India signs an agreement to acquire five lithium mines in Argentina (Business Standard)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Indian govt. signed an agreement to acquire five lithium brine blocks for exploration and development in Argentina.
Context:
- The Mines Ministry, operating through KhanijBidesh India Limited (KABIL), has entered into an agreement with Argentina's state-owned CAMYEN for the development of five lithium blocks.
- CAMYEN, officially known as Catamarca Minera Y Energetica Sociedad Del Estado, is headquartered in the Catamarca province of the Latin American nation.
- Key Points: KABIL, a government-owned entity, will initiate the exploration and development activities for five lithium brine blocks—Cortadera-I, Cortadera-VII, Cortadera-VIII, Cateo-2022-01810132, and Cortadera-VI, collectively spanning an area of approximately 15,703 hectares.
- As part of its expansion, KABIL is planning to establish a branch office in Catamarca, Argentina.
- This marks a significant milestone as it represents the first lithium exploration and mining project undertaken by a government company in India.
- Argentina, situated within the global "Lithium Triangle" alongside Chile and Bolivia, collectively possesses more than half of the world's total lithium resources.
Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL):
- It is a Joint Venture Company among National Aluminium Company (NALCO), Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL) and Mineral Exploration Corporation Limited (MECL).
- It has been formed in August 2019.
- KABIL is focusing on identifying and sourcing battery minerals like Lithium and Cobalt.
- KABIL is a joint venture company focused on identifying, acquiring, developing, processing and making commercial use of strategic minerals in overseas locations for supply in India.
Current Statistics About Lithium in India:
- India has recently discovered 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves in Jammu & Kashmir and ranks seventh globally.
- The primary lithium reserve in India has been discovered in the Salal-Haimana area of Reasi District in Jammu and Kashmir, with additional smaller reserves identified in Karnataka.
- Presently, India fulfils its entire lithium demand through imports.
- In the fiscal year 2023, there was a notable increase in lithium imports in India, reaching approximately $3 billion (around ?24,900 crore), indicating a 58% growth compared to the figures in FY22.
- More than 95% of India's lithium imports are sourced from China and Hong Kong.
Global Reserves of Lithium:
- Approximately half of the world's lithium resources are concentrated in Latin America, primarily in countries such as Bolivia, Argentina and Chile along with significant deposits in USA, Australia and China.
- Bolivia has the highest identified lithium resources in the world with 20 million tonnes, as per the US Geological Survey data.
- Argentina has the second-largest lithium reserve estimated to be close to 20 million tonnes.
- The United States follows Argentina with 12 million tonnes of lithium reserves.
- Chile ranks fourth globally with 11 million tonnes of lithium reserves.
- Australia occupies the fifth spot with 7.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves, according to the available data.
- China, the largest country in Asia, ranks sixth globally with 6.8 million tonnes of lithium reserve. China, without having the largest lithium reserves, continues to dominate lithium mining and processing in the world.
- Argentina holds a substantial portion, accounting for 20% of the world's total lithium resources, making it the second-largest contributor after Bolivia.
- Argentina is a key participant in the 'Lithium Triangle,' alongside Chile and Bolivia.
- Collectively, these three nations possess over two-thirds of the global lithium resources.
- The Lithium Triangle is a region in the Andes known for its rich lithium reserves.
- Notably, Argentina ranks second globally in terms of lithium resources, third in lithium reserves, and fourth in lithium production.
Importance of the Agreement:
- This agreement holds strategic value as it enables India to enhance its lithium supply, fostering the growth of both countries' lithium mining and downstream sectors.
- It contributes to the diversification of the supply chain for essential materials, aligning with the pursuit of Global Net Zero objectives.
- Given that a significant portion, approximately 54%, of India's lithium imports are currently sourced from China, which dominates 80% of the global supply, this deal helps reduce dependence on a single supplier.
- The initiative aligns with the Mineral Security Partnership (MSP), of which India is an active participant.
Union Minister Rao Inderjit Singh launches the MPLADS e-SAKSHI Mobile Application for the Revised Fund Flow Procedure under the MPLAD Scheme (PIB)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) Rao Inderjit Singh launched the MPLADS e-SAKSHI Mobile Application at Khurshid Lal Bhawan, New Delhi.
What is the e-SAKSHI Mobile Application?
- The e-SAKSHI mobile application was devised for the revamped fund flow procedure within the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLAD).
- It is poised to revolutionize the way Members of Parliament (MPs) engage with and oversee development projects in their constituencies.
Key Features of e-SAKSHI:
- Convenience and Accessibility: MPs can seamlessly propose, track, and supervise projects with the application, ensuring convenience and accessibility at their fingertips.
- Real-time Access: The application provides real-time access, enhancing decision-making by enabling swift responses to emerging needs or issues.
- Streamlined Communication: e-SAKSHI facilitates streamlined communication between MPs and relevant authorities, promoting an efficient exchange of information.
- Transparency: MPs receive instant updates on the status and progress of proposed projects, promoting transparency in the implementation process.
- Budget Management: The application includes features for budget management, empowering MPs to monitor expenditures effectively.
Key Points about the MPLAD Scheme:
- Introduced in 1993, MPLAD is a fully funded Government of India scheme where funds are released directly to district authorities as grants-in-aid.
- The funds are non-lapsable, allowing the carry-forward of entitlement not released in a specific year to subsequent years, subject to eligibility.
- MPs have an annual entitlement of ?5 crore per constituency, with their role limited to recommending works.
- District authorities are responsible for sanctioning, executing, and completing the recommended works within stipulated timelines.
- Lok Sabha members recommend works in their respective constituencies, while Rajya Sabha members can recommend works anywhere in their elected state.
- Nominated members can recommend works nationwide.
- MPLADS works can be implemented in areas affected by various natural calamities, ensuring a flexible and responsive approach to development needs.
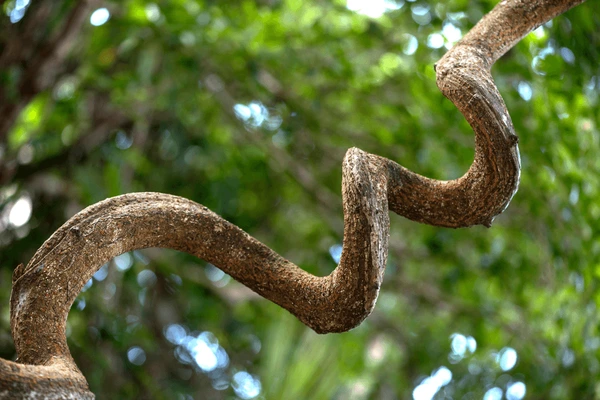
In Assam, creeper conservation rides revived Karbi traditional game (The Hindu)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A dying traditional game, given a fresh lease of life at the ongoing Karbi Youth Festival (KYF) in central Assam’s Karbi Anglong district, has fuelled a drive for conserving a creeper with an African connection.
About African Dream Herb:
- The African dream herb, also known by various names such as Giant sea bean, snuff box, and Entada rheedii, is a perennial climbing vine valued by African traditional healers for its ability to induce vivid dreams, facilitating efficient communication with ancestors.
- Indigenous to Africa, Asia, Australia, and Madagascar, this vine thrives in tropical lowlands, along coastlines, river banks, woodlands, thickets, and riverine rainforests.
- Uses: A paste derived from its leaves, bark, and roots serve purposes ranging from wound cleaning to treating burns and addressing jaundice in children.
- The plant's tea, made from its entirety, aids in improving blood circulation to the brain and healing the aftermath of a stroke.
- The bark is employed to treat ailments such as diarrhoea, dysentery, and parasitic infections.
- This vine produces dark brown, spherical seeds, almost the size of a human patella or kneecap, used in the traditional game 'Hambi Kepathu,' associated with the origin of the Karbi community.
What is Hambi Kepathu?
- Also known as Simrit in some regions of Karbi Anglong, Hambi Kepathu is played on three rectangular courts with two teams of three members each.
- In this male-only game, players place a 'hambi' (glazed creeper seed) vertically on the midpoint of the boundary line for opponents to hit with their 'hambi.'
- The name Hambi Kepathu is derived from the first syllables of the names of a Karbi sister-brother duo, adding to the array of traditional Karbi games such as 'Pholong' (spinning top), 'Thengtom Langvek' (torch swimming), and 'Kengdongdang' (bamboo stilt race).
PM pays homage to Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji on his Parkash Utsav (The Hindu)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
January 17 marks the 357th birth anniversary of Guru Gobind Singh, the revered Sikh leader born in Patna, Bihar.
About Guru Gobind Singh:
- Guru Gobind Singh, the 10th and the last Guru of the Sikhs, was born as Gobind Rai on December 22, 1666, in Patna, Bihar, to Guru Teg Bahadur, the ninth Guru of Sikhism.
- Following the martyrdom of his father by the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in 1675, Guru Gobind Singh assumed leadership at the age of nine.
- Renowned as a warrior, poet, and prophet, Guru Gobind Singh is cherished by Sikhs for his defence of faith and advocacy for equality and justice.
- In 1699, Guru Gobind Singh formed the institution of the Khalsa and introduced the Five Ks — Kesh (uncut hair), Kangha (wooden comb), Kara (iron or steel bracelet), Kirpan (sword), and Kacchera (short breeches).
- He fought 14 wars against his oppressors and tyrants, but with ethical and moral principles, never taking captives, nor damaging places of worship; he was never the first to be the aggressor.
- The notable conflicts include the Battle of Bhangani, the Battle of Nadaun, the Battle of Anandpur, the Battle of Chamkaur, the Battle of Muktsar, and the Battle of Khidrana
- While continuing to lead with steely determination, Guru Gobind Singh faced with fortitude, the execution of his two sons, Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh.
- The duo was bricked alive at Sirhind by the then-governor.
- He lost two more sons in the battle of Chamkaur Sahib, yet he stayed true to his goal.
- When the Mughal army, numbering over a lakh, marched against his troop of 40 soldiers, he marched on bravely, penning his famous hymn, mitr pyare nu haal muridan da kehna (Oh beloved friend of the Lord, see the plight of your disciples).
- Guru Gobind is credited with finalising the manuscript of Guru Granth Sahib, declaring it to be the ultimate Guru of the Sikhs.
- His metaphysical, sublime and exquisite poetry has been immortalised in his composition, Dasam Granth, reflected in Jaap Sahib, Chandi Di Vaar, Tav Prasad savaiye and Benti Chaupai, among others.
- He wrote in Punjabi, Arabic, Braj Bhasa, Sanskrit and Persian and remains a much-revered guru.
- He was assassinated in 1708, at the age of 41.
Defence upgrade roadmap: Apex body led by Prime Minister, MoD sci-tech unit (Indian Express)
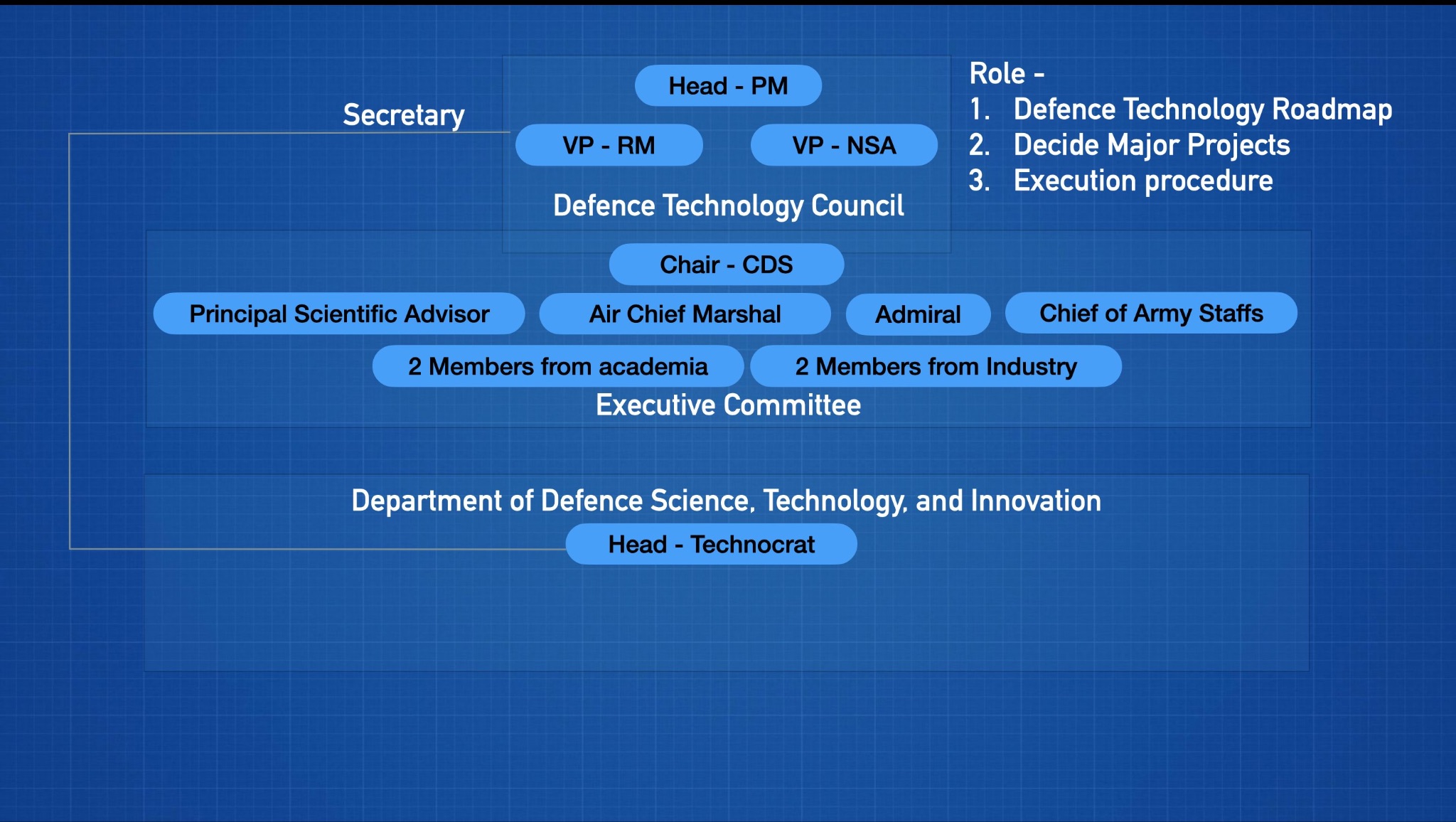
- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The expert committee, led by Vijay Raghavan, the former principal scientific advisor, proposed that the country's defence technology roadmap be overseen by an apex body called the Defence Technology Council, with the Prime Minister serving as its chair.
The context in which the Vijay Raghavan Committee was Established:
- Formed by the government last year, the committee was tasked with assessing the functioning of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The committee's report, submitted this month, follows the government's initiative to address significant delays in various DRDO projects.
- This scrutiny comes in response to concerns raised by the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence, which noted that 23 out of 55 mission mode projects faced substantial delays.
- In 2022, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) highlighted that 67% of the 178 scrutinized projects failed to meet their initially proposed timelines.
- The CAG attributed these delays to factors such as persistent alterations in design specifications, delays in completing user trials, and delays in placing supply orders.
- The prevalent practice of seeking multiple extensions for projects, particularly those designated under the Mission Mode category, has been identified as undermining the intended purpose of these initiatives.
Major Recommendations of the Vijay Raghavan Committee:
- Establishment of the Defence Technology Council: Headed by the Prime Minister, with the Defence Minister and the National Security Advisor serving as Vice Presidents.
- This council is envisioned to play a pivotal role in charting the nation's defence technology roadmap, deciding on significant projects, and overseeing their execution.
- An executive committee, led by the Chief of Defence Staff, is proposed, featuring members such as the Principal Scientific Advisor, the three service chiefs, their vice chiefs, and representation from academia and industry.
- Creation of the Department of Defence Science, Technology, and Innovation: To be led by a technocrat, this department aims to foster defence research and development within the academic and startup ecosystem.
- Additionally, it is designated as the secretariat for the Defence Tech Council chaired by the Prime Minister.
- Drawing expertise from scientists in the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and academia, it will compile a knowledge repository on production expertise, conduct background research for the Defence Tech Council, and contribute to informed decisions on technology production.
- Restructuring of DRDO's Focus: Recommends that DRDO concentrate on its original mission of research and development for defence purposes.
- The suggestion is for DRDO to abstain from involvement in productization, production cycles, and product management, tasks deemed more suitable for the private sector.
- Currently, DRDO is engaged in all aspects of its projects, spanning from research and development to production.
