Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS)

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exporters seeking to avail duty concessions on shipments to the UK will have to adhere to the new British rules under the Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS).
What is the Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS)?
- The Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS) is a preferential trading scheme introduced by the United Kingdom to promote trade with developing countries and support their economic growth.
- The DCTS is designed to support sustainable growth in these countries through a more generous unilateral offer compared to the current Generalised Scheme of Preferences (GSP).
Key provisions of the DCTS include:
- Tariff Reduction: Lowering tariffs facilitates easier exportation of goods from developing countries to the UK market.
- Liberalized Rules of Origin: Simplifying rules of origin requirements streamlines trade between developing nations and the UK.
- Simplified Conditions: The scheme's conditions are simplified to facilitate easier access for developing nations.
- The DCTS extends to countries currently benefiting under the UK's GSP, encompassing 47 Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and 18 additional low-income (LIC) and lower-middle-income (LMIC) countries or territories identified by the World Bank.
- However, it excludes countries classified as upper-middle income by the World Bank for three consecutive years or those with a free trade agreement (FTA) with the UK.
- The UK government's policy response to the DCTS introduction is structured into four sections, addressing rules of origin, tariffs, goods graduation, and scheme conditions.
- Overall, the DCTS signifies the UK's commitment to bolstering trade opportunities and sustainable growth in developing countries by providing improved market access and favorable trade terms.
Significance For India:
- The Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS) has significant implications for India, as it offers preferential access to the United Kingdom's market.
- India, being classified as a lower-middle-income country by the World Bank, is eligible to benefit from the DCTS.
- Trade opportunities: The scheme provides reduced or eliminated tariffs on various goods, making it easier for Indian exporters to access the UK market.
- This results in enhanced trade opportunities and increased competitiveness for Indian products.
- Economic growth: By improving access to a major global market, the DCTS can contribute to India's economic growth, creating jobs and boosting the country's export sector.
- Diversification: The scheme encourages Indian businesses to diversify their export portfolio, helping to reduce reliance on specific sectors or trading partners.
- Sustainable development: Through its focus on promoting sustainable development and economic growth in participating countries, the DCTS aligns with India's own goals to foster inclusive and sustainable economic progress.
Overall, the DCTS presents a positive outlook for trade between India and the UK. It offers Indian exporters improved access to the UK market, reduced trade barriers, and a conducive environment for sustainable growth. India can leverage the opportunities provided by the DCTS to strengthen its trade relationship with the UK and potentially increase its exports, benefiting its economy and the livelihoods of its people.
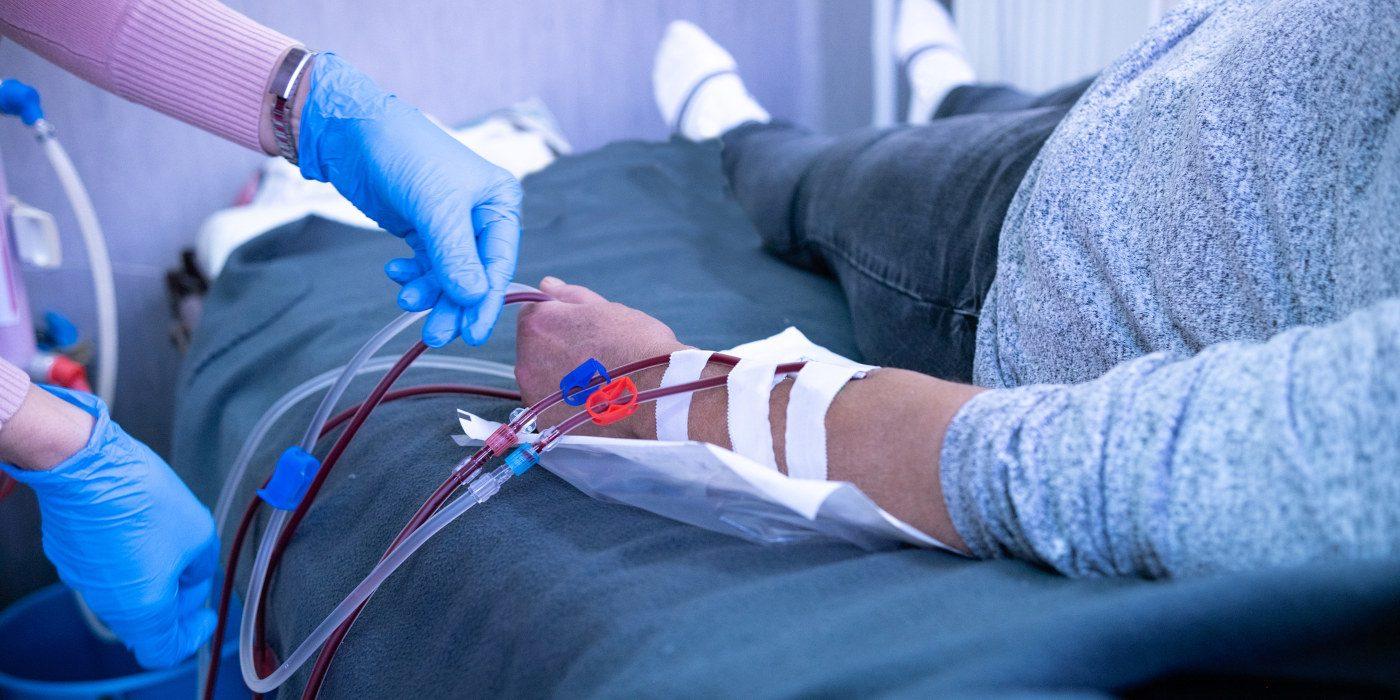
Haemodialysis
- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Findings from a nationwide private hemodialysis network show that there is a variation in the survival of patients receiving hemodialysis in India depending on various factors, and stress on the need to standardize dialysis care across centers.
What is Hemodialysis?
- Haemodialysis, also known as dialysis, is a medical procedure that helps individuals with kidney failure by removing waste products and excess fluid from their blood.
- This procedure essentially performs the functions of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste and maintaining the body's electrolyte balance.
Key points about hemodialysis:
- Process: During hemodialysis, a patient's blood is circulated through a machine with a semipermeable membrane, called a dialyzer or an artificial kidney.
- The dialyzer filters out waste products, such as urea and creatinine, and excess fluid from the blood, which is then discarded, while essential components are returned to the patient's bloodstream.
- Access: To perform hemodialysis, a patient typically requires vascular access, which is a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein, usually in the arm.
- This connection allows for the efficient flow of blood from the patient to the dialysis machine and back.
- Duration: Haemodialysis treatment typically lasts for around 3-5 hours and is performed several times per week, depending on the patient's needs and kidney function.
- Indications: Haemodialysis is prescribed for patients with end-stage kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), who need immediate intervention while waiting for a kidney transplant or when a transplant is not a suitable option.
- Side effects: Some common side effects of hemodialysis include low blood pressure, muscle cramps, itching, and fatigue.
- Complications such as infection, access problems, and blood clotting may also occur, but these risks can be minimized with proper medical supervision and management.
- In summary, hemodialysis is a life-sustaining treatment for patients with kidney failure, offering a means to maintain their health and well-being despite the loss of kidney function.
SAKHI App To Assist Gaganyaan Crew

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) facility at Thumba in Thiruvananthapuram, has developed a multi-purpose app that will help astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission carry out a range of tasks such as looking up vital technical information or communicating with one another.
About SAKHI App:
- The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), an ISRO facility in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, has created the versatile 'SAKHI' app for astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission.
- SAKHI stands for 'Space-borne Assistant and Knowledge Hub for Crew Interaction'.
Purpose:
- During the mission, the app will assist Gaganyaan crew members in various tasks such as accessing vital technical information and communicating with each other.
Utility:
- Health Monitoring: It will monitor key health parameters like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, providing crucial insights into the crew's physical condition during the mission.
- Additionally, it will remind them of hydration, dietary schedules, and sleep patterns.
- Connectivity:
- Astronauts can use the app to maintain mission logs in various formats, including voice recordings, texts, and images.
- It will ensure seamless communication between the crew, the onboard computer, and ground-based stations.
- Current Status: An engineering model of the custom-built hand-held smart device featuring SAKHI has been tested, with the development of a flight model underway.
About the Gaganyaan Mission:
- The primary objective of the mission is to demonstrate the capability to launch and safely return three crew members to low Earth orbit.
- The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) is designated as the launch vehicle for the Gaganyaan mission.
- Crew Escape System (CES): A vital component of the mission, CES is powered by quick-acting, high-burn rate solid motors.
- It ensures the safe evacuation of the Crew Module and crew in case of emergencies during launch or ascent.
- Orbital Module: Comprising the Crew Module (CM) and Service Module (SM), the Orbital Module orbits the Earth, providing safety and support throughout the mission phases.
- Crew Module (CM): Designed to offer a habitable space with Earth-like conditions for the crew during their time in space.
- Service Module (SM): This module supports the CM during orbit, containing essential systems such as thermal, propulsion, power, avionics, and deployment mechanisms.
- This will mark ISRO's inaugural manned spaceflight mission, joining the ranks of the US, Russia, and China, which have previously conducted human spaceflights.
Nilgiris Forest Fire

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has deployed its assets to aid the local administration in dousing the raging forest fire that started recently in Tamil Nadu's Nilgiris district.
What is a Forest Fire?
- A forest fire, also known as a wildfire, is an uncontrolled fire that occurs in forested areas or other vegetated landscapes.
- These fires can spread rapidly, fueled by dry vegetation, high temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds.
- Once ignited, they can quickly grow in size, consuming vast areas of land, vegetation, and wildlife habitat.
- Wildfires pose significant risks to human safety, property, ecosystems, and air quality.
Causes of Forest Fire:
- Forest fires are caused by Natural causes as well as man-made causes.
- Natural causes: Many forest fires start from natural causes such as lightning which sets trees on fire.
- However, rain extinguishes such fires without causing much damage. High atmospheric temperatures and dryness (low humidity) offer favorable circumstances for a fire to start.
- Man-made causes: Fire is caused when a source of fire like naked flame, cigarette or bidi, electric spark, or any source of ignition comes into contact with inflammable material.
- Natural causes: Many forest fires start from natural causes such as lightning which sets trees on fire.
Types of forest fire:
- Surface Fire: This type of forest fire spreads primarily along the ground, consuming surface litter such as dry leaves, twigs, and grasses.
- The flames engulf the forest floor as they advance.
- Underground Fire: Underground fires, also known as muck fires, burn with low intensity beneath the surface, consuming organic matter and surface litter.
- These fires often spread slowly and can continue burning for months, destroying vegetative cover.
- Ground Fire: Ground fires occur in sub-surface organic fuels such as duff layers under forest stands or organic soils of swamps.
- They burn herbaceous growth and organic matter beneath the surface, often transitioning from smoldering underground fires.
- Crown Fire: Crown fires involve the burning of the crowns of trees and shrubs, sustained by a surface fire.
- They are particularly hazardous in coniferous forests, where resinous material can fuel intense flames.
Frequency of Forest Fire in India:
- Seasonality: Forest fires in India are prevalent from November to June, with peak activity typically occurring in April and May, encompassing both small-scale and large-scale incidents.
- Vulnerability: The 2019 India State of Forest Report (ISFR) highlighted that over 36% of the country's forest cover is susceptible to frequent fires, with 4% categorized as extremely prone and an additional 6% as highly fire-prone.
- Affected Regions: Dry deciduous forests experience severe fires, with Northeast India, Odisha, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Uttarakhand being particularly vulnerable areas.
- Recent Incidents: Notable fire outbreaks occurred in 2021 across Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Nagaland-Manipur border, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, including wildlife sanctuaries.
- In 2023, Goa faced large bushfires under investigation for potential human causes.
- 2024 Trends: Recent reports indicate heightened fire activity in Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Meghalaya, and Maharashtra, with increased incidents along the Konkan belt, coastal Gujarat, southern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, coastal Odisha, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Southern India: While Andhra Pradesh and Telangana witness fire incidents, forests in southern India, primarily evergreen or semi-evergreen, are less prone to fires, although Tamil Nadu has experienced recent wildfires.
Reasons Behind This Year's Fires:
- Climate Factors: Dry conditions, high temperatures, clear skies, and light winds have fueled forest fires in southern India.
- Temperature Trends: February 2024 was exceptionally hot, making it the hottest month in southern India since 1901.
- Heat Accumulation: Above-average temperatures over the past months led to a buildup of heat, drying out biomass in forests ahead of the summer season.
- Excess Heat Factor: Western Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are experiencing higher-than-normal EHF values, increasing the risk of heat waves.
- Mild Aridity: Lack of rain and high temperatures have classified most districts in southern India as mildly arid.
World Air Quality Report 2023

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India had the third worst air quality out of 134 countries in 2023 after Bangladesh and Pakistan according to the World Air Quality Report 2023 by IQAir.
About World Air Quality Report 2023:
- The World Air Quality Report is an annual publication by IQAir, a Swiss air quality monitoring firm.
- The report provides an in-depth analysis of global air quality, shedding light on the impact of air pollution on human health and the environment.
Key highlights from the report include:
- India ranks third in poor air quality: With an average annual particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) concentration of 54.4 micrograms per cubic meter, India trails only Bangladesh and Pakistan in terms of poor air quality.
- South Asian dominance in pollution rankings: Bangladesh and Pakistan occupy the top two positions in the air pollution rankings, while ten out of the eleven most polluted cities in the world are in India.
- Delhi's alarming status: For the fourth consecutive year, Delhi has been identified as the world's most polluted capital city.
- Additionally, Bihar's Begusarai has been termed the world's most polluted metropolitan area.
- India's widespread exposure: An overwhelming 96% of the Indian population experiences PM2.5 levels more than seven times the WHO annual PM2.5 guideline, emphasizing the need for urgent interventions to mitigate the health impacts of air pollution.
What is Particulate Matter (PM)?
- Particulate Matter (PM) is a term used to describe a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
- These particles can be made up of various components such as dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and organic chemicals.
- They are classified based on their size, with PM2.5 and PM10 being the most commonly referenced categories.
- PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less, which is about 30 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
- These particles are produced by various sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and wildfires.
- Due to their small size, they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, posing significant health risks.
- PM10, on the other hand, refers to coarse particulate matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less.
- These particles are larger and primarily originate from activities such as construction, road dust, and agricultural practices.
- While not as harmful as PM2.5, they can still enter the respiratory system and cause health problems.
