e-Migrate Portal

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministers for External Affairs and Labour and Employment launched the upgraded e-Migrate portal and mobile app, aimed at enhancing the migration experience for Indian workers seeking employment abroad. This initiative reflects the Indian government's commitment to ensuring the safety and welfare of its migrant workforce, aligning with global migration goals under the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
About e-Migrate Portal
The e-Migrate portal is an online platform designed to facilitate and manage the migration of Indian workers. It promotes safe and legal mobility channels by providing a transparent framework for migrant workers, including:
- Information Access: Comprehensive resources to help migrants understand the migration process.
- Documentation Support: Tools to assist with necessary paperwork.
- Helpline Support: A 24/7 multilingual helpline that addresses issues faced by workers, particularly in the Gulf region.
- Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to educate workers about their rights and responsibilities abroad.
The upgraded version of the portal, launched in October 2024, features enhanced functionality to better serve Indian migrants.
Key Features of e-Migrate v2.0
- Multilingual Helpline: Offers real-time support in multiple languages, ensuring that urgent issues are resolved efficiently.
- Integration with Digilocker: Facilitates secure, paperless submission of essential documents, such as passports and employment contracts.
- Social Security Net: Enhances social security measures for migrants, including insurance policies and partnerships with the State Bank of India for fee-free digital payment services.
- Mobile App: Introduced for the first time, this app provides easy access to services, including a job search marketplace for overseas employment opportunities.
- Rural Accessibility: Collaboration with Common Service Centres (CSCs) aims to expand immigration services to rural areas in local languages, making the platform more accessible to diverse populations.
Significance
The e-Migrate portal aligns with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 10, which promotes orderly and responsible migration. By fostering safe migration practices, this initiative seeks to empower Indian workers and protect their rights while contributing to the country's international workforce.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has officially launched its first two initiatives: the Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG) and the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission. These initiatives aim to enhance India’s research landscape and support innovation in critical sectors.
Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG)
- Objective: The PMECRG is designed to empower early career researchers by providing flexible funding and support for high-quality innovative research. It aims to foster creativity and drive technological progress, positioning India as a global leader in science and technology (S&T).
- Significance: This grant recognizes the essential role of young researchers in advancing India's scientific agenda. By investing in their development, ANRF aims to cultivate a vibrant research ecosystem that encourages groundbreaking discoveries.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission
- Focus: The MAHA-EV Mission targets the development of key technologies for electric vehicles, specifically in areas such as tropical EV batteries, power electronics, machines and drives (PEMD), and charging infrastructure.
- Goals:
- Reduce Import Dependency: By fostering domestic innovation in EV components.
- Global Leadership: Positioning India as a leader in the electric vehicle sector, aligning with the government's Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- Collaboration: The mission is designed to encourage multi-institutional and multi-disciplinary collaboration to address critical scientific challenges, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of India's EV sector.
Significance of Both Initiatives
- Bridging Gaps: Both initiatives aim to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial applications, a key goal of ANRF. This alignment is crucial for translating research into practical applications that benefit society.
- Strategic Interventions: These programs reflect the discussions held during the ANRF's Governing Board meeting, which emphasized global positioning in key sectors, capacity building, and fostering an innovation ecosystem.
- Long-term Vision: The initiatives contribute to India's goal of achieving a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047, accelerating the country's progress toward a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
The launch of the PMECRG and MAHA-EV Mission marks a significant step in enhancing India's research ecosystem. By supporting early career researchers and advancing electric vehicle technologies, ANRF is poised to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and strengthen India’s position on the global scientific stage. These initiatives reflect a commitment to sustainable development and technological leadership, paving the way for transformative advancements in various sectors.
Haber-Bosch process
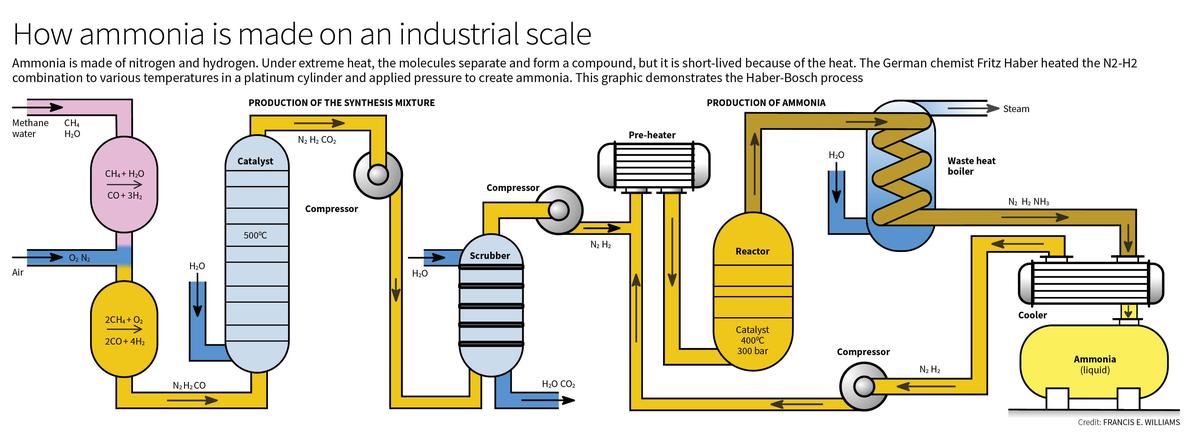
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Haber-Bosch process has fundamentally transformed agricultural practices and global food production, enabling the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is essential for fertilizers.
The Nitrogen Molecule
- Composition: Nitrogen primarily exists as molecular nitrogen (N?) in the atmosphere, where two nitrogen atoms are bonded with a strong triple bond. This bond is very stable and requires significant energy (946 kJ/mol) to break, rendering N? largely inert and unavailable for direct use by plants.
Nitrogen in Nature
- Natural Fixation: In nature, the energy required to break the N? bond is typically provided by phenomena like lightning, which converts nitrogen to reactive forms such as nitrogen oxides (NO and NO?). These can subsequently form nitric acid when they react with water, depositing reactive nitrogen through rainfall.
- Microbial Processes: Certain bacteria, including Azotobacter and Rhizobia, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into reactive forms, supporting plant growth. Azolla, a fern with a symbiotic cyanobacterium, also helps in nitrogen fixation.
The Nitrogen Cycle
- Plant Uptake: Plants absorb reactive nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH??) and nitrate (NO??) from the soil, essential for synthesizing proteins and other vital compounds. Humans and animals rely on plants for their nitrogen intake.
- Cycle Completeness: While nitrogen is returned to the soil through excretion and decomposition, some is lost back to the atmosphere as N?. This loss contributes to the depletion of soil nitrogen, especially in crops that do not fix their own nitrogen.
Ammonia Production
- Haber-Bosch Process: This process synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature, using a catalyst to enhance efficiency. Initially developed by Fritz Haber and scaled by Carl Bosch, this method became the backbone of modern fertilizer production.
Benefits and Downsides of Fertilizers
- Food Security: The Haber-Bosch process has significantly increased food production, contributing to a remarkable rise in global food supply and preventing widespread hunger. It is estimated that one-third of the world’s population relies on fertilizers produced via this process for their food.
- Environmental Impact: The widespread use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to environmental issues:
- Excess Nutrients: Over-application can result in nutrient runoff into water bodies, causing eutrophication, which depletes oxygen and harms aquatic life.
- Acid Rain: Reactive nitrogen can contribute to acid rain, affecting soil health and biodiversity.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous fertilizer use without adequate replenishment of nutrients can degrade soil quality over time.
While the Haber-Bosch process is crucial for modern agriculture and food security, it also presents significant environmental challenges. The balance between using fertilizers effectively and sustainably is essential to ensure that technological advancements do not come at the cost of ecological health. As such, addressing food security requires not just technological innovation, but also thoughtful political and social engagement to manage resources responsibly.
India's Renewable Energy Capacity Hits 200 GW Milestone
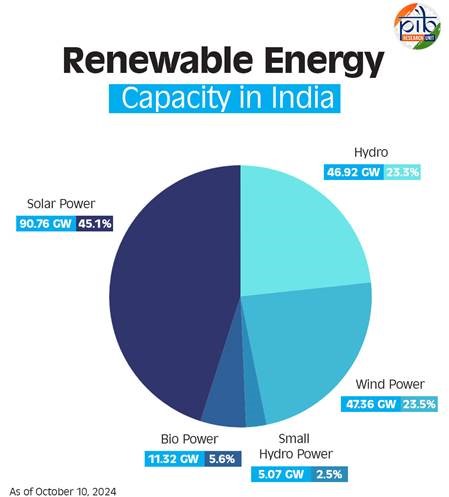
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
India has recently celebrated a landmark achievement in its renewable energy sector, with its total renewable energy capacity surpassing 200 GW as of October 10, 2024. This milestone, reported by the Central Electricity Authority, showcases the country’s growing commitment to clean energy and its strategic shift towards a more sustainable future.
Overview of India’s Renewable Energy Landscape
As of October 2024, India's total electricity generation capacity stands at 452.69 GW, with renewable sources contributing a substantial 201.45 GW, representing 46.3% of the overall capacity. This shift highlights India’s increasing reliance on cleaner, non-fossil fuel energy.
Key contributors to this capacity include:
- Solar Power: Leading with 90.76 GW, capitalizing on India's abundant sunlight.
- Wind Power: Following closely at 47.36 GW, leveraging the country’s vast wind corridors.
- Hydropower: Large hydro projects add 46.92 GW, while small hydro contributes an additional 5.07 GW.
- Biopower: Incorporating biomass and biogas energy, contributing 11.32 GW.
Together, these resources are pivotal in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
Leading States in Renewable Energy Capacity
Certain states are at the forefront of this renewable energy expansion:
- Rajasthan: 29.98 GW, benefiting from ample land and sunlight.
- Gujarat: 29.52 GW, driven by robust solar and wind initiatives.
- Tamil Nadu: 23.70 GW, utilizing favorable wind conditions.
- Karnataka: 22.37 GW, supported by a mix of solar and wind projects.
Key Schemes and Programs
The Indian government has introduced numerous initiatives to accelerate renewable energy capacity, aiming for 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030. Notable programs include:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission
- PM-KUSUM Scheme
- PM Surya Ghar Scheme
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) for solar PV modules
These efforts reflect the government's commitment to fostering a sustainable energy future while addressing the challenges posed by climate change and energy security. Here are some other ongoing key initiatives:
- Notification of a trajectory for renewable energy power bids of 50 GW per annum by Renewable Energy Implementation Agencies (REIAs) from FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Foreign Direct Investment permitted up to 100 percent under the automatic route to attract investments.
- Waiver of Inter-State Transmission System charges for solar and wind power projects commissioned by June 30, 2025; green hydrogen projects until December 2030; and offshore wind projects until December 2032.
- Announced Renewable Purchase Obligation trajectory until 2029-30, including separate RPO for Decentralized Renewable Energy.
- A Project Development Cell has been established to attract and facilitate investments in the renewable sector.
- Standard Bidding Guidelines issued for tariff-based competitive bidding for procurement of power from grid-connected solar, wind, and wind-solar projects.
- Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Parks are being set up to provide land and transmission for large-scale renewable energy projects.
- Cabinet approval for a Viability Gap Funding scheme for offshore wind energy projects, facilitating the installation and commissioning of 1 GW of offshore wind energy capacity along the coasts of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Issued Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020, for net-metering up to 500 kilowatts or the electrical sanctioned load, whichever is lower.
- The “National Repowering and Life Extension Policy for Wind Power Projects, 2023” has been released.
- “Strategy for Establishment of Offshore Wind Energy Projects” outlines a bidding trajectory of 37 GW by 2030.
- Offshore Wind Energy Lease Rules, 2023, notified to regulate the grant of leases for offshore wind energy development.
- Procedure for Uniform Renewable Energy Tariff (URET) has been established.
- Standard & Labelling (S&L) programs for Solar Photovoltaic modules and grid-connected solar inverters have been launched.
- A transmission plan has been prepared to augment transmission infrastructure until 2030.
- The Electricity (Late Payment Surcharge and Related Matters) Rules have been notified.
- Green Energy Open Access Rules 2022 have been issued to promote renewable energy.
- Launched the Green Term Ahead Market (GTAM) to facilitate the sale of renewable energy power through exchanges.
- Orders issued to ensure that power is dispatched against Letters of Credit or advance payment for timely payments to renewable energy generators.
ITU World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly 2024

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated ITU WTSA 2024 and India Mobile Congress 2024, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- First Time in India: WTSA hosted for the first time in India and the Asia-Pacific region.
- Participants: Over 3,000 industry leaders, policy-makers, and tech experts from more than 190 countries expected.
ITU WTSA 2024
- Significance: Governing conference for the standardization work of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), held every four years.
- Focus Areas: Discussion on standards for next-generation technologies including:
- 6G
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Cybersecurity
- Opportunities for India: Enhances India’s role in shaping the global telecom agenda; insights into Intellectual Property Rights and Standard Essential Patents for startups and research institutions.
India Mobile Congress 2024
- Theme: "The Future is Now"
- Technological Focus: Highlight advancements in:
- Quantum Technology
- Circular Economy
- 6G and 5G use cases
- Cloud and Edge Computing
- IoT and Semiconductors
- Cybersecurity
- Green Technology
- Satellite Communication and Electronics Manufacturing
Importance for India
- Showcase of Innovation: A platform for India’s innovation ecosystem, demonstrating advancements in digital technology.
- Global Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between government, industry, and academia to address global telecommunication challenges.
