Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
- 12 Nov 2025
In News:
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare but usually fatal infection of the central nervous system (CNS), affecting the brain and spinal cord. Recent advisories issued during the monsoon season, including warnings by the Kerala government, have brought renewed attention to this disease due to favourable environmental conditions for the causative organism.
Causative Organism
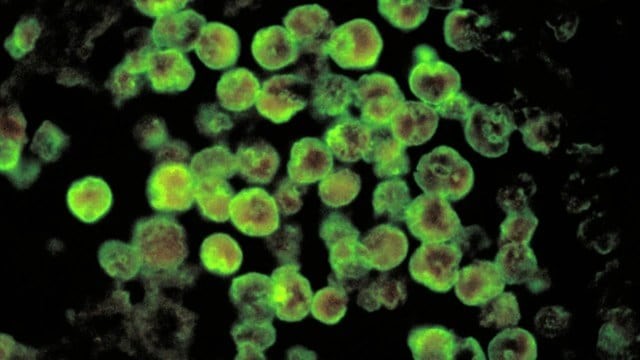
- PAM is caused by Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba.
- Amoebae are single-celled eukaryotic organisms belonging to the kingdom Protista, characterised by their ability to change shape and move using pseudopodia.
Habitat and Transmission
- Naegleria fowleri thrives in warm freshwater environments, especially:
- Lakes, rivers, ponds
- Hot springs
- Stagnant or slow-moving water
- Poorly maintained swimming pools, water parks, hot tubs, and spas
- Mode of entry:
- The amoeba enters the human body through the nose, not by drinking water.
- Activities such as swimming, diving, or nasal irrigation with untreated water can force contaminated water into the nasal passages.
- From the nose, the amoeba migrates along the olfactory nerves to the brain.
Pathogenesis
- Once inside the brain, Naegleria fowleri:
- Rapidly multiplies
- Invades brain tissue and meninges
- Feeds on nerve and glial cells
- This leads to severe inflammation, necrosis (cell death), haemorrhage, and swelling of brain tissue.
- The disease progresses very rapidly.
Symptoms
- Incubation period: Usually 1–9 days after exposure.
- Early symptoms (often resemble bacterial meningitis):Fever, Severe headache, Nausea and vomiting, and Sensitivity to light
- Advanced symptoms:Stiff neck, Confusion and hallucinations, Seizures, and Loss of consciousness and coma
- Fatality:PAM is frequently fatal within days to weeks of symptom onset.Very few survivors have been reported worldwide.
Treatment Status
- There is no standard or definitive treatment for PAM.
- Current management relies on combination therapy, including anti-parasitic and supportive drugs, with limited success.
- Early diagnosis remains a major challenge due to rapid disease progression.
Prevention and Public Health Measures
- Avoid swimming or diving in warm, stagnant freshwater bodies, especially during summer or monsoon.
- Use nose clips or keep the nose closed while swimming.
- Ensure proper chlorination and maintenance of swimming pools and water parks.
- Use only treated or sterile water for nasal cleansing or irrigation.
- Health authorities advise prompt medical consultation if symptoms like prolonged fever, headache, neurological signs, or altered consciousness appear after freshwater exposure.
Differentiation from Other Amoebic Infections
- PAM should not be confused with granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE), another rare CNS infection caused by Acanthamoeba or Balamuthia mandrillaris, which has a slower disease course.
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
Kerala’s Kozhikode district has reported three recent cases of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), including the death of a nine-year-old girl. A three-month-old infant and another child are currently receiving treatment. Following these incidents, the state health department has issued an alert to prevent further infections.
About Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM):
- Definition: PAM is a rare but severe infection of the brain and its protective membranes, caused by the free-living amoeba Naegleria fowleri, popularly called the “brain-eating amoeba.”
- Transmission: The amoeba thrives in warm, fresh water, soil, hot tubs, and improperly maintained swimming pools. Infection occurs when contaminated water enters the nose, allowing the pathogen to reach the brain and meninges. Dust or soil exposure can also serve as potential sources.
- Symptoms: Include headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, hallucinations, and neurological deterioration. PAM progresses rapidly, often proving fatal within days.
- Treatment: Early diagnosis and administration of specific antibiotics can sometimes save lives, but recovery is rare. Globally, the disease has a 97% fatality rate, whereas Kerala has reduced it to 25% due to prompt medical interventions and protocols.
Other Amoebic Infections:
- Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis (GAE): Caused by Acanthamoeba or Balamuthia mandrillaris, GAE progresses more slowly than PAM but is equally deadly if untreated. Unlike PAM, GAE does not necessarily require water exposure for infection.
Epidemiology in Kerala:
- The first PAM case in India was reported in 1971, and Kerala’s first case occurred in 2016. From 2016 to 2023, eight cases were confirmed in the state.
- Last year, Kerala recorded 36 positive cases with nine deaths, prompting the development of the state’s first standard operating procedure (SOP) for managing amoebic meningoencephalitis.
- Notably, in July 2024, a 14-year-old boy in Kozhikode became the first Indian to survive PAM, only the 11th survivor globally.
Factors Contributing to Recent Cases:
- Increased testing for acute encephalitis syndrome (AES).
- Environmental changes, including climate change and pollution.
- Greater awareness and proactive healthcare measures, leading to earlier detection and treatment.
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A five-year-old girl from Malappuram district in Kerala who had been undergoing treatment for amoebic meningoencephalitis at the Government Medical College Hospital Kozhikode has died.
What is the Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis?
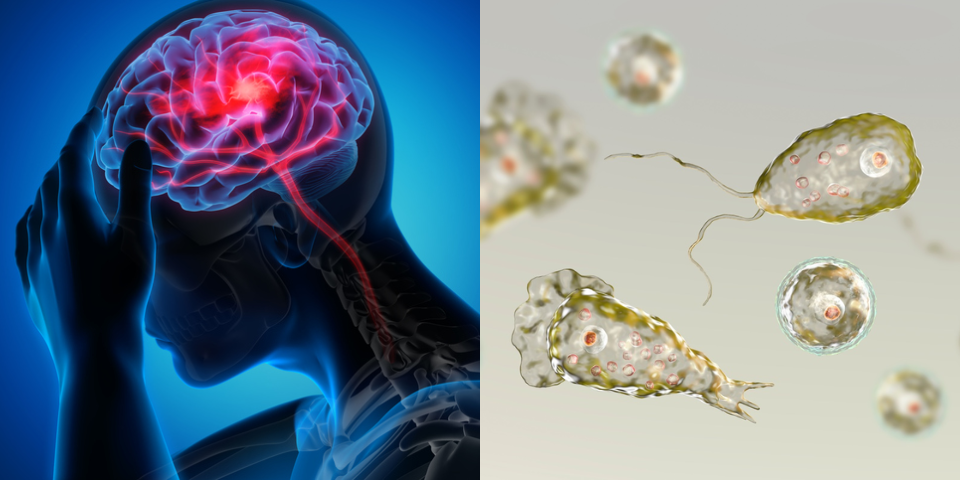
- Primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare brain infection that is caused by Naegleria fowleri.
- It is a free-living amoeba or a single-celled living organism.
- Naegleria fowleri lives in warm fresh water and soil around the world and infects people when it enters the body through the nose.
- Higher temperatures of up to 115°F (46°C) are conducive to its growth and it can survive for short periods in warm environments.
- The amoeba can be found in warm freshwater, such as lakes and rivers, swimming pools, splash pads, surf parks, or other recreational venues that are poorly maintained or minimally chlorinated.
How does Naegleria fowleri infect people?
- Naegleria fowleri enters the body through the nose, usually when people are swimming. It then travels up to the brain, where it destroys the brain tissue and causes swelling.
- Notably, people cannot get infected with Naegleria fowleri from drinking water contaminated with the amoeba.
- PAM is also non-communicable.
Symptoms of PAM:
- In the initial stage, the symptoms include headache, fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Later on, the patient may have a stiff neck and experience confusion, seizures, hallucinations and slip into a state of coma.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “Most people with PAM die within 1 to 18 days after symptoms begin.
- It usually leads to coma and death after 5 days.”
What is the treatment for primary amoebic meningoencephalitis?
- As earlier reported, scientists haven’t been able to identify any effective treatments for the disease yet.
- At present, doctors treat it with a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
