Golden trevally Fish

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The golden trevally, a popular marine fish on Tamil Nadu’s coastline, has been successfully bred in captivity by scientists at ICAR-CMFRI’s Visakhapatnam station.
What is Golden trevally Fish?
- The Golden Trevally (Gnathanodon speciosus), also known as the Golden Kingfish or Banded Trevally, is a popular and fascinating marine fish species found in the Indo-Pacific and Eastern Pacific regions.
- It typically inhabits deep lagoons and seaward reefs, often in association with larger fish species.
- This fish is highly sought-after for both consumption and ornamental purposes due to its faster growth rates, good meat quality, and attractive appearance.
- According to fish landing observations in India, golden trevally are primarily landed at reef area fishing grounds in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Kerala, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
About the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI):
- CMFRI was established in 1947 under India's Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It joined the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) in 1967.
The institute's primary objectives include:
- Monitoring exploited marine fisheries resources and assessing under-exploited resources within India's Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Understanding fluctuations in marine fisheries resources in response to environmental changes.
- Developing sustainable mariculture technologies for finfish, shellfish, and other organisms to supplement capture fishery production.
- The CMFRI's notable achievements include developing the "Stratified Multistage Random Sampling Method" for estimating fishery catch and effort along India's 8,000 km coastline.
- Headquartered in Kochi, Kerala, the institute continues to contribute significantly to the growth and development of India's marine fisheries sector.
State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Asia is warming faster than the global average, it is witnessing more extreme weather, climate, and water-related events than any other region across the world.
Highlights of the State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report:
- The 2023 State of the Climate in Asia Report, spearheaded by the World Meteorological Organization, sheds light on significant climate trends and events across the continent:
- In 2023, Asia witnessed 79 extreme climate events, affecting over nine million individuals, making it the most disaster-affected region.
- Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide soared to unprecedented levels in 2022.
- Oceans have absorbed approximately a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted annually into the atmosphere since 1960, resulting in record-high ocean heat content in 2023.
- Tropical cyclone activity over the North Indian Ocean surpassed the average.
- 2023 marked Asia's second-highest mean temperature on record, with Japan and Kazakhstan experiencing record warmth.
- Glacial retreat accelerated in 2023, particularly in the East Himalayas and Central Asia's Tian Shan mountains, due to elevated temperatures and arid conditions.
About the World Meteorological Organisation:
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations with a membership of 193 member states and territories.
- It is the UN system's authoritative voice on the state and behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, its interaction with the oceans, the climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
- WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization, the roots of which were planted at the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23 March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences a year later.
- The Secretariat, headquartered in Geneva, is headed by the Secretary-General.
- Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress.
Psychoanalysis
- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Sudhir Kakar, a pioneering Indian psychoanalyst, author, and cultural critic, passed away on Monday at the age of 85.
What is Psychoanalysis?
- Psychoanalysis is a set of psychological theories and therapeutic methods that focus on the unconscious mind, as well as the role of repressed emotions and desires in shaping behavior and mental health.
- Developed by Sigmund Freud in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, psychoanalysis is based on the idea that many of our thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by unconscious motives and conflicts, often rooted in childhood experiences.
- Psychoanalysis has three core components:
- A method of investigation of the mind and the way one thinks.
- A systematized set of theories about human behavior.
- A method of treatment for psychological and emotional issues.
- Key concepts in psychoanalysis include the id, ego, and superego (the structural model of the psyche), the Oedipus complex, defense mechanisms (such as repression, denial, and projection), and dream interpretation.
- During psychoanalysis therapy, a patient works closely with a therapist to explore and understand unconscious thoughts and feelings, often by discussing dreams, memories, and other experiences.
- The goal is to bring repressed emotions to the surface and address any underlying conflicts in order to alleviate mental distress and improve overall well-being.
- While psychoanalysis has had a significant influence on psychology and mental health treatment, it remains a controversial approach due to its lack of scientific rigor and emphasis on subjective interpretation.
- Nevertheless, many of its concepts have been adapted or integrated into other forms of therapy, and psychoanalysis remains an important part of the history and development of psychology.
Significance:
- It has profoundly impacted the fields of psychology and mental health treatment, as well as culture, literature, and the arts. Its significance can be understood through the following points:
- Foundational Role: Psychoanalysis provided a groundbreaking approach to understanding the human mind and behavior, shifting the focus from conscious experiences to unconscious mental processes.
- Influence on Psychology: Many concepts introduced by psychoanalysis, such as the unconscious mind, defense mechanisms, and the influence of early childhood experiences, have been adopted and adapted by various schools of psychology, including cognitive-behavioral, humanistic, and psychodynamic approaches.
- Therapeutic Approach: Psychoanalysis revolutionized the way mental health issues were treated, moving away from a purely medical model and emphasizing the importance of talking therapy in addressing psychological problems.
- Cultural Impact: The ideas of psychoanalysis have permeated culture, literature, and the arts, influencing our understanding of human motivations, relationships, and emotions. Concepts like Freudian slips, dream interpretation, and the Oedipus complex have become part of everyday language.
- Interdisciplinary Applications: The principles of psychoanalysis have been applied in fields beyond psychology, including sociology, anthropology, literature, and film studies.
- Despite criticisms and revisions, psychoanalysis remains a significant and influential theory that has shaped our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
- It continues to contribute to the development of psychological theories and therapeutic approaches, enriching our comprehension of mental health and human nature.
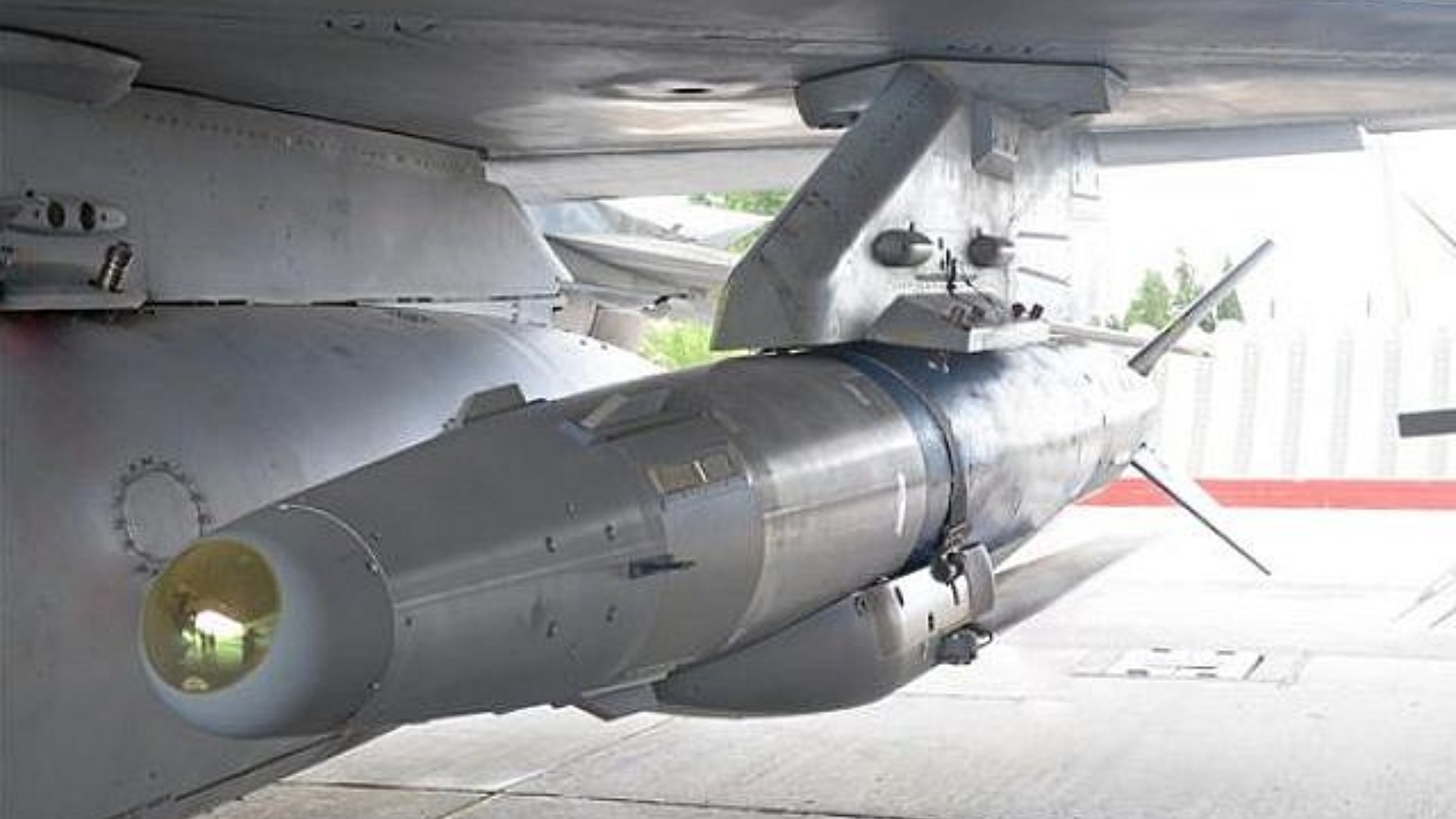
Crystal Maze-2 Missile

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force achieved a milestone by successfully test-firing an air-launched ballistic missile, ROCKS or Crystal Maze 2, capable of hitting targets over 250 kilometers away.
About Crystal Maze-2 Missile:
- Crystal Maze 2 missile also known as ROCKS is an advanced air-launched missile developed by Israel, designed for precision strikes on high-value targets.
- This missile is capable of engaging heavily fortified positions from long distances, ensuring minimal collateral damage.
- It is renowned for its accuracy and reliability in combat scenarios, making it a preferred choice for missions requiring surgical precision.
- The missile’s integration into various platforms enhances its operational flexibility and effectiveness in diverse combat environments.
Features:
- Crystal 2 operates effectively in GPS-denied areas and can breach regions secured by air defense systems.
- This system allows for the choice between penetration or blast fragmentation warheads, making it suitable for targeting both surface and heavily fortified underground facilities.
- With a striking distance of over 250 kilometers, it offers versatility with options for either penetration or blast fragmentation warhead, ensuring the destruction of above-ground or well-protected underground targets.
- India is currently developing the Crystal Maze 2 missile.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative.
- This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
Marburg virus disease (MVD)
- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kitum cave in Mount Elgon National Park, Kenya, is known as the world's deadliest cave which may have some really dangerous viruses inside, like Ebola and Marburg.
What is Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)?
- Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg hemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
- It affects both people and non-human primates.
- Marburg and Ebola viruses are both members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus).
- Though caused by different viruses, the two diseases are clinically similar.
- Both diseases are rare and can cause outbreaks with high fatality rates.
- The average MVD case fatality rate is around 50%.
- Rousettus aegyptiacus, fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family, are considered to be natural hosts of the Marburg virus.
Transmission:
- Human infection with MVD typically occurs after prolonged exposure to Rousettus bats inhabiting mines or caves.
- The virus can then spread through human-to-human transmission via direct contact with infected bodily fluids, contaminated materials, or broken skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms:
- After an incubation period of 2-21 days, symptoms arise abruptly, including fever, chills, headache, and muscle pain.
- A maculopapular rash may appear around day five, most visible on the chest, back, and stomach.
- Other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, chest pain, sore throat, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, can manifest, with severity increasing to potentially include jaundice, organ dysfunction, severe weight loss, delirium, and massive hemorrhaging.
- The average MVD case fatality rate is around 50%, varying between 24% and 88% in past outbreaks.
Treatment:
- There is currently no specific treatment for MVD, but early supportive care involving rehydration and symptom management improves survival rates.
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs):
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fever (VHFs) is a group of diseases caused by several distinct families of viruses that affect multiple organ systems in the body.
- These illnesses range from mild to severe and life-threatening, with many having no known cure or vaccine.
- VHFs negatively impact the cardiovascular system and reduce overall bodily function.
