Kiru Hydropower Corruption Case: CBI Searches J&K Ex-Governor Satya Pal Malik’s Premises

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The CBI conducted searches at the premises of former Jammu and Kashmir governor Satya Pal Malik and 29 other locations recently in connection with alleged corruption in the Rs 2,200-crore Kiru Hydropower project.
What are the Corruption Allegations Surrounding the Kiru Hydel Project?
- During his tenure as the governor of Jammu and Kashmir from August 23, 2018, to October 30, 2019, Satya Pal Malik claimed that he was offered a Rs 300-crore bribe to approve two files, one of which pertained to the project.
- In 2022, the J&K government requested a CBI investigation into alleged misconduct, previously highlighted by Satya Pal Malik, in the awarding of two government contracts.
- Concerns have been raised regarding the award of civil works, particularly to Patel Engineering Ltd, a prominent infrastructure and construction company established in 1949.
- The CBI has initiated action against the former CVPPPL chairman, MD, and Directors, as well as Patel Engineering.
- According to the FIR, an inquiry by the J&K Anti-Corruption Bureau and the Power Department had been conducted.
- The FIR alleges non-compliance with e-tendering guidelines in the awarding of civil works for the project.
- Additionally, accusations of substandard work and failure to employ local youth have been levelled against the hydel project.
What is the Kiru Hydel Power Project?
- The 624MW Kiru hydroelectric project is being developed as a run-of-river scheme in the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory in India.
- Location of the Kiru project: The Kiru hydropower project is being built along the Chenab River near the villages of Patharnakki and Kiru, approximately 42 km from Kishtwar.
- It will be located between the Kirthai II hydroelectric project to its upstream and the Kwar hydroelectric project to its downstream.
- The project is being developed by the Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPPPL) joint venture (JV) between:
- National Hydroelectric Power (NHPC, 49%)
- Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development (JKSPDC, 49%) and
- The Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%)
- The Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) awarded environmental clearance for the hydroelectric project in 2016 while the foundation stone was laid in February 2019.
- The project is being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 4,287 crore and is expected to start commercial operations in July 2025.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the investment in the project in March 2019.
- Apart from helping address the energy demand across northern India and the state’s rural areas, it could aid small-scale and cottage industries.
Advantages of the Kiru Hydroelectric Power Project:
- This project aims to alleviate the energy shortage in Northern India while also enhancing the transportation, education, healthcare, and road infrastructure in the area.
- By bringing electricity to rural communities, the project will lessen the reliance of residents on alternative energy sources.
- The heightened power availability will foster the growth of small-scale and cottage industries, generating employment opportunities and revenue for the local populace.
What is a Run-of-river Project?
- Run-of-river hydropower is a facility that channels flowing water from a river through a canal or penstock to spin a turbine.
- Typically a run-of-river project will have little or no storage facility.
- Run-of-river provides a continuous supply of electricity (base load), with some flexibility of operation for daily fluctuations in demand through water flow that is regulated by the facility.
Race to the global eradication of Guinea worm disease nears the finish line
- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
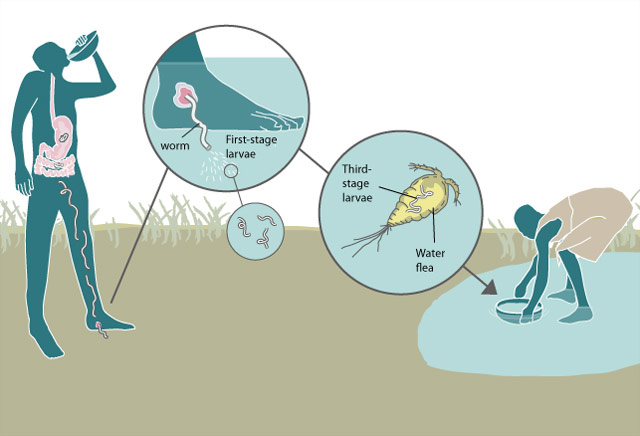
The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease. There were more than 3.5 million cases of this disease in the 1980s, but according to the WHO, they dwindled to 14 cases in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just six in 2023.
What is Guinea Worm Disease?
- Dracunculiasis is also called guinea worm disease (GWD).
- It is an infection caused by a parasite called Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm).
- This parasite is an organism that survives by deriving nutrients and feeding off another organism.
- GWD spreads through drinking contaminated water.
- It is presently eradicated in most parts of the world but is still seen in remote parts of Africa and some remote rural areas in the world where there is no access to clean drinking water.
- GWD is considered endemic in three African countries, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Mali.
- In recent years, a few cases of GWD in animals, especially dogs, have been reported in developed countries as well.
- GWD is a serious condition, that causes debilitating pain and complications, affecting the quality of life
Symptoms:
- People infected with Guinea worm don’t typically have any symptoms until about a year after they're first infected.
- It’s not until the worm is about to erupt from the skin that people start to feel sick.
- What that happens, the symptoms of Guinea worm disease can include Fever, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhoea, Shortness of breath, Burning, itching, pain, and swelling where the worm is in the body (often the legs and feet) and Blister where the worm breaks through the skin.
Impact:
- Guinea worm disease isn’t often deadly, but it can cause serious complications, lifelong disabilities, and financial hardship for those involved.
- The pain involved is often so intense that it’s difficult for people to work, go to school, or care for themselves or others.
- This lasts an average of 8.5 weeks, though lifelong disability is common.
Dracunculiasis Treatment:
- There is no vaccine or drug developed to prevent or treat this disease.
- The only means available is the management of the disease which is removing the whole worm and caring for the wound caused by it and avoiding infection in the process or exposure to the guinea worm larvae at all costs, especially by avoiding contaminated drinking water and stagnant water sources.
- Without proper treatment, wounds caused by the worm can become infected by bacteria, leading to sepsis, septic arthritis, and contractures (when joints lock and deform).
- In some cases, these infections become life-threatening.
Earth’s early evolution: Fresh insights from rocks formed 3.5 billion years ago

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exploring ancient cratons such as the Singhbhum Craton in India, alongside similar formations in South Africa and Australia, provides unparalleled insights into the early stages of our planet's development, reaching back approximately 3.5 billion years.
What is Singhbhum Craton?
- The Singhbhum Craton encompasses a vast expanse of rugged terrain, primarily spanning regions in Jharkhand and Odisha, situated between the Chhota Nagpur plateau and the Eastern Ghats.
- Dating back approximately 3.5 billion years, this ancient segment of the Earth's crust offers valuable insights into early geological processes.
- Its oldest rock formations consist predominantly of volcanic and sedimentary rocks, referred to as greenstone successions.
- Greenstones are characterised by submarine volcanic rocks with minor sedimentary components.
- Geologically akin to greenstone belts in South Africa's Barberton and Nondweni regions and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, these areas experienced extensive submarine mafic volcanic activity, rich in magnesium oxide, between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago, with preserved features like pillowed lava and komatiites.
Significance:
- The Singhbhum Craton sheds light on early tectonic activities during the Archaean era, enhancing our understanding of the Earth's formative stages.
- Its distinctive geological characteristics, particularly the presence of greenstone belts, yield invaluable data on surface and atmospheric processes crucial for theorising about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life on Earth.
What are Cratons?
- A craton is a stable and ancient part of Earth's lithosphere that has experienced long-term tectonic and geomorphic stability.
- It is considered to be the nucleus of a continent and is characterised by its thick and cold lithosphere.
- Cratons can undergo destruction, which is defined as a geological process resulting in the loss of craton stability due to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
- The mechanisms responsible for craton destruction include oceanic plate subduction, rollback and retreat of subducting plates, stagnation and dehydration of subducting plates in the mantle transition zone, melting of the mantle caused by dehydration of stagnant slabs, non-steady flow in the upper mantle induced by melting, and changes like the lithospheric mantle.
- Craton destruction can lead to crustal thinning, surface uplift, and the concentration of mineral deposits.
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY)

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Social Justice and Empowerment, being the Nodal Department for the welfare of senior citizens, develops and implements programmes and policies for these groups in close collaboration with State Governments, Non-Governmental Organisations and civil society.
About the Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme to improve the quality of life of the Senior Citizens.
- The project is implemented by the Department of Social Justice and Empowerment.
Aims and Objectives:
- The main objective of the Scheme is to improve the quality of life of Senior Citizens by providing basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and entertainment opportunities and by encouraging productive and active ageing through providing support for capacity building of State/ UT Governments/Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) / local bodies and the community at large.
The components of the AVYAY Scheme are as under:-
-
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC)
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC)
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY)
- Elderline – National Helpline for Senior Citizens
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE)
- Geriatric Caregivers Training
Components of the AVYAY Scheme:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC): Grant aid is provided to Non-Governmental/ Voluntary Organizations for running and maintenance of Senior Citizens' Homes (old age homes), continuous care homes, etc.
- Facilities like shelter, nutrition, medicare and entertainment are provided free of cost to indigent senior citizens.
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC): Grant in aid is released to States/ UTs for the creation of a pool of trained Geriatric Caregivers for senior citizens, for carrying a special drive for Cataract Surgeries for Senior Citizens and State Specific Activities for the welfare of senior citizens, especially who are indigent in the States/UTs.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): To provide for senior citizens, suffering from any age-related disability/infirmity such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and loco-motor disabilities.
- The eligible senior citizens under this component are those who are in the BPL Category or have monthly income up to Rs.15000/.
- Generic and non-generic devices are distributed to the senior citizens through the camps.
- Elderline: National Helpline for Senior Citizens (14567): The Ministry has set up the National Helpline for Senior Citizens to provide free information, Guidance, Emotional Support and field intervention in cases of abuse and rescues.
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE): To promote out-of-the-box and innovative solutions for commonly faced problems, innovative start-ups are identified and encouraged to develop products, processes and services for the welfare of the elderly under this initiative.
- The initiative is implemented through IFCI Venture Capital Funds Ltd. (Investment Manager).
- Geriatric Caregivers Training: To bridge the gap in supply and increasing demand in the field of geriatric caregivers and also to create a cadre of professional caregivers in the field of geriatrics.
- The component is implemented through the National Institute of Social Defence and at present 3,180 geriatric caregivers have been trained.
In a first, CERN scientists carry out laser cooling of Positronium

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a first, an international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
About Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS):
- AEgIS is an experiment at the Antiproton Decelerator facility at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- It is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- In 2018, AEgIS demonstrated the first pulsed production of antihydrogen atoms, by interacting pulse-produced positronium (an atom consisting of only an electron and a positron) with cold, trapped antiprotons.
- The primary scientific goal of the Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) is the direct measurement of the Earth's gravitational acceleration, g, on antihydrogen.
What is Positronium?
- Positronium is a bound state system of a positron and an electron, similar to the hydrogen atom, where an electron orbits around a proton.
- In the case of positronium, the positron and the electron orbit around their common centre of mass.
- The system is unstable, and the two particles eventually annihilate each other, releasing two or more gamma ray photons.
- Positronium has two possible states:
- The singlet state (para-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are antiparallel and the system has a shorter lifetime, and
- The triplet state (ortho-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are parallel, and the system has a longer lifetime.
- Positronium has been studied extensively in experimental and theoretical physics because it provides a simple system for testing quantum electrodynamics (QED) and for studying the properties of matter and antimatter.
- It also has potential applications in fields such as material science, plasma physics, and astrophysics.
What is Antimatter?
- Antimatter shares similarities with ordinary matter, except for its opposite electric charge.
- Often referred to as "mirror" matter, antimatter pairs with ordinary matter particles.
- For example, while an electron possesses a negative charge, its antimatter counterpart is a positron, which carries a positive charge and has the same mass as an electron.
- Positrons, antiprotons, and antineutrons are the antimatter counterparts of electrons, protons, and neutrons, respectively, collectively known as antiparticles.
- These antiparticles can combine to form anti-atoms and theoretically could lead to the formation of antimatter regions within our universe.
- However, the coexistence of matter and antimatter is short-lived due to their tendency to annihilate upon contact, resulting in the release of substantial energy in the form of gamma rays or elementary particles.
- Antimatter, like matter, emerged during the Big Bang.
- Scientists have produced antimatter particles through high-speed collisions in large particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider operated by CERN outside Geneva.
- Additionally, antiparticles are sporadically generated throughout the universe through natural processes.
