Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
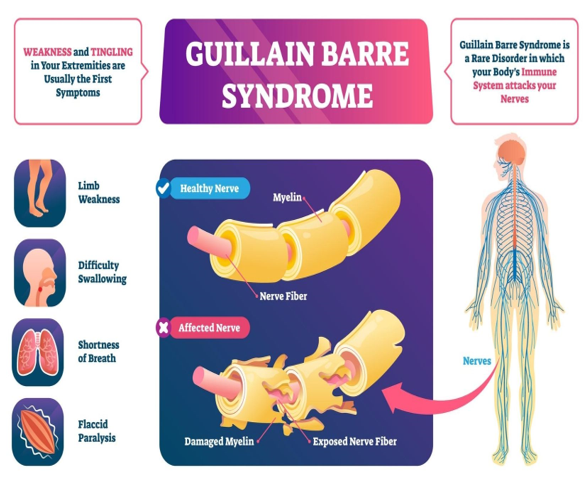
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
