SEBI’s Sachetisation of Mutual Funds
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed the “sachetisation” of mutual fund investments to promote financial inclusion, especially among low-income and first-time investors.
What is Sachetisation?
- Originating from the FMCG sector (e.g., shampoo sachets), sachetisation refers to offering financial products in small, affordable units, enhancing accessibility and affordability.
- In capital markets, it implies micro-level investment options, particularly through low-ticket SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans).
Objectives:
- Promote financial inclusion and empower economically underserved sections.
- Expand mutual fund penetration to semi-urban and rural areas.
- Encourage long-term savings and wealth creation among new investors.
- Reduce dependency on large institutional or foreign investors by broadening the domestic retail base.
Key Features of SEBI’s Sachet SIP Proposal:
Feature Details
Minimum SIP Amount ?250 per month
Eligibility Only for new mutual fund investors
Investment Limit Up to 3 sachet SIPs across different AMCs
Excluded Schemes Debt funds, sectoral/thematic, small-cap, mid-cap equity funds (due to higher risk)
Commitment Period Encouraged to commit for 5 years (60 SIPs), but premature withdrawal allowed
Payment Modes Only via auto-pay mechanisms such as UPI Autopay and NACH
Cost Incentives AMCs to receive subsidies from SEBI’s Investor Education and Awareness Fund
Distributor Incentive ?500 per investor after completion of 24 monthly SIPs
Significance:
- Democratizes investment access by lowering the entry barrier for mutual funds.
- Encourages behavioral shift towards long-term financial planning and discipline.
- Stabilizes domestic markets by broadening and diversifying the retail investor base.
Supports SEBI’s vision of making capital markets inclusive, tech-enabled, and accessible.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES)

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launched in April 2015, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) offers subsidised interest rates on pre- and post-shipment export credit to Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs.
- The Commerce Ministry has sought a Rs 3,000 crore extension of the scheme beyond December 2024, with emphasis on supporting MSME exporters amidst global economic challenges.
Objectives of IES:
- Reduce Cost of Credit: Offers 3% to 5% interest subvention to make export credit affordable.
- Boost Export Competitiveness: Enables Indian exporters, especially MSMEs, to match international pricing.
- Encourage Export Diversification: Supports MSMEs in exploring new markets and products.
- Enhance Financial Inclusion: Promotes access to formal credit systems for small exporters.
Key Features:
- Interest Subsidy:
- 3% for MSME manufacturer exporters.
- 2% for merchant and manufacturer exporters of 410 specified tariff lines.
- Coverage: Initially limited to select products, later extended to all MSME exporters.
- Implementation:
- Managed by the RBI, in coordination with DGFT and authorized banks.
- Subsidy reimbursed to banks offering export credit at reduced rates.
- Banks exceeding Repo Rate + 4% are excluded.
Need for Extension:
- The scheme expired in December 2024, but exporters are demanding continuation due to:
- Rising global inflation and logistics disruptions (e.g., Red Sea crisis).
- Increase in credit duration demands from foreign buyers (120–150 days).
- Decline in export credit availability despite higher demand.
- FIEO reports a drop in outstanding export credit from ?2.27 lakh crore (2023) to ?2.17 lakh crore (2024).
- MSMEs operate on thin margins, and the subvention can make or break deals.
Significance for MSMEs:
- MSMEs contribute ~45% to India’s total exports and often struggle with high borrowing costs and limited financial access.
- Affordable credit via IES allows MSMEs to:
- Remain price competitive.
- Take larger and longer-term orders.
- Invest in product innovation and value addition.
- Improve market diversification and resilience.
Challenges in Accessing Credit:
- Stringent eligibility norms and collateral requirements.
- Complex administrative procedures for availing benefits.
- Limited awareness among small enterprises about the scheme.
- Slow disbursal and inconsistent application by banks.
Policy Implications and the Way Forward:
- A revamped, MSME-focused IES can ensure inclusive growth and boost India’s export-led development.
- Calls for:
- Simplification of procedural norms.
- Higher interest subvention limits or removal of caps (e.g., ?50 lakh per IEC holder).
- Longer validity (multi-year horizon) for predictability and planning.
- Aligns with the broader goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and achieving $1 trillion in exports by 2030.
QS World Future Skills Index 2025

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The QS World Future Skills Index 2025, released by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), evaluates countries' readiness to meet the evolving demands of the global job market. It assesses nations based on skill development, education, and economic transformation, highlighting their preparedness for emerging technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and sustainability.
India’s Performance in the Index:
- Overall Ranking: India is ranked 25th globally, categorizing it as a “Future Skills Contender.”
- Future of Work Category: India ranked 2nd, only behind the United States, reflecting its preparedness for AI, digital, and green jobs.
- Economic Transformation: India scored 58.3, the lowest among the top 30 countries, reflecting challenges in innovation and sustainability.
- Skills Fit: India received a score of 59.1, the weakest among the top 30 nations, indicating a gap between workforce skills and industry requirements.
- Academic Readiness: India’s education system is struggling to keep pace with employer demands, necessitating curriculum reforms and stronger academia-industry collaboration.
Key Findings from the Report:
Strengths:
- Digital Readiness: India has demonstrated strong capabilities in integrating digital talent into the workforce.
- Youth Advantage: A large, young population provides a demographic dividend for sustained economic growth.
- Startup Ecosystem: India’s startup culture and government initiatives support technological advancement and innovation.
Weaknesses:
- Higher Education-Industry Gap: Mismatch between education and employer requirements, particularly in AI, green skills, and entrepreneurship.
- Limited R&D Investment: India’s research and development spending is 0.6% of GDP, far below the global average of 2.7%.
- Low Innovation in Sustainability: India scored 15.6 out of 100, ranking poorly in future-oriented innovation for sustainability.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) estimates a 29 million skilled workforce gap in critical sectors such as healthcare, semiconductor manufacturing, and AI.
- Low Employability Rates: Only 25% of management professionals, 20% of engineers, and 10% of graduates meet global employability standards.
- Higher Education Accessibility: Many students face difficulties in accessing quality tertiary education, particularly in skill-intensive fields.
Opportunities for Growth:
- Leverage Demographic Dividend: India can capitalize on its young workforce to dominate skill-based industries while other nations struggle with aging populations.
- Policy Support:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on modular education and reskilling initiatives.
- ULLAS Program: Aims to expand lifelong learning and skill development.
- Technological Integration: Advancements in AI and digital learning can help modernize academic curricula and improve job readiness.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Enhancing Academia-Industry Collaboration: Universities should prioritize problem-solving, entrepreneurship, and creativity to align education with employer needs.
- Increasing R&D Investment: Raising spending on research and development to promote innovation and sustainability.
- Expanding Access to Education: Bridging regional disparities in tertiary education through flexible and modular learning.
- Strengthening Policy Implementation: Ensuring effective execution of skilling programs to reduce the workforce-employability gap.
Global Economic Prospects (GEP) Report 2025
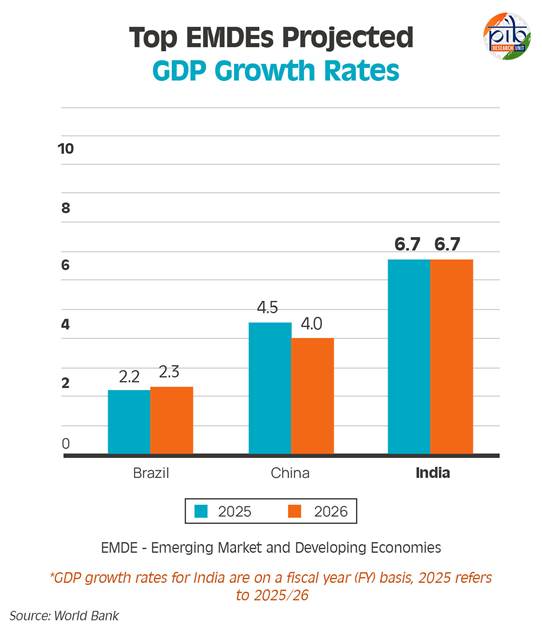
- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Bank has released its Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report for 2025, a flagship biannual publication analyzing trends and projections in the global economy, with a focus on emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). The report highlights economic growth forecasts, trade dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Outlook
- The world economy is projected to expand at a steady yet subdued rate of 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, maintaining the pace of 2024.
- Inflation, which peaked above 8% in recent years, is expected to stabilize at an average rate of 2.7% in 2025 and 2026, aligning with central bank targets.
- Despite growth, the global economy remains 0.4 percentage points below the 2010-2019 average, raising concerns about its ability to tackle poverty effectively.
Challenges and Risks
- Trade Restrictions: New trade restrictions imposed in 2024 were five times higher than the 2010-19 average, contributing to a slowdown in global trade and economic growth.
- Rising Protectionism: Increased fragmentation in global trade policies is limiting exports and hampering economic integration.
- Policy Uncertainty: Adverse policy shifts, sluggish progress in reducing inflation, and weaker performance in major economies pose downside risks to global recovery.
- Debt and Investment Concerns: Developing economies are experiencing sluggish investment growth and high debt levels, exacerbated by climate change-related costs.
Emerging Markets and Developing Economies (EMDEs)
- EMDEs have significantly evolved since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
- The three largest EMDEs—India, China, and Brazil—have accounted for approximately 60% of annual global growth over the past two decades.
- Growth in low- and middle-income developing countries is expected at 4.1% in 2025 and 4% in 2026, with a notable slowdown compared to the early 2000s.
- Low-income countries are projected to rebound to 5.7% in 2025 and 5.9% in 2026, aided by easing conflicts in some regions.
- The world's poorest nations, with annual per capita incomes below USD 1,145, recorded growth of 3.6% in 2024, impacted by conflicts in regions like Gaza and Sudan, alongside lingering effects of COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions.
India-Specific Highlights
- Fastest-Growing Major Economy: India is expected to maintain its position as the world’s fastest-growing major economy, with a projected growth rate of 6.7% in both 2025 and 2026.
- Sectoral Growth: The services sector will remain robust, while manufacturing activity is expected to strengthen.
- Investment Growth: Supported by rising private investment, improved corporate balance sheets, and favorable financing conditions, investment growth in India is expected to remain steady.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Innovation-driven initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- Expansion of the digital economy and financial inclusion efforts.
- Rural Demand and Consumption: Growth in rural demand and a recovery in farm production have bolstered consumer spending, although urban consumption remains affected by inflation and slow credit growth.
Great Nicobar Island Development Project
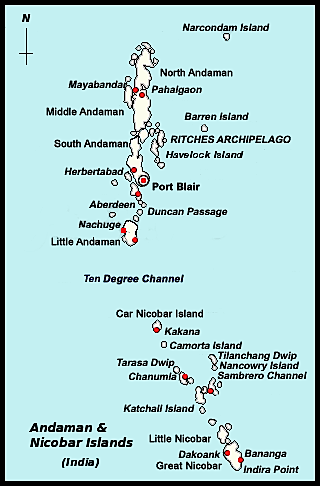
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
An international cruise terminal to facilitate a “global” port-led city, “high-end” tourism infrastructure, and a ship-breaking yard are among the new additions to the ?72,000 crore mega-infrastructure project in Great Nicobar Island proposed by the Union Shipping Ministry.
Overview of the Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island Development Project is a ?72,000-crore initiative to transform the southernmost island of India into a hub for defense, logistics, commerce, eco-tourism, and infrastructure development.
- It is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd (ANIIDCO) over 16,610 hectares of land.
- The project includes multiple components like an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), an international airport, greenfield cities, a mass rapid transport system, and a free trade zone.
Key Proposed Developments:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): To make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: To improve connectivity and serve as a strategic airport.
- Greenfield Cities: New urban settlements to support the infrastructure.
- Coastal Mass Rapid Transport System: An advanced transportation network along the coast.
- Free Trade Zone: To facilitate international trade activities.
- International Cruise Terminal (new addition): To attract global tourists and facilitate cruise tourism.
- Ship Breaking Yard (new addition): To establish a facility for ship building and breaking.
Geographical and Ecological Context:
- Great Nicobar Island is the largest island in the Nicobar group, located at the southern tip of India. It is covered in rainforests and hosts diverse species, including endangered ones like the leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode.
- The island's ecosystem is rich in biodiversity, with extensive mangroves, coral reefs, and rainforests.
Significance of the Project:
- Geo-strategic Importance: The island’s location near the Malacca Strait offers a strategic maritime advantage, enhancing India’s global maritime presence.
- National Security: With increasing Chinese influence in the region, the project aims to strengthen India's maritime security.
- Economic Growth: The ICTT and other infrastructure will boost economic activities, making the region a vital trade hub.
- Job Creation: The development will lead to numerous job opportunities for locals, especially in sectors like tourism, ports, and transport.
- Tourism Development: With eco-tourism at its core, the project is expected to generate substantial income through tourism, improving the local economy.
- Social Infrastructure: It will lead to improvements in healthcare, education, and digital services through initiatives like telemedicine and tele-education.
LEADS 2024 Report

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launch of the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report and the Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield (LEAPS) 2024 awards in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of LEADS 2024 Report:
- Evaluate logistics performance across Indian states and union territories.
- Provide actionable insights for logistics reforms to foster competitive federalism.
- Assess logistics infrastructure, services, regulatory environment, and sustainability efforts.
- Performance Evaluation:
Region Achievers Fast Movers Aspirers
Coastal States Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh, Goa Kerala, West Bengal
Landlocked States Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand
North-Eastern States Assam, Arunachal Pradesh Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura Manipur
Union Territories Chandigarh, Delhi Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Ladakh
Lakshadweep, Puducherry
- Key Remarks:
- Action Plans for Better Logistics: States should develop regional and city-level logistics plans, including for last-mile connectivity, to attract investments.
- Green Logistics: Advocate for sustainable logistics practices to ensure environmentally responsible growth.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encourage PPPs to promote multi-modal hubs and streamline logistics infrastructure.
- Technological Integration: Push for the adoption of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics to enhance efficiency in logistics operations.
- Skill Development & Gender Inclusivity: Focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development to boost sectoral growth. Promote gender diversity in logistics.
- LEAD Framework: Urge logistics sectors to embrace the LEAD framework (Longevity, Efficiency, Accessibility, Digitalisation) for transformation.
- LEAD Framework and Recommendations:
- Longevity, Efficiency, and Effectiveness: Improve long-term logistics strategies.
- Accessibility and Accountability: Ensure better reach and transparent logistics practices.
- Digitalisation: Enhance digital transformation across logistics processes.
- About LEADS:
- Full Form: Logistics Ease Across Different States.
- Launched: 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Purpose: To assess and improve logistics infrastructure and services across Indian states and UTs.
- Methodology: Based on over 7,300 responses from a pan-India survey and inputs from over 750 stakeholder consultations.
- LEAPS 2024 Awards: Recognized excellence in the logistics sector across categories such as air, rail, road, maritime freight service providers, startups, MSMEs, and educational institutions.
- PM GatiShakti Course: Launched a 15-hour online course on “PM GatiShakti Concept for Efficient Infrastructure Planning and National Development”, hosted on iGOT Karmayogi platform and UGC SWAYAM portal.
- Logistics Cost Framework Report: Unveiled a report on the logistics cost framework, aiming to accurately estimate logistics costs in India through a hybrid methodology, incorporating both EXIM and domestic cargo data.
- Significance of LEADS:
- Provides critical insights into logistics performance, helping States and UTs to improve infrastructure, services, and regulatory practices.
- Plays a key role in India's vision of becoming a $32 trillion economy by 2047 by improving logistics efficiency, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The CPPS aims to enhance pension accessibility and simplify the disbursement process for over 7.85 million pensioners in India.
- Key Benefit: Pensioners can now receive their pension from any bank or branch across India, eliminating the need for physical verifications and providing seamless nationwide pension disbursement.
Key Highlights:
- Key Features:
- No need for physical verification: Pensioners do not have to visit the bank for verification at the time of pension commencement.
- Seamless pension disbursement: Upon release, the pension amount is credited immediately.
- Nationwide access: Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank or branch, without needing to transfer Pension Payment Orders (PPO) when relocating or changing banks.
- Significance:
- Eliminates the decentralised pension system, where each regional office maintained separate agreements with a few banks.
- Ensures pension portability, especially for pensioners who move or change banks.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO):
- Overview:
- EPFO is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952, and works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Structure:
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Government (Central & State)
- Employers
- Employees
- The Central Board of Trustees is chaired by the Union Minister of Labour and Employment.
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Key Schemes Operated by EPFO:
- Employees’ Provident Funds Scheme, 1952 (EPF): A savings scheme for workers.
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (EPS): A pension scheme for employees after retirement.
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976 (EDLI): Provides life insurance coverage to workers.
- Global Coverage: EPFO is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries, offering reciprocal social security benefits to international workers from countries with such agreements.
- Impact: The EPFO schemes cover Indian workers and international workers from countries with which EPFO has signed bilateral agreements.
Key Facts:
- CPPS improves the convenience and accessibility of pension services for millions of pensioners across India by simplifying the pension disbursement process and providing nationwide access without the need for physical verifications.
- EPFO, a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, plays a crucial role in managing provident funds, pensions, and insurance schemes for both domestic and international workers, fostering social security across India.
Project VISTAAR

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
IIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources). MoU signed between the Ministry and IIT Madras to integrate information about agricultural start-ups into the VISTAAR platform.
Key Highlights:
Project Objectives:
- Digitalisation of Agricultural Extension: To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the agricultural extension system through digital platforms.
- Access to Start-Up Innovations: Provide farmers easy access to over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors, connecting them to technological solutions and innovations.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Focus on making farming more sustainable and climate-resilient by promoting adoption of innovative technologies.
Key Features of VISTAAR:
- Integration of start-up data via IIT Madras' startup information platform and its incubatee, YNOS Venture Engine.
- Advisory services covering:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- Information on government schemes for agriculture, allied sectors, and rural development.
- Real-time, contextual, and accurate information to enhance decision-making and improve farming practices.
Significance of the Project:
- The platform will expand the outreach of agricultural extension services, providing support to farmers across India.
- It will ensure farmers access high-quality advisory services that are critical for improving productivity and income.
- Integration of start-up-driven innovations will aid in the adoption of climate-resilient farming practices.
- Timely and accurate information will empower farmers to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency of agricultural processes.
Impact on Farmers:
- Digitalisation will provide farmers with easier access to expert advice and resources, enhancing productivity.
- Improved access to government schemes ensures farmers can avail themselves of financial and technical support for development.
- The project aligns with national objectives of enhancing agriculture’s contribution to India’s economy and ensuring food security.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
RBI's Report on State Finances (2024-25)

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) report titled "State Finances – A Study of Budgets of 2024-25" provides a comprehensive analysis of the fiscal position of Indian states.
Key Highlights
- States' Performance Post-Pandemic
- Improved Tax Revenue: The average tax buoyancy has increased significantly from 0.86 (2013-2020) to 1.4 (2021-2025), reflecting enhanced tax collection efficiency.
- Capital Expenditure: There is a consistent rise in capital expenditure, which increased from 2.4% of GDP in 2021-22 to 2.8% in 2023-24 and is budgeted at 3.1% in 2024-25. This indicates a growing focus on investment in infrastructure like highways and bridges.
- Fiscal Discipline and Debt Levels
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD): The gross fiscal deficit is projected at 3.2% of GDP in 2024-25, a slight increase from 2.9% in 2023-24.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: While states' debt-to-GDP ratio decreased from 31.0% in March 2021 to 28.5% in March 2024, it remains higher than the pre-pandemic level of 25.3% in 2019.
- Increased Borrowing and Debt Pressure
- Market Borrowings: States' reliance on market borrowings has increased, accounting for 79% of the GFD in FY25. Gross market borrowings surged by 32.8%, totaling Rs 10.07 trillion in FY23-24.
- Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs): Continued losses in DISCOMs, accumulating Rs 6.5 lakh crore by 2022-23 (2.4% of India's GDP), continue to strain state finances.
- Rising Subsidy Burden
- Many states are offering subsidies and loan waivers, such as farm loan waivers and free services (electricity, transport, etc.), which risk diverting funds away from critical infrastructure projects. This includes significant subsidies for income transfers to farmers, women, and youth.
- Fiscal Transparency Concerns
- Revenue Generation Issues: Revenue growth from non-tax sources and central grants is slowing. The pace of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) growth has also slowed down, which impacts overall state revenues.
- Lack of Fiscal Transparency: Inadequate reporting of off-budget liabilities obfuscates the true fiscal position, leading to a lack of clarity and accountability in state finances.
Recommendations by the RBI
- Debt Consolidation: States are encouraged to create clear and transparent debt reduction paths, with consistent reporting of off-budget liabilities to improve fiscal accountability.
- Expenditure Efficiency: Focus on outcome-based budgeting, ensuring funds are directed towards productive and sustainable investments, particularly in climate-sensitive areas.
- Subsidy Rationalization: States should contain and optimize subsidies to ensure they don't overshadow essential growth-promoting expenditure.
- Efficient Borrowings: Reduce over-reliance on market borrowings to control fiscal deficits and minimize financial risks.
- Revenue Generation: Improve collection mechanisms for SGST, strengthen non-tax revenue sources, and increase grants to reduce dependence on borrowings.
Balancing Subsidies and Fiscal Discipline
- Importance of Subsidies: Welfare programs like subsidies for healthcare, food security (e.g., Public Distribution System), and LPG connections (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana) play a crucial role in human development and economic equality by supporting vulnerable populations.
- Importance of Fiscal Discipline: Excessive welfare spending without corresponding revenue generation can lead to high deficits and public debt, threatening long-term fiscal stability. Maintaining fiscal discipline ensures sustainable public finances, promotes investor confidence, and supports economic growth.
Green fixed deposits

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
Green fixed deposits (FDs) are a type of investment scheme offered by banks and financial companies, aimed at environmentally-conscious investors. They function similarly to traditional fixed deposits, where funds are locked in with a bank for a fixed tenure. The primary distinction between green and regular deposits lies in the allocation of funds. While regular deposits are pooled into a common fund, the funds from green deposits are exclusively allocated to projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Green Fixed Deposits:
- Investment Purpose: The funds raised through green FDs are directed towards environmentally beneficial projects, such as renewable energy initiatives (solar and wind power), clean technology, organic farming, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Eligibility: Green deposits are available to various entities, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), societies, clubs, non-profit organizations, and sole proprietorships.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on green deposits may or may not differ from regular deposits, depending on the policies set by the lending institution. Some banks and financial institutions, like IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank, DBS Bank India, and HDFC Ltd., offer green deposits, with Bank of Baroda recently launching the BOB Earth Green Term Deposit with an interest rate of up to 7.15% per annum.
- Safety: Like regular fixed deposits, green deposits are insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) under the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961, ensuring the safety of the investment.
- Overdraft Facility: Banks may offer overdraft facilities against green deposits, providing more flexibility to investors.
- Premature Withdrawal: If the investor chooses to withdraw the deposit before the agreed tenure (after six months), the green FD will be converted into a regular fixed deposit.
- Denomination: Green deposits are denominated in Indian Rupees only.
Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program

- 21 Dec 2024
On December 20, 2024, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $350 million policy-based loan aimed at expanding India's manufacturing sector and improving the resilience of its supply chains. This loan is part of the Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program.
Key Points:
- Loan Agreement Signatories:
- Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance, Government of India
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- SMILE Program:
- Goal: Strengthen the logistics ecosystem to enhance India's manufacturing sector and improve supply chain resilience.
- Structure: The program includes two subprograms focusing on strategic reforms in logistics and infrastructure development.
- Key Features of the SMILE Program:
- Strengthening Multimodal Infrastructure: Enhances logistics infrastructure at the national, state, and city levels.
- Standardization: Improves warehousing and other logistics assets to attract private sector investment.
- External Trade Logistics: Enhances efficiencies in external trade logistics.
- Smart Systems: Adopts systems for efficient, low-emission logistics to promote sustainability.
- Expected Outcomes:
- Cost Reduction & Efficiency: Strategic reforms will reduce logistics costs and improve efficiency.
- Job Creation: Infrastructure development and reforms are expected to generate substantial employment opportunities.
- Gender Inclusion: The program promotes gender inclusion through economic growth initiatives.
- Impact on India’s Economy:
- The transformation of India’s logistics sector will enhance the competitiveness of the manufacturing sector and drive sustainable economic growth.
About the Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- Established: December 19, 1966.
- Members: 69 countries, including both regional (e.g., India, China) and non-regional (e.g., USA, Japan) members.
- Function: ADB promotes social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific, providing loans, grants, and technical assistance for development projects.
- Key Shareholders:
- Japan: 15.57%
- USA: 15.57%
- India: 6.32%
- China: 6.43%
- Australia: 5.77%
Specialised Investment Fund (SIF)
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
SEBI has introduced a new asset class called Specialised Investment Fund (SIF), designed to bridge the gap between Mutual Funds (MFs) and Portfolio Management Services (PMS). This new asset class is targeted at informed investors who are willing to take on higher risks.
SIFs offer a blend of the flexibility seen in PMS and the regulatory framework governing MFs, making them suitable for investors seeking more customized and riskier investment strategies.
Key Features of SIF:
- Minimum Investment: The minimum investment threshold for SIFs is Rs. 10 lakh. However, accredited investors (who meet specific eligibility criteria) can invest with lower amounts.
- Expense Structure: SIFs will follow the same expense structure as mutual funds. For equity schemes up to Rs 500 crore in size, the maximum allowable fee is 2.25% of assets under management (AUM), with the cap decreasing as the fund size grows. This ensures transparency and keeps management fees in line with existing mutual fund norms.
- Investment Strategies: SIFs can offer a mix of open-ended, close-ended, and interval investment strategies. Specific details on permissible strategies will be released by SEBI in the future.
- Investment Restrictions:
- For debt instruments, a single issuer's exposure is capped at 20% of the total AUM. However, this can be raised to 25% with approval from the Asset Management Company (AMC)’s trustees and board of directors. Government securities are exempt from this limit.
- For equities, the exposure is capped at 10% of the total AUM, in line with the norms for mutual funds.
- Ownership in Companies: The maximum permissible ownership in any company is raised to 15%, including the MF exposure.
- REITs and InvITs: SIFs can invest a maximum of 20% of their AUM in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). However, the exposure to a single issuer in these areas is limited to 10%.
- Branding and Marketing: SEBI mandates AMCs to distinguish SIFs clearly from MFs through distinct branding, advertising, and website presence. This helps in creating a clear differentiation between the two products for investors.
- Risk Management and Compliance: AMCs managing SIFs are required to have robust risk management systems, internal control systems, and expertise to handle the investments effectively. Trustees are responsible for ensuring that the AMC complies with all risk management, investor protection, and disclosure norms.
Regulatory Context:
- The regulations on SIFs are similar to those governing mutual funds, including taxation and other compliance requirements.
- SEBI also introduced the Mutual Fund Lite regulations to encourage the growth of passively managed funds, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds. These regulations are designed to reduce compliance burdens and lower the barriers to entry for new players in the mutual fund industry.
Significance of SIFs:
- Targeted Audience: SIFs cater to investors who are knowledgeable and willing to take on riskier investments, thereby filling a gap between traditional MFs (which are more conservative) and PMS (which offer highly customized solutions).
- Higher Flexibility: While SIFs maintain some regulations of MFs, they offer more flexibility in investment choices, allowing AMCs to explore more dynamic strategies.
- Investor Protection: By maintaining the same expense structure as mutual funds and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks, SEBI aims to protect investor interests while allowing for higher returns that come with riskier investments.
India Maritime Heritage Conclave 2024

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The 1st India Maritime Heritage Conclave (IMHC 2024), a landmark event organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) was recently held.
Key Highlights:
Event Overview:
- Organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), held on December 11-12, 2024.
- Theme: "Towards Understanding India's Position in Global Maritime History."
- Celebrated India’s maritime legacy and future vision as a maritime powerhouse.
India’s Maritime Heritage:
- Deeply rooted in ancient traditions; references in Rig Veda, mythology, literature, and archaeology.
- Modern India boasts a 7,500 km coastline, 13 major ports, 200 non-major ports, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Ports handle 1,200 million tonnes of cargo annually, vital for economic growth.
Key Features of IMHC 2024:
- International Participation: Dignitaries from 11 countries, including Greece, Italy, UK.
- Exhibition: Showcased ancient shipbuilding techniques, navigation systems, historical trade routes.
- Cultural Program: Celebrated coastal traditions with performances and festivities.
- Key Focus: Sustainable maritime innovation, skill development, youth engagement, and cultural preservation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC):
- Location: Lothal, Gujarat – an ancient Harappan site (2600 BCE).
- Significance: Home to the world’s oldest dry-dock (2400 BCE).
- Future Vision: NMHC to showcase maritime history with 14 galleries, open aquatic gallery, lighthouses, and a research institute.
Modern Maritime Significance:
- India’s Global Maritime Ranking: 16th largest globally, 3rd largest in ship recycling.
- Trade Backbone: 95% of India's trade by volume, 70% by value handled by maritime sector.
- Port Performance: India ranks 22nd in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2023).
Future Maritime Vision:
- Sustainable Blue Economy: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, green shipping, and maritime tourism.
- Skill Development: Training programs to empower local communities and boost maritime workforce.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading ports and shipping infrastructure under the Sagar Mala Program.
- Policy Framework: Integrated policies for maritime heritage preservation and economic development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Focus on increasing maritime capacity and sustainability.
- SAGAR: Security and Growth for All in the Region initiative.
- Ship Repair & Recycling Mission: Promote India as a global leader in ship recycling.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: Development of eco-friendly maritime infrastructure.
Oilfields Amendment Bill, 2024

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
To encourage domestic production of petroleum and other mineral oils, along with private investment in these sectors to reduce import dependence, the Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
Key Details:
- Objective:
- Encourage domestic petroleum production.
- Reduce import dependence by promoting private investment in the oil sector.
- Key Amendments:
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- The Bill separates petroleum and mineral oil production from mining activities.
- The Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948, is amended to focus on mineral oils, distinct from the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Expanded Definition of Mineral Oils:
- Includes hydrocarbons in various forms (natural gas, crude oil, petroleum, coal bed methane, and shale gas/oil).
- Excludes coal, lignite, and helium from the definition (falling under the Mines and Minerals Act).
- Petroleum Lease:
- Replaces the term "mining lease" with "petroleum lease."
- Covers activities such as exploration, development, production, and transportation of mineral oils.
- Private Investment:
- Provisions to attract private investment by clarifying rules for petroleum leases.
- Current mining leases remain valid without altering terms to the lessee's disadvantage.
- Decriminalization and Penalties:
- Replaces criminal punishment with financial penalties.
- Fines can go up to Rs. 25 Lakh, with additional penalties for ongoing violations.
- Rule-making Power of Central Government:
- Expands the Centre's authority over petroleum lease regulations, conservation, royalties, mergers, facility sharing, environmental protection, and dispute resolution.
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- Significance of the Bill:
- Energy Access and Security: Ensures energy security by boosting domestic production.
- Attracting Investment: Creates a conducive environment for private sector investment.
- Environmental Safeguards: Provisions to control carbon emissions and promote renewable energy in oilfields.
- Opposition Criticism:
- State Rights on Mining: Concerns raised by opposition parties, particularly the DMK, about the reduction of state control over resource taxation (taxing mineral rights).
- Impact on Federal Balance: States traditionally manage mining rights under the Constitution’s State List (Entry 50). The Bill may shift control to the Union List (Entry 53), creating constitutional concerns.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Opposition figures like P.P. Suneer (CPI) argue for prioritizing public companies like ONGC, fearing privatization may worsen environmental governance.
- Adjudication of Disputes:
- Appeals against penalty decisions will be handled by the Appellate Tribunal, as per the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Broader Significance:
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on fuel imports, fostering energy security and economic stability.
- Regulation: Strengthens the enforcement mechanism for petroleum operations while encouraging private participation.
Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB):
- Formation: Established under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Functions: Regulates refining, transportation, distribution, storage, marketing, and sale of petroleum products and natural gas.
- Role in the Bill: Ensures competitive markets for gas and handles appeals regarding regulatory decisions.
India’s Semiconductor Market Projected to Surpass $100 Billion by 2030
- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
India's semiconductor market is poised to exceed $100 billion by 2030, according to a report from the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association and Counterpoint Research. Currently valued at $45 billion in 2023, the market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 13%, driven by demand in mobile handsets and IT sectors, which together account for over 75% of revenues.
Key Highlights:
- Growth Drivers: The growth is supported by strong demand for electronics and government initiatives like the production-linked incentive scheme. Semiconductors are essential for various industries, including electronics, defense, healthcare, and automotive.
- Importance of Semiconductors: These materials, which include silicon and germanium, are crucial for electronic devices. They can conduct electricity under certain conditions, making them fundamental in transistors, integrated circuits, and devices like LEDs and solar cells.
- Global Context: The global semiconductor supply chain has shown vulnerabilities, particularly during the chip shortage of 2021. Major producers include Taiwan (44% market share), China (28%), South Korea (12%), the U.S. (6%), and Japan (2%). Countries are now focusing on building domestic chip industries to reduce dependency on a few key suppliers.
Factors Favoring India's Growth in Semiconductors:
- Skilled Workforce: India has a vast pool of STEM graduates, providing a skilled workforce for semiconductor manufacturing and design.
- Cost Advantage: Lower labor costs and efficient supply chains position India favorably for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Diversification: India is becoming a hub for back-end assembly and testing operations, with potential for front-end manufacturing.
- Government Support: Initiatives like Semicon India and the India Semiconductor Mission aim to create a robust semiconductor ecosystem, offering substantial fiscal incentives for companies.
Government Initiatives:
- Semiconductor Fab Scheme: Provides 50% project cost support for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Display Fab Scheme: Offers similar support for display manufacturing.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: Trains 85,000 engineers across academic and R&D institutions.
- Recent approvals for the establishment of semiconductor plants in Gujarat and Assam further bolster this initiative.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Prime Minister commended the completion of three years of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, calling it a transformative initiative for India’s infrastructure development.
- Key Benefits: The plan enhances multimodal connectivity and improves efficiency across various sectors, contributing to logistics, job creation, and innovation.
Overview of PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Launch Date: October 2021
- Objective: A transformative initiative worth ?100 lakh crore aimed at revolutionizing India’s infrastructure over five years.
- Development Tool: Created as a Digital Master Planning tool by the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
- GIS Platform: Utilizes a dynamic Geographic Information System to integrate action plans from various ministries into a comprehensive database.
- Goals: Accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by addressing inter-ministerial challenges.
Key Features
- Digital Integration: A digital platform coordinating the efforts of 16 ministries for seamless infrastructure planning.
- Multi-Sector Collaboration: Incorporates initiatives from major programs like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
- Economic Zones Development: Focuses on key areas such as textile clusters and pharmaceutical hubs to boost productivity.
- Technology Utilization: Employs advanced spatial planning tools and ISRO satellite imagery for data-driven project management.
Core Sectors Driving the Plan
- The National Master Plan is centered around seven primary sectors that enhance economic growth and connectivity, supported by sectors like energy transmission and social infrastructure.
Six Pillars of PM GatiShakti
- Comprehensiveness: Integrates various initiatives through a centralized portal, ensuring efficient planning.
- Prioritisation: Allows ministries to prioritize projects based on national importance and resource allocation.
- Optimisation: Identifies infrastructure gaps and selects the most efficient transportation routes.
- Synchronisation: Ensures coordinated efforts across ministries to avoid delays.
- Analytical Capabilities: Offers extensive data layers for improved spatial planning and decision-making.
- Dynamic Monitoring: Uses satellite imagery for real-time project tracking and adjustments.
Achievements of PM GatiShakti
- District-Level Expansion: Extended to 27 aspirational districts, with plans for 750 in the near future.
- Technological Integration: Enhanced real-time infrastructure planning using geospatial tools.
- Global Outreach: The GatiShakti tool showcased to 30 countries and highlighted at international conferences.
- Social Sector Benefits: Identified areas for new healthcare facilities and improved planning in various districts.
- Rural and Urban Development: Implemented projects for irrigation and city logistics in multiple states.
- Employment Initiatives: Utilized for setting up training institutes near industrial clusters.
India's BRAP 2024 Alignment with World Bank's B-READY Index

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian government plans to align indicators of the BRAP 2024 index with the World Bank’s B-READY index to enhance business readiness rankings.
- State Involvement: States have been instructed to address gaps identified in the B-READY evaluations to improve their global rankings.
- Indicators Included: The upcoming 2024 BRAP rankings, prepared by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, will incorporate specific indicators from the B-READY index.
- Enterprise Survey Launch: An enterprise survey for the B-READY index in India is set to start in October, with support from the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- Participation Timeline: Although B-READY rankings will commence in 2024, India’s participation will begin in 2026. The initial rankings will cover 54 countries, expanding to 120 in 2025 and 180 in 2026.
- Successor to Previous Rankings: The B-READY index replaces the Ease of Doing Business rankings, which were discontinued in 2021 due to irregularities. It considers a broader range of factors in its assessments.
- Benchmark for Global Institutions: The B-READY framework will serve as a benchmark for global financial institutions and multinational companies to evaluate a country’s regulatory and policy environment.
- Historical Improvement: India improved its Ease of Doing Business ranking from 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2020.
- Technical Understanding: A team of government officials is tasked with understanding the technical aspects of the B-READY index to formulate strategies for improving India’s score.
- Lifecycle Parameters: The new index tracks ten parameters throughout a firm's lifecycle, including business entry, utility services, and labor, focusing on real-world applications rather than just legal changes.
- Recent BRAP Rankings: The BRAP 2022 rankings were recently announced, with Andhra Pradesh and Kerala achieving the top positions.
Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
INDIA TO SUPPORT TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO IN DEVELOPING UPI-LIKE PAYMENT SYSTEM
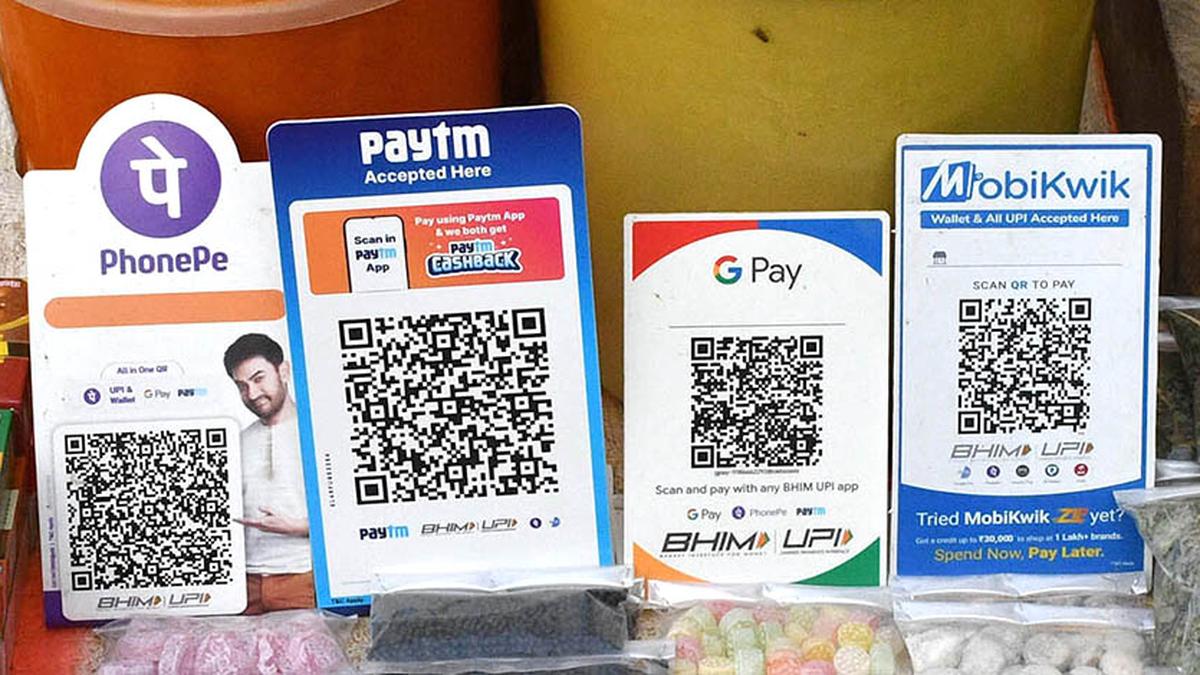

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- NPCI International Payments Limited (NIPL) has partnered with Trinidad and Tobago's Ministry of Digital Transformation to create a payment platform for person-to-person and person-to-merchant transactions.
- Modeling on UPI: The new digital payments system will be based on India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which is widely recognized as a leading digital payment solution.
- Role of NPCI: NIPL, a quasi-government body under the Reserve Bank of India, manages India’s retail payment systems, including UPI.
Previous Initiatives
- Global Expansion: Earlier in 2024, NIPL also committed to establishing digital payment systems in Peru and Namibia, leveraging the UPI model.
- Ongoing Talks: NIPL is exploring opportunities with additional countries in Africa and South America to assist in building their payment infrastructures.
Significance:
- UPI has emerged as a transformative force in India's financial landscape, registering nearly 15 billion transactions in August 2024, with an estimated value of USD 245 billion.
- This strategic partnership aims to empower Trinidad and Tobago to establish a reliable and efficient real-time payments platform for both person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions, expanding digital payments in the country and fostering financial inclusion.
10 YEARS OF MAKE IN INDIA

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The “Make in India” initiative has completed 10 years. It was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on September 25, 2014.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The ‘Make in India’ campaign aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best in class manufacturing infrastructure.
- “Make in India” was designed to transform India into a global hub for design and manufacturing.
- Seen as an important ‘Vocal for Local’ initiative, its objective is twofold. Firstly, to boost India’s manufacturing capabilities and secondly to showcase its industrial potential on a global stage.
- The “Make in India 2.0” phase encompassing 27 sectors – both manufacturing and service.
4 pillars of “Make in India” initiative:
- New Processes: To enhance the business environment, promote entrepreneurship and startups – ‘ease of doing business’ became a crucial factor.
- New Infrastructure: Development of industrial corridors, smart cities, integrating state-of-the-art technology and high-speed communication to create world-class infrastructure, improving intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure etc.
- New Sectors: Opening of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in sectors like Defence Production, Insurance, Medical Devices, Construction, and Railway infrastructure.
- New Mindset: In order to support industrial growth and innovation – the government embraced a role as a facilitator rather than a regulator. The Government partners with industry in the economic development of the country.
Key Initiatives to enable Make in India initiative
Production linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: The primary goals of the PLI Schemes are to attract substantial investments, incorporate advanced technology, and ensure operational efficiency. These schemes cover 14 key sectors aimed at fostering investment in cutting-edge technology and promoting global competitiveness.
PM GatiShakti: It is a strategic initiative aimed at achieving Aatmanirbhar Bharat and a US $5 trillion economy by 2025 through the creation of multimodal and last-mile connectivity infrastructure. PM GatiShakti is a transformative approach for economic growth and sustainable development. The approach is driven by 7 engines, namely:
- Railways
- Roads
- Ports
- Waterways
- Airports
- Mass Transport
- Logistics Infrastructure
Semiconductor Ecosystem Development: It encompasses four key schemes:
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Semiconductor Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Display Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, Sensors Fabs, and Discrete Semiconductors, along with Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP) / OSAT Facilities in India
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
It aims to foster the development of a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
The Semicon India Programme aims to provide a significant impetus to semiconductor and display manufacturing by facilitating capital support and promoting technological collaborations.
National Logistics Policy: Introduced to complement the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan. It focusses on enhancing the soft infrastructure of India’s logistics sector.
The Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) was rolled out. The key areas which it addresses are logistics systems, standardization, human resource development, state engagement, and logistics parks.
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme: Aims to create “Smart Cities” and advanced industrial hubs.
Startup India: Several programs aimed at supporting entrepreneurs, building a robust startup ecosystem, and transforming India into a country of job creators instead of job seekers were rolled out.
Implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST): As India’s tax reforms, it is seen as crucial in the context of the Make in India initiative.
Unified Payments Interface: For India’s digital economy growth, it is seen as one of the key initiatives to enable ease of doing business.
Ease of Doing Business: The efforts aim to simplify regulations, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and create a more business-friendly environment, significantly boosting investor confidence and supporting the objectives of the Make in India initiative.
PM Modi Inaugurates 'Sudarshan Setu', India's Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge
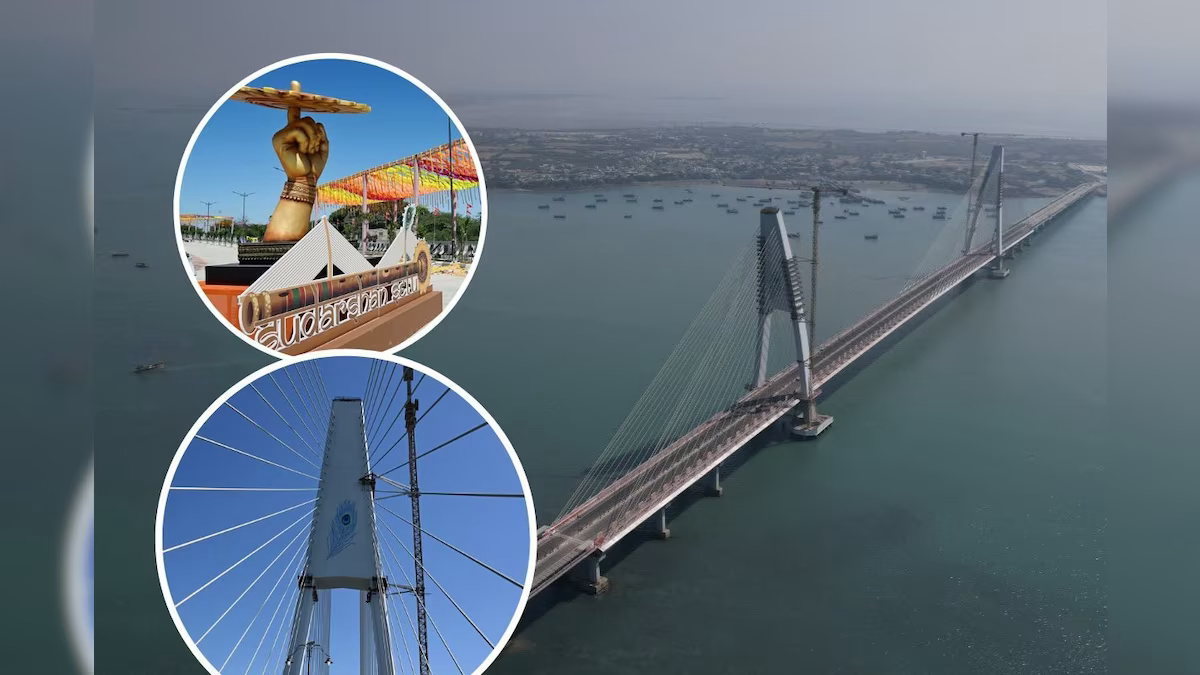

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently inaugurated the Sudarshan Setu, a four-lane cable-stayed bridge connecting Okha to Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
About the Sudarshan Setu:
- 'Sudarshan Setu' is the country's longest cable-stayed bridge 2.32 km on the Arabian Sea connecting Beyt Dwarka island to mainland Okha in Gujarat's Devbhumi Dwarka district.
- It boasts a unique design, featuring a footpath adorned with verses from the Bhagavad Gita and images of Lord Krishna on both sides.
- It also has solar panels installed on the upper portions of the footpath, generating one megawatt of electricity.
- The 2.32 km bridge, including 900 metres of a central double-span cable-stayed portion and a 2.45 km long approach road, has been constructed at a cost of Rs 979 crore.
About Beyt Dwarka:
- Bet/Beyt (pronounced ‘Bait’ Dwarka also known as Shankhodara, is an island located near the shores of Okha which is situated around 30 km from Dwarka, in the Gulf of Kutch.
- It said that Lord Krishna resided here while Dwarka was his constitutional seat.
History:
- Bet Dwarka derived its name from the word ‘bet’ which translates to ‘gift’ and is believed that Lord Krishna received it from his friend Sudama.
- In the ancient epic, Mahabharata, Bet Dwarka is known by the name of ‘Antardvipa’ to which people of the Yadava clan needed to travel by boat.
- Explorations and excavations carried out under the sea have revealed the presence of settlements whose age can be traced back to the era of the Harappan civilisation and that of the Mauryan rule.
- In the later years, the region was under the administration of the Gaekwad clan of the state of Baroda.
- During the revolt of 1857, Vaghers attacked the region and captured it, but had to concede defeat in two years and return the region back to the Gaekwads.
Unauthorised online lending apps high on the FSDC scanner

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fresh measures to curb unauthorised online lending apps’ operations could be on the anvil, following deliberations on the issue at the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently.
About the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC):
- The Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) is a high-level body established by the Government of India in 2010 to address macroeconomic and financial stability issues.
- Although not a statutory body, it operates under the Financial Stability Division of the Department of Economic Affairs within the Ministry of Finance.
Background:
- In response to the global financial crisis of 2008, recommendations were made by the Raghuram Rajan Committee for the creation of a centralised regulatory body to oversee India's financial system.
- The establishment of FSDC reflects India's proactive approach to enhance preparedness for future financial challenges.
Composition:
- Chaired by the Union Finance Minister, the council comprises key stakeholders including the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), finance and economic affairs officials, regulatory body chairpersons, and other relevant authorities.
- The Secretary of the Department of Economic Affairs serves as the council's secretary.
Responsibilities:
- FSDC is entrusted with the task of promoting financial stability, coordinating policy responses to systemic risks, and fostering the development of India's financial sector.
Concerns and Future Directions:
- Concerns have been raised about potential encroachment on the autonomy of sectoral regulators due to FSDC's leadership by the Union Finance Minister.
- To address this, it's crucial to safeguard the independence of regulatory bodies and establish clear guidelines to ensure effective coordination without undermining regulatory authority.
What is Digital Lending?
- Digital lending refers to the process of accessing credit online, facilitated through web platforms or mobile applications.
- This approach leverages technology across various stages of the lending process, including customer acquisition, credit assessment, approval, fund disbursement, recovery, and customer service.
Key Features:
- Utilises technology for end-to-end lending operations, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
- Offers flexibility in credit options and facilitates swift transactions, appealing to modern borrowers.
- Prominent examples include Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) schemes, which provide short-term financing for purchases, allowing consumers to defer immediate payments.
Drivers of Growth:
- Increased adoption is driven by widespread smartphone usage and the convenience of online transactions.
- Flexibility in credit offerings and simplified application processes contribute to the popularity of digital lending platforms.
- BNPL services, in particular, cater to consumers seeking deferred payment options for purchases and services.
Centre increases Fair and Remunerative Prices of sugarcane

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs recently approved ?340/quintal as the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for the sugar season 2024-25 at a sugar recovery rate of 10.25%.
What is the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)?
- FRP was introduced by the government in 2009 by an amendment to the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966.
- It replaced the Statutory Minimum Price (SMP) on the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) consultation.
- The FRP system assured timely payment to farmers, irrespective of the profit and loss to sugar mills.
- Further, the new system made it mandatory for sugar mills to pay the farmers within 14 days of delivery of sugarcane.
- Additionally, the FRP system introduced grading on the basis of sugar recovery rate from sugarcane wherein a premium was paid to the farmer on higher recovery and a reduction in rates on lower recovery.
- The FRP is based on the Rangarajan Committee report on reorganising the sugarcane industry.
Factors Considered for Announcing FRP:
-
- Cost of production of sugarcane
- Return to the growers from alternative crops and the general trend of prices of agricultural commodities
- Availability of sugar to consumers at a fair price
- The price at which sugar produced from sugarcane is sold by sugar producers
- Recovery of sugar from sugarcane
- The realisation made from the sale of by-products viz. molasses, bagasse and press mud or their imputed value
- Reasonable margins for the growers of sugarcane on account of risk and profits
Effect of the New FRP:
- Sugar production in India was hit hard in the October-December 2023 quarter as production fell by 11.21 million metric tonnes;
- It was 12 million in the same quarter the previous year.
- The increase in FRP is going to increase the cost for producers.
- The increased FRP will benefit over five crore sugarcane farmers in the country, however, the increase in production cost could affect end-consumers as well.
- Factors such as FRP hikes, akin to MSP, make it attractive to farmers but also increase prices in the local market as mills pass on that cost to consumers
