Risk weight (LiveMint)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Spooked by the strong growth in unsecured loans to consumers, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has increased the cost of funds for banks and non-bank financial companies (NBFCs), by increasing the risk weight of such loans.
What are Risk Weights?
- Every rupee lent by the bank is a cost or has an implication on its capital position.
- Depending on the nature of the loan and the inherent risk associated with it, risk weights are attributed.
- Banks have to ensure that their capital is enough to cover these risk-weighted assets.
- Total assets as disclosed in the financials and total risk-weighted assets are different things.
- Each asset class has varying risk weights.
- For instance, risk weights for home loans could range from 50 percent to 75 percent, for gold loans it is 75 percent.
- Corporate loans are charged 100 percent given the risk they carry.
How do they affect borrowers?
- Lower the risk weight, and lower the rate of interest. This is the thumb rule.
- Therefore, risk weights impact borrowers indirectly and are felt through the pricing of loans.
- For instance, home loans have the lowest interest rate among retail products because lower risk weights allow banks to pass on the advantage of capital consumption.
- Personal loans and credit cards have the highest interest rate because of their tenure and charge on capital.
Cloud Seeding (LiveMint)
- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Delhi government is mulling the use of artificial rain through cloud seeding this month to combat the air pollution crisis in the national capital.
What is Cloud Seeding?
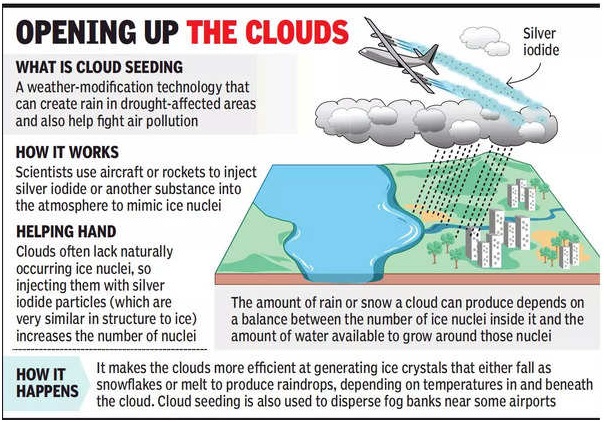
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique aimed at increasing precipitation by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei.
- The primary goal is to encourage the formation and growth of precipitation particles within clouds.
- Commonly used substances for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide, and liquid propane.
There are two main types of cloud seeding:
- Static cloud seeding: This type of seeding is used to increase precipitation in areas that are experiencing drought
- It involves releasing silver iodide or dry ice into clouds that are already producing precipitation.
- The silver iodide or dry ice acts as ice nuclei, which causes water droplets in the clouds to freeze and form snowflakes.
- The snowflakes then grow larger and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
- Dynamic cloud seeding: This type of seeding is used to increase the amount of precipitation that falls from clouds that are not yet producing precipitation.
- It involves releasing silver iodide into clouds that are still in the development stage.
- The silver iodide acts as condensation nuclei, which causes water vapor in the clouds to condense and form water droplets.
- The water droplets then grow larger and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
- Cloud seeding is typically done using aircraft, but it can also be done using ground-based generators or rockets.
- The aircraft or other seeding platform will fly into the clouds and release the silver iodide or dry ice.
- The seeding material will then spread throughout the cloud and begin to alter the microphysical processes.
- The effectiveness of cloud seeding is debated.
- Some studies have shown that it can increase precipitation by up to 30%, while other studies have shown that it has little or no effect.
- The effectiveness of cloud seeding is likely to vary depending on the type of clouds being seeded, the atmospheric conditions, and the seeding method used.
- Cloud seeding is used in a variety of countries around the world, including the United States, China, Russia, and Australia.
The Hindu Parliament security breach | 14 Opposition MPs suspended from House amid face-off (LiveMint)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Fourteen MPs have been suspended for "unruly conduct" as stormy scenes played out in Parliament in the wake of the massive security breach recently.
Context:
- A total of 14 MPs, 13 from Lok Sabha and one from Rajya Sabha, were suspended from Parliament on Thursday for the remainder of the Winter Session.
- This follows after stormy scenes played out in Parliament on Thursday, December 14, in the wake of the massive security breach a day before.
- Earlier in the day, TMC member Derek O'Brien was suspended from the Rajya Sabha for the remainder of the Winter session for "unruly behaviour" and "misconduct".
Suspension of MPs:
- The Presiding Officer, whether the Speaker of the Lok Sabha or the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, plays a crucial role in maintaining order for the smooth functioning of the House.
- Empowered to uphold proper proceedings, the Speaker/Chairman has the authority to compel a Member to withdraw from the House, ensuring the orderly conduct of parliamentary affairs.
What are the Rules under which the Presiding Officer/Chairman acts?
- In Lok Sabha: Rule 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business empowers presiding officers to direct an MP to withdraw for disorderly conduct.
- The suspended Member must remain absent for the remainder of the day's sitting.
- Rules 374 and 374A are invoked for more persistent disruptions.
- Rule 374 allows the Speaker to name legislators for continued disruptions, leading to a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Rule 374A, added in December 2001, facilitates automatic suspension for five days or the remaining session part.
- In Rajya Sabha: Rule 255 grants the Chairman the authority to immediately direct withdrawal for disorderly conduct.
- Rule 256 enables the Chairman to name members persistently disregarding the Chair's authority or abusing Council rules.
- The House may then pass a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Unlike Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha cannot suspend members without a formal motion.
Judicial Oversight in MP Suspension Cases:
- While Article 122 of the Indian Constitution shields parliamentary proceedings from judicial review, there are instances of courts intervening in legislative procedures.
- In a case involving the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly's 2021 Monsoon Session, where 12 BJP MLAs were suspended for a year, the Supreme Court stepped in.
The Court ruled that the assembly's resolution had legal limitations and was only applicable for the duration of the Monsoon Session, underscoring the judiciary's role in assessing the legality and effectiveness of legislative actions.
Hike in US Federal Reserve Interest and Impact on Indian Economy (Live Mint)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The US Federal Reserve is expected to raise benchmark rates by 25 bps to the 5.25-5.50 percent range on Wednesday. Investors will be watching for cues on inflation and rate hike trajectory.
About US Federal Reserve:
- The US Federal Reserve, also known as the Fed, serves as the central banking system of the United States, offering a secure, adaptable, and steady monetary and financial framework.
- It operates through 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, each responsible for a designated U.S. geographic area.
- The Fed's primary functions encompass conducting national monetary policy, overseeing and regulating banks, ensuring financial stability, and delivering banking services.
Impacts of US Federal Reserve Interest Hike:
- The US Fed's Significance: As the world's most powerful central bank, the decisions taken by the US Federal Reserve regarding interest rates have significant implications worldwide. These decisions influence both developed and emerging economies across the globe.
- Global Effects: Changes in US interest rates have a ripple effect that extends beyond the nation's borders. The adjustments impact various economies worldwide, leading to shifts in investment patterns and financial flows.
- Appeal of American Assets: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, American assets become more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Consequently, there is a possibility of capital outflows from emerging and riskier markets to the US.
- Impact on Capital-Intensive Sectors: Sectors heavily reliant on Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of a US interest rate hike. The increased cost of borrowing may affect their growth prospects.
- Global Liquidity Tightening: Higher US interest rates can lead to a tightening of global liquidity. Foreign investors may face challenges in obtaining affordable funds, which could have implications for their investment decisions and overall economic activities.
Potential Impacts on the Indian Economy:
- Interest Rate Differential: Following a rate hike by the US Federal Reserve, the gap between interest rates in the US and India narrows, adversely affecting currency trade and financial flows.
- Foreign Investor Response: With higher returns available in the US due to increased interest rates and attractive Dollar and US Treasury yields, foreign investors may be inclined to withdraw investments from the Indian market, leading to capital outflows.
- Currency and RBI Response: The relative strengthening of the US currency (Dollar) makes the Indian rupee weaker, prompting the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to consider a rate hike domestically.
- RBI's Action to Curb Outflows: To mitigate the outflows of funds from Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and safeguard the rupee's stability, the RBI may find it necessary to increase interest rates within India.
- Forex Reserve Management: In the event of a significant decline in the rupee's value, the RBI might be compelled to sell some of its Dollar reserves to support the domestic currency. This action, however, depletes the country's foreign exchange reserves.
Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (LiveMint)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RoDTEP scheme, which initially lasted until September 30, 2023, will now continue until June 30, 2024, with the same rates for products that are already being exported.
Facts About:
- The RoDTEP Scheme, officially known as the Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products, plays a crucial role in helping Indian exporters.
- It became operational on January 1, 2021, replacing the earlier export incentive program called Merchandise Exports from India (MEIS).
- This change was necessary because the World Trade Organization (WTO) found that the MEIS scheme violated WTO rules by providing export subsidies for a wide range of goods.
- How it Works: Under the RoDTEP Scheme, exporters receive a rebate based on a percentage of the value of their exports (known as FOB or Freight On Board value).
This rebate is given in the form of a transferable duty credit/electronic scrip (e-scrip), and the details of these credits are maintained digitally by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
The RoDTEP Committee, which operates within the Department of Revenue, is responsible for reviewing and recommending the maximum rates for different export sectors under this scheme.
- Main Objective: The primary goal of the RoDTEP Scheme is to offer comprehensive support to exporters by refunding the duties and taxes incurred during the production and distribution of exported products.
Importantly, it covers taxes, duties, and levies imposed at the central, state, and local levels, which are not reimbursed through other existing mechanisms.
- Financial Support: In the fiscal year 2023-24, the Indian Government has allocated a substantial budget of Rs. 15,070 crores to support the RoDTEP Scheme.
- Engaging with Stakeholders: The RoDTEP Committee has recently started its work by collaborating with Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and Chambers of Commerce.
Brent Crude (LiveMint)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Brent crude oil has recently surged to its highest point in 10 months, exceeding $93 per barrel.
Facts About:
- Brent Crude is the primary benchmark used to determine oil prices globally.
- The name "Brent" originates from the Brent oil field, which was discovered in the 1970s and became a major source of oil production.
- Roughly two-thirds of all internationally traded crude oil is priced relative to Brent, making it the most widely recognized benchmark.
- It's a type of light, sweet crude oil extracted from oil fields in the North Sea.
- Brent crude's special characteristics, such as its low density and low sulfur content, make it easier to refine into products like gasoline.
- Since it's transported by sea, it's convenient to move Brent crude oil to distant locations.
- The price of Brent Crude is influenced by several factors, including shifts in supply and demand, geopolitical events, production interruptions, and economic conditions.
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
