IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
How the Shock Syringe Works:
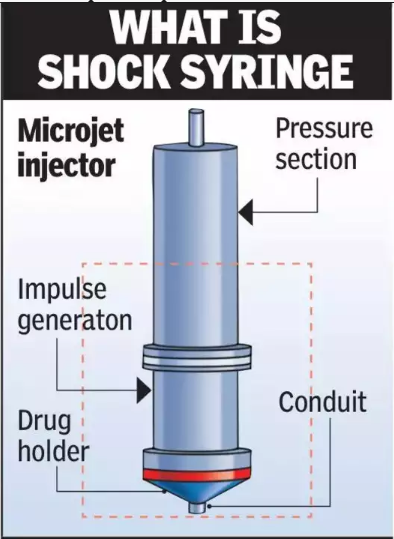
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
