RBI tweaks norms related to the Regulatory Sandbox scheme

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank recently tweaked guidelines for the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme under which participating entities will have to comply with digital personal data protection norms.
About the Regulatory Sandbox Scheme:
- The Regulatory Sandbox scheme denotes a controlled regulatory environment where new products or services can undergo live testing.
- Functioning as a "safe space" for businesses, regulators may offer certain relaxations for testing purposes within this environment.
- It serves as a structured platform for regulators to engage with the industry and develop regulations that foster innovation and enable the delivery of cost-effective financial products.
- The scheme holds potential as a tool for creating dynamic regulatory environments that adapt to emerging technologies through evidence-based learning.
Objectives:
- Offering innovative technology-led entities an opportunity for limited-scale testing of new products or services, potentially involving regulatory relaxations before broader implementation.
- At its core, the Regulatory Sandbox is a formal program allowing market participants to test new products, services, or business models in live settings, under appropriate oversight.
- Proposed financial services under the scheme should leverage new or emerging technology to address consumer needs or offer benefits.
- The overarching goal is to promote responsible innovation in financial services, enhance efficiency, and deliver consumer benefits.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the 'Enabling Framework for Regulatory Sandbox' in August 2019 after extensive consultations.
- The updated framework mandates compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act of 2023 for sandbox entities.
- Furthermore, the timeline for various stages of the Regulatory Sandbox process has been extended from seven to nine months.
- Fintech companies, including startups, banks, financial institutions, and other entities providing support to financial services businesses, are among the target applicants for entry into the Regulatory Sandbox.
PM Modi lays stone for India’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam
- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the country’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam in Tuticorin district recently.
About Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- The Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport is a forthcoming space launch facility located in Kulasekarapattinam, a coastal village near the temple town of Tiruchendur in Thoothukudi district, southern Tamil Nadu.
- It will become the second operational spaceport in India after the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, established in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, in 1971, and will feature two launch pads.
- The primary focus of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport will be to facilitate the commercial launch of Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs).
- Spanning 2,350 acres, the spaceport will comprise 35 essential facilities, including a launch pad, rocket integration facilities, ground range and checkout facilities, and a mobile launch structure (MLS) equipped with checkout computers.
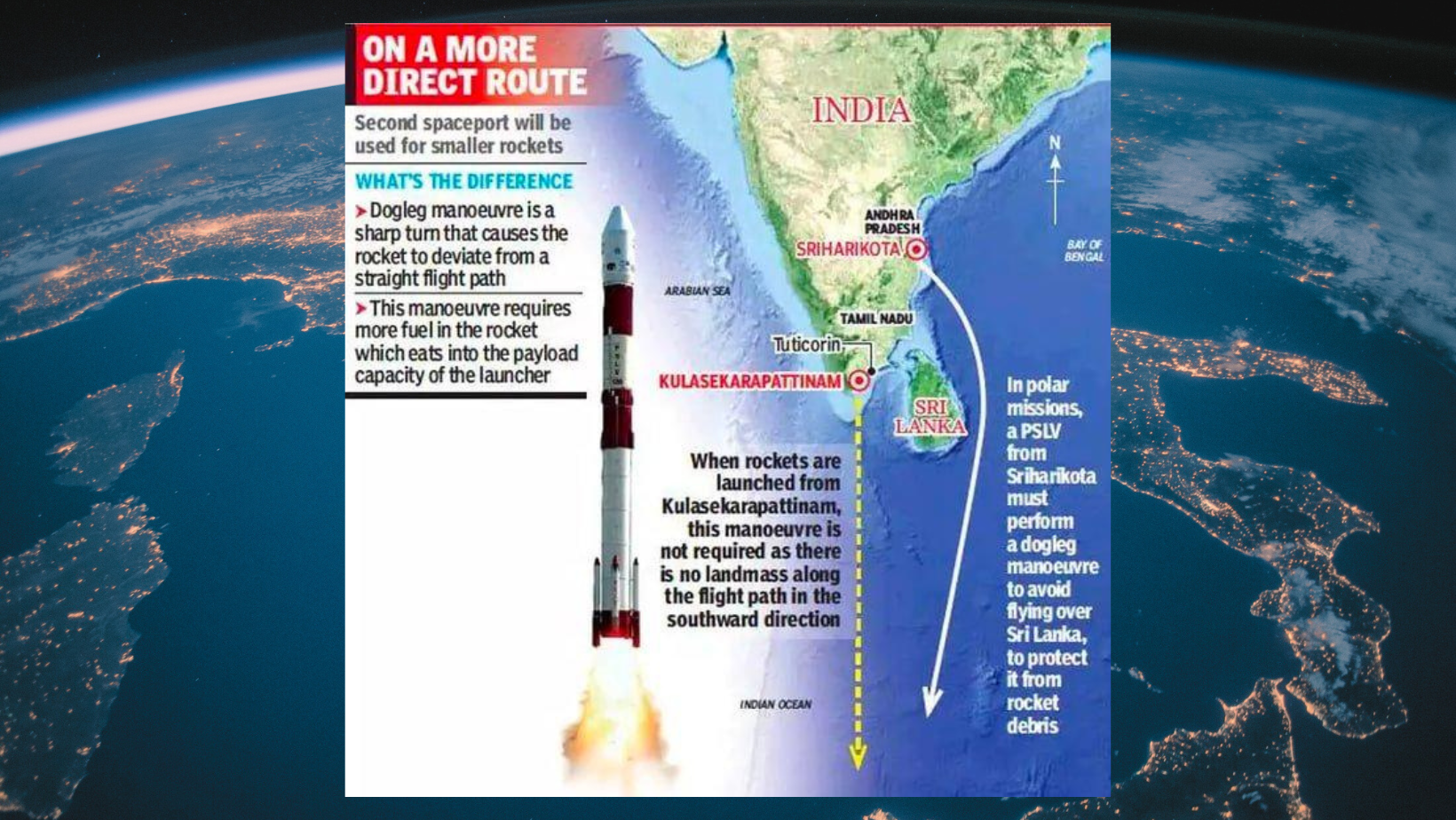
- With the capability to launch up to 24 satellites annually using a mobile launch structure, it offers a strategic advantage by enabling direct southward launches over the Indian Ocean, thus conserving fuel for small rocket launches.
- This stands in contrast to the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, where launching into a polar orbit necessitates additional fuel due to the curved trajectory required to avoid crossing landmasses, particularly Sri Lanka.
- The estimated cost of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport project is Rs. 986 crore.
About the Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs):
- The SSLV, or Small Satellite Launch Vehicle, is a three-stage launch vehicle characterized by three solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) serving as a terminal stage.
- Measuring 2 meters in diameter and 34 meters in length, the SSLV boasts a lift-off weight of 120 tonnes.
- Designed for versatility, the SSLV can effectively launch a 500kg satellite into a 500 km planar orbit.
- Notable features of the SSLV include its cost-effectiveness, rapid turnaround time, ability to accommodate multiple satellites, feasibility for launch-on-demand, and minimal infrastructure requirements.
New waste management technology could improve life in rural India

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new waste management technology that allows pyrolysis at a community level could help rural Indians cut indoor air pollution, improve soil health, and generate clean power, a recent study has claimed.
What is BioTRIG?
- BioTRIG represents a novel waste management technology centered around pyrolysis, poised to mitigate indoor air pollution, enhance soil quality, and foster clean energy generation across rural India.
- This community-oriented pyrolysis system is ingeniously crafted to utilize locally generated waste, offering a sustainable solution tailored to village environments.
- The innovative process yields three valuable by-products: bio-oil, syngas, and biochar fertilizer, presenting multifaceted benefits for rural communities, from cleaner energy sources to enhanced agricultural productivity.
- Moreover, the self-sustaining nature of BioTRIG enables the utilization of syngas and bio-oil to fuel subsequent pyrolysis cycles, with excess electricity catering to local energy needs, fostering self-reliance and sustainability.
- By harnessing the clean-burning properties of bio-oil and the soil-enriching qualities of biochar, BioTRIG empowers rural households to transition away from traditional cooking fuels while concurrently enhancing agricultural resilience and carbon sequestration efforts.
Significance:
- Computer simulations indicate that the BioTRIG system holds the potential to significantly mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from communities, potentially reducing them by nearly 350 kg of CO2-eq per capita per year.
- This projection underscores a noteworthy positive influence on both climate emissions and public health.
- The BioTRIG technology could mark a paradigm shift in waste management practices and energy generation methods within rural India, promising transformative benefits for communities.
What is Pyrolysis?
- Pyrolysis is a transformative chemical recycling method that disassembles residual organic matter into its fundamental molecular components.
- This innovative process entails confining the waste within an oxygen-deprived enclosure and subjecting it to temperatures exceeding 400 degrees Celsius.
Education Minister launches SWAYAM Plus platform

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Dharmendra Pradhan recently launched the ‘SWAYAM Plus’ platform to offer courses developed collaboratively with the industry.
About the SWAYAM Plus Platform:
- SWAYAM is a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform providing educational opportunities by bringing the best teaching and learning resources to everyone.
- Operated by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Madras, this platform aims to extend educational opportunities to both traditional students and working professionals, aligning with the provisions of the NEP 2020 for flexible entry and exit points in education.
- By enabling individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, SWAYAM Plus empowers them to enhance their skills and career prospects, thus contributing to India's knowledge economy.
Objectives and features:
- SWAYAM Plus primarily focuses on achieving the following:
- Building an ecosystem for all stakeholders in professional and career development, including learners, course providers, industry, academia, and strategic partners;
- Enabling a mechanism that provides credit recognition for high?quality certifications and courses offered by the best industry and academia partners;
- Reaching a large learner base by catering to learning across the country, with a focus on reaching learners from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas and Offering employment-focused courses, based on learner needs – across chosen disciplines with options to learn through resources in vernacular languages.
- Enhanced employability: SWAYAM Plus empowers individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, enhancing skills and career prospects.
- Industry partnerships: Courses are tailored to industry requirements in collaboration with industry leaders.
Key features:
- Multilingual content, AI guidance, credit recognition, and pathways to employment are prominent features.
Implementation and reach:
- SWAYAM Plus aims to offer high-quality courses with credit recognition, reaching learners nationwide, especially from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas.
Value-added services:
- Value-added services like mentorship, scholarships, and job placements will be provided, creating a digital ecosystem for upskilling and reskilling at all education levels.
- SWAYAM, launched in 2017, had enrolled 72 lakh learners by 2023.
- Now, in line with the NEP 2020, SWAYAM Plus will incorporate courses tailored to industry requirements, developed in collaboration with industry leaders like L&T, Microsoft, and CISCO.
European Parliament adopts nature restoration law

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Parliament recently adopted the first European Union (EU) law to restore degraded ecosystems across the 27-nation political and economic bloc.
About the Nature Restoration Law:
- The Nature Restoration Law is hailed as a significant stride toward rejuvenating Europe’s natural habitats, with a staggering 81% currently classified as being in poor health.
- It sets a pioneering example for global emulation, emphasizing the criticality of safeguarding and revitalizing our natural environment for the welfare of forthcoming generations.
Objectives:
- This legislation aims to rejuvenate ecosystems, habitats, and species across the European Union's (EU) terrestrial and marine domains, fostering the enduring recuperation of diverse and robust nature.
- Additionally, it endeavors to contribute to the EU's climate mitigation and adaptation objectives while fulfilling international commitments.
- These directives aspire to encompass a minimum of 20% of the EU's land and marine territories by 2030, with the ultimate goal of restoring all ecosystems in need by 2050.
Specific Targets:
- Wetlands, forests, grasslands, rivers, lakes, heath & scrub, rocky habitats, and dunes: The objective is to enhance and restore biodiverse habitats on a large scale, fostering the recovery of species populations through habitat improvement and expansion.
- Pollinating Insects: The target is to reverse the decline of pollinator populations by 2030, aiming for a positive trajectory in pollinator numbers.
- Forest Ecosystems: The aim is to promote an upward trend in standing and fallen deadwood, varied aged forests, forest connectivity, common forest bird populations, and organic carbon reserves.
- Urban Ecosystems: The objective is to achieve zero net loss of green urban spaces by 2030 and expand the total area covered by green urban spaces by 2040 and 2050.
- Agricultural Ecosystems: The goal is to bolster grassland butterfly and farmland bird populations, increase organic carbon reserves in cropland mineral soils, and augment the proportion of agricultural land featuring diverse landscape characteristics.
About the European Union (EU):
- The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 European countries that collaborate on various issues, including trade, security, and environmental protection.
- Founded after World War II to promote peace and economic cooperation, the EU has evolved into a complex organization with its own institutions, laws, and currency (the euro).
- It operates on the principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, with the European Commission, European Parliament, and European Council among its key decision-making bodies.
- The EU's single market allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people across member states, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Additionally, the EU plays a prominent role in global affairs, advocating for multilateralism, sustainable development, and climate action.
