Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
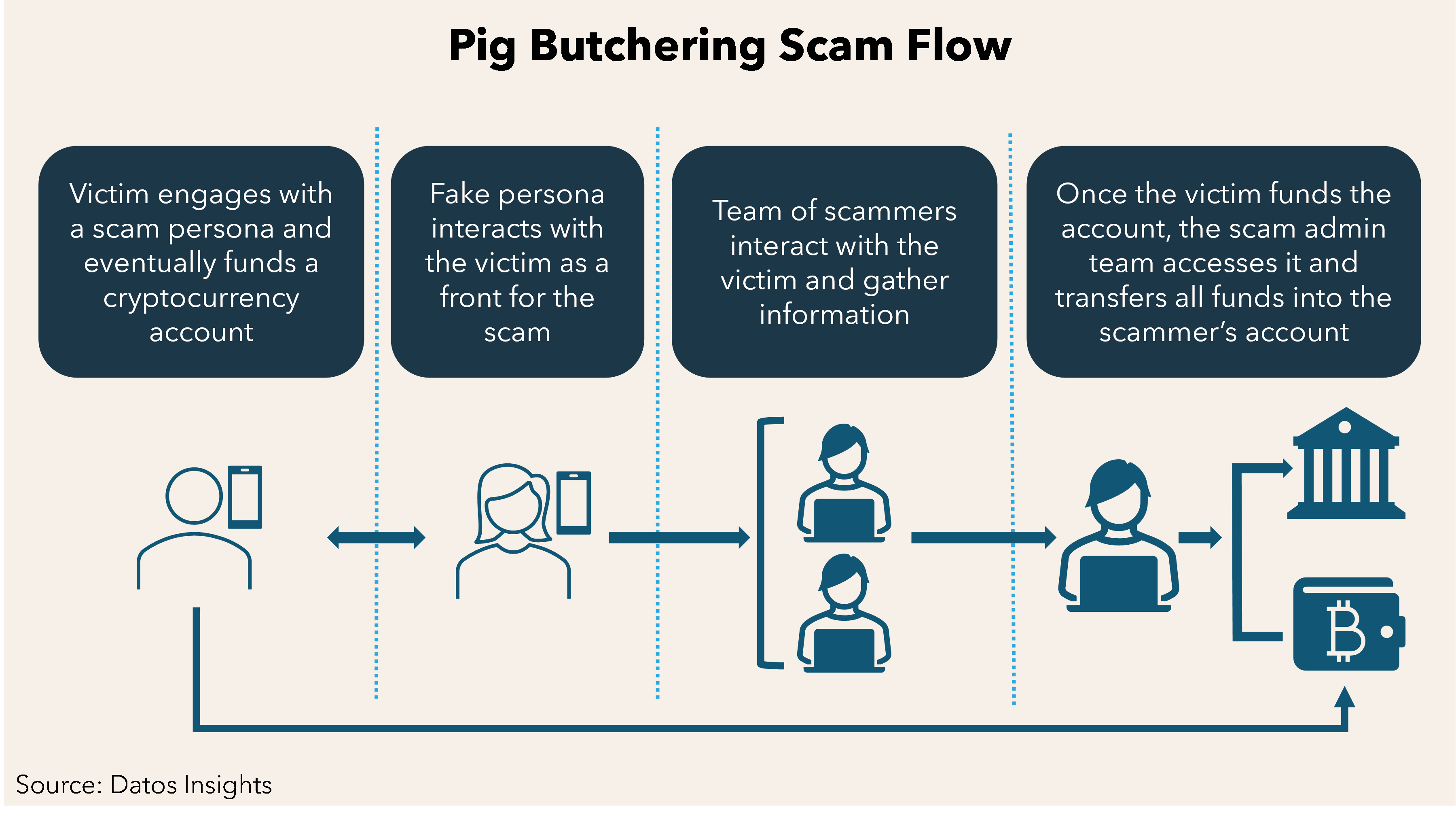
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
