El Niño and La Nina
- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Last month, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) forecasted above-normal rain in the upcoming monsoon season in India, with “favourable” La Nina conditions expected to set in by August-September.
What are El Niño and La Nina?
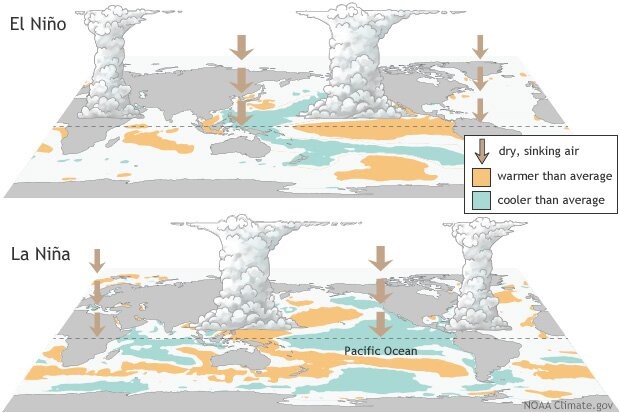
- El Niño (meaning “little boy” in Spanish) and La Nina (meaning “little girl” in Spanish) are climate phenomena that are a result of ocean-atmosphere interactions, which impact the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean which affects global weather.
- The Earth’s east-west rotation causes all winds blowing between 30 degrees to the north and south of the equator to slant in their trajectory.
- As a result, winds in the region flow towards a southwesterly direction in the northern hemisphere and a northwesterly direction in the southern hemisphere which is known as the Coriolis Effect.
- Due to this, winds in this belt (called trade winds) blow westwards on either side of the equator.
- Under normal ocean conditions, these trade winds travel westwards along the equator from South America towards Asia.
- Wind movement over the ocean results in a phenomenon called upwelling, where cold water beneath the ocean surface rises and displaces the warm surface waters.
- At times, the weak trade winds get pushed back towards South America and there is no upwelling.
- Thus, warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures are recorded along the equatorial Pacific Ocean, and this is known as the emergence of El Niño conditions.
- Conversely, during La Nina, strong trade winds push warm water towards Asia.
- Greater upwelling gives rise to cold and nutrient-rich water towards South America.
- Thus, climatologically, El Niño and La Nina are opposite phases of what is collectively called the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- It also includes a third neutral phase.
- El Niño events are far more frequent than La Nina ones.
- Once every two to seven years, neutral ENSO conditions get interrupted by either El Niño or La Nina.
- Recently, La Nina conditions prevailed between 2020 and 2023.
How could the incoming La Nina impact global weather?
- La Niña, driven by the cooling of ocean waters due to the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation) cycle, can significantly influence global weather patterns.
- The air circulation loop in the region, affected by these temperature changes, impacts precipitation levels in neighbouring areas and can alter the Indian monsoon.
- Currently, the El Niño event that began in June last year has significantly weakened.
- Neutral ENSO conditions are expected to be established by June.
- Following this, La Niña conditions are anticipated to emerge, with its effects likely becoming apparent from August.
La Nina’s Impact on India:
- With above normal rain forecast, the seasonal rainfall is expected to be 106 per cent of the Long Period Average (LPA), which is 880mm (1971-2020 average).
- Except in east and northeast India, all remaining regions are expected to receive normal or above-seasonal rainfall.
- Heavy rains could result in some regions witnessing riverine and urban flooding, mudslides, landslides and cloudbursts.
- East and northeast India region, during La Nina years, receive below average seasonal rainfall.
- Therefore, there may be a shortfall in water reserves there this year.
- During La Nina years, incidents of thunderstorms generally increase.
- “The east and northern India regions could experience thunderstorms accompanied by lightning.
- With increased farming activities undertaken during the July and August rainy months, which coincides with the season’s enhanced lightning and thunderstorms, there is a high risk of fatalities in these regions.
- In addition to ENSO, there are other parameters that can impact the monsoon.
- However, in a La Nina year, a deficit monsoon over India can be easily ruled out.
La Nina’s Impact on the World:
- Similar to India, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and their neighbouring countries receive good rainfall during a La Nina year.
- This year, Indonesia has already witnessed floods.
- On the other hand, droughts are common in southern regions of North America, where winters become warmer than usual.
- Canada and the northwestern coast of the United States see heavy rainfall and flooding.
- Southern Africa receives higher than usual rainfall, whereas eastern regions of the continent suffer below-average rainfall.
- ENSO has a huge impact on hurricane activity over the Atlantic Ocean.
- During a La Nina year, the hurricane activity here increases.
- For instance, the Atlantic Ocean churned out a record 30 hurricanes during the La Nina year 2021.
Is Climate Change Affecting ENSO?
- Over India, El Niño is known to suppress the southwest monsoon rainfall and drive higher temperatures and intense heat waves, like the present summer season.
- In the past, monsoon seasons during years following an El Niño were 1982-1983 and 1987-1988, with both 1983 and 1988 recording bountiful rainfall.
- At present too, a similar situation could play out.
- The 2020-2023 period witnessed the longest La Nina event of the century.
- Thereafter, ENSO neutral conditions developed, which soon gave way to El Niño by June 2023 which has been weakening since December last year.
- Scientists say that climate change is set to impact the ENSO cycle.
- Many studies suggest that global warming tends to change the mean oceanic conditions over the Pacific Ocean and trigger more El Niño events.
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has also said that climate change is likely to affect the intensity and frequency of extreme weather and climate events linked to El Niño and La Nina.
Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) will now be open to new members and observers after a historic first charter of the grouping came into force on 20 May.
What is BIMSTEC?
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a multilateral regional organization that brings together seven member states located in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal, forming a contiguous regional unity.
- Aims: The primary aim of BIMSTEC is to accelerate shared growth and cooperation among littoral and adjacent countries in the Bay of Bengal region.
- Formation: The organization was initially founded as BIST-EC in June 1997, following the adoption of the Bangkok Declaration.
- The founding members included Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- With Myanmar's entry in late 1997, the organization evolved into BIMST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- In 2004, the inclusion of Nepal and Bhutan led to the formation of BIMSTEC, as we know it today.
- The current member states comprise five South Asian nations: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, and two Southeast Asian nations: Myanmar and Thailand.
- BIMSTEC's Permanent Secretariat is situated in Dhaka, Bangladesh, serving as a hub for regional cooperation and coordination among member states.
Areas of cooperation:
- BIMSTEC functions as a sector-driven cooperative organization, initially focusing on six key sectors: Trade, Technology, Energy, Transport, Tourism, and Fisheries.
- Over time, the scope of cooperation has expanded, and as of now, BIMSTEC has identified 14 priority areas of cooperation.
- The inclusion of Climate Change in 2008 marked the 14th priority area.
- Within these priority areas, each member country takes responsibility for leading specific sectors.
- This allows for focused efforts and utilization of regional expertise.
- India, for example, is the leading country in several crucial areas, including Transport & Communication, Tourism, Environment & Disaster Management, and Counter-Terrorism & Transnational Crime.
- This leadership role involves coordinating initiatives, sharing best practices, and driving collaborative efforts within these sectors to enhance regional development and cooperation.
Planetary Alignment

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Next month, on June 3, there will be a planetary alignment that may actually allow you to witness six planets align in the sky.
What is a Planetary Alignment?
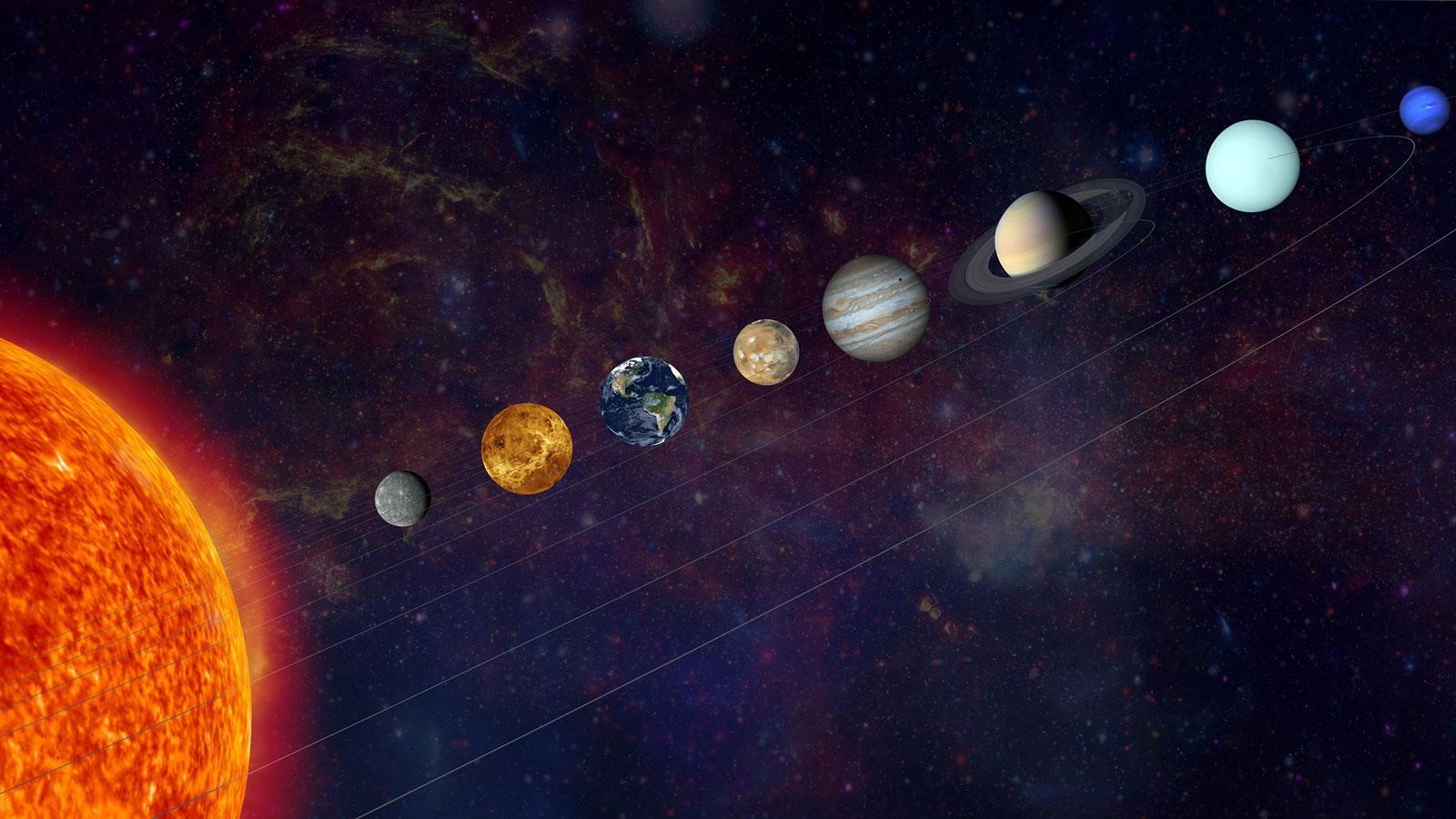
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that's Earth.
- It is an astronomical event that happens when, by coincidence, the orbits of several of the planets of the Solar System bring them to roughly the same side of the Sun at the same time.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- It’s important to emphasise that the planets aren’t forming a straight line in space – that’s a much rarer astronomical event called a syzygy.
- However, because all the planets, including the Earth, orbit around the Sun in roughly the same orientation (moving in which we call the “Plane of the Ecliptic”), when they’re on the same side of the Sun as each other, they appear to form a line in the sky when we view them from Earth.”
- Planetary alignments are rather common within themselves, especially when two, three, or even four planets align in the sky.
- Five or more planets aligning, however, is less common.
- April 8, 2024, was the last time the planets were all in alignment.
Which planets will align?
- Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will form a near-straight line, offering an extraordinary opportunity to witness this cosmic phenomenon.
Which planets will be visible?
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Economic Capital Framework (ECF)

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Central Board of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved a record surplus transfer of Rs 2.11 lakh crore to the Central government for the fiscal year 2023-24, determined based on the Economic Capital Framework (ECF).
What is the Economic Capital Framework (ECF)?
- The Economic Capital Framework (ECF) is an objective, rule-based, transparent methodology for determining the appropriate level of risk provisions (fund allocation to capital reserve) that is to be made under Section 47 of the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) developed an Economic Capital Framework (ECF) for determining the allocation of funds to its capital reserves so that any risk contingency can be met as well as to transfer the profit of the RBI to the government.
- There are two clear objectives for the ECF.
- First, the RBI as a macroeconomic institution has the responsibility to fight any disorder especially a crisis in the financial system. Here, to meet such a crisis, the RBI should have adequate funds attached under the capital reserve.
- Second, is transferring the remaining part of the net income to the government.
- The process of adding funds to the capital reserve is a yearly one where the RBI allots money out of its net income to the capital reserve.
- How much funds shall be added to the capital reserve each year depends upon the risky situation in the financial system and the economy.
- The process of allocation of funds is technically called as provisioning (risk provisioning etc.,) to the reserves.
- After allotting money to the capital reserve, the remaining net income of the RBI is transferred to the government as profit.
- Since the government is the shareholder of the RBI, the latter’s income (means profit) should be transferred to the Government (Section 47 of the RBI Act).
- Previously, there were several attempts to frame an ECF for the RBI. However, under the changed circumstances, the RBI central board constituted a new committee (under Bimal Jalan) to design an ECF in 2018.
What is a Bimal Jalan Committee?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in November 2018 had constituted a six-member committee, chaired by former governor Dr Bimal Jalan, to review the current economic capital framework (ECF), after the Ministry of Finance asked the central bank to follow global practices.
What did the Bimal Jalan Committee Recommend?
- According to the Committee, a better distinction between the two components of RBI's economic capital, realised equity and revaluation balances, was needed.
- The realised equity can be used as a buffer in meeting losses, whereas the revaluation balances will be used only during market risks as they are unrealised valuation gains and cannot be distributed.
- The Committee has recommended the adoption of Expected Shortfall (ES) under stressed conditions for measuring the RBI’s market risk and asked to adopt a target of ES 99.5 per cent confidence level.
- It also asked to maintain a Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB) within 6.5 per cent and 5.5 per cent of RBI's balance sheet.
- The Jalan Committee recommended a surplus distribution policy that follows the realised equity maintained by the RBI.
- The panel also suggested that the RBI’s ECF should be reviewed every five years.
- In August 2019, the Central Board of the RBI, chaired by Governor Shaktikanta Das, finalised the RBI’s accounts for 2018-19 using the revised framework to determine risk provisioning and surplus transfer. According to the reports, the RBI had over Rs 9 trillion of surplus capital with it.
Personality Rights

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Hollywood actress Scarlett Johansson has said she was “shocked” and “angered” to hear the voice of GPT-4o, OpenAI’s latest AI model, as it sounded “eerily similar” to her own voice.
What are Personality Rights?
- Personality rights or publicity rights are a subset of “celebrity rights” – a much broader term used to refer to certain rights enjoyed by celebrities.
- Besides personality rights, celebrities also have “privacy rights”, which include the right to be left alone.
- The name, voice, signature, images, or any other feature easily identified by the public are markers of a celebrity’s personality and are referred to as “personality rights.”
- These could include poses, mannerisms, or any other distinct aspect of their public persona.
- Several celebrities register aspects of their personalities as trademarks to use them commercially.
- For instance, footballer Gareth Bale trademarked the heart shape he makes with his hands as part of goal celebrations.
- The rationale behind such rights is that only the creator or owner of the unique features can gain commercial benefit from them.
- Therefore, unauthorised use could lead to revenue losses.
- In India, actors such as Rajnikanth, Anil Kapoor and Jackie Shroff have approached the courts over “personality rights” in India.
- Recently, the Delhi HC protected the personality and publicity rights of actor Jackie Shroff while restraining various e-commerce stores, AI chatbots, and social media from misusing Shroff’s name, image, voice, and likeness without his consent.
How are Personality Rights Protected in India?
- Although personality rights or their protection are not explicitly defined in Indian statutes, they usually fall under the right(s) to privacy and property.
- Concepts in intellectual property rights cases, such as passing off and deception, are usually applied in such cases while ascertaining if protection is warranted.
- Protection can be given through damages and injunctions.
