Dark Oxygen
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
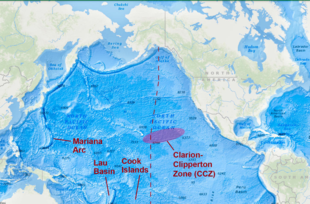
Where was it discovered?
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
