Mitogenome
- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found South African leopards originated from two unique clades in southern and central Africa approximately 0.8 million years ago.
What is a Mitogenome?
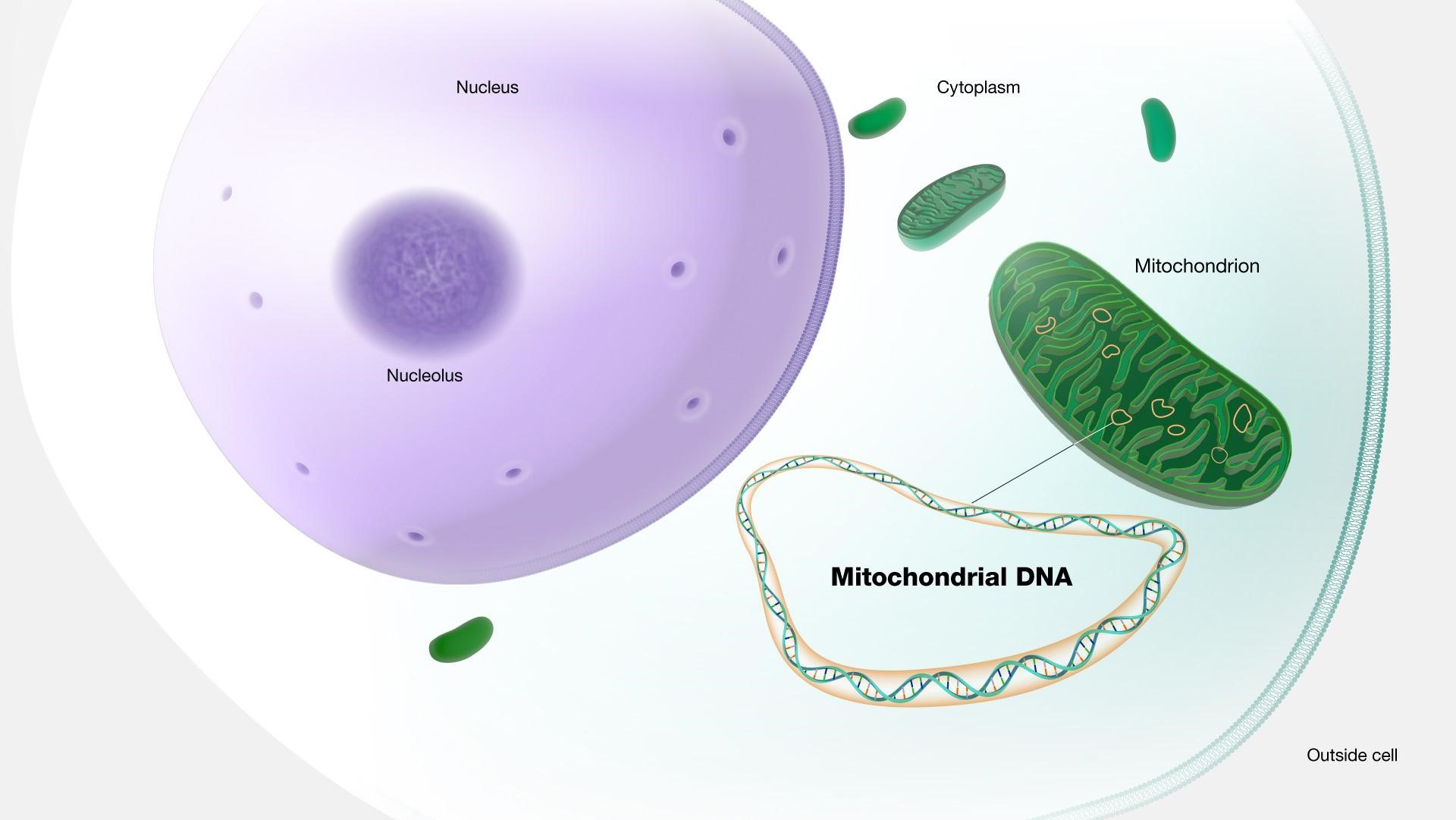
- DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and also in the mitochondrial genome, or mitogenome.
- Mitogenomes are DNA molecules that float around outside the nucleus of a cell.
- They store their own set of genetic information and are maternally inherited, which means they are only passed on from mother to offspring.
- Mitogenomes are a “genomic by-catch” when sequencing the whole genome.
- They are so abundant in cells that it is very easy to extract them.
- Studying mitogenomes is a reliable way to track the ancestry of a species.
- This is because genes mutate (change) at a regular rate over time.
- The changes in the mitogenome provide a picture of any species' evolution over hundreds of thousands of years.
What is DNA?
- DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid is the genetic material that codes the information for all the different processes that make an organism living like growth, replication, metabolism, etc.
- DNA is present in each cell (except for some viral species, RBCs, sieve cells, etc.) and is passed down from parents to their offspring. DNA is comprised of units called nucleotides.
- DNA is self-replicating, a long stretch of nucleotides.
- DNA is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four major macromolecules that make up the living system.
- In eukaryotic cells, it is found in the nucleus of the cell whereas in prokaryotes it is found free-floating in the cell cytoplasm.
- Other than the nucleus DNA is also found in mitochondria, chloroplast, and in smaller forms called plasmid in certain bacterial species.
