Lenacapavir
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Wednesday approved Lenacapavir (LEN), the most promising HIV prevention medicine to be made so far.
What is Lenacapavir (LEN)?
- Type: Antiretroviral drug used as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV prevention.
- Mechanism: Prevents HIV infection in HIV-negative individuals at high risk.
- Efficacy: Clinical trials show it prevents 99.9% of HIV transmissions.
- Dosage: Injectable form, administered twice a year.
Recent Development
- Approved by: United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) – June 2025.
- Brand name: To be marketed as Yeztugo by Gilead Sciences.
- Described as the most promising HIV prevention drug to date.
Global and Indian Context
Global Need
- LEN could be a game-changer in ending the global HIV/AIDS epidemic.
- However, cost remains a barrier—initially priced at over $40,000 per person/year, now reduced to $28,218.
Indian Reality
- Despite India's 92% contribution to global ART supply, PrEP is yet to be rolled out under India’s National AIDS Control Programme (NACP).
- The National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) has not yet integrated PrEP or LEN into national policy.
India’s Role in Equitable Access
Expert View:
- India must take the lead in making LEN accessible, affordable, and timely.
- Equitable distribution is critical to preventing new infections and achieving AIDS elimination targets.
- Urges Indian regulators and generic companies to fast-track licensing and manufacturing.
Why this matter?
Public Health Impact
- LEN could stop HIV transmission at scale if made widely available in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- Its twice-a-year injectable nature increases adherence, especially in vulnerable populations.
Cost Savings
- Prevention through PrEP like LEN is more cost-effective than providing lifelong ART after infection.
India’s Strategic Position
- India already serves as the global hub for HIV treatment through its generic pharmaceutical capacity.
- India’s leadership is central to global HIV prevention strategies including:
- Treatment as Prevention (TasP)
- Test and Treat
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
Policy Recommendations
- Fast-track regulatory approvals for generic LEN in India.
- Integrate PrEP and injectable LEN into NACO guidelines.
- Ensure price transparency and accessibility through public-private collaboration.
- Collaborate with global health bodies (WHO, UNAIDS, Global Fund) to position India as the equitable access leader.
Libia Lobo Sardesai

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, at the age of 100, Libia Lobo Sardesai was awarded the Padma Shri for her pivotal role in Goa’s liberation struggle from Portuguese colonial rule.
About Libia Lobo Sardesai
- Born: 25 May 1924, in Portuguese-ruled Goa; raised in Mumbai.
- Profession: Freedom fighter, broadcaster, and Goa’s first Director of Tourism post-liberation.
- Legacy: Symbol of courage and resistance, known as the “voice of Goa’s liberation.”
Role in Goa’s Liberation Movement
- Involvement: Joined the Goan nationalist movement during her college years.
- Underground Radio:
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Goenche Sodvonecho Awaz (Voice of Freedom of Goa) – Konkani
- Voz de Liberdade – Portuguese
- Operated from Amboli (Maharashtra) and Castle Rock (Karnataka) in the Western Ghats.
- Purpose: Counter Portuguese censorship and propaganda; broadcast news, updates, and morale-boosting messages to Goans.
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Final Broadcast:
- On 19 December 1961, Libia flew over Panaji in an IAF plane, announcing Goa’s liberation with the message:
“Rejoice brothers and sisters, Rejoice! Today, after 451 years of alien rule, Goa is free and united with the Motherland.”
Goa Liberation Movement: Background
- Colonial Rule: Goa was under Portuguese rule for over 451 years (from 1510 to 1961).
- Key Phases:
- 1954: India imposed an economic blockade after Portuguese crackdown on satyagrahis.
- August 1955: Mass satyagraha met with violent repression by Portuguese forces.
- Censorship: Portuguese regime enforced total censorship; only official Portuguese narratives were allowed.
- 1961 – Operation Vijay:
- Initiated on 17 December 1961 by the Indian Army under Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri.
- Portuguese forces surrendered by 19 December 1961, marking Goa’s official liberation.
Notable Leaders of the Movement
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia: Sparked initial resistance against Portuguese rule.
- Libia Lobo Sardesai: Voice of the resistance via underground broadcasting.
- Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri: Led military operations during Operation Vijay.
Significance
- Libia Lobo Sardesai represents the unsung contributions of civil resistance and communication warfare in India’s decolonization.
- Her work sustained nationalist morale, informed citizens under censorship, and shaped the narrative of a liberated Goa.
Aero India 2025
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of India’s premier aerospace and defence exhibition, is scheduled from February 10–14, 2025, at the Yelahanka Air Force Station, Bengaluru.
Organised by the Ministry of Defence and the Defence Exhibition Organisation (DEO), the event continues to be a vital forum for promoting India's indigenous defence capabilities and fostering international collaboration.
Evolution of Aero India: From Showcase to Strategic Asset
- Inception (1996): Launched as a modest exhibition to attract foreign investments and highlight India’s aerospace potential.
- Growth Phase (2005–2015): Marked by the entry of global giants like Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, and Dassault Aviation. Indigenous platforms like LCA Tejas began gaining prominence.
- Current Phase (2015–Present): Aligned with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’, Aero India has become a symbol of India's defence self-reliance and a magnet for global partnerships.
Aero India 2025 Highlights
1. International Participation and Strategic Displays
- Participation from 15+ countries and major OEMs.
- Russia’s Su-57 and USA’s F-35—two of the world’s most advanced 5th-generation fighters—will be showcased together, reflecting India’s growing strategic importance.
- Other prominent platforms: KC-135 Stratotanker, Embraer C-390, and Light Combat Helicopter Prachand.
2. Indigenous Innovation
- Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA): India’s 5th-generation stealth fighter, developed by HAL and ADA, will be unveiled.
- Indigenous platforms like LCA Mk2, LUH, HTT-40, ALH, and Naval Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter will also be featured.
3. Start-Up Integration via 'Manthan'
- Through the iDEX initiative, Aero India is promoting start-ups working in AI, unmanned systems, cybersecurity, and electronic warfare.
- Start-ups will showcase innovations including jetpack suits, robotics, and defence software tools.
4. Business & Public Engagement
- Business Days: February 10–12, 2025
- Public Days: February 13–14, 2025
- Over 7 lakh visitors expected; the event offers aerial displays, seminars, tech expos, and networking forums.
5. Defence Diplomacy and Deals
- Aero India 2023 had seen over ?80,000 crore worth of MoUs. A similar or higher scale of defence agreements is expected in 2025.
- High-level participation from defence ministers, air chiefs, and CEOs of OEMs, signalling deepening international defence cooperation.
Strategic Significance for India
- Geopolitical Leverage: Participation of both US and Russian defence firms signals India’s strategic autonomy and balanced defence diplomacy.
- Self-Reliance Boost: The event enhances domestic manufacturing by integrating MSMEs, promoting co-development and co-production with foreign partners.
- Global Recognition: Positions India as an emerging aerospace hub in the Indo-Pacific.
- Technological Edge: Demonstrates advancements in stealth technology, avionics, and unmanned systems.
Theme of Aero India 2025: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities” — highlighting India’s expanding defence manufacturing capabilities and its aim to integrate with the global supply chain.
Whip System in Indian Parliament

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar recently criticized the party whip system, arguing that it curtails the freedom of expression of Members of Parliament (MPs) and enforces servility by mandating strict adherence to the party line. His remarks have sparked a renewed debate on the balance between party discipline and individual autonomy in a parliamentary democracy.
What is a Party Whip?
A whip in parliamentary parlance is both a directive and a designated official of a political party. The directive instructs legislators on voting behavior on specific issues such as bills, motions, or resolutions. The designated whip ensures attendance, adherence, and discipline within the party ranks.
- The term “whip” originated from England’s hunting tradition, where a “whipper-in” kept hounds within the pack.
- The political usage dates back to Edmund Burke in the British Parliament.
- In India, the whip system has been in place since the start of parliamentary governance.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- The whip system is not mentioned in the Constitution, Rules of Procedure, or any statute, but functions through parliamentary conventions.
- The Anti-Defection Law (52nd Amendment, 1985) enforces the whip by allowing disqualification of MPs/MLAs for defying it, thus preserving political stability and party integrity.
Quorum Requirement: As per Article 100 of the Constitution, quorum in Parliament is one-tenth of the total membership:
- Lok Sabha: 55 members
- Rajya Sabha: 25 members
Types of Whips
- One-Line Whip: Informational—members may abstain.
- Two-Line Whip: Requires presence but does not dictate voting.
- Three-Line Whip: Strictest—mandates attendance and voting as directed.
- Violation can lead to disqualification under the Anti-Defection Law, unless two-thirds of the party members dissent together.
Functions and Significance
- Ensures Attendance: Maintains quorum during critical votes.
- Secures Support: Helps pass or oppose legislation.
- Maintains Discipline: Prevents cross-voting or defection.
- Internal Monitoring: Identifies discontent among MPs and informs party leadership.
- Party Cohesion: Acts as a channel between MPs and party high command.
- Democratic Functioning: Ensures government stability, especially during division voting, where numbers decide the fate of motions like the No-Confidence Motion.
For ruling coalitions, a united stance during such votes is crucial to showcase majority strength.
Chief Whip and Institutional Structure
- The Chief Whip is the most critical functionary in enforcing the whip.
- In the Lok Sabha, the Minister of Parliamentary Affairs usually acts as the government’s chief whip.
- In the Rajya Sabha, it is the Minister of State for Parliamentary Affairs.
- Whips also coordinate which MPs speak, when, and on what issues.
The All-India Whips Conference, held since 1952, allows whips from all parties to discuss coordination strategies and share parliamentary practices.
Criticism and Contemporary Debate
- Critics, including the Vice President, argue that whips limit deliberative democracy, reduce MPs to mere rubber stamps, and suppress individual judgment.
- However, supporters claim that whips are essential to prevent chaos, ensure smooth functioning, and uphold mandated party ideologies, especially in a system where governments often hinge on narrow majorities.
Former Lok Sabha Speaker Sumitra Mahajan defended the whip, stating that MPs elected on a party ticket must uphold the party’s collective ideology and decisions, even if personal disagreement exists.
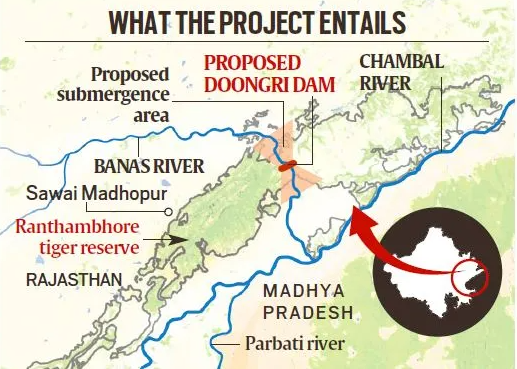
PKC-ERCP: Rajasthan’s River-Linking Project
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP), part of the National Interlinking of Rivers (ILR) programme, aims to address water scarcity in 23 districts of Rajasthan, potentially benefiting 3.45 crore people. However, it has raised serious concerns over its ecological impact, particularly on the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
About the PKC-ERCP Project:
Aspect Details
Objective To channel surplus water from the Chambal basin for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
Estimated Cost ?72,000 crore (90% funded by the Central Government)
Water Allocation 4,100 MCM to Rajasthan and 3,000 MCM to Madhya Pradesh
Rivers Involved Chambal, Parbati, Kalisindh, Banas, and tributaries
Major Structure 39 m high, 1.6 km long dam across the Banas River, a Chambal tributary, near Doongri village, ~30 km from Sawai Madhopur
Submergence and Environmental Concerns:
- Total Submergence: ~408.86 sq km in Rajasthan.
- Reservoir Impact: 227 sq km to be submerged under the proposed dam across Banas River.
- Impact on Tiger Reserve:
- 37.03 sq km of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (total area: 1,133 sq km) to be submerged.
- This includes parts of Ranthambore National Park (392 sq km) and Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary (674 sq km).
- May fragment the reserve, disrupting wildlife corridors and tiger movement.
- Ranthambore’s Significance:
- Home to ~57 tigers, it is one of India’s most prominent conservation areas.
- Situated at the Aravalli-Vindhya junction, with rich biodiversity, including leopards, hyenas, sloth bears, and iconic flora like Dhok trees.
- Encompasses the UNESCO-listed Ranthambore Fort and the Great Boundary Fault.
Arguments For the Project:
- Addresses chronic water scarcity in eastern Rajasthan.
- Promotes agricultural productivity, drinking water security, and industrial development.
- Aims to optimize water use by diverting surplus flows.
Arguments Against the Project:
- Biodiversity loss due to habitat submergence and reserve fragmentation.
- Risks to tiger conservation efforts.
- Potential violation of environmental safeguards under the Wildlife Protection Act and Forest Conservation norms.
Long-term ecological costs may outweigh short-term developmental gains.
ILO World Employment and Social Outlook 2025
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The global economy is slowing down, making it harder for labour markets to recover fully since the outbreak of the COVID 19 pandemic, according to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) report, World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2025, released in Geneva
Global Employment Trends
- Unemployment Rate (2024): Remained steady at 5%.
- Youth Unemployment: High at 12.6%, particularly severe in upper-middle-income countries (16%).
- Global Jobs Gap:
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- 186 million unemployed
- 137 million temporarily unavailable
- 79 million discouraged workers
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- NEET Population (2024):
- 259.1 million globally:
- 173.3 million young women (28.2%)
- 85.8 million young men (13.1%)
- 259.1 million globally:
Economic Growth and Labour Recovery
- Global Growth (2024): 3.2% (↓ from 3.3% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2022)
- Forecast (2025): Similar growth expected, with gradual deceleration ahead.
- Recovery Remains Uneven:
- High-income countries see rise in labour force participation.
- Low-income countries (LICs) face challenges creating decent jobs, with informal work returning to pre-pandemic levels.
- India’s GDP Growth:
- 6.9% in 2024, forecast at 6.4% in 2025
- Driven by monetary easing, domestic demand, and public investment
- Southern Asia: Growth pegged at 6.2% in 2024, 5.8% in 2025, mainly due to India.
- Labour Participation:
- Significant increase in female labour force participation, especially in India.
Key Labour Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions
- Climate Change Costs
- Unresolved Debt Issues
- ~70 countries at risk of debt distress
- Many LICs spend more on debt servicing than on education/health
- Stagnant Real Wages
- Post-pandemic wage recovery mostly in advanced economies
- Vulnerable Jobs in Developing Regions
- Sub-Saharan Africa: 62.6% households live on <USD 3.65/day
- Employment is mainly informal, lacking security
Green and Digital Transitions
- Green Jobs Growth:
- Employment in renewables rose from 13.7 million (2022) to 16.2 million (2023)
- 46% of green energy jobs are in China
- Digital Economy:
- Offers promise, but infrastructure and skills gap limit benefits in many countries.
ILO Recommendations for Social Justice & SDG 2030 Goals
- Boost Productivity & Job Creation: Invest in skills training, education, and infrastructure
- Expand Social Protection: Better access to social security and safe work conditions
- Leverage Private Capital: LICs should channel remittances and diaspora funds into development
- Structural Transformation: Focus on modern services and manufacturing for quality jobs
- Youth Skill Development: Promote education for emerging sectors like green tech and digital economy
- Global Collaboration: Foster inclusive fiscal and monetary policies for equitable recovery
About ILO
- Established: 1919 | UN Agency
- Members: 187 countries
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Unique Tripartite Structure: Brings together governments, employers, and workers to set labour standards and promote decent work for all.
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
Rabbit Fever
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Tularemia, commonly known as "rabbit fever," is a rare but highly infectious bacterial disease caused by Francisella tularensis. Though uncommon, it can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. Over recent years, cases of tularemia have been on the rise in the United States, drawing attention to the broader environmental and epidemiological factors influencing the disease’s spread.
Rising Incidence of Tularemia
Between 2011 and 2022, the United States saw a 56% increase in the annual average incidence of tularemia infections compared to the previous decade, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vulnerable populations include children aged 5 to 9, older men, and individuals of American Indian or Alaska Native descent. The increasing number of reported cases highlights the growing concern over this disease, despite its rarity.
Transmission Pathways
Tularemia is primarily transmitted through:
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: Common carriers include rabbits, hares, and rodents, particularly those infected with Francisella tularensis. This presents a risk for individuals working closely with wildlife, such as hunters.
- Insect Bites: Ticks, especially in regions with high tick populations, and deer flies can spread the disease.
- Contaminated Food or Water: Consuming undercooked meat from infected animals or untreated water can lead to infection.
- Inhalation of Contaminated Dust or Droplets: This is a potential risk in agricultural or laboratory settings and can result in pulmonary tularemia.
Contributing Factors to the Rise in Cases
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of tularemia:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are increasing tick activity and extending breeding seasons, allowing the bacteria to spread more easily.
- Habitat Encroachment: Deforestation and increased human interaction with wildlife are amplifying exposure to infected animals.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Advances in surveillance and testing methods have made it easier to detect tularemia, leading to more reported cases.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tularemia symptoms can vary depending on the route of infection. Symptoms typically appear 3 to 5 days post-exposure and may include:
- Sudden high fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Chills, fatigue, and body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially near the site of infection (e.g., under the arms or in the groin)
There are four primary forms of tularemia:
- Ulceroglandular: Characterized by skin ulcers and swollen lymph nodes.
- Glandular: Swollen lymph nodes without ulcers.
- Pneumonic: Lung infection, often resulting from inhalation.
- Typhoidal: A more systemic form, with symptoms like fever and abdominal pain.
Differentiating tularemia from other conditions such as flu, pneumonia, or lymphadenitis is key for diagnosis. A skin ulcer or swollen lymph nodes in individuals with recent exposure to wildlife or ticks is a critical diagnostic clue.
Treatment and Prognosis
Tularemia is treatable with antibiotics. First-line treatment includes streptomycin or gentamicin, while doxycycline or ciprofloxacin may be used for milder cases. Treatment typically lasts 10 to 21 days, and when initiated promptly, the disease has a high recovery rate and minimal complications. However, untreated cases can lead to chronic infections, lung abscesses, pneumonia, or severe sepsis, with mortality rates of 1-2% under treatment. Untreated severe cases can result in mortality rates between 30% and 60%.
Tularemia in India: A Potential Concern?
Tularemia is extremely rare in India, mainly due to the country's differing ecological conditions and limited interaction with the primary reservoirs of Francisella tularensis. However, awareness remains crucial, especially for individuals traveling to endemic regions or working in wildlife settings. Despite its rarity in India, the rising global incidence and changing environmental factors warrant continued vigilance.
Quad 20th Anniversary
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Quad Foreign Ministers reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific. Marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, originally formed to respond to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
Key Highlights:
- What is the Quad?
- A strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Founded on shared principles of democracy, human rights, rule of law, and countering China's influence.
- Origins:
- Quad traces its origins to the 2004 Tsunami relief efforts.
- Formed formally in 2007, but Australia withdrew in 2008 due to regional tensions. It rejoined in 2017 following strengthened US-Australia ties.
- Commitment to Regional Security:
- Focus on countering China’s assertive behavior in the Indo-Pacific.
- Ensuring maritime security, countering illegal fishing, promoting infrastructure, and advancing economic cooperation.
- Key Initiatives:
- IPMDA: Real-time monitoring of maritime activities.
- MAITRI: Capacity-building for maritime security.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate-level STEM education in member countries.
- Open RAN: Promoting secure 5G infrastructure.
- Cancer Moonshot: Focus on cervical cancer prevention.
- Military and Naval Cooperation:
- Malabar Exercises: Joint naval drills between India, Japan, the US, and Australia.
- ASEAN and Regional Cooperation:
- Emphasis on ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Support for the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Future Developments:
- India to host the next Quad Summit in 2025.
- Continued focus on sustainable regional development, scientific collaboration, and disaster relief efforts.
- Significance of the Quad for India:
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides a platform to counter China's assertive policies, especially in the South China Sea and the "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Maritime Security: Ensures freedom of navigation and counters illegal activities like piracy and illegal fishing in India’s maritime domain.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Strengthens cooperation on infrastructure projects and trade initiatives, such as the Blue Dot Network.
- Post-COVID, Quad may aid India in attracting manufacturing units shifting from China.
- Scientific and People-to-People Collaboration: Supports STEM education and enhances soft power diplomacy through academic and cultural exchanges.
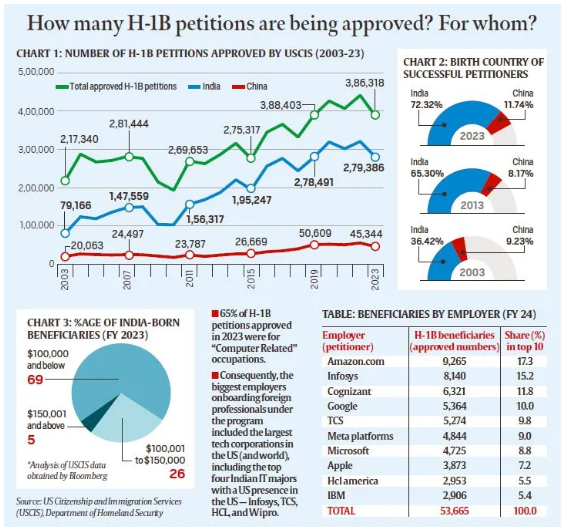
H-1B Visa
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
Tamil Nadu's First Glass Bridge in Kanyakumari
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu inaugurated India’s first glass bridge over the sea in Kanyakumari, connecting the Thiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial.
- The bridge provides a safe and scenic walking route between these two iconic landmarks, eliminating the need for ferry trips.
Key Highlights:
- Dimensions and Design
- The bridge is 77 meters long and 10 meters wide, offering uninterrupted views of the sea from a unique vantage point.
- Designed to withstand marine conditions like corrosion and strong winds, ensuring durability and safety for visitors.
- Tourism Investment
- The bridge was built at a cost of ?37 crore, marking a significant investment in tourism infrastructure for Kanyakumari.
- This project aligns with the state’s vision to boost tourism and modernize amenities in the region.
- Significance as a Tourist Attraction
- The bridge is set to become a landmark tourist attraction, enhancing the visitor experience by providing a direct, scenic route between the two monuments.
- It is expected to play a pivotal role in boosting tourist footfall and the local economy.
About Thiruvalluvar Statue
- Location and Design
- The Thiruvalluvar Statue stands on a rock near the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari.
- It is a symbol of wisdom, officially named the Statue of Wisdom by the Tamil Nadu government.
- Physical Specifications
- The statue stands at a total height of 133 feet (41 meters), with the statue itself measuring 95 feet (29 meters) and the pedestal adding 38 feet (12 meters).
- Weight: The statue weighs approximately 7000 tonnes and is designed in a hollow structure.
About Vivekananda Rock Memorial
- Location and Significance
- Situated on a rock in the Laccadive Sea, around 500 meters from the mainland in Kanyakumari.
- The memorial commemorates Swami Vivekananda, who represented India’s spiritual legacy at the 1893 Parliament of World’s Religions in Chicago.
- Historical and Religious Importance
- The rock is believed to be the site where Swami Vivekananda attained enlightenment.
- It is also associated with goddess Kanyakumari, who is said to have prayed to Lord Shiva on this rock, with an imprint of her feet preserved there.
- Architectural Features
- The memorial incorporates diverse architectural styles, including the Sripada Mandapam and the Vivekananda Mandapam.
- A life-sized bronze statue of Swami Vivekananda is located at the memorial.
- The rock is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea, where these three water bodies converge.
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has recently been renamed MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), reflecting a shift in understanding of the disease's root causes and its broader implications.
Why the Name Change?
- The primary reason for renaming NAFLD to MASLD is to highlight the metabolic dysfunction as the primary cause of the disease.
- Previously, the term NAFLD focused on the absence of alcohol consumption, which inadvertently shifted attention away from the true contributors, like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- The term MASLD eliminates the stigma associated with "non-alcoholic," which may have misled people into thinking alcohol consumption was the only factor, even though metabolic issues are the central cause.
- The term MASLD shifts the focus towards metabolic dysfunction, making it easier for healthcare professionals to understand, diagnose, and treat the condition more effectively.
The Connection to Metabolic Dysfunction
- MASLD is strongly associated with metabolic issues such as abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood sugar. These metabolic problems are key contributors to liver fat accumulation.
- People with abdominal obesity are 2-3 times more likely to develop fatty liver disease. MASLD affects about 25% of the global population, and the rates increase significantly (up to 50-70%) in individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity.
- By focusing on metabolic dysfunction, MASLD encourages addressing the root causes rather than just the symptoms, offering a more effective approach to treatment and prevention.
How is MASLD Diagnosed?
Advancements in non-invasive diagnostic methods have improved the ability to diagnose MASLD more easily and accurately, including:
- FibroScan: A non-invasive, painless test to measure liver fat and stiffness, replacing the need for liver biopsy.
- MRI and Ultrasound Techniques: Reliable methods for assessing liver fat and scarring.
- Blood Tests: Common tests like ALT, AST, and GGT assess liver function. Researchers are also exploring new markers like CK-18 fragments and the ELF score (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis) to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Implications for Patient Care
The renaming of NAFLD to MASLD has important implications for patient care:
- Targeted Treatments: By focusing on the metabolic roots, treatments such as weight loss, blood sugar management, and cholesterol control can be prioritized. These interventions help reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, liver failure, and cirrhosis.
- Earlier Diagnosis: MASLD encourages earlier recognition of the condition, which can lead to better management and improved long-term outcomes.
Prevention
Preventing MASLD involves avoiding foods that exacerbate liver fat buildup. Dr. Punit Singla, director at Marengo Asia Hospitals, emphasizes limiting or avoiding:
- Fast food, junk food, and processed foods
- Foods high in sugar, including red and processed meats
A healthier lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can significantly help prevent or manage MASLD.
Pegasus Spyware

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
For the first time, a court in the US has held Israel’s NSO Group liable for its intrusive spyware Pegasus, which could set up a measure of accountability for the company that it has, for long, allegedly downplayed.
Overview:
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
- It has been used for surveillance, allegedly targeting journalists, activists, politicians, and government officials across the world, including India.
Recent Legal Developments:
- US Court Ruling (2024):
- A US court held NSO Group liable for using Pegasus to surveil 1,400 WhatsApp users, including 300 from India.
- NSO Group violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the California Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA).
- The ruling may revive debates on the accountability of spyware use and its implications on privacy.
Use of Pegasus in India:
- Targeted Individuals (2021):
- 300 Indian numbers allegedly targeted, including journalists, politicians, Union Ministers, and civil society members.
- High-profile targets included opposition leaders, constitutional authorities, and activists.
- Government Denial:
- The Indian government denied involvement, stating allegations lacked substance.
- In Parliament, IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw rejected claims, asserting India’s surveillance laws prevent unauthorized surveillance.
- NSO Group Response:
- NSO Group denied the allegations, calling them “false and misleading” and citing doubts about the sources.
Investigations and Legal Actions:
- Supreme Court Inquiry:
- The Supreme Court appointed a committee of technical experts in 2021 to investigate claims.
- August 2022 Report: Found no conclusive evidence of spyware use on examined devices but noted lack of cooperation from the government.
- State-Level Investigations:
- West Bengal: Set up a Commission of Inquiry into Pegasus surveillance, later halted by the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh: The issue became political, with allegations that the previous government used Pegasus to monitor opposition figures.
Pegasus Spyware Features:
- Capability: Can hack iOS and Android devices to collect data, record conversations, capture photos, and access app data.
- Exploitation Method: Uses zero-day vulnerabilities to exploit iOS and Android devices covertly.
- Invisibility: Operates without user knowledge, often only detected through signs like browser closings after phishing links are clicked.
Controversial Use of Pegasus:
- Global Use: Though intended for fighting terrorism and crime, Pegasus has been misused for spying on journalists, politicians, human rights activists, and opposition leaders.
- India Specifics:
- Pegasus Project: Targeted Indian citizens, including activists, journalists, and politicians.
- Amnesty International: Confirmed use of Pegasus to target Indian phones.
India's Legal Framework for Surveillance:
- Telecommunications Act (2023): Empowers the government to control telecom services during emergencies, but requires authorization for lawful interceptions.
- IT Act (2000): Allows the government to monitor, intercept, or decrypt information through computer resources under certain conditions.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act (2023): Aims to protect personal data, including provisions on surveillance, data breaches, and rights of individuals over their data.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns:
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Surveillance infringes on the right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Freedom of speech and expression (Article 19) may be curtailed, with surveillance being used to suppress dissent.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Surveillance often occurs without judicial or parliamentary oversight, leading to potential executive overreach.
- Inability to Seek Legal Remedies:
- Citizens targeted by surveillance cannot challenge it due to lack of awareness, undermining constitutional rights.
- Executive Overreach and Suppression of Free Expression:
- Pegasus revelations have raised concerns about surveillance targeting constitutional functionaries, suppressing free speech, and stifling open discourse.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
Empowering ASHA Workers

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
ASHAs (Accredited Social Health Activists) are critical to India's healthcare system, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Since the program's launch in 2005, ASHAs have been integral in improving maternal health, increasing immunization rates, and promoting family planning and sanitation awareness. The network of ASHAs has grown to nearly 1 million members, making it one of the largest community health worker programs in the world.
Role of ASHAs: ASHAs work as community health activists, beyond basic healthcare delivery, by:
- Promoting health awareness.
- Mobilizing local participation in health programs.
- Increasing the utilization of existing health services.
They play a central role in improving maternal and child health, and their efforts have led to increased institutional deliveries and improved immunization rates in rural India.
Challenges Faced by ASHAs: Despite their essential role, ASHAs face several challenges:
- Inadequate compensation and delayed payments, which undermine motivation.
- Heavy workloads with insufficient support and resources.
- Social and economic marginalization, often leading to a lack of recognition and respect.
- Punitive systems that emphasize compliance and record-keeping, hindering autonomy.
This environment limits ASHAs' capacity to act as independent change agents, reducing their effectiveness in driving long-term health improvements.
Psychological Empowerment of ASHAs: To address these challenges, it's essential to empower ASHAs not just financially, but psychologically. Research in motivation theory, particularly Self-Determination Theory (SDT), provides a framework to achieve this. SDT emphasizes the importance of three key psychological needs:
- Autonomy: The need for ownership over one's work.
- Competence: The need to feel capable and effective in performing tasks.
- Relatedness: The need for social connection and recognition.
By fostering these three needs, ASHAs can become more intrinsically motivated and empowered to take ownership of their roles.
Strategies for Empowerment:
- Autonomy: Giving ASHAs more control over their work and decision-making can improve their engagement and efficacy. This can be achieved by reducing rigid monitoring and compliance systems.
- Competence: Providing continuous, quality training and resources will help ASHAs build the skills and confidence needed to perform their roles effectively. Digital tools and modern training programs can be used to enhance their capabilities.
- Relatedness: ASHAs should receive direct feedback from the communities they serve, fostering a sense of connection and accomplishment. Encouraging networks among ASHAs will also help combat isolation and provide peer support.
Government Efforts and Initiatives: The Indian government has recognized the need to support ASHAs through several initiatives:
- Increased remuneration and performance-based incentives.
- Insurance coverage under schemes like Ayushman Bharat.
- Training programs for skill development under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- Village Health Mapping and digital engagement platforms to enhance outreach and feedback mechanisms.
Moving Forward:
To further empower ASHAs, several key steps should be taken:
- Formalizing employment status: Transitioning ASHAs from volunteers to formal workers with benefits can ensure more stability and recognition.
- Improving compensation: Ensuring timely and adequate payments along with performance bonuses will incentivize ASHAs and increase job satisfaction.
- Enhancing infrastructure: Ensuring ASHAs have access to the necessary tools, medical supplies, and transportation to perform their tasks effectively.
- Digital integration: Expanding digital tools for data collection and communication can streamline their work and improve coordination with healthcare systems.
Turner Prize

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
Jasleen Kaur, a 38-year-old Indian-origin Scottish artist, has won the prestigious Turner Prize 2024 for her exhibition "Alter Altar". This win highlights Kaur’s unique ability to weave together personal, political, and spiritual elements into a cohesive artistic expression. The exhibition explores themes such as plurality, migration, and cultural identity, drawing from Kaur’s own family history and experiences.
Exhibition Overview:
"Alter Altar," which was first showcased in Glasgow, features an array of everyday objects and cultural symbols, including:
- A vintage red Ford Escort covered in a large crocheted doily, symbolizing her father’s migrant aspirations.
- Worship bells, Irn-Bru orange resin, an Axminster carpet, and family photographs.
- Soundtracks, including music from Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan and Bob Marley, which reflect Kaur’s multicultural upbringing.
The exhibition blends these elements to examine migration, identity, and belonging. The jury, chaired by Alex Farquharson, Director of Tate Britain, praised Kaur’s ability to combine different voices through unexpected and playful material combinations, creating a visual and aural experience that evokes both solidarity and joy.
Personal and Political Reflection:
Kaur’s work reflects on the Sikh concept of Miri Piri, which represents the balance between the political and the spiritual. This duality is central to her exploration of cultural practices and the effects of violence, colonialism, and empire on these traditions. In her acceptance speech, Kaur also addressed political issues, calling for a ceasefire in Gaza and an end to institutional complicity in Israel's actions.
About the Turner Prize:
The Turner Prize, established in 1984, is one of the most prestigious awards in contemporary British art. It aims to recognize recent developments in British art. Kaur’s win is particularly significant as it marks the 40th anniversary of the award. Previous winners include renowned Indian-origin artists such as Anish Kapoor (1991).
RBI's Stance on De-dollarisation and Risk Diversification

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
- Governor Shaktikanta Das clarified that India is not pursuing "de-dollarisation," but rather aiming to diversify risk in trade. Measures like local currency trade agreements and Vostro accounts are intended to reduce reliance on the US dollar without eliminating it entirely.
- Objective: The goal is to de-risk India's trade, not to fully replace the dollar, especially amidst rising geopolitical tensions.
Key Highlights:
Vostro Accounts and Local Currency Trade:
- Vostro Accounts: These accounts, held by foreign banks in Indian rupees, facilitate transactions in local currencies, helping mitigate the risks of dollar dependency.
- International Currency Trade: By promoting trade in local currencies, the RBI seeks to reduce exposure to fluctuations in the dollar's value. However, these efforts have faced challenges due to India’s limited international presence in goods and services trade.
Gold Purchases by Central Banks:
- Surge in Gold Purchases: Global central banks, including the RBI, have significantly increased gold holdings. India added 27 tonnes in October 2024 alone, the largest increase among central banks.
- Motivations for Gold: The surge in gold buying reflects growing concerns about geopolitical risks, including the Ukraine war, and the potential for secondary sanctions. Gold is seen as a safe haven asset that diversifies reserves away from the US dollar.
Decline in Dollar Dominance:
- Global Shift: The share of the US dollar in global reserves has been gradually declining, partly due to the rise of the Chinese yuan. Central banks are increasingly turning to gold and alternative currencies as part of a diversification strategy.
- Impact on Emerging Markets: Countries like India are particularly motivated to reduce reliance on the dollar due to geopolitical tensions and economic vulnerabilities linked to the dollar’s dominance.
India’s Domestic Currency Trade Initiatives:
- Trade with Russia and UAE: India is actively exploring trade in domestic currencies with countries like Russia and the UAE to reduce dependence on the dollar. However, these efforts have faced slow uptake due to India’s trade deficit with most countries except the US.
- Challenges in Adoption: Despite efforts to internationalize the rupee, high transaction costs and lack of sufficient demand for rupee-based trade are significant barriers.
BRICS and Shared Currency Discussions:
- Geopolitical Complexity: BRICS nations, due to their geographical and economic diversity, have discussed the possibility of a shared currency, but no consensus has been reached.
- Reluctance Toward Yuan: India has resisted using the Chinese yuan for transactions, particularly for Russian oil imports, despite the yuan’s growing acceptance. This reflects India’s desire to maintain economic sovereignty and avoid over-reliance on a single currency.
Regional Implications of Dollar Volatility:
- Neighbourhood Impact: Countries like Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan have experienced significant financial distress due to declining dollar reserves and surging oil prices, exacerbated by the Ukraine war.
- India’s Resilience: India’s strong dollar reserves have helped it maintain economic stability, but the country remains cautious of dollar volatility, particularly as oil prices rise.
Conclusion:
- Strategic Balance: India’s approach reflects a strategic balance of mitigating risks while ensuring global trade stability. The RBI’s emphasis on gold accumulation and pushing for rupee-based trade demonstrates a desire to reduce exposure to the dollar, but challenges like trade deficits and high transaction costs still hinder the full realization of these goals.
- Economic Sovereignty: Through these measures, India seeks to safeguard its economic sovereignty and financial stability in an increasingly unpredictable global economy.
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India, Will Assume Office on November 11
- Appointment:
- Justice Sanjiv Khanna has been appointed as the 51st Chief Justice of India by President Droupadi Murmu.
- He is set to take office on November 11, 2024, succeeding Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, who is retiring on November 10, 2024.
- Tenure:
- Justice Khanna's tenure will be relatively short, lasting only six months, as he is scheduled to retire on March 13, 2025.
Career and Background
- Education and Early Career:
- Justice Khanna is a graduate of Delhi University’s Campus Law Centre.
- He enrolled as an advocate in 1983 and primarily practiced before the Delhi High Court.
- Prior to his elevation to the Delhi High Court in 2005, he served as the Senior Standing Counsel for the Income Tax Department and the standing counsel for civil matters for the Delhi government.
- Judicial Career:
- Supreme Court Appointment: Justice Khanna was appointed to the Supreme Court in January 2019, despite not having served as Chief Justice of a High Court. He was elevated over other senior judges from the Delhi High Court, such as Justices Rajendra Menon and Pradeep Nandrajog, whose names were initially recommended but not forwarded to the government.
- Key Contributions:
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- February 2024: Part of the five-judge bench that struck down the Electoral Bond Scheme as unconstitutional.
- 2023: Contributed to upholding the abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution.
- 2023: Authored a ruling granting the Supreme Court the power to directly grant divorce under Article 142 on the grounds of "irretrievable breakdown of marriage."
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- Administrative Role:
- Justice Khanna currently serves as the Executive Chairman of the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
Process of Appointment of Chief Justice of India (CJI)
- Seniority Principle: The CJI is typically the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court.
- Memorandum of Procedure (MoP): The Law Ministry requests a recommendation from the outgoing CJI for his successor.
- Presidential Appointment: After receiving the recommendation, the President of India formally appoints the new CJI.
- Tenure and Retirement: The CJI serves until the age of 65. Upon retirement, the senior-most judge becomes the next CJI.
- Merit and Integrity Considerations: In addition to seniority, merit and integrity play crucial roles in the selection process for the CJI.
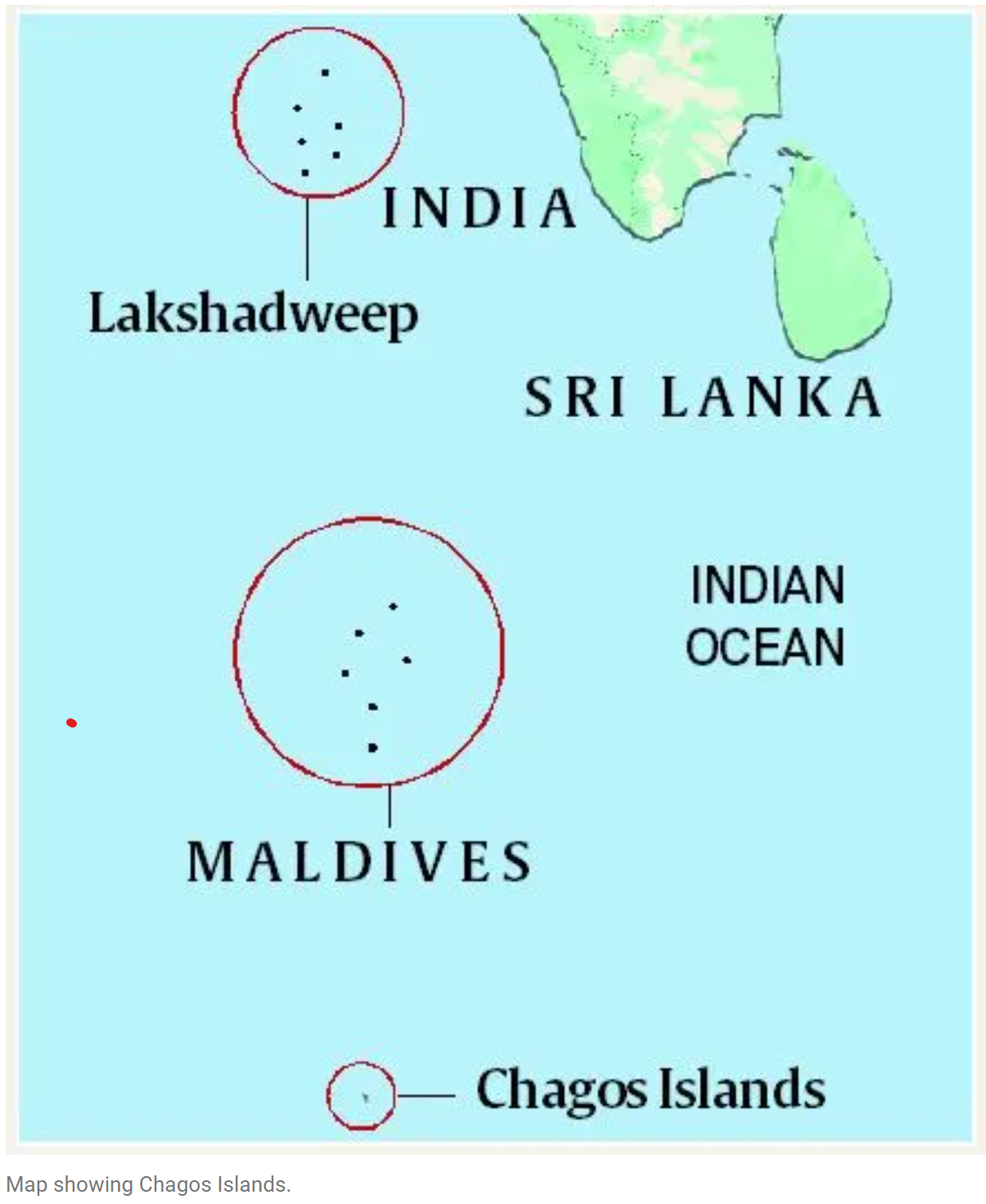
UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Kingdom said it would cede sovereignty of the strategically important Chagos Islands to Mauritius, calling it a “historic political agreement”. The UK has long controlled Chagos and the Diego Garcia military base located there, jointly operating it with the United States.
Background of the Chagos Archipelago
Historical Context
- The Chagos archipelago consists of 58 islands located about 500 km south of the Maldives.
- Initially uninhabited, the islands were populated in the late 18th century through the importation of slave labor.
- The islands were ceded to Britain from France in 1814, and in 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which includes Chagos.
Controversy Over Sovereignty
- Mauritius, a former British colony, claims that the detachment of Chagos from its territory during its independence in 1968 was illegal.
- The UK compensated Mauritius with a grant but retained control, establishing a military base on Diego Garcia.
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
Military Significance
- Diego Garcia has been a crucial U.S. military base since its operational status began in 1986.
- It played a key role in U.S. military operations during conflicts in the Gulf, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The base enables rapid response to crises and supports regional security, especially in light of U.S. interests in monitoring key trade routes like the Malacca Strait.
Geopolitical Implications
- The presence of the U.S. military in the Indian Ocean is vital for countering security threats, particularly regarding China's growing influence.
Recent Developments: The UK-Mauritius Agreement
Key Features of the Treaty
- On October 3, 2023, the UK agreed to cede sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, marking a significant political shift.
- The treaty allows Mauritius to resettle Chagossians (excluding Diego Garcia) and establishes a trust fund for their benefit.
- Despite this, the UK retains control over Diego Garcia for an initial period of 99 years.
Implications of the Agreement
- The resolution of the sovereignty issue may strengthen Western commitments to a stable and free Indo-Pacific region.
- If unresolved, tensions could push Mauritius toward seeking alliances with alternative powers like China.
India’s Position and Interests
Support for Mauritius
- India has historically supported Mauritius in its claims over Chagos, reflecting its stance against colonial legacies.
- In 2019, India voted in favor of Mauritius at the UN General Assembly regarding the Chagos dispute.
Strategic Partnerships
- With increasing Chinese assertiveness in the Indian Ocean, India has been strengthening its ties with Mauritius.
- Recent initiatives include the inauguration of an India-built airstrip and jetty in Agaléga, enhancing connectivity and support for Mauritius.
Conclusion
The UK-Mauritius treaty over the Chagos Archipelago marks a significant turning point in colonial legacies and geopolitical alliances in the Indian Ocean. For India, supporting Mauritius aligns with its broader strategic interests and enhances its influence in a region marked by competing global powers. As the dynamics evolve, India's role in fostering regional stability and partnerships will be crucial.
India-U.S. MoU on Critical Minerals Supply Chains

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The sixth Commercial Dialogue took place in Washington on October 4, 2024, led by Indian Union Minister of Commerce Piyush Goyal and U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo.
- MoU Signing: A day prior, the leaders signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) aimed at expanding and diversifying critical minerals supply chains to enhance resilience.
- Focus Areas:
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Exploration
- Extraction
- Processing and refining
- Recycling and recovery
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Context: This agreement follows China's export restrictions on gallium and germanium, critical for the semiconductor industry, and its ban on technology related to rare earth magnets and critical materials extraction.
- Strategic Goals:
- Promote open supply chains, technology development, and investment flows for green energy.
- Explore collaboration with other mineral-rich countries, particularly in Africa and South America.
- Progress on Semiconductor Supply Chains:
- Continued efforts to establish resilient semiconductor supply chains since the previous MoU.
- Completion of a "readiness assessment" by the U.S. Semiconductor Industry Association and India Electronics Semiconductor Association.
- Commitment to foster investments, joint ventures, and technology partnerships.
- Innovation Handshake: Success of roundtables in San Francisco and New Delhi aimed at enhancing innovation ecosystems and startup collaboration.
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership: Discussions from the EIN Roundtable in March 2024 informed the U.S.-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership meeting.
- IPEF Supply Chain Agreement: Significant progress noted in the IPEF ministerial meeting, focusing on semiconductors, chemicals, and critical minerals, particularly batteries and healthcare products.
- Future Collaborations:
- Focus on expanding U.S. Department of Commerce presence in India with approximately 70 Foreign Commercial Service staff.
- Plans for a U.S. trade mission to India in March 2025 aimed at supporting U.S. SMEs owned by underserved communities.
- Domestic Solar Manufacturing Protection: India reinstated the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) order to protect local solar PV module production against cheaper imports from China.
- Economic Context:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights China's expanding manufacturing trade surplus and its restrictive actions affecting India's access to solar equipment.
- India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes have invested over $4.5 billion to bolster clean energy manufacturing but require additional policies to safeguard these investments.
Status of Elephant in India 2022-23

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- Shelved Census Report: The Environment Ministry has delayed the release of the elephant census report, “Status of Elephant in India 2022-23,” due to a lag in the Northeast census, with publication on hold until at least June 2025.
- Population Decline: Preliminary data from the report indicates significant drops in elephant populations across several regions:
- Southern West Bengal: 84% decline
- Jharkhand: 64% decline
- Odisha: 54% decline
- Kerala: 51% decline
- Developmental Threats: The report cites “mushrooming developmental projects,” including unregulated mining and infrastructure development, as major threats to elephant populations.
- Methodological Concerns: The Environment Ministry noted that refined counting methods could explain some discrepancies, suggesting new data may not be directly comparable to previous censuses conducted every five years since the 1990s.
- Old Counting Methods:
- Pre-2002: Elephants were counted using the “total direct count” method, which involved simple head counts but lacked scientific rigor for larger populations.
- 2002: Introduction of the “indirect dung count” method, where dung samples were used to estimate density based on decay rates.
- Sample Block Counts: Modified methods involved surveying limited areas (5 sq km) to improve detection accuracy.
- Elephants vs. Tigers: In 2021, a harmonized approach for estimating elephant and tiger populations was proposed, utilizing a similar block and co-variate methodology for both species.
- Genetic Mark-Recapture: The 2022-23 elephant census employed a genetic mark-recapture model using dung samples to identify individual elephants.
- Impact of Delay: Experts argue that withholding the available data hinders conservation efforts and governance. Delays could exacerbate the plight of elephant populations, particularly in regions facing specific threats, such as mining in Odisha.
Key Findings of the Unreleased Report:
- Overall Decline: The overall elephant population has decreased by 20% since 2017, with some areas reporting reductions of up to 41%.
- Regional Impact:
- Southern West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha have seen losses of nearly 1,700 elephants.
- The Western Ghats region indicates an 18% decline.
- Northeast Region: The census for this area relies on extrapolated data from 2017, with approximately one-third of India's elephants located there.
- Contributing Factors: Habitat fragmentation, poaching, and human-elephant conflicts due to developmental activities are major threats.
- Conservation Recommendations: Strategies to strengthen elephant corridors, restore habitats, and enhance community involvement in conservation are vital.
- Challenges in the Northeast: Urban development, mining, and agriculture significantly threaten elephant movement and survival, underscoring the need for targeted conservation strategies.
- Conservation Status of Elephants in India:
- Leading States: Karnataka, Assam, and Kerala have the highest elephant populations.
- Conservation Status: Elephants are classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and are protected under multiple international conventions.
- Threats to Elephants:
- Habitat Loss: Rapid human population growth is diminishing elephant habitats.
- Fragmentation: Habitat disruption from construction and development projects is prevalent.
- Unlawful Killing: Human-elephant conflict often leads to retaliatory killings.
- Poaching: Targeting of male elephants for tusks continues to threaten genetic diversity.
- Conservation Measures:
- Financial support under various government schemes for habitat conservation and human-elephant conflict resolution.
- Establishment of 33 Elephant Reserves across 14 states.
- Collaborative efforts with railways and power departments to mitigate risks.
- Regular elephant census every five years by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) for monitoring populations.
La Nina and North India’s pollution
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research by scientists at the National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) has underlined the links between climate change, La Niña and air quality.
Key Points on Air Quality Outlook for Delhi and North India
- Delayed La Niña & Monsoon Retreat:
- Erosion of optimism for improved air quality this winter in Delhi.
- Significant pollution challenges anticipated in early winter months.
- Possible relief in December and January, contingent on La Niña strengthening.
- Impact of Stubble Burning:
- If stubble burning occurs at half the intensity of previous years, November air quality may deteriorate.
- Research Insights:
- Study by National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) links climate change, La Niña, and air quality.
- Notable air quality improvement in winter 2022-23 was linked to La Niña conditions.
- Late onset of La Niña contributes to air quality uncertainty.
- Changing Pollution Dynamics:
- Shift from local emission-centric views to broader climatological factors is necessary.
- Air quality in Delhi worsens during winter due to high humidity, calm winds, and poor pollutant dispersion.
- La Niña Delays:
- Delayed La Niña onset means weak winds and stagnant conditions, worsening pollution.
- Expected development between September and November 2024.
- Effects of Stubble Burning:
- North-north-westerly winds could carry pollution from stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana into Delhi.
- Potential Outcomes of Late La Niña Onset:
- If La Niña develops in December or January, may improve air quality slightly.
- However, a longer, severe winter could exacerbate pollution issues due to lower inversion layers.
- NIAS-SAFAR Model Predictions:
- Early La Niña could have worsened air quality in the peninsular region.
- Early onset might have improved northern air quality.
- Link to Climate Change:
- Evidence suggests extreme air pollution correlates with climate change.
- Emphasizes the need for rigorous mitigation efforts and broader airshed management.
- Call for Rethinking Air Quality Strategies:
- Focus on integrating larger climatic factors into air quality policies.
- Prioritize health-centric measures through collaborative efforts with scientific bodies.
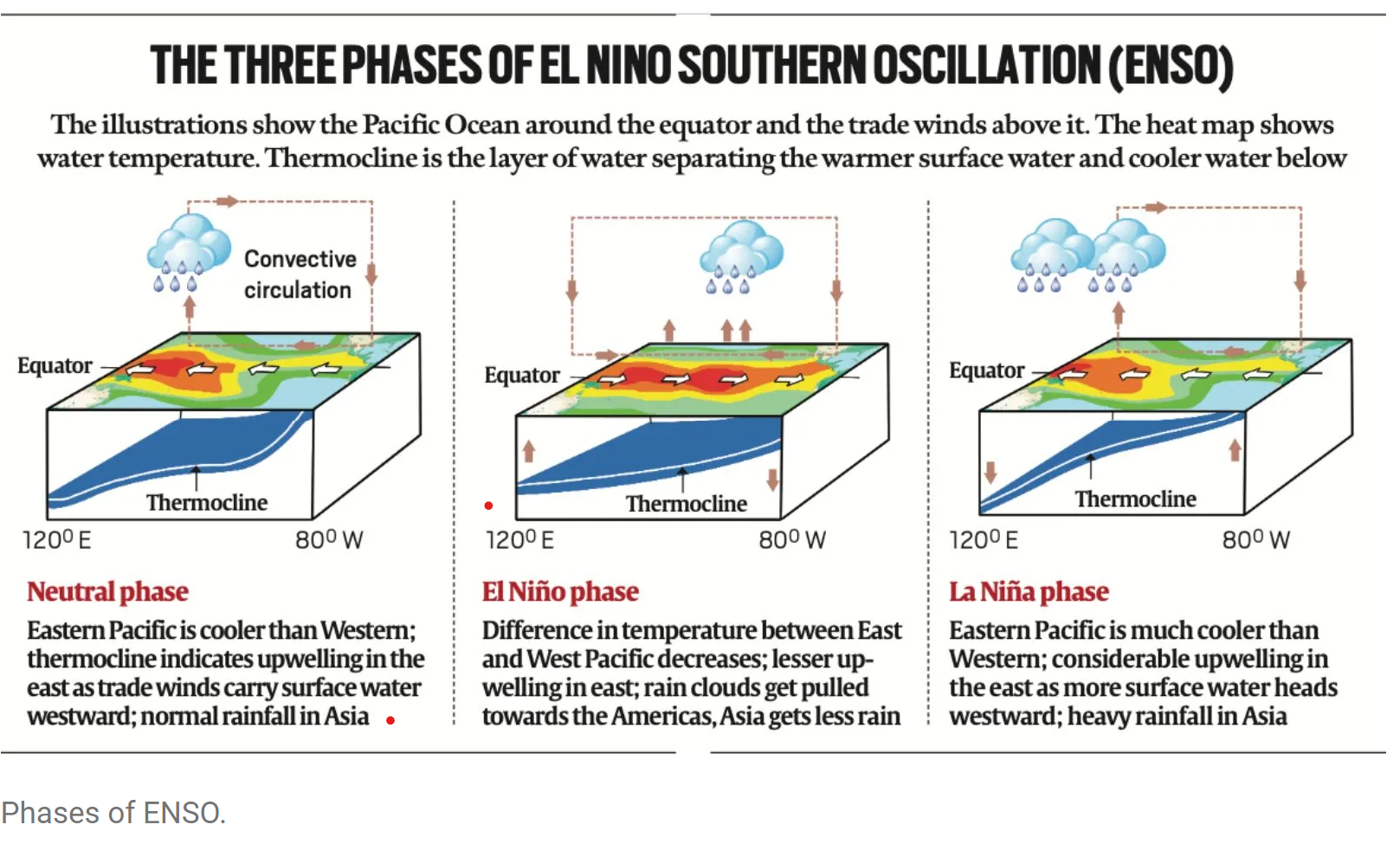
What is La Niña?
- La Niña (or ‘The Little Girl’ in Spanish) is a phase of what climatologists refer to as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a phenomenon that is a key driver of global natural climate variability.
- ENSO is characterised by changes in sea temperatures along the tropical Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric fluctuations overhead. These changes alter and interfere with the global atmospheric circulation, and influence weather worldwide.
- Occurring in irregular cycles of anywhere between two to seven years, ENSO has three phases — warm (El Niño or ‘The Little Boy’ in Spanish), cool (La Niña), and neutral.
- During the neutral phase, the eastern Pacific (off the northwestern coast of South America) is cooler than the western Pacific (around Philippines and Indonesia). This is because prevailing trade winds — caused by Earth’s rotation, between 30 degrees north and south of the equator — move east to west, sweeping warmer surface water along with them. The relatively cool waters from below rise to the surface to replace the displaced water.
- These wind systems weaken in the El Niño phase, leading to lesser displacement of warmer waters off the American coasts. Consequently, the eastern Pacific becomes warmer than usual. The opposite happens in the La Niña phase i.e. trade winds become stronger than usual and push larger quantities of water to the western Pacific.
WORLD TOURISM DAY 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Tourism celebrated World Tourism Day on September 27, 2024, under the theme “Tourism and Peace.” The focus was on how tourism fosters global peace by encouraging cross-cultural interactions and understanding.
Key Details:
- World Tourism Day, established in 1980 by the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO), celebrates the global impact of tourism and raises awareness about its economic, social, and cultural significance.
- This day celebrates the diverse experiences that tourism offers and commits to making travel more inclusive, sustainable, and beneficial for all; here’s all you need to know about the day.
- The date, September 27, was chosen to commemorate the adoption of UNWTO statutes in 1975
- The theme for World Tourism Day 2024 is “Tourism and Peace,” which will highlight the association between tourism and world peace, with the United Nations emphasising the significance of comprehending diverse cultures and encouraging sustainable tourism.
World Tourism Day: Significance and Celebrations
- World Tourism Day is a global event that celebrates the role of tourism in bridging cultural gaps, enhancing mutual understanding, and driving economic development.
- It focuses on responsible tourism practices, celebrating diverse cultural heritage, and addressing environmental sustainability and fair distribution of benefits.
- Events include seminars, workshops, and conferences on the theme of the year, cultural festivals, exhibitions, and public performances.
- Educational campaigns and community outreach activities raise awareness about responsible travel, supporting local economies, and protecting natural environments.
Note:
- The World Economic Forum, in its recently released Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI), shares the top countries gaining popularity in the travel and tourism industry.
- Notably, in Southeast Asia, India ranks 39th as the TTDI’s top lower-middle-income economy. India’s strong Natural (6th), Cultural (9th) and Non-Leisure (9th) resources drive its travel industry, with the country’s being only one of three to score in the top 10 for all the resources pillars.
- The TTDI measures the set of factors and policies that enable the sustainable and resilient development of the T&T sector, which in turn contributes to the development of a country. Among the 119 countries, here are the top 10 countries for travel and tourism in 2024 attracting travellers from all over the globe.
10 YEARS OF MAKE IN INDIA

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The “Make in India” initiative has completed 10 years. It was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on September 25, 2014.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The ‘Make in India’ campaign aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best in class manufacturing infrastructure.
- “Make in India” was designed to transform India into a global hub for design and manufacturing.
- Seen as an important ‘Vocal for Local’ initiative, its objective is twofold. Firstly, to boost India’s manufacturing capabilities and secondly to showcase its industrial potential on a global stage.
- The “Make in India 2.0” phase encompassing 27 sectors – both manufacturing and service.
4 pillars of “Make in India” initiative:
- New Processes: To enhance the business environment, promote entrepreneurship and startups – ‘ease of doing business’ became a crucial factor.
- New Infrastructure: Development of industrial corridors, smart cities, integrating state-of-the-art technology and high-speed communication to create world-class infrastructure, improving intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure etc.
- New Sectors: Opening of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in sectors like Defence Production, Insurance, Medical Devices, Construction, and Railway infrastructure.
- New Mindset: In order to support industrial growth and innovation – the government embraced a role as a facilitator rather than a regulator. The Government partners with industry in the economic development of the country.
Key Initiatives to enable Make in India initiative
Production linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: The primary goals of the PLI Schemes are to attract substantial investments, incorporate advanced technology, and ensure operational efficiency. These schemes cover 14 key sectors aimed at fostering investment in cutting-edge technology and promoting global competitiveness.
PM GatiShakti: It is a strategic initiative aimed at achieving Aatmanirbhar Bharat and a US $5 trillion economy by 2025 through the creation of multimodal and last-mile connectivity infrastructure. PM GatiShakti is a transformative approach for economic growth and sustainable development. The approach is driven by 7 engines, namely:
- Railways
- Roads
- Ports
- Waterways
- Airports
- Mass Transport
- Logistics Infrastructure
Semiconductor Ecosystem Development: It encompasses four key schemes:
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Semiconductor Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Display Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, Sensors Fabs, and Discrete Semiconductors, along with Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP) / OSAT Facilities in India
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
It aims to foster the development of a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
The Semicon India Programme aims to provide a significant impetus to semiconductor and display manufacturing by facilitating capital support and promoting technological collaborations.
National Logistics Policy: Introduced to complement the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan. It focusses on enhancing the soft infrastructure of India’s logistics sector.
The Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) was rolled out. The key areas which it addresses are logistics systems, standardization, human resource development, state engagement, and logistics parks.
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme: Aims to create “Smart Cities” and advanced industrial hubs.
Startup India: Several programs aimed at supporting entrepreneurs, building a robust startup ecosystem, and transforming India into a country of job creators instead of job seekers were rolled out.
Implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST): As India’s tax reforms, it is seen as crucial in the context of the Make in India initiative.
Unified Payments Interface: For India’s digital economy growth, it is seen as one of the key initiatives to enable ease of doing business.
Ease of Doing Business: The efforts aim to simplify regulations, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and create a more business-friendly environment, significantly boosting investor confidence and supporting the objectives of the Make in India initiative.
INDO-PACIFIC ECONOMIC FRAMEWORK (IPEF)

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
India signed agreements within the US-led 14-member IPEF focused on a clean and fair economy.
- Objectives:
- Facilitate development, access, and deployment of clean energy and climate-friendly technologies.
- Strengthen anti-corruption measures and promote tax transparency among member countries.
- Clean Economy Agreement:
- Aims to accelerate energy security and mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Focuses on innovative methods to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote technical cooperation.
- Fair Economy Agreement:
- Seeks to create a transparent and predictable business environment to enhance trade and investment.
- Emphasizes information sharing, asset recovery facilitation, and strengthening cross-border investigations.
- Funding Mechanisms:
- IPEF offers platforms for technical assistance and concessional funding.
- IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund: Initial grant of $33 million aimed to catalyze $3.3 billion in private investments.
- PGI Investment Accelerator: Received $300 million from the US International Development Finance Corporation.
- Concerns Raised:
- Experts highlighted concerns over the secrecy of IPEF negotiations with limited public input.
- Expressed hope that India has not agreed to a non-derogation clause that could limit domestic regulatory flexibility for national projects.
- Potential Risks:
- Most standards discussed in IPEF are aligned with those in the US and OECD countries.
- India risks compliance pressures in future trade deals if it adopts these standards without adequate preparation.
- Strategic Importance of IPEF:
- Involves 14 member countries, focusing on economic cooperation through four key pillars: trade, supply chain resilience, clean economy, and fair economy.
- Represents 40% of the global economy and 28% of world trade, highlighting India's commitment to regional partnerships alongside the US, Japan, Australia, and other Indo-Pacific nations.
Bacterial Pathogens Priority List (BPPL)

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently released its updated Bacterial Priority Pathogens List (BPPL) 2024.
What is the Bacterial Pathogens Priority List?
- The Bacterial Pathogens Priority List (BPPL) is a crucial tool in the global effort to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Background:
- In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) created the first BPPL to guide investment in the research and development (R&D) of new antibacterial treatments, listing 13 bacterial pathogens (phenotypes).
- The list was developed using the Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) method, a scientific approach that evaluates and ranks alternatives based on multiple criteria, ensuring systematic and transparent decision-making.
- The 2024 WHO BPPL expands to cover 24 pathogens across 15 families of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, categorizing them into critical, high, and medium priority groups to guide R&D and public health efforts.
Significance:
- The BPPL directs priorities for R&D and investment in AMR, highlighting the necessity for region-specific strategies to combat resistance effectively.
- It is aimed at developers of antibacterial medicines, academic and public research institutions, research funders, public-private partnerships involved in AMR R&D, and policymakers responsible for AMR policies and programs.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the ability of microorganisms to persist or grow in the presence of drugs designed to inhibit or kill them.
- These drugs, called antimicrobials, are used to treat infectious diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoan parasites.
- When microorganisms become resistant to antimicrobials, standard treatments are often ineffective, and in some cases, no drugs provide effective therapy.
- Consequently, treatments fail and this increases illness and mortality in humans, animals and plants.
- For agriculture, this causes production losses, damages livelihoods and jeopardizes food security.
- Moreover, AMR can spread among different hosts and the environment, and antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms can contaminate the food chain.
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major global threat of increasing concern to human and animal health.
- It also has implications for food safety, food security and the economic well-being of millions of farming households.
Chausath Khamba

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Characterized by its marble pillars and intricate latticework, Chausath Khamba (64 pillars) stands adjacent to the Nizamuddin dargah, a 14th-century shrine erected in honor of the revered Sufi saint Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
About the Chausath Khamba:
- Chausath Khamba was built in AD 1623 - 24 to serve as a tomb for Mirza Aziz Koka, the foster brother of Mughal Emperor Akbar.
- It is so called on account of the 64 (chausath) monolithic marble pillars (khamba) and stands close to his father, Atgah Khan’s tomb, at the edge of the Dargah of Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
- The tomb enclosure is entered through a lofty arched gateway and has a large sunken forecourt.
- The mausoleum is unique on account of it being built entirely of marble, with 25 marble domes supporting the flat roof of the structure.
- The plan for Chausath Khamba could have been inspired by the wooden garden pavilions from Persia - such as the Chihil Sutun, and in turn, the Chausath Khamba seems to have inspired the architectural design for Emperor Shahjahan’s Diwan-i-Aam, Hall of Audience.
- Each facade of the square structure has five marble arches inset with marble jaallis or lattice screens and a doorway in the central arch providing access to the tomb.
- The column capitals are intricately carved with simple yet striking pendentives bridging the square floor plan to the circular dome above.
- The structure also finds mention in Sir Gordon Risley Hearn’s book The Seven Cities of Delhi.
- As per author and historian Sam Dalrymple, the edifice embodies the architectural style of Gujarat and Ahmedabad within Delhi, serving as the Urs Mahal for hosting festivities during the commemoration of Nizamuddin's passing.
- This illustrates the historical dissemination of regional architectural influences across India over centuries.
Google Deepmind’s new AI that can play video games with you

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google DeepMind recently revealed its latest AI gaming agent called SIMA or Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent, which can follow natural language instructions to perform tasks across video game environments.
What is SIMA?
- Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) is an AI Agent, which is different from AI models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google Gemini.
- AI models are trained on a vast data set and are limited when it comes to working on their own.
- On the other hand, an AI Agent can process data and take action themselves.
- SIMA can be called a generalist AI Agent that is capable of doing different kinds of tasks.
- It is like a virtual buddy who can understand and follow instructions in all sorts of virtual environments – from exploring mysterious dungeons to building lavish castles.
- It can accomplish tasks or solve challenges assigned to it.
- It is essentially a super-smart computer program that can be thought of as a digital explorer, having the ability to understand what you want and help create it in the virtual world.
How does SIMA work?
- SIMA can understand commands as it has been trained to process human language.
- So when we ask it to build a castle or find the treasure chest, it understands exactly what these commands mean.
- One distinct feature of this AI Agent is that it is capable of learning and adapting.
- SIMA does this through the interactions it has with the user.
- The more we interact with SIMA, the smarter it gets by learning from its experiences and improves over time.
- This makes it better at understanding and fulfilling user requests.
- Based on the current stage of AI development, it is a big feat for an AI system to be able to play even one game.
- However, SIMA goes beyond that and can follow instructions in a variety of game settings.
- This could potentially introduce more helpful AI agents for other environments.
Honoring, the Architect of Mumbai (Bombay)

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maharashtra cabinet recently decided to ask the Ministry of Railways to rename Mumbai Central Station after Nana Jagannath Shankarseth.
Who was Nana Jagannath Shankarseth?
- Nana Jagannath Shankarseth was a social reformer, educationist, and philanthropist and often described as the “architect” of Mumbai (then Bombay).
- He made extremely valuable contributions in terms of both ideas and money to multiple sectors, to lay a strong foundation for the city.
- Shankarseth was greatly inspired by the legendary merchant and philanthropist Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy.
- As a social reformer and community leader, Shankarseth earned the goodwill of both Indians and the British.
- He became the first Indian to be nominated to the Legislative Council of Bombay.
Shankarseth’s Most Significant Contributions:
- Education: Shankarseth was deeply committed to the growth and spread of education in Bombay, and donated land owned by his family for educational institutions.
- Like many social reformers of his age, he believed that Indians could progress through education.
- He also worked for the education of girls and women.
- Shankarseth founded the Native School of Bombay, which was renamed first as the Bombay Native Institution, and then as the Board of Education.
- Finally, this institution evolved into the prestigious Elphinstone College.
- Museum, Temples: Shankarseth was among the wealthy donors who helped promote Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum in Byculla, which was designed by a famous London-based architect.
- The Bhawani Shankar Temple near Nana Chowk was Shankarseth’s tribute to his late mother Bhawanibai Murkute.
- He also built a Ram temple.
- Railways: The first train in India ran between Boribunder and Thane on April 16, 1853.
- The 34-km project was undertaken by the Great Indian Peninsular Railway Company.
- The committee that gave the project impetus included Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and Nana Shankarseth.
Lab to monitor seawater quality and testbed to track monsoon systems inaugurated

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India commissioned the atmospheric testbed facility near Bhopal, equipped with high-end instruments to record vital parameters for enhancing weather models and conducting advanced studies on the Indian monsoons, with construction commencing in early 2018.
What is the Atmospheric Research Testbed (ART)?
- The ART is an open-field, focused observational and analytical research programme at Silkheda.
- The facility aims to conduct ground-based observations of weather parameters like temperature, wind speeds, etc., and in-situ (on-site) observations of the transient synoptic systems – like low-pressure areas and depressions that form in the Bay of Bengal – during the southwest monsoon season from June to September.
- Studying these systems and their associated cloud parameters will be used to generate high volumes of data over a long period.
- It can then be compared with the existing weather models so that improvements can be made to obtain accurate rainfall predictions.
- The setup at ART will also be used for calibrating and validating various satellite-based observations, part of weather predictions and forecasting.
- Spread over 100 acres, the ART has been developed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences for Rs 125 crore.
- The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, is in charge of the operations.
- Under the first phase, remote sensing-based and in-situ measurements using 25 meteorological instruments have commenced.
- In the second phase, ART will deploy instruments such as a radar wind profiler and balloon-bound radiosonde, and soil moisture and temperature measuring equipment.
What instruments are ART equipped with?
- To obtain continuous observations of convection, clouds, and precipitation, and monitor the major modes of variabilities, the ART is equipped with over two dozen high-end instruments, radars, and more.
- At 72 meters, ART will house India’s tallest meteorological tower.
- Some of the instruments deployed are an aethalometer for performing aerosol studies, a cloud condensation nuclei counter, a laser ceilometer to measure cloud sizes, a micro rain radar to calculate raindrop size and its distribution, and a Ka-band cloud radar and a C-band Doppler weather radar to help track the movement of rain-bearing systems over this zone.
Why is having an Atmospheric Research Testbed important?
- At present, 45% of India’s labor force is employed in the agriculture sector and much of Indian agriculture is rain-fed.
- Cultivation along the Monsoon Core Zone (MCZ), which spans the central India region from Gujarat to West Bengal, is primarily rainfall-fed.
- The southwest monsoon season accounts for 70 percent of the country’s annual average rainfall (880mm).
- Throughout India, the majority of Kharif cultivation is undertaken between July and August, which see an average monthly rainfall of 280.4mm and 254.9mm (1971–2020 average), respectively.
- During this four-month-long season, several rain-bearing synoptic systems, namely the low pressures or depressions, develop in the Bay of Bengal.
- Inherently, these systems move westwards/northwestwards over to the Indian mainland and pass through the MCZ, causing bountiful rainfall.
Why is it important to have data about monsoons over central India?
- Studies have correlated the all-India rainfall performance to the rainfall received over the central India region, highlighting its importance.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issues rainfall forecasts for the country’s four homogeneous regions – north, west, east, and south peninsular India.
- In addition, it issues a special rainfall forecast for the MCZ, which is considered India’s food bowl.
- However, there is still limited understanding of the role of these synoptic systems, their associated cloud physics, cloud properties, and their overall role in enhancing the monsoon rainfall.
- Central India, therefore, acts as a natural laboratory for scientists and meteorologists to perform a hands-on study of the Indian monsoons.
- They can record data and make observations about the allied systems, clouds, and other associated physical and atmospheric parameters.
- Additionally, climate change is driving erratic rainfall patterns in tropical regions, like India.
- It has also strengthened the low-pressure systems, which are aided by high temperatures.
- This results in very heavy rainfall recorded along their trajectory during the monsoons.
- Now, with ART, scientists will be able to generate and obtain long-term observations on cloud microphysics, precipitation, convection, and land-surface properties, among a host of other parameters.
- This information will be assimilated and fed into the numerical weather models to enhance forecast output, especially the rainfall forecasts.
- More accurate forecasts will ultimately help the farming community plan their activities better.
Why Madhya Pradesh?
- The ART has been established at Silkheda, a location that falls directly in line with the path of major rain-bearing synoptic systems.
- This will facilitate direct monitoring and tracking.
- Besides, the locality is pristine and free of anthropogenic and other pollutants, making it the best site in central India for setting up sensitive, high-end meteorological instruments and observatories for recording data.
Bengaluru's Rameshwaram cafe blast puts the spotlight on IEDs

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least nine people were injured after an explosion at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area recently, possibly by an improvised explosive device (IED).
What is Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)?
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) refers to a makeshift explosive device constructed and deployed unorthodoxly or improvised.
- These devices are typically crafted using commonly available materials, including explosives, triggers, and containers, often to cause destruction, injury, or death.
- IEDs can vary widely in design and complexity, ranging from simple pipe bombs to more intricate devices incorporating timers, remote controls, or even cellular communication for activation.
- IEDs can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- Due to their adaptable nature, IEDs are commonly used by insurgents, terrorists, and other malicious actors to carry out attacks against both military and civilian targets.
- Their unpredictable nature and often concealed placement make them particularly challenging for security forces to detect and mitigate.
- Efforts to counter IED threats involve a combination of technological advancements, intelligence gathering, and counterinsurgency strategies aimed at identifying and neutralizing these devices before they can cause harm.
Types of IEDs:
- Vehicle-Borne IEDs: Among the most destructive forms of IEDs are those concealed within vehicles. These can be driven to specific locations and detonated, causing massive explosions capable of levelling buildings.
- Suicide Bombings: Suicide bombings involve individuals strapping IEDs to their bodies, becoming human carriers of destruction. This method inflicts maximum damage in densely populated areas.
- Package IEDs: Package IEDs are small devices hidden in innocuous-looking packages. They are often placed in public spaces, targeting unsuspecting victims.
Methods of IED Initiation:
- Remote Control: IEDs can be remotely triggered using various methods, such as cell phones or radio signals, allowing attackers to maintain a safe distance from the explosion.
- Pressure Activation: Pressure-sensitive IEDs detonate when a certain amount of pressure is applied, making them lethal traps for those who inadvertently trigger them.
- Timers: IEDs can also be equipped with timers, which delay the explosion to occur at a specific time, further complicating detection and prevention.
The Devastating Impact of IEDs:
- The aftermath of IED explosions is often catastrophic, leading to loss of life, severe injuries, and widespread damage to infrastructure.
- The psychological impact on survivors and affected communities can be long-lasting.
Detection Technologies and Challenges:
- Detection technologies such as (Metal Detectors, X-ray and Imaging Scanners, Explosive Trace Detection (ETD), and Sniffer Dogs) play a critical role in countering the threat of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), but they also face numerous challenges due to the evolving nature of these devices.
Ladakh: Centre agrees to examine demand for statehood, inclusion in Sixth Schedule of Constitution

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Centre has agreed to examine whether the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution can be implemented in Ladakh.
What is the Sixth Schedule?
- The Sixth Schedule under Article 244 provides for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions — Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) — that have some legislative, judicial, and administrative autonomy within a state.
- ADCs have up to 30 members with a term of 5 years and can make laws, rules and regulations with regard to land, forest, water, agriculture, village councils, health, sanitation, village- and town-level policing, inheritance, marriage and divorce, social customs and mining, etc.
- The Bodoland Territorial Council in Assam is an exception with more than 40 members and the right to make laws on 39 issues.
- The Sixth Schedule applies to the Northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram (three Councils each), and Tripura (one Council).
Why does Ladakh want to be part of the Sixth Schedule?
- There was much enthusiasm initially, mostly in Leh, after the August 5, 2019 decisions that created two new Union Territories.
- The Buddhist-dominated Leh district had long demanded UT status because it felt neglected by the erstwhile state government, which was dominated by politicians from Kashmir and Jammu.
- This development has sparked concerns among locals regarding potential challenges related to identity preservation, resource allocation, and administrative oversight.
- Also, the changed domicile policy in Jammu and Kashmir has raised fears in the region about its own land, employment, demography, and cultural identity.
- The UT has two Hill councils in Leh and Kargil, but neither is under the Sixth Schedule.
- Their powers are limited to the collection of some local taxes such as parking fees and allotment and use of land vested by the Centre.
- The Sixth Schedule empowers the Governor of the State to designate specific areas as administrative units within the Autonomous Districts and Autonomous Regions.
Can Ladakh be included in the Sixth Schedule?
- In September 2019, the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes recommended the inclusion of Ladakh under the Sixth Schedule, noting that the new UT was predominantly tribal (more than 97%), people from other parts of the country had been restricted from purchasing or acquiring land there, and its distinct cultural heritage needed preservation.
- Notably, no region outside the Northeast has been included in the Sixth Schedule.
- In fact, even in Manipur, which has predominantly tribal populations in some places, the autonomous councils are not included in the Sixth Schedule.
- Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, which are totally tribal, are also not in the Sixth Schedule.
- “Ladakh’s inclusion in the Sixth Schedule would be difficult.
- The Constitution is very clear, the Sixth Schedule is for the Northeast.
- For tribal areas in the rest of the country, there is the Fifth Schedule.
- However, it remains the prerogative of the government — it can, if it so decides, bring a Bill to amend the Constitution for this purpose.
Kiru Hydropower Corruption Case: CBI Searches J&K Ex-Governor Satya Pal Malik’s Premises

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The CBI conducted searches at the premises of former Jammu and Kashmir governor Satya Pal Malik and 29 other locations recently in connection with alleged corruption in the Rs 2,200-crore Kiru Hydropower project.
What are the Corruption Allegations Surrounding the Kiru Hydel Project?
- During his tenure as the governor of Jammu and Kashmir from August 23, 2018, to October 30, 2019, Satya Pal Malik claimed that he was offered a Rs 300-crore bribe to approve two files, one of which pertained to the project.
- In 2022, the J&K government requested a CBI investigation into alleged misconduct, previously highlighted by Satya Pal Malik, in the awarding of two government contracts.
- Concerns have been raised regarding the award of civil works, particularly to Patel Engineering Ltd, a prominent infrastructure and construction company established in 1949.
- The CBI has initiated action against the former CVPPPL chairman, MD, and Directors, as well as Patel Engineering.
- According to the FIR, an inquiry by the J&K Anti-Corruption Bureau and the Power Department had been conducted.
- The FIR alleges non-compliance with e-tendering guidelines in the awarding of civil works for the project.
- Additionally, accusations of substandard work and failure to employ local youth have been levelled against the hydel project.
What is the Kiru Hydel Power Project?
- The 624MW Kiru hydroelectric project is being developed as a run-of-river scheme in the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory in India.
- Location of the Kiru project: The Kiru hydropower project is being built along the Chenab River near the villages of Patharnakki and Kiru, approximately 42 km from Kishtwar.
- It will be located between the Kirthai II hydroelectric project to its upstream and the Kwar hydroelectric project to its downstream.
- The project is being developed by the Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPPPL) joint venture (JV) between:
- National Hydroelectric Power (NHPC, 49%)
- Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development (JKSPDC, 49%) and
- The Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%)
- The Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) awarded environmental clearance for the hydroelectric project in 2016 while the foundation stone was laid in February 2019.
- The project is being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 4,287 crore and is expected to start commercial operations in July 2025.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the investment in the project in March 2019.
- Apart from helping address the energy demand across northern India and the state’s rural areas, it could aid small-scale and cottage industries.
Advantages of the Kiru Hydroelectric Power Project:
- This project aims to alleviate the energy shortage in Northern India while also enhancing the transportation, education, healthcare, and road infrastructure in the area.
- By bringing electricity to rural communities, the project will lessen the reliance of residents on alternative energy sources.
- The heightened power availability will foster the growth of small-scale and cottage industries, generating employment opportunities and revenue for the local populace.
What is a Run-of-river Project?
- Run-of-river hydropower is a facility that channels flowing water from a river through a canal or penstock to spin a turbine.
- Typically a run-of-river project will have little or no storage facility.
- Run-of-river provides a continuous supply of electricity (base load), with some flexibility of operation for daily fluctuations in demand through water flow that is regulated by the facility.
