H-1B Visa
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
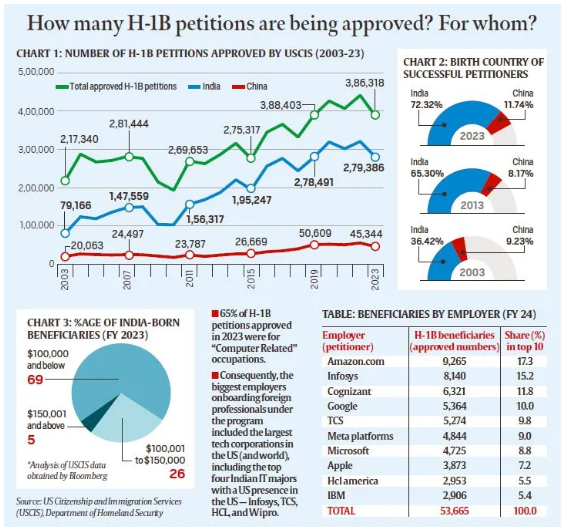
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
