Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
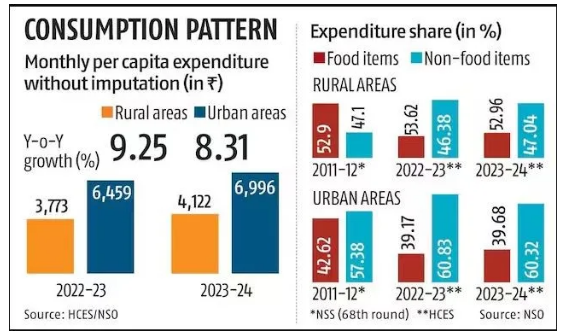
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
