Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
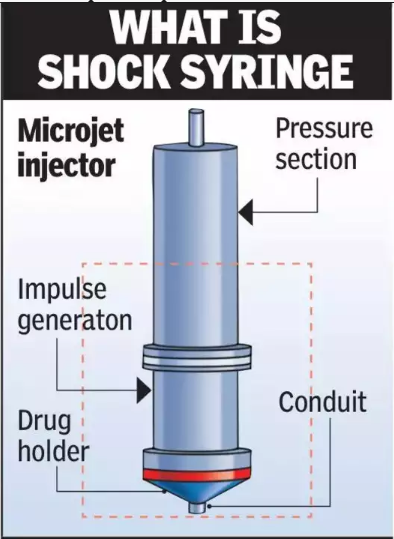
How the Shock Syringe Works:
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
UN Approves New AU Force to Combat Al-Shabaab in Somalia
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- On January 19, 2024, the UN Security Council approved a new African Union (AU) force in Somalia to counter the Al-Shabaab terrorist group.
- The resolution was supported by 14 of 15 members, with the US abstaining due to concerns about funding.
- The new force will replace the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) after its mandate ends on December 31, 2024.
New Mission - AUSSOM:
- The new mission is named African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
- AUSSOM will continue supporting Somali forces in stabilizing the nation and combating terrorism.
- The mission's objective is to enhance security and stability in Somalia, addressing the challenges posed by Al-Shabaab and ISIL.
Mandate and Operations:
- AUSSOM allows for the deployment of up to 12,626 personnel, including 1,040 police officers, until June 2025.
- The force will focus on counterterrorism, maintaining security, and assisting the Somali government in stabilizing the country.
Financing:
- A hybrid funding approach will be used:
- 75% of the mission’s costs will be covered by the UN, and 25% will come from African Union and partner countries.
- The US raised concerns about the UN's disproportionate funding of the mission, which led to its abstention from voting.
Contributing Countries:
- Egypt has announced its participation in the new force.
- Burundi and Ethiopia will not be contributing troops to AUSSOM.
- Ethiopia has its own ongoing disputes with Somalia, particularly regarding its maritime deal with the breakaway Somaliland region.
Background on Somalia's Challenges:
- Somalia has faced decades of civil war, an insurgency by Al-Shabaab, and recurring climate disasters.
- The country is one of the poorest in the world, and its internal conflicts are exacerbated by clannism, which has fragmented its political and social structure.
Historical Context of Peace Missions in Somalia:
- Previous UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia (1992-1995) faced significant failures, notably the Battle of Mogadishu and the failure to prevent the 1993 massacre.
- The rise of Al-Shabaab in the mid-2000s has further escalated the conflict, and the mission of AUSSOM aims to address these continuing threats.
The Role of Clannism:
- Clannism has hindered the establishment of a unified government in Somalia, with clan rivalries leading to a lack of national cohesion.
- Clannism refers to the prevalence of clan-centric politics, where allegiance to clan and sub-clan interests often takes precedence over national cohesion. In Somalia, the major clans are Darod, Hawiye, Dir, and Rahanweyn.
Importance of AUSSOM:
- AUSSOM represents a strategic shift in the international approach to stabilizing Somalia, relying more on African-led initiatives for peace and security in the region.
Global Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN peacekeeping mission has been active globally, with over 1 million personnel deployed across 70+ operations.
- Success stories like Sierra Leone (1999-2005) and Liberia (2003-2018) demonstrate the potential impact of well-executed peace missions, but past failures like in Somalia (1992-1995) and Rwanda (1994) underline the challenges faced.
India’s Contribution:
- India has contributed significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, deploying over 253,000 personnel in 49 operations since 1948.
- India’s contributions to missions in Somalia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Sudan reflect its active role in global peacekeeping efforts.
ASI Decodes Sanskrit Inscription Found in Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK)

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
An ancient Sanskrit inscription found in Gilgit (PoK) was decoded by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
About the Inscription:
- Location:
- Gilgit (PoK): Written in Brahmi script, dating back to 4th century CE.
- Peshawar (Pakistan): Written in Sharada script, dating to 10th century CE.
- Details of Gilgit Inscription:
- Mentions Pushpasingha, who installed a Mahesvaralinga for the merit of his guru.
- Written in Brahmi script, which was prevalent during the 4th century CE.
- Religious Context: Indicates significant religious connection, particularly with Shaivism.
- Details of Peshawar Inscription:
- Fragmentary: Engraved on a slab.
- Written in Sharada characters (10th century CE).
- Mentions Buddhist Dharini (chants), particularly referring to Da (Dha) rini in line six.
- The inscription is partially damaged, and further details are unclear.
- Earlier Discoveries:
- This is not the first Sanskrit inscription decoded from Pakistan. In the past, Sanskrit inscriptions have been found in various parts of Pakistan.
- Swat Valley: Known for numerous Buddhist rock inscriptions in Sanskrit using Nagari script, which were part of the Gupta Empire (circa 240–550 CE).
- Religious and Cultural Implications:
- The Gilgit inscription provides evidence of Shaivism as a prominent religious practice in the region during the 4th century CE.
- The Peshawar inscription suggests Buddhist influences, particularly related to Buddhist chants and rituals.
- Swat Valley's Role: The inscriptions found here highlight its importance as a center of Buddhist learning and cultural exchange.
