Addressing Vertical Fiscal Imbalance: The Role of the 16th Finance Commission
- 06 Sep 2024
In India, the financial relationship between the Union government and the States is characterized by vertical fiscal imbalance (VFI), where the Union government holds most of the revenue while States shoulder significant expenditure responsibilities. The 16th Finance Commission has a pivotal role in addressing this imbalance. Here's how it should approach the issue:
Understanding Vertical Fiscal Imbalance (VFI)
- Current Situation:
- States incur 61% of revenue expenditure but collect only 38% of revenue receipts.
- States rely heavily on transfers from the Union government, leading to a pronounced VFI.
- VFI Definition:
- VFI arises when the expenditure responsibilities of States exceed their revenue-raising capabilities, necessitating transfers from the Union.
Reasons to Address VFI
- Constitutional Allocation:
- Revenue duties and expenditure responsibilities are constitutionally divided.
- Union government collects Personal Income Tax, Corporation Tax, and part of indirect taxes for efficiency.
- States are better positioned to deliver publicly provided goods and services effectively.
- Historical Context:
- The 15th Finance Commission highlighted that India has experienced a rising VFI, exacerbated by crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Finance Commission's Role:
- The Commission addresses VFI by determining how to allocate taxes collected by the Union to the States and how to distribute these among States.
Finance Commission Recommendations
- Tax Devolution:
- The Commission recommends devolving a portion of Union taxes to States.
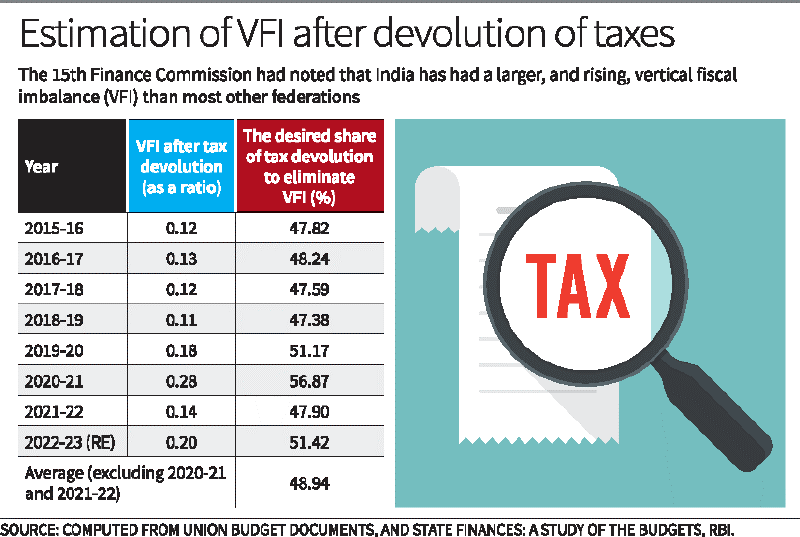
- The 14th and 15th Finance Commissions recommended devolving 42% and 41% of net proceeds, respectively.
- To eliminate VFI, devolution should be around 48.94%.
- Grants and Transfers:
- The Commission also suggests grants under Article 275 for specific purposes.
- Transfers under Article 282, such as centrally sponsored and central sector schemes, are tied and include conditionalities, which are not untied resources.
Calculation and Recommendations for VFI
- Estimating VFI:
- Ratio = (Own Revenue Receipts + Tax Devolution) / Own Revenue Expenditure.
- A ratio less than 1 indicates insufficient revenue to meet expenditure, showing the VFI deficit.
- Empirical Findings:
- To address VFI, the share of net proceeds devolved to States should be around 49%.
- This increase would ensure that States have more untied resources, enhancing their ability to meet local needs and priorities.
Implications of Increased Tax Devolution
- Enhanced State Capacity:
- A higher share of tax devolution would empower States with more resources for untied expenditures.
- It would improve the alignment of State expenditures with local needs and priorities.
- Improved Efficiency:
- Enhanced devolution would lead to better efficiency in expenditure by allowing States to respond more effectively to jurisdictional requirements.
- Strengthened Fiscal Federalism:
- Addressing VFI through increased tax devolution contributes to a more balanced and cooperative fiscal federalism.
Conclusion: The 16th Finance Commission should focus on increasing the share of tax devolution to around 50% to address the vertical fiscal imbalance. This adjustment will provide States with the necessary resources to manage their expenditure responsibilities more effectively and ensure a more equitable distribution of fiscal resources in India’s federal structure.
