Ring of Fire
- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nine people died and more than 1,000 were injured in Taiwan after the island was hit by its biggest earthquake in at least 25 years on Wednesday (April 4) morning.
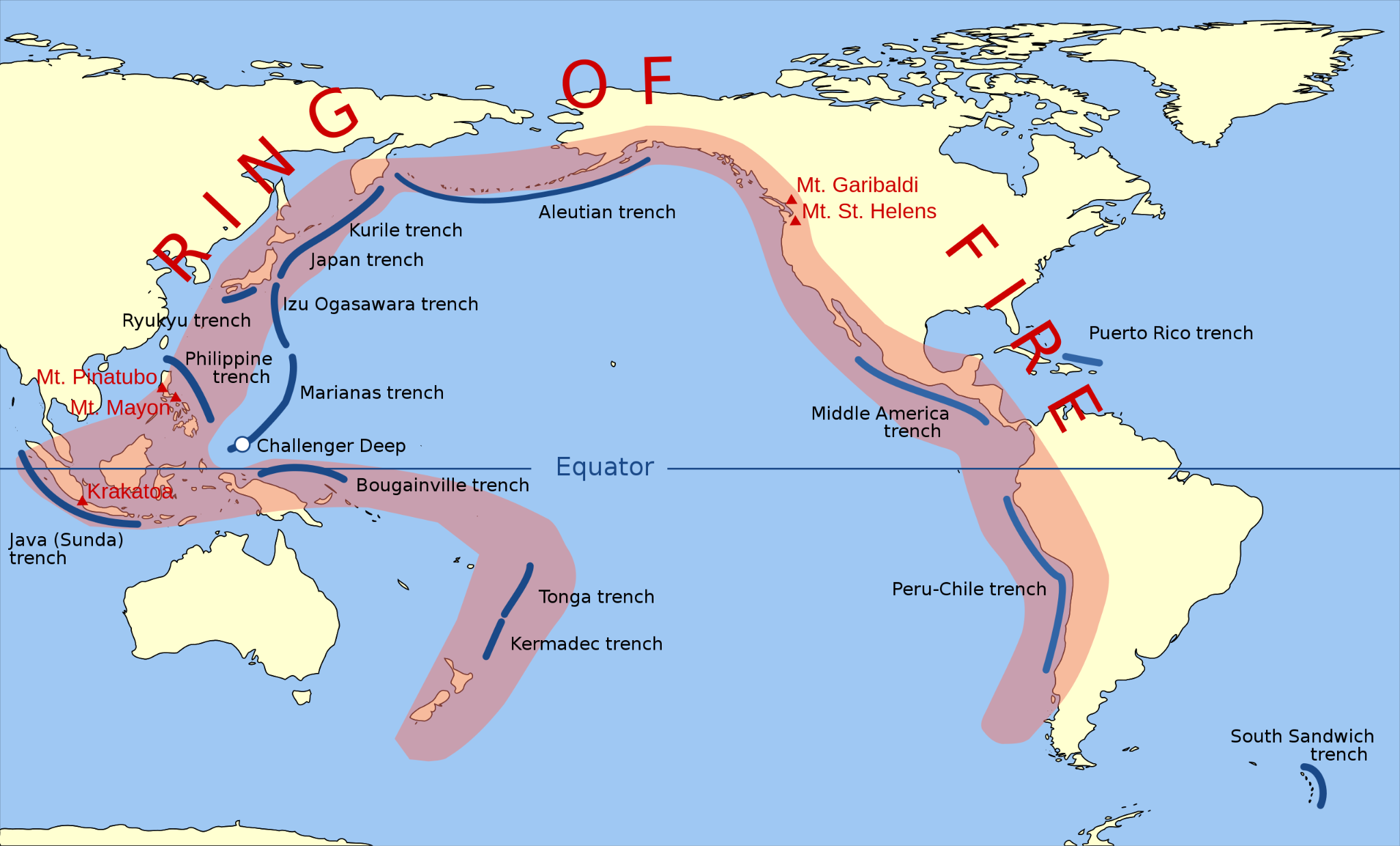
What is the Ring of Fire?
- The Ring of Fire is essentially a string of hundreds of volcanoes and earthquake sites that run along the Pacific Ocean.
- It is a semicircle or horseshoe in shape and stretches nearly 40,250 kilometers.
- The Ring of Fire traces the meeting points of numerous tectonic plates, including the Eurasian, North American, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Caribbean, Nazca, Antarctic, Indian, Australian, Philippine, and other smaller plates, which all encircle the large Pacific Plate, according to a report by National Geographic.
- It runs through 15 more countries including the USA, Indonesia, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Guatemala, Russia, Chile, Peru, and the Philippines.
Why is the Ring of Fire Vulnerable to Earthquakes?
- The Ring of Fire witnesses so many earthquakes due to constant sliding past, colliding into or moving above or below each other of the tectonic plates.
- As the edges of these plates are quite rough, they get stuck with one another while the rest of the plate keeps moving.
- An earthquake occurs when the plate has moved far enough and the edges unstick on one of the faults.
Why are There so Many Volcanoes in the Ring of Fire?
- The existence of volcanoes in the Ring of Fire is also due to the movement of tectonic plates.
- Many of the volcanoes have been formed through a process known as subduction.
- It takes place when two plates collide with each other and the heavier plate is shoved under each other, creating a deep trench.
- “When a ‘downgoing’ oceanic plate [like the Pacific Plate] is shoved into a hotter mantle plate, it heats, volatile elements mix, and this produces the magma.
- The magma then rises through the overlying plate and spurts out at the surface,” which leads to the formation of volcanoes, according to a report by DW.
- Most of the subduction zones on the planet are located in the Ring of Fire and that’s why it hosts a large number of volcanoes.
Why is Taiwan so Exposed to Earthquakes?
- Taiwan lies along the Pacific “Ring of Fire,” the line of seismic faults encircling the Pacific Ocean where most of the world’s earthquakes occur.
- The area is particularly vulnerable to temblors due to the tension accumulated from the interactions of two tectonic plates, the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate, which may lead to sudden releases in the form of earthquakes.
- The region’s mountainous landscape can magnify the ground shaking, leading to landslides.
myCGHS App

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government has launched the 'myCGHS' app for iOS to provide Central Government Health Scheme beneficiaries access to electronic health records, information, and resources.
About myCGHS app:
- The Union Health Ministry launched the myCGHS app for iOS (Apple Users) to provide easy access for the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) beneficiaries to their Electronic Health Records, information, and other resources.
- The myCGHS iOS app is developed by the technical teams of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) Himachal Pradesh and the NIC Health Team.
- It is a convenient mobile application offering features aimed at enhancing information and accessibility for CGHS beneficiaries.
- The app is said to offer a range of services including:
- Online appointment booking and cancellation
- Downloading CGHS card and index card
- Accessing lab reports from CGHS labs
- Checking medicine history
- Monitoring medical reimbursement claim status
- Accessing referral details
- Locating nearby wellness centers
- Staying updated with news and highlights, and
- Finding nearby impaneled hospitals, labs, and dental units.
- Additionally, users can access the contact details of wellness centers and offices conveniently.
- To ensure data security, the app also features security measures such as two-factor authentication and mPIN function to be able to access the app once they are logged in.
- Users on the Apple ecosystem can find the app on the App Store and download it free of charge.
- The myCGHS app has been available for Android users since February 2022.
Key Highlights of the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS):
- CGHS provides healthcare services to registered employees and pensioners of the Central Government of India.
- Enrolled members receive reimbursement and cashless healthcare facilities through this scheme.
- It encompasses healthcare services from various systems of medicine including Allopathy, Homeopathy, Ayurveda, and Unani.
- CGHS beneficiaries have the flexibility to undergo treatment at any impaneled private hospital of their preference.
Ahobilam Temple

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Forest Department and Sri Lakshmi Narasimha Swamy Devasthanam (SLNSD) at Ahobilam have imposed certain restrictions on visitors arriving at the shrine, which is composed of nine different temples, situated within the Nallamala forest.
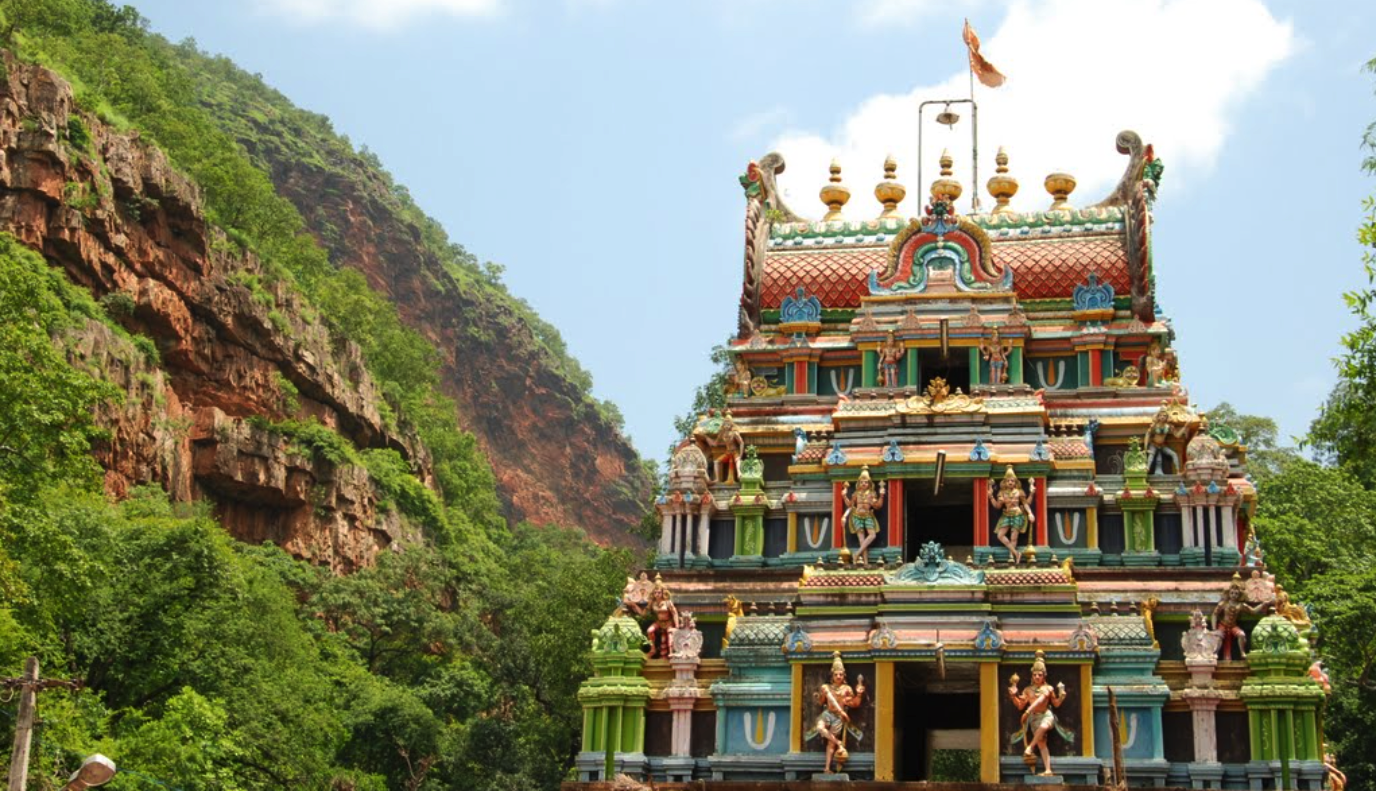
About Ahobilam Temple:
- The Ahobilam is a famous temple situated on the Nallamalai ranges in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The Nallamalai ranges south of river Krishna, down to Tirupati, and are called `Sesha Parvatha`.
- Sesha is the name of the king of serpents.
- The hood of the sesha is at Tirupati, the tail is at Srisailam, and the middle is situated at Ahobilam.
- Nallamalais at the tail are called Sringiri
- In the middle are called Vedagiri and
- Garudagiri referred to as the hood
- The shrine of the Ahobilam temple is situated on the top of the first range and is referred to as Upper Ahobilam and down below is called Lower Ahobilam.
- A huge temple surrounded by several buildings can be seen at the Upper Ahobilam.
- The main shrine or the "sacro sanctum" at Upper Ahobilam was carved out of a big egg-like rock with mandapams.
- There is a tank here, which supplies water to the residents of the Upper Ahobliam temple.
- There is a Lower Ahobilam in the below with a big temple and enclosures, It was built according to the South Indian style (Dravidian architecture).
Significance:
- Ahobilam is traditionally regarded as the place where Vishnu in the form of Narasimha killed the Rakshasa Hiranyakashipu to save his devotee Prahlada.
- The legend says that Narasimha emerged from a rock pillar to slay the Rakshasa.
- The moment is represented in several murtis in the various temples.
- Also, Garuda prayed for a vision of Narasimha in the form of Avathara, to fulfill his wish, and settled in nine forms across the hills in Ahobilam.
About Nallamala Forest:
- Nallamala Forest is among South India's largest expanses of untouched woodland, besides the Western Ghats.
Location:
- Situated across five districts in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, it sprawls across the Nallamala Hills, a segment of the Eastern Ghats, south of the Krishna River.
- Part of the forest falls within the Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, the nation's largest tiger reserve, boasting a significant tiger population.
Climate:
- Experiencing warm to hot conditions year-round, with scorching summers and mostly cool, dry winters.
- The majority of rainfall occurs during the southwest monsoon.
Vegetation:
- Tropical dry deciduous.
Flora:
- Nallamala Forest is rich in endemic species like Andrographis nallamalayana, Eriolaena lushingtonii, Crotalaria madurensis var, Dicliptera beddomei, and premna hamitonii.
Fauna:
- Home to over 700 animal species, including tigers, leopards, black bucks, wild hogs, peacocks, pangolins, Indian Pythons, King Cobras, and numerous rare bird species.
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Uttarakhand government has constituted two teams of experts to evaluate the risk posed by five potentially hazardous glacial lakes in the region.
What is Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)?
- A GLOF denotes the sudden release of meltwater from a moraine or ice-dammed glacial lake, typically due to dam failure.
- These events pose significant hazards, often resulting in catastrophic flooding downstream, leading to substantial loss of life and property.
- GLOF can be triggered by several factors, including earthquakes, heavy rains, and avalanches.
Key Features of GLOFs:
-
- Sudden water releases.
- Rapid occurrences lasting hours to days.
- Large downstream river discharges.
Threats Posed by GLOFs in the Himalayan Regions:
- Climate Change Impact: Climate change-induced glacier melt accelerates the formation or expansion of glacial lakes, heightening the risk of GLOFs.
- Vulnerability of Moraines and Dams: Glacial lakes situated behind unstable moraines or natural dams are prone to breaching, as evidenced by events like the Kedarnath floods in 2013.
- Immediate Flood Risks: Abrupt water releases trigger massive floods, causing extensive damage to homes, and infrastructure, and triggering landslides and sedimentation.
Mitigation Strategies for GLOFs:
- Risk Assessment and Zonation: Identify high-risk areas and implement necessary mitigation measures, including mapping and modeling, as outlined in the 'Guidelines for Preparation of Disaster Management Plans for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOF)'.
- Early Warning Systems: Establish monitoring networks with sensors to detect changes in glacial lakes and provide timely warnings to vulnerable communities.
- Utilization of Technology: Leverage remote sensing and GIS-based tools for monitoring glacial lakes and surrounding areas.
- Regulation of Construction: Implement construction codes to regulate development in high-risk zones, exemplified by the 'Guidelines for the Construction of Earthquake Resistant Buildings' developed by the NDMA.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Enhance skills and resources through training programs conducted by institutions like the National Centre for Disaster Management, in collaboration with the private sector and NGOs.
- Infrastructure Development: Invest in infrastructure to redirect potential floodwaters away from communities and critical infrastructure.
The Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA)

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Officials recently emphasized that India's shrimp export value chain is certified by the Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA), ensuring that abusive conditions are not tolerated at shrimp farms.
About the Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA):
- The Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA) was set up by an act of Parliament in 1972.
- The erstwhile Marine Products Export Promotion Council established by the Government of India in September 1961 was converged into MPEDA on 24th August 1972.
- MPEDA is given the mandate to promote the marine products industry with special reference to exports from the country.
- It is the nodal agency for the holistic development of the seafood industry in India to realize its full export potential as a nodal agency.
- Based on the recommendations of MPEDA, the Government of India notified new standards for fishing vessels, storage premises, processing plants, and conveyances.
- MPEDA’s focus is mainly on Market Promotion, Capture Fisheries, Culture Fisheries, Processing Infrastructure & Value addition, Quality Control, Research and Development.
- It is envisaged that this organization would take all actions to develop and augment the resources required for promoting the exports of “all varieties of fishery products known commercially as shrimp, prawn, lobster, crab, fish, shellfish, other aquatic animals or plants or part thereof and any other products which the authority may, by notification in the Gazette of India, declare to be marine products for (the) Act”.
- The Act empowers MPEDA to regulate exports of marine products and take all measures required for ensuring sustained, quality seafood exports from the country.
- MPEDA is given the authority to prescribe for itself any matters that the future might require for protecting and augmenting the seafood exports from the country.
- It is also empowered to inspect marine products, their raw materials, fixing standards, specifications, and training as well as take all necessary steps for marketing the seafood overseas.
Major Functions of MPEDA:
-
- Infrastructure registration for seafood export trade.
- Trade information collection and dissemination.
- Promotion of Indian marine products overseas.
- Assistance for infrastructure development and modernized processing.
- Aquaculture promotion for export production augmentation.
- Deep-sea fishing project promotion and equipment upgrade.
- Market promotion and publicity activities.
- Inspection of marine products and raw materials, setting standards.
- Training for fishermen, fish processing workers, and aquaculture farmers.
- Research and development through RGCA.
- Extension activities through NETFISH and NaCSA.
- Matters related to protecting and increasing seafood exports.
- Headquarters of MPEDA is located in Kochi, Kerala.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It has Trade Promotion offices in New Delhi, Tokyo, and New York.
