Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Researchers from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed an innovative “self-actuating” drug delivery system that targets rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by delivering therapeutic agents only when needed. This approach offers a revolutionary alternative to conventional systemic treatments.
About Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Definition: RA is a chronic autoimmune and inflammatory disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, particularly the joints, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Hands, wrists, and knees — often multiple joints simultaneously.
- Symptoms:
- Inflammation of joint lining
- Chronic pain and joint deformity
- Unsteadiness or balance issues
- May affect lungs, heart, and eyes
- Cause: The exact cause remains unknown, but it involves an immune response attacking the body’s own tissues.
- Traditional Treatment:
- Involves Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate
- Requires frequent dosing
- May lead to systemic side effects and inefficient drug retention
Breakthrough: Self-Actuating Drug Delivery System
Key Features:
- Targeted Drug Release: Releases medication only in response to biochemical signals in the inflamed synovial environment of RA-affected joints.
- Precision and Safety: Reduces side effects by limiting drug release to flare-ups, minimizing exposure to unaffected areas.
- Main Drug Used: Methotrexate, a widely used anti-rheumatic drug.
Mechanism:
- Microspheres are engineered using polymer-lipid hybrid micro-composites:
- Lipid Component (Soya Lecithin): Ensures high drug encapsulation efficiency.
- Polymer Component (Gelatin): Reacts to Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) — enzymes present during RA inflammation.
- Action:
- Enzymes like MMP-2 and MMP-9 increase during RA flare-ups.
- These enzymes cleave the gelatin, triggering controlled, pulsatile release of methotrexate.
- Outcome in Animal Studies:
- Reduced joint swelling and cartilage damage
- Promoted joint repair
- Improved drug bioavailability and retention in joints
Significance
- Improved Patient Outcomes:
- Long-lasting relief with fewer doses
- Reduced systemic toxicity
- Personalized therapy based on inflammation levels
- Enhanced joint function and slower disease progression
- Research Publication: The findings were published in the journal Biomaterial Advances.
Wider Applications
- Potential Use in:
- Other inflammatory conditions like synovitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Veterinary medicine for arthritis in animals
- Regenerative medicine and personalized drug delivery
Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
As of early 2025, 60% of the construction of the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is complete. The telescope is expected to begin its first scientific observations by the end of 2028.
About ELT
The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is poised to become the world’s most powerful ground-based optical and infrared telescope, with revolutionary capabilities to explore the universe.
- Location: Cerro Armazones, Atacama Desert, northern Chile
- Altitude: 3,046 meters above sea level
- Managing Body: European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Project Cost: Approximately $1.51 billion (around 1.3 billion euros)
- Completion Target: Late 2020s
- Primary Mirror: Diameter of 39 meters (128 feet) — the largest of its kind
- Constructed from 798 hexagonal segments, each 1.5 m across and 5 cm thick
Key Scientific Objectives
- Exoplanet Exploration
- Direct imaging of Earth-like exoplanets in habitable zones of nearby stars
- Analysis of atmospheric biosignatures such as oxygen, water vapor, and methane, aiding the search for extraterrestrial life
- Understanding the Early Universe
- Observation of the first stars and galaxies formed post-Big Bang
- Investigation of dark matter and dark energy, crucial for understanding cosmic expansion and the universe’s fate
- Detailed Study of Stars and Galaxies
- Identification and characterization of individual stars in distant galaxies
- Analysis of the formation, evolution, and structure of galaxies over cosmic time
- Black Holes and Cosmic Structures
- Study of supermassive black holes at galactic centers
- Understanding their role in galaxy dynamics and structure
Why Chile’s Atacama Desert?
- Dry Climate: Very low humidity and cloud cover, ensuring clearer skies
- High Altitude: Thin atmosphere reduces atmospheric interference with incoming light
- Minimal Light Pollution: Remote location offers dark skies critical for deep-space observation
- Dome Structure: Protects sensitive instruments from harsh desert conditions
About the European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Nature: Leading intergovernmental science and technology organization in the field of astronomy
- Headquarters: Garching, Germany
- Members: 16 countries including Austria, Belgium, Brazil, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom
- Facilities in Chile:
- La Silla
- Paranal
- Chajnantor
- Mandate: Design, construction, and operation of advanced ground-based telescopes to promote international collaboration and facilitate path-breaking astronomical research
Cabinet Approves Establishment of ‘Third Launch Pad’ at ISRO's Sriharikota Facility

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, has approved the establishment of a Third Launch Pad (TLP) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), located at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This project marks a significant step in enhancing India’s space capabilities and will support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV) for ISRO’s evolving space exploration programs.
Key Features of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP will be built with an adaptable design, capable of supporting NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic propulsion. The launch pad will also serve as a standby for the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Sriharikota. This addition will help ISRO meet its growing launch capacity needs, particularly for future human spaceflight missions and space exploration projects. It will facilitate higher launch frequencies, thus boosting the Indian space ecosystem.
Implementation Strategy and Timeline
The Third Launch Pad is planned to be developed within 48 months (4 years), with the total cost pegged at ?3984.86 Crore. The development will involve maximized industry participation and will utilize existing infrastructure at the launch complex. The project will also leverage ISRO’s experience gained from establishing the earlier launch pads.
The Importance of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP is designed to support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV), a key part of ISRO’s vision for space exploration. The facility will not only accommodate heavier vehicles but will also ensure standby capacity for the Second Launch Pad (SLP). Its strategic location at Sriharikota ensures several advantages:
- Proximity to the Equator: This offers a substantial increase in payload capacity due to the additional push provided by the Earth's rotation.
- Safety and Accessibility: The site is free from major international maritime or airline routes, ensuring a safe flight path.
- Geographical Advantage: The launch pad is situated on the eastern coast, enabling launches in an easterly direction, maximizing the benefits of Earth’s rotational speed.
Future Plans for Indian Space Exploration
The establishment of the Third Launch Pad is crucial for the expanded vision of India’s space program, particularly in line with the Amrit Kaal period. ISRO aims to achieve ambitious milestones, such as the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040. The NGLV will play a pivotal role in these plans, with features like:
- A three-stage vehicle and reusable first stage.
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion, using refined kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will increase payload capacity by three times at 1.5 times the cost of current vehicles.
The Role of Sriharikota in India’s Space Program
Sriharikota, the hub of ISRO’s launch operations, has been integral to India’s space exploration. Currently, the Indian Space Transportation Systems rely on two operational launch pads:
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Established over 30 years ago for PSLV and SSLV missions, FLP continues to support Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Built primarily for GSLV and LVM3 vehicles, SLP also serves as a standby for PSLV. Over its 20 years of operation, SLP has supported several national missions, including Chandrayaan-3, and is preparing for the Gaganyaan missions.
Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Twigstats

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The tracing of genetic ancestry remains a challenging task due to the statistical similarity among populations across geographical regions. However, recent advances in genetic analysis, particularly the development of the Twigstats tool, are significantly enhancing our ability to reconstruct genetic histories at a very high resolution.
Key Insights from Genetic Research:
- Ancient DNA (aDNA): Prehistoric human ceremonial burials, mass grave mounds, and war graves are rich sources of ancient genetic material, offering key insights into population dynamics. These samples help us understand past migrations, cultural transitions, and the genetic legacy of ancient groups.
- Challenges in Ancestry Tracing:
- Populations often share many genetic similarities, complicating the task of tracing ancestry across regions.
- Ancient DNA samples are typically of lower quality compared to modern samples, limiting the precision of past genetic studies.
- The movement of genes across time and space, through processes like gene flow, adds complexity to the understanding of population ancestry.
Traditional Genetic Techniques:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Used to identify natural genetic variations, SNP analysis has been central to reconstructing genetic histories. However, it is limited by its reliance on high-quality samples and struggles with closely related groups.
- Haplotypes and Genealogical Trees: By analyzing shared DNA segments (haplotypes) and rare variants, researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of population structure and ancestry, which can reveal shifts in population over time.
The Emergence of Twigstats:
- What is Twigstats?
- Twigstats is an advanced analytical tool that enhances the precision of ancestry analysis through time-stratified ancestry analysis, a method that allows for a more fine-grained look at genetic data.
- It is designed to address the limitations of traditional methods by integrating SNPs, haplotypes, and rare genetic variants, providing a more holistic view of ancestry.
- The tool is powered by statistical languages R and C++, which help researchers better manage and analyze complex genetic data.
- How It Works: Twigstats builds family trees by analyzing shared genetic mutations, identifying recent mutations that offer a clearer understanding of historical periods and events. It helps trace the evolution of populations and offers insights into their migrations, mixing, and cultural shifts.
Key Features and Impact of Twigstats:
- Time-Stratified Ancestry Analysis: Allows researchers to study how populations evolved over time, with a focus on specific historical periods.
- Enhanced Precision: Reduces statistical errors and enhances the precision of individual-level ancestry reconstruction.
- Higher-Resolution Mapping: Provides high-resolution genetic maps of migration patterns and admixture events across centuries.
Applications of Twigstats:
- Historical Case Studies: The tool has been used to study ancient genomes from Europe, particularly the Iron, Roman, and Viking Ages (500 BC to 1000 AD). It revealed the fine-scale genetic history of populations in regions like northern and central Europe, including the movement of Germanic and Scandinavian peoples.
- Viking Age Insights: Researchers were able to trace the early presence of Scandinavian-like ancestry in regions such as Britain and the Baltic before the traditionally believed start of the Viking Age. This suggests earlier interactions and migrations from Scandinavia, which aligns with historical records of Anglo-Saxon and Viking movements.
- Cultural Transitions: The analysis identified shifts in population genetics corresponding to cultural changes, such as the shift from the Corded Ware culture to the Bronze Age and the influence of the Wielbark culture.
Genetic Methods Used in the Study:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Commonly used to trace ancestry but requires high-quality samples.
- Haplotypes and Rare Variants: Offer more nuanced insights into population movements by considering combinations of genetic markers inherited together.
- Genealogical Tree Inference: Applied to both ancient and modern genomes, it provides detailed demographic and ancestry information, supporting the reconstruction of high-resolution genetic histories.
Case Study: India’s Genetic History (2009 Study)
- Researchers used SNP analysis to trace the genetic history of India, revealing two major ancestral groups:
- Ancestral North Indians (ANI): Genetically closer to Central Asian, European, and Middle Eastern populations.
- Ancestral South Indians (ASI): A distinct genetic group, showcasing India’s diverse population structure.
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
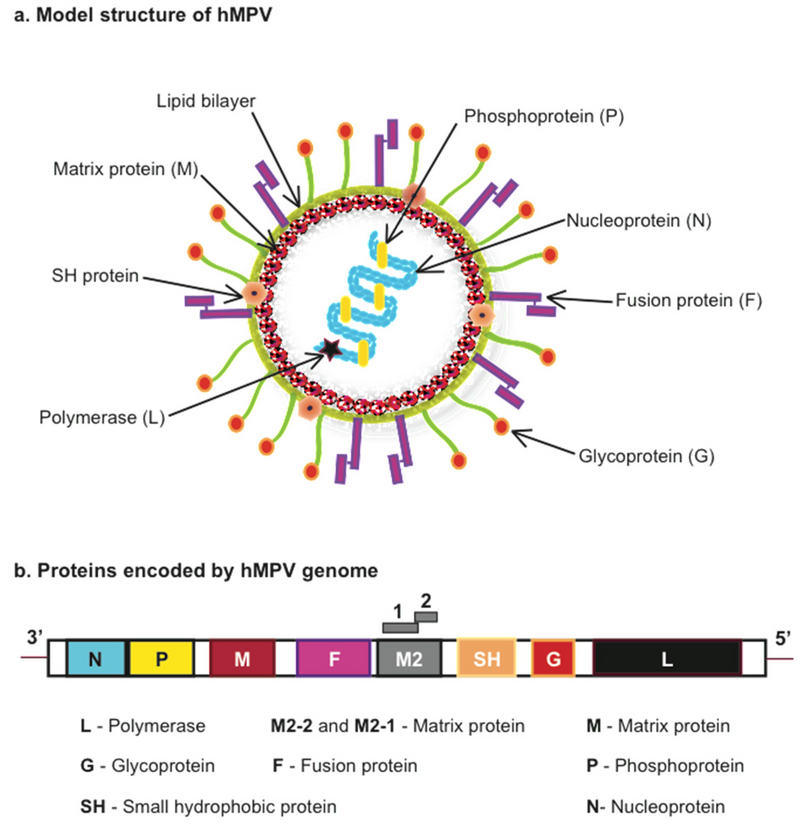
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
Rabbit Fever
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Tularemia, commonly known as "rabbit fever," is a rare but highly infectious bacterial disease caused by Francisella tularensis. Though uncommon, it can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. Over recent years, cases of tularemia have been on the rise in the United States, drawing attention to the broader environmental and epidemiological factors influencing the disease’s spread.
Rising Incidence of Tularemia
Between 2011 and 2022, the United States saw a 56% increase in the annual average incidence of tularemia infections compared to the previous decade, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vulnerable populations include children aged 5 to 9, older men, and individuals of American Indian or Alaska Native descent. The increasing number of reported cases highlights the growing concern over this disease, despite its rarity.
Transmission Pathways
Tularemia is primarily transmitted through:
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: Common carriers include rabbits, hares, and rodents, particularly those infected with Francisella tularensis. This presents a risk for individuals working closely with wildlife, such as hunters.
- Insect Bites: Ticks, especially in regions with high tick populations, and deer flies can spread the disease.
- Contaminated Food or Water: Consuming undercooked meat from infected animals or untreated water can lead to infection.
- Inhalation of Contaminated Dust or Droplets: This is a potential risk in agricultural or laboratory settings and can result in pulmonary tularemia.
Contributing Factors to the Rise in Cases
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of tularemia:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are increasing tick activity and extending breeding seasons, allowing the bacteria to spread more easily.
- Habitat Encroachment: Deforestation and increased human interaction with wildlife are amplifying exposure to infected animals.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Advances in surveillance and testing methods have made it easier to detect tularemia, leading to more reported cases.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tularemia symptoms can vary depending on the route of infection. Symptoms typically appear 3 to 5 days post-exposure and may include:
- Sudden high fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Chills, fatigue, and body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially near the site of infection (e.g., under the arms or in the groin)
There are four primary forms of tularemia:
- Ulceroglandular: Characterized by skin ulcers and swollen lymph nodes.
- Glandular: Swollen lymph nodes without ulcers.
- Pneumonic: Lung infection, often resulting from inhalation.
- Typhoidal: A more systemic form, with symptoms like fever and abdominal pain.
Differentiating tularemia from other conditions such as flu, pneumonia, or lymphadenitis is key for diagnosis. A skin ulcer or swollen lymph nodes in individuals with recent exposure to wildlife or ticks is a critical diagnostic clue.
Treatment and Prognosis
Tularemia is treatable with antibiotics. First-line treatment includes streptomycin or gentamicin, while doxycycline or ciprofloxacin may be used for milder cases. Treatment typically lasts 10 to 21 days, and when initiated promptly, the disease has a high recovery rate and minimal complications. However, untreated cases can lead to chronic infections, lung abscesses, pneumonia, or severe sepsis, with mortality rates of 1-2% under treatment. Untreated severe cases can result in mortality rates between 30% and 60%.
Tularemia in India: A Potential Concern?
Tularemia is extremely rare in India, mainly due to the country's differing ecological conditions and limited interaction with the primary reservoirs of Francisella tularensis. However, awareness remains crucial, especially for individuals traveling to endemic regions or working in wildlife settings. Despite its rarity in India, the rising global incidence and changing environmental factors warrant continued vigilance.
