Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The WHO–WMO joint report (2025), Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress, warns that rising global temperatures are creating an unprecedented occupational health and productivity crisis. The year 2024 was the warmest on record, with global average temperatures 1.45°C above pre-industrial levels, and the decade 2015–2024 being the hottest ever recorded.
Key Findings
- Productivity Losses: Each 1°C rise in Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) above 20°C reduces global worker productivity by 2–3%. Sun exposure further raises WBGT by 2–3°C, amplifying risk.
- Scale of Exposure: Over 2.4 billion workers are directly exposed; annually, 22.85 million injuries, 18,970 deaths, and 2.09 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) are linked to workplace heat stress (ILO estimates).
- Geographical Hotspots: South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and the Middle East face the highest risks. Heat stress now affects 30% of the global population seasonally or daily.
- Health Impacts: More than one-third of workers in hot conditions report physiological heat strain (hyperthermia, kidney dysfunction, dehydration, neurological problems). WHO safety guidance (1969) recommends that core body temperature during an 8-hour shift not exceed 38°C, a threshold increasingly breached.
- Climate Change Dimension: Daytime peaks of 40–50°C are becoming frequent even outside the tropics. Europe’s 2023 heatwave saw worker fatalities, showing that occupational heat stress is no longer limited to equatorial regions.
India’s Experience
In India, informal workers in brick kilns, construction, agriculture, and power looms are the most affected. Many begin work before sunrise to avoid peak heat, yet still suffer dehydration, dizziness, and lost wages as work hours shrink. Indoor workplaces with poor ventilation often become “furnaces,” leading to chronic fatigue, kidney strain, and even fatalities. By 2030, the ILO projects India could lose 34 million full-time equivalent jobs, particularly in agriculture and construction, due to heat stress.
Wider Implications
- Public Health Burden – Rising cases of heat stroke, cardiovascular collapse, and chronic kidney disease (26.2 million cases in 2020 alone) strain already weak health systems.
- Economic Losses – Developing economies face shrinking GDP as productivity drops; agriculture and construction are most vulnerable.
- Social Inequality – The poor, migrant labourers, and women are disproportionately at risk due to unsafe working conditions and lack of social protection.
- Climate Justice – Regions contributing least to emissions, like Bangladesh and Sub-Saharan Africa, suffer the harshest effects, deepening global inequities.
- Food Security – Agricultural labour productivity loss disrupts crop cycles and threatens farmer incomes, worsening hunger and malnutrition.
- Legal Burden – Rising occupational illness cases risk overwhelming compensation systems and highlight gaps in labour safety laws.
Adaptation Strategies
- Occupational Heat Action Plans: Early warning systems, rescheduling work timings, shaded shelters, and worker training.Example: The Ahmedabad Heat Action Plan (India) has reduced heatwave mortality through alerts, shelters, and training.
- Infrastructure & Technology: Cooling shelters, hydration points, and mechanisation to reduce manual strain.Example: Bangladesh’s garment sector has piloted low-cost ventilation and cooling fans, lowering worker fatigue.
- Labour Policy Reforms: Enforcing heat-index-based work-hour rules, mandatory rest breaks, and compensation for heat-linked illnesses.Example: Qatar bans outdoor work between 10 am–3:30 pm during peak summer.
- Public Health Measures: Hydration protocols, health screenings, and recognition of heat stress as an occupational disease.Example: US OSHA’s “Water–Rest–Shade” campaigninstitutionalises hydration and rest breaks.
- Global & National Coordination: Mainstreaming heat stress into ILO conventions, COP climate talks, and SDG frameworks, with climate finance support for vulnerable economies.Example: Australia integrates climate projections into mining and agriculture workplace safety standards.
Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025 began in Bonn, Germany, with over 5,000 delegates from governments, international organisations, civil society, and scientific bodies. It serves as a crucial platform for setting the technical and political groundwork ahead of COP29.
What is the Bonn Climate Conference?
- A mid-year climate summit held annually under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Also referred to as the Sessions of the UNFCCC Subsidiary Bodies (SBs).
- First held in 1995, after the UNFCCC was signed in 1992.
- Hosted in: Bonn, Germany (home of the UNFCCC headquarters).
- Organised by: The UNFCCC Secretariat.
Main Objectives
- Prepare for COP Summits: Provides a platform for technical discussions that shape the COP agenda (COP29 in this case).
- Review of Commitments: Tracks implementation of earlier climate agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Science–Policy Integration: Connects IPCC research with policymaking processes.
- Support for Developing Nations: Discusses climate finance and technology transfer mechanisms.
- Inclusive Participation: Engages Indigenous communities, NGOs, experts, and private stakeholders.
Subsidiary Bodies of the UNFCCC
- SBI (Subsidiary Body for Implementation):
- Reviews how climate commitments are implemented.
- Facilitates support for developing countries.
- SBSTA (Subsidiary Body for Scientific and Technological Advice):
- Provides scientific guidance.
- Bridges IPCC reports with UNFCCC decision-making.
Key Focus in 2025
Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA)
- Originally mentioned in the Paris Agreement (2015).
- Received major progress only during COP28 (Dubai).
- Aim: Establish a global, measurable, and equitable adaptation framework, similar to the 1.5°C target for mitigation.
- Bonn 2025 focuses on operationalising this goal, especially for climate-vulnerable nations.
Importance of the Bonn Conference
- Pre-COP Platform: Decisions taken here set the tone and agenda for COP summits.
- Technical + Political Dialogue: Encourages cooperation between scientists, policymakers, and climate negotiators.
- Influences Global Climate Action: Outcomes impact the direction of global climate governance.
Mount Kenya’s Rapid Glacier Retreat due to Climate Change

- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
Mount Kenya, Africa’s second-highest peak after Kilimanjaro, is witnessing a dramatic loss of its glacial cover due to accelerating climate change. Scientists warn that the mountain may become completely ice-free by 2030.
Key Findings:
- The Lewis Glacier, once one of the most prominent ice bodies on Mount Kenya, has experienced substantial shrinkage.
- A 2011 study by the University of Innsbruck (Austria) reported a 90% volume loss in Lewis Glacier between 1934 and 2010.
- A 2023 satellite analysis revealed that only 4.2% of the ice present in 1900 remains today.
About Mount Kenya:
- Location: Central Kenya, just south of the Equator.
- Elevation:5,199 meters (17,058 feet) at its highest peak, Batian.
- Geological Nature: An extinct stratovolcano, heavily eroded over millennia.
- Glaciers: Includes Lewis Glacier and Tyndall Glacier, among the last surviving tropical glaciers in Africa.
- UNESCO Status: Declared a World Heritage Site in 1997 for its ecological and cultural value.
ICJ Hearing on Landmark Climate Change Case

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has begun hearings on a landmark climate change case, seeking an advisory opinion on the obligations of countries under international law regarding climate change.
- The case stems from a UN General Assembly (UNGA) resolution initiated by Vanuatu in March 2023, co-sponsored by 132 countries.
Background:
- Vanuatu, a small island nation, faces existential threats from rising sea levels.
- The resolution was passed to clarify climate obligations in light of international laws, including the UNFCCC, Paris Agreement, and other legal instruments like the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas, and the Universal Declaration on Human Rights.
Global Impact of the Case:
- The outcome of the case could influence global climate governance, particularly in the context of climate negotiations.
- It may broaden the legal basis for climate obligations and underscore the legal consequences for non-compliance.
India’s Position:
- India has voiced concerns about the judicial process being the best approach to tackle climate issues, advocating for diplomatic efforts.
- India is scheduled to make its submission on December 5, highlighting its preference for a collaborative, non-top-down approach in climate discussions.
Implications for Developed and Developing Countries:
- The case highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries for climate change due to their higher emissions.
- The ICJ's advisory opinion could reinforce the argument that developed countries' obligations extend beyond the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, incorporating broader international legal frameworks.
Climate Litigation and Precedent:
- The ICJ ruling could set a precedent for climate litigation, potentially influencing over 2,600 ongoing climate lawsuits globally.
- Notable rulings include the European Court of Human Rights, which held Switzerland accountable for failing to meet emissions targets, and India's Supreme Court recognizing the right to be free from adverse climate impacts in 2023.
Record Participation and Importance of the Case:
- The ICJ has received over 90 written submissions, with 97 countries and 12 international organizations participating in the hearings.
- The case is significant for the growing number of climate-related lawsuits and the evolving nature of international climate law.
Future Prospects:
- The ICJ’s advisory opinion, though non-binding, could significantly impact future climate negotiations, particularly in terms of responsibility sharing and climate finance.
- The outcome could also influence calls for compensation for climate damages, especially from vulnerable states like small island nations.
Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI 2025) report was released at the annual UN climate conference in Baku.
Key Highlights:
- It is published by think tanks German watch, New Climate Institute, and Climate Action Network International.It was first published in 2005.
- It tracks the progress of the world’s largest emitters in terms of emissions, renewables, and climate policy.
India's Ranking in Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- India's Rank: 10th (Dropped two places from the previous year).
- Key Factors for India's High Rank:
- Low per capita emissions: 2.9 tons of CO2 equivalent (global average: 6.6 tons).
- Rapid deployment of renewables: India is a leader in solar energy projects, including large-scale solar and rooftop solar schemes.
- Renewable energy targets: Aims for 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Energy efficiency standards: Introduced, but coverage remains inadequate.
- Electric vehicle (EV) deployment: Significant progress, especially in two-wheelers.
- Challenges for India:
- Heavy reliance on coal: India remains one of the top 10 countries with the largest developed coal reserves.
- Growth-oriented approach: Economic growth and energy demand continue to drive climate action, with limited change in climate policy expected.
- Future Pledges:
- Net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Global leadership in green energy.
CCPI 2025 Rankings Overview
Rank
Country
Key Points
1-3
Empty
No country performed well enough to achieve a "very high" rating.
4
Denmark
Leading climate actions but ranks 4th technically.
5
Netherlands
Strong climate performance, follows Denmark.
6
U.K.
Notable improvement due to coal phase-out and halting new fossil fuel licenses.
10
India
High performer, despite challenges like reliance on coal.
55
China
Largest emitter, heavily reliant on coal, ranks 55th despite promising plans.
57
U.S.
Second-largest emitter, ranks 57th with insufficient climate targets.
59
Argentina
Major climate policy setbacks, including potential exit from Paris Agreement.
64-67
Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Russia
Lowest-ranked, major oil and gas producers with weak climate policies.
General Findings of the Report
- CCPI Methodology: Assesses 63 countries (plus the EU) responsible for 90% of global emissions based on their emissions, renewable energy efforts, and climate policies.
- Global Trends:
- No country has been able to secure a "very high" rating across all categories.
- Denmark and Netherlands are among the top performers.
- The U.K. shows significant progress with its coal phase-out and fossil fuel policies.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
Emissions Gap Report 2024

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently published the Emissions Gap Report 2024, in anticipation of the COP29 meeting of the UNFCCC to be held in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Key Highlights:
- Current Trajectory of Global Warming:
- If countries continue with current environmental policies, global temperatures are expected to rise by 3.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- This is significantly higher than the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, with an effort to cap it at 1.5°C.
- Paris Agreement at Risk:
- Even if all Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are fully implemented (including both unconditional and conditional emissions reduction targets), the world would still experience 2.6°C of warming by 2030.
- This presents a major challenge to achieving the Paris Agreement’s climate goals.
- Urgent Need for Action:
- To limit global warming to 1.5°C, greenhouse gas emissions must peak before 2025 and decline by 43% by 2030.
- The report highlights the emission gap between current pledges and what is required to meet the 1.5°C goal.
- Record High Emissions:
- Global greenhouse gas emissions hit a record 57.1 gigatons of CO? equivalent in 2023.
- This represents an increase of 1.3% compared to 2022, continuing the upward trend from the previous decade.
- India’s Emissions:
- India’s greenhouse gas emissions grew by 6.1% between 2022 and 2023.
- Per capita emissions in India were 2.9 tCO?e in 2022, significantly lower than China (11 tCO?e) and the U.S. (18 tCO?e).
- G20 Countries’ Contribution:
- G20 countries, excluding the African Union, contributed 77% of global emissions in 2023.
- The six largest emitters (including China, U.S., and India) were responsible for 63% of global emissions.
- This shows a significant imbalance in emissions, with developed countries having much higher per capita emissions compared to developing nations like India and Africa.
- Necessary Emissions Cuts:
- To keep the 1.5°C target within reach, global emissions need to be cut by at least 7.5% annually until 2035.
- Cost of bridging the emissions gap: Achieving net-zero by 2050 will require USD 900 billion to USD 2.1 trillion annually, approximately 1% of global GDP.
- Emission Reduction Pathways:
- Renewable Energy: Scaling up solar and wind energy technologies could contribute up to 27% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Forest Conservation: Protecting and restoring forests could provide 20% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Other crucial measures include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to electric vehicles, and focusing on fuel switching in key sectors like transport, industry, and buildings.
- Disparities in Emissions:
- Despite changes over the past two decades, large disparities remain between emissions across regions.
- Developed countries have three times higher per capita emissions compared to the global average, while India, the African Union, and least developed countries continue to have much lower emissions.
- Call to Action:
- UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen urged countries to act now, stating: “No more hot air, please.” The urgency is to ramp up climate pledges and ensure stronger actions in the upcoming COP29 talks in Baku, Azerbaijan (November 2024), where nations must work to get on a 1.5°C pathway.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Established: 1972, following the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm.
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya.
- Governing Body: The United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), which is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on environmental matters, with 193 Member States.
- Programs & Initiatives: UNEP leads global efforts on climate action, ecosystem restoration, clean seas, and supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Reports: UNEP publishes crucial assessments like the Emissions Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, and Adaptation Gap Report, influencing global environmental policies.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
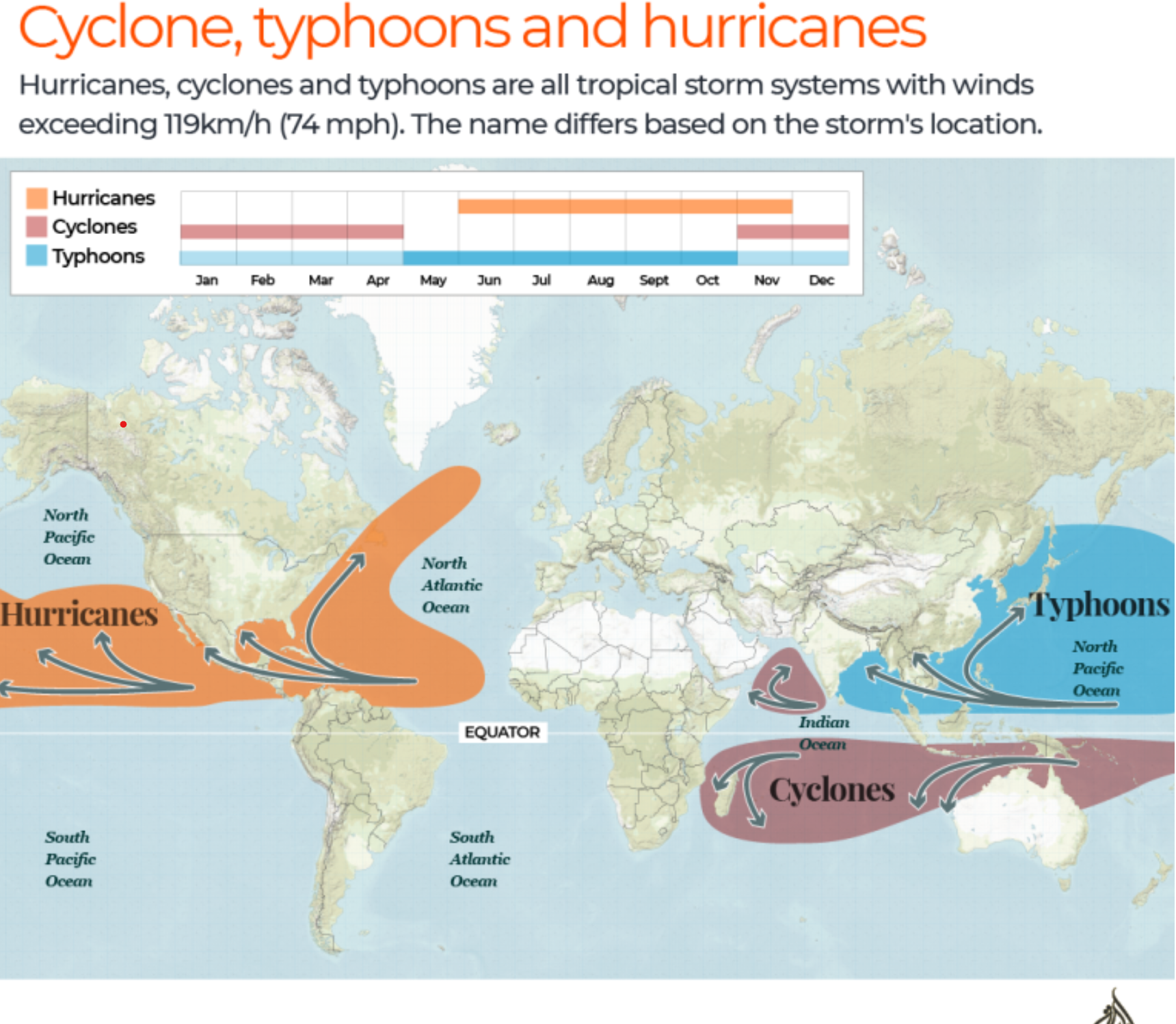
Increasing Frequency of Typhoons in Southeast Asia
- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Overview of Typhoons
- Definition: A typhoon is a type of cyclone with wind speeds of 119 km/h or more, forming over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- Mechanism: As warm, moist air rises from the ocean, it creates a low-pressure system, leading to the characteristic circular wind patterns: anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Recent Typhoon Events
- Typhoon Yagi: The most powerful tropical cyclone in Asia in 2024, with peak winds of 260 km/h. It caused significant destruction across Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand, displacing around 631,000 people and resulting in over 500 fatalities.
- Typhoon Bebinca: Reached wind speeds of 151 km/h, classified as a Category 1 storm, impacting eastern China with heavy rainfall and forcing evacuations for over 414,000 residents.
- Typhoon Shanshan: Affected Japan, bringing severe weather conditions.
Why are Typhoons more frequent?
- Rising Sea Surface Temperatures:
- Global warming has raised ocean temperatures, providing more energy for typhoon formation and intensification.
- Atmospheric Circulation Changes:
- Alterations in patterns, such as the weakening of the Walker Circulation, affect the frequency and paths of typhoons.
- El Niño and La Niña Effects:
- The El Niño-Southern Oscillation significantly influences typhoon activity. El Niño years often lead to increased typhoon occurrences in Southeast Asia, while La Niña can enhance cyclone activity in the Western Pacific.
- Increased Atmospheric Moisture:
- Higher global temperatures result in more evaporation, adding moisture to the atmosphere, which fuels stronger storms and increases rainfall intensity.
- Geographical Vulnerability:
- Southeast Asia’s location near warm ocean currents makes it a hotspot for typhoon activity, particularly along its extensive coastlines.
- Marine Heat Waves:
- Climate change has led to more frequent marine heat waves, causing extreme ocean warming, which contributes to intensified storms.
- Weaker Land-Sea Temperature Gradients:
- Changes in temperature differences between land and sea can prolong storm duration and severity.
- Urbanization and Environmental Degradation:
- Rapid urban development and the destruction of coastal ecosystems, like mangroves, diminish natural barriers against storm impacts.
Humanitarian Impact and Response
- The increasing intensity and frequency of typhoons have precipitated severe humanitarian crises in affected regions. The need for international cooperation in disaster response has become critical, involving collaboration among governments, civil societies, and humanitarian organizations to provide aid and support for those affected.
- Understanding the multifaceted reasons behind the rising frequency of typhoons is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts and enhance community resilience in Southeast Asia.
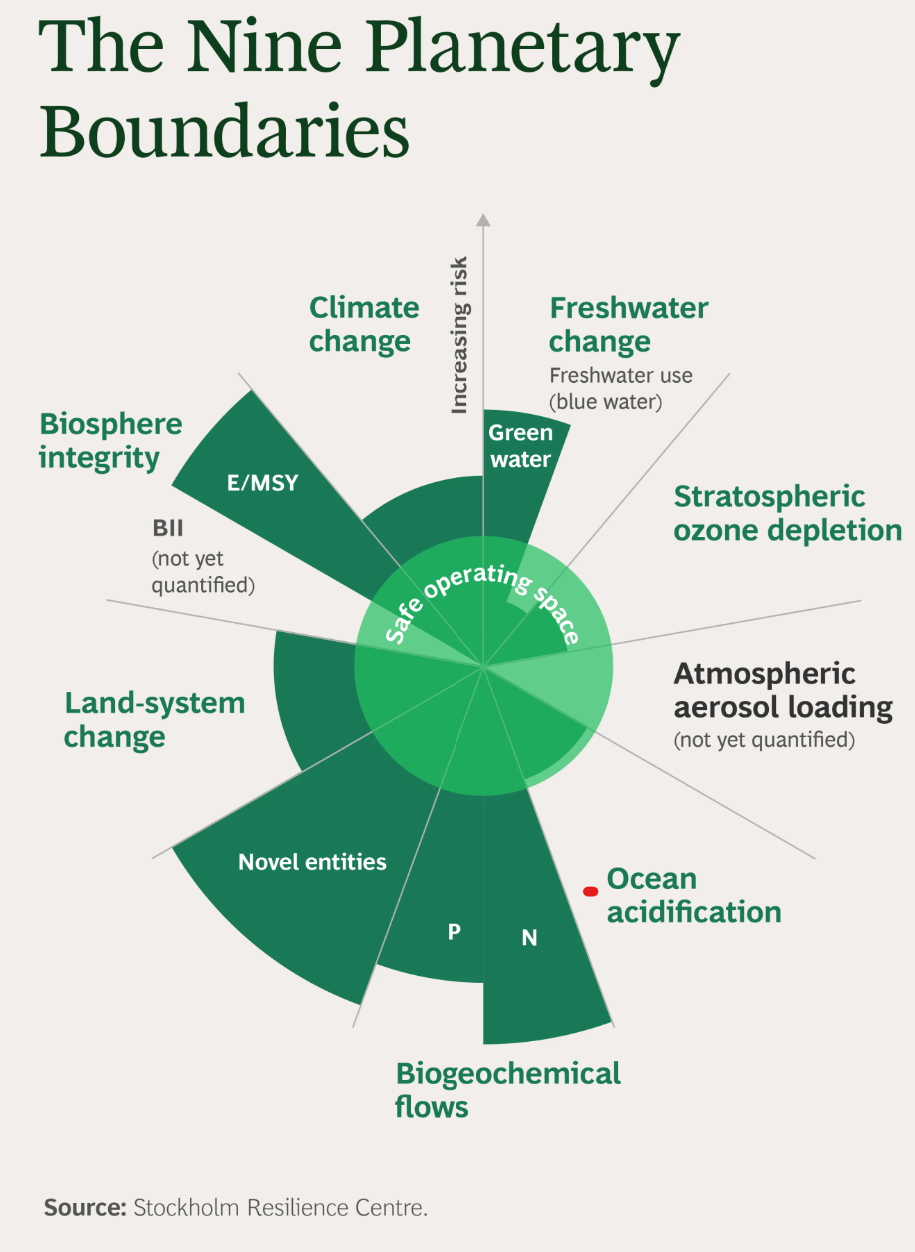
PLANETARY BOUNDARIES AND OCEAN ACIDIFICATION
- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
A new report from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) indicates that the world's oceans are nearing critical acidity levels.
- Key Findings:
- Nine Crucial Factors: The report identifies nine essential elements for sustaining life on Earth.
- Exceeded Limits: Six of these factors have already surpassed safe limits due to human activities.
- Ocean Acidification: This is poised to become the seventh boundary breached.
- Crossed Boundaries:
- Factors Affected:
- Climate change
- Loss of natural species and habitats
- Depletion of freshwater resources
- Increase in pollutants, including plastics and agricultural chemicals
- Factors Affected:
- Causes of Ocean Acidification:
- Primarily driven by rising carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels (oil, coal, gas).
- Implications of Acidification:
- Damage to corals, shellfish, and phytoplankton, disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Threats to food supplies for billions of people.
- Reduced capacity of oceans to absorb CO2, exacerbating global warming.
- Ozone Layer Status:
- Currently not close to being breached; showing recovery since the banning of harmful chemicals in 1987.
- Air Quality Concerns:
- A ninth boundary related to particulate matter is near danger limits.
- Improvements in air quality are noted, but industrializing nations still face pollution risks.
- Tipping Points:
- Crossing these boundaries could lead to irreversible and catastrophic consequences for humanity and future generations.
- All boundaries are interconnected; breaching one can destabilize the entire system.
- Opportunities for Solutions:
- Addressing critical issues, such as limiting temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, can have widespread benefits across multiple environmental challenges.
Planetary boundaries
- The planetary boundaries were introduced in 2009 to define the global environmental limits within which humans can safely live.
- Johan Rockström, former director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre, led a group of 28 renowned scientists to identify the nine processes that regulate the stability and resilience of the Earth system.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gas concentrations, primarily CO2, are the primary metric here. Exceeding the recommended levels risks amplifying global warming.
- Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorb CO2, leading to decreased pH levels. This boundary measures the carbonate ion concentration, vital for marine life like corals.
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion: The ozone layer protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation. This boundary emphasizes the ozone concentration in the stratosphere.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycles: Excess nitrogen and phosphorus, often from fertilizers, can disrupt ecosystems. Here, the focus is on their flow into the environment.
- Freshwater Use: Freshwater is vital for life. This boundary pinpoints the annual consumption of freshwater resources.
- Land-System Change: As we modify landscapes, particularly through deforestation, we alter habitats and carbon storage capabilities. This threshold concerns the amount of forested land remaining.
- Biodiversity Loss: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem resilience. This metric observes the extinction rate of species.
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading: Aerosols influence climate and human health. This boundary examines their density in the atmosphere.
- Chemical Pollution: Synthetic chemicals can harm ecosystems and human health. This boundary reviews their concentration and spread.
GREENLAND LANDSLIDE AND GLOBAL SEISMIC WAVES

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Massive Greenland landslide sent seismic waves around earth for 9 days. One year ago, roughly 25 million cubic metres of ice and rock splashed into the Dickson Fjord in Greenland and displaced the water enough to give rise to a 200-metre high mega-tsunami; in this way, a melting glacier led to a planet-wide tremor, and researchers warn that it may not be the last
Seismic Observations
- Detection: Unusual seismic signals recorded by stations worldwide, characterized by a single frequency, unlike typical earthquake vibrations.
- Classification: Initially termed a "USO" (unidentified seismic object) due to its atypical properties.
- Duration: Waves persisted for nine days, unlike typical aftershock patterns.
Investigation Efforts
- Collaboration: Involved over 68 researchers from 40 universities across 15 countries.
- Data Sources: Combined seismic data, satellite imagery, water level monitors, and a classified bathymetric map from the Danish Navy.
- Conclusion: The seismic waves resulted from a massive landslide caused by the collapse of Hvide Støvhorn peak, which triggered a series of events leading to the tsunami.
Mega-Tsunami and Seiche
- Tsunami Details:
- Created by the avalanche crashing into the fjord, displacing water significantly.
- Resulted in waves that reflected off fjord walls, reaching heights of nearly 110 meters due to the fjord's unique shape.
- Seiche Phenomenon:
- Oscillations in the fjord persisted for over nine days, reflecting the energy from the landslide.
- Maximum amplitude of the seiche recorded at 7.4 meters, with a frequency of 11.45 MHz.
Climate Context
- Global Warming Impact: Thinning glaciers contributed to instability in the region, making such landslides more likely.
- Future Predictions: Researchers warn of increased frequency and scale of similar events as climate change continues to affect Arctic and subarctic regions.
Key Takeaways
- The Greenland landslide serves as a reminder of the unpredictable consequences of climate change, including massive geological events.
- The incident highlights the interconnectedness of natural systems and the potential for localized events to have global repercussions.
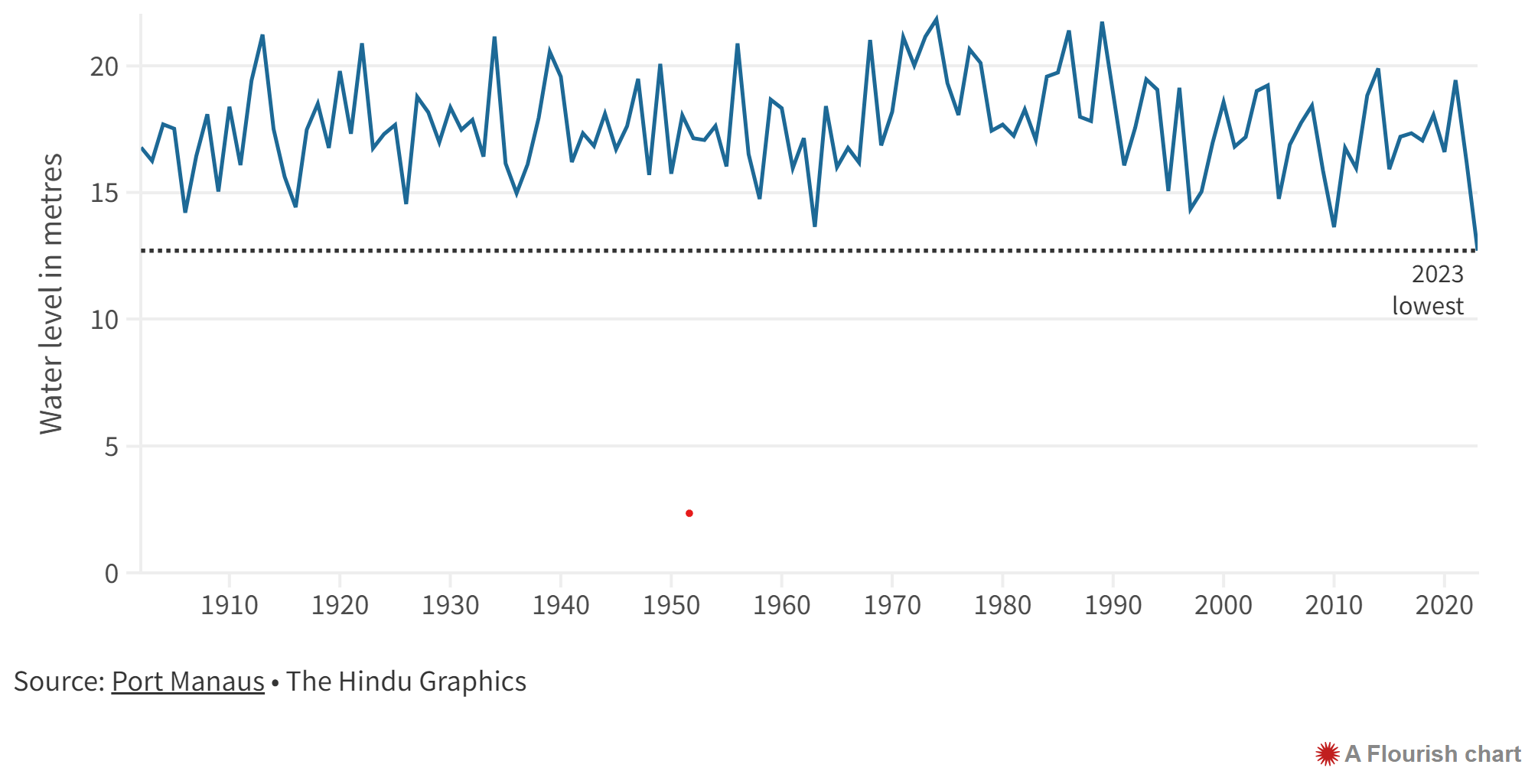
Climate change drives Amazon rainforest's record drought, study finds
- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
The drought that hit all nine Amazon rainforest countries - including Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Peru - is expected to worsen in 2024
Role of Climate Change:
- Likelihood Increase: Climate change made the drought 30 times more likely.
- Temperature and Rainfall: It drove extreme high temperatures and contributed to lower rainfall.
Future Projections:
- Expected Worsening: The drought is predicted to worsen in 2024, with the rainy season expected to recede in May.
Impact on Ecosystems:
- River Levels: Rivers have reached their lowest levels on record, with the Rio Negro river falling to its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) since records began in 1902.
- Dolphin Deaths: At least 178 endangered pink and gray Amazon river dolphins died due to low water levels and high temperatures.
- Fish Deaths: Thousands of fish died from low oxygen levels in Amazon tributaries.
Impact on Human Life:
- Disruptions: Waterways dried up rapidly, forcing people to undertake long journeys across dried river sections to access essential goods like food and medicine.
Contributing Factors:
- El Niño Influence: Periodic warming in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (El Niño) contributed to decreased rainfall but not to higher temperatures.
Potential Consequences:
- Forest Fires and Biome Health: The drought could exacerbate forest fires, combined with climate change and deforestation, potentially pushing the Amazon toward a point of no return where it ceases to be a lush rainforest.
- Previous Droughts: While the region has experienced at least three intense droughts in the past 20 years, this one’s impact on the entire Amazon basin is unprecedented.
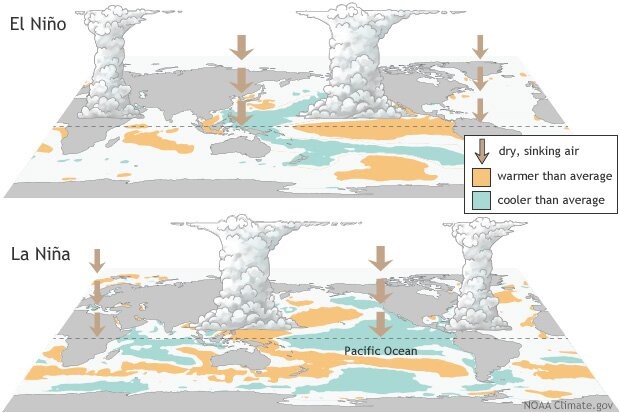
El Niño and La Nina
- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Last month, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) forecasted above-normal rain in the upcoming monsoon season in India, with “favourable” La Nina conditions expected to set in by August-September.
What are El Niño and La Nina?
- El Niño (meaning “little boy” in Spanish) and La Nina (meaning “little girl” in Spanish) are climate phenomena that are a result of ocean-atmosphere interactions, which impact the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean which affects global weather.
- The Earth’s east-west rotation causes all winds blowing between 30 degrees to the north and south of the equator to slant in their trajectory.
- As a result, winds in the region flow towards a southwesterly direction in the northern hemisphere and a northwesterly direction in the southern hemisphere which is known as the Coriolis Effect.
- Due to this, winds in this belt (called trade winds) blow westwards on either side of the equator.
- Under normal ocean conditions, these trade winds travel westwards along the equator from South America towards Asia.
- Wind movement over the ocean results in a phenomenon called upwelling, where cold water beneath the ocean surface rises and displaces the warm surface waters.
- At times, the weak trade winds get pushed back towards South America and there is no upwelling.
- Thus, warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures are recorded along the equatorial Pacific Ocean, and this is known as the emergence of El Niño conditions.
- Conversely, during La Nina, strong trade winds push warm water towards Asia.
- Greater upwelling gives rise to cold and nutrient-rich water towards South America.
- Thus, climatologically, El Niño and La Nina are opposite phases of what is collectively called the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- It also includes a third neutral phase.
- El Niño events are far more frequent than La Nina ones.
- Once every two to seven years, neutral ENSO conditions get interrupted by either El Niño or La Nina.
- Recently, La Nina conditions prevailed between 2020 and 2023.
How could the incoming La Nina impact global weather?
- La Niña, driven by the cooling of ocean waters due to the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation) cycle, can significantly influence global weather patterns.
- The air circulation loop in the region, affected by these temperature changes, impacts precipitation levels in neighbouring areas and can alter the Indian monsoon.
- Currently, the El Niño event that began in June last year has significantly weakened.
- Neutral ENSO conditions are expected to be established by June.
- Following this, La Niña conditions are anticipated to emerge, with its effects likely becoming apparent from August.
La Nina’s Impact on India:
- With above normal rain forecast, the seasonal rainfall is expected to be 106 per cent of the Long Period Average (LPA), which is 880mm (1971-2020 average).
- Except in east and northeast India, all remaining regions are expected to receive normal or above-seasonal rainfall.
- Heavy rains could result in some regions witnessing riverine and urban flooding, mudslides, landslides and cloudbursts.
- East and northeast India region, during La Nina years, receive below average seasonal rainfall.
- Therefore, there may be a shortfall in water reserves there this year.
- During La Nina years, incidents of thunderstorms generally increase.
- “The east and northern India regions could experience thunderstorms accompanied by lightning.
- With increased farming activities undertaken during the July and August rainy months, which coincides with the season’s enhanced lightning and thunderstorms, there is a high risk of fatalities in these regions.
- In addition to ENSO, there are other parameters that can impact the monsoon.
- However, in a La Nina year, a deficit monsoon over India can be easily ruled out.
La Nina’s Impact on the World:
- Similar to India, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and their neighbouring countries receive good rainfall during a La Nina year.
- This year, Indonesia has already witnessed floods.
- On the other hand, droughts are common in southern regions of North America, where winters become warmer than usual.
- Canada and the northwestern coast of the United States see heavy rainfall and flooding.
- Southern Africa receives higher than usual rainfall, whereas eastern regions of the continent suffer below-average rainfall.
- ENSO has a huge impact on hurricane activity over the Atlantic Ocean.
- During a La Nina year, the hurricane activity here increases.
- For instance, the Atlantic Ocean churned out a record 30 hurricanes during the La Nina year 2021.
Is Climate Change Affecting ENSO?
- Over India, El Niño is known to suppress the southwest monsoon rainfall and drive higher temperatures and intense heat waves, like the present summer season.
- In the past, monsoon seasons during years following an El Niño were 1982-1983 and 1987-1988, with both 1983 and 1988 recording bountiful rainfall.
- At present too, a similar situation could play out.
- The 2020-2023 period witnessed the longest La Nina event of the century.
- Thereafter, ENSO neutral conditions developed, which soon gave way to El Niño by June 2023 which has been weakening since December last year.
- Scientists say that climate change is set to impact the ENSO cycle.
- Many studies suggest that global warming tends to change the mean oceanic conditions over the Pacific Ocean and trigger more El Niño events.
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has also said that climate change is likely to affect the intensity and frequency of extreme weather and climate events linked to El Niño and La Nina.
Carbon Farming

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Carbon farming offers a versatile solution applicable across diverse agro-climatic regions, simultaneously addressing issues such as soil degradation, water scarcity, and climate variability challenges.
What is Carbon Farming?
- Carbon farming refers to a set of agricultural practices designed to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the soil.
- The primary goal is to mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon capture and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Through strategic land management, farmers can play a crucial role in offsetting carbon emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
Principles of Carbon Farming:
- Carbon Sequestration: The core principle involves capturing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and storing it in the soil.
- This is achieved by promoting the growth of plants and trees that absorb carbon from the atmosphere.
- Reduced Emissions: Carbon farming emphasizes practices that minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
- This includes optimizing fertilizer use, adopting no-till farming, and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Integrating diverse crops and promoting agroforestry practices contribute to biodiversity conservation.
- This enhances ecosystem resilience and supports sustainable agricultural systems.
- Soil Health: Improving soil health is fundamental to carbon farming.
- Practices like cover cropping and rotational grazing not only sequester carbon but also enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient cycling.
Benefits of Carbon Farming:
- Climate Change Mitigation: The primary benefit is the significant contribution to mitigating climate change.
- Carbon farming helps offset carbon emissions, acting as a natural solution to reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Improved Soil Fertility: The focus on soil health leads to increased fertility and productivity.
- Healthy soils contribute to better crop yields, reduced erosion, and enhanced resilience to climate-related challenges.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Carbon farming practices support biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse plant and animal species.
- This contributes to ecological balance and resilience in the face of environmental changes.
- Economic Opportunities: Farmers engaged in carbon farming may access new revenue streams through carbon offset programs.
- These initiatives incentivize sustainable practices and provide financial benefits to farmers.
Challenges in Carbon Farming:
- Transition Period: Implementing carbon farming practices often requires a transition period, during which farmers may face initial costs and adjustments to new techniques. Financial support and education are crucial during this phase.
- Market Access: Connecting farmers to carbon offset markets can be challenging. Developing transparent and accessible markets for carbon credits is essential for the success of carbon farming initiatives.
- Education and Awareness: Many farmers may not be familiar with carbon farming practices.
- Education and awareness programs are necessary to disseminate information, build capacity, and encourage widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Carbon farming is a dynamic and evolving approach to agriculture that holds immense promise in the fight against climate change. By understanding its principles, benefits, and challenges, farmers and stakeholders can actively contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future. The key terms associated with carbon farming provide a foundation for navigating this innovative landscape and embracing practices that benefit both the environment and agriculture.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global trade dynamics are expected to remain sluggish in 2024, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has warned.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- UNCTAD’s latest projections indicate global growth of 2.6 percent in 2024, slightly slower than in 2023.
- This marks the third consecutive year in which the global economy will grow at a slower pace than before the pandemic when the average rate for 2015–2019 was 3.2 percent.
India’s growth is expected to be marginally lower than in 2023:
- Regarding India, the report stated that the economy grew at 6.7 percent in 2023 and is expected to be marginally lower at 6.5 percent in 2024.
- It noted that the expansion in 2023 was influenced by strong public investment and the services sector, which received a boost from robust local demand for consumer services along with assured external demand for business services exports.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to keep interest rates constant in the near term, while strong public investment expenditures will offset restrained public consumption spending.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1964 to promote the interests of developing countries in global trade.
- With its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD has 195 member states and collaborates with numerous nongovernmental organizations worldwide.
- The organization focuses on formulating policies related to various aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance, and technology.
- UNCTAD plays a crucial role in addressing the concerns of developing countries regarding international institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank.
- By providing a platform for these countries to discuss and tackle their unique challenges, UNCTAD contributes to global economic development and reduces inequalities.
- Some notable achievements of UNCTAD include the establishment of the Global System of Trade Preferences (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), which reduces tariffs and removes non-tariff trade barriers, the Common Fund for Commodities, providing financial assistance to countries dependent on commodity exports, and various agreements for debt relief.
- In recent years, UNCTAD has focused on addressing globalization challenges and helping the least developed countries integrate into the global economy.
Equity Issues in IPCC Reports

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a study published recently, researchers analyzed more than 500 future emissions scenarios the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessed in its latest reports.
About the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC):
- The IPCC was created in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It is the leading international body for the assessment of climate change.
- It is a key source of scientific information and technical guidance to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement.
- The IPCC provides governments with scientific information for use in developing climate policies.
- The IPCC currently has 195 members.
- The IPCC does not undertake new research. Instead, it synthesizes published and peer-reviewed literature to develop a comprehensive assessment of scientific understanding.
- These assessments are published in IPCC reports.
- They are subject to multiple drafting and review processes to promote an objective, comprehensive, and transparent assessment of current knowledge.
- The IPCC’s work is guided by principles and procedures that govern all main activities of the organization.
- IPCC member governments and observer organizations nominate experts and the IPCC's scientific governing body, the IPCC Bureau, selects authors and editors with expertise in a range of scientific, technical, and socio-economic fields.
What are IPCC Assessment Reports?
- Typically, IPCC reports comprise three Working Group reports:
- One on physical science
- One on climate adaptation, and
- One on mitigation action.
- One synthesis report consolidates findings from the three Working Group reports.
- Then there are thematic special reports.
- Each report assesses climate-related scientific literature to capture the state of scientific, technical, and socio-economic knowledge on climate change.
- The IPCC is currently in its Seventh Assessment cycle (AR7).
How Does it Assess Future Scenarios?
- The IPCC uses ‘modelled pathways’ to estimate what it will take to limit the warming of the earth’s surface.
- These pathways are drawn using Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) that describe human and earth systems.
- IAMs are complex models that examine possible futures of the energy and climate systems and economies.
- Its macroeconomic models can point to future growth levels in terms of GDP;
- Its energy models can project future consumption
- Vegetation models can examine land-use changes; and
- Earth-system models use the laws of physics to understand how climate evolves.
- With such integration across disciplines, IAMs are meant to provide policy-relevant guidelines on climate action.
- However, these models also have shortcomings. They prioritize least-cost assessments — for example, the absolute cost of setting up a solar plant or undertaking afforestation in India is lower than in the U.S.
- However, experts have said they could exercise the option of enabling countries to equitably share the burden of action, where the richest undertake more drastic mitigation action more immediately.
About the Latest Study:
- Conducted by a team of specialists from Bengaluru and Chennai, the study scrutinized 556 scenarios outlined in the IPCC's AR6 report.
- Their findings indicate that by 2050, per-capita GDP in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, West Asia, and other parts of Asia will remain below the global average.
- Collectively, these regions account for 60% of the global population.
- Additionally, the study highlighted disparities in the consumption of goods and services, as well as energy and fossil fuel consumption, between the Global North and the Global South.
Why Does Equity Matter?
- Equity is crucial in climate action as per the UNFCCC, which mandates developed nations to lead in combating climate change.
- However, current modeling approaches often overlook equity, burdening poorer nations disproportionately.
- Researchers highlight the need for modeling techniques that prioritize climate justice and equitable distribution of responsibilities.
- They argue that mitigation pathways should ensure developed regions accelerate towards net negative emissions and allocate carbon budgets to less developed regions.
- Addressing this gap requires a paradigm shift in scenario building, emphasizing both equity and environmental sustainability.
- This approach is vital for fostering global cooperation and achieving meaningful climate action.
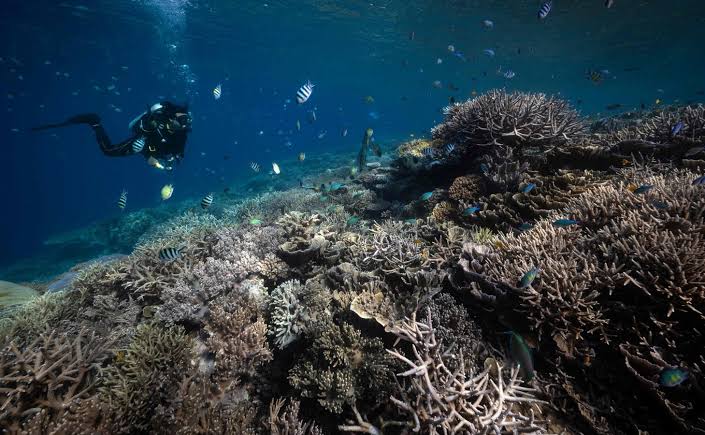
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
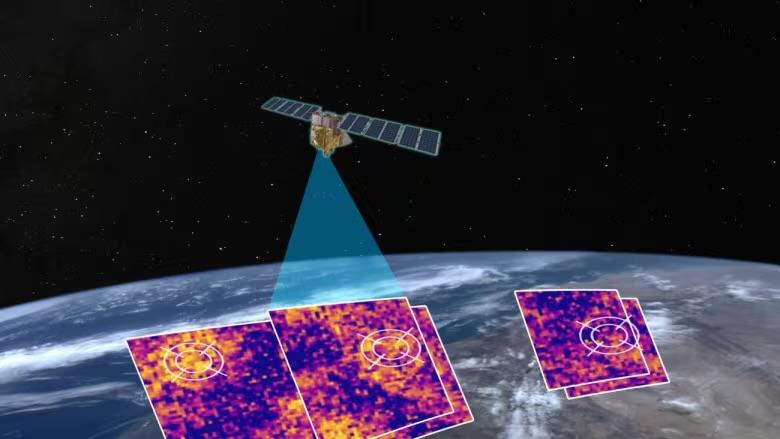
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
Carbon Capture and How it Can Help Save the Planet

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Germany has recently declared its approval for carbon capture and offshore storage for specific industrial sectors.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage?
- CCS refers to a host of different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large point sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- Notably, CCS is different from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), where CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
- CCS involves three different techniques of capturing carbon, including: Post-combustion, Pre-combustion, and Oxyfuel combustion.
- In post-combustion, CO2 is removed after the fossil fuel has been burnt. By using a chemical solvent, CO2 is separated from the exhaust or ‘flue’ gasses and then captured.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel. “First, the fossil fuel is partially burned in a ‘gasifier’ to form synthetic gas. CO2 can be captured from this relatively pure exhaust stream,” according to a report by the British Geological Survey. The method also generates hydrogen, which is separated and can be used as fuel.
- In oxyfuel combustion, the fossil fuel is burnt with almost pure oxygen, which produces CO2 and water vapor. The water is condensed through cooling and CO2 is separated and captured. Out of the three methods, oxyfuel combustion is the most efficient but the oxygen burning process needs a lot of energy.
- Post-combustion and oxyfuel combustion equipment can be retro-fitted in existing plants that were originally built without them. Pre-combustion equipment, however, needs “larger modifications to the operation of the facility and are therefore more suitable to new plants.
- After capture, CO2 is compressed into a liquid state and transported to suitable storage sites.
- Although CO2 can be transported through ship, rail, or road tanker, pipeline is the cheapest and most reliable method.
Can Carbon Capture Help Save the world?
- Operational CCS projects generally claim to be 90 percent efficient, meaning they can capture 90 per cent of carbon and store it.
- Studies, however, have shown that a number of these projects are not as efficient as they claim to be.
- For example, a 2022 study by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) found most of the 13 flagship CCS projects worldwide that it analyzed have either underperformed or failed entirely.
- Moreover, CCS technologies are quite expensive.
- When CCS is attached to coal and gas power stations it is likely to be at least six times more expensive than electricity generated from wind power backed by battery storage.
- It is far cheaper and more efficient to avoid CO2 emissions in the first place.
- There are also only a few operational CCS projects across the world even though the technology has been pushed for decades.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there were 40 operational CCS projects in 2023, which captured more than 45 metric tonnes (Mt) of CO2 annually.
- To ensure the planet doesn’t breach the 1.5 degree Celsius temperature increase limit, it would take an “inconceivable” amount of carbon capture “if oil and natural gas consumption were to evolve as projected under today’s policy settings.
- It added that the electricity required to capture that level of carbon as of 2050 would be more than the entire planet’s use of electricity in 2022.
- Therefore, there couldn’t be an overreliance on carbon capture as a solution to tackle climate change.
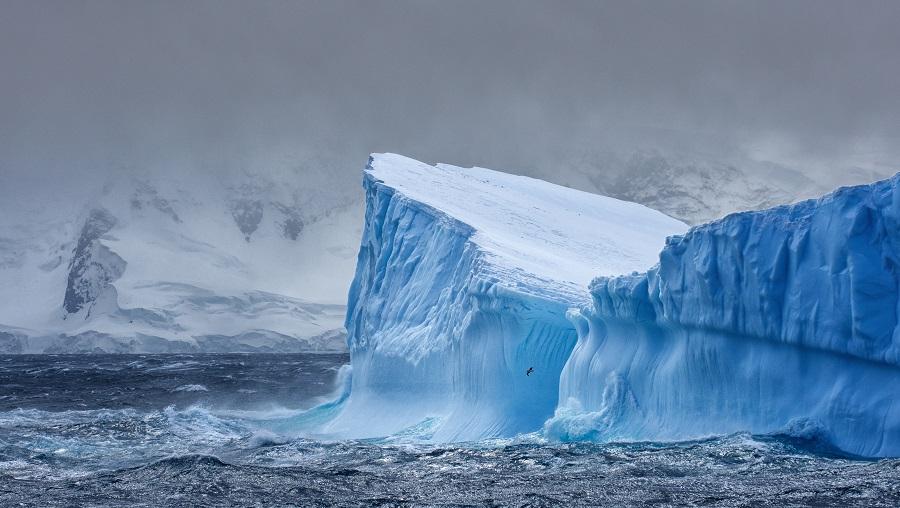
Doomsday Glacier has lost 50 billion tons of ice, melting began 80 years ago

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Antarctica's Doomsday Glacier, the world's widest glacier, has lost over 50 billion tons of ice and the melting rate is on the rise as the continent gets warmer.
What is Doomsday Glacier?
- The Thwaites Glacier (also known as Doomsday Glacier), a massive and world’s widest glacier is located in West Antarctica.
- The Doomsday nickname reflects the potential for catastrophic flooding if the glacier were to collapse completely.
- Scientists are particularly concerned about Thwaites Glacier because of its size and location.
- If it were to collapse or significantly retreat, it could lead to a more rapid flow of ice from the interior of West Antarctica into the ocean, contributing to rising sea levels.
- The collapse could lead to a 65 cm rise in global sea level.
- The ice loss in the region has been observed to be accelerating since the 1970s, however, so far it remained unclear as to when this retreat began.
- The significant glacial retreat began in the 1940s and the findings coincide with previous work that studied retreat on Pine Island Glacier and found glacial retreat began in the ‘40s as well.
- This change is not random nor specific to one glacier but It is part of a larger context of a changing climate.
Why Did the Melting Begin?
- The meeting was kicked off by an extreme El Nino climate pattern that warmed the west Antarctic, and since then the glacier has not been able to recover from the damage.
- It is significant that El Niño only lasted a couple of years, but the two glaciers, Thwaites and Pine Island remain in significant retreat.
- Once the system is kicked out of balance, the retreat is ongoing.
- The Doomsday Glacier's melting remains one of the most crucial events triggered and accelerated by climate change and could lead to the submergence of several coastal regions of the world.
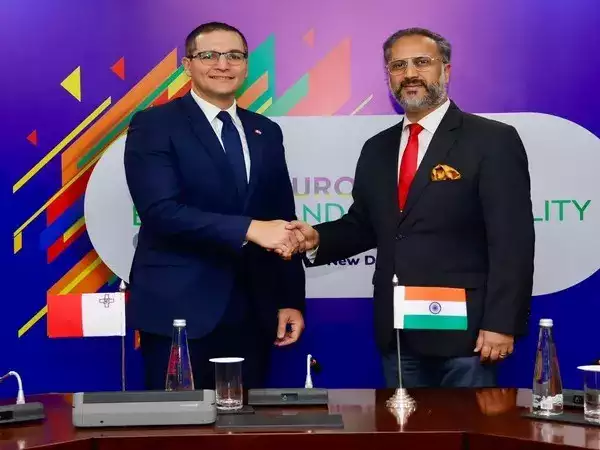
Malta becomes the 119th member of the International Solar Alliance

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Malta became the 119th country to join the International Solar Alliance recently.
About the International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an alliance of more than 120 signatory countries that aims to reduce the dependence on non-renewable sources of energy like fossil fuels.
- Currently, 118 countries are signatories to the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- The platform strives to develop and deploy cost-effective and transformational energy solutions powered by the sun to help member countries develop low-carbon growth trajectories, with a particular focus on delivering impact in countries categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and the Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was conceptualised on the sidelines of the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
Role of India:
- As a founding member, India holds a pivotal position within the alliance, serving both as a host nation and a major contributor to achieving its objectives.
- The ISA marks a historic milestone as the first international organisation to establish its secretariat in India.
- With a target of generating 100 GW of solar energy by 2022, India's commitment represents a significant portion of the ISA's overall goal.
Recent Developments:
- The ISA was granted Observer Status by the UN General Assembly, fostering closer collaboration between the alliance and the United Nations to advance global energy growth and development.
- The approval of the 'Solar Facility' by the ISA introduces a payment guarantee mechanism aimed at incentivizing investments in solar projects, further driving progress towards sustainable energy initiatives.
Warming up to climate change: How does climate change impact extreme weather events?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Extreme weather is becoming more frequent and more intense in many places around the world because of climate change.
How Does Climate Change Impact Extreme Weather Events?
- The Earth's average temperature has gone up by at least 1.1 degrees Celsius since 1850, mostly because of human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- This temperature rise has led to more frequent and stronger extreme weather events worldwide, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires.
- It's hard to directly blame one single weather event on climate change because there are many factors involved.
- However, studies can tell us if climate change made a particular event worse or more likely to happen.
- For example, after a deadly heatwave in Western Europe in 2019, a study found that climate change made that heatwave five times more likely to occur.
- In India, heatwaves have become longer because of global warming, and they're expected to get even worse in the future.
- Climate models predict that by the 2040s, heatwaves might become 12 times more common.
- Higher temperatures also make droughts worse.
- In East Africa, for instance, a severe drought happened between 2020 and 2022, leading to famine and displacing millions of people.
- A report found that climate change made droughts like this at least 100 times more likely in that region.
- Warmer temperatures also contribute to wildfires by drying out land and making it easier for fires to start and spread.
- In Canada, for example, a study showed that climate change doubled the chances of extreme fire conditions.
- This was particularly concerning because Canada recently faced its worst wildfire season ever.
- As temperatures rise, the air can hold more moisture, leading to heavier rainfall and more flooding during storms.
- Warm air can also dry out the soil, making droughts worse. But when warm, moist air meets cooler air, it can lead to more intense storms and flooding.
- There's also evidence that climate change is making hurricanes stronger and more frequent.
- Warmer oceans provide more energy for hurricanes to form and intensify.
- The oceans have absorbed a lot of the extra heat from greenhouse gases, making them warmer.
- This, in turn, leads to stronger storms and more damage when they hit land.
- So, while climate change doesn't directly cause any single weather event, it's making extreme weather events more common and more severe, putting people and ecosystems at risk.
Why Kashmir and Ladakh are without snow this winter, its implications (Indian Express)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Himalayas are experiencing an unusual lack of snowfall this winter, impacting ski resorts and prompting holiday cancellations.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Unprecedented precipitation deficit: December witnessed an alarming 80% precipitation deficit in the western Himalayan region.
- The ongoing dry spell in January is attributed to the absence of active western disturbances this winter season, as reported by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Impact on freshwater resources: Experts warn of potential impacts on freshwater availability in the Himalayan region.
- The extended dry spell poses a threat to horticulture and agricultural production, raising concerns among experts.
- Unseasonal blooming and alarming temperature anomalies: Despite being peak winter, Ladakh and Kashmir experienced unusually warm temperatures, leading to early crop blooming.
- A report by IMD scientists reveals maximum temperatures 5-8 degrees Celsius below normal over the northern plains since December 29.
- Challenges to water levels and ecosystems: Experts also highlight the significance of the Chillai Kalan snowfall period as the only freshwater source.
- The prolonged dry spell has resulted in reduced water levels in rivers and streams, posing challenges to the region's ecosystems.
Factors contributing to severe weather conditions:
- Scientists attribute the severe weather to three main factors:
- Lack of active western disturbances
- Prevailing El Nino conditions, and
- A strong jet stream.
- El Nino, characterised by abnormal warming in the central Pacific Ocean, contributes to altered weather patterns.
- Mechanics of fog formation: Scientists explain the three conditions required for fog formation: weak low-level winds, moisture, and overnight cooling.
- The lack of strong western disturbances disrupts these conditions, contributing to the prolonged fog.
- Persistent jet streams and cold wave conditions: Strong jet streams prevailing over north India for the last five days have led to the subsidence of cold air, enhancing cold wave/cold day conditions.
These conditions are expected to continue over the next five days, intensifying the challenges posed by the ongoing weather anomalies.
Migratory Birds Arrive in Odisha’s Chilika Before Winter (DownToEarth)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Migratory birds have started their annual journey to Chilika Lake—India’s largest waterbird habitat in Odisha — ahead of winter this year.
About Chilika Lake:
- Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lake and a shallow lagoon with estuarine character spread across the districts of Puri, Khurda and Ganjam in the state of Odisha in eastern India.
- It is considered to be the largest lagoon in India and is counted amongst the largest lagoons in the world.
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory waterfowl found anywhere on the Indian sub-continent.
- It is one of the hotspots of biodiversity in the country, and some rare, vulnerable and endangered species listed in the IUCN Red List of threatened Animals inhabit the Lake area for at least part of their life cycle.
- On account of its rich bio-diversity, Chilika Lake was designated as a "Ramsar Site", i.e. a wetland of International Importance.
- The Nalaban Island within the lake is notified as a Bird Sanctuary under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The National Wetlands, Mangroves and Coral Reefs Committee of the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India, have also identified the lake as a priority site for conservation and management.
- The Lake is a highly productive ecosystem, with rich fishery resources.
- The rich fishing grounds sustain the livelihood of more than 0.2 million fisherfolk who live in and around the lake.
- It has a great heritage value and maritime trade to the far east countries used to take place from here.
- It is the largest winter ground of migratory birds in the Indian sub-continent and home to more than 150 highly threatened Irrawaddy dolphins, which is the largest lagoonal population globally.
- It supports some of the largest congregation of migratory birds from large parts of Asia, particularly during the winters that arrive from as far as the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea, remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia, Central and South East Asia, Ladakh and the Himalayas to feed and breed in its fertile waters.
Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) (Indian Express)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Union Environment, Forest and Climate Change Minister Bhupender Yadav on Thursday launched a Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC), conceptualised under India’s G20 Presidency, to promote the practices of resource efficiency and circular economy globally.
About Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC):
- RECEIC was launched in 2023 at Chennai, Tamil Nadu, with the honorable presence of Shri Bhupender Yadav, Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- The launch event witnessed the participation of distinguished guests, including the Commissioner on Environment from the European Union and esteemed Ministers from Canada, France, Italy, Denmark, Mauritius, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Industry-Driven Initiative:
- RECEIC is an industry-led initiative with a primary goal of fostering global resource efficiency and circular economy practices.
- Embracing the circular economy model, RECEIC promotes production and consumption practices involving sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to maximize their utility.
- Sustainable Impact:
- The coalition is envisioned to be a self-sustaining entity, committed to lasting environmental sustainability, beyond India's G20 Presidency.
- Founding Members:
- With 39 companies headquartered in 11 different countries, the coalition boasts a diverse group of founding members.
- As a collaborative platform, RECEIC fosters knowledge-sharing, best practice exchange, and the adoption of sustainable approaches among participating industries.
Haploclastus Nilgirinus (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists warned that Haploclastus nilgirinus, a tarantula species, may face endangerment due to habitat loss and the effects of climate change.
About Haploclastus Nilgirinus:
- This tarantula species, known as Haploclastus nilgirinus, is a venomous and rarely seen spider that burrows in the Nilgiri hills of the Western Ghats.
- Notably, there is a significant difference in size between males and females of this species, with the males being considerably smaller.
- The primary threats to Haploclastus nilgirinus are illegal wildlife trade and the impact of climate change.
What is a tarantula?
- Tarantulas are a type of large, hairy spider belonging to the Theraphosidae family.
- They are found all around the world, except for Antarctica.
- These spiders move slowly on their eight hairy legs but are skilled nocturnal predators.
- Adult tarantulas typically measure around five inches (13 centimeters) in length, and when their legs are fully extended, their span can reach up to 11 inches (28 centimeters).
