Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Paris-based International Energy Agency highlighted India’s Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), 2017 as something that sets it apart from other developing economies where “energy efficiency in buildings stands out as a laggard”.
About Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC):
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) Released by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- It was first released in 2007 and again updated in 2017.
- The purpose of ECBE is to set minimum energy standards for commercial buildings, with the objective of enabling energy savings of between 25 and 50% in compliant buildings.
- Commercial buildings include hospitals, hotels, schools, shopping complexes and multiplexes which have a connected load of 100 kW or more, or contract demand of 120 kVA or more.
- Also the code is for both new buildings and retrofitting existing buildings.
- Assessment Parameters: The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) primarily looks at parameters like building design including envelope (walls, roofs, windows), lighting systems, and renewable energy integration among others.
- Tagging of buildings: Compliant buildings are assigned one of three tags in ascending order of efficiency, namely ECBC, ECBC Plus, and Super ECBC.
- 23 out of 28 states have notified ECBC rules. But only 15 states have notified rules based on the latest ECBC,2017.
- Five states — Gujarat, Maharashtra, J&K, Ladakh, and Manipur — are yet to notify ECBC rules.
Aurora (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, NASA shared this incredible image of an aurora taken from the International Space Station.
What is Aurora?
- An aurora is a natural light display that shimmers in the sky.
- They are only visible at night, and usually only appear in lower polar regions.
- Auroras come in colors like blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- They're mostly visible near the Arctic and Antarctic Circles, known as the aurora borealis and aurora australis, respectively.
- These natural light shows occur when the solar wind from the sun meets Earth's magnetic field, creating a beautiful halo of light around the poles.
- This collision between solar wind ions and Earth's atmosphere atoms leads to stunning auroras.
- Their color depends on altitude and the atoms involved.
- Red comes from oxygen ions higher up, while the familiar green-yellow hues arise from interactions at lower altitudes.
- Sometimes, reddish and bluish tints appear, created by ions colliding with nitrogen atoms.
- The most active auroras happen when the solar wind is strongest, affected by solar weather changes, which follow an 11-year cycle.
- Equinoxes and magnetic storms can cause auroras to be seen even in mid-latitudes, affecting communication signals and occasionally causing disruptions.
- Auroras are a natural spectacle, painted by the collision of solar wind and Earth's atmosphere, creating these dancing lights in the night sky.
Bioluminescent Fungi 'Mycena Chlorophos' (The New Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A team of researchers and the forest department have found a rare bioluminescent mushroom in the Kanyakumari Wildlife Sanctuary (KKWLS).
About Mycena chlorophos:
- Mycena chlorophos is a species of bioluminescent fungus, meaning that it can produce its light.
- It is primarily found in subtropical Asia, including India, Japan, Taiwan, Polynesia, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka, as well as in Australia and Brazil.
- The bioluminescence is produced through a chemical reaction that involves luciferin, a light-emitting molecule, and the enzyme luciferase.
- Luciferase catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, which produces light.
- The luciferin in Mycena chlorophos is a compound called trans-3-hydroxyhispidin.
- This compound is also found in other bioluminescent fungi, such as Neonothopanus nambi and N. gardneri.
- The bioluminescence of Mycena chlorophos is thought to serve several functions.
- It may help the fungus to attract insects, which can help to disperse its spores.
- It may also help the fungus to ward off predators.
What is Bioluminescence?
- It is the ability of living organisms to emit light.
- It occurs due to a biochemical reaction between luciferins, oxygen, and the enzyme luciferase.
- The benefit of bioluminescence in fungi is to attract insects to facilitate their spore dispersal.
Radiative Cooling Paint (The Hindu)
- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
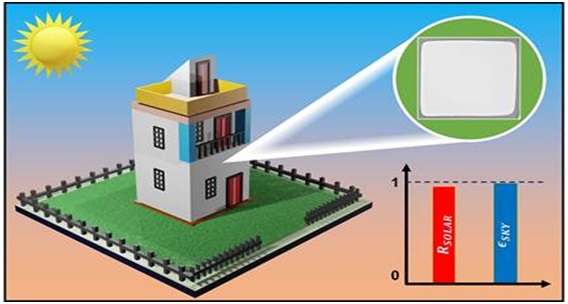
Researchers from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) have developed a radiative cooling paint, which is specifically engineered to cool structures like buildings, pavers, and tiles in hot weather conditions.
What is Radiative Cooling Paint?
- Material Composition: Radiative Cooling Paint is composed of a mix of magnesium oxide (MgO) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), derived from easily accessible, cost-effective, and safe materials.
- The optimized MgO-PVDF with dielectric nanoparticles resulted in a large solar reflectance of 96.3% and a record high thermal emission of 98.5% due to Mg?O bond vibrations, and other stretching/bonding vibrations from the polymer.
- Cooling Mechanism: This paint stands out not only for its appearance but for its function.
- It reflects nearly all of the sun's heat and emits a significant amount of its heat, effectively maintaining cooler surfaces.
- Heat Management: Tailored for hot climates, it efficiently reduces the need for excessive electricity use to cool buildings during sweltering days.
- Temperature Reduction: Once applied, it notably lowers surface temperatures by approximately 10 degrees under intense sunlight, surpassing the performance of regular white paint.
- Application Ease: Additionally, it showcases water-resistant properties and excellent adhesion to various surfaces, simplifying the application process on structures like walls and roofs.
Green Firecrackers (The Hindu)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Both government agencies and conscious citizens in Bengaluru are actively ensuring that only less polluting green crackers are being sold and bought this Deepavali.
What are Green firecrackers?
- Green firecrackers are a type of fireworks designed to produce fewer pollutants and emissions compared to traditional firecrackers.
- They are crafted to be more environmentally friendly by using cleaner ingredients, and emitting less smoke and harmful chemicals upon combustion.
- There are mainly three types of green firecrackers: SWAS, SAFAL, and STAR.
- They are not only eco-friendly but 15-20 % cheaper than the conventional ones.
- In 2018, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-NEERI) introduced the idea of green crackers.
What are they made of?
- Green firecrackers are marked by reduced size of shell, elimination of ash usage, reduced usage of raw material in the compositions, and have a uniformly acceptable quality.
- They use additives as dust suppressants to reduce emissions with specific reference to particulate matter (PM).
- These crackers lack the barium compounds responsible for their unique green hue.
- Barium, a metallic oxide, is known to contribute to air pollution and noise pollution.
- When green crackers are ignited, they produce water vapor, thereby minimizing dust emissions.
- In terms of sound levels, green firecrackers generate noise ranging from 110 to 125 decibels, making them significantly quieter than traditional firecrackers, which typically produce around 160 decibels, resulting in nearly 30% less noise.
