Ngada Festival

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Rengma Naga tribe concluded a two-day celebration of the Ngada festival-cum-Mini Hornbill Festival at the Tseminyu RSA ground in Nagaland.
Ngada Festival Overview:
- Celebration: It is an annual celebration observed by the Rengma Naga tribe, marking the end of the agricultural cycle.
- Duration: Typically, an eight-day festival, it is celebrated towards the end of November.
- Significance: It is a festival of thanksgiving, joy, and cultural unity, with a focus on gratitude for the harvest and remembrance of departed souls.
Cultural and Ritual Aspects:
- Rituals: The festival involves rituals for protection from misfortunes, such as fire and evil spirits, as well as prayers for peace and prosperity in the community.
- Agricultural Link: The festival is celebrated after the harvest season, symbolizing the end of the agricultural cycle and the beginning of the storage of crops.
- Official Announcement: The village priest announces the start of the festival, and preparations begin shortly after.
Importance of Ngada:
- Gratitude for the Harvest: The festival is a celebration of the hard work of the agricultural year and the bountiful harvest.
- Cultural Identity: The festival serves as a vital reminder of the Rengma Naga’s cultural heritage and traditions, helping to preserve them for future generations.
- Symbol of Unity: It fosters cultural unity and strengthens community bonds within the tribe.
Tribal Demographics:
- Population: The Rengma Naga tribe has a population of around 62,951 in Nagaland and 22,000 in Assam (according to the 2011 Census of India).
- Ethnic Identity: The Rengmas belong to the Tibeto-Burman ethnic group and identify themselves as Njong or Injang.
Historical and Cultural Background:
- Migration: It is believed that the Rengmas, along with other Naga tribes, migrated from Southeast Asia, crossing the Yunnan Mountain ranges, and eventually settled in the upper Burma region.
- Slavery: Historically, slavery was practiced among the Rengmas, with slaves known as menugetenyu and it sakesa. However, by the time the British arrived, slavery was in decline, and no Rengma tribespeople were known to be slaves.
Economy:
- Agricultural Lifestyle: The Rengma Naga are primarily agriculturalists, relying on Jhum cultivation (shifting cultivation) and wet rice cultivation.
- Crops Grown: They grow staple crops like paddy, along with seasonal crops and fruits.
Religion:
- Traditional Beliefs: Traditionally, the Rengma Naga worship supernatural beings.
- Christianity: Today, most of the Rengma tribe has converted to Christianity.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
'Bal VivahMukt Bharat' Campaign

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Minister for Women and Child Development launched the “Bal VivahMukt Bharat” campaign aimed at eradicating child marriage in India.
- Goal: Reduce child marriage rates to below 5% by 2029.
- Focus: Engage multiple stakeholders, raise awareness, and leverage technology for eradication.
Target Areas:
- Target States: West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Tripura, Assam, Andhra Pradesh.
- High-Burden Districts: Nearly 300 districts with higher rates of child marriage.
Child Marriage Free Bharat Portal:
- A digital platform to raise awareness, report cases, and track progress on child marriage prevention.
- Real-time tracking by Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPOs).
Monitoring and Accountability:
- Central nodal officers and CMPOs will oversee the campaign’s implementation at state and district levels.
- The portal facilitates citizens’ participation by allowing complaints and providing information on legal remedies.
Progress and Impact:
- Child marriage rates have reduced from 47.4% (2005-06) to 23.3% (2019-21).
- The goal is to reduce these rates further to below 5% by 2029.
Awareness and Community Engagement:
- Public campaigns and community mobilization to challenge societal norms and change attitudes towards child marriage.
- The campaign will continue through various channels, including the BetiBachaoBetiPadhao initiative.
Legal Framework:
- Strengthening the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006, which sets the legal marriage age at 18 for women and 21 for men.
- Penalties for those involved in child marriage include imprisonment and fines.
Key Challenges for Child Marriage:
- Poverty: Families may view early marriage as a financial relief.
- Cultural Norms: Deep-rooted societal beliefs about preserving family honor.
- Gender Inequality: Patriarchal systems view girls as burdens.
- Lack of Education: Limited access to schooling forces early marriages.
- Fear of Sexual Assault: Misguided belief that early marriage protects girls.
- Weak Law Enforcement: Corruption and inadequate resources hinder the law’s implementation.
- Pandemic Impact: Economic hardships during COVID-19 led to an increase in child marriages.
Related Initiatives:
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006: Strengthens child marriage laws and establishes CMPOs.
- Success Stories: Individuals like BuchaRamanamma, Durga, and Roshni Perween have inspired others by stopping their own child marriages and advocating for change.
Campaign and National Vision:
- The campaign aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision for a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
- It aims to empower women and girls, providing them with opportunities for education, health, and safety.
- Collective effort from the government, social organizations, and citizens is crucial to eliminating child marriage.
Eklavya Digital Platform
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
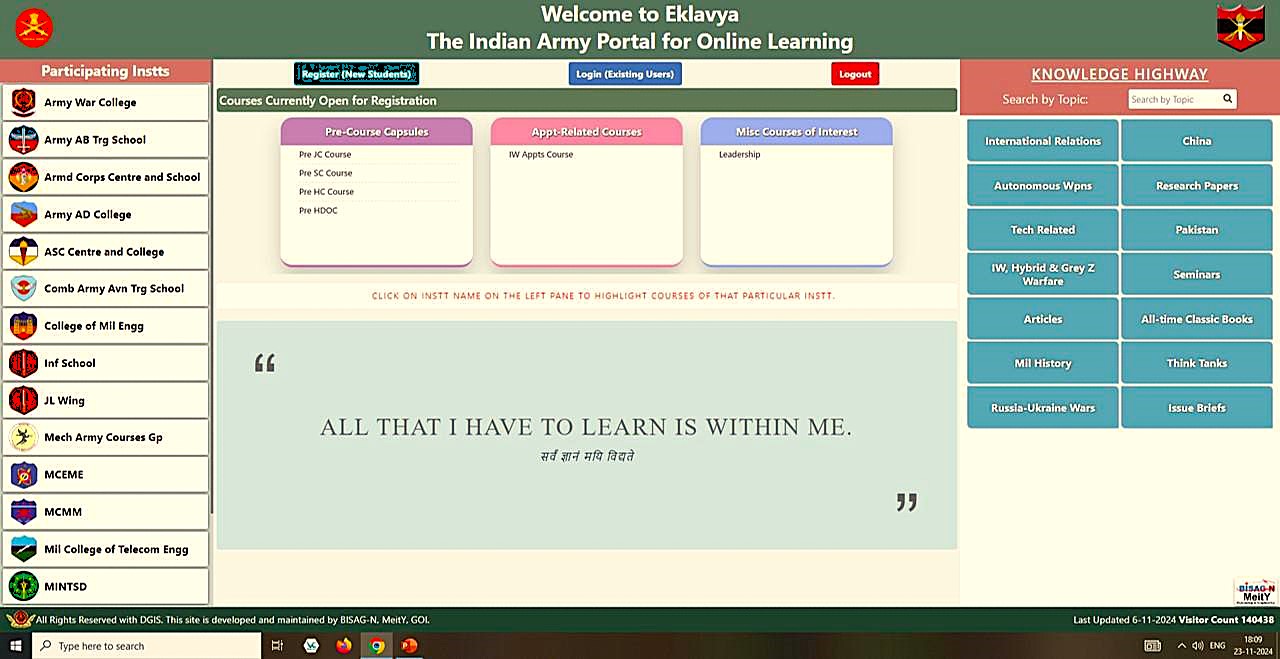
- The Indian Army launched the “Eklavya” online learning platformnmunder the leadership of General Upendra Dwivedi, Chief of the Army Staff (COAS).
- It is part of the Army’s “Decade of Transformation” initiative and aligns with the theme for 2024, “Year of Technology Absorption.”
Platform Development:
- Developed by the Army Training Command (ATC) and sponsored by the Army War College.
- Created at zero cost in collaboration with the Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), Gandhinagar.
- Hosted on the Army Data Network with scalable architecture to integrate various training establishments.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple courses from 17Category ‘A’ Training Establishments of the Army.
- Allows student officers to register for several courses simultaneously.
- Aims to decongest physical courses and integrate contemporary, application-focused content.
Categories of Courses:
- Pre-Course Preparatory Capsules: Online study material for physical courses, allowing focus on contemporary topics during offline training.
- Appointment-Specific Courses: Online courses for officers appointed to specialized roles (e.g., information warfare, financial planning, etc.), helping them gain domain-specific expertise before posting.
- Professional Development Suite: Includes courses on strategy, leadership, operational art, finance, emerging technologies, etc., focusing on holistic officer development.
Knowledge Highway:
- A searchable database featuring journals, research papers, and articles to support continuous professional education and development.
Impact:
- Promotes continuous professional military education.
- Enhances the efficiency and specialization of officers, particularly in emerging domains.
- Streamlines training processes and integrates modern technology in the Army’s educational system.
