World’s 1st Functioning AI-designed Viral Genome

- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
Scientists at Stanford University and the Arc Institute have created the world’s first artificially designed viral genome using Artificial Intelligence (AI), marking a major milestone in computational biology and synthetic genomics. The breakthrough demonstrates AI’s capability to generate an entirely new and functional virus—one that can infect and kill bacteria.
About the Discovery
The AI-generated virus was designed using a genomic model called Evo, which functions like a “language model” for DNA. Evo was trained on nearly two million viral genomes, learning the patterns and grammar of genetic sequences—akin to how language models learn human syntax and semantics.
The model was guided to mimic the bacteriophage ΦX174 (phi-X-174), a virus that infects E. coli bacteria. This phage was chosen because:
- It has a small yet complex genome (about 5,386 DNA letters and 11 overlapping genes).
- It was the first genome ever sequenced (1977) and the first synthesized from scratch (2003)—now it is the first AI-designed genome.
How It Was Done
- Training the AI: Evo was trained on millions of viral sequences to understand gene order, composition, and regulatory logic.
- Design Phase: Using prompts, Evo generated thousands of potential genome designs.
- Screening & Testing: Researchers filtered these using software checks to ensure each genome contained the necessary genes and functional proteins.
- Lab Validation: Hundreds of genomes were synthesized and inserted into E. coli bacteria. Out of 302 attempts, 16 fully functional viruses emerged.
- Results:
- These viruses contained over 392 mutations never seen in nature.
- Some designs achieved functions human scientists had failed to engineer, such as borrowing DNA-packaging proteins from unrelated viruses.
- Cryo-electron microscopy confirmed the structural integrity of these AI-designed proteins within the viral shell.
What is a Virus?
A virus is a microscopic infectious agent made of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) enclosed within a protein coat (capsid).
- It cannot replicate independently and must hijack a host cell’s machinery to reproduce.
- Many viruses cause diseases like COVID-19, AIDS, measles, and smallpox.
What is a Genome?
The genome is the complete set of DNA instructions in an organism.
- In humans, it comprises 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus plus mitochondrial DNA.
- It encodes all genetic information required for growth, development, and functioning.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Redefining Synthetic Biology:The experiment represents a leap from reading and writing genomes to designing them. AI is now capable of generating entirely new, functional genetic blueprints.
- Advancing Phage Therapy:The AI-designed bacteriophages could revolutionize phage therapy—the use of viruses to target and kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a major global health threat.
- Accelerating Biotechnology:This development showcases how AI can drastically accelerate genetic innovation, enabling rapid design and testing of new biological entities.
- Proof of Concept for AI-Driven Evolution:AI-generated viruses adapted to bacterial defenses faster than natural ones, indicating potential for directed evolution through computational models.
- Ethical and Regulatory Implications:While promising, the creation of new synthetic organisms underscores the need for global biosafety, biosecurity, and ethical frameworks to govern AI-driven genetic design.
Semiconductor Designers Power India’s Chip Dreams

- 24 Sep 2025
In News:
India’s semiconductor ecosystem is witnessing a transformative shift — from being a consumer-driven electronics market to an emerging design and manufacturing hub. While the country’s large-scale semiconductor fabrication projects are still in early stages, the chip design sector is already thriving, positioning India as a critical player in the global semiconductor value chain.
Policy Framework: Semicon India Mission
The turning point came in 2021, when the Government of India launched the ?76,000 crore Semicon India Programme, aimed at developing India into a global hub for electronics design and manufacturing.
- Manufacturing Push:The mission provides 50% capital support for semiconductor fabrication (fab) and assembly, testing, marking, and packaging (ATMP/OSAT) facilities, with states adding 20–25% additional incentives.
- Ten major projects have been approved across Gujarat, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Assam.
- Notably, Micron’s ?22,500 crore ATMP facility in Gujarat is under construction and expected to begin operations in 2024.
- Design Support:The Design Linked Incentive (DLI) and Chips to Startup (C2S)programmes aim to nurture a new generation of semiconductor designers.
- The C2S initiative provides free access to high-end Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools from Siemens, Cadence, and Synopsys, while targeting the training of 85,000 engineers in five years.
India’s Edge in Semiconductor Design
- India today accounts for 20% of the global semiconductor design workforce, hosting around 1.25 lakh chip designers who develop nearly 3,000 chips annually.
- Multinational firms like NVIDIA, Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm run large R&D operations from India, spread across Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune, and Noida.
- Even as the world faces a projected shortage of one million chip designers by 2030 (Deloitte), India’s deep talent pool offers a natural advantage.
- The country produces over 8 lakh engineering graduates annually, with around 5.7 lakh enrolled in electronics and related disciplines (2021–22).
Academia–Industry Collaboration: Bridging the Gap
- Despite government efforts, experts underline a persistent disconnect between academia and industry. Indian industries invest only 0.4% of profits in academic R&D, compared to 5–6% in the U.S. and South Korea.
- Strengthening collaboration — through joint research, funded Ph.D. programs, and internship pipelines — is essential to make graduates industry-ready and sustain innovation.
- Institutions like IITs, IISc, and IIITs have begun partnerships with leading toolmakers such as Synopsys, Lam Research, and Cadence to enable frontier-level projects at sub-10 nanometer design nodes.
Economic and Strategic Implications
- High-Value Employment: Semiconductor jobs have a multiplier effect of 6.7, driving indirect employment in allied sectors.
- Export Potential: Electronics exports are projected to quintuple by 2026, narrowing India’s trade deficit.
- Strategic Autonomy: Domestic chip capacity reduces dependence on foreign suppliers, vital for defence, telecom, and automotive sectors.
- Innovation Push: With rising patent filings and homegrown IP, India is consolidating its role in the global tech value chain.
Riyadh Design Law Treaty (DLT)

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- India reaffirms its commitment to inclusive growth and strengthening its intellectual property (IP) ecosystem.The signing of the treaty comes after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Highlights:
Purpose of the DLT:
- Aims to harmonize industrial design protection frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
- Improves efficiency and accessibility of design registration processes.
Key Features of the DLT:
- Grace Period: A 12-month grace period after the first disclosure of the design, ensuring its validity for registration.
- Flexibility for Applicants: Provides relief measures such as relaxed deadlines, reinstatement of lost rights, and flexibility in adding priority claims.
- Simplified Processes: Includes simplified procedures for design renewals, assignment, and license recording.
- E-Filing Systems: Promotes the adoption of electronic filing systems and exchange of priority documents.
Benefits of DLT:
- Empowering SMEs and Startups: Helps small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups protect designs globally, enhancing competitiveness and market growth.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Standardizes procedures, making the design protection process less complex, more predictable, and affordable.
- Support for Developing Countries: Offers technical assistance for implementation in developing and least-developed countries.
Significance for India:
- India’s rich heritage of design and craftsmanship underscores the importance of design protection for sustainable economic growth.
- Design registrations in India have surged, with a 120% increase in domestic filings over the last two years.
Supporting Programs:
- The treaty’s provisions align with India’s initiatives like Startup India and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) Scheme to boost the protection and commercialization of designs for Indian innovators.
Broader Impact:
- DLT aims to integrate design protection with traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, further enhancing protection for India’s diverse creative sectors.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a specialized UN agency established in 1967, promoting IP rights globally.
- India is a member of WIPO, which has 193 member countries.
Overview of Intellectual Property (IP):
- IP includes creations like inventions, industrial designs, literary and artistic works, symbols, and more, which are used in commerce.
- IP rights protect creators, allowing them to benefit from their work when commercially exploited.
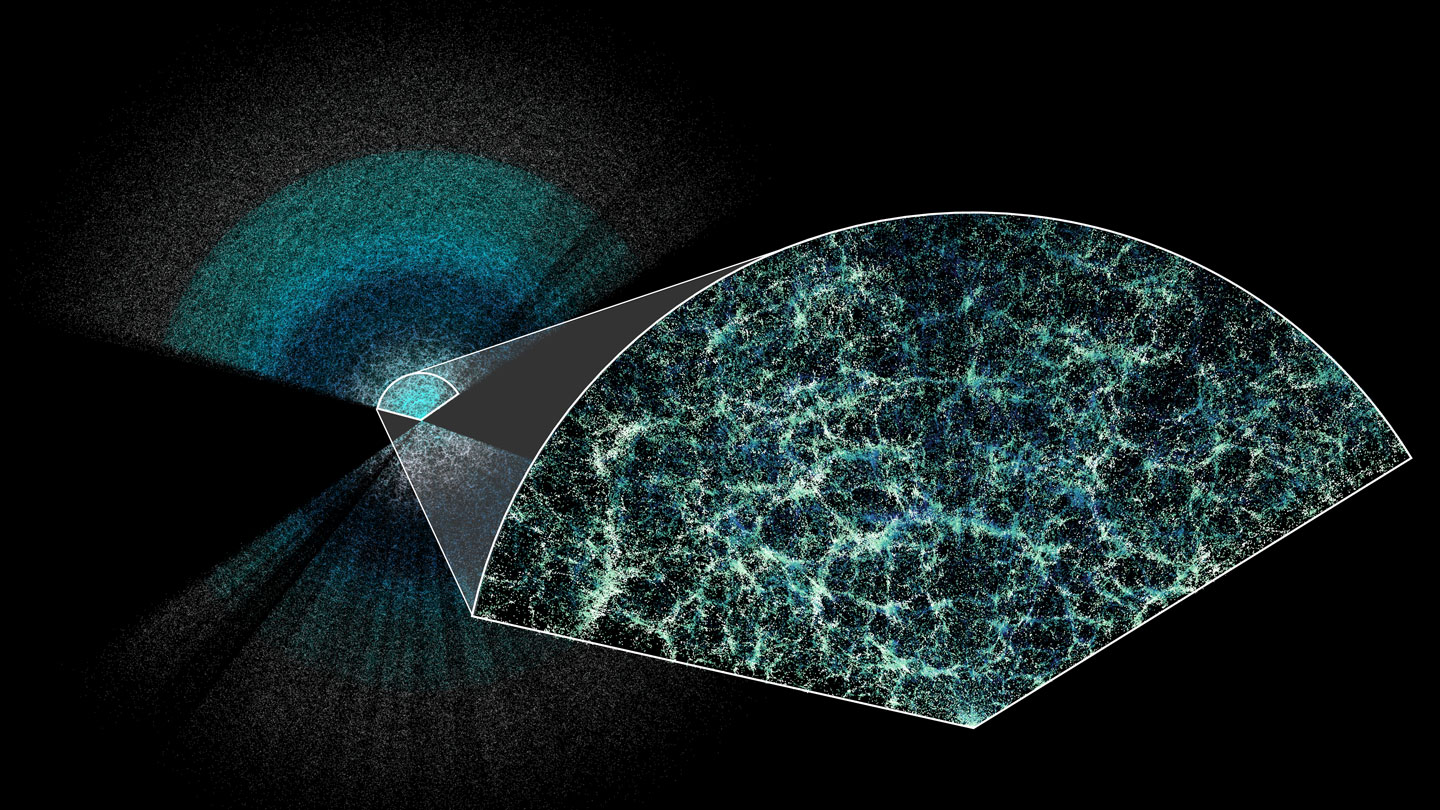
3D Cosmic Map May Open Window To Dark Energy
- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of researchers has just released the most comprehensive “three-dimensional” map of the universe, which, scientists hope, could reveal some clues about dark energy, the mysterious force that is believed to be causing the universe to expand uncontrollably.
Context:
- An international team of researchers has unveiled an extensive 3D map of the universe, aiming to unlock secrets about dark energy, the enigmatic force thought to be driving the universe's rapid expansion.
- Led by Shadab Alam from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in Mumbai, the team collaborated on this groundbreaking project, utilizing the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), a specialized tool capable of simultaneously gathering light from 5,000 galaxies when attached to a telescope.
- The DESI collaboration has measured that the expansion rate of the universe was increasing by 68.5 km per second after every 3.26 million light-years of distance, a unit astronomers define as megaparsec.
About Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI):
- The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is a remarkable tool designed to capture light from an impressive 5,000 galaxies simultaneously when attached to a telescope.
- This collaborative effort involves over 900 researchers from institutions worldwide, with the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) representing India's sole participating institution.
- DESI, stationed atop the Mayall 4-Meter Telescope in Arizona, United States, has enabled researchers to analyze light emissions from an astounding six million galaxies, some dating as far back as 11 billion years ago.
- This wealth of data has facilitated the creation of the most intricate map of the universe to date.
Dark Energy Vs Dark Matter:
- Dark energy and dark matter are two distinct yet mysterious components of the universe, with vastly different properties and effects on cosmic structures.
Nature and Composition:
- Dark Energy: Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe.
- It is often associated with a cosmological constant or Einstein's "cosmological antigravity."
- Dark energy is thought to exert a repulsive force that counteracts gravity on cosmic scales, driving galaxies away from each other at an accelerating rate.
- However, its precise nature remains one of the greatest mysteries in modern physics.
- It's important to note that dark energy does not matter; rather, it's an energy density inherent in space itself.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter is a form of matter that does not emit, absorb, or reflect electromagnetic radiation, making it invisible and detectable only through its gravitational effects.
- Unlike dark energy, dark matter exerts an attractive gravitational force, influencing the motion of galaxies and other cosmic structures.
- It interacts with ordinary matter and with itself only through gravity and possibly through weak nuclear force, but not through electromagnetic forces like photons.
- Various astrophysical observations strongly suggest the existence of dark matter, but its precise composition and particle nature are still unknown.
Effects on the Universe:
- Dark Energy: The primary effect of dark energy is to drive the accelerated expansion of the universe.
- This expansion results in the increasing separation between galaxies over time. Dark energy is thought to dominate the energy density of the universe, comprising approximately 68% of the total mass-energy content.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter plays a crucial role in the formation and structure of galaxies and larger cosmic structures.
- Its gravitational influence binds galaxies together and provides the framework for the large-scale cosmic web.
- While dark matter does not emit or interact with light, its presence can be inferred from gravitational lensing, galaxy rotation curves, and the large-scale distribution of matter in the universe.
- Dark matter is estimated to constitute about 27% of the total mass-energy content of the universe.
Detectability:
- Dark Energy: Dark energy is challenging to detect directly because it does not interact with electromagnetic radiation.
- Its existence is inferred from the observational data related to the accelerating expansion of the universe, such as measurements of distant supernovae and the cosmic microwave background radiation.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter is also challenging to detect directly due to its non-interaction with light.
- However, its gravitational effects on visible matter and radiation allow astronomers to indirectly infer its presence.
- Various experimental efforts, such as those involving particle accelerators and underground detectors, aim to detect dark matter particles directly, though success has not yet been achieved.
Project GR00T

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI chip leader Nvidia on Tuesday (March 19) announced Project GR00T or Generalist Robot 00 Technology, which promises to revolutionize the evolution of humanoid robots.
What is Project GR00T?
- Project GR00T stands for Generalist Robot 00 Technology.
- It is essentially a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots.
- This ambitious project aims to create a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots, enabling them to understand natural language, learn new skills from observing humans, and solve various tasks in real-time.
- Robots built on this platform are designed to understand natural language and emulate movements by observing human actions, such as instantly learning coordination, dexterity, and other skills.
- This can help the robots navigate and engage with the real world around them.
- The goal of Project GR00T is to advance the field of embodied artificial general intelligence (AGI) and drive breakthroughs in robotics.
- NVIDIA intends to leverage its expertise in AI and its technological resources to develop this foundational model, which would provide humanoid robots with human-like abilities, such as emotion, reaction, and movement.
The Potential Consequences of Project GR00T and Humanoid Robots in the Workforce:
- As humanoid robots, such as those envisioned by NVIDIA's Project GR00T, become more advanced and capable of handling various hazardous or repetitive tasks, concerns arise over potential job displacement.
- For instance, Nvidia's partnership with Hippocratic AI to develop AI-powered healthcare agents may lead to a reduction in the demand for nurses.
- However, proponents argue that these robots can serve as valuable aids for humans, enhancing their quality of life and complementing their skills rather than supplanting them entirely.
- Consequently, the impact of humanoid robots on the workforce may ultimately depend on their successful integration into existing labor structures, as well as the willingness and ability of society to adapt to this transformative technology.
The need to overhaul a semiconductor scheme (The Hindu)
- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The semiconductor Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme, set to undergo a mid-term appraisal, has so far approved only seven start-ups, falling significantly short of its intended goal of supporting 100 over a span of five years since its announcement.
About Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme:
- Under the DLI scheme, government will provide financial incentives and design infrastructure to domestic companies, start-ups and MSMEs focussed on semiconductor design.
- The DLI scheme has been announced by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) to offset the disabilities in the domestic industry involved in semiconductor design in order to not only move up in value-chain but also strengthen the semiconductor chip design ecosystem in the country.
- C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing), a scientific society operating under MeitY, will serve as the nodal agency for implementation of the DLI scheme.
Objectives:
-
- Nurturing and facilitating the growth of the domestic companies, startups and MSMEs.
- Achieving significant indigenization in semiconductor content and IPs involved in the electronic products deployed in the country, thereby facilitating import substitution and value addition in the electronics sector.
- Strengthening and facilitating access to semiconductor design infrastructure for startups and MSMEs.
Duration: The scheme shall initially be for three (3) years from 01-01-2022.
- The scheme has three components – Chip Design infrastructure support, Product Design Linked Incentive and Deployment Linked Incentive.
- Under the Chip Design infrastructure support, C-DAC will set the India Chip Centre to host the state-of-the-art design infrastructure (viz. EDA Tools, IP Cores and support for MPW (Multi Project Wafer fabrication) & post-silicon validation) and facilitate its access to supported companies.
- Under the Product Design Linked Incentive component, reimbursement of up to 50% of the eligible expenditure subject to a ceiling of ?15 Crore per application will be provided as fiscal support to the approved applicants who are engaged in semiconductor design.
- Under the Deployment Linked Incentive component, an incentive of 6% to 4% of net sales turnover over 5 years subject to a ceiling of ?30 Crore per application will be provided to approved applicants whose semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor linked design are deployed in electronic products.
- The DLI Scheme will also take a graded and pre-emptive approach to Identify the Products of national priorities and implement strategies for their complete or near complete indigenisation & deployment thereby taking steps towards the import substitution & value addition in strategic & societal sectors.
ENCORE (NewsOnAIR)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) has developed in-house software named ‘ENCORE’ designed for efficient candidate and election management.
About ‘ENCORE’:
- The Election Commission of India has designed in-house software for complete Candidate and election management through ‘ENCORE’ which stands for Enabling Communications on Real-time Environment.
- This provides a seamless facility for Returning Officers to process candidate nomination, affidavit, Voter turnout, counting, results and data management.
- The ENCORE counting application is an end-to-end application for returning officers to digitize the votes polled, tabulate the round-wise data and then take out various statutory reports of counting.
- An additional application, the ENCORE Scrutiny Application, allows Returning Officers to scrutinize online nominations submitted by candidates.
- This process involves verifying and marking the status of nominations as Accepted, Rejected, or Withdrawn, facilitating the creation of the final list of contesting candidates and symbol assignment.
- The ECI offers an online portal for candidate nomination and affidavit submission.
- Candidates can create accounts, complete nomination forms, submit security deposits, and plan their visits to the Returning Officer through this portal.
- The Candidate Affidavit portal is designed to display information about a candidate's financial assets and liabilities, offering transparency in candidates' financial disclosures.
- The ENCORE Nodal App serves as a platform for various government departments, including fire, education, police, environment, and CPWD, to issue 'no objection' certificates.
- These certificates are required before granting permission for political parties or candidates to hold rallies, road shows, and meetings, ensuring that all necessary clearances are obtained before public events.
