Ranikhet Disease in India

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
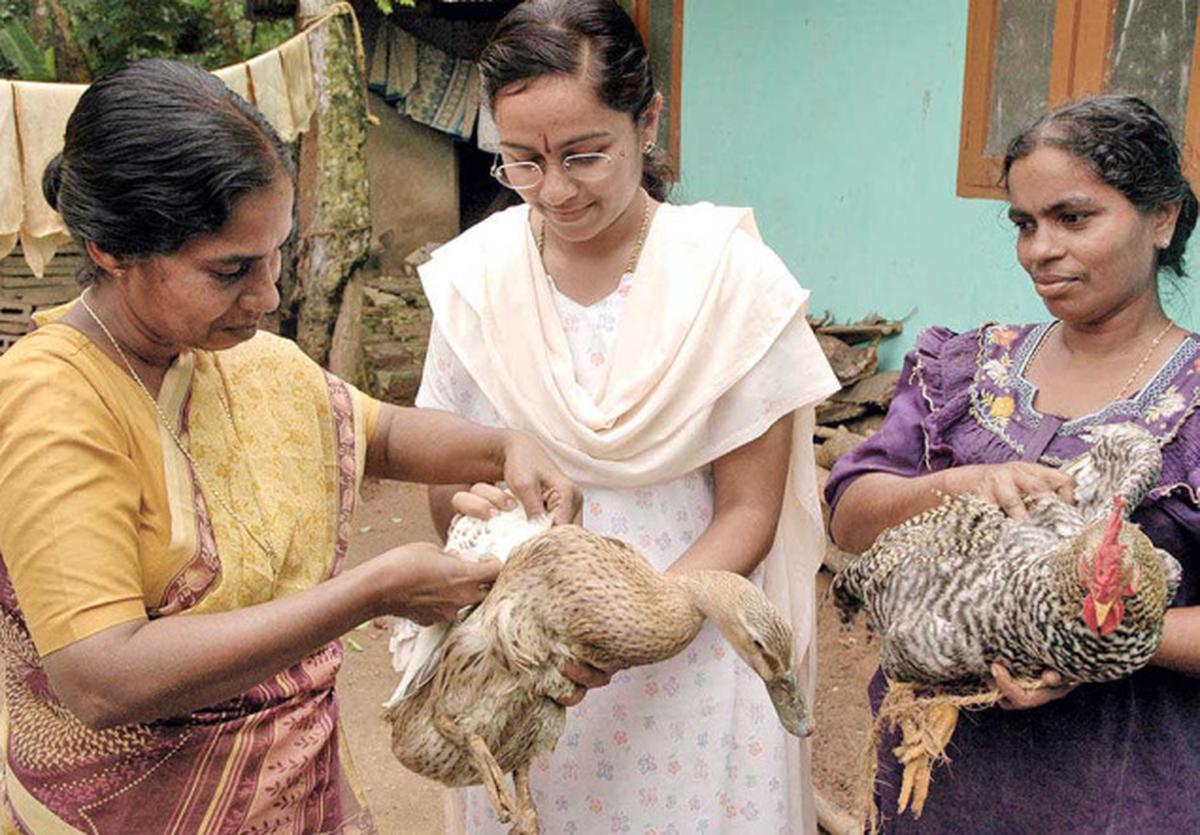
Recent outbreaks of suspected Ranikhet disease (Newcastle Disease) have caused the death of approximately 1.5 lakh chickens in poultry farms across Andhra Pradesh (Eluru, Guntur, Prakasam, and the Godavari districts) and Haryana (Barwala and Raipur Rani in Panchkula). These outbreaks have raised alarms about biosecurity measures, especially in regions that are major poultry producers.
About Ranikhet Disease:
- Also known as: Newcastle Disease (ND)
- Causative Agent: Avian avulavirus 1 (also called Avian Paramyxovirus-1 or APMV-1)
- Affected Species: Primarily chickens, but also turkeys, ducks, pigeons, crows, geese, guinea fowls, partridges, doves, and even hedgehogs (suspected reservoirs).
- Nature of Disease: Highly contagious and fatal viral disease.
- Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bird secretions (especially feces)
- Contaminated feed, water, equipment, clothing, and environment
- ND virus can survive for weeks in cool environments, increasing risk in winter.
Symptoms and Impact:
- In Birds:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing, gasping
- Nervous symptoms: Droopiness, loss of coordination
- Digestive symptoms: Diarrhea
- Mortality rate: Ranges from 50% to 100%
- Production impact: Drop in egg production and fertility
- In Humans:
- Mild zoonotic effect, primarily conjunctivitis in people handling infected birds or lab samples.
- Usually self-limiting and non-fatal.
Recent Outbreaks and Investigations:
Andhra Pradesh:
- Approximately 1.5 lakh birds have died across multiple districts.
- Suspected cause: Highly virulent strain of Ranikhet Disease.
Haryana (Barwala–Raipur Rani belt):
- This belt houses around 115 poultry farms and is the second-largest poultry producer in Asia.
- Previously affected by bird flu outbreaks in 2006 and 2014.
- Northern Regional Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (NRDDL), Jalandhar collected 40 new samples from affected farms after being unsatisfied with earlier ones.
- Preliminary suspicion points toward Ranikhet Disease; however, cold wave conditions and the presence of older birds (not replaced due to COVID-19 restrictions) may have also contributed.
- The region falls in the path of migratory birds, whose droppings can spread avian flu viruses, complicating disease identification.
Current Challenges:
- Lack of effective treatment: No curative treatment exists. Management relies on preventive vaccination, biosecurity measures, and good poultry housing practices.
- Diagnostic delays: Require reliable sampling and laboratory testing to confirm the cause.
- Climate sensitivity: Poultry are vulnerable to extreme cold, especially if housing and care are inadequate.
- Pandemic aftershocks: COVID-19 disruptions prevented the routine replacement of older birds, increasing vulnerability.
Golden-headed Cisticola

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
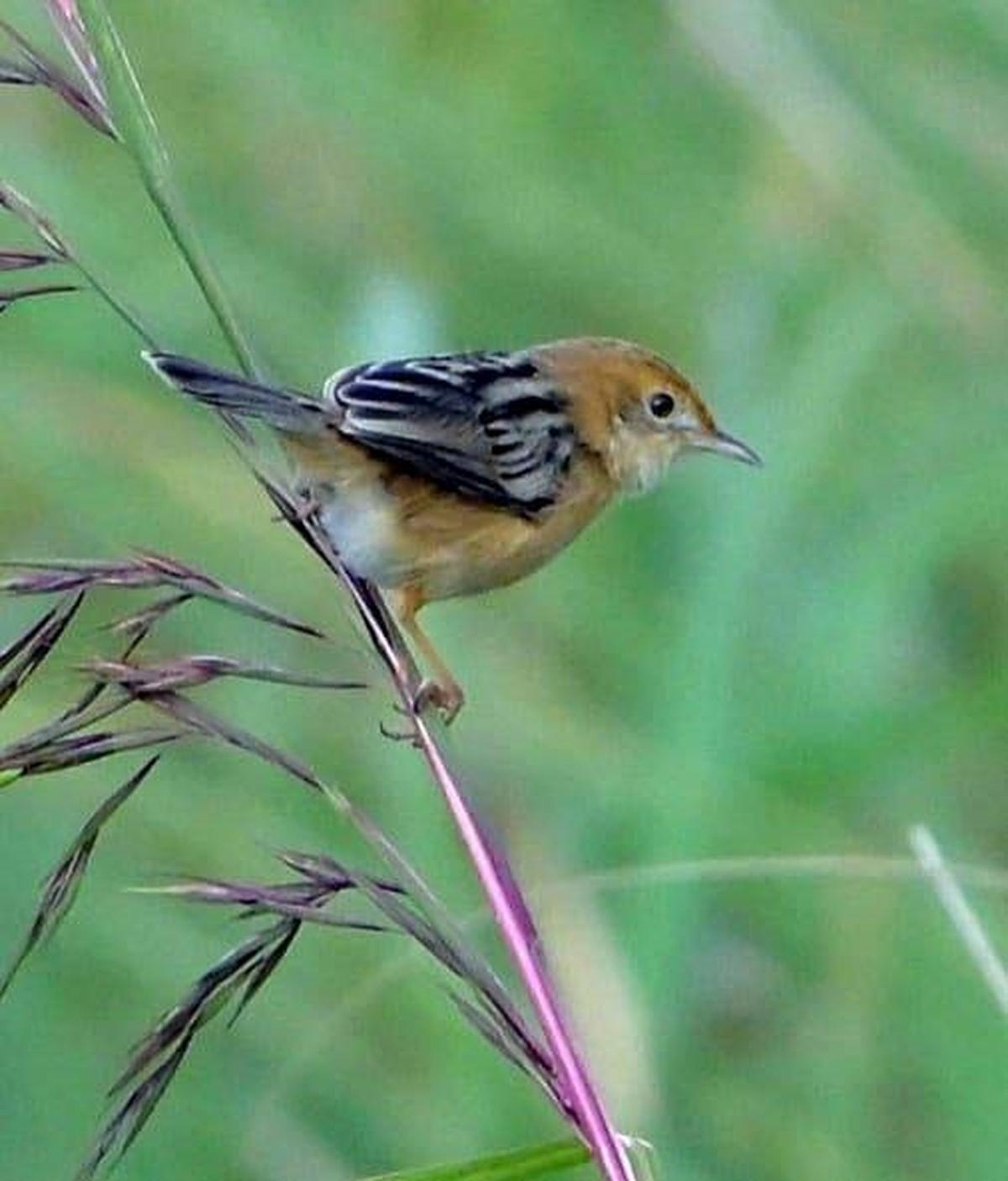
In a remarkable ornithological development, the Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis) has been sighted in the Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki district, Kerala, marking its first recorded presence in the southern Western Ghats after a significant gap.
The finding underscores the ecological richness of the region and highlights the need for intensified avian research in the Western Ghats.
About Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis)
- Also known as the bright-capped cisticola, it is a small warbler belonging to the family Cisticolidae.
- It is an omnivorous bird, feeding primarily on invertebrates such as insects and small slugs, along with grass seeds.
- The species is typically found in grassland habitats within mountain ranges, and has been previously recorded in parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala, notably in Banasura Hills, Wayanad. However, this is the first confirmed sighting in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap.
Physical features of breeding males include:
- Golden-orange plumage on the head, neck, and chest
- Pinkish beaks
- Black streaks on the back
- A distinctive call that aids identification
Habitat and Distribution
- It is widely distributed across Australia and several Asian countries.
- In India, its presence had been limited to select regions of the Western Ghats, making its recent sighting in Mathikettan Shola both rare and ecologically significant.
Conservation Status
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Golden-headed Cisticola is classified as Least Concern. Despite this, the new finding calls for further research into its habitat preferences and conservation needs within India.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park
Located in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Mathikettan Shola is a vital biodiversity hotspot.
- It comprises evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, shola grasslands, and semi-evergreen vegetation.
- The park hosts three major streams: Uchillkuthi Puzha, Mathikettan Puzha, and Njandar, which are tributaries of the Panniyar River.
- Its highest point is Kattumala, located at the eastern border adjoining Tamil Nadu.
- The Muthavan tribal community resides near the park’s northeastern boundary, reflecting the intricate human-nature interface in the region.
Scientific and Conservation Importance
The rediscovery has been documented in the journal Malabar Trogon by the Malabar Natural History Society, bringing attention to the importance of long-term monitoring and baseline studies in underexplored ecosystems.
It emphasizes:
- The ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The importance of citizen science, as local birdwatchers played a key role in the finding.
- The need for enhanced habitat protection and ornithological research in grassland ecosystems of high-altitude regions.
Aroma Mission

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Aroma Mission, also known as the Lavender Revolution, is emerging as a transformative initiative for regions like Jammu & Kashmir and the North East, prioritised under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for inclusive development.
It aims to harness the untapped potential of India’s biodiverse regions through the scientific cultivation of aromatic crops and production of essential oils, with the dual goals of economic upliftment and sustainable innovation.
Key Objectives and Features:
- Launched By: Ministry of Science & Technology
- Nodal Agency: CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP), Lucknow
- Started In: Jammu & Kashmir, now extended to the North East
- Known As: Lavender Revolution
- Purpose: Boost India’s aroma industry by promoting the cultivation of high-value aromatic crops and increasing the production of essential oils.
Major Focus Areas:
- Crops Cultivated: Lavender, lemongrass, citronella, palmarosa, vetiver, patchouli, rose, peppermint, and chamomile
- Target Sectors: Cosmetics, aromatherapy, pharmaceuticals, and food flavouring industries
Impact and Achievements:
- Over 5,000 hectares brought under aromatic crop cultivation in the North East.
- Establishment of 39 essential oil distillation units.
- Distribution of 1 lakh agarwood saplings planned to boost the region's share in global aromatic plant trade.
- Expected annual essential oil production: 2,000 tonnes, valued at over ?300 crores.
- Estimated to generate 60 lakh man-days of rural employment.
- Projected increase in farmers’ income by ?60,000–?70,000 per hectare annually.
Institutional Support: IICON – Incubation and Innovation Complex
- Location: CSIR-North East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat, Assam
- Launched By: Dr. Jitendra Singh (Minister of Science & Technology)
- Purpose: Provide technical assistance, advanced facilities, and business incubation support for startups, MSMEs, and SHGs.
- Facilities: Access to 27 cutting-edge technologies for up to two years to help refine production and marketing strategies.
Integrated Development Approach:
The Aroma Mission exemplifies the “whole-of-government” approach, aligning with various flagship programmes such as:
- Start-Up India
- MSME Development
- Doubling Farmers’ Income
- Women Empowerment (e.g., through Rural Women Technology Parks)
- Act East Policy (enhancing North East's connectivity and trade potential)
Over 25 startups and self-help groups have already been empowered through access to facilities and entrepreneurial training at IICON, contributing to local innovation ecosystems.
Strategic Significance:
- Regional Empowerment: Converts underutilised natural resources into economic assets, especially in remote regions like J&K and the North East.
- Environmental Sustainability: Encourages eco-friendly cultivation and reduces pressure on traditional farming.
- Economic Diversification: Supports India’s transition to a bio-economy, with aromatic plant industries offering export potential and rural employment.
- Vision India@2047: Positions the North East as a hub for biotechnology, essential oils, innovation, and trade, aligning with long-term national growth goals.
RBI Payment System Report 2024

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
The Payment System Report – December 2024 is a bi-annual publication by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
It analyses trends in digital and retail payment systems over the last five calendar years (up to CY-2024) and highlights India's transformation into a global leader in payment innovation and inclusion.
Growth in Digital Transactions
- Exponential Growth: Digital payment transactions rose 94 times in volume (from 222 crore in 2013 to 20,787 crore in 2024) and 3.5 times in value (from ?772 lakh crore to ?2,758 lakh crore).
- Recent CAGR (2019–2024):
- Volume: 45.9% CAGR
- Value: 10.2% CAGR
- Retail Digital Payments: From 162 crore transactions in FY13 to 16,416 crore in FY24 — a 100-fold increase in 12 years.
- Digital Payments Index (DPI): Surged from a base of 100 in March 2018 to 445.50 in March 2024, indicating massive digital adoption.
UPI: A Game-Changer
- Launched in 2016 by NPCI, UPI has revolutionized mobile-based payments.
- CAGR (Last 5 Years):
- Volume: 74.03%
- Value: 68.14%
- Monthly Transactions: UPI processes over 16 billion transactions monthly, ranking among the largest globally.
- Inclusive Innovations:
- UPI Lite & UPI Lite X: For offline/small-value payments.
- UPI123Pay: For feature phone users.
- UPI 2.0: Includes auto-debit and recurring payment functionalities.
Credit and Debit Card Trends
- Credit Cards:
- Growth: More than doubled from 5.53 crore (Dec 2019) to 10.80 crore (Dec 2024).
- Debit Cards:
- Stable Usage: Marginal increase from 80.53 crore to 99.09 crore in the same period.
Cross-Border Payment Integration
- RBI is actively enhancing cross-border payments by integrating India's UPI with international Fast Payment Systems (FPSs), addressing high costs, delays, and limited access.
- Key Developments:
- UPI-PayNow Linkage (Feb 2023): India-Singapore real-time cross-border payments.
- UPI-enabled QR Payments: Available in Bhutan, France, Mauritius, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, UAE.
- Project Nexus:
- A BIS-conceptualized multilateral project.
- Aims to interlink FPSs of India, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand for seamless retail payments.
Institutional and Legal Framework
- Legal Backbone: Payments and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act) empowers RBI to:
- Regulate, supervise, and license payment system operators.
- Authorize systems like NPCI, card networks, ATM operators, etc.
- Governing Body:
- Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS) under RBI.
- Chairperson: RBI Governor; Vice-Chairperson: Deputy Governor (in charge of DPSS).
- Payment Ecosystem Entities:
- RBI-regulated: RTGS, NEFT, Cheques (CTS).
- NPCI-managed: UPI, IMPS, AePS, BBPS, NETC, NACH, Cards.
- Other PSOs: TReDS, PPIs.
Strategic Significance
- Financial Inclusion: Payment systems are critical tools for promoting inclusive growth by ensuring last-mile delivery of services and direct benefit transfers.
- Global Competitiveness: RBI’s regulatory foresight and innovation have placed India among the global frontrunners in digital payments.
PKC-ERCP: Rajasthan’s River-Linking Project
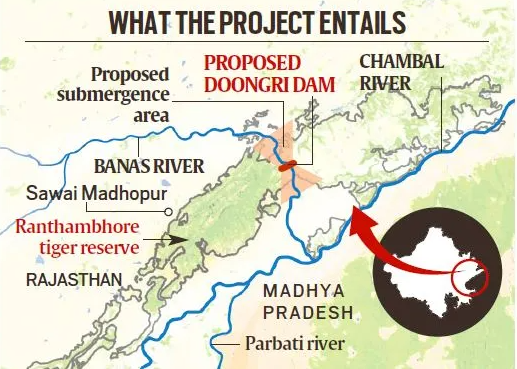
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP), part of the National Interlinking of Rivers (ILR) programme, aims to address water scarcity in 23 districts of Rajasthan, potentially benefiting 3.45 crore people. However, it has raised serious concerns over its ecological impact, particularly on the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
About the PKC-ERCP Project:
Aspect Details
Objective To channel surplus water from the Chambal basin for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
Estimated Cost ?72,000 crore (90% funded by the Central Government)
Water Allocation 4,100 MCM to Rajasthan and 3,000 MCM to Madhya Pradesh
Rivers Involved Chambal, Parbati, Kalisindh, Banas, and tributaries
Major Structure 39 m high, 1.6 km long dam across the Banas River, a Chambal tributary, near Doongri village, ~30 km from Sawai Madhopur
Submergence and Environmental Concerns:
- Total Submergence: ~408.86 sq km in Rajasthan.
- Reservoir Impact: 227 sq km to be submerged under the proposed dam across Banas River.
- Impact on Tiger Reserve:
- 37.03 sq km of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (total area: 1,133 sq km) to be submerged.
- This includes parts of Ranthambore National Park (392 sq km) and Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary (674 sq km).
- May fragment the reserve, disrupting wildlife corridors and tiger movement.
- Ranthambore’s Significance:
- Home to ~57 tigers, it is one of India’s most prominent conservation areas.
- Situated at the Aravalli-Vindhya junction, with rich biodiversity, including leopards, hyenas, sloth bears, and iconic flora like Dhok trees.
- Encompasses the UNESCO-listed Ranthambore Fort and the Great Boundary Fault.
Arguments For the Project:
- Addresses chronic water scarcity in eastern Rajasthan.
- Promotes agricultural productivity, drinking water security, and industrial development.
- Aims to optimize water use by diverting surplus flows.
Arguments Against the Project:
- Biodiversity loss due to habitat submergence and reserve fragmentation.
- Risks to tiger conservation efforts.
- Potential violation of environmental safeguards under the Wildlife Protection Act and Forest Conservation norms.
Long-term ecological costs may outweigh short-term developmental gains.
Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
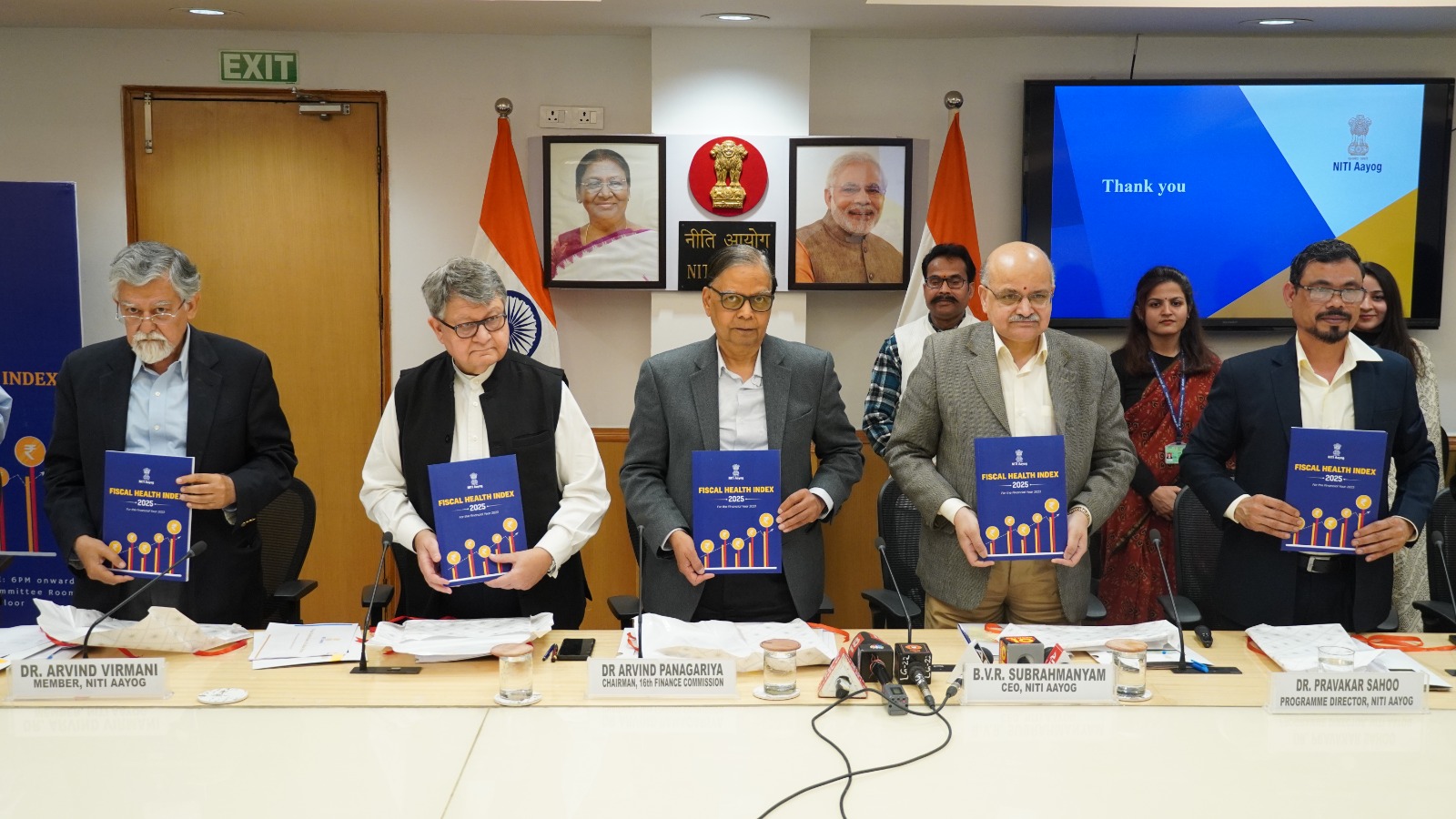
NITI Aayog launched the inaugural Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025 on 24 January 2025 in the presence of the 16th Finance Commission Chairman, Dr. Arvind Panagariya. The index evaluates the fiscal performance of 18 major Indian states using FY 2022–23 as the base year.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To assess, monitor, and improve the fiscal health of Indian states and foster balanced regional development, economic resilience, and fiscal transparency. It aims to support the national goal of Viksit Bharat @2047.
- Developed by:
- NITI Aayog, with data sourced from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- Designed as an annual publication to promote informed and targeted state-level policy reforms.
- Evaluation Parameters:
The index comprises five sub-indices that collectively offer a holistic picture of fiscal health:
- Quality of Expenditure – Efficiency in developmental and social sector spending (e.g., health, education).
- Revenue Mobilization – Tax and non-tax revenue generation capacity.
- Fiscal Prudence – Adherence to fiscal deficit targets and sound financial management.
- Debt Index – Absolute level of public debt.
- Debt Sustainability – Debt-to-GSDP ratio and interest burden on revenues.
Key Highlights from FHI 2025:
Top Performing States (Achievers):
Rank State FHI Score Strengths
1. Odisha 67.8 Low fiscal deficit, strong debt management, effective capital expenditure
2. Chhattisgarh 55.2 Revenue growth from mining, fiscal prudence
3. Goa 53.6 High tax efficiency and non-tax revenue
Aspirational States (Facing Challenges):
- Punjab, West Bengal, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh
- Issues: High debt-to-GSDP ratios, revenue deficits, poor revenue mobilization
Sub-Index Insights:
- Revenue Mobilization: Odisha, Goa, and Chhattisgarh excelled; Bihar and West Bengal lagged due to low own-tax revenues.
- Quality of Expenditure: Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh prioritized social sectors; Punjab and Rajasthan underperformed in capital investment.
- Debt Management: Maharashtra and Gujarat maintained robust practices; Punjab and Haryana faced rising interest burdens.
- Debt Sustainability: Odisha and Chhattisgarh displayed strong sustainability; West Bengal and Punjab showed fiscal stress.
- Fiscal Prudence: Odisha and Jharkhand maintained low deficits, enabling better public investment.
Significance for Policy & Governance:
- Encourages healthy interstate competition and promotes cooperative federalism.
- Provides data-driven insights for targeted fiscal reforms.
- Reinforces the need for decentralized and transparent financial governance.
- Offers a benchmark for fiscal performance aligned with national transformation goals.
Recommendations:
- Enhance revenue base via tax reforms and tapping into non-tax sources.
- Boost capital expenditure in infrastructure, health, and education.
- Strengthen debt sustainability frameworks and reporting mechanisms.
- Institutionalize fiscal responsibility through better compliance and accountability.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The President of India conferred the National Panchayat Awards 2024 on 45 outstanding Panchayats for their contributions to inclusive growth, environmental sustainability, and rural development. The event was held on 11th December 2024 (postponed from 24th April due to General Elections).
About the Awards
- Launched to commemorate: 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, which gave constitutional status to Panchayats as institutions of local self-governance.
- Usual celebration date: 24th April — observed as National Panchayati Raj Day.
- Revamped in 2022 to align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) via Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
Objectives
- Recognize best practices in rural governance.
- Encourage healthy competition among Panchayats.
- Promote effective implementation of LSDGs and quality service delivery.
Evaluation Structure
- Multi-level assessment: Block → District → State/UT → National level.
- Evaluation based on 9 LSDG themes, including:
- Poverty-Free & Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean & Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just & Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
Award Categories
Award Category Focus Area
Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP) Top 3 GPs under each LSDG theme
Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar Top 3 GPs, Block Panchayats & District Panchayats with highest scores across all themes
Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs promoting renewable energy adoption
Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs achieving net-zero carbon emissions
Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar Institutions providing exemplary support to PRIs in implementing LSDGs
Key Highlights of 2024:
- Total Awards: 45 Panchayats
- Women Leadership: 42% of award-winning Panchayats led by women.
- Participation: 1.94 lakh Gram Panchayats competed.
- Prize Money: ?46 crore transferred digitally to awardees.
- Booklet Released: Best Practices of Awardee Panchayats.
- Film Showcased: Highlighting success stories and capacity-building.
State-wise Recognition
- Notable awardees from: Odisha, Tripura, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Telangana, Assam, etc.
- Tripura & Odisha stood out in total recognitions.
- GPs from Maharashtra, Odisha, and Tripura received special awards for energy and carbon neutrality.
Other Key Initiatives for PRIs
Initiative Purpose
SVAMITVA Scheme (2020) Mapping rural property to provide Record of Rights.
e-Gram Swaraj (e-FMS) Work-based accounting to promote transparency.
mActionSoft Geo-tagging Panchayat assets via GPS-enabled photos.
Citizen Charter Portal “Meri Panchayat Mera Adhikaar” – Service delivery assurance to citizens.
Ratnagiri Buddhist Site

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has resumed excavations at the ancient Buddhist site of Ratnagiri in Odisha’s Jajpur district, unveiling monumental discoveries that underline its rich religious, cultural, and maritime legacy. This renewed effort comes more than 60 years after the site was first excavated between 1958 and 1961.
About Ratnagiri
- Meaning: Ratnagiri translates to “Hill of Jewels.”
- Location: Situated on a hill between the Brahmani and Birupa rivers, northeast of Bhubaneswar.
- Part of the Diamond Triangle: Along with Lalitgiri and Udaygiri, Ratnagiri forms Odisha’s famed “Diamond Triangle” of Buddhist heritage sites.
- Historical Period: Flourished between the 5th and 13th centuries CE, peaking under the Bhauma-Kara dynasty (8th–10th century CE).
- Buddhist School: An important centre for Mahayana and especially Vajrayana (Tantrayana) Buddhism.
- It possibly rivalled Nalanda in prominence as a Buddhist learning centre.
- The monastery complex at Ratnagiri is the only one in India with a curvilinear roof, once housing about 500 monks.
Recent Discoveries by ASI
- Three colossal Buddha heads, each measuring 3–4 feet.
- A massive palm sculpture, 5 feet in size.
- Hundreds of votive stupas, sculptures of Buddhist deities.
- A monolithic elephant statue, 5 feet long and 3.5 feet tall.
- Pottery, inscribed stones, beads, stone pillars, and a brick wall believed to be part of a larger structure.
- Rich ceramic assemblages, which may shed light on the region’s cultural and technological evolution.
These artefacts are estimated to date back to the 8th and 9th centuries CE and are believed to enhance understanding of Buddhism’s evolution in Odisha and its linkages with other cultures.
Buddhism in Odisha & Southeast Asian Links
- Buddhism gained a strong foothold in Odisha after Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) in 261 BCE, a turning point that led him to embrace Buddhism.
- Though Buddha never visited Odisha, the region became instrumental in spreading Buddhism to Southeast Asia, especially during the Bhauma-Kara period.
- The state maintained robust maritime trade and cultural links with regions like Java, Bali, Sumatra, Borneo, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
- Baliyatra Festival: A vibrant annual event held in Cuttack, commemorating Odisha’s ancient seafaring ties with Bali and other Southeast Asian regions.
- According to some studies, Chinese monk Hiuen Tsang may have visited Ratnagiri during his travels in India (638–639 CE).
Significance of the Renewed Excavations
- The ASI aims to uncover partially visible structures, complete the site’s mapping, and contextualize the findings within the broader Buddhist history of India and Southeast Asia.
- Researchers hope to discover signs of foreign architectural or cultural influences, further confirming ancient Odisha’s global Buddhist and trade connections.
- The discoveries reaffirm Ratnagiri’s importance as a cornerstone of Buddhist learning and art, potentially on par with other renowned ancient centres like Nalanda and Vikramashila.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES)

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launched in April 2015, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) offers subsidised interest rates on pre- and post-shipment export credit to Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs.
- The Commerce Ministry has sought a Rs 3,000 crore extension of the scheme beyond December 2024, with emphasis on supporting MSME exporters amidst global economic challenges.
Objectives of IES:
- Reduce Cost of Credit: Offers 3% to 5% interest subvention to make export credit affordable.
- Boost Export Competitiveness: Enables Indian exporters, especially MSMEs, to match international pricing.
- Encourage Export Diversification: Supports MSMEs in exploring new markets and products.
- Enhance Financial Inclusion: Promotes access to formal credit systems for small exporters.
Key Features:
- Interest Subsidy:
- 3% for MSME manufacturer exporters.
- 2% for merchant and manufacturer exporters of 410 specified tariff lines.
- Coverage: Initially limited to select products, later extended to all MSME exporters.
- Implementation:
- Managed by the RBI, in coordination with DGFT and authorized banks.
- Subsidy reimbursed to banks offering export credit at reduced rates.
- Banks exceeding Repo Rate + 4% are excluded.
Need for Extension:
- The scheme expired in December 2024, but exporters are demanding continuation due to:
- Rising global inflation and logistics disruptions (e.g., Red Sea crisis).
- Increase in credit duration demands from foreign buyers (120–150 days).
- Decline in export credit availability despite higher demand.
- FIEO reports a drop in outstanding export credit from ?2.27 lakh crore (2023) to ?2.17 lakh crore (2024).
- MSMEs operate on thin margins, and the subvention can make or break deals.
Significance for MSMEs:
- MSMEs contribute ~45% to India’s total exports and often struggle with high borrowing costs and limited financial access.
- Affordable credit via IES allows MSMEs to:
- Remain price competitive.
- Take larger and longer-term orders.
- Invest in product innovation and value addition.
- Improve market diversification and resilience.
Challenges in Accessing Credit:
- Stringent eligibility norms and collateral requirements.
- Complex administrative procedures for availing benefits.
- Limited awareness among small enterprises about the scheme.
- Slow disbursal and inconsistent application by banks.
Policy Implications and the Way Forward:
- A revamped, MSME-focused IES can ensure inclusive growth and boost India’s export-led development.
- Calls for:
- Simplification of procedural norms.
- Higher interest subvention limits or removal of caps (e.g., ?50 lakh per IEC holder).
- Longer validity (multi-year horizon) for predictability and planning.
- Aligns with the broader goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and achieving $1 trillion in exports by 2030.
Exercise La Perouse 2025
- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
India is participating in the fourth edition of the multinational naval exercise La Perouse, hosted by France in key maritime straits—Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok. The Indian Navy's INS Mumbai, an indigenously built guided-missile destroyer, represents India.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Countries: Navies from India, France, Australia, USA, UK, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Canada.
- Objectives:
- Enhance maritime situational awareness.
- Promote tactical interoperability through joint training.
- Conduct surface warfare, anti-air warfare, air defence, and VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations.
- Strengthen cooperation on maritime surveillance, air operations, and information sharing.
- Significance:
- Demonstrates commitment to a rules-based international order in the Indo-Pacific.
- Reflects India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Counters increasing presence of Chinese naval forces in the Indo-Pacific.
Strategic Location: Key Straits in Focus
- Strait of Malacca
- Connects: Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) to South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Geography: Lies between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra, near Singapore.
- Significance: One of the world’s busiest trade routes.
- Choke Point: Narrowest part (Philips Channel) is only 2.8 km wide.
- Sunda Strait
- Connects: Java Sea (Pacific) to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Java and Sumatra (Indonesia).
- Challenges: Volcanic islands (e.g., Krakatoa), shallow depths (20–100 m).
- Importance: Secondary maritime route, strategic in times of congestion in Malacca.
- Lombok Strait
- Connects: Java Sea to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Bali and Lombok islands.
- Depth: 250–1,300 meters – suitable for large vessels.
- Unique Feature: Part of the Wallace Line, a major ecological boundary.
Sanchar Saathi App

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
In a landmark move to enhance telecom accessibility, security, and empowerment across India, the Union Minister of Communications launched a suite of citizen-focused initiatives. Key highlights of the event included the launch of the Sanchar Saathi Mobile App, National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0 and the inauguration of the Intra Circle Roaming facility at DBN Funded 4G Mobile Sites.
Sanchar Saathi Mobile App
- Launched by: Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
- Platforms: Available on Android and iOS.
- Objective: Strengthen telecom security, empower citizens, and combat telecom fraud.
- Key Features:
- Chakshu (SFC): Report suspected fraud communications (calls/SMS).
- Know Your Mobile Connections: Identify and manage all mobile numbers issued in one’s name.
- Block Lost/Stolen Devices: Swiftly block, trace, and recover lost/stolen mobile phones.
- Verify Handset Genuineness: Confirm the authenticity of mobile handsets before purchase.
Impact so far (via Sanchar Saathi Portal, launched May 2023):
- 2.75 crore fraudulent connections disconnected.
- 25+ lakh lost/stolen devices blocked.
- 12.38 lakh WhatsApp accounts linked to cybercrimes disengaged.
- 11.6 lakh mule bank accounts frozen.
- 90% spoofed international calls blocked within 2 months of new prevention system.
National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0
- Launched by: Union Minister of Communications, builds upon NBM 1.0 (2019–2024).
- Part of: National Digital Communications Policy, 2018.
- Aim: Digitally empower citizens and bridge the digital divide to realize the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Targets (by 2030):
- 2.70 lakh villages to be connected with OFC (from ~50,000 now).
- 90% broadband connectivity to anchor institutions (schools, PHCs, Panchayats, Anganwadis).
- Fixed broadband speed: Increase national average from 63.55 Mbps (2024) to 100 Mbps.
- Right of Way (RoW) disposal time: Reduce from 60 days to 30 days.
- Rural internet subscribers: Increase from 45 to 60 per 100 population.
- 30% of mobile towers to be powered by sustainable energy.
- 100% mapping of PSU fiber networks on PM GatiShakti National Master Plan by 2026.
- Enhanced use of “Call Before u Dig (CBuD)” app to protect underground telecom infrastructure.
- Facilitate 5G rollout, and prepare infrastructure for 6G and common telecom ducts in all linear projects.
- Leverage power sector (e.g. Optical Ground Wire - OPGW) for broadband in remote/hilly areas.
Intra Circle Roaming (ICR) at DBN-Funded 4G Sites
- Launched by: Ministry of Communications.
- Implemented under: Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN), formerly USOF.
- Objective: Allow subscribers of multiple telecom service providers (TSPs) (e.g., BSNL, Airtel, Reliance) to access 4G services from a single DBN-funded tower.
- Impact:
- Eliminates need for duplicate towers.
- Covers 27,000+ towers across 35,400 remote villages.
- Enhances user choice, reduces cost, and ensures efficient infrastructure use.
Global Risks Report 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the 20th edition of the Global Risks Report 2025, outlining the most pressing global risks over short-term (1-2 years) and long-term (10 years) horizons.
- The report, based on the Global Risks Perception Survey (GRPS) 2024-2025, categorizes risks across economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal, and technological domains.
Key Findings of the Report
Short-Term Risks (1-2 Years)
- Misinformation and Disinformation – Undermines trust in governance and institutions, complicating global cooperation.
- Extreme Weather Events – Rising costs and frequency due to climate change.
- State-Based Armed Conflict – Geopolitical tensions, including conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine war.
Long-Term Risks (10 Years)
- Extreme Weather Events – Ranked as the most significant long-term risk.
- Biodiversity Loss & Ecosystem Collapse – Drastic impact on food security and natural systems.
- Critical Changes to Earth Systems – Irreversible environmental shifts.
Evolving Global Risk Landscape
The risk landscape is shaped by four structural forces:
- Technological Acceleration – Rapid advancements in AI and digital platforms.
- Geostrategic Shifts – Increasing global polarization and armed conflicts.
- Climate Change – Rising environmental hazards.
- Demographic Bifurcation – Aging populations and labor shortages.
Specific Risks and Trends
Environmental Risks
- Pollution: Increasing air, water, and land contamination due to unsustainable production.
- Natural Disasters: Wildfires in the U.S. projected to cause over $200 billion in damages.
- Water Supply Shortages: A major concern for countries like India.
Economic and Trade Risks
- Escalating Trade Protectionism: Increase in tariffs and restrictions (e.g., Make in India, U.S. Inflation Reduction Act).
- Economic Uncertainty: Global inflation projected to decrease to 3.5% by 2025, but trade tensions may reignite financial instability.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Decline: A 10% drop in 2023 due to trade fragmentation.
Technological Risks
- Misinformation & Disinformation: AI-generated content fuels societal polarization.
- Cybersecurity Threats: AI-driven cyberattacks and algorithmic biases in governance.
- Surveillance & Censorship: Increased digital monitoring with inadequate legal safeguards.
Geopolitical and Societal Risks
- Erosion of Human Rights: Increasing authoritarian surveillance and control.
- Migration & Resource Shortages: Climate-induced migration is a rising global concern.
- Pension Crisis: Aging populations in countries like Japan and Germany threaten economic stability.
India-Specific Risks
- Water Shortages – Critical impact on agriculture and urban development.
- Misinformation & Disinformation – Threatens democratic institutions and governance.
- Pollution (Air, Water, Soil) – Major environmental and health hazard.
- Labor & Talent Shortages – Workforce challenges due to demographic shifts.
- Erosion of Civic Freedoms – Concerns over digital surveillance and censorship.
Policy Recommendations
Global and Domestic Strategies
- Strengthen Multilateral Cooperation: WTO reforms and global trade dispute resolutions.
- Boost Domestic Resilience: Investment in infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
- Combat Pollution: Stricter regulations on air and water pollutants.
- Address Algorithmic Bias: Global standards for AI governance and accountability.
- Ethical Oversight for Biotech: WHO-led regulations for human genome editing.
Long-Term Sustainability Measures
- Flexible Work Policies: Encouraging non-linear career paths.
- Pre-Retirement Health Programs: Improving lifestyle choices to reduce healthcare costs.
- Pension System Reforms: Raising retirement ages and ensuring financial security for retirees.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and the focus on this month underscores the critical importance of preventing cervical cancer, a disease responsible for significant mortality among women in India. At the heart of this prevention is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which is recognized as the most effective measure to prevent cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Despite its potential, the HPV vaccine remains out of reach for many due to its high cost and the need for greater awareness.
HPV and its Impact in India
HPV is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide, making it one of the primary causes of cancer in women. In India, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women, accounting for about 6-29% of all cancers in women. As of GLOBOCAN 2020, India alone has 20% of the global burden of cervical cancer, with over 123,000 cases and a 9.1% mortality rate.
Additionally, HPV can lead to several other cancers, including anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and throat cancers, making its vaccination vital for overall cancer prevention.
The HPV Vaccine: A Game-Changer
The HPV vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent infections caused by the virus and reduce the incidence of associated cancers. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the virus before it can cause damage. There are different types of vaccines authorized in India, including:
- Gardasil (protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18)
- Cervarix (a bivalent vaccine targeting HPV 16 and 18)
- Cervavac (India's first HPV vaccine, developed by the Serum Institute of India)
The vaccine is recommended for both males and females between 9 and 26 years, with a special focus on children aged 12 to 13 years, as the vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to the virus. It’s also suitable for people who are immunocompromised or HIV-infected.
Challenges to HPV Vaccination in India
Despite the obvious benefits, the uptake of the HPV vaccine in India faces several barriers:
- High Costs: The price of the vaccine remains prohibitively high. For example:
- Gardasil 9 costs ?10,850 per dose.
- Gardasil 4 is priced between ?2,000 to ?4,000 per dose.
- Cervavac, the Indian-made vaccine, costs around ?2,000 per dose, which is more affordable but still out of reach for many.
- Awareness and Cultural Perceptions: There is a lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Cultural factors, particularly around reproductive health, can also create reluctance to vaccinate, especially in rural or conservative areas.
- Limited Access: Currently, the vaccine is available through private practitioners and is not part of the National Immunisation Programme (NIP), limiting access to the broader population.
The Way Forward: National Immunisation and Awareness Campaigns
The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) has recommended that the HPV vaccine be included in India’s National Immunisation Programme (NIP). This would enable broader access and affordability, especially for girls aged 9–14 years and ensure that a routine vaccination schedule is implemented at the age of 9 years. Some states like Punjab and Sikkim have already taken steps to introduce the vaccine in their state-level immunization programs.
Additionally, a nationwide HPV vaccination campaign could raise awareness about the vaccine and its benefits, helping to overcome the challenges of cost, safety concerns, and cultural perceptions. Regular cervical cancer screenings (such as Pap smears and HPV tests) should also be encouraged to identify precancerous changes early.
Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Odisha has become the 34th state to implement the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The National Health Authority (NHA) of the Union Ministry of Health signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Odisha to onboard the state under the scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme will be implemented alongside the existing Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana in Odisha.
- It provides health coverage of Rs. 5 lakh per family per annum, with an additional Rs. 5 lakh for women members.
- Approximately 1.03 crore families will be covered under the scheme.
- Shri JP Nadda, Union Health Minister, emphasized that the scheme is the world’s largest and fastest-growing health coverage initiative.
- Shri Mohan Charan Majhi, Chief Minister of Odisha, highlighted that people will now have access to cashless treatment in over 29,000 empaneled hospitals.
About Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY:
- Launched in 2018 under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoH&FW).
- Targets 12 crore families (~55 crore beneficiaries).
- Provides cashless hospital coverage for secondary and tertiary care.
- Fully funded by the government, with cost-sharing between the Centre and states.
- Covers nearly 2,000 medical procedures, including major surgeries.
Since its inception, over 8.19 crore hospital admissions have been recorded, with ?1.13 lakh crore spent on healthcare for marginalized sections.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity
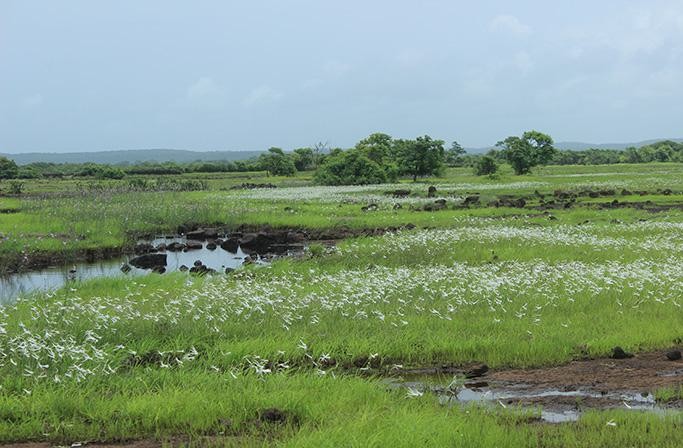

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals
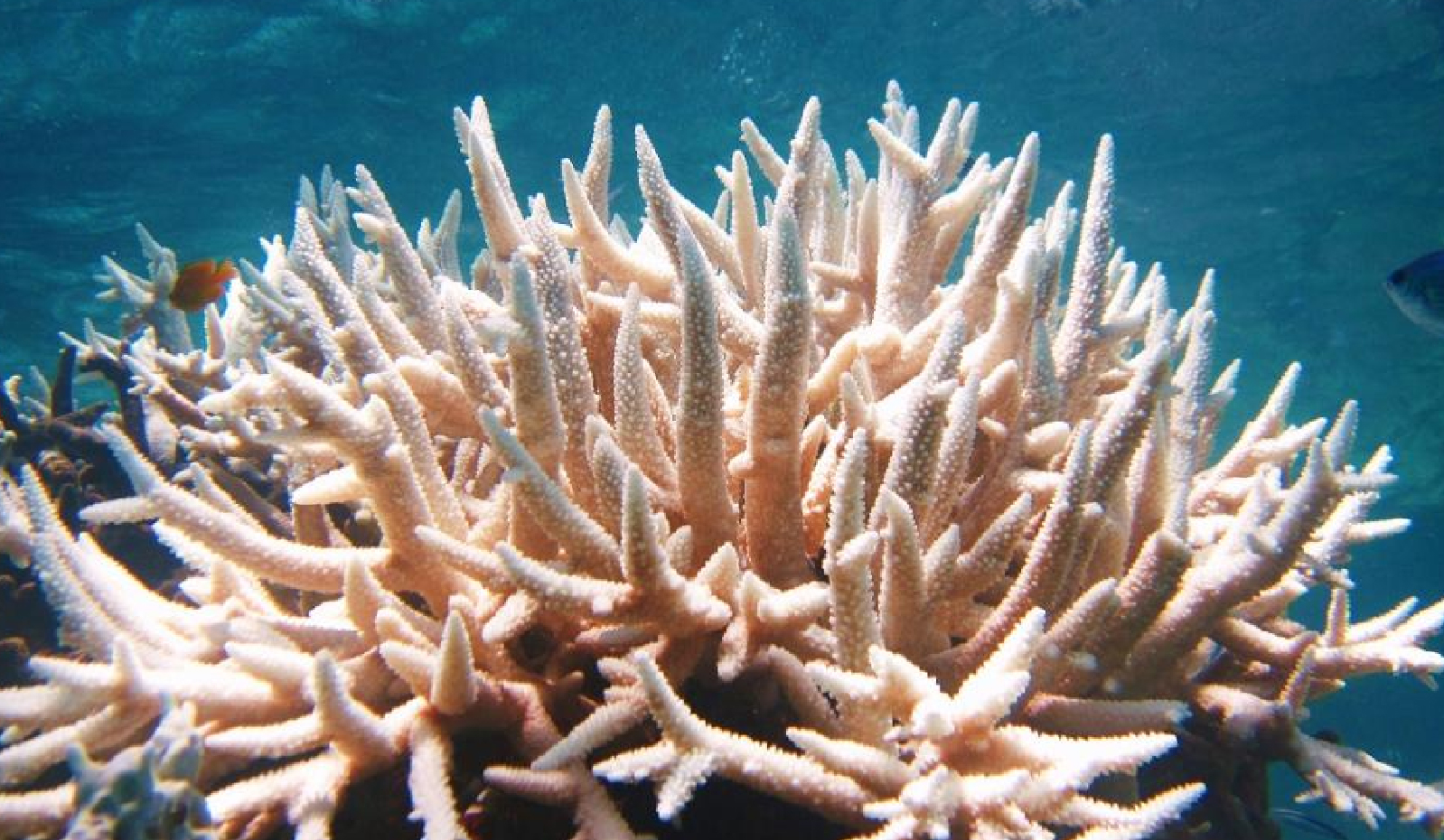

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
India Joins the UN-CEBD

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- India has recently joined the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD), marking a significant step in strengthening its role in global statistical frameworks.
- The inclusion is a result of India's recent membership in the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC), signaling the nation's growing influence in global data governance.
Key Highlights
- India's Growing Influence: India’s entry into the UN-CEBD highlights its growing stature in the international statistical community, emphasizing its commitment to utilizing big data and data science for informed decision-making.
- Strategic Opportunity: This membership allows India to contribute to shaping global standards in leveraging big data for official statistical purposes, especially in tracking Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is UN-CEBD?
- UN-CEBD is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014 to explore the benefits and challenges of using big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- It was established under the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC).
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states (including India) and 16 international organizations.
Key Objectives
- Monitor SDGs: Use big data to track progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Address Data Challenges: Overcome challenges in utilizing non-traditional data sources, such as satellite imagery, Internet of Things (IoT), and private sector data.
- Promote Big Data Use: Encourage practical applications of big data across borders while addressing associated challenges.
Governance and Functions
- Advisory Board: Provides strategic direction, convening four times a year.
- UN Bureau: Manages day-to-day operations.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Vision and direction for utilizing big data in global official statistics.
- Capacity Building: Enhance capabilities through training, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- Public Trust: Establish confidence in using big data for official statistics.
Big Data: Definition and Importance
What is Big Data?
- Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional data management systems.
- It enables enhanced decision-making and improved processes for policy formulation, product development, and governance.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP): Facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Big Data Management Policy: Defines strategies for managing large datasets within government agencies.
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics: Centralizes official data for better access and analysis.
The 6Vs of Big Data
- Volume: Large amounts of data.
- Velocity: Speed of data generation and processing.
- Variety: Different types of data.
- Veracity: Accuracy of data.
- Value: Significance of the data.
- Variability: Fluctuations in data.
India’s Role in the UN-CEBD
Contribution to Global Standards
- India's initiatives such as the Data Innovation Lab and the use of satellite imagery and machine learning will be shared with other members, fostering global collaboration in statistical innovations.
- India will contribute to shaping international standards for the use of big data in monitoring SDGs.
Enhancing Statistical Processes
- Modernization of Data: India aims to modernize its statistical processes by incorporating IoT, satellite data, and private-sector data.
- Real-time Insights: Providing policymakers with timely and accurate data to address key socio-economic issues.
- Improving Estimates: Using big data to enhance the accuracy of official statistics, improving governance and policymaking.
Strategic Goals of India's Engagement
- Streamline Statistical Production: Innovation in data collection, processing, and analysis to reduce delays in data availability.
- Improve Decision-Making: Provide real-time, evidence-based insights to policymakers.
- Foster International Collaboration: Share India’s expertise and learn from global best practices to build future-ready statistical systems.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
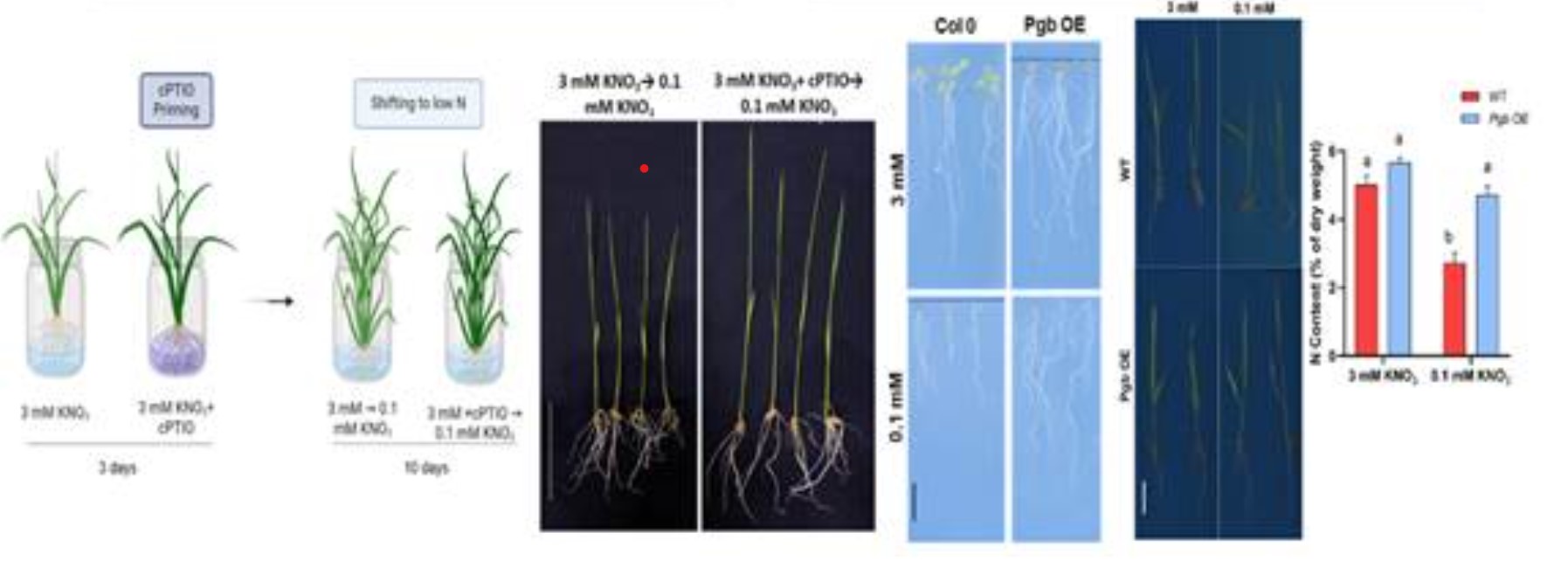
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
Bhashini Initiative
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
e-Shram Portal, which aims to provide social security benefits to unorganised workers, has been upgraded with multilingual functionality for all 22 scheduled languages of India. This development, supported by the Bhashini Initiative, ensures that unorganised workers from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access the portal more easily and benefit from government welfare schemes.
About Bhashini Initiative:
- Launched in: July 2022
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Aim: To eliminate language barriers in accessing digital services by making AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools publicly available.
Key Features:
- Local Language Translation: Bhashini offers AI-powered translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages to ensure that digital platforms like e-Shram are accessible to everyone in their native languages.
- Open AI and NLP Resources: These tools are made available to Indian MSMEs, startups, and innovators to create a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
- Crowdsourcing Platform (Bhashadaan): A platform for people to contribute to building linguistic datasets through initiatives like Suno India, Likho India, Bolo India, and Dekho India, furthering language diversity in digital services.
- National Digital Public Platform: Aimed at providing universal access to digital content in all Indian languages, facilitating smoother communication across regions.
e-Shram Portal: A One-Stop Solution for Unorganised Workers
- Purpose: The e-Shram portal was created to provide unorganised workers with access to social security benefits and welfare schemes.
Recent Upgrade:
- Multilingual Functionality: The portal has now been upgraded to support 22 scheduled languages, making it more inclusive and user-friendly for workers who speak various regional languages.
- Previous Version: Previously, the portal was only available in English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi. The integration of 22 languages is a significant improvement, enabling broader participation.
Importance of the e-Shram Portal for Unorganised Workers:
- Welfare Access: The portal provides access to government schemes designed for the welfare, livelihood, and well-being of unorganised workers, including gig and platform workers and building and construction workers.
- Integration of Social Security Schemes:
- As of now, the portal facilitates access to 12 government schemes, with plans to integrate even more, including state-level programs.
- Future plans include launching a mobile app, a single application form, and the integration of payment gateways for faster disbursement of benefits.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
