Will India reassess its position on China-backed Asian trade bloc RCEP? (Business Standard)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is keeping a watchful eye on its neighbour countries’ recent deliberations to join the China-backed Asian trade bloc, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), although the government is yet to “re-evaluate” the position it took four years ago.
What is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)?
- RCEP, or the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, is a proposed agreement involving ASEAN member states and their free trade agreement partners.
- Introduced in 2011, negotiations started in 2012, aiming to finalize the deal by November 2019.
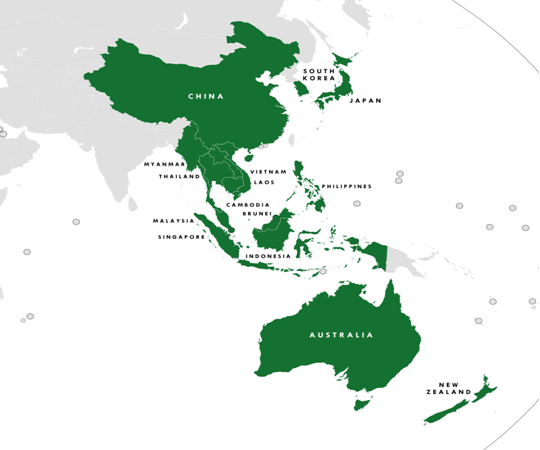
- After the withdrawal of India, there are 15 members of RCEP, which includes 10 ASEAN countries and 5 other countries, namely:
- Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- RCEP's objective is to establish an integrated market, facilitating the availability of products and services across the region.
- The negotiations cover trade, investment, intellectual property, dispute settlement, e-commerce, SMEs, and economic cooperation.
- Initially proposed by Beijing in 2012 to counter the Trans-Pacific Partnership, RCEP became a key tool for China after the U.S. withdrew from the TPP in 2016.
- India chose not to sign the RCEP in 2019 due to concerns about its industries competing with China and potential flooding of Indian markets.
- Despite some sectors anticipating gains, India emphasized the need for a deal favorable to all countries and sectors.
