India Ranks 93 on Corruption Perceptions Index 2023 (The Hindu)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
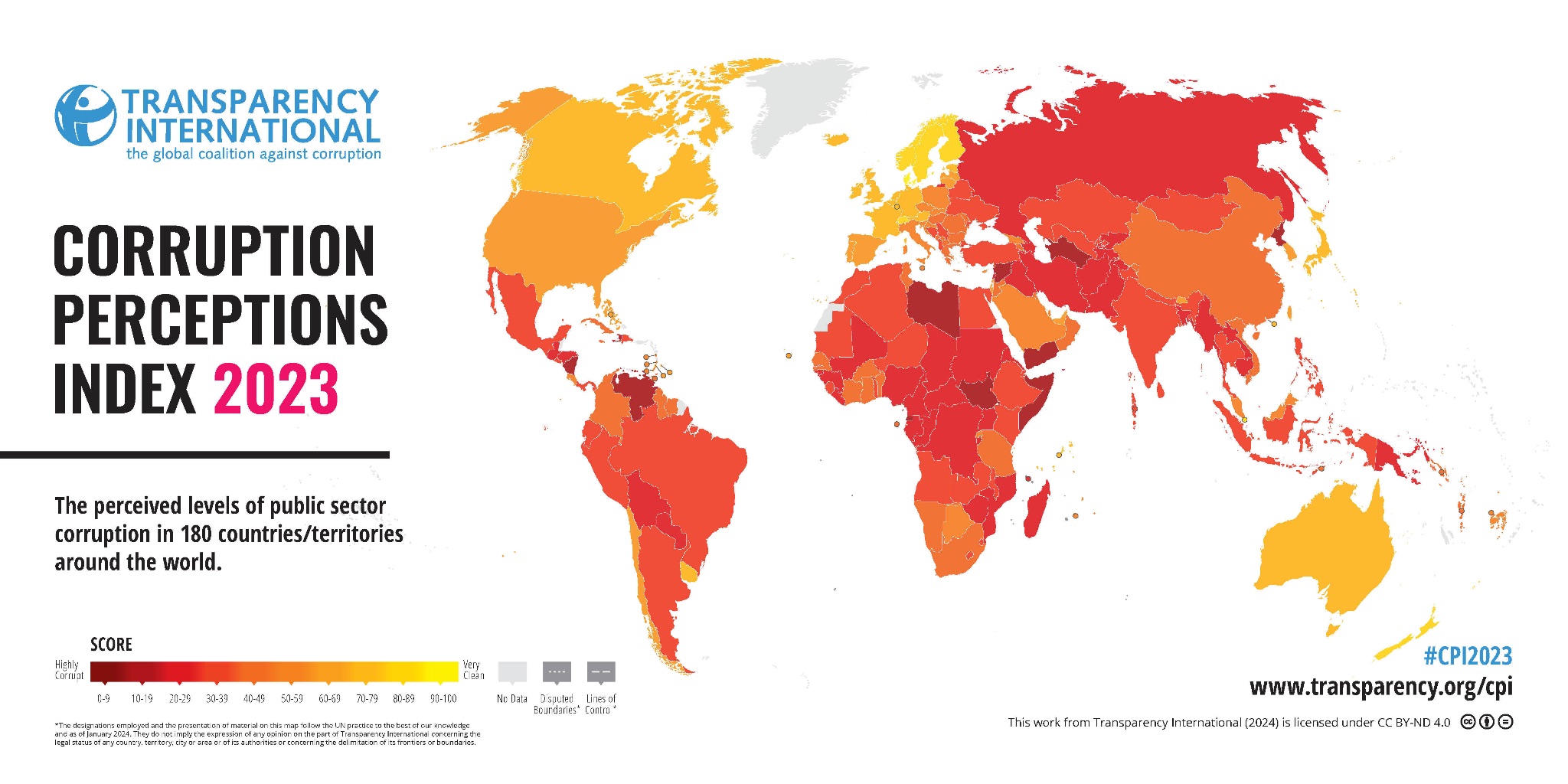
India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 as its overall score remained largely unchanged, according to a Transparency International report.
Key Facts About Corruption Perceptions Index 2023:
- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 tied with Maldives, Kazakhstan, and Lesotho also ranking at 93 out of 180 countries.
- In 2023, India's overall score was 39 while in 2022, it was 40.
- India's rank in 2022 was 85.
- Denmark (90) tops the index for the sixth consecutive year, with Finland and New Zealand.
- In South Asia, both Pakistan (133) and Sri Lanka (115) grapple with their respective debt burdens and ensuing political instability.
- Bangladesh (149) emerges from the least developed country (LDC) status, with economic growth supporting a continued reduction in poverty and improving living conditions.
- China (76), with its aggressive anti-corruption crackdown, has punished more than 3.7 million public officials for corruption over the last decade.
- Somalia (11), Venezuela (13), Syria (13), South Sudan (13) and Yemen (16) take the bottom spots in the index.
What is the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)?
- The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) scores and ranks countries/territories based on how corrupt a country’s public sector is perceived to be by experts and business executives.
- It is a composite index, a combination of 13 surveys and assessments of corruption, collected by a variety of reputable institutions including the World Bank, World Economic Forum, private risk and consulting companies, think tanks and others.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and the results are given on a scale of 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- The CPI is released annually by Transparency International, an independent nonprofit organization that aims to fight corruption, especially in the public sector.
- Transparency International is a global independent, nongovernmental nonprofit organization (NPO) that aims to stop corruption by promoting transparency in various sectors of society.
- The organization's international secretariat is located in Berlin and it has national chapters in more than 100 countries.
- The agency is funded through donations from governments, individuals, private donors, and other organizations.
- The organisation conducts research, and advocacy work, and undergoes various projects in its fight against corruption.
- In 1995, the organization created the first Corruption Perceptions Index, ranking 45 countries based on how much corruption they were perceived to have in the public sector.
Economic Impact of Corruption:
- Corruption continues to be a big hurdle to political, economic, and social development.
- Those who are economically challenged are the most affected by the effects of corruption and related fraud.
- That's because they often rely heavily on public services and can't afford to pay bribes.
- The International Finance Corporation also cites increases in the cost of business as a result of corruption.
Elon Musk's Neuralink implants Brain Chip in First Human (Indian Express)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Elon Musk announced his brain chip company, Neuralink, has completed its first implant on a human patient.
What is Neuralink?
- Neuralink is an upcoming medical device called a brain-computer interface that can help paralysed persons or amputees regain some sense of movement.
- It will decode signals from a part of the brain that plans movements.
- These signals will then be used to control external devices such as computers and mobile phones, allowing the participants to browse the web or play online games with just their thoughts even as their limbs are immobile.
- Under the PRIME Study (short for Precise Robotically Implanted Brain-Computer Interface) an N1 implant will be surgically placed by an R1 robot in the brain.
- The N1 implant has 1,024 electrodes distributed across 64 threads that are thinner than human hair.
- The R1 robot has been designed to insert these threads very accurately in a specific region of the brain.
Current Scenario in the Brain-Computer Interface?
- Recent breakthroughs in brain-computer interfaces have led to remarkable advancements, including systems capable of translating neural signals into speech at nearly the speed of natural speech and bi-directional interfaces that offer sensory feedback to the brain.
- In a notable development, researchers in Switzerland documented a case involving a man paralyzed from the waist down who regained the ability to walk.
- This feat was achieved through the use of a digital bridge that bypassed the damaged portion of his spinal cord.
- By employing a brain-spine interface, the signals from his brain were converted into stimulation for his spine, enabling him to walk again.
- While it may take several years before such devices are commercially available, the scientific progress in this field is remarkable.
- These advancements hold promise for individuals paralyzed due to accidents, offering potential mobility with the assistance of spinal implants.
What are the Challenges?
- One of the main challenges of the technology is establishing the connection between the brain and the chips, allowing it to reliably interpret the signals from the brain.”
- The use of conventional electronics for developing brain-computer interfaces results in a “mismatch with the soft tissue of the brain.”
- This can lead to tissue damage and immune response to the sensors.
- Flexible electronics with tissue-like properties can help build interfaces that do not face these problems.
- It can also help the systems adapt to changes in the brain volume during development, ageing and disease.
Eravikulam National Park to Close From February 1 for Nilgiri Tahr Breeding Season (The Hindu)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eravikulam National Park (ENP), the natural habitat of the Nilgiri tahr, will be closed for the calving season of the species from February 1 to March 31.
About Eravikulam National Park:
- Eravikulam National Park also known as Rajamala National Park, is located in Kerala's Idukki district.
- The park is administered under the Kerala Forest and Wildlife Department and became a National park in 1978.
- It is a 97 km2 national park located along the Western Ghats, Kerala.
- Anamudi, the highest peak in south India was located on the southern side of the park.
- This is also the land of "Neelakurinji", a flower that blooms once in twelve years.
- Wildlife in the Park: The park holds the maximum viable population of the endangered Nilgiri Tahr including other little-known fauna Nilgiri marten, ruddy mongoose, small clawed otter, dusky striped squirrel etc.
- Flora: Important flora includes Microtropis ramiflora, Actinodaphne bourdilloni, Pittosporum tetraspermium, Chrysopogon Zelanieus, Strobilanthus Kunthianus (Neela Kurinji) etc.
- Mostly the park is busted with rolling grasslands, but several patches of shola forests are also found in the upper part of the valley.
- The shola grasslands are exceptionally rich in balsams and orchids including the long thought extinct variety Brachycorythis wightii.
- The Atlas moth, the largest of its kind in the world, is seen in this park.
Key Facts about Nilgiri Tahr:
- Nilgiri Tahr is a rare mountain animal found only in the southern part of the Western Ghats.
- Scientific Name: Nilgiritragus hylocrius
- Local Name: Varayaadu
- They are famous for their ability to climb steep cliffs, which has earned them the nickname Mountain Monarch.
- It is the official state animal of Tamil Nadu.
- Distribution: Nilgiri Tahrs are mainly found in Kerala and Tamil Nadu, covering only about 5% of the Western Ghats.
- Eravikulam National Park in Kerala is home to the largest population of Nilgiri Tahrs.
- Habitat: They live in open grasslands at elevations between 1200 and 2600 meters in the South Western Ghats.
- Characteristics: Nilgiri Tahrs have a sturdy body with short, coarse fur and a rough mane.
- Both males and females have curved horns, with males having larger horns, up to 40 cm long.
- Adult males have a light grey area on their backs, known as a 'saddle,' hence the name 'saddlebacks.'
- They have a short grey-brown or dark coat.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972: Schedule I
Employer Rating Survey to Assess Women Participation in Workforce (Business Standard)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
To bolster the representation of women in the workforce and advance gender equality, various ministries of the central government issued a series of advisories and surveys on Tuesday, aimed at industries and employers.
About the Survey:
- This survey aims to evaluate the prevalence of women-friendly practices across the nation's workplaces.
- The government is collecting information on several key aspects, including the establishment of internal complaints committees (ICC) for preventing sexual harassment, the provision of childcare facilities, ensuring pay equity, offering flexible or remote work options for women, and providing safe transportation during late hours.
- Additionally, various ministries of the Central government have issued advisories to enhance women's representation in the workforce.
Factors Affecting Low Women Workforce Participation:
- Cultural and Social Norms: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations often discourage women from pursuing full-time employment due to responsibilities for caregiving and homemaking, limiting their participation in the workforce.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to quality education can hinder women from acquiring the necessary skills and qualifications for certain jobs, further reducing their workforce participation.
- Gender Pay Gap: Disparities in wages between men and women discourage women from entering or remaining in the workforce, contributing to lower participation rates.
- Structural Constraints: India's manufacturing and service sectors often have rigid structures that limit employment opportunities, particularly in the informal sector where many women work.
- Security Concerns: Instances of sexual harassment in the workplace create safety concerns for women, acting as a barrier to their participation in the labour force.
Government Initiatives Supporting Women's Empowerment:
- Code on Wages, 2019: Ensures equal pay for equal work without discrimination based on gender, fostering fairness in wage practices across establishments.
- Code on Occupational Safety, Health And Working Conditions (OSH), 2020: Proposes amendments to improve employment conditions for women workers, particularly in above-ground mines, ensuring their safety and well-being.
- Maternity Benefit Act, 2017: Enhances maternity benefits and fosters a healthier work environment for pregnant and nursing women, promoting their well-being and work-life balance.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh (RMK): A national organization offering microfinance services to empower economically disadvantaged women, supporting their livelihood projects and economic independence.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Focuses on creating sustainable self-employment opportunities for rural women through skill training, capacity building, and financial assistance, enabling them to engage in income-generating activities.
- MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act): Guarantees 100 days of wage employment annually to rural households, actively encouraging women's participation and ensuring equitable employment opportunities.
Way Forward
Continued government initiatives aimed at empowering women in the workforce through skill development and expanded employment opportunities have yielded positive results, as evidenced by the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the Labour Bureau in 2023. This survey indicated a notable increase in women's participation, rising from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23.
Draft Indian Stamp Bill, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre has proposed repealing the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 and bringing in a new law for the stamp duty regime in the country.
What is Stamp Duty?
- A stamp duty is essentially a government tax, which is levied to register documents, like an agreement or transaction paper between two or more parties, with the registrar.
- Usually, the amount specified is fixed based on the document’s nature or is charged at a certain percentage of the agreement value stated in the document.
- Stamp duties can be levied on bills of exchange, cheques, promissory notes, bills of lading, letters of credit, policies of insurance, transfer of shares, debentures, proxies and receipts.
- Accepted as valid evidence in a court of law, stamp duties are levied by the Centre but appropriated by the concerned states within their territories under Article 268 of the Constitution.
Notable Provisions of the Draft Indian Stamp Bill, 2023:
Several provisions of the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 have now become “redundant” or “inoperative” Therefore, the ministry has proposed repealing the existing Act and substituting it with new legislation to “reflect the present realities and objectives.”
- The draft Bill has introduced provisions for digital e-stamping.
- “Electronic stamp” or “e-stamp” means an electronically generated impression denoting the payment of stamp duty by electronic means or otherwise, according to Section 2 (18) of the Bill.
- There are also provisions for digital signatures.
- Section 2 (17) of the Bill states that the words “executed” and “execution”, used for instruments, will mean “signed” and “signature” and include attribution of electronic records and electronic signatures, as defined under the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000.
- The IT Act defines “electronic records” as “data, record or data generated, image or sound stored, received or sent in an electronic form or micro film or computer generated microfiche.”
- Meanwhile, digital or electronic signature refers to the authentication of any electronic record by a subscriber through an electronic method or procedure.
- The draft Bill also proposes to raise penalties.
- It seeks to increase the maximum penalty amount from Rs 5,000 to Rs 25,000 for contravening any provisions of the law and impose Rs 1,000 per day for repeated offences.
What is the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899?
- The Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 is a fiscal or money-related statute that lays down the law relating to tax levied in the form of stamps on instruments recording transactions.
- Under Section 2 of the Act, an instrument includes every document by which any right or liability is or purports to be, created, transferred, limited, extended, extinguished or recorded.
- According to this Act, a “stamp” has been defined as “any mark, seal or endorsement by any agency or person duly authorised by the State Government, and includes an adhesive or impressed stamp, for the purposes of duty chargeable under this Act”.
- Section 3 of the 1899 Act prescribes that certain instruments or documents shall be chargeable with the amount indicated in Schedule 1 of the Act.
- These include bills of exchange or promissory notes.
Framework for Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector (Down To Earth)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The central government recently launched a framework to promote voluntary carbon markets in the agriculture sector.
What are Carbon Markets?
- Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought.
- Companies or individuals can use carbon markets to compensate for their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing carbon credits from entities that remove or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- One tradable carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas reduced, sequestered or avoided.
- When a credit is used to reduce, sequester, or avoid emissions, it becomes an offset and is no longer tradable.
Why are Carbon Markets Important?
- Scientists warn that 2°C of warming will be exceeded during the 21st century unless we achieve deep reductions in GHG emissions now.
- Effective action will require concerted and sufficient investment, knowing also that the costs of inaction will be far higher.
- The latest IPCC report finds all countries are falling way short, with financial flows three to six times lower than levels needed by 2030 – and even starker differences in some regions of the world.
- Many countries are turning to carbon markets as a key component in driving and financing the necessary transformation to tackle the climate crisis.
How Many Types of Carbon Markets Are There?
- There are broadly two types of carbon markets: compliance and voluntary.
- Compliance markets are created as a result of any national, regional and/or international policy or regulatory requirement.
- Voluntary carbon markets (VCM)– national and international – refer to the issuance, buying and selling of carbon credits, on a voluntary basis.
- The current supply of voluntary carbon credits comes mostly from private entities that develop carbon projects, or governments that develop programs certified by carbon standards that generate emission reductions and/or removals.
Importance of Establishing a VCM Framework in the Agricultural Sector:
- Emission Concerns: Agriculture in India contributes approximately 15% of the nation's greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the urgent need for mitigation strategies.
- Vulnerability: With around 50% of cultivated land being rainfed and more than 80% of farmers categorized as small or marginal, the sector is highly susceptible to the impacts of climate change.
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (2010): This initiative focuses on promoting adaptation measures such as agroforestry, micro irrigation, and soil health management, which not only reduce emissions but also offer opportunities for carbon sequestration.
- Additional Income Opportunities: Through the implementation of these practices, farmers can potentially generate additional income streams.
'Maratha Military Landscapes' to be India's nomination for UNESCO World Heritage List for 2024-25 (The Hindu)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
'Maratha Military Landscapes' representing extraordinary fortification and military system envisioned by the Maratha rulers will be India's nomination for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List for the 2024-25 cycle, the Culture Ministry said on January 29.
About Maratha Military Landscapes:
- Developed between the 17th and 19th centuries, the nomination comprises the 12 components of Salher Fort, Shivneri Fort, Lohgad, Khanderi Fort, Raigad, Rajgad, Pratapgad, Suvarnadurg, Panhala Fort, Vijaydurg, Sindhudurg in Maharashtra, and Gingee Fort in Tamil Nadu.
- These components are strategically distributed across diverse geographical and physiographic regions, highlighting the military prowess of the Maratha rule.
- The landscapes showcase the integration of landscape, terrain, and physiographic characteristics distinctive to the Sahyadri mountain ranges, the Konkan Coast, the Deccan Plateau, and the Eastern Ghats in the Indian Peninsula.
- Out of the more than 390 forts in Maharashtra, only 12 have been chosen under the 'Maratha Military Landscapes of India'.
- The inception of the Maratha Military ideology dates back to the 17th century during the reign of the Maratha King Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, continuing through subsequent rules until the Peshwa rule of 1818 CE.
UNESCO Nomination Criteria:
- There are two categories of nomination- cultural and natural criteria.
- The Maratha Military Landscapes is nominated under cultural criteria.
- To fulfil this criterion, a site should bear unique testimony to cultural tradition, it should be an outstanding example of a type of building, architectural or technological ensemble, or landscape that illustrates significant stage(s) in human history and it should be directly or tangibly associated with events or living traditions, ideas or beliefs, artistic and literary works of outstanding universal significance.
World Heritage Sites In India:
- India presently boasts 42 World Heritage sites, with 34 cultural sites, 7 natural sites, and 1 mixed site.
- Maharashtra alone has six World Heritage Sites including:
- The Ajanta Caves
- Ellora Caves
- Elephanta Caves
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus
- Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai, and
- The Western Ghats (a natural site)
Tentative List Recognition:
- The Maratha Military Landscapes of India, included in the Tentative List of World Heritage sites in 2021, is the sixth cultural property nominated for inclusion in the World Heritage List from Maharashtra.
Govt Brings Non-urea Fertilisers Under Price Control (Indian Express)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Modi government has brought di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), muriate of potash (MOP) and all other fertilisers that receive nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) support under “reasonable pricing” controls.
What is the Central Government's Decision on Non-Urea Fertilizers?
- The Department of Fertilisers (DoF) under the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilisers has issued comprehensive guidelines for assessing the fairness of Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs) for all non-urea fertilisers covered by the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme.
- Effective from April 1, 2023, these guidelines set maximum allowable profit margins for different types of fertilizer companies: 8% for importers, 10% for manufacturers, and 12% for integrated manufacturers.
- Companies deemed to be earning excessive profits beyond these thresholds during a financial year (April-March) are required to reimburse the surplus to the DoF by October 10 of the following fiscal year.
- Failure to comply within the specified timeframe will result in the imposition of a 12% per annum interest rate on the refund amount, calculated from the day after the end of the financial year.
- Any unreasonable profits will be deducted from future fertilizer subsidy payments by the government.
How will Companies Unreasonable Profit be Determined?
- Fertilizer companies are required to conduct a self-assessment of unreasonable profits, using cost auditor's reports and audited cost data approved by their board of directors.
- This information must be submitted to the Department of Fertilisers (DoF) by October 10 of the subsequent fiscal year.
- The DoF will then review the reasonableness of Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs) submitted by companies by February 28 for each completed previous financial year.
- Subsequently, it will prepare a report on any unreasonable profits earned and to be recovered from the companies.
Significance of the New DoF Guidelines:
- Non-urea fertilizers are already informally price-controlled, a measure expected to continue until the conclusion of the Lok Sabha elections.
- The new guidelines establish indirect MRP controls on non-urea fertilizers by limiting the profits companies can earn from their sales.
- These limits will be based on the total cost of sales, encompassing production or import costs, administrative overheads, selling and distribution expenses, as well as net interest and financing charges.
- Essentially, the new guidelines extend the detailed cost monitoring and price control regime currently applied to urea to other fertilizers.
What is the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme?
- NBS fertilisers are technically decontrolled unlike urea, whose maximum retail price (MRP) is fixed by the government.
- Under the NBS scheme, introduced in April 2010, their MRPs are supposed to be market-determined and set by the individual companies selling them.
- The government merely pays a fixed per-tonne subsidy on each of these fertilisers, linked to their nutrient content or specific percentage of nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), potassium (K) and sulphur (S).
- Unlike the previous system, where subsidies were product-specific, the NBS Scheme encourages balanced fertilization by discouraging excessive use of high-nutrient fertilizers like urea, DAP, and MOP.
- It aims to promote innovation in fertilizer products and encourages the use of complex fertilizers and single super phosphate to address nutrient imbalances.
- However, the scheme faced challenges as urea consumption increased significantly, leading to nutrient imbalances and subsequent failure.
Delhi HC Upholds Validity of Anti-profiteering Provision of CGST Act (TOI)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi High Court has upheld the constitutional validity of the anti-profiteering clause in the GST law, which mandates companies to pass on the benefit of lower taxes and input tax credits to consumers.
What is an ‘Anti-profiteering’ Activity?
- Any reduction in the rate of GST tax on any supply of goods or services or the benefit of input tax credit should have been passed on to the recipient by way of a commensurate reduction in prices.
- The wilful action of not changing the final price of the good or service by various means, despite the reduction in the rate of the tax for that particular good or service, amounts to “profiteering”.
How is the Anti-profiteering Mechanism Under the CGST Act?
- CGST mandate a 3-tier structure for investigation and adjudication of the complaints regarding profiteering.
- a) National Anti-profiteering
- b) Authority Directorate General of Safeguards
- c) State-level screening committees and standing committee
How Does the Screening Committee and Standing Committee Work?
- GST council may constitute a standing committee, having members from both state and central government.
- Every state shall constitute one state-level screening committee.
- It will have one member from the state government and one member from the central government as nominated by the respective appropriate authority.
- The complaints or issues of local nature will be first examined by the screening committee.
- State-level screening and standing committee will examine the complaint and determine the prime facie evidence to support the validity of the complaint.
- If any committee satisfies that the supplier has contravened section 171 of the CGST Act, the case shall be transferred to DG Safeguards for further investigation.
- The committees shall complete the investigation within a period of a month from the date of the receipt of the application.
What is the Role of DG Safeguards in the Anti-profiteering Mechanism?
- DG safeguards are the main investigation arm in the anti-profiteering mechanism.
- It can summon the interested parties make inquiries or call the relevant documents.
- It can seek help from technical experts in the due course of investigation.
- DG Safeguards shall complete the investigation within a period of three months from the date of receipt of the report from either screening or standing committee.
- The period can be extended for another three months.
Who Can File the Complaint Against Profiteering?
- Any consumer or organisation experiencing a non-reduction in the price of the goods or service despite the reduction in the rate of GST can file a complaint with proper evidence.
- Any supplier, trader, wholesaler or retailer, who could not get the benefit of input tax credit on account of a reduction in the rate of GST, can also file the complaint with proper evidence.
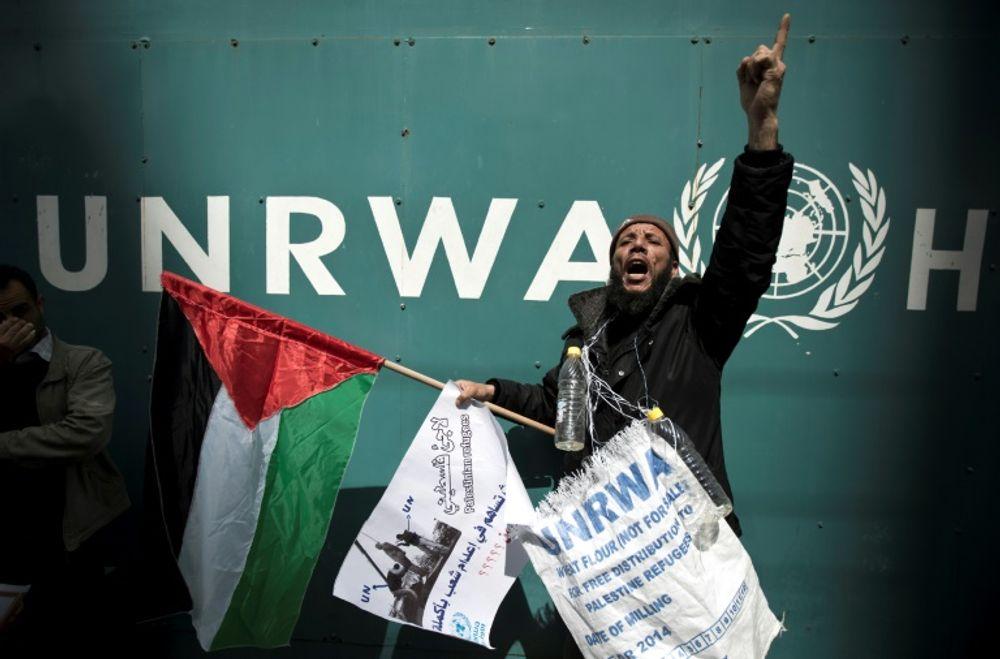
Western Countries Halt UNRWA Funding Amid Gaza War (Indian Express)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
UN officials recently urged countries to reconsider their decision to suspend funding for UNRWA, promising strict action against any staff member implicated in Hamas’ October 7 attack on Israel.
Context:
- Recently UN officials urged countries to reconsider their decision to suspend the funding for the United Nations agency for Palestinian refugees (UNRWA).
- The agency highlighted that two million Palestinians in Gaza are dependent on UNRWA services.
- The US and eight other Western countries, which together provided more than half of UNRWA’s 2022 budget, cut the money after Israel accused some of the agency’s staff members of involvement in the October 7 attack.
What is the United Nations Refugee Agency for Palestinians (UNRWA)?
- UNRWA stands for UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East.
- It was founded in 1949 to provide aid to about 700,000 Palestinians who were forced to leave their homes in what is now Israel during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
- The UN agency operates in Gaza and the Israeli-occupied West Bank, as well as Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan — countries where the refugees took shelter after their expulsion.
- It runs education, health, relief and social services, microfinance and emergency assistance programmes inside and outside refugee camps based in the aforementioned areas.
- Currently, around 5.9 million Palestine refugees — most of them are descendants of original refugees — access the agency’s services.
- Over 1 million are sheltering in UNRWA schools and other facilities in Gaza.
- Funding: UNRWA is funded almost entirely by voluntary contributions by donor states like the US.
- It also gets a limited subsidy from the UN, which is used only for administrative costs, the agency’s website said.
What has Israel accused UNRWA of?
- Israel has alleged that 12 staff members of UNRWA were involved in the October 7 attack.
- It has also claimed that Hamas siphons off funds given to UNRWA and fights from in and around the agency’s facilities.
- Israel has alleged that “Hamas tunnels (are) running next to or under UNRWA facilities and accuses the agency of teaching hatred of Israel in its schools.
How has UNRWA Responded?
- The UNRWA has denied all the allegations, saying it has no links to Hamas.
- In the statement, UN officials said out of 12 staff members who were accused of being involved in the attack, nine have been terminated.
- One is confirmed dead and the identity of the two others is being clarified.
What Happens Now?
- UNRWA is crucial for the survival of people living in Gaza, which has plunged into a humanitarian crisis after the outbreak of the conflict.
- The agency has been the main supplier of food, water and shelter to civilians of the enclave.
- UNRWA, however, would run out of money needed for its aid work within weeks if the funding isn’t restored.
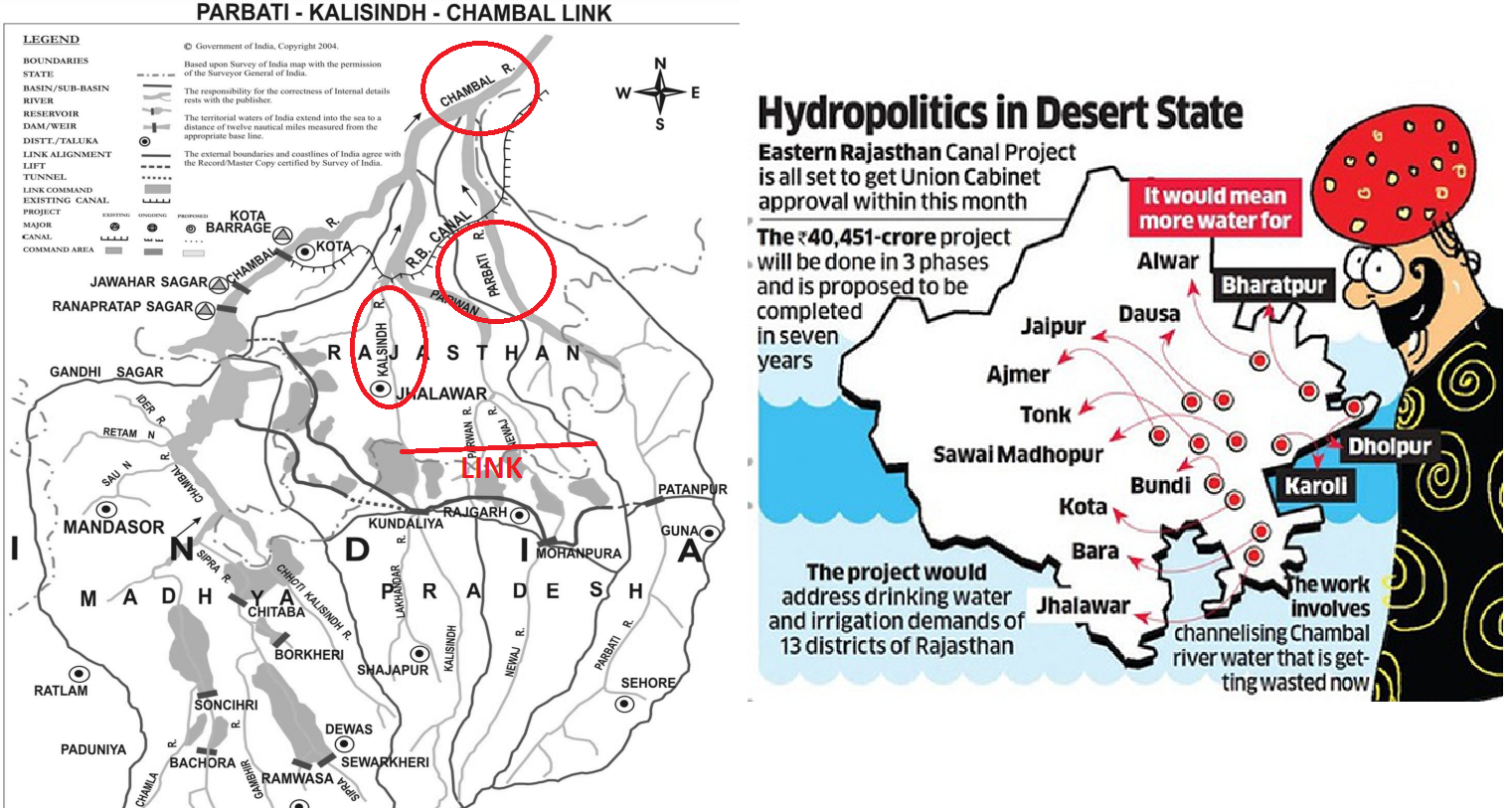
Modified Parbati-Kalisindh- Chambal-ERCP (PKC-ERCP) Link Project (Indian Express)
- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An MoU was signed by Rajasthan and MP with the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti Sunday for implementation of the Modified Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-ERCP (Modified PKC-ERCP) Link Project.
What is the Modified PKC-ERCP?
- The Modified PKC-ERCP is an inter-state river linking project.
- A Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) will be finalised among Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Centre, covering the sharing of water, exchange of water, sharing of costs and benefits, implementation mechanisms, arrangements for management and control of water in the Chambal basin, etc.
What is the PKC link project?
- The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) link project is one of the 30 links included in the National Perspectives Plan formulated by the erstwhile Union Ministry of Irrigation (now Ministry of Water Resources) and the Central Water Commission in the year 1980.
- As per the National Water Development Agency (NWDA), the preliminary feasibility report of the Kalisindh-Chambal link canal project was prepared and circulated to the states concerned in September 1991.
- The report proposed the diversion of water from river Newaj (a tributary of Kalisindh) and Kalisindh to the river Chambal at either the Rana Pratap Sagar dam or the Gandhi Sagar dam.
- Rajasthan came up with the proposal of the ERCP in 2019, and to utilise water resources optimally, the Task Force for Interlinking of Rivers (TFILR) discussed its merger with the PKC link project.
- This integration was approved by the Special Committee for Interlinking of Rivers in December 2022.
What is the ERCP?
- The Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) is aimed at the intra-basin transfer of water within the Chambal basin, by utilising surplus monsoon water available in the Kalisindh, Parvati, Mej and Chakan subbasins and diverting it into water deficit sub-basins of Banas, Gambhiri, Banganga and Parbati.
- This will provide drinking and industrial water to 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan, namely Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, Sawai-Madhopur, Dausa, Jaipur, Ajmer, Tonk, Bundi, Kota, Baran, and Jhalawar.
What are the benefits of the modified project?
- According to the Jal Shakti Ministry, the link project proposes to provide drinking and industrial water in 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan, and Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh, apart from providing irrigation in 2.8 lakh ha. area (or more) each in both states (total of 5.6 lakh ha or more).
What is River Interlinking?
- River Interlinking involves the creation of artificial channels to connect rivers and water bodies, facilitating the transfer of water from regions of surplus to those facing deficits.
- Importance of River Interlinking:
- Disaster Management: River Interlinking plays a crucial role in mitigating floods and droughts, aiding in effective disaster management strategies.
- Economic Benefits: It offers economic advantages such as enhanced irrigation facilities, increased hydro-power generation capacity, and improved inland navigation, contributing to regional development.
- Ecological Restoration: River Interlinking initiatives contribute to the restoration of river ecosystems and provide support to biodiversity in water-deficient regions, fostering ecological balance.
- Concerns Associated with River Interlinking:
- Biodiversity Loss: One major concern revolves around the potential loss of biodiversity resulting from altering natural river courses and habitats.
- Community Displacement: Another significant issue is the displacement of communities residing in areas affected by river interlinking projects, highlighting social and humanitarian challenges.
About the National Perspective Plan:
- The National Perspective Plan was formulated in 1980 under the purview of the Ministry of Irrigation (currently known as the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and the Central Water Commission.
- Objective:
- The plan aims to address regional disparities by facilitating the inter-basin transfer of water resources, thereby minimizing imbalances across different regions of the country.
- Components:
- The plan consists of 30 link projects categorized into two main components:
- the Himalayan component, comprising 14 projects, and
- the Peninsular component, consisting of 16 projects.
- The plan consists of 30 link projects categorized into two main components:
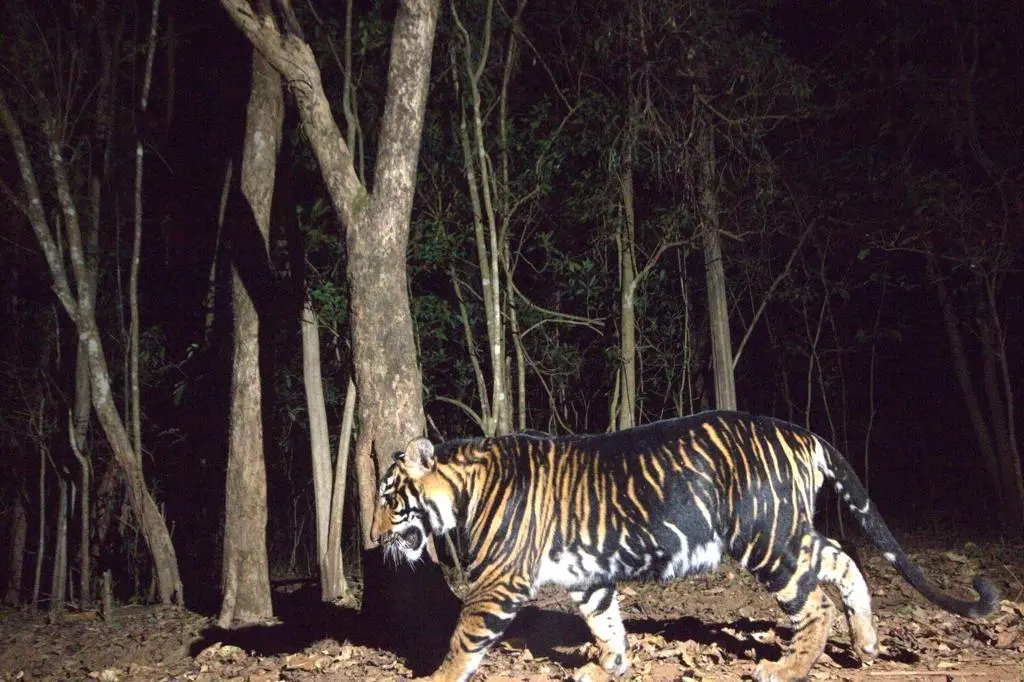
World's First 'Black Tiger Safari', to be Established in Odisha (TOI)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha is gearing up to provide an unparalleled experience to visitors through its upcoming black tiger safari, offering a rare glimpse into the lives of these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
What are Black Tigers or Melanistic Tigers?
- Black tigers, also known as melanistic tigers, are a unique phenomenon resulting from a genetic condition called melanism.
- Melanism causes an increased production of melanin, a pigment responsible for hair, eye, and skin colouration, resulting in black or nearly black skin, feathers, or hair in animals.
- In Simlipal Tiger Reserve, many royal Bengal tigers belong to a distinct lineage characterized by higher-than-normal levels of melanin.
- These tigers exhibit black and yellow interspersed stripes on their coats, though they are not entirely black.
- Therefore, they are more accurately described as pseudo-melanistic.
- As per the 2022 All-India Tiger Estimation, 16 tigers were recorded in Similipal Tiger Reserve, out of which 10 were melanistic.
- However, ongoing tiger surveys conducted by the state government suggest that the actual number of royal Bengal tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve may be higher than reported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Factors Contributing to (Pseudo) Melanism:
- Research conducted by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) in Bengaluru indicates that a single mutation in the gene Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) is responsible for the enlargement or spreading of black stripes into the yellow background of black tigers.
- Genetic analyses and computer simulations suggest that Similipal's black tigers may have originated from a very small founding population of tigers and are likely inbred.
- Additionally, the isolation of tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve leads to breeding within the population, further contributing to the prevalence of melanism among these tigers.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal, which derives its name from the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree, is a national park and a Tiger Reserve situated in the northern part of Orissa’s Mayurbhanj district.
- It spans an expansive area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 square miles), bordering Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a key component of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which encompasses three protected areas:
- Similipal Tiger Reserve
- Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biodiversity: Similipal is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of wildlife including the majestic Bengal tiger, the iconic Asian elephant, the formidable gaur, and the elusive chausingha.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves site since 2009, it stands as Asia's second-largest biosphere reserve, following the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- Notably, Similipal Tiger Reserve holds the distinction of being the sole natural habitat in India for melanistic royal Bengal tigers, adding to its ecological significance.
The Procedure of Appointment of a Chief Minister (The Hindu)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Janata Dal (United) president Nitish Kumar took oath as Bihar Chief Minister for a record ninth time on Sunday, returning to the BJP-led National Democratic Alliance just 18 months after he left it, in his fifth switch in political loyalties since 2015.
About Chief Minister:
- According to Article 163 of the Indian Constitution, each state shall have a Council of Ministers led by the Chief Minister (CM) to assist and provide advice to the Governor in carrying out the state's functions.
- In the parliamentary system of governance, the Chief Minister holds the actual executive authority within states.
- While the Governor serves as the ceremonial head of the state, the Chief Minister serves as the head of the government.
- In the Indian political framework, the Chief Minister's role is analogous to that of the Prime Minister at the national level.
Appointment Process of Chief Minister:
- The Constitution of India does not lay down specific criteria for the appointment of a Chief Minister.
- Article 164 of the Indian Constitution stipulates that the Governor is responsible for appointing the Chief Minister, albeit with certain limitations.
- Traditionally, the leader of the largest party in the state legislature is typically chosen as the Chief Minister, following parliamentary conventions.
- Even individuals who are not members of the state legislature (both Houses) can be appointed as Chief Minister for a temporary period of six months, during which they must secure election or nomination (in the case of a bicameral legislature).
- In situations where no single party or pre-poll coalition secures a majority in the assembly (known as a hung assembly), the Governor exercises discretionary powers to appoint the Chief Minister, relying on individual judgment.
- The Constitution does not mandate the Chief Minister-elect to demonstrate majority support in the state assembly before assuming office.
- However, after the formation of the ministry, the Governor may request the Chief Minister to prove majority support within a reasonable timeframe.
Oath and Affirmation of Chief Minister:
- The third Schedule of the Indian Constitution outlines the "Forms of Oaths or Affirmations" to be taken by public officials.
- Typically, the Chief Minister's oath, solemnly administered by the Governor, constitutes a formal commitment to uphold the constitution and execute the responsibilities of the position with integrity and diligence.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Chief Minister:
- The Chief Minister serves as the principal advisor to the Governor on matters pertaining to the convening and adjournment of state legislative sessions.
- As the head of the State Legislative Assembly, the Chief Minister acts as the primary liaison between the Governor and the Council of Ministers.
- The Chief Minister possesses the authority to propose the dissolution of the legislative assembly to the Governor when deemed necessary.
- Additionally, the Chief Minister assumes the role of vice-chairman of the relevant zonal council on a rotational basis, serving a term of one year.
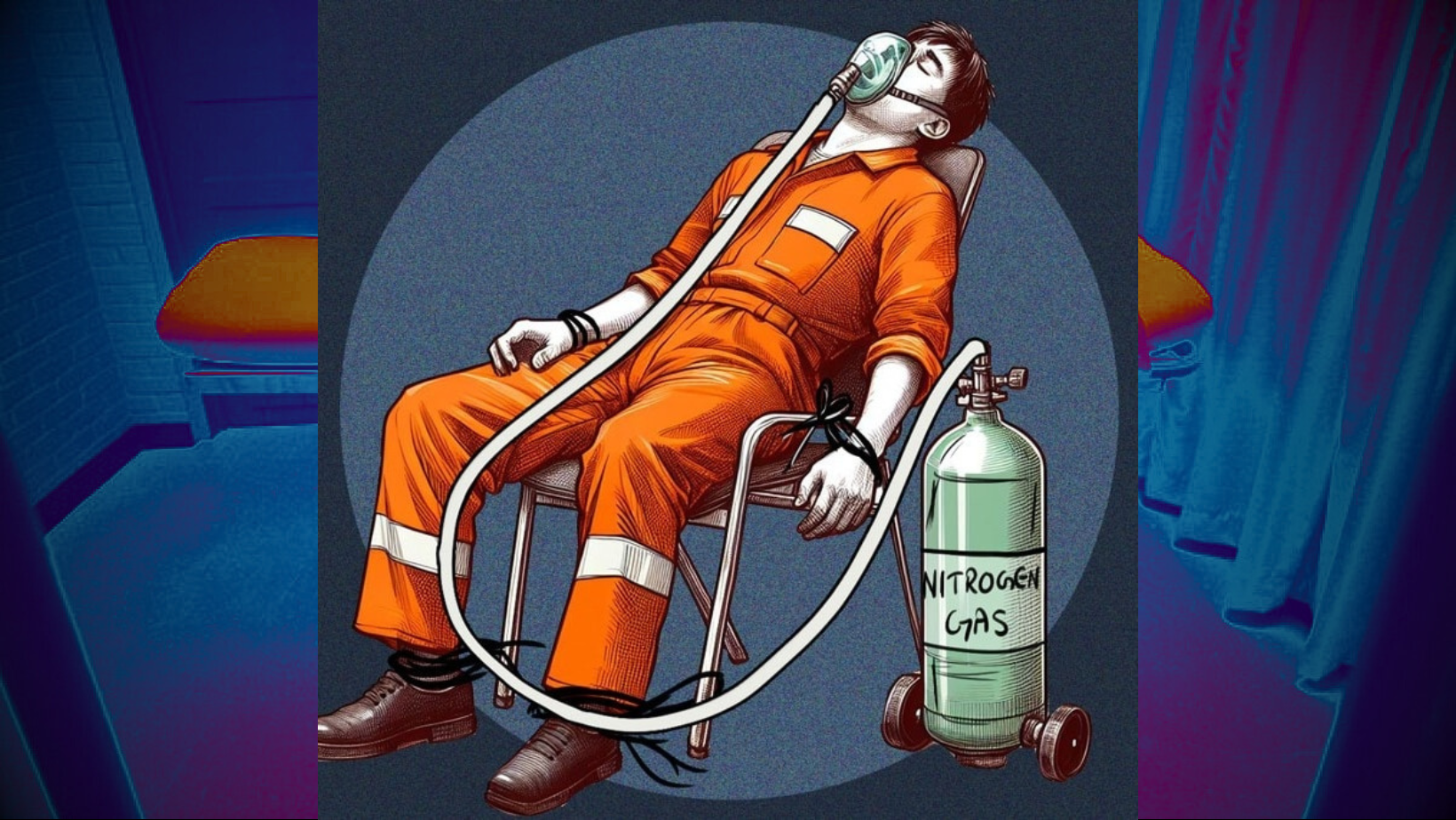
Alabama in USA Carried Out the First Ever Execution Using Nitrogen Gas (Indian Express)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Alabama inmate Kenneth Smith was executed on January 25 by nitrogen hypoxia, marking the United States’ first execution using the method, and the first time in over four decades that a new method of execution was introduced since lethal injection was first used in 1982.
News Summary:
- An Alabama death row inmate has been put to death by nitrogen gas, in the first known execution of its kind in the US.
- His case marks the first known execution by nitrogen hypoxia, which his lawyers had argued amounted to a form of “cruel and unusual punishment”.
- Death by nitrogen gas is an untested procedure, and its opponents say it can cause unnecessary suffering.
- Kenneth Smith, 58, was a contract killer who had been on the death row since 1996.
What is Nitrogen Hypoxia?
- Nitrogen hypoxia is a style of execution wherein an inmate is made to inhale nitrogen instead of oxygen, leading to gradual asphyxiation.
- To achieve this, a respirator mask is placed over the head of the inmate on death row.
- While the air we breathe is made up of 80 per cent nitrogen, it exists in combination with oxygen, rendering the colourless, odourless gas harmless.
- However, if a person is deprived of oxygen and made to breathe in just nitrogen, the gas proves lethal.
- When a high concentration of nitrogen is inhaled, it replaces the oxygen in the body and disables the respiratory system, causing death.
Why Nitrogen Hypoxia?
- Nitrogen hypoxia is the first new method of execution to be introduced since 1982 when lethal injections began being used.
- The drug needed to administer lethal injections to inmates on death row became harder to access over time, pushing authorities to scout for alternatives.
- Further, there were reports of a surge in complications associated with the procedure as well.
- As of now, only three states in the United States have approved the use of nitrogen gas to execute death row inmates, namely, Alabama, Oklahoma, and Mississippi.
Is Nitrogen Hypoxia Ethical?
- There is little research regarding death by nitrogen hypoxia.
- When the State is considering using a novel form of execution that has never been attempted anywhere, the public has an interest in ensuring the State has researched the method adequately and established procedures to minimise the pain and suffering of the condemned person.
- The risks associated with this method of execution include the risks surrounding the chances of a gas leak if the mask is not secured well on the inmate.
- The law requires that this execution not be cruel.
Key facts about Nitrogen:
- The air around us, the atmosphere, is made up of about 78% nitrogen and only 21% oxygen.
- The rest comprises water vapour, argon, neon, helium, hydrogen and xenon.
- Those are known as "permanent gases".
- There is also a range of "variable gases" in the atmosphere.
- They include methane, ozone and carbon dioxide — with concentrations that can vary from day to day and region to region.
- At a concentration of 78% in the atmosphere, nitrogen is safe to breathe.
- But it grows dangerous and potentially fatal once levels of nitrogen reach 80% or more.
- Nitrogen has no odour, is tasteless, and colourless.
- Nitrogen gas is inert, but certain soil bacteria can "fix" nitrogen into a usable form for plants and animals.
- French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisier named nitrogen azote, meaning without life.
- Nitrogen was sometimes referred to as 'burnt' or 'dephlogisticated' air.
- Nitrogen compounds are found in foods, fertilizers, poisons, and explosives.
- It is responsible for the orange-red, blue-green, blue-violet, and deep violet colours of the aurora.
- Nitrogen has a valence of 3 or 5.
- Discovery: Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772
- Nitrogen is the fifth most abundant element in the universe.
PM Modi Inaugurates the Diamond Jubilee Celebration of the SC (The Hindu)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Sunday said ?800 crore has been approved for the expansion of the Supreme Court building complex while underlining that “ease of justice is the right of every Indian citizen and the Supreme Court is its medium”.
About the Supreme Court of India (SC):
Historical Context:
- The Supreme Court of India, inaugurated on January 26, 1950, coinciding with India's Republic Day, stands as the apex judicial body of the nation.
- Article 124 of the Constitution states that “There shall be a Supreme Court of India.”
- Situated on Tilak Marg, New Delhi, it initially operated from the Parliament House before relocating to its current edifice.
- The present building of the Supreme Court was inaugurated on August 4, 1958, by the first President of India, Dr. Rajendra Prasad.
Judicial Composition:
- The original Constitution envisioned a Supreme Court comprising a Chief Justice and seven puisne Judges, with subsequent increments authorized by Parliament to meet the burgeoning caseload.
- Presently, the Supreme Court consists of 34 Judges, including the Chief Justice, who convene in smaller benches of two or three, while larger benches of five or more, known as Constitution Benches, address critical constitutional matters or resolve conflicting decisions.
Jurisdiction and Powers:
- Endowed with original, appellate, and advisory jurisdiction, the Supreme Court serves as the final interpreter of the Constitution and the ultimate court of appeal.
- Its exclusive original jurisdiction extends to disputes between the Government of India and States or between States (Article 131), while Article 32 empowers it to safeguard Fundamental Rights through writs.
- Additionally, the Supreme Court exercises appellate jurisdiction over High Courts and other judicial bodies, with the power to entertain appeals on substantial questions of law and issue special leave to appeal under Article 136.
- Special advisory jurisdiction is vested in the Supreme Court under Article 143, allowing it to deliberate on matters referred by the President of India.
Judicial Powers and Enforcement:
- Empowered to issue writs and directions for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights, the Supreme Court wields authority to punish for contempt of court, including self-contempt.
- It can reconsider its final judgments through curative petitions and holds the authority to transfer cases between High Courts and adjudicate on election petitions.
Binding Authority:
- As the apex judicial body, judgments rendered by the Supreme Court carry binding precedent on all subordinate courts and tribunals across India, ensuring uniformity and consistency in legal interpretation and application.
AISHE report shows higher enrollment of women in higher education for 8 consecutive years (Indian Express)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the last eight years, more women have enrolled in higher education compared to men, according to the 2021-22 All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) released recently.
Major Highlights of the AISHE Report 2021-22:
- The All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) for 2021–2022 has recently been released, and it highlights a notable change in enrolment trends.
- Women have enrolled in higher education at a higher rate than men during the last eight years, which is a significant step toward gender parity in academic fields.
Women Lead the Surge:
- According to the AISHE report, women now constitute 55 percent of the total increase in higher education enrollment, accounting for a staggering 91 lakh individuals since the academic year 2014-15.
- The latest statistics indicate that out of the overall enrollment of 4.33 crore, 48 percent, or 2.07 crore, are women—a marginal uptick from the 2.01 crore recorded in the previous academic year.
- The trend, characterized by a continuous surge in female enrollment since 2014-15, is particularly noteworthy.
- The report highlights an 18.7 percent increase in the enrollment of women from 2017-18 to 2021-22, showcasing a consistent upward trajectory.
Narrowing the Gender Gap:
- The gender gap in higher education is steadily narrowing, with the science stream standing out as a domain where women are making significant strides.
- Notably, 52.1 percent of the 57.18 lakh students enrolled in science at the undergraduate, postgraduate, MPhil, and PhD levels are women.
- The undergraduate level alone witnesses 51 percent of women in the science stream.
- However, disparities persist in certain disciplines, such as engineering and technology, where female enrollment lags significantly behind.
- The AISHE survey reveals that of the total students in undergraduate engineering programs, only 11.3 lakh are females, while 27.6 lakh are males.
- In addition to undergraduate programs, the report sheds light on postgraduate and PhD levels, showcasing a remarkable 61.2 percent of women in postgraduate science programs and a significant 62 percent representation in PhD programs in the sciences.
- State-wise Enrolment: The top 6 states in terms of student enrollment are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, and Rajasthan, constituting 53.3% of total enrollment.
- Number of Foreign Students: There are 46,878 foreign students enrolled in higher education, with the highest share from Nepal (28%).
- Teaching Staff in Higher Education: The total number of faculty/teachers in 2021-22 is 15.98 lakh, with about 56.6% male and 43.4% female, showing an increase of 46,618 teachers over 2020-21.
- This emerging trend is not only indicative of changing societal dynamics but also underlines the need for continued efforts to foster inclusivity and equal opportunities within the realm of higher education.
- The report serves as a testament to the progress made while emphasizing the areas that still require attention and intervention.
About the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) Report:
- The All India Survey on Higher Education serves as the primary source of comprehensive data regarding the state of higher education in India.
- Published by the Ministry of Education, this survey has been ongoing since 2011, covering all higher educational institutions across the country.
- It gathers detailed information on various aspects including student enrollment, faculty data, infrastructure, and finances.
- The report relies on voluntary data submission by higher education institutions listed on the aishe.gov.in portal, with the accuracy of the data overseen by the respective institution's Nodal Officers.
What are incestuous ‘sapinda’ marriages, and why has the Delhi High Court reaffirmed the ban on them? (Indian Express)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi High Court this week rejected a challenge to the constitutionality of Section 5(v) of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 (HMA), which prohibits marriage between two Hindus if they are “sapindas” of each other — “unless the custom or usage governing each of them permits of a marriage between the two”.
What was the Case?
- In 2007, the marriage of a woman was declared void after her husband proved it was a sapinda marriage and she did not come from a community where such marriages were customary.
- This decision was challenged in the Delhi High Court, which dismissed the appeal in October 2023.
- The woman then petitioned the High Court again, challenging the legality of the sapinda marriage ban.
- She claimed that sapinda marriages take place even when there is no evidence of custom.
- As a result, Section 5(v), which prohibits sapinda marriages unless an established custom exists, violates the right to equality guaranteed by Article 14 of the Constitution.
- The petitioner also claimed the marriage had received the consent of both families, demonstrating its legitimacy.
What are Sapinda Marriages?
- A sapinda marriage is one between two people who are related to each other to some extent.
- According to Section 3(f)(ii), “Two persons are said to be sapindas of each other if one is a lineal ascendant of the other within the limits of sapinda relationship, or if they have a common lineal ascendant who is within the limits of sapinda relationship with reference to each of them.”
- According to the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA), on the mother's side, a Hindu person cannot marry anyone within three generations of them in the "line of ascent".
- On the father's side, this prohibition applies to anyone within five generations of the individual.
- This means that on their mother's side, a person cannot marry their sibling (first generation), parents (second generation), grandparents (third generation), or anyone else who shares this ancestry within the three generations.
- On their father's side, this prohibition would apply to their grandparents' grandparents as well as anyone within five generations of this ancestry.
Exceptions to the Prohibition Against Sapinda Marriages?
- The only exception can be found within the same provision.
- An exception arises when the customs of the individuals involved permit sapinda marriages.
- The term "custom" is defined in Section 3(a) of the HMA.
- According to this section, a custom must have been consistently and uniformly practised for an extended period and must have gained sufficient recognition among Hindus in a specific locality, community, or family to be deemed legally binding.
Are Marriages Similar to Sapinda Marriages Allowed in Other Countries?
- In several European countries, the laws on relationships that are considered incestuous are less stringent than in India.
- In France, the crime of incest was abolished under the Penal Code of 1810, so long as the marriage was between consenting adults.
- Portuguese law also does not criminalise incest.
- Under Italian law, incest is a crime only if it causes a “public scandal”.
- In the United States, incestuous marriages are banned in all 50 states, though incestuous relationships between consenting adults are allowed in New Jersey and Rhode Island.
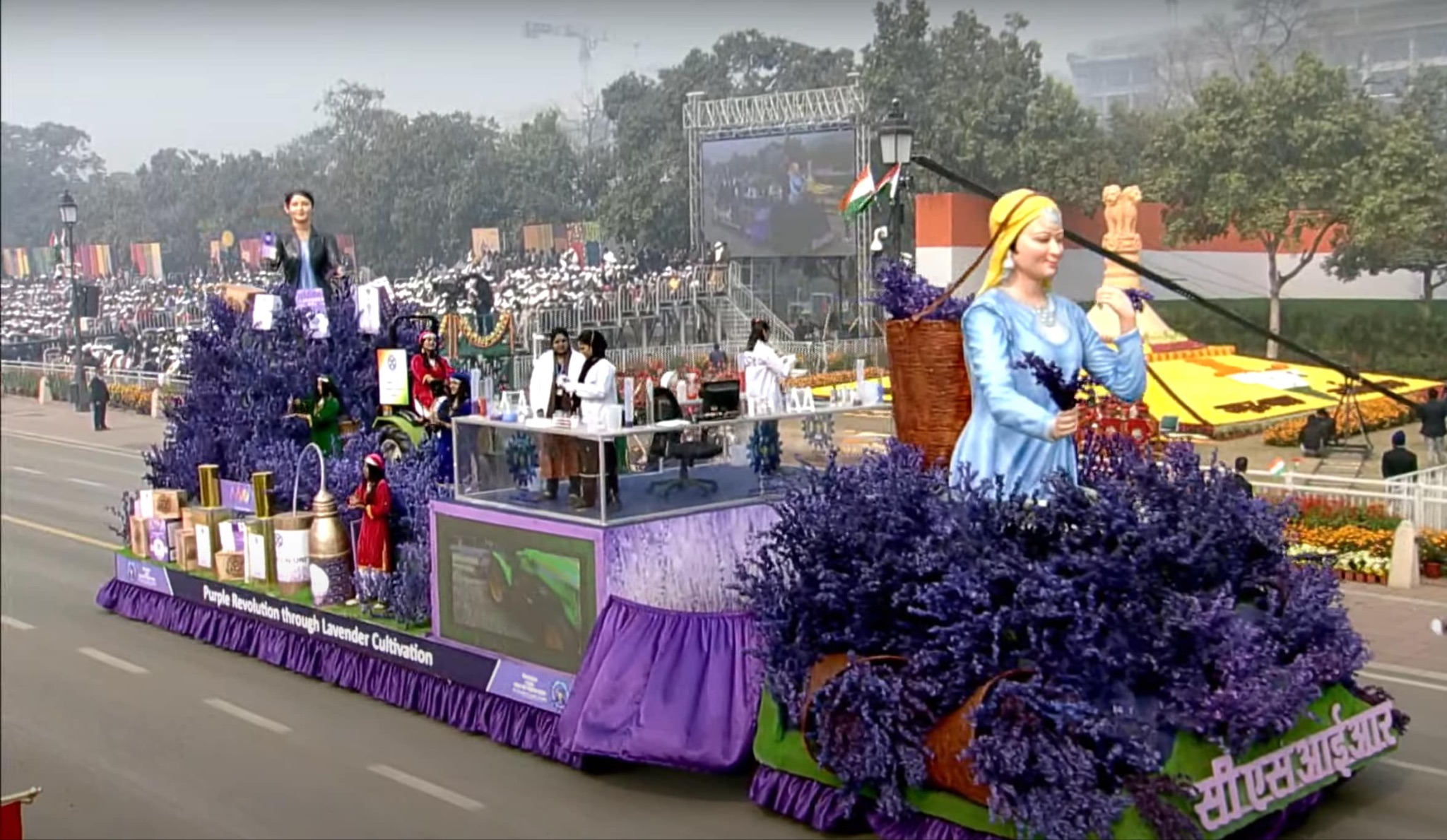
CSIR’s Republic Day Tableau highlights the Purple Revolution through Lavender Cultivation in Jammu & Kashmir (PIB)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Council of Scientific & Industrial Research's Republic Day Tableau highlighted the unleashing of a Purple Revolution ushered through Lavender cultivation in Jammu & Kashmir.
What is the Purple Revolution?
- The Purple Revolution or Lavender Revolution, launched by the Ministry of Science & Technology, aims to promote the indigenous aromatic crop-based agro-economy through the ‘aroma mission’ of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- The mission aims to increase the income of the farmers and promote lavender cultivation on a commercial scale.
- Lavender oil, which sells for, at least, Rs. 10,000 per litre, is the main commodity.
- Other popular products include medicines, incense sticks, soaps, and air fresheners.
- The cultivation of lavender is very cost-effective as it yields revenue immediately.
- Jammu and Kashmir’s climatic conditions are conducive to lavender cultivation since the aromatic plant can withstand both chilly winters and pleasant summers.
- Additionally, it is a low-maintenance crop, which can be used from its second year of plantation and blossoms for fifteen years.
- In its entirety, lavender production gives better returns when compared to other traditional crops.
- Under the One District One Product-Districts as Export Hubs (ODOP-DEH) initiative, lavender cultivation in Jammu and Kashmir has experienced a significant boom.
- Lavender has been designated by the central government as a "Doda brand product" to promote the rare aromatic plant and boost the morale of farmers, entrepreneurs, and agribusinesses involved in its cultivation as part of this Aroma Mission.
- The Aroma Mission through the Purple Revolution aims to bring about a revolutionary change in the fragrance industry, consequently promoting the expansion of the aroma sector and generating rural employment, through targeted interventions during cultivation, product refinement, market development and curating an expansion strategy for the lavender crop.
About Aroma Mission:
- The Aroma Mission, launched in 2016, aims to enhance the cultivation of plants like lavender, Aloe Vera, Mehndi, Menthol, and Mint, known for their aromatic and medicinal properties.
- Developed by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), this mission employs new technologies.
- It seeks to revolutionize the aroma sector by improving agricultural practices, processing methods, and product development.
- Additionally, it provides technical and infrastructure support to farmers and growers nationwide, ensuring fair prices through buy-back mechanisms.
- The mission targets to expand cultivation by 30,000 hectares and catalyze aromatic crop cultivation in 60,000 hectares overall.
- This expansion is expected to yield an extra 700 tonnes of essential oils used in perfumery, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, creating a business worth at least 200 crores.
Interim Budget 2024: Exporters seek higher allocation for MAI scheme (Business Standard)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the interim Budget 2024, exporters have urged the government to allocate funds worth $3.88 billion for the Market Access Initiative (MAI) scheme to promote Indian exports and help them hit the ambitious $2 trillion target by 2030.
What is the Market Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme?
- The Market Access Initiative (MAI) Scheme is an Export Promotion Scheme envisaged to act as a catalyst to promote India’s exports on a sustained basis.
- The scheme is formulated on a focus product-focus country approach to evolve specific markets and specific products through market studies/surveys.
- Assistance would be provided to Export Promotion Organizations/Trade Promotion Organizations/National Level Institutions/ Research Institutions/Universities/Laboratories, Exporters etc., for enhancement of exports through accessing new markets or through increasing the share in the existing markets.
- Under the Scheme, the level of assistance for each eligible activity has been fixed.
- The following activities will be eligible for financial assistance under the Scheme:
- Marketing Projects Abroad
- Capacity Building
- Support for Statutory Compliances
- Studies
- Project Development
- Developing Foreign Trade Facilitation Web Portal
- To support Cottage and handicraft units
How does the MAI Scheme work?
- The scheme’s primary goal is to facilitate export growth by enabling entities to enter new markets or enhance their presence in existing markets.
- To accomplish this, the scheme provides predetermined levels of assistance for each eligible activity.
- By directing attention to key products and specific markets, the MAI Scheme serves as a catalyst for driving India’s export expansion in a sustainable and strategic manner.
Who is eligible to receive assistance under the MAI Scheme?
- Various entities are eligible to receive financial assistance under the MAI Scheme, including:
- Export promotion organizations
- Trade promotion organizations
- National level institutions
- Research institutions
- Universities
- Laboratories
- Individual exporters
- Start-ups
Who administers the MAI Scheme?
- The MAI Scheme is administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, through the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
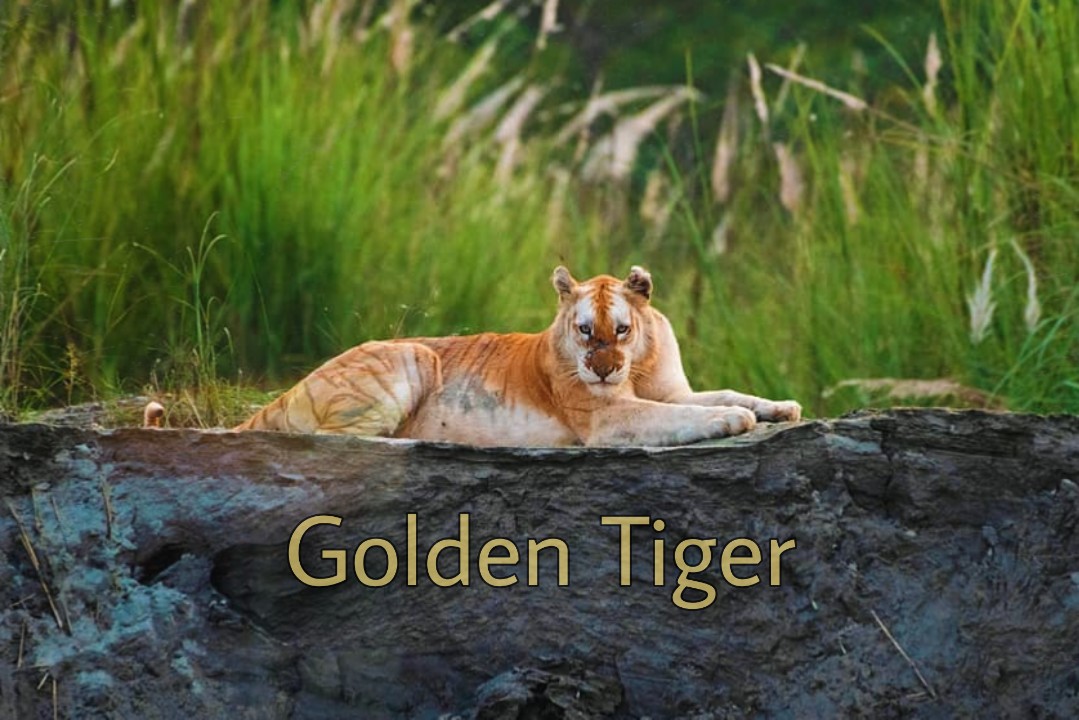
Rare Golden Tiger takes a stroll in Assam’s Kaziranga National Park, video stuns people (HT)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A rare golden tiger was recently spotted in Kaziranga National Park taking a stroll and is the only known golden big cat in India.
What is a Golden Tiger?
- A Golden Tiger, also called a Golden Tabby Tiger, is a Bengal tiger with a unique colour variation caused by a recessive gene.
- The tiger looks golden because it has a mutation or a genetic variant.
- Basically, tigers have three colours: black, orange and white.
- In the Golden Tiger, the black colour is missing and it is slightly faded.
- The golden colouring of these tigers comes from a recessive trait called 'wideband,' affecting how black pigments are produced during hair growth.
- Golden tigers are not a distinct subspecies but rather a product of genetic diversity among Bengal tigers.
- They are extremely rare in the wild and even more so in captivity.
About Kaziranga National Park:
- Kaziranga National Park lies partly in the Golaghat District and partly in the Nagaon District of Assam.
- It is the oldest park in Assam and covers an area of 430 sq km along the river Brahmaputra on the North and the Karbi Anglong hills on the South.
- The National Highway 37 passes through the park area and tea estates, hemmed by table-top tea bushes.
- Kaziranga National Park a world heritage site is famous for the Great Indian one-horned rhinoceros, the landscape of Kaziranga is of sheer forest, tall elephant grass, rugged reeds, marshes & shallow pools.
- It was declared a National Park in 1974.
- It is one of the last areas in eastern India undisturbed by a human presence.
- It is inhabited by the world's largest population of one-horned rhinoceroses, as well as many mammals, including tigers, elephants, panthers and bears, and thousands of birds.
- Vegetation: Due to the difference in altitude between the eastern and western areas of the park, mainly four main types of vegetation’ like alluvial inundated grasslands, alluvial savanna woodlands, tropical moist mixed deciduous forests, and tropical semi-evergreen forests.
- Flora: Kumbhi, Indian gooseberry, cotton tree, and elephant Apple are among the famous trees that can be seen in the park.
- Fauna: The forest region of Kaziranga Park is home to the world’s largest population of Indian Rhinoceros.
- Other animals that can be seen in the elephant grass, marshland and dense tropical moist broadleaf forests of Kaziranga are Hoolock Gibbon, Tiger, Leopard, Indian Elephant, Sloth Bear, Wild water buffalo, swamp deer, etc.
- Also in this park the good number of migratory bird species from Central Asia.
- With the increase in tiger population every year, the government authorities declared Kaziranga a Tiger Reserve in the year 2006.
As Army launches Op Sarvashakti, recalling Sarpvinash of 2003, that crushed terror base in Pir Panjal (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Army has launched Operation Sarvashakti in the Rajouri-Poonch sector of Jammu and Kashmir, deploying forces on both sides of the Pir Panjal range to target terrorists who have carried out a series of attacks on troops in the area.
What is Operation Sarvashakti?
- In a bid to combat increasing terrorist activities in Jammu and Kashmir, the Army has initiated Operation Sarvashakti, under which terrorists operating on both sides of the Pir Panjal mountain ranges in the Union Territory will be neutralised.
- There were three major attacks on the security forces in 2023, and over the past few years, 20 soldiers have been killed in terrorist ambushes in this area.
- Operation Sarvashakti, as part of which at least three brigades of additional troops are being deployed in the sector from various reserve and strike corps formations in order to increase the density of troops and, therefore, the likelihood of contact with terrorists, recalls an earlier operation by the Army in the same forests more than two decades ago.
- Back in 2003, Indian forces launched Operation Sarpvinash to flush out terrorists who had infiltrated from across the border and set up camps in the thick forests south of the Pir Panjal range, especially in the Hilkaka area in Poonch.
What was Operation Sarpvinash?
- Operation Sarpvinash, launched in April 2003, marked a significant counter-insurgency effort in Jammu and Kashmir.
- In response to intelligence indicating over 300 foreign terrorists establishing secure camps in Surankote and Hilkaka post-infiltration across the Line of Control (LoC), the three-month-long operation involved 10,000 troops in a challenging 150 sq km area.
- Employing helicopters and ground forces, the operation neutralized approximately 100 terrorists, dismantled bunkers, and recovered weapons, explosives, and supplies.
- Operation Sarpvinash successfully restored peace to the region until 2017-18, impacting the region's security dynamics.
- However, since 2021, there has been a resurgence of high-intensity attacks on security forces in this area.
Why is this area important strategically?
- The areas south of Mendhar leading to the Pir Panjal range through Hilkaka constitute among the shortest routes of access for infiltrators from across the LoC into the Kashmir valley.
- The terrorists chose this region to set up camps because dominating this area can potentially provide a conduit to personnel in the event of a military operation by the Pakistanis, and easier infiltration of terrorists.
- The dense forests and steep mountain slopes offer both adequate cover and visual domination of the area.
- Terrorists were able to merge with the foliage whenever Indian troops carried out searches in the area and inflicted casualties in case of contact.
- All of these locational advantages for terrorists remain intact to some degree even now.
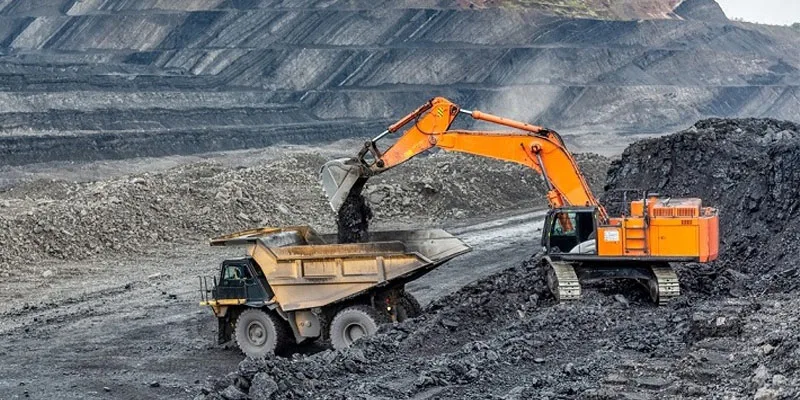
Centre approves incentive of Rs 8,500 crore for coal gasification projects (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to achieve the target of coal gasification of 100 million tonnes (MT) of coal by 2023 in India, the government recently approved Rs 8,500 crore incentives.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a thermo-chemical procedure wherein the pressure and heat of the gasifier disintegrate coal into its chemical components.
- The resulting "syngas" are mostly carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen, with some other gaseous substances thrown in for good measure.
- Coal gasification is an in-situ method wherein oxygen is infused into the seam together with water and ignited at high temperatures, causing coal to partly oxidised into hydrogen, CO, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
- Ex-situ reactors are designed to simulate the gasification process above the ground's surface.
- Sulphur in coal is transformed to H2S and trace volumes of carbonyl sulphide during the gasification process (COS).
- Acid gas removal technology can easily and cost-effectively discard these sulphur compounds.
- There is no scrubber sludge produced by coal gasification plants, which necessitates careful and expensive disposal.
- The majority of the wash water is reprocessed, and residual wastewater from gasification plants can be treated effectively.
- As a result, coal gasification is regarded as a cleaner coal technology when compared to coal combustion.
- Furthermore, coal could be used to generate a range of products using clean coal innovations such as hydrogen, methanol, and fertilisers via coal gasification.
- Carbon fibres and plastic composites made from coal power plant ash/residue.
How can it be used?
- Syngas, according to proponents of coal gasification, can be used to generate power, in energy-efficient fuel cell technology, or as chemical "building components" for industrial applications.
- The hydrogen can also be extracted and used to power a hydrogen economy.
- Coal gas can also be transformed into a transportation fuel to be used in automobiles as a replacement for gasoline, but it is less efficient than the current output and combustion of petroleum-based gasoline.
- Coal gasification is said to be more efficient than traditional coal burning since it can use the gases two times: the coal gases are first purified of contaminants before being fired inside a turbine to produce energy.
- The gas turbine exhaust heat can be then collected and used to produce steam for a steam turbine generator.
- This is known as a combined process, and according to DOE, a coal gasification processing facility using this dual method can possibly attain an efficiency of 50% or higher, compared to the customary coal power plant, which is typically just above 30%.
Significance of Coal Gasification:
- India announced environmental targets as its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement in 2016.
- In order to meet these objectives, coal gasification aids in the decrease of emission levels and the advancement of non-fossil fuel-based energy resources.
- The syngas produced by coal gasification can be used to generate urea and a variety of products such as methanol, Dimethyl ether (DME), and olefins, allowing India to minimise imports and become self-sufficient.
- Syngas CO and H2 are essential reducing agents for steel production and are regarded as an environmentally friendly technique of steel production because they reduce the import of furnace oil.
- India has ambitious plans to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) domestically rather than importing them from China.
- As a result, the potential of Syngas requirement for making APIs, as well as methanol as a solvent, is being investigated.
- The synthesis gas can be used in an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) system to generate electricity in an efficient and environmentally friendly manner.
Initiatives taken by India:
- The Ministry of Coal, through Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan, has taken the initiative, National Coal Gasification Mission, that is to utilise coal through coal gasification, with the goal of achieving 100 MT coal gasification by 2030.
- It has also been recommended that all coal companies assign a nodal officer and formulate a plan for gasifying at least 10 per cent of their coal production.
- SHAKTI policy was implemented in coal gasification projects to minimise operating costs by allocating long-term coal linkages through auction.
What is National Voters’ Day?: Govt plans events around theme for 2024 (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India today is celebrating its 14th National Voters’ Day. It is celebrated annually on January 25 since 2011 to mark the foundation day of the Election Commission of India. The ECI was founded on January 25, 1950.
Why is National Voters’ Day celebrated?
- National Voters’ Day aims to promote people’s participation in elections by encouraging and felicitating young voters and increasing voter enrolment.
- It is also utilised to spread awareness among voters and to promote informed participation in the electoral process.
- The day is celebrated at the national, state, district, constituency and polling booth levels, which makes it one of the largest celebrations in the country.
- The date chosen for National Voters' Day commemorates the formation of the Election Commission of India (ECI) on January 25, 1950.
- The ECI is an autonomous constitutional body under Article 324 entrusted with the sacred responsibility of conducting free, fair, and credible elections across the country.
- Since its inception, the ECI has played a pivotal role in upholding the democratic principles of India, ensuring the voice of every citizen is heard.
- The first National Voters’ Day was celebrated in 2011 under the leadership of the then Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) S Y Quraishi.
- Emulating India’s example, six countries, including Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal and Bhutan, have started celebrating National Voters Day.
- National Voters’ Day pledge: As a part of the celebrations, all government offices, autonomous bodies, and organisations take a pledge on the day.
- Schools and educational Institutions across the country are encouraged to conduct activities such as debates, discussions, and competitions on the theme of Voters’ Day.
What is the theme for National Voters’ Day 2024?
- The theme for this year is ‘Nothing Like Voting, I Vote For Sure’, which is a continuation of last year’s theme, and conveys an individual’s feeling and aspiration towards participation in the electoral process through the power of their vote.
- The logo for this year’s theme is designed in such a way that it showcases the festivity and inclusivity of the electoral process.
- The Ashoka Chakra in the background represents the largest democracy in the world, whereas the inked finger represents the participation of each and every voter of the country.
- The tick mark in the logo stands for informed decision-making by the voter.
A shallow lake in Canada could reveal how life on Earth began (Space.com)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have discovered a lake that could be a good match for Darwin's "warm little ponds" where life got started on the primordial Earth.
What is a Soda Lake?
- A soda lake is a lake with a pH value of more than the usual measure of 6 or 7, usually between 9 and 11.
- High carbonate concentration, especially sodium carbonate, is responsible for the alkalinity of the water.
- A soda lake may also contain a high concentration of sodium chloride and other salts making it saline or hypersaline Lake.
- Soda lakes are highly productive ecosystems compared to freshwater lakes with a global primary production rate of over 10 grams of carbon per square meter per day.
- Therefore Soda lakes are the most productive aquatic environment on Earth because of the availability of dissolved carbon dioxide.
- Soda lakes occur naturally in both arid and semi-arid areas.
Geology And Genesis Of Soda Lakes:
- A topography that limits the outflow of water from the lake is needed.
- An endorheic basin is formed when the water is confined without the outflow.
- The pH of the water in the depression rises through the evaporation of the lake which requires a suitable climate like the desert climate to balance between the inflow and evaporation.
- The rate at which carbonate salt dissolves in the lake water depends on the ecology of the surrounding area.
- The relative absence of magnesium and calcium is critical in the formation of the soda lake since magnesium or calcium is likely to dissolve quickly and displace the carbonate ion thus neutralizing the PH of the lake water.
Biodiversity Of Soda Lakes:
- Soda lakes are inhabited by a rich diversity of microbial life making them a productive ecosystem.
- They are permanent and seasonal habitats for algae which are visible in many of the lakes.
- Soda lakes are dominated by prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea, especially in lakes with higher levels of alkalinity.
- Multicellular organisms such as brine shrimp and fish are found in plenty if not most of the soda lakes.
- Soda lakes also harbour unique species which are adapted to the alkali conditions.
- These organisms which are adapted to the high alkalinity are called haloalkaliphiles.
Examples Of Soda Lakes:
- Africa and Asia have the highest number of soda lakes since the two continents have vast desert conditions which are perfect for the formation of soda lakes.
- Most of the soda lakes in Africa are located in Eastern Africa, especially in Kenya, Tanzania, and Ethiopia.
- Lake Natron in Tanzania is one of the most outstanding soda lakes in Africa because of the high PH of water which is always about 12.
- India and China have the highest number of soda lakes in Asia.
- Some of the soda lakes in India include Tso Kar Salt Lake, Pangong Salt Lake, and Lonar Lake.
NFRA to inspect Big 4, others in 2024 too (Financial Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is going to inspect the Big Four audit firms as well as other top auditors of large listed entities in 2024, an official familiar with the development told FE.
What is the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)?
- The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is a statutory body and was constituted on 1st October 2018 by the Government of India under Sub Section (1) of section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- It is responsible for setting accounting standards in the country.
- The Punjab National Bank fraud prompted the government to establish an NFRA as the legal regulator for the auditing profession.
- Its mandate is to improve the quality and consistency of financial statements in the country and ensure that businesses and financial institutions disclose accurate and fair information.
- The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is located in New Delhi.
- The chairperson since March 2022 is Ajay Bhushan Pandey.
- The NFRA can probe listed as well as unlisted public companies.
- Companies must have a paid-up capital of ?500 crores and an annual turnover of ?1,000 crores.
Functions and Duties:
- As per Sub Section (2) of Section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013, the duties of the NFRA are to:
- Recommend accounting and auditing policies and standards to be adopted by companies for approval by the Central Government;
- Monitor and enforce compliance with accounting standards and auditing standards;
- Oversee the quality of service of the professions associated with ensuring compliance with such standards and suggest measures for improvement in the quality of service;
- Perform such other functions and duties as may be necessary or incidental to the aforesaid functions and duties.
Composition of the NFRA:
- As mandated by the Companies Act, NFRA is comprised of a chairperson appointed by the Central Government and a maximum of 15 members.
- The individuals selected for these roles must possess expertise in accountancy, auditing, finance, or law.
- Furthermore, they are required to declare to the Central Government that there is no conflict of interest or lack of independence in their appointment.
Membership Qualifications:
- All members, including the chairperson, who are in full-time employment, are prohibited from association with any audit firm (including related consultancy firms) during their term of office and for a period of two years after the completion of their term.
Powers of the NFRA:
- The NFRA has the same powers as the Civil Court.
- The NFRA has the authority to investigate matters of misconduct involving CAs and Chartered Accountants.
- It can impose a penalty of not less than ?1 lakh but not exceeding 5 times the fees collected.
- Also, the NFRA may also investigate and take action against individuals who violate the rules of professional conduct.
- It has the power to initiate investigations on its own and upon referral from the Central Government.
What is end-to-end encryption? How does it secure information? (The Hindu)
- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
There are several ways to encrypt information depending on the level of secrecy and protection required.
What is End-to-end Encryption (E2EE)?
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a type of messaging that keeps messages private from everyone, including the messaging service.
- When E2EE is used, a message only appears in decrypted form for the person sending the message and the person receiving the message.
- The sender is one "end" of the conversation and the recipient is the other "end"; hence the name "end-to-end."
How Does Encryption Work?
- Encryption works by altering data so that only someone who possesses a specific piece of knowledge — known as the key — can interpret the data.
- Keys can take different forms in different contexts.
- With communications over the Internet, a key is a string of bits that plays a role in the complex mathematical equations used to scramble and unscramble data.
- With E2EE, the key that can encrypt and decrypt messages remains saved on a user's device.
What Kind of Encryption Does E2EE Use?
- End-to-end encryption uses a specialized form of encryption called public key encryption (also sometimes called asymmetric encryption).
- Public key encryption enables two parties to communicate without having to send the secret key over an insecure channel.
- Public key encryption relies on using two keys instead of one: a public key and a private key.
- While anyone, including the messaging service, can view the public key, only one person knows the private key.
- Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key (not the public key).
- This contrasts with symmetric encryption, where only one key is used to both encrypt and decrypt.
How Does End-to-end Encryption Support Privacy?
- E2EE ensures that no one can see messages except for the two people who are communicating with each other.
- When implemented properly, it does not require users to trust that a service will handle their data properly.
- Thus, E2EE gives people total control over who can read their messages, enabling them to keep their messages private.
What are the Limitations of End-to-end Encryption?
- E2EE keeps messages secure in transit (as they pass from one person to another).
- But it does not protect messages once they reach their destination.
- E2EE is not guaranteed to be future-proof. When implemented correctly, modern encryption methods are strong enough to resist encryption-breaking efforts from even the most powerful computers in the world.
- But the more powerful in the future like Quantum computers, if developed, would be able to crack modern encryption algorithms.
- Using E2EE keeps messages secure in the present, but it may not keep them secure permanently.
The need to overhaul a semiconductor scheme (The Hindu)
- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The semiconductor Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme, set to undergo a mid-term appraisal, has so far approved only seven start-ups, falling significantly short of its intended goal of supporting 100 over a span of five years since its announcement.
About Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme:
- Under the DLI scheme, government will provide financial incentives and design infrastructure to domestic companies, start-ups and MSMEs focussed on semiconductor design.
- The DLI scheme has been announced by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) to offset the disabilities in the domestic industry involved in semiconductor design in order to not only move up in value-chain but also strengthen the semiconductor chip design ecosystem in the country.
- C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing), a scientific society operating under MeitY, will serve as the nodal agency for implementation of the DLI scheme.
Objectives:
-
- Nurturing and facilitating the growth of the domestic companies, startups and MSMEs.
- Achieving significant indigenization in semiconductor content and IPs involved in the electronic products deployed in the country, thereby facilitating import substitution and value addition in the electronics sector.
- Strengthening and facilitating access to semiconductor design infrastructure for startups and MSMEs.
Duration: The scheme shall initially be for three (3) years from 01-01-2022.
- The scheme has three components – Chip Design infrastructure support, Product Design Linked Incentive and Deployment Linked Incentive.
- Under the Chip Design infrastructure support, C-DAC will set the India Chip Centre to host the state-of-the-art design infrastructure (viz. EDA Tools, IP Cores and support for MPW (Multi Project Wafer fabrication) & post-silicon validation) and facilitate its access to supported companies.
- Under the Product Design Linked Incentive component, reimbursement of up to 50% of the eligible expenditure subject to a ceiling of ?15 Crore per application will be provided as fiscal support to the approved applicants who are engaged in semiconductor design.
- Under the Deployment Linked Incentive component, an incentive of 6% to 4% of net sales turnover over 5 years subject to a ceiling of ?30 Crore per application will be provided to approved applicants whose semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor linked design are deployed in electronic products.
- The DLI Scheme will also take a graded and pre-emptive approach to Identify the Products of national priorities and implement strategies for their complete or near complete indigenisation & deployment thereby taking steps towards the import substitution & value addition in strategic & societal sectors.
Rahul Gandhi prevented from visiting Batadrava Than Significance of this Assam shrine (Indian Express)

- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Congress leader Rahul Gandhi recently prevented from visiting Assam’s Batadrava Than, where he was going as part of his Bharat Jodo Nyay Yatra.
What is the Batadrava Than?
- The Batadrava Than, or Bordowa Than, is a temple complex at the birthplace of revered Vaishnavite reformer-saint Srimanta Sankardeva (1449-1568).
- Located in Nagaon district, the Batadrava Than, or Bordowa Than, is one of the most sacred sites for Assamese Vaishnavites.
- Sankardeva founded the first-ever Kirtan Ghar at Bordowa in 1494 AD to practise and preach the neo-Vaishnavite faith during the fifteenth century in Assam and propagated the Ek Saran Naam Dharma.
- Various structures within the campus include Natghar (drama hall), Alohighar (guest room), Sabhaghar (assembly hall), Rabhaghar (music room), Hatipukhuri, Aakashi Ganga, Doul mandir (festive temple), and more.
- There is also a mini-museum displaying historical articles and artefacts.
- Bordowa Than has a history of disputes over ownership, leading to its division into two satras: Narowa and Salaguri. In 1958, it was reunified under the banner of 'Bordowa Than,' with both former Satras combined, and a single Namghar was established.
What was Srimanta Sankardeva’s Philosophy?
- He propagated the Ek Saran Naam Dharma.
- The Ek Saran Naam Dharma focussed on worship in the form of bhakti (devotion) to Lord Krishna, through singing and congregational listening of His name and deeds.
- Sankardeva espoused a society based on equality and fraternity, free from caste differences, orthodox Brahmanical rituals and sacrifices.
- His teaching focused on prayer and chanting (naam) instead of idol worship. His dharma was based on the four components of deva (god), naam (prayers), bhakats (devotees), and guru (teacher).
- The Neo-Vaishnavite reformist movement that Sankardeva started is behind the monastic institutions called Thans/Sattras that dot Assam.
- As the saint travelled across Assam, spreading his teachings, these Sattras/Thans were established as centres of religious, social and cultural reforms in the 16th century.
- Today, the Sattras promulgate Sankardeva’s unique “worship through art” approach with music (borgeet), dance (xattriya) and theatre (bhauna).
- Each Sattra has a naamghar (worship hall) as its nucleus and is headed by an influential “Sattradhikar”.
Literary Contributions:
- Srimanta Sankardev's significant literary works include 'Kirtan Ghosa' and 'Gunamala.'
- He is credited with composing sacred songs known as 'Borgeet.'
- His penned dramas, recognized as 'Ankia Naat,' featured Sattriya Dance as an integral component during that era.
- In these 'Ankia Naats,' Srimanta Sankardev employed a narrative style through drama, often portraying the lives of Lord Krishna and Lord Rama.
- His inaugural dramatic piece was 'Chihnajatra,' followed by others like 'Kaliya Daman' and 'Patni Prasad.'
- Remarkably, at the age of twelve, when he commenced formal education, he crafted a poem extolling Lord Vishnu titled 'Karatala Kamala Kamala Dala Nayana.'
- Notably, during this early phase, he composed the poem using only consonants, having not yet learned about vowels.
First meeting of Social Audit Advisory Body reviews social justice schemes (ET)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first meeting of the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) was held last week at the conference hall, Dr Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
What is the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB)?
- Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) is a first-of-its-kind advisory body in India.
- It is set up under the National Institute of Social Defence (NISD), which functions under the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment (DoSJE), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It will guide the Ministry as it institutionalizes social audits for each of its programs.
- It will support the Social Justice Cell of the Social Audit Unit members in developing their abilities.
What is a Social Audit:?
- A social audit is a procedure that involves looking over and evaluating a plan or program.
- People actively participate in the process, which involves comparing government data with actual ground realities.
- Important tenets of SA include:
- Protection of citizens (Suraksha)
- Participation (Bhagidari), and
- Information access (Jaankari).
Implementation of Social Audit:
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), among other hallmark programs, now include the provision of Social Audit (SA) with the efforts of the Union Government.
- In order to guarantee SA through specialized Social Audit Units at the state level, DoSJE developed the National Resource Cell for Social Audit (NRCSA).
- The first state to put a social audit statute into effect was Meghalaya.
Significance: Promote transparency and accountability,
-
- strengthen institutions at the grassroots level etc.
Challenges: Lack of awareness among stakeholders, apathetic attitude of implementing agency etc.
Steps for SocialAudit:
- Orientation and Sensitization:: Conducted by the implementing agency.
- Presentation: Creating a social audit team.
- Verification: Verifying information with beneficiaries, inmates, stakeholders, and institution staff.
- Validation: Presenting the initial report for validation.
- Presentation and Action: Sharing findings at the district level with all stakeholders present.
Restoring Lake Victoria: CSE, Tanzanian authorities hold multi-nation stakeholder consultation (DownToEarth)
- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Lake Victoria, the largest freshwater lake in Africa and the world’s second-largest faces numerous environmental challenges that demand collective efforts for restoration and conservation.
About Lake Victoria:
Geography:
- Located in East Africa and bordered by Tanzania, Uganda, and Kenya.
- Africa's largest lake by area (approximately 59,947 km²) and the world's second-largest freshwater lake after Lake Superior.
- Lies in a shallow depression within the East African Rift Valley.
- The average depth of 40 meters, maximum depth of 80-81 meters.
Hydrology:
- The main source of water is rainfall, supplemented by rivers like the Kagera.
- The only outlet is the Victoria Nile, which flows into the White Nile and ultimately the Nile River.
- Plays a crucial role in the water supply and livelihoods of millions of people in East Africa.
Ecology:
- Supports a diverse ecosystem with over 200 fish species, including the Nile perch and Nile tilapia.
- Important habitat for birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
- Facing challenges like pollution, overfishing, and invasive species.
History and Culture:
- Named after Queen Victoria by British explorer John Hanning Speke in 1858.
- Has been a vital source of transportation, trade, and food for centuries.
- Plays a significant role in the cultural traditions and folklore of the surrounding communities.
With no iron or steel, Ayodhya temple is a study in sandstone (The Hindu)
- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new landmark of India — both structural and spiritual — rose on Ayodhya's horizon on January 22 in the form of a new-age architectural marvel of elegant sandstones, diligently carved by craftspeople with dedication and devotion to Lord Ram.
Major Features of the Ram Temple:
- No iron or steel has been used in the construction of the grand structure.
- Stones have been sourced from Rajasthan's Bansi Paharpur area.
- The entire temple superstructure will eventually be three storeys — ground plus two floors.
- Nagara style: The temple complex, built in the traditional Nagara style, will be 380 feet long from the east to the west, 250 feet wide and 161 feet high.
- Each floor of the temple will be 20 feet high and have a total of 392 pillars and 44 gates.
- Images of Lord Hanuman, other deities, peacocks and flower patterns have been carved onto the stones, lending the structure a divine look.
- Unique feature: Around the grand temple is a rectangular periphery called percota, a feature found in temples in south India, but not generally in north India.
- The percota will be 14 feet wide and the periphery span 732 metres.
- The temple will be nestled within the percota periphery.
- Ornate statues of elephants, lions, Lord Hanuman and Garuda were installed at the main entrance leading to the temple.
- These statues have also been made using sandstone brought from Bansi Paharpur.
- An ancient Shiva temple that exists on the Kuber Tila has also been revitalised.
- Green Complex: About 70 per cent of the complex will be a green area.
- "The green area includes portions which are very dense and, in some segments, even sunlight hardly filters through.
- The complex will have two sewage treatment plants — a water treatment plant and a dedicated electricity line from the powerhouse.
- The fire brigade post will be able to source water from an underground reservoir.
Additional Architectural Aspects:
- A time capsule, located approximately 2,000 feet below the ground beneath the temple, houses a copper plate inscribed with pertinent information about the Ram Mandir, Lord Rama, and Ayodhya.
- The objective of this time capsule is to preserve the temple's identity for posterity, preventing it from fading into obscurity in the years to come.
- Engineered as an earthquake-resistant structure, the temple boasts an estimated age of 2500 years.
PM Modi extends his greetings to the people of India on Parakram Diwas (Indian Express)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi extended greetings to the people of India on Parakram Diwas on 23rd January.
Why Parakram Diwas is Celebrated?
- The government officially announced on January 19, 2021, that January 23 be observed as Parakram Diwas in order to pay tribute to Netaji’s relentless pursuit of India’s freedom.
- The government of India has decided to celebrate his birthday on the 23rd day of January every year as “PARAKRAM DIWAS” to inspire people of the country, especially the youth, to act with fortitude in the face of adversity as Netaji did, and to infuse in them a spirit of patriotic fervour,” the Centre had said in a notification.
- Parakram Diwas, which translates to “Day of Valour”.
- In 2021, the first event took place at Victoria Memorial Hall, Kolkata.
- In 2022, a hologram statue of Netaji was unveiled at India Gate, and in 2023, the 21 largest unnamed islands of Andaman & Nicobar Islands were named after the 21 Param Vir Chakra awardees and a model of National Memorial dedicated to Netaji which was supposed to be built on Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose Dweep, was unveiled.
Key Facts About Subhas Chandra Bose:
- Born on January 23, 1897, in Cuttack, Orissa.
- In 1920, he successfully passed the civil service examination but resigned from his position in April 1921 after learning about the nationalist turmoil in India.
- A prominent Indian nationalist leader, he played a pivotal role in the Indian independence movement against British colonial rule.
- Joined the Indian National Congress and actively participated in the struggle for independence.
- Elected president of the Indian National Congress for two consecutive terms but resigned due to ideological conflicts with Mahatma Gandhi.
- In 1939, Bose founded the Forward Bloc, an organization aimed at unifying anti-British forces in India.
- Fled from India at the beginning of World War II, travelling to the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan in pursuit of an alliance against British forces in India.
- With Japanese assistance, reorganized and led the Indian National Army, comprising Indian prisoners-of-war and plantation workers from Southeast Asia.
- Established the Azad Hind Government in exile with Japanese support, leading the Indian National Army in battles against the allies in Imphal and Burma.
PM Modi announces solar roof-top scheme for one crore households (HT)
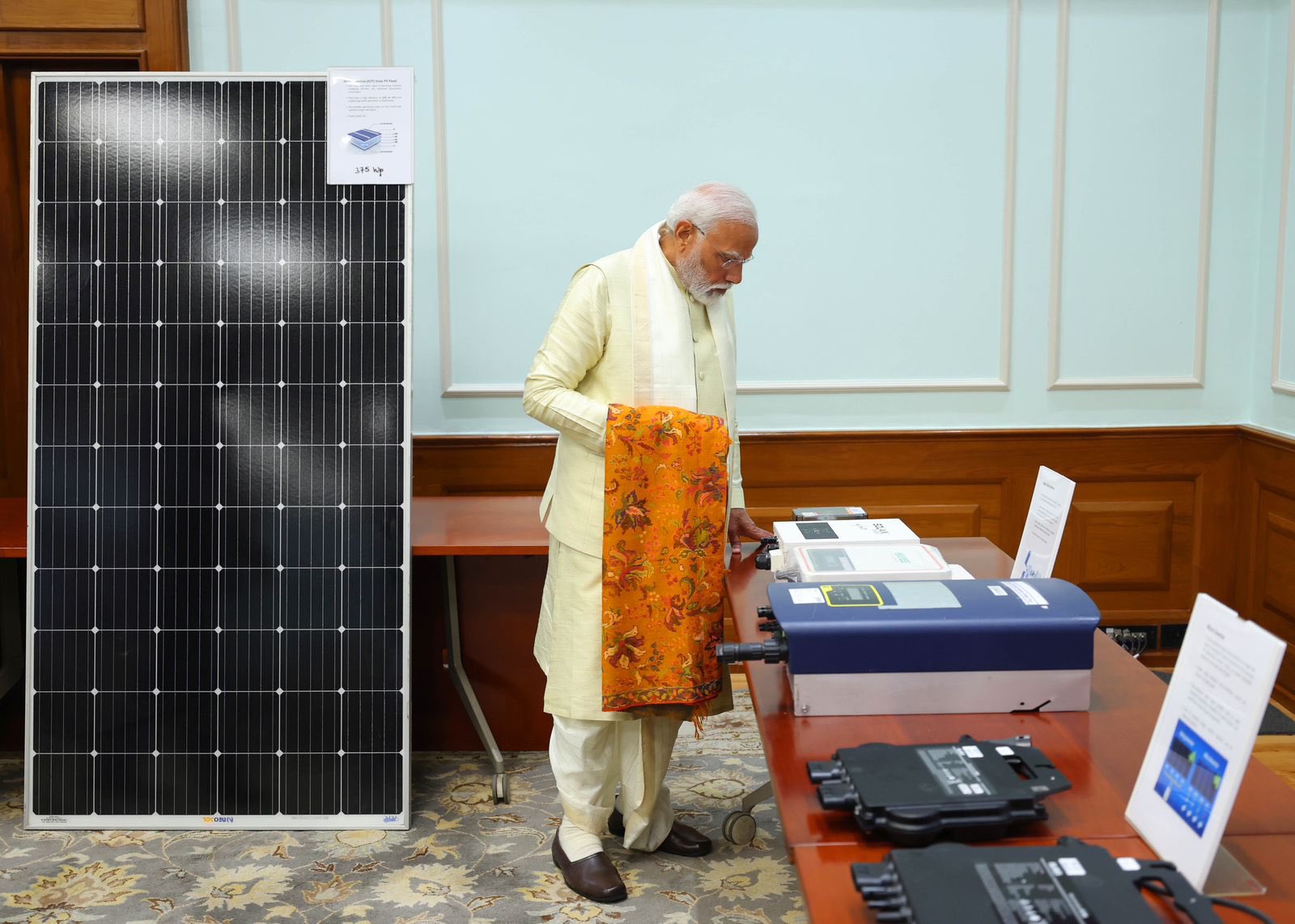

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Monday announced the 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana' under which one crore households will get rooftop solar across the nation.
What is 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana'?
- The scheme aims to equip one crore poor to middle-class households with rooftop solar panels in a bit to provide electricity from solar energy.
- The scheme would not only reduce the electricity bill of the poor and middle class but would also make India self-reliant in the energy sector.
- Rooftop solar panels are the photovoltaic panels installed on the roof of a building which is connected to the main power supply unit.
- Thus, it reduces the consumption of grid-connected electricity and saves electricity costs for the consumer.
- In a solar rooftop system, there is only an upfront capital investment and minimal cost for maintenance.
- Under this scheme, one crore households will get solar rooftops.
- Moreover, it will offer additional income for surplus electricity generation.
- The consumer can choose any vendor on the national portal and after installation, the subsidy is sent directly to the bank account of the consumer.
- The Pradhanmantri Suryodaya Yojana is a new scheme but very similar to the previously announced Rooftop Solar Programme in 2014.
- The previous scheme had aimed to produce 40,000 megawatts (MW) or 40 gigawatts (GW) of solar power by 2022.
India's Advancements in Solar Energy:
- At the end of last year, 2023, India’s solar power generation stood at 73.31 GW, up from 2022’s 63.3 GW.
- However, rooftop solar power generation only stands at around 11.08 GW as of December 2023.
- The total solar power generated in the nation, Rajasthan leads the pack with 18.7 GW while Gujarat follows with 10.5 GW.
- However, when talking about rooftop solar power, Gujarat is at peak position — with 2.8 GW — followed by Maharashtra at 1.7 GW.
- India has more than 300 million households and an average of 300 sunny days each year, which has tremendous potential for rooftop solar installations in residential spaces.
- However, experts note that despite several measures, India’s rooftop solar power generation is not where it should be, listing reasons for the situation.
- The primary reason for rooftop solar not becoming popular is that it is still an expensive option for many.
- There is also a lack of awareness.
Importance of Solar Power to India:
- Harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity is important to India for multiple reasons.
- If India wants to achieve its aim of becoming net zero by 2070, it has to look towards the sun.
- In fact, at COP26, in November 2021, India committed to meet 50 per cent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030.
- For these aims to be met, India has to harness the full capacity of the sun.
- Moreover, India’s share of global energy demand is predicted to double to 11 per cent in 2040, making it imperative to enhance energy security and self-sufficiency in power generation without increasing environmental costs.
- This increase in power demand is likely to increase India’s reliance on coal, oil and natural gas as a source of energy.
- However, additional imports of oil and increased domestic production of coal will not only fall short of energy demand but will also entail economic and environmental costs.
- The expansion of solar power units and increased reliance on solar power allow India to enhance energy security in the face of rising demand.
- Furthermore, India is already facing depleting groundwater levels, owing to which the nation must shift its energy resources away from water.
Davos meeting 2024: 5 key takeaways (Indian Express)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
This year’s edition of the World Economic Forum (WEF) annual meeting was held from January 15 to January 19.
Key Highlights from Davos Meeting 2024:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The focal point of discussion at this year's World Economic Forum (WEF) meeting was Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Conversations delved into its transformative potential for human welfare, addressing concerns such as the necessity for regulation, apprehensions about job losses, risks associated with impersonation and misinformation, and the potential exacerbation of inequalities.
- Despite acknowledging these challenges, participants generally agreed that the positive aspects of AI outweigh the negatives, with no substantial threat to human intelligence.
- War and Uncertainty: The summit underscored the risks emanating from a delicate geopolitical landscape, ongoing conflicts in the Middle East and Europe, threats to global supply chains, and uncertainties surrounding food security.
- Notably, the head of the Palestine Investment Fund estimated a requirement of at least $15 billion solely for the reconstruction of houses in Gaza.
- However, Arab states asserted their reluctance to fund reconstruction without a guarantee of lasting peace.
- Climate: The imperative for businesses to adapt to climate change and nations to collaborate despite differences in combating it emerged as another key theme.
- Discussions emphasized the necessity for developed countries to assist in financing climate action in developing nations to prevent a widening inequality that could result in winners and losers.
- China's Economy: Against the backdrop of a slowing economy, China sought increased investment from the West, which has experienced some cooling.
- With a GDP growth of 5.2% in 2023, still below pre-pandemic levels, China grappled with efforts by the United States to isolate it, particularly evident in the semiconductor trade standoff.
- India-Specific Observations: McKinsey and Company's assessment of Davos 2024 highlighted India's rapid transformation as one of the fastest-growing large economies globally.
- The summit marked the launch of the Global Good Alliance for Gender Equity and Equality, endorsed by the WEF and the Government of India.
- Originating from the G20 Leaders' Declaration, the alliance aims to bring together global best practices, knowledge sharing, and investments in women's health, education, and enterprise.
- Supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the alliance will be hosted by the CII Centre for Women Leadership, with the World Economic Forum as a 'Network Partner' and Invest India as an 'Institutional Partner.'
About the World Economic Forum:
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It was established in 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- It is a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
Reports released by WEF:
-
- Global Gender Gap Index
- Global Risks Report
- Fostering Effective Energy Transition Report
- Global Cyber Security Outlook
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Travel and Tourism Development Index
About Davos Meet:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) organizes a meeting annually at the end of January in Davos, a mountain resort in Graubünden, in the eastern Alps region of Switzerland.
- The Annual Meeting, also known as the Davos Agenda, has the objective of orienting global leaders on the imperatives of the year ahead.
- This year's theme for the Annual Meeting in Davos is 'From Lab to Life: Science in Action'.
MeitY signs MoU with Cuba for cooperation on digital public infrastructure (ET)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Cuba have signed an MoU for cooperation in the field of sharing successful digital solutions implemented at the population scale for digital transformation.
India and Cuba Bilateral Relations:
- India and Cuba share a robust and longstanding diplomatic camaraderie, marked by warmth and amity.
- In a gesture of early support, India was among the first nations to acknowledge and establish relations with the new Cuban government post the revolutionary events in January 1959.
- Trade Dynamics: The bilateral trade engagement, while moderate, exhibits a diverse array of commodities.
- India exports pharmaceutical products, organic chemicals, plastic goods, medical equipment, engineering items, textiles, metal products, mineral oil products, and tools to Cuba.
- Conversely, Cuba primarily imports pharmaceuticals and tobacco products from India.
- Energy Partnership: A pivotal facet of India-Cuba relations is their collaboration in the energy sector.
- As a member country and Vice-President of the Latin America & the Caribbean region at the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Cuba plays a significant role in fostering energy cooperation between the two nations.
- Advancements in Science & Technology, Biotechnology, and Health: The bilateral relations in the domains of science, technology, and health have been fortified through ministerial-level visits from both nations.Development Collaboration: Prioritizing development assistance has been a cornerstone of their bilateral ties.
- India has extended disaster relief assistance to Cuba in the aftermath of hurricanes that have afflicted the region over the years.
- Cultural Relations: Cuban appreciation for Indian culture and civilization is evident, with figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Rabindranath Tagore holding a special place in Cuban hearts.
- Indian Diaspora: Although the Indian community in Cuba is relatively small, it includes descendants of Indians who migrated to Cuba in the early twentieth century from Jamaica and other parts of the West Indies to contribute to sugarcane plantations.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- DPI is a digital network that enables countries to safely and efficiently deliver economic opportunities and social services to all residents.
- DPI can be compared to roads, which form a physical network that connects people and provides access to a huge range of goods and services.??
- DPI allows people to open bank accounts and receive wages faster and more easily.
- It allows governments to support citizens more quickly and efficiently, especially during emergencies.
- And it enables entrepreneurs to reach customers far and wide.??
- A strong DPI has three foundational systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—that together can make life easier in important ways.?
- When the three core systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—exist simultaneously and can talk to one another, people, businesses, and governments can reap the full benefits of DPI.
- Over time, safe and inclusive DPI creates vibrant and competitive economies.?
Indigenous mobile hospital saves life at ‘Pran Pratishta’ event in Ayodhya (The Hindu)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An Indigenous mobile hospital at the 'Pran Pratishta' event in Ayodhya played a life-saving role as 65-year-old Dharmacharya Pramukh and VHP member Ramkrishna Srivastava, experiencing a heart attack and sudden medical emergency, collapsed unconscious.
What is Aarogya Maitri Aid Cube?
- It is India’s first portable hospital that can be airlifted to a disaster area and assembled in an hour.
- This “flatpack” field hospital consists of 72 small cubes equipped with tents and customised medical equipment.
- It is built under the Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita and Maitri (BHISHM) and the hospital is reportedly designed to treat up to 200 patients.
- The cubes, each of which weighs below 15kg and measures 38cm x 38cm x 38cm, are resilient enough to be dropped from a plane or helicopter.
- The ‘Aarogya Maitri Cube Cage’ has three frames containing 12 mini-cubes.
- A single cage can fit a total of 36 mini-cubes.
- At least five trained people are needed to assemble the cubes into a functional hospital in an hour.
- These cubes can be flown to a war zone or a remote area hit by natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods.
- The product was developed under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ambitious ‘Project BHISHM’ which aims to support developing countries affected by natural disasters or humanitarian crises.
How the portable hospital will help?
- The portable hospital is capable of facilitating life-saving surgery on remote and tough terrains.
- The 72 cubes contain different equipment such as portable ventilators, solar panel-based generators, ultrasound machines, digital imaging radiography machines, defibrillators, high-mounted OT lights, stretchers, modern surgical devices, and portable laboratories.
- A line of Ayurvedic products was added to the list of items in the cubes at the suggestions of PM Modi.
- “HLL Life Care is the government’s nodal agency for sourcing the Aarogya Maitri Cube, whereas the manufacturing has been undertaken by multiple sellers as it includes a variety of products.
- Billed as the “world’s first portable disaster hospital”, the kit is waterproof and corrosion-proof.
- A tablet computer is installed inside the cube pack to prevent mistakes while setting up the structure.
- If the immediate need at the site is for life-saving surgery, then the operating theatre can be assembled first. This takes just 10 minutes. The doctors can start surgery while the remaining cubes are assembled.”
- The portable hospital can “provide critical medical care to 100 survivors for up to 48 hours, making it a lifeline on remote and tough terrains where immediate medical attention is needed. The cubes [which are self-sustained healthcare units] can handle bullet, burn, head, spinal and chest injuries, fractures, and major bleeding.
- India is now equipped and ready to supply this to any country in need.
- t can also be utilised in regions across India that need medical support due to epidemics, high elevations, or challenging landscapes.
- This could play a significant role in the management of public health.
- As a goodwill gesture, India has already given two Aarogya Maitri Cubes to Myanmar and one is being prepared for Sri Lanka.
After tiny chopper Ingenuity, NASA planning to send giant fixed-wing plane Maggie to Red Planet (TOI)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In its pursuit of extensively exploring Mars to find signs of water, Nasa is considering a proposed idea to send a giant fixed-wing plane to the Red Planet.
What is Ingenuity Mars Helicopter?
- The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter is a small, autonomous aircraft that is part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission.
- It was deployed to the surface of Mars on April 3, 2021, and made its first powered, controlled flight on another planet on April 19, 2021.
- Ingenuity is a technology demonstration mission, and its main goal is to show that powered flight is possible on Mars.
- The helicopter has four carbon-fiber blades creating enough lift to overcome the thin Martian atmosphere.
- It is powered by solar cells and can fly for up to 90 seconds at a time.
- Since its first flight, Ingenuity has completed 72 flights, far exceeding its original planned five flights.
- It has flown a total of 17 km and reached an altitude of 24 m.
- The helicopter has also helped to scout ahead for the Perseverance rover, taking images and collecting data from areas that the rover cannot reach.
- Ingenuity's success has paved the way for future aerial exploration of Mars.
- Future helicopters could be used to scout for landing sites, study the Martian surface in more detail, and even carry small payloads of scientific instruments.
About Perseverance Rover:
- Perseverance is a robotic rover exploring Jezero Crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission.
- Launched on July 30, 2020, it successfully landed on February 18, 2021, making it the most sophisticated and heaviest rover ever sent to Mars.
Mission Highlights:
- Seeking signs of ancient microbial life: Perseverance is equipped with several instruments to analyze Martian rocks and soil for potential signs of past life.
- Collecting rock samples: The rover drills and collects rock samples that will be cached on Mars for potential return to Earth by future missions.
- Testing technology for future missions: Perseverance is demonstrating new technologies that will be crucial for future human exploration of Mars, such as the MOXIE instrument that produces oxygen from the Martian atmosphere and the Ingenuity helicopter, the first powered aircraft to fly on another planet.
- Perseverance Achievements:
- Finding evidence of an ancient lake in Jezero Crater that may have been habitable for microbial life.
- Collecting the first rock samples from Mars that will be returned to Earth.
- Demonstrating the feasibility of using a helicopter on Mars (the Ingenuity helicopter hitched a ride with Perseverance).
Indian Immunologicals rolls out indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine (Financial Express)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) recently announced that it has launched India’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine, Havisure.
About Havisure Vaccine:
- The vaccine is effective in preventing the disease and is recommended for children in routine immunization.
- It is a two-dose vaccine wherein the first dose is administered at above 12 months of age and the second dose is given at least after 6 months of the first dose.
- The vaccine is also recommended for individuals who are at risk of exposure or travel to the regions with high hepatitis A prevalence.
- In addition to this people with occupational risk of infection and suffering from chronic liver diseases also need Hepatitis A vaccination.
Key Facts About Hepatitis A:
- Hepatitis A is an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV).
- The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person.
- The disease is closely associated with unsafe water or food, inadequate sanitation, poor personal hygiene and unprotected sex.
- Unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver disease but it can cause debilitating symptoms and rarely fulminant hepatitis (acute liver failure), which is often fatal.
- Hepatitis A occurs sporadically and in epidemics worldwide, with a tendency for cyclic recurrences.
- Epidemics related to contaminated food or water can erupt explosively, such as the epidemic in Shanghai in 1988 that affected about 300,000 people.
- They can also be prolonged, affecting communities for months through person-to-person transmission.
- Hepatitis A viruses persist in the environment and can withstand food production processes routinely used to inactivate or control bacterial pathogens.
- Geographical distribution: Infection is common in low- and middle-income countries with poor sanitary conditions and hygienic practices, and most children (90%) have been infected with the hepatitis A virus before the age of 10 years, most often without symptoms.
- Transmission: The hepatitis A virus is transmitted primarily by the fecal-oral route; that is when an uninfected person ingests food or water that has been contaminated with the feces of an infected person.
- In families, this may happen through dirty hands when an infected person prepares food for family members.
- Waterborne outbreaks, though infrequent, are usually associated with sewage-contaminated or inadequately treated water.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of hepatitis A range from mild to severe and can include fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin).
- Not everyone who is infected will have all the symptoms.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A.
- Recovery from symptoms following infection may be slow and can take several weeks or months.
- Prevention: Improved sanitation, food safety and immunization are the most effective ways to combat hepatitis A.
Police think tank Bureau of Police Research and Development warns users of scams, data-breach acts on WhatsApp (The Hindu)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) has warned users of different scams perpetrated through messaging platform WhatsApp.
About the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD):
- The Bureau of Police Research & Development (BPR&D) was set up in 1970 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to identify the needs and problems of the police in the country.
- It was also mandated to keep abreast of the latest developments in the fields of science and technology, both in India and abroad, to promote the use of appropriate technology in police work.
- Over the years, the BPR&D has also been entrusted with the responsibility of monitoring the training needs and quality of training in the States and Central Police Organisations and assisting the same, as also assisting the States in modernization of the State Police Forces and Correctional Administration.
- In the process, the BPR&D has also been tasked to assist the Ministry of Home Affairs and the CPFs, etc., in the development of Standards, Quality Requirements (QRs), etc., concerning various types of equipment and items about infrastructure.
- More recently, the BPR&D has also been entrusted with the responsibility of anchoring and coordinating the work of the National Police Mission.
BPRD's Roles and Responsibilities:
- The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) plays a crucial role in elevating the functioning of police forces across the nation:
- Policy Formulation and Guidance: Assists in formulating policies and strategies for police development.
- Guides to enhance the efficiency of police forces.
- Interdepartmental Interface: Acts as a bridge between the police and other government departments for efficient resource and technology sharing.
- Financial Assistance: Offers financial support to state governments for surveys, studies, and the development of specialized infrastructure and training.
- Training and Awareness: Conducts seminars and workshops to educate police personnel on crime prevention and effective policing.
- Promotes awareness of policing importance and public order maintenance.
- Development of Systems: Works towards developing systems like Community Policing, modern investigations, and effective technology and data management.
BPRD's Vision and Mission:
- Vision: To facilitate the optimal deployment of police forces and related activities, enabling them to meet contemporary challenges.
- Mission: To enhance police capabilities and those of stakeholders by providing resources and research-based knowledge, bridging gaps between evidence-based practice, policy formulation, and public outreach.
- Focus Areas: BPRD prioritizes innovation, knowledge initiatives, and research in policing, public order, security, and related fields, creating models relevant to contemporary needs.
- Overall Objective: BPRD is committed to developing capacity, fostering police professionalism, and promoting safety and public order in India through research, innovation, and strategic initiatives.
How the new Education Ministry guidelines will affect the coaching institutes (HT)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Taking cognisance of coaching centres charging exorbitant fees from students, promoting unhealthy competition and stress among students, and a rise in student suicides and other malpractices, a set of new guidelines were released by the Education Ministry.
Guidelines for Registration and Regulation of Coaching Centers 2024:
- The guidelines define a 'coaching centre' as an establishment providing coaching for study programs, competitive exams, or academic support to more than 50 students at the school, college, and university levels, established, run, or administered by any person.
Key aspects of the guidelines include:
- Registration Process: Coaching centres must apply for registration within their local jurisdiction, adhering to specified forms, fees, and document requirements.
- Each branch of a coaching centre is considered a separate entity, requiring individual registration.
- Marketing Standards: Coaching centres are prohibited from making misleading promises or guarantees regarding ranks or marks.
- Transparency is mandated, with centres required to maintain an updated website containing detailed information.
- Student Enrollment: Students below the age of 16 are not permitted for enrolment, and entry is allowed only after the completion of secondary school examinations.
- Fee Structure: Tuition fees must be fair, with detailed receipts provided.
- A comprehensive prospectus must include information on courses, duration, facilities, fees, and refund procedures. Any fee increase during the course is prohibited.
- Exit Policy: Pro-rata refunds are mandated within 10 days for mid-course withdrawals.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Coaching centres must allocate a minimum of one square meter per student.
- Compliance with fire safety and building codes is essential, along with proper electrification, ventilation, lighting, security measures, and medical assistance.
- Study Hours: Classes should not coincide with school hours, and weekly off for students and tutors is mandatory.
- Class sizes must align with a healthy teacher-student ratio.
- Mental Wellbeing: Centers should establish mechanisms for immediate intervention and counselling for students in distress.
- Complaint Mechanism: Students, parents, or tutors/employees can file complaints, to be resolved within thirty days by the competent authority or an inquiry committee.
- Penalties: Penalties for violations include ?25,000 for the first offence, ?1 lakh for the second, and registration revocation for subsequent breaches.
PM declares Khelo India Youth Games 2023 open in Chennai (Indian Express)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently declared the Khelo India Youth Games 2023 open at the Nehru Indoor Stadium in Chennai.
What is Khelo India?
- The Khelo India programme has been introduced to revive the sports culture in India at the grassroots level by building a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establishing India as a great sporting nation.
- Talented players identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels by the High-Powered Committee will be provided annual financial assistance of INR 5 lakh per annum for 8 years.
About the Khelo India Youth Games 2023:
- The 6th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games is being hosted by Tamil Nadu, marking the first occurrence of the Games in South India.
- Spanning from January 19th to 31st, 2024, the event will unfold across four cities in Tamil Nadu – Chennai, Madurai, Trichy, and Coimbatore.
- With over 5600 athletes participating in more than 275 competitive events spanning 26 sports disciplines and one demo sport, this edition introduces Silambam, a traditional sport of Tamil Nadu, as a demo sport and includes Squash for the first time.
- Archery, athletics, badminton, and squash have been introduced first time in this edition.
- The mascot, 'Veera Mangai,' pays tribute to Rani Velu Nachiyar, an Indian queen who courageously resisted British colonial rule.
- The logo integrates the image of the poet Thiruvalluvar.
- Objectives: The overarching objective of the Khelo India Youth Games is to rejuvenate India's grassroots sports culture, aiming to build a robust framework for all sports and position the nation as a prominent sporting entity.
- Organized by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, the Games have been an annual tradition since their inception in 2018 in Delhi.
What is the Nagara style, in which Ayodhya’s Ram temple is being built (Indian Express)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ram temple in Ayodhya will be inaugurated on January 22. Chandrakant Sompura, 81, and his son Ashish, 51, have designed the complex in the Nagara style of temple architecture.
What is the Nagara style?
- Originating around the 5th century AD, the Nagara style influenced temple architecture in several regions of India, from Northern India to Karnataka to parts of Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Gujarat, giving it its pan-India appeal.
- Given that the temple will attract Hindu devotees from across the country, this is the most "inclusive" architectural style of Hinduism in that respect.
- The word “Nagara” means “city,” and the style's close association with urban architectural principles made it suitable for a bustling town like Ayodhya while retaining Hindu temple elements that are familiar to devotees.
- With carved pillars and towering spires, it seeks to echo the magnificent craftsmanship of the Khajuraho temples of Madhya Pradesh and the Sun Temple in Odisha’s Konark.
- The Nagara style is not confined to a specific period — it flourished during the Gupta dynasty but continued to evolve through various regional kingdoms and empires that ruled over the northern parts of India.
- The temple's architecture is characterised by its tower-like structures, known as 'shikhara' or spires, which rise vertically, symbolising the sacred mountain, Mount Meru, considered to be the centre of the physical, metaphysical and spiritual dimensions in Hindu, Jain and Buddhist cosmology.
- This temple architecture is also closely associated with both the Shaivite and Vaishnavite sects of Hinduism and known for its sculptural elements that echo scenes from Hindu epics like Ramayana and Mahabharata.
The typical Nagara temple layout:
- The layout of Nagara-style temples follows a distinct pattern, reflecting the cosmic order and the journey of the soul towards liberation
The typical plan of the Nagara-style temple:
- Vastu Purusha Mandala: At the core of Nagara temple design is the concept of Vastu Purusha Mandala, a sacred diagram representing the cosmic man.
- The temple’s plan is aligned with this mandala, ensuring that the deity’s sanctum aligns with the cosmic forces.
- This alignment reflects the belief that the temple is a microcosm of the universe, establishing a cosmic resonance.
- Garbhagriha (Sanctum Sanctorum): The sanctum sanctorum, or garbhagriha, is the innermost and holiest chamber where the principal deity resides and is always located directly below the highest Sikhara.
- Often square, this chamber is a symbol of the womb of creation.
- The placement of the deity within this sacred space is meticulously calculated to maintain harmony with cosmic energies.
- Pradakshina Patha (Circumambulation): Around the garbhagriha, there is a circumambulatory path called the pradakshina patha.
- This path allows devotees to walk in a clockwise direction around the deity, as a symbolic act of paying respect, seeking blessings, and expressing devotion.
- The pradakshina patha may be enclosed within the temple or form an outer pathway surrounding the main temple complex.
- It is believed that circumambulation harmonizes the individual with the divine and creates a spiritual connection.
- Vimana (Tower): The Vimana, or tower, is the crowning glory of Nagara temples.
- The shikhara, as the main spire, represents Mount Meru, the mythical abode of the gods, meant to symbolize the ascent from the earthly realm to the celestial plane, creating a visual narrative of the soul’s journey towards spiritual awakening.
- Mandapa (Congregation Hall): The mandapa, or congregation hall, serves as a communal space for rituals, gatherings, and celebrations. Supported by intricately carved pillars, the mandapa’s design is often open, allowing devotees to participate in ceremonies.
- The pillars themselves are adorned with sculptures depicting deities, mythological narratives, and celestial beings, contributing to the immersive spiritual experience.
- Antarala (Vestibule): The antarala acts as a transitional space between the garbhagriha and the mandapa.
- It serves functional and symbolic purposes, symbolising the journey from the material to the divine.
- The antarala may house additional deities or intricate sculptures, further enhancing the spiritual ambience.
- Ardhamandapa (Entrance Porch): The ardhamandapa, or entrance porch, serves as the threshold between the external world and the sacred interior.
- Often featuring ornate pillars and intricate carvings, the ardhamandapa is a visual prelude to the architectural splendour within.
- Devotees traverse this space as they enter the sanctified realm of the temple.
- Peripheral Structures: Surrounding the central shrine are often smaller shrines and subsidiary structures, creating a complex architectural ensemble.
- These structures, known as subsidiary shrines or parivara devatas, pay homage to various deities associated with the main deity.
- The arrangement of these structures follows a harmonious pattern, contributing to the overall visual appeal of the temple complex.
Regional variations:
- As a pan-India style, the Nagara architecture has regional variations that reflect the cultural ethos of where it is built.
- Odisha: The Nagara style in the state is characterised by its exquisite stone carvings and towering spires.
- The temples of Bhubaneswar, Puri, and Konark in the state of Odisha exemplify this style.
- The temples showcase carvings of deities, mythical creatures, dancers, and musicians, evoking a sense of dynamic movement.
- Gujarat: Known for its elegance and simplicity, the Gujarati Nagara style is epitomised by the Sun Temple in Modhera and the famous Somnath Temple.
- The main 'shikhara' in the state's temples are relatively modest in height compared to northern iterations.
- The emphasis is on the overall harmony of the temple’s complex measurements and the sculptural beauty.
- Rajasthan: The style in this state has been noticeably influenced by distinctive elements of Rajput architecture — from fortified walls and ornate entryways.
- Look no further than the Dilwara Temples in Mount Abu and the Sun Temple of Ranakpur for examples of this style.
- Distinct features include marble carvings and delicate detailing.
- Karnataka: Nagara temples in the South have subdued shikharas compared to their northern temples.
- What is more, the emphasis is on pillar carvings and the subject matter is often famous scenes from mythology.
- The Virupaksha Temple in Hampi and the Lepakshi Veerabhadra Temple are notable Nagara-style temples in the south.
- Madhya Pradesh: Central Indian temples often feature a variety of spires, emphasising the stepped shape.
- The sculptures focus on a wide range of themes, including mythological narratives, daily life, and spiritual pursuits.
- The Khajuraho complex, including the Lakshmana Temple, exemplifies the Nagara style in Central India.
- Combining spiritual principles with aesthetics and craftsmanship, the Nagara style is an indelible part of India’s cultural and religious legacy.
- The Ram temple draws from this same architectural legacy of Hinduism to create a religious monument that seeks to inspire the same awe that the centuries-old Indian temples continue to do.
Comparison to Dravida style:
- The Dravida counterpart to the shikhara is the vimana. There exists, however, a fundamental difference.
- In the Dravida-style temples, vimanas are typically smaller than the great gatehouses or gopurams, which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex.
- Moreover, while shikharas are mentioned in southern Indian architectural sources, they refer to only the dome-shaped crowning cap atop the vimana.
- The existence of gopurams also points to another unique feature of the Dravida style — the presence of a boundary wall.
- A few Nagara-style temple complexes are lined with distinctive boundary walls that are a part of the temple’s design.
- This is one of Ayodhya’s Ram temple’s ‘hybrid’ features — although no elaborate gopuram has been built (citing paucity of space), a 732m long wall runs around the temple compound.
Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival begins in Arunachal; effective conservation of iconic birds urged (DTE)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 9th edition of the Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival (PPHF) commenced in the town of Seijosa in Arunachal Pradesh’s Pakke Kessang district on January 18, 2024, with a call to protect and conserve hornbills.
About Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival:
- The first Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival (PPHF) took place in 2015 with the primary goal of acknowledging the Nyishi tribal group's significant role in hornbill conservation within the Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR).
- Additionally, the festival aimed to generate alternative sources of income for the region and raise awareness across India about the marvels of PTR and its surroundings.
- The current year's festival is themed "Domutoh Domutoh, Paga hum Domutoh," meaning 'Let Our Hornbills Remain' in the Nyishi language.
- The focus of this year's festival is to emphasize the crucial importance of preserving these iconic birds.
About the Great Indian Hornbill:
- The Great Indian Hornbill is a bird family found in tropical and subtropical Africa, Asia, and Melanesia.
- It is the state bird of Kerala and Arunachal Pradesh in India.
- The Great Indian Hornbill is now considered “Vulnerable” due to high hunting pressure, habitat loss, and deforestation.
Key Facts About Pakke Tiger Reserve:
- Pakke Tiger Reserve is located in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is bordered by the Tenga Reserve Forest to the North, the Doimara Reserve Forest to the West, and Nameri National Park and Tiger Reserve (Assam) to the South.
- The region exhibits high species diversity and endemicity, acting as a transitional zone between the Indian and Malayan ecoregions.
- Located North of the Brahmaputra River, Pakke Tiger Reserve is positioned in the transition zone between the Assam plains and the hilly forests of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Vegetation primarily comprises tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen forests.
- Flora: Notable flora includes Polyalthia simiarum, Pterospermum acerifolium, Sterculia alata, Stereospermum chelonioides, Ailanthus grandis, and Duabanga grandiflor. Additionally, about eight species of bamboo are found in the area.
- Fauna: The fauna of the reserve includes iconic species like the Tiger and elephant, as well as predators such as the Leopard and the Clouded leopard, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the region.
ISRO develops second-generation Distress Alert Transmitter (The Hindu)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed an improvised Distress Alert Transmitter (DAT) with advanced capabilities and features for the fishermen at sea to send emergency messages from fishing boats.
What is a Distress Alert Transmitter (DAT)?
- The first version of DAT has been in operation since 2010, allowing fishermen at sea to send emergency messages from their fishing boats.
- These messages are transmitted via a communication satellite to the Indian Mission Control Centre (INMCC), the central control station, where the alert signals are decoded to determine the identity and location of the distressed fishing boat.
- The extracted information is then relayed to Maritime Rescue Coordination Centres (MRCCs) under the Indian Coast Guard (ICG), enabling coordinated Search and Rescue operations to assist fishermen in distress.
About the Second Generation DAT (DAT-SG):
- Leveraging advancements in satellite communication and navigation technology, ISRO has enhanced DAT into the Second Generation DAT (DAT-SG). DAT-SG not only allows fishermen to send distress alerts but also provides them with acknowledgements, assuring them that rescue operations are underway.
- In addition to transmitting distress signals, DAT-SG can receive messages from control centres.
- This feature enables the sending of advance alert messages to fishermen about adverse weather conditions, cyclones, tsunamis, or other emergencies.
- Moreover, the system transmits information on Potential Fishing Zones (PFZs) to fishermen at regular intervals.
- DAT-SG can be connected to mobile phones using a Bluetooth interface, and messages can be read in the native language through a mobile app.
- The central control centre employs a web-based network management system called "SAGARMITRA," which maintains a database of registered DAT-SGs.
- This system assists MRCCs in accessing real-time information about distressed boats, allowing the Indian Coast Guard to initiate Search & Rescue operations promptly during distress situations.
Why Kashmir and Ladakh are without snow this winter, its implications (Indian Express)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Himalayas are experiencing an unusual lack of snowfall this winter, impacting ski resorts and prompting holiday cancellations.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Unprecedented precipitation deficit: December witnessed an alarming 80% precipitation deficit in the western Himalayan region.
- The ongoing dry spell in January is attributed to the absence of active western disturbances this winter season, as reported by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Impact on freshwater resources: Experts warn of potential impacts on freshwater availability in the Himalayan region.
- The extended dry spell poses a threat to horticulture and agricultural production, raising concerns among experts.
- Unseasonal blooming and alarming temperature anomalies: Despite being peak winter, Ladakh and Kashmir experienced unusually warm temperatures, leading to early crop blooming.
- A report by IMD scientists reveals maximum temperatures 5-8 degrees Celsius below normal over the northern plains since December 29.
- Challenges to water levels and ecosystems: Experts also highlight the significance of the Chillai Kalan snowfall period as the only freshwater source.
- The prolonged dry spell has resulted in reduced water levels in rivers and streams, posing challenges to the region's ecosystems.
Factors contributing to severe weather conditions:
- Scientists attribute the severe weather to three main factors:
- Lack of active western disturbances
- Prevailing El Nino conditions, and
- A strong jet stream.
- El Nino, characterised by abnormal warming in the central Pacific Ocean, contributes to altered weather patterns.
- Mechanics of fog formation: Scientists explain the three conditions required for fog formation: weak low-level winds, moisture, and overnight cooling.
- The lack of strong western disturbances disrupts these conditions, contributing to the prolonged fog.
- Persistent jet streams and cold wave conditions: Strong jet streams prevailing over north India for the last five days have led to the subsidence of cold air, enhancing cold wave/cold day conditions.
These conditions are expected to continue over the next five days, intensifying the challenges posed by the ongoing weather anomalies.
National Quantum Mission to call for proposals to set up four tech hubs (PTI)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will set up a coordination cell to implement the National Quantum Mission (NQM) with a focus on establishing four technology hubs in the format of consortia of academia, research and development labs and industry.
What is the National Quantum Mission (NQM)?
- The National Quantum Mission (NQM) will assist India take a giant leap into the future of technology.
- India has entered the ranks of the select few nations actively pursuing the advancement of quantum technology by establishing this programme.
- In 2023, the government sanctioned the National Quantum Mission (NQM), spanning from 2023-24 to 2030-31, with the following key features:
- The mission aims to initiate, foster, and amplify scientific and industrial research and development in Quantum Technology (QT), establishing a dynamic and innovative ecosystem.
- Its ultimate goal is to propel quantum technology-led economic growth, foster the QT ecosystem, and position India as a leading nation in the field of Quantum Technologies & Applications.
- It willl be implemented by the Department of Science & Technology (DST) under the Ministry of Science & Technology.
Key Objectives:
- Develop intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 physical qubits across platforms like superconducting and photonic technology within eight years.
- Implement satellite-based secure quantum communications over a 2000-kilometre range within India, ensuring long-distance secure quantum communications with other countries.
- Establish inter-city quantum key distribution over 2000 km and multi-node Quantum networks with quantum memories.
- Develop highly sensitive magnetometers in atomic systems and Atomic Clocks for precision timing, communications, and navigation.
- Support the design and synthesis of quantum materials like superconductors, novel semiconductor structures, and topological materials for quantum device fabrication.
- Develop single photon sources/detectors and entangled photon sources for applications in quantum communications, sensing, and metrology.
Implementation:
- The mission involves the establishment of four Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) in leading academic and National R&D institutes, focusing on Quantum Computing, Quantum Communication, Quantum Sensing & Metrology, and Quantum Materials & Devices.
- These hubs will concentrate on generating new knowledge through basic and applied research and promote R&D in their respective domains.
Significance:
- NQM has the potential to elevate India's Technology Development ecosystem to global competitiveness.
- It is expected to significantly benefit various sectors such as communication, health, finance, and energy, with applications ranging from drug design to space, banking, and security.
- The mission aligns with national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, Skill India, Stand-up India, and Start-up India, and contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
- With the launch of this mission, India will be the seventh country to have a dedicated quantum mission after the US, Austria, Finland, France, Canada and China.
What is Quantum Technology?
- The term "quantum technology" is used to describe the research and development of techniques to build supercomputers with enhanced speed, security, and efficiency in data processing above conventional computers.
- Quantum mechanics, which governs the behaviour of subatomic particles, is used to design these novel systems.
- The peculiar characteristics of subatomic particles are the key to quantum technology's capabilities in processing massive quantities of information concurrently.
Telco body seeks USOF, tax reliefs in FY25 Union Budget (Live Mint)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Telecom services providers have urged the Ministry of Finance to suspend the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) till the existing corpus is exhausted.
About Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF):
- The USOF was established through a parliamentary amendment to the Indian Telegraph (Amendment) Act, 2003.
- Its primary goal is to ensure non-discriminatory access to affordable telecom services in rural and remote areas, thereby narrowing the digital gap between urban and rural regions.
- For financially unviable rural and remote areas, the USOF provides subsidy support in the form of Net Cost or Viability Gap Funding (VGF).
- This encourages telecom service providers to expand their services to these areas, enhancing telecommunications and broadband accessibility.
- Funding Mechanism: Telecom operators contribute to the USOF through a Universal Service Levy (USL), a percentage of their Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR).
- Administration: The USOF is overseen by the Administrator, USO Fund, appointed by the Central Government.
- It operates as an attached office under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF):
- Launched by USOF on October 1st, 2022, the TTDF Scheme targets domestic companies and institutions engaged in designing, developing, and commercializing telecommunication products and solutions.
- The scheme aims to facilitate affordable broadband and mobile services in rural and remote areas.
- The initiative fosters connections between schools and diverse volunteers from the Indian Diaspora, including young professionals, retired teachers, retired government officials, NGOs, private sector companies, corporate institutions, and more.
- Under the scheme, USOF is committed to developing standards to meet nationwide requirements and establishing an ecosystem for research, design, prototyping, use cases, pilots, and proof-of-concept testing.
- The scheme provides grants to Indian entities, encouraging the integration of indigenous technologies tailored to domestic needs.
Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI)
- The Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI), was constituted in 1995 as a non-governmental society registered under the Societies Act, 1860.
- The Association is dedicated to the advancement of modern communications through the establishment of a world-class cellular infrastructure and to delivering the benefits of affordable mobile communication services to the people of India.
- Today it is regarded as an important interface between the main stakeholders of the Indian Telecom Ecosystem, i.e. Government, Operators, Consumers, Equipment Manufacturers, and Content Providers.
- COAI provides a forum for discussions and exchange of ideas between Service Providers, Policy Makers, Regulators, Technologists, etc., who share a common interest in the development of mobile telephony in the country.
India’s first graphene centre becomes reality (Indian Express)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union government recently launched India’s first graphene centre ‘India Innovation Centre for Graphene (IICG)’ at Maker Village Kochi.
About India Innovation Centre for Graphene (IICG):
- India Innovation Centre for Graphene (IICG) is India’s first Graphene Centre.
- It is a joint venture of the Digital University of Kerala, the Centre for Materials for Electronics Technology (C-MET) and Tata Steel Limited.
- Key Aspects: IICG is committed to advancing research and development, fostering product innovation, and enhancing capacity building in the field of Graphene and two-dimensional materials (2DM).
- With a vision to bridge the gap between research and commercialization, IICG actively supports the Graphene-Aurora program initiated by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- This program aims to provide a comprehensive facility for startups and industries to facilitate seamless progression from research and development to commercialization.
About Graphene:
- Graphene is a one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, serves as the fundamental building block of Graphite, utilized in various applications, including pencil tips.
- Scientists first isolated Graphene in 2004.
Properties of Graphene:
- Recognized as the world's thinnest material, Graphene boasts a thickness of only one atom, making it one million times thinner than human hair.
- Despite its extreme thinness, Graphene exhibits exceptional strength, surpassing even steel and diamond.
- It functions as an outstanding conductor of both heat and electricity, surpassing copper in electrical conductivity.
- Remarkably transparent, Graphene absorbs only 2% of light.
- Impermeable to gases, including lightweight gases like hydrogen and helium.
Applications:
- Mechanical Strength: Used to enhance the strength of various materials.
- Thermal Applications: Ideal for creating heat-spreading solutions, such as heat sinks or heat dissipation films.
- This has applications in microelectronics (e.g., improving the efficiency and lifespan of LED lighting) and larger applications like thermal foils for mobile devices.
- Energy Storage: Due to its minimal thickness, Graphene possesses an exceptionally high surface-area-to-volume ratio, making it promising for use in batteries and supercapacitors.
- It holds the potential to enable energy storage devices, including batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells, with increased energy storage capacity and faster charging capabilities.
- Future Potential: Graphene shows promise in various potential applications, including anti-corrosion coatings and paints, precise sensors, efficient electronics, flexible displays, solar panels, accelerated DNA sequencing, drug delivery systems, and more.
Telangana signs agreement with WEF for setting up C4IR in Hyderabad (The Hindu)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Telangana has signed an agreement with the World Economic Forum (WEF) to establish the Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR) in the state capital, Hyderabad.
About the Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR):
- C4IR is a global initiative of the World Economic Forum (WEF) to collaborate with governments, businesses, academia, and civil society to address the challenges and opportunities posed by the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR).
- The focus of this collaboration is to use technology for advancements in the life sciences and healthcare sector, particularly aiming to meet healthcare targets for the state’s population.
- Telangana aims to become a hub for health technology and a global centre for healthcare services.
About Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR):
- Klaus Schwab, the executive chairperson of the World Economic Forum (WEF), coined the term 4IR in 2016.
- This term refers to advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, 5G technology, the Internet of Things, robotics, biotechnology, quantum computing, and more.
- These technologies offer new possibilities for organizations, allowing them to dream big and expand into areas that were previously unimaginable.
The World Economic Forum
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It was established in 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- It is a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
Jagannath Temple corridor | An attempt to counter BJP’s Hindutva push ahead of elections (The Hindu)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik on Wednesday unveiled a sprawling heritage corridor around the Jagannath Temple in Puri, a project being seen as an attempt to counter the BJP’s Hindutva push ahead of the Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections later this year.
About the Puri Heritage Corridor Project:
- The Shree Jagannath Heritage Corridor, officially named Shree Mandir Parikrama, is a 75-metre-long heritage corridor around the Jagannath Temple in Puri, Odisha.
- Initiated in 2016, the Puri Heritage Corridor Project aims to enhance pilgrim amenities, bolster the temple's safety, and contribute to Puri's transformation into a world heritage city.
- The comprehensive project entails the redevelopment of significant areas within the town and in proximity to the temple, catering to the needs of both visitors and tourists.
- A phased implementation of 22 distinct projects is planned under the Augmentation of Basic Amenities and Development of Heritage and Architecture at Puri (ABADHA) scheme.
- The project also aims to provide ample facilities and amenities for pilgrims and visitors, ensuring a hassle-free and memorable experience, while strengthening the safety and security of the temple and its devotees.
About Jagannath Temple:
- Jagannath Temple believed to be built in the 12th century by King Anatavarman Chodaganga Deva of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty.
- People call it ‘Yamanika Tirtha’ because they believe that the presence of Lord Jagannath nullifies the power of ‘Yama,’ the god of death, in Puri.
- The temple, also known as the “White Pagoda” and part of the Char Dham pilgrimages, has four gates:
- The main Eastern ‘Singhdwara’ with two crouching lions,
- Southern ‘Ashwadwara,’
- Western 'Vyaghra Dwara,' and
- Northern ‘Hastidwara.’
- Each gate has unique carvings representing different forms.
- In front of the entrance stands the Aruna stambha or sun pillar, originally from the Sun Temple in Konark, adding to the historical and artistic significance of the Jagannath Temple.
An ancient system that could bring water to dry areas (DownToEarth)
- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Some of Africa’s dry areas face serious water shortages due to minimal rainfall. An ancient system of drawing water from aquifers, the “qanat system”, could help.
What is the Qanat system?
- The qanats have been used for centuries in arid and semi-arid parts of North Africa, the Middle East and Asia, where water supplies are limited.
- It’s known by a variety of names, “foggara” in North Africa, “falaj” in Oman and “qarez” in parts of Asia.
- It’s thought to have been developed in Persia in the first millennium BC.
- As the Islamic Empire spread across the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, north Africa and parts of Europe from 661 to 750 CE, so did knowledge about qanats.
- Today, some of the region’s qanat systems, like those in Iran, are protected under heritage status.
- Some of these qanats, although declining in number, are still used.
- They are largely protected for historical and cultural reasons.
How does the qanat system work?
- There are bodies of water underground known as aquifers, some of which can be found at the tops of valleys or near mountains.
- A qanat system taps these aquifers and, using underground tunnels, moves the water, using gravity, over many kilometres.
- The tunnel then exits at a lower-lying area.
- When the water exits the tunnel, farmers can use it to irrigate their crops.
- People can also access the water along the stretch of the tunnel using wells.
- It’s a system that’s managed by everyone and its benefits are shared.
- Everybody has a vested interest and a role to play and community bonds can be strengthened.
Advantages of qanat systems:
- Efficient use of water: Qanats allow for the extraction and transport of groundwater from deep underground sources to the surface.
- This allows for a more efficient use of water resources, as the water is extracted and transported to the surface for irrigation and other purposes.
- Sustainable water supply: Qanats can provide a reliable and sustainable source of water for communities, even in arid regions where surface water is scarce.
- Cool and humid air supply: The cool and humid air that flows through the qanat can be used to provide a natural air conditioning system for buildings, as well as to irrigate crops and orchards.
- Low maintenance: Qanats require minimal maintenance once they are constructed, making them a cost-effective and long-lasting water supply solution.
- Disaster resilience: Qanats are resilient to natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods, as they are located underground and protected from damage.
Who are the Shankaracharyas — and who was Adi Shankara? (Indian Express)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the four Shankaracharyas have said they will not attend the inauguration of the Ram temple in Ayodhya on January 22.
Who are the Shankaracharyas?
- The Shankaracharyas are the "supreme authority" in Hinduism and for interpreting Hindu scriptures.
- The shankaracharyas head the four principal monasteries or mutts that were established by the eighth-century Hindu saint Adi Shankara.
- They are based in Uttarakhand, Odisha, Karnataka and Gujarat.
- Each mutt, called peetha or pitha in Sanskrit, was tasked to serve as the custodian of one Veda each and keep alive Vedic literature.
- Govardhan Math in Puri is the custodian of the Rig Veda.
- Dwarka Sharada Peetham in Gujarat is responsible for the Sam Veda.
- The Sringeri Sharada Peetham in Karnataka is responsible for the Yajur Veda and
- Jyotir Math in Uttarakhand's Joshimath for the Atharva Veda.
- All the peethas are situated in the four cardinal directions and are amongst the most-revered pilgrimages in India.
Who was Adi Shankara?
- The title "Shankaracharya", in fact, is derived from Adi Shankara, a Vedic scholar credited with reforming and reviving Hinduism during a time when Buddhists and Jains wielded influence.
- Adi Shankara was born in Kalady village on the bank of the River Periyar in today Kerala’s Ernakulam district in the month of Vaishakha in 788 CE.
- Also known as Jagadguru, Shankara had a short life (it is believed he died when he was just 32) but he had a big impact on Hindu religion.
- Revered as an avatar of Lord Shiva, it is believed that he mastered the Vedas when he was just 16.
- At a very young age, Shankara started criss-crossing the length and breadth of India to spread his commentaries on Brahama Sutras, Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita amid a rise in Jainism and Buddhism.
What is the legacy of Shankara?
- Shankara’s legacy today transcends his contributions to metaphysics and theology.
- His travels across the subcontinent have often been interpreted as a near-nationalistic project where faith, philosophy and geography are yoked together to imagine a Hindu India which transcended the political boundaries of his time.
- And his four mathas, located in the North and South, East and West of India, are seen as the ultimate examples of this project.
- His mathas are thus also seen as keepers of Hindu faith and traditions.
What is Advaita Vedanta?
- Shankara is most associated with Advaita Vedanta, a school of Hindu philosophy and spiritual discipline.
- Advaita Vedanta articulates an ontological position of radical nondualism — it posits that all that we perceive is ultimately illusory (maya) and that the principle of Brahman (not the caste Brahmin) is the only true reality of all things, transcending empirical plurality.
- The fundamental thrust of Advaita Vedanta lies in the unity of atman or individual consciousness, and brahman or the ultimate reality.
Four Peethas aren't the four Dhams
- The four peethas established by Adi Shankara should not be confused with the four dhams.
- The four dhams, known as Char Dham, were also established by Adi Shankara.
- The four dhams are at;
- Badrinath
- Dwarka
- Puri and
- Rameswaram.
- The peethas are basically associated with the preservation and propagation of Hindu philosophy.
Union Minister Rao Inderjit Singh launches the MPLADS e-SAKSHI Mobile Application for the Revised Fund Flow Procedure under the MPLAD Scheme (PIB)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) Rao Inderjit Singh launched the MPLADS e-SAKSHI Mobile Application at Khurshid Lal Bhawan, New Delhi.
What is the e-SAKSHI Mobile Application?
- The e-SAKSHI mobile application was devised for the revamped fund flow procedure within the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLAD).
- It is poised to revolutionize the way Members of Parliament (MPs) engage with and oversee development projects in their constituencies.
Key Features of e-SAKSHI:
- Convenience and Accessibility: MPs can seamlessly propose, track, and supervise projects with the application, ensuring convenience and accessibility at their fingertips.
- Real-time Access: The application provides real-time access, enhancing decision-making by enabling swift responses to emerging needs or issues.
- Streamlined Communication: e-SAKSHI facilitates streamlined communication between MPs and relevant authorities, promoting an efficient exchange of information.
- Transparency: MPs receive instant updates on the status and progress of proposed projects, promoting transparency in the implementation process.
- Budget Management: The application includes features for budget management, empowering MPs to monitor expenditures effectively.
Key Points about the MPLAD Scheme:
- Introduced in 1993, MPLAD is a fully funded Government of India scheme where funds are released directly to district authorities as grants-in-aid.
- The funds are non-lapsable, allowing the carry-forward of entitlement not released in a specific year to subsequent years, subject to eligibility.
- MPs have an annual entitlement of ?5 crore per constituency, with their role limited to recommending works.
- District authorities are responsible for sanctioning, executing, and completing the recommended works within stipulated timelines.
- Lok Sabha members recommend works in their respective constituencies, while Rajya Sabha members can recommend works anywhere in their elected state.
- Nominated members can recommend works nationwide.
- MPLADS works can be implemented in areas affected by various natural calamities, ensuring a flexible and responsive approach to development needs.
In Assam, creeper conservation rides revived Karbi traditional game (The Hindu)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A dying traditional game, given a fresh lease of life at the ongoing Karbi Youth Festival (KYF) in central Assam’s Karbi Anglong district, has fuelled a drive for conserving a creeper with an African connection.
About African Dream Herb:
- The African dream herb, also known by various names such as Giant sea bean, snuff box, and Entada rheedii, is a perennial climbing vine valued by African traditional healers for its ability to induce vivid dreams, facilitating efficient communication with ancestors.
- Indigenous to Africa, Asia, Australia, and Madagascar, this vine thrives in tropical lowlands, along coastlines, river banks, woodlands, thickets, and riverine rainforests.
- Uses: A paste derived from its leaves, bark, and roots serve purposes ranging from wound cleaning to treating burns and addressing jaundice in children.
- The plant's tea, made from its entirety, aids in improving blood circulation to the brain and healing the aftermath of a stroke.
- The bark is employed to treat ailments such as diarrhoea, dysentery, and parasitic infections.
- This vine produces dark brown, spherical seeds, almost the size of a human patella or kneecap, used in the traditional game 'Hambi Kepathu,' associated with the origin of the Karbi community.
What is Hambi Kepathu?
- Also known as Simrit in some regions of Karbi Anglong, Hambi Kepathu is played on three rectangular courts with two teams of three members each.
- In this male-only game, players place a 'hambi' (glazed creeper seed) vertically on the midpoint of the boundary line for opponents to hit with their 'hambi.'
- The name Hambi Kepathu is derived from the first syllables of the names of a Karbi sister-brother duo, adding to the array of traditional Karbi games such as 'Pholong' (spinning top), 'Thengtom Langvek' (torch swimming), and 'Kengdongdang' (bamboo stilt race).
PM pays homage to Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji on his Parkash Utsav (The Hindu)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
January 17 marks the 357th birth anniversary of Guru Gobind Singh, the revered Sikh leader born in Patna, Bihar.
About Guru Gobind Singh:
- Guru Gobind Singh, the 10th and the last Guru of the Sikhs, was born as Gobind Rai on December 22, 1666, in Patna, Bihar, to Guru Teg Bahadur, the ninth Guru of Sikhism.
- Following the martyrdom of his father by the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in 1675, Guru Gobind Singh assumed leadership at the age of nine.
- Renowned as a warrior, poet, and prophet, Guru Gobind Singh is cherished by Sikhs for his defence of faith and advocacy for equality and justice.
- In 1699, Guru Gobind Singh formed the institution of the Khalsa and introduced the Five Ks — Kesh (uncut hair), Kangha (wooden comb), Kara (iron or steel bracelet), Kirpan (sword), and Kacchera (short breeches).
- He fought 14 wars against his oppressors and tyrants, but with ethical and moral principles, never taking captives, nor damaging places of worship; he was never the first to be the aggressor.
- The notable conflicts include the Battle of Bhangani, the Battle of Nadaun, the Battle of Anandpur, the Battle of Chamkaur, the Battle of Muktsar, and the Battle of Khidrana
- While continuing to lead with steely determination, Guru Gobind Singh faced with fortitude, the execution of his two sons, Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh.
- The duo was bricked alive at Sirhind by the then-governor.
- He lost two more sons in the battle of Chamkaur Sahib, yet he stayed true to his goal.
- When the Mughal army, numbering over a lakh, marched against his troop of 40 soldiers, he marched on bravely, penning his famous hymn, mitr pyare nu haal muridan da kehna (Oh beloved friend of the Lord, see the plight of your disciples).
- Guru Gobind is credited with finalising the manuscript of Guru Granth Sahib, declaring it to be the ultimate Guru of the Sikhs.
- His metaphysical, sublime and exquisite poetry has been immortalised in his composition, Dasam Granth, reflected in Jaap Sahib, Chandi Di Vaar, Tav Prasad savaiye and Benti Chaupai, among others.
- He wrote in Punjabi, Arabic, Braj Bhasa, Sanskrit and Persian and remains a much-revered guru.
- He was assassinated in 1708, at the age of 41.
Defence upgrade roadmap: Apex body led by Prime Minister, MoD sci-tech unit (Indian Express)
- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The expert committee, led by Vijay Raghavan, the former principal scientific advisor, proposed that the country's defence technology roadmap be overseen by an apex body called the Defence Technology Council, with the Prime Minister serving as its chair.
The context in which the Vijay Raghavan Committee was Established:
- Formed by the government last year, the committee was tasked with assessing the functioning of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The committee's report, submitted this month, follows the government's initiative to address significant delays in various DRDO projects.
- This scrutiny comes in response to concerns raised by the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence, which noted that 23 out of 55 mission mode projects faced substantial delays.
- In 2022, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) highlighted that 67% of the 178 scrutinized projects failed to meet their initially proposed timelines.
- The CAG attributed these delays to factors such as persistent alterations in design specifications, delays in completing user trials, and delays in placing supply orders.
- The prevalent practice of seeking multiple extensions for projects, particularly those designated under the Mission Mode category, has been identified as undermining the intended purpose of these initiatives.
Major Recommendations of the Vijay Raghavan Committee:
- Establishment of the Defence Technology Council: Headed by the Prime Minister, with the Defence Minister and the National Security Advisor serving as Vice Presidents.
- This council is envisioned to play a pivotal role in charting the nation's defence technology roadmap, deciding on significant projects, and overseeing their execution.
- An executive committee, led by the Chief of Defence Staff, is proposed, featuring members such as the Principal Scientific Advisor, the three service chiefs, their vice chiefs, and representation from academia and industry.
- Creation of the Department of Defence Science, Technology, and Innovation: To be led by a technocrat, this department aims to foster defence research and development within the academic and startup ecosystem.
- Additionally, it is designated as the secretariat for the Defence Tech Council chaired by the Prime Minister.
- Drawing expertise from scientists in the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and academia, it will compile a knowledge repository on production expertise, conduct background research for the Defence Tech Council, and contribute to informed decisions on technology production.
- Restructuring of DRDO's Focus: Recommends that DRDO concentrate on its original mission of research and development for defence purposes.
- The suggestion is for DRDO to abstain from involvement in productization, production cycles, and product management, tasks deemed more suitable for the private sector.
- Currently, DRDO is engaged in all aspects of its projects, spanning from research and development to production.
The last batch of Mizoram Bru refugees permanently settled in Tripura (The Hindu)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Tripura government has allocated land for the rehabilitation of the last batch of Mizoram Bru refugees, who were granted permanent settlement in Tripura through a Home Ministry-initiated quadripartite agreement signed on January 16, 2020.
Who are Bru refugees?
- Brus, also referred to as Reangs, are a tribal community indigenous to northeast India and have historically resided in parts of Mizoram, Tripura, and Assam.
- In the state of Tripura, the Brus are a designated Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- Most Brus residing in Tripura today have suffered more than two decades of internal displacement, fleeing ethnic persecution primarily from the neighbouring state of Mizoram.
Bru-Reang Refugee Crisis:
- It all started in 1995 when the Young Mizo Association and the Mizo Students' Association demanded that Brus be eliminated from Mizoram’s electoral rolls as they were not indigenous inhabitants.
- Being ethnically distinct from the majority of Mizos, the Brus are often referred to as “Vai” in the state, meaning outsiders or non-Mizos.
- Tensions escalated after the Brus retaliated against the Mizos’ attempts to disenfranchise them, and organized themselves into an armed group, the Bru National Liberation Front, and a political entity, the Bru National Union.
- They also demanded the creation of a separate Bru Autonomous District Council (ADC) in western Mizoram as per the provisions of the sixth schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- However, their attempts at seeking greater autonomy were foiled and resultant ethnic clashes forced many Reangs in Mamit, Kolasib and Lunglei districts of Mizoram to migrate to neighbouring Tripura in 1997.
- Today, roughly 35,000 Reangs continue to reside in north Tripura’s Kanchanpur camp as refugees, as per Home Ministry estimates.
Have there been any attempts to resettle the Brus?
- The state governments, along with the union government have made multiple attempts to send Brus back to their homeland in Mizoram.
- But until 2014, following eight rounds of resettlement, only an estimated 5,000 individuals, or 1622 Bru-Reang families returned to Mizoram in various batches.
- In July 2018, the governments of Tripura, Mizoram, and the central government concluded a quadripartite pact with Bru community representatives to resettle refugees in Mizoram.
- This was however opposed by not only native Mizo groups but also by the Reangs who feared threats to life and further ethnic repression in their home state.
- Efforts were still made to pursue the terms of this pact. The supply of free ration to relief camps was halted on instructions of the Home Ministry in a bid to hastily complete the repatriation of refugees, which resulted in at least six starvation deaths.
- Sensing a failure of the 2018 pact, the four groups once again came together in January 2020 to sign another quadripartite pact to resettle the Brus, this time in the state of Tripura.
- The central government earmarked a Rs 600 crore package to aid the rehabilitation efforts, and the Bru families were promised a residential plot, a fixed deposit of Rs 4 lakh, a Rs 1.5 lakh grant to construct their houses, as well as free ration and a monthly stipend of Rs 5,000 for a period of two years.
- Additionally, the renewed 2020 pact also promised to include the displaced Reangs in the electoral rolls in Tripura.
Darjeeling zoo’s success with snow leopards: Why wild cats are fussy breeders (Indian Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP) in Darjeeling has made headlines for successfully breeding 77 snow leopards since the 1980s, placing it next only to New York’s Bronx Zoo, which has produced 80 snow leopard cubs since it started breeding experiments with the species in the 1960s.
About Snow Leopard:
- The snow leopard, also known as the ounce, is a large Asian cat belonging to the family Felidae, classified as Panthera uncia.
- It preys on various animals, including marmots, wild sheep, ibex, and domestic livestock. As the apex predator in the mountain ecosystem, snow leopards serve as vital indicators of ecosystem health.
- Habitat: Native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia, snow leopards are found in India, specifically in the western Himalayas covering Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh in the eastern Himalayas.
- Threats to Survival: With an estimated 4,000 to 6,500 snow leopards remaining in the wild, around 500 of them are in India.
- Human settlement expansion, particularly livestock grazing, has escalated conflicts.
- Climate change, causing a rise in average temperatures across their habitat, poses an additional threat.
- Poaching, driven by illegal trades in pelts and body parts used in traditional Chinese medicine, further endangers their lives.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Conservation Efforts: The Government of India initiated Project Snow Leopard in 2009 to safeguard and conserve the snow leopard population and their habitats through participatory policies.
- Under the UNDP's SECURE Himalaya project in 2020, India's first Snow Leopard Conservation Centre was launched in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand, promoting conservation efforts in the region.
About Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP):
- Formerly known as the Himalayan Zoological Park, the PNHZP was established in August 1958 in Darjeeling, West Bengal.
- Dedicated to the preservation of ecological balance in the Eastern Himalayas, the park pursues the following objectives:
- Ex-situ Conservation and Captive Breeding: The park focuses on the ex-situ conservation and captive breeding of endangered Himalayan animal species.
- Awareness and Education: Aiming to educate and motivate both local residents and visitors, the park conducts awareness campaigns highlighting the significance of Himalayan ecosystem conservation.
- Applied Research: The PNHZP initiates applied research in animal biology, behaviour, and healthcare, contributing to a better understanding of these aspects.
- Conservation Pioneering: Recognized as a conservation pioneer, the zoo initiated the first ex-situ conservation breeding program in 1986, commencing with the Snow Leopard conservation breeding project.
- The Red Panda project followed suit in 1990.
- High-Altitude Zoo: The PNHZP holds the distinction of being the largest high-altitude zoo in the country, making significant strides in the conservation of endangered Eastern Himalayan species in India.
How do flights land safely despite fog and low visibility? The wizardry tech that makes it possible! (Financial Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the past few days, the Delhi airport has experienced chaos, resulting in over 100 flight delays, 10 flights being diverted, and some even cancelled due to low visibility caused by dense fog conditions affecting flying operations.
What is an Instrument Landing System?
- Fog, which is the suspension of water droplets near the ground, poses a considerable obstacle to aircraft operations during instances of reduced visibility.
- This atmospheric condition results in thick mist which hampers flight operations, necessitating the reliance on instruments like the “Instrument Landing System” (ILS) to navigate through the obscured surroundings.
- ILS is a standard International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) precision landing aid that is used to provide accurate azimuth (angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system) and descent guidance signals for guidance to flight for landing on the runway under adverse weather conditions.
- To put things in perspective, ILS operates in tandem with ground-based equipment and avionic components on the aircraft, providing precise guidance to pilots during the critical phases of approach and landing.
- The ILS guiding system helps planes land in low visibility with the help of radio signals and also sometimes high-intensity lighting arrays.
- Among the various categories of ILS, Category 3 (CAT III) is the most significant due to its capability to support landing operations in low visibility conditions, thereby enhancing flight safety and operational efficiency.
- At present, airports like Delhi, Amritsar, Jaipur, Lucknow, and Kolkata among others use CAT IIIB technology in India.
- However, the absence of pilots or the ILS technology can lead to massive delays and cancellations.
- Moreover, a lot of financial and logistics are required to operate the technology which is still a distant dream at many airports around the country.
How does this system work?
- Consisting of two main components—the localizer and the glide slope—the CAT safe system functions by transmitting radio signals that help pilots align their aircraft with the correct runway and maintain the appropriate descent path.
- The localizer ensures lateral alignment, guiding the aircraft along the correct azimuth toward the runway centerline.
- Simultaneously, the glide slope provides vertical guidance, aiding pilots in maintaining the proper descent angle for a safe landing.
- Together, these components create a reliable and accurate navigational reference, allowing pilots to execute precision landings even when external visibility is severely compromised.
- Notably, ILS-equipped runways are equipped with ground-based transmitters positioned at the end of the runway, emitting signals that are received by the aircraft’s onboard ILS receiver.
- As the aircraft approaches the runway, the pilot uses the visual and audible cues provided by the ILS to make real-time adjustments, ensuring that the aircraft remains aligned with the desired glide path.
- In essence, the technology significantly enhances aviation safety and operational reliability by enabling pilots to conduct precise landings even in conditions that would otherwise pose a considerable risk.
NHAI cracks down on multiple FASTags for a single vehicle, launches ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ program (Financial Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) announced on Monday (January 15) that FASTags with valid balances but incomplete KYC will be deactivated by banks after January 31, 2024.
What is the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ Program?
- In a bid to enhance the efficiency of the electronic toll collection system and facilitate seamless movement at toll plazas, NHAI has initiated the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ program, discouraging the use of a single FASTag for multiple vehicles or linking multiple FASTags to a particular vehicle.
- NHAI encourages FASTag users to complete the ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) process for their latest FASTag, aligning with RBI guidelines.
- To prevent inconvenience, users must ensure KYC completion for their latest FASTag and discard all previously issued FASTags through their respective banks.
- The initiative aims to deactivate or blacklist previous tags after January 31, 2024.
- Ensuring seamless and comfortable journeys: The ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ initiative, coupled with the high penetration rate of FASTag at around 98% and over 8 crore users, is poised to streamline toll operations, ensuring efficient and comfortable journeys on national highways.
About FASTags:
- FASTag serves as an electronic toll collection system in India, administered by the NHAI.
- Utilising Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, it facilitates toll payments directly from the linked prepaid or savings account or directly from the toll owner.
- FASTag utilizes Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, allowing seamless toll payments while the vehicle is in motion.
- Windscreen Affixation: FASTag is affixed on the vehicle's windscreen, providing a hassle-free experience for customers to drive through toll plazas without the need to stop for payments.
- Automatic Deduction: Toll fares are automatically deducted from the linked account of the customer, ensuring a swift and cashless transaction.
- Vehicle Specific: Once affixed to a vehicle, FASTag becomes vehicle-specific, preventing transferability to another vehicle.
- Purchase from NETC Member Banks: FASTag can be conveniently purchased from any of the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) Member Banks.
- Prepaid Account Recharge: In the case of linking FASTag to a prepaid account, customers need to recharge or top-up the tag based on their usage.
Govt cuts windfall tax on petroleum crude to Rs 1,700 per tonne (The Hindu)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has cut the windfall tax on domestically-produced crude oil to ?1,700 per tonne from ?2,300 per tonne with effect from January 16.
What is Windfall Tax?
- A Windfall Tax is imposed by governments on specific industries that experience exceptionally high profits due to economic conditions surpassing the norm.
- The term "windfall" denotes an unforeseen surge in profits, leading to the imposition of the windfall tax on the excess gains.
- Imposition Criteria: Governments impose the Windfall Tax when there is a sudden and substantial increase in an industry's revenue.
- Notably, this increase must be unrelated to the company's intentional actions, such as business strategies or expansions, but instead linked to external events beyond its control.
- A Windfall Tax is typically triggered by external occurrences, such as the unexpected surge in profits observed in the oil and gas industries amid the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Tax Rates: Governments tax these windfall gains at rates higher than the standard tax rates applicable to regular profits.
- Target Industries: Commonly, industries such as oil, gas, and mining become targets for windfall gains tax.
Objectives:
- Redistribution of Gains: To redistribute unexpected profits, especially when high prices benefit producers at the expense of consumers.
- Funding Social Welfare Schemes: Utilizing the windfall tax revenue to support social welfare initiatives.
- Supplementary Revenue Source: Acting as an additional revenue stream for the government.
- Addressing Trade Deficit: Providing a means for the government to mitigate the widening trade deficit in the country.
When Did India Introduce Windfall Tax?
- To address the shortage of energy products on the domestic market, the Indian government added a special additional excise duty on the export of gasoline and diesel, known as the Windfall Tax, on July 1st, 2022.
Why are Countries Levying Windfall Taxes Now?
- Since the past few years, gasoline prices, crude oil, gas, and coal have significantly increased.
- COVID-19 and the conflict between Ukraine and Russia made this increase even more pronounced.
- Because of this, energy companies profited handsomely at the expense of consumers, who now pay much higher prices for their energy use.
- The UN Secretary-General, therefore, encouraged nations to impose windfall taxes on those companies that have greatly benefited from the rise in the price of fossil fuels.
- As a result, many countries, including the UK, Germany, and others, besides India, are considering imposing Windfall Taxes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a windfall tax is a tax that a government may impose or an additional tax that may be imposed on a business when it generates a sizable unanticipated profit, particularly if the company has benefited from favourable economic conditions.
Companies in specific economic sectors, such as the oil and gas industry, that profit from circumstances like commodity shortages that significantly drive up the cost of their goods at the expense of consumers may be subject to windfall taxes.
Goyal asks FCI officers to turn whistleblowers to curb corruption (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Food Minister said the role of FCI is not only to deliver ration but also to instil confidence in farmers and beneficiaries by bringing in transparency, efficiency and accountability.
About the Food Corporation of India (FCI):
- FCI is a statutory body with multifaceted objectives aimed at ensuring national food security.
- It was established through the enactment of the Food Corporation Act, of 1964 by the Parliament.
- As part of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, FCI plays a pivotal role in supporting farmers, managing food distribution, and maintaining strategic food grain stocks.
Key Objectives:
- Effective Price Support Operations: FCI focuses on safeguarding farmers' interests through efficient price support operations.
- Public Distribution System (PDS): The distribution of food grains nationwide for the PDS forms a crucial aspect of FCI's mandate.
- Operational and Buffer Stocks: FCI is entrusted with maintaining optimal levels of operational and buffer stocks to ensure national food security.
Role in Ensuring Food Security:
- Procurement at Minimum Support Price (MSP): FCI actively engages in procuring food grains, primarily wheat and paddy, under the Price Support Scheme to guarantee MSP for farmers and provide affordable food to vulnerable sections.
- Coarse Grains Procurement: Additionally, FCI oversees the procurement of coarse grains, such as Jowar and Bajra, in coordination with state government agencies.
- Storage Capacity: To meet storage obligations, FCI boasts an extensive network of storage depots and silos strategically positioned across the country.
- Movement and Distribution: FCI undertakes the movement of food grain stocks from surplus to deficit regions, ensuring planned delivery through PDS, creating buffer stocks, and supplying food grains for defence, paramilitary forces, and natural calamities.
In conclusion, FCI's multifaceted role encompasses procurement, storage, and distribution, contributing significantly to the nation's food security and the well-being of farmers.
Medical care on India’s trains is running late, with passengers at risk (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Balasore train accident in June 2023 raised important concerns about rail safety, but it was largely about accident-related safety.
Provision of Medical Care in Railway:
- In 1995, a ‘Special first aid box’ was provided in long-distance superfast trains, Shatabdi and Rajdhani trains.
- In 1996, as part of a pilot project, Railways stationed a medical team in two long-distance trains.
- This team consisted of a medical officer, a male nurse, and an attendant.
- The Railways subsequently discontinued the service – but to make healthcare accessible, it decided to give doctors travelling on trains a 10% discount if they were willing to provide medical services en route.
- In 2017, the Supreme Court directed the Railways to set up a committee consisting of experts from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) to recommend further measures.
- Based on the committee’s recommendations, the Railways decided to modify the contents of the first aid boxes and provide them at all railway stations and in all passenger-carrying trains.
- It also mandated first-aid training for railway staff at the time of joining and once every three years.
- In 2021, the Railways launched an integrated helpline number – 139 – for all queries concerning the railways, including medical assistance.
Way Forward
- Railways should ensure the updated 88-item first-aid list is in place on all trains and that passengers are aware of these services.
- Periodic inspections are necessary to maintain the quality of care as well.
- Finally, the Railways need to install a system to capture data on the healthcare needs of people travelling on trains and use that to inform policy.
In a big push for India's energy security, ONGC makes two significant gas discoveries in the Mahanadi basin block (Business World)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant stride towards bolstering India's energy security, the state-owned Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) has successfully unearthed two substantial natural gas reserves within the Mahanadi basin block in the Bay of Bengal.
About the Mahanadi River Basin:
- Ranked as the 8th largest river basin in the country, the Mahanadi River Basin boasts a substantial catchment area spanning 139,681.51 sq. km, representing approximately 4.28% of the total geographical area of India.
- Encompassing significant portions of Chhattisgarh and Odisha, along with smaller segments of Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh, this basin stretches across diverse terrains and is surrounded by the Central India hills to the north, the Eastern Ghats to the south and east, and the Maikala range to the west.
- The basin's physiographic features are categorized into four regions:
- The northern plateau
- The Eastern Ghats
- The coastal plain (a fertile delta area), and
- The erosional plains of the central tableland.
- Notably, the basin receives about 90% of its rainfall during the monsoon season.
- Agriculture dominates the landscape, covering 54.27% of the total area, while water bodies occupy 4.45%. Predominant soil types include red and yellow soils.
Key Characteristics of the Mahanadi River:
- As one of the major east-flowing peninsular rivers in India, the Mahanadi River originates from the Sihawa range of hills in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh.
- Water Potential: Second only to the Godavari River in terms of water potential among peninsular rivers, the Mahanadi River spans a total length of 851 km, with 357 km flowing through Chhattisgarh and 494 km through Odisha.
- Tributaries: The river is augmented by left bank tributaries including the Seonath, Hasdeo, Mand, and Ib, while the right bank receives contributions from the Ong, Tel, and Jonk.
- Hirakud Dam: An engineering marvel, the Hirakud Dam, recognized as the world's longest earthen dam at 26 km, is strategically located about 15 km from Sambalpur in Odisha, providing essential water management for the region.
- The Mahanadi River plays a crucial role in the hydrology of Chilika Lake, designated as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Approximately 61% of the lake's inland flow originates from the Mahanadi River system, mainly through its distributaries, Daya and Bhargabi.
Global surgery: why access to essential surgery is important (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global surgery is the neglected stepchild in global health. The neglect is more shocking in South Asia which has the largest population globally lacking access to essential surgery.
What is global surgery?
- Global surgery focuses on equitable access to emergency and essential surgery.
- While it predominantly focuses on low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), it also prioritises access disparities and under-served populations in high-income countries (HICs).
- These “surgeries” include essential and emergency surgeries such as surgery, obstetrics, trauma, and anaesthesia (SOTA).
- Despite small differences, there is largely a consensus across multiple international groups on about thirty or so procedures that fall under the umbrella of emergency and essential surgery.
The Global Scenario:
- As per the Lancet Commission on Global Surgery (LCoGS), more than 70% of the global population, which amounts to five billion individuals, lacks timely access to safe and affordable surgical care.
- Notably, over 1.6 billion of these individuals reside in South Asia. Access gaps are particularly acute, with 99% and 96% of people in low- and lower-middle-income countries (LLMICs), respectively, facing challenges compared to 24% in high-income countries (HICs).
Concerns and Impact:
- In 2010, surgically treatable conditions contributed to around 17 million deaths, surpassing the combined mortality burden of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria.
- The global disease burden also translates into a significant economic impact, with a projected cumulative loss of $20.7 trillion to the GDP across 128 countries by 2030 if the scale-up of surgical care remains inadequate.
Measures implemented for Global Surgery:
- India's Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana has played a pivotal role by providing millions of surgeries at either zero or negligible cost, specifically benefiting the bottom 40% of the Indian population.
- In South Asia, Pakistan has developed a National Surgical Care Vision, while Nepal has initiated a comprehensive National Plan Encompassing Surgical, Obstetric, and Anaesthesia Care (NSOAP).
Way Ahead
- Addressing global surgery challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, emphasizing research, innovation, policy focus, and sustained financing.
- Key stakeholders, including organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and various non-profit groups, hold significant potential in advancing and supporting global surgery initiatives.
- Collaborative efforts on these fronts are crucial for ensuring equitable and accessible surgical care on a global scale.
India celebrates 76th Army Day with pride and gratitude (TOI)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Droupani Murmu conveyed their warm wishes to Indian Army personnel on the occasion of Army Day.
Why is Army Day celebrated?
- On January 15, KM Cariappa took charge of the Indian Army from General Sir Francis Roy Bucher in 1949, who was the last British-serving Army chief.
- KM Cariappa became the first-ever Indian General to command the Army in its long eventful journey.
- Later, General Cariappa also became the Field Marshal of India.
- KM Cariappa, who is popularly known as Kipper, received King's commission in 1919 and was part of the first group of Indian cadets at the Royal Military College in Sandhurst, UK.
- He was the first Indian who attended Staff College in Quetta and the first one to command a battalion.
- In 1942, Cariappa raised the 7th Rajput Machine Gun which was later known as 17 Rajput.
- He was conferred with Field Marshal Rank in 1986 and passed away in 1993 at the age of 94.
Indian Army Day 2024: Theme
- The theme of the Indian Army Day 2024 is “In Service of the Nation”.
- The theme of 2024 focuses on the main essence of the Army.
- This year’s theme also resembles the motto of the Indian Army, “Service Before Self.”
- This year marks the 76th Army Day.
- The parade will be held under the command of the Army's Central Command, which is headquartered in Lucknow.
Indian Army Day 2024: Significance
- Indian Army Day is also known as Bhartiya Sena Diwas.
- The day promises a grand celebration to honour the valour and service of the Army officers.
- It also proves to be a day dedicated to spreading awareness and enthusiasm among the youth of the nation to join the Bhartiya Sena and serve the country selflessly.
- Army Day is dedicated to appreciating and acknowledging the sacrifice and dedication of the Indian Army towards protecting the country from the illegal invasion of enemies and attacks.
Indian Army Day 2024: History
- The Indian Army was established on 1 April 1895 by the British.
- Initially, the Indian Army was known as the Royal Indian Army.
- India attained Independence on 15 August 1947.
- On 15 January 1949, the first Commander-in-Chief of India General K.M. Cariappa took over the rule of British Army Official General Sir Francis Roy Bucher. Since then, this historic moment has been celebrated as Bhartiya Sena Divas.
- India is following the tradition of celebrating this grand day with great zeal and patriotism.
- Since 15 January 1949, India has been self-reliant in the field of defence.
The first-ever IUCN assessment of the Himalayan Wolf is out. And it is grim (DownToEarth)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Himalayan Wolf is a prominent lupine predator found across the Himalayas the taxonomic status which was a puzzle till late, has been assessed for the first time in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List.
Key Findings:
- Population Decline: The IUCN assessment highlights a persistent reduction in the habitat area, extent, and quality of Himalayan wolves.
- The estimated total population ranges from 2,275 to 3,792 mature individuals, with 227 to 378 in India.
Primary Threats:
- Depredation Conflict: Arising from habitat modification, encroachment, and depletion of wild prey populations.
- Hybridization with Dogs: Particularly in Ladakh and Spiti, where feral dog populations are on the rise.
- Illegal Hunting: Driven by trade in fur and body parts, including paws, tongues, and heads.
About the Himalayan Wolf (Canis lupus chanco):
- It is also called Tibetan wolves, which live at more than 4,000 metres altitudes.
- Habitat: It is found in the Himalayas (Nepal and India) and the Tibetan Plateau.
- Exhibits genetic adaptations to cope with hypoxic conditions.
- Characteristics: Adorned with thick fur, displaying brown colouration on the back and tail, complemented by paler yellows on the face, limbs, and underside.
- Larger than Indian and European wolves.
- Shows a preference for wild prey over domestic options.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN’s Red List: Categorized as Vulnerable.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I.
- CITES: Included in Appendix I.
Recommended Actions for the Conservation of Himalayan Wolves:
- Ensure the preservation and restoration of robust wild prey populations and their natural habitats.
- Foster collaborative transboundary initiatives to safeguard and conserve the species across its range of countries.
- Integrate the Himalayan Wolf into comprehensive conservation programs for enhanced protection and sustainable management.
How GM mustard was developed, why the question of its approval has now reached the Supreme Court (Indian Express)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently questioned the Centre on why reports of the court-appointed Technical Experts Committee (TEC) on the biosafety of genetically modified (GM) crops were not looked into by the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
Context:
- The Supreme Court has raised concerns about the approval process for the transgenic mustard hybrid DMH-11, developed by Delhi University with herbicide-tolerant traits through genetic modification.
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) had recommended its environmental release in 2022, but the court questioned whether the reports from the court-appointed Technical Experts Committee (TEC) were adequately considered before approval.
- DMH-11 contains two alien genes isolated from a soil bacterium called Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
- Indian scientists improvised the barnase/barster male sterility technique to produce the DMH-11.
-
- Barnase/barster male sterility technique is a 1990s breeding innovation technique pioneered in Belgium.
- Indian scientists arranged the genes in a way that will allow a large number of high-yielding varieties of mustard to be developed, which is normally not possible.
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) undergo genome alterations, and transgenic organisms result from the introduction of foreign DNA sequences.
- Approval process for transgenic crops:
-
- Safety assessments by committees are conducted before the open field tests.
- Transgenic plants must be better than non-GM variants and environmentally safe for commercial clearance.
- GEAC recommends environmental release.
- Final approval by MoEFCC.
- Benefits of GM crops:
-
- Resistance against plant diseases.
- Improved yields
- Increased food security.
About the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC):
- Establishment: GEAC operates as a statutory body mandated by the Environment Protection Act of 1986.
- Responsibility: It holds the responsibility for evaluating proposals concerning the environmental release of Genetically Modified (GM) organisms and associated products.
- GEAC operates under the purview of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
SC directs UOI to frame a policy to phase out heavy-duty diesel vehicles & replace them with BS VI (The New Indian Express)
- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court has directed the Centre to frame a policy within six months to replace heavy-duty diesel vehicles and replace them with BS VI vehicles, observing that the right to clean air is not the entitlement of people living in Delhi alone.
What are BS-VI Norms?
- Bharat stage (BS) emission standards are laid down by the government to regulate the output of air pollutants from internal combustion engines and spark-ignition engine equipment, including motor vehicles.
- The central government has mandated that vehicle makers must manufacture, sell and register only BS-VI (BS6) vehicles from April 1, 2020.
- The first emission norms were introduced in India in 1991 for petrol and in 1992 for diesel vehicles.
- Following this, the catalytic converter became mandatory for petrol vehicles and unleaded petrol was introduced in the market.
What is the Difference Between BS4 and BS6?
- Both BS-IV and BS-VI are unit emission norms that set the maximum permissible levels for pollutants that an automotive or a two-wheeler exhaust can emit.
- Compared to the BS4, BS6 emission standards are stricter
- Whereas makers use this variation to update their vehicles with new options and safety standards, the biggest modification comes in the permissible emission norms.
What area unit BSI, BSII, BSIII, BSIV, and BSVI emission norms?
- The abbreviation BS refers to ‘Bharat Stage’.
- It is prefixed to the iteration of the actual emission norms.
- The primary rules with the soubriquet Asian nation 2000 were introduced in the year 2000, with the second and third iterations being introduced in 2001 and 2005 with the soubriquet BSII (BS2) and BSIII (BS3), respectively.
- The fourth iteration, BSIV, was introduced in 2017 and therefore the delay between the introduction of BS3 and BS4 resulted in fast-tracking the BSVI or BS6 emission norms rather than BSV (BS5) norms.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- Carmakers were not prepared for this transition and in a subsequent judgment, the implementation of Euro II was deferred.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- In 2002, the government accepted the report submitted by the Mashelkar committee, which proposed a road map for the rollout of Euro-based emission norms in India.
- It also recommended a phased implementation of future norms, with regulations being implemented in major cities first and extended to the rest of the country after a few years.
- Based on the recommendations of the committee, the National Auto Fuel policy was announced officially in 2003.
- The road map for the implementation of the BS norms was laid out in 2010.
- The policy also created guidelines for auto fuels, reduction of pollution from older vehicles and R&D for air quality data creation and health administration.
- The standards and the timeline for implementation are set by the Central Pollution Control Board under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Since October 2010, Bharat Stage (BS) III norms have been enforced across the country.
- BS-IV emission norms were put in place in 13 major cities from April 2010, and the entire country from April 2017.
- In 2016, the government announced that the country would skip the BS-V norms altogether and adopt BS-VI norms by 2020.
Science Ministry team visits Hawaii to take stock of international telescope project (The Hindu)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a signal of renewed enthusiasm for a global scientific project, an official delegation from the Department of Science and Technology visited Mauna Kea, an inactive volcano on the island of Hawai’i in the United States, to discuss “challenges” to the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project.
About Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) Project:
- The name "Thirty Metre" denotes the telescope's substantial 30-meter mirror diameter, composed of 492 glass segments seamlessly integrated.
- It is an international collaboration involving institutions such as CalTech, the Universities of California, Canada, Japan, China, and India, facilitated by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Significance: Upon completion, it will surpass the world's largest existing visible-light telescope in width by threefold.
- A larger mirror enables greater light collection, enhancing the telescope's capability to observe distant, faint objects.
- It is projected to be over 200 times more sensitive than current telescopes and possess 12 times the resolving power of the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Application: The TMT's primary purpose includes the study of exoplanets, specifically exploring whether their atmospheres contain water vapour or methane, potential indicators of extraterrestrial life.
- Opposition against Construction: The proposed site, Mauna Kea in Hawaii, is contested due to its sacred significance to native Hawaiians, who perceive such projects as desecrating the mountain.
Contribution of India:
- India expects to be a major contributor to the project and will provide:
- Hardware (segment support assemblies, actuators, edge sensors, segment polishing, and segment coating)
- Instrumentation (first light instruments), and
- Software (observatory software and telescope control systems) worth $200 million.
- Of the 492 precisely polished mirrors that the telescope needs, India will contribute 83.
- The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAP) is leading the consortium of Indian institutions that are involved with the TMT project.
India gears up for HPV vaccine drive against cervical cancer (Indian Express)
- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to reduce cases of cervical cancer, the government is likely to roll out an immunisation campaign against Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in the second quarter of the year.
What Is Cervical Cancer?
- Cervical cancer starts in the cells lining the cervix -- the lower part of the uterus (womb).
- Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control.
- It typically develops slowly, primarily caused by persistent infection with certain high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection which can affect the skin, genital area and throat.
- Women living with HIV are 6 times more likely to develop cervical cancer compared to women without HIV.
- Cervical cancer can be cured if diagnosed at an early stage and treated promptly.
- According to WHO, countries around the world are working to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer in the coming decades, with an agreed set of three targets to be met by 2030.
How does the vaccine prevent cancers?
- The quadrivalent vaccines, including the Serum Institute of India’s Cervavac, prevent the entry of four of the most common types of HPV 16, 18, 6 and 11 thereby preventing infections, genital warts, and eventually cancer.
- At least 14 HPV types have been identified to have the potential to cause cancer.
-
- Among these, HPV types 16 and 18 are considered to be the most oncogenic, causing about 70 per cent of all cervical cancer cases globally.
- Universal immunisation of girls also reduces the transmission of the infection to boys and protects them from other cancers.
Who should get the HPV vaccine?
- The vaccine has to be administered to adolescent girls before they are sexually active.
- This is because the vaccine can only prevent the entry of the virus.
- “HPV is a very common infection and 90% of sexually active women already have it.
- Other than that, the response to the vaccine is also better in adolescents.
- This is the reason a booster is needed for girls over the age of 15 years who get the shot.
- Although not covered by the planned government campaign, the vaccine can also be administered to adolescent boys and is recommended for men who have sex with men.
Why is an HPV vaccination campaign important?
- More than 95% of all cervical cancer cases are linked to persistent infection with certain high-risk strains of HPV.
- What this essentially means is vaccination can be effectively used to prevent the infection and thereby cervical cancer cases.
- This is especially necessary in a country like India which accounts for nearly a fifth of the cervical cancer cases globally.
-
- India reports around 1.25 lakh cases and about 75,000 deaths each year.
- “The vaccine is 97% effective in preventing cervical cancer. This is the reason more than 100 countries have now implemented HPV vaccination programmes and they have seen a decline in the incidence as well.
Ganga mission gets the power to allow treated sewage into water bodies (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), the Centre’s nodal agency responsible for the abatement of pollution in river Ganga and its tributaries, has assumed new powers under which it may now permit the discharge of treated sewage and effluent that conforms to the prescribed “norms” into the river, canal or water bodies.
About the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The National Clean Ganga Mission (NMCG) is a flagship programme developed by the National Council for the Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of the Ganga River, also known as the National Ganga Council.
- It is registered as a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It came into existence on August 12th 2011 and is supported by the State-Level Program Management Groups (SPMGs) in Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- The Government of India established this body to encourage a coordinated effort by the listed states to tackle the contamination of the Ganga River by offering financial and technological assistance.
Key objectives of the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The project entails rehabilitating and boosting existing STPs and immediate short-term action to reduce pollution at the exit points on the riverfront in order to control the inflow of sewage.
- To preserve the consistency of the water cycle without altering the fluctuations of the natural season.
- Restore and control surface and groundwater supply.
- Regenerate and preserve the natural flora of the city.
- To preserve and invigorate the aquatic biodiversity and the riparian biodiversity of the Ganga River basin.
- Enable the public to engage in the process of protecting, rejuvenating and maintaining the water.
Major functions of the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- Execution of the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) work program
- Integration of the National Ganga River Basin Project supported by the World Bank
- Supervise and manage the execution of projects approved by the Government of India under NGRBA
- To perform some additional research or duties as may be delegated by MoWR, RD & GJ in the context of restoration of the Ganga River
- Layout regulations and procedures for the conduct of NMCG affairs and contribute or revise, vary or amend them as and when required
- Grant or accept financial aid, loan securities or properties of any kind, and undertake and approve the management of any endowment trust, fund or gift that is not incompatible with the objectives of the NMCG.
- Take all such action and take any other action that might seem appropriate or relevant to the accomplishment of the goals of the NGRBA.
Article 30 Not Intended To Ghettoise Minorities, Minority Institution Can Include Others In Administration: Supreme Court In AMU Case Hearing (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent observation, the Supreme Court, headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud, highlighted that the right granted to religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer their educational institutions under Article 30(1) of the constitution was not intended to "ghettoise" them.
What is Article 30 of the Indian Constitution?
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution states the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- It says: “All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.”
When was Article 30 adopted?
- Article 30 was adopted on December 8, 1948.
Features of Article 30 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 30 of the Indian constitution consists of provisions that safeguard various rights of the minority community in the country keeping in mind the principle of equality as well.
- Article 30(1) says that all minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Article 30(1A) deals with the fixation of the amount for the acquisition of property of any educational institution established by minority groups.
- Article 30(2) states that the government should not discriminate against any educational institution on the ground that it is under the management of a minority, whether based on religion or language while giving aid.
The debate around Article 30:
- On December 8, 1948, the Constituent Assembly debated the need for imparting primary education in one's mother tongue.
- One of the members of the Assembly moved an amendment to restrict the scope of this article to linguistic minorities.
- He argued that a secular state should not recognise minorities based on religion.
- Another member of the Assembly proposed to guarantee linguistic minorities the fundamental right to receive primary education in their language and script.
- He was concerned about the status of minority languages, even in regions which had a significant minority population.
- The Constituent Assembly rejected the proposals.
What is Article 29 of the Indian Constitution?
- Both Article 29 and Article 30 guarantee certain rights to minorities.
- Article 29 protects the interests of minorities by making a provision that any citizen/section of citizens having a distinct language, script or culture has the right to conserve the same.
- Article 29 mandates that no discrimination would be done on the grounds of religion, race, caste, language or any of them.
Concept of Minority in the Indian Constitution:
Religious minorities:
- While Article 30 and Article 29 of the Constitution do not specify 'minorities' in India, it is classified into religious minorities and linguistic minorities.
Religious Minorities in India:
- The basic ground for a community to be nominated as a religious minority is the numerical strength of the community.
- For example, in India, Hindus are the majority community.
- As India is a multi-religious country, it becomes important for the government to conserve and protect the religious minorities of the country.
- Section 2, clause (c) of the National Commission of Minorities Act, declares six communities as minority communities. They are:
- Muslims
- Christians
- Buddhists
- Sikhs
- Jains and
- Zoroastrians (Parsis)
Linguistic Minorities:
- A class or group of people whose mother language or mother tongue is different from that of the majority groups is known as the linguistic minority.
- The Constitution of India protects the interests of these linguistic minorities.
Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023 | Surat, Indore are the cleanest cities (The Hindu)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The President of India recently presented the ‘Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023’ at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
What is Swachh Survekshan?
- Conducted annually, Swachh Survekshan is a comprehensive evaluation of cleanliness, hygiene, and sanitation standards in cities and towns throughout India.
- This initiative was launched as an integral component of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, specifically falling under the urban segment (SBA-Urban).
- Initiated by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the survey is executed in collaboration with the Quality Council of India (QCI).
- The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, launched on October 2, 2014, aims to achieve cleanliness and the eradication of open defecation in India by October 2, 2019.
- The campaign is bifurcated into rural (SBA-Gramin, overseen by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and urban (SBA-Urban, supervised by MoHUA).
- Recently, on October 1, 2021, SBM-U 2.0 was introduced, focusing on ensuring universal access to sanitation facilities. Within this framework, the vision of attaining a Garbage-Free India has been emphasized.
- Commencing with the first survey in 2016, covering 73 cities, Swachh Survekshan has expanded significantly to encompass 4242 locations in the 2020 survey.
- The evaluation methodology centres on two primary criteria: citizen feedback and field assessment.
- Objectives of Swachh Survekshan: The primary goal of Swachh Survekshan is to encourage large-scale citizen participation and create awareness amongst all sections of society about the importance of working together towards making towns and cities better places to reside in.
About Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023:
- Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023 were presented by President Droupadi Murmu at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, under the auspices of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The theme for the year 2023 centred around "Waste to Wealth" emphasizing sustainable waste management practices.
- For 2024, the theme is “Reduce, Reuse and Recycle”.
- Indore (Madhya Pradesh) and Surat (Gujarat) jointly clinched the title of the cleanest cities in the country, with Navi Mumbai (Maharashtra) securing the third position.
- Remarkably, Indore maintained its top-ranking status for the seventh consecutive year.
- In the category of clean cities with a population of less than 1 lakh, Sasvad, Patan, and Lonavala secured the top three positions, while Madhyamgram, Kalyani, and Haora in West Bengal found themselves at the bottom.
- The cleanest cantonment was declared as Mhow Cantonment Board in Madhya Pradesh, and Chandigarh earned the SafaiMitra Surakshit Sheher recognition.
- In the Ganga Towns category, Varanasi and Prayagraj secured the first and second positions, respectively.
- Acknowledging overall cleanliness efforts, Maharashtra claimed the title of the best-performing state, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh in the second and third positions.
- Odisha secured the fourth spot, with Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Sikkim, Karnataka, Goa, Haryana, and Bihar following suit.
- Conversely, Rajasthan, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh found themselves at the lower end of the ranking.
Govt’s ZED scheme for MSMEs hits 1 lakh certification milestone; check scheme’s details (Financial Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zero Effect, Zero Defect scheme (ZED) by the MSME Ministry, which aims to encourage environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices among MSMEs, has achieved the 1 lakh certification milestone
What is the Zero Effect, Zero Defect (ZED) Scheme?
- Launched in October 2016 and revamped in April 2022, the ZED scheme offers certification for environmentally conscious manufacturing under three certification levels (gold, silver and bronze) classified according to 20 performance-based parameters such as quality management, timely delivery, process control, waste management, etc.
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to 75 per cent of the total cost of certification, with a maximum subsidy ceiling of Rs 50,000 along with up to Rs 2 lakh support for handholding/consultancy to achieve the next certification level.
- For technology upgradation, the scheme offers assistance of up to Rs 3 lakhs for moving towards zero effect solutions/pollution control measures/cleaner technology.
- MSMEs are charged Rs 10,000 for bronze certification, Rs 40,000 for silver certification, and Rs 90,000 for gold certification.
- In December 2023, the MSME Ministry made the ZED scheme free for women-led MSMEs.
- In addition, the government will now make a guaranteed payment of 100 per cent financial support for the certification cost under the scheme.
- The ZED certification is valid for three years and the MSME units are required to re-apply for the certificate as per the validity of the scheme.
- Currently, the scheme is applicable for manufacturing MSMEs only.
- The government hasn’t announced the scheme’s model for services MSMEs yet.
- The scheme is in line with the government’s plan to reduce the country’s CO2 emissions by 1 billion tons by 2030, reduce carbon intensity below 45 per cent by 2030 and finally make way for achieving a Net-Zero emission target by 2070.
- The ZED Certification envisages the promotion of Zero Defect Zero Effect (ZED) practices amongst MSMEs so as to:
- Encourage and enable MSMEs to manufacture quality products using the latest technology, and tools & to constantly upgrade their processes for the achievement of high quality and high productivity with the least effect on the environment.
- Develop an Ecosystem for ZED Manufacturing in MSMEs, to enhance competitiveness and enable exports.
- Promote the adoption of ZED practices and recognise the efforts of successful MSMEs.
- Encourage MSMEs to achieve higher ZED Certification levels through graded incentives.
- Increase public awareness of demanding Zero Defect and Zero Effect products through the MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification.
- Identify areas to improve upon, thereby assisting the Government in policy decisions and investment prioritization.
Mamata asks PM to officially list Bengali as a ‘classical language’ (The Hindu)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
West Bengal Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee in a letter to Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Thursday asked the central government to officially list Bengali as a “classical language”
About the Classical Languages in India:
- The Ministry of Culture plays a significant role in providing guidelines concerning Classical languages.
- At present, six languages in India hold the status of 'Classical.'
- These include:
- Tamil (2004)
- Sanskrit (2005)
- Kannada (2008)
- Telugu (2008)
- Malayalam (2013) and
- Odia (2014)
- All these Classical Languages find a place in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
The criteria for designating a language as 'Classical' encompass several key factors:
- Historical Significance: A language must boast high antiquity, with early texts or recorded history spanning 1500-2000 years.
- Rich Literary Heritage: The language should possess a substantial body of ancient literature or texts considered a valuable heritage by successive generations of speakers.
- Originality: The literary tradition of the language should be original, not borrowed from another speech community.
- Distinctive Identity: A Classical language and its literature must maintain a distinct identity from modern iterations, potentially featuring a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or derivatives.
Upon achieving Classical status, the Human Resource and Development Ministry extends various benefits to promote the language, including:
- International Recognition: Two significant annual international awards are instituted for scholars of eminence in classical Indian languages.
- Centers of Excellence: Establishing a dedicated Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages.
- Academic Support: Encouraging the University Grants Commission to initiate Professional Chairs for Classical Languages, particularly in Central Universities, to foster academic research and development.
The Bengali Language:
- Bengali serves as the official language of West Bengal and holds the same status in Bangladesh.
- It stands as the second most spoken language in India and ranks as the seventh most spoken language globally.
- As an Indo-Aryan language indigenous to the Bengal region of South Asia, Bengali employs a script derived from Brahmi, an ancient Indian script.
- Notably, Bengali is written from left to right.
World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 Report (The Hindu)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The global unemployment rate is set to increase in 2024 while growing social inequalities remain a concern, according to the International Labour Organisation’s (ILO) World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 report released in Vienna recently.
Key Findings:
- Employment Trends: Joblessness and the jobs gap have both decreased below pre-pandemic levels, but global unemployment is expected to rise in 2024.
- The macroeconomic environment witnessed a significant deterioration in 2023.
- Global Economic Challenges: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and persistent inflation led to frequent and aggressive actions by central banks.
- Monetary authorities in both advanced and emerging economies implemented the fastest interest rate increases since the 1980s, with widespread global repercussions.
- Economic Slowdown in Key Economies: China, Türkiye, and Brazil experienced notable slowdowns, adversely affecting global industrial activity, investment, and trade.
- Despite the economic slowdown, global growth in 2023 surpassed expectations, and labour markets displayed unexpected resilience.
- Unemployment Dynamics: The global unemployment rate in 2023 improved modestly to 5.1% compared to 2022.
- Labour market participation rates largely recovered from pandemic lows, but concerns arise about structural imbalances persisting.
- Wage Trends: Real wages declined in most G20 countries as increases failed to keep pace with inflation.
- Workers living in extreme poverty (earning less than US$2.15 per day per person in PPP terms) increased by about one million globally in 2023.
- Positive real wage growth was observed in China, the Russian Federation, Mexico, India, and Türkiye.
Recommendations As per the Report:
- Inclusive Labor Policies: Policymakers in rapidly ageing countries should focus on supporting the participation of groups with weak labour market attachment, including youth, women, and older workers.
- Investment and Skills Strategies: Investment and skills policies should aim to enhance productivity, and potential growth, and promote a more productive utilization of technological progress.
- Sectoral Improvements: Motivating workers who leave due to low pay and challenging working conditions can be achieved by improving conditions in sectors and occupations with these challenges.
- International Workforce Matching: Facilitating the matching of internationally mobile workers to suitable jobs could alleviate some of the shortages in the labour market.
- Long-Term Engagement: Recognizing that structural challenges in labour market adjustment are unlikely to vanish in the short term, it is crucial for governments and social partners to engage in ongoing efforts to address these challenges.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) stands as the United Nations agency dedicated to the world of work.
- Mission: The core mission of the ILO is to promote social and economic justice by establishing and advancing international labour standards.
- Motto: At the heart of the ILO's mission is the pursuit of Decent Work for all, encapsulating the commitment to fostering conditions that are fair and dignified.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, the ILO operates from its global headquarters.
- Parent Organization: Functioning under the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations, the ILO is a vital component of the UN system.
- Additionally, it is a member of the United Nations Development Group (UNDP), collaborating with other UN organizations to achieve Sustainable Development Goals.
- Historical Background: Established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles, following the conclusion of World War I, the ILO was conceived with the conviction that enduring and universal peace could only be realized through a foundation of social justice.
- In 1946, it transitioned into a specialized agency within the newly formed United Nations.
- Membership: The ILO boasts a diverse membership, with 187 member states, encompassing 186 out of the 193 UN member states along with the Cook Islands.
- Organizational Structure: Distinguishing itself as the only tripartite U.N. agency, the ILO brings together representatives from governments, employers, and workers of its 187-member states, fostering collaborative efforts in shaping global labour standards and policies.
The Process of Selecting Tableaux for the Republic Day Parade (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India’s Republic Day celebrations are incomplete without colourful tableaux cantering down the Kartavya Path (formally Rajpath). Showcasing India’s rich and diverse cultural heritage, they add colour to the grand event on January 26.
Who can send tableaux to the Republic Day parade?
- According to the Ministry of Defence (MoD), each year, a select number of “State Governments/UT Administrations/Central/Ministries/Departments” send their tableaux to the Republic Day parade.
- There is a rigorous application process which begins with interested parties submitting a concept note, along with design blueprints to the MoD.
How does the selection process work?
- The tableaux proposals received are evaluated by a committee of experts appointed by the MoD, comprising prominent persons in the fields of art, culture, painting, sculpture, music, architecture, choreography, etc. The selection process happens in a phased manner.
- STAGE 1 involves the assessment of the initial proposals and the design sketch/blueprint.
- The Committee sits alongside official representatives of the participants and suggests modifications, if necessary.
- A number of proposals may be rejected in this stage itself.
- STAGE 2 involves the assessment of three-dimensional models of the proposals.
- If the Committee is satisfied with the model, then the tableau is selected and further sent for fabrication.
- The Committee can also suggest changes to models before selection.
- Crucially, while the process is envisioned to be collaborative, the Committee has the final say on which tableaux are chosen, and can order any modifications they feel are required.
What is the basis of selection?
- Selection depends upon a combination of factors including but not limited to visual appeal, impact on the masses, idea/theme of the tableaux, degree of detailing involved in the tableaux, music accompanying the tableaux, local artists used etc.
- Each year, the MoD comes up with an overarching theme, under which, participants can showcase elements relevant to their respective state/UT/department in their tableaux.
- This year’s theme is “Viksit Bharat” (Developed India) and “Bharat: Loktantra ki Matrika” (India: the Mother of Democracy).
- The Defence Ministry also shares the basic guidelines about what all the tableaux can or should include.
- The participating entities must engage “young qualified designers from renowned institutions”, electronic display walls for a bright display of images or content, moving elements using robotics or mechatronics, 3D printing could be used for certain elements, use of augmented or virtual reality, and special effects to improve the optics and visual effects of the tableau.
- Extra weightage is given to tableaux which conform to these guidelines.
- Importantly, the tableaux of two different states/ UTs must not be too similar, and eco-friendly materials must be used for their construction.
'Report Fish Disease' to Monitor Fish Diseases (TOI)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A mobile app titled ‘Report Fish Disease’ has been introduced to help aquaculture farmers to report diseases on their farms.
What is the 'Report Fish Disease' App?
- The mobile application is designed to empower fish farmers by offering a convenient and effective platform for reporting diseases on their farms.
- Developed as part of the NSPAAD project, with the lead institute being ICAR-NBFGR and a collaborative partnership with the Central Institute of Fisheries Technology (CIFT), this app brings a host of features and benefits.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: The app provides fish farmers with an intuitive and user-friendly interface, ensuring easy accessibility.
- Efficient Disease Reporting: A simplified reporting format allows farmers to easily report disease outbreaks by providing essential information such as location, affected species, observed symptoms, and images.
Significance:
- Swift Response through Geo-tagging: Utilizing geo-tagging technology, the app facilitates a rapid response from authorities.
- Farmers receive real-time updates on the status of their reported cases, ensuring transparency and accountability in disease management.
- Information Hub: Beyond reporting, the app serves as an information hub, offering farmers valuable resources on disease prevention, treatment, and best aquaculture practices.
- Comprehensive Disease Management: The app is a comprehensive package aimed at diagnosing, preventing, controlling, and treating aquatic animal diseases.
- It provides solutions to encourage aquaculture farmers to maintain the health of their stocks.
Anticipated Impact:
- By transforming disease management in aquaculture, the app aims to enhance the sustainability and productivity of this critical sector.
- It achieves this through early disease detection, data-driven decision-making, capacity building, and efficient resource allocation.
The ultimate goals of the app include:
- Improved Livelihood: Enhancing the livelihood of fish farmers through proactive disease management.
- Food Security: Safeguarding the nation’s food security by ensuring the health and well-being of aquatic animal stocks.
- Industry Growth: Contributing to the sustainable growth of the aquaculture industry by fostering a proactive approach to disease prevention and management.
Henley Passport Index 2024 (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Henley Passport Index, which ranks the world’s most travel-friendly passports, has released its list for 2024, with European nations of France, Germany, Italy and Spain, and Asia’s Japan and Singapore sharing the number one spot.
Highlights of Henley Passport Index 2024:
- The Henley Passport Index for 2024 ranks different passports according to the number of destinations their holders can visit without a prior visa or can avail of a visa on arrival, a visitor’s permit, or an electronic travel authority (ETA) on entering the destination.
- The rankings are based on the analysis of data provided by the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- It then provides a ‘Visa-free score’ which, essentially, is the number of destinations that the holders of that particular passport can travel to without a prior visa or can avail of a visa on arrival or other similar permits.
- For instance, those holding the passports of the countries in the #1 spot had access to 194 visa-free destinations while those holding the Afghanistan passport ranked last at #104, had visa-free access to only 28 of them.
- As per the latest rankings, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Singapore, and Spain hold the top spot as the world's most powerful passports, allowing visa-free entry to 194 global destinations.
- Finland, Sweden and South Korea shared the second rank, while Austria, Denmark, Ireland and Netherlands occupied the third spot.
- India, meanwhile, has improved its ranking and moved up to the 80th position from the previous year’s ranking of 84.
- Those holding an Indian passport have visa-free access to 62 destinations.
- World’s least powerful passports:
- Afghanistan (Score: 28) - visa-free access to only 28 destinations
- Syria (Score: 29) - visa-free access to only 29 destinations
- Iraq (Score: 31) - visa-free access to only 31 destinations
- Pakistan ( (Score: 34) - visa-free access to only 34 destinations
About Henley Passport Index:
- The Henley Passport Index is the original, authoritative ranking of all the world’s passports according to the number of destinations their holders can access without a prior visa.
- The index is based on exclusive data from the International Air Transport Association (IATA) – the largest, most accurate travel information database – and enhanced by Henley & Partners’ research team.
- It started in 2006 as the Henley & Partners Visa Restrictions Index (HVRI).
- The Henley Passport Index compares the visa-free access of 199 different passports to 227 travel destinations.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India has flagged concerns relating to sensitive and confidential trade data of its exporters getting compromised while complying with the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
What Is Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- CBAM is a policy tool introduced by the European Union (EU) to reduce carbon emissions by imposing a carbon tax on imported products, ensuring that they are subject to the same carbon costs as products produced within the EU.
- It is part of the EU's "Fit for 55 in 2030 package" to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
- The aim of CBAM is to prevent carbon-intensive imports from undermining the EU's climate objectives and to encourage the adoption of cleaner production practices around the world.
- To implement CBAM, importers will need to declare the quantity of goods imported and their greenhouse gas emissions on an annual basis.
- They will need to surrender a corresponding number of CBAM certificates to offset these emissions, and the price of these certificates will be based on the weekly average auction price of EU Emission Trading System (ETS) allowances in Euro/tonne of CO2 emitted.
- It encourages non-EU countries to adopt stricter environmental regulations, reduce global carbon emissions, and prevent carbon leakage by discouraging companies from moving to countries with weaker environmental regulations.
- Additionally, the revenue generated from CBAM will be used to support EU climate policies, which can serve as an example for other countries to promote green energy.
Impact of CBAM on India:
- The EU's carbon border adjustment mechanism will have a negative impact on India's exports of metals such as iron, steel, and aluminium products.
- The mechanism will subject these exports to extra scrutiny and impose carbon levies ranging from 19.8% to 52.7%, which could threaten India's major exports to the EU.
- From 1st January 2026, the EU will start collecting the carbon tax on each consignment of steel, aluminium, cement, fertilizer, hydrogen and electricity, which could further harm India's exports to the EU.
- The high carbon intensity of Indian products, due to coal being the dominant energy source, is a concern for the country as it may result in higher carbon tariffs from the EU.
- India's use of coal is much higher than the EU and the global average, with coal-fired power accounting for almost 75% of India's energy consumption.
- This makes direct and indirect emissions from industries like iron, steel and aluminium a significant worry for India.
- The lack of a domestic carbon pricing scheme in India poses a risk to its export competitiveness, particularly for sectors such as refined petroleum products, organic chemicals, pharma medicaments, and textiles, which are among the top 20 goods imported by the EU from India.
- Countries with a carbon pricing system may have a competitive advantage as they may pay less carbon tax or receive exemptions.
- This risk could expand to other sectors in the future.
What can be done?
- India can take a multi-pronged approach to mitigate the impact of the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) on its exports.
- One of the ways is to implement a Decarbonization Principle, which refers to reducing or eliminating greenhouse gas emissions from human activities such as transportation, power generation, manufacturing, and agriculture.
- The government could complement its existing schemes such as the National Steel Policy and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme with a Decarbonization Principle.
- This would encourage industries to focus on carbon efficiency, making their products more competitive in a carbon-conscious world.
- Another way is to negotiate with the EU to recognize its energy taxes as equivalent to a carbon price.
- India could also negotiate with the EU to transfer clean technologies and financing mechanisms to aid in making India's production sector more carbon efficient.
- One way to finance this is to propose that a portion of the EU's CBAM revenue could be set aside to support India's climate commitments.
- Additionally, India could begin preparing for the new system by establishing a Carbon Trading System, as China and Russia do.
- India can encourage sustainable and eco-friendly production by providing incentives, which will enable the country to stay competitive in a more carbon-conscious future while achieving its 2070 Net Zero Targets. This will help India pursue its developmental goals and economic aspirations without any compromise.
DRDO anti-drone tech ready, handed over to BEL, private firms (The Hindu)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The counter-drone system developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is ready for production and has already been demonstrated to armed services and other internal security agencies with some orders already placed.
Key Highlights from the Report:
- The Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has successfully engineered an indigenous counter-drone technology designed to counter various types of drone attacks, encompassing both soft and hard kill capabilities, particularly effective against micro drones.
- Significance: This cutting-edge system employs a laser-based kill mechanism for the detection and destruction of drones in the airspace.
- Notably, it can proficiently detect and disrupt micro drones within a range of 3 kilometres, employing laser signals to neutralize targets situated at distances between 1 to 2.5 kilometres.
- The technology has been seamlessly transferred to private industries, including Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Adani, Larsen & Toubro (L&T), and Icom.
- This strategic transfer enhances collaboration between the public and private sectors for the continued advancement and deployment of this crucial anti-drone technology.
What are Counter-Drone Systems?
- Counter-drone systems serve as defensive mechanisms designed to thwart potential drone attacks through the processes of detection, identification, and neutralization.
- These systems are broadly categorized as kinetic or non-kinetic.
- Kinetic Systems: Kinetic counter-drone systems employ projectiles, such as bullets or missiles, to destroy an intruding drone.
- They integrate advanced sensors like radar for drone detection, coupled with a motorized platform to precisely aim and fire the weapon.
- Non-Kinetic Systems: Non-kinetic counter-drone systems focus on disrupting flight capabilities or corrupting signals crucial for control and navigation.
- This is achieved by emitting noise signals at specific frequencies, rendering the drone incapable of receiving command signals.
- Additionally, non-kinetic systems may transmit false GPS signals, creating confusion in the drone's navigation system.
Centre asks Manipur government to study representation on removing Kuki-Chins from ST list (The Hindu)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Manipur government has been asked by the Centre to examine a representation seeking deletion of the “Nomadic Chin-Kuki” from the list of Scheduled Tribes in Manipur.
Context:
- The petition advocates that the primary criterion for categorizing Scheduled Tribes in the country should be based on Indigeneity, referencing a Supreme Court ruling dated January 2011.
- The petition specifically highlights the case of the "Zou" tribe, asserting that their origin in Myanmar's Chin state, a foreign territory, was not documented in pre-independence Indian Censuses.
- Consequently, the plea argues against the inclusion of the "Zou" tribe in the Scheduled Tribe list of Manipur.
About Kuki and Zomi Tribes:
- The Kuki-Zomi Tribes represent an ethnic group originating from the Bangladesh region, primarily residing in Manipur and Mizoram in India.
- Also recognized as Chin or Mizo people, they share a unified ancestry and culture.
- Their communication is conducted through various dialects within the Chin-Kuki-Mizo language family, belonging to the Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
- The Kuki-Zomi Tribes are interconnected with the broader Zo people, alongside other tribes such as Chin and Mizo.
What is the Process of amendment in the ST List?
- The inclusion or exclusion of any tribe or tribal community from the Scheduled Tribes list is exclusively governed by legislation enacted by the Parliament of India.
- Amendments to the list are effectuated through notifications issued under clause (1) of Article 342, specifying Scheduled Tribes.
- According to a Supreme Court ruling, the authority to modify, amend, or alter the Scheduled Tribes list specified in the notification under Article 342(1) is not vested in State governments, courts, tribunals, or any other entity.
- Contrary to this, the central government asserts that the initiation of proposals for inclusion or exclusion from the ST list must originate from the respective State government.
- The Parliament then takes action based on this proposal.
- The Lokur Committee, in 1965, laid down the criteria employed by the government to designate communities as Scheduled Tribes, and these criteria persist in use today.
- They encompass primitive traits, distinctive culture, geographical isolation, shyness of contact with the larger community, and backwardness.
PM Modi wishes Indian diaspora on Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas (The Hindu)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has extended his wishes to the Indian diaspora on the Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas and said their dedication towards preserving our rich heritage and strengthening global ties is commendable.
What is Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas?
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), also known as Non-Resident Indian (NRI) Day, is celebrated on January 9 to mark the contribution and achievements of the overseas Indian community to the development of India.
- The day also commemorates the return of Mahatma Gandhi, the greatest Pravasi, from South Africa to India in 1915, who led India's freedom struggle and changed the lives of Indians forever.
- Its format was later revised in 2015 to celebrate the event once every two years and to hold theme-based conferences during the intervening period with participation from overseas diaspora experts, policy-makers, and stakeholders.
- The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is the flagship event of the Ministry of External Affairs.
- It is held in different cities, to showcase the diversity and progress of different regions of India.
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas: History
- Pravasi Bharatiya Diva was first celebrated in 2003.
- It was an annual event earlier, but in 2015, the government revised its format to celebrate PBD once every two years.
- To date, 17 conventions have been held.
- The last Pravasi Bharatiya Divas was celebrated in the Indore of Madhya Pradesh in 2023.
Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards:
- Another aspect of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is the Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards.
- The awards were initiated in 2003 by the Indian Government to recognize the achievements and contributions of NRIs and PIOs in various fields such as education, science and technology, arts and culture, social work, public service, trade and industry, and philanthropy.
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas: Significance
- These conventions provide a platform for the overseas Indian community to engage with the Indian government and people of the land of their ancestors for mutually beneficial activities.
- These conventions are also very useful in networking among the overseas Indian community residing in various parts of the world and enable them to share their experiences in various fields.
Switzerland’s decision to eliminate import duties limits FTA utility for India’ (Indian Express)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Switzerland’s policy to allow tariff-free entry for all industrial goods from all countries significantly limits India’s prospects of gains from India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) free trade agreement (FTA) that is currently being negotiated.
Context:
- Within the broader context, the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) asserts that Switzerland's approach of granting tariff-free entry to all nations places constraints on the benefits India could potentially derive from the envisioned trade agreement with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- This limitation arises as Switzerland has eliminated tariffs on various products, encompassing chemicals, consumer goods, vehicles, and clothing.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
- The organization operates in parallel with the European Union (EU), and all four member states participate in the European Single Market and are part of the Schengen Area.
- They are not, however, party to the European Union Customs Union.
- It was established in 1960.
- Trade Dynamics with India:
- In 2022, the combined merchandise trade between EFTA and India exceeded USD 6.1 billion.
- The predominant EFTA imports included organic chemicals (27.5%), with machinery (17.5%) and pharmaceutical products (11.4%) constituting the primary exports to India.
India’s Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) with EFTA:
- Negotiations on the trade deal commenced in 2008 and resumed in 2016.
- The latest rounds covered diverse aspects such as trade in goods and services, rules of origin, Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), trade and sustainable development, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, technical barriers to trade, trade remedies, and customs and trade facilitation.
Impact of Switzerland’s Policy on India's Gains under EFTA:
- Effect on Negotiations: Switzerland's decision significantly alters the dynamics of the ongoing India-EFTA trade agreement negotiations, posing implications for India's potential gains.
- Increase in Market Competitiveness: Switzerland, as India's primary export destination in EFTA, has eliminated import duties, intensifying competition for Indian products despite the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with EFTA.
- No Gains in Agricultural Exports: Exporting agricultural produce to Switzerland remains challenging due to tariff complexities, quality standards, and approval requirements. EFTA, including Switzerland, has shown reluctance to eliminate tariffs on basic agricultural produce.
- Trade Deficit with Switzerland: In FY2023, India faced a substantial trade deficit with Switzerland, with imports totalling $15.79 billion compared to exports of $1.34 billion. Switzerland's policy is anticipated to widen this trade deficit further.
- In essence, Switzerland's tariff-free policy introduces complexities in India's negotiations and hampers potential gains, particularly in the realm of agricultural exports, impacting the overall trade balance with EFTA.
: In a first, India set to chair, and host UNESCO's World Heritage Committee session in Delhi (HT)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic development, India is poised to chair and host UNESCO's World Heritage Committee session in New Delhi from July 21 to 31 this year, the Permanent Representative of India to UNESCO.
About the World Heritage Committee:
- The World Heritage Committee operates as a subsidiary of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- Its primary responsibilities encompass executing the World Heritage Convention, determining the utilization of the World Heritage Fund, and disbursing financial assistance in response to requests from States Parties.
- The committee holds authoritative decision-making power regarding the inscription of properties on the World Heritage List, scrutinizes reports on the conservation status of listed properties, and prompts States Parties to rectify mismanagement issues.
- Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in determining the inclusion or removal of properties on the List of World Heritage in Danger.
- Structure:
- Comprising representatives from 21 States Parties elected by their General Assembly, the Committee operates with members serving six-year terms.
- However, many state parties opt for a four-year term voluntarily, allowing other state parties an opportunity to participate on the committee.
- Bureau of the World Heritage Committee:
- The Bureau, consisting of seven state parties elected annually by the Committee, includes a Chairperson, five Vice-Chairpersons, and a Rapporteur.
- This body is responsible for coordinating the Committee's activities, determining meeting schedules, and organizing the agenda.
What is UNESCO?
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) stands as a specialized agency within the United Nations (UN), dedicated to fostering global peace and security through collaborative efforts in education, arts, sciences, and culture.
- Established in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation, UNESCO boasts a membership of 193 states and 11 associate members, along with partnerships in the non-governmental, intergovernmental, and private sectors.
- The organization is headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris.
- UNESCO's foundational mission is to promote peace, sustainable development, and human rights by fostering cooperation and dialogue among nations.
- It pursues this overarching goal through five primary program areas: Education, Natural Sciences, Social/Human Sciences, Culture, and Communication/Information.
- The governance of UNESCO lies in the hands of the General Conference, comprising member states and associate members, convening biannually to establish the agency's programs and budget.
- The General Conference also elects members of the Executive Board, responsible for managing UNESCO's initiatives.
- Every four years, the Director-General is appointed by the General Conference to serve as the chief administrator of UNESCO.
- India has been a founding member of UNESCO, having ratified UNESCO’s Constitution on 4th November 1946.
The logic behind momentum investing (The Hindu)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Traditionally, experts have advised investors to buy assets when they are selling at low prices, such as during times of a financial crisis, as assets could be found selling at prices well below their intrinsic value. Momentum investing is in stark contrast to this traditional logic.
What is Momentum investing?
- Momentum investing refers to a style of investing wherein investors purchase assets such as stocks or bonds that are consistently rising in price while selling assets whose prices are falling.
- Momentum investors buy assets with rising prices in the hope that the upward price momentum of these assets would continue, thus allowing them to sell these assets at higher prices in the future to make profits.
- Similarly, they sell assets that are falling in price expecting the fall in prices to continue for some time.
- Momentum investing is based on the philosophy that there can be discernible trends in asset prices and that these trends tend to persist over time.
- The persistence of such trends gives investors an opportunity to recognise and participate in them early enough to make significant profits from their investments.
What is the Counter-logic?
- Momentum investors often invest money in assets whose prices have scaled new all-time highs, even if these assets are trading at prices that are far above their intrinsic value.
- Many academic studies have shown that momentum investing can generate high returns that comfortably beat the benchmark indices.
- Momentum investors generally do not conduct a deep analysis of the fundamental or intrinsic value of the assets in which they invest their money.
- They invest purely based on whether the price of an asset is showing a strong trend, either upward or downward, that they can ride on.
- For this reason, many critics argue that momentum investing can cause an unsustainable rise or fall in prices as momentum investors are blind to the actual value of these assets.
- This, they argue, can eventually lead to heavy losses for investors who are late to sell when the prices of these momentum-driven assets suddenly catch up with the assets’ intrinsic value.
- Some investors may combine value investing, which is based on assessing the intrinsic value of an asset, with momentum investing.
- These investors believe that taking into account the existing trend in the price of an asset can help save time and boost investment returns.
- It should be noted that traditional value investors believe in purchasing assets that are undervalued and selling them when the price of the asset has risen to match the asset’s intrinsic value.
- It might, however, take many years before the price of an asset rises to fully match its intrinsic value.
- Investors who combine value investing with momentum investing may be able to purchase an undervalued asset at just about the time when its price starts to trend towards its intrinsic value.
- This prevents investor money from being locked in for years in assets whose prices go nowhere.
Land Ports Authority Releases Report on Gender-Inclusive Framework for Cross-Border Trade in India (NewsOnAIR)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Land Ports Authority of India (LPAI) today released a report on 'Engendering Land Ports in India' in New Delhi. The main objective of the report is to develop a framework for gender-inclusive cross-border trade and tourism through land Ports in the country.
About the Land Ports Authority of India (LPAI):
- LPAI was established In 2012 as a statutory body under the LPAI Act of 2010.
- It comes under the purview of the Department of Border Management, Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Mandate: LPAI is entrusted with the development of cutting-edge infrastructure for its land ports.
- This infrastructure includes the construction of a Cargo Terminal Building, Passenger Terminal Building, deployment of mechanized equipment for cargo handling, implementation of security and surveillance measures at land ports, and the provision of forex counters.
- Growth: From its inception with just two land ports in 2012, LPAI has played a significant role in expanding India's operational land ports to 11, facilitating connections across the country's land borders with Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Land Ports in India:
- Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) are the official designations for land ports in India.
- The country currently boasts 11 operational land ports, namely Attari, Agartala, Dawki, Petrapole, Raxaul, Rupaidiha, Jogbani, Moreh, Sutarkandi, Srimantapur, and the Passenger Terminal Building (PTB) at Dera Baba Nanak.
- In the year 2023, significant trade activities were conducted through seven primary land ports: Attari, Agartala, Petrapole, Raxaul, Jogbani, Sutarkandi, and Srimantapur.
- These land ports played a crucial role in facilitating trade valued at Rs 76,000 crore and accommodating the movement of approximately 24 lakh passengers in the year 2023.
Why there is a Need for Land Ports in India?
- Given its strategic central location, India shares an extensive international land border spanning over 15,000 kilometres with seven South Asian countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Numerous specified entry and exit points facilitate cross-border movements involving individuals, goods, and vehicles.
- However, the persistent challenge of inadequate infrastructure at these designated border checkpoints has posed a significant hurdle to regional trade, adversely affecting the smooth transit of both commodities and passengers.
- Recognizing this obstacle, the Committee of Secretaries recommended the establishment of Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) in 2003.
- These ICPs were envisioned to offer state-of-the-art infrastructure facilities, addressing the deficiencies in the existing border infrastructure and promoting more efficient cross-border interactions.
Launch of the Traditional Medicine Morbidity codes of Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani Chapter in International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11 as Module 2 (PIB)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The launch event for Module 2 of the World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11 TM Morbidity Codes is scheduled to take place in New Delhi on January 10, 2024.
What is the International Classification of Diseases?
- Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) serves as a global standard for classifying diseases.
- The existing global data on diseases is primarily rooted in modern biomedicine practices, guiding diagnoses within healthcare systems worldwide.
- ICD plays a significant role on a global scale, offering crucial insights into the prevalence, causes, and consequences of human diseases and mortality.
- It achieves this by incorporating reported and coded data, forming the basis for clinical terms in health records and disease statistics across primary, secondary, and tertiary care, as well as cause-of-death certificates.
- The data and statistics derived from ICD coding contribute to various essential functions, including supporting payment systems, aiding in service planning, facilitating quality and safety administration, and driving health services research.
- Moreover, the standardized data collection associated with ICD categories allows for large-scale research initiatives.
- It's important to note that the WHO ICD series currently does not include the classification of data and terminology related to diseases based on Ayush systems such as Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, etc.
- The Central Bureau of Health Intelligence (CBHI), operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, serves as the WHO Collaboration Centre for ICD-related activities.
- The CBHI plays a crucial role in collecting and disseminating data on various diseases and mortality.
What is the TM2 module of ICD11?
- The Ministry of Ayush has introduced the Code for Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani Medicine, utilizing the National Ayush Morbidity and Standardised Electronic Portal (NAMASTE).
- In partnership with the World Health Organization (WHO), the Ministry of Ayush has collaboratively developed a comprehensive categorization of data and terminology about diseases based on Ayush systems, namely Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani, within the TM2 module of the ICD11 series.
- Furthermore, the Ministry of Ayush has formalized this collaboration by signing a Donor Agreement with the World Health Organization for the implementation of these initiatives.
Karnataka High Court bans mining around KRS Dam in Mandya: ‘can’t turn Nelson’s eye to possible danger’ (Indian Express)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka High Court has suspended all mining licenses for stone quarrying within a 20-km radius of the Krishna Raja Sagar (KRS) Dam in the Mysore-Mandya region of the state under provisions of the Dam Safety Act, 2021.
About the Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam:
- Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam is a gravity dam strategically positioned beneath the confluence of the Kaveri River with its tributaries, Hemavati and Lakshmana Tirtha, in Karnataka's Mandya district.
- Usage: The dam serves crucial roles, providing water for irrigation in Mysore and Mandya while acting as a primary drinking water source for Mysore, Mandya, and Bengaluru.
- Additionally, it facilitates power generation at the Shivanasamudra hydroelectric power station.
- Water released from the KRS Dam travels into Tamil Nadu and is stored in the Mettur Dam in the Salem district.
- History: Constructed during the reign of Maharaja Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV, the dam, completed in 1931, bears his name.
- The eminent Indian engineer Sir M. Visvesvaraya designed this impressive structure, commencing construction in 1911.
- Features: Built with a combination of surki mortar and limestone, the dam spans 2,621 meters (8,600 ft) in length and stands 40 meters (130 ft) high.
- Exhibiting an arch type, it boasts 177 iron sluices, some equipped with automatic doors.
- The reservoir covers about 130 square kilometres, making it the largest in Asia at the time of construction.
- A captivating addition to the site is the Brindavan Gardens, an ornamental garden intricately linked with the dam.
Key Details About the Kaveri River:
- Kaveri River, also spelt Cauvery, is a revered river in southern India, often referred to as the Ganga of South India.
- Origin: The river originates from the Brahmagiri Hill in the Western Ghats of southwestern Karnataka.
- Course: Flowing southeastward for a span of 765 km, Kaveri traverses through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, descending the Eastern Ghats with impressive cascades.
- Basin Coverage: The Kaveri basin spans the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Outflow: Ultimately, the river empties into the Bay of Bengal at Poompuhar in the Mayiladuthurai district of Tamil Nadu.
- Left Bank Tributaries: Notable left bank tributaries include Harangi, the Hemavati, the Shimsha, and the Arkavati.
- Right Bank Tributaries: Major right bank contributors encompass Lakshmantirtha, the Kabbani, the Suvarnavati, the Bhavani, the Noyil, and the Amaravati.
Autonomous systems becoming the preferred choice in Order of Battle for nations across the globe: Navy Chief (The Hindu)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chief of Naval Staff Admiral R Hari Kumar officially initiated the maiden indigenously produced Drishti 10 'Starliner' Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for the Indian Navy.
What is Drishti 10 Starliner UAV?
- Drishti 10 Starliner Unmanned Aerial Vehicle is an advanced intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) platform, developed by Adani Defence and Aerospace, and represents a significant leap forward in India’s defence technology.
- The Drishti 10 Starliner boasts an impressive 36 hours of endurance and a substantial 450 kg payload capacity.
- It stands out as the only all-weather military platform certified with NATO’s STANAG 4671 (standardized agreement 4671) for airworthiness, allowing it to operate in both segregated and unsegregated airspace.
- The UAV is equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, an extended endurance of 36 hours, and advanced communication capabilities.
- Its incorporation of new-age technologies such as Automatic Take Off and Landing (ATOL) positions it as a formidable asset.
- Notably, this UAV is a home-assembled version of the Hermes-900 MALE UAV, featuring an impressive 70% indigenous content.
- A notable feature of the Drishti 10 'Starliner' is its low maintenance demands, contributing to cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
- This quality enhances operational readiness, minimizing downtime and optimizing deployment opportunities.
- The Drishti 10 is outfitted with cutting-edge communication systems, encompassing satellite communication and Line-of-Sight (LOS) data links, guaranteeing dependable and secure data transmission.
What is Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)?
- A drone, also referred to as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), is an aircraft that operates without a human pilot, crew, or passengers on board.
- UAVs are integral components of unmanned aircraft systems, comprising a ground-based controller and a communication system linked with the UAV.
Drones are categorized based on their weight, adhering to existing regulations:
- Nano: Equal to or less than 250 grams
- Micro: Between 250 grams and 2 kilograms
- Small: From 2 kilograms to 25 kilograms
- Medium: Between 25 kilograms and 150 kilograms
- Large: Exceeding 150 kilograms
Ram Temple opening brings fresh hope to Moradabad brass traders as orders for idols shoot up (The Hindu)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The industry, which till now produced utensils and home decorative items with intricate designs, is now flooded with orders for idols of Ram, Sita, Laxman and Hanuman
Brassware Industry Moradabad:
- Moradabad was founded in 1600 by Murad, the son of Mughal Emperor Shahjahan, and hence became known as Moradabad.
- It is well-known for its brass work and has made a name for itself in the global handicraft market.
- Moradabad, often referred to as the "Brass City" or Peetal Nagri, exports brassware to countries like the US, Britain, Canada, Germany, the Middle East, and Asia.
- Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, holds historical significance due to its exceptional hardness and workability.
- In the 1980s, the industry witnessed diversification with the introduction of various metal wares such as brass, iron, and aluminum.
- This expansion brought new technologies like electroplating, lacquering, and powder coating to Moradabad's art industry.
- Notably, Moradabad Metal Craft (Word Mark) has received a geographical indication (GI) tag, emphasizing its unique identity and craftsmanship.
- In the 18th century, Moradabad’s brass industry was boosted when the British East India Company began ordering large quantities of brass products for export.
- The demand for Moradabad’s brassware continued to grow throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, making it one of the most critical industries in the city.
What Categories of Brass are made in Moradabad?
Moradabad’s manufacturers produce a wide range of brass products, including:
- Brass utensils: It includes a variety of brass utensils, such as pans, kettles, and jugs.
- Brass lamps: Moradabad is also known for its brass lamps, which are used for decoration and lighting homes and businesses.
- Brass statues: Brass spiritual suppliers also produce a wide range of brass God idols, Goddess statues, and Home decor statues.
- Other brass products: In addition to the items mentioned above, Moradabad’s manufacturers also produce various other brass products, such as vases, ashtrays, candlesticks, and door knockers.
How AI can help detect cancer and why India’s biggest cancer treatment hospital is utilising it (Indian Express)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Given the escalating cases of cancer, the shortage of specialists poses a significant challenge in curbing fatalities. To address this gap, Mumbai’s Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), the biggest cancer hospital in India, is turning to artificial intelligence (AI).
Context:
- With the rising cancer cases, a notable challenge is the shortage of specialists, impacting efforts to reduce fatalities.
- To tackle this issue, Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH) in Mumbai, India, the country's largest cancer hospital, is embracing artificial intelligence.
- The hospital is leveraging deep learning to establish a Bio-Imaging Bank for cancer, employing AI to develop a tailored algorithm specific to cancer diagnosis.
What is the Role of AI in Cancer Detection and Treatment?
- Early Detection through Identification of Tissue Changes and Potential Malignancies: AI analyzes radiological and pathological images, learning from extensive datasets to recognize unique features associated with various cancers.
- This technology facilitates early detection by identifying tissue changes and potential malignancies.
- Predictive Models for Tumor Survival and Treatment Guidance: Comprehensive imaging generates longitudinal patient data, aiding in understanding behavior, treatment response, disease recurrence, and overall survival.
- AI and machine learning protocols utilize this data to develop predictive models for tumor survival and guide treatment aggressiveness.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Chemotherapy: The creation of a tumor image bank allows for the development of algorithms for different tumors, assessing treatment responses directly from images and avoiding unnecessary chemotherapy for predicted non-responders.
- Maintaining Diagnostic Quality while Decreasing Radiation Exposure: Tata Memorial Hospital has added data from 60,000 patients to the biobank over the past year.
- Using this data, AI successfully reduces radiation by enhancing images with AI algorithms, ensuring a significant decrease in radiation exposure to children without compromising diagnostic quality.
- Potential to Reduce Cancer Fatalities in the Future:
- AI is poised to play a transformative role in cancer treatment, particularly in mitigating fatalities in rural India.
- Its potential lies in tailoring treatment approaches based on diverse patient profiles, optimizing therapy outcomes.
- AI swiftly detects cancer, eliminating the need for extensive tests and enabling even general practitioners to diagnose complex cancers.
- This technology is set to significantly enhance precision in cancer solutions.
What is Bio-Imaging Bank?
- The overarching objective is to establish a robust repository incorporating radiology and pathology images intricately linked with clinical information, outcome data, treatment specifics, and additional metadata.
- This strategic design aims at facilitating the training, validation, and rigorous testing of AI algorithms.
- Functioning: In conjunction with creating the database, the project involves training and testing multiple AI algorithms using the accumulated data.
- It is tailored to address medically relevant tasks, including screening for lymph node metastases, nucleus segmentation and classification, biomarker prediction, and therapy response prediction.
- Institutions Involved: The multi-institutional project receives funding from the Department of Biotechnology and collaborates with IIT-Bombay, RGCIRC-New Delhi, AIIMS-New Delhi, and PGIMER-Chandigarh.
From red ant chutney to black rice, the 7 Odisha products that have bagged GI tags (Indian Express)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Seven products from Odisha, ranging from the Similipal Kai chutney made with red weaver ants to the embroidered Kapdaganda shawl, have bagged the coveted Geographical Indication (GI) tag in recognition of their exclusivity to the state.
What is Geographical Indication (GI) Tag?
- Geographical Indications of goods refer to the place of origin of a product.
- Such tags are accorded as they convey an assurance of quality and distinctiveness, attributable to the fact of its origin in a specific geographical locality, region or country.
- In India, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, awards GIs.
- A GI registration is given to an area, not a trader, but once a product gets the registration, traders dealing in the product can apply to sell it with the GI logo.
- Authorised traders are each assigned a unique GI number.
- If any unauthorised trader tries selling the product under that name, they can be prosecuted under The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- A marker of authentic products, the GI tags also help protect the interests of the local growers and artisans by preventing duplicity of the products and sale from unauthorised traders.
- Consumers, through the tags, can know which goods are certified.
The Seven Products and Their Distinctiveness:
- Kapdaganda shawl: Woven and embroidered by the women of the Dongria Kondh tribe, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) in the Niyamgiri hills in Odisha’s Rayagada and Kalahandi districts, the shawl reflects the rich tribal heritage of the Dongria Kondhs.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Green symbolises the mountains and hills, and yellow stands for peace and happiness.
- Red stands as the symbol of blood.
- The motifs in the shawls are mostly lines and triangles, believed to be a reflection of the importance of mountains for the community.
- The shawl is worn by both men and women and the Dongrias gift it to their family members as a token of love and affection.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Lanjia Saura Painting: The painting is also known as Idital. The artworks are famous for their beauty, aesthetics, ritualistic association and iconography.
- The art form belongs to the Lanjia Saura community, a PVTG largely residing in the Rayagada district.
- These paintings are in the form of exterior murals painted on the mud walls of homes.
- White paintings figure over a crimson-maroon background.
- It is believed that the Lanjia Sauras paint their walls with Idital artworks to show gratitude to their deities and forefathers, and also for the well-being of their community.
- Reflecting the love and affection of the primitive tribes for nature, they feature subjects like tribal humans, trees, animals, birds, the Sun and the Moon.
- Koraput Kala Jeera Rice: The black-coloured rice variety, also known as the ‘Prince of Rice’, is famous for its aroma, taste, texture and nutritional value.
- Tribal farmers of the Koraput region have preserved the rice variety for around 1,000 years.
- As the rice grains resemble cumin seeds, it is also called Kala Jeera. Consumption of the rice variety helps in increasing haemoglobin levels and improves metabolism in the body.
- The farmers and producers of Koraput Kala Jeera rice have followed the traditional knowledge and practices in cultivation.
- Similipal Kai chutney: The chutney made with red weaver ants is a traditional delicacy of the tribals in Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district.
- The ants are found in the forests of Mayurbhanj, including in the Similipal forests – Asia’s second-largest biosphere.
- Rich in medicinal and nutritional value, the chutney is believed to be a good source of nutrients like protein, calcium, zinc, vitamin B-12, iron, magnesium, potassium, etc.
- The tribals prepare the Kai chutney by grinding the ants manually on a Sil Batta or the grinding stone.
- Mayurbhanj’s tribals also earn their livelihood by selling the red ants and the chutney made from the ants.
- They believe that its consumption helps boost immunity and prevents diseases.
- Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal: Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal is known for its prickly thorns on the stems and the whole plant.
- The green and round fruits contain more seeds as compared to other genotypes.
- It is famous for its unique taste and relatively short quick cooking time. The plants are resistant to major insects and can be grown with minimal pesticide.
- It is being widely cultivated in Nayagarh district of the state.
- Odisha Khajuri Guda: Odisha’s “Khajuri Guda” or jaggery is a natural sweetener extracted from date palm trees and has its origin in the Gajapati district.
- Traditionally, the jaggery is prepared in a trapezoidal form called ‘Patali Gur’ and is organic by nature.
- It is dark brown and has a unique taste.
- Dhenkanal Magji: Dhenkanal Magji is a type of sweet made from cheese from buffalo milk, with distinct characteristics in terms of appearance, taste, flavour, shape, and size.
- It also has unique nutritional values that distinguish it from other cheese-based sweets.
- The sweet is prepared by draining moisture from the cheese and then frying it, finally forming balls from the mixture.
‘Deep tech’ policy to be sent to Cabinet for approval, says scientific adviser (The Hindu)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government will be sending a note, on a new ‘deep tech’ policy for India in the coming weeks to the Union Cabinet for approval, said Prof. Ajay Kumar Sood, Principal Scientific Advisor at a public event on January 5.
Key Details in the Draft NDTSP:
- The Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) stands out through its key highlights, enhancing the existing Startup India policies by fostering an environment conducive to the growth of deep tech startups.
- It addresses the unique challenges these startups face.
- The draft NDTSP introduces new policy instruments and recommends essential policy changes under several themes, including nurturing research, development, and innovation, strengthening the intellectual property regime, facilitating access to funding, enabling shared infrastructure and resource sharing, creating supportive regulations, standards, and certifications, attracting human resources, initiating capacity building, promoting procurement and adoption, ensuring policy and program interlinkages, and sustaining deep tech startups.
India's 'Deep Tech' Startup Ecosystem faces significant challenges as outlined in the draft 'deep tech' policy:
- As of May 2023, the DPIIT recognizes 10,298 startups, but only about 10% fall under the 'deep tech' category, indicating a need for more effort and support.
- A major hurdle is the inadequate funding for 'deep tech' startups. Unlike fintech or retail software startups that require comparatively smaller funds, 'deep tech' startups demand significantly larger financial investments.
- This financial gap poses a notable obstacle to their growth and development.
What is Deep Tech?
- Deep technology, often referred to as "deep tech," encompasses advanced technologies rooted in substantial scientific or engineering innovations.
- These innovations are considered "deep" due to their sophisticated and highly advanced nature, providing solutions to complex challenges or issues.
- Examples of breakthroughs in deep tech include genomics, robotics, nanotechnology, and clean energy initiatives emerging from research labs and academia.
- Deep-tech startups and companies are characterized by their pursuit of solutions to intricate problems through technologies and processes involving lengthy research and development cycles.
- Importantly, businesses and startups that rely on easily replicable ideas do not qualify as deep tech startups.
- Deep tech stands apart from high tech, which denotes a broader scope of technical innovations and advancements.
- Unlike high-tech companies, those in deep tech are primarily focused on profound scientific or engineering breakthroughs.
Isro’s futuristic fuel cell system could power space station (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, a futuristic fuel cell-based power system was successfully tested by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to provide a sustainable and reliable power source for space stations.
What is a Fuel Cell?
- Fuel cells, intricate devices powered by chemical reactions, have diverse applications spanning transportation, industrial sectors, commercial and residential buildings, and reversible grid energy storage systems.
- Operationally, fuel cells consist of two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in an electrolyte.
- The anode, supplied with hydrogen fuel, undergoes oxidation to produce hydrogen ions and electrons.
- Simultaneously, the cathode, exposed to an oxidizer like oxygen, results in the production of water as hydrogen ions absorb electrons.
- The voltage per unit cell is determined by the energy level disparity at the electrodes. While a single fuel cell generates a modest amount of direct-current electricity, practical use often involves assembling stacks of these cells.
- Advantages: Advantages of fuel cells include lower or zero emissions, particularly with hydrogen fuel cells emitting only water, addressing climate concerns by avoiding carbon dioxide emissions.
- They operate quietly with few moving parts, achieve higher efficiencies compared to combustion engines, and resemble batteries but offer prolonged electrical energy due to continuous external fuel and air/oxygen sources.
- This longevity distinguishes them from batteries that rely on finite fuel material and oxidant, making fuel cells a sustainable and efficient choice for various applications.
About ISRO:
- The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is the pioneer space exploration agency of the Government of India, headquartered at Bengaluru.
- ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development, while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research.
- ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, considered amongst the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
BRO Implements Indigenous Technology for Road Construction Near China Border in Arunachal Pradesh (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
In order to improve operational capacity of the defence forces in the high-altitude areas along the Indo-China border in Arunachal Pradesh, the BRO will build bituminous roads using an indigenous technology, “Rejupave” developed by India’s oldest and premier road research organisation, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI).
What is Rejupave Technology?
- CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI), India's oldest road research organization, developed the Rejupave Technology.
- It is beneficial for constructing high-altitude bituminous roads in low and sub-zero temperatures.
- The technology actively reduces production and rolling temperatures of bituminous mixes by 30 to 400 degrees Celsius, ensuring minimal heat loss during transit in snowy conditions and long haulage times.
- The bio-oil-based asphalt modifier of this technology significantly lowers the heating requirements of bituminous mixes and preserves mix temperature during transit.
- In cold climatic regions, the 'Rejupave' asphalt modifier enhances long-term durability and resistance to thermal cracking under low-temperature conditions.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the eco-sensitive mountainous environment of Arunachal Pradesh.
About CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI):
- Established in 1952, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) stands as a premier national laboratory under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- CRRI's major research and development programs encompass a range of projects, including the design, construction, and maintenance of roads and runways, traffic and transportation planning for large and medium cities, management of roads in diverse terrains, improvement of marginal materials, utilization of industrial waste in road construction, and landslide control.
- The institute extends its expertise by providing technical and consultancy services to various organizations both within India and internationally.
- CRRI actively contributes to capacity building in highway engineering, empowering human resources to undertake and execute road and runway projects.
High-frequency waves detected in the Martian Upper Atmosphere could help understand plasma processes over Mars (PIB)
- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, scientists have detected the existence of high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian Upper Atmosphere with novel narrowband and broadband features that can help to understand plasma processes in the Martian plasma environment.
What are Plasma Waves?
- Plasma waves, commonly observed in Earth's magnetosphere, denote short-time scale fluctuations in electric and magnetic fields.
- These waves play a crucial role in energizing and transporting charged particles within Earth's magnetosphere.
- Specific plasma waves, like electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves, serve as a safeguard, cleansing Earth's radiation belt, known to pose threats to satellites.
- Researchers, intrigued by this phenomenon, seek to understand the presence of diverse plasma waves around planets without intrinsic magnetic fields, such as Mars.
Key Observations:
- Scientists utilized high-resolution electric field data from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission (MAVEN) spacecraft to examine high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian environment.
- These waves manifest as either parallel-propagating electron oscillations (Langmuir waves) or perpendicular-propagating electron oscillations (upper-hybrid type waves) in Mars' magneto sheath region.
- Two distinct wave modes, below and above the electron plasma frequency, were observed in the Martian magnetosphere.
- Broadband and narrowband waves exhibited identifiable features in the frequency domain, with broadband waves displaying periodic patchy structures at intervals of 8–14 milliseconds.
Significance:
- The presence of these waves offers a valuable tool to investigate how electrons gain or dissipate energy within the Martian plasma environment.
Cabinet clears PRITHVI initiative for ease of research in earth sciences (Indian Express)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government Friday approved an initiative that will give it the flexibility to pursue research and use funds allocated to five different sub-schemes related to earth sciences over a five-year period.
About the PRITHVI Scheme:
- The PRITHVI Scheme is an initiative by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) designed to deepen our understanding of the Earth and its essential indicators.
- With a substantial allocation of Rs 4,797 crore spanning 2021-26, this comprehensive initiative aims to significantly advance research, modeling, and service delivery in critical domains like weather, climate, oceans, and polar regions.
- The scheme amalgamates five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training, and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Collectively, these programs strive to deepen our comprehension of Earth's vital signs and translate scientific knowledge into practical services for the benefit of society, the environment, and the economy.
Objectives:
- A primary aim of PRITHVI is to enhance and sustain long-term observations across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth.
- This facilitates the recording and monitoring of vital signs and changes within the Earth System.
- The scheme places emphasis on developing predictive models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards while advancing our understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring polar regions and high seas is a significant aspect, targeting the discovery of new phenomena and resources.
- The scheme underscores the development of technology for exploring and sustainably harnessing oceanic resources for societal applications.
Implementation:
- Various components of the PRITHVI scheme are interdependent, executed in an integrated manner through the collective efforts of the institutes under the MoES.
10th century Kadamba inscription written in Kannada, Sanskrit found in Goa (The Hindu)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An inscription written in Kannada and Sanskrit and said to be of 10th century A.D. Kadamba period has been discovered in the Mahadeva temple at Cacoda in southern Goa.
About the Kadamba Inscription:
- Discovery and Study of the Inscription: The inscription illuminates the Kadamba period in Goa, commencing with the auspicious phrase 'Be it well' (Swasthi Shri).
- It was discovered between the temples of Mahadev and Sateri-Betal at Cacoda in Goa.
- Epigraphic Details: It chronicles the story of Gundayya, Talara Nevayya's son, who vowed to fulfill his father's desire by capturing a Gopura in the port of Goa.
- The inscription is engraved in Kannada and Nagari characters.
- Its literary style mirrors the Talangre inscription of Jayasimha I from the same period.
- The deciphering of the Kadamba stone inscription has brought to light its historical and socio-cultural importance.
- Historical Narrative: The Kadambas of Goa served as subordinates to the Chalukyas.
- Kadamba Shasthadeva, appointed as Mahamandaleshwara of Goa by Chalukyan emperor Tailapa II, played a key role in overthrowing the Rashtrakutas.
- In 960 A.D., Kadamba Shasthadeva conquered Chandavara and the port of Gopakapattana (present Goa).
- Gundayya, Talara Nevayya's son, actively participated in the battle, successfully securing the port but sacrificing his own life.
- To commemorate his son's heroic fight, Talara Nevayya erected a memorial stone with the inscription in the Mahadev temple at Cacoda.
- Socio-cultural Importance: Cacora village, situated near navigable waterways, establishes connections to the Upper Ghat region through the ancient route of Diggi ghat leading to Karnataka.
- Currently a census town under the Municipality of Curchorem Cacora in Goa, Cacoda hosts the Mahadev temple with its affiliated deities, showcasing the cultural richness and historical significance of the area.
Justice Gavai nominated as SC Legal Services Committee Chairman: What law says on free legal aid in India (Indian Express)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Supreme Court judge Justice BR Gavai has been nominated as the Chairman of the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee (SCLSC), replacing Justice Sanjiv Khanna – the seniormost judge of the top court after the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
What is the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee?
- The Supreme Court Legal Services Committee was constituted under Section 3A of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, to provide “free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of society”, in cases falling under the top court’s jurisdiction.
- Section 3A of the Act states that the Central Authority (the National Legal Services Authority or NALSA) shall constitute the committee.
- It consists of a sitting SC judge, who is the chairman, along with other members possessing the experience and qualifications prescribed by the Centre.
- Both the chairman and other members will be nominated by the CJI. Further, the CJI can appoint the Secretary to the Committee.
Who does the SCLSC comprise?
- As of date, the SCLSC consists of chairperson BR Gavai and nine members nominated by the CJI.
- The Committee, in turn, can appoint officers and other employees as prescribed by the Centre, in consultation with the CJI.
- Besides this, Rule 10 of the NALSA Rules, 1995, entails the numbers, experience, and qualifications of the SCLSC members.
- Under Section 27 of the 1987 Act, the Centre is empowered to make rules in consultation with the CJI, by notification, to carry out the provisions of the Act.
What is the need for legal services and how is it dispensed to the people?
- The need for providing legal services has been underlined in many provisions of the Indian Constitution.
- Article 39A states, “The State shall secure that the operation of the legal system promotes justice, on a basis of equal opportunity, and shall, in particular, provide free legal aid, by suitable legislation or schemes or in any other way, to ensure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of economic or other disabilities.”
- Moreover, Articles 14 (right to equality) and 22(1) (rights to be informed of grounds for arrest) also make it obligatory for the State to ensure equality before the law and a legal system that promotes justice based on equal opportunity.
- Although the idea of a legal aid programme was earlier floated in the 1950s, it was in 1980 that a committee at the national level was established under the chairmanship of then SC judge Justice PN Bhagwati.
- The Committee for Implementing Legal Aid Schemes started monitoring legal aid activities throughout India.
What the Legal Services Authorities Act says?
- In 1987, the Legal Services Authorities Act was enacted to give a statutory base to legal aid programmes.
- It aims to provide free and competent legal services to eligible groups, including women, children, SC/ST and EWS categories, industrial workers, disabled persons, and others.
- Under the Act, NALSA was constituted in 1995 to monitor and evaluate the implementation of legal aid programmes and to lay down policies for making legal services available.
- A nationwide network has been envisaged under the Act for providing legal aid and assistance.
- It also disburses funds and grants to State Legal Services Authorities and NGOs for implementing legal aid schemes and programmes.
- Subsequently, in every state, State Legal Services Authorities (SLSA) were established to implement NALSA’s policies and directions, give free legal services to people, and conduct Lok Adalats.
- An SLSA is headed by the Chief Justice of the respective High Court and includes the senior HC judge as its Executive Chairman.
- While the HC Chief Justice is the patron-in-chief of the SLSA, the CJI is the patron-in-chief of NALSA.
- Similarly, District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) and Taluk Legal Services Committees were established in districts and most taluks.
- Situated in the District Courts Complex in every district, each DLSA is chaired by the District Judge of the respective district.
- The Taluka or Sub-Divisional Legal Services Committees are headed by a senior civil judge.
- Collectively, these bodies organise legal awareness camps, provide free legal services, and supply and obtain certified order copies and other legal documents, among other functions.
How graphene semiconductors can revolutionise electronics and computing (Front Line)
- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, Scientists have made a breakthrough in electronics, creating the world’s first functional semiconductor made from graphene—a material known for being tough, flexible, light and with a high resistance.
What is Graphene?
- Graphene is a single sheet of carbon atoms—a 2D material held together by the strongest chemical bonds known.
- These carbons are arranged in tessellated hexagons, much like honeycomb.
- It is an incredibly strong material. It’s so strong we can hold up a football with just one atomic layer of graphene.
- Graphene is also incredibly flexible, making it ideal for use in electrical devices and batteries, or even printed on glass, plastics or fabrics.
Keys Properties of Graphene:
- Strength: it is the strongest material ever measured, about 200 times stronger than steel.
- This is because the strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms in the hexagonal lattice make it very difficult to break apart.
- Conductivity: Graphene is also an excellent conductor of heat and electricity.
- In fact, it is the best conductor of heat at room temperature of any known material.
- This is because the electrons in graphene can move freely through the lattice without encountering any obstacles.
- Transparency: Graphene is almost completely transparent to light, absorbing only about 2.3% of visible light.
- This makes it a promising material for use in transparent electronics and solar cells.
- Flexibility: Graphene is also incredibly flexible, and can be bent and folded without breaking.
- This makes it a good candidate for use in flexible electronics, such as wearable devices.
- These properties make graphene a potential game-changer for a wide range of industries, including electronics, energy, transportation, and medicine.
Potential Applications of Graphene:
- Electronics: Graphene could be used to make transistors that are much faster and more efficient than the silicon transistors used in today's electronics.
- This could lead to the development of smaller, lighter, and more powerful devices.
- Energy: Graphene could be used to make solar cells that are more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity.
- It could also be used to make batteries that are lighter and have longer lifespans.
- Transportation: Graphene could be used to make lighter and stronger airplanes and cars.
- It could also be used to make more efficient batteries for electric vehicles.
- Medicine: Graphene could be used to make sensors that can detect diseases at an early stage.
- It could also be used to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells.
Drawback of Graphene:
- Graphene has major drawbacks, which has prevented its use in electronics.
- One major issue is known as the “band gap problem.”
- The band gap is a crucial electronic property that allows semiconductors to switch on and off.
- Graphene didn’t have a band gap—until now.
- Despite its promise, graphene is still a relatively new material and there are a number of challenges that need to be overcome before it can be widely used.
- One challenge is that it is difficult and expensive to produce large sheets of high-quality graphene.
- Another challenge is that graphene is very sensitive to its environment, and its properties can be easily affected by the presence of even small amounts of impurities.
- However, researchers are making rapid progress in overcoming these challenges, and it is likely that graphene will become a common material in the near future.
- With its unique properties, graphene has the potential to revolutionize many different industries and improve our lives in countless ways.
PM’s school becomes base for week-long residential programme for students (The Hindu)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Ministry of Education on Thursday launched ‘Prerana’, an experiential learning programme, which will operate from the vernacular school in Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s birthplace Vadnagar, Gujarat where Mr. Modi studied when he was a student.
Context:
- The Department of School Education & Literacy, operating under the Ministry of Education, Government of India, has unveiled 'Prerana: An experiential learning program.'
- This innovative initiative is specifically crafted to deliver a profound, distinctive, and motivational learning experience to its participants.
- The overarching goal of this program is to cultivate and nurture leadership qualities among the individuals involved, thereby contributing to their holistic development and empowering them with the skills necessary for effective leadership in various contexts.
What is ‘Prerna’ Program?
- Prerana is driven by a strong commitment to integrate principles of Indian education system and the philosophy of value-based education which is a corner stone of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- It is a week-long residential program for selected students of class IX to XII.
- It is an experiential and inspirational learning program for students with the best-in-class technology where heritage meets innovation.
- A batch of 20 selected students (10 boys and 10 girls) will attend the program, every week from various parts of the country.
- Prerana program will run from a Vernacular School, established in 1888, in one of the oldest living cities of India, Vadnagar, district Mehsana, Gujarat.
- The curriculum of Prerana School prepared by IIT Gandhi Nagar is rooted in nine value based themes:
- Swabhiman and Vinay
- Shaurya and Sahas
- Parishram and Samarpan
- Karuna and Sewa
- Vividhta and Ekta
- Satyanishtha and Shuchita
- Navachar and Jigyasa
- Shraddha aur Vishwas, and
- Swatantrata and Kartavya.
- The program based on above themes will inspire the youth and foster respect for Bharat's unity in diversity, embodying the spirit of "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam" and will contribute by making the youth of today, a flame holder for Viksit Bharat.
- Towards this endeavour, the participants will be guided by mentors from prestigious institutions.
- Selection Procedure: Students can register through the portal, wherein applicants can fill the requisite details to be a part of the ambitious and aspirational Prerana program.
- The registered applicants will go through a selection process, as prescribed on the portal.
- Applicants can also join the selection procedure conducted at the School/block level, on designated ‘Prerana Utsav’ day, through various activities based on the ethos of Prerana to evaluate for well rounded personalities keen to shape the future of our nation.
- Upon selection, the 20 participants (10 boys and 10 girls) will be attending the Prerana program and embark on a journey of inspiration, innovation, and self-discovery.
- After the program, the participants will carry the ethos of Prerana into their respective communities, become change makers and spark positive change to inspire others.
Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change submits proposals for Wetland City Accreditation under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands for cities of Indore, Bhopal and Udaipur (The New Indian Express)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
MoEF&CC has submitted three nominations from India for Wetland City Accreditation (WCA) of Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh) & Udaipur (Rajasthan) under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
What is Wetland City Accreditation (WCA)?
- Recognizing the importance of wetlands in urban and peri-urban environments and to take appropriate measures to conserve and protect these wetlands, the Ramsar Convention during COP12 held in the year 2015 approved a voluntary Wetland City Accreditation system under Resolution XII.10.
- It recognizes cities which have taken exceptional steps to safeguard their urban wetlands.
- The Wetland City Accreditation scheme aims to further promote the conservation and wise use of urban and peri-urban wetlands, as well as sustainable socio-economic benefits for local populations.
- Additionally, the Accreditation seeks to encourage cities that are close to and dependent on wetlands.
- Primarily Wetlands of International Importance, but also wetlands with other conservation category status, to develop and strengthen a positive relationship with these valuable ecosystems.
- To be formally accredited, a candidate for the Wetland City Accreditation should satisfy the standards used to implement each of the six international criteria mentioned Operational Guidance for WCA of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
- This voluntary scheme provides an opportunity for cities that value their natural or human-made wetlands to gain international recognition and positive branding opportunities for their efforts in demonstrating strong positive relationships with wetlands.
- The ongoing Amrit Dharohar initiative of the MoEF&CC announced as part of this year’s budget also aims to achieve similar goals by promoting unique conservation values of Ramsar Sites.
- In this context, WCA will not only generate public awareness about conservation of urban and peri-urban wetlands but will also help in implementation of Amrit Dharohar across the country.
The Three Nominated Cities Include:
- Indore: Founded by Holkars, Indore is the cleanest city in India and the recipient of India’s Smart City Award 2023 for its best sanitation, water and urban environment.
- Sirpur Lake, a Ramsar Site in the city, has been recognised as an important site for water bird congregation and is being developed as a Bird Sanctuary.
- A strong network of more than 200 wetland mitras is engaged in bird conservation and sensitising local community to protect Sarus Crane.
- Bhopal: One of the cleanest cities in India that has proposed conservation zones around the wetlands in its draft City Development Plan 2031.
- Bhoj Wetland, Ramsar Site is the city’s lifeline, equipped with the world-class wetlands interpretation centre, Jal Tarang.
- Additionally, the Bhopal Municipal Corporation has a dedicated Lake Conservation Cell.
- A network of more than 300 wetland mitras is engaged in wetland management and conservation of Sarus Crane.
- Udaipur: Located in Rajasthan, the city is surrounded by five major wetlands, namely, Pichola, Fateh Sagar, Rang Sagar, Swaroop Sagar, and Doodh Talai.
These wetlands are an integral part of the city’s culture and identity, help maintain the city’s microclimate, and provide a buffer from extreme events.
India to use SpaceX rocket to launch communications satellite (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is gearing up for the launch of its communication satellite GSAT-20, weighing 4,700kg, an initiative marking India's entry into a new era of satellite technology.
Context:
- The commercial arm of ISRO, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) will launch GSAT-20 (renamed as GSAT-N2), on-board SpaceX’s Falcon-9 during the second quarter of 2024.
- ISRO's current flagship rocket, the LVM3, holds a maximum carrying capacity of four tons.
- Falling short by 700kg for the GSAT-20.
- This satellite will cater to cellular backhaul service needs particularly to remote and unconnected regions.
What is GSAT 20 Satellite?
- GSAT-20 is an Indian geostationary Ka-band high-throughput communications satellite.
- GSAT 20 is built on the I-3K unified modular bus with electric-only propulsion.
- It will be India's first satellite to rely entirely on electric propulsion, which can be five to six times more efficient than chemical-based propulsion.
- It features a Ka × Ka high-throughput communications payload with 70 Gbps throughput utilizing 32 spot beams with each 2 polarisations providing broadband services across the Indian region.
- The satellite was initially set for a 2020 launch on a GSLV Mk.3 (2) rocket but got moved up to 2019 on an Ariane-5ECA+.
- In 2021, the plan returned to a GSLV Mk.3 (2) launch.
- In early 2024, a contract with SpaceX was signed for a Falcon-9 v1.2 (Block 5) launch.
What is SpaceX’s Falcon-9 Rocket?
- Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX “for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond".
- It is the world’s first orbital-class reusable rocket.
- Reusability allows SpaceX to re-fly the most expensive parts of the rocket, which in turn drives down the cost of space access," it added.
- Till now, it has undertaken 285 launches, 243 landings, and 217 re-flights.
Centre, SEBI will regulate short selling, Solicitor-General tells Supreme Court (The Hindu)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court judgement records a statement made by Solicitor General Tushar Mehta that the Union government and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) will take measures to regulate short selling.
What is Short Selling?
- Short selling is a financial strategy where an investor or trader borrows securities, such as stocks, from a broker and sells them in the market with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price in the future.
- Short selling is regulated by a circular notified by SEBI in December 2007.
- This technique is employed by individuals who anticipate a decline in share prices, aiming to profit from their predictions.
- The process involves selling shares that the trader does not own.
- To initiate a short position, the trader borrows shares from a broker, who lends them with an agreement for return at the settlement time.
- The borrowed stocks are then sold at the prevailing market rate, creating a short position.
- Subsequently, the trader waits for the prices to decrease before buying back the shares to close the position.
- The ultimate goal of short selling is to 'sell high and buy low.'
- Profits are made when share prices fall, and the trader benefits from the difference between the selling and repurchasing prices.
- Conversely, if the trader's analysis is incorrect and share prices rise, they incur a loss.
How Does Short Selling Work?
Short selling is an activity that allows market participants to profit from the fall in the price of a financial instrument. It involves borrowing an asset from a broker, selling it in the market, and then repurchasing it later at a hopefully lower price to return it to the lender.
- Borrowing the Asset: The trader borrows the asset (usually stocks) from a broker or another trader.
- This borrowed asset is typically done through a margin account, where the investor agrees to certain terms and pays a fee or interest for the borrowed amount.
- Selling the Asset: After obtaining the borrowed asset, the trader immediately sells it on the market.
- This is where they take advantage of their belief that the asset's price will decrease.
- Waiting for Price Drop: The trader waits for the price of the asset to fall. If the price drops as anticipated, the investor can buy back the asset at a lower price.
- Repurchasing the Asset: Once the price has dropped, the trader uses the proceeds from the initial sale to repurchase the same asset at a lower price.
- Returning the Borrowed Asset: Finally, the trader returns the borrowed asset to the lender, typically the broker, from whom they originally borrowed it.
- Profit or Loss: The profit or loss in short selling is the difference between the price at which the asset was sold and the price at which it was repurchased, minus any borrowing fees, interest, or transaction costs.
Short selling is considered a more advanced and riskier trading strategy, and it requires careful monitoring of market conditions. It is often used by experienced investors or hedge funds seeking to profit from anticipated price declines in specific securities or markets.
A first in 100 years, the Indian Science Congress was postponed amid a tussle between organisers, Govt (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Science Congress, the largest gathering of scientists and students of science in the country and a permanent annual fixture in the calendar of the participant group for more than a century has been postponed.
Postponement of the Indian Science Congress:
- Unprecedented Interruption: The postponement of the Indian Science Congress holds unprecedented significance.
- Since its inception in 1914, the Congress has been an annual event, except for the years immediately following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022).
- Tradition and Prime Ministerial Engagement: A cornerstone of scientific tradition, the Indian Science Congress is inaugurated by the Prime Minister, making it a fixture on the PM's calendar.
- Typically, it stands as the Prime Minister's first public engagement of the new year.
Why has the Science Congress Been Postponed This Year?
- This year's postponement stems from a protracted dispute between the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), the organizing body, and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) within the Union Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The DST, a key funding entity, withdrew support in September 2023, citing financial irregularities.
- The ISCA refuted the allegations and contested the DST's directive prohibiting government funds for Science Congress-related expenses, leading to an impasse that has resulted in the postponement.
- A legal challenge to the DST's decision is currently pending.
What is the Indian Science Congress (ISC)?
- The Indian Science Congress (ISC) is a unique event in the country that serves as a platform for scientific communities to interact with students and the general public on science-related matters.
- Organized by the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), an independent body supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in the central government, the Science Congress is an annual five-day event from January 3 to 7, considered a permanent fixture on the Prime Minister’s calendar.
- The inaugural session of the Indian Science Congress took place in 1914 at the premises of the Asiatic Society, Calcutta.
- In recent years, the Indian Science Congress (ISC) has faced criticism due to issues such as a lack of substantial discussions, the promotion of pseudoscience, and outlandish claims by certain speakers.
- This has led to concerns among prominent scientists, with some advocating for the discontinuation of the event or, at the very least, the withdrawal of government support.
- While the government provides an annual grant for organizing the Science Congress, it does not play a direct role in its organization.
Namibian cheetah Aasha gives birth to 3 cubs in Kuno; ‘indicator that animals are acclimatising’ (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a Namibian cheetah named Aasha has given birth to three cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
About Kuno National Park (KNP):
- Location: Situated in the Sheopur district of Madhya Pradesh, Kuno National Park is nestled near the Vindhyan Hills.
- The park is aptly named after the Kuno River, a significant tributary of the Chambal River that traverses its expanse.
- Originally designated as a wildlife sanctuary, Kuno National Park attained the status of a national park in 2018.
- This transformation aligns with its pivotal role in the 'Action Plan for Introduction of Cheetah in India.'
- Vegetation and Flora: Kuno predominantly features a grassland landscape, punctuated by occasional rocky outcrops.
- The flora encompasses a diverse mix, including dominant species such as Kardhai, Salai, and Khair trees.
- The park boasts a rich composition with 123 tree species, 71 shrub species, 32 exotic and climbing species, and 34 bamboo and grass species.
- Fauna: The protected region of Kuno National Park shelters an array of wildlife, including the jungle cat, Indian leopard, sloth bear, Indian wolf, striped hyena, golden jackal, Bengal fox, and dhole.
- The park also delights bird enthusiasts with a habitat supporting over 120 bird species.
What is Project Cheetah?
- The Wildlife Trust of India started talks in 2009 to bring the cheetah back to India.
- Over five years, 50 cheetahs will be imported from African nations and placed in various national parks as part of the "Action Plan for Reintroduction of Cheetahs in India."
- Prime Site Selection - Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP): Among the surveyed sites in central Indian states, Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh emerged as the most suitable location.
- This acclaim is attributed to its conducive habitat and ample prey base.
- KNP is deemed capable of supporting 21 Cheetahs, uniquely standing as a wildlife site where villages have been entirely relocated from within the park.
- Moreover, Kuno offers the prospect of harmoniously accommodating four of India's prominent big cats - tiger, lion, leopard, and Cheetah.
- Additional Recommended Sites: The project identifies other potential sites, including Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh), Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary - Bhainsrorgarh Wildlife Sanctuary complex (Madhya Pradesh), Shahgarh bulge in Jaisalmer (Rajasthan), and Mukundara Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan).
- Implementation Progress: As a significant stride in the project's realization, 20 Cheetahs, comprising 8 from Namibia and 12 from South Africa, were introduced to Kuno Palpur National Park last year.
- This marks a historic initiative to establish a free-ranging Cheetah population in India, reviving their presence after a 70-year absence.
PM inaugurates Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Optical Fibre Connection (PIB)
- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently, in Kavaratti, Lakshadweep, inaugurated the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands submarine optical fibre connection (KLI-SOFC) project including various developmental projects worth more than Rs 1,150 crore.
Background-Kochi-Lakshadweep Submarine OFC (KLI) Project:
- The need for digitally connecting the Lakshadweep Islands through a high-capacity submarine cable link with the mainland has been felt for some time.
- Earlier, the only means of communication with the Islands was through Satellite medium, which had limited bandwidth capacity and was not able to meet the growing bandwidth demand.
- In the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Cable (KLI) project submarine cable connectivity from Mainland (Kochi) to eleven Lakshadweep Islands namely, Kavaratti, Agatti, Amini, Kadmat, Chetlet, Kalpeni, Minicoy, Androth, Kiltan, Bangaram and Bitra has been extended.
- The project is funded by the Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF), Department of Telecommunication.
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) was the Project Executing Agency and the work was awarded to NEC Corporation India Pvt Ltd.
- Major activities related to the project include Marine Route Survey, Submarine Cable laying, Civil Construction of CLS stations, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of End Terminals (SLTE).
- Highlights of the KLI Project:
- Total link distance: 1,868 kilometres.
- Total cost of project: Rs 1072 crore
???????Benefits of the KLI Project:
- The project will play a significant role in achieving the objective of ‘Digital India’ and ‘National Broadband Mission’ and in rolling out various e-governance projects of the Government of India in Lakshadweep Islands.
- E-Governance, Tourism, Education, Health, Commerce and Industries will get a boost
- It will also help in further improvement in the standards of living of the people on the Island and will accelerate overall social and economic development in these areas.
- The population of Lakshadweep Islands will be provided high-speed wireline broadband connectivity.
- High-speed broadband will be provided through FTTH and 5G/4G Mobile networks.
- The bandwidth created under this project will be available to all Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) to strengthen their telecom services in the Lakshadweep Islands.
Govt ready with rules for CAA, set to be notified before Lok Sabha polls announcement (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The rules for the Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019 are ready with the central government and will be notified "much before" the announcement of the Lok Sabha elections.
What is the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) 2019?
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019 proposes amendments to the definition of illegal immigrants, specifically benefiting Hindu, Sikh, Parsi, Buddhist, Jain, and Christian immigrants (excluding Muslims) from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh.
- These individuals, residing in India without documentation, are eligible for expedited Indian citizenship within 5 years (reduced from 11 years).
Key Provisions:
- Cancellation of OCI Registration: The Act empowers the cancellation of Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) registration if the holder violates Citizenship Act provisions or other applicable laws.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Forced Migration: The CAA 2019 applies to those compelled to seek refuge in India due to religious persecution.
- Cut-off Date: Applicants must have entered India on or before December 31, 2014.
- Exceptions: The Act excludes areas under the Constitution's sixth schedule (autonomous tribal regions in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram) and states with an inner-line permit regime (Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and Mizoram).
- Implementation Status: Despite lacking notified rules, leading to non-implementation, the government has repeatedly sought extensions for rule formulation.
Rules for the the CAA:
- The authorities have finalized the rules, and the online portal is operational.
- Upon issuing the rules, the authorities can implement the law, granting Indian citizenship to eligible individuals.
- The entire application process will be conducted online, allowing applicants to apply, even using their mobile phones.
- Applicants must declare the year of their entry into India without travel documents, with no requirement for additional documents.
- Requests from applicants who applied after 2014 will be processed according to the new rules.
Factors Contributing to the Delay in CAA Implementation:
- The CAA has encountered robust opposition, particularly in states like Assam and Tripura, leading to significant delays in its implementation.
- Demographic Concerns in Assam: In Assam, concerns have arisen over the perceived demographic impact of the CAA, with fears that it might contradict the 1985 Assam Accord's provisions.
- Assam Accord Violation Perception: The CAA is viewed in Assam as a potential breach of the 1985 Assam Accord, which permits citizenship for migrants arriving between January 1, 1966, and March 25, 1971.
- Nationwide Protest: Protests initially concentrated in the northeast expanded nationwide, contributing to a complex socio-political environment surrounding the CAA.
- Legal Challenges: The Supreme Court is handling petitions, including one from the Indian Union Muslim League, challenging the constitutional validity of the CAA.
- Allegations of Selectivity: Critics argue that the law is discriminatory, excluding persecuted communities like Rohingya, Tibetan Buddhists, and Sri Lankan Tamils, raising concerns about its arbitrary nature.
Counterarguments Responding to CAA Petitions:
- Basis of Classification: The government asserts that the CAA's classification is not based on religion but on addressing "religious discrimination" faced by minorities in neighbouring countries with a state religion.
- Parliamentary Deliberation: Emphasizing over seven decades of deliberation, the government highlights that the Parliament has considered issues related to minorities and enacted the CAA as a targeted amendment.
- Specific Problem Resolution: The CAA is portrayed as a focused amendment designed to address a specific issue prevalent in identified countries, rather than serving as a comprehensive solution for global challenges.
- Limited Legislative Scope: It is clarified that the legislation has a delimited scope, addressing the specific concerns of minorities in certain nations.
- The Indian Parliament is not obligated to address potential persecutions worldwide.
Another eye in the sky, on the ground: India is now part of the world’s largest radio telescope project (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian government’s recent approval to join the SKA project, accompanied by a financial commitment of Rs 1,250 crore, marks the initial step towards this ratification.
What is the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO)?
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy and is headquartered in the UK.
- At the moment, organisations from ten countries are a part of the SKAO.
- These include Australia, Canada, China, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, the Netherlands and the UK.
What is significant about the SKA telescope?
- The telescope, proposed to be the largest radio telescope in the world, will be located in Africa and Australia whose operation, maintenance and construction will be overseen by SKAO.
- The completion is expected to take nearly a decade at a cost of over £1.8 billion.
- Some of the questions that scientists hope to address using this telescope include:
- Beginning of the universe
- How and when the first stars were born
- The life cycle of a galaxy
- Exploring the possibility of detecting technologically-active civilisations elsewhere in our galaxy and
- Understanding where gravitational waves come from.
- As per NASA, the telescope will accomplish its scientific goals by measuring neutral hydrogen over cosmic time, accurately timing the signals from pulsars in the Milky Way, and detecting millions of galaxies out to high redshifts.
- Significantly, the development of SKA will use the results of various surveys undertaken using another powerful telescope called the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is developed and operated by the country’s science agency CSIRO.
- This telescope, which has been fully operational since February 2019 mapped over three million galaxies in a record 300 hours during its first all-sky survey.
- ASKAP surveys are designed to map the structure and evolution of the Universe, which it does by observing galaxies and the hydrogen gas that they contain.
What are radio telescopes?
- Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can detect invisible gas and, therefore, they can reveal areas of space that may be obscured by cosmic dust.
- Significantly, since the first radio signals were detected by physicist Karl Jansky in the 1930s, astronomers have used radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by different objects in the universe and explore them.
- According to NASA, the field of radio astronomy evolved after World War II and became one of the most important tools for making astronomical observations.
- The Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico, which was the second-largest single-dish radio telescope in the world, collapsed in December 2020.
- The telescope was built in 1963 and because of its powerful radar, scientists employed it to observe planets, asteroids and the ionosphere, making several discoveries over the decades, including finding prebiotic molecules in distant galaxies, the first exoplanets, and the first millisecond pulsar.
Prime Minister pays tributes to Savitribai Phule and Rani Velu Nachiyar on their Jayanti (PIB)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi paid tributes to Savitribai Phule and Rani Velu Nachiyar on their Jayanti.
Who is Savitribai Phule?
- Recognized as India's first woman teacher, Savitribai Phule was a pioneer who defied prevailing societal conventions to advance women's education, equality, and justice.
- She was a Dalit lady from the Mali community and was born on January 3, 1831, in Satara District's Naigaon (Maharashtra).
- Despite prevailing norms that limited education to affluent men, the Phules established India's first girls' school in Bhidewada, Pune, in 1848.
- Savitribai's commitment to social reform led to the establishment of Mahila Seva Mandal in 1852, advocating for women's rights.
- In 1860, she initiated a strike against shaving the hair of widowed women.
- Savitribai actively promoted inter-caste marriages, and widow remarriage, and fought against social issues like child marriage, sati, and dowry.
- In collaboration with Jyotirao, she founded the Balhatya Pratibandhak Griha, offering support to pregnant widows.
- The couple further established the Satyashodhak Samaj in 1873, aimed at dismantling caste, religion, and class hierarchies.
- Her literary contributions include "Kavya Phule" (1854), her first collection of poems, and "Bavan Kashi Subodh Ratnakar" (1892).
- Savitribai Phule's enduring legacy lies in her unwavering commitment to education and social reform, making her a pioneering figure in Indian history.
About Rani Velu Nachiyar:
- Rani Velu Nachiyar, born on January 3, 1730, in Ramanathapuram, Tamil Nadu, India, holds the distinction of being the first queen to actively resist British rule, predating the Sepoy Mutiny.
- Revered as Veeramangai among Tamils, she was extensively trained in martial arts, including Valari, Silambam, horse riding, archery, and various languages such as French, English, and Urdu.
- Married to King Muthuvaduganathaperiya Udaiyathevar of Sivagangai, Rani Velu Nachiyar entered the battlefield when her husband fell victim to British soldiers.
- Collaborating with Hyder Ali and Gopala Nayaker, she waged a successful war against the British, displaying exceptional military prowess.
- In 1780, she delegated authority to the Marudu brothers for the administration of the country.
- Rani Velu Nachiyar's courageous stand against colonial rule and her strategic alliances in the face of adversity mark her as an iconic figure in India's history of resistance and resilience.
Protesting new hit-and-run law, truckers dial down after talks with Home Secretary (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The All India Motor Transport Association (AIMTC) decided to end the nationwide truck drivers protests against the new hit-and-run law, after a meeting with Union Home Secretary Ajay Bhalla.
What is the New Hit-and-run Law?
The recently enacted Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita introduces stringent penalties for hit-and-run incidents in India.
- The law specifies that an accused individual causing a fatal crash and fleeing the scene without reporting to authorities could face imprisonment for up to 10 years along with a fine of Rs 7 lakh.
- Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita has established two distinct categories under the umbrella of "causing death by negligence."
- The first category addresses causing death through any rash or negligent act that does not amount to culpable homicide.
- Offenders in this category may face imprisonment for up to five years and a fine.
- The second category deals with causing death through rash and negligent driving, not amounting to culpable homicide.
- If the individual escapes without promptly reporting the incident to a police officer or magistrate, they could be subjected to up to 10 years of imprisonment and a fine.
What was the Hit-and-run Law Before?
- The old, British-era Indian Penal Code (IPC) did not have a specific provision for hit-and-run cases.
- Actions in such cases were taken under Section 304 A of the IPC.
- According to that section, a person causing the death of another due to a rash or negligent act could invite a jail term of a maximum of 2 years or be fined.
- "Whoever causes the death of any person by doing any rash or negligent act not amounting to culpable homicide, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to 2 years, or with fine, or with both," the section stated.
- All cases of hit-and-run along with other forms of activities that came under the ambit of causing death by a "rash and negligent act" were lodged under Section 304 A of the IPC.
South Africa files genocide case against Israel at ICJ: Why the African nation supports Gaza so strongly (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid international criticism of Israel for its continued bombing of Gaza, South Africa recently moved the International Court of Justice (ICJ), for an urgent order declaring that Israel was in breach of its obligations under the 1948 Genocide Convention.
About the International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations (UN).
- It was established in June 1945 by the Charter of the United Nations and began work in April 1946.
- The seat of the Court is at the Peace Palace in The Hague (Netherlands).
- Of the six principal organs of the United Nations, it is the only one not located in New York (United States of America).
- The Court’s role is to settle, in accordance with international law, legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies.
- Its official languages are English and French.
- Powers and Functions: The ICJ handles two types of cases—contentious cases, involving legal disputes between States, and advisory proceedings, responding to legal questions referred by UN organs and specialized agencies.
- Contentious cases involve only UN member States or other States that have accepted the Court's jurisdiction.
- While the Court's judgments in contentious cases are final and binding, advisory opinions are not binding.
- Deciding disputes in line with international law, the ICJ relies on conventions, international custom, general principles, judicial decisions, and expert writings.
- Composition: The Court is composed of 15 judges, who are elected for terms of office of nine years by the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- It is assisted by a Registry, its administrative organ.
- To be elected, a candidate must secure an absolute majority in both UNGA and UNSC.
- The Court sees one-third of its composition renewed every three years, and judges are eligible for re-election.
- Once elected, judges declare their commitment to the impartial and conscientious exercise of their powers.
- They act independently, detached from any governmental influence.
- This comprehensive structure ensures the ICJ's role as a pivotal entity in the international legal landscape, providing judgments on contentious matters and advisory opinions on significant legal questions.
About the Genocide Convention 1948:
- The term 'genocide,' often casually employed in reference to attacks on various communities globally, finds its precise definition in the UN's Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide, presented to the General Assembly in 1948.
- According to this Convention, genocide entails any of the following acts carried out with the intent to wholly or partially destroy a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group:
- Killing members of the group.
- Causing serious bodily or mental harm to group members.
- Deliberately inflicting conditions of life to bring about the group's physical destruction.
- Imposing measures to prevent births within the group.
- Forcibly transferring children of one group to another.
- This Convention categorizes genocide as a crime, applicable irrespective of whether it occurs during wartime or peacetime. India ratified the convention in 1959, although no specific legislation addressing genocide has been enacted to date.
NREGS payments: Aadhaar-based system mandatory now, Govt says may consider exemptions on case basis (Indian Express)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
With the Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) now mandatory for payment of wages to NREGS workers, the Government on Monday said it may consider exemptions on a “case-by-case basis” should any gram panchayat face “technical issues”.
What is the Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS)?
- The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) is a payment service that allows a bank customer to use Aadhaar as his/her identity to access his/her Aadhaar-enabled bank account and perform basic banking transactions like balance enquiry, cash withdrawal, remittances through a Business Correspondent.
- It is a service developed by the National Payments Corporation of India.
Key features of AePS:
- Aadhaar-linked transactions: AePS enables Aadhaar card holders to make transactions through their Aadhaar-linked bank accounts, similar to debit/credit card transactions.
- Biometric authentication: Transactions are completed by submitting the Aadhaar number and biometric details (iris or fingerprint scan) at Points of Sale (PoS) or micro ATMs, using Aadhaar authentication.
- Bank account privacy: Users are not required to share their bank account details during the transaction, enhancing privacy and security.
- Fund transfers: AePS allows users to transfer funds between bank accounts, providing a convenient way to send and receive money.
- Secure transactions: AePS transactions are considered safe and secure as they require biometric authentication, ensuring the identity of the user.
- By leveraging the Aadhaar infrastructure, AePS simplifies and secures financial transactions, making it accessible to a wide range of individuals, particularly those who may not have access to traditional banking services.
ABPS Implementation for NREGS:
- Since 2017, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) has adopted the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (ABPS).
- This system involves linking workers' 12-digit Aadhaar numbers with their job cards and NREGS workers' bank accounts.
- With nearly universal coverage of Aadhaar numbers among the adult population, the Government of India opted to expand ABPS for beneficiaries within the scheme.
- Payments are exclusively directed through ABPS to the associated accounts, ensuring a secure and swift method of fund transfer.
- Out of the total 14.33 crore active beneficiaries, Aadhaar has been successfully linked for 13.97 crore individuals.
- Among these Aadhaar-linked beneficiaries, 13.34 crore Aadhaar authentications have been completed, making 81.89% of active workers eligible for ABPS.
- In July 2023, approximately 88.51% of wage payments were executed through the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System.
Mandatory Adoption of ABPS for NREGS Workers:
- Initially mandated by the Rural Development Ministry starting from February 1, 2023, the implementation of the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (ABPS) witnessed several extensions, ultimately being permitted until December 31, 2023.
- As of January 1, 2024, ABPS has become obligatory for NREGS workers, with no further extensions granted to states beyond December 31.
- The integrated approach of ABPS and the National Automated Clearing House (NACH), an interbank system, will be employed for bulk payments, including subsidies and salaries.
- The use of ABPS for wage payments to unskilled workers ensures the seamless transfer of benefits to their bank accounts, even in instances of frequent changes in the beneficiary's bank account.
Exemption Decision in the Event of Technical Issues:
- If a gram panchayat encounters technical or Aadhaar-related challenges, the Government of India may evaluate exemptions from Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (ABPS) requirements on a case-by-case basis until the resolution of the issue.
- This announcement followed criticism from opposition parties, labeling ABPS as a harsh New Year measure that could potentially exclude millions of the most vulnerable and marginalized Indians from accessing basic income.
- The government was accused of "weaponizing technology, especially Aadhaar.
India, Pakistan exchange list of nuclear installations and facilities (ET)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Pakistan exchanged the list of nuclear installations and facilities, covered under the Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities between the two countries.
About the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities:
- The Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities, also known as the India-Pakistan Non-Attack Agreement, was signed on 31 December 1988 and became effective on 27 January 1991.
- It was signed by the then Pakistani PM Benazir Bhutto and Indian PM Rajiv Gandhi.
- According to this agreement, both India and Pakistan are required to annually communicate the list of nuclear installations and facilities covered by the agreement on the first of January of each calendar year.
- The agreement stipulates that neither party shall engage, directly or indirectly, in any actions aimed at causing destruction or damage to any nuclear installation or facility in the other country.
- The term 'nuclear installation or facility' encompasses nuclear power and research reactors, fuel fabrication, uranium enrichment, isotopes separation, reprocessing facilities, as well as any other installations involving fresh or irradiated nuclear fuel and materials in any form, along with establishments storing significant quantities of radioactive materials.
Need for the Agreement:
- In 1986, heightened concerns arose when the Indian army conducted a large-scale exercise named 'Brasstacks,' prompting fears of a potential assault on nuclear facilities.
- Subsequently, negotiations ensued between the two nations aimed at fostering an understanding regarding the management of nuclear weapons, ultimately leading to the formulation of the treaty.
Importance of the Agreement:
- Both nations reiterate their dedication to enduring peace and the cultivation of amicable and harmonious bilateral relations.
- They recognize the significance of confidence-building measures in fostering such relations built on mutual trust and goodwill.
- The potential consequences of even a limited nuclear exchange between India and Pakistan are grave, with the potential to cause the loss of 20 million lives within a week.
Radiocarbon dating brought the first verifiable way to keep time to many fields of science, significantly transforming them (The Hindu)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
From thermodynamics to GPS, from social systems theory to studies of consciousness, time plays an essential role in how we study, interpret, and understand the natural universe and the peoples and technologies that occupy it.
What is radiocarbon dating?
- Radiocarbon dating is a technique employed to determine the age of an object by utilizing radiocarbon, a specific isotope known as carbon-14.
- Formation of Carbon-14: Carbon-14 is generated in the Earth's atmosphere through a process initiated by cosmic rays—energetic streams of charged particles originating from outer space.
- These cosmic rays collide with atmospheric gas atoms, releasing neutrons in the process.
- When these neutrons interact with nitrogen-14 isotopes, carbon-14 is produced.
- Given the continuous influx of cosmic rays penetrating the Earth's atmosphere, a constant production of carbon-14 takes place.
- Subsequently, this newly formed carbon-14 readily combines with atmospheric oxygen, resulting in the creation of radioactive carbon dioxide.
- The carbon-14 compound enters various ecosystems through the carbon cycle, including plants (via photosynthesis), animals (through the consumption of plants), and other forms of biomass.
- It assumes the form of carbon dioxide and other carbon compounds, facilitating its diffusion into the Earth's diverse ecosystems.
- This ensures that the concentration of carbon-14 in the atmosphere remains comparable to its concentration in the planet's other biospheres.
How does radiocarbon dating work?
- The process of radiocarbon dating hinges on the principles of carbon exchange within living organisms, such as the human body.
- While alive, these organisms continuously interact with their environment by engaging in activities like breathing, consuming food, excreting, and shedding skin.
- During these dynamic processes, carbon-14 is both released from the body and replenished, maintaining a relatively constant concentration within the organism that is in equilibrium with its surroundings.
- However, upon death, the cessation of these activities results in a diminishing concentration of carbon-14 in the body due to radioactive decay.
- As time elapses, the quantity of carbon-14 steadily decreases, and its decay rate can be theoretically predicted.
- Radiocarbon dating assesses the age of an object by measuring the remaining amount of carbon-14, a value used by scientists or computers to estimate the time since the organism's demise.
- In contemporary radiocarbon dating methodologies, advanced techniques are employed, with one of the most sensitive approaches being accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS).
- This sophisticated method allows for the analysis of organic samples as minute as 50 mg, enhancing the precision and accuracy of radiocarbon dating.
What are the limitations of carbon-14 dating?
- Age Restriction: Carbon-14 dating is effective for dating organic materials up to approximately 60,000 years old.
- Sample Size Requirements: Conventional radiocarbon dating necessitates relatively large samples, typically ranging from 10 to 100 grams (0.35 to 3.5 ounces), depending on the material being analyzed.
- Advancements in Sample Size: While newer dating methods have emerged that can work with smaller sample sizes, allowing for analyses with quantities as low as 20 to 50 milligrams (0.0007 to 0.0018 ounces).
- Contamination Sensitivity: Radiocarbon samples are highly susceptible to contamination, making it crucial for accurate dating that they remain clean and well-preserved throughout the analysis process.
Two-Month-Old Infant Breaks Records as Youngest to Undergo Successful Bone Marrow Transplant in Mumbai (Times Now)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A two-month-old girl, diagnosed with the rare disease ‘bubble baby syndrome,' becomes the youngest to receive a bone marrow transplant from an unrelated donor at Bai Jerbai Wadia Hospital for Children in Parel.
What is Bubble Baby Syndrome?
- 'Bubble baby syndrome,' medically known as Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of rare, life-threatening diseases that cause a child to be born with very little or no immune system.
- As a result, the child’s body is unable to fight off infections and can become very sick from infections like chickenpox, pneumonia and meningitis and can die within the first year of life.
- This condition falls under the category of primary immune deficiencies.
- The term "Bubble Baby Syndrome" is derived from the necessity for affected individuals to live in a highly controlled environment, as exposure to ordinary surroundings can pose fatal risks to children with SCID.
- What happens in Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)?
- In the developing fetus, the immune system originates in the bone marrow, where versatile stem cells can differentiate into three crucial types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets.
- Among these, white blood cells, particularly lymphocytes, play a vital role in safeguarding the body against infections.
- Lymphocytes consist of two main types: B-cells and T-cells.
- T-cells identify, attack, and eliminate invaders, while B-cells produce antibodies that "remember" infections for future defence.
- SCID is classified as a "combined" immunodeficiency as it impacts both of these infection-fighting white blood cell types.
- In SCID, the child's immune system exhibits either an insufficient quantity of lymphocytes or dysfunctional lymphocytes.
- Consequently, the compromised immune system struggles to combat various germs such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, leading to recurrent and severe infections.
- Causes: SCID results from inherited mutations in multiple genes, with one or both birth parents passing down the condition to their child.
- Symptoms: Although infants with SCID may initially appear healthy, signs of the disorder may manifest shortly after birth. These symptoms include
- Failure to thrive
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Frequent, often severe respiratory infections
- Oral thrush (a type of yeast infection in the mouth)
- Other challenging-to-treat bacterial, viral, or fungal infections
- Treatment: SCID is considered a pediatric emergency, and without prompt intervention, affected babies are unlikely to survive beyond their first birthday.
- The primary treatment method involves a stem cell transplant, also known as a bone marrow transplant.
- In this procedure, the child receives stem cells from a donor with the hope that these new cells will reconstruct the compromised immune system, offering a chance for a healthier and more sustainable life.
Bone marrow transplant
- The most common treatment for SCID is an allogeneic bone marrow transplant, which will introduce normal infection-fighting cells into your child’s body.
- Allogeneic transplants use stem cells from a relative or an unrelated donor from the National Marrow Donor Program.
- An allogeneic bone marrow transplant involves taking cells from the bone marrow (the soft, spongy tissue found in bones) of a healthy donor and giving them to a child after the child’s diseased bone marrow has been eliminated.
- Doctors at Children’s Hospital will screen your child’s family for potential bone marrow matches.
- While a tissue-matched sibling offers the greatest chance of curing SCID, they are not often available.
- Instead, most patients receive bone marrow donations from their parents or unrelated matched donors.
Govt extends PLI scheme for the auto sector by a year with 'partial amendments' (Business Standard)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of Heavy Industries announced the extension of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Automobile and Auto Components by one year with "partial amendments".
PLI Scheme for Automobile Sector:
- The Union Cabinet approved the PLI-Auto Scheme in 2021, allocating a budgetary outlay of Rs. 25,938 crore for five years (FY2022-23 to FY2026-27).
- Aimed at enhancing the production of Advanced Automotive Technology (AAT) Products, the PLI-AUTO Scheme is designed to promote extensive localisation for AAT products and facilitate the development of both domestic and global supply chains.
- This scheme primarily targets Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEVs), specifically Battery Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles.
- In a recent amendment, the incentive period was extended to cover five consecutive financial years, commencing from the financial year 2023-24, with disbursement scheduled for the subsequent financial year, 2024-25.
- The amended scheme stipulates that approved applicants can avail benefits for five consecutive financial years, but the eligibility period will not extend beyond the financial year ending on March 31, 2028.
- Additionally, the amendments specify that if an approved company fails to meet the determined threshold for an increase in Determined Sales Value over the initial year's threshold, it will not receive any incentives for that particular year.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Programme?
- Around 5 years ago, the Indian government aimed to stimulate domestic manufacturing by encouraging more companies to produce goods.
- Recognizing manufacturing as a crucial driver of economic growth with a multiplier effect, wherein each job and investment in manufacturing positively influences other sectors, the government introduced the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme.
- Under the PLI scheme, both foreign and domestic companies engaged in manufacturing receive financial incentives from the government.
- The annual incentive payout is determined as a percentage of the revenue generated by these companies and is applicable for a period of up to five years.
10th phase of Sagar Parikrama covering AP and Puducherry coastal districts to start from Mon (PIB)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Parshottam Rupala along with Minister of State Dr L Murugan will participate in the Sagar Parikrama (Phase X) event being organized from 1st January 2024 to 6th January 2024 at various locations of Andhra Pradesh and Puducherry
About Sagar Parikrama Phase-10:
- Sagar Parikrama Phase-X is poised to be a pivotal event in the ongoing efforts to promote sustainable fisheries, empower stakeholders, and contribute to the economic growth of coastal communities.
- It will continue and cover the remaining coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh namely Nellore, Prakasam, Bapatla, Krishna, West Godavari, Konaseema, Kakinada, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram, Srikakulam and Yanam (Union Territory of Puducherry).
What is “Sagar Parikrama”?
- Sagar Parikrama is a testament to the transformative power of visionary leadership for the welfare of the fishing community and coastal development.
- It is an initiative taken by the Government, with an aim to resolve the issues of the fishers, and other stakeholders and facilitate their economic upliftment through various fisheries’ schemes and programs being implemented by the Government such as Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) and Kisan Credit Card for Fisheries (KCC).
- It represents a transformative voyage along the coastal belt, symbolizing unity with fisherfolk, fish farmers, and all stakeholders in the spirit of the 75th Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- The Sagar Parikrama Yatra features the interactions of ministers with fishermen, fish farmers and other relevant stakeholders.
- State fisheries officials, fishermen representatives, fish farmers, entrepreneurs, fishermen cooperative society leaders, professionals, scientists, and other stakeholders from across the nation will accompany the events.
- The journey of the first phase of “Sagar Parikrama” started from Mandvi, Gujarat on 5th March 2022.
- So far, the total 9 phases of Sagar Parikrama have been covered in the coastal States/UTs of Gujarat, Daman & Diu, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andaman & Nicobar, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and part of Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh during initiation of its tenth phase.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- Sagar Parikrama is making a notable impact on improving the quality of life and economic well-being of the fishing community.
- By providing a platform for direct interaction with Ministers and senior government officials, the initiative ensures that the concerns and issues of fishermen and fish farmers are addressed promptly.
How two choke points could turn into a perfect storm for global trade (Indian Express)
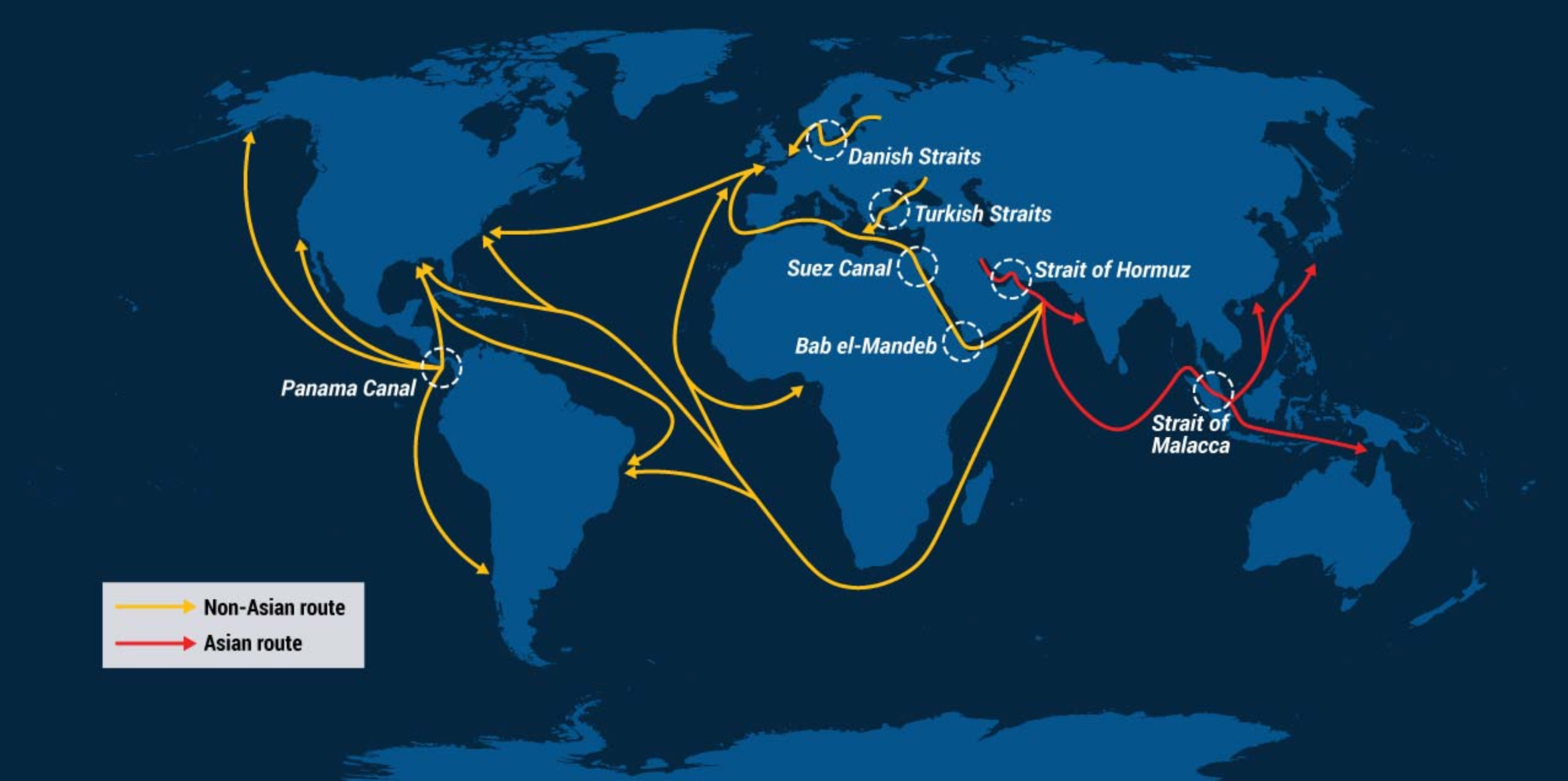
- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Shipping giant Maersk on Sunday suspended passage of its vessels through the Red Sea route for 48 hours after fresh attacks by Yemen-based Houthi rebels. This comes barely a week after the company announced plans to resume operation citing the deployment of a US-led military operation to guard the crucial sea route.
What do the ongoing Red Sea and Panama Canal crises mean for world trade?
- A disruption in maritime transport is a crucial concern for the world economy, as over 80 per cent of the global goods trade is carried by sea.
- The share of trade via sea is much higher for developing countries such as India.
- Currently, two important shipping routes are facing blockages.
- Bab-el-Mandeb Strait which leads to the Suez Canal in the Red Sea region connects Asia and parts of North East and East Africa to Europe.
- The 100-year-old Panama Canal connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Both these routes are among the busiest in the world and a blockage results in forcing global shipping lines to take longer alternate routes, pushing up freight rates.
- The disruption at the Red Sea route, for instance, is estimated to push the prices of Indian agricultural products by 10 to 20 per cent, as shipments would be routed around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope.
- This comes at a time when much of the West is witnessing higher interest rates to curb inflation.
- Higher prices could further fuel demand concerns for global and Indian exporters.
Why is trade via the Panama Canal slowing?
- Shipping via the Panama Canal has dropped by over 50 per cent due to drought conditions at the 51-mile stretch.
- Due to the shortage of water, ships moving from Asia to the US are being forced to use the Suez Canal, which takes six more days compared to the Panama Canal.
- Moreover, Panama is facing its driest rainy season in decades, raising fears of prolonged canal bottlenecks.
How have the attacks impacted freight rates?
- Ever since the attacks along the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait began, global shipping firms have begun imposing war risk surcharges over and above the normal freight rates.
- Indian exporters said that freight rates for Indian shipments headed to Europe and Africa could surge as much as 25-30 per cent if the ongoing security concern along the Red Sea trade route continues.
- This is troubling, as the European Union is one of India’s second-largest export destinations.
- Slowing demand from the region has impacted India’s labour-intensive sectors, such as textiles, gems and jewellery exports.
Panama Canal
- It is an artificial canal that spans the Isthmus of Panama and links the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- Together with the Suez Canal, it is one of the two most strategically important man-made waterways in the world.
- It has a length of around 80 kilometres.
- The United States constructed the canal between 1904 and 1914, and on August 15, 1914, it was formally inaugurated.
- Since 1999, when control of the Canal was moved from the United States to Panama, it has been owned and operated by the Republic of Panama.
- To make it easier for ships to cross the continental divide, the Panama Canal is made up of a network of locks that raise and decrease the water level.
Over 1 lakh people availed free treatment under Delhi Arogya Kosh scheme till October (Indian Express)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
As many as 1.13 lakh people have availed of free health treatment being provided under the city Government’s ‘Delhi Arogya Kosh’ scheme, till October last year, according to government data.
What is the 'Delhi Arogya Kosh' Scheme?
- Constituted in 2011, the Delhi Arogya Kosh (DAK) has five components/schemes:
- Financial assistance to EWS patients
- Free High-End Radiological Diagnostic Test Scheme
- Cashless Specified Surgeries scheme
- RTA (Road Traffic Accident) Scheme (‘i.e. Farishtey Scheme’) and
- Cashless Dialysis Scheme.
- There are 4 schemes under the name of Delhi Arogya Kosh which include financial support from the government for medical implants, various types of surgeries, 136 types of medical tests and the Farishtey scheme for treatment of accident victims.
- Under this scheme, if any citizen of Delhi goes to Delhi government hospitals for treatment and has to face a waiting period for examination or treatment and the patient needs immediate care, then the patient can avail the above-mentioned services in a private hospital with a doctor’s reference.
- Cashless check-ups and treatment will be provided for them in all the empanelled hospitals and the cost of this will be borne by the government.
- Under this scheme, every citizen of Delhi who has Delhi's voter card can get treatment.
- Children below 19 years of age can avail this facility based on their parents' voter cards.
Schemes Under 'Delhi Arogya Kosh':
- Financial assistance up to 5 lakh for different types of medical implants: Under this scheme, the government provides financial assistance up to Rs 5 lakh to the patients.
- To avail of the benefit of this scheme, patients need to submit their application and relevant documents.
- After their screening, the government bears the cost of implants and the treatment of the patient up to Rs 5 lakh.
- It is a cashless scheme.
- 136 free medical test facilities at private labs for patients: In the case of a long waiting list at government hospitals, patients can get the tests done at private hospitals or labs.
- Under this scheme, patients can get about 136 types of medical tests done for free.
- Under this, while waiting in a government hospital, patients can get all medical tests from private hospitals and labs free of cost, including X-ray, MRI, PET scan, CT scan and ultrasound.
- Free Surgery Scheme for patients to get the surgery done in private hospitals: If a patient goes to Delhi government hospital for treatment and has to undergo surgery but the waiting time is more than 30 days, then patients can avail free surgery in private hospitals under the 'Free Surgery Scheme' under this scheme.
- The government bears all the expenses incurred in the surgery.
- Accident victims’ free treatment : The Farishtey Scheme is also covered under Delhi Arogya Kosh.
- Under this scheme, if a person meets with an accident, he or she is provided immediate treatment in a government hospital for free and if the patient gets admitted within 72 hours of an accident, he or she can also avail treatment at a private hospital for free.
-
- All the expenses of patients will be borne by the Delhi government.
SC’s translation projects raced ahead in 2023 as retd. HC judges and law clerks help AI (The Hindu)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court’s monumental project of translating all of its 36,000 judgments into Scheduled Languages achieved unprecedented speed in 2023, with the E-SCR portal starting with just 2,238 translated judgments in January and ending the year with over 31,000.
Background:
- In 2023, the Supreme Court of India embarked on a groundbreaking venture to translate its extensive archive of 36,000 judgments into Scheduled Languages.
- This innovative initiative, powered by collaboration between retired High Court judges, law clerks, and artificial intelligence, has made significant strides.
- However, concerns linger regarding the practical application of these translated judgments and the absence of a standardized legal vocabulary across diverse regional languages.
- The launch of the E-SCR portal in 2023 marked a modest beginning with 2,238 translated judgments in January, reaching a commendable milestone of over 31,000 rulings translated by the year's end.
- Recent statistics reveal that Hindi leads with the highest number of translated judgments at 22,396, followed by Punjabi (3,572), Kannada (1,899), Tamil (1,172), and Gujarati (1,112).
- While the translation speed witnessed a significant improvement in 2023, legal experts express concerns about the practical utility of translated judgments, particularly when High Courts, except in the Hindi-speaking States, cannot conduct proceedings in regional languages.
What is the Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software (SUVAS)?
- SUVAS was introduced in November 2019 by the then-Chief Justice of India (CJI) S.A. Bobde.
- It was created to encourage and ensure the use of regional languages in judicial proceedings.
- It is an artificial intelligence (AI)--trained machine translation tool.
- Constitutional Standing: While Article 348(1)(a) of the Indian Constitution mandates that proceedings in the Supreme Court and every High Court be conducted in English, Article 348(2) provides a provision.
- It allows a State Governor, with the President's consent, to authorize the use of Hindi or another state language in the High Court of that particular State.
- In this context, SUVAS is vested with authority under Article 348, serving as a pivotal tool to promote linguistic diversity within the constitutional framework.
Planning to invest in green deposits? RBI releases latest guidelines to explain key provisions (Live Mint)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent guideline, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) don’t need to raise green deposits.
What are Green Deposits?
- A green deposit is essentially a fixed-term deposit designed for individuals seeking to invest in eco-friendly projects.
- Similar to a standard Fixed Deposit scheme, the green deposit offers interest to investors and has a predetermined term.
Key Features:
- Allocation to Green Finance: The funds deposited in a green deposit are specifically earmarked for allocation to green finance initiatives, promoting environmentally conscious investments.
- Environmentally Friendly Focus: Also referred to as an environmentally friendly fixed deposit, this financial instrument encourages sustainable development by directing funds toward projects related to renewable energy, clean technology, and other environmentally beneficial initiatives.
- Priority Sector Classification: Green activities or projects financed through this framework may be classified under the priority sector, provided they meet the requirements outlined in the Priority Sector Lending (PSL) guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Overdraft Facility: Banks are permitted to offer overdraft facilities to customers against their Green Deposits, providing added flexibility.
- Currency Denomination: As per the current framework, green deposits can only be denominated in Indian Rupees.
- Insurance Coverage: Deposits raised under this framework are covered by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) in accordance with the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961, and the relevant regulations.
- Renewal or Withdrawal: Upon maturity, depositors have the option to either renew or withdraw their green deposits, providing flexibility and choice.
Advantages of Green Deposits:
- Contribution to Climate-Friendly Initiatives: Green deposits empower depositors to actively participate in climate-friendly initiatives, aligning with India's net-zero goals and promoting environmental sustainability.
- Support for Socially Responsible Activities: Although higher interest rates may not be the primary focus, depositors indirectly contribute to socially and environmentally responsible endeavours.
- Their funds play a pivotal role in supporting activities that benefit the community and the planet.
- Positive Environmental Impact: By investing in green deposits, depositors contribute to positive outcomes such as reduced emissions, improved air quality, and sustainable resource allocation.
- These actions foster positive externalities, creating a healthier environment for all.
- Contribution to Reduced Income Inequality: The support for eco-friendly initiatives and fair resource allocation facilitated by green deposits contributes to long-term reductions in income inequality, fostering a more equitable and sustainable society over time.
Challenges Associated with Green Deposits:
- Design Limitations: Flaws in the design of green deposit frameworks may restrict the scope of eligible green projects that banks can invest in, limiting the diversity of environmentally beneficial initiatives.
- Perceived Reality vs. Impact: There is a concern that some green investment products may serve more as a psychological boost for investors rather than delivering substantial environmental benefits.
- The actual impact on the environment may not align with the positive perception created.
- Uncertain Project Sustainability: The long-term sustainability of green projects funded by banks remains uncertain, raising questions about the enduring impact of investments in environmentally friendly initiatives.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient awareness among bank staff can result in delays in the process of acquiring green deposits, hindering the seamless integration of eco-friendly financial products into banking operations.
- Lower Interest Rate Perception: Investors often prioritize high returns, and the perception that green deposits may offer lower interest rates could deter them from choosing environmentally conscious financial products.
Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increases by 7.8% (provisional) in Nov 2023 as compared to the Index of Nov 2022 (PIB)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The combined Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increased by 7.8 per cent (provisional) in November 2023 as compared to the Index of November 2022.
About the Index of Industrial Production (IIP):
- The IIP is a comprehensive index that assesses the growth rate of industry groups, categorized into:
- Broad sectors: Mining, Manufacturing, and Electricity.
- Use-based sectors: Basic Goods, Capital Goods, and Intermediate Goods.
- In India, the initiation of computing the IIP predates international recommendations. The Central Statistical Organization, now known as the National Statistics Office (NSO), assumed the responsibility for compilation and publication in 1951.
- The Ministry responsible for this process is the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
Key Information:
- Base Year: The base year was changed to 2011-12 from 2004-05 in the year 2017.
- Sources of Data: The NSO compiles the IIP using secondary data from 14 source agencies across various Ministries/Departments and their attached/subordinate offices.
- The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) contributes a significant portion of the data for the calculation.
- Utilization of IIP Data: The Industrial Production Index (IIP) is a valuable resource employed by several entities, including government bodies like the Ministry of Finance and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), as well as private firms and analysts.
- It serves as a critical tool for analytical purposes.
- Additionally, the data is instrumental in computing the quarterly Gross Value Added (GVA) of the manufacturing sector within the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
About the Index of Eight Core Sectors:
- The Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) assesses the combined and individual production performance of eight vital industries.
- Together, these sectors account for 40.27% of the items measured in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- Listed in descending order of their weightage, the eight core industries are:
- Refinery Products, Electricity, Steel, Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Cement, and Fertilizers.
162 cases of Covid sub-variant JN.1 detected in India; highest from Kerala, Gujarat: INSACOG (Live Mint)
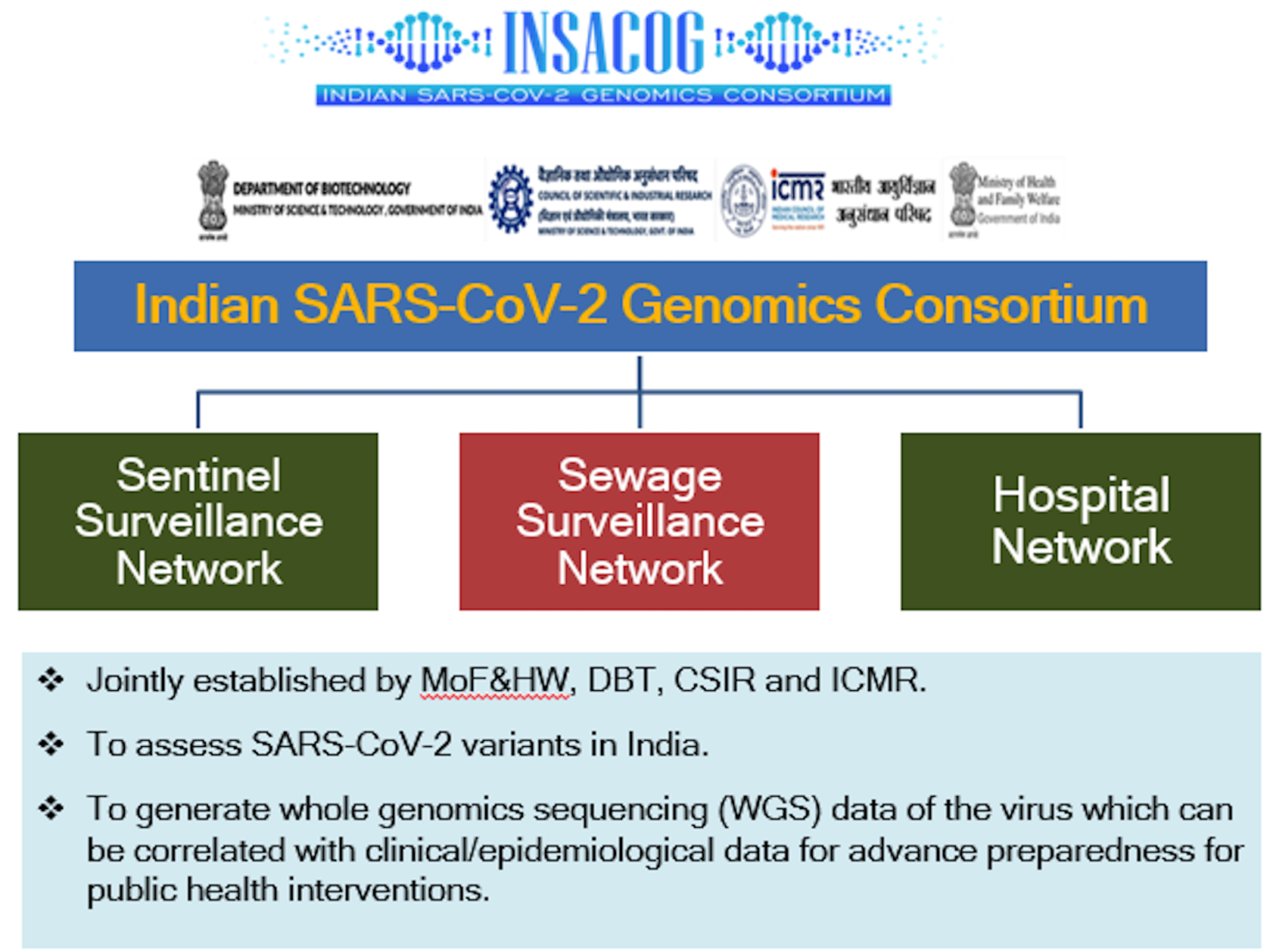
- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India reported a total of 109 JN.1 COVID variant cases in the country as of December 26, Health Ministry sources recently said.
What is Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)?
- Established in December 2020, INSACOG is a collaborative initiative involving the Union Ministry of Health, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Council for Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- The consortium's primary mission is to expand whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus responsible for Covid-19, across India.
- This initiative aims to comprehend the virus's spread and evolution.
- INSACOG initially engaged 10 national research laboratories of the central government and has grown into a network of 38 labs, including private labs, following a hub-and-spoke model.
- The consortium's Genome Sequencing Laboratories guide new laboratories, working in tandem to monitor genomic variations through sentinel sequencing facilitated by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) under the Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP) of the central government.
- Beyond sequencing efforts, INSACOG endeavors to establish a systematic correlation between genome sequencing and clinical outcomes.
- It is actively building a nationwide hospital network to investigate clinical correlations in mild versus severe cases of Covid-19.
- Additionally, the consortium is conducting a longitudinal study to comprehend long-term post-Covid complications and changes in immunity.
- Looking ahead, INSACOG is exploring sewage surveillance as an early detection tool and assessing the spread of variants in hotspot localities.
Minister Bhupendra Yadav launches NTPS, a unified system for forest goods’ transport across India (Indian Express)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The central government on Friday launched the National Transit Pass System (NTPS) to facilitate seamless transit of forest goods across the country through a single permit.
About the National Transit Pass System (NTPS):
- The National Transit Pass System (NTPS) is established to facilitate the smooth transit of timber, bamboo, and other forest produce across the country.
- Currently, transit permits are issued based on state-specific rules, leading to a fragmented system.
- The NTPS aims to implement a "One Nation-One Pass" regime, ensuring seamless transit across the entire nation.
- This initiative streamlines the issuance of timber transit permits by providing a unified online platform for tree growers and farmers engaged in agroforestry, contributing to a more business-friendly environment.
Key Features of NTPS:
- Unified Online Platform: The NTPS offers a unified, online mode for obtaining timber transit permits, simplifying the process for tree growers and farmers involved in agroforestry nationwide.
- Record Management: It manages records for both inter-state and intra-state transportation of timber, bamboo, and other forest produce from various sources, including private lands, government-owned forests, and private depots.
- QR Coded Transit Permits: The system generates QR coded transit permits, enabling check gates across states to verify the permits' validity and ensure seamless transit.
- User-Friendly Applications: NTPS provides desktop and mobile applications for easy registration and permit applications, enhancing user convenience.
- Regulated Species and Exemptions: Transit permits are issued for regulated tree species, while users can self-generate No Objection Certificates for exempted species.
- State Participation: Presently, 25 States and Union Territories have adopted the unified permit system, simplifying interstate business operations for producers, farmers, and transporters.
- Nodal Ministry: The NTPS operates under the guidance of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
