India’s Burden of Zero-Dose Children in 2023
- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
According to a recent Lancet study based on Global Burden of Disease data, India ranked second globally in terms of the number of unvaccinated or “zero-dose” children in 2023, trailing only Nigeria.
What Are Zero-Dose Children?
- The term “zero-dose children” refers to those who have not received even a single dose of any routine childhood vaccine.
- In 2023, 1.44 million children in India were identified as zero-dose, highlighting significant immunisation gaps.
Global and National Trends:
- Nigeria topped the list with approximately 2.5 million zero-dose children.
- Eight countries, including India and Nigeria, together accounted for over 50% of the global zero-dose burden.
- Globally, the number of zero-dose children dropped from 58.8 million in 1980 to 14.7 million in 2019, reflecting long-term progress.
Challenges in India:
- Despite the Universal ImmunisationProgramme (UIP) covering 12 vaccine-preventable diseases, several challenges persist:
- COVID-19 pandemic led to significant disruptions in routine immunisation.
- Vaccine hesitancy continues to undermine public health efforts.
- Geographical and socio-economic inequalities limit access to health services in certain regions.
- Between 2010 and 2019, measles vaccine coverage declined in over 100 countries, including India, further exacerbating public health risks.
Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000–2023

- 11 Apr 2025
In News:
A recent United Nations report titled ‘Trends in Maternal Mortality 2000–2023’, released by the Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group (MMEIG), highlights global progress and setbacks in maternal health. While acknowledging India's significant gains, the report places India second in global maternal deaths, behind Nigeria.
India’s Maternal Mortality Statistics (2023)
- Maternal deaths in India: 19,000(7.2% of global total)
- Rank: Second globally, tied with the Democratic Republic of Congo
- MMR: Reduced from 362 per 1 lakh live births (2000) to 80 in 2023 — a 78% decline
- Global average decline: 40% (2000–2023), but India achieved 86% decline
- Comparison with Nigeria:
- Nigeria: 75,000 deaths, contributing 28.7% of global maternal deaths
- India's Health Ministry deemed the comparison unfair given population differences (India: 145 crore, Nigeria: 23.26 crore)
Definition and Importance of MMR
According to WHO, Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) refers to:
“The death of a woman during pregnancy or within 42 days of termination, from pregnancy-related causes excluding accidental ones.”
MMR is a critical indicator for assessing healthcare quality and maternal well-being.
UN Global Findings
- Estimated maternal deaths globally (2023): 260,000
- Daily deaths: Over 700 women; about one death every two minutes
- Leading causes: Post-partum haemorrhage, hypertensive disorders, infections
- SDG 3.1 Target: Reduce MMR to <70 per 1 lakh live births by 2030
India-Specific Causes of Maternal Deaths
- Medical reasons:
- Post-partum haemorrhage
- Hypertensive disorders (e.g. pre-eclampsia)
- Infections related to pregnancy
- Co-morbidities: Anaemia, diabetes, hypertension
- Systemic challenges:
- Inadequate emergency obstetric care at Primary Health Centres (PHCs) and Community Health Centres (CHCs)
- Lack of infrastructure, trained personnel, and referral systems
- Socio-economic backwardness and poor access to healthcare in northern India
Concerns Highlighted in the Report
- Slowing progress post-2016 despite early improvements
- Humanitarian funding cuts impacting:
- Health worker retention
- Facility operations
- Availability of essential drugs (for haemorrhage, malaria, pre-eclampsia)
- Disruption in maternal care supply chains, especially in low-resource regions
India’s Stand
The Union Health Ministry has contested comparisons with smaller nations like Nigeria, asserting that India's maternal health progress is notable given its large population. The Ministry emphasized the 86% decline in MMR since 1990, as opposed to a global decline of 48% in the same period.
RBI’s 6th Remittance Survey (2023–24)
- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
India remains the world’s top recipient of remittances, with total inward remittances doubling from USD 55.6 billion in 2010–11 to USD 118.7 billion in 2023–24, as per the Reserve Bank of India’s Sixth Round of the Remittances Survey.
Shift in Sources of Remittances
- A significant trend in 2023–24 is the growing dominance of Advanced Economies (AEs) over traditional Gulf sources.
- The United States emerged as the largest contributor with a 27.7% share, followed by the United Arab Emirates (UAE) at 19.2%.
- AEs including the UK, Singapore, Canada, and Australia now account for over 50% of India’s total remittance inflows.
- The UK’s share increased notably from 3.4% (2016–17) to 10.8% (2023–24).
- Australia contributed 2.3%, reflecting rising skilled migration.
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain) collectively contributed 38%, a decline from 47% in 2016–17.
Reasons for the Shift
- Robust Job Markets in AEs: High-paying jobs for skilled Indian migrants in the US, UK, Canada, and Australia.
- UK-India Migration and Mobility Partnership (MMP) tripled Indian migration to the UK from 76,000 in 2020 to 250,000 in 2023.
- Favorable immigration policies in Canada (Express Entry) and Australia boosted skilled migration.
- Declining Opportunities in GCC:
- Post-pandemic return of Indian migrants and reduced demand for low-skilled labor due to automation and economic diversification.
- Nationalization policies (e.g., Nitaqat in Saudi Arabia, Emiratization in UAE) favor local employment.
- Changing Migration Patterns:
- Southern states (Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana) now prefer AEs due to higher education levels.
- Northern states (Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan) still send migrants to GCC, but limited by lower skill levels.
- Rise in Education-Driven Migration:
- Many Indian students pursue higher education abroad and stay back for employment.
- Indian students abroad: Canada (32%), US (25.3%), UK (13.9%), Australia (9.2%).
State-Wise Remittance Distribution (2023–24)
- Maharashtra: 20.5%
- Kerala: 19.7%
- Tamil Nadu: 10.4%
- Telangana: 8.1%
- Karnataka: 7.7%
- Notable increases observed in Punjab and Haryana.
Mode of Transfers
- The Rupee Drawing Arrangement (RDA) remains the dominant channel.
- Other channels include direct Vostro transfers and fintech platforms.
- Digital transactions account for 73.5% of remittance flows.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
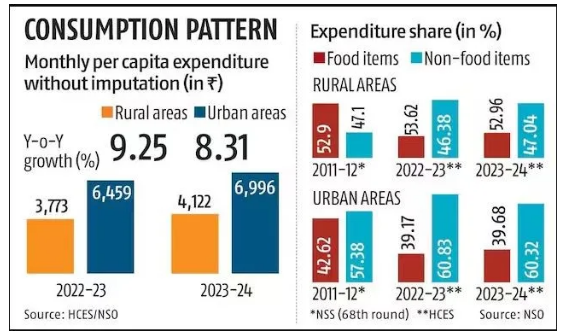
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
2023 National Tansen Samman

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
- The prestigious National Tansen Samman for 2023 was conferred upon Pt. Swapan Choudhary, a renowned tabla maestro from Kolkata, at the National Tansen Festival held in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tansen Festival: This festival, renowned for its celebration of classical music, is organized annually in Gwalior, which is considered the music capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Prize Details: As part of the honor, Pt. Swapan Choudhary was presented with an honorarium of five lakh rupees, a citation plaque, and a shawl-shriphal.
- About the Award:
- The National Tansen Samman was established in 1980 by the Madhya Pradesh government to recognize exceptional contributions to Indian classical music.
- It is named after Tansen, one of India's most celebrated classical musicians.
- The award is the highest national honor in the field of Indian classical music.
- Additional Award:
- Raja Mansingh Tomar Samman for 2023 was awarded to Sanand Nyas, an institution from Indore. This institution has been active for 35 years in the promotion of classical music, drama, and cultural festivals.
- Pt. Swapan Choudhary’s Remark: In response to receiving the honor, Pt. Choudhary expressed his gratitude and pride in joining the ranks of distinguished artists awarded the National Tansen Samman.
About Tansen: The Iconic Musician
- Legacy: Tansen, also known as Miyan Tansen, was a prominent Indian classical musician, composer, and vocalist. He is credited with popularizing several ragas and revolutionizing the Indian classical music tradition.
- Role at Akbar’s Court: Tansen was one of the Navaratnas (nine jewels) in the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He held the title of Mian, meaning "learned man," bestowed upon him by Akbar.
- Contributions:
- Tansen is famous for his compositions, including the introduction of notable ragas such as Miyan ki Malhar, Miyan ki Todi, and Darbari.
- He also improved the plucked rabab, which is of Central Asian origin, enhancing its role in Indian classical music.
- Historical Influence: Tansen's life and work are surrounded by extensive legend, and his contributions remain deeply influential in the development of Indian classical music today.
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
- It was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences, PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy, and Space, along with Shri V. Srinivas, the Secretary of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- This initiative, conceptualized by DARPG, aims to evaluate and rank central Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal mechanisms.
Key Aspects of GRAI 2023:
- Objective: GRAI 2023 was designed to provide a comparative assessment of Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal systems. It was created based on recommendations from the Parliamentary Standing Committee of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Assessment Method: The index evaluates 89 Central Ministries and Departments across four dimensions:efficiency, feedback, domain&organisational Commitment
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Group A: Ministries/Departments with more than 10,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Group B: Ministries/Departments with 2,000 to 9,999 grievances (33 Ministries/Departments)
- Group C: Ministries/Departments with fewer than 2,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Top Performers:
- Group A: The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare topped the rankings.
- Group B: The Office of the Comptroller & Auditor General of India led.
- Group C: The Department of Investment & Public Asset Management ranked first.
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Analysis: GRAI 2023 includes an in-depth analysis of the root causes of effective grievance redressal for each Ministry/Department, presented in a color-coded, easily understandable format.
- Advancements: The report outlines a roadmap for improving grievance redressal, emphasizing:
- Utilization of advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analytics and data analysis.
- The introduction of features like IGMS 2.0 and TreeDashboard within CPGRAMS.
- Improved training for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) and more rigorous audits to increase accountability.
- Expansion of CPGRAMS integration to local governments, enhancing the grievance redressal system across all levels of governance.
Commonwealth Secretariat recognized CPGRAMS as a best practice in grievance redressal at its meeting in April 2024.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
National Water Awards 2023

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
The Hon’ble President of India Smt. Droupadi Murmu will confer the 5th National Water Awards 2023 on October 22nd 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
Organizing Body:
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Department: Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR)
- Purpose: To recognize and honor individuals, organizations, and bodies that have made significant contributions to water conservation and management.
Award Categories
- Best State
- Best District
- Best Village Panchayat
- Best Urban Local Body
- Best School or College
- Best Industry
- Best Water User Association
- Best Institution (other than school or college)
- Best Civil Society Organization
Winners
- Best State:
- 1st Prize: Odisha
- 2nd Prize: Uttar Pradesh
- 3rd Prize (joint): Gujarat & Puducherry
- Other Awards: Winners in the remaining categories have been recognized, with citations, trophies, and cash prizes provided in certain categories.
Objectives of the National Water Awards
- Promote Water Conservation: Raise awareness about the importance of water and encourage effective water usage practices.
- Recognize Efforts: Celebrate the work of individuals, institutions, and organizations contributing to the government’s vision of a ‘Jal Samridh Bharat’ (Water-rich India).
- National Campaign: Under the guidance of Hon’ble Prime Minister, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has been working to spread awareness on water management and conservation through extensive national campaigns.
History and Background
- The National Water Awards (NWAs) were launched in 2018 by the DoWR, RD & GR to foster awareness and action on water-related issues.
- Awards were given for 2019, 2020, and 2022, but there were no awards in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The awards aim to inspire best practices in water usage, conservation, and management across India, involving government bodies, industries, communities, and civil society.
Significance
- The National Water Awards serve as a platform to recognize the innovative initiatives taken by various stakeholders in addressing water challenges.
The awards contribute to furthering the government’s mission of achieving sustainable water management practices across the nation.
Global Report on Internal Displacement 2024 (GRID-2024)

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Floods, cyclones, earthquakes and other disasters triggered over half a million internal displacements in India in 2023, according to Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC).
About Global Report on Internal Displacement 2024:
- The Global Report on Internal Displacement (GRID) 2024, published by the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) based in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is the authoritative source for data and analysis on the state of internal displacement for the previous year.
- Each year, IDMC presents the validated estimates of internal displacements by conflict and disasters, and the total cumulative numbers of IDPs worldwide.
- The GRID also provides an overview of the year’s most significant internal displacement situations, highlighting potential measures to address the issue across the humanitarian, development, disaster risk reduction and climate change agendas.
- The 2024 Global Report on Internal Displacement (GRID) report presents the data and analysis behind the 75.9 million people living in internal displacement as of the end of 2023.
- It is the ninth edition of the GRID and includes global and regional insights into the risk, scale and impacts of internal displacement.
Highlights of the GRID 2024:
- Rising Numbers of (IDPs): In 2023, the number of internally displaced persons (IDPs) reached 75.9 million, up from 71.1 million the previous year.
- Causes of Displacement: Disasters contributed to 7.7 million displacements, with earthquakes being responsible for one-fourth of these.
- Conflict and violence led to 68.3 million displacements.
- High-Displacement Countries: Sudan, Syria, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Colombia, and Yemen account for almost half of the world's IDP population.
- Significant Increases: Sudan had the highest number of IDPs recorded for a single country in 2023, reaching 1 million.
- The majority of new displacements occurred in Sudan, the Palestinian territories, and the DRC, accounting for nearly two-thirds of all cases.
- South Asia Displacement: Approximately 3 million people across South Asia experienced internal displacement due to conflict and violence, with 80% of them located in Afghanistan.
- Manipur violence resulted in 67,000 displacements, marking the highest number of conflict and violence-related displacements in India since 2018.
- Impact of Natural Disasters: There was a notable decrease in internal displacement due to natural disasters in India in 2023, dropping from 2.5 million in 2022 to 528,000.
About Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC):
- Established in 1998, the IDMC is the leading source of information and analysis on internal displacement.
- It was created to address a significant gap in knowledge on global patterns and scales of internal displacement.
- IDMC defines internal displacement as the number of forced movements of people within their own country over a given year.
- The IDMC is a part of the Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC), an independent, non-governmental humanitarian organization.
- Primary Roles: The IDMC serves as a global monitor and advocate for evidence-based policy and action.
- It aims to influence governments, UN agencies, donors, international organizations, and NGOs.
- As the official repository of data and analysis on internal displacement, the IDMC's GRID provides critical insights into the global internal displacement crisis and aids in developing informed solutions.
State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Asia is warming faster than the global average, it is witnessing more extreme weather, climate, and water-related events than any other region across the world.
Highlights of the State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report:
- The 2023 State of the Climate in Asia Report, spearheaded by the World Meteorological Organization, sheds light on significant climate trends and events across the continent:
- In 2023, Asia witnessed 79 extreme climate events, affecting over nine million individuals, making it the most disaster-affected region.
- Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide soared to unprecedented levels in 2022.
- Oceans have absorbed approximately a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted annually into the atmosphere since 1960, resulting in record-high ocean heat content in 2023.
- Tropical cyclone activity over the North Indian Ocean surpassed the average.
- 2023 marked Asia's second-highest mean temperature on record, with Japan and Kazakhstan experiencing record warmth.
- Glacial retreat accelerated in 2023, particularly in the East Himalayas and Central Asia's Tian Shan mountains, due to elevated temperatures and arid conditions.
About the World Meteorological Organisation:
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations with a membership of 193 member states and territories.
- It is the UN system's authoritative voice on the state and behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, its interaction with the oceans, the climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
- WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization, the roots of which were planted at the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23 March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences a year later.
- The Secretariat, headquartered in Geneva, is headed by the Secretary-General.
- Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress.
State of Global Climate Report 2023

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with a host of observations by climate agencies in the preceding three months, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has officially confirmed 2023 to be the hottest year on record.
About the State of Global Climate Report 2023:
- Published annually by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the State of Global Climate Report provides a detailed analysis of the Earth's climate system.
- Contributors to the report include various UN organizations, National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, Global Data and Analysis Centers, Regional Climate Centres, the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), and more.
Highlights of the 2023 Report:
- Record-Breaking Global Temperatures: 2023 was the hottest year on record, with a global average near-surface temperature of 1.45°Celsius (±0.12°C) above the pre-industrial baseline.
- The past ten years were also the warmest decade recorded.
- Extensive Marine Heatwaves: Nearly one-third of the global ocean experienced a marine heatwave on an average day in 2023.
- Over 90% of the ocean had faced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, negatively impacting ecosystems and food systems.
- Unprecedented Glacier Ice Loss: Preliminary data reveals the largest loss of ice since 1950 for the global set of reference glaciers, driven by extreme melt in western North America and Europe.
- Surge in Renewable Energy Capacity: Renewable capacity additions in 2023 increased by almost 50% from 2022, totaling 510 gigawatts (GW) and marking the highest rate in the past two decades.
- These findings emphasize the pressing need to address climate change through effective international cooperation, policymaking, and sustainable practices.
About the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that fosters international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Founded in 1950, WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization established in 1873 to facilitate the exchange of weather data and research.
- Today, WMO comprises 193 member countries and territories and promotes the free exchange of meteorological and hydrological data, information, and research.
- By collaborating with various partners, WMO contributes to environmental protection, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
World Air Quality Report 2023

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India had the third worst air quality out of 134 countries in 2023 after Bangladesh and Pakistan according to the World Air Quality Report 2023 by IQAir.
About World Air Quality Report 2023:
- The World Air Quality Report is an annual publication by IQAir, a Swiss air quality monitoring firm.
- The report provides an in-depth analysis of global air quality, shedding light on the impact of air pollution on human health and the environment.
Key highlights from the report include:
- India ranks third in poor air quality: With an average annual particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) concentration of 54.4 micrograms per cubic meter, India trails only Bangladesh and Pakistan in terms of poor air quality.
- South Asian dominance in pollution rankings: Bangladesh and Pakistan occupy the top two positions in the air pollution rankings, while ten out of the eleven most polluted cities in the world are in India.
- Delhi's alarming status: For the fourth consecutive year, Delhi has been identified as the world's most polluted capital city.
- Additionally, Bihar's Begusarai has been termed the world's most polluted metropolitan area.
- India's widespread exposure: An overwhelming 96% of the Indian population experiences PM2.5 levels more than seven times the WHO annual PM2.5 guideline, emphasizing the need for urgent interventions to mitigate the health impacts of air pollution.
What is Particulate Matter (PM)?
- Particulate Matter (PM) is a term used to describe a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
- These particles can be made up of various components such as dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and organic chemicals.
- They are classified based on their size, with PM2.5 and PM10 being the most commonly referenced categories.
- PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less, which is about 30 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
- These particles are produced by various sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and wildfires.
- Due to their small size, they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, posing significant health risks.
- PM10, on the other hand, refers to coarse particulate matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less.
- These particles are larger and primarily originate from activities such as construction, road dust, and agricultural practices.
- While not as harmful as PM2.5, they can still enter the respiratory system and cause health problems.
India Ranks 93 on Corruption Perceptions Index 2023 (The Hindu)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
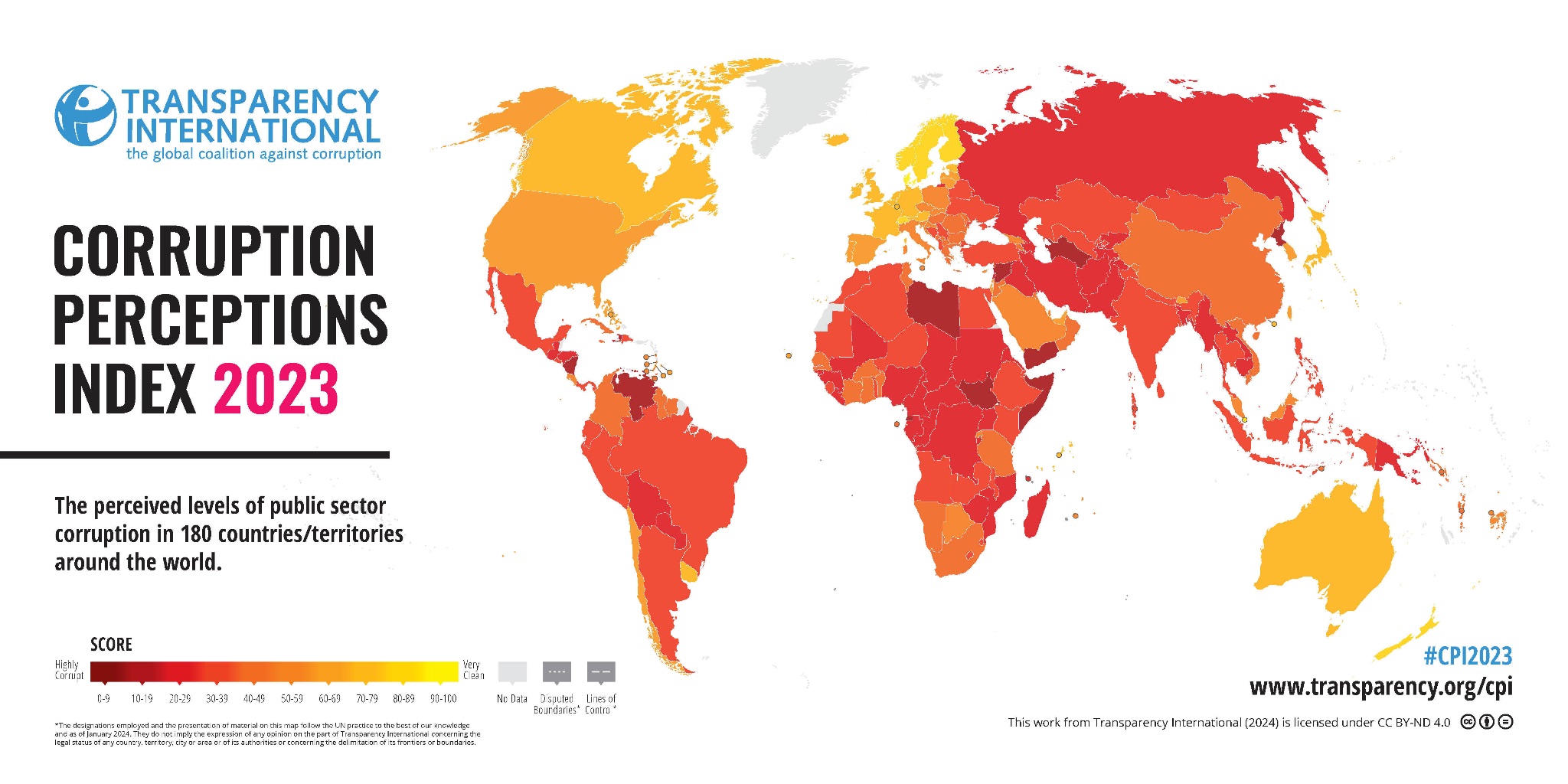
India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 as its overall score remained largely unchanged, according to a Transparency International report.
Key Facts About Corruption Perceptions Index 2023:
- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 tied with Maldives, Kazakhstan, and Lesotho also ranking at 93 out of 180 countries.
- In 2023, India's overall score was 39 while in 2022, it was 40.
- India's rank in 2022 was 85.
- Denmark (90) tops the index for the sixth consecutive year, with Finland and New Zealand.
- In South Asia, both Pakistan (133) and Sri Lanka (115) grapple with their respective debt burdens and ensuing political instability.
- Bangladesh (149) emerges from the least developed country (LDC) status, with economic growth supporting a continued reduction in poverty and improving living conditions.
- China (76), with its aggressive anti-corruption crackdown, has punished more than 3.7 million public officials for corruption over the last decade.
- Somalia (11), Venezuela (13), Syria (13), South Sudan (13) and Yemen (16) take the bottom spots in the index.
What is the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)?
- The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) scores and ranks countries/territories based on how corrupt a country’s public sector is perceived to be by experts and business executives.
- It is a composite index, a combination of 13 surveys and assessments of corruption, collected by a variety of reputable institutions including the World Bank, World Economic Forum, private risk and consulting companies, think tanks and others.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and the results are given on a scale of 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- The CPI is released annually by Transparency International, an independent nonprofit organization that aims to fight corruption, especially in the public sector.
- Transparency International is a global independent, nongovernmental nonprofit organization (NPO) that aims to stop corruption by promoting transparency in various sectors of society.
- The organization's international secretariat is located in Berlin and it has national chapters in more than 100 countries.
- The agency is funded through donations from governments, individuals, private donors, and other organizations.
- The organisation conducts research, and advocacy work, and undergoes various projects in its fight against corruption.
- In 1995, the organization created the first Corruption Perceptions Index, ranking 45 countries based on how much corruption they were perceived to have in the public sector.
Economic Impact of Corruption:
- Corruption continues to be a big hurdle to political, economic, and social development.
- Those who are economically challenged are the most affected by the effects of corruption and related fraud.
- That's because they often rely heavily on public services and can't afford to pay bribes.
- The International Finance Corporation also cites increases in the cost of business as a result of corruption.
PM declares Khelo India Youth Games 2023 open in Chennai (Indian Express)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently declared the Khelo India Youth Games 2023 open at the Nehru Indoor Stadium in Chennai.
What is Khelo India?
- The Khelo India programme has been introduced to revive the sports culture in India at the grassroots level by building a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establishing India as a great sporting nation.
- Talented players identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels by the High-Powered Committee will be provided annual financial assistance of INR 5 lakh per annum for 8 years.
About the Khelo India Youth Games 2023:
- The 6th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games is being hosted by Tamil Nadu, marking the first occurrence of the Games in South India.
- Spanning from January 19th to 31st, 2024, the event will unfold across four cities in Tamil Nadu – Chennai, Madurai, Trichy, and Coimbatore.
- With over 5600 athletes participating in more than 275 competitive events spanning 26 sports disciplines and one demo sport, this edition introduces Silambam, a traditional sport of Tamil Nadu, as a demo sport and includes Squash for the first time.
- Archery, athletics, badminton, and squash have been introduced first time in this edition.
- The mascot, 'Veera Mangai,' pays tribute to Rani Velu Nachiyar, an Indian queen who courageously resisted British colonial rule.
- The logo integrates the image of the poet Thiruvalluvar.
- Objectives: The overarching objective of the Khelo India Youth Games is to rejuvenate India's grassroots sports culture, aiming to build a robust framework for all sports and position the nation as a prominent sporting entity.
- Organized by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, the Games have been an annual tradition since their inception in 2018 in Delhi.
Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023 | Surat, Indore are the cleanest cities (The Hindu)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The President of India recently presented the ‘Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023’ at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
What is Swachh Survekshan?
- Conducted annually, Swachh Survekshan is a comprehensive evaluation of cleanliness, hygiene, and sanitation standards in cities and towns throughout India.
- This initiative was launched as an integral component of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, specifically falling under the urban segment (SBA-Urban).
- Initiated by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the survey is executed in collaboration with the Quality Council of India (QCI).
- The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, launched on October 2, 2014, aims to achieve cleanliness and the eradication of open defecation in India by October 2, 2019.
- The campaign is bifurcated into rural (SBA-Gramin, overseen by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and urban (SBA-Urban, supervised by MoHUA).
- Recently, on October 1, 2021, SBM-U 2.0 was introduced, focusing on ensuring universal access to sanitation facilities. Within this framework, the vision of attaining a Garbage-Free India has been emphasized.
- Commencing with the first survey in 2016, covering 73 cities, Swachh Survekshan has expanded significantly to encompass 4242 locations in the 2020 survey.
- The evaluation methodology centres on two primary criteria: citizen feedback and field assessment.
- Objectives of Swachh Survekshan: The primary goal of Swachh Survekshan is to encourage large-scale citizen participation and create awareness amongst all sections of society about the importance of working together towards making towns and cities better places to reside in.
About Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023:
- Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023 were presented by President Droupadi Murmu at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, under the auspices of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The theme for the year 2023 centred around "Waste to Wealth" emphasizing sustainable waste management practices.
- For 2024, the theme is “Reduce, Reuse and Recycle”.
- Indore (Madhya Pradesh) and Surat (Gujarat) jointly clinched the title of the cleanest cities in the country, with Navi Mumbai (Maharashtra) securing the third position.
- Remarkably, Indore maintained its top-ranking status for the seventh consecutive year.
- In the category of clean cities with a population of less than 1 lakh, Sasvad, Patan, and Lonavala secured the top three positions, while Madhyamgram, Kalyani, and Haora in West Bengal found themselves at the bottom.
- The cleanest cantonment was declared as Mhow Cantonment Board in Madhya Pradesh, and Chandigarh earned the SafaiMitra Surakshit Sheher recognition.
- In the Ganga Towns category, Varanasi and Prayagraj secured the first and second positions, respectively.
- Acknowledging overall cleanliness efforts, Maharashtra claimed the title of the best-performing state, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh in the second and third positions.
- Odisha secured the fourth spot, with Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Sikkim, Karnataka, Goa, Haryana, and Bihar following suit.
- Conversely, Rajasthan, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh found themselves at the lower end of the ranking.
Horticulture boost: Litchi cultivation has expanded to 19 Indian states, according to officials (DownToEarth)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Litchi which is synonymous with India's hot summers, is now under cultivation in 19 Indian states, extending beyond its traditional confinement to Muzaffarpur in Bihar.
About Litchi Cultivation:
- Litchi, a delicious and succulent fruit of superior quality, belongs to the Sapindaceae family from a botanical perspective.
- Its translucent and flavorful aril, or edible flesh, is widely enjoyed as a table fruit in India.
- Agro-climatic Requirements: Litchi is a sub-tropical fruit that thrives optimally in moist sub-tropical climates.
- Ideally cultivated at low elevations, it can be grown up to an altitude of 800 meters.
- The crop flourishes in deep, well-drained loamy soil rich in organic matter, with an ideal pH range of 5.0 to 7.0.
- Temperature: The crop's temperature tolerance ranges from avoiding extremes, not exceeding 40.5 degrees Celsius in summer and staying above freezing point in winter.
- Rainfall: Prolonged rainfall, especially during flowering, can be detrimental as it interferes with pollination.
- Young trees necessitate protection from frost and hot winds until firmly established, although some temperature variation is necessary for proper fruiting.
- Frost during winter and intense summer heat are limiting factors for successful cultivation.
- Traditionally, commercial cultivation in India was confined to the northern foothills of the Himalayas from Tripura to Jammu & Kashmir, and the plains of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- However, due to increasing demand and the crop's viability, commercial cultivation has expanded to various states such as Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, etc.
- India ranks second in the world in production of Litchi production after China.
- Other significant producers include Thailand, Australia, South Africa, Madagascar, and the US.
- Statewise, Bihar tops in Litchi production followed by West Bengal (12 % of the total) and Jharkhand (10 %).
About National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL):
- The National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL) serves as the leading national institute dedicated to research and development in the field of litchi.
- It plays a pivotal role in providing national leadership, serving as a repository for comprehensive information on litchi production, processing, value addition, and extending consultancy services to end-users.
MEA’s Flagship ‘Know India Programme’ for youth diaspora completes 20 years (MEA GOI)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The flagship programme of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for the youth diaspora, the ‘Know India Programme’, has completed 20 years.
About the Know India Programme (KIP):
- The Know India Programme is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of External Affairs designed to enhance awareness about India, its cultural heritage, and art, and to familiarize participants with various aspects of contemporary India and their ancestral homeland.
- This program is open to Persons of Indian Origin (21-35 years) (excluding non-resident Indians) from all over the world, with a preference for youth from Girmitiya countries, such as those from Mauritius, Fiji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago, South Africa, and Jamaica.
- The program has been in existence since its inception in 2003.
Features of Know India Programme (KIP):
- It is a 21 days’ programme (excluding international travel) during which the participant will visit Delhi, Agra and a select state in India alongwith visits to places of historical, cultural, and religious significance.
- KIP participants will also have a 2-day orientation programme in New Delhi.
- Participants will meet opinion makers, leaders, and officials to get an overview of India’s economy, society and ongoing growth and development story.
- Participants are provided local hospitality e.g. boarding and Internal transportation in India, return air tickets from their country of residence to India provided participants bear 10% of the cost of total air fare.
- Gratis visa shall be granted to participants by the Indian Missions/Posts abroad.
- Some of the key elements of the Programme include:
- Visits to places of historical and cultural importance;
- Familiarisation with Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical forms of Music and Dance;
- Visit to institutions of democracy and governance like Parliament of India, Election Commission of India, Rashtrapati Bhawan;
- Interaction with leading educational institutions;
- Exposure to flagship economic and development schemes like Digital India, StartUp India, and Make in India; and
- visits to industrial sites, public and private firms to highlight India’s strength in Manufacturing & Service sector.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Minimum qualification required for participating in KIP is graduation from a recognized University /Institute or enrolled for graduation and the ability to speak in English.
- The applicant should not have visited India through any previous Programme of Government of India.
- Those who have not visited India before will be given preference.
- Applicant must provide documentary evidence to prove Indian origin or an undertaking about Indian origin which must be countersigned by the Indian Embassy/High Commission/Consul General.
States Returning to OPS Pose Significant Financial Burden: RBI (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the RBI released a report saying, the return to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) by a few states would put a huge burden on their finances, restricting them from undertaking capital expenditure to drive the growth.
What is the Old Pension Scheme (OPS)?
- The Old Pension Scheme (OPS), popularly OPS, is for state and central government employees who have completed 10 or more years of service.
- The appeal of the Old Pension Scheme lies in its commitment to provide a guaranteed or 'defined' benefit to retirees, classifying it as a 'Defined Benefit Scheme.'
- It provides government employees with pensions based on their final salary, amounting to 50% of the last drawn salary.
- For instance, if a government employee's final monthly salary upon retirement was Rs 10,000, they would receive a guaranteed pension of Rs 5,000.
- Similar to government employees' salaries, pension payouts increased with government-declared dearness allowance (DA) hikes.
- The Central government discontinued OPS in 2003.
What were the issues with the OPS?
- The primary concern was the unfunded nature of the pension liability, lacking a dedicated corpus that could grow over time to meet payment needs.
- The annual Government of India budget allocated funds for pensions without a clear strategy for sustaining future payments.
- The 'pay-as-you-go' approach raised inter-generational equity concerns, burdening the present generation with the escalating load of pension responsibilities.
- Recently, the RBI expressed alarm over some states, including Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan, reverting to the OPS, citing it as a significant fiscal challenge.
- The RBI warned that by deferring current expenses to the future, states risk accumulating unfunded pension liabilities in the years to come.
What is the New Pension Scheme (NPS)?
- Introduced by the Central government in 2004 as an alternative to OPS, NPS is accessible to employees across public, private, and unorganized sectors, excluding those in the armed forces.
- This pension initiative encourages individuals to invest in a pension account regularly during their employment.
- Upon retirement, subscribers can withdraw a specific percentage of the accumulated corpus.
- The remaining amount is disbursed as a monthly pension post-retirement.
- Regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA).
How does NPS differ from OPS?
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS) ensures a fixed and guaranteed pension amount.
- In contrast, the National Pension Scheme (NPS) is an investment-cum-pension scheme, exposing returns to market volatility.
- NPS contributions are defined, but benefits are contingent on market performance.
Why Rural India Needs Women Drone Pilots? (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The NAMO Drone Didi Scheme provides new work opportunities to women and makes them the backbone of the rural economy.
What is the NAMO Drone Didi Scheme?
- The Prime Minister has recently approved the Central Sector Scheme (NAMO Drone Didi Scheme) for providing Drones to the Women Self Help Groups (SHGs), with an outlay of Rs. 1261 Crore.
- The scheme aims to provide drones to 15,000 selected Women SHGs during the period 2023-24 to 2025-2026 for providing rental services to farmers for agriculture purposes.
- The scheme seeks to empower women Self Help Groups (SHGs) and bring new technologies through drone services in the agriculture sector.
The highlights of this scheme are as follows:
- Departments involved: The scheme converges the resources and efforts of the Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW); Department of Rural Development (DoRD); Department of Fertilizers (DoF); Women SHGs and Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Identification of SHGs: The women SHGs would be identified from the total 89 lakh SHGs formed under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana.
- Financial Assistance:
- Central Financial Assistance covering 80% of drone costs up to a maximum of Rs. 8 Lakh will be provided.
- The remaining amount can be raised through the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with a provision of interest subvention @ 3% on the AIF loan.
- Training:
- One of the members of SHGs will be trained in drone piloting skills and agriculture purposes of nutrient and pesticide application.
- Another member will be trained as a drone technician.
- This will allow them to not just operate the drone but also repair and maintain it.
- Nano Fertilizers: The scheme also promotes the use of Nano Fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP through drone services.
- Opportunities for Start-ups: The scheme not only empowers women but also opens avenues for dynamic start-ups in the field of drone aeronautics, tapping into significant untapped potential in this emerging sector.
Significance of the NAMO Drone Didi Scheme:
- Empowering Rural Women: Fosters technological empowerment of rural women, positioning them as the backbone of the rural economy.
- Places drone technology in the hands of women pilots from Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Modernizing Agricultural Practices: Addresses the imperative to modernize agricultural practices.
- Aims to elevate agricultural productivity through cutting-edge technology, contributing to a new agricultural revolution.
- Job Opportunities in Drone Aeronautics: Creates opportunities in the emerging field of drone aeronautics with substantial untapped potential.
- Opens avenues for rural women as pilots, mechanics, and spare-part dealers.
- Efficient Fertigation System Development: Facilitates the development of an efficient fertigation system.
- Introduces innovative liquid fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP with foliar application.
- Time-Efficient Spraying System: Automation of the spraying system through agri-drones ensures a time-saving and efficient application system.
- Equitable Agrarian Family Culture: Contributes to making the agrarian family culture more equitable and robust.
Article 356 of the Indian Constitution (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently held that the declaration of State emergency under Article 356 and the subsequent actions of the President should have a “reasonable nexus”.
What is Article 356 of the Indian Constitution?
Article 356 of the Constitution of India is based on Section 93 of the Government of India Act, 1935. According to Article 356, the President's Rule can be imposed on any state of India on the grounds of the failure of the constitutional machinery.
There are two types:
- If the President receives a report from the state's Governor or otherwise is convinced or satisfied that the state's situation is such that the state government cannot carry on the governance according to the provisions of the Constitution.
- Article 365: As per this Article, President's Rule can be imposed if any state fails to comply with all directions given by the Union on matters it is empowered to.
In simple words, President's Rule is when the state government is suspended and the central government directly administers the state through the office of the governor (centrally appointed. It is also called State Emergency or Constitutional Emergency.
President's Rule:
- Parliamentary approval is necessary for the imposition of the President's Rule on any state.
- The proclamation of President's Rule should be approved in both Houses of Parliament within two months of its issue.
- The approval is through a simple majority.
- The President's Rule is initially for a period of six months.
- Later, it can be extended for a period of three years with parliamentary approval, every six months.
- The 44th Amendment to the Constitution (1978) brought in some constraints on the imposition of the President's Rule beyond a period of one year. It says that the President's Rule cannot be extended beyond one year unless:
- There is a national emergency in India.
- The Election Commission of India certifies that it is necessary to continue the President's Rule in the state because of difficulties in conducting assembly elections in the state.
What happens after the President's Rule is imposed?
- The governor carries on with the administration of the state on behalf of the President. He or she takes the help of the state's Chief Secretary and other advisors/administrators whom he or she can appoint.
- The President has the power to declare that the state legislature's powers will be exercised by the Parliament.
- The state legislative assembly would be either suspended or dissolved by the President.
- When the Parliament is not in session, the President can promulgate ordinances with respect to the state's administration.
When is the President's Rule imposed?
- President's Rule is typically imposed when any of the following circumstances occur:
- The state legislature is unable to elect a leader as the Chief Minister within the time prescribed by the state's governor.
- Breakdown of a coalition in the state government, resulting in the Chief Minister having minority support in the legislature, and the CM is unable to prove a majority within the time prescribed by the governor.
- A vote of no confidence in the legislative assembly leads to a loss of majority.
- Postponement of elections due to unavoidable reasons such as a natural disaster, epidemic, or war.
Revocation of President's Rule:
- President's Rule can be revoked anytime after such a proclamation has been made by a subsequent proclamation by the President.
- A proclamation of revocation does not require approval by the Parliament.
- This occurs when the leader of a political party produces letters indicating majority support for him in the assembly and stakes his claim to form the state government.
How do web browsers work? (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Web browsers are our digital passports to the vast universe of the internet. Their simplicity is deceptive: beneath their user-friendly interfaces lies a world of intricate processes that transform clicks into the web pages we interact with every day.
What are web browsers?
- Fundamentally, the browser is an application that people use to send and receive messages via the internet.
- In other words, the browser is a program that runs on our device, with its purpose being to fetch information in different formats from the internet and show it on the device.
- It also does the reverse, receiving your input (say, a click), translating it to code, and transmitting it to some other machine across the internet.
- In the year 1990, the English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee introduced the concept of the World Wide Web also named ‘WorldWideWeb’.
What Constitutes a Web Browser?
Web browsers today comprise numerous essential components, each representing a sophisticated technology. Additionally, they depend on various supporting technologies and adhere to established standards governing the functioning of the Internet.
- Request and Response: When we enter a website's URL, the browser sends a request to a server, asking for the specific web page.
- The server processes the request and sends back a response containing the information needed to construct the page.
- This response, akin to a digital blueprint, travels back to our browser.
- Deconstructing the Response: The server's response comprises various files encoded in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- HTML outlines the webpage structure, CSS adds style and aesthetics, while JavaScript brings interactivity, making the page dynamic and engaging.
- Rendering: The browser deciphers HTML, applies CSS for styling, and executes JavaScript for interactivity, rapidly assembling the final webpage.
- Rendering engines are crucial technology enabling quick and cohesive visual presentation.
- Managing Data: Browsers use cookies for retaining site preferences and cache for storing frequently accessed files.
- Cookies act like post-it notes, preserving login status and preferences, while the cache accelerates page loading by retrieving stored files instead of downloading them again.
- Security: Browsers prioritize security by employing encryption protocols like HTTPS for data exchange.
- They create secure 'tunnels' to shield information during transmission. Warning systems alert users about potential threats, enhancing overall online safety.
As technology advances, web browsers are on a trajectory of continuous evolution. They are integrating state-of-the-art technologies such as WebAssembly, facilitating near-native performance within the browser. The future holds promises of support for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences, offering immersive online interactions. Privacy features are also being fortified, empowering users with enhanced control over their digital presence.
Oil Producers Water Down Provision on Fossil Fuel Phase-out (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After four days of deadlock, a new draft agreement text emerged at the COP28 climate meeting that severely watered down earlier provisions on fossil fuel elimination but singled out coal for a rapid phase-down, which could be problematic for India.
Context:
- The 28th Conference of the Parties (COP 28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is underway in the United Arab Emirates from November 30 to December 12, 2023.
- During the climate meeting on December 10, negotiators took an initial step toward enhancing action on adapting to climate change.
- A draft text outlining potential "global goals" on adaptation was introduced for the first time, serving as a starting point for further negotiations.
- Negotiators are actively discussing various topics, including the contentious issue of fossil fuel phase-out, in informal sessions to find common ground.
- The draft document is titled 'Global Goal on Adaptation' (GGA) and aims to establish a shared global objective for adaptation, similar to the global goal of limiting temperature rise below the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold for mitigation.
- This initiative addresses a longstanding demand from developing countries, emphasizing the need for increased focus and resource mobilisation for adaptation efforts.
- Notably, the draft removes the term 'phasing out' of fossil fuels but includes stronger language against coal, urging a "rapid phase-down of unabated coal," a point that may face objections from major consumers like India, Indonesia, and China, all developing countries heavily reliant on coal power.
Responses to the Draft Text 'Global Goal on Adaptation':
- The European Union (EU) and certain small island states promptly dismissed the draft agreement text.
- The EU climate commissioner criticized the overall insufficiency of the text, deeming it inadequate in addressing the climate change challenge.
- Primary dissatisfaction arose from the weakening of a provision related to the use of fossil fuels.
- The draft initially urged countries to "reduce both consumption and production of fossil fuels, in a just, orderly, and equitable manner."
- Notably, fossil fuels, responsible for nearly 80 percent of greenhouse gas emissions, have never been explicitly mentioned in prior COP decisions.
- While previous decisions emphasized the need to cut emissions, they avoided specifying actions for emission reduction.
- COP28 marked the first formal discussion of a fossil fuel phase-out but attempts to incorporate a robust provision faced resistance from oil-producing nations like Saudi Arabia and Russia.
- India, while not offering an immediate reaction to the draft agreement, has consistently asserted that singling out coal for accelerated reduction is discriminatory.
Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi) (NewsOnAir)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
YUVAi Student Finalists to showcase their AI-enabled social impact projects at the GPAI summit.
About Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi) Initiative:
- YUVAi is aimed at fostering a deeper understanding of AI, to equip school students from classes 8th to 12th across the nation with AI skills, and to empower them to become human-centric designers and users of AI.
- In addition, the program offers an applied learning experience for students to understand and identify how AI technology can tackle critical problems and lead to the inclusive development of the nation.
- It is a collaborative initiative of the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India and Intel India.
- The objectives of YUVAi are to :
- Foster a deeper understanding of AI-tech and social skills
- Enable youth to develop AI-enabled solutions as a sign of achievement
- Empower youth to become human-centric designers and users of AI
- The program will be conducted in three phases.
- In the initial phase, teachers will be selected to identify students from their respective schools and share their details with the organizing team.
- Next, online orientation sessions will be conducted for registered students around core AI concepts by experts to facilitate understanding of the ideation process.
- Finally, students will be encouraged to submit ideas (individually or in teams of 2) through a 120-second video explaining a proposed AI-enabled solution for any one of the eight core themes- agriculture, healthcare, education, environment and clean energy, transportation, rural development, smart cities and law and justice.
- Shortlisted students will attend online deep dive AI training in the second phase.
- A 3-day face-to-face boot camp will be organized to provide adequate mentorship and guidance by YUVAi coaches.
- After the mentorship camps, students will use this newly gained knowledge to develop AI-enabled innovations/projects on any of the eight core themes and submit final entries.
- Finally, the most innovative AI-based solutions will be announced and invited to a national showcase and felicitation ceremony.
- Rewards: Upon a successful idea submission, students will be awarded a Certificate of Appreciation.
Protein from Budgett’s frog can block enzymes of disease-causing pathogens (The Hindu)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science’s (IISc.) molecular biophysics unit in a study have identified that peptides (short protein) produced from Budgett’s frog can combat enzymes of disease-causing pathogens.
Key Research Findings:
- The research focused on peptides, or short proteins, derived from amphibian skin, a subject of prolonged study due to their capacity to counter adverse environmental conditions, including harmful pathogens.
- A peptide secreted by frogs demonstrated inhibitory effects on two crucial enzymes, namely subtilisin Carlsberg and proteinase K, which are produced by pathogens.
- These enzymes play a crucial role in fostering infections by breaking down specific protective proteins within the infected individual.
- The studied peptide exhibited its inhibitory action through a slow-tight binding pathway, proving to be as effective as SSI, a well-established subtilisin inhibitor.
- The researchers illustrated the formation of a Michaelis complex—an intact, noncovalent complex with the inhibitor—during the process.
About Budgett’s frog:
- Budgett’s frogs exhibit high intelligence and a notably assertive nature.
- When alarmed, they employ a defensive strategy by inflating themselves, standing on short legs, and, if necessary, lunging at potential threats with an open, imposing mouth accompanied by a distinctive shriek.
- During the dry season, these frogs take refuge in burrows they construct at the bottoms of water pools.
- Within these burrows, they shed multiple layers of skin to create a waterproof cocoon, ensuring their moisture retention.
- Equipped with exceptional night vision and a keen sensitivity to movement, Budgett’s frogs showcase effective hunting skills.
- Habitat/Range: Found in proximity to permanent or seasonal bodies of water, Budgett’s frogs inhabit regions across Paraguay, Argentina, and Bolivia.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Classified as Least Concern.
Royal Bengal Tiger spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary (PTI)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a Royal Bengal Tiger was spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim at an altitude of 3,640 metres.
Context
- Royal Bengal Tiger has been sighted in the Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim roaming at an altitude of 3,640 meters.
- The Royal Bengal Tiger was captured by trap cameras of a team of the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) which is conducting a study in the sanctuary in collaboration with the Sikkim Forest Department.
- It was under a larger project called "Conservation and Use of Five Wetlands in three Himalayan States to Secure Habitats of Birds Migrating within the Central Asian Flyway (CAF)."
- This project was sanctioned under the National Mission on Himalayan Studies (NMHS), and aims to protect and conserve wetland sites in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Sikkim.
About Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary is located at the tri-junction of Sikkim, Bengal and Bhutan and is spread over 128 square kilometres.
- The sanctuary is strategically located in the East Sikkim district, connecting the forests of Bhutan and the Neora Valley National Park in West Bengal.
- It is the largest wildlife sanctuary in Sikkim.
- Vegetation: The Sanctuary has typical alpine-temperate-subtropical vegetation with high-altitude lakes around Jelep La.
- Flora: Rhododendron, Silver Fir, Juniper forest and associated ground flora, moss-filled oak forests with dense bamboo thickets etc.
- Fauna: It is home to various species, including red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan musk deer, Himalayan goral, and Himalayan black bears.
EU’s Landmark Deal on Artificial Intelligence Regulation (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently European Union policymakers agreed on a provisional deal on landmark rules governing the use of artificial intelligence (AI).
On December 8, EU member states and lawmakers reached a consensus on the formulation of "historic" rules governing artificial intelligence models like ChatGPT, concluding prolonged negotiations.
However, these rules are slated to come into effect no earlier than 2025, allowing room for technological advancements in the interim.
Key Highlights:
- The inception of the Artificial Intelligence Act dates back to 2021, aiming to instil transparency, trust, and accountability in AI practices.
- Its overarching goal is to establish a framework to address risks to safety, health, fundamental rights, and democratic values within the EU.
- Featuring a two-tier approach, the Act imposes transparency requirements on all general-purpose AI models, with more stringent measures for the more powerful ones.
- The Act proposes the creation of an EU-wide database cataloguing high-risk AI systems, with provisions for the inclusion of future technologies meeting high-risk criteria.
- The legislation seeks a delicate balance between fostering AI adoption and preventing or mitigating harms associated with specific applications of the technology.
Global Perspectives on Artificial Intelligence Governance:
- The dynamic evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) development has prompted diverse global perspectives on the regulation of these technologies.
- In May 2023, members of the European Parliament reached a preliminary agreement on a revised draft of the European Union's ambitious Artificial Intelligence Act.
- This Act envisions the creation of an EU-wide database for high-risk AI systems and outlines criteria for the inclusion of future technologies that meet these high-risk parameters.
- In contrast, the United States currently lacks comprehensive AI regulations and has adopted a relatively hands-off approach.
- On the opposite end of the spectrum, China has, in the past year, introduced some of the world's initial nationally binding regulations specifically targeting certain types of algorithms and AI.
- It has implemented a law to govern recommendation algorithms, with a particular focus on how these algorithms disseminate information.
India’s Position on Artificial Intelligence:
- Initially, the Union Minister for Electronics and Information Technology stated that the government was not contemplating any legislation to oversee the development of AI in India.
- However, in the lead-up to the G20 summit in September 2023, the Indian government hinted at the potential regulation of AI.
- Officials indicated that the forthcoming Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2022 would extend to AI developers engaged in creating and facilitating AI technologies.
- Given the substantial data collection and utilization by AI developers to train their algorithms and enhance AI solutions, they may be classified as data fiduciaries and held accountable for the responsible use of personal data.
- Prime Minister Modi recently expressed India's aspiration to "take a giant leap in AI to empower its citizens and actively contribute to its evolution."
- India is gearing up to host the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi from December 12-14.
- As a co-founder of GPAI, India, along with 28 member countries and the EU, is committed to guiding the responsible development and utilization of AI.
India's Ambitious Initiative to Expand Renewable Energy Capacity (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has proposed an exemption for green hydrogen developers from adhering to its list of authorised manufacturers to enable them to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China.
What Does The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) Propose?
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is exploring the option of granting an exemption to green hydrogen developers from its list of authorized manufacturers.
- This proposed exemption would enable these developers to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China, aiming to enhance the competitiveness of green hydrogen exports.
- It's noteworthy that Chinese manufacturers are presently absent from MNRE's Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) and Revised List of Models and Manufacturers (RLLM).
The MNRE’s Proposal Background:
- After the 2020 Galwan Valley skirmishes, the Indian government issued directives to restrict the involvement of Chinese vendors in public procurement.
- Recently, the Indian procurement portal GeM announced the removal of hundreds of Chinese vendors over the past three years.
- At a time when energy companies are intensifying efforts to mass-produce green hydrogen, essential for which are renewable energy equipment and electrolysers, the government has sidelined Chinese manufacturers.
- This aligns with the MNRE's policy to enhance domestic manufacturing of renewable energy equipment.
- While central PSUs may face restrictions on importing electrolysis machinery from China, others continue to do so.
- In FY23, India witnessed a 40% increase, in importing machines and apparatus for electroplating, electrolysis, and electrophoresis, worth $45.61 million, compared to the preceding fiscal year.
What is the Significance of the MNRE’s Proposal?
- ??The proposal to import solar PV modules from China carries significance in bolstering the supply chain and enhancing the global competitiveness of Indian green hydrogen exports.
- Central PSUs such as Indian Oil Corporation Ltd and NTPC Ltd, both actively involved in green hydrogen projects, would benefit by sourcing equipment from Chinese manufacturers.
- This move is poised to strengthen India's position in the global green hydrogen market, aligning with the objectives outlined in the National Green Hydrogen Mission and facilitating the achievement of set targets.
Painkiller Meftal could cause DRESS syndrome (Financial Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has recently issued a drug safety alert for doctors and patients about the use of the commonly used painkiller mefenamic acid, popularly sold under the brand name Meftal.
Context:
- The Pharma standard body, Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) in its preliminary analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) from the PvPI database revealed that Meftal can lead to Drug Reactions with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome.
- According to doctors, this syndrome causes a diverse array of clinical symptoms, anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks after initiating the offending drug.
What is DRESS syndrome?
- DRESS syndrome (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) is an adverse reaction term that is currently used to describe a hypersensitivity reaction.
- Experts classify DRESS syndrome as a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- It is a serious drug reaction affecting the skin and other organs, with a mortality rate of up to 10%.
- It manifests when the immune system excessively responds to specific medications, leading to a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- This reaction can manifest with various symptoms across the body, including fever, abnormalities in blood, and inflammation of organs.
What are the symptoms of DRESS syndrome?
- Patients diagnosed with DRESS syndrome typically present with a rash, fever, and eosinophilia but can have a variety of symptoms including liver, lung, or kidney involvement.
- “DRESS syndrome should be suspected if a diffuse rash erupts and is accompanied by fever, facial edema, and enlarged lymph two to six weeks after starting a new high-risk medication.
How to treat DRESS Syndrome?
- The most important step to treat DRESS Syndrome is to stop the medication involved in the reaction, and sometimes, no further treatment is needed.
- Topical steroids can be given to treat the rash and in certain cases, further treatment is needed to protect the organs from damage, such as with steroids, which can be given either intravenously or orally.
- “Treatment with steroids can be needed for weeks or even months, and lab work is monitored carefully during this time.
- The average time to recovery is six to nine weeks.
Odisha Invokes ESMA to Ban Strikes by Health Department Staffs (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha Government invoked the Orissa Essential Services (Maintenance) Act (ESMA) prohibiting strikes by paramedical staff, including nurses, pharmacists, technicians, Class III and IV employees, to ensure that medical services are not disrupted.
About Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA):
The Indian Parliament enacted ESMA in 1968 to ensure the continuous provision of critical services crucial to people's daily lives. This legislation prohibits employees in essential services from striking, regardless of bandhs or curfews.
- Designated Essential Services: Public conservation, sanitation, water supply, hospitals, national defense, petroleum, coal, electricity, steel, fertilizer production, and banking-related services fall under the ambit of essential services.
- Communication, transportation, and government initiatives for food grain acquisition and distribution are also covered.
- State-Specific Application: State governments, individually or collaboratively, can enforce ESMA within their territories, each having its own version with slightly varied provisions.
- This allows states to address disruptions that impact specific regions.
- Central Government Activation: In the case of a nationwide disruption, especially in sectors like railways, the central government may invoke ESMA.
- Consequences for Striking Employees: Employees engaging in illegal strikes under ESMA can face disciplinary action, including dismissal. Legal consequences may involve arrests without a warrant, with imprisonment for up to one year, fines, or both for those participating or instigating the strike.
UN Secretary-General Invokes Article 99 on Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid Israel’s ongoing military attacks on the Gaza Strip, particularly in its southern region, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter in a bid to establish a ceasefire.
Context:
- The United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has decided to invoke Article 99 of the UN Charter as the death toll in Israeli bombardments on Gaza crosses 16,000.
- He also urged the UN Security Council to act on the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- The development comes as Israel increased the intensity of its operations, especially in the areas of southern Gaza with Israel's defence leadership claiming that “half of Hamas’ battalion commanders" are killed.
What is Article 99 of the UN Charter?
- The Secretary-General may bring to the attention of the Security Council any matter which in his opinion may threaten the maintenance of international peace and security.”
- It is seen as a discretionary power.
- The responsibility it confers upon the Secretary-General will require the exercise of the highest qualities of political judgment, tact and integrity” according to a 1945 report of the Preparatory Commission of the United Nations.
- According to the UN, the President of the Security Council is under the obligation to call a meeting of the Council if the Secretary-General brings to the attention of the Council any matter under Article 99.
When has Article 99 Been Activated in the Past?
- 1960: Following the Congo Crisis, Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld invoked Article 99 to address the aftermath of Belgium's withdrawal and the ensuing internal conflict.
- 1971: Amid the Bangladesh Liberation War, Secretary-General U Thant activated Article 99 to draw attention to the humanitarian crisis, urging international intervention.
- 1979: In response to the Iranian Revolution and hostage crisis, Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim triggered Article 99 to underscore the seriousness of the situation and the necessity for a peaceful resolution.
- 1989: Confronted with the ongoing Lebanese Civil War and hostage abductions, Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar invoked Article 99 to emphasize the requirement for international support and engagement.
‘Garba Of Gujarat’ Declared as Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Garba, the folk art of Gujarat, receives the intangible cultural heritage of humanity (ICH) tag from Unesco.
Context:
- 'Garba of Gujarat' has been inscribed in the Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of Humanity by UNESCO.
- The decision was taken at the 18th session of the UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage held in the Republic of Botswana.
- Garba of Gujarat is the 15th ICH element from India to join this list.
- This inscription underscores Garba’s pivotal role as a unifying force that fosters social and gender inclusivity.
About Garba Dance:
- Garba is a ritualistic and devotional dance deeply rooted in the traditions of Gujarat, India.
- This vibrant dance is a central part of the nine-day Navratri festival, dedicated to the worship of feminine energy or Shakti.
- The cultural richness of Garba vividly expresses the divine feminine through its performances and visuals.
- Taking place in various settings, from homes and temple courtyards to public spaces, streets, and open grounds, Garba transforms into a widespread, inclusive community celebration.
- Beyond its religious significance, Garba serves as a social equalizer, breaking down barriers related to socio-economic status, gender, and sect divisions.
- This inclusive dance form fosters community unity, bringing together diverse and marginalized groups and reinforcing social bonds.
- Notably, Garba holds the distinction of being the 15th cultural element from India to be recognized by UNESCO.
What is Intangible Cultural Heritage?
- Cultural heritage extends beyond physical structures and object collections.
- It encompasses traditions and living expressions transmitted from our forebears to descendants.
- This includes oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, and the knowledge associated with nature, the universe, as well as the skills involved in traditional craftsmanship.
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module Retraces Steps to Earth Orbit (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have brought the Propulsion Module (PM) of the Chandrayaan-3 mission , which initially brought the Vikram lander to within 100 km of the Moon's surface before detaching and executing a historic controlled descent on August 23, back into Earth orbit.
What is a Propulsion Module in Chandrayaan-3?
- The Propulsion Module is a rectangular component of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, equipped with solar panels for power.
- Its primary purpose was to transport the Lander module to the lunar polar circular orbit and facilitate its separation.
- Following separation, the SHAPE payload within the Propulsion Module was activated.
- Initially intended for a three-month operation during the mission, the ISRO announced on December 4th that the Chandrayaan-3's Propulsion Module had been manoeuvred out of lunar orbit.
- Placed high above Earth for an additional mission, the module is currently sustained by residual fuel.
- This bonus mission will showcase technologies crucial for future lunar sample retrieval, according to ISRO.
- As of now, the ISRO has not disclosed its plans for the spacecraft once it depletes its fuel.
Importance of Propulsion Module's Return to Earth's Orbit:
- ISRO highlighted the key achievements resulting from the return manoeuvres conducted on the Propulsion Module (PM) in connection to upcoming missions:
- Planning and executing the trajectory and manoeuvres for the return journey from the Moon to Earth.
- Developing a software module for planning such manoeuvres, along with its initial validation.
- Planning and executing a gravity-assisted flyby around a planet or celestial body.
- Preventing uncontrolled crashing of the PM onto the Moon's surface at the end of its life, aligning with the requirement of avoiding debris creation.
What is Chandrayaan-3 Mission?
Mystery of megamouth shark solved after one washes up in Philippines (Business Insider)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a dead 18-foot megamouth shark that washed up on the beach in the Philippines was pregnant, confirming for the first time that these mysterious creatures give birth to live young.
About Megamouth Shark:
- Researchers have found Megamouth sharks to be particularly elusive.
- Since their discovery in 1976, there have been fewer than 300 sightings of these deep-sea sharks.
- Uncovering fewer than 150 specimens, scientists have identified them as the smallest of three species of filtering sharks.
- Their scientific name is Megachasma pelagios.
- Similar to their relatives, the basking sharks, Megamouth sharks feed on krill suspended in seawater, utilizing their oversized mouths to sieve their food.
- Although most sightings have occurred near the Philippines and Taiwan, these sharks have been observed around the world.
- These sharks are found in deep, warm oceanic water and inhabit the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans.
- Characterized by their substantial size, Megamouth Sharks can reach weights of up to 2700 pounds (1215 kg) and lengths ranging from 425 to 515 cm. Females are generally larger than males.
- Easily recognizable by their large, soft head and anteriorly positioned mouth, their colouration varies from grey to bluish-black above and pale grey below.
- They possess small, hooked teeth along both top and bottom jaws.
- As filter feeders, they swim with their mouths continuously wide open, filtering their preferred planktonic prey.
- The inside of their mouths is equipped with light-producing organs that may attract pelagic crustaceans and other potential prey.
- On the conservation front, the Megamouth Shark is listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List.
Closest-ever Sun photo captured by Solar Orbiter (India Today)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The European Space Agency's Solar Orbiter has captured the most detailed image of the Sun's full disc and outer atmosphere, the corona, to date.
What is the Solar Orbiter?
- Solar Orbiter is a Sun-observing satellite, equipped with 10 state-of-the-art science instruments, that aims to provide unprecedented insights into the workings of the Sun.
- It intends to conduct an in-depth study of both the Sun and the inner heliosphere, exploring the uncharted regions closest to our Solar System.
- A collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, it represents the most intricate scientific laboratory ever dispatched to study the Sun.
- Distinguished by its capability to capture images of the Sun from a closer vantage point than any preceding spacecraft, it also marks the first exploration of the Sun's previously uncharted polar regions.
- Launched on February 10, 2020, the mission unveiled its initial images in June of the same year.
- Following gravitational assist manoeuvres at Earth and Venus, it commenced full science operations in December 2021.
- Solar Orbiter actively orbits the Sun in an elliptical trajectory, with its closest point, the perihelion, located approximately 25 million miles (40 million kilometres) from the Sun—closer than the orbit of Mercury.
- In terms of instrumentation, it actively carries six remote-sensing instruments for observing the Sun and the solar corona, along with four in-situ instruments for measuring the solar wind, energetic particles, and electromagnetic fields.
- The mission actively aims to continue its scientific operations until at least 2027.
Panchayat Development Index (PIB)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj recently informed Lok Sabha about the Panchayat Development Index.
About the Panchayat Development Index:
- The Panchayat Development Index serves as a comprehensive and versatile metric designed to actively evaluate the holistic advancement, efficacy, and ongoing progress of panchayats.
- This index actively considers a spectrum of socio-economic indicators and parameters, offering an actively nuanced understanding of the well-being and developmental status of local communities within the panchayat's jurisdiction.
- Objectives: The primary objective is to actively play a pivotal role in assessing performance and progress towards actively achieving Sustainable Development Goals at the grassroots level.
- An active component of this initiative is the Local Indicators Framework, which encompasses nine key themes for actively localising Sustainable Development Goals.
- These themes actively encompass creating poverty-free and thriving livelihoods, ensuring health and actively child-friendly environments, actively promoting water sufficiency, actively fostering clean and green spaces, actively developing self-sufficient infrastructure, actively establishing socially just and secure communities, actively promoting good governance, and actively creating women-friendly villages.
How Ranking Works?
- Ranks within the index are actively assigned based on scores, actively categorising panchayats into four grades.
- Those actively scoring below 40 percent are actively classified as Grade D,
- 40-60 percent as Grade C,
- 60-75 percent as Grade B
- 75-90 percent as Category A
- and those actively surpassing 90 percent are actively designated as A+.
- Significance of this Index: The significance of this index lies in its ability to actively offer valuable insights into areas requiring attention and improvement within rural areas under panchayat jurisdiction.
- It actively aids in identifying disparities, gauging the achievement of development goals, and actively crafting targeted policies and interventions to elevate the overall well-being and quality of life in rural communities.
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) (DST Gov)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The study by ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), Izatnagar, Bareilly has found the exact status of EEHV and its subtypes circulating among the Asian elephant population in India.
What is Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)?
- Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is responsible for one of the most devastating viral infectious diseases in elephants worldwide, especially young Asian elephants.
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is classified in the family Herpesviridae.
- The mortality rate is very high (70-85%) and death occurs within a short period (2-4 days).
- In India, the incidence of EEHV-HD was first reported in 1997.
- 9 of 15 potential cases were confirmed from Southern India in wild free-ranging calves in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu forest reserves, and Madras Zoo.
- Transmission of the disease: EEHV is mostly spread through mucosal secretions which include:
- Saliva, Breast milk, Nasal secretions, Trunk to trunk contacts etc
- The disease can only affect elephants and is not infectious to humans or other animals.
- Symptoms: Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- Treatment: Treatment involves a combination of strategies such as antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy to counter haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C and E, as well as antipyretics and analgesics to manage fever.
- It's important to note that there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses in animals or humans since these viruses typically enter a latent state.
Scientists uncover seismic clues in Kopili Fault zone, advancing earthquake preparedness (PIB)
- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have detected seismogenic liquefaction characteristics within the dynamically active Kopili Fault (KF) zone.
About Kopili Fault Zone:
- The Kopili Fault extends from the western part of Manipur up to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It covers a distance of about 400 km and is closer to the Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- The Kopili fault bisects the Meghalaya Plateau and isolates the Mishmi block from the main part of the plateau.
- The Kopili fault is almost passing through the Kopili River.
- The river Kopili rises in the North Cachar Hills District in Borail Range at an altitude of 1525 meters.
- From a field study, it is observed that the Kopili Fault region is moving in the northeast direction at an average velocity of 28.397N mm/yr and 40.227E mm/yr.
- This region is characterized by heightened seismic activity, classified within the most critical Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- The geological dynamics are attributed to collisional tectonics, where the Indian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture, producing dextral strike-slip earthquakes in the lower crust.
- The Kopili fault zone, a tectonic depression filled by the alluvium of the Kopili River and its tributaries, has experienced numerous seismic events, notable among them being the 1869 earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1943 earthquake (magnitude 7.3).
Iyothee Thass Pandithar (The Hindu)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin on Friday unveiled a statue of late anti-caste activist Iyothee Thass Pandithar installed at the Gandhi Mandapam campus at Guindy in Chennai.
About Iyothee Thass Pandithar:
- Iyothee Thass Pandithar was an important anti-caste activist and practiced Siddha medicine.
- He was born on 20 May 1845 in Madras presidency.
- In the 1870s, Thass brought together the Todas and other tribes of the Nilgiri Hills for the freedom movement.
- In 1876, he started the Advaidananda Sabha and, with Rev. John Rathina, launched a magazine called Dravida Pandian.
- In 1891, he founded the "Dravida Mahajana Sabha'' with Rettamalai Srinivasan.
- Also, he established the Sakya Buddhist Society in Madras, which had branches all over South India.
- This society, also known as the Indian Buddhist Association, was formed in 1898.
- To organize and oversee the society's activities, he began a weekly magazine, Tamizhan, in 1907.
INS Trinkat (Indian Express)
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Navy has appointed the first woman commanding officer in a naval ship in line with the Navy’s philosophy of “all roles-all ranks” to deploying women in the service, Navy Chief Admiral R Hari Kumar said on Friday.
About INS Trinkat:
- INS Trinkat is a patrol vessel crafted by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers in Kolkata, West Bengal, and serves the Indian Navy.
- The role of the INS Trinkat is for anti-poaching operations, counter-insurgency operations, and Search and Rescue Operations in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands, and India's Exclusive Economic Zone.
- It is capable of detecting and destroying fast-moving surface craft.
- It can also carry out policing anti-smuggling and fisheries protection operations.
- These patrol vessels are aptly named after Trinkat Island, one of the 24 islands constituting the Nicobar Islands chain situated in the northeast Indian Ocean, between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
About Group Captain Shaliza Dhami:
- Group Captain Shaliza Dhami, is an esteemed officer in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- She holds the distinction of being the first woman officer in the IAF to secure a permanent commission and the pioneer woman to attain the role of a Flight Commander.
- Adding to her achievements, she became the first woman IAF officer selected for a front-line combat unit.
- Shaliza Dhami is an officer who is a qualified navigation instructor and has been involved in training observers inducted into the Navy.
- She is also learned to be the first woman officer who served as an observer in the Navy’s Tupolev Tu-142 maritime patrol aircraft.
- It's noteworthy that she is poised to make history once again by assuming command of a ship, marking a significant milestone in her career.
Sub-Neptune Planets (The Hindu)
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently astronomers have discovered an uncommon star system located just 100 light-years away from us, with six planets huddled immensely close to their host star.
What about sub-Neptunes?
- Sub-Neptunes are generally any planet that has a smaller radius than Neptune, although some could still be more massive.
- There are no sub-Neptunes in our solar system even though they are now known to be more common around other stars than Neptune-sized worlds.
- They might be rocky planets with thick atmospheres of hydrogen and helium gas, planets made of rock and ice bearing warm and water-rich atmospheres.
- These sub-Neptune planets were Initially detected in 2020 by NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and are about two to three times as big as Earth.
What are the findings?
- The newly discovered sub-Neptunes range from 1.9 to 2.9 times Earth's diameter.
- All appear to possess a large atmosphere.
- They and their star are located around 100 light-years from Earth.
- A light year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
- The system has six planets, all about the same size and they've barely changed since its formation up to 12 billion years ago.
- Their star, called HD110067, is visible in Earth's night sky in the northern constellation Coma Berenices.
- These undisturbed conditions make it ideal for learning how these worlds formed and whether they host life.
Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL) (The Hindu)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Bank of England (BoE) on Friday signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) concerning cooperation and exchange of information in relation to the Clearing Corporation of India Ltd (CCIL).
About Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL):
- The Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) was set up in April 2001 to provide guaranteed clearing and settlement functions for transactions in Money, G-Secs, Foreign Exchange, and Derivative markets.
- Objective: The prime objective has been to improve efficiency in the transaction settlement process, insulate the financial system from shocks emanating from operations-related issues, and undertake other related activities that would help to broaden and deepen the money, debt, and forex markets in the country.
- Promoters of CCIL: State Bank of India, IDBI Bank Ltd, ICICI Bank Ltd, Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), Bank of Baroda, and HDFC Bank Ltd.
- The company was incorporated with an authorised equity share capital of Rs. 50 crores.
- CCIL’s adherence to the stringent principles governing its operations as a Financial Market Infrastructure (FMI) has resulted in its recognition as a Qualified Central Counterparty (QCCP) by the Reserve Bank of India in 2014.
- CCIL is also the trade repository for all OTC transactions in the Forex, Interest Rate, and Credit derivative transactions.
- Through its fully owned subsidiary, Clearcorp Dealing Systems Limited (CDSL), CCIL has introduced various platforms for the electronic execution of deals in various market segments.
- Further, CDSL has developed, implemented, and manages the NDS-OM, the RBI-owned anonymous electronic trading system for dealing in G-Secs and also for reporting OTC deals, as well as the NDS-CALL platform, which facilitates electronic dealing in the Call, Notice & Term Money market.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Exercise Milan (The Hindu)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Navy To Conduct One Of Its Largest Naval Exercises — MILAN — Next February; More Than Fifty Countries Expected To Participate
About Exercise Milan:
- Exercise Milan is a biennial multilateral naval exercise that began in 1995, and has since significantly expanded in scope and scale to become the largest exercise held by India.
- Initially involving only Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, it has evolved significantly in terms of participants and exercise complexity.
- Aligned with India's 'Look East Policy' initially, Milan expanded under the 'Act East Policy' and Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative, welcoming Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs).
- The mid-planning conference for Milan-24 occurred in October.
- The last edition of Milan, which is held off Visakhapatnam, saw participation from over 40 countries showcasing its substantial growth in scale and international engagement.
- The next edition of Exercise MILAN is scheduled to be held in February 2024 and is expected to see the participation of over 50 countries.
- It reflects the significant expansion of the Navy’s engagements as well as its capacity to assist countries in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) as the first responder and Preferred Security Partner.
Sindhudurg Fort (Financial Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is gearing up to showcase its operational prowess in a significant ‘Operational Demonstration’ scheduled for December 4, 2023, at Sindhudurg Fort in Maharashtra.
About Sindhudurg Fort:
- Sindhudurg Fort is a historically significant stronghold situated on an islet in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in western India.
- Positioned on Kurte Island near Malvan town in Sindhudurg District within the Konkan region of Maharashtra, this formidable fortress was commissioned and constructed under the reign of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj of the Maratha Empire in 1664.
- The primary objective behind its construction was to counteract the escalating influence of foreign colonizers, including English, Dutch, French, and Portuguese merchants, and to curb the rise of the Siddis of Janjira.
- The Bakhar (a form of historical narrative written in Marathi prose) written by Chitragupta aptly mentions this fort as the most invaluable asset to Shivaji Maharaj.
Key Features:
- The fort spans 48 acres and boasts fortified walls that are 29 feet high and 12 feet thick, extending for a distance of two miles.
- Guarding these walls are 52 bastions equipped with embrasures for cannons.
- Access to the fort is through the Dilli Darwaja, the main gate, uniquely designed to blend seamlessly with the walls and visible only from close quarters.
- The fort is surrounded by several smaller forts, including Padmagad, Rajkot, and Sarjekot.
- An intriguing feature within the fort is a slab bearing the handprint and footprint of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Additionally, a small temple dedicated to the Maratha King is situated within the fort's bounds
Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Delhi High Court has criticized the forest department's proposal to hold a walkathon and cyclathon in a wildlife sanctuary, calling it a "haphazard exercise."
About Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary covers 32.71 sq. km on the Southern Delhi Ridge of the Aravalli hill range, bordering Delhi and Haryana.
- It's in Southern Delhi and parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts in Haryana.
- It's a part of the Sariska-Delhi Wildlife Corridor, linking Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan to Delhi Ridge.
- The sanctuary gets its name from the contiguous Asola village near Tughlaqabad in the Delhi NCR.
- Vegetation: The vegetation is classified as Northern Tropical Thorn Forests, known for thorny appendages and special leaves.
- The climate has extreme summer heat and significant winter cold due to its inland position.
- Flora: The main exotic plant is Prosopis juliflora, and the primary native plant is Diospyros montana.
- Fauna: The sanctuary is home to various animals like Golden Jackals, striped hyenas, Indian Crested Porcupines, Civets, Jungle Cats, Snakes, Monitor Lizards, and Mongoose.
- This sanctuary plays a crucial role in connecting wildlife across different areas.
World AIDS Day 2023 (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the World AIDS Day 2023, observed each year on December 1, the World Health Organisation emphasised recognising and remembering the contribution of communities in controlling HIV-AIDS.
About World AIDS Day 2023:
- World AIDS Day which is observed every year on December 1 is a global movement to unite people in the fight against HIV and AIDS.
- Since 1988, when the World Health Organisation (WHO) recognised the day, communities have stood together on World AIDS Day to show strength and solidarity against HIV stigma and to remember lives lost.
- It is an opportunity to reflect on the progress made to date and raise awareness about the challenges that remain to achieve the goals of ending AIDS by 2030.
- The theme of World AIDS Day 2023 is– “Let Communities Lead"
What is HIV/AIDS?
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, compromising the body's ability to fight off infections and diseases.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by severe immune system damage.
- Transmission: HIV spreads through unprotected sexual contact, sharing contaminated needles, and from an infected mother to her child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Treatment: Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) is the primary treatment for HIV/AIDS, managing the virus and supporting the immune system.
- Lifelong adherence is essential, ensuring viral suppression.
- Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is vital, and global challenges such as stigma and healthcare access persist in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant Safety) System (New Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
"In a first", through cutting-edge indigenous technology, the Indian Railways has successfully developed a system, preliminarily called as ‘Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant safety) system’ to prevent elephant–train collisions in the forest areas.
About Gajraj Suraksha:
- Gajraj Suraksha uses an AI-based algorithm and a network of sensitive optical fiber cables to detect elephants approaching railway tracks, aiming to address elephant fatalities resulting from train accidents.
- How this will work?
- The system functions by sensing pressure waves generated by elephant movements along the tracks.
- As elephants move, the optical fibers detect vibrations from their footsteps, triggering signals within the fiber network.
- This enables the system to identify elephants up to 200 meters ahead of their arrival on the track.
- The Optical Fibre Cable (OFC)-based Intrusion Detection System sends alarms to station masters upon detecting movement along the tracks.
- The network is designed to accurately track elephant movement, allowing prompt communication to nearby station masters.
- This ensures timely information to locomotive drivers, facilitating the slowing down or stopping of trains to prevent potential collisions with elephants.
- The Indian Railway plans to introduce this system in West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Kerala, certain parts of Chhattisgarh, and Tamil Nadu.
Digital Crop Survey System (Indian Express)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Emphasizing the current manual nature of crop area and production estimation, the Central Government has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to transition to a digital approach by implementing the Digital Crop Survey System starting in July next year.
About the Digital Crop Survey:
- As a part of the Digital Crop Survey initiative, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (MoA&FW) has instructed states to capture data on essential parameters, encompassing:
- Village name, year, season, farmer ID, farm ID,
- Crop name (at the farm plot level),
- Crop variety,
- Crop sown area (at the farm plot level),
- Geotags of crop photos,
- Geotags of the farm boundary where the crop is cultivated,
- Sowing/planting date (at the farm plot level),
- Irrigation type (at the farm plot level), and
- Irrigation source (at the farm plot level).
- This directive follows the introduction of a pilot Digital Crop Survey across multiple states earlier this year.
- In a parallel initiative, the MoA&FW has also revised the release timelines for crop estimates.
- Previously conducted in five phases, the ministry has streamlined the process by eliminating the fourth phase traditionally released in August.
- The ministry now plans to unveil comprehensive final estimates encompassing all states and seasons (kharif, rabi, summer) in September-October, departing from the earlier practice of releasing final estimates in February of the subsequent year.
Guidelines for the Digital Crop Survey:
- According to sources, the Economics, Statistics and Evaluation Division (ESED) under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW), has finalised the guidelines.
- According to the guidelines, all states/ UTs shall automate/digitise the process of area enumeration/girdawari of crops at field level, i.e., Digital Crop Survey, from 2024-25 Agricultural Year.
- In India, the agriculture year begins in July and ends in June, the following year.
- Under the guidelines, states and UTs shall use GPS-enabled mobile applications for collecting crop-sown data of each plot for each season and share the village-level aggregated data with DA&FW through API only.
Need for the Digital Crop Survey:
- The current methodology for gathering and consolidating crop statistics relies entirely on manual processes across most states, leading to delays and human errors in the data compilation.
- Only a handful of states, such as Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh, have embraced a digital approach to data collection through GPS-enabled mobile applications, particularly for the recording of crop area and Collection of Cost of Cultivation and Equipment Survey (CCEs) data directly from the fields.
- While Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh have implemented digital systems, they are primarily focused on recording crop areas.
- India faces a challenge due to the lack of dependable agricultural production estimates, accentuating the necessity for a "real-time assessment estimate" of crops.
- Recognizing this gap, there is a compelling need to modernize the current production estimation system by incorporating technological interventions.
Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) (The Hindu)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has recently requested the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) to provide access to "essential documents" related to the accusations of stock manipulation and accounting fraud against the Adani Group.
About the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP):
- The Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) is a nonprofit investigative reporting platform that collaborates with over 50 independent media outlets worldwide, producing over 100 investigations annually.
- Established in 2006, its mission is to conduct transnational investigative reporting and advocate for technology-based approaches to expose organized crime and corruption on a global scale.
- The organization strives to cultivate and empower a global network of investigative journalists, publishing their stories to shed light on crime and corruption, enabling the public to hold those in power accountable.
Vision:
- OCCRP envisions a world where lives, livelihoods, and democracy are not jeopardized by crime and corruption.
- The organization is committed to exposing malfeasance so that the public can actively hold institutions accountable.
Core Initiatives:
- Global Investigative Network: OCCRP facilitates a global network of investigative journalists, providing them with essential resources and tools.
- This includes digital and physical security measures, enabling journalists covering sensitive topics to collaborate effectively with trusted editors.
- An investigative data platform, OCCRP Aleph empowers journalists to search and cross-reference over three billion records, unveiling criminal connections and patterns.
- This platform facilitates efficient cross-border collaboration among journalists.
- Training and Skill Development: OCCRP offers training programs to reporters and partners, equipping them with advanced journalism techniques, and enhancing their investigative capabilities.
- Partnerships for Change: OCCRP collaborates with advocacy groups, arming civil society with information to advocate for justice and transformative change.
- The organization also uncovers evidence that empowers law enforcement to take meaningful action.
Kati Bihu (PIB)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister, Narendra Modi recently extended best wishes on the auspicious occasion of KatiBihu to the people of Assam.
About Kati Bihu:
- Kati Bihu is an annual celebration observed in the state of Assam, signifying the relocation of rice saplings.
- The term "Kati" translates to cutting, representing the agricultural activity during this period.
- Also known as Kongali Bihu, with "Kongali" connoting a state of poverty, the festival holds cultural significance in Assam alongside two other Bihu festivals—Bhogali or Magh Bihu in January and Rongali or Bohag Bihu in April.
Significance:
- In this month, food resources are scarce, prompting people to celebrate by illuminating their homes with earthen lamps or candles.
- Lighting lamps near the Tulsi plant are a central aspect of the festival, signifying devotion and auspiciousness.
- People light a special lamp known as "Akash Banti" (Sky candle) in their paddy fields. Fueled by mustard oil, these lamps are elevated on bamboo poles.
- The belief prevails that the illuminated lamps guide the spirits of ancestors toward their heavenly abode.
Bhimashankar Temple (HT)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Tensions escalated at the Bhimashankar temple recently as a dispute unfolded between two groups of religious leaders, referred to as pujaris, regarding the leadership of the puja ceremony, leading to a brawl.
Bhimashankar Temple Overview:
- The Bhimashankar Temple is an ancient Hindu shrine dedicated to Lord Shiva, located amidst the Sahyadri hills in the Pune District of Maharashtra.
- Recognized as one of the 12 holy Jyotirlinga shrines in India, it holds immense spiritual significance.
- In recent times, it has gained additional importance as it was designated a "Wildlife Sanctuary," forming part of the Western Ghats and serving as the source of the Bhima River.
Historical Significance:
- Constructed around the 13th century, the temple is a testament to the craftsmanship of Vishwakarma sculptors.
- Subsequent enhancements, including the addition of spires (shikhara) by Maratha Empire statesman Nana Phadnavis in the 18th century, contribute to its historical evolution.
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, the Maratha ruler, is believed to have played a role in fostering worship at the temple through his endowments.
Architectural Marvel:
- A blend of old and new structures in the Nagara style of architecture, the Bhimashankar Temple boasts spacious courtyards, intricate wall carvings, and imposing pillars.
- The sanctum, or Garbhgriha, houses the sacred Jyotirlinga, positioned at a lower level. The Swayambhoo, a self-emanated Shiv Linga, holds a central place in the Sanctum Sanctorum.
- Exquisite mythological carvings adorn the massive pillars and doorframes, depicting divine figures and sacred symbols.
- Additionally, the temple encompasses an ancient shrine dedicated to Lord Shani, considered auspicious by devotees, and features the revered Nandi statue at its entrance.
What are Jyotirlingas?
- Jyotirlingas are shrines where Lord Shiva is worshipped in the form of a Jyotirlingam, representing different manifestations of the deity.
- Among the 12 main Jyotirlingas in India, Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga is one.
- Each of these sacred shrines is named after its presiding deity and holds unique spiritual significance for devotees across the country:
- Somnath Jyotirlinga in Gir, Gujarat
- Mallikarjuna Jyotirlinga in Srisailam, Andhra Pradesh
- Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh
- Omkareshwar Jyotirlinga in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh
- Baidyanath Jyotirlinga in Deoghar, Jharkhand
- Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga in Maharashtra
- Ramanathaswamy Jyotirlinga in Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu
- Nageshwar Jyotirlinga in Dwarka, Gujarat
- Kashi Vishwanath Jyotirlinga in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
- Trimbakeshwar Jyotirlinga in Nasik, Maharashtra
- Kedarnath Jyotirlinga in Rudraprayag, Uttarakhand
- Ghrishneshwar Jyotirlinga in Aurangabad, Maharashtra
Siena Galaxy Atlas (SGA) (Space)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Astronomers have recently crafted a stunning atlas comprising 400,000 galaxies situated in the cosmic vicinity of the Milky Way, aptly named the Siena Galaxy Atlas.
About the Siena Galaxy Atlas:
- It is a digital atlas designed to help learn more about our universe by highlighting a number of well-known galaxies.
- It was produced using information gathered from three astronomical surveys conducted at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) between 2014 and 2017. These surveys collectively are referred to as the DESI Legacy Surveys.
Distinguishing Features:
- Setting itself apart from previous atlases, the Siena Galaxy Atlas relies on state-of-the-art digital images captured by advanced technology.
- Unlike its predecessors, which utilized outdated equipment and photographic plates, this atlas leverages highly sensitive instruments to produce the most precise and accurate data available.
- Notably, it marks the first cosmic atlas to showcase the light profiles of galaxies—a curve illustrating the variation in brightness from the galaxy's brightest point to its dimmest.
Significance:
- The introduction of the Siena Galaxy Atlas carries immense importance in astronomical exploration for several reasons:
- By relying on digital images captured with advanced instruments, the atlas ensures a level of precision and detail that surpasses previous methods, enhancing the overall quality of data.
- Light Profiles of Galaxies: A pioneering feature, the inclusion of light profiles in the atlas provides a unique perspective, allowing astronomers to glean valuable insights into the structure and characteristics of galaxies.
- Pattern Recognition: Cosmic atlases, such as the Siena Galaxy Atlas, play a pivotal role in aiding astronomers in identifying patterns.
- This capability is particularly valuable in categorizing phenomena like transient events, such as stars that exhibit sudden flares and then disappear.
- The atlas facilitates the identification of celestial objects worthy of more detailed follow-up studies, enabling astronomers to delve deeper into specific areas of interest.
- From unravelling the mysteries surrounding the birth and evolution of galaxies to investigating the distribution of dark matter and the propagation of gravitational waves through space, the Siena Galaxy Atlas serves as a versatile tool for astronomers in their cosmic pursuits.
AERA Warns Indian Airport Operators Against Charging Unapproved Tariffs (TOI)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Airport Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA) issued a warning to major airports about levying aeronautical charges without approval.
About Airports Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA):
- Airports Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA), established under the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008, is a statutory body entrusted with the crucial task of regulating tariffs and associated charges for aeronautical services at major airports.
- This includes overseeing air traffic management, aircraft landing and parking, and ground handling services.
- The designation of an airport as "major" hinges on the 2008 Act, considering an annual passenger traffic threshold of at least 15 lakh.
- An amendment in 2019 elevated this criterion to 35 lakh annual passengers.
- For other airports, tariff determination falls under the purview of the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- As an independent economic regulator, AERA operates with the objective of creating an equitable playing field, fostering healthy competition among major airports, promoting investment in airport facilities, and ensuring transparent regulation of aeronautical service tariffs.
- This initiative arose from the recognition of the need for an independent regulatory body capable of safeguarding the interests of both service providers and consumers.
- Headquartered in Delhi, AERA's history traces back to a time when most Indian airports were under the governance of the central government.
- The shift towards private sector participation in airport infrastructure development prompted the need for a distinct regulator.
- The Naresh Chandra Committee set up in 1997, recommended the establishment of an independent regulatory authority.
- Subsequently, the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008 (AERA Act), was enacted, leading to the creation of AERA.
About Airports Authority of India (AAI):
- Airports Authority of India (AAI), established through an Act of Parliament on April 1, 1995, resulted from the merger of the National Airports Authority and the International Airports Authority of India.
- Entrusted with a significant role, AAI is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining, and managing civil aviation infrastructure both on the ground and in the airspace of the country.
- Main Functions of AAI Include
- Construction, modification, and management of passenger terminals.
- Development and management of cargo terminals.
- Development and maintenance of apron infrastructure, encompassing runways, parallel taxiways, aprons, etc.
- Provision of Communication, Navigation, and Surveillance, involving DVOR / DME, ILS, ATC radars, visual aids, etc.
- Provision of air traffic services.
- Provision of passenger facilities and related amenities at its terminals.
Bihar’s Only Ramsar Site 'Kanwar Lake' Drying Up (DownToEarth)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Bihar’s only wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention lies neglected and is on the brink of drying up, even as the state is pitching other waterbodies for classification.
About Kanwar Lake:
- Kanwar Taal, known as Kabar Taal or Kabartal Wetland, is an oxbow lake in Begusarai district, Bihar, India.
- It is the largest freshwater oxbow lake in Asia, covering an area of 67.5 km².
- The lake was established as a bird sanctuary in 1987 and is now a designated Ramsar site since 2020.
- Covering the majority of the Indo-Gangetic plains in northern Bihar, this lake was declared a Ramsar site in 2020, making it the first wetland in Bihar to be included in the Ramsar convention.
- Kanwar Taal is a significant wetland in Bihar and is an essential stopover for migratory waterbirds along the Central Asian Flyway.
- The lake provides vital flood absorption during the monsoon season and supports agriculture during the dry season.
- It also houses five critically endangered species and over 50 fish species.
- Biodiversity: Kanwar Taal is rich in biodiversity.
- It is home to a wide range of plant and animal species.
- It supports 165 plant species and 394 animal species, including 221 species of birds.
- These bird species include both resident and migratory birds, with the lake serving as an important stopover point for migratory waterbirds travelling along the Central Asian Flyway.
- Flood Absorption: The wetland plays a crucial role in flood absorption during the monsoon season.
- It helps in reducing the impact of floods in the region by absorbing excess water, which is important for flood control and the protection of nearby areas.
- Agricultural Support: During the dry season, Kanwar Taal supports agriculture in the surrounding areas.
- The water from the lake is used for irrigation, benefiting local farmers and contributing to the region's agricultural productivity.
- Endangered Species: The wetland is home to five critically endangered species, highlighting its significance in conserving rare and threatened wildlife.
- Additionally, it hosts over 50 fish species, contributing to the aquatic biodiversity of the region.
What are Oxbow Lakes?
- Oxbow lakes are crescent-like water bodies formed due to erosion and deposition in meanders of rivers.
- Meanders are loops or curved structures formed in the course of a river due to friction or tectonic activity.
- The speed of water flow in the outer section of this meander is more than the inner part causing its neck to become narrower over time.
- Eventually, the size of this loop increases making it harder for the river to flow through it so it opts for a straight path.
- Finally, the ends of this meandered loop are separated by deposition of sediments or silt separating the river and a horseshoe-like structure called oxbow lake.
Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” Portal Launched (PIB)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Development of the North-East Region virtually launched the “MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” portal at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi recently.
About Poorvottar Sampark Setu Portal:
- The Poorvottar Sampark Setu portal is a robust tool designed to streamline and improve the monitoring of Union Ministers' fortnightly visits to the North Eastern Region (NER)
Key features include:
- Insightful Dashboard: The portal offers a comprehensive dashboard presenting valuable insights and graphical information on state-wise/district-wise visits to NER by Union Ministers, serving as a centralized resource for stakeholders.
- Curated Minister List: It generates a curated list of Ministers eligible for nomination for visits to NER in the upcoming months, facilitating efficient planning.
- Online Tour Reporting: After their visit, Ministers can conveniently submit tour reports and recommendations online, streamlining the reporting process.
- Recommendation Analysis: MDoNER (Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region) can analyze and forward the received recommendations to respective line Ministries, Departments, and State Governments for prompt action.
- Summary Report Generation: The portal offers a one-click summary report generation feature, simplifying the overview of visits for effective decision-making.
What is the MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard?
- The MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard is a comprehensive platform integrating data from 112 schemes across 55 Departments and Ministries.
Its key benefits include:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Empowers stakeholders with data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations, ensuring a seamless and efficient workflow.
- Centralized Monitoring: Provides a centralized hub for monitoring diverse schemes and initiatives.
- Policy-Level Decision Tool: Functions as a valuable tool for crafting policies based on robust data analysis.
- Information Integration: Integrates information seamlessly, fostering coherence and accessibility.
- Focused Monitoring: Keeps a vigilant eye on NER Aspirational districts, North East border districts, and the most backward districts in NER for targeted interventions.
Modi’s Visit to Gunji Irks Nepal Opposition (Indian Express)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Gunji near Kalapani, Uttarakhand has triggered an uproar in Nepal.
About Gunji Village:
- Gunji Village, situated in the Dharchula tehsil of Pithoragarh district in northern Uttarakhand, holds a strategic location near the borders of Tibet and Nepal.
- Nestled at an altitude of 3500 meters, it marks the confluence of the Kuthi Yankti and Kalapani Rivers at the eastern end of the Kuthi Valley, offering stunning views of Mount Api in Nepal.
- Covering a geographical area of 188.9 hectares, Gunji is a seasonal abode for its inhabitants.
- During winters, the residents, totalling 335 people in 194 households as per the 2011 census, migrate to lower altitudes, primarily to Dharchula within the same district.
- The village is under the administration of a Sarpanch, the elected head.
- Renowned for its connection to the traditional Indian/Nepalese route to Kailas–Manasarovar, Gunji attracts visitors seeking its breathtaking vistas.
- To embark on a journey to Gunji, obtaining an Inner Line permit is a prerequisite.
What is an Inner line permit (ILP)?
- An Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document issued by the Government of India, facilitating the inward travel of Indian citizens into a protected area for a limited duration.
- It is mandatory for Indian citizens residing outside these specific states to secure a permit before entering the designated state.
- This document serves as a regulatory measure by the government to manage and monitor the movement of individuals into areas located in proximity to India's international borders.
- The concept originates from the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulations of 1873, designed to safeguard the Crown's interests in trades such as tea, oil, and elephants by restricting the entry of "British subjects" into these designated "Protected Areas.
- In 1950, the term "British subjects" was replaced by "Citizen of India."
- ILPs come in various types, including those for tourists and others intended for individuals planning extended stays, often for employment purposes.
CSIR-CCMB Study to Understand the Genetics Behind Diseases (The Hindu)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The project — “Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP)” — aims to uncover the effects of genomic and environmental diversity on disease risk observed in people across the world, including those in Asia, Africa and North and South America.
About the Project, The Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP):
- The Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP) is a pioneering genomics and epigenomics initiative aimed at unravelling the genetic underpinnings of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) in diverse populations, including South Asians.
- This five-year international project seeks to illuminate the impact of genomic and environmental diversity on disease risk across global populations, spanning Asia, Africa, and North and South America.
- Researchers will examine individuals from varied genetic and environmental backgrounds, analyzing DNA methylation patterns to discern their contributions to disease risk within each context.
- The study involves the development of software, infrastructure, and advanced statistical analyses to create new resources, integrated with existing international health and genetics databases for assessing trends in DNA methylation variation.
- This initiative holds significance as it aims to identify common and region-specific disease-causing mechanisms, addressing questions about the universal effectiveness of medicines and paving the way for targeted interventions to reduce global health disparities.
What is DNA methylation?
- DNA methylation is a molecular process involving the attachment of chemical groups to DNA, influencing the activation and deactivation of genes.
- This epigenetic modification plays a crucial role in enabling the body to respond to environmental signals, thereby contributing to overall systemic health and disease status.
- The intricate interplay between DNA methylation, genetics, and the environment is essential for unravelling the pathways that underlie health and disease, providing insights into their interconnected consequences.
DGCA Implements New Rules for Hang Gliders (Business Standard)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Aviation regulator DGCA has issued amended norms for operating powered hang gliders in the country.
About Hang Gliders:
- A hang glider is a distinctive type of aircraft that relies on air currents to remain airborne, setting it apart from conventional aircraft with engines and propellers.
- These aerodynamic marvels depend on wind dynamics for lift rather than propulsion.
- Operational Mechanics: Due to their unpowered nature, hang gliders necessitate launching from elevated points such as hills or mountains.
- Gravity, acting as the primary force, encompasses the weight of both the pilot and the wing.
- This weight generates thrust, propelling the aerofoil through the air.
- The aerofoil's distinctive shape prevents the hang glider from descending rapidly and facilitates lift.
- The aerofoil's design manipulates airflow, compelling the air above the wing to move faster, creating a low-pressure area.
- Simultaneously, the wing's downward and forward motion compresses the air beneath, fostering lift as the aerofoil is drawn into the low-pressure zone.
- Pilots maintain control during flight by manipulating the trapeze and adjusting direction and speed.
- Powered Hang Gliders: In a departure from traditional hang gliders, powered hang gliders integrate features of both hang gliders and powered aircraft.
- Equipped with a small engine, these variants enable pilots to take off and sustain flight without relying on natural elements like thermals or wind conditions, making them accessible to less-experienced aviators.
DGCA Regulations for Powered Hang Gliders:
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) mandates strict regulations governing powered hang gliders:
- Operation Authorization: Individuals must obtain prior authorization from a DGCA-approved examiner or instructor before operating a powered hang glider.
- Examiner Qualifications: Approved examiners must possess a minimum of 50 hours of experience on powered hang gliders, including at least 10 hours on a dual machine.
- Test Flight Criteria: Individuals conducting test flights must meet specific criteria, holding a valid Commercial Pilot Licence (CPL) with at least 25 hours of flying experience on a powered hang glider or authorization with 50 hours of flying experience.
- Transaction Certification: The sale or transfer of a powered hang glider requires a DGCA-issued certificate following a background check conducted by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Lease and Operation Restrictions: Owners or operators are prohibited from leasing, renting, or lending powered hang gliders.
- The use of certain equipment and devices is strictly regulated, with explicit permissions required.
- Safety Protocols: Security measures endorsed by the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) are obligatory at parking and operational locations, ensuring compliance with established guidelines for safe flight operations.
Is Halley’s Comet returning? (India Today)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The celestial calendar for 2023 is set to offer a spectacular show as the Orionid meteor shower is expected to rain down its greatest number of meteors on the mornings of October 21 and 22.
About the Orionid Meteor Shower:
- An annual celestial spectacle illuminating the night sky every October, the Orionid meteor shower is a captivating phenomenon with a fascinating origin.
- This cosmic event transpires as Earth traverses the remnants of debris left by Halley's Comet, officially designated as 1P/Halley.
- Halley's Comet, on a roughly 76-year orbit around the sun, sheds dust particles from its nucleus during each passage through the inner solar system.
- This process creates a distinctive trail of debris along its path.
- In late October each year, Earth intersects this celestial trail, giving rise to the mesmerizing display known as the Orionid meteor shower.
- Measuring about five by nine miles in size, Halley's Comet undergoes a remarkable transformation, losing between three to ten feet of material with each journey through the inner solar system.
- The resulting debris becomes the source of the Orionid meteors.
- This celestial event offers a visual treat for observers in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres, particularly during the post-midnight hours.
- It provides an opportunity to witness the graceful streaks of light as the meteors traverse the night sky.
What are Meteors?
- Meteors, often referred to as "shooting stars," are a captivating manifestation of meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at high speed and subsequently burning up.
- Meteor showers, occurring annually or at regular intervals, are linked to the Earth passing through the dusty debris trail left behind by a comet.
- In the case of the Orionid meteor shower, the meteors are named after the constellation Orion, close to where these luminous streaks appear in the sky.
- This annual celestial event not only captivates observers with its dazzling display but also serves as a reminder of the dynamic interactions between Earth and the celestial bodies that grace our cosmic neighbourhood.
Microalgae are Adapting to Warming Climate (DownToEarth)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study finds microalgae are firing up a light-responsive protein to use sunlight for growth.
What is the Microalgae?
- Microalgae are microscopic algae prevalent in freshwater and marine environments, consisting of unicellular species that can exist independently or in chains and groups.
- Comprising unicellular algal varieties such as green algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates, these organisms exhibit sizes ranging from a few micrometres to several hundred micrometres.
- Their colour, determined by predominant pigments, categorizes them into groups like green, red, or brown.
- Unlike higher plants, microalgae lack roots, stems, or leaves, and they predominantly engage in photosynthesis, fueled by photosynthetic pigments.
- Heterotrophic microalgae, lacking these pigments, rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Significance:
- Microalgae play a foundational role in the aquatic food chain, offering vital nutrients for zooplankton, small fish, and various aquatic organisms.
- They serve as a primary food source for filter-feeding organisms.
- Moreover, photosynthetic microalgae contribute significantly to global carbon and oxygen cycles, absorbing carbon dioxide and generating oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Approximately half of atmospheric oxygen is produced by these organisms.
- Microalgae can also establish symbiotic relationships, as seen in their association with corals (zooxanthellae), providing nutrients through photosynthesis.
- Certain microalgae, like Nostoc, Anabaena, and Oscillatoria, exhibit nitrogen-fixing capabilities.
- Additionally, microalgae are rich in nutrients and can be consumed by humans. Notable examples like Spirulina and Chlorella are often utilized as dietary supplements.
What are Macroalgae?
- Macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds, are marine plants engaging in photosynthesis but reproducing without flowers.
- Visible to the naked eye, in contrast to microalgae, they typically grow attached to the seabed or reef substrate.
- These macroscopic algae play crucial roles in reef ecosystems, providing both food and habitat for a diverse array of species while contributing significantly to nutrient dynamics.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
RISC-V Technology (The Hindu)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Chip designer Qualcomm said on Tuesday it is partnering with Alphabet's Google to make wearable devices like smartwatches using chips based on RISC-V technology.
What is RISC-V Technology?
- RISC-V technology, colloquially pronounced as "risk five," stands as a pioneering open-source initiative in computer architecture.
- Functioning as an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), it serves as the foundation for crafting customized processors tailored to various end applications.
- Positioned as the fifth generation of processors rooted in the Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) philosophy, RISC-V originated as a project at UC Berkeley.
- Initially conceived for academic purposes, it has since matured into a robust standard now overseen by RISC-V International.
- RISC-V operates as an open-standard architecture, with its definition shaped collaboratively by member companies associated with RISC-V International—a global nonprofit organization steering the ISA.
- This collaborative approach fosters innovation and design freedom among member companies, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in processor technology.
- At its core, RISC-V features a concise set of instructions upon which all software designs run.
- This streamlined architecture empowers designers to tailor and construct processors in alignment with the specific requirements of their intended applications.
Key Advantages:
- The merits of RISC-V extend beyond its technical specifications. Its open-standard nature facilitates industry-wide collaboration and innovation, enabling diverse stakeholders to contribute to the evolution of processor technology.
- Moreover, the entire RISC-V architecture is subject to scrutiny in the public domain, mitigating concerns related to back doors and concealed channels.
Applications:
- RISC-V finds application across a broad spectrum of industries, including wearables, industrial processes, Internet of Things (IoT), home appliances, smartphones, automotive systems, high-performance computing (HPC), and data centres.
- Its versatility makes it a compelling choice for diverse technological landscapes, showcasing its adaptability and efficacy across various domains.
Life through geometry in Warli (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Warli Whisperers, an exhibition by the Inherited Arts Forum, traces the artistic journey of the celebrated Mashe family from Maharashtra.
About the Warli Art:
- Origin: Warli art is a tribal form originating from the North Sahyadri region of Maharashtra, with roots dating back to the 10th century AD.
- However, it gained recognition for its unique style in the early 1970s.
- Practitioners: Traditionally, Warli art was practiced by Suvasinis, the women of the Warli tribe, who adorned the Lagn Chowk or wedding square with their artistic expressions.
- Characteristics: Warli artists draw inspiration from nature, depicting scenes of farming, food gathering, village life, and elements from the natural world.
- These paintings are mainly dominated by basic geometric shapes like circles, triangles and squares.
- These geometric shapes stand as a symbol of natural elements in our environment.
- For example, the circles represent the sun and moon, the triangles represent the mountains and the squares are considered as the central motifs of the painting.
- Techniques and Materials: The paintings showcase triangles, circles, and lines in stark white against a mud brown background, narrating stories of village life, customs, and traditions.
- Modified bamboo sticks serve as paintbrushes, and the colours are derived from nature, such as brown and orange from henna, indigo from dye, red from bricks, and white from thick rice paste.
- Warli art serves as a vibrant portrayal of the everyday and social occurrences within the Warli tribe of Maharashtra, serving as a means to adorn the walls of village houses.
- Concerns: It was not recognised as an art form even though it was in practice for centuries.
Warli Tribe
- The Warli tribe, categorized as indigenous Adivasis, inhabit both the mountainous and coastal regions near the Maharashtra-Gujarat border.
- Their communication is conducted through an unwritten Varli language, classified within the southern zone of Indo-Aryan languages.
SC Collegium recommends names for Chief Justices of five High Courts (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court Collegium headed by Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud has recommended the appointment of Chief Justices to five High Courts.
What is the Collegium System?
- It is a system under which appointments and transfers of judges are done in the Supreme Court and High Courts.
- It is not rooted in the Constitution, iInstead, it has evolved through judgments of the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme Court Collegium, headed by the Chief Justice of India, consists of the court's four other most senior judges.
- Similarly, the High Court Collegium is chaired by its Chief Justice, along with the four other most senior judges of that specific high court.
Appointment of Judges: Constitutional Framework
- Constitutional Provision: Under Article 217, the President holds the authority to appoint judges of a high court.
- The appointment of the Chief Justice involves consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the respective state's governor.
- Similarly, consultation with the Chief Justice of the concerned high court is essential for appointing other judges.
- In cases where a high court serves multiple states, the President consults with the governors of all relevant states.
- No Minimum Age Requirement: The Constitution does not specify a minimum age for the appointment of high court judges.
- Qualifications of Judges: To qualify for a high court judge, an individual must:
- Be a citizen of India.
- Have held a judicial office within India's territory for ten years; or
- Have been an advocate of a high court (or successive high courts) for ten years.
Supreme Court Judgements:
- Second Judges Case (1993): The Supreme Court decreed that the appointment of a high court judge must align with the Chief Justice of India's opinion.
- Third Judges Case (1998): The Supreme Court emphasized that for the appointment of high court judges, the Chief Justice of India should consult a collegium comprising the two most senior judges of the Supreme Court.
- The consultation process involves more than the Chief Justice of India's individual opinion.
Is Pegasus spyware targeting journalists in India? (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amnesty International and Washington Post recently announced that it has found the presence of Pegasus spyware, sold only to governments, on two Indian journalists’ phones.
What is Pegasus Spyware, and How Does it Infiltrate Devices?
- Pegasus is a sophisticated form of malware, covertly designed to gather information without the user's knowledge.
- Developer: Developed by the Israeli security firm NSO Group.
- Objectives: Pegasus serves three primary purposes:
- Collecting historical data on a device discreetly.
- Continuously monitoring user activities and gathering personal information.
- Transmitting the collected data to third parties.
Infiltration Mechanisms:
- Pegasus utilizes "zero-click exploits," exploiting vulnerabilities in popular apps like iMessage and WhatsApp.
- Notably, zero-click exploits require no user interaction, differentiating them from typical cyberattacks.
- Network injection attacks are another method employed by Pegasus, where unsecured websites are used to infiltrate devices within milliseconds of the user's visit.
What is a Zero-click exploit?
- A zero-click exploit involves the installation of malicious software on a device without the device owner's consent.
- Notably, it does not require any action from the device owner to initiate or complete the installation.
Specific Exploit in the Recent Case with Indian Journalists:
- The particular exploit reportedly used in the incidents is known as BLASTPAST (previously identified as BLASTPASS), unfolding in two phases.
- Initial Phase: The attack aims to establish a connection with Apple HomeKit, a platform enabling users to control various smart devices on their network.
- The primary objective of this phase might be to assess how the device could be vulnerable to exploitation or to maintain visibility for potential future attacks.
- Second Phase: Malicious content is sent through the iMessage app to the target device.
- This stage is pivotal as it delivers the complete spyware payload, enabling extensive surveillance and data collection.
Mines Ministry unveils draft rules for offshore minerals auction (The Hindu Business Line)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s Mines Ministry has proposed a new set of rules for the auction of offshore mineral blocks. It is also in the process of identifying such mineral blocks, including those in exclusive economic zones beyond territorial waters.
Context:
- To implement the amended Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act), the ministry has unveiled two draft rules:
- Offshore Areas Mineral Auction Rules: These rules delineate provisions governing the auctioning of production leases.
- Offshore Areas Existence of Mineral Resources Rules: These rules set forth norms for the exploration of minerals and deposits in offshore areas.
Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act):
- The OAMDR Act governs the development and regulation of mineral resources in India's territorial waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zones, and other maritime zones.
About Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
- The Bill proposes amendments to the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, governing mining activities in India's maritime zones.
Key highlights include:
- Empowering the government to reserve offshore areas without operating rights.
- Granting the administering authority the discretion to issue composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Eliminating the provision for renewing production leases and setting a fixed fifty-year period, aligning with the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Mandating the grant of production leases to the private sector through competitive bidding.
- Allowing non-competitive bidding for operating rights in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government for government entities or corporations.
- Restricting the grant of exploration licenses or production leases for atomic minerals to government or government corporations.
- Introducing a four-year timeline for the commencement of production and dispatch after executing a composite license or production lease, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement after discontinuation.
- Authorizing the central government to establish rules for mineral conservation, systematic development, and environmental protection in offshore areas, preventing or controlling pollution from exploration or production operations.
India's Maritime Zone Mineral Resources:
- India's maritime zone hosts diverse mineral resources, including lime mud off the Gujarat and Maharashtra coasts within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Additionally, the region boasts construction-grade sand along the Kerala coast and heavy mineral placers in the inner-shelf and mid-shelf regions off Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra.
- Phosphorite is found in the Eastern and Western continental margins, while the Andaman Sea and Lakshadweep Sea house Polymetallic Ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) nodules and crusts.
Govt issues PMLA notice to Binance, 8 other offshore crypto firms, asks IT Min to block URLs (Indian Express)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's Financial Intelligence Unit has issued show cause notices to nine offshore crypto-currency operators, including Binance, for not complying with the anti-money laundering PML Act.
About the Financial Intelligence Unit India:
- Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND) was set by the Government of India in November 2004 as the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions.
- FIU-IND is also responsible for coordinating and strengthening efforts of national and international intelligence, investigation and enforcement agencies in pursuing the global efforts against money laundering and financing of terrorism.
- It is an independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC) headed by the Finance Minister.
Key Functions of FIU-IND:
- Information Collection: Act as the central hub for receiving various reports, including Cash Transaction Reports (CTRs), Non-Profit Organisation Transaction Reports (NTRs), Cross Border Wire Transfer Reports (CBWTRs), Reports on the Purchase or Sale of Immovable Property (IPRs), and Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) from diverse reporting entities.
- Information Analysis: Analyze the received information to unveil transaction patterns indicative of potential money laundering and associated criminal activities.
- Information Sharing: Collaborate by sharing intelligence with national intelligence/law enforcement agencies, national regulatory authorities, and foreign Financial Intelligence Units, fostering a collective effort against financial crimes.
- Central Repository: Establish and maintain a national database by consolidating reports received from reporting entities.
- Coordination: Strengthen the collection and sharing of financial intelligence through efficient national, regional, and global networks to combat money laundering and related crimes.
- Research and Analysis: Conduct ongoing monitoring and identification of strategic areas related to money laundering trends, typologies, and developments.
What are Virtual Digital Assets?
- As per the Income Tax Act, a 'virtual digital asset' is described as any information, code, number, or token (excluding Indian currency or foreign currency) generated through cryptographic means and blockchain technologies.
- These assets can be electronically transferred, stored, or traded.
- The definition explicitly covers non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or tokens of a similar nature, regardless of nomenclature.
Forest Department Relies on Muthuvan Tribe's Indigenous Knowledge for Nilgiri Tahr Conservation (The Hindu)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Members of the Muthuvan tribe of the Anamalai hills, who are known for coexisting with the wildlife with their traditional knowledge, have joined hands with the Tamil Nadu Forest Department for a unique task.
About the Muthuvan Tribe:
- Inhabiting the border hill forests of Kerala and Tamil Nadu, the Muthuvan tribe is distributed across this region.
- The tribe communicates in distinct dialects, identifying themselves as Malayalam Muthuvan and Pandi Muthuvan.
- Cultural Beliefs: Embracing animism and spirit worship, the Muthuvan tribe venerates forest gods and attributes the spirits of their ancestors as the initial settlers in the hill forests.
- Renowned for their harmonious coexistence with wildlife, the Muthuvan people leverage traditional knowledge to navigate their relationship with the natural environment.
- Unique Governance System - 'Kani System': Operating under the 'Kani System,' each village is overseen by a 'Kani' responsible for village administration, reflecting their distinctive form of governance.
- Traditional Medicine Expertise: Proficient in traditional medicines, the Muthuvan tribe safeguards their effective remedies, preserving and passing down this knowledge across generations.
- Occupation: Agriculture serves as the primary occupation for Muthuvan tribes, yielding various products such as ragi, cardamom, and lemongrass.
About Project Tahr:
- Project Tahr aims to enhance comprehension of the Nilgiri Tahr population through surveys and radio telemetry studies.
- The initiative focuses on reintroducing Tahrs to their historical habitat, fostering their return to natural landscapes.
- Addressing immediate threats, the project employs strategic measures to mitigate challenges facing the Nilgiri Tahr.
- A key component involves intensifying public awareness efforts to garner support and understanding for the conservation of this species.
- Project Tahr is slated for a comprehensive 5-year implementation, spanning from 2022 to 2027.
INS Sumedha Visits Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (PIB)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Naval Ship INS Sumedha recently made a port visit at Lagos, Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (GoG).
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is the third vessel among the indigenously crafted Saryu-class Naval Offshore Patrol Vessels (NOPV).
- Constructed and designed domestically, Goa Shipyard Limited played a pivotal role in the indigenous creation of INS Sumedha.
- The vessel officially joined the Indian Navy's fleet on March 7, 2014.
- Operational Base: A key asset of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet, INS Sumedha operates from its base in Visakhapatnam.
- Primary Functions: The vessel is tasked with a diverse range of functions, including EEZ surveillance, anti-piracy patrols, fleet support operations, maritime security provision to offshore assets, and execution of escort operations for high-value assets.
- Features:
- With a displacement of 2,230 tonnes, INS Sumedha boasts dimensions of 105 meters in length and 12.9 meters in beam.
- Equipped with a cutting-edge weapon and sensor package, the vessel ensures enhanced operational capabilities.
- Designed to carry an Advanced Light Combat Helicopter onboard, adding to its versatility in maritime operations.
- Powered by two of the largest diesel engines deployed in the Indian Navy, INS Sumedha attains a top speed of 25 knots.
- Featuring a remarkable range of 6,000 nautical miles (11,000 km) at 16 knots (30 km/h), the offshore patrol vessel is well-suited for prolonged missions and operations.
About the Gulf of Guinea:
- Location: Situated as the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Guinea is positioned off the western coast of the African continent.
- The Gulf lies at the confluence of the Prime Meridian and the Equator, specifically at 0°0’N and 0°0'E.
- Extent and Coastline: Encompassing an area of 2.3 million square kilometres, the Gulf features an extensive coastline stretching approximately 6,000 kilometres.
- Characterized by a narrow continental shelf, it boasts a distinctive coastal landscape.
- Oceanic Conditions: The Gulf of Guinea experiences warm tropical waters characterized by relatively low salinity, influenced by the inflow of rivers and high regional rainfall.
- Notable tributaries include the Volta and Niger rivers.
- Coastal Countries: 16 countries border the Gulf of Guinea, including Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Republic of Congo, Guinea, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Gabon, Nigeria, Ghana, São Tomé and Principe, Togo, and Sierra Leone.
- Topography: The coastal region is predominantly low-lying, featuring mangrove swamps, marshes, and lagoons.
- Geological Significance: The Gulf's coastline bears a striking resemblance to the continental margin of South America, affirming the theory of continental drift.
- Holding over 35% of the world’s petroleum reserves, the Gulf of Guinea is a significant global repository of petroleum.
- Security Challenges: Regrettably, the Gulf of Guinea has gained notoriety as one of the world’s most perilous gulfs due to widespread piracy, significantly impacting West African countries and attracting international concern.
BCCC Cautions Entertainment Channels on Depicting SCs, STs. (Business Standard)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Broadcasting Content Complaint Council (BCCC) on Tuesday asked entertainment channels to exercise "extreme caution" while portraying the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes in television programmes to avoid hurting the sentiments of the members of the two communities.
About the Broadcasting Content Complaints Council (BCCC):
- The Indian Broadcasting and Digital Foundation (IBDF) established the BCCC in June 2011 as an independent self-regulatory body.
- Regulatory Role: The primary function of the BCCC is to enforce self-regulatory guidelines for non-news channels, covering general entertainment, kids, and special interest channels.
- Formulation of Guidelines: Guidelines address crucial areas, including national interest, racial and religious harmony, treatment of children, social values, explicit content (sex and nudity), violence, crime, gambling, drugs, smoking, tobacco, alcohol, defamation, harm, and offence.
- Complaint Lodging Process: Any viewer can file a complaint regarding television programs, non-news channels, and digital content of IBDF India members.
- Composition of BCCC:
- The council comprises 13 members, including a chairperson, four non-broadcast members, four representatives from national-level statutory commissions, and four members from the broadcast industry.
- Functioning Mechanism: Upon receiving a valid complaint, the concerned channel is required to present its viewpoint on the contested content within one working week.
- If the BCCC committee finds the channel's response unsatisfactory, it holds the authority to issue directives, mandating modifications or withdrawal of the content.
- Reporting to Authorities: In case of non-compliance with directives, the BCCC promptly submits a detailed report to the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting within 24 hours.
Key Details about the Indian Broadcasting & Digital Foundation (IBDF):
- Founded in 1999, the Indian Broadcasting Foundation initially served as the apex body for broadcasters.
- Recently rebranded as the Indian Broadcasting and Digital Foundation (IBDF) to encompass digital platforms, consolidating oversight over all digital over-the-top streaming firms.
- Representative Role: Recognized as the official spokesperson for the Indian broadcasting industry, IBDF plays a crucial role in articulating industry perspectives.
- IBDF's membership includes a diverse range of channels, covering both news and non-news categories such as General Entertainment Channels (GEC), sports, music, movies, and infotainment.
- Actively involved in providing research-based legislative inputs to the government, IBDF engages in advocacy efforts on various fronts, including fiscal, regulatory, and business issues.
- The organization plays a pivotal role in facilitating the formulation of favourable policies, addressing industry challenges, and advocating for essential changes in the overall system.
New Plant Species Curcuma kakchingense Discovered in Manipur (HT)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
In a remarkable botanical discovery, a team of researchers from the Department of Life Sciences at Manipur University and Kwaklei and Khonggunmelei Orchids Pvt. Ltd. has unveiled a hitherto unknown plant species named "Curcuma kakchingense."
About Curcuma Kakchingense:
- Recently identified flowering plant species in Manipur, belong to the Zingiberaceae family.
- Member of the angiospermic family Zingiberaceae, which includes well-known plants like turmeric, gingers, and cardamom.
- Plant Characteristics: Robust plant reaching a height of eight feet, characterized by large terminal inflorescence.
- Natural Habitat: Thrives along the banks of the Sekmai River in the Kakching District of Manipur.
- Resemblance to Other Species: Bears a striking resemblance to local "Yaingung" (Curcuma longa) and Curcuma phrayawan from Thailand.
- Distinguished by lemon-yellow rhizomes with a notably bitter taste.
- IUCN Red List Classification: Classified as "Data Deficient" (DD) under the IUCN Red List category.
Importance of Curcuma Plants:
- Culinary and Traditional Uses: Various Curcuma species, including turmeric (Curcuma longa), play a vital role in cuisines, traditional medicines, spices, and dyes.
- Biological Activities: Curcumin and curcuminoids found in Curcuma species are nontoxic polyphenolic compounds with diverse biological activities.
- Pharmacological Properties: Essential oil of Curcuma species possesses pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, anti-diabetic, and anti-microbial effects.
- Versatile Applications: Widely utilized in cosmetics, perfumes, and as ornamental plants, contributing to various industries and daily life.
New Artificial Intelligence System BTSbot Discovers Supernova (India Today)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international team led by Northwestern University has successfully created an artificial intelligence (AI) tool Bright Transient Survey Bot (BTSbot) that can detect, identify, and classify supernovae.
What is the Bright Transient Survey Bot (BTSbot)?
- The Bright Transient Survey Bot operates as a machine-learning algorithm, undergoing training with a vast dataset comprising over 1.4 million images from nearly 16,000 sources.
- Utilizing data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF), it successfully identified the recently discovered supernova named SN2023tyk.
- Functionality: The algorithm seamlessly automates the process of seeking potential supernovae across the night sky.
- In the case of SN2023tyk, it autonomously requested the supernova's spectrum from the Palomar Observatory.
- Subsequently, the Spectral Energy Distribution Machine (SEDM), another robotic telescope, performed comprehensive observations to obtain the source's spectrum.
- Advantages: This innovative system not only streamlines the entire workflow of searching, detecting, confirming, classifying, and announcing new supernovae but also eradicates human error, significantly enhancing the speed of the process.
- The Bright Transient Survey Bot showcases the potential of automated technology in advancing astronomical discoveries.
What is artificial intelligence?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the interdisciplinary field of computer science dedicated to developing algorithms and computational models that emulate human cognitive processes.
- Rooted in machine learning and advanced data analytics, AI aims to create systems capable of reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- AI involves the study and design of intelligent agents, encompassing areas like natural language processing, computer vision, and expert systems.
- It seeks to enhance machines' ability to learn from experience, adapt to new information, and perform tasks that traditionally necessitate human intelligence, fostering innovation across diverse domains, including healthcare, finance, and robotics.
Chennai's Pallikaranai Wetlands Welcoming Migratory Bird Flocks (The Hindu)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
With over 150 garganeys, and several other species, including waders and raptors, flocking the Pallikaranai marshland, the curtain for the migratory season has been raised.
About Pallikaranai Marshland:
- Location: Pallikaranai marshland is a freshwater and partly saline wetland, located approximately 20 kilometres south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- The eastern border of the marsh is flanked by the Buckingham Canal.
- Rich Ecosystem: The diverse ecosystem of Pallikaranai supports an impressive array of wildlife, including 115 bird species, 10 mammals, 21 reptiles, 10 amphibians, 46 fish, nine molluscs, five crustaceans, and seven butterfly species.
- Notable Species: Among the diverse wildlife are noteworthy species such as the Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis), glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), grey-headed lapwings (Vanellus cinereus), and Pheasant-tailed jacana (Hydrophasianus chirurgus).
- Biodiversity Significance: Beyond its biodiversity, the marshland serves a crucial role in flood prevention for Chennai, absorbing water during wet periods and releasing it during dry spells.
- Environmental Threats: Despite its ecological importance, the site faces threats from invasive non-native species, household sewage, urban wastewater, and periodic droughts.
- Ramsar Designation: Acknowledging its ecological significance, Pallikaranai marshland holds the status of being one of India's Ramsar sites, recognized for its importance in wetland conservation on an international scale.
INS Beas to Be Upgraded (PIB)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Defence signed a contract on October 16, 2023, in New Delhi for the life Upgrade and Re-Powering of "INS Beas" with Kochi-based M/S Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) at an overall cost of Rs. 313.42 Cr.
Context:
- The INS Beas is gaining attention as the first Brahmaputra Class Frigate to undergo a transition from steam to diesel propulsion.
- The completion of its Mid-Life Upgrade and Re-Powering in 2026 is expected to result in the INS Beas joining the active fleet of the Indian Navy, equipped with a modernized weapon suite and upgraded combat capabilities.
About INS Beas:
- INS Beas (F37) stands as a Brahmaputra-class frigate within the Indian Navy, constructed at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- Commissioned on July 11, 2005, it is the second ship in the Indian Navy to carry this name, with the first being a Leopard-class frigate commissioned in 1960 and decommissioned in 1992.
- Role: Functioning as a versatile warship, INS Beas is proficient in various missions, encompassing anti-aircraft, anti-submarine, and anti-ship warfare.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in patrolling, surveillance, and safeguarding India's maritime interests.
- Features: The ship's design and construction are wholly Indian, derived from the modification of the Godavari-class frigate.
- With a displacement of about 3,850 tonnes, INS Beas boasts a length of 126 meters (413 feet) and a beam width of 14.5 meters (48 feet).
- Propulsion: Powered by 2 steam turbines, INS Beas demonstrates remarkable agility, capable of reaching speeds exceeding 30 knots during naval operations.
- Technology: Equipped with modern sensor suites and matching weapon systems, the ship embodies cutting-edge technology to enhance its operational capabilities.
Amazon River Hits Lowest Levels in a Century Amid Drought in Brazil (Business Standard)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Amazon River fell to its lowest level in over a century on Monday at the heart of the Brazilian rainforest as a record drought upended the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and damaged the jungle ecosystem.
About the Amazon River:
- The Amazon River holds the distinction of being the world's largest river in terms of both water volume and width.
- Length and Course: Spanning an impressive 6,400 kilometres, it is the second-longest river globally, surpassed only by the Nile.
- Originating high in the Andes Mountains, the river courses its way eastward through vast rainforests and lowlands before reaching its culmination at the northeastern coast of Brazil, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Dynamic Width: During the dry season, the Amazon River exhibits a width ranging from 4 to 5 kilometres, expanding significantly to 50 kilometres in certain areas during the wet season.
- Unparalleled Drainage Area: The Amazon boasts the largest drainage area globally, with its watershed spanning across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
- Approximately two-thirds of the Amazon's mainstream and the majority of its basin lie within the borders of Brazil.
- Water Discharge and Global Impact: With a staggering water discharge of 300,000 cubic meters per second into the Atlantic Ocean, the Amazon contributes one-fifth of the total freshwater volume entering the world's oceans.
- This immense water flow plays a pivotal role in regulating global oxygen and carbon cycles.
- Extensive Tributaries: Featuring over 1,100 tributaries, including seventeen exceeding 1,500 kilometres in length, notable contributors include the Rio Negro, the Madeira River, and the Xingu River.
- Environmental Significance: The Amazon Rainforest, constituting approximately half of the Earth's remaining rainforest, stands as the largest repository of biological resources.
- Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet's oxygen and carbon balance.
US Says Egypt Border Crossing to Gaza to Reopen (Business Today)
- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Hundreds of tons of aid from multiple countries have been stationed in Egypt's Sinai Peninsula, awaiting an agreement for secure transportation to Gaza for several days.
About the Sinai Peninsula:
- Geographical Location: The Sinai Peninsula is a triangular landmass located in northeastern Egypt, serving as a critical land bridge that connects the continents of Asia and Africa.
- Size and Sovereignty: Encompassing an expansive area of 23,500 square miles (61,000 square km), the Sinai Peninsula is recognized as a sovereign territory within the boundaries of Egypt.
- Geographical Boundaries: It is bordered to the north by the Mediterranean Sea and to the east by Israel and the Gaza Strip.
- The Suez Canal lies to the west, acting as a separation from the African part of Egypt.
- To the southwest, the Gulf of Suez and the Red Sea border the peninsula, while the Gulf of Aqaba marks its southeastern boundary.
- Egypt shares maritime borders in the Sinai with Jordan and Saudi Arabia.
- Historical Significance: In the late 19th century, including the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt became part of the British Empire until gaining independence in 1922.
- During the Six-Day War of June 1967, the peninsula was occupied by Israeli forces and returned to Egypt in 1982 as part of the peace treaty signed in 1979.
- Diverse Geography: The Sinai Peninsula is characterized by a diverse landscape, featuring mountain ranges, deserts, plateaus, and coastal regions.
- Population Composition: With a relatively sparse population, the Sinai is home to about 600,000 people, predominantly consisting of Arab Egyptians and Bedouins.
Hailstorms Damage Apple Orchards in Kulgam, Shopian (HT)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A hailstorm in the evening caused massive damage to the crops and fruits in south Kashmir’s Kulgam and Shopian districts. Residents said the hailstorm damaged the apple fruit which was ready for harvesting.
What are Hailstorms?
- Hail, a solid form of rain composed of ice balls or lumps, leads to the formation of hailstorms when they descend to the ground.
- Typically lasting around 15 minutes, these storms can inflict injuries and damage to structures, vehicles, and more, particularly prevalent in midlatitude regions.
- Hailstorms occasionally coincide with other severe weather phenomena such as cyclones and tornadoes.
- The size of hailstones varies widely, ranging from small pellets under 1/4 inch to larger stones measuring several inches in diameter.
- Conditions: Conditions conducive to hailstorm occurrence involve the presence of highly developed Cumulonimbus clouds, massive anvil-shaped formations observed during thunderstorms that can reach heights of up to 65,000 feet.
- Strong updrafts, or ascending air currents within these clouds, and high concentrations of supercooled liquid water are essential elements.
- Formation of Hail: Hail formation begins with a water droplet lifted by an updraft inside a thundercloud.
- As it ascends, supercooled water droplets adhere to its surface, creating layers of ice.
- With continued ascent, the hail embryo grows by accumulating more supercooled particles until gravity pulls it down.
- Large hailstones often display alternating layers of clear and opaque ice due to irregular rates of freezing during their development.
Vice President Interacted With Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) President During P20 Summit (PTI)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar recently hosted a lunch for heads of parliamentary delegations attending the G20 Parliamentary Speakers' Summit (P20) and also interacted with Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) President Duarte Pacheco.
About the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU):
- Established in 1889 in Paris, the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) is the international organization of Parliaments, dedicated to promoting representative democracy and world peace.
- It serves as the first multilateral political organization globally, fostering cooperation and dialogue among all nations.
- Mission and Slogan: The IPU's mission revolves around parliamentary diplomacy, empowering parliaments, and parliamentarians to advance peace, democracy, and sustainable development worldwide.
- Its slogan, "For democracy. For everyone," encapsulates its commitment to democratic values.
- Membership and Promotion of Democracy: Currently comprising 179 member parliaments and 13 associate members, the IPU actively promotes democracy by strengthening parliaments, and fostering youth inclusion, gender balance, and diversity.
- A dedicated committee defends the human rights of parliamentarians globally.
- Headquarters and Funding: The IPU relocated its headquarters to Geneva in 1921.
- Financed primarily by its members using public funds, the organization sustains its operations and initiatives.
Organizational Structure:
- IPU Assembly: Principal statutory body expressing IPU views on political issues.
- Gathers parliamentarians to study international problems and make actionable recommendations.
- Governing Council: Plenary policymaking body composed of three representatives from each member parliament.
- Establishes the IPU's annual program, and budget, and considers substantive issues.
- Executive Committees: A 17-member body overseeing IPU administration and advising the Governing Council.
- Fifteen members elected by the Council for a four-year term.
- Standing Committees: Three committees set up by the Governing Council to assist the Assembly in its work.
- Meeting of Women Parliamentarians: A separate organ meeting during the first round of Statutory Meetings, reporting to the Governing Council.
- Attended by parliamentarians of both sexes, focusing on specific substantive items for debate within the Assembly's competence.
India, Sri Lanka Launch Ferry Service Across Palk Strait (The Hindu)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international, high-speed passenger ferry service between Nagapattinam on the eastern coast of Tamil Nadu and Kankesanthurai in the northern province of Sri Lanka, has resumed as of Saturday, October 14, 2023, after a gap of nearly four decades.
About the Palk Strait:
- Palk Strait, situated between the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the island nation of Sri Lanka, derives its name from Robert Palk, the governor of Madras Presidency (1755-1763) during the British Raj.
- Bounded by Pamban Island (India), Adam's (Rama's) Bridge, the Gulf of Mannar, and Mannar Island (Sri Lanka) to the south, the strait serves as a crucial link connecting the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with the Gulf of Mannar in the southwest.
- The southwestern segment of the strait is referred to as Palk Bay.
- Spanning 40 to 85 miles (64 to 137 km) in width, 85 miles in length, and with a depth of less than 330 feet (100 meters), it features the inflow of several rivers, including Tamil Nadu's Vaigai River.
- The port of Jaffna, serving as the commercial hub for northern Sri Lanka, is situated along this significant waterway.
Facts About Adam's Bridge:
- Adam's Bridge, also recognized as Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu, constitutes a series of limestone shoals situated between Pamban Island (Rameswaram Island) off the south-eastern coast of Tamil Nadu, India, and Mannar Island off the north-western coast of Sri Lanka.
- Geological evidence supports the idea that this bridge once formed a land connection between India and Sri Lanka.
- Extending over 50 km, it delineates the separation between the Gulf of Mannar to the southwest and the Palk Strait to the northeast.
- Featuring dry sandbanks and shallow waters ranging from 1 to 10 meters in depth, hindering navigation, scientists posit that Ram Setu is a natural formation resulting from tectonic movements and the entrapment of sand in corals.
- Significantly, this structure holds cultural significance in Hindu and Muslim mythology.
- Hindus believe it to be the bridge constructed by Lord Ram and his army for their journey to Lanka to confront Ravan.
- According to Islamic legend, Adam traversed this bridge to reach Adam’s Peak in Sri Lanka, where he purportedly stood on one foot in repentance for 1,000 years.
Manipur to Conduct Census of Amur Ffalcon (The New Indian Express)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Manipur Forest Department will conduct the first-ever Amur falcon census. This initiative in India is one of the several programs the agency is running to safeguard migrating birds.
About Amur Falcon:
- The Amur Falcon, a diminutive member of the falcon family locally known as Akhuipuina, predominantly frequents Manipur and Nagaland.
- Originating from southeastern Siberia and northern China, these birds embark on extensive migrations in vast formations to winter in Southern and East Africa, covering a one-way journey of approximately 20,000 km through India twice a year.
- In terms of conservation, the Amur Falcon is safeguarded by the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, listed under Schedule IV.
- Hunting or possession of its meat is subject to legal repercussions, including imprisonment for up to three years, a fine of up to 25,000, or bonds.
- Initiating a conservation effort in 2018, the forest department employed radio tagging to study the birds' migratory routes.
- As per the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Amur Falcon is categorized as "Least Concern."
- Despite this, the species faces threats such as illegal trapping and killing during migration, along with habitat loss due to agricultural practices and land reclamation.
Egypt is Racing to Eliminate Hepatitis C (The Hindu)
- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently the WHO announced that Egypt had made “unprecedented progress” towards eliminating hepatitis C.
Context:
- As per the World Health Organization (WHO), Egypt has attained a significant milestone by becoming the inaugural country to reach the "gold tier" status in its pursuit of eliminating hepatitis C, meeting the criteria established by the global health organization.
- Egypt has successfully identified 87% of individuals with hepatitis C and has administered curative treatment to 93% of those diagnosed, surpassing the WHO's gold-tier benchmarks.
- These targets include diagnosing a minimum of 80% of individuals with hepatitis C and offering treatment to at least 70% of those identified, marking a commendable achievement for Egypt in the global effort against the disease.
What is Hepatitis C?
- Hepatitis C is a viral infection impacting the liver, causing both acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) illnesses that can be life-threatening.
- Transmission occurs through contact with infected blood, such as sharing needles, unsafe medical procedures like unscreened blood transfusions, and vertical transmission from an infected mother to her baby.
- It can also be transmitted through certain sexual practices involving blood exposure.
- Contrary to misconceptions, Hepatitis C is not spread through breast milk, food, water, or casual contact like hugging, kissing, or sharing food/drinks with an infected person.
- Symptoms encompass fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
- Geographically, this viral infection is present in all WHO regions, with the Eastern Mediterranean Region and European Region bearing the highest disease burden.
- New infections often lack symptoms, making diagnosis challenging, and chronic infections may remain asymptomatic for decades until severe liver damage prompts noticeable symptoms.
- While no vaccine exists for Hepatitis C, antiviral medications offer effective treatment options.
What is Gold Tier Status?
- Gold tier status involves fulfilling distinct criteria, which encompass:
- Guaranteeing 100% blood and injection safety, with a commitment to maintaining a minimum of 150 needles/syringes annually for individuals who inject drugs (PWID).
- Achieving a diagnosis rate of over 80% for individuals living with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- Providing treatment to over 70% of individuals diagnosed with HCV.
- Instituting a sentinel surveillance program for hepatitis sequelae, with a focus on conditions such as liver cancer.
Centre Notifies Green Credit Programme and Ecomark Scheme (DownToEarth)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change on October 13, 2023, notified the ‘green credit’ programme, a first-of-a-kind market-based instrument designed to incentivise individuals, industries and local bodies for their voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors.
About Green Credit Programme (GCP):
- Green Credit Program (GCP ) is an innovative market-based mechanism designed to incentivize voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors, by various stakeholders like individuals, communities, private sector industries, and companies.
- The GCP's governance framework is supported by an inter-ministerial Steering Committee and The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) serves as the GCP Administrator, responsible for program implementation, management, monitoring, and operation.
- In its initial phase, the GCP focuses on two key activities: water conservation and afforestation.
- A user-friendly digital platform will streamline the processes for registration of projects, verification, and issuance of Green Credits.
- The Green Credit Registry and trading platform, being developed by ICFRE along with experts, would facilitate the registration and thereafter, the buying and selling of Green Credits.
- To obtain Green Credits, individuals and entities must register their activities through the central government's dedicated app/website www.moefcc-gcp.in.
- The Administrator will verify the activity through a designated agency, with self-verification for small projects.
- Once verification is complete, the Administrator will grant a Green Credit certificate which will be tradable on the Green Credit platform.
What is the Ecomark Scheme?
- The Ecomark Scheme provides accreditation and labelling for household and consumer products that meet specific environmental criteria while maintaining quality standards as per Indian norms.
- Products accredited under the Ecomark Scheme will adhere to specific environmental criteria, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
- It will build consumer awareness of environmental issues and encourage eco-conscious choices.
- It will also motivate manufacturers to shift towards environmentally friendly production. The scheme seeks to ensure accurate labelling and prevent misleading information about products.
- The Central Pollution Control Board administers the Ecomark Scheme in partnership with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), which is the national body for standards and certification.
Both initiatives mark significant steps in promoting sustainable living, and environmental conservation, and, through individual and collective choice, embody eco-friendly practices in India. They align with global sustainability goals and reflect the government's commitment to conservation and protection of the environment.
A New Discovery: Unveiling an Underwater Mountain Range in the Southern Ocean (India Today)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have discovered an ancient underwater mountain range hidden within the world's strongest ocean current, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
Context:
- During a recent research expedition, scientists discovered a previously unknown mountain range deep beneath the Southern Ocean’s surface.
- Using state-of-the-art sonar technology, researchers were able to map out the underwater landscape with astonishing accuracy, revealing a vast range of peaks, ridges, and valleys.
- This newfound mountain range spans hundreds of miles and is estimated to be millions of years old.
- Geological Significance: This discovery holds immense importance for our understanding of the Earth’s geological history.
- The underwater mountain range provides key evidence of plate tectonics and the movement of Earth’s crust, as well as the formation of new landmasses.
- By studying the composition and structure of these underwater formations, scientists will be able to gain insights into the geological processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
- Moreover, the discovery raises intriguing questions about the relationship between underwater mountains and the surface landscapes they may be connected to.
- Researchers are eager to investigate whether similar mountain ranges exist on land and whether they share a common origin.
- Implications for Climate and Ecosystems: The newfound underwater mountain range also has significant implications for climate and marine ecosystems.
- These underwater peaks can act as barriers, influencing ocean currents and affecting nutrient distribution.
- Understanding the impact of these formations on ocean dynamics is crucial for predicting climate patterns and better managing marine resources.
- Additionally, these underwater mountains create a unique habitat for a diverse range of marine species.
- The ridges and valleys provide sheltered zones where marine life can thrive, with the potential for new species discoveries.
- Protecting these habitats will be critical in preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
About the Southern Ocean:
- The Southern Ocean, also referred to as the Antarctic Ocean is one of the Earth's five major ocean basins.
- Its formation traces back approximately 34 million years when Antarctica and South America underwent a gradual separation, resulting in the creation of the Drake Passage.
- This passage, situated between the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and South America, delineates the Southern Ocean from the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, encompassing their tributary seas surrounding Antarctica below the 60° S latitude.
- Physiography: The ocean floor structure features a continental shelf, typically less than 160 miles (about 260 km) wide, expanding to a maximum width exceeding 1,600 miles (2,600 km) near the Weddell and Ross seas.
- Renowned for its robust winds, intense storms, marked seasonal variations, and frigid temperatures, the Southern Ocean is predominantly influenced by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC).
- This current, the longest, strongest, and deepest-reaching on Earth, follows a clockwise circulation around the continent, surpassing all others in the volume of water it transports globally.
- Biodiversity: The Southern Ocean sustains diverse flora and fauna, with a majority of marine life relying on the nutrient-rich phytoplankton found in the Antarctic Convergence.
- Notable species include whales, penguins, orcas, and seals, contributing to the region's rich biodiversity.
A new non-invasive formaldehyde sensor can detect adulterated fish at room temperature (DST GOI)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A new low-cost sensor made of metal oxide nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide composite can detect formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature in a non-invasive way. The sensor shows long-term stability with a low detection limit.
Context:
- A sensor designed for the detection of formalin in fish has been developed by the Nanomaterials and Nanoelectronics Laboratory at Guwahati University, Assam.
- The formalin sensor utilizes a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide, synthesized through a process involving the wet chemical approach for Graphene Oxide (GO) and the hydrothermal route followed by calcination for the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Testing of the sensor has been conducted both at the laboratory scale and on fish procured from the fish markets in the Guwahati region, specifically targeting potential adulteration.
- This groundbreaking research has received support from DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence) and has been documented in the journal ACS Appl. Nano Mater.
- Research Support: The research behind this innovative sensor is backed by DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence).
About Non-Invasive Formaldehyde Sensor:
- This non-invasive formaldehyde sensor incorporates a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2) as its key materials.
- While reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has been widely utilized for detecting various toxic gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), tin oxide (SnO2) has demonstrated notable efficacy in formaldehyde detection, both in its pristine form and when combined with different compounds, including graphene.
- This combination is favoured for its heightened stability and sensitivity to low concentrations of formaldehyde.
- Synthesis Process: The fabrication process involves a wet chemical approach for the production of graphene oxide (GO), followed by the hydrothermal route and subsequent calcination to synthesize the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Comparison with Existing Sensors: Unlike commercial formalin sensors for fish, which are primarily electrochemical-based or colorimetric-based and often invasive, this novel sensor, made from metal oxide nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide, offers a cost-effective and non-invasive method for detecting formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature.
- Challenges with Existing Sensors: Traditional electrochemical sensors, though widely used, tend to be expensive, and colourimetric sensors, while more cost-effective, share the invasive nature of their electrochemical counterparts. Both face challenges related to low-level and selective detection.
- Significance of the New Sensor: The development of gas sensors based on 2D materials, such as graphene, opens up new possibilities for the effective detection of toxic vapours at room temperature.
- These sensors hold promise for accurately detecting formalin emanating from adulterated food products.
What is Formaldehyde?
- Formaldehyde (CH?O) is an odorless, colorless gas with high toxicity and flammability under standard room temperature conditions.
- Primary Applications:
- Production of fertilizers, paper, plywood, and certain resins.
- Utilized as a food preservative.
- Found in glues, resins, dyes, textiles, disinfectants, building materials, automotive components, embalming processes, and laboratory settings.
- Incorporated into household items like antiseptics, medications, and cosmetics.
- Potential Health Effects:
- Exposure to formaldehyde may result in irritation of the skin, throat, lungs, and eyes. Additionally, formaldehyde is recognized as a carcinogenic substance.
For Huntington’s disease clues, scientists are looking in fruit flies (The Hindu)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists at the University of Szeged in Hungary have made significant progress in advancing our understanding of Huntington's disease through the study of fruit flies.
What is Huntington’s Disease?
- Huntington’s disease (HD) is a brain disorder that is passed down in families from generation to generation.
- It is caused by an error in the DNA instructions that build our body and keep it running.
- DNA is made up of thousands of genes, and people with HD have a small defect in a gene called huntingtin.
- Over time, this error causes damage to the brain and causes symptoms of Huntington’s disease.
- Huntington’s disease causes a person’s physical, mental and emotional abilities to deteriorate, usually during their prime at work, and there is currently no cure.
- Most people start developing symptoms in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50, but HD can also occur in children and young adults.
- Huntington’s disease is known as a family disease because each child of a parent with HD has a 50/50 chance of inheriting the defective gene.
Huntington’s Disease Symptoms:
- Symptoms of Huntington’s disease can vary greatly from person to person but typically include:
- Personality changes, mood swings and depression
- Forgetfulness and impaired judgment
- Unsteady gait and involuntary movements (chorea)
- Slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and significant weight loss.
- Symptoms typically worsen over the course of 10 to 25 years, affecting the ability to reason, walk, and speak.
- The person with HD or their friends and family may notice difficulty planning, remembering, and concentrating on the task.
- They can develop mood swings such as depression, anxiety, irritability, and anger.
- Most people with Huntington’s disease become “fidgety” and develop facial and limb movements known as chorea, which they cannot control.
- The symptoms of Huntington’s disease are sometimes described as ALS, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s all at the same time.
Huntington’s Disease Treatment:
- No treatment can stop or reverse the progression of Huntington’s disease.
- Antipsychotic medications can relieve chorea and help control hallucinations, delusions, and violent outbursts.
- Huntington’s disease causes disability that gets worse over time.
How the PM JANMAN scheme can help Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (Indian Express)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN), aimed at providing PVTG households and habitations with basic facilities such as safe housing, clean drinking water and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
What is the PM-JANMAN Scheme?
- PM-JANMAN is a government initiative aimed at integrating tribal communities into the mainstream of development.
- The scheme, comprising both Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes, will be executed collaboratively by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, State governments, and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) communities.
Key Features:
- Implementation Scope: The scheme focuses on 11 critical interventions managed by 9 line Ministries, ensuring the effective execution of existing schemes within villages inhabited by PVTGs.
- Sectoral Coverage: PM-JANMAN spans various sectors, encompassing initiatives such as ensuring safe housing through the PM-AWAS Scheme, access to clean drinking water, improved healthcare, education, nutrition, road and telecommunications connectivity, and the promotion of sustainable livelihoods.
- Special Initiatives: The plan includes specific initiatives such as the establishment of Van Dhan Vikas Kendras to facilitate the trade of forest produce, deployment of off-grid solar power systems for 1 lakh households, and installation of solar street lights.
- Objectives: PM-JANMAN aims to enhance the quality of life and overall well-being of PVTGs by addressing the various forms of discrimination and exclusion they face.
- Additionally, it recognizes and values the unique and significant contributions of PVTGs to both national and global development.
How Does PM-JANMAN Differ?
- Distinctive Identification and Recognition: Criticism has arisen over outdated criteria for identifying Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- The presence of repetitive names and discrepancies in recognition across states has led to confusion and exclusion.
- Addressing these concerns, PM-JANMAN introduces a Human Development Index for PVTGs, aiming to enhance proper identification and tailored development planning based on updated and comprehensive data.
- Participatory Bottom-Up Approach: In a departure from the 'one-size-fits-all' approach, PM-JANMAN adopts customised strategies that respect the unique needs and priorities of PVTGs.
- Emphasizing a participatory bottom-up approach, the scheme actively involves PVTGs in decision-making processes, particularly regarding land rights, social inclusion, and cultural preservation.
- Livelihood Promotion: PM-JANMAN focuses on sustainable livelihoods for PVTGs by providing skills training, essential resources such as land and credit, and implementing the Forest Rights Act (FRA) to secure land titles, particularly under Section 3(1)(e) for primitive tribal groups and pre-agricultural communities.
- The scheme encourages the preservation of cultural heritage through the promotion of traditional technologies and skill enhancement via industry partnerships.
- Health, Nutrition, and Education: To address the unique challenges faced by PVTGs, PM-JANMAN incorporates Mobile Medical Health Units for healthcare outreach in remote areas.
- The scheme also emphasizes cultural sensitivity in education by integrating PVTG culture and language into the curriculum, providing transportation, and training teachers about PVTG cultural contexts.
- Infrastructure Development: Recognizing that PVTG habitations may not meet standard criteria for existing schemes, PM-JANMAN relaxes guidelines for infrastructure schemes like Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, and Jal Jeevan Mission.
- This ensures improved access to housing, water, sanitation, electricity, and connectivity for PVTGs.
What are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- PVTGs represent the most vulnerable segments within tribal communities, facing heightened challenges in various aspects of development.
- Due to their distinct vulnerabilities, more developed and assertive tribal groups often receive a significant portion of tribal development funds, necessitating a focused allocation of resources for the advancement of PVTGs.
- The designation of PVTGs dates back to 1975 when, based on the recommendations of the Dhebar Commission, the Government of India identified 52 tribal groups with unique vulnerabilities.
- Presently, there are 75 PVTGs among the 705 Scheduled Tribes in India.
- Geographically, PVTGs are distributed across 18 states and one Union Territory, as per the 2011 census, with Odisha having the highest number, exceeding 2.5 lakh individuals.
- Distinctive Characteristics of PVTGs:
- Stagnant or declining trends.
- Primarily pre-agricultural practices.
- Exceptionally low educational attainment.
- Predominantly subsistence level, indicating a reliance on basic, self-sustaining economic activities.
How Japan’s moon-landing attempt in January will affect Chandrayaan 4 (The Hindu)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the “Moon Sniper” lander developed by Japan’s space agency successfully entered lunar orbit.
About the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) Mission:
- The Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) is a spacecraft crafted and launched by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) on September 7, 2023, from the Tanegashima spaceport.
- Remarkably lightweight at 590 kg, SLIM embarked on its mission alongside XRISM, a cutting-edge X-ray space telescope, on an H-2A rocket.
- Upon launch, SLIM assumed an elliptical orbit around the moon within a span of approximately three minutes.
- Notably, the apogee (farthest point) of this orbit extends to 4,000 km, while the perigee (closest point) hovers at 600 km above the lunar surface.
Objectives of SLIM on the Lunar Surface:
- Before its lunar descent, SLIM is programmed to release two compact rovers known as Lunar Excursion Vehicle (LEV) 1 and 2.
- Working in tandem with SLIM, LEV-1, and LEV-2 are tasked with conducting a comprehensive study of the lunar surface near the designated landing area.
- Their mission encompasses the collection of temperature and radiation readings, as well as endeavours to investigate the moon's mantle.
- This collaborative effort by SLIM and its rovers aims to enhance our understanding of lunar conditions and contribute valuable insights to lunar exploration.
What is the XRISM Mission:
- The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) is a collaborative effort between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with valuable contributions from the European Space Agency (ESA).
- Mission Objective: XRISM is designed to observe X-rays emanating from deep space, aiming to precisely identify their wavelengths with an unprecedented level of accuracy.
- The mission employs cutting-edge spectroscopy techniques to measure changes in the brightness of celestial objects across various wavelengths.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging state-of-the-art spectroscopy, XRISM can detect X-rays within a broad energy spectrum ranging from 400 to 12,000 electron volts.
- To provide a perspective, the energy of visible light typically falls within the 2 to 3 electron volts range.
- This expanded energy range enables astrophysicists to gain novel insights into some of the universe's most dynamic regions, vast structures, and entities characterized by formidable gravitational forces.
India, Russia ink pacts on the construction of future power units of the Kudankulam nuclear plant (The Hindu)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a major boost to their time-tested partnership, India and Russia recently signed some "very important" agreements related to the construction of the future power-generating units of the Kudankulam nuclear power plant.
About the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project:
- The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project is India's largest nuclear power plant situated in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu.
- It is being developed by the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) in collaboration with Russia's Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation.
- The construction began in March 2002.
- Since February 2016, the first power unit of the Kudankulam NPP has been steadily operating at its design capacity of 1,000 MW.
- The plant is expected to start operating at full capacity in 2027.
- Water-Water Energy Reactor: The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project employs VVER (Water-Water Energy Reactor) technology, a pressurized water reactor design developed in the former Soviet Union, known for its safety and reliability.
- Power Generation Capacity: The current power generation capacity is 2×1,000 MWe VVER, expected to significantly increase with the construction of four additional reactors, estimated at ?89,470 crore.
- All units are subject to International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) safety analysis, except the Kalpakkam nuclear plant, reserved for strategic use under the India-US Nuclear Agreement.
What is the 3-Stage Nuclear Programme of India?
- India's nuclear program is structured into three stages, strategically designed to harness the extensive Thorium deposits within the country, constituting approximately 25% of the world's total reserves.
- This focus on Thorium is crucial as India possesses limited Uranium reserves, accounting for about 2% of the global uranium reserves.
- 1st Stage: The initial stage employs Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors that operate on natural uranium, consisting of 99.3% U-238 and 0.7% U-235.
- The fissile U-235 triggers a chain reaction, while the non-fissile U-238 transforms into Pu-239 as a byproduct (spent fuel).
- This Pu-239 is subsequently utilized in the Fast Breeder Reactors in the 2nd stage.
- 2nd Stage: Fast Breeder Reactors primarily rely on Plutonium, utilizing a combination of Plutonium-239 from the 1st stage and the abundant U-238 found on Earth to generate additional Plutonium inside the reactor.
- As U-238 does not initiate a chain reaction, the reactors are termed Breeder reactors.
- To maximize the chances of neutron interaction with U-238, these reactors, known as Fast Breeder Reactors, omit a moderator to slow down neutrons.
- Once Plutonium-239 is fully consumed, Thorium is introduced to convert it into U-233, to be used in the 3rd stage.
- 3rd Stage: Thermal Breeder Reactors utilize U-233 produced in the 2nd stage, incorporating thorium-232.
- Notably, Thorium is non-radioactive and non-fissile. Since these reactors also generate U-233 from Thorium-232, they are classified as breeder reactors.
- India's significant reserves of thorium, particularly in the form of monazite sand, emphasize the critical role of the 3rd stage in India's nuclear energy portfolio.
PM Narendra Modi calls upon religious leaders and social organizations to launch a mass movement against drugs (NewsOnAir)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Veer Bal Diwas in New Delhi, PM Narendra Modi calls upon religious leaders and social organizations to launch a mass movement against drug menace.
Drug Menace in India:
- Alcohol, cannabis, opium, and heroin constitute the primary drugs abused in India.
- Approximately 13% of substance abusers in the country are under 20 years old.
- Adolescence is identified as a critical-risk period for the initiation of substance use.
- Children impacted by substance abuse fall under the category of children in need of care and protection as per the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015.
- In various regions, including Punjab, Assam, Mizoram, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Bihar, Delhi, etc., drug abuse prevalence is notably high.
- Key causes of drug abuse include factors such as poverty, peer pressure, illiteracy, low self-esteem, and genetic predisposition.
Challenges in Combating the Drug Menace:
- India, strategically located between the Death Triangle (Thailand, Myanmar, and Laos) and Death Crescent (Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran), is a prominent hub for drug trafficking, particularly in major opium production regions globally.
- Porous borders exacerbate the problem, and technological advancements, such as the utilization of the dark net and cryptocurrency for drug trafficking, further complicate law enforcement efforts.
- Criminalizing drug abuse contributes to social stigma for addicts, deterring them from seeking essential medical assistance.
- There is a notable absence of comprehensive studies assessing the societal impact of drug abuse, hindering the formulation of informed strategies.
Efforts to Combat the Drug Menace:
- The Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act of 1985 outlines measures for identification, treatment, and rehabilitation.
- The Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan targets 272 highly vulnerable districts with a focus on community outreach.
- The Seizure Information Management System (SIMS) portal facilitates the management of cases involving substantial drug seizures.
- The National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) spanning 2018-2025 adopts a comprehensive, multi-pronged strategy.
- Furthermore, adherence to international conventions, including the Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961) and the Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971), reinforces India's commitment to addressing the global issue of drug abuse.
Atomic watchdog report says Iran is increasing production of highly enriched uranium (Indian Express)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Iran has increased the rate at which it is producing near weapons-grade uranium in recent weeks, reversing a previous slowdown that started in the middle of this year, the International Atomic Energy Agency said in a report.
What is Uranium Enrichment?
- Natural uranium is comprised of two isotopes, with approximately 99% being U-238 and only about 0.7% being U-235.
- U-235 is a fissile material capable of sustaining a chain reaction within a nuclear reactor.
- The enrichment process involves increasing the proportion of U-235 through isotope separation, effectively isolating U-238 from U-235.
- For the production of nuclear weapons, enrichment is necessary up to 90% or more, referred to as weapons-grade uranium.
- Low-enriched uranium, typically containing a 3-5% concentration of U-235, is suitable for generating fuel for commercial nuclear power plants.
- In contrast, highly enriched uranium, boasting a purity of 20% or more, finds application in research reactors.
Key Facts About Uranium:
- Discovered in 1789 by the German chemist Martin Klaproth, Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element found in the periodic table, characterized by its atomic number 92.
- This element holds the distinction of having the highest atomic weight among all naturally occurring elements.
- Naturally present in low concentrations in soil, rock, and water, uranium is commercially extracted from minerals like uraninite.
- The mining of uranium ore can be undertaken through open pits or underground excavations, followed by crushing and processing at a mill to isolate the valuable uranium.
- An alternative method involves the direct dissolution of uranium from ore deposits in the ground, known as in-situ leaching, with the extracted uranium then pumped to the surface.
About the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- The International Atomic Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- Established as an autonomous entity through its international treaty, the IAEA Statute, the organization, nonetheless, reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria, the IAEA collaborates with its Member States and various global partners to advance the safe and peaceful utilization of nuclear technologies.
- It employs nuclear safeguards, encompassing monitoring, inspection, information analysis, and other measures, to ensure the peaceful nature of nuclear activities and to detect and deter any potential diversion towards weapons-related purposes.
- The IAEA plays a crucial role in implementing comprehensive safeguards agreements mandated by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), acting as a frontline defense against nuclear weapons proliferation.
- Additionally, the agency facilitates the exchange of scientific and technical information among its Member States.
- A key function of the IAEA is to bolster national, regional, and international capabilities to respond effectively to nuclear and radiological incidents, thereby minimizing their impact.
Zombie deer disease: Why are scientists concerned over its transmission to humans? (TOI)
- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers in the US have warned that Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) spreading among wildlife across North America, could also spread to humans.
What is Zombie Deer Disease??
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Zombie deer disease or chronic wasting disease is a prion disease that affects deer, elk, reindeer, sika deer and moose.
- Prion diseases affect both humans and animals and are distinguished by long incubation periods.
- In the case of chronic wasting disease or the zombie deer disease, "it may take over a year before an infected animal develops symptoms.
- History of the Disease?: The zombie deer disease was first discovered in Colorado (USA) in 1967.
- Until now, reports of humans getting affected have not come to the fore.
- However, the findings of several studies suggest that it can easily jump to human beings.
Why are health experts and scientists worried about a possible transmission??
- Experts are giving examples of the mad cow disease or the Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE).
- “The BSE outbreak in Britain provided an example of how, overnight, things can get crazy when a spillover event happens from livestock to people.
Symptoms of the Disease:
- The common signs of the disease are drastic weight loss (wasting), stumbling, and other neurologic symptoms.
- Other symptoms seen in animals infected with this disease are listlessness, drooling, excessive thirst or urination, drooping ears, and lack of fear of people.
It is difficult to eradicate this disease??
- The chronic wasting disease is extremely difficult to eradicate from the environment once the infection has started.
- It can persist for years in dirt or on surfaces, and it is resistant to disinfectants, formaldehyde, radiation, and incineration at 600C (1,100F).
- Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) is fatal to animals, and there are no treatments or vaccines.
Prevention?:
- To avoid the spread of the disease, humans should avoid shoot, handling, or eating meat from deer and elk that look sick or are acting strangely or are found dead.
- Individuals should wear latex or rubber gloves when dressing the animal or handling the meat.
Speed up measures for a new dam at Mullaperiyar, Kerala tells Central Water Commission (The Hindu)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently the State government of kerala has urged the Centre to speed up measures for building a new dam at Mullaperiyar in the Idukki district at a meeting with the Central Water Commission.
About the Central Water Commission (CWC):
- The Central Water Commission (CWC) is a leading technical organization in India dedicated to water resources management.
- Currently operating as an attached office of the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India, it plays a pivotal role in overseeing various aspects of water resource management nationwide.
Key Functions:
- Initiation and Coordination: The Commission is responsible for initiating, coordinating, and advancing schemes in collaboration with concerned State Governments.
- These schemes focus on controlling, conserving, and utilizing water resources for Flood Control, Irrigation, Navigation, Drinking Water Supply, and Water Power Development.
- Investigation and Execution: The CWC undertakes the investigation, construction, and execution of water resource schemes as deemed necessary.
- Leadership and Structure: The Commission is led by a Chairman, holding the status of Ex-Officio Secretary to the Government of India.
- The organizational structure includes three wings:
- Designs and Research (D&R) Wing
- River Management (RM) Wing
- Water Planning and Projects (WP&P) Wing
- Each wing is overseen by a full-time member with the status of Ex-Officio Additional Secretary to the Government of India.
- Headquarters: The headquarters of the Central Water Commission is located in New Delhi.
Key Facts About Mullaperiyar Dam:
- The Mullaperiyar Dam is a masonry gravity dam, situated on the Periyar River in Thekkady, Idukki district of Kerala.
- Situated at an elevation of 881 meters above sea level, it graces the Cardamom Hills within the Western Ghats.
- The dam is strategically located at the convergence of the Mullayar and Periyar rivers.
- Its construction, led by the British Corps of Royal Engineers under Pennycuick, commenced in 1887 and concluded in 1895.
- Utilizing limestone and "Surkhi" (a blend of burnt brick powder, sugar, and calcium oxide), the dam serves the purpose of redirecting west-flowing River Periyar waters to the rain shadow regions of Theni, Madurai, Sivaganga, and Ramanathapuram districts in Tamil Nadu.
- The Periyar National Park is located around the dam's reservoir.
- Despite its location in Kerala, the dam is operated and maintained by Tamil Nadu under a 999-year lease agreement established during British rule.
New Toad Species Discovered in Dampa Tiger Reserve of Mizoram (HT)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A group of scientists from India and the United Kingdom have discovered a new species of toads, the third of a genus found only in a very narrow area in northeast India.
About the Recently Discovered Toad Species:
- This newfound toad species, belonging to the bufoides genus, marks the third identified within a limited area in northeast India.
- Distinguished by its interdigital webbing, unique colouration, skin tuberculation, and the existence of ovoid, tuberculated, and depressed parotid glands, this species adds to the diversity of its genus.
- The preceding species from the same genus, Bufoides meghalayanus and Bufoides kempi, were previously identified in the region of Meghalaya.
- In recognition of its discovery and to honour the significant contributions of the renowned herpetologist S. Bhupathy, this new species has been aptly named after him.
About the Dampa Tiger Reserve:
- Situated in the Lushai Hills on the western side of Mizoram, the Dampa Tiger Reserve holds significance for its unique features.
- Establishment: Designated as a tiger reserve in 1994 under the Project Tiger initiative.
- Geographical Boundaries: Bordered on the west by the Chittagong hill tracts (Sazek hill range) of Bangladesh.
- The terrain is characterized by hills, with elevations ranging from 49 to 1095 meters above mean sea level.
- Prominent peaks include Chhawrpialtlang (1095m), Dampatlang (869m), and Pathlawilunglentlang (780m).
- Vegetation Diversity: Encompassing tropical evergreen to semi-evergreen forests, the reserve boasts a diverse range of vegetation.
- River Systems: Drained by the Khawthlangtuipui River in the west and the Teirei River in the east, with tributaries like Keisalam, Seling, and Aivapui flowing through the reserve.
- Fauna: Diverse mammalian species inhabit the reserve, including Hoolock Gibbon, Rhesus Macaque, Assamese Macaque, Pig-Tailed Macaque, Stump-Tailed Macaque, and Phayre’s Leaf Monkey.
- Flora: The reserve boasts a rich flora, featuring species such as Dipterocarpus turbinatus, Dipterocarpus marcocarpus, Terminalia myriocarpa, and Michelia champaca, among others.
Project Nilgiri Tahr’ Launched in Tamil Nadu (The Hindu)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Consolidating efforts towards the conservation of Tamil Nadu’s State Animal, Chief Minister M.K. Stalin on Thursday, October 12, 2023, launched the ‘Project Nilgiri Tahr’ from the Secretariat in Chennai.
About Nilgiri Tahr:
- The Nilgiri Tahr, scientifically known as Nilgiritragus hylocrius, is an endangered mountain ungulate that is native to the southern part of the Western Ghats.
- Locally referred to as 'Varayaadu,' these creatures are renowned for their remarkable climbing abilities on steep cliffs, earning them the moniker "Mountain Monarch."
- Notably, the Nilgiri Tahr holds the distinction of being the state animal of Tamil Nadu.
Distribution:
- The current range of Nilgiri Tahrs is confined to approximately 5% of the Western Ghats in southern India, specifically in the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- The Eravikulam National Park in Kerala is home to the highest density and the largest surviving population of Nilgiri Tahrs.
Habitat:
- Nilgiri Tahrs inhabit open montane grassland habitats, thriving at elevations ranging from 1200 to 2600 meters in the South Western Ghats.
Distinctive Features:
- Characterized by a stocky body, short coarse fur, and a bristly mane, Nilgiri Tahrs exhibit sexual dimorphism, with mature males being larger and darker in colour.
- Both males and females possess curved horns, with males having larger ones measuring up to 40 cm, while females' horns reach approximately 30 cm.
- Adult males develop a light grey area or 'saddle' on their backs, leading to the term 'saddlebacks.' The species is recognized by its short grey-brown or dark coat.
Conservation Status:
- The Nilgiri Tahr is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, signifying the critical need for conservation efforts.
- Additionally, it is accorded the highest protection under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972, listed in Schedule I.
ICRISAT Joins One CGIAR Global Initiative (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), a Hyderabad-based international research institute with a focus on tropical dryland agrifood system innovation, has joined the One CGIAR integrated partnership.
What is One CGIAR Global Initiative?
- The One CGIAR global initiative is designed to establish a cohesive approach to transform food, land, and water systems in response to the challenges posed by the climate crisis.
- This collaborative effort involves the CGIAR System Organisation and 12 research centres operating under the umbrella of One CGIAR.
- CGIAR is a publicly-funded network of research centres focused on agrifood systems, operating in over 80 countries.
Key Facts about ICRISAT:
- ICRISAT, a non-profit, non-political international research organization, is dedicated to agricultural research for development in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Its mission is to support farmers by providing improved crop varieties and hybrids, particularly aiding smallholder farmers in arid regions to combat climate change.
- The organization specializes in research on five highly nutritious, drought-tolerant crops: chickpea, pigeonpea, pearl millet, sorghum, and groundnut.
- Recognized for its impactful work, ICRISAT was awarded the 2021 Africa Food Prize for the Tropical Legumes Project, contributing to improved food security across 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
- ICRISAT is headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana State, India, with two regional hubs in Nairobi, Kenya, and Bamako, Mali.
- Through its research and initiatives, ICRISAT plays a crucial role in addressing agricultural challenges and promoting sustainable development in diverse regions.
India Ranks 111 in Global Hunger Index (The Hindu)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
India ranks 111 out of a total of 125 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023, with its progress against hunger nearly halted since 2015, reflecting a global trend.
Key Findings of Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023:
- India holds a Global Hunger Index score of 28.7 on a 100-point scale, categorizing its severity of hunger as "serious."
- The global GHI score for 2023 is 18.3, considered moderate.
- Latin America and the Caribbean stand out as the only region in the world where GHI scores have deteriorated between 2015 and 2023.
- South Asia and Africa South of the Sahara emerge as the global regions with the highest hunger levels, each having GHI scores of 27.0.
About the Global Hunger Index:
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool designed to comprehensively measure and track hunger at global, regional, and national levels, reflecting multiple dimensions of hunger over time.
- The GHI is intended to raise awareness and understanding of the struggle against hunger, provide a way to compare levels of hunger between countries and regions and call attention to those areas of the world where hunger levels are highest and where the need for additional efforts to eliminate hunger is greatest.
- It is prepared jointly by Irish aid agency Concern Worldwide and the German organisation Welt Hunger Hilfe.
- How the GHI Is Calculated?
- Each country’s GHI score is calculated based on a formula that combines four indicators that together capture the multidimensional nature of hunger:
- Undernourishment: the share of the population whose caloric intake is insufficient;
- Child stunting: the share of children under the age of 5 who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition;
- Child wasting: the share of children under the age of five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition; and
- Child mortality: the share of children who die before their 5th birthday, reflecting in part the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
- The indicators included in the GHI formula reflect caloric deficiencies as well as poor nutrition.
- The undernourishment indicator captures the food access situation of the population as a whole, while the indicators specific to children reflect the nutrition status within a particularly vulnerable subset of the population for whom a lack of dietary energy, protein, and/or micronutrients (essential vitamins and minerals) leads to a high risk of illness, poor physical and cognitive development, and death.
- The inclusion of both child wasting and child stunting allows the GHI to document both acute and chronic undernutrition.
- By combining multiple indicators, the index minimizes the effects of random measurement errors.
- These four indicators are all part of the indicator set used to measure progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Good Governance Day: Govt launches 3 new features on iGOT Mission Karmayogi platform (TOI)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Good Governance Day, Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi by introducing three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform that include My iGOT, Blended Programs and Curated Programs..
About Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmayogi, the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), is geared towards equipping Civil Servants with enhanced creativity, constructiveness, and innovation, utilising transparency and technology to prepare them for future challenges.
- This innovative program serves as a cornerstone for the country's civil servants, emphasizing a balanced approach between 'on-site learning' and traditional 'off-site learning.'
- Approved by the Government on September 2, 2020, Mission Karmayogi encompasses six key pillars:
- Policy Framework
- Institutional Framework
- Competency Framework
- Digital Learning Framework (iGOT-Karmayogi)
- The electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS), and
- The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework.
- Encompassing all civil servants, including contractual employees, across various ministries, departments, organizations, and agencies of the Union Government, the program introduces three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform:
- My iGOT: Delivers targeted training courses on the home page of individual officers, directly addressing their unique capacity-building needs identified in the Capacity-Building Plan for their Ministries/Departments.
- Blended Programs: Facilitates equitable access to training methodologies across all levels by integrating traditional offline (in-person) classroom courses with online learning components.
- This approach enables officers and faculty to benefit from both the flexibility of online courses and the invaluable interactions of face-to-face classroom sessions.
- Curated Programs: Designed to cater to diverse learning needs of Ministries/Departments and Training Institutions, offering a custom approach to address the specific requirements of different segments within the civil services.
Six armed poachers, timber mafia held by forest officials at Similipal National Park (New Indian Express)
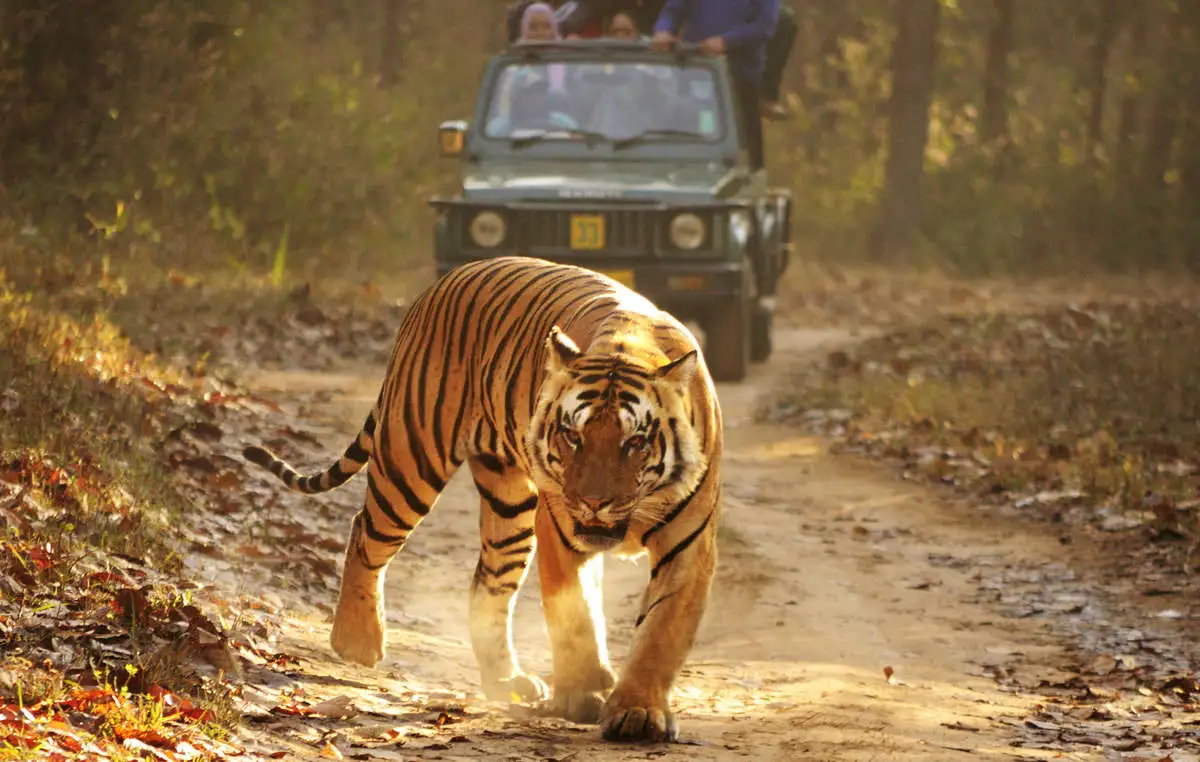

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a significant breakthrough, forest officials at Similipal National Park apprehended four armed poachers and two members of the timber mafia in separate locations on Saturday night.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is located within the Mayurbhanj District, in the Northernmost part of Odisha.
- Declared a 'Tiger Reserve' in 1956, STR became a part of the national conservation initiative 'Project Tiger' in 1973.
- Recognized by UNESCO in 2009, STR, along with a transitional area covering 2250 sq. km, was included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- Terrain: Surrounded by high plateaus and hills, STR boasts the twin peaks of Khairiburu and Meghashini, reaching 1515m above mean sea level.
- The undulating and hilly terrain features open grasslands and wooded areas, with the inclined plateau rising abruptly from the low coastal plains.
- Hydrography: The region is crisscrossed with perennial water sources, contributing to rivers like Budhabalanga, Salandi, and various tributaries of the Baitarani River.
- Vegetation: STR encompasses a diverse mix of forest types and habitats, with Northern tropical moist deciduous dominating alongside semi-evergreen patches.
- Notably, it hosts the world's only landscape with melanistic tigers.
- Tribes: The vicinity of STR is inhabited by various tribes, including Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara.
- Flora: Home to an impressive 1078 plant species, including 94 orchid species, STR is characterized by the dominance of Sal trees.
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including leopard, gaur, elephant, langur, barking and spotted deer, sloth bear, mongoose, flying squirrel, porcupine, turtle, monitor lizard, python, sambar, pangolin, and more.
What is the Special Tiger Protection Force (STPF)?
- Realizing the importance of ‘tiger protection’ in biodiversity conservation, the Finance Minister announced policy initiatives in February 2008, for constituting the ‘Special Tiger Protection Force’ (STPF).
- Based on the one-time grant of Rs. 50 crore was provided to the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) for raising, arming and deploying a Special Tiger Protection Force, the proposal for the said force has been approved by the competent authority for 13 tiger reserves.
- The STPF has been made operational in the States of Karnataka (Bandipur), Maharashtra (Pench, Tadoba-Andhari, Nawegaon-Nagzira, Melghat), Rajasthan (Ranthambhore), Odisha (Similipal) and Assam (Kaziranga), out of 13 initially selected tiger reserves, with 60% central assistance under the ongoing Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Project Tiger (CSS-PT).
Goan Cashew (kernel) Got the Geographical Indication (GI) Tag (Indian Express)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Goa Chief Minister Pramod Sawant hailed the recognition as a great opportunity for the cashew industry in the state and “a milestone towards the Swayampurna Goa mission”.
About Goan cashew:
- Cashew is one of the most important plantation crops in India, with significant cultivation in the state of Goa.
- Its introduction to India traces back to the 16th century (1570) when the Portuguese brought it from its native region in northeast Brazil, Latin America.
- Originally recognized for afforestation and soil conservation, cashews quickly gained prominence in Goa, occupying the largest area among horticultural crops.
- The climatic conditions conducive to its growth are well-suited to the Indian coastal areas, thriving under hot and humid circumstances.
Climatic Conditions:
- Soil and Climate: Well-drained deep sandy loam soils, ranging from sandy to laterite, prove to be ideal for cashew cultivation.
- Goa, known for its sandy loam, is a particularly favourable region for this crop.
- Adaptability: Cashew exhibits excellent adaptability to the coastal regions of India, thriving under temperatures ranging from 20 to 38 degrees Celsius.
- The relative humidity in the range of 60 to 95% is also conducive to its growth.
- Rainfall: Annual precipitation between 2000 to 3500mm supports the cultivation of cashews, ensuring optimal growth and development.
- Geographical Expansion: While traditionally associated with Goa, the cultivation of cashews is expanding to non-traditional areas in the plains of Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and some parts of the Northeast hill region.
- Cashew's journey from its introduction by the Portuguese to becoming a vital crop in Goan agriculture highlights its adaptability and significance in the diverse agro-climatic regions of India.
What is a Geographical Indication Tag?
- A Geographical Indication (GI) tag is a distinctive emblem affixed to products originating from a specific geographical area, signifying unique qualities or a reputation inherently tied to that origin.
- Primarily employed for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts, and industrial items, the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in India aims to facilitate the registration and enhanced safeguarding of geographical indications associated with various goods.
- Under this act, the granted GI tag holds validity for a period of 10 years, with the provision for renewal upon expiration.
Union Health Minister Launches MedTech Mitra Platform to Empower Medical Technology Innovators (NewsOnAir)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Health Minister Dr Mansukh Mandaviya has launched MedTech Mitra - a strategic initiative to empower MedTech innovators and advance healthcare solutions.
What is the MedTech Mitra Portal?
- The MedTech Mitra portal is an online platform designed to support medtech innovators by assisting in clinical evaluation, regulatory facilitation, and the adoption of new products in the medical technology sector.
- This collaborative initiative is overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), operating under the direction/guidance of NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission.
Significance:
- In conjunction with recent policies and incentive schemes, such as the medical devices policy and the production-linked incentive scheme, the MedTech Mitra platform aims to catalyze growth in the medical devices sector and promote domestic manufacturing.
- These initiatives seek to foster the indigenous development of affordable and high-quality MedTech devices and diagnostics, thereby significantly reducing the sector's reliance on imports.
- The platform is envisioned to streamline the innovation process and facilitate research and development for emerging start-ups, ensuring a smoother journey from concept to product.
- By offering comprehensive guidance, including support for animal and clinical trials, the platform aims to bridge gaps for startups and promote ease of innovation.
- The MedTech Mitra portal is poised to foster collaborations between engineers, scientists, and clinicians, addressing a previously existing gap in partnerships within the sector.
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) serves as the apex institution in India responsible for formulating, coordinating, and advancing biomedical research.
- With a primary mandate to conduct, coordinate, and implement medical research for societal benefit, ICMR is dedicated to translating medical innovations into tangible products and processes, subsequently integrating them into the public health system.
- Financial support for ICMR is provided by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
AstroSat detects millisecond X-ray bursts from high magnetic field neutron stars (DD News)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s first multi-wavelength space-based observatory, AstroSat, has detected intense sub-second X-ray bursts emanating from a neutron star with an ultrahigh magnetic field, known as a magnetar.
What is X-ray Bursts?
- X-ray bursts manifest in low-mass X-ray binary systems featuring a neutron star and a low-mass main sequence star orbiting each other.
- The occurrence of these bursts is intricately linked to the gravitational dynamics of the neutron star and its companion.
- In this system, the proximity and intense gravitational forces of the neutron star cause the companion star to exceed its Roche-lobe, leading to the formation of an accretion disk around the neutron star.
- This disk becomes a repository for hydrogen drawn from the overflowing companion star.
- As hydrogen accumulates on the neutron star's surface, the extreme temperatures and pressures prevailing there catalyze its transformation into helium.
- This ongoing process results in the formation of a thin surface layer of helium.
- When this helium layer reaches a critical mass, a sudden explosive ignition occurs, elevating the entire neutron star's surface temperature to several tens of millions of degrees and releasing a burst of X-rays.
- Following the outburst, the binary system returns temporarily to a quiescent state, allowing the neutron star to reaccumulate the helium surface layer gradually.
- This cyclic process leads to the recurrence of X-ray bursts, typically unfolding at regular intervals separated by several hours or days.
About Indias’ AstroSat:
- AstroSat stands as India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory, pioneering a mission focused on the simultaneous study of celestial sources across X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands.
- Launched with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, AstroSat took flight aboard the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota on September 28, 2015.
- It entered a 650 km orbit, inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The Mission Operations Complex (MOX) at ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru oversees the satellite throughout its mission life.
- With a minimum useful life of around 5 years, AstroSat is dedicated to achieving the following scientific objectives:
- Understanding high-energy processes in binary star systems housing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimating magnetic fields associated with neutron stars.
- Investigating star birth regions and high-energy processes in star systems beyond our galaxy.
- Detecting new, briefly bright X-ray sources in the celestial sphere.
- Conducting a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
India shedding mentality of slavery, says PM Modi (The Hindu)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Speaking at a "Veer Bal Diwas" event to commemorate the martyrdom of two sons of Guru Gobind Singh, PM Modi said their sacrifices are not only being remembered in India but also globally through programmes in other countries as well
About Veer Bal Diwas:
- Veer Bal Diwas is observed annually on December 26th to commemorate the valour and sacrifice of the four sons of Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh guru.
- The four sons, named Zorawar Singh, Fateh Singh, Jai Singh, and Kulwant Singh, played a significant role in resisting the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his army.
- Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh were captured by the Mughals at the ages of six and nine, respectively, after defending the fort of Anandpur Sahib from a siege.
- Subsequently, they were taken to Sirhind, where, steadfast in their faith, they refused to convert to Islam and were sentenced to a tragic death by being bricked alive in 1705.
- Jai Singh and Kulwant Singh, also captured at Anandpur Sahib, managed to escape from Sirhind with the assistance of loyal followers.
- They later joined their father in his final battle at Sirhind, where Guru Gobind Singh was wounded by a musket shot.
- The unwavering courage and sacrifice of Guru Gobind Singh's sons became a symbol of inspiration for generations of Sikhs, reflecting their dedication to the cause of Sikhism.
About Guru Gobind Singh:
- Guru Gobind Singh, the last of the ten Sikh Gurus, was born on December 22, 1666, in Patna, Bihar.
- His birth anniversary is observed according to the Nanakshahi calendar.
- Assuming the role of Sikh Guru at the tender age of nine after the passing of his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, he served until his assassination in 1708.
Contributions:
- Religious: Guru Gobind Singh made profound contributions to the Sikh religion, introducing practices such as wearing a turban to cover hair.
- He laid the foundation for the Khalsa (1699), embodying the Five 'K's: kesh (uncut hair), kanga (wooden comb), kara (iron or steel bracelet), kirpan (dagger), and kachera (short breeches).
- These articles of faith became integral to the identity of a Khalsa.
- Establishing various rules for Khalsa warriors, including abstaining from tobacco, alcohol, and halal meat, Guru Gobind Singh emphasized their duty to protect innocent people from persecution.
- Guru Gobind Singh designated Guru Granth Sahib as the spiritual guide for both the Khalsas and Sikhs.
- Martial: Engaging in the battle of Muktsar in 1705, Guru Gobind Singh fiercely opposed the Mughals.
- The Battle of Anandpur in 1704 resulted in the tragic loss of the Guru's mother and two minor sons, who were executed. His eldest son also fell in battle.
- Literary: Guru Gobind Singh's legacy includes compositions like Jaap Sahib, Benti Chaupai, and Amrit Savaiye.
- Notably, he wrote the Zafarnama, a letter addressed to the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, showcasing his literary prowess and resilience.
‘Dunki’ and immigration: How the first modern passports came to be (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The recently released Shah Rukh Khan’s movie ‘Dunki’ is said to be based on the ‘donkey route’ or ‘donkey flight’ that lakhs of Indians take to reach countries like the US, the UK or some other European countries.
What is a Donkey Journey?
- Dunki is the Punjabi idiom that means to "hop from place to place", according to the Migration Policy Institute (MPI).
- It is a colloquial term for "donkey flights" or the "donkey flights method", which is a dangerous illegal immigration technique involving crossing a country's borders through a backdoor route via multiple stops in other countries.
How does the donkey flight method or dunki work?
- The desire for a higher quality of life has given rise to an industry driven by "agents" who charge exorbitant fees to help smuggle people to the country of their choice.
- Some agents may even run legitimate businesses while offering this dangerous option.
- The agents can offer various services, from fake papers to help through otherwise legal migration processes to smuggling people through ship containers.
Which countries are most targeted using the Dunki method?
- While donkey flight can be used to enter any country, the US, Canada, and the UK are some of the most popular destinations undertaken by Indian immigrants.
- According to a report, between February 2019 and March 2023, as many as 149,000 Indians were detained for attempting to enter the US illegally.
- Of this, most of those detained were from Gujarat and Punjab.
Risks involved in the dunki method:
- Dunki comes with tremendous risks, including the risk of capture, imprisonment, and deportation.
- When facilitated by an agent, the system is highly exploitative.
- Many sell off their assets, including ancestral land, to pay these agents.
- Agents may also withhold people's passports or other important documents to extort more money and assets.
- Moreover, smuggled migrants are also more vulnerable to becoming victims of other crimes during the smuggling process.
- The terrains of the places through which immigrants may have to travel pose a range of risks, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrains, and access to basic resources like food and water.
- It must be noted that migrant smuggling is not the same as human trafficking.
- However, these crimes may sometimes interlink, adding another layer of risk for those engaging in illegal immigration.
About Passports:
- Rooted in history, passports trace back to mentions in the Hebrew Bible and structured systems in nations like France and the UK.
- The evolution into modern passports was catalyzed by the British Nationality and Status of Aliens Act in 1914, introducing features such as photographs and distinctive characteristics.
- The League of Nations' 1920 conference sought to standardize passport regulations, contributing to the establishment of a common British system.
- During the 1920s, the United States linked immigration laws to passports, imposing limitations on inflows.
- Despite initial reservations, passports have persisted as an integral element of contemporary citizenship.
- Indian Passports: The initiation of issuing Indian passports dates back to the First World War (1914-1918) through the Defence of India Act, as mandated by the British government for travel.
Assam-Meghalaya panels for boundary dispute to submit reports by December 31 (The Hindu)
- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The regional committees on the boundary dispute between Assam and Meghalaya have been asked to submit their reports by December 31, a Meghalaya government official said on Friday, December 22.
What is the Assam-Meghalaya Border Dispute?
- The Assam and Meghalaya have a longstanding dispute in 12 stretches of their 884-km shared border.
- The areas include Upper Tarabari, Gazang Reserve Forest, Hahim, Langpih, Borduar, Boklapara, Nongwah, Matamur, Khanapara-Pilangkata, Deshdemoreah Block I and Block II, Khanduli, and Retacherra.
Historical Context:
- During British rule, undivided Assam encompassed present-day Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Mizoram.
- Meghalaya was delineated in 1972, following the Assam Reorganisation (Meghalaya) Act of 1969, but differing interpretations of the border emerged.
- In 2011, Meghalaya identified 12 disputed areas, covering approximately 2,700 sq km.
Key Point of Contention:
- A focal point of discord is Langpih in West Garo Hills, bordering Kamrup district in Assam.
- Post-Independence, Langpih transitioned from Kamrup district to Garo Hills and Meghalaya.
- Assam contends it's part of the Mikir Hills, while Meghalaya questions the inclusion of Blocks I and II of the Mikir Hills (now Karbi Anglong) in Assam.
Efforts to Resolve Dispute:
- In 1985, an official committee, led by former Chief Justice of India Y V Chandrachud, was formed but didn't yield a resolution.
- Both states identified six out of 12 disputed areas for resolution, resulting in a Memorandum of Understanding in March 2022.
- The second round of discussions for the remaining areas commenced in November 2022.
Potential Solutions:
- Utilizing satellite mapping for precise border demarcation.
- Leveraging constitutional provisions like Article 263 for the Inter-state Council to advise on disputes and coordinate policies.
- Reviving Zonal Councils to address common concerns among states in each zone, including border disputes and economic planning.
- Embracing the spirit of cooperative federalism to strengthen India's unity in diversity.
IIT Guwahati researchers devise mathematical model to help prevent riverbank erosion (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati has developed a new award-winning mathematical model to help prevent erosion of rivers like Brahmaputra.
What is BRAHMA-2D?
- BRAHMA-2D (Braided River Aid: Hydro-Morphological Analyzer) is a sophisticated mathematical model designed for assessing the flow dynamics of expansive braided rivers such as the Brahmaputra.
- Functioning as a quasi-3D river flow model, BRAHMA-2D offers insights into water velocity at various depths within the river and the circulation patterns around structures like spurs, crucial for preventing river bank erosion.
- Developed through collaboration between researchers at IIT Guwahati and the Brahmaputra Board under the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti, this innovative model plays a pivotal role in the design of sustainable hydraulic structures.
- Engineers can leverage BRAHMA-2D to create effective structures like spurs, river bends, and other protective measures to combat river bank erosion.
- The model's successful validation on the Brahmaputra River near Majuli Island in Assam, a region prone to river bank erosion, underscores its practical applicability.
- BRAHMA-2D integrates a two-dimensional water movement model with entropy theory, focusing on disorder or randomness.
- Notably, it identifies a unique dip phenomenon near spurs, where water flows underneath intensifies—a phenomenon absent at points away from these structures.
- Beyond erosion prevention, BRAHMA-2D extends its utility to environmental studies by assessing the habitat suitability of aquatic species, particularly endangered ones.
- This assessment is based on factors such as required depth and flow velocity, showcasing the model's versatility in addressing multifaceted challenges in river ecosystems.
About Brahmaputra River:
- Originating as Siang or Dihang from the Chemayungdung glacier in the Kailash range near Mansarovar Lake, the Brahmaputra enters India to the west of Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Dibang, Lohit, Siang, Burhi Dihing, Tista, and Dhansari contribute to its flow.
- This perennial river exhibits distinctive features influenced by its geography and prevailing climatic conditions.
- Experiencing biannual flooding, the first occurs from the melting Himalayan snow in summer, and the second is a consequence of monsoon flows.
- Climate change has amplified the frequency and intensity of these floods, posing a threat to populations and food security in the lower riparian states of India and Bangladesh.
- Known for its dynamism, the Brahmaputra undergoes frequent changes in course, driven by landslides and geological activities.
Three heritage projects in Punjab and Haryana bag UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards 2023 (Business Standard)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The resilient urban revitalisation of Rambagh Gate and Ramparts in Punjab, and heritage conservation projects related to Haryana's Church of Epiphany and Delhi's Bikaner House won Unescoawards on Thursday.
About Rambagh Gate & Ramparts:
- A three-story architectural marvel, the Rambagh Gate underwent meticulous restoration employing traditional building techniques.
- Locally sourced materials, including Nanak Shahi bricks set in lime mortar, were integral to the restoration process.
About Pipal Haveli, Gurdaspur:
- Pipal Haveli in Gurdaspur stands as a testament to ecological and traditional building methods, incorporating locally sourced materials and embracing vernacular architectural language.
- Notably, it actively promotes women's empowerment through initiatives like the BaRi Collective, offering programs that enhance women's livelihoods through environmentally conscious craft practices.
What is the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation?
- UNESCO aims to promote private sector engagement and foster collaborations between the public and private sectors to preserve the cultural heritage of the Asia-Pacific region for the benefit of present and future generations.
- Since the year 2000, the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation have been acknowledging the accomplishments of private sector entities and public-private initiatives in effectively conserving or restoring structures, places, and properties of significant heritage value in the region.
- Noteworthy, among the recognized sites, five are located in China, six in India, and one in Nepal.
- Highlights of Award-Winning Sites in India:
- Rambagh Gate in Amritsar: Received the prestigious "Award of Excellence," the highest recognition across all categories.
- Pipal Haveli in Punjab: Honored for its sustainable development as a heritage rural homestay.
- Karnikara Mandapam at Kunnamangalam Bhagawati Temple in Kerala: Earned the esteemed "Award of Distinction."
- Epiphany in Haryana, David Sassoon Library and Reading Room in Mumbai, and Bikaner House in New Delhi: Recognized with the "Award of Merit" for their outstanding contributions to cultural heritage conservation.
CISF to take over security of Parliament complex after Lok Sabha breach | What's the plan (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Home Ministry has approved the deployment of the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) in the Parliament complex, according to a government order.
News Summary:
- Following the security breach on December 13, the Union Home Ministry has given the green light for CISF deployment in the Parliament complex.
- Collaborating with Parliament Security Services, CISF will oversee access control for both the new and old Parliament buildings.
What are the Current Security Arrangements in Parliament?
- The Delhi Police currently handles access control, including frisking and baggage scanning.
- In response to the recent incident, eight Delhi Police security personnel responsible for these duties were suspended.
- In the event of armed intervention, the Parliament Duty Group (PDG), an armed unit of the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), is deployed.
- The overall responsibility for security lies with the Parliament Security Service under the Lok Sabha Speaker.
About Central Industrial Security Force (CISF):
- Established under the Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968, CISF is a key Central Armed Police Force (CAPF).
- Initially formed in 1969 with three battalions, it has evolved into a versatile organization boasting a current strength of 1,63,590 personnel.
- Operating under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Home Affairs, CISF's headquarters is situated in New Delhi.
Key Operations:
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: Safeguarding 353 establishments nationwide, including Atomic Power Plants, Space Installations, Defence Production Units, Mines, Oil Fields, and Refineries.
- Fire Protection: Maintaining a dedicated Fire Wing catering to 104 establishments for fire safety services.
- VIP Security: Mandated to provide security to VIP protectees categorized as Z+, Z, Y, and X across the country.
- Airport Security: Entrusted with the specialized task of airport security since 2000, following the hijacking of Indian Airlines Flight IC-814 to Kandahar.
- Private Sector Security: Authorized by an amendment to the CISF Act, the force offers security services, on a payment basis, to vital private and joint venture industrial entities contributing to the nation's security and economy.
- Examples include Infosys campuses, Patanjali Food and Herbal Park, and the Reliance refinery.
- Overseas Deployment: Contributing contingents to the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH).
- CISF stands out as the only Central Armed Police Force with a daily public interface, playing a crucial role in securing airports, the Delhi Metro, and iconic monuments.
NSG Takes on Invasive Vilayati Kikar/Prosopis Juliflora (Indian Express)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The National Security Guard (NSG) is actively combating the encroachment of the invasive plant species known as vilayati kikar at its Manesar campus, situated near the Delhi-Ajmer highway.
What is Prosopis Juliflora?
- Prosopis juliflora, a shrub or small tree belonging to the Fabaceae family and classified as a type of mesquite, is indigenous to Mexico, South America, and the Caribbean.
- Introduced to Delhi by the British in the 1920s during the construction of the national capital, this species is locally known by various names in India, including Bellary jaali, seemai karuvelam, seemai jaali, gando baval, and vilayati kikar.
- Known for its high ecological adaptability, Prosopis juliflora can thrive in diverse soil types, ranging from sand dunes to clay, and from saline to alkaline soils.
- It exhibits a wide altitude range, growing below 200 to above 1500 meters above sea level, with a mean annual rainfall varying from 50 to 1500 mm.
- However, despite its adaptability, it is recognized as an invasive plant with a propensity for vigorous growth, enabling it to outcompete indigenous plant species.
Impacts on the Environment: This invasive species pose significant environmental challenges:
- Prosopis juliflora absorbs more than four litres of water to produce one kilogram of biomass.
- The plant generates less oxygen and more carbon dioxide, making it less conducive to supporting bird habitats.
- It has the potential to contaminate groundwater, posing risks to the overall quality of this vital resource.
- The species contributes to land erosion by displacing grasslands that serve as habitats for native plants and animals.
- The invasive nature of Prosopis juliflora raises concerns about its ecological impact and necessitates efforts to manage and control its spread in affected regions.
Govt Notifies Changes in PLI Scheme for White Goods (Business Standard)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The central government has introduced changes to the rules governing the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for white goods, specifically air conditioners and light-emitting diode lights, with the goal of ‘simplifying the scheme’s operations’ and promoting the ease of doing business, according to an official statement on Wednesday.
What are White Goods?
- Major home appliances, commonly known as white goods, encompass substantial household devices like stoves, refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, tumble dryers, dishwashers, and air conditioners.
- While these durable consumer durables were initially available only in white, contemporary options offer a variety of colours, yet they persistently retain the term "white goods."
- Renowned for their robustness and extended lifespan, white goods are engineered to endure the rigours of daily use.
- Additionally, the term "white goods" may extend to white fabrics, particularly linen or cotton, including items like curtains, towels, or sheets, which historically were crafted from white cloth.
- In the beverage industry, the term "white goods" refers to colourless spirits such as vodka or gin.
What is Brown Goods?
- Brown goods refer to relatively lightweight electronic consumer durables, including computers, digital media players, TVs, and radios.
- In contrast to large household appliances (white goods), brown goods are primarily geared towards entertainment, communication, and convenience.
- Typically featuring electronic components, these devices are designed to deliver audio, video, or data-related services as their primary functions.
What is Grey Goods?
- When a commodity is traded through distribution channels, which are unofficial but legal are known as the grey goods.
- They are goods that are traded in a specific area, where the manufacturer does not intend to sell the product, but with different specifications.
- Grey goods are sold without the knowledge of the original manufacturer.
- They are typically less costly than the ones that are available by the authorised distributor.
- Also, they might be made to pertain to some jurisdiction.
- Example: A factory-unlocked version of the iPhone. It is made to suit US standards but is sold in India for a lesser price than the iPhone made for Indian standards.
- When it comes to such Grey goods, the manufacturer does not provide any warranty for the product.
Migratory Birds Arrive in Odisha’s Chilika Before Winter (DownToEarth)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Migratory birds have started their annual journey to Chilika Lake—India’s largest waterbird habitat in Odisha — ahead of winter this year.
About Chilika Lake:
- Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lake and a shallow lagoon with estuarine character spread across the districts of Puri, Khurda and Ganjam in the state of Odisha in eastern India.
- It is considered to be the largest lagoon in India and is counted amongst the largest lagoons in the world.
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory waterfowl found anywhere on the Indian sub-continent.
- It is one of the hotspots of biodiversity in the country, and some rare, vulnerable and endangered species listed in the IUCN Red List of threatened Animals inhabit the Lake area for at least part of their life cycle.
- On account of its rich bio-diversity, Chilika Lake was designated as a "Ramsar Site", i.e. a wetland of International Importance.
- The Nalaban Island within the lake is notified as a Bird Sanctuary under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The National Wetlands, Mangroves and Coral Reefs Committee of the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India, have also identified the lake as a priority site for conservation and management.
- The Lake is a highly productive ecosystem, with rich fishery resources.
- The rich fishing grounds sustain the livelihood of more than 0.2 million fisherfolk who live in and around the lake.
- It has a great heritage value and maritime trade to the far east countries used to take place from here.
- It is the largest winter ground of migratory birds in the Indian sub-continent and home to more than 150 highly threatened Irrawaddy dolphins, which is the largest lagoonal population globally.
- It supports some of the largest congregation of migratory birds from large parts of Asia, particularly during the winters that arrive from as far as the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea, remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia, Central and South East Asia, Ladakh and the Himalayas to feed and breed in its fertile waters.
NASA Recently Shared a Satellite Image of Deception Island (Tribune India)
- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) recently shared a satellite image of Deception Island, one of the only places in the world where a ship can sail directly into the centre of an active volcano.
About Deception Island:
- Deception Island is situated within the South Shetland Islands, forming part of an archipelago northwest of the Antarctic Peninsula.
- This volcanic island is notable for its dynamic features and distinct geography.
- Originating from a colossal volcanic eruption, Deception Island's formation resulted in the collapse of its central structure, allowing seawater to inundate the resulting caldera.
- The landscape is characterized by desolate volcanic slopes, steaming beaches, and glaciers adorned with ash layers, creating a unique horseshoe-shaped entrance to the sea via Neptune’s Bellows.
- The island encircles Port Foster, recognized as one of the safest harbours in the Antarctic, offering vessels a rare opportunity to navigate into the heart of an active volcano.
- Among the few places globally where this is possible, Deception Island has experienced over twenty eruptions since the 19th century.
- Notably, the island witnessed three volcanic eruptions from 1967 to 1970, leading to the destruction of Chilean and British stations.
- Presently, Argentina and Spain maintain summer scientific stations on the island.
- Deception Island is safeguarded under the Antarctic Treaty, designating it as a protected area with restricted human visits and minimized environmental impact.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of an Autonomous Body Mera Yuva Bharat (PIB)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has approved the establishment of an autonomous body Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat).
About Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat):
- Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat), an autonomous body will benefit the youth in the age group of 15-29 years, in line with the definition of ‘Youth’ in the National Youth Policy.
- In the case of programme components specifically meant for adolescents, the beneficiaries will be in the age group of 10-19 years.
- It will help in Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and to make the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- It will be launched on 31st October 2023 on National Unity Day.
Objective:
- The primary objective of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) is to make it a whole of Government platform for youth development.
- With access to resources & connection to opportunities, youth would become community change agents and nation builders allowing them to act as the Yuva Setu between the Government and the citizens.
- It seeks to harness the immense youth energy for nation-building.
The establishment of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) would lead to:
- Leadership Development in the Youth:
- Improve leadership skills through experiential learning by shifting from isolated physical interaction to programmatic skills.
- Investing more in youth to make them social innovators, and leaders in the communities.
- Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and making the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- Better alignment between youth aspirations and community needs.
- Enhanced efficiency through Convergence of existing programmes.
- Act as a one-stop shop for young people and Ministries.
- Create a centralized youth database.
- Improved two-way communication to connect youth government initiatives and activities of other stakeholders that engage with youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem.
Why There is a Need for Such Initiative?
- India’s youth are to play a critical role in defining the future of the nation.
- There is a need to establish a new contemporary technology-led platform for the Government to engage with the present-day youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem
- Mera Yuva Bharat supported by a technology platform would help to increase the Youth outreach efforts of the Department of Youth Affairs.
Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan Now Opens for Safari Tours (TOI)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The forest department started the inaugural jungle safari at the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on Monday, which marks the beginning of organised tiger reserve tours for tourists in four locations across the state.
About Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, also known as Darrah Wildlife Sanctuary, spans across four districts – Bundi, Kota, Jhalawar, and Chittorgarh in Rajasthan.
- The reserve is nestled in a valley formed by two parallel mountains, Mukundra and Gargola.
- Establishment: In 2013, the tiger reserve was formed, encompassing Mukandra National Park, Dara Sanctuary, Jawahar Sagar Sanctuary, and a section of Chambal Sanctuary.
- Initially, it served as a hunting preserve for the Maharaja of Kota.
- River: Positioned on the eastern bank of the Chambal River, the reserve is crisscrossed by its tributaries.
- Vegetation: The reserve features a Dry Deciduous Forest.
- Flora: The dominant species is Kala Dhok or Kaladhi (Anogeissus pendula), accompanied by Khair, Ber, Kakan, Raunj, and more.
- On elevated slopes, Anogeissus pendula gives way to Anogeissus latifolia, coexisting with Bel, Salar, Uum, and Shisham.
- Fauna: Noteworthy fauna include Leopard, Sloth bear, Nilgai, Chinkara, Spotted Deer, Small Indian Civet, Toddy Cat, Jackal, Hyena, Jungle Cat, and Common Langur, among others.
- The region is also home to various reptiles and amphibians, such as Pythons, Rat Snake, Buff-striped keelbacks, Green keelbacks, crocodiles, turtles, Gharial and Otters.
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Says Unemployment Rate Declined (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) has reported that the unemployment rate in the country has shown a decrease between April and June 2023.
Key Observations of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Improved Work Metrics: Both the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) and Worker-Population Ratio (WPR) showed positive trends in the recent period.
- Urban Employment Trends: In urban areas, LFPR increased from 47.5% (April-June 2022) to 48.8% (April-June 2023) for individuals aged 15 and above.
- The WPR in urban areas rose from 43.9% (April-June 2022) to 45.5% in the corresponding months this year.
- Gender-specific Changes:
- Male LFPR increased from 68.3% to 69.2%.
- Female LFPR showed notable growth from 18.9% to 21.1% during the observed period.
What is the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Conducted by the National Sample Survey (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Launched in April 2017 by the National Statistical Office (NSO) to provide more frequent labour force data.
Objectives:
- Estimate key employment and unemployment indicators every three months for urban areas.
- Annually estimate indicators for both 'Usual Status' and 'Current Weekly Status' in rural and urban areas.
- Key Indicators:
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): Percentage of individuals in the population who are part of the labour force (working, seeking, or available for work).
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): Percentage of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): Percentage of unemployed persons among those in the labour force.
- Current Weekly Status (CWS): Activity status determined based on the activities in the last 7 days before the survey.
India to Hold Satellite Spectrum Auctioning (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Elon Musk vs Mukesh Ambani battle on whether to auction or allocate satellite spectrum has attracted intervention from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
What is Satellite Spectrum?
- The satellite spectrum is like a special section of radio waves reserved for satellites when they're up in space.
- It's part of the larger family of radio waves that we use for things like Wi-Fi, TV, and radio.
- This spectrum serves as a vital resource for countries, facilitating satellite broadcasting, communication, and weather services.
Key Points:
- Limited Resource: The satellite spectrum is finite, allocated for activities like satellite broadcasting and communication.
- It plays a crucial role in facilitating services provided by communication satellites and weather satellites.
- Frequency Bands: The spectrum is categorized into different frequency bands, chosen based on diverse applications.
- The frequency assigned during a satellite's construction remains unchanged post-launch.
- Impact on Data Transfer: The frequency of a signal dictates the speed of data transfer.
- Higher frequencies enable faster data transmission, but they also entail shorter wavelengths, leading to signal attenuation over distances and increased interference risks.
- Frequency Range: Satellites typically transmit in the frequency range of 1.5 to 51.5 gigahertz.
- High-speed broadband operations often use the higher end of this spectrum.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Founded in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, later becoming a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Functions:
- Allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordinates and sets technical standards for telecommunication/ICT.
- Strives to enhance ICT access in underserved communities globally.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- India's Association with ITU: India has actively participated in the ITU since 1869, maintaining a consistent presence on the ITU Council since 1952.
New Species of Bagworm Moth discovered From Idukki (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers from the Zoology Department at St. Thomas College (Autonomous), Thrissur, have discovered a new species of bagworm moth, Wizard Bagworm, from near the Nariyampara Falls in the Idukki district.
What is a Bagworm Moth?
- Belonging to the family of moths in the order Lepidoptera, bagworm moths are recognized for their protective larval cases.
- These moths are distributed globally, with notable populations in North America and Africa.
- In their larval stage, these perennial moths inhabit various evergreen trees and junipers.
- They derive their name from the bag-like cases constructed by the larvae around themselves.
- The larvae can pose a threat to trees, particularly evergreens.
About Eumasia Venefica:
- This recently identified species earned its name due to the unique shape of its bag, resembling a wizard's hat.
- It is the fourth species within this genus to be documented in India.
- Distinctive Features:
- The species exhibits effective camouflage techniques to evade predators.
- Larval cases of Eumasia venefica are discovered attached to rocks adorned with lichens.
- These cases join together, forming a colony covered with lichens.
- The larval bags bear a resemblance to a 'witch's hat,' featuring a disc-like anterior and a tubular posterior part.
- Unlike polyphagous pests, the larvae of this species exclusively feed on algae and mosses present on rocks.
Pontus Tectonic Plate: Geologist Unexpectedly Finds Remnants of a Lost Mega-Plate (Science Daily)
- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Geologists have reconstructed a massive and previously unknown tectonic plate that was once one-quarter the size of the Pacific Ocean.
About Pontus Tectonic Plate:
- Recently discovered in the west Pacific Ocean, the Pontus Tectonic Plate is a long-lost geological plate that holds significance in Earth's history.
- Believed to have measured about 15 million square miles at its zenith, roughly equivalent to one-quarter of the Pacific Ocean, this massive tectonic plate dates back as far as 160 million years, with more recent traces extending to approximately 20 million years ago.
- Over millions of years, the Pontus Plate underwent a gradual subduction process, pulled downward beneath a neighbouring plate by the force of gravity.
How was this Discovery Made?
- The subducting process involves the plate sinking into Earth's mantle due to its higher density compared to the surrounding mantle.
- Traces of a subducted plate are discernible in the form of rock fragments concealed in mountain belts.
- During subduction, upper portions of the plate are occasionally scraped off.
- Researchers employed geological data and computer modelling to reconstruct the movements of current plates, revealing a substantial area potentially vacated by the subducted Pontus Plate.
- Utilizing magnetic techniques, scientists identified basalt remnants in Borneo as Pontus relics, suggesting that this fragmentary evidence was left behind during the plate's subduction some 85 million years ago.
What is Plate Tectonics?
- Tectonic plates are large, rigid pieces of Earth's lithosphere, the outer shell comprising the crust and uppermost part of the mantle.
- These plates, which vary in size and shape, constantly move and interact, shaping the Earth's dynamic surface.
- The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several major plates, such as the Pacific, North American, and Eurasian plates, among others.
- The interactions at plate boundaries result in various geological phenomena, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- Plate tectonics, the theory explaining these movements, underscores how heat-driven convective currents in the Earth's mantle cause plates to diverge, converge, or slide past each other.
- Tectonic plate movements influence the planet's topography, seismic activity, and the distribution of continents and oceans, playing a fundamental role in Earth's geological evolution.
Reliance General gets ?923cr GST notices from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) (TOI)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Reliance General Insurance Company (RGIC), a subsidiary of the Anil Ambani-led Reliance Capital, has received multiple show-cause notices worth Rs 922.58 crore from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI).
About Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI):
- Formerly known as the Directorate General of Central Excise Intelligence (DGCEI), the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) stands as a premier intelligence organization operating under the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs, within the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Its primary focus is on collecting, collating, and disseminating intelligence pertaining to Goods and Services Tax (GST) evasion and duties related to Central Excise and Service Tax on a pan-India basis.
- Evolution: Originally designated as the Directorate General of Anti-Evasion (DGAE), it was established in 1979 as an independent wing under the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, New Delhi.
- Became a full-fledged Directorate in 1983, headed by a Director.
- In 1988, attained the status of Directorate General under a Director General.
- Currently comprises 04 offices of the Director General (East, West, North, and South), 26 Zonal Units, and 40 Regional Units.
Key Responsibilities:
- Intelligence Gathering: Collects information from various sources, including GST returns, financial statements, and other documents, to identify potential GST law violations.
- Investigation: Empowered to conduct investigations into suspected cases of GST evasion or non-compliance, involving summoning individuals, examining records, and executing searches and seizures.
- Enforcement: Enforces provisions of the GST law, taking legal action against offenders, imposing penalties, and recovering taxes or duties owed.
- Additional Functions: Collaborates with agencies like the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) and State GST authorities for effective GST law implementation.
- Plays a crucial role in raising awareness about GST compliance and educating taxpayers on their legal obligations.
- Provides technical and legal assistance to field officers and other government entities involved in GST administration.
Mandarin-Trained Territorial Army Inducted At LAC (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently the Territorial Army (TA) has inducted its first batch of Mandarin-trained officers to support the regular Army's efforts to enhance expertise in the Chinese language.
What is the Territorial Army (TA)?
- The Indian Territorial Army (TA) acts as the second line of defence, complementing the regular Indian Army.
- It is distinct in its role, being neither a profession, occupation, nor a source of employment.
- Reserved for individuals engaged in mainstay civilian professions, gainful employment or self-employment in a civil field is a prerequisite for joining the TA.
Key Roles:
- Relieving Regular Army: Primarily tasked with relieving the Regular Army from static duties.
- Assistance in Emergencies: Provides crucial assistance to civil authorities during natural calamities and tragedies.
- Essential Services: Aids civil administration in delivering essential services, particularly in areas facing stretched state machinery or security threats.
Service Commitment:
- Part-Time Service: TA volunteers typically serve in uniform for a few days annually, ensuring their readiness to bear arms for national defence during emergencies.
Historical Background:
- Established by the British in 1920 through the Indian Territorial Act, organized into 'The Auxiliary Force' for Europeans & Anglo-Indians and 'The Indian Territorial Force' for Indian Volunteers.
- The Territorial Army Act of 1948 formalized the TA, inaugurated by the first Indian Governor General, Shri C Rajagopalachari, on 9th October 1949.
- Motto: Savdhani Va Shoorta (Vigilance and Valour).
Eligibility Criteria:
- Nationality: Open to Indian citizens (Men & Women).
- Age: 18 to 42 years.
- Education: Graduate from any recognized university.
- Physical Standards: Must be physically and medically fit.
- Employment: Gainful employment in civilian professions.
- Exclusions: Serving members of the Regular Army/Navy/Air Force/Police/GREF/Para Military and similar forces are ineligible.
New Ensign for the Indian Air Force (HT)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Air Force (IAF) Chief Air Chief Marshal (ACM) Vivek Ram Chaudhari on Sunday unveiled a new Ensign for the force, as it marked its 91st anniversary, by the inclusion of the Air Force Crest in the top right corner of the Ensign, towards the fly side.
About the Indian Air Force (IAF) Ensign:
- The new IAF Ensign exclusively incorporates the IAF Crest, featuring distinctive elements that symbolize the spirit and ethos of the Indian Air Force.
Key Elements:
- IAF Crest: The crest prominently showcases the national symbol, the Ashoka Lion, atop, with "Satyamev Jayate" in the Devanagari script beneath.
- Himalayan Eagle: Positioned below the Ashoka Lion, a Himalayan eagle with outstretched wings symbolizes the formidable fighting spirit of the IAF.
- Light Blue Ring: Encircling the Himalayan eagle, a light blue ring bears the words "Indian Air Force."
- IAF Motto: Derived from the Bhagavad Gita, the motto "Nabha Sparsham Deeptam" (touching the sky with glory) is inscribed in golden Devanagari below the eagle.
- The IAF crest serves as a powerful symbol of inspiration and encouragement.
Variations:
- IAF has adopted various crests for commands, squadrons, and other establishments, all adhering to a standard frame featuring the formation sign and a motto at the foot.
Historical Evolution:
- British Era: During the British era, the IAF was known as the Royal Indian Air Force, and its ensign featured the Union Jack and the RIAF roundel.
- Post-Independence: The current IAF Ensign, created post-independence, replaces the Union Jack with the Indian tricolour and the RAF roundels with the IAF tri-colour roundel in the lower right canton.
Govt Mulling Incentives for ASHA Workers (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The government is planning to give incentives to ASHA health activists for mobilising eligible individuals for sickle cell disease screening and distribution of sickle cell cards for prevention and early detection of the disease.
About Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA):
- ASHA serves as a trained female community health activist integral to the National Rural Health Mission initiated by the Government of India.
- Selected from the community and accountable to it, ASHA is trained to bridge the gap between the community and the public health system.
Key Functions:
- Acts as a care provider at the community level.
- Facilitates access to healthcare, medicine, and sanitation services.
- Health Awareness: Raises awareness of health issues among marginalized sections within the community.
- Advocate for Women's Health: Champions female health and hygiene standards.
- Advocates for a health-conscious approach to livelihood.
Implementation:
- The ASHA scheme is operational in all States/UTs, except Goa.
- States are mandated to employ at least one ASHA worker per every 1000 people.
- Inclusive Selection Process: The selection process involves various community groups, self-help groups, Anganwadi Institutions, and local committees.
Selection Criteria:
- Rural ASHA: Preferably a literate woman resident, married/widowed/divorced, aged 25 to 45 years, and preferably educated up to the 10th standard.
- Urban ASHA: Identified from vulnerable clusters, belonging to specific vulnerable groups, with good communication and leadership skills.
Compensation:
- Primarily an honorary volunteer compensated for specific situations.
- Ranges from Rs 2,000 to Rs 7,000, depending on the state.
- Incentives: Eligible for incentives under various national health programs.
Adani Ports' Flagship Mundra Port Completes 25 Years (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Mundra Port in Gujarat has completed 25 years of its operations, highlighting its expansion and evolution as one of the largest ports globally.
About Mundra Port:
- Mundra Port stands as India's largest private and container port, situated on the north shores of the Gulf of Kutch near Mundra in the Kutch district of Gujarat.
- As a deep-draft, all-weather port, it holds the distinction of being a Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
- Managed by Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ), the port is a pivotal player in India's cargo movement, accounting for nearly one-fourth of the nation's total.
- Mundra Port plays a crucial role in managing 33% of the country's container traffic.
- Key Features: Strategic Location: Positioned on the Gulf of Kutch, Gujarat.
- Handling Capacity: With an impressive capacity of 260 MMT, the port efficiently manages over 155 MMT (FY 2022-23), contributing to almost 11% of India's maritime cargo.
- Infrastructure: Boasting 26 berths and two single-point moorings, the port accommodates diverse vessels and handles various cargo types, including containers, dry bulk, break bulk, liquid cargo, and automobiles.
- Coal Import Terminal: Home to the nation's largest coal import terminal, Mundra facilitates swift cargo evacuation with minimal turnaround time.
- Rail Connectivity: The port's rail network is seamlessly integrated into the national rail network, ensuring efficient cargo handling for destinations across India.
SUGAM REC Mobile App for 54EC Bonds Investors (PIB)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, REC Limited, the Maharatna Central Public Sector Enterprise launched a SUGAM REC mobile application.
What is the SUGAM REC App?
- The SUGAM REC App caters exclusively to current and prospective investors in REC's 54EC Capital Gain Tax Exemption Bonds.
- Users can conveniently download e-bond certificates, apply for new investments, access essential forms for KYC updates, and connect with REC's Investor Cell through call, email, or WhatsApp.
What are 54EC Bonds?
- Also known as Capital Gain Bonds, these fixed-income instruments offer capital gains tax exemption under section 54EC.
- Investors can save on income tax for long-term capital gains by investing in these bonds within six months of the gain.
- With a fixed lock-in period of 5 years, the bonds can be held in either Physical or Demat form.
- Issued by government-managed institutions, they fund specific capital projects and derive their name from the relevant section of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Key Facts about REC Limited:
- A 'Maharatna' company under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- Registered with RBI as a non-banking finance company (NBFC), Public Financial Institution (PFI), and Infrastructure Financing Company (IFC).
- Established in 1969 to address severe drought and famine, focusing on energizing agricultural pump sets for irrigation and reducing reliance on monsoons.
- Provides long-term loans and financing products to State, Centre, and Private Companies for infrastructure asset creation.
- It is the nodal agency for initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGAYA), Deen Dayal Upadhaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY), and National Electricity Fund (NEF) Scheme.
NGT Investigates Removal of Invasive Mussels in Ennore-Pulicat Wetland (The Hindu)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Southern Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has asked the Fisheries Department and the Tamil Nadu State Wetland Authority to file a detailed report on the removal of invasive mussel species from the Ennore-Pulicat wetland.
What is Mytella strigata?
- Mytella strigata is a moderately large mussel known for its symmetrical shell, commonly found in the middle intertidal and subtidal waters of estuaries and coastal areas.
- These mussels attach to surfaces using byssus threads.
- Appearance: Individual mussels display diverse external colours such as black, dark bluish, brown, grey, orange, and occasionally green.
- The species exhibits various shell patterns, including zigzags, spots, or concentric bands.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found in dense clusters on hard substrates and in epibenthic habitats, Mytella strigata is prevalent along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of tropical South and Central America.
- It has also expanded its presence to regions like Taiwan, the Philippines, Singapore, the Gulf of Thailand, the west coast of India, and the southeastern United States.
- Threats: These mussels pose a threat as they spread across river bottoms, forming carpets that hinder prawns from grazing or burying themselves in the sediment.
About Pulicat Lake:
- Pulicat is an extensive brackish-to-saline lagoon with marshes and a brackish swamp on the north.
- This is the second-largest saltwater lagoon in India and a Ramsar site (internationally recognized wetland under the Ramsar Convention).
- Only 16% of the lagoon is in Tamil Nadu; the rest is in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is fed by the Araani River at the southern tip and the Kalangi River from the northwest.
- Buckingham Canal, a navigation channel, passes through the lagoon.
- On the eastern boundary of this lagoon is Shriharikota Island, which separates the lagoon from the Bay of Bengal.
- The lagoon is shallow with large areas of mudflats and sandflats.
Watermeal May Become an Essential Food for Astronauts (India Today)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists from Mahidol University in Thailand have been exploring the potential of watermeal, the smallest flowering plant on Earth, as a source of nutrition and oxygen for astronauts.
What is Watermeal?
- The Watermeal scientifically known as Wolffia, is often mistaken for algae, but they're actually the smallest flowering plants in the world!
- Its simplicity and rapid growth rate make it an ideal candidate for studying the effects of altered gravity on plant development.
- this tiny plant is aquatic, predominantly floating on the surface of water bodies.
- Because watermeal doesn’t have any roots, stems or leaves, it is basically just a sphere floating on a body of water.
- It's a prolific producer of oxygen through photosynthesis and belongs to the duckweed family (Lemnaceae).
- Each individual watermeal plant is extremely small, roughly the size of a pinhead.
- It has a simple, globular, and rootless structure, often appearing like minute green grains on the water.
- Watermeal thrives in quiet, nutrient-rich freshwater environments like ponds, lakes, and marshes.
- The plant is found globally, with a significant presence in Asia and Thailand.
- Watermeal is known to be a rich source of protein, making it a nutritious foodstuff.
- In Thailand, it has been part of the local diet for generations, appearing in dishes ranging from soups to salads.
Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission (HT)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Dr Aroh Barjatya, an Indian-origin scientist is set to lead the multi-institution NASA rocket mission on October 14.
About Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission:
- The APEP mission entails the launch of three rockets, each equipped with scientific instruments, to explore changes in the upper atmosphere during a solar eclipse, particularly during the critical phase of sudden light reduction.
- Mission Objective: To investigate alterations in the ionosphere induced by the abrupt decrease in sunlight during an eclipse, leading to the generation of waves in this atmospheric layer.
- Measurements will encompass changes in electric and magnetic fields, as well as variations in density and temperature.
- Launch Details: The launch site is the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, with a specific focus on studying the ionosphere's response during an eclipse.
- Potential Impact on Communications: NASA notes projections indicating a temperature and density reduction in the ionosphere during the eclipse, potentially causing disruptive wave disturbances that could affect GPS and satellite communications.
- Process: Rockets will be strategically positioned just beyond the path of annularity, where the Moon directly aligns with the Sun.
- Each rocket will deploy four compact scientific instruments designed to capture data on electric and magnetic fields, density, and temperature changes.
- NASA's primary objective is to achieve unprecedented simultaneous measurements from multiple ionospheric locations during a solar eclipse.
- Rationale for Rocket Selection: Sounding rockets were chosen for their precision in pinpointing and measuring specific regions of space.
- Their ability to investigate lower altitudes, inaccessible to satellites, makes them ideal for this mission.
- Sounding rockets offer precise data recording as they ascend and descend during suborbital flights, covering altitudes ranging from 45 to 200 miles (70 to 325 kilometres) above Earth's surface along their flight path.
Gangetic River Dolphin (The Hindu)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A recent publication by scientists and researchers has revealed that 19 Gangetic river dolphins had been rescued from the irrigation canals of the Ganga-Ghagra basin in Uttar Pradesh between 2013 and 2020.
About Gangetic River Dolphin:
- The Gangetic River dolphin is a freshwater species, representing one of the rare river dolphins worldwide.
- Distribution: It thrives in the river systems of Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu, spanning across Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Common Names: Known by various names such as Blind dolphin, Ganges dolphin, Ganges susu, hihu, side-swimming dolphin, and South Asian River Dolphin.
- Designated as India's National Aquatic Animal.
- Physical Features: Characterized by a long, thin snout, rounded belly, stocky body, and large flippers.
- Primarily feeds on fish, often found in counter-current systems of the main river channel.
- Eyes lack a lens, earning it the moniker 'blind dolphin.'
- Possesses an advanced bio-sonar system for effective hunting, even in murky waters.
- Requires surfacing every 30-120 seconds for breathing; its audible breathing sounds have led to the affectionate term 'Susu.'
- Conservation Status: IUCN categorizes it as Endangered.
- Protected under Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act.
- Listed in CITES Appendix I.
Ayushman Arogya Mandir (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Government has decided to rename the current Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) as 'Ayushman Arogya Mandir.'
About Ayushman Arogya Mandir:
- The government has decided to rename the Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centres as 'Ayushman Arogya Mandir'
- The rebranded AB-HWCs will also have a new tagline -- 'Arogyam Parmam Dhanam'.
- Under the Government of India's flagship Ayushman Bharat Yojana, more than 1.6 lakhs AB- HWCs have been successfully established across states and UTs over the last five years with 219 crore footfalls so far.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir is an attempt to move from a selective approach to health care to deliver a comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative care.
- It has two components which are complementary to each other.
- Under its first component, 1,50,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandir will be created to deliver Comprehensive Primary Health Care, that is universal and free to users, with a focus on wellness and the delivery of an expanded range of services closer to the community.
- The second component is the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) which provides health insurance cover of Rs. 5 lakhs per year to over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families seeking secondary and tertiary care.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs are envisaged to deliver an expanded range of services that go beyond Maternal and child health care services.
- It includes care for non-communicable diseases, palliative and rehabilitative care, Oral, Eye, and ENT care, mental health, and first-level care for emergencies and trauma , including free essential drugs and diagnostic services
- More than 2.71 crore wellness sessions have been held at these centers.
Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently gave its approval for the three-year extension of fast-track courts that are specifically used to handle sexual offense cases.
About Fast Track Special Court (FTSC):
- The Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) initiative started in August 2019 as a centrally sponsored scheme to handle cases related to rape and the POCSO Act.
- Originally planned for one year, it got extended to March 2023, and now it's extended further until March 2026 with a financial allocation of Rs. 1952.23 crore from the Nirbhaya Fund.
- These specialized courts, totaling 761, including 414 exclusive POCSO Courts, operate across all States and Union Territories.
- The Department of Justice, Ministry of Law & Justice, oversees their implementation.
- The primary aim is to expedite justice, offering quick relief to victims and reinforcing the nation's commitment to ending sexual and gender-based violence.
- The expected outcomes of this scheme are significant.
- They include a substantial reduction in pending cases related to Rape & POCSO Act, providing swift access to justice for victims through improved facilities and expedited trials, and reducing the burden on the judicial system by managing the number of cases effectively.
Angkor Wat Temple (TOI)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Angkor Wat, in the heart of Cambodia, has beaten Pompeii in Italy to become the eighth Wonder of the World.
About Angkor Wat Temple:
- Angkor Wat is among the most significant archaeological sites of Southeast Asia, located in the northern province of Siem Reap in Cambodia.
- The temple was constructed by the Khmer King Suryavarman II in the early 12th century.
- It was originally built as a Hindu temple, dedicated to Lord Vishnu by the Khmer Emperor Suryavarman II, it was converted into a Buddhist temple by his successor Jayavarman VII, who also built the famous Buddhist temple of Bayon nearby.
- The transition from Hinduism to Buddhism is evident in the intricate carvings that adorn the temple walls, depicting scenes from Hindu and Buddhist mythology.
- An interesting fact about Angkor is that it is also known as Yasodharapura.
- The name Angkor is derived from nokor, a Khmer word meaning "kingdom," which is derived from Sanskrit nagara, which means "city."
- Angkor Wat is said to represent Mount Meru, the home of the gods, according to both Hindu and Buddhist faiths.
- It is also famous for its statue of eight-armed Vishnu, also revered by the locals as their protecting deity.
- It holds the Guinness World Record for being the largest religious structure in the world, spread across some 400 km sq.
- In 1992 the temple complex was named a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Syrian Golan/Golan Heights (The Hindu)
- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India has voted in favour of a draft resolution in the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) that expressed deep concern over Israel not withdrawing from the Syrian Golan.
About the Syrian Golan/Golan Heights:
- Location: Situated in south-western Syria, the Golan Heights is a rocky plateau sharing borders with Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan.
- The elevated terrain overlooks the Jordan Rift Valley, housing the Sea of Galilee and the Jordan River, with Mount Hermon as a dominant feature.
- Demography: Over 40,000 people reside in the Israeli-occupied Golan, with a majority being Druze, an Arab minority practicing a distinct form of Islam.
- Although Israel offered Druze residents citizenship after annexation, most identified as Syrian and declined.
- Additionally, about 20,000 Israeli settlers live in the region.
- History of Conflict: Originally part of Syria, Israel captured the Golan Heights in 1967 during the Six-Day War and formally annexed it in 1981.
- Syria attempted to reclaim the area in the 1973 Middle East war but was unsuccessful.
- While an armistice was signed in 1974, international recognition of Israel's annexation is lacking, and Syria insists on the territory's return.
- Significance of Golan Heights: Israel argues that maintaining the Golan as a buffer zone is vital due to the Syrian civil war, protecting Israeli towns from neighboring instability.
- Concerns also include the fear of Iran, an ally of the Syrian president, establishing a permanent presence near the border for potential attacks on Israel.
- Both nations value the Golan's water resources and fertile soil.
The Booker Prize 2023 (Indian Express)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The 2023 Booker Prize has been awarded to Prophet Song, a dystopian vision of Ireland in the grips of totalitarianism.
Key Facts:
- Irish author Paul Lynch won the 2023 Booker Prize for his novel "Prophet Song," a dystopian work about an Ireland that descends into tyranny.
- Set in Dublin, it tells the story of a family grappling with a terrifying new world in which the democratic norms they are used to begin to disappear.
- He becomes the fifth Irish writer to win the high-profile literary prize, which has propelled to fame countless household names, including past winners Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, and Hilary Mantel.
What is a Booker Prize?
- The Booker Prize is a literary prize awarded every year to the best novel written in the English language which is published in the UK or Ireland.
- It is a high-profile literary prize and thus, is much anticipated among book lovers.
- Background: It was established in 1969 by Booker McConnell Ltd, the prize transitioned to the Booker Prize Foundation in 2002, sponsored by the Man Group.
- Initially, the award was £21,000, increased to £50,000 in 2002.
- Selection Process: An advisory committee, comprising diverse literary figures, appoints a judging panel annually.
- BOOKER PRIZE winners: Indians
- VS Naipaul, In a Free State (1971)
- Salman Rushdie, Midnight’s Children (1981)
- Arundhati Roy, The God of Small Things (1997)
- Kiran Desai, The Inheritance of Loss (2006)
- Aravind Adiga, The White Tiger (2008)
Parthenon Sculptures (Indian Express)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A diplomatic row sparked between Greece and the UK recently after British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak canceled a meeting with his Greek counterpart Kyriakos Mitsotakis over the status of the Parthenon Sculptures housed at the British Museum.
What are the Parthenon Sculptures?
- The Parthenon Sculptures at the British Museum are more than 30 ancient stone sculptures from Greece that are more than 2,000 years old.
- Most of them originally adorned the walls and grounds of the Parthenon temple on the rocky Acropolis hill in Athens.
- Completed in 432 BC, the temple is dedicated to the goddess Athena and is seen as the crowning glory of Athens’ Golden Age.
- While one notable sculpture, which is 75 meters long, depicts a procession for the birthday of Athena, others show gods, heroes, or mythical creatures.
How did the sculptures reach Britain?
- They were removed from the Parthenon in the early 19th century by Thomas Bruce, the 7th Earl of Elgin and then-British ambassador to the Ottoman Empire.
- The marbles were taken to Britain and purchased by the British Museum in 1816.
Swine Flu (TOI)
- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
UK public health officials recently said they had confirmed a first human case of a swine flu strain similar to one that has been circulating in pigs.
About Swine Flu:
- Swine flu, scientifically known as H1N1 influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by the H1N1 virus that commonly affects pigs.
- However, this virus can also infect humans, leading to a range of symptoms from mild to severe, and in some cases, it can be fatal.
- The virus spreads among humans through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes, making it highly transmissible.
- Swine flu symptoms resemble those of seasonal influenza, including fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, and fatigue.
- In severe cases, individuals may experience respiratory distress and pneumonia.
- One of the distinctive features of the H1N1 virus is its ability to affect younger age groups more severely compared to typical seasonal flu viruses.
- The World Health Organization declared a global pandemic of H1N1 influenza in 2009, emphasizing the need for international cooperation in monitoring and controlling the spread of the virus.
- Oseltamivir is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B.
Comet P12/Pons-Brooks (The Hindu)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Astronomers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have used the Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) in Hanle, Ladakh, to photograph the Comet P12/Pons-Brooks.
About Comet P12/Pons-Brooks:
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is a Halley-type periodic comet that was first discovered by Jean-Louis Pons on July 12, 1812.
- It is nicknamed the 'Devil Comet' or likened to the 'Millennium Falcon' for its distinctive appearance.
- It has an orbital period of about 71.3 years.
- During its closest approach to the Sun or perihelion, the comet comes within about 0.78 astronomical units (AU) of the Sun, while at its furthest point, or aphelion, it is located at a distance of about 17.2 AU.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is also known for being the probable parent body causing the κ-Draconids meteor shower.
- It will make its return in 2024 and it is expected to reach its maximum brightness (potentially visible to the naked eye) during the month of April.
- With its closest approach occurring just a few days before a total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, it presents a unique opportunity for skywatchers to potentially view the comet during the eclipse.
- However, since the comet's brightness can be unpredictable, there is no guarantee it will be visible.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is currently in the constellation of Lyra Constellation.
Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) (PIB)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, GoI is organizing the 19th Working Party on Data Collection and Statistics (WPDCS19) of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) from 28th November to 2nd December 2023.
About the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission:
- The Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for the management of tuna and tuna-like species in the Indian Ocean.
- It works to achieve this by promoting cooperation among its Contracting Parties (Members) and Cooperating Non-Contracting Parties in order to ensure the conservation and appropriate utilisation of fish stocks and encouraging the sustainable development of fisheries.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations adopted the Agreement for the Establishment of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission during its 105th Session in Rome on 25 November 1993.
- The Indian Ocean holds the position as the second-largest tuna fishery globally, making it a crucial focus for the IOTC.
- Currently, the IOTC boasts 31 contracting parties, including countries and two cooperating non-contracting parties, Liberia and Senegal.
- Membership is open to Indian Ocean coastal countries, countries or regional economic integration organizations that are UN members, countries that are members of UN special organizations, and countries involved in tuna fishing in the Indian Ocean.
- India is an active member of the IOTC, with its headquarters located in Victoria, Seychelles.
INS Imphal (Business Standard)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently unveiled the crest of the Indian Navy's stealth-guided missile destroyer Imphal.
About INS Imphal:
- INS Imphal is the third ship in the Visakhapatnam-class stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- INS Imphal is the third of the four Project 15B stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- It's one of the biggest destroyers made in India, measuring 164 meters long and weighing over 7500 tonnes.
- Powered by Combined Gas and Gas (COGAG) propulsion, the ship is capable of achieving speeds in excess of 30 knots (56 km/hour).
- It's equipped to handle various tasks in maritime warfare.
- The ship boasts a high indigenous content of approximately 75 percent that includes BrahMos surface-to-surface missiles, medium-range surface-to-air missiles, anti-submarine indigenous rocket launchers, and 76mm super rapid gun mount.
- "Designed by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau and built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited, Imphal is a hallmark of indigenous shipbuilding and is amongst the most technologically advanced warships in the world.
- The crest design on the ship represents the Kangla Palace and 'Kangla-Sa.'
- The Kangla Palace is a historical and archaeological site in Manipur, serving as the traditional seat of the past kingdom.
- On the right side of the crest, 'Kangla-Sa' is depicted—a mythical being with a dragon's head and lion's body from Manipur's history, symbolizing the guardian of its people.
- ‘Kangla-Sa' is also the state emblem of Manipur.
- Interestingly, INS Imphal is the first capital warship named after a city in the northeast—Imphal, the capital of Manipur.
Himalayan Black Bear (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
An animal keeper died after being attacked by a Himalayan black bear in the animal’s enclosure of Indira Gandhi Zoological Park (IGZP) here recently.
About Himalayan Black Bear:
- The Himalayan black bear (Scientific Name: Ursus thibetanus laniger) is a subspecies of the Asian black bear found in the Himalayas of India, Bhutan, Nepal, China, and Pakistan.
- In India, habitat covers the entire Himalayan range from Jammu & Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh, extending to hilly areas in other northeastern states.
- Habitat: Thrives in heavily forested regions with broadleaved and coniferous forests.
- It utilizes orchards, agricultural fields, and human habitats to navigate between forest patches.
- Physical Features: Possesses soft and shiny fur, featuring a distinctive white V patch on the chest.
- Average length ranges from 1.4 to 1.7 meters, weighing between 90 to 200 kg (higher weight typically before hibernation).
- Life Span: In the wild, their life expectancy is approximately 25 to 30 years.
- Diet: Omnivorous nature, consuming acorns, nuts, fruit, honey, roots, and various insects like termites and beetle larvae.
- Behavior: Primarily diurnal by nature but often shifts to a nocturnal lifestyle to avoid human contact.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List classification: Vulnerable
- Due to encroachment of human population, forest fires and the timber industries; these have all reduced the bear's habitat.
- There is also a high mortality rate among the newborn.
ISRO's AstroSat (PTI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's AstroSat space telescope has achieved a significant milestone by detecting more than 600 Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB), each marking the death of a massive star or merging of neutron stars.
About ISRO’s AstroSat:
- AstroSat is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- One of the unique features of the AstroSat mission is that it enables the simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is expected to be 5 years.
- It carried a total of five scientific payloads, enabling imaging and studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra-galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- The scientific objectives of AstroSat’s mission are:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
- At present, all the payloads are operational and are observing the cosmic sources.
Rythu Bandhu Scheme (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission recently canceled the Telangana government's approval to give money to farmers through the Rythu Bandhu Scheme.
About Rythu Bandhu Scheme:
- Rythu Bandhu Scheme, also known as the Farmer's Investment Support Scheme (FISS), was initiated by the Telangana government in 2018.
- Objectives:
- Provide timely cash grants for the initial investment needs of farmers.
- Prevent farmers from falling into the debt trap.
- Financial Assistance: Rs 5,000 per acre per farmer per season directly transferred to their accounts.
- Distribution: Biannual support for both kharif and rabi harvests.
- Usage: Farmers can use funds for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, labor, and other field operations of their choice.
- Eligibility: Open to all resident land-owning farmers, including those in forest areas with a Record of Forest Rights (ROFR).
- Special Inclusion: Farmers in forest areas, mainly from Scheduled Tribe communities, with a ROFR document, are eligible for benefits.
- It’s India's first direct farmer investment support scheme, providing cash directly to beneficiaries.
Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a new plant species belonging to the 'Impatiens' genus (Balsaminaceae) has been identified in the Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Tirunelveli.
About Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- The Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, is situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- This reserve combines three major sanctuaries:
- The Kalakkad Sanctuary
- The Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of the Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The Agasthyamalai Hills, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu, forms the sanctuary's core and is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- This reserve is also recognized as the “River Sanctuary,” with 14 rivers originating from it.
- Flora: The flora in this region exhibits a gradual transition from dry thorn forest to dry deciduous, moist deciduous, and a patch of West Coast wet evergreen forests at higher elevations.
- Fauna: Diverse fauna includes species such as Lion-tailed Macaque, Nilgiri Tahr, Nilgiri Pipit, Grey Headed Bulbul, Blue Winged Parakeet, and more.
Details about the New Plant Species:
- The species, named 'Impatiens Karuppusamyi,' pays tribute to S. Karuppusamy for his significant contributions to the taxonomy of South Indian angiosperms.
- This particular plant is exclusively found in the Agasthyamalai region within the southern Western Ghats.
- Belonging to the scapigerous group (stemless group), the plant is observable only during the monsoon season, lasting for a few weeks.
- Impatiens, a genus comprising over 1,000 flowering plant species, is widely distributed across tropical Africa, Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, and China.
Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar linking the Mediterranean and the Atlantic for shipping (The Hindu)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea unless Israel stops bombing Gaza.
About the Strait of Gibraltar:
- The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow water passage that serves as a crucial link connecting Europe and Africa, facilitating the connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Historical Significance: Prior to the inauguration of the Suez Canal in 1869, the Strait of Gibraltar held exclusive prominence as the sole gateway to the Mediterranean Sea.
- Geographical Borders: Positioned between Spain and the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar in the north, and Morocco and the Spanish exclave of Ceuta in the south, the strait spans approximately 58 km and reaches a width of about 13 km at its narrowest point.
- Depth and Geological Formation: With depths ranging from 300 to 900 meters, the strait constitutes a significant divide between the elevated plateau of Spain and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa.
- Geological studies indicate that the strait originated from the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate.
- High Maritime Activity: Recognized as one of the world's busiest waterways, the Strait of Gibraltar witnesses the daily transit of around 300 ships, equivalent to approximately one ship every 5 minutes.
- The Moroccan port of Tanger-Med, situated near Tangier, is a prominent port along the strait.
- Pillars of Heracles: Marking the eastern extremity of the strait, the area between the Rock of Gibraltar in the north and Mount Hacho or Jebel Moussa in the south spans approximately 23 km.
- These two land features referred to as the Pillars of Heracles, hold historical and geographical significance.
About the Mediterranean Sea:
- The Mediterranean Sea, an intercontinental body of water, is flanked by Europe to the north, Asia to the east, and Africa to the south.
- In the western expanse, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the narrow Strait of Gibraltar.
- To the extreme northeast, it links to the Black Sea via the Dardanelles Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Bosporus Strait.
- In the southeast, the Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal.
- Historical Significance: Recognized as the cradle of Western civilization, the Mediterranean Sea has played a pivotal role in the development of ancient cultures.
- Notable civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire, flourished along its shores.
- Countries and Territories Along the Coast: A total of 22 countries, along with one territory (Gibraltar, a British Overseas Territory), have coastlines along the Mediterranean Sea.
- European nations with Mediterranean coastlines include Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, and Greece.
- Countries from the West Asian (Middle Eastern) region bordering the Mediterranean Sea include Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine (Gaza Strip), and the divided island of Cyprus.
- Additionally, five North African nations, namely Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt, have coastlines along the Mediterranean.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia (Indian Express)
- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
What is Mycoplasma Pneumonia?
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that can cause illness by damaging the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, windpipe).
- It acts more like a virus and spreads faster from person to person.
- It is a common cause of pneumonia in children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Vulnerable groups, who already have respiratory issues, are prone to developing this infection in a severe form.
- Most people with respiratory infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae don’t develop pneumonia.
- For this reason, MP is known as an atypical pneumonia and is sometimes called walking pneumonia.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can include:
- Fever, Cough, Headache, Sore throat, Fatigue, Muscle aches, and Shortness of breath
- In most cases, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is mild and goes away on its own within a few weeks.
- However, some people may develop more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- It spreads through close contact with an infected person, such as through coughing or sneezing.
- It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- There is no vaccine to prevent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection however there are multiple antibiotics that effectively cure this infection.
PM to release ‘Collected Works of Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya’ on 25th December (PIB)

- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of the 162nd birth anniversary of Mahamana Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi will release the first series of 11 volumes of ‘Collected Works of Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya’, on 25th December, 2023.
About Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya:
- Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya, born on December 25, 1861, in Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, made significant contributions to India's education system and actively participated in the Indian Independence movement.
- Acknowledged as a venerable soul, Mahatma Gandhi bestowed upon him the title of 'Mahamana,' considering him an elder brother.
- In 2014, posthumously, Pandit Malviya was honoured with the Bharat Ratna, the highest civilian award in the country.
- In tribute to his legacy, the Indian Railways launched the Varanasi-New Delhi Mahamana Express in 2016.
Significant Contributions:
- Banaras Hindu University: In 1916, Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya played a pivotal role in the Indian independence struggle against British rule and established the Banaras Hindu University (BHU).
- Serving as the Vice-Chancellor at BHU from 1919 to 1938 showcased his dedication to education and leadership.
- Hindu Mahasabha: A founding member of the Hindu Mahasabha in 1906, Malaviya demonstrated his early leadership in this organization.
- As a social reformer and accomplished legislator, he contributed significantly during his 11-year tenure (1909–20) as a member of the Imperial Legislative Council.
- Scout and Guide Movement: Pandit Malviya was instrumental in establishing the Scout and Guide movement in India, showcasing his commitment to youth development and character building.
- 'Satyamev Jayate': Renowned for coining the famous slogan 'Satyamev Jayate,' Pandit Malviya proclaimed it during the 1918 Indian National Congress session when he served as the President.
- President of INC: Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya's leadership extended to the Indian National Congress, where he held the position of President for four sessions (1909, 1913, 1919, and 1932).
- His active role in the Civil Disobedience and Non-cooperation movements, led by Mahatma Gandhi, underscored his commitment to India's struggle for independence.
- Media Role: From 1924 to 1946, Pandit Malviya served as the Chairman of Hindustan Times and also founded several Hindi and English newspapers, including The Leader, Hindustan Dainik, and Maryada.
- Advocacy for Education and Social Causes: Malaviya championed free and compulsory primary education, opposed the system of indentured labour in the British Empire, and advocated for the nationalization of railways, reflecting his dedication to societal progress and reform.
“FLip” mutations of SARS-COV-2 may be evading immunity and leading to a surge in COVID cases, suggest researchers (DownToEarth)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The omicron subvariant JN.1. is likely to soon become the dominant lineage of the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide, according to researchers at the University of Tokyo. The subvariant has a mutation in its spike protein, L455S, also called a “FLip” mutation.
Context:
- The mutations denoted as L455S and L455F are termed "FLip" mutations due to their role in interchanging the positions of amino acids F and L within the spike protein.
- These mutations enhance the virus's transmissibility.
- The substitution associated with these mutations reduces the receptor binding capacity of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a protein present in epithelial cells across various body parts, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys.
- ACE2 serves as a crucial entry point for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, binding through its spike-like protein on the virus's surface.
- The FLip mutations, specifically L455F and F456L, are characterized by the swapping of positions between two amino acids, F and L, within the spike protein.
What is Flip Mutation?
- A flip mutation, also known as bit flip mutation, is a genetic operator used in evolutionary algorithms, particularly genetic algorithms (GAs).
- It works by randomly flipping the values of individual genes (bits) within a chromosome, introducing small changes to the genetic makeup of an individual.
- Imagine a chromosome as a string of 0s and 1s, representing the genetic code for a specific trait or characteristic.
- A flip mutation randomly selects one or more of these bits and changes their values.
- For example, a 0 might be flipped to a 1, or vice versa.
- The following image depicts flip mutation:
How does it work:?
- Individual selection: An individual is selected from the population.
- Gene selection: One or more genes (bits) within the individual's chromosome are randomly chosen.
- Bit flipping: The value of each selected gene is flipped. This means that a 0 is changed to a 1, and vice versa.
World Climate Action Summit 2023 (NewsOnAir)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi will be on a two-day visit to Dubai, UAE from 30th November to attend the World Climate Action Summit.
About World Climate Action Summit:
- The World Climate Action Summit is the High-Level Segment of the 28th Conference of Parties (COP-28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- COP-28 is being held from 28 November to 12 December 2023 under the Presidency of the UAE.
- The Conference of Parties to the UNFCCC provides a unique opportunity to impart momentum for collective action towards combating the shared challenge of climate change.
- The World Climate Action Summit will bring together heads of state and governments, leaders from civil society, business, youth, indigenous peoples' organisations, frontline communities, science, and other sectors.
- The summit aims to facilitate discussions on actions and plans to scale climate action.
- The COP 28 will focus on four paradigm shifts:
- Fast-tracking the energy transition and slashing emissions before 2030;
- Transforming climate finance, by delivering on old promises and setting the framework for a new deal on finance;
- Putting nature, people, lives, and livelihoods at the heart of climate action; and
- Mobilizing for the most inclusive COP ever.
- The summit may witness intense negotiations on unfulfilled promises of financial aid, particularly the yet-to-materialize $100 billion pledged by rich countries by 2020.
- Additionally, some countries, notably the European Union, are expected to advocate for a global deal to phase out unabated fossil fuels during COP28.
- During COP-26 in Glasgow, the Prime Minister announced five specific targets, titled "Panchamrit”, as India’s unprecedented contribution to climate action.
- The Prime Minister also announced Mission Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE) on that occasion.
- Climate change has been an important priority area of India’s G20 Presidency, and significant new steps have been captured in the New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration and other outcomes during our Presidency.
- COP-28 will provide an opportunity to take forward these successes.
Odisha Government has declared Leprosy as a 'Reportable Disease' in the State (New Indian Express)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha government on Friday declared leprosy a reportable disease in the state and asked hospitals and persons dealing with diagnosis and treatment, institutions imparting medical education and providing diagnostic services to report all cases to the respective district health authorities.
What is Leprosy?
- Leprosy, often referred to as Hansen's disease, is a persistent infectious illness brought on by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae.
- The skin, eyes, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract, and peripheral nerves are the main areas affected by this condition.
- If left untreated, the condition has the potential to produce gradual and irreversible impairments.
- Prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, leprosy qualifies as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) found in over 120 countries.
- Its occurrence spans all age groups, encompassing early childhood to advanced age.
- Transmission of Disease: Transmission of leprosy transpires through droplets from the nose and mouth, necessitating prolonged, close contact with an untreated individual.
- Contrary to misconceptions, casual interactions such as handshakes, hugs, shared meals, or proximity do not facilitate transmission.
- Symptoms: Symptoms usually manifest 3 to 5 years post-exposure to the leprosy-causing bacteria.
- Red patches on the skin.
- Skin Lesion
- Numbness in arms, hands, and legs.
- Ulcers on the soles of feet.
- Muscle Weakness and excessive weight loss.
- Nerve damage can result in loss of sensation in limbs and potential mucous membrane complications like a stuffy nose or nosebleeds.
- Treatment: Leprosy is curable through Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT), with early intervention crucial in preventing disability.
- Importantly, the commencement of treatment not only aids in recovery but also halts the transmission of the disease.
About the National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP):
- The National Leprosy Eradication Programme is a centrally sponsored Health Scheme under the National Health Mission of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India.
- The Programme is headed by the Deputy Director of Health Services (Leprosy ) under the administrative control of the Directorate General Health Services, Govt. of India.
- While the NLEP strategies and plans are formulated centrally, the programme is implemented by the States/UTs.
- The major concern of the Programme is to detect cases of leprosy at an early stage and provide complete treatment, free of cost, in order to prevent the occurrence of Grade II Disability (G2D) in affected persons.
- India has achieved the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at the National level in 2005.
- However, there are few districts within States where leprosy is still endemic.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
SEBI on Saturday decided to bring entities facilitating fractional investment in real estate under a regulatory framework, whereby they will be required to operate as Small and Medium Real Estate Investment Trusts.
About Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
- A Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) is a company that owns and typically operates income-generating real estate or related assets.
- It pools funds from investors, directing them into various commercial real estate ventures, including office buildings, shopping malls, apartments, hotels, resorts, self-storage facilities, warehouses, and mortgages or loans.
- In contrast to conventional real estate firms, REITs don't develop properties for resale; rather, they acquire and develop properties primarily for inclusion in their investment portfolio.
- REITs offer individual investors an opportunity to share in the income generated by commercial real estate without the need to directly purchase such properties.
- Typically specializing in specific real estate sectors, REITs may focus on diversified or specialty portfolios, encompassing various property types like office and retail spaces.
- Most REITs are publicly traded on stock exchanges, similar to stocks, providing high liquidity compared to physical real estate investments.
- This stock-like nature allows investors to buy or sell REIT shares on the exchange at any time.
Sports Ministry requests IOA to constitute an ad-hoc committee to manage WFI affairs (Indian Express)

- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After suspending the newly elected Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) body on Sunday, the Sports Ministry have requested the Indian Olympic Association to constitute an ad-hoc committee to manage and control the affairs of the federation.
News Summary:
- Three days after the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) elected a new governing council to run the sport in India, the Union Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports directed the body to suspend all activities.
- It issued a letter to the Indian Olympic Association (IOA) to create an ad-hoc committee to manage and control the affairs of the WFI.
About the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI):
- Established in 1958 and headquartered in New Delhi, the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) serves as the governing body for wrestling.
- Mission: WFI plays a pivotal role in nurturing and promoting wrestling talent for prestigious events such as the Olympics, Asian Games, National Wrestling Championships, and World Wrestling Championships.
- Affiliation: As an integral part of the Indian Olympic Association (IOA), WFI operates in accordance with the rules and regulations set forth by both the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and United World Wrestling (UWW).
- The UWW, recognized as the international governing body for wrestling, holds responsibilities ranging from overseeing wrestling competitions at the World Championships to ensuring adherence to standards at the Olympic level.
- WFI's Contract System for Wrestlers: In a groundbreaking move in 2018, WFI introduced an innovative contract system designed to support wrestlers.
- This system categorizes wrestlers into four grades:
- Grade A, providing financial assistance of 30 lakh rupees.
- Grade B offers a financial support package of 20 lakh rupees.
- Grade C, extending support amounting to 10 lakh rupees.
- Grade D provides a support package of 5 lakh rupees.
- To ensure relevance and fairness, the contracts undergo a thorough review on an annual basis, reflecting WFI's commitment to the ongoing development and support of wrestling talent.
About Indian Olympic Association (IOA):
- The Indian Olympic Association acts as the governing body overseeing the Olympic Movement and the Commonwealth Games within India.
- It holds affiliation with prominent international bodies, including the International Olympic Committee (IOC), Commonwealth Games Federation (CGF), Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), and Association of National Olympic Committees (ANOC).
- In fulfilling its role, the IOA manages key aspects of sports governance and prioritizes the welfare of athletes across the nation.
- Responsibilities: As a recognized entity by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, the IOA undertakes the crucial responsibility of coordinating the representation of athletes and teams in major international multi-sport events such as the Olympic Games, Commonwealth Games, Asian Games, and others sanctioned by the IOC, CGF, OCA, and ANOC.
- Historical Perspective: Established in 1927 with Sir Dorabji Tata serving as the Founding President and Dr. A.G. Noehren as the Secretary-General, the IOA operates as a Non-Profit Organization under the Societies Registration Act of 1860.
- This history underscores its enduring commitment to the promotion of sports.
- Governance Structure: Currently governed by a 32-member Executive Council, the IOA is led by a President.
- Elections for the Executive Council occur once every four years, emphasizing democratic and periodic leadership changes within the organization.
Supplementary Grants (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supplementary Demands for Grants (SDG) are likely to see additional allocation for fertliser, food and fuel subsidy along with Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme.
About Supplementary Grants:
- According to Article 115 of the Indian Constitution, there's a provision for additional funds known as supplementary, additional, or excess grants.
- When the funds approved by the Parliament are not enough for the planned expenses, an estimate is submitted to the Parliament for extra grants.
- These additional grants are reviewed and approved by the Parliament before the conclusion of the financial year.
- If the actual spending surpasses the approved grants, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Railways make a request for an Excess Grant after the financial year ends.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India highlight these excesses to the Parliament.
- The Public Accounts Committee then examines these cases and provides recommendations to the Parliament.
- The Demand for Excess Grants is presented to the Parliament after the financial year, once the actual expenditures have been incurred.
High-energy Particle "Amaterasu" (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have detected one of the most powerful cosmic rays ever slamming into Earth but they have no idea what caused it or where it came from.
What is Amaterasu?
- The particle, named Amaterasu after the sun goddess in Japanese mythology, is one of the highest-energy cosmic rays ever detected.
- The Amaterasu particle has an energy exceeding 240 exa-electron volts (EeV).
- It is millions of times more than particles produced in the Large Hadron Collider, the most powerful accelerator ever built, and equivalent to the energy of a golf ball traveling at 95mph.
- It comes only second to the Oh-My-God particle, another ultra-high-energy cosmic ray that came in at 320 EeV, detected in 1991.
- Amaterasu appears to have emerged from the Local Void, an empty area of space bordering the Milky Way galaxy.
What are Cosmic Rays?
- Cosmic rays are high-energy particles, primarily protons and atomic nuclei, that originate from outer space and bombard Earth from all directions.
- They possess extraordinary energies, often exceeding those achievable in human-made accelerators.
- Created through various astrophysical processes, such as supernova explosions and the remnants of massive stars, cosmic rays travel through the vast expanse of space.
- Upon entering Earth's atmosphere, they collide with air molecules, initiating cascades of secondary particles.
- These rays play a crucial role in astrophysics, providing insights into the universe's most energetic phenomena.
- They contribute to our understanding of cosmic structures, magnetic fields, and the dynamics of celestial bodies.
- Despite their significance, the origins of certain ultra-high-energy cosmic rays remain mysterious, prompting ongoing research to unveil the secrets of these enigmatic particles.
Ministry of Textiles launches “Paat-Mitro” application to facilitate jute farmers (PIB)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
To provide important information about MSP and agronomy to jute farmers, the Ministry of Textiles launched “Paat-Mitro” - a mobile application, developed by The Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) during the ‘Jute Symposium’.
What is Paat Mitro?
- Paat Mitro is a mobile application crafted by the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) with the primary aim of furnishing vital information on Minimum Support Prices (MSP) and agronomy to jute farmers.
Key Features:
- The application is accessible in six languages, ensuring inclusivity.
- All functionalities within the app are provided to users free of charge.
- Paat Mitro offers a comprehensive range of information, encompassing the latest agronomic practices, MSP details, Jute Gradation Parameters, farmer-centric schemes like ‘Jute-ICARE,’ weather forecasts, locations of JCI’s Purchase Centres, and Procurement Policies.
- Farmers can conveniently track the payment status for the raw jute they sell to JCI under the MSP Operation.
- The app integrates advanced technology features such as a Chatbot, facilitating farmers in resolving queries effectively.
Key Information about the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI):
- Established in 1971 under the aegis of the Government of India, the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) serves as the official agency dedicated to ensuring minimum support prices (MSP) for jute cultivators.
- JCI functions as the executing body for several Government of India initiatives aimed at enhancing the jute crop and the welfare of jute growers.
- It operates under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Textiles.
- The geographical reach of JCI spans seven states renowned for jute cultivation in India, including West Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Orissa, and Andhra Pradesh.
- With an authorized and paid-up capital of Rs. 5 crore, JCI plays a pivotal role in implementing the government's policy decisions, obligatorily purchasing any quantity of jute offered by growers at support rates without quantitative limitations.
- Incurred losses during policy implementation by JCI are subject to reimbursement by the Government of India.
Rating agencies too subjective, loaded against India, need reform: CEA (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Credit rating agencies need to reform their sovereign rating process to correctly reflect the default risk of developing economies, saving billions in funding costs, the government’s chief economic adviser, V Anantha Nageswaran, said recently.
What is a Sovereign Credit Rating?
- A Sovereign Credit Rating serves as an assessment of a government's ability to meet its debt obligations, with a lower rating reflecting higher credit risk.
- Rating agencies typically consider multiple factors such as growth rate, inflation, government debt, short-term external debt as a percentage of GDP, and political stability.
- A positive credit rating not only boosts credibility but also indicates a history of timely loan repayments, aiding banks and investors in evaluating loan applications and determining appropriate interest rates.
- The global credit rating industry is dominated by three major agencies: Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Despite India's ascent from the 12th to the 5th largest economy globally in 2023, with the second-highest growth rate among comparable economies, its credit ratings from S&P and Fitch stand at BBB, while Moody's rates it at Baa3—indicating the lowest investment-grade level.
Concerns Regarding Credit Rating Methodology:
- A quantitative examination revealed that more than 50% of credit ratings rely on qualitative components.
- Institutional Quality, predominantly gauged through the World Bank’s Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs), emerges as the primary factor influencing the credit rating of a developing economy.
- This poses a challenge as these metrics are often non-transparent, perception-driven, and derived from a limited group of experts, making them inadequate in representing the sovereign's willingness to meet its financial obligations.
- The non-trivial impact of these indicators on ratings implies that developing economies must exhibit progress along subjective indicators to secure a credit rating upgrade.
CEA's Suggestions for Credit Rating Reform:
- The Chief Economic Advisor (CEA) proposed a shift towards primarily considering a country's historical debt repayment record as a key determinant of its 'willingness to pay,' in contrast to relying on potentially suboptimal qualitative information.
- Embracing such a model would significantly enhance the credibility of Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs).
- The use of qualitative information and judgment should only be a last resort when genuine, verifiable data options are unavailable.
- If governance indicators are to be employed, they should be grounded in clear, well-defined, and measurable principles, steering away from subjective assessments by CRAs.
- CRAs possess a comprehensive database of global best practices, influencing their judgments.
- Sharing this knowledge with the countries they assess would empower sovereigns to take targeted actions to enhance their creditworthiness.
Kambala (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the weekend of November 25 and 26, 160 pairs of buffaloes and their jockeys will race on specially made slush tracks for Kambala races at City Palace Grounds in Bengaluru.
What is Kambala?
- Kambala is a folk sport rooted in coastal Karnataka, particularly in areas where Tulu speakers are predominant.
- In the past, families and groups used to organize races in the muddy paddy fields after the harvest season.
- For many families, especially those from the Bunt community in coastal regions, Kambala holds significant prestige.
- Throughout the year, they groom pairs of buffaloes with the aim of winning major Kambala events and other races.
Kambala consists of four main categories:
- Negilu (plough): Lighter ploughs are used to tie buffaloes for the race.
- This category is for entry-level buffalo pairs participating in their first Kambala race.
- Hagga (rope): Buffaloes are raced by jockeys with just a rope tied to both buffaloes.
- Adda Halage: Participants stand over a horizontal plank dragged by buffaloes.
- Unlike Hagga and Negilu, where jockeys run behind the animals, buffaloes drag the jockeys in Adda Halage.
- Kane Halage: A wooden plank is tied to buffaloes.
- The plank, on which jockeys stand, has two holes through which water gushes out as it is dragged along the slush tracks.
- The height of water splashes determines the winner of the event.
Coming soon, a ‘Cafeteria’ for oil spill-hit birds at Ennore Creek (The Hindu)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Experts from the Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) and the Besant Memorial Animal Dispensary (BMAD) are planning to establish feeding stations for birds at the creek, where contamination due to an oil spill from industries in Manali has brought down the bird population drastically.
About Ennore Creek:
- Ennore Creek, situated in Thiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu, is a backwater channel branching off from the Kosathalaiyar River.
- It merges with the Bay of Bengal at Mugathwara Kuppam, while its northern channel links to Pulicat Lake, the country's second-largest brackish water lake.
- For generations, this creek has been a lifeline for communities in the neighbouring villages, designated as CRZ IV (Water Body) in the coastal zone management plan by the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority.
- Its significance is heightened for local fisherfolk, alongside the Buckingham Canal and the broader Pulicat water system.
- The Ennore Creek has historically fostered a robust aquatic ecosystem renowned for its biodiversity.
- This ecologically sensitive area once boasted extensive mangrove swamps, contributing not only to sustainable fish resources but also playing a crucial role in flood mitigation during periods of heavy rainfall, high tides, and cyclones.
About the Wildlife Trust of India:
- Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) is an Indian Non-profit Organisation (NGO) committed to nature conservation.
- Motto: In Service of Nature
- It was formed in November 1998, in response to the rapidly deteriorating condition of the country's wildlife.
- Its mission is to:
- Conserve wildlife and its habitat and
- Work for the welfare of individual wild animals, in partnership with communities and governments.
- WTI has earned recognition for accomplishing significant conservation milestones, including the recovery of populations for critically endangered species, successful species translocation, and the mitigation of human-animal conflicts.
How an AI tool can make weather forecasts more accurate and help tackle climate change (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
At the recent COP28, NASA and IBM announced that an Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool called watsonx.ai would be available on the open-source AI platform Hugging Space.
What is watsonx.ai?
- Watsonx.ai is a collaborative Artificial Intelligence tool developed by IBM and NASA.
- Its primary function is to enable users to monitor Earth from space, assessing past environmental changes and offering predictions about future occurrences.
- User-Friendly Interface: The tool is designed for simplicity, requiring users to select a location and a date.
- Watsonx.ai then highlights changes in floodwater, reforestation efforts, and other pertinent factors.
Functionality:
- Watsonx.ai is built on a foundation model trained on a diverse set of uncategorized data, allowing it to extrapolate information from one context to another.
- NASA provides datasets in the form of satellite images, and IBM developed the foundation model to interpret these visual inputs.
- The model's training involves comprehending visual sequences over time by reconstructing images with blank areas. This process enhances its ability to understand the connections between photos.
- Adjustments were made to the model for specific tasks such as segmenting and categorizing photos.
Additional Components:
- Watsonx.data: A specialized data store optimized for governed data and AI workloads.
- It facilitates the scaling of AI workloads by leveraging the entire data landscape.
- Watsonx.governance: An end-to-end toolkit encompassing both data and AI governance. It aids clients in establishing responsible, transparent, and explainable AI workflows.
- The toolkit provides governance capabilities for model management throughout the AI lifecycle.
Why rain and flood woes have hit Tamil Nadu hard in December (Indian Express)
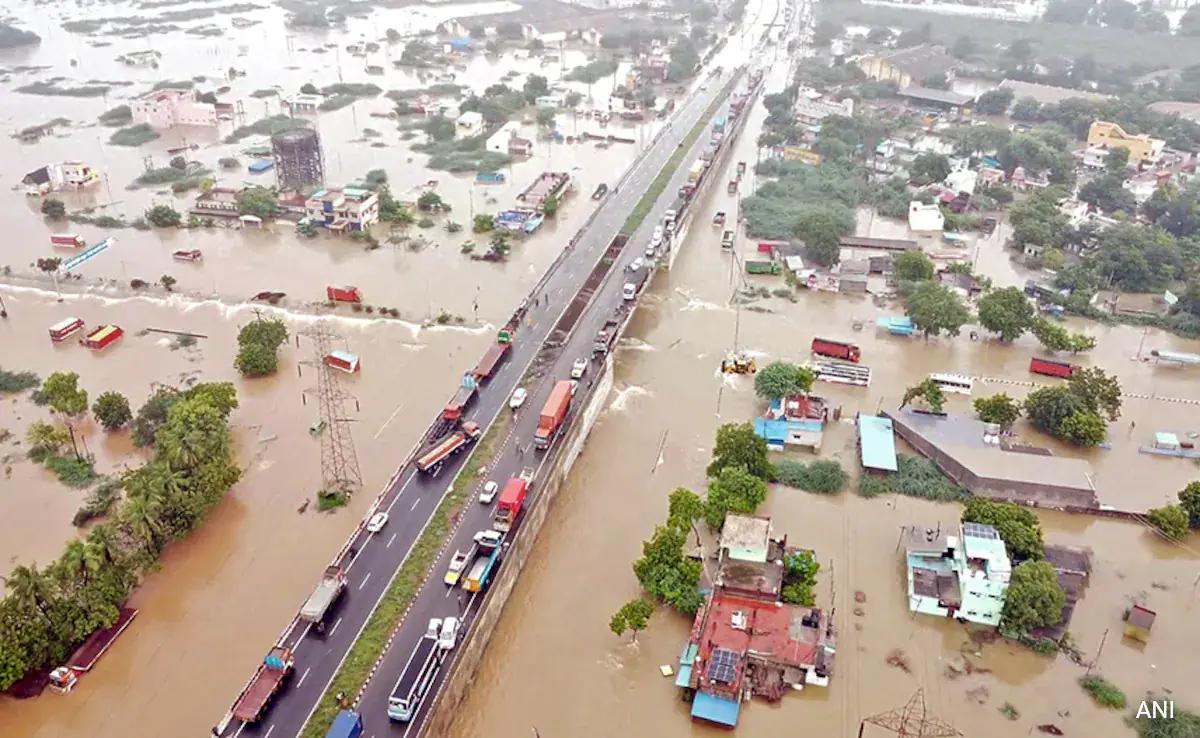

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu has battled heavy rainfall throughout December. At the beginning of the month, parts of Chennai and its neighbourhood experienced massive flooding because of Cyclone Michaung.
News Summary:
- Tamil Nadu has experienced significant rainfall, recording 450mm since October 1.
- Among the 38 districts, only 14 have reported deficient rainfall until December 20.
Seasonal Rainfall Norms:
- December rainfall is typical for Tamil Nadu, with the northeast monsoon being crucial for the region.
- Nearly 48% of the annual rainfall (443.3mm) in Tamil Nadu occurs from October to December, impacting rabi cultivation.
Recent Rainfall Patterns in Southern Tamil Nadu:
- Three districts in southern Tamil Nadu witnessed 'exceptionally' heavy rainfall from December 17 to 19.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported a 100% or more surplus during this period compared to the previous week (December 6-13, 2023).
Factors Contributing to Record Rainfall:
- Vigorous northeast monsoon over Tamil Nadu and Kerala, particularly in the southern regions.
- Development of a cyclonic circulation in the southwest Bay of Bengal on December 16, enhancing northeast monsoon winds.
- The persistence of this system over southern Tamil Nadu on December 18 and 19, led to heavy cloud convection and hefty rainfall.
IMD's Forecast:
- The cyclonic circulation has moved away from the Indian landmass, currently positioned over the southeast Arabian Sea.
- No significant rainfall is expected in Tamil Nadu, but the IMD predicts light to moderate intensity rainfall (up to 64mm in 24 hours) in certain areas of southern Tamil Nadu.
What is Northeast Monsoon?
- The northeast monsoon stands as a significant and permanent element within the Indian subcontinent's climate system.
- Its nomenclature originates from the prevailing direction of the monsoon winds—blowing from the northeast to the southwest.
- In their trajectory, these winds accumulate moisture from the Bay of Bengal, subsequently depositing it over southern states such as Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, south Telangana, and Karnataka.
- This monsoon is alternatively known as the winter monsoon, retreating monsoon, or reverse monsoon.
- Period: The northeast monsoon maintains activity throughout the three-month span from October to December.
- Causes and Influences: One of the primary instigators of the northeast monsoon is the southward shift of the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
- The ITCZ, a dynamic belt near the Equator, marks the convergence of trade winds from the northern and southern hemispheres.
- The southward displacement of the ITCZ, coupled with the warming of the Indian Ocean, induces a reversal in the lower-atmosphere moisture-laden winds' direction—from southwest to northeast—thereby triggering the Northeast Monsoon (NEM).
Sangai Deer (Indian Express)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Manipur Government has expressed its reservations to the Centre over a hydro-electric modernisation plan in the state’s famous Loktak Lake saying it could be detrimental to the endangered species of Sangai deer apart from disturbing the biodiversity of the lake.
About Sangai Deer:
- The sangai is an endemic and endangered subspecies of Eld's deer found only in Manipur, India.
- It is also the state animal of Manipur.
- Its common English name is Manipur brow-antlered deer or Eld's deer and the scientific name is Rucervus eldii eldii.
- It is believed to have originated from a common ancestor of the brow-antlered deer family, which is thought to have existed in the region during the Pleistocene epoch, around 12,000 years ago.
- Its original natural habitat is the floating marshy grasslands of the Keibul Lamjao National Park, located in the southern parts of the Loktak Lake, which is the largest freshwater lake in eastern India.
- Appearance: is a medium-sized deer that is unique in appearance and behavior.
- The Sangai deer is a slender and graceful deer, with long legs and a thin neck. They have a height of around 90-100 cm at the shoulder and can weigh between 70 to 120 kg.
- Food Habits: The Sangai deer is primarily found in the marshy wetlands of the Loktak Lake in Manipur, where they feed on the vegetation growing on the floating biomass called “Phumdis.”
- They are known to feed on a wide variety of plants, including grasses, sedges, and herbs.
- Vulnerable Species: The Sangai is an endangered species and is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- The population of Sangai deer has been severely threatened due to habitat loss, hunting, and poaching.
- In the 1950s, the population of the Sangai deer was estimated to be around 600-700 individuals.
- However, by the 1970s, the population had declined to less than 100 individuals due to extensive hunting and habitat loss.
- The Government of India and the State Government of Manipur took several conservation measures, including the establishment of the Keibul Lamjao National Park in 1977, to protect and conserve the Sangai deer.
- The Sangai deer is a social animal and is usually found in small herds of 2-20 individuals.
- Protecting and conserving their natural habitats is one of the most effective ways to ensure the survival of these species.
- This can be achieved through the creation and management of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, and the restoration of degraded habitats.
Digital Twins (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Survey of India (SoI) and Genesys International, a prominent Indian mapping company, revealed a strategic collaboration for the implementation of a three-dimensional (3D) digital twin-mapping initiative in India.
About Digital Twin:
- Digital twins are digital representations of physical objects, people or processes.
- They aid decision-making through high-fidelity simulations of the twinned physical system in real-time and are often equipped with autonomous control capabilities.
- These replicas serve as dynamic and detailed counterparts, providing a real-time, data-driven simulation of their physical counterparts.
- The concept of digital twins has gained prominence with the advent of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and machine learning.
- In essence, a digital twin continuously collects and processes data from its physical counterpart, offering a comprehensive view of its behavior, status, and interactions.
- This real-time synchronization enables organizations to monitor, analyze, and understand the performance of physical assets or processes more effectively.
Applications:
- Manufacturing Sector: One primary application of digital twins is in the manufacturing sector.
- Manufacturers use digital twins to create virtual models of products and production processes.
- This allows for simulation, analysis, and optimization before physical prototypes are built, leading to reduced development costs and improved product quality.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, digital twins are employed to create personalized models of patients.
- These models, based on individual health data, help in predicting health outcomes, optimizing treatment plans, and advancing medical research.
- Transportation: Transportation industries utilize digital twins for optimizing logistics and predictive maintenance.
- For example, digital twins of aircraft engines can simulate performance under various conditions, aiding in proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Urban Planning: Urban planning benefits from digital twins by creating virtual models of entire cities.
- This assists in designing and optimizing infrastructure, managing resources efficiently, and planning for future growth and development.
- Industries: In industrial settings, digital twins of production processes enable real-time monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
Farlowichnus rapidus (The Hindu)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Brazil's geological service recently announced a new species of dinosaur, a speedy animal that lived in the desert during the early Cretaceous period.
About Farlowichnus Rapidus:
- The new species of dinosaur was a small carnivorous animal about the size of a modern-day seriema bird, or about 60-90 cm (2-3 feet) tall.
- it was a very fast reptile that ran across the ancient dunes.
- These fossilized dinosaur "trackways," were first found in the 1980s by Italian priest and paleontologist Giuseppe Leonardi in the city of Araraquara, in Sao Paulo (Brazil).
- It lived during the early Cretaceous period.
About Cretaceous Period:
- The Cretaceous Period, spanning from approximately 145 to 66 million years ago, represents the third and final epoch of the Mesozoic Era.
- It is characterized by significant geological and biological events.
- The climate was generally warm, and the world's continents were positioned closer to their present locations.
- The Cretaceous witnessed the proliferation of diverse and iconic dinosaurs, including the formidable Tyrannosaurus rex and the enormous herbivorous sauropods.
- Additionally, flowering plants, or angiosperms, experienced a remarkable evolutionary expansion during this period, transforming terrestrial ecosystems.
- Towards the end of the Cretaceous, a catastrophic event, possibly a large asteroid impact, led to the mass extinction of dinosaurs and numerous other species, marking the boundary between the Cretaceous and the subsequent Paleogene Period.
- This extinction event profoundly shaped the course of Earth's biological evolution.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The annual tiger census in West Bengal’s Sundarbans is scheduled to commence on November 27.
About Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR) is situated in the coastal districts of West Bengal, i.e. South 24- -Parganas and part in North 24-Parganas.
- It lies at the southernmost extremity of the lower Gangetic delta bordering the Bay of Bengal.
- It is one of the first nine Tiger Reserves declared under the Project Tiger scheme in the year 1973.
- It is the only mangrove forest throughout the world (besides Bangladesh) to harbour a significant tiger population.
- Borders: The Sundarbans Tiger Reserve is bound on the east by the international boundary with Bangladesh formed by the rivers Harinbhanga, Raimangal, and Kalindi.
- On the south lies the Bay of Bengal.
- The western border is formed by the river Matla, which acts as a common boundary with the territorial Forest Division of South 24- Parganas.
- Towards the northwest, the area is bound by rivers Bidya and Gomdi.
- The Sundarban Tiger Reserve is a part of the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve.
- It harbours significant populations of the river terrapin (Batagur baska), which was once believed to be extinct.
- It is the nesting ground for marine turtles like Olive Ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea), Green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas), and Hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata).
- Flora: These comprise true mangroves or major elements, minor elements of mangroves or/and mangrove associates, shrubs, non-halophytic non-mangrove associates, halophytic herbs, shrubs, weeds, epiphytes, and parasitic plants.
- Fauna: It is to a large number of endangered and globally threatened species like the tiger (Panthera tigris tigris), fishing cat (Prionailurus viverrina), and estuarine crocodile (Crocodilus porosus), Gangetic (Platanista gangetica) and Irrawaddy Dolphin (Oracella brevirostris), king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah), water monitor lizard (Varanus salvator), etc.
Black-spotted Croaker, or the Ghol Fish (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The black-spotted croaker, or the ghol fish — considered a fisherman’s lottery — was declared the state fish of Gujarat on Tuesday.
About Ghol Fish:
- The Ghol fish is a rare and valuable marine species known for its richness in essential nutrients such as iodine, omega-3, DHA, EPA, iron, taurine, magnesium, fluoride, and selenium.
- Habitat: Typically found in the Indo-Pacific region, stretching from the Persian Gulf to the Pacific Ocean, the Ghol fish thrives in the marine areas of Gujarat and Maharashtra in India, exhibiting a distinctive golden-brown color.
- Size and Price: With a length of around one-and-a-half meters, the Ghol fish's price increases with its size, reaching up to Rs 5 lakh per unit length.
- Referred to as 'Sea Gold,' the Ghol fish earns this moniker due to a pouch in its stomach with potent medicinal properties, making it highly valued in the overseas market.
- Health Benefits:
- Eye Health: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins, the Ghol fish contributes to maintaining eyesight.
- Anti-Ageing: The collagen content in the fish helps prevent wrinkles, preserving skin elasticity.
- Cognitive Development: The omega-3 content supports the growth of brain cells, enhancing the IQ of infants if consumed regularly.
- Muscle Toning: The fish is known for its muscle-toning properties.
- Economic Value: In high demand for both its meat and air bladder (sold separately), the Ghol fish serves various purposes, from culinary use to making beer and wine, with its air bladder finding applications in pharmaceuticals.
Psyche Mission (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A NASA experiment on the Psyche spacecraft has beamed back a near-infrared laser that contains test data from almost 16 million kilometers away.
About the Psyche Mission:
- Psyche is a NASA mission to study a metal-rich asteroid ‘Psyche’, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- The mission launched on October 13, 2023, from Kennedy Space Center and will arrive at Psyche in August 2029.
- The spacecraft will orbit the asteroid for about two years, studying its geology, composition, and magnetic field.
- Scientists believe that Psyche may be the exposed core of an early planet that never fully formed.
- If so, studying Psyche could provide important insights into the formation of our solar system.
- It is also the first in a series of NASA science missions to be the primary payload launched on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
- The goals of the Psyche mission are to:
- Understand the composition and structure of a metallic asteroid.
- Determine how Psyche formed and evolved.
- Learn more about the formation of planetary cores.
- The Psyche spacecraft is a solar-powered spacecraft that uses Hall effect thrusters for propulsion.
- The spacecraft also carries a suite of scientific instruments, including:
- A magnetometer to measure Psyche's magnetic field.
- A spectrometer to measure the composition of Psyche's surface.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer to measure the abundance of elements on Psyche's surface.
Mythimna Separata (DownToEarth)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Persistent high temperatures over an extended period might be responsible for the severe infestation of the Mythimna separata pest in Assam, causing damage to paddy crops in at least 15 districts.
About Mythimna Separata:
- This is a common long-distance migratory insect and a significant pest for various grain crops.
- Distribution: Mythimna separata is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, including China, Japan, Southeast Asia, India, and eastern Australia.
- It has also been introduced to New Zealand and some Pacific islands.
- In India, it was initially identified as a sporadic pest in Tamil Nadu in 1937 and later in Kerala and Odisha in 1957.
- Known by various names such as the ear-head-cutting caterpillar, rice ear-cutting caterpillar, or armyworm, this pest feeds on leaves and has the capability to cut off panicles from the base of a crop plant.
- Its feeding habits often leave the field resembling it has been grazed by cattle.
- During an outbreak, the pest multiplies rapidly and moves in swarms from one field to another, similar to an army, causing harm to crops.
- The pest population tends to increase under favorable conditions, particularly when there is a rise in temperatures coupled with dryness.
Investor Risk Reduction Access platform (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the chairperson of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) launched the Investor Risk Reduction Access platform.
About the Investor Risk Reduction Access Platform:
- The Investor Risk Reduction Access Platform is created to make investing safer, especially when technical issues occur at the trading member's end, both at the primary site and the disaster recovery site.
- Its purpose is to let investors close their open positions and cancel pending orders using the IRRA platform when technical problems or unexpected outages make the trading member's site inaccessible.
- It's designed to minimize risks for investors involved in the market.
- The platform is not for making new positions or orders;
- its role is solely to cancel pending orders.
- This platform is accessible to trading members supporting internet-based trading (IBT) and Security Trading through Wireless Technology (STWT) for their investors.
- However, it is not available for algo trading and institutional clients.
- All major stock exchanges – BSE, NSE, NCDEX, MCX, and Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India (MSE) – have collaborated to develop this platform.
- Stock exchanges can keep an eye on factors such as connectivity, order flow, and social media updates.
- They can independently activate the IRRA service if necessary, without waiting for a request from the trading member.
Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (Financial Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister announced the launch of two India-led initiatives: the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository and a Social Impact Fund aimed at promoting the development of Social Impact Fund to advance Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in the Global South during the Virtual G20 Leaders’ Summit on 22nd November 2023.
About the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository:
- It was developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is an extensive resource center that combines knowledge and insights from G20 members and visiting countries.
- Its primary objective is to fill the knowledge gap in the decision-making processes and methodologies necessary for designing, constructing, deploying, and governing Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs).
- The GDPIR presents information in a standardized format from countries and organizations that have successfully implemented DPIs on a large scale.
- This includes elements such as maturity scales, source codes (where available), and governance frameworks.
- Currently, the GDPIR showcases 54 DPIs from 16 countries.
- The DPIs from India featured in the GDPIR include
- Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), eSanjeevani, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DigiLocker, Umang, Co-WIN, Government e-marketplace, API Setu, Diksha, E-Hospital and Poshan Tracker etc.
What about the Social Impact Fund?
- The fund will financially support countries developing DPIs, providing “upstream technical and non-technical assistance”.
- The platform allows other governments, international organisations, and philanthropies to contribute to the fund too.
- India has pledged an initial commitment of $25 million (USD) to the fund.
Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended to the authorities that the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary abutting the Bandipur Tiger Reserve be declared as a core critical tiger habitat.
About Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Heggadadevanakote Taluk of Mysore district in Karnataka and comprises the Lakshmanapura State Forest.
- In 1974, Nugu was declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary and later during the year 2003-2004, the area of Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary was added to the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
- On the western side of the sanctuary lies the backwater of Nugu Dam which forms the part of the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary.
- On the southwestern side, the area touches the Alaganchi State Forest which comes under the Bandipur Tiger Reserve.
- During the summer, elephants migrate from the adjoining area and congregate on the foreshore area because here, the backwater recedes and the area becomes temporary vast grassland due to the availability of fodder and water.
Geology of Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Nugu region has red loamy type of soil with boulders.
The climate of Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The climate in the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary is of moderate type with the temperature ranging between14°C to 38°C.
- The area receives rainfall both from southwest and northeast monsoons.
- The average amount of rainfall received in this area is 1000mm.
- Flora: The flora of the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary is similar to that of the Bandipur National Park.
- The forests comprise southern mixed deciduous trees and dry deciduous scrubs.
- Some of the tree species found in this region include Dipterocarpus indicus, Calophyllum tomentosum, and Hopea parviflora.
- Fauna: Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary has a vast list of fauna with a wildlife population that includes elephants, wild boar, jungle cats, tigers, leopard, bonnet macaque, small Indian civet, back nappe hare, along with reptiles like the marsh crocodile, monitor lizard, cobra, rat snake, etc.
- With the adoption of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, hunting and poaching is banned and illegal in this sanctuary.
- In recent times, the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary has been declared to be an eco-sensitive zone, which means there will be no commercial or industrial activity including mining in this area.
Tantalum (NewsOnAir)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Armed Forces contingent comprising 81 personnel departed for Australia on Wednesday to take part in the second edition of Joint Military Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23.
About Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23:
- Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23 was established in 2022, with its first edition held in Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- It is planned as an annual training event, alternating between India and Australia.
- The primary goal of the exercise is to cultivate collaborative partnerships and share best practices between the two sides.
- This year, the exercise is scheduled to take place in Perth, Australia, spanning from November 22nd to December 6th, 2023.
- The Indian Army contingent, consisting of 60 personnel from a Gorkha Rifles battalion, will actively participate in this exercise.
- A key focus is on promoting interoperability during multi-domain operations in urban and semi-urban terrain, aligned with Chapter VII of the United Nations on peacekeeping operations.
- The joint exercise serves as a platform for exchanging ideas and collectively rehearsing tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting tactical operations.
- Additionally, the exercise contributes to fostering understanding between the two militaries, further strengthening defense cooperation between the two friendly nations.
Other Exercises between India and the Aus:
- AUSINDEX - Naval exercise between India and Australia
- Exercise Pitch Black - It is a biennial warfare exercise hosted by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
Inter Command Ocean Sailing Race 2023 (NewsOnAir)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The second edition of the Inter-Command Ocean Sailing Race to Goa was flagged off from the Naval Base in Kochi on Wednesday.
About the Inter Command Ocean Sailing Race 2023:
- The Inter Command Ocean Sailing Race 2023 features four 40-footer sailboats for an exciting journey in the Arabian Sea which was:
- INSV Bulbul
- INSV Neelkanth
- INS Kadalpur, and
- INSV Hariyal
- Each boat has a team of eight people from three naval commands and a combined team from Andaman and Nicobar Command, including the Delhi area.
Details of the Race:
- Distance and Route: The race covers around 667km from Naval Base, Kochi, to Goa in about five days.
- Engine-Free Journey: Boats will use the wind to reach Goa without engines.
- Inclusive Crew: This edition includes both men and women officers and sailors, promoting equal opportunities.
- Competition: With 32 participants, each competing for the title, the boats will navigate through the Arabian Sea's currents and winds.
Organizational Framework:
- Event Host: The Southern Naval Command organizes the race with the Indian Naval Sailing Association in New Delhi.
- Coordination: The Indian Navy’s Offshore Sailing Club in Kochi and the Ocean Sailing Node in INS Mandovi, Goa, coordinate the event.
- Purpose: The race helps the Navy improve risk management and technical skills while fostering a spirit of adventure among the crew.
Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) (Financial Express)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The AIM and NITI Aayog have recently introduced a new accelerator known as Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) aimed at providing support to startups in the circular economy sector in both Australia and India.
About Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE):
- RISE, a collaborative initiative between Australia’s national science agency (CSIRO), and Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), the Government of India’s flagship initiative for fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, is a dedicated accelerator.
- This program is designed to support startups and small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India and Australia focusing on circular economy technologies and solutions.
Key Highlights:
- Focus Themes: The RISE Accelerator targets startups in India and Australia engaged in circular economy technologies, specifically in:
- Climate Smart Agriculture
- Clean Energy
- Circular Economy and Waste Management, and
- Climate Smart Mobility.
- Nine-Month Program: Over the course of nine months, the RISE Accelerator aims to assist startups in navigating early steps in a new region, establishing connections with the right partners, customers, and talent, and building credibility to succeed in international markets.
- First Round Focus: In its initial round, the accelerator concentrates on supporting startups and SMEs involved in technologies and solutions related to waste and the circular economy.
- Financial Support: Participating startups have the opportunity to receive up to INR 40,00,000 in non-equity grants.
- Future Rounds: Subsequent rounds of the accelerator will shift focus to climate-smart agriculture, clean energy, and climate-smart mobility.
New Frog Species- Music Frog (The Hindu)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered a new species of 'music frog' in Arunachal Pradesh.
About the New Frog Species:
- Scientists discover a new 'music frog,' Nidirana noadihing, in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Both male and female frogs are vocal with a unique call pattern of two-three notes.
- The discovery was made during field surveys in the Changlang and Lohit districts in August-September.
- Male frogs with 'robust' bodies were found calling loudly in vegetation near water bodies.
- The new species is named after the Noa-Dihing River, near where it was discovered.
- The species confirms the presence of the Nidirana genus in India for the first time.
- Nidirana species are known in Japan, Taiwan, China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.
- Appearance: The amphibians have "irregularly shaped and sized spots" on their eyelids and they have dark stripes around their moderately large eyes.
- Their pupils are gold-rimmed and their irises are dark brown and have a golden spackle.
- Habitat: Noa-Dihing Music Frogs inhabit swamps, ponds, and paddy fields, constructing nests for egg laying.
- The discovery emphasizes the importance of exploring specialized habitats like marshlands, often overlooked in scientific studies.
Naval Anti-Ship Missile Short Range (NASM-SR) (TOI)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy successfully test-fired an indigenous anti-ship missile over the Arabian Sea, marking a significant step in India's efforts towards self-reliance in defense technologies.
About Naval Anti-Ship Missile Short Range (NASM-SR):
- This revolutionary missile NASM-SR, entirely developed by Indian scientists and engineers, represents a huge stride in the indigenization of India's defense infrastructure.
- The project is a collaborative effort between various esteemed agencies, including the Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The successful trial brings a sense of pride and accomplishment to India's defense realm.
- Launch Capability: This advanced missile is designed for launch from attack helicopters, presenting a versatile addition to the naval arsenal.
- Replacement for Sea Eagle: NASM-SR is slated to replace the existing Sea Eagle missiles currently in use by the Navy, aligning with the imperative of modernization and technological advancement.
- Integration with MH-60R Helicopters: As Sea King helicopters are phased out, the NASM-SR is anticipated to integrate seamlessly with the new MH-60R multi-role helicopters, a pivotal component of the Navy's evolving fleet.
Key Features:
- The missile incorporates a state-of-the-art guidance system and integrated avionics.
- It introduces indigenous launcher technology tailored for helicopter deployment.
- Possessing a striking range of approximately 60 km.
- Travels at a speed of Mach 0.8, slightly below the speed of sound.
- Equipped with a 100kg warhead, rendering it capable of neutralizing patrol boats and causing substantial damage to larger warships.
- Employs an imaging infrared seeker to target heat emissions, enhancing precision in homing onto its designated targets.
- During the approach to its target, the NASM-SR operates at just 5 meters above sea level, a strategic feature known as sea skimming.
- This low-level approach minimizes the susceptibility to detection, tracking, and interception by enemy radars or surface-to-air missiles.
Exercise Vajra Prahar 2023 (The Hindu)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A joint exercise of the special forces of India and the United States commenced in Meghalaya’s Umroi Cantonment on Tuesday.
About Exercise Vajra Prahar 2023:
- Exercise Vajra Prahar is a collaborative effort between the Indian Army and the US Army Special Forces.
- It is the 14th such exercise aimed at sharing the best practices and experiences in areas such as joint mission planning and operational tactics
- Representing the US, personnel from the 1st Special Forces Group (SFG) of the US Special Forces are actively engaged.
- The Indian Army contingent, led by Special Forces personnel from the Eastern Command, contributes to this joint training effort.
- The first edition took place in India in 2010, and the 13th edition occurred at the Special Forces Training School (SFTS), Bakloh (HP).
- This continuity highlights the longstanding commitment to strengthening Indo-US defense ties.
- The 14th edition is currently underway at Umroi Cantonment, Meghalaya, spanning from 21st November to 11th December 2023.
- This location serves as the backdrop for intensive training and cooperation.
- Exercise Vajra Prahar serves as a crucial platform to enhance inter-operability between the Indian and US armies.
- This emphasis on seamless coordination aims to bolster defense cooperation and strategic alignment.
Other Exercises between India and the USA:
- YUDHABHAYAS- Army
- VAJRA PRAHAR- Army
- Exercise MALABAR (Multilateral)- Indian Navy
- RED FLAG 16-1- Air Force
- Exercise COPE India 23- Air Force
Risk weight (LiveMint)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Spooked by the strong growth in unsecured loans to consumers, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has increased the cost of funds for banks and non-bank financial companies (NBFCs), by increasing the risk weight of such loans.
What are Risk Weights?
- Every rupee lent by the bank is a cost or has an implication on its capital position.
- Depending on the nature of the loan and the inherent risk associated with it, risk weights are attributed.
- Banks have to ensure that their capital is enough to cover these risk-weighted assets.
- Total assets as disclosed in the financials and total risk-weighted assets are different things.
- Each asset class has varying risk weights.
- For instance, risk weights for home loans could range from 50 percent to 75 percent, for gold loans it is 75 percent.
- Corporate loans are charged 100 percent given the risk they carry.
How do they affect borrowers?
- Lower the risk weight, and lower the rate of interest. This is the thumb rule.
- Therefore, risk weights impact borrowers indirectly and are felt through the pricing of loans.
- For instance, home loans have the lowest interest rate among retail products because lower risk weights allow banks to pass on the advantage of capital consumption.
- Personal loans and credit cards have the highest interest rate because of their tenure and charge on capital.
Gambusia Fish (The Hindu)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Government and non-government groups in Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Punjab have recently put Gambusia fish into local water sources to deal with mosquito issues.
About Gambusia fish:
- Gambusia, also known as mosquitofish, is a genus of small, freshwater fish in the family Poeciliidae.
- There are over 40 species of Gambusia, most of which are found in North America, Central America, and the Caribbean.
- Gambusia fish are known for their voracious appetite for mosquito larvae, and they have been widely introduced around the world for mosquito control.
- They are small, with females typically reaching a maximum length of 7 cm and males a maximum length of 4 cm.
- They have a slender body with a pointed snout and a small mouth.
- They are typically green or silver in color, with some species having dark spots on their sides.
- Gambusia fish are livebearers, meaning that they give birth to live young.
- Females can produce up to 1,000 fries (baby fish) per year.
- They are opportunistic feeders and will eat a variety of foods, including mosquito larvae, small insects, and zooplankton.
- Gambusia fish have been introduced to many parts of the world for mosquito control.
- However, they have also been shown to have negative impacts on native fish populations.
- In some cases, Gambusia fish have been known to outcompete and displace native fish species.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) declares Gambusia one of the 100 worst invasive alien species in the world.
Tantalum (Indian Express)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Ropar has found the presence of tantalum, a rare metal, in the Sutlej river sand in Punjab.
What is Tantalum?
- Tantalum is a rare metal with the atomic number 73.
- Tantalum was first discovered by Anders Gustaf Ekenberg, a Swedish chemist, in 1802.
- It has been named after a Greek mythological figure Tantalus.
Properties:
- It’s grey, heavy, very hard, and one of the most corrosion-resistant metals in use today.
- It possesses high corrosion resistance because when exposed to air, it forms an oxide layer that is extremely difficult to remove, even when it interacts with strong and hot acid environments.
- When pure, tantalum is ductile, meaning it can be stretched, pulled, or drawn into a thin wire or thread without breaking.
- Moreover, it “is almost completely immune to chemical attack at temperatures below 150°C, and is attacked only by hydrofluoric acid, acidic solutions containing the fluoride ion, and free sulphur trioxide.
- Notably, tantalum also has an extremely high melting point, exceeded only by tungsten and rhenium.
Applications:
- Tantalum is most prominently used in the electronic sector.
- The capacitors made from tantalum are capable of storing more electricity in smaller sizes without much leakage than any other type of capacitor.
- This makes them ideal for use in portable electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and digital cameras.
- As tantalum has a high melting point, it is frequently used as a substitute for platinum, which is more expensive.
- The rare metal is also used to make components for chemical plants, nuclear power plants, aeroplanes, and missiles.
- Tantalum does not react with bodily fluids and is used to make surgical equipment and implants, like artificial joints.
Government bans anti-cold drug combination for kids aged under four (Indian Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has prohibited the use of anti-cold fixed drug combinations in children below four years of age.
What are Fixed Dose Combination (FDC) Drugs?
- Fixed-dose combination (FDC) drugs, also referred to as combination products, embody a formulation containing two or more active drugs within a single dosage form.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) defines a combination product as a composition involving a drug and a device, a biological product and a device, or a combination of a drug, device, and biological product.
- While the conventional approach favours formulating drugs as single compounds, the acceptance of fixed-ratio combination products hinges on two key criteria:
- Dosage Requirements: Each ingredient in the combination must meet the dosage criteria tailored to a specific population group.
- Proven Advantages: The combination should demonstrate a clear advantage over administering individual compounds separately in terms of therapeutic effect, safety, or compliance.
- FDCs have witnessed significant popularity in the Indian pharmaceutical market, experiencing notable growth in recent years.
About the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO):
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) serves as the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) in India, overseeing the medical devices industry per the Drugs & Cosmetics Rules.
- Positioned under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, it is led by the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) with its headquarters situated in New Delhi.
- Operationalizing under the provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is entrusted with several crucial responsibilities, including the approval of new drugs, the facilitation of clinical trials, the establishment of standards for drugs, ensuring control over the quality of imported drugs, and coordination of activities among State Drug Control Organizations.
- One of its significant roles lies in collaboration with state regulators for granting licenses related to specialized categories of critical drugs.
- These encompass vital medical components such as blood and blood products, I.V. fluids, vaccines, and sera.
- The CDSCO plays a pivotal role in upholding standards, ensuring quality, and fostering coordination across the regulatory landscape for the benefit of public health in India.
Why the UK banned Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad ads over ‘greenwashing’ claims (Indian Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Earlier in December, the United Kingdom’s ad regulator banned advertisements from Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad for allegedly misleading consumers regarding the environmental impact of air travel.
What is Greenwashing?
- Greenwashing is the deceptive practice of creating a false impression or providing misleading information about the environmental sustainability of a company's products.
- It involves making unverified claims to lead consumers to believe that a company's products are more environmentally friendly or have a more positive impact on the environment than is accurate.
- Furthermore, greenwashing can occur when a company highlights the sustainable aspects of a product to divert attention from its involvement in environmentally harmful practices.
- Companies may employ greenwashing tactics by using vague claims that lack substantiated data or scientific validation.
- For instance, a car vendor might assert that a vehicle is eco-friendly due to increased fuel efficiency, conveniently overlooking or downplaying the broader environmental impact of vehicle manufacturing processes.
What are the Concerns With Greenwashing?
The practice of greenwashing raises apprehensions on several fronts:
- Authenticity of Climate Goals: There is a risk of undermining the authenticity of climate goals when misleading or exaggerated information about environmental initiatives is presented.
- Unwarranted Recognition and Benefits: Entities involved in greenwashing may receive undeserved recognition or benefits, potentially rewarding irresponsible behaviour and discouraging genuine sustainability efforts.
- Market Distortion: Greenwashing can distort markets by creating an uneven playing field.
- Entities engaging in deceptive practices might gain an unfair advantage over those genuinely adhering to stringent environmental standards.
- Lack of Comprehensive Regulations: The absence of comprehensive regulations and standards for environmental claims allows greenwashing to persist without adequate scrutiny, contributing to a lack of transparency.
- Challenges to Carbon Credit Systems: The practice of greenwashing introduces challenges to the integrity of carbon credit systems.
- This is particularly evident in informal markets, where the expansion of credit sources and certification by unofficial entities raise concerns about transparency and reliability.
- It's crucial to note that in the context of carbon credits, one credit represents the removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
- The concept of carbon credits was introduced by the Kyoto Protocol, providing rewards to countries or firms surpassing emission reduction mandates.
Global Initiatives Addressing Greenwashing:
- During the 27th Conference of Parties (COP27), the United Nations Secretary-General declared a zero-tolerance stance against greenwashing.
- Private corporations were urged to rectify their practices to align with genuine environmental efforts.
- In a landmark move in October 2023, the European Union approved the world's first green bond standards.
- These standards, under the "European Green Bond" label, mandate transparency and direct 85% of funds towards sustainable activities within the EU.
- The legislation aims to support the EU's transition to climate neutrality.
Laws in India:
- In India, greenwashing is classified as an unfair trade practice under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- This legislation prohibits deceptive claims and outlines penalties and remedies for consumers adversely affected by such misleading practices.
- In February 2023, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) issued guidelines for issuers of green debt securities.
- These guidelines are designed to ensure transparency, prevent greenwashing, protect investors, and regulate the development of the securities market.
- The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI), a voluntary self-regulatory organization, plays a crucial role in monitoring advertising practices.
- It holds jurisdiction over allegations of greenwashing, ensuring that ads are not only legal but also honest and fair.
- The ASCI's regulatory efforts aim to safeguard consumer interests and promote fair competition within the Indian advertising landscape.
Bhoomi Rashi Portal is revolutionizing land acquisition for Highway projects – Here’s how (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari revealed in a recent statement to the Rajya Sabha that the Bhoomi Rashi portal is instrumental in expediting the development of highway infrastructure in India.
About the Bhoomi Rashi Portal:
- The acquisition of land was done manually before the year 2018. The data files were moved physically, leading to some limitations. This included delays in issuing notices, errors in land details, etc.
- To overcome the issues, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways came up with a system.
- It is known as “Bhoomi Rashi”.
- The portal came into force on 1st April 2018
- The system is digital and automates the whole land acquisition (LA) process.
- It made and still makes the LA process more transparent and error-free.
- The portal processes the notices at every stage on a real-time basis.
Key Objectives:
- Acceleration of Land Acquisition: The primary goal is to facilitate a quicker and more efficient land acquisition process for National Highways.
- Centralized Processing: Acting as a singular online platform, it consolidates the processing of land acquisition notifications, contributing to the swift development of highway infrastructure projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensures transparency and accountability throughout the land acquisition process.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Facilitates the electronic transfer of benefits directly to the accounts of the beneficiaries involved in the land acquisition.
Salient Features:
- Bilingual application with Hindi and English for easy usability
- Preparation of interface for adding basic details of the project, including land acquisition sanction details
- Preparation of interface for Land Acquisition locations. villages
- Preparation of Interface for Competent Authority for Land Acquisition (CALA) details. CALA is a revenue functionary of the State Government appointed for each NH Project.
- Interface for generating land acquisition notification
- Interface for land Details
- Interface for generation of notification: organisational email IDS for all those involved in the process flow to ensure smooth e-office management
- Interface for Objections and processing
- Interface for compensation determination and finalisation
- Interface for land owners and affected parties
- Interface for reports generation
The portal is seamlessly integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Ministry of Finance, ensuring real-time deposit of compensation into the accounts of affected/interested individuals.
What is Land Acquisition?
- Land acquisition is the governmental process, whether at the state or union level, through which private land is procured for infrastructure development, urbanization, or industrialization.
- In exchange, the government provides appropriate compensation to the landowner based on market value and assumes responsibility for the rehabilitation and resettlement of those affected by the land acquisition.
SAT quashes Sebi's order against Kishore Biyani, and others (Live Mint)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) on Wednesday quashed regulator Sebi's order banning Future Retail chairperson Kishore Biyani and some other promoters from the securities market for one year in an insider trading case.
About the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT):
- Established as a statutory and autonomous entity under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act, 1992, the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) serves as a crucial forum for adjudicating appeals against decisions made by SEBI or its adjudicating officers.
Key Functions:
- Appeals Jurisdiction: Primarily tasked with hearing appeals against orders issued by SEBI or its adjudicating officers under the SEBI Act.
- Extended Jurisdiction: Additionally, SAT entertains appeals concerning orders from the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) related to cases filed before them.
Composition:
- Presiding Officer: A retired or sitting Supreme Court judge, Chief Justice of a High Court, or a High Court judge with at least seven years of service.
- Judicial Member: High Court judge with a minimum of five years of service.
- Technical Member: Individual with expertise and a minimum of 15 years of experience in the financial sector, including securities market, pension funds, commodity derivatives, or insurance.
- This member can be a senior official in the Central or State Government or a person of proven ability and integrity.
Appointment and Tenure:
- Appointments made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India or its nominee.
- Presiding Officer and members serve a term of five years, eligible for reappointment for an additional term of up to five years.
- No member shall hold office after reaching the age of 70.
Powers and Authority:
- They are empowered with the same powers as a civil court under the code of civil procedure when adjudicating suits.
- Appeals to SAT can be made by any person aggrieved by SEBI or adjudicating officer orders, excluding those made with the consent of all parties.
Appeals Process:
- Appeals against SAT decisions can be filed in the Supreme Court, limited to questions of law.
- No appeal is permissible against orders made with the consent of all parties.
- The SAT, with its specific mandate and composition, plays a pivotal role in ensuring fairness and justice in the regulatory framework of the securities market in India.
What is Insider Trading?
- Insider trading is the act of buying or selling securities of a publicly traded company based on material information not yet disclosed to the public.
- Material information encompasses any data that could significantly influence an investor's decision to buy or sell the security.
- For instance, Consider a scenario where a government employee, possessing knowledge about an upcoming regulation that would favour a sugar-exporting company, takes advantage of this information by purchasing the company's shares before the regulation becomes public knowledge.
MSME Ministry launches 3 sub-schemes under RAMP programme; makes ZED scheme free for women (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
MSME Minister Narayan Rane recently launched three sub-schemes under the ministry’s existing RAMP ((Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity) programme.
About the RAMP Programme:
- The Raising & Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) program, supported by the World Bank and inaugurated in 2022, is dedicated to enhancing the performance of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) across India.
Program Objectives:
- Market and Credit Access: Facilitate improved access to markets and credit for MSMEs.
- Institutional Strengthening: Enhance institutional and governance structures at both central and state levels.
- Center-State Collaborations: Foster improved linkages and partnerships between central and state entities.
- Delayed Payment Issues: Address challenges related to delayed payments within the MSME sector.
- Greening of MSMEs: Promote sustainable practices and the adoption of green technologies within MSMEs.
- The National MSME Council has been set up by the Ministry to work as an administrative and functional body of the RAMP Programme.
Sub Schemes under RAMP:
- MSME GIFT Scheme: Aims to support MSMEs in adopting green technology through interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance.
- MSE SPICE Scheme: Focuses on promoting circular economy projects, with credit subsidy mechanisms, aligning with the MSME sector's goal of achieving zero emissions by 2070.
- MSE ODR Scheme: A pioneering initiative leveraging modern IT tools and Artificial Intelligence to address delayed payment incidents for Micro and Small Enterprises.
- Implementing Agencies for Sub Schemes:
- MSME GIFT and MSME SPICE Schemes: Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- MSE ODR Scheme: National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI)
- These sub-schemes, under the RAMP umbrella, signify a comprehensive effort to fortify and propel the growth of MSMEs, incorporating technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Chimaeras (The Hindu)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a recent landmark study, scientists reported successfully generating a live chimaera in non-human primates
About Chimaeras:
- A genetic chimaera is a single organism made up of cells from more than one distinct genotype (or genetic makeup).
- Examples of varying degrees of chimerism exist in the animal kingdom.
- For instance, the half-sider budgerigar, a common pet parakeet, displays different colors on each side of its body due to chimerism.
- In anglerfish, the male fuses with the female, eventually being absorbed, creating a single animal with a merged genetic makeup.
- Marine sponges are known to have up to four distinct genotypes in one organism.
- In humans, natural chimaeras occur when the genetic material in one cell changes, leading to a clonal population of cells different from the rest.
- Fusion of two fertilized zygotes early in embryonic development can result in a condition where two genetic makeups coexist in a single individual.
- Chimerism can also arise from twin or multiple pregnancies evolving into a single fetus or a twin fetus being absorbed into a singleton.
Hard Currency (Financial Express)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) said in a statement that Conditions are not ripe to make INR a hard currency.
What is Hard Currency?
- Usually, developed countries issue hard currency, and this currency is easier to trade and receive funds from other countries or investors from other nations.
Key characteristics of hard currencies:
- Hard currency means a stable currency, and its value does not fluctuate much in the international markets.
- It makes hard money currency easily tradable.
- It is issued by a sound economy. Developed countries issue hard currency and it is accepted by all nations across the world.
- It is highly liquid and several countries prefer to accept hard currency instead of local currency as it has lesser fluctuations and can be easily converted to local currency.
- Hard currency is universally accepted and international investors have a sense of faith in hard currency for trading.
- Countries across the globe consider hard currency as a foreign currency reserve, further adding to its value.
- As hard currency is easily convertible and stable, it is widely used in international exchanges.
- The value of the hard currency does not change much in response to global events.
- When domestic currencies struggle, people start holding on to hard currencies to protect their wealth.
Examples of hard currencies:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF) etc.
The E Prime Layer (HT)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an international team of scientists found a new mysterious layer called the E prime layer on the outer part of the Earth's core.
About the E Prime Layer:
- Before, it was thought that there's only a small exchange of materials between the Earth's core and mantle.
- However, experiments showed that when water reaches the boundary between the core and mantle, it reacts with silicon in the core and creates silica.
Development of this Layer:
- New research proposes that over billions of years, tectonic plates carrying surface water transported it deep into the Earth.
- When this water reaches about 1,800 miles below the surface at the core-mantle boundary, it triggers significant chemical changes, affecting the core's structure.
- Scientists observed that under high pressure, subducted water chemically reacts with core materials.
- This reaction forms a hydrogen-rich, silicon-depleted layer on the outer core, resembling a film.
- Silica crystals produced in this process rise and mix into the mantle, impacting the overall composition.
- Changes in the liquid metallic layer could potentially lead to reduced density and altered seismic characteristics, consistent with anomalies detected by seismologists.
Importance of this Discovery:
- This finding deepens researchers' understanding of the Earth's internal workings, revealing a more extensive and complex global water cycle than previously known.
- The altered core layer has significant implications for the interconnected geochemical processes that link surface water cycles with the deep metallic core.
What is ROV ‘Daksh’? (HT)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Defence Research Development Organisation's robotics team utilized the Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Daksh to aid in the ongoing rescue operations during the Uttarakhand tunnel collapse.
What is ROV Daksh?
- Daksh is a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), designed by the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) for the recovery of unexploded bombs.
- It can negotiate various hurdles in an urban setting and can also be utilised to survey and monitor nuclear and chemical contamination levels.
- 90% of its components are indigenous.
- It has ladder climbing abilities and can function for three continuous hours, with the capability to operate over distances exceeding 100 to 500 meters.
- It serves the bomb disposal units (BDU) of an army, police, and paramilitary forces, aiding in handling IEDs and other dangerous substances.
- Its manipulator arm can handle hazardous objects weighing up to 20kg from 2.5 meters and 9kg from 4 meters away.
- Daksh demonstrates the ability to climb stairs and maneuver steep slopes, with durable rubber wheels capable of withstanding blast impacts.
- It is equipped with multiple cameras, IED handling tools, nuclear biological chemical (NBC) reconnaissance systems, a master control station (MCS), and a shotgun.
- The equipment is specifically designed for use on a motorized pan-tilt platform, which can help reach the risky terrain.
Atmospheric Waves Experiment (Indian Express)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Atmospheric Waves Experiment is a first-of-its-kind NASA experimental attempt aimed at studying the interactions between terrestrial and space weather.
What is the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE)?
- AWE is a first-of-its-kind NASA experimental attempt aimed at studying the interactions between terrestrial and Space weather.
- Planned under NASA’s Heliophysics Explorers Program, the $42 million mission will study the links between how waves in the lower layers of the atmosphere impact the upper atmosphere, and thus, Space weather.
- AWE will be launched and mounted on the exterior of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS).
- From the vantage point, it will look down at the Earth and record the colourful light bands, commonly known as airglow.
- It will try to understand the combination of forces that drive the Space weather in the upper atmosphere.
- “AWE could open a new window of study, wherein scientists are attempting to understand if Space weather is affected by terrestrial and bottom-up forces.
- It will measure the airglow at mesopause (about 85 to 87 km above the Earth’s surface), where the atmospheric temperatures dip to minus 100 degrees Celsius.
- At this altitude, it is possible to capture the faint airglow in the infrared bandwidth, which appears the brightest enabling easy detection.
- AWE will be able to resolve waves at finer horizontal scales than what satellites can usually see at those altitudes, which is part of what makes the mission unique.
- The health of the ionosphere, whose lower layers sit at the edge of Space, is important for maintaining seamless communication.
- It is still not fully understood if the ionosphere is affected by the transient events or intense perturbations resulting from hurricanes or tornadoes.
- It was expected to launch in the month of August 2022, but the fresh launch is planned for later this month.
Rhododendron (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently rhododendron blooms in parts of Uttarakhand in November, worries experts.
About Rhododendron:
- Rhododendron is a diverse genus of flowering plants, encompassing over a thousand species, which include trees, shrubs, and creepers.
- These woody flowering plants belong to the heath family (Ericaceae) and are recognized for their appealing flowers and handsome foliage.
- Habitat: Rhododendrons thrive in various habitats, ranging from alpine regions and coniferous and broadleaved woodlands to temperate rainforests and even tropical areas.
- Distribution: Native to temperate regions of Asia, North America, and Europe, as well as tropical regions in Southeast Asia and northern Australia, rhododendrons have a broad geographical distribution.
- They flourish in slightly acidic soil conditions.
- Diversity: This genus displays an extensive range of sizes and shapes, from low-growing prostrate ground covers to towering trees exceeding 100 feet in height.
- In India, there are 132 taxa, including 80 species, 25 subspecies, and 27 varieties of rhododendrons.
- Local Names and Significance: In the local language, rhododendrons are known as "Lali Guras."
- Notably, they hold cultural significance as the national flower of Nepal and the state tree of Uttarakhand in India.
Nitrogen-9 Nucleus (Indian Express)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers have found "compelling evidence" supporting the existence of the uncommon nitrogen-9 isotope. This discovery challenges previous interpretations and provides a fresh perspective on subatomic structures.
About Nitrogen-9 Nucleus:
- Nitrogen-9 is a radioactive isotope of nitrogen.
- This means that it is unstable and will eventually decay into a different isotope of nitrogen or a different element.
- It is considered unusual because it has an uncommon combination of seven protons and two neutrons (7:2) in its atomic nucleus.
- This creates an unusually high ratio of protons to neutrons.
- Generally, elements have a balanced ratio for stability, but Nitrogen-9’s high proton content makes it less stable, challenging the conventional stability thresholds.
- This oddity raises questions about its existence in this state and how it maintains stability, introducing complexity to our understanding of atomic nuclei.
- The reason for nitrogen-9's short half-life is that the strong force, which is responsible for holding nuclei together, is not strong enough to overcome the Coulomb repulsion between the positively charged protons in the nitrogen-9 nucleus.
- The discovery of nitrogen-9 is a major breakthrough in our understanding of nuclear physics.
- It showed that nuclei with very high proton-to-neutron ratios can exist, even if they are only for a very short time.
- This discovery has led to new research into the limits of nuclear stability and the role of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in holding nuclei together.
What is an Isotope?
- An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in its atomic nucleus.
- This variance in neutron count results in different atomic masses for isotopes of the same element.
- Isotopes of an element share similar chemical properties but may exhibit differences in physical properties, such as stability and radioactivity.
Onattukara Sesame (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Efforts are being made to expand the cultivation of geographical indication (GI)-tagged Onattukara sesame.
About Onattukara Sesame:
- Onattukara sesame is a special sesame seed variety native to the Onattukara region of Kerala.
- It is renowned for its distinctive flavor, rich aroma, and exceptional nutritional and health value.
- In 2023, it received a geographical indication (GI) tag, recognizing its unique characteristics and link to the Onattukara region.
- This recognition serves as a testament to the exceptional qualities of Onattukara sesame and is expected to propel its demand and further empower the farmers of the region.
- Onattukara sesame distinguishes itself from other sesame varieties through its unique flavor profile.
- This distinctive flavor profile makes Onattukara sesame an indispensable ingredient in traditional Kerala cuisine, where it graces a variety of dishes, from curries and chutneys to sweet snacks.
- Distinguishing Features:
- Flavor and Aroma: Onattukara sesame has a nutty, slightly sweet flavor and a rich, earthy aroma.
- Nutritional Value: It is a rich source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and iron.
- It also contains healthy fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
- Medicinal Properties: Traditionally, Onattukara sesame oil has been used in Ayurveda for its medicinal properties, including its ability to promote skin health, reduce inflammation, and relieve joint pain.
Freemartins (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Farmers in agricultural settings often identify freemartins by observing their physical and/or behavioral traits since these animals are unable to reproduce.
About Freemartins:
- A freemartin is an infertile female cattle with masculinized behavior and non-functioning ovaries.
- This condition is caused by the exchange of cells between female and male twins in utero.
- The male twin produces a hormone called anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), which suppresses the development of the female reproductive tract.
- As a result, the female twin is born with an underdeveloped reproductive system and is unable to reproduce.
- Freemartinism occurs in about 90% of female cattle twins that share a placenta with a male twin.
- This is because the placentas of cattle twins are often fused together, allowing cells to move between the two fetuses.
- The fusion of placentas usually occurs between 40 and 120 days of gestation.
- In addition to being infertile, freemartins may also exhibit some masculine characteristics, such as a deeper voice, coarser hair, and a more muscular build.
- This is because they have been exposed to AMH from their male twin.
- There is no treatment for freemartinism, as the animal is infertile and cannot produce offspring.
- However, freemartins can still be used for other purposes, such as meat production or draft work.
Sophisticated Analytical & Technical Help Institutes (SATHI) Initiative (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The cancellation of a call for proposals under the Department of Science and Technology's SATHI program by the Centre has raised concerns among higher education institutions.
About Sophisticated Analytical & Technical Help Institutes (SATHI) initiative:
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) is starting a project to create a shared Science and Technology infrastructure facility called Sophisticated Analytical & Technical Help Institute (SATHI).
- This facility will be available for use by academic institutions, startups, manufacturing units, industries, and R&D labs.
- The goal is to offer efficiently managed services with high transparency, accessibility, and effectiveness all in one place, catering to the needs of industries, startups, and academia.
- In the first phase, SATHI facilities will be set up at IIT-Delhi, IIT-Kharagpur, and BHU-Varanasi.
- This initiative aims to benefit less-endowed organizations like MSMEs, startups, state universities, and colleges, fostering a strong culture of research collaboration across different institutions and disciplines.
Aims & Objectives of SATHI:
- Provide shared, professionally managed Science and Technology services and infrastructure.
- Ensure efficiency, accessibility, and transparency for the demands of faculty, researchers, scientists, and students from various institutes and organizations.
- Enable round-the-clock R&D activities with minimal downtime.
- Offer facilities for fabrication work, rapid prototyping, material testing, characterisation, device fabrication, smart manufacturing, and more.
- Attract and support R&D labs, industrial R&D, MSMEs, Incubators, Start-ups, etc.
- Organize short-term courses, workshops, seminars, and hands-on training programs on the use and application of various instruments and techniques.
- Provide technical help and scientific knowledge to both external and internal users/researchers.
- Train technicians for maintaining and operating sophisticated scientific instruments.
- Maintain a record of trained personnel for better societal outreach and utilization of trained manpower across different SATHI centers when needed.
State of the Cryosphere Report 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
As per the 2023 State of the Cryosphere report, the anticipated disappearance of almost all tropical glaciers, a significant majority of mid-latitude glaciers, and polar regions is expected, even if global efforts successfully limit the rise in temperatures to 2 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels.
About the State of the Cryosphere Report 2023:
- The State of the Cryosphere Report annually assesses the condition of Earth's snow and ice regions, and has been reviewed and endorsed by over 60 leading cryosphere scientists.
- This report is published by The International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI.)
- The cryosphere is a term for the regions of our globe that are covered in ice and snow – either seasonally or year-round.
- The Report describes how a combination of melting polar ice sheets, vanishing glaciers, and thawing permafrost will have rapid, irreversible, and disastrous impacts worldwide.
Key findings in the report on the impact of 2°C of warming include:
- Ice sheets: nearly all of Greenland, much of West Antarctica, and even vulnerable portions of East Antarctica will be triggered to very long-term, inexorable sea-level rise.
- Glaciers: extensive, irreversible ice loss from the world’s glaciers in many major river basins, with some disappearing entirely.
- As glaciers melt, risks of catastrophic events such as landslides, sudden ice shears, and glacial lake outburst floods increase.
- Sea ice: extensive sea ice loss at both poles, with severe feedback to global weather and climate.
- By 2°C, the Arctic Ocean will be sea ice-free in summer every year, potentially for several months.
- Permafrost: extensive permafrost thaw and resulting greenhouse gas emissions will cause temperatures to continue to rise, even once human emissions reach zero.
- At 2°C, annual total permafrost emissions (both CO2 and methane) would total the size of the entire European Union’s emissions from 2019.
- Polar ocean acidification: year-round, permanent corrosive ocean acidification conditions in many regions of Earth’s polar and near-polar seas.
- Shell-building animals and commercial fisheries that rely on them in the food chain may not survive.
About International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI):
- It was formed in 2009 following COP-15 in Copenhagen
- ICCI is a network of senior policy experts and researchers working with governments and organizations to create, shape, and implement initiatives designed to preserve as much of the Earth’s cryosphere as possible.
- ICCI programs target the unique climate dynamics at work in the cryosphere, while at the same time lending increased urgency to global climate efforts aimed at CO2 and other greenhouse gases by communicating the unexpected rapidity and global implications of cryosphere warming.
Dwarf Planet Eris (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered the inside structure of the enigmatic dwarf planet Eris.
About Dwarf Planet Eris:
- This new dwarf planet is the largest object found in orbit around the sun since the discovery of Neptune and its moon Triton in 1846.
- It was discovered on Jan. 5, 2005, and It is larger than Pluto, discovered in 1930.
- Like Pluto, the new dwarf planet is a member of the Kuiper belt, a swarm of icy bodies beyond Neptune in orbit around the sun.
- Eris is named for the ancient Greek goddess of discord and strife.
- The surface of Eris is extremely cold, so it seems unlikely that life could exist there.
- With a radius of about 1,163 kilometers, Eris is about 1/5 the radius of Earth.
- Eris, like Pluto, is a little smaller than Earth's Moon.
- Eris takes 557 Earth years to make one trip around the Sun.
- As Eris orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 25.9 hours, making its day length similar to ours.
- Moons: Eris has a very small moon called Dysnomia.
- Dysnomia has a nearly circular orbit lasting about 16 days.
- Eris most likely has a rocky surface similar to Pluto.
- Atmosphere: The dwarf planet is often so far from the Sun that its atmosphere collapses and freezes, falling to the surface as snow.
- As it gets closest to the Sun in its faraway orbit, the atmosphere thaws.
Card-on-File Tokenisation (CoFT) (Business Standard)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Visa has highlighted that the primary advantage of tokenization is a decreased risk of data breaches.
What is Card-on-File Tokenisation?
- Tokenisation is a process where the cardholder’s original card number, one which is written on the card and is extensively used for transactions and card identification, is replaced with a surrogate term called ‘token.’
- This process allows enhanced card protection by converting the customers’ card numbers into tokens.
- The exchange of tokens happens between the token requestor and the network, which empowers customers to receive a secure and reliable online payment experience.
- All relationship evidence of such exchange between token and crucial card information is securely saved in a vault that is only accessible to the card networks.
- Resultantly, the customers’ card details will be highly protected from online fraud and hackers.
How Does Card-on-File Tokenisation Work?
- When a customer makes a transaction by using their card at a tokenisation-based-authentication server:
- A credit/debit card is used for transactions at a POS device or an e-commerce website
- The tokenisation system receives and interprets the credit card number
- The tokenisation system goes on to replace the original credit card number with a 16-digit random character token for security
- The tokenisation system then provides the converted 16-digit random token number to the e-commerce marketplace and replaces the user’s credit card number with the same in their system
- For instance, card number (example): 4018 2255 6984 7854 will be replaced with token number: 4325 5214 8574 6658.
- The tokenisation system is an important tool for separating crucial data in ecosystems and databases while also offering enhanced card protection to cardholders.
Measles (Indian Express)
- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
An estimated 11 lakh children in India missed their crucial first dose of measles vaccine in 2022, according to a report by the World Health Organization and US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What is Measles?
- Measles is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus.
- It is caused by the Morbillivirus of the Paramyxoviridae family.
- It spreads easily when an infected person breathes, coughs, or sneezes.
- It can cause severe disease, complications, and even death.
- Measles can affect anyone but is most common in children.
- Measles infects the respiratory tract and then spreads throughout the body.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include a high fever, cough, runny nose, and a rash all over the body.
- Measles typically starts with a strong fever about 10 to 14 days after getting infected.
- In the beginning, it starts with a runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, and small white spots inside the cheeks.
- After a few days, a rash appears, usually on the face and upper neck.
- This rash spreads over about three days, reaching the hands and feet, and lasts for five to six days before fading away.
- Any non-immune person (not vaccinated or vaccinated but not developed immunity) can become infected.
- If a woman catches measles during pregnancy, this can be dangerous for the mother and can result in her baby being born prematurely with a low birth weight.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for measles.
Amazon Yellow Spotted River Turtle (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In the Peruvian Amazon, an extended heat wave and drought have shortened the incubation period for thousands of turtle hatchlings released into the river by biologists as part of a local environmental program.
About Amazon Yellow Spotted River Turtle:
- This species is one of the largest South American river turtles.
- It is characterized by its dark upper shell and yellow spots on the head, which fade with age.
- They are considered side-necked turtles because they cannot pull their heads into their shells.
Native Habitat:
- Yellow-spotted River turtles are native to the Amazon River basin and can be found in the Amazon and Orinoco river systems in Venezuela, eastern Colombia, eastern Ecuador, northeastern Peru, the Guianas, Brazil and northern Bolivia.
- These turtles spend time basking along the riverbanks and in the calm waters of big rivers and streams.
- They avoid fast-moving waters.
Food/Eating Habits:
- They are omnivorous, feeding on both vegetation and small animals.
Reproduction and Development:
- Females lay their eggs in the peak of the dry season and the nests are sometimes destroyed by rising flood waters.
Sleep Habits:
- The turtles are diurnal, meaning they are most active in mid-morning and afternoon.
Lifespan:
- The oldest known yellow-spotted Amazon River turtle living in human care reached 23 years of age.
- They can live up to 70 years.
Exercise MITRA SHAKTI (PIB)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A joint military exercise, “Exercise MITRA SHAKTI-2023” is being conducted from November 16th to 29th, 2023, in Aundh (Pune).
About Exercise MITRA SHAKTI:
- Exercise MITRA SHAKTI is the ninth edition of a joint military exercise between the Indian and Sri Lankan armies.
- The Indian contingent, consisting of 120 personnel mainly from the MARATHA LIGHT INFANTRY Regiment, is participating alongside personnel from the Indian Air Force and the Sri Lankan Air Force.
- This exercise is the first bilateral and bi-service endeavor between the two countries.
- The primary goal is to jointly practice sub-conventional operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, emphasizing coordinated responses in counter-terrorism operations.
- The exercise includes training in Army Martial Arts Routine (AMAR), combat reflex shooting, Yoga, and the use of Drones and Counter Unmanned Aerial Systems, along with helicopters.
- Joint drills will cover securing helipads and conducting casualty evacuation during counter-terrorist operations.
- The collective focus is on enhancing interoperability among troops, minimizing risks to life and property, and prioritizing the interests and agenda of the UN in peacekeeping operations.
- Additionally, the exercise aims to strengthen bilateral relations between the neighboring nations.
Sickle Cell Disease (TOI)
- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The UK's medicines regulator has granted approval for the world's first gene therapy treatment for sickle cell disease.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
- Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a blood disorder that is passed through the genes and results in abnormal hemoglobin.
- (Hemoglobin is a part of the red blood cells that carry oxygen through the body.)
- People with SCD have red blood cells that sickle or change shape when exposed to low oxygen levels in the cell.
- These sickled cells also become stiff and sticky compared to normal red blood cells.
- They can block blood flow, leading to tissue damage and pain.
- Over time, these blockages can lead to organ dysfunction and result in other serious medical complications.
Sickle Cell Disease Types
- There are several different forms of sickle cell disease, and it is different for each person.
- Hemoglobin SS, also known as sickle cell anemia
- Hemoglobin SC disease
- Hemoglobin sickle beta-thalassemia
- The most common and usually the most severe form is sickle cell anemia.
- The SCD type affects the severity and frequency of complications.
- The type of SCD also impacts the timing of complications.
- Some people have symptoms at a very young age while others will not show symptoms until adulthood.
Sickle Cell Disease Symptoms
- Anemia: Sickled blood cells are less able to carry oxygen, leading to anemia.
- Symptoms can include fatigue, weakness, dizziness, headache, shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Bone Pain: Decreased blood flow to the bones leads to periodic spikes in bone pain known as bone crises.
- SCD can also cause avascular necrosis, which is a breakdown of the bone and joint.
- Eye Disease or Blindness: Sickled blood cells can damage the fragile blood vessels in the back of the eye, leading to retina damage called retinopathy. This can lead to blindness.
- Infections: The spleen fails in SCD patients at a young age, decreasing the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Kidney Issues: Blood in the urine (papillary necrosis), frequent urination, kidney disease.
Treatments:
- A bone marrow transplant (stem cell transplant) can cure sickle cell disease.
- However, there are treatments that can help relieve symptoms, lessen complications, and prolong life.
- Gene therapy is also being explored as another potential cure. The UK recently became the first country to approve gene therapy treatment for sickle cell disease
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) (Business Standard)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Among 1.39 million cyber security cases last year, vulnerable services made up 875,892 of the total incidents tackled by Cert-In
What is CERT-In?
- CERT-In stands for the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team.
- It is a government agency that functions under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It was established in January 2004 with the objective of securing Indian cyberspace.
- It is the national nodal agency for dealing with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing.
- It strengthens the security-related defence of the Indian Internet domain.
- The Information Technology Act of 2000 designated CERT-In to serve as the national agency to perform the following functions in the area of cyber security:
- Prevention of cyber attacks: CERT-In works to prevent cyber attacks by issuing advisories and guidelines to organizations and users.
- It also conducts vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and remediate security weaknesses.
- Incident response: It provides technical assistance to organizations that have been affected by cyber-attacks.
- It helps them to contain and recover from the incident, and to minimize the damage.
- Cyber security awareness: It raises cyber security awareness among the Indian public through various initiatives, such as workshops, seminars, and online resources.
- Coordination with other agencies: CERT-In coordinates with other cyber security agencies in India and around the world to share information and best practices.
- The constituency of CERT-In is the Indian cyber community and Indian cyberspace.
- CERT-In provides services to organisations in the Government, Public, and Private sectors.
- In addition, CERT-In provides services to individuals and home users as well.
- Disclosure of information will be followed in accordance with Indian Constitutional laws.
Worldwide Governance Indicators (Indian Express)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Chief Economic Adviser recently expressed worry about credit rating agencies using the World Bank's Worldwide Governance Indicators to assess ratings, particularly for developing countries.
About Worldwide Governance Indicators:
- The Worldwide Governance Indicators is based on a long-standing research programme of The World Bank.
- It was first established in 1996 to measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries.
- These aggregate indicators are derived from over 30 individual data sources produced by a variety of survey institutes, think tanks, non-governmental organizations, international organizations, and private sector firms.
- The indicators capture six key dimensions of governance including:
- Voice and Accountability
- Political Stability and Absence of Violence
- Government Effectiveness
- Regulatory Quality
- Rule of Law
- Control of Corruption
- According to The World Bank, corruption is the single greatest obstacle to economic and social development.
About The World Bank:
- The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries around the world.
- Its goals are to reduce poverty and support development.
- It helps by offering a growing range of free tools, research, and knowledge to help people address the world’s development challenges, for instance, comprehensive, downloadable indicators about development in countries around the globe.
Wasp-107b (TOI)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In its latest discovery, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a planet "Wasp-107b" where specks of sand fall as rain.
What is “Wasp-107b”?
- WASP-107b is a warm exoplanet with Neptune’s mass and Jupiter’s radius.
- This makes it ‘fluffy’ compared to the giant gas planets in our Solar System.
- This unusual size-to-mass ratio has given astronomers a unique opportunity to probe its atmosphere roughly 50 times deeper than more dense planets like Jupiter.
- This gas giant, often referred to as a "super-Neptune," holds several remarkable characteristics that set it apart from other known exoplanets.
Key Characteristics of WASP-107b:
- Size and Mass: WASP-107b is roughly the size of Jupiter, but with only about 12% of Jupiter's mass.
- This makes it one of the least dense exoplanets ever discovered.
- Orbit and Proximity: WASP-107b orbits its host star, WASP-107, very closely, completing an orbit in just 5.7 days.
- It is located about 200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo.
- Sand Rain: WASP-107b exhibits a unique water cycle similar to Earth's, but with a peculiar twist: instead of water droplets, the planet experiences sand rain.
- These sand grains, composed of silicates, rise from lower atmospheric levels and condense into clouds before falling back down.
- Atmosphere: WASP-107b possesses a puffy atmosphere, likely due to its low density.
- In 2018, scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope detected helium in its atmosphere, marking the first detection of this element in an exoplanet's atmosphere.
- Potential for Atmospheric Characterization: WASP-107b's large size and proximity to its star make it a promising target for future atmospheric characterization studies.
- Scientists hope to glean more insights into the composition and dynamics of its atmosphere.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) Scheme (TOI)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi released the 15th installment of the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme worth over Rs 18,000 crore to more than 8 crore farmers on November 15, 2023.
About Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN):
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- Under the scheme, income support of Rs. 6,000 per year in three equal installments is provided to all land-holding farmer families, providing them with socio-economic security.
- The amount is directly transferred to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries without any involvement of intermediaries, making it one of the largest Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) schemes in the world.
- So far, more than Rs. 2.42 lakh crore have been disbursed to over 11 crore farmers.
- As per the study by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), PM-KISAN had numerous benefits for the farmers and agriculture sector.
- It addresses the liquidity constraints of farming households, enabling essential input procurement.
- The scheme boosts modern cultivar adoption through Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
- The cash transfer to farmers increases their total net income and enhances their risk-taking capacity, leading to productive investments.
- PM-KISAN has empowered the farmers by boosting agriculture investments, easing credit constraints, and spurring rural economic growth.
- Consequently, farmers have been able to invest in their farms, including purchasing seeds, fertilizers, and necessary equipment, leading to increased agricultural production and improved crop yields.
Voice of Global South Summit (NewsOnAir)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate the second Voice of Global South Summit on November 17. This will be the second Voice of Global South Summit in less than a year hosted by India.
About ‘Voice of Global South Summit’ 2023:
- India is hosting the ‘Voice of Global South Summit’ 2023 in virtual format.
- The theme of the inaugural Leaders’ Session is "Together, for Everyone’s Growth, with Everyone’s Trust” and that of the Concluding Leaders’ Session is "Global South: Together for One Future”.
- The Summit will focus on sharing with the countries of the Global South, the key outcomes achieved in various G20 meetings over the course of India’s Presidency.
- The Summit will serve as a platform to discuss ways to sustain the momentum generated toward the common aspiration of a more inclusive, representative, and progressive world order.
What is the Voice of Global South Summit?
- Voice of Global South Summit has been India's endeavor to provide a common platform to deliberate on the concerns, interests, and priorities that affect the developing countries and also to exchange ideas and solutions, and most importantly, to unite in voice and purpose in addressing the concerns and priorities.
- The initiative is inspired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, and Sabka Prayaas, and is underpinned by India’s philosophy of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”.
- India will work to ensure that the valuable inputs generated from partner countries in the Voice of Global South Summit deliberations receive due cognizance globally.
What is Global South?
- he term ‘Global South’ began by loosely referring to those countries that were left out of the industrialization era.
- These countries had a conflict of ideology with the capitalist and communist countries, accentuated by the Cold War.
- It includes countries that are in Asia, Africa, and South America.
- ‘Global South’ is just the opposite of ‘Global North’, defined essentially by an economic division between the rich and poorer countries.
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra (The Hindu)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the programme "Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra" across the country on November 15 to promote the Centre’s welfare schemes.
On the occasion of the Janjatiya Gaurav Divas (15th Nov), marking the birth anniversary of tribal icon Birsa Munda, Prime Minister Narendra Modi flagged off the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra from Khunti, Jharkhand.
About Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra:
- The central idea of Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra is to publicise schemes, to get data on those who have benefitted from these schemes, and to mark those who are eligible but haven't got the schemes yet.
- It aims to cover over 2.55 lakh Gram Panchayats and over 3,600 urban local bodies by January 25, 2024, touching every district of the country.
- Its focus will be on reaching out to people and creating awareness about the benefits of welfare schemes like sanitation facilities, essential financial services, electricity connections, access to LPG cylinders, housing for the poor, food security, proper nutrition, reliable healthcare, clean drinking water, etc.
- Five specially designed IEC (Information, Education, and Communication) Vans has been flagged off marking the launch of the massive outreach programme of the government.
- The IEC Vans have been branded and customised to enable dissemination of information through audio visuals, brochures, pamphlets, booklets, and flagship standees in Hindi and state languages showcasing the major schemes, highlights and their achievements at the national, state and district level.
- The schemes being publicised include Ayushman Bharat, PMJAY, PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihoods Mission, PM Awas Yojana (Rural), PM Ujjwala Yojana, PM Vishwakarma, PM Kisan Saman, Kisan Credit Card (KCC), PM Poshan Abhiyan, Har Ghar Jal - Jal Jeevan Mission, Survey of villages and mapping with improvised technology in village areas (SVAMITVA), Jan Dhan Yojana, Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Suraksha Bima Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana, PM PRANAM, Nano Fertiliser.
- Since schemes are aimed at tribals, specific concerns of tribal areas such as the Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, Enrolment in Eklavya Model Residential Schools, Scholarship Schemes, Forest Right Titles, Individual and Community Land, Van Dhan Vikas Kendra, Organising Self Help Groups are also being addressed.
- The officers in charge will make sure that they reach out to the tribals and give out information about schemes meant for them.
India International Science Festival (PIB)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 9th edition of the India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023 will be held at Faridabad, Haryana from January 17th-20th, 2024.
About the India International Science Festival (IISF):
- The India International Science Festival (IISF) is an annual science festival organized by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Earth Science, and Vijnana Bharati in India.
- The festival aims to promote science and technology in India and to showcase the latest advancements in these fields.
- The IISF has been held every year since 2007.
- The festival typically lasts for four days and features a variety of events, including exhibitions, seminars, workshops, and competitions.
- The exhibitions feature displays of scientific and technological innovations from India and around the world.
- The seminars and workshops provide opportunities for scientists and technologists to share their knowledge with the public.
- The competitions encourage students to participate in science and technology.
- The IISF is a major event in the Indian scientific community and has been praised for its role in promoting science education and public awareness of science.
- The festival has also been successful in attracting international participation, with scientists and technologists from around the world attending the event.
- The 2022 IISF was held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, from January 21 to 24.
India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023:
- It will be held at the Campus of Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) and Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB) of the Department of Biotechnology in Faridabad.
- Theme: 'Science and Technology Public Outreach in Amrit Kaal'.
- IISF 2023 will have a total of 17 themes to showcase scientific achievements, offering diverse benefits to participants and the general public.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) (Indian Express)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India, the US, and 12 other members of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) on Wednesday entered into a supply chain resilience agreement that aims to cut dependence on China and help shift manufacturing of crucial goods to member nations.
About Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF):
- The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) is an economic initiative launched by U.S. President Joe Biden in Tokyo on May 23, 2022.
- The framework aims to strengthen economic cooperation among countries in the Indo-Pacific region, which is home to over 40% of the world's population and generates nearly 60% of global GDP.
- Except Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar, other Southeast Asian nations are a part of the IPEF.
- It has currently 14 members including Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, the United States, and Vietnam.
- The IPEF has four pillars:
- Trade;
- supply chains;
- clean energy, decarbonisation and infrastructure;
- tax and anti-corruption.
- IPEF Significance: The IPEF is a significant development in the Indo-Pacific region.
- It is the first major economic initiative launched by the United States in the region since the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) negotiations collapsed in 2017.
- The IPEF is also unique in that it is open to all countries in the Indo-Pacific region, regardless of their economic development level.
- India and IPEF: India has been actively involved in the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) since its launch in May 2022.
- The country has joined three of the four pillars of the framework: supply chains, clean energy, and fair economy.
- However, India has not yet joined the trade pillar, which is the most sensitive and contentious pillar of the framework.
- There are a number of reasons why India has been hesitant to join the trade pillar.
- One concern is that the pillar could lead to tariff cuts on agricultural products, which would harm Indian farmers.
- India is also concerned about the potential for the trade pillar to lead to increased data flows, which could raise privacy concerns.
Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A dominant tiger named Bajrang said to have sired at least 50 cubs during his lifetime, recently died in a territorial fight with another powerful tiger, Chhota Matka, in the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR).
About Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve is the oldest and largest National Park in the Chandrapur district of Maharashtra.
- It is one of India's 47 project tiger reserves existing in India.
- The total area of the tiger reserve is 1,727 Sq.km, which includes the Tadoba National Park, created in the year 1955.
- The Andhari Wildlife Sanctuary was formed in the year 1986 and was amalgamated with the park in 1995 to establish the present Tadoba Andheri Tiger Reserve.
- The word 'Tadoba' is derived from the name of God "Tadoba" or "Taru," which is praised by local tribal people of this region, and "Andhari" is derived from the name of the Andhari river that flows in this area.
- Tadoba is presently home to more than 115 tigers, which is one of the highest in India.
- The vegetation of Tadoba forest is of Southern tropical dry deciduous type and is spread on around 626 sq. km.
- Teak is the prominent tree species in the forest.
- The Tadoba Tiger Reserve is rich in flora and fauna
- Flora: Some of the famous and widely seen flora of this park include Teak, Ain, Bija, Bamboo, Black Plum, and many others.
- Fauna: Tigers, Indian leopards, Sloth bears, Gaur, Nilgai, Striped Hyena, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer, Marsh Crocodile, etc.
Igla-S Missiles (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Russia has announced that it will supply the Igla-S man-portable air defense missile system to the Indian armed forces through licensed production by an Indian private company.
About Igla-S Missile System:
- The Igla-S is a man-portable air-defense system (MANPADS) developed by Russia.
- It is a surface-to-air missile (SAM) system which is also known as SA-24 Grinch in the West.
- The Igla-S entered service in 2004 and is currently in service with over 30 countries, including Russia.
- It is a highly effective and versatile weapon system that can be used to engage a wide variety of targets, including fixed- and rotary-winged aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and cruise missiles.
- The Igla-S has a range of 5 km and an altitude of 3,500 meters including a speed of Mach 2.5.
- It is a "fire-and-forget" weapon, meaning that the operator does not need to track the target after launch.
- The missile's infrared homing seeker automatically guides it to the target.
- It is a very compact and lightweight weapon system, making it ideal for use by infantry troops.
- It can be easily transported and deployed in a matter of minutes.
- The Igla-S is used by a number of countries, including Algeria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Libya, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nicaragua, North Korea, Peru, Poland, Russia, Serbia, Syria, Venezuela, and Vietnam.
INS Sumedha (Financial Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a strategic move as part of the Indian Navy’s mission-based deployment to West Africa and the Atlantic, INS Sumedha conducted a port call at Walvis Bay, Namibia recently.
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is a Saryu-class, Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel (NOPV) of the Indian Navy.
- It is the third ship of the class to be commissioned and was built by Goa Shipyard Limited in India.
- The ship was commissioned in March 2014.
- INS Sumedha is designed to undertake a variety of missions, including fleet support operations, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance, and monitoring of sea lines of communication and offshore assets.
- The ship is also capable of carrying out humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR) operations.
- INS Sumedha has been deployed on a number of operational missions, including:
- Operation Kaveri, the evacuation of Indian citizens from Sudan in April 2023.
- The ship has also participated in a number of international exercises, including Exercise Bright Star 2023 in Egypt.
About Walvis Bay:
- Walvis Bay is a city on the coast of Namibia, in the Erongo Region.
- It is the second-largest city in Namibia, after Windhoek, and is the capital of the Erongo Region.
- It is a major port city, and is the main port for Namibia.
- The port is home to a number of shipping companies and is a major export center for Namibian goods, such as fish, minerals, and diamonds.
- Originally a German enclave during the colonial era, Walvis Bay became a vital part of Namibia after gaining independence in 1990.
- The official language of the city is English, but Afrikaans, German, and Portuguese are also spoken.
Asian Development Bank (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The central government recently signed a USD 400 million policy-based loan with the Manila-based Asian Development Bank (ADB) to support its urban reform agenda to create high-quality urban infrastructure, improve service delivery, and promote efficient governance systems.
About Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
- It was established in 1966 to promote economic development and cooperation in Asia and the Pacific.
- The ADB's primary goal is to reduce poverty in its member countries.
- The bank provides loans, grants, technical assistance, and policy advice to its member countries.
- It also mobilizes private sector investment through its private sector arm, the Asian Development Bank Private Sector Operations.
- It has 68 member countries, including 49 countries in Asia and the Pacific, and 19 non-regional developed countries.
- The ADB's annual lending volume is around $32 billion.
- As of 2022, ADB's five largest shareholders are Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People's Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
- Source of Funding: It relies on member contributions, retained earnings from lending, and the repayment of loans for the funding of the organization.
The bank's strategy is focused on four key areas:
- Promoting sustainable growth: The ADB is committed to supporting its member countries in achieving their sustainable development goals by financing infrastructure, clean energy, and climate change mitigation and adaptation projects.
- Tackling poverty and inequality: The ADB is providing financing for education, health, social protection, and other programs that benefit the poor and vulnerable to reduce poverty and inequality in its member countries.
- Strengthening regional cooperation: The ADB is promoting regional cooperation and integration in Asia and the Pacific.
- The bank is supporting its member countries in developing regional infrastructure, trade, and investment projects.
- Responding to crises and disasters: The ADB is helping its member countries prepare for and respond to crises and disasters by providing finances for disaster risk reduction and resilience projects.
One Station One Product’ scheme (New Indian Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Railway has established more than a thousand outlets in railway stations across the nation under its ‘One Station One Product’ (OSOP) initiative which aimed at providing a platform for skilled artisans to sell their indigenous products.
About One Station One Product’ (OSOP):
- The OSOP scheme is a unique initiative by the Indian Railways and aims to provide livelihood opportunities through skill development to local artisans, potters, weavers, and craftsmen.
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- The scheme, designed by the National Institute of Design, Ahmedabad, provides distinctive outlets that give high visibility to indigenous products, benefiting local craftsmen.
- Railways allot the outlets at its stations through a tendering process.
- The scheme’s outreach measures include advertising, social media, public announcements, press notifications, and personal visits to artisans.
- The products at these outlets range from artifacts and handicrafts to textiles and traditional appliances, indigenous to the region, and are crafted by local artisans or tribals.
- They also include locally made or grown food products in processed or semi-processed forms.
- It provides uniquely designed sale outlets for locals to sell indigenous products, and is now operational at 1,037 stations nationwide.
PM PVTG Development Mission (NewsOnAir)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi is going to launch the PM PVTG (Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups) Development Mission in a huge step to empower tribal people.
About PM PVTG Development Mission:
- The PM PVTG Development Mission plans to saturate PVTG families and habitations with basic facilities such as road and telecom connectivity, electricity, safe housing, clean drinking water, and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
- The Mission will be implemented through the convergence of 11 interventions of nine Ministries.
- In addition, saturation will be ensured for schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojna, Sickle Cell Disease Elimination, TB Elimination, 100 percent immunisation, PM Surakshit Matritva Yojana, PM Matru Vandana Yojana, PM Poshan, and PM Jan Dhan Yojana.
Who are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- PVTGs, or Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, represent the most vulnerable subsets within India's diverse tribal communities, requiring heightened support and development efforts.
- There are 75 PVTGs in 18 States and Union Territories living in 22 thousand 544 villages having a population of around 28 lakhs.
- These tribes stay in scattered, remote, and inaccessible habitations, often in forest areas.
- The Government of India employs specific criteria for their identification, encompassing pre-agricultural technological levels, low literacy rates, economic disadvantages, and either a declining or stagnant population.
- The origin of the PVTG category dates back to 1975 when the government identified 52 vulnerable tribal groups, later augmented by an additional 23 in 1993.
- Notable examples of PVTGs include:
- the Cholanaikayan in Kerala
- Kathodi in Gujarat
- Jarawas in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands and
- Koraga in Karnataka
- The distinctive classification of PVTGs underscores a commitment to addressing the unique challenges faced by these marginalized tribal communities, aiming to uplift them through targeted support and development initiatives.
Cloud Seeding (LiveMint)
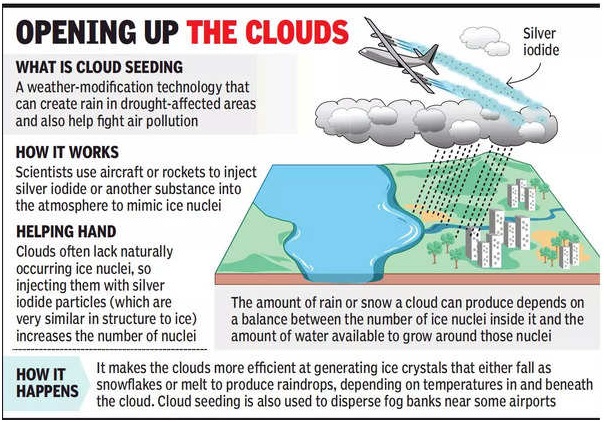
- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Delhi government is mulling the use of artificial rain through cloud seeding this month to combat the air pollution crisis in the national capital.
What is Cloud Seeding?
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique aimed at increasing precipitation by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei.
- The primary goal is to encourage the formation and growth of precipitation particles within clouds.
- Commonly used substances for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide, and liquid propane.
There are two main types of cloud seeding:
- Static cloud seeding: This type of seeding is used to increase precipitation in areas that are experiencing drought
- It involves releasing silver iodide or dry ice into clouds that are already producing precipitation.
- The silver iodide or dry ice acts as ice nuclei, which causes water droplets in the clouds to freeze and form snowflakes.
- The snowflakes then grow larger and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
- Dynamic cloud seeding: This type of seeding is used to increase the amount of precipitation that falls from clouds that are not yet producing precipitation.
- It involves releasing silver iodide into clouds that are still in the development stage.
- The silver iodide acts as condensation nuclei, which causes water vapor in the clouds to condense and form water droplets.
- The water droplets then grow larger and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
- Cloud seeding is typically done using aircraft, but it can also be done using ground-based generators or rockets.
- The aircraft or other seeding platform will fly into the clouds and release the silver iodide or dry ice.
- The seeding material will then spread throughout the cloud and begin to alter the microphysical processes.
- The effectiveness of cloud seeding is debated.
- Some studies have shown that it can increase precipitation by up to 30%, while other studies have shown that it has little or no effect.
- The effectiveness of cloud seeding is likely to vary depending on the type of clouds being seeded, the atmospheric conditions, and the seeding method used.
- Cloud seeding is used in a variety of countries around the world, including the United States, China, Russia, and Australia.
GPS Anklets (Indian Express)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time in India, a prisoner in J&K has been given bail on the condition that his movements are monitored constantly.
About GPS Anklets/Tracker:
- The GPS tracker is a compact wearable gadget secured around the ankle, offering real-time location details.
- It is designed to be tamper-proof, triggering an alarm if any attempt is made to interfere with it.
- Removal by the wearer or any unauthorized individual without causing damage is virtually impossible.
- This versatile tracker can be attached to either the ankle or the arm, presenting as GPS anklets or GPS bracelets.
- While commonplace for bail conditions in countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Malaysia, this marks the inaugural use of GPS trackers for this purpose in India.
What is GPS?
- GPS, or the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system with a global reach.
- It functions through a network of satellites orbiting Earth, transmitting signals to GPS receivers.
- This technology has revolutionized navigation, offering precise location and time information for diverse applications, from driving to hiking.
- Originally developed for military purposes, GPS is now widely used in civilian life, integrated into smartphones for location-based services and emergency response.
- Its applications extend to real-time tracking of vehicles and assets, contributing to enhanced security and efficient management.
- Ongoing advancements ensure that GPS remains a crucial tool in modern navigation.
Vadhavan Port (HT)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Vadhavan Port Project Ltd. (VPPL) has started the procedures to build a port with an estimated cost of ?76,220 crore. Public hearings are expected to commence in the coming months.
About Vadhavan Port:
- The Vadhavan Port is a proposed deep-sea port to be located in Palghar District, Maharashtra.
- It is expected to be one of the largest ports in the world, with a capacity to handle over 20 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) of containers per year.
- The port is being developed by a joint venture between the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) and the Maharashtra Maritime Board (MMB).
- The Vadhavan Port is being designed as a "green port" with a focus on sustainability.
- The port will use renewable energy sources and implement energy efficiency measures.
- The port will also have a dedicated waste management system to minimize environmental impact.
- It is expected to be operational by 2040 and is a critical project for India's economic growth and development.
- The Vadhavan Port is expected to be a major boost to the Indian economy.
- It will create thousands of jobs and attract billions of dollars in investment.
- The port will also help to reduce congestion at the JNPA, which is currently India's busiest container port.
- The Vadhavan Port is a major infrastructure project that is expected to have a significant impact on India's economy and society.
Birsa Munda (New Indian Express)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On Birsa Munday's birthday on Nov. 15th, PM Modi is scheduled to visit Ulihatu village, where the great leader's descendants live in an asbestos house.
About Birsa Munda:
- Birsa Munda was a tribal leader and folk hero who belonged to the Munda tribe.
- He was born on November 15, 1875, in the village of Ulihatu in the present-day Khunti district of Jharkhand.
- Birsa Munda is known for leading a rebellion against British colonial rule and the exploitation of tribal communities in the late 19th century.
- He was a charismatic leader and a devout Hindu.
- He preached a message of social and religious reform and advocated for the revival of traditional Munda culture and values.
- He also led a campaign against the conversion activities of Christian missionaries.
- In 1895, Birsa Munda launched a rebellion against the British.
- He and his followers attacked police stations, government buildings, and the homes of zamindars (landlords).
- The British responded with a heavy crackdown, and Birsa Munda was arrested in 1897.
- He was released from prison in 1898 but was rearrested in 1900 after he resumed his rebellion.
- Birsa Munda died in prison on June 9, 1900, at the age of 25.
- Birsa Munda's rebellion was a watershed moment in the history of the Indian independence movement.
- It inspired other tribal leaders to rise up against the British, and it helped to raise awareness of the plight of tribal communities in India.
- Birsa Munda is revered as a hero by tribal communities across India, and he is considered to be one of the pioneers of the Indian independence movement.
- In addition to his political activism, Birsa Munda was also a religious reformer.
- He founded a new religious movement called Birsait, which combined elements of Hinduism and tribal animism.
- Birsaitism is still practiced by some tribal communities in Jharkhand today.
- Birsa Munda's legacy continues to inspire people today, and he is remembered as one of the greatest heroes of the Indian independence movement.
- To honor Birsa Munda's significant influence on the national movement, the state of Jharkhand was established on his birthday in 2000.
- Recognizing his contributions, the Central Government declared November 15 as 'Janjatiya Gaurav Divas' in 2021.
Saturn’s Rings (Earth.com)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
According to a recent report, Saturn's rings will vanish in just 18 months.
What are Saturn’s Rings?
- Saturn’s ring system is made up of countless small particles, ranging from micrometers to meters in size, that orbit the planet.
- These particles are mostly made of ice, with a smaller amount of rocky debris and dust.
- The rings are named alphabetically in the order they were discovered, with the main rings being A, B, and C.
- The rings are also home to countless icy fragments and are shrouded in a layer of cosmic dust.
- Recent research suggests that these objects might be relatively new in the cosmic timeline, potentially forming a mere 400 million years ago, making them younger than one-tenth of Saturn’s age.
About the Planet Saturn:
- Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the solar system, after Jupiter.
- Saturn is a gas giant composed primarily of hydrogen and helium.
- It has a radius about nine times that of Earth, although it has a low density and is only about 95 times more massive than Earth.
- It has the highest number of satellites or moon, i.e., 146 in the solar system.
- Pioneer 11 and Voyagers 1 and 2 conducted flybys of Saturn, but Cassini extensively orbited the planet, completing 294 orbits from 2004 to 2017.
Exercise ‘CORPAT’ And ‘Bongosagar’ (NewsOnAir)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Exercise CORPAT and BONGOSAGAR between the Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy were conducted in the Northern Bay of Bengal from 07 - 09 Nov 2023.
About Exercise CORPAT and Bongosagar:
- The 4th edition of the Bilateral Exercise between the Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy, BONGOSAGAR-23, and the 5th edition of Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT) by the two navies were held at Visakhapatnam.
- Ships and aircraft from both navies undertook joint patrolling along the International Maritime Boundary Line and maritime exercises to enhance interoperability.
- Indian Navy Ships Kuthar, Kiltan, and Maritime Patrol Aircraft (MPA) Dornier participated in the exercise.
- The ships undertook communication drills, surface gun-shoots, tactical maneuvers, and other exercises.
- INS Kuthar is an indigenously built guided-missile Corvette, whereas INS Kiltan is an indigenously built anti-submarine Corvette.
- Both ships are part of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet based at Visakhapatnam, which functions under the operational command of the FOCINC ENC.
- CORPAT-23 also included the maiden Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief drills held between the two navies.
- The bilateral exercises and coordinated patrols have strengthened mutual understanding and cooperation between the two navies.
India-OPEC Energy Dialogue (PIB)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue took place on 9 November 2023, at the OPEC Secretariat in Vienna, Austria
Highlights of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue 2023:
- The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue took place on November 9th, in Vienna, Austria.
- The Meeting was co-chaired by HE Haitham Al Ghais, Secretary General of OPEC, and Hardeep Singh Puri, Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas and Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs of India.
- Discussions revolved around ensuring availability, affordability, and sustainability in energy markets, emphasizing India's crucial role in global economic growth and energy demand.
- The 6th High-Level Meeting concluded with both parties underscoring the importance of fostering enhanced cooperation between India and OPEC moving forward.
- It was agreed to hold the next High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue during the course of 2024 in India.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries(OPEC):
- OPEC, or the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent international organization comprising oil-exporting nations.
- Its core mission is to coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- This coordination aims to stabilize oil prices in global markets, working towards eliminating harmful and unnecessary price fluctuations.
- It was established in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela, OPEC has since expanded to include 13 members.
- Member countries are Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela.
- With the addition of another 11 allied major oil-producing countries including Russia, the grouping is known as OPEC+.
- The organization's headquarters is located in Vienna, Austria.
World Energy Outlook 2023 (IEA)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released the World Energy Outlook (WEO) Report 2023.
About World Energy Outlook 2023:
- This flagship publication of the International Energy Agency (IEA) has appeared every year since 1998.
- It provides in-depth analysis and strategic insights into every aspect of the global energy system.
- This year, the report delves into how changes in economies and energy usage are meeting the increasing demand for energy amid geopolitical tensions and fragile energy markets.
- It evaluates the evolution of energy security fifty years after the establishment of the IEA and looks at what's necessary at the COP28 climate conference in Dubai to support the 1.5 °C goal.
- The publication analyzes today's energy trends, covering areas like investment, trade flows, electrification, and energy access.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an independent inter-governmental organization operating within the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Its mission involves collaborating with governments and industry to create a secure and sustainable energy future.
- Established in 1974 to safeguard oil supplies, it was a response to the 1973-1974 oil crisis, which exposed the vulnerability of industrialized nations to oil import dependencies due to an oil embargo.
- Comprising 31 member countries and eleven association countries, IEA candidates must be OECD members.
- India joined as an Associate member in 2017.
- The IEA publishes reports such as the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, World Energy Statistics, and Net Zero by 2050.
AAINA Dashboard for Cities’ Portal (PIB)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
‘AAINA Dashboard for Cities’ portal aims to create a robust database of key performance metrics of Urban Local Bodies
About AAINA Dashboard for Cities:
- AAINA – Dashboard for cities, an initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) is being envisaged which would serve as a tool for comparing similarly placed Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and promoting peer learning amongst ULBs.
- This dashboard will inspire the ULBs by pointing to possibilities and areas of improvement and providing them the opportunity to learn and engage with frontrunners.
- It will provide information on the status and progress of the cities on five broad thematic areas viz.
- Political and Administrative Structure
- Finance
- Planning
- Citizen Centric Governance and
- Delivery of Basic Services.
- Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) can voluntarily submit their key data through a simple form on the portal.
- ULBs will submit audited accounts and performance metrics, which they can update when needed.
- The dashboard aims to be a permanent platform for ULB data, regularly updated for stakeholders and eventually open for public view.
- The Ministry, through the Digital India Corporation, will help ULBs/States with the data submission process.
- Currently, information about all the ULBs in the country isn’t available on one platform.
- The idea is to provide a platform for ULBs to learn from each other and also have critical data, which can be used in the future for planning new schemes and taking policy decisions
Attenborough's Long-beaked Echidna (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
An elusive echidna feared extinct after disappearing for six decades has been rediscovered in a remote part of Indonesia, on an expedition that also found a new kind of tree-dwelling shrimp.
About Attenborough's long-beaked echidna:
- Attenborough's long-beaked echidna (Zaglossus attenboroughi), also known as Sir David's long-beaked echidna or the Cyclops long-beaked echidna.
- It is an egg-laying mammal native to the Cyclops Mountains in the northern Indonesian region of Papua.
- It is one of three species of long-beaked echidna, and is the smallest and most threatened of the three.
- The echidna was named after naturalist Sir David Attenborough.
- The echidna is a nocturnal animal, and it is most active at night.
- It spends its days sleeping in burrows, and it emerges at night to forage for food.
- The echidna's diet consists of ants, termites, beetles, and other insects.
- Attenborough's long-beaked echidna is classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
5th Annual India- US ‘2+2’ Dialogue (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India and the U.S. on November 10 held extensive deliberations to further expand their global strategic partnership through greater defence industrial ties, enhancing engagement in the Indo-Pacific and boosting cooperation in key areas such as critical minerals and high technology.
Context:
- The fifth annual ‘2+2’ dialogue between India and the United States is underway in New Delhi.
- The U.S. delegation at the 2+2 ministerial talks was led by U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken and U.S. Defence Secretary Lloyd Austin.
- External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar and Defence Minister Rajnath Singh headed the Indian side.
What is the 2+2 Dialogue?
- The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, an annual diplomatic summit being held since 2018, brings together India's foreign and defence ministers with their US counterparts.
- Its purpose is to address and collaborate on common concerns to enhance and strengthen India–United States relations.
- A 2+2 ministerial dialogue enables the partners to better understand and appreciate each other’s strategic concerns and sensitivities taking into account political factors on both sides, in order to build a stronger, more integrated strategic relationship in a rapidly changing global environment.
- India has 2+2 dialogues with four key strategic partners: the US, Australia, Japan, and Russia.
- Besides Russia, the other three countries are also India’s partners in the Quad.
- The US is India’s oldest and most important 2+2 talks partner.
Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS) (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS) of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) did not effectively disseminate mass alerts during natural disasters, despite recent testing.
About Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS):
- The Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS) is a public warning system that uses mobile networks to send emergency alerts to mobile phones within a specific geographic area.
- It is a one-way messaging system that allows authorized authorities to send short messages to all mobile phones within a designated area, regardless of whether the recipients are subscribed to the mobile network or not.
Benefits of CBAS:
- Rapid and widespread dissemination of information: CBAS can reach a large number of people within a short period of time, making it an effective tool for communicating critical information during emergencies.
- No user interaction required: CBAS messages are automatically displayed on mobile phones, so there is no need for users to take any action to receive them.
- Effective for reaching all mobile phone users: CBAS messages can be received by all mobile phone users, regardless of whether they are subscribed to a particular mobile network or not.
- Not affected by network congestion: CBAS messages are not affected by network congestion, so they can be delivered even when network traffic is heavy.
CBAS can be used to send a variety of emergency alerts, including:
- Weather warnings: CBAS can be used to warn people of impending severe weather, such as tornadoes, hurricanes, and flash floods.
- Amber Alerts: CBAS can be used to broadcast information about missing children.
- Public safety alerts: CBAS can be used to warn people of other public safety threats, such as fires, terrorist attacks, and chemical spills.
Phreatomagmatic Eruptions (TOI)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently a new island emerged near Japan's Ogasawara island chain after an undersea volcano erupted.
What is Phreatomagmatic Eruption?
- A phreatomagmatic eruption is a volcanic eruption caused by the interaction of magma and water.
- They differ exclusively from magmatic and phreatic eruptions.
- Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) debris.
- Large explosive eruptions typically contain magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.
- Phreatomagmatic ash is formed by the same mechanism over a wide range of basic and acidic compositions.
- A blocky and uniform crust with low vesicle content is formed.
- Deposits from phreatomagmatic eruptions are thought to be better classified and finer-grained than those from magmatic eruptions.
- This is the result of higher fragmentation of phreatomagmatic eruptions.
About Ogasawara Islands:
- The Ogasawara Islands are a group of more than 30 small subtropical islands in the North-Western Pacific Ocean roughly 1,000 km south of the main Japanese Archipelago.
- It is also known as the Bonin Islands.
- It is one of the famous UNESCO World Heritage sites of Japan.
Vampire Viruses (TOI)
- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time, several ‘vampire viruses have been detected in the soil samples in the USA recently.
About Vampire Viruses:
- "Vampire viruses", also known as virophages, are viruses that parasitize other viruses.
- They have been known to science for decades, but this is the first time they have been discovered in the United States.
- The viruses were found in soil samples from Maryland and Missouri.
- Virophages are thought to attach themselves to other viruses and inject their own genetic material into the host-virus.
- This genetic material then takes over the host virus's replication machinery, allowing the virophage to reproduce itself.
- The host-virus is eventually destroyed in the process.
- Virophages could be used to control harmful viruses that infect crops or livestock.
- They could also be used to design new antiviral drugs that target viruses in a more specific way than current drugs.
- However, the discovery of virophages also raises some concerns.
- Virophages could potentially kill beneficial viruses that play an important role in the environment.
- For example, some viruses help to break down organic matter in soil, while others help to control populations of harmful bacteria.
Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Paris-based International Energy Agency highlighted India’s Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), 2017 as something that sets it apart from other developing economies where “energy efficiency in buildings stands out as a laggard”.
About Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC):
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) Released by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- It was first released in 2007 and again updated in 2017.
- The purpose of ECBE is to set minimum energy standards for commercial buildings, with the objective of enabling energy savings of between 25 and 50% in compliant buildings.
- Commercial buildings include hospitals, hotels, schools, shopping complexes and multiplexes which have a connected load of 100 kW or more, or contract demand of 120 kVA or more.
- Also the code is for both new buildings and retrofitting existing buildings.
- Assessment Parameters: The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) primarily looks at parameters like building design including envelope (walls, roofs, windows), lighting systems, and renewable energy integration among others.
- Tagging of buildings: Compliant buildings are assigned one of three tags in ascending order of efficiency, namely ECBC, ECBC Plus, and Super ECBC.
- 23 out of 28 states have notified ECBC rules. But only 15 states have notified rules based on the latest ECBC,2017.
- Five states — Gujarat, Maharashtra, J&K, Ladakh, and Manipur — are yet to notify ECBC rules.
Aurora (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, NASA shared this incredible image of an aurora taken from the International Space Station.
What is Aurora?
- An aurora is a natural light display that shimmers in the sky.
- They are only visible at night, and usually only appear in lower polar regions.
- Auroras come in colors like blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- They're mostly visible near the Arctic and Antarctic Circles, known as the aurora borealis and aurora australis, respectively.
- These natural light shows occur when the solar wind from the sun meets Earth's magnetic field, creating a beautiful halo of light around the poles.
- This collision between solar wind ions and Earth's atmosphere atoms leads to stunning auroras.
- Their color depends on altitude and the atoms involved.
- Red comes from oxygen ions higher up, while the familiar green-yellow hues arise from interactions at lower altitudes.
- Sometimes, reddish and bluish tints appear, created by ions colliding with nitrogen atoms.
- The most active auroras happen when the solar wind is strongest, affected by solar weather changes, which follow an 11-year cycle.
- Equinoxes and magnetic storms can cause auroras to be seen even in mid-latitudes, affecting communication signals and occasionally causing disruptions.
- Auroras are a natural spectacle, painted by the collision of solar wind and Earth's atmosphere, creating these dancing lights in the night sky.
Bioluminescent Fungi 'Mycena Chlorophos' (The New Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A team of researchers and the forest department have found a rare bioluminescent mushroom in the Kanyakumari Wildlife Sanctuary (KKWLS).
About Mycena chlorophos:
- Mycena chlorophos is a species of bioluminescent fungus, meaning that it can produce its light.
- It is primarily found in subtropical Asia, including India, Japan, Taiwan, Polynesia, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka, as well as in Australia and Brazil.
- The bioluminescence is produced through a chemical reaction that involves luciferin, a light-emitting molecule, and the enzyme luciferase.
- Luciferase catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, which produces light.
- The luciferin in Mycena chlorophos is a compound called trans-3-hydroxyhispidin.
- This compound is also found in other bioluminescent fungi, such as Neonothopanus nambi and N. gardneri.
- The bioluminescence of Mycena chlorophos is thought to serve several functions.
- It may help the fungus to attract insects, which can help to disperse its spores.
- It may also help the fungus to ward off predators.
What is Bioluminescence?
- It is the ability of living organisms to emit light.
- It occurs due to a biochemical reaction between luciferins, oxygen, and the enzyme luciferase.
- The benefit of bioluminescence in fungi is to attract insects to facilitate their spore dispersal.
Radiative Cooling Paint (The Hindu)
- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) have developed a radiative cooling paint, which is specifically engineered to cool structures like buildings, pavers, and tiles in hot weather conditions.
What is Radiative Cooling Paint?
- Material Composition: Radiative Cooling Paint is composed of a mix of magnesium oxide (MgO) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), derived from easily accessible, cost-effective, and safe materials.
- The optimized MgO-PVDF with dielectric nanoparticles resulted in a large solar reflectance of 96.3% and a record high thermal emission of 98.5% due to Mg?O bond vibrations, and other stretching/bonding vibrations from the polymer.
- Cooling Mechanism: This paint stands out not only for its appearance but for its function.
- It reflects nearly all of the sun's heat and emits a significant amount of its heat, effectively maintaining cooler surfaces.
- Heat Management: Tailored for hot climates, it efficiently reduces the need for excessive electricity use to cool buildings during sweltering days.
- Temperature Reduction: Once applied, it notably lowers surface temperatures by approximately 10 degrees under intense sunlight, surpassing the performance of regular white paint.
- Application Ease: Additionally, it showcases water-resistant properties and excellent adhesion to various surfaces, simplifying the application process on structures like walls and roofs.
Green Firecrackers (The Hindu)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Both government agencies and conscious citizens in Bengaluru are actively ensuring that only less polluting green crackers are being sold and bought this Deepavali.
What are Green firecrackers?
- Green firecrackers are a type of fireworks designed to produce fewer pollutants and emissions compared to traditional firecrackers.
- They are crafted to be more environmentally friendly by using cleaner ingredients, and emitting less smoke and harmful chemicals upon combustion.
- There are mainly three types of green firecrackers: SWAS, SAFAL, and STAR.
- They are not only eco-friendly but 15-20 % cheaper than the conventional ones.
- In 2018, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-NEERI) introduced the idea of green crackers.
What are they made of?
- Green firecrackers are marked by reduced size of shell, elimination of ash usage, reduced usage of raw material in the compositions, and have a uniformly acceptable quality.
- They use additives as dust suppressants to reduce emissions with specific reference to particulate matter (PM).
- These crackers lack the barium compounds responsible for their unique green hue.
- Barium, a metallic oxide, is known to contribute to air pollution and noise pollution.
- When green crackers are ignited, they produce water vapor, thereby minimizing dust emissions.
- In terms of sound levels, green firecrackers generate noise ranging from 110 to 125 decibels, making them significantly quieter than traditional firecrackers, which typically produce around 160 decibels, resulting in nearly 30% less noise.
Cops lose Rs 12 crore in chit fund scheme, probe on (TOI)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Around 70 persons belonging to AP special police have lost nearly Rs 12 crore in a chit fund scheme in Mangalagiri, said the police. Mangalagiri police registered a case and launched an public sector investigation.
What are Chit Funds?
- Chit funds, also known as Kuri and Chitty, serve as versatile financial instruments encompassing both borrowing and saving components.
- In this financial arrangement, a group of individuals collectively contributes a fixed sum at regular intervals, with the understanding that one member will receive the total pooled amount during each interval.
- This process repeats until every member has received their share.
- Typically managed by a chit-fund company, this financial instrument operates by having a group of contributors make regular contributions toward the chit value for a duration equivalent to the total number of subscribers.
- The recipient of the pooled money is determined through an auction or lucky draw, employing a reverse auction system where the individual willing to accept the lowest amount is chosen.
- The sum forfeited by the winning bidder is distributed among other bidders, deducting a foreman's charges and commission.
- The share each bidder receives is termed a dividend. Interestingly, a winning bidder can continue to invest in subsequent intervals, even after claiming their sum.
Types of Chit Funds:
Chit funds can be categorized into three types:
- Chit Funds Run by State Governments:
- Managed and regulated by state governments.
- Public sector undertakings (PSUs) also fall under this category.
- These funds are considered safe, with limited chances of loss. Business processes are transparent and well-regulated.
- Private Registered Chit Funds:
- Registered under the Chit Funds Act of 1982.
- Typically initiated by well-established financial institutions or business entities.
- While participation in these funds may not be as secure as state-run or public-sector funds, the calculated risk is manageable due to their association with reputable private-sector entities.
- Unregistered Chit Funds:
- These chit-funds lack legal recognition, and participation involves a higher risk.
- Commonly found throughout India, they are often formed by a close-knit group of associates.
- Participation in unregistered chit funds is discouraged due to the potential for disputes, which rely heavily on the integrity and honesty of the members involved.
What is Saradha Chit Fund Scam?
- The Saradha scam, also known as the Saradha Group financial scandal, was a major financial scam that surfaced in 2013.
The Saradha scheme:
- The scheme, run by Saradha Group (an umbrella company with 200 private players), was launched in the early 2000s by businessman Sudipto Sen.
- Aimed at small investors, the scheme became popular in a very short time as it promised high returns.
- The money was collected through a wide network of agents, who were paid commissions of over 25 per cent.
- The Saradha Group raised about Rs 2,500 crore in a few years time.
- The company used varied marketing means to build its brand.
- Apart from popular marketing techniques like celebrity endorsements, the company used to sponsor cultural events such as Durga Puja and invest in popular football clubs to attract more investors.
- The scheme soon expanded to Odisha, Assam, and Tripura, and the number of investors reached close to 1.7 million.
US launches Red Sea force as ships reroute to avoid attacks (The Hindu)
- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin on Tuesday announced the creation of a multinational operation to safeguard commerce in the Red Sea following a series of missile and drone attacks by Yemen's Iran-aligned Houthis.
Context:
- The U.S. Defense Secretary recently revealed the establishment of a multinational operation to protect commerce in the Red Sea.
- This decision comes in response to a string of missile and drone attacks by Yemen's Iran-aligned Houthis.
- The gravity of these attacks has prompted several shipping companies to instruct their vessels to remain stationary and avoid entering the Bab el-Mandeb Strait until the security concerns are addressed.
About the Red Sea:
- The Red Sea is a narrow waterway extending southeastward from Suez, Egypt, to the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
- The Bab-el-Mandeb Strait links the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, providing a connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Sea.
- Essentially, it is a narrow inland sea positioned between the Arabian Peninsula and Africa.
- The Red Sea acts as a boundary, separating the coastlines of Egypt, Sudan, and Eritrea from those of Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
- The Gulf of Aqaba, an extension to the northeast, stretches into southern Israel and southwestern Jordan.
- Significance: The Red Sea boasts some of the planet's hottest and saltiest seawater.
- It stands as one of the most heavily traversed water routes globally, facilitating maritime traffic between Europe and Asia.
- Relevance for India:
- Potential disruptions along this route could lead to a significant surge, up to 25-30%, in freight rates for Indian shipments bound for Europe and Africa.
- For India, the Red Sea trade route serves as the most direct path for ships traveling from Asia to Europe.
- India heavily depends on the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait for crucial aspects such as crude oil, LNG imports, and trade with regions in West Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- This passage is critical, accounting for 30% of global container traffic.
Who are the Houthi Rebels?
- The Houthis are a Shiite Muslim sect with roots that date back centuries in Yemen.
- Members of the religion are a minority in Yemen, which is predominantly Sunni Muslim, but they are a significant one, numbering in the hundreds of thousands and making up as much as a third of the overall population.
- Named after the Houthi tribe, they adhere to Zaydi Shia beliefs within Islam, emphasizing the lineage of Prophet Muhammad's family as the political leaders of the state.
- Also recognized as Ansar Allah, translating to "Supporters of God."
- Involvement in Yemen's Civil War: A major faction in Yemen's nearly decade-long civil war, starting in 2014 when Houthi insurgents seized control of Yemen's capital, Sanaa.
- By early 2015, Saudi Arabia, supported by other Gulf states and the U.S., conducted airstrikes against the Houthis, who have backing from Iran.
- Although a ceasefire was signed in 2022, it lapsed after six months, with the parties involved not returning to full-scale conflict.
- Houthi Attacks on Red Sea Ships:
- Iran-backed Houthi rebels from Yemen have targeted ships in the Red Sea in response to Israel's military actions in Gaza.
- The Houthis, supporting Hamas, declared on November 19 their intent to attack vessels they believe are traveling to and from Israel.
Full-blown late blight attack damages potato crops in Punjab (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Days after the experts from Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) had cautioned farmers against the late blight disease attack on potato crop, the worst fears of the potato farmers have come true.
About Late Blight Disease:
- Late Blight disease is attributed to the fungus Phytophthora infestans and stands as a significant threat to potato crops, potentially causing rapid failures if appropriate control measures are not implemented.
- Common in humid regions with specific temperature conditions, this disease manifests with initial symptoms of small, light to dark green, circular to irregular water-soaked spots.
- In cool, moist weather, these spots rapidly expand into large, dark brown or black lesions, often exhibiting a greasy appearance.
- A pale green to yellow border typically surrounds these lesions.
- The spread of Late Blight is facilitated by infected tubers and soil, acting as a primary source of infection.
- Infected tubers play a crucial role in the disease's persistence from one crop to another. Airborne infection occurs through sporangia.
- Effective control measures involve the prompt destruction of infected crop residue in the field to prevent the disease from spreading to nearby areas.
Diseases Caused by Bacteria on Potato Crops:
- Ring Rot
- Brown Rot
Diseases Caused by Fungi on Potato Crops:
- Late Blight
Diseases Caused by Virus on Potato Crops:
- Leaf Roll
- Mosaic
First Prehistoric Pictorial Cave Art Found in Madagascar Offers Clues Regarding Ancient Connections Between Borneo, Egypt (The Hindu)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, distinctive prehistoric rock art depictions were unearthed within the Andriamamelo Cave in western Madagascar.
Key Discoveries:
- Within this cave's truly pictorial art, human-like and animal-like figures depicting scenes from nature have been revealed.
- The remarkable findings unveiled surprising cultural connections, with some scenes directly linking to Egyptian religious motifs from the Ptolemaic period (300-30 BCE).
- Additionally, symbols and inscriptions on the cave walls indicated connections to the Ethiopian and Afro-Arab regions.
- Furthermore, the prevalent symbology and motifs echoed a cave art style from Borneo dating back two millennia.
- Notably, depictions within the cave may include three extinct animals of Madagascar — a giant sloth lemur, an elephant bird, and a giant tortoise.
- The potential connection to Egypt is suggested by eight significant images, including representations of a falcon (Horus), the bird-headed god Thoth, the ostrich goddess Ma`at, and two human-animal figures resembling Anubis, the ancient Egyptian god typically portrayed with a canine head.
About Andriamamelo Cave:
- The Andriamamelo Cave is situated in western Madagascar, nestled within the karstified limestone of the Paysage Harmonieux Protege de Beanka.
- This cave is a component of a vast karst region that encompasses the UNESCO World Heritage site, Parc National de Bemaraha, to the south, and the less-explored Antsingimavo karst area to the north.
Goa Liberation Day: Why India waited for 14 years after independence to move troops to Goa (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Goa Liberation Day is commemorated annually on December 19. In 2023, we observe the 62nd anniversary of the liberation of Goa.
Key Highlights:
- This day commemorates the liberation of Goa in 1961 by the Indian armed forces, ending 450 years of Portuguese rule.
- Portuguese colonization in India began in 1510, but by the late 19th century, their colonies were limited to Goa, Daman, Diu, Dadra, Nagar Haveli, and Anjediva Island.
- After India's independence in 1947, attempts to persuade Portugal to cede their territories were unsuccessful.
- The Goa liberation movement gained momentum from small-scale revolts, peaking between 1940 and 1960.
- In 1961, diplomatic efforts failed and Operation Vijay was executed, leading to the annexation of Daman, Diu, and Goa to the Indian mainland on December 19.
About Operation Vijay:
- Operation Vijay, a 36-hour military initiative initiated on December 18, 1961, and concluded on December 19, 1961, aimed at liberating the Portuguese territories of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- This marked a significant milestone as possibly the first tri-service operation by the Indian armed forces.
- The Indian Air Force executed bombings on the Portuguese airbase at Dabolim, complementing the army's advancement from the north and east into Goa.
- Simultaneously, the Indian Navy played a crucial role in preventing hostile actions by Portuguese warships, securing access to Mormugao harbor, and establishing control over the Anjadip Island off the coast of Karwar.
- By the evening of December 19, 1961, Portuguese Governor General Vassalo De Silva signed the surrender document as the Indian armed forces, led by the army with support from the air force and navy, had effectively outnumbered and outgunned the Portuguese forces.
Granting Statehood to Goa after Liberation:
- Following its liberation, Goa came under the administration of the Indian government, becoming a constituent of the Indian Union as the Union Territory of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- However, in 1967, a plebiscite was conducted to decide on the potential merger of the state with Maharashtra.
- The majority of Goans voted against the merger, leading to the continuation of its status as a Union Territory.
- This arrangement persisted until 1987 when Goa was accorded statehood, emerging as the 25th state of India.
- Meanwhile, Daman and Diu retained their status as a Union Territory.
Electoral Trusts (ET) Scheme (Indian Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
After a three-day hearing, the Supreme Court has reserved its judgment on the challenge to the Central government’s Electoral Bonds Scheme.
About Electoral Trusts (ET):
- As per Section 17CA of Income Tax Rules (1962), an Electoral Trust (ET) is a non-profit organization established for the orderly receipt of voluntary contributions from any person for distributing the same to political parties, registered under Section 29A of the Representation of People Act, 1951.
- This Scheme was notified in January 2013 by the then UPA government.
- Objective of Electoral Trust:
- Electoral Trusts are designed to bring more transparency in the funds provided by corporate entities to the political parties.
- The objective of an Electoral trust is not to receive any profit or pass on any direct or indirect benefit to its members or contributors.
- An Electoral trust will distribute funds only to eligible Political parties.
- These trusts are approved by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) in accordance with the Electoral Trust Scheme of 2013.
- The ET may receive voluntary contributions from:
- an Individual (citizen of India)
- a Company registered in India
- a Firm or HUF or Associations of Persons or Body of Individuals resident in India
- The electoral trusts have to apply for renewal every three financial years.
INDUS-X Initiative (Financial Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On the eve of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the inaugural INDUS-X Investors Meet was held in New Delhi.
What is the INDUS X Initiative?
- The INDUS-X initiative, also known as the India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem, was launched in June 2023 during the State Visit of the Prime Minister of India to the United States.
- Its primary objective is to expand the strategic technology partnership and defense industrial cooperation between the governments, businesses, and academic institutions of India and the United States.
- INDUS-X is envisioned as a defense innovation bridge, encompassing Joint Challenges, a Joint Innovation Fund, academia engagement, industry-startup connections, private sector investment in defense projects, mentorship by experts, and niche technology projects, among other initiatives.
- This collaborative effort holds the promise of ushering in a new era of defense innovation and cooperation between India and the United States.
About INDUS X Investors Meet:
- The first-ever INDUS-X Investors Event brought all the stakeholders including Startups, Investors, Incubators, and Industry from both sides under one roof to discuss the collaborative agendas and opportunities thereon.
- The event also had focused panel discussions with a select audience of 50 thought leaders, including start-ups, investors, government officials, and business leaders from the defence industry.
- The panel discussed ‘Investment Opportunities in the Defence Sector’, elaborating upon establishing a sustainable commercial foundation for defence collaboration and co-production.
- The INDUS-X Educational Series (Gurukul) was also launched during the event.
- The Gurukul initiative is aimed at helping innovators and startups to navigate the defence eco-system of the US and India.
Palamu Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A recently captured image in the Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR) reveals a new tiger, distinct from the one caught earlier this year.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve:
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve is located on the western side of Latehar district on the Chhotanagpur plateau in Jharkhand.
- It is one of the first 9 tiger reserves established in the country at the inception of ‘Project Tiger’, in the year 1973 in India and the only one in the state of Jharkhand.
- This reserve forms a part of the Betla National Park.
- The total area of the Tiger Reserve is 1129.93 sq. km
- It is the first reserve in the world in which a tiger census was carried out as a pugmark count, as early as 1932 under the supervision of J.W. Nicholson.
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve is very important for its biodiversity.
- The project area is constituted mainly of Sal forests, mixed deciduous forests, and bamboo groves.
- The reserve zone is the watershed area for 3 important rivers Koel, Burha, and Auranga.
Hermes 900 Star Liner (The Hindu)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Adani Aerospace and Defence in partnership with Elbit Systems manufactures the complete carbon composite aerostructures for Hermes 900 and Hermes 450 in Hyderabad.
About Hermes 900 Starliner:
- The Hermes 900 StarLiner is an Israeli-made, medium-size, multi-payload, medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed for tactical missions.
- It is also known as the Hermes 900 Heavy-Fuel Engine (HFE).
- It is developed by Elbit Systems.
- It is a successor to the Hermes 450 series of drones, one of the most widely used military drones in the world.
- The aircraft has a service ceiling of 30,000ft and offers a flight endurance of up to 36 hours.
- The Hermes 900 has a wingspan of 15 m (49 ft) and can carry a range of multi-sensor payloads weighing up to 450kg for multiple applications.
- Payload options include electro-optical/infrared sensors, synthetic-aperture radar/ground-moving target indication, communications and electronic intelligence, electronic warfare, and hyperspectral sensors.
- The drone has direct and indirect lighting strike capability and can perform missions under instrument flight rules (IFR) in all weather conditions.
'World's Largest Meditation Centre': PM Modi inaugurates Swarved Mahamandir in Varanasi (ET)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the world’s largest meditation centre, Swarved Mahamandir, in Varanasi on December 18.
About the Swarved Mahamandir:
- The Swarved Mahamandir stands as the world's largest meditation centre, accommodating 20,000 individuals in collective contemplation.
- Situated in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, this spiritual haven aspires to cast a luminous spiritual aura, enveloping the globe in a state of tranquil attentiveness.
- Named after the Swarved, a profound spiritual text penned by Sadguru Shri Sadafal Deoji Maharaj, the visionary behind Vihangam Yoga and an enduring yogi, the temple serves as a bastion for disseminating Swarveda teachings.
- Emphasizing Brahma Vidya, a profound body of knowledge, it guides spiritual seekers toward sustaining an unwavering equilibrium of peace and happiness.
- Architecturally, the Mahamandir is an imposing seven-floor superstructure, adorned with a captivating design featuring 125-petal lotus domes.
- Crafted from teakwood, the intricate carvings embellishing the ceiling and doors add to its allure.
- Pink sandstone envelops the temple walls, complemented by an enchanting garden featuring medicinal herbs.
- Imprinted on the Mahamandir's walls are verses from the Swarveda, serving as an enduring testament to the spiritual wisdom that resonates within its sacred confines.
What is Vihangam Yoga?
- Vihangam Yoga, an indigenous form of Yoga and meditation, was established by Sadguru Sadafal Deo Ji Maharaj in 1924.
- The nomenclature of this practice is derived from two foundational words: "Vihag," signifying bird, and "Yog," denoting union.
- The name encapsulates the profound concept of a bird ascending from the terrestrial realm, soaring high and unbounded in the sky.
- This symbolism mirrors the ultimate aim of Vihangam Yoga – the liberation of the soul from attachments to the material world, allowing it to recognize and embrace its innate, unshackled essence.
- Only through this liberation can an individual's consciousness seamlessly merge with the universal consciousness, often referred to as the Supreme Being, leading to a state of enduring tranquillity and bliss.
Telecommunications Bill, 2023: The changes it seeks in the telecom sector, why some have raised concerns (Indian Express)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Telecommunications Bill, 2023, was introduced in the Lok Sabha on Monday. The bill allows the government to take over, manage or suspend telecommunication services or a network over national security.
Key Features of the Telecommunications Bill, 2023
- Repeal of Existing Laws: The bill annuls the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, the Indian Wireless Telegraphy Act, 1933, and the Telegraph Wires (Unlawful Possession) Act, 1950, while introducing amendments to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Act, 1997.
- Authorization for Telecom Activities: Central government approval is mandatory for telecommunication services, network establishment, operation, maintenance, expansion, or possession of radio equipment.
- Existing licenses remain valid for their granted period or five years if unspecified.
- Spectrum Assignment: Spectrum allocation, except for specific purposes, will be through auction.
- Exceptions include national security, disaster management, and services by state-owned entities.
- Interception and Search Powers: Messages may be intercepted, monitored, or blocked for public safety, emergencies, or specified grounds like state security and prevention of offences.
- Government's Extraordinary Powers: The government can take temporary possession of telecom infrastructure during public emergencies, with the authority to suspend telecom services.
- Authorized officers may search for unauthorized equipment.
- Standards Specification Authority: The central government can prescribe standards for telecom equipment, infrastructure, networks, and services.
- Right of Way for Telecom Infrastructure: Facility providers can seek a right of way over public or private property for telecom infrastructure on a non-discriminatory basis.
- User Protection Measures: The government may implement measures to protect users, including consent for specific messages, creation of Do Not Disturb registers, and a mechanism for reporting malware.
- TRAI Appointments and Experience Requirements: Amendments allow individuals with at least 30 years of professional experience to serve as TRAI chairperson and those with at least 25 years of membership.
- Digital Bharat Nidhi: The Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) is renamed Digital Bharat Nidhi, allowing its use for research and development (R&D).
- Adjudication Process: An adjudicating officer, of the rank of joint secretary and above, will handle inquiries and orders against civil offences.
- Appeals can be made to the Designated Appeals Committee and further to TDSAT.
- Offences and Penalties: The Bill outlines criminal and civil offences, imposing penalties and imprisonment for unauthorized telecom services, network access, and equipment possession.
- Civil penalties apply for breaches of authorization terms.
What are the Reasons behind the introduction of the Telecommunications Bill, of 2023?
- The telecommunications sector plays a pivotal role in fostering economic and social progress, serving as the conduit for digital services.
- Given its significance, the security of our nation relies substantially on the robustness of telecommunication networks.
- Hence, there is an imperative to establish a legal and regulatory structure that prioritizes the security and resilience of telecommunication networks, fostering a digitally inclusive trajectory for growth.
- The dynamic evolution of telecommunication, its patterns of use, and underlying technologies in recent years underscores the necessity for legislation that aligns with the evolving needs of our society.
Stable Auroral Arc (SAR) (New Indian Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a rare phenomenon, researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have recorded the auroral activity that is normally witnessed over the North Pole- at Hanle and Merak in Ladakh through the all-sky cameras recently.
What is Stable Auroral Arc (SAR)?
- An aurora is a glorious curtain of light that is usually seen at high latitudes like in the Scandinavian countries, and they are not expected to occur at lower latitudes.
- They occur due to the interaction between the Earth’s magnetosphere and the incoming solar wind that carries charged particles and magnetic fields.
- They are typically several hundred kilometers wide and can extend for thousands of kilometers.
- A Stable Auroral Arc (SAR) is red in colour as opposed to the usual green-blue curtains of light seen from high latitudes.
- It is a rare phenomenon and it was not exactly an aurora-like one witnessed from close to the North Pole.
- SAR arcs are typically subvisual, meaning that they cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- However, they can be detected using specialized instruments, such as photometers and spectrographs.
- It was observed in Ladakh during a strong G3-class geomagnetic storm and this event was registered in many parts of the world.
Mines Ministry to Launch National Geoscience Data Repository Portal To Foster Innovation in Exploration (PIB)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines is to launch the National Geoscience Data Repository (NGDR) Portal on 19th December 2023 in a ceremony in New Delhi.
What is the National Geoscience Data Repository Portal?
- This extensive online platform facilitates the retrieval, exchange, and examination of geospatial information nationwide.
- Spearheaded by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the Bhaskaracharya Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), the NGDR initiative marks a notable advancement in democratizing crucial geoscience data.
- It empowers stakeholders in various industries and academia by providing unparalleled access to invaluable resources.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) originated in 1851 with the primary objective of identifying coal deposits for the Railways.
- Since its inception, GSI has transformed into a repository of geo-scientific information, achieving international recognition for its contributions.
- The organization is dedicated to creating and updating national geoscientific data, conducting mineral resource assessments, and providing impartial geological expertise crucial for policy decisions, commercial ventures, and socio-economic needs.
- GSI focuses on comprehensive documentation of geological processes, employing state-of-the-art techniques in geological, geophysical, and geochemical surveys.
- As an attached office of the Ministry of Mines, GSI operates from its headquarters in Kolkata, with six regional offices in Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong, and Kolkata, along with state unit offices across India.
About BISAG (N):
- Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) operates as an Autonomous Scientific Society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, falling under the MeitY, Government of India.
- Its multifaceted mission encompasses technology development and management, research and development, fostering national and international collaboration, capacity building, and facilitating technology transfer and entrepreneurship development in the realm of geospatial technology.
- BISAG-N has played a pivotal role in implementing GIS and geospatial technologies for major ministries and nearly all states, integrating diverse technological domains such as geo-spatial science, information science systems, and mathematics science systems.
- The institute operates as a state agency under the Department of Science and Technology, Government of Gujarat, situated in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
mRNA, easy to customise, is the next frontier for personalised medicine (The Hindu)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The therapeutic use of messenger RNA (mRNA) has fueled great hope to combat a wide range of incurable diseases.
What is mRNA?
- mRNA, or messenger RNA, represents a type of nucleic acid responsible for conveying genetic instructions.
- Within cells, mRNA serves as a messenger, transporting codes from the DNA located in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, where ribosomes are situated.
- The genetic information in DNA undergoes transcription, or copying, into mRNA before proteins can be synthesized.
- Each mRNA molecule encodes information for a specific protein, with every sequence of three nitrogen-containing bases dictating the inclusion of a particular amino acid in the protein.
Advantages of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Scalability: The production of mRNA in the laboratory is highly scalable, as the method for generating mRNA remains consistent across different types.
- This contrasts with traditional drugs, where each compound has distinct chemistry, requiring varied manufacturing methods.
- Patient-Centric: mRNA, being naturally degradable by cells when no longer needed, allows for flexible dosage adjustments to cater to changing patient requirements.
- Broad Therapeutic Potential: mRNA-based medicine holds promise for addressing a wide range of diseases rooted in cellular errors, such as the production of incorrect proteins, mutant protein versions, or insufficient normal protein levels.
- By delivering corrected mRNA to affected cells, scientists aim to facilitate the production of the correct proteins.
Prospects of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Diverse Treatment Applications: The future of mRNA-based medicine extends to addressing conditions like heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and bone loss, among others.
- Enhanced Wound Healing: mRNA drugs exhibit the potential to stimulate the formation of new blood vessels.
- This capability is particularly beneficial for diabetic patients with compromised blood circulation, reducing the risk of amputation.
- Treatment for Rare Conditions: mRNA-based medicine holds promise in treating rare disorders like propionic acidaemia, characterized by insufficient levels of liver proteins crucial for preventing the accumulation of toxic by-products in the body, especially in children.
Way Forward
- The capacity to tailor and manufacture mRNA easily enhances its prospects as a potent and personalized therapy, offering the potential for reduced side effects and widespread applicability.
- Despite these advancements, mRNA-based therapeutics are in the early stages of development, facing challenges such as the short lifespan of mRNA in cells and limited protein production duration.
- Addressing these hurdles is crucial to optimizing mRNA effectiveness and minimizing the quantity of mRNA needed.
MoEFCC has launched the Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme to promote sustainable forest management and agroforestry practices across the country (Indian Express)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid rising international concerns about deforestation and illicit trade in timber, the government has launched its own “national” forest certification scheme to validate entities that adhere to sustainable practices in the management of forests and their products.
About the Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme (IFWCS):
- The Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme (IFWCS) serves as the national forest certification initiative, focusing on fostering sustainable forest management and the sustainable utilization of Trees outside Forests (TOF) across India.
- Voluntary Participation: The scheme provides a voluntary third-party certification mechanism to encourage agroforestry practices within the country.
- Alternatives to Foreign Certifications: IFWCS presents an indigenous alternative to foreign certification agencies that have been prevalent in the Indian market for the past two decades.
- Applicability: The certification applies nationwide, covering both forest areas and TOF plantations on government, private, agroforestry, and other lands.
- It encompasses both timber and non-timber forest produce (NTFP).
- Necessity: With major export markets like Europe and the United States imposing stricter rules on forest product imports due to deforestation concerns related to climate change, IFWCS can provide market incentives for entities practising responsible forest management.
- Significance: The scheme aims to enhance trust, transparency, and international acceptability of Indian forest-based products.
- It is especially beneficial for state forest departments, individual farmers, or Farmer Producer Organizations engaged in agroforestry.
- Compliance and Legal Status: While the certification may gain recognition from various regulatory authorities, it does not serve as legal advice on compliance with specific laws, regulations, or requirements.
- Foundation: Forest Management certification relies on the Indian Forest Management Standard, a crucial component of the National Working Plan Code 2023, introduced this year.
- The Indian Forest and Wood Certification Council, acting as a multi-stakeholder advisory body, will supervise the scheme.
- The council comprises members from esteemed institutions like the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education, Forest Survey of India, and the Indian Institute of Forest Management, along with representatives from relevant ministries.
- Implementation: The Indian Institute of Forest Management in Bhopal will serve as the scheme's operating agency.
- Certification bodies conducting independent audits will be accredited by the National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies under the Quality Council of India.
Management of Forests in India:
- The administration of forests in India aligns with individual working plans specific to each forest area.
- Recently, these plans have undergone revisions incorporating the newly formulated Indian Forest Management Standards.
- Comprising 8 criteria, 69 indicators, and 254 verifiers, these standards are obligatory for implementation across all forest divisions nationwide.
- While forest divisions are not compelled to obtain certification, adhering to these standards renders them eligible.
- The decision to pursue certification is contingent upon specific requirements and considerations.
India's Akash missile engages four targets at once at 25km, a global first (ET)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India demonstrated the capability of the Akash missile system to engage four aerial targets simultaneously at a range of 25 kilometres, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) said on Sunday.
Context:
- During the recent Exercise Astrashakti 2023, a solitary unit of the Akash weapon system demonstrated its capability by effectively engaging and eliminating four unmanned targets simultaneously.
- This showcase positions India as the pioneer, being the first country to showcase the proficiency of engaging multiple targets at considerable distances concurrently through command guidance from a single firing unit.
About the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System:
- The Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System is a Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (SRSAM) designed to safeguard vulnerable areas and points from airborne threats.
- Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), it boasts several notable features:
- Versatility: Capable of simultaneously engaging multiple targets and effectively neutralizing manoeuvring threats, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles, and helicopter-launched missiles.
- Electronic Counter-Counter Measures (ECCM): Equipped with built-in ECCM features, enhancing its resilience against electronic countermeasures.
- Flexible Deployment: The entire system is configured for launch from both static and mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, ensuring adaptable deployment options.
- Transportability: Road and rail transportable, with swift mobilization and deployment capabilities, facilitating rapid response scenarios.
- Range: Capable of engaging aerial targets at a distance of approximately 25 km.
- Altitude of Operation: Ranging from 100 meters up to 20 km.
- Weight: 710 kg.
- Guidance System: Command Guidance.
- Automation: Fully automatic with a quick response time from target detection to neutralization.
- Open-System Architecture: Designed with an open-system architecture, ensuring adaptability to current and future air defence environments.
What is ‘noma’, the latest addition to WHO’s list of neglected tropical diseases (DownToEarth)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) on December 15, 2023, added one of the world’s most under-recognised health challenges, noma, to its official list of neglected tropical diseases (NTD).
About the Noma disease:
- Noma is a severe gangrenous disease of the mouth and face with a mortality rate of approximately 90 per cent.
- It is also known as cancrum oris or gangrenous stomatitis and is often associated with extreme poverty, malnutrition and poor access to sanitation and oral hygiene.
- The name of the disease comes from the Greek word “nom?”, meaning “to devour”, as noma eats away facial tissue and bones if not treated early.
- Noma mainly affects children aged 2-6 years old and is found most commonly among those living in poor communities.
- The illness’s ‘hidden’ or neglected nature is most likely due to the fact that it affects the world’s most marginalised children.
- Noma is associated with a number of risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, weakened immune systems, infections, and extreme poverty.
- While the disease is not contagious, it prefers to attack when the body’s defences are weak.
- The NTD often starts as an ulcer on the mucous membrane lining, commonly after a bout of measles or other diseases, stated another 2003 study.
- “It quickly develops into a massive necrosis, moving from the inside outward, often involving major portions of the face.
- Treatment: “Early treatment with antibiotics, rehydration, correction of electrolytic imbalances, and administering nutritional supplements will halt the disease.
- The patients who survive face many consequences, like significant facial disfigurement, spasms of the jaw muscles, oral incontinence and speech problems.
- The disease is also called the ‘face of poverty’, as effective drugs like sulfonamides and penicillin and adequate surgical treatment for the effects remain inaccessible for many due to extreme poverty.
- “The recognition of noma as an NTD aims to amplify global awareness, catalyse research, stimulate funding, and boost efforts to control the disease through multisectoral and multi-pronged approaches.
Surat Diamond Bourse to create 150,000 jobs! Modi is confident ‘world’s largest office building’ will be a boon for artisans and businessmen (Financial Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the inauguration ceremony of the Surat diamond bourse in Gujarat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi revealed plans for the creation of 150,000 new jobs, emphasising the bourse’s role as a “one-stop shop” for artisans and businessmen.
About Surat Diamond Bourse:
- Established in February 2015 by the former Chief Minister of Gujarat, Smt. Anandiben Patel, the Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is a prominent diamond trade centre situated in DREAM (Diamond Research and Mercantile) city, Surat, Gujarat.
- Recognized as the "diamond city" due to its diamond industry, which processes 85 to 90% of the world's rough diamonds, the SDB stands as the world's largest diamond trading hub, spanning an expansive floor space of 660,000 square meters and surpassing The Pentagon as the largest office building globally.
- Themed around the 'panch tatva,' symbolizing the five elements of nature – air, water, fire, earth, and sky, the SDB is designed with thematic landscaping.
- As a global centre for both rough and polished diamond and jewellery trading, it unifies various facets of the diamond industry, including cutting, polishing, and trading activities, within its vast expanse.
- The Bourse features a state-of-the-art 'Customs Clearance House' for Import-Export, a Jewelry mall for retail jewellery business, and facilities for International Banking and Safe Vaults.
Importance of the SDB Project:
- The Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is set to accommodate a diverse range of diamond-related enterprises, encompassing the sale of both rough and polished diamonds, diamond manufacturing machinery, diamond planning software, diamond certificate firms, lab-grown diamonds, and more.
- Anticipated to be a major contributor to employment, the SDB is poised to generate substantial job opportunities.
- With an expected direct employment impact on over 1.5 lakh individuals across various roles within the diamond industry, it aims to bolster economic activity and livelihoods.
- Acknowledging its commitment to environmental responsibility, the complex has earned pre-certification as a green building by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
- This recognition is a testament to the SDB's implementation of eco-friendly and sustainable practices in its operations.
What is DREAM City?
- DREAM City, short for Diamond Research and Mercantile City, is an emerging business district located in Surat.
- Encompassing 810 hectares (2,000 acres) of land near Khajod, it follows the model of the Gujarat International Finance Tec (GIFT) City and Dholera Smart City near Ahmedabad.
- Envisioned as a comprehensive urban development, DREAM City is slated to feature office spaces, residential areas, and associated amenities.
- The project is under the purview of a special-purpose vehicle established by the Government of Gujarat.
- With an anticipated opening in 2030, DREAM City is poised to become Gujarat's third smart city, aligning with the state's commitment to fostering modern and sustainable urban environments.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
How Indian states fare on logistics: What the Centre’s latest survey says (Indian Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) perception survey, released by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry, flags some challenges in logistics and states performance on a regional basis.
Key highlights of the Report:
- Only five states namely Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Telangana continue to make up 70 per cent of exports. Over the years this has caused a widening gap in income and job generation between the landlocked states and coastal states.
- Performance of Landlocked States: Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh have received low perception scores on these counts while user satisfaction in Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab improved.
- Notably, Jharkhand saw below-average scores across all indicators, encompassing infrastructure, services, and operating and regulatory categories.
- Performance of North-East Group: In Manipur, user satisfaction levels for the state are generally lower than the average of the North-East Group for all indicators across pillars.
- The data indicated relatively high stress in the ‘easy of entry’ category.
- While Assam performed better than average on most counts, the user performance assessment was also below the average of North-East Group in the case of Meghalaya.
- Odisha, West Bengal Lag Among Coastal States: Indian coastal states including Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal account for 75 per cent of total exports from the country and have fared well in logistics historically.
- Gujarat accounts for 33% followed by Maharashtra with 16% and Tamil Nadu with 9% share.
- However, the survey showed that Goa, Odisha and West Bengal continue to perform below the average among coastal states.
- In the case of Odisha, the survey said that there has been an improvement in the overall perception of the state’s logistics ecosystem since 2019 but despite this, the indicator averages for this year have remained below the Coastal Group average.
What is Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS)?
- Initiated in 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, LEADS draws inspiration from the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- Unlike the LPI, which relies solely on perception-based surveys, LEADS incorporates both perception and objectivity, thereby enhancing the robustness and comprehensiveness of its evaluation.
- LEADS focuses on three pivotal pillars:
- Logistics Infrastructure
- Logistics Services, and
- Operating and Regulatory Environment.
- The recently released 5th edition, LEADS 2023, illuminates the evolving performance of states and union territories across these pillars.
- It provides valuable insights into the enhancement of logistics performance at the State/UT level, emphasizing an augmented stakeholder perception and the impact of various reforms.
- This report not only signals a positive transformation in the performance of states but also empowers State/UT Governments with region-specific insights, facilitating informed decision-making and comprehensive growth.
Importance of the LEADS Initiative:
- The LEADS report serves as a catalyst in fostering healthy competition among States/UTs, driving improvements in logistics performance.
- Notably, 23 States/UTs have aligned their State Logistics Policies with the National Logistics Policy, while 16 have accorded industry status to logistics, collectively contributing to the elevation of India's global positioning in the logistics ecosystem.
- This initiative significantly enhances the overall competitiveness of India's logistics sector, as evidenced by the country's ascent by six places to the 38th position in the 2023 Logistics Performance Index.
- Integral to this success are digital reforms like PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP), and GST, which have propelled India's improved global ranking.
- Developed collaboratively and through a consultative approach, the LEADS report introduces objectivity in assessing both infrastructure development and process-related reforms.
Saint Lucia’s Tax Inspectors without Borders (TIWB) programme launched in partnership with India (ET)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India will help Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and sharing best practices under the ‘Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) programme’.
Key Highlights:
- India has been chosen as the Partner Administration and will provide Tax Experts for this programme.
- This programme is expected to be of 12-18 months’ duration in which India, in collaboration with the TIWB Secretariat and support of the UNDP Country Office, Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean, aims to aid Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and through sharing of best practices.
- The focus of the programme will be on the effective use of automatic exchange of information under the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) framework.
What is Tax Inspectors without Borders programme?
- Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) is a joint initiative of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is designed to support developing countries to build tax audit capacity.
- TIWB facilitates well-targeted, specialised tax audit assistance in developing countries around the world.
- Under TIWB, tax audit experts work alongside local officials of developing country tax administrations on tax audit and tax audit-related issues.
- TIWB aims to transfer technical know-how and skills to developing countries’ tax auditors, as well as share general audit practices.
- The host administrations of developing countries are the lead partners in TIWB programmes, clearly specifying their needs and scope of work.
- A dedicated central unit (TIWB Secretariat) jointly managed by OECD and UNDP operates as a clearing house to match the demand for auditing assistance with appropriate expertise.
- TIWB is a capacity-building programme.
State Bank of India (SBI) has raised its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) by up to 10 basis points for selected tenures (Financial Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
State Bank of India (SBI) on Friday hiked its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) on various tenures by 5-10 basis points (bps), a move that could make consumer loans, such as auto or home loans, more expensive for borrowers.
What is the Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR)?
- The MCLR, or Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate, represents the minimum lending rate below which a bank is not authorized to lend.
- This mechanism aims to facilitate the calculation of the minimum interest rate applicable to various types of loans offered by banks.
- Introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on April 1, 2016, the MCLR methodology serves to improve the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission and enhance transparency in the interest rate-setting process, replacing the earlier base rate structure established in July 2010.
- Calculation of MCLR: MCLR is internally determined by the bank, considering the remaining period for the loan repayment. This rate is closely tied to actual deposit rates and is calculated based on four key components:
- The marginal cost of funds
- Negative carry-on account of the cash reserve ratio
- Operating costs
- Tenor premium
- Under the MCLR framework, banks have the flexibility to offer loans at fixed or floating interest rates across all categories.
- The actual lending rates for various loan categories and tenors are determined by adding the components of spread to the MCLR.
- Consequently, the bank is restricted from lending at a rate lower than the MCLR for a specific maturity concerning all loans linked to that benchmark.
- Banks review and publish MCLRs for different maturities on a monthly basis.
- Certain loan rates, such as those for fixed-rate loans with tenors exceeding three years and special loan schemes offered by the government, remain unaffected by MCLR fluctuations.
Difference Between MCLR and Base Rate:
MCLR stands as a more evolved iteration of the base rate, presenting several distinctions between the two:
- Origin and Regulation: The base rate is the RBI-set minimum interest rate, and financial institutions cannot lend below this rate.
- MCLR, on the other hand, is an internal benchmarking system used by financial institutions, allowing them to set lending rates based on a predetermined spread.
- Cost Calculation: The base rate relies on the average cost of funds.
- MCLR is rooted in the marginal or incremental cost of money, providing a more dynamic reflection of the current cost scenario.
- Impact of RBI's Repo Rate: The base rate remains unaffected by changes in the RBI's repo rate.
- MCLR, however, is directly influenced by revisions in the repo rate, adjusting accordingly.
- Consideration Factors: The base rate typically considers the minimum rate of return or profit margin.
- In contrast, when determining the MCLR, factors such as the tenor premium are taken into account, resulting in a more nuanced rate-setting process.
‘Sacrifice forever etched in our hearts’: PM Modi, leaders across parties pay tributes on Vijay Diwas (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Leaders across the political lines paid tributes to the soldiers who fought in the 1971 war, on the occasion of 52nd Vijay Diwas on Saturday.
About Vijay Diwas:
- Vijay Diwas, observed on December 16 annually, is a commemoration honouring the triumph of the Indian armed forces over Pakistan in the 1971 war and paying tribute to the soldiers who made the ultimate sacrifice for their country.
- This day is also recognized in Bangladesh as 'Bijoy Dibos' or Victory Day, symbolizing the nation's formal independence from Pakistan.
Historical Background:
- The roots of the 1971 war lay in the genocide perpetrated by the oppressive Pakistani military regime, led by General Yahya Khan, against the people of East Pakistan.
- The conflict emerged following the victory of the Sheikh Mujibur Rahman-led Awami League in the 1970 elections.
- Post-elections, the Pakistani military used force to manipulate the results, resulting in a mass exodus from East Pakistan.
- India intervened during this critical period, with then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi offering refuge to those fleeing from the other side of the border.
- Tensions escalated on December 3, 1971, when Pakistan initiated air strikes on 11 Indian airbases.
- In response, Indira Gandhi instructed India's Army Chief, General Sam Manekshaw, to launch a full-scale war against Pakistan.
- India supported Bangladesh nationalist groups and executed 'Operation Trident,' led by the Indian Navy, to target Karachi Port.
- After a 13-day battle, India achieved a decisive victory on December 16, 1971, leading to the establishment of Bangladesh from the former East Pakistan.
- On this momentous day, General Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi of Pakistan signed the Instrument of Surrender, capitulating with 93,000 Pakistani soldiers before the Indian Army and the Mukti Bahini of Bangladesh, marking the most substantial military surrender post-World War II.
How the hottest summer ever affected the Arctic: 5 things you need to know (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Rising temperatures in the Arctic have led to unprecedented wildfires that forced communities to evacuate, a decline in sea ice extent, devastating floods, food insecurity, and a rise in sea level.
Highlights from the Arctic Report Card 2023:
- The period from October 2022 to September 2023 ranked as the sixth-warmest year in the Arctic since the initiation of record-keeping in 1900.
- Notably, this timeframe aligns with the Arctic monitoring year, spanning from October to September to cover the region's cold season.
- This marks the 14th consecutive year wherein Arctic temperatures surpassed the average recorded between 1991 and 2020.
- The elevated temperatures observed in the northern polar region had significant consequences, including unprecedented wildfires necessitating community evacuations, a reduction in sea ice coverage, severe floods, concerns about food security, and an elevation in sea levels.
The most severe consequences of the soaring temperatures in the Arctic:
- Thawing of Subsea permafrost: Subsea permafrost is essentially frozen soil beneath the seabed that contains organic matter.
- While it has been gradually thawing for thousands of years, warmer ocean temperatures are accelerating this process.
- When subsea permafrost thaws, the organic matter it contains decays and releases methane and carbon dioxide – greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming and worsen ocean acidification.
- Food insecurity: Due to the impact of climate change on freshwater bodies and marine ecosystems, Western Alaska recorded another year of extremely low numbers of Chinook and chum salmon. The size of adult salmon has also decreased.
- It led to fishery closures, worsened user conflicts, and had profound cultural and food security impacts in Indigenous communities that have been tied to salmon for millennia.
- Interestingly, while the population of Chinook and chum salmon declined, sockeye salmon increased in Western Alaska.
- According to scientists, the diverging impacts are affecting Indigenous communities that depend on the salmon for food, and challenging fishery managers as the different species respond in unique ways to the warming climate.
- Raging wildfires: Canada with 40% of its land mass is considered Arctic and Northern was among the worst affected regions when it comes to wildfires.
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record with fires burning more than 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories.
- This happened as high temperatures dried up vegetation and soil, coupled with below-average rainfall, creating perfect conditions for wildfires.
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record with fires burning more than 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories.
- Severe flooding: Rising temperatures have led to dramatic thinning of the Mendenhall Glacier, located in Alaska, over the past 20 years.
- As a result, over the years, the meltaway water has annually caused floods in the region.
- One such disaster took place in August 2023, when a glacial lake on a tributary of the Mendenhall Glacier burst through its ice dam.
- It caused unprecedented flooding and severe property damage” in Alaska’s Juneau.
- Greenland ice sheet melting: The highest point on Greenland’s ice sheet experienced melting for only the fifth time in the 34-year record.
- Not only this, the ice sheet continued to lose mass despite above-average winter snow accumulation.
- Between August 2022 and September 2023, it lost roughly 350 trillion pounds of mass.
- Notably, Greenland’s ice sheet melting is the second-largest contributor to sea-level rise.
India joins the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for flying wing technology in tailless configuration (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully carried out a flight trial of the Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator, an indigenous high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) from the Aeronautical Test Range, Chitradurga in Karnataka.
About the Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator:
- The Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator is a domestically developed high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) crafted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s Aeronautical Development Establishment.
- Its inaugural flight took place in July 2022, marking significant progress in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems, real-time integration, hardware-in-loop simulation, and an advanced Ground Control Station.
- The project team successfully optimized avionic systems, integration processes, and flight operations, culminating in the seventh and final flight in the ultimate configuration.
- Constructed with a complex arrowhead wing platform, the UAV prototype utilizes a lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- A noteworthy feature is the autonomous landing capability, eliminating the need for ground radars, infrastructure, or a pilot.
- This unique capability demonstration allows take-off and landing from any runway with surveyed coordinates.
- This technology demonstrator has been developed for India's secretive stealth combat drone called Ghatak.
- The successful flight in a tailless configuration has propelled India into the prestigious group of nations that have perfected the controls for the Flying wing configuration
Indian Joins Elite Club:
- With this flight in the tailless configuration, India has joined the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for the flying wing technology.
- These flight tests led to achievements in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems; integrated real-time and hardware-in-loop simulation, and a state-of-the-art Ground Control Station, informed the DRDO.
Aatmanirbharta
- The DRDO team had optimised the avionic systems, integration and flight operations towards the successful seventh flight in the final configuration.
- The aircraft prototype, with a complex arrowhead wing platform, is designed and manufactured with lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- Also, the composite structure, impregnated with fibre interrogators for health monitoring, is a showcase of ‘Aatmanirbharta’ in aerospace technology.
'Pralay' Missile (The Hindu)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India on November 7 successfully test-fired its surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) 'Pralay' from the Abdul Kalam Island off the Odisha coast.
About the Pralay missile:
- The Pralay missile is a short-range ballistic missile developed by India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO).
- It is similar in design and functionality to Russia’s Iskander-M quasi-ballistic missile.
- With a range that can vary from 150-500 km, the Pralay is equipped with a 500 kg payload that gives it a reach of 400 km.
- One of the key features of the Pralay missile is its ability to switch from a ballistic to a flat trajectory after launch.
- This quasi-ballistic trajectory, combined with high speeds and terminal maneuvering capabilities, makes it incredibly difficult for adversary air defense systems to intercept.
- The Pralay missile is a land mobile quick reaction system, launched from storage and transportation canisters and housed in either a 12×12 or an 8×8 launcher configuration.
- Furthermore, the missile’s jet vane system allows for evasive maneuvers in the terminal phase of flight, and it is even speculated that the Pralay has the capability to release decoys, adding an additional layer of defense.
- Its indigenously developed Fused Silica Radar-dome (RADOME) further enhances its radar transparency, making it even more challenging for enemy radars to detect.
- With the Pralay missile, India is reaffirming its commitment to developing and deploying advanced defense systems that can effectively counter adversary air defense systems.
- In an era where stealth technology is being challenged, the Pralay missile presents a formidable solution for striking targets deep behind enemy lines with minimal risk.
Treaty of Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) (Indian Express)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
NATO on Tuesday announced the formal suspension of a key Cold War-era security treaty in response to Russia’s pullout from the deal.
About Treaty of Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE):
- During the final years of the Cold War, negotiators signed the CFE, a treaty that placed restrictions on the deployment of military equipment to maintain a military balance between the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the then-Warsaw Pact countries.
- The treaty's purpose was to prevent the rapid build-up of forces that could be used in a swift assault.
- On November 19, 1990, twenty-two member states from both NATO and the Warsaw Pact came together in Paris to sign the agreement, a year after the fall of the Berlin Wall.
- The CFE finally entered into force on November 9, 1992, following the disintegration of the Warsaw Pact.
- The Treaty set specific limits on the number of battle tanks, armored combat vehicles, artillery pieces, combat aircraft, and attack helicopters that NATO and Warsaw Pact states could have on their respective territories.
- To meet these limits, CFE state parties destroyed over 50,000 weapons systems over subsequent years.
- These actions were monitored through a compliance mechanism that involved information sharing and reciprocal inspections.
- Furthermore, the treaty's scope was expanded to cover troop numbers in a 1992 follow-up agreement known as the CFE-1A.
- This arrangement arranged limits on military personnel levels.
- In 1999, during the Istanbul summit of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), CFE Treaty partners reached an agreement on an updated and modified arrangement known as the Adapted CFE Treaty.
- One significant change was that limitations on conventional weapon systems were no longer linked to two military blocs but to the territorial borders of individual states.
- However, Russia suspended its participation in the treaty in 2007 and ceased active participation in 2015.
Krishi 24/7 7 (The Hindu Business Line)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Union Agriculture Ministry partnered with the Wadhwani Institute for Artificial Intelligence (Wadhwani AI) to create a solution known as Krishi 24/7.
About Krishi 24/7:
- Krishi 24/7 is a groundbreaking AI-powered solution developed with support from Google.org, designed for automated monitoring and analysis of agricultural news.
- Key Features:
- This tool scans news articles in various languages and translates them into English for easy access.
- It extracts crucial information from news articles, including headlines, crop details, event types, dates, locations, severity, summaries, and source links.
- This ensures that the ministry receives timely updates on relevant events found on the internet.
- Significance:
- Krishi 24/7 addresses the vital need for an efficient system to identify and manage agricultural news articles.
- This aids in making timely decisions.
- It serves the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) by identifying pertinent news, delivering timely alerts, and facilitating swift action to protect the interests of farmers and promote sustainable agricultural growth through informed decision-making.
Vaigai Dam (The Hindu)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The third and final flood warning has been issued for five southern districts after the water level in Vaigai dam touched 69 feet (full reservoir level 71 ft) at 7 a.m. on Wednesday, November 8.
About Vaigai Dam:
- Built across the Vaigai River, the Vaigai Dam is located near Andipatti in Tamil Nadu's Theni district.
- The dam was inaugurated by then Chief Minister K. Kamaraj on January 21, 1959, and is often referred to as the lifeline of the people of this region.
- The farmers in the region are completely dependent on the water from the dam for irrigation purposes.
- With a height of 111 feet, the dam has the capacity to store up to 71 feet of water.
- Its main purpose is to provide irrigation water for the Madurai and Dindigul districts, as well as drinking water for Madurai and Andipatti residents.
- Close to the dam, the Government of Tamil Nadu has established an Agricultural Research Station dedicated to crop research.
- Additionally, there is a charming garden called Little Brindavan situated near the dam, offering a delightful place for visitors.
Project Dolphin (The Hindu)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In an effort to conserve dolphins and their habitat, the Tamil Nadu government has issued orders to implement Project Dolphin under the Union government’s Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats scheme.
About Project Dolphin:
- Project Dolphin is a national conservation initiative approved in 2019 during the first meeting of the Prime Minister-led National Ganga Council (NGC) and launched in 2021 to safeguard both riverine and oceanic dolphin species.
- It's part of the larger Arth Ganga program, which is a government initiative.
- It is modeled after Project Tiger, the successful conservation program that has played a significant role in the resurgence of tigers in India.
- The Project Dolphin will strengthen the marine ecology and overall health of the marine Environment and will be implemented at a cost of Rs.8.13 crore.
- The major habitats of the dolphins are found in the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu).
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change is responsible for implementing Project Dolphin.
- The main goal is to ensure the long-term survival of these dolphins and, by extension, the overall health of the river's aquatic life.
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) started a dolphin conservation program in 2016 to work towards this important mission.
- Dolphins play an important role in keeping the marine environment in balance.
- Dolphins worldwide face various natural and human-induced threats which include hunting, entanglement in fishing nets, overfishing, climate change, ship strikes, tourism activities, toxic contamination, noise pollution, oil and gas development, and habitat degradation.
- The conservation of dolphins and their aquatic habitat through the use of modern technology by engaging with fishermen and other ocean-dependent populations is proposed under the project.
- The project will focus on key activities including strengthening of protection activities through better patrolling anti-poaching activities and strengthening of the surveillance and patrolling teams with modern equipment and technology;
- Rescue and rehabilitation activities through the strengthening of veterinary services, patrolling and training, etc;
- Dolphin habitat improvement through the restoration of coastal eco-system like mangroves, corals, sea grass, etc;
- Removal of ghost nets and reduction of pollution in coastal areas;
- enhancing awareness through the celebration of “National Dolphin Day”
Euclid Mission (NASA)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Euclid mission, which will investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, released its first five science images recently.
About Euclid Mission:
- Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by European Space Agency (ESA), with contributions from NASA.
- Euclid is designed to give important new insights into the "dark side" of the universe -- namely dark matter and dark energy, both thought to be key components of our cosmos.
- It was launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, (USA) on 1 July 2023 and the launch vehicle used was ‘SpaceX Falcon 9’.
- The mission derives its name from Euclid of Alexandria, an ancient Greek mathematician from around 300 BC, who laid the foundations of geometry.
- Euclid Mission Objective: The primary goal of the Euclid mission is to create a three-dimensional map of the universe, with time as the third dimension.
- This will be achieved by observing billions of galaxies, extending up to 10 billion light-years away, and covering over a third of the celestial sphere.
- Euclid will explore how the Universe has expanded and how structure has formed over cosmic history, revealing more about the role of gravity and the nature of dark energy and dark matter.
- The Euclid Consortium – consisting of more than 2,000 scientists from 300 institutes in 13 European countries, the U.S., Canada, and Japan – is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis.
- NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP.
- Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.
World Local Production Forum (WLPF) (PIB)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian delegation led by Shri Bhagwant Khuba, Union Minister of State for Chemicals and Fertilizers participated in the Second World Local Production Forum (WLPF) held in Hague, Netherlands.
About the World Local Production Forum (WLPF):
- The World Local Production Forum (WLPF) is an initiative by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The inaugural WLPF took place virtually in 2021.
- Main Objective: The core aim of this forum is to enhance access to essential medicines and other health technologies.
- Role and Function: The WLPF serves as a regular platform for Member States and the global community to collaboratively develop strategies, mobilize collective efforts, and establish partnerships.
- These actions are directed towards promoting sustainable local production, ensuring timely and equitable access to high-quality health products.
- Secretariat: The Local Production and Assistance (LPA) Unit at the WLPF is responsible for overseeing the forum's activities.
- Second WLPF Goals: The second WLPF has several key objectives:
- To create a global platform for discussions addressing the primary challenges related to local production and technology transfer.
- To explore opportunities and mechanisms for overcoming obstacles in this regard.
- To champion sustainable local production capabilities that lead to improved access to safe, effective, and high-quality health products and technologies.
Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) initiative (The Hindu)
- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Navy Chief Admiral recently stated that the Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) effort demonstrates the commitment to a free, open, inclusive, and rules-based Indo-Pacific region.
About the Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) initiative:
- Announcement: It was announced at the 2022 Quad Leaders’ Summit in Tokyo.
- The primary objective is to track "dark shipping" and develop a more comprehensive, timely, and precise understanding of maritime activities in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Geographic Coverage: IPMDA integrates three critical regions in the Indo-Pacific:
- the Pacific Islands, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean region.
- Purpose: IPMDA is a technology and training initiative aimed at enhancing maritime domain awareness in the Indo-Pacific.
- It seeks to increase transparency in critical waterways in the region.
- Technology Utilized: Innovative technology, including the collection of commercial satellite radio frequency data, is employed.
- The goal is to provide partners across Southeast Asia, the Indian Ocean region, and the Pacific with near real-time information on activities occurring in their maritime zones.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) (Indian Express)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
As the Air Quality Index (AQI) in the National Capital Region reaches 'severe' levels, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) activated Stage 4 measures from the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) recently.
What is the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)?
- GRAP is a set of emergency measures that kick in to prevent further deterioration of air quality once it reaches a certain threshold in the Delhi-NCR region.
- Approved in 2016 after the Supreme Court’s order in M. C. Mehta vs. Union of India (2016) and notified in 2017.
- The Supreme Court-appointed Environment Pollution (Prevention & Control) Authority (EPCA) to implement GRAP measures till 2020.
- However, the EPCA was dissolved and replaced by the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in 2020.
- From 2021, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM), a statutory body responsible for implementing GRAP.
- CAQM relies on air quality and meteorological forecasts by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM).
- GRAP is incremental in nature and thus, when the air quality dips from ‘poor’ to ‘very poor,’ measures listed under both sections have to be followed.
- Stage 1 of GRAP is activated when the AQI is in the ‘poor’ category (201 to 300),
- Stage 2 is when it’s in the ‘Very poor’ category (301-400),
- Stage 3 is when the AQI is the ‘Severe’ category (401-450) and finally
- Stage 4 is when it rises to the ‘Severe +’ category (more than 450).
Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
According to a new report, global climate finance is on the rise, yet it is not increasing at a scale and pace sufficient to address the climate crisis effectively.
About Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023:
- The Global Landscape of Climate Finance is an annual report published by the Climate Policy Initiative (CPI).
- It provides the most comprehensive overview of global climate-related primary investment, covering both public and private finance.
- The report tracks climate finance flows across a range of sectors, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, transport, climate adaptation, and mitigation.
- This report concludes by calling for governments and investors to increase their support for climate finance, particularly for adaptation finance.
- It also recommends that more data be collected on climate finance flows to better understand where the gaps are and how to address them.
- It is an important tool for tracking global progress on climate finance and identifying areas where further investment is needed.
- It is an essential resource for policymakers, investors, and other stakeholders who are working to finance the transition to a low-carbon and climate-resilient economy.
- Key findings from the 2023 edition of the Global Landscape of Climate Finance report:
- Global climate finance reached an estimated USD 1.3 trillion on an annual average in 2021/2022, up from USD 653 billion in 2019/2020.
- The majority of climate finance is still directed towards mitigation activities, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency.
- There was a significant increase in climate finance for adaptation activities in 2021/2022.
- The growth in global climate finance was concentrated in a handful of geographies, with China, the US, Europe, Brazil, Japan, and India receiving 90% of increased funds.
- Private finance accounted for 60% of global climate finance in 2021/2022, up from 52% in 2019/2020.
Guindy National Park (The Hindu)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Guindy National Park, packed with blackbucks and birds, is one of the few national parks located in an Indian metropolis.
About the Guindy National Park:
- Guindy National Park is a protected area, located in the heart of Chennai’s metropolitan area of Tamil Nadu.
- It's the 8th smallest national park in India, covering an area of 2.70 square kilometers (1.04 square miles).
- This national park is unique because it is situated within the city of Chennai and is an extension of the grounds around Raj Bhavan, which was formerly known as the 'Guindy Lodge' and serves as the official residence of the governor of Tamil Nadu.
- Guindy National Park plays a crucial role in both ex-situ and in-situ conservation efforts.
- It provides a habitat for various wildlife species, including 400 blackbucks, 2,000 spotted deer, 24 jackals, numerous snakes, geckos, tortoises, and over 130 bird species.
- Flora: Guindy National Park features a diverse range of vegetation, including dry evergreen scrub and thorn forests, grasslands, and water bodies.
- Fauna: The park is home to 14 mammal species, over 60 species of butterflies and spiders each, and a wide variety of invertebrates such as grasshoppers, ants, termites, crabs, snails, slugs, scorpions, mites, earthworms, and millipedes.
Cnemaspis Rashidi (The Hindu)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A new species of gecko has been found recently in Tamil Nadu's Western Ghats, near Rajapalayam.
About Cnemaspis Rashidi:
- Cnemaspis Rashidi, also known as Rashid's dwarf gecko, is a recently discovered species of gecko in the Western Ghats of India.
- It is the smallest species in the genus Cnemaspis, measuring approximately two inches long from its snout to the vent.
- It is characterized by its beautiful color patterns of yellow, white, and black on its back.
- Cnemaspis rashidi is endemic to the Western Ghats.
- It was discovered in 2023 by a team of scientists from the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Pune and the Madras Crocodile Bank Trust.
- The scientists found the gecko at an altitude of 1,245 meters at the Kottamalai estate near Rajapalayam in Tamil Nadu.
- This is the 94th species of gecko that has been identified to date, out of 93 that have been reported.
- It is also a reminder of the rich biodiversity of the Western Ghats, which is one of the world's most important biodiversity hotspots.
National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) (PIB)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Shri Nagendra Nath Sinha, Secretary, Ministry of Steel, unveiled a groundbreaking ceremony for the Mining operations at Mount Celia Gold Project located in Western Australia.
About National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC):
- National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC), a Navratna Public Sector Enterprise under the Ministry of Steel, Government of India.
- It is the single largest producer of iron ore in India.
- It owns and operates highly mechanized iron ore mines in Chhattisgarh and Karnataka.
- The registered office is situated in Hyderabad, Telangana.
- NMDC is considered to be one of the low-cost producers of iron ore in the world.
- It also operates the only mechanized diamond mine in India at Panna, Madhya Pradesh.
- The company is involved in the exploration of a variety of minerals, including iron ore, copper, rock phosphate, limestone, dolomite, gypsum, bentonite, magnesite, diamond, tin, tungsten, graphite, and beach sands.
- Most of the high-quality iron ore produced by NMDC is sold to the Indian domestic steel industry through long-term contracts.
Zanzibar (Indian Express)
- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
An IIT-Madras campus was inaugurated in Zanzibar on Monday, becoming the first campus of an IIT to be opened abroad.
Context:
- The first IIT campus outside of India was inaugurated on Monday with the opening of the IIT-Madras campus in Zanzibar.
- The pioneering venture is part of the central government’s initiative to project India’s education system onto the global stage.
- The campus is located in Bweleo district, a short distance from Zanzibar Town.
- The Zanzibar campus will benefit from an array of academic collaborations, including study abroad programs, internships with companies, and opportunities at the IIT-Madras campus in Chennai.
- It is open to students of all nationalities.
Key facts about Zanzibar (Tanzania):
- Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago in the Indian Ocean, 25–50 kilometers located off the coast of east-central Africa and a semi-autonomous province of Tanzania.
- It comprises the main island of Unguja (informally referred to as Zanzibar), and Pemba Island, along with numerous smaller islands.
- Zanzibar City, on Unguja, is the archipelago's capital and largest city.
- The official languages of Zanzibar are Swahili and English.
- Zanzibar has a rich history, dating back to the 1st century AD.
- It was once a major center for the trade of spices, slaves, and ivory.
- The archipelago has been ruled by various empires and dynasties over the centuries, including the Portuguese, Omanis, and British.
- In 1964, Zanzibar gained independence from Britain and merged with Tanganyika to form the United Republic of Tanzania.
- Stone Town, the historic center of Zanzibar City, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The raised sands and sandstones with varied residual deposits are found on Zanzibar and Pemba islands which are similar to the alluvial deposits present on the African mainland.
- It is known for its vast wilderness areas.
- They include the plains of Serengeti National Park, populated by the “big five” game (elephant, lion, leopard, buffalo, rhino), and Kilimanjaro National Park, home to Africa’s highest mountain.
GST Amnesty Scheme (TOI)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The finance ministry has come out with an amnesty scheme for filing appeals against Goods and Services Tax (GST) demand orders.
What is the GST Amnesty scheme?
- The GST Amnesty scheme was introduced by the Centre to help businesses comply with the Goods and Services Tax laws in the country.
- Every entity that needs to file its GST returns must conduct the process in a sequential manner.
- If the taxpayer misses the last date, they may have to pay penalties for not filing the returns.
- In such a situation, the GST Amnesty scheme helps taxpayers file their returns without hefty penalties.
- The plan also aids businesses whose registration stands canceled for non-filing of returns.
- Under the GST Amnesty scheme, taxpayers can file for the revocation of their cancellation as well.
How can one benefit from the GST Amnesty scheme?
- Taxpayers cannot file the GST return for a particular period without submitting the previous ones.
- A heavy penalty will also be levied on them for missing their filings.
- The GST Amnesty scheme allows taxpayers to file their pending returns without incurring a hefty fine.
- It will help them in complying with the indirect taxation laws of the country.
- It also aids business entities to appeal against the cancellation of their registration if they have not submitted the GST returns for three consecutive quarters.
- The scheme will be open till January 31, 2024.
Pavana River (TOI)
- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently residents of Thergaon area in Pune, are worrieda a lot owing to the thick layer of toxic foam on Pavana river near Kejudevi temple.
About the Pavana River:
- Location: The Pavana River is in the western part of Maharashtra, specifically in the Pune District.
- It crosses Pune City and acts as a natural boundary between Pune City and the Pimpri-Chinchwad area.
- Origin: The river begins in the Western Ghats, approximately 6 kilometers south of Lonavala.
- It's a tributary of the Bhima River and meets the Mula River within Pune city.
- Initially flowing east, it turns south and passes through the suburbs of Dehu, Chinchwad, Pimpri, and Dapodi before joining the Mula River.
- There is a dam is built on this river at Pavana Nagar, called the "Pavana Nagar Dam".
- The Pavana Nagar Dam is an earthfill gravity dam.
- It's 1,329 meters (4,360 feet) long and 42.37 meters (139.0 feet) high.
- The dam has a total storage capacity of 30,500.00 cubic kilometers.
- Its main purpose is to supply sufficient water to the nearby areas and is a crucial water source for the region.
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) (HT)
- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A controversy over alleged engineering lapses in the ?1 lakh crore Kaleshwaram lift irrigation project on the Godavari river triggered an electoral slugfest in poll-bound Telangana.
About Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP):
- Location: The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) is situated at Kaleshwaram village in Telangana, along the Godavari River.
- Confluence Point: It is located at the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari Rivers.
- At this confluence, the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers also meet, forming the seventh-largest drainage basin in the subcontinent.
- Originally called Pranahita-Chevella project in erstwhile Andhra Pradesh, it was redesigned, extended and renamed as Kaleshwaram project in Telangana in 2014.
- KLIP is known as the world's largest multi-stage and multi-purpose lift irrigation project.
- A significant feature of KLIP includes a series of underground and surface water pumping stations, claimed to be the world's largest of their kind.
- This lift irrigation system stretches over 300 kilometers and moves large volumes of water from rivers or reservoirs to be distributed through channels and additional reservoirs before reaching the next stations.
- Objective: The project's goal is to provide water to 45 lakh acres of land in Telangana for irrigation and drinking water.
- KLIP started in 2016 and will utilise approximately 283 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) of water from the Godavari River to serve 13 districts in Telangana.
Adaptation Gap Report 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Adaptation Gap Report states that funding for adaptation measures in developing nations has been declining and is insufficient of what is required.
About the Adaptation Gap Report:
- The Adaptation Gap Report (AGR) is an annual United Nation Enviroment Programme (UNEP) flagship publication.
- The report's primary objective is to inform the negotiators of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Member States, and the broader UNFCCC constituency, about the status and trends within climate adaptation at global and regional levels.
- AGR offers science-based recommendations to policymakers and decision-makers to enhance climate adaptation efforts in key climate-sensitive sectors.
- Since 2014, UNEP has been producing these assessments to support effective adaptation responses aligned with the UNFCCC's temperature and adaptation goals.
- The "adaptation gap" refers to the difference between actual adaptation efforts and the goals set by society, influenced by factors like climate change impacts, available resources, and competing priorities.
Key Findings of the Report:
- Adaptation costs are expected to rise significantly by 2050, especially in high-warming scenarios.
- The financial needs for adaptation are 10-18 times higher than the current international public adaptation fund flows.
- Urgent action is required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance adaptation efforts to protect vulnerable populations worldwide.
- In 2021, funding from developed countries to support adaptation projects in developing countries decreased by 15% compared to previous years.
- The report suggests seven strategies to bridge the adaptation gap, including increasing international financial support and mobilizing domestic resources.
- It also calls for a reform of the global financial system to facilitate easier access to climate-related funding from multilateral agencies such as the World Bank or the IMF.
Lucy Mission (NASA) (Indian Express)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently NASA's Lucy mission has discovered that the asteroid Dinkinesh is actually a binary system of two asteroids.
About Lucy Mission:
- The Lucy Mission is a NASA space probe designed to explore the Trojan asteroids.
- These are the asteroids that share an orbit with Jupiter around the Sun.
- It's on a twelve-year journey to visit eight different asteroids and the entire mission costs around $981 million.
- It was launched on October 16, 2021, from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station or Kennedy Space Centre in Florida.
- The Lucy Mission is named for the fossilized skeleton of a human ancestor, which was named for the Beatles song "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds."
- The mission's scientists hope that Lucy will help them to better understand our own origins, just as the Lucy fossil helped us to better understand our evolutionary history.
- The Lucy spacecraft is equipped with a suite of instruments that will be used to study the asteroids it encounters. These instruments include:
- A high-resolution visible camera
- A near-infrared spectrometer
- A thermal emission spectrometer
- A dust detector
- A radio occultation instrument
- Lucy's mission will provide new insights into the diversity of the Trojan asteroids, their formation, and their role in the early solar system.
- The mission will also test new technologies for deep space exploration, such as a solar-powered propulsion system and a terminal tracking system.
- It made its first gravity assist from Earth on October 16, 2022, and on November 1, 2023, it flew by its first asteroid, Dinkinesh, a binary asteroid in the main belt.
- Lucy will make another gravity assist from Earth in 2024, and in 2025, it will fly by the inner main-belt asteroid 52246 Donaldjohanson.
World Food India 2023 (HT)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated that India's food diversity benefits investors worldwide as he inaugurated the second edition of "World Food India 2023" at Bharat Mandapam in Delhi recently.
What is World Food India 2023?
- World Food India 2023 provides a gateway of access to the Indian food market, promoting collaborations between domestic and foreign investors.
- It is organized by India's Ministry of Food Processing Industries in New Delhi from November 3rd to 5th.
- Objective: It aims to exhibit India's rich food culture and attract global investments in the food processing sector.
- The event brings together manufacturers, producers, investors, policymakers, and organizations from around the world involved in the food industry.
- Key Areas of Focus: The event is focused on leveraging millets as a superfood, positioning India as a global hub for food processing, unlocking growth potential in strategic segments, establishing an efficient ecosystem, and promoting sustainable development.
- India's Vision: This event aligns with India's vision to become a global leader in the food processing industry, highlighting the country's production, consumption, and export potential across various food sectors.
- India is taking steps to create an inclusive and sustainable ecosystem, attract foreign investment, and improve the ease of doing business in the food processing sector.
- Notably, the first edition of World Food India took place in 2017.
- India is a global leader in the production of various agricultural products, such as milk, bananas, mangoes, papayas, guavas, ginger, okra, and buffalo meat.
- It also ranks second in the production of rice, wheat, potatoes, garlic, and cashew nuts.
- Moreover, the United Nations has declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets (IYM 2023) with the goal of increasing millet production and consumption worldwide.
ENCORE (NewsOnAIR)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) has developed in-house software named ‘ENCORE’ designed for efficient candidate and election management.
About ‘ENCORE’:
- The Election Commission of India has designed in-house software for complete Candidate and election management through ‘ENCORE’ which stands for Enabling Communications on Real-time Environment.
- This provides a seamless facility for Returning Officers to process candidate nomination, affidavit, Voter turnout, counting, results and data management.
- The ENCORE counting application is an end-to-end application for returning officers to digitize the votes polled, tabulate the round-wise data and then take out various statutory reports of counting.
- An additional application, the ENCORE Scrutiny Application, allows Returning Officers to scrutinize online nominations submitted by candidates.
- This process involves verifying and marking the status of nominations as Accepted, Rejected, or Withdrawn, facilitating the creation of the final list of contesting candidates and symbol assignment.
- The ECI offers an online portal for candidate nomination and affidavit submission.
- Candidates can create accounts, complete nomination forms, submit security deposits, and plan their visits to the Returning Officer through this portal.
- The Candidate Affidavit portal is designed to display information about a candidate's financial assets and liabilities, offering transparency in candidates' financial disclosures.
- The ENCORE Nodal App serves as a platform for various government departments, including fire, education, police, environment, and CPWD, to issue 'no objection' certificates.
- These certificates are required before granting permission for political parties or candidates to hold rallies, road shows, and meetings, ensuring that all necessary clearances are obtained before public events.
Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary (New Indian Express)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a first-of-its-kind, over 50 grass species were identified during a two-day workshop and survey on ‘Grasses Identification and Grassland Management’ at the Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary in the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR).
About Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: It is located in the Kurnool & Prakasam of Andhra Pradesh with an area of 1194 sq km.
- Located between two important hill passes known as "Mantralamma kanuma" and "Nandi kanuma".
- The Northern part of this Sanctuary forms a major part of the Southern boundary for Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve.
- River: The Gundlakamma River stretches across the sanctuary.
- It also has many, mesic sites and ancient rock formations.
- Indicator Species: Tiger, Panther, Wild dog, Bats, Fig trees.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary on September 18, 1990.
- Forest Type: Dry mixed deciduous forest, moist dry deciduous, semi-evergreen, dry deciduous scrub forest and dry savannahs.
- Flora: The forest is an adobe to medicinal plants of which 10 are critically endangered, 21 are Endangered and 27 species are vulnerable.
- The plants like Madhuca longifolia, Dellenia pentagyna, Aristolochia indica, Terminalia arjuna, Pithecolobium ducle, Adina cordifolia, Vanda spp; etc; thrive here.
- Fauna: Wildlife like Tiger, Leopard, Flying squirre. angur, jungle cat, panther, tiger, mouse deer, hyena, bonnet monkey etc; are found here.
Hydroclimate Extremes (PIB)
- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study conducted at Banaras Hindu University explored the impact of global warming on hydroclimate extremes in the Indian River Basins (IRBs).
About Hydroclimate Extremes:
- Hydroclimatic extremes are severe events with significant impacts on both human societies and ecosystems.
- These events encompass phenomena such as floods, droughts, heat waves, and heavy rainstorms.
Key Findings:
- The research utilized highly detailed simulated precipitation data derived from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project-6 (CMIP6) experiments.
- The study's results suggest an anticipated rise in the frequency of extreme rainfall in the Western Ghats and Northeast River basins.
- Additionally, heavy rainfall intensity is predicted to increase in the Upper Ganga and Indus basins.
- The research sheds light on an agricultural drought in the lower Ganga basin, attributed to a reduction in average rainfall.
Importance:
- This study underscores the importance of policymakers creating strategies to address both excess and shortage of water resources.
- It anticipates a 4% to 10% rise in intense rainfall in the western regions of Indian river basins, along with noteworthy shifts in precipitation patterns in specific areas.
- These alterations in hydroclimate extremes could greatly impact agriculture, public health, and socio-economic conditions.
- Furthermore, the research identifies critical areas prone to urban flooding in densely populated cities, emphasizing the need for policymakers to devise tailored climate adaptation and mitigation plans.
- These should encompass policies related to water management and emergency services to mitigate the risks posed by extreme events in these basins.
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) (TOI)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
??The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OHCA), on Friday, launched an emergency aid appeal seeking $1.2 billion to help some 2.7 million people in Gaza and the West Bank.
About the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA):
- OCHA is part of the United Nations (UN) and focuses on humanitarian issues.
- It coordinates and leads UN responses to humanitarian crises worldwide.
- It was established by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1991.
- OCHA's goal is to save lives, protect people, and help those affected by disasters and conflicts.
- It works with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and other partners to respond to emergencies.
- It provides funding to support relief efforts in crisis-affected regions.
- There are two types of pooled funds:
- The Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF) can provide financial support for emergencies anywhere on the globe.
- Country-Based Pooled Funds (CBPFs) are specific to individual countries.
- These funds operate from two central hubs located in Geneva and New York, serving as global operational centres.
- The office works to ensure that humanitarian aid reaches those in need.
- It has two headquarters locations, Geneva and New York, which act as centres of global operations.
- It helps plan and manage humanitarian responses, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness.
- OCHA promotes coordination among humanitarian organizations to avoid duplication and ensure better outcomes.
Bletchley Declaration 2023 (Indian Express)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The United Kingdom hosted a major Artificial Intelligence (AI) meeting, bringing together political leaders and technological professionals to explore the potential benefits and risks of this fast-evolving technology.
About the Bletchley Declaration:
- The Bletchley Declaration provides a comprehensive overview of the worldwide perspective on the potential benefits and risks associated with artificial intelligence (AI).
- It underlines the necessity of aligning AI systems with human intentions and encourages a deeper exploration of AI's full capabilities.
- Furthermore, the document acknowledges the potential for significant harm caused by AI, whether intentional or unintentional, including the possibility of catastrophic consequences.
- The Bletchley Declaration places great emphasis on safeguarding human rights, promoting transparency, ensuring explainability, upholding fairness, ensuring accountability, establishing regulation, prioritizing safety, incorporating human oversight, adhering to ethical standards, addressing bias issues, safeguarding privacy, and protecting data.
- This document is a reflection of the intricate negotiations between nations with differing interests and legal systems, encompassing countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and China.
- The Bletchley Declaration highlights the crucial role of civil society in addressing AI safety concerns, despite some criticism from civil society groups that felt excluded from the summit.
- It also places a significant responsibility on companies engaged in the development of cutting-edge AI systems, emphasizing the need to ensure their safety through rigorous testing, evaluation, and the implementation of appropriate measures.
Global Stocktake should account for failures of developed nations: BASIC nations at COP28 (The Hindu)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The BASIC grouping, comprising Brazil, South Africa, India and China, has pushed during annual climate talks here that the Global Stocktake should also account for the failures of the developed nations.
About Global Stocktake:
- The global stocktake serves as a mechanism for nations and stakeholders to collectively assess their progress in achieving the objectives outlined in the Paris Climate Change Agreement, highlighting areas of success and areas needing improvement.
- In essence, it is akin to taking inventory on a global scale.
- Essentially, the global stocktake involves a comprehensive examination of everything related to the world's status regarding climate action and support.
- It entails identifying gaps and collaboratively strategizing to steer a more effective course towards accelerating climate action.
- This evaluation occurs every five years, with the inaugural stocktake scheduled to conclude at COP28.
- Background: In 2015, during COP21 in Paris, it became obligatory for all countries to establish emissions reduction targets and adapt to climate change impacts, known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- The agreement mandated that countries evaluate their progress, starting in 2023 and subsequently every five years.
- Initial Assessment: The UN released a technical report on the first Global Stocktake in September 2023.
- According to this report, while the global community demonstrated some progress, it fell short of the necessary scale.
- The report emphasizes the need to expedite implementation, adopting an all-of-society approach to enhance ambition across all aspects, aligning with the goals of the Paris Agreement and addressing the climate crisis.
- The report acknowledges existing progress but underscores the urgency for more concerted efforts.
- Recognizing well-known gaps, the technical findings also spotlight opportunities and creative solutions, addressing both current challenges and those emerging.
- Additionally, the report notes that the average global temperature has risen by nearly 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times.
INCOIS wave rider buoy washes ashore in Gopalpur (New Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A wave rider buoy, equipped belonging to the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), with GPS and various weather-related instruments, was found ashore at the Gopalpur Military Station in Ganjam district on Saturday.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), New Delhi.
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999.
- The ESSO operates as an executive arm of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for its policies and programmes.
- It is mandated to provide the best possible ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies and the scientific community through sustained ocean observations and constant improvement through systematic and focused research.
What is the Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO)?
- Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO) is a virtual organisation set up by the Ministry of Earth Sciences GOI in 2007 and it is the executive arm of MoES.
- It has three major branches of earth sciences viz.,
- Ocean Science & Technology
- Atmospheric Science & Technology
- Geosciences and Technology.
- The overall vision of the ESSO is to excel in knowledge and technology enterprise for the earth system science realm towards the socio-economic benefit of the Indian sub-continent and in the Indian Ocean region.
- The ESSO contributes to the areas of Weather (General) and Weather advisories specific to agriculture, aviation, shipping, sports, etc. Monsoon, Disasters (cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis, sea level rise), Living and non-living resources (fishery advisory, poly-metallic nodules, gas hydrates, freshwater etc), Coastal and Marine Ecosystems and Climate Change, Underwater Technology.
Scientists Create Tiny Robots Called 'Anthrobots' From Human Cells (India Times)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have created 'Anthrobots' , tiny living robots from human cells and the robots are able to move around in a lab dish and one day may be helpful in healing wounds or damaged tissue.
What is an Anthrobots?
- Anthrobots are self-assembling biological robots made from human tracheal cells, capable of movement and encouraging neuron growth.
- They can be created from adult human cells without genetic modifications, making them a potential patient-specific therapeutic tool.
- Anthrobots represent a significant advancement in regenerative medicine, potentially aiding in treating a variety of diseases and injuries.
- The multicellular robots, ranging in size from the width of a human hair to the point of a sharpened pencil, were made to self-assemble and shown to have a remarkable healing effect on other cells.
- The discovery is a starting point for the researchers’ vision to use patient-derived biobots as new therapeutic tools for regeneration, healing, and treatment of disease.
What are Tracheal cells?
- Tracheal cells come from the lining of the bronchi and trachea, forming the network of tubes that transport air to the lungs.
- These cells, a type of epithelial cell, are crucial for producing lubricating mucus to maintain the functionality of the airways.
- They are responsible for generating not only mucus but also various other compounds, all of which play a vital role in the process of respiration.
Is White Lung Syndrome caused by a new pathogen? Here is what you need to know (Indian Express)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
An outbreak of a respiratory illness in northern China and Ohio in the US — the White Lung Syndrome as people are calling it — has sparked speculation online of a new pandemic threat after COVID-19.
About White Lung Syndrome:
- “White lung syndrome” is a term used to describe a severe form of pneumonia characterized by the appearance of white patches on chest X-rays.
- While the term suggests a specific disease, it is actually used to describe a variety of conditions that cause similar symptoms.
- Symptoms: The specific symptoms of white lung syndrome can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Cough, feThere is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- ver, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, loss of appetite and wheezing
- In severe cases, white lung syndrome can lead to respiratory failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
- Causes: There are many different causes of white lung syndrome, including:
- Viral infections: These are the most common cause of white lung syndrome, including viruses like influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and COVID-19.
- Bacterial infections: These are less common than viral infections, but can still cause white lung syndrome.
- Fungal infections: These are rare, but can occur in people with weakened immune systems.
- Inhalation of harmful substances: This can include inhaling dust, fumes, or chemicals.
- Autoimmune diseases: These are diseases in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues.
- Prevention: There is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- However, there are vaccines available for some of the viruses that can cause white lung syndrome, such as influenza and COVID-19.
- Treatment: The treatment for white lung syndrome depends on the underlying cause.
- In some cases, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed.
- In more severe cases, oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
11 bodies recovered after the volcanic eruption in Indonesia, and 12 climbers are still missing (Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The bodies of 11 climbers were recovered on Monday a day after a furious eruption of the Mount Marapi volcano as Indonesian rescuers searched for 12 apparently still missing.
About Mount Marapi:
Don't confuse it with Mount Merapi, which is located on Java Island.
- ‘Mount Marapi’ located is a volcanic mountain located in West Sumatra of Indonesia.
- It also known as Marapi or Gunuang Marapi in Minangkabau.
- According to legend, the mountain is the site first settled by the Minangkabau people after their ship landed on the mountain when it was the size of an egg and surrounded by water.
- There are large numbers of upright burial stones in the region which are oriented in the direction of the mountain, indicating its cultural significance.
- A significant eruption occurred in 1979, and in April-May 2018, ashfalls to the southeast were recorded.
About Mount Merapi:
- Mount Merapi is a volcanic mountain on the island of Java in Indonesia and is the most active volcano in Indonesia (out of a total of 30 active volcanoes).
- Although Mount Merapi was discovered by humans in 1754, geologists have estimated that the volcanic mountain is over 400,000 years old.
- The last major eruption of Mount Merapi back in 2010. This eruption took the lives of 347 people, and a further 20,000 locals were forced to evacuate the area.
- The local name for Mount Merapi is Gunung Merapi which can be translated to Fire Mountain or Mountain of Fire.
- Mount Merapi is considered sacred by local people. They believe that a supernatural kingdom exists there.
- Mount Merapi has erupted countless times, which haven't been recorded in modern history.
- However, we do know that Merapi has erupted over 68 since 1548.
- Merapi has now been active for approximately 10,000 years.
PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" launched under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 Crore supports 2 lakh micro food processing enterprises following One District One Product (ODOP) approac

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
As part of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) is implementing a centrally sponsored "PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" for providing financial, technical and business support for setting up / upgradation of micro food processing enterprises in the country.
About PM Formalisation of Micro food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme:
- Launched on 29th June 2020, PMFMPE is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- It is designed to address the challenges faced by the micro-enterprises and to tap the potential of groups and cooperatives in supporting the upgradation and formalization of these enterprises.
- Aims:
- Enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry and promote formalization of the sector; and
- Support Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), and Producers Cooperatives along their entire value chain.
- Objectives: To build the capability of microenterprises to enable:
- Increased access to credit by existing micro food processing entrepreneurs, FPOs, Self Help Groups, and Co-operatives.
- Integration with an organized supply chain by strengthening branding & marketing.
- Support for the transition of existing 2,00,000 enterprises into a formal framework.
- Increased access to common services like common processing facilities, laboratories, storage, packaging, marketing, and incubation services.
- Strengthening of institutions, research, and training in the food processing sector; and
- Increased access for the enterprises, to professional and technical support.
- Outlay:
- The scheme envisages an outlay of ? 10,000 crores over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- The expenditure under the scheme would be shared in a 60:40 ratio between Central and State Governments, in a 90:10 ratio with the North
- In Eastern and the Himalayan States, a 60:40 ratio with UTs with the legislature and 100% by the Center for other UTs.
- Coverage:
- Under the scheme, 2,00,000 micro food processing units will be directly assisted with credit-linked subsidies.
- Adequate supportive common infrastructure and institutional architecture will be supported to accelerate the growth of the sector.
The Supreme Court directed the governments to provide details on “the estimated inflow of illegal migrants into India.. after March 25, 1971”. (Indian Express)
- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Thursday asked the Centre and Assam government to provide details on the “estimated inflow of illegal migrants” to Assam and other Northeastern states after March 25, 1971, and the status of border fencing.
News Summary:
- During the hearing of petitions, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court expressed concerns about the perceived 'unlimited influx' of illegal migrants from Bangladesh, impacting demographics and straining resources for Indian citizens.
- The court questioned the application of Section 6A, granting Indian citizenship benefits to illegal migrants, solely in Assam and not in West Bengal, which shares a larger border with Bangladesh.
- The Supreme Court directed the Home Secretary to submit an affidavit by May 11, 2023, detailing the estimated inflow of illegal migrants, steps taken to address illegal immigration, and specifics on border-fencing extent and timelines.
- The government was also instructed to provide information on illegal immigration along the West Bengal border post on March 25, 1971.
Why Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955 is Under Challenge?
- Presently, a Supreme Court bench is reviewing petitions from indigenous Assamese groups challenging Section 6A of the Citizenship Act.
- These groups assert that the special provision serves as a 'beacon' for illegal entrants to settle in Assam, gain Indian citizenship, and subsequently deprive locals of political, and economic rights, jeopardizing Assamese cultural identity.
- The petitioners question the constitutional validity of Section 6A, claiming it is arbitrary, specifically singles out Assam, violates Article 14, and has led to an influx of illegal migrants from Bangladesh.
- They advocate for establishing 1951 as the cutoff date for inclusion in the National Register of Citizens instead of 1971.
- The primary petitioner, Assam Sanmilita Mahasangha (ASM), argues that Section 6A is discriminatory, arbitrary, illegal, and infringes upon the rights of indigenous Assamese people by establishing a different citizenship cutoff date for Assam compared to the rest of India (July 1948).
What are the Arguments of the Central Government?
- The central government refutes the accusation of unfairly burdening the state with the responsibility of handling illegal migrants, contending that different states of India can be classified differently based on historical and geographical factors.
- According to the government, the classification implied in Section 6-A is founded on intelligible differentia.
- Dismissing claims of arbitrariness, the Centre asserts that the guarantee against non-arbitrariness under Article 14 does not mandate universal application for every law, irrespective of dissimilarity or the nature of the individuals it pertains to.
Global River Cities Alliance with 267 river cities including India, USA and Denmark to be launched on December 10, 2023 (PIB)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) on behalf of River Cities Alliance (RCA), has signed a Memorandum of Common Purpose (MoCP) with the Mississippi River Cities and Towns Initiative (MRCTI), representing 124 cities/towns situated along the banks of the Mississippi River, USA.
What is River Cities Alliance (RCA)?
- The River Cities Alliance (RCA) is a joint initiative of the Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) & the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), with a vision to connect river cities and focus on sustainable river centric development.
- Beginning with 30 member cities in November 2021, the Alliance has expanded to 109 river cities across India and one international member city from Denmark.
- 30 cities include Dehradun, Rishikesh, Haridwar, Srinagar, Varanasi, Kanpur, Prayagraj, Farrukhabad, Mirzapur, Mathura, Bijnor, Ayodhya, Patna, Bhagalpur, Begusarai, Munger, Sahibganj, Rajmahal, Howrah, Jangipur, Hugli-Chinsurah, Berhampore, Maheshtala, Aurangabad, Chennai, Bhubaneshwar, Hyderabad, Pune, Udaipur and Vijayawada.
- The Alliance is open to all river cities of India. Any river city can join the Alliance at any time.
- Objective: To provide the member cities with a platform to discuss and exchange information on aspects that are vital for sustainable management of urban rivers, sharing best practices and supporting innovation.
- It focuses on three broad themes- Networking, Capacity Building and Technical Support.
- The Secretariat of the Alliance is set up at the National Institute for Urban Affairs (NIUA) Delhi.
About the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India, established the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) as a registered society to take proactive measures for preventing, controlling, and abating environmental pollution in the Ganga River.
- Its mission includes ensuring a continuous and adequate flow of water to rejuvenate the river.
- Initially serving as the implementation arm of the dissolved National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA), NMCG aims to achieve effective pollution abatement and river rejuvenation through a river basin approach, promoting inter-sectoral coordination and environmentally sustainable development.
- Post the dissolution of NGRBA in 2016, NMCG continues its objectives through the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management of River Ganga, also known as the National Ganga Council.
- The mission focuses on maintaining minimum ecological flows in the Ganga to ensure water quality and sustainable development.
- Structure: NMCG follows a two-tier management structure comprising the Governing Council and the Executive Committee, both led by the Director General.
- The Executive Committee holds the authority to approve projects up to Rs. 1000 crores.
- At the state level, State Programme Management Groups (SPMGs) serve as the implementing arms of State Ganga Committees.
- The Director General of NMCG holds the position of Additional Secretary in the Government of India.
Mining for critical minerals: what is the auction process, and why is it important? (Indian Express)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A total of twenty critical mineral blocks are currently open for commercial bidding by private entities. The auction process commenced on November 29, and interested parties have the opportunity to submit bids until January 22 of the following year.
What are Critical Minerals?
- A mineral attains critical status when there is a relatively higher risk of supply shortage and its impact on the economy compared to other raw materials.
- These minerals play a pivotal role in economic development and national security, and their scarcity, concentration in specific geographic locations, or limited extraction/processing options may pose potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain.
- Critical minerals, including lithium, graphite, cobalt, titanium, and rare earth elements, are indispensable for advancements in various sectors such as high-tech electronics, telecommunications, transport, and defense.
- They are integral to strategic value chains, including initiatives for clean technologies (e.g., zero-emission vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels), information and communication technologies (e.g., semiconductors), and advanced manufacturing inputs and materials (e.g., defense applications, permanent magnets, ceramics).
What are the Estimated Reserves of Key Critical Minerals in these Blocks?
- J&K Block: In the J&K block, there is an inferred reserve of 5.9 million tonnes of bauxite, containing over 3,400 tonnes of lithium metal content.
- Additionally, this block boasts more than 70,000 tonnes of titanium metal content.
- Odisha Block: In the Odisha block, the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) estimates an inferred value of 2.05 million tonnes of nickel ore, equivalent to 3,908 tonnes of nickel metal content.
- Chhattisgarh Block: While the Chhattisgarh block contains lithium and rare earth elements (REEs), no drilling has been conducted to assess total reserves as of yet.
- Other Blocks: Nickel ore reserves have been identified in three blocks, situated in Bihar, Gujarat, and Odisha.
- However, drilling has not been carried out for the Bihar and Gujarat blocks.
How does India presently source these minerals?
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, India imported 2,145 tonnes of lithium carbonate and lithium oxide.
- Lithium carbonate, containing up to 19% lithium, and lithium oxide, typically converted to lithium hydroxide and containing 29% lithium, were part of the imports.
- Additionally, India imported 32,000 tonnes of unwrought nickel and 1.2 million tonnes of copper ore during the same period.
- Notably, India is entirely dependent on imports for its lithium and nickel demand, while for copper, this reliance stands at 93%.
Recent Initiatives by the Indian Government to Boost the Critical Minerals Sector:
- Identification of 30 Critical Minerals: In July 2023, the Indian government released a list of 30 critical minerals, including Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium, and Cadmium.
- Mining Permissions: The government amended a key law, allowing for the mining of three critical minerals – lithium, niobium, and REEs.
- New royalty rates for critical minerals, aligning with global benchmarks, were specified to attract bidders.
- Geological Survey of India's Exploration: The Geological Survey of India initiated 125 projects in the current fiscal to explore critical mineral reserves.
- Notably, it estimated 5.9 million tonnes of lithium ore in the Salal-Haimna areas (Reasi district, J&K).
- In the preceding eight fiscal years, a total of 625 mineral exploration projects were undertaken.
- Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals: The Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals recommended establishing a Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals to formulate policies and incentives for creating a comprehensive value chain of critical minerals in the country.
- Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL): A joint venture company, Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL), is mandated to identify and acquire overseas mineral assets of a critical and strategic nature, such as lithium and cobalt, to ensure a secure supply.
- Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): India joined the US-led Mineral Security Partnership (MSP), a collaboration of 14 countries aiming to catalyze public and private investment in critical mineral supply chains globally.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (Indian Express)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this year, a South Korean laboratory unveiled a significant advancement that holds promise as a potential solution to the energy crisis.
What is Google DeepMind's Project?
- Google has introduced the Graph Networks for Materials Exploration (GNoME), an AI tool developed by DeepMind.
- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence, GNoME successfully predicted the structures of over 2 million new materials.
- The potential applications span diverse sectors, including renewable energy, battery research, semiconductor design, and enhanced computing efficiency.
How does GNoME operate?
- GNoME functions as an advanced graph neural network model (GNN), where input data takes the form of a graph resembling connections between atoms.
- The model employs 'active learning,' initially training on a small specialized dataset and later incorporating new targets for machine learning with human assistance.
- This adaptability suits the algorithm well for material discovery, as it involves identifying patterns not present in the original dataset.
Operational Mechanism of GNoME:
- GNoME employs two pipelines for discovering stable materials with low energy.
- The structural pipeline generates candidates with structures akin to known crystals, while the compositional pipeline follows a more randomized approach based on chemical formulas.
- Outputs from both pipelines undergo evaluation using established Density Functional Theory calculations, contributing to the GNoME database and guiding subsequent rounds of active learning.
- Consequently, the model has significantly improved its precision rate for predicting material stability, reaching around 80%, up from an initial 50%.
- DeepMind's research, encompassing 380,000 stable predictions, is equivalent to nearly 800 years of knowledge, facilitating further breakthroughs in materials discovery for researchers.
What is the Significance of GNoME?
- This breakthrough in artificial intelligence dramatically expands the inventory of 'stable materials,' multiplying it by tenfold in a single stride.
- These materials encompass inorganic crystals crucial for a spectrum of modern technologies, from computer chips to batteries.
- Stability is paramount for these crystals, as any instability could lead to decomposition.
- While the synthesized and tested processes still lie ahead, DeepMind has shared a curated list of 381,000 crystal structures from the predicted 2.2 million, offering a promising foundation for advancing new technologies.
- In comparison, human experimentation over the last decades has revealed the structures of around 28,000 stable materials, catalogued in the Inorganic Crystal Structures Database, representing a noteworthy advancement in material discovery.
Food versus Fuel: What’s happening with Centre’s ethanol blending scheme (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After banning sugar exports, the Centre has taken the next step towards augmenting domestic availability – restricting the diversion of the sweetener for ethanol production.
What is the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme?
- The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) programme was launched in January 2003.
- The programme sought to promote the use of alternative and environment-friendly fuels and to reduce import dependency for energy requirements.
- Effective from April 1, 2019, across the nation (excluding UTs of Andaman Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands), Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) sell petrol blended with up to 10% ethanol.
- The average ethanol blending in petrol has surged from 1.6% in 2013-14 to 11.8% in 2022-23.
- India targets a 20% ethanol blending ratio by 2025, revised from the initial 2030 deadline per the NITI Aayog's roadmap.
- Benefits of the EBP Programme:
- Reducing India’s import bill.
- Mitigating environmental pollution.
- Augmenting farm income.
- Offering a biofuel option with minimal additional investment for manufacturers.
- Challenges for 20% Ethanol Blending:
- Engine modifications are required to process petrol blended with 20% ethanol.
- Ethanol combustion yields no CO2, yet it doesn't address nitrous oxide emissions.
- Concerns about inefficient land use in ethanol production and the substantial water demand for cultivating crops.
- Food security considerations due to uncertainties about future agricultural output.
Why is the Restriction on Sweetener Diversion for Ethanol Production Imposed?
- Sugar Supply Concerns: Closing the 2022-23 sugar year with stocks slightly exceeding 57 lakh tonnes (lt), the lowest since 2016-17 (39.4 lt), raises apprehensions.
- The stock level falls significantly below the peak of 143.3 lt in 2018-19.
- Uncertainties surround the sugar production for the ongoing 2023-24 year, with Maharashtra and Karnataka anticipating substantial declines due to insufficient rainfall and low reservoir water levels in key cane-growing regions.
- Key Implication of the Decision: The recent decision, coupled with the ban on sugar shipments since May 2023, underscores a clear priority.
- Governments emphasize domestic supply over exports, favouring consumers over producers and prioritizing food over fuel.
Strategies to Boost Ethanol Production without Compromising Food Security:
- Diversification of Feedstocks: The government's ethanol policy, marked by favourable pricing and the incorporation of alternative feedstocks such as 2G ethanol sources, has been instrumental.
- The historical dependence on sugarcane-based feedstocks, which constituted 100% of ethanol sources (reduced to 76% in 2022-23), is no longer the sole reliance of the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program.
About Ethanol:
- Ethanol, an anhydrous ethyl alcohol having the chemical formula of C2H5OH, can be produced from sugarcane, maize, wheat, etc which have high starch content.
- In India, ethanol is mainly produced from sugarcane molasses by fermentation process.
- Ethanol can be mixed with gasoline to form different blends.
- As the ethanol molecule contains oxygen, it allows the engine to more completely combust the fuel, resulting in fewer emissions and thereby reducing the occurrence of environmental pollution.
- Since ethanol is produced from plants that harness the power of the sun, ethanol is also considered a renewable fuel.
This explosion in space, will now form a new solar system! James Webb Telescope captures Cassiopeia A in its latest discovery (Business Today)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The James Webb Space Telescope by NASA has recently documented a striking image of a star that underwent a supernova explosion within the Cassiopeia A (Cas A) supernova remnant.
What is Cassiopeia A?
- Cassiopeia A is the aftermath of a colossal star's explosion approximately 340 years ago, standing as the most recently formed remnant of its kind in our galaxy.
- Renowned for its status as a prototypical type of supernova remnant, it has been the subject of extensive exploration by various ground- and space-based observatories.
- Encompassing around 10 light-years, this remnant resides 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation, offering valuable insights into the intricate dynamics of supernovae.
What is Supernova?
A supernova is a powerful and catastrophic stellar explosion that occurs during the final stages of a massive star's life cycle. This extraordinary event releases an immense amount of energy, temporarily outshining entire galaxies and producing luminosities that can briefly outshine an entire galaxy.
What happens during a supernova explosion?
- Massive stars: Supernovas typically occur in massive stars, at least 8 times the mass of our sun.
- These stars burn brightly and fiercely, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores.
- Nuclear fusion: As the star ages, it runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core.
- The core starts to collapse inwards due to gravity, while the outer layers expand and cool.
- This increased pressure and temperature trigger the nuclear fusion of heavier elements, like carbon and oxygen, releasing immense energy.
- Bounce and shockwave: The core's collapse eventually leads to a sudden rebound, called the core bounce.
- This bounce creates a shockwave that rips through the star's outer layers, ejecting them outwards in a violent explosion.
Types of supernovae: There are two main types of supernovae:
- Core-collapse supernovae: The explosion blows away the star's outer layers, leaving behind a neutron star or, if the mass is even greater, a black hole.
- Type Ia supernovae: These occur in binary systems where a white dwarf, the remnant of a low-mass star, siphons material from its companion star.
- This builds up mass on the white dwarf until it reaches a critical point and undergoes thermonuclear runaway, leading to a massive explosion.
Significance of supernovae: Supernovae play a crucial role in the universe's evolution.
- Enrich the interstellar medium with heavy elements: The ejected material from supernovae is rich in elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, which are essential for the formation of new stars and planets.
- Trigger star formation: The shockwaves from supernovae can compress surrounding gas clouds, triggering the formation of new stars.
- Create black holes and neutron stars: The most massive stars leave behind black holes or neutron stars, incredibly dense objects with fascinating properties.
Calling for caution, PM flags need for ethics, democratic values in AI (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document on the proper use of AI, the guardrails for the technology, and how it can be democratised.
Context:
- India is currently hosting the 4th Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi, scheduled from December 12-14, 2023.
- The first three GPAI summits were held in Montreal, Paris and Tokyo, respectively.
- Prime Minister Modi emphasized the dual nature of AI, portraying it as a significant development tool for the 21st century but also highlighting potential risks.
- He called for a global framework to ensure responsible AI use and urged caution in deployment.
- Addressing concerns like deepfakes, cybersecurity, and cyber-terrorism, he proposed an audit mechanism categorizing AI tools based on their capabilities.
- PM Modi is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document outlining proper AI use, technology guardrails, and democratization.
- Recognizing AI's role in economic growth, he announced India's upcoming AI mission, focusing on AI computing power for startups and innovators, with applications in agriculture, health, and education.
- The mission aims to extend AI skills to Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- PM Modi stressed ethical AI use as a guiding principle and suggested the inclusion of development and deployment protocols for high-risk AI systems in the global framework.
- He underscored AI's potential for connecting people and envisioned its ethical use in promoting economic growth, equality, and social justice.
About the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit:
- The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit is a three-day event starting December 12, which will see representatives from 28 member countries and the European Union.
- India is the Lead Chair for the alliance in 2024.
- The founding members of the GPAI: are Australia, Canada, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, Slovenia, the UK, the US, and the EU.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the summit on December 12.
- The objective of this summit is to bridge the gap between theory and practice on AI by supporting cutting-edge research and applied activities on AI-related priorities.
- It will feature a number of seminars covering a wide range of subjects, including AI and global health, education and skill development, AI and data governance, and machine learning workshops.
- More than 150 speakers from various nations will be present at the summit, including more than fifty GPAI experts.
- Moreover, leading global AI innovators such as Intel, Google, Meta, Microsoft, etc will be taking part in these events.
- Additionally, start-ups and students who win under the YUVA AI programme will present their AI models and solutions.
Missiles from rebel territory in Yemen miss a ship near key Bab el-Mandeb Strait, US official says (TOI)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two missiles fired by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Context:
- Two missiles fired from territory held by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the key Bab el-Mandeb Strait on Wednesday.
- An American warship also shot down a suspected Houthi drone flying in its direction during the incident.
- The ship was carrying Indian-manufactured jet fuel and was heading for either Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
- It was coming from Mangalore in southern India and had an armed security crew on board.
- The Houthis have carried out a series of attacks on vessels in the Red Sea and launched drones and missiles targeting Israel.
About Bab el-Mandeb Strait:
- The Bab-el-Mandeb is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a chokepoint between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East and is a strategic link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is one of the world's most important routes for global seaborne commodity shipments, particularly crude oil and fuel.
- The Perim Island divides the strait into two channels, of which the eastern is known as the Bab Iskender (Alexander's Strait), while the western is known as Dact-el-Mayun.
What is the Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa, the world's fourth-largest peninsula, is located in Northeast Africa, extending eastwards from the African mainland and bordered by the Red Sea, Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- Positioned equidistantly from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer, it encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Ethiopian Plateau, Ogaden desert, and Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region has experienced historical complexities, including imperialism, neo-colonialism, the Cold War, ethnic tensions, intra-African conflicts, poverty, disease, and famine.
India’s first Pompe disease patient passes away: What is this rare genetic disorder? (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Nidhi Shirol, India’s first Pompe disease patient, passed away last month at the age of 24 years after battling the disease. She spent the last six years in a semi-comatose state.
What is Pompe Disease?
- Pompe disease is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) and is also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II.
- This enzyme is crucial for breaking down glycogen into glucose within the lysosomes of cells.
- Its prevalence estimates range from 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 300,000 births and occur across diverse ethnicities and populations.
- The age of onset and severity can vary, leading to a spectrum of clinical presentations.
How does Pompe disease affect an individual?
The severity of the condition and the progression of symptoms may differ among individuals. Some key symptoms are:
- Muscle weakness: Progressive muscle weakness is a primary feature of Pompe disease.
- It affects both skeletal and smooth muscles, leading to difficulties in mobility and daily activities.
- Weakness in the respiratory muscles can result in breathing difficulties, especially during physical exertion or even while lying down.
- Motor skill delay: Children with the disease may experience delays in achieving motor milestones, such as sitting, crawling, and walking.
- The degree of motor skill delay can vary, and some individuals may never attain certain motor milestones.
- Degenerative impact on bones: Prolonged muscle weakness and reduced mobility can have a degenerative impact on bones, leading to joint contractures and skeletal deformities.
- Respiratory complications: The weakening of respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, can have an impact.
- Patients may experience shortness of breath, respiratory infections, and in severe cases, respiratory failure.
- Cardiac involvement: In some cases, Pompe disease can affect the heart muscles, leading to complications.
- Symptoms such as heart palpitations, fatigue, and chest pain, may manifest.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Pompe disease can cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, characterised by the thickening of the heart muscle walls.
- This can lead to impaired heart functions and cardiovascular symptoms.
- Implications for daily living: Patients may face challenges in performing daily activities independently due to muscle weakness and respiratory limitations.
- Assistive devices such as wheelchairs and respiratory support equipment may become necessary.
How is Pompe disease diagnosed?
- Diagnosing Pompe disease involves a multi-faceted approach.
- Enzyme assays are conducted to measure the activity of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), the deficient enzyme.
- Genetic testing identifies mutations in the responsible GAA gene.
- Clinical evaluations consider the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
- Enzyme tests, often performed on blood or skin cells, provide crucial insights into GAA deficiency.
- Genetic analysis confirms the presence of specific mutations associated with Pompe Disease.
- The combination of these diagnostic tools enables healthcare professionals to accurately identify and confirm the disease, helping achieve timely intervention and management.
Is Pompe disease curable?
- While there is currently no cure for Pompe disease, treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is a standard treatment, involving the infusion of the missing enzyme to alleviate glycogen buildup.
Data | Sharp rise in Indians illegally crossing U.S. northern border from Canada (The Hindu)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the last ten years, the number of unauthorized Indian migrants entering the U.S. has surged significantly, climbing from a mere 1,500 a decade ago to an astonishing 96,917 in 2023, as reported by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
What are the Implications for India Amidst the Surge in Illegal Migrants?
- Bilateral Relations: The surge in illegal migration poses potential challenges to bilateral relations between India and the USA, impacting areas such as trade negotiations, security cooperation, and strategic partnerships.
- Economic Factors: India faces the risk of a brain drain, as skilled individuals seek illegal entry, potentially affecting sectors with a demand for skilled labour and impacting the country's economy.
- The outflow of skilled and educated individuals through illegal migration can have adverse effects on India's economy, leading to a depletion of talent and expertise.
- Labour Market Challenges: The departure of skilled or semi-skilled workers may create labour shortages in specific sectors, affecting India's workforce and economic productivity.
- Policy Repercussions: India may need to institute stringent policies to address the root causes of illegal migration, potentially diverting resources and attention from other developmental priorities.
What are the Causes Behind the Surge in Illegal Indian Migrants to the USA?
- Pull Factors: The USA's reputation for offering improved employment prospects, higher wages, and career advancement acts as a significant attraction for migrants.
- The allure of quality education and prestigious academic institutions in the USA attracts students and families in search of educational opportunities.
- The desire to reunite with family members or relatives already settled in the USA motivates some migrants to seek illegal entry for proximity to loved ones.
- Push Factors: Numerous push factors, including limited job opportunities and economic prospects in India, drive individuals to seek better employment opportunities abroad.
- Social conflicts or a lack of confidence in India's governance structure may prompt some individuals to search for a more stable environment elsewhere.
- Visa Backlogs and Alternative Routes: Smugglers adapt their methods, providing sophisticated services to facilitate illegal entry into America.
- Prolonged visa backlogs prompt individuals to explore alternative, albeit illegal, pathways to enter the USA due to extended waiting times and limited legal entry options.
- Global Migration Trends: The overall increase in global migration post-pandemic contributes to this surge as individuals seek improved opportunities and security in different countries.
- Misinformation: Social media and deceptive travel agencies disseminate misinformation, misleading desperate migrants and encouraging them to embark on perilous journeys guided by multiple facilitators across continents.
- Desperate migrants may undertake complex, multi-leg journeys through various continents and countries, facing numerous risks and challenges along the way.
What can be Done?
Prioritizing economic stability, job creation, and social welfare programs to alleviate distress and offer improved opportunities within India. Initiating diplomatic dialogues to comprehend and address concerns that contribute to migration, fostering collaboration with other nations to safeguard the rights of migrants.
In a monthly report, the IEA projected that India's oil product demand growth would slow to 2.5% next year from 4.1% in 2023. (ET)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said recently that the "explosive growth" in Indian oil product consumption may be coming to an end.
About International Energy Agency:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an autonomous intergovernmental organization founded in 1974 in Paris, France.
- Its primary focus revolves around energy policies, emphasizing economic development, energy security, and environmental protection, collectively known as the '3 E’s of IEA.'
- The IEA Clean Coal Centre is dedicated to providing independent information and analysis on making coal a cleaner energy source in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Originating in response to the oil crisis of 1973-1974, the IEA's mandate has evolved to include tracking global energy trends, advocating sound energy policies, and fostering international energy technology cooperation.
- Mission: The IEA's mission is to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- Focus Areas: Key focus areas include energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and global engagement.
- The IEA collaborates closely with non-member countries, particularly major producers and consumers, to find solutions to shared energy and environmental concerns.
- IEA’s Membership: The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries. Four countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel and Lithuania.
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership Criteria:
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- These reserves, accessible to the government even if not directly owned, should be readily deployable to address disruptions in the global oil supply.
- Demand Restraint Program: Candidates are required to implement a demand restraint program aimed at reducing national oil consumption by up to 10%.
- Emergency Response Capability: Member countries must have legislation and organizational frameworks in place to operate Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis.
- Transparent Reporting: Legislation and measures should be established to ensure that all oil companies under the jurisdiction of the candidate country promptly report information upon request.
- Collective Action Capability: Measures must be in place to guarantee the country's capability to contribute its share in collective actions initiated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- India joined this organization in 2017 as an Associate member.
- However, in 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) invited India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, to become its full-time member.
- Major reports published by the IEA include the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, World Energy Statistics, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, and the India Energy Outlook Report.
NASA all set to launch of PACE mission to study air quality, key climate factors and more (NASA)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
NASA is ready to enhance our understanding of Earth’s atmosphere with the upcoming Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission, scheduled for launch in early 2024.
What is NASA's PACE Mission?
- The mission will leverage advanced polarimeters to investigate the intricate interactions of light, aerosols, and clouds, enhancing our understanding of their impact on both air quality and climate.
- Beyond aerosol analysis, the PACE mission will delve into the study of ocean colour.
- At its core, the Ocean Colour Instrument (OCI) serves as the primary science instrument for PACE, designed to measure the ocean's colour across a spectrum ranging from ultraviolet to shortwave infrared.
- The mission includes two polarimeters:
- The Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and
- The Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2)
- Working in tandem, these instruments offer complementary spectral and angular sampling, ensuring polarimetric accuracy and extensive spatial coverage.
- This integrated approach aims to deliver enhanced atmospheric correction and a comprehensive dataset on aerosols and clouds, surpassing the capabilities of OCI alone.
- The collaborative payload of OCI, SPEXone, and HARP2 is poised to achieve significant breakthroughs in aerosol-cloud-ocean research.
What are Aerosols and their Effect?
- Aerosols are comprised of liquid or solid particles suspended in a gaseous or liquid medium.
- In the atmosphere, these particles are predominantly found in the lower layers (< 1.5 km) since aerosol sources are terrestrial.
- However, specific aerosols may extend into the stratosphere, particularly those ejected by volcanoes at high altitudes.
- Sources of Aerosols:
- Natural Sources: Generated from breaking waves (sea salt), wind-blown mineral dust from the surface, and volcanic emissions.
- Anthropogenic Aerosols: These include sulphate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols, primarily originating from fossil fuel combustion.
- Effects of Aerosols:
- Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry.
- Reduction of Visibility.
- Significance for Air Quality and Human Health: Aerosols can adversely affect the heart and lungs.
- Role as Nuclei: Serve as nuclei for cloud droplets or ice crystals in ice clouds.
Mumps outbreak: Worrying symptoms to watch out for, preventive tips (India TV)
- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A mumps outbreak has recently been reported in several states across the country, causing concern among public health officials.
What is Mumps Disease?
- Mumps is a contagious disease caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family.
- It typically involves painful swelling in the parotid salivary glands, located on the sides of the face below and in front of the ears.
- These swollen glands often give the infected person a characteristic "chipmunk-cheek" appearance.
- Humans are the only known host for the mumps virus, which is spread via direct contact or by airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract of infected individuals.
- Transmission of mumps: Mumps is spread through contact with the saliva or respiratory droplets of an infected person. This can happen through coughing, sneezing, kissing, sharing utensils, or close contact.
- Symptoms:
- Mumps typically manifest after an incubation period of 2 to 4 weeks, starting with nonspecific symptoms like myalgia, headache, malaise, and low-grade fever.
- Within days, these initial symptoms progress to the swelling of the parotid salivary glands, either unilaterally or bilaterally, with other salivary glands affected in 10% of cases.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent mumps is to get vaccinated with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine.
- The MMR vaccine is safe and effective for most people.
- Other preventive measures include practising good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick people, and covering your coughs and sneezes.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for mumps. Most people recover on their own within a few weeks.
- Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as with pain relievers and fever reducers.
- In general, mumps is a mild, self-limiting disease that resolves without lasting effects.
- However, complications can arise, including encephalitis or sensorineural deafness.
- Orchitis, a painful inflammation of the testes, occurs in approximately 20% of young adult males who contract mumps.
The Hindu Parliament security breach | 14 Opposition MPs suspended from House amid face-off (LiveMint)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Fourteen MPs have been suspended for "unruly conduct" as stormy scenes played out in Parliament in the wake of the massive security breach recently.
Context:
- A total of 14 MPs, 13 from Lok Sabha and one from Rajya Sabha, were suspended from Parliament on Thursday for the remainder of the Winter Session.
- This follows after stormy scenes played out in Parliament on Thursday, December 14, in the wake of the massive security breach a day before.
- Earlier in the day, TMC member Derek O'Brien was suspended from the Rajya Sabha for the remainder of the Winter session for "unruly behaviour" and "misconduct".
Suspension of MPs:
- The Presiding Officer, whether the Speaker of the Lok Sabha or the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, plays a crucial role in maintaining order for the smooth functioning of the House.
- Empowered to uphold proper proceedings, the Speaker/Chairman has the authority to compel a Member to withdraw from the House, ensuring the orderly conduct of parliamentary affairs.
What are the Rules under which the Presiding Officer/Chairman acts?
- In Lok Sabha: Rule 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business empowers presiding officers to direct an MP to withdraw for disorderly conduct.
- The suspended Member must remain absent for the remainder of the day's sitting.
- Rules 374 and 374A are invoked for more persistent disruptions.
- Rule 374 allows the Speaker to name legislators for continued disruptions, leading to a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Rule 374A, added in December 2001, facilitates automatic suspension for five days or the remaining session part.
- In Rajya Sabha: Rule 255 grants the Chairman the authority to immediately direct withdrawal for disorderly conduct.
- Rule 256 enables the Chairman to name members persistently disregarding the Chair's authority or abusing Council rules.
- The House may then pass a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Unlike Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha cannot suspend members without a formal motion.
Judicial Oversight in MP Suspension Cases:
- While Article 122 of the Indian Constitution shields parliamentary proceedings from judicial review, there are instances of courts intervening in legislative procedures.
- In a case involving the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly's 2021 Monsoon Session, where 12 BJP MLAs were suspended for a year, the Supreme Court stepped in.
The Court ruled that the assembly's resolution had legal limitations and was only applicable for the duration of the Monsoon Session, underscoring the judiciary's role in assessing the legality and effectiveness of legislative actions.
Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) (The Hindu)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Centre has decided to deploy National Level Monitors (NLM) to oversee the implementation of its livestock schemes including the National Livestock Mission and Rashtriya Gokul Mission.
About Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM):
- The Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) has been implemented for the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- The scheme is important in enhancing milk production and productivity of bovines to meet the growing demand for milk and making dairying more remunerative to the rural farmers of the country.
- The scheme is also continued under the umbrella scheme Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna from 2021 to 2026 with a budget outlay of Rs.2400 crore.
- The RGM will result in enhanced productivity and benefit of the programme, percolating to all cattle and buffaloes of India, especially with small and marginal farmers.
- This programme will also benefit women in particular since over 70% of the work involved in livestock farming is undertaken by women.
Objectives:
- To enhance the productivity of bovines and increase milk production in a sustainable manner using advanced technologies.
- To propagate the use of high genetic merit bulls for breeding purposes.
- To enhance Artificial insemination coverage through strengthening the breeding network and delivery of Artificial insemination services at farmer’s doorstep.
- To promote indigenous cattle & buffalo rearing and conservation in a scientific and holistic manner.
India’s First ‘City Of Literature’ (NewsOnAir)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently India-born author Nandini Das is the winner of 2023 British Academy Book Prize for Global Cultural Understanding.
About the British Academy Book Prize:
- The British Academy Book Prize, formerly known as the Nayef Al Rodhan Prize for Global Cultural Understanding, is a prestigious annual award given to the best non-fiction book that, in the opinion of the judges, contributes to global cultural understanding for a wider public audience.
- The prize was established in 2013 in partnership with Professor Nayef Al-Rodhan and is worth £25,000.
- The British Academy is the UK's national academy for the humanities and social sciences, and the prize is one of its most prestigious awards.
- It is a testament to the importance of these disciplines in helping us to understand ourselves and the world around us.
- Eligible books must be non-fiction, and come from the subjects that fall within the humanities and social sciences, from archaeology, history and psychology to philosophy, languages and cultural studies.
- Nandini Das who is a Professor in the English faculty at the University of Oxford, won the award for her book ‘Courting India: England, Mughal India and the Origins of Empire’
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, in the Bargarh area of Odisha's Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary, two rare and elusive wild dogs, known as Dholes, have been spotted.
About Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is Located between the Hirakud Dam (on the Mahanadi River) and the Reservoir in Odisha.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1985.
- It's also famous because the freedom fighter Veer Surendra Sai used 'Barapathara' within the sanctuary as his base during his struggle against the British.
- It covers an area of 347 square kilometres and is home to a variety of wildlife, including Indian Bison, Wild Boars, Sambhar, and Peacocks.
- The dry deciduous forest attracts many migratory birds during the winter season.
- The sanctuary also houses the endangered four-horned antelope, known as Chousingha.
- Additionally, it's internationally significant due to its notable population of Leopards, Bisons, and Chousingha.
State Food Safety Index (SFSI) (Indian Express)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) published the State Food Safety Index in which 15 out of 20 states recorded lower 2023 scores compared to 2019.
About the State Food Safety Index:
- Since 2019, FSSAI has released the State Food Safety Index (SFSI) each year on June 7 on the occasion of World Food Safety Day.
- SFSI scores are given out of a total of 100 points that are calculated based on five parameters with different weightages:
- Human Resources and Institutional Data
- Compliance
- Food Testing Infrastructure
- Training and Capacity Building
- Consumer Empowerment.
- In the 2023 index, a new parameter called ‘Improvement in SFSI Rank’ was added, which assesses improvement in each state’s rank from the year before.
- The primary goal of this index is to ensure that citizens have access to safe and nutritious food.
- This index is a dynamic and comprehensive system that offers an objective way to assess food safety across all states and UTs.
- States and UTs are categorized into three groups: large states, small states, and UTs, for evaluation and comparison.
Key findings from the report:
- 19 out of 20 large states — including Maharashtra, Bihar, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh — recorded a drop in their 2023 scores from 2019.
- The most substantial drop was observed in the 'Food Testing Infrastructure' category, with states like Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh receiving lower scores in this aspect.
- Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Jharkhand also had reduced scores in the 'Compliance' category.
- In the 2023 index, the 'Human Resources and Institutional Data' category was given the third-highest importance, accounting for 18% of the evaluation (it was 20% in previous years).
- The only category that showed notable improvement was 'Training and Capacity Building,' which was given the least importance, 8%, in the 2023 index (compared to 10% in previous years).
Future Leaders Scholarship Programme (Indian Express)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Imperial College London recently announced a new scholarship programme for Indian students that aims to nurture the country’s most talented Master’s scholars over the next three years.
About the Future Leaders Scholarship Programme:
- Imperial College London unveils the Future Leaders Scholarship Programme for Indian students.
- It aims to support 30 highly talented Master's students in India for the next three years.
- This scholarship will cover all tuition and living expenses.
- It is available for Master's students in fields such as engineering, natural sciences, business, and medical research.
- Notably, half of the scholarships are set aside for female scholars.
- The program creates an opportunity for India's brightest students to further their education and gain valuable experiences at a top international university.
- In addition to this scholarship, the university has partnered with the UK government's Chevening Scholarships programme to sponsor an extra three Master's scholars from India in the next three years.
One Nation, One Registration Platform (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The National Medical Commission (NMC)will launch its “One Nation, one registration platform’‘ for doctors across the country
About One Nation, One Registration Platform:
- The National Medical Commission (NMC) will launch a patch trial of the National Medical Register (NMR), in which physicians will receive a unique identification number and, based on their location, be able to apply for a license to practice in any State within the next six months.
- The change was announced by the commission in a gazette notification earlier this year under the title "Registration of Medical Practitioners and Licence to Practice Medicine Regulations, 2023."
- The NMR will receive the data of almost 14 lakh doctors who are currently registered in the system.
- Objectives: The goal is to supply undergraduate students on the NMR with a masked ID, and based on when they complete their course, the ID is unmasked and assigned.
- It will eliminate duplication and red tape while also providing the public with access to information on any physician practising in India.
Features of the NMR:
- The public will have access to the NMR via the NMC website, which will take the role of the current Indian Medical Register (IMR). It will provide detailed information about registered doctors, such as:
- Unique Identification Number (UID): Each doctor will be assigned a unique identification number.
- Registration Number: The doctor’s registration number for verification.
- Qualifications: Information about the doctor’s educational qualifications.
- Specialization: The doctor’s area of expertise.
- Name and Place of Work: Details of the doctor’s name and workplace.
- Institute/University: The name of the institution or university where the qualifications were obtained.
Tamil Lambadi Embroidery (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For almost 60 years, the Porgai Artisan Association Society has been producing and distributing embroidered clothing in an effort to raise awareness of the art form and ensure that it is passed down to future generations.
About Tamil Lambadi Embroidery:
- The Lambadi community has a long-standing tradition of practising Lambadi embroidery.
- This craft is used to embellish their clothing and household items and it holds significant cultural and identity value for the Lambadis.
- Traditionally, Lambadi women use colourful cotton threads to create intricate embroidery on cotton and silk fabrics.
- Embroidery Designs: The traditional Lambadi embroidery designs are characterized by geometrical patterns, including squares, rectangles, and circles.
- These designs have also been influenced by elements from the local environment, such as forests, birds, fruits, and flowers.
Facts About the Lambadi Community:
- They are also known as Lambadis or Banjaras.
- Historically they are nomadic tribes, originating from Afghanistan and settling in regions including Rajasthan, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- They also assisted Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in transporting goods in the 17th century.
- Speak 'Gor Boli' or 'Lambadi,' which is often written in Devanagari or local languages.
- Many members of the Lambani community are bilingual or multilingual to communicate in the predominant language of their region in India.
- The elderly women within the Lambadi community continue to wear the Petia, a traditional five-piece dress.
- The Petia is made using Mushru silk from Kutch, showcasing the enduring connection to their heritage and craftsmanship.
Black Stork (TOI)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time, a Black Stork, a species rarely seen, has been spotted in the Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary in Uttar Pradesh recently.
About Black Stork:
- The black stork (Ciconia nigra) is a large bird in the stork family Ciconiidae.
- It is usually found in marshy areas, rivers or inland waters.
- It is a long-distance migrant, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent.
- The black stork is considered to be a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, but its actual status is uncertain.
- Despite its large range, it is nowhere abundant, and it appears to be declining in parts of its range, such as in India, China and parts of Western Europe, though increasing in others such as the Iberian Peninsula.
- Various conservation measures have been taken for the black stork, like the Conservation Action Plan for African black storks by Wetlands International.
- It is also protected under the African-Eurasian Waterbird Agreement and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) 'Prachand' (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Army's Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) Prachand has conducted the first-ever day-and-night firing of 20 mm turret guns and 70 mm missiles.
About Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) 'Prachand':
- The LCH is the only assault helicopter in the world that has the ability to land and take off at 5,000 meters while carrying a sizable payload of fuel and weaponry.
- The helicopter features a frame and landing gear that are largely crash-proof, and it uses material that absorbs radar waves to reduce its radar signature.
- For protection against nuclear, biological, and chemical (NBC) emergencies, a pressurised compartment is available.
- The helicopter is protected from enemy radars and infrared seekers of enemy missiles by a countermeasure dispensing mechanism.
- LCH is powered by two French-origin Shakti engines manufactured by the HAL.
- The helicopter will be equipped with Helina missiles, the air force version of which is called Dhruvastra.
- It is capable of combat duties such as enemy air defence destruction, counter-insurgency warfare, combat search and rescue, anti-tank, and counter-surface force operations.
India’s First ‘City Of Literature’ (Money Control)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Kozhikode, in Kerala, was named the ‘City of Literature’ by the Unesco Creative Cities Network (UCCN), making it the first such city in India.
About India’s First ‘City Of Literature’:
- Kozhikode (Kerala), has achieved global recognition by joining the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
- It is now known as the 'City of Literature,' making it the first Indian city to receive this prestigious title.
- This recognition was awarded on World Cities Day, (31 October) along with Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, which was designated a 'City of Music.'
- Prague was the first city to receive the 'City of Literature' title in 2014.
About UNESCO Creative Cities Network:
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network is a global initiative established by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to recognize and promote cities that have made significant contributions to the development of creative industries and culture.
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network now comprises 350 creative cities from over 100 countries.
- These cities represent seven creative fields, including Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gastronomy, Literature, Media Arts, and Music.
- Participation in the UNESCO Creative Cities Network provides cities with opportunities for international collaboration, knowledge sharing, and the exchange of best practices in creative and cultural endeavours.
- These cities serve as hubs for artistic expression, cultural preservation, and economic growth, making them vital players in the global creative economy.
- Through this network, cities work together to harness the power of culture and creativity to address common challenges and promote sustainable development, ultimately enhancing their status on the global stage.
Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) (NewsOnAir)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Health Authority (NHA) has recently declared the extension of its Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) until the 31st of December 2023.
About Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS):
- Launched in December 2022, the DHIS became effective from 1st January 2023.
- The scheme is implemented by the National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Its primary objectives include giving a further impetus to digital health transactions across the country through the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
Salient Features of DHIS:
- The scheme offers incentives of up to four crore rupees, determined by the number of digital health records created and linked to patients' Ayushman Bharat Health Account numbers.
- Incentives are extended to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and providers of digital health solutions, including Hospital/Health Management Information Systems (HMIS) and Laboratory Management Information Systems (LMIS).
- Health facilities (hospitals and diagnostic labs) registered with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission's Health Facility Registry (HFR) and meeting the specified eligibility criteria can avail of the incentives.
Benefits of DHIS:
- Incentives for Digitization: Healthcare facilities and Digital Solution Companies participating in the scheme can earn incentives to cover expenses related to digitization.
- Enhanced Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery: DHIS streamlines the healthcare process, eliminating hassles in registration, appointment scheduling, consultations, IPD admission, discharge, and more.
- Robust Digital Health Ecosystem: The scheme contributes to the development of a strong digital health ecosystem, encompassing various levels of healthcare facilities.
- Improved Quality of Care: DHIS facilitates evidence-based, accessible, and high-quality healthcare services, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missiles (TOI)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Israel's Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) anti-tank guided missiles were recently delivered to the Indian Air Force.
About the Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile:
- The Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile (ATGM) is a sophisticated fire-and-forget missile designed for anti-tank and anti-personnel purposes.
- It features a tandem-charge high-explosive warhead.
- Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, an Israeli defense technology company, the Spike NLOS ATGM comes in man-portable, vehicle-launched, and helicopter-launched variants.
- The missile is currently in use by the defense forces of Israel and 38 other countries, including India, Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Peru, Spain, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, the UK, Philippines, and Singapore.
- Key features of the Spike NLOS ATGM:
- Striking range of up to 30 kilometers
- Weight of 71 kg, and
- An electro-optical seeker that offers superior target visibility compared to radar or infrared-guided missiles.
- The missile's seeker is equipped with a datalink, enabling the launch operator to maintain control over the missile during flight.
- This capability allows for precise targeting, including attacking different parts of a tank or engaging an alternative target, or aborting the strike if necessary.
- The Spike NLOS ATGM can be armed with various types of warheads, making it versatile for destroying tanks, and air defense systems, or for use in urban combat scenarios.
Perucetus colossus (Indian Express)
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Perucetus colossus, whose fossils were discovered in Peru, maybe the heaviest discovered animal ever, even heavier than the blue whale.
About Perucetus colossus:
- The whale species Perucetus colossus is known from a recently described fossil dating back over 38 million years.
- Despite potentially being shorter in length, scientists believe that this ancient whale species might have been heavier than the modern blue whale.
- Researchers estimate that the weight of the Perucetus colossus could have ranged from 85 to an astonishing 340 tonnes.
- The fossilized bones of this species exhibited an unusual combination of large volume and extreme density, a characteristic known as pachyosteosclerosis.
- Pachyosteosclerosis is not observed in living whales, dolphins, and porpoises, but it is present in sirenians, a marine mammal group that includes sea cows.
- Unlike deep-diving whales, Perucetus colossus likely lived in shallow coastal areas, suggesting that it might have dived with air in its lungs.
- However, diving with air in the lungs would make it challenging to stay near the seafloor.
- The heavy bones of the Perucetus colossus might have played a crucial role in enabling it to do so.
- The skeletal mass of the Perucetus colossus is estimated to have been between five and eight tons, double that of a modern blue whale.
Study in India (SII) portal (Indian Express)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Study In India (SII) portal was recently introduced by the Education Ministry, aiming to promote Indian education among international students.
About the Study in India (SII) portal:
- The Study in India (SII) portal serves as a dedicated website offering comprehensive information about higher education institutions (HEIs) in India.
- The main objective of the portal is to establish India as a global education hub and attract students from diverse backgrounds.
- The portal showcases a wide range of academic programs available in the HEIs, including undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral courses, along with courses related to the Indian Knowledge System (IKS), such as Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical arts.
- Detailed information about the academic facilities, research support, and other related offerings in the institutes is provided on the portal.
- It acts as a convenient one-stop platform for students, enabling them to register, apply for a visa, select desired courses, and receive offer letters from their chosen institutes.
- The portal allows students to apply to multiple institutes or courses of their preference, simplifying the application process.
- Study in India (SII) offers a streamlined and well-organized application process, providing international students with easy access to higher education opportunities in India.
What is Study in India (SII) Programme?
- The Study in India (SII) program is a prominent initiative initiated by the education ministry in 2018 with the aim of positioning India as a premier education destination for international students.
- The program seeks to attract foreign students to pursue higher education in India, providing them with valuable educational opportunities offered by renowned Indian universities.
Great Nicobar Island Project (DownToEarth)
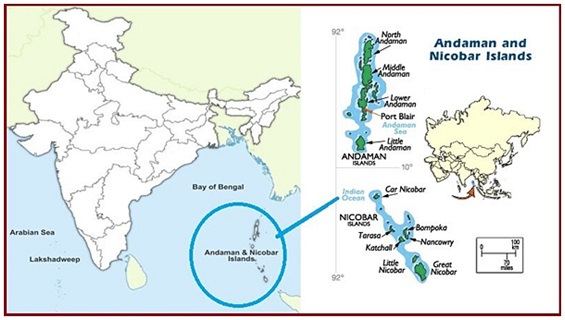
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change's statement in the Rajya Sabha, approximately 964,000 trees are expected to be cut down for the implementation of the Great Nicobar Island Project.
About Great Nicobar Island Project:
- Ministry:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Implementing Agency:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- The project is a massive undertaking with a budget of ?72,000 crore and is spearheaded by NITI Aayog, known as NITI Aayog's Project for Great Nicobar Island.
- Objective:
- The primary goal of the project is to achieve holistic development for the Great Nicobar Island (GNI).
- The project's vision is to transform the Great Nicobar Island, situated in the Bay of Bengal, into a modern, sustainable, and self-sufficient territory, thus facilitating the comprehensive development of Great Nicobar.
The plan comprises four key components:
- A transshipment port at Galathea Bay with an investment of ?35,000 crore.
- Development of a dual-use military-civil international airport.
- Establishment of a power plant.
- Creation of a township to support the overall project.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) (TOI)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) has reported that three private sector satellite manufacturers plan to launch their earth observation satellites during this fiscal year.
About Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe):
- IN-SPACe serves as a single-window, independent, and autonomous agency within the Department of Space (DOS).
- It was established as part of the Space sector reforms to encourage and facilitate the active involvement of private players in the space industry.
- IN-SPACe's responsibilities include promoting, enabling, authorizing, and supervising various space activities of non-governmental entities, such as manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites, providing space-based services, and utilizing space infrastructure and facilities.
- Acting as an intermediary between ISRO and Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs), the agency assesses opportunities for leveraging India's space resources effectively and enhancing space-based initiatives.
- Also, IN-SPACe addresses the specific needs and demands of private players, including educational and research institutions, while working in collaboration with ISRO.
- The headquarters of IN-SPACe is located in Bopal, (Ahmedabad).
Samudrayaan (IndiaToday)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
India's ambitious Samudrayaan project, aimed at exploring the deep ocean and its resources, is set to send three personnel to a depth of 6000 meters in a submersible vehicle.
About Samudrayaan Project:
- India's inaugural manned mission to delve into the depths of the ocean for exploration.
- Its primary objectives include studying deep ocean resources and conducting biodiversity assessments.
- The mission is designed to ensure minimal disturbance to the ecosystem, focusing solely on exploration.
- Part of the comprehensive Deep Ocean Mission aligned with the Central Government's Blue Economy policy.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) leads the implementation of this ambitious, multi-institutional endeavor.
What is the Blue Economy?
- Blue economy refers to the sustainable use of marine resources for exploration, economic growth, improved livelihoods, and transport while preserving the health of marine and coastal ecosystems.
- In India, the blue economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including shipping, tourism, fisheries, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana (PIB)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
In the Lok Sabha, the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas provided details about the Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN scheme.
About Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana:
- The scheme was officially notified in March 2019.
- Its main objective is to extend financial support to integrated bio-ethanol projects, facilitating the establishment of Second Generation (2G) ethanol projects using lignocellulosic biomass and other renewable feedstocks.
- It has a financial outlay of Rs. 1969.50 crore, spanning the period from 2018-19 to 2023-24.
- Financial assistance of Rs. 150 crore is offered per project for commercial projects, while demonstration projects receive Rs. 15 crore per project.
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas serves as the nodal ministry for this scheme.
What is Lignocellulosic Biomass?
- Abundant Source: It is found in agricultural and forestry residues, as well as dedicated energy crops.
- Biofuels and Bio-based Products: Lignocellulosic biomass holds promise as a sustainable feedstock for producing biofuels like second-generation ethanol and various bio-based products.
- Challenges: Efficiently breaking down its complex structure to release sugars for fermentation or chemical conversion is a key challenge.
- Innovative Technologies: Researchers are exploring enzymatic hydrolysis and thermochemical treatments to unlock its energy potential.
- Green and Sustainable Future: Utilizing lignocellulosic biomass can reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and mitigate environmental impacts linked to conventional energy production.
Himalayan vulture bred (The Hindu)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The first-ever instance of captive breeding of the Himalayan vulture in India has been successfully recorded at the Assam State Zoo in Guwahati by researchers.
About Himalayan Vulture:
- Scientific Name: Gyps himalayensis
- It is a rare and the largest bird species native to the Himalayas.
- Habitat:
- The Himalayan vulture primarily inhabits higher regions of the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, typically found at elevations above 1500 meters.
- This species has a distribution range that extends from western China, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to the eastern part of the Himalayan mountain range, including India, Nepal, and Bhutan, and further to central China and Mongolia.
- Description:
- This vulture is impressively large, featuring a sandy brown plumage with a pale, featherless head. In flight, it displays black primaries and a distinctive small-headed, squared-winged appearance.
- Himalayan vultures are usually spotted alone or in small groups, but they gather in large flocks when feeding on a carcass.
- Conservation status:
- The Himalayan vulture is categorized as "Near Threatened" on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
- To ensure its preservation, the species is covered under the Multi-species Action Plan (MsAP) for the conservation of African-Eurasian vultures and is also included in national Action Plans in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Cambodia.
- Threats:
- The most significant potential threat to this vulture species is believed to be mortality resulting from the ingestion of diclofenac and other vulture-toxic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), commonly used in livestock, particularly in South Asia.
India to launch female robot astronaut 'Vyommitra' ahead of manned mission (IndiaTV News)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Minister of Science & Technology, Dr Jitendra Singh, announced on Wednesday that India is set to launch Vyommitra, a female robot astronaut, into space as part of the ambitious Gaganyaan project.
What is Vyommitra?
- Vyommitra is an AI-enabled female robot.
- It was introduced at the inaugural session of the "Human Spaceflight and Exploration — Present Challenges and Future Trends" event in January 2020.
- The name is a combination of two Sanskrit words: Vyoma (Space) and Mitra (Friend), and it was created for the unmanned Gaganyaan mission.
- Because she lacks legs, she is described as a half-humanoid robot.
- She may, however, bend to the sides and forward.
- The ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) designed, developed, and integrated the robot.
- At the same time, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), a sister Isro facility based in Thumba, built its fingers.
- This robot is designed to ride aboard a rocket and survive stress and vibrations while in flight.
- With the ability to speak, see, and make facial expressions, it has been created to resemble a human.
- Vyommitra will also acquire a digital twin.
- The twin would be built through collaboration with academic institutions such as the IITs.
- Vyommitra will accompany astronauts on manned missions in addition to the unmanned Gaganyaan mission.
- Vyommitra's mission is to perform specific tasks in order to analyse how astronauts might behave.
- She will mimic every action that astronauts are required to take and respond to them in two languages.
- She will monitor via module parameters, alert, carry out life support procedures, carry out tasks like operating switch panels, and imitate other human actions in space throughout the uncrewed flight.
What is the Gaganyaan mission?
- Named after the Sanskrit word for craft or vehicle to the sky, the Gaganyaan project has been developed at the cost of ?90 billion.
- If it succeeds, India will become only the fourth country to send a human into space after the Soviet Union, the US, and China.
- Under the Gaganyaan Mission, ISRO will be sending three humans to an orbit of 400 km for a 3-day mission and bring them back safely to Earth.
- Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk III, also called the LVM-3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3,) the three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle, will be used to launch Gaganyaan as it has the necessary payload capability.
- Training Collaboration with Russia: In June 2019, ISRO's Human Space Flight Centre partnered with Russia's Glavkosmos, a government-owned entity, under a contract encompassing comprehensive astronaut training.
- However, four astronauts selected for the Gaganyaan have been undergoing mission-specific training at the Astronaut Training Facility in Bengaluru.
CHD1L gene (DownToEarth)
- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A new study indicates that some individuals of African descent have a CHD1L gene variant that may be involved in controlling the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
What is the CHD1L gene?
- The CHD1L gene encodes proteins that aid in repairing DNA damage within the body.
- A specific variant of the CHD1L gene is found predominantly in the African population and has been associated with a decreased viral load (amount of HIV in the blood) of HIV-1, the most common and severe type of HIV compared to HIV-2.
- Through the analysis of DNA from nearly 4,000 people of African descent living with HIV-1, researchers identified the presence of a gene variant of CHD1L located on chromosome 1.
- Individuals carrying this particular gene variant exhibited a low viral load, reducing their risk of transmitting the virus and slowing the progression of their own HIV-related illness.
- The study suggests that between 4% and 13% of people with African origins could be carrying this specific CHD1L gene variant.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (India Today)
- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has reported a significant anthrax outbreak in Zambia, marking an alarming spread of the disease across nine out of the country's ten provinces.
What is anthrax?
- According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), anthrax is a highly infectious disease that is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- Although it affects animals like cows, sheep, and goats, humans can get sick if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Anthrax is not contagious, which means we can't catch it from another person like the cold or flu.
Symptoms of anthrax:
- The disease manifests in three forms depending on the route of infection: cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and inhalational.
- Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, presents with itchy bumps that develop into black sores, often accompanied by fever and muscle aches.
- Gastrointestinal anthrax resembles food poisoning initially but can escalate to severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhoea.
- Inhalational anthrax, the deadliest form, starts with cold-like symptoms before progressing to severe respiratory distress and shock.
How is anthrax diagnosed?
- Anthrax can be diagnosed by identifying Bacillus anthracis in blood, skin lesions, or respiratory secretions through laboratory culture, PCR, or ELISA tests.
- While there is no specific test to determine exposure to anthrax, public health investigations play a crucial role in identifying potential cases.
Treatment for anthrax:
- Treatment for anthrax is available and includes antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, or levofloxacin.
- If diagnosed early, antibiotic treatment can cure most anthrax infections.
- In severe cases, hospitalisation and treatments like continuous fluid drainage and mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
- Vaccines are also available for both livestock and humans, although human vaccines are typically reserved for those at high occupational risk.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (The Hindu)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Road traffic deaths fell by 5% to 1.19 million fatalities annually worldwide between 2010 and 2021, with 108 UN member nations reporting a drop, a report by the World Health Organization (WHO) said. India, however, registered a 15% increase in fatalities.
News Summary:
- The fifth edition of the WHO Global Status Report on Road Safety, released in 2023, serves as a comprehensive assessment of progress in mitigating road traffic deaths.
- This report evaluates advancements made between 2010 and 2021, establishing a foundation for meeting the ambitious target of the United Nations Decade of Action 2021–2030—to cut road traffic fatalities in half by 2030.
- Declared by the United Nations General Assembly in September 2020, the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030 strives to achieve a 50% reduction in road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- Generous support from Bloomberg Philanthropies has played a crucial role in producing this report.
- Since 2007, Bloomberg Philanthropies has committed $500 million to facilitate road safety initiatives in low- and middle-income countries and cities worldwide
Key Insights from the Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023:
- Countries Achieving Over 50% Reduction in Road Traffic Deaths: Ten countries, including Belarus, Brunei Darussalam, Denmark, Japan, Lithuania, Norway, Russian Federation, Trinidad and Tobago, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, have successfully reduced road traffic deaths by more than 50%.
- Additionally, 35 more countries have made commendable progress, achieving a reduction in road traffic deaths ranging from 30% to 50%.
- Leading Cause of Death for Children and Youth: As of 2019, road traffic crashes have become the primary cause of death for children and youth aged five to 29 years.
- Globally, these crashes rank as the 12th leading cause of death across all age groups.
- 5% Reduction in Road Traffic Fatalities in the Last Decade: Despite a population growth of nearly 14 billion over the last decade, there has been a 5% reduction in the absolute number of road traffic fatalities.
- The road fatality rate has declined from 18 per 1 lakh people in 2010 to 15 per 1 lakh in 2021, marking a 16% decrease in the road traffic death rate since 2010.
- Regional Distribution of Traffic Deaths: The regional breakdown indicates that:
- 28% of global road traffic deaths occurred in the WHO’s South-East Asia Region
- 25% in the Western Pacific Region
- 19% in the African Region
- 12% in the Region of the Americas
- 11% in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, and
- 5% in the European Region.
- The situation in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Nine out of 10 road traffic deaths transpire in low- and middle-income countries, with fatalities in these nations being disproportionately higher (three times) in comparison to the number of vehicles and roads they possess.
- Countries Meeting WHO Best Practices for Risk Factors: Only six countries have legislation aligning with WHO best practices for all risk factors (speeding, drunk driving, and the use of motorcycle helmets, seatbelts, and child restraints).
- Meanwhile, 140 countries, constituting two-thirds of UN Member States, have such laws governing at least one of these risk factors.
- India-Specific Observation: In India, the reported deaths due to road crashes increased from 1,50,785 in 2018 to 1,53,792 in 2021.
- Notably, the number stood at 1.3 lakh in 2010.
Lunar Codex (The Guardian)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Lunar Codex program has the potential to bestow immortality upon an assorted collection of human-created art.
About Lunar Codex:
- The Lunar Codex is a remarkable collection of art curated by artists worldwide, intended to endure on the lunar surface as a timeless testament to human creativity, even amid tumultuous times like wars, pandemics, and economic crises.
- At the helm of this endeavor is Samuel Peralta, a semi-retired physicist and art enthusiast from Canada.
- Comprising diverse forms of digitized art, the Lunar Codex will be dispatched to the moon to serve as a permanent record of human ingenuity. Memory cards and NanoFiche, an updated 21st-century version of film-based microfiche, guarantee the safe arrival of these artistic expressions to the lunar surface.
- Carefully assembled from contributions by 30,000 artists, writers, filmmakers, and musicians representing 157 countries, the collection spans an array of art forms, including images, magazines, books, podcasts, movies, and music.
- The art is divided into four capsules:
- The first capsule, the Orion collection, has already encircled the moon after being launched aboard NASA's Artemis 1 mission via the Orion spacecraft last year.
- In the months ahead, multiple lunar landers will transport the Lunar Codex capsules to distinct locations, including craters at the moon's South Pole and the lunar plain known as Sinus Viscositatis, ensuring the enduring legacy of human creativity on Earth's celestial neighbor.
Here to enhance partnership between EFTA, India: Norway's trade minister (Business Standard)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Norway's Minister of Trade and Industry Jan Christian Vestre has said his India visit aims to enhance collaboration between European free trade partners and India and improve framework conditions for job creation, value creation, and investments.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Its core objective is to foster free trade and economic integration among its member countries, both within Europe and on a global scale.
- Member Countries: EFTA comprises four member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- These nations are characterized by open, competitive economies, demonstrating a shared commitment to progressively liberalize trade both within multinational forums and through individual free trade agreements.
- Customs Distinction: Unlike the European Union (EU), EFTA operates differently as it is not a customs union.
- This key distinction allows each EFTA State the autonomy to establish its own customs tariffs and formulate foreign trade measures independently concerning non-EFTA States.
- Association Responsibilities:
- EFTA manages various aspects crucial to its objectives, including:
- Facilitating free trade among EFTA countries.
- Overseeing EFTA's engagement in the European Economic Area (EEA), encompassing the European Union and three EFTA countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, excluding Switzerland).
- Managing EFTA's extensive network of free trade agreements globally.
- Free Trade Agreement Network: EFTA member countries boast one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) globally.
- This comprehensive network spans over 60 countries and territories, incorporating the European Union among others.
EFTA plays a pivotal role in promoting economic collaboration, free trade, and global engagement, distinguishing itself from the EU through its approach to customs and foreign trade measures.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more nations aimed at lowering barriers to imports and exports among them.
- In a free trade scenario, goods and services can move across international borders with minimal government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or restrictions hindering their exchange.
- The principle of free trade stands in contrast to trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs come in various forms, including Preferential Trade Agreements, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements, and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA).
COP28: What was the most important deal short (Indian Express)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
COP28: The annual climate conference this year saw some key resolutions on fossil fuels, methane emissions, and funds to fight global warming, among others. However, many concerns remain.
Context:
- The 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also referred to as COP28 took place from November 30 to December 12 at Expo City in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
- While the event yielded significant outcomes, it, akin to its predecessors, fell short of meeting the anticipated expectations.
Key Outcomes of COP28:
- Fossil Fuel Transition Ambiguity: Acknowledging the role of fossil fuels in global warming for the first time, the agreement calls for countries to contribute to transitioning away from fossil fuels to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
- However, the lack of specific time schedules and targets disappointed some nations that expected a more explicit commitment to a "fossil fuel phase-out."
- Renewable Energy Tripling: The agreement calls on countries to contribute to tripling the global installed capacity of renewable energy and doubling annual improvements in energy efficiency.
- This measure is expected to result in emissions avoidance of approximately 7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent by 2030.
- However, the global nature of this target raises questions about individual country responsibilities.
- Coal Phase-Down Continuation: The agreement reiterates the commitment to the phase-down of coal, following up on the decision made at COP26.
- While there were considerations to impose restrictions on new coal-fired power plants without carbon capture and storage, these were dropped due to resistance from countries like India, China, and South Africa.
- The agreement lacks specifics on measurement criteria or baseline for this phase-down.
- Methane Emission Challenges: Despite the significance of methane as a greenhouse gas, responsible for nearly 25% of emissions and is 80 times more potent than CO2, the agreement avoids setting targets for methane emission cuts in 2030.
- Countries like India are opposed to mandates due to the agricultural sector's major role in methane emissions.
- Operational Loss & Damage Fund: A significant outcome for vulnerable nations, COP28 operationalized the Loss and Damage Fund, established in COP27.
- Commitments, totaling around US$ 800 million, were made during the conference to assist countries recovering from climate-induced disasters.
- Global Goal on Adaptation Establishment: COP28 adopted a global framework for adaptation, addressing a historic imbalance where adaptation efforts received less attention and resources compared to mitigation activities.
- The framework, though established, lacks financial provisions, necessitating further strengthening in subsequent years.
- Adaptation Challenges: While the global adaptation framework is a positive step, there is still work to be done, particularly in defining indicators for measuring progress on each global goal.
- Adaptation efforts historically focused on local initiatives, and the agreement aims to garner more attention and resources for these endeavours on a global scale.
- Climate Action Acceleration Shortcomings: The final agreement falls short of providing sufficient impetus for the acceleration of climate action in the immediate term.
What is the Conference of the Parties (COP)?
- In 1992, Rio Earth Summit, 154 countries joined an international treaty, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, as a framework for international cooperation to combat climate change by limiting average global temperature increases and the resulting climate change, and coping with impacts that were, by then, inevitable.
- The COP is the supreme decision-making body of the Convention.
- All States that are Parties to the Convention are represented at the COP, at which they review the implementation of the Convention and any other legal instruments that the COP adopts and take decisions necessary to promote the effective implementation of the Convention, including institutional and administrative arrangements.
- Currently, there are 198 'parties' or signatories of the Convention.
JALDOST airboat (The Hindu)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) recently revealed its latest creation, the JALDOST airboat.
What is JALDOST?
- JALDOST is an innovative airboat specifically designed for water operation, aimed at effectively removing excess aquatic weed and floating waste from various water bodies.
- The airboat features a closed, airtight pontoon-type hull, ensuring its inherent unsinkability.
- Notably, the JALDOST incorporates a hybrid propulsion system, combining air propulsion and paddle wheel propulsion, making it versatile and efficient in its movements.
- Operating through weed with ease, JALDOST serves as an ideal platform for collecting and transporting these undesirable aquatic plants to the shore.
- It achieves this through a steel mesh belt conveyor system situated at the front, which gathers the waste and deposits it on the horizontal deck conveyor.
- Upon reaching the shore, the collected waste is efficiently unloaded using a rear conveyor system, facilitating easy transfer to trucks or tractors.
- The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has introduced two versions of the airboat, namely JALDOST Mark-1 and an upgraded version, JALDOST Mark-2, further enhancing its capabilities.
Green Rising initiative launched at RewirEd summit to empower Youth-Led climate solutions (DD News)

- 09 Dec 2023
What is the Green Rising Initiative?
- The "Green Rising" initiative focuses on engaging youth for impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level, aligning with the global effort to address the severe impacts of climate change.
- This initiative encompasses both the global "Green Rising" initiative and the "Green Rising India Alliance," a collaborative endeavor that brings together UNICEF, Generation Unlimited, and a diverse network of public, private, and youth partners.
- The primary objective is to mobilize millions of young individuals globally, encouraging their active engagement in green initiatives aimed at addressing and adapting to the profound impacts of climate change within their communities.
- In India, this effort is channelled through the YuWaah campaign, which specifically focuses on harnessing the energy and commitment of the youth to drive impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level.
About UNICEF:
UNICEF, or the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, is a specialized agency of the United Nations committed to promoting the well-being and rights of every child globally.
- Foundation and Establishment: Established in 1946 by the United Nations General Assembly, UNICEF was originally designed to provide emergency food and healthcare to children in countries devastated by World War II.
- Over time, UNICEF's scope evolved to include long-term developmental programs, focusing on education, healthcare, nutrition, clean water, sanitation, and protection for children in need.
- UNICEF is governed by an Executive Board consisting of 36 members who are elected to terms of three years by the United Nations Economic and Social Council.
- Universal Presence: UNICEF operates in over 190 countries and territories worldwide, making it one of the most extensive and widely recognized humanitarian organizations globally.
- Child Rights Advocacy: UNICEF is a leading advocate for children's rights, working to ensure that every child has the right to survive, thrive, and reach their full potential, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Emergency Response: In times of crises, including natural disasters, conflicts, and pandemics, UNICEF plays a crucial role in providing immediate and life-saving assistance to affected children and communities.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: UNICEF collaborates with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), other UN agencies, and the private sector to implement its programs and maximize its impact.
- Funding Mechanism: UNICEF is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from governments, private donors, businesses, and the general public. It relies on these funds to carry out its programs and respond to emergencies.
- Focus on Equality and Inclusion: UNICEF emphasizes the importance of equality and inclusion, working to address disparities and ensure that the most vulnerable children, including those with disabilities or from marginalized communities, are not left behind.
- Global Campaigns: UNICEF spearheads global campaigns to address critical issues affecting children, such as vaccination drives, education initiatives, and efforts to eliminate child labour and violence against children. These campaigns aim to rally public support and create awareness about the challenges faced by children worldwide.
- It was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1965 for the “promotion of brotherhood among the nations”.
- Headquarters: New York City
India is expected to withstand global shocks as its current account deficit improves due to falling crude oil prices. (ET)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After two years of battling inflation and growth pangs, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was in for a pleasant surprise when the economic growth trumped its expectations to hit 7.2 per cent in the last month.
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has unveiled its most recent monetary policy report, projecting a robust economic recovery for the country in the current fiscal year.
- Anticipating a significant upswing, the central bank foresees the gross domestic product (GDP) to expand by 7 percent in 2021-22, a notable rebound from the 7.3 percent contraction witnessed in the preceding year.
- However, the RBI issues a cautionary note about the challenges posed by inflation, which has consistently exceeded the target range of 2-6 percent over several months.
- The report attributes inflationary pressures to supply-side disruptions, escalating commodity prices, increased fuel taxes, and demand-related factors.
- The RBI anticipates inflation to remain elevated in the short term before gradually moderating in the latter half of the year.
- The RBI's stance mirrors a delicate equilibrium, emphasizing the intricate balance between fostering economic growth and managing inflation, often characterized as the Goldilocks Effect.
- This effect alludes to a scenario where the economy is neither excessively overheated nor excessively sluggish but rather poised for optimal growth with minimal inflationary pressures.
What is the Goldilocks Effect?
- The Goldilocks Effect, also known as the Goldilocks Principle, posits that individuals have a predisposition to seek an amount that is 'just right' for their specific needs or preferences.
- This concept, derived from the children's story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears, reflects a preference for options that are neither too extreme nor too moderate, falling within an optimal and desirable range.
- This principle finds application across various fields and disciplines, encompassing psychology, hard sciences, economics, marketing, and engineering, each incorporating its unique interpretation of the principle.
- Goldilocks Pricing: One notable application of the Goldilocks Effect is in Goldilocks Pricing, a psychological pricing strategy grounded in concepts such as product differentiation, comparative pricing, and bracketing.
- Product differentiation involves distinguishing certain products from others, a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage the Goldilocks Effect.
- This differentiation is then coupled with comparative pricing, where businesses simultaneously offer multiple versions of a product with varying quality levels attached to corresponding price points.
- The strategy hinges on providing three options: one priced too high for most, one priced too low for most, and one priced just right.
- When executed effectively, this approach enables businesses to appeal to diverse segments of the market, capturing premium buyers, standard consumers, and discount seekers.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which is marking its 75th anniversary? (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Seventy-five years ago on Sunday, the UN General Assembly approved the Universal Declaration of Human Rights at a meeting in Paris – laying one of the foundation stones of the international order that emerged following the horrors of World War II.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)?
- On 10 December 1948, during a session in Paris, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously endorsed the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), marking a pivotal moment in shaping the post-World War II international order.
- The UDHR emerged as a response to wartime atrocities and aimed to establish a shared understanding of the fundamental rights and freedoms inherent to all individuals.
- A concise yet impactful document, the declaration comprises a preamble and 30 articles that delineate essential rights and freedoms.
- These 30 articles encompass a comprehensive spectrum of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Emphasizing their universality, these rights are deemed applicable to all individuals, irrespective of nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status.
- While not legally binding, the UDHR has functioned as a guiding force inspiring the development of international human rights law.
Key Features:
- Preamble: The preamble elucidates the reasons behind adopting the declaration, underscoring the inherent dignity and the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family.
- Articles: The UDHR articulates 30 articles outlining a wide array of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. Examples of these rights include:
- The right to life, liberty, and security of person.
- The right to freedom of religion, expression, and assembly.
- The right to work and education.
- The right to an adequate standard of living.
- The declaration asserts that "all are equal before the law" and emphasizes the entitlement of everyone to "a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal."
- It also affirms the right of "everyone to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution.
Achievements of UNDHR:
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UNDHR) is acknowledged for its significant impact, having served as the inspiration and foundation for over 70 human rights treaties at both global and regional levels, as noted by the United Nations.
- It played a pivotal role in inspiring movements such as decolonization, the anti-apartheid movement, and various struggles for freedom worldwide, including those related to gender, LGBTIQ+ rights, and opposition against racism.
What is the Current Situation?
- As the 75th anniversary is commemorated, human rights face challenges amid conflicts such as the Israel-Hamas war, Russia's actions in Ukraine, internal strife in Myanmar and Sudan, and numerous other global situations.
- UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has remarked that the Universal Declaration has been frequently misused and abused, exploited for political gain, and often ignored by those who should uphold it.
- Contrastingly, Amnesty International asserts that the declaration serves as living proof that a global vision for human rights is attainable and can be realized.
- Despite instances of neglect or exploitation, the declaration remains relevant, and the world is encouraged to recognize its successes while learning from its failures.
Amit Shah to chair 26th meeting of Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar on Sunday (Business Standard)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah will chair the 26th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar's capital on Sunday, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) said on Saturday.
What are Zonal Councils?
- The conceptualization of Zonal Councils can be attributed to the visionary initiative of India's first Prime Minister, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru, in 1956.
- These councils are statutory bodies established by an Act of Parliament, namely the States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- The act delineated the country into five zones (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern), assigning a Zonal Council to each.
Present Composition of Zonal Councils:
- Northern Zonal Council: Includes Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi, and Union Territory of Chandigarh.
- Central Zonal Council: Encompasses Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Eastern Zonal Council: Comprises Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and West Bengal.
- Western Zonal Council: Involves Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- Southern Zonal Council: Consists of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Exclusion and Special Council: The North Eastern States (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Nagaland) are not part of Zonal Councils.
- Instead, their unique challenges are addressed by the North Eastern Council, established under the North Eastern Council Act of 1972.
- Sikkim was included in the North Eastern Council in 2002.
Organizational Structure:
- Chairman: The Union Home Minister serves as the Chairman for each Zonal Council.
- Vice Chairman: Chief Ministers of the states in each zone act as Vice-Chairman, rotating annually.
- Members: Chief Minister and two nominated Ministers from each state, along with two members from Union Territories in the zone.
- Advisers: Planning Commission nominees, Chief Secretaries, and another officer/Development Commissioner from each state in the zone.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of Zonal Councils include promoting national integration and curbing acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism, and particularistic tendencies.
- Additionally, they aim to facilitate cooperation, idea exchange, and a climate of collaboration among states for the successful execution of development projects.
Functions:
- Zonal Councils function as advisory bodies, empowered to discuss common interests between the Union and represented states.
- They can recommend courses of action to the Central Government and individual state governments.
- Specific areas of discussion may include economic and social planning, border disputes, linguistic minorities, inter-state transport, and matters arising from the reorganization of states under the States Reorganisation Act.
Navy plans to get undersea chariots, made in India, for special operations (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is planning to acquire indigenously made swimmer delivery vehicles — also known as underwater chariots and midget submarines — as part of efforts to modernise and strengthen the capabilities of its Marine Commandos (MARCOS) for special undersea operations.
News Summary:
- In a strategic move, the Indian Navy set to deploy domestically manufactured undersea chariots for specialized operations.
- These innovative vessels, designed to accommodate a crew of at least six, will be equipped with cutting-edge lithium-ion batteries for enhanced performance.
- The significant size of these undersea chariots opens up new possibilities, allowing divers to transport larger cylinders.
- This advancement translates to extended underwater missions, thereby amplifying operational capabilities in shallow waters.
- Moreover, the spacious design of these chariots facilitates the carriage of extra weaponry, providing the Navy with increased flexibility for diverse and complex operations.
- This development signifies a noteworthy stride in bolstering the Navy's underwater capabilities through indigenous technological advancements.
What are Chariots?
- Nearly all modern navies in the world use chariots, which are extremely specialized platforms.
- These self-propelled vehicles can be deployed from ships or submarines, tailored to their size and designated roles.
- Notably, during World War II, manned human torpedoes were commonly referred to as chariots.
- Functionality: Chariots prove invaluable for naval operations in shallow waters, offering a spectrum of missions.
- These include shallow-water surveillance, targeted assaults on adversary coastal installations, and even engagements with ships in harbours.
- Particularly advantageous is their ability to grant marine commandos access to areas close to adversary harbours—locations that submarines, constrained by shallow waters, may find challenging to reach.
- Furthermore, these chariots facilitate the efficient transportation of weapons and equipment to operational zones.
- Utilization in India: While detailed information on the swimmer delivery vehicles employed by the Indian Navy is not widely available, some sources suggest the utilization of Italian-made chariots for several years.
- Around 2012, recognizing the strategic importance of these platforms, the Ministry of Defence entrusted Hindustan Shipyard Limited with the construction of two such submarines, underscoring India's commitment to enhancing its maritime capabilities.
What are Marine Commandos (MARCOS)?
- The Marine Commandos, known by the acronym MARCOS and formally recognized as the Marine Commando Force (MCF), stand as the specialized forces within the Indian Navy entrusted with the execution of special operations.
- Established in February 1987, MARCOS possesses versatile capabilities to operate effectively across diverse environments, encompassing sea, air, and land.
- Over time, the force has accumulated valuable experience, earning an esteemed international reputation for its high level of professionalism.
- MARCOS routinely engage in specialized maritime operations in regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, navigating the Jhelum River and Wular Lake with precision and expertise.
Iberian wolf (DownToEarth)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
As per the regional government, the Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus) has been declared extinct in the historical region of Andalusia, located in the southernmost part of Iberia, since the year 2020.
About the Iberian Wolf:
- The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the Grey wolf, distinguished by its prolonged isolation from other wolf populations for over a century.
- With the largest wolf population in Western Europe, this magnificent species is native to the Iberian Peninsula, encompassing Spain and Portugal.
- Thriving in diverse habitats, Iberian wolves inhabit forests, inland wetlands, shrublands, grasslands, pastures, and mountainous areas.
- These wolves lead a social lifestyle, living, hunting, and traveling in small packs.
- Each pack includes the alpha male and female, along with their young and older offspring.
- The alphas serve as the pack leaders, responsible for establishing territory, selecting den sites, tracking down, and hunting prey.
- Primarily carnivorous, the Iberian wolf's diet comprises various animal species.
- With regard to conservation, the Iberian wolf holds the status of "Vulnerable" according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Schemer (Indian Express)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry has recently announced a fresh target for its PM SVANidhi scheme, focusing on empowering street vendors.
About PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme:
- Launched on June 01, 2020, by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the PM SVANidhi Scheme aims to assist street vendors affected by the Covid-19 lockdown in reviving their livelihoods.
- As a micro-credit initiative, it provides street vendors with a collateral-free loan of Rs. 10,000 at a low-interest rate (below 12%) for one year, facilitating their financial recovery.
- Originally scheduled until March 2022, the scheme has now been extended till December 2024 with a focus on expanding the affordable loan corpus, encouraging digital transactions, and promoting holistic socio-economic development for street vendors and their families.
- Eligibility for the loan requires street vendors who were vending on or before March 24, 2020, and hold a certificate of vending issued by the Town Vending Committees (comprising local authorities and vendors) after conducting a survey.
- The scheme offers several benefits, including an interest subsidy of 7% per annum on timely loan repayment, no penalty on early repayment, cash back incentives up to Rs. 100 per month to promote digital transactions, and the possibility of credit limit escalation for prompt loan repayment.
- The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) serves as the implementation agency for the scheme, ensuring efficient delivery and monitoring of financial support to street vendors across the country.
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) (Indian Express)
- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Telangana High Court's division bench recently conveyed its discontentment over the absence of specific information regarding measures taken to manage the outbreak of Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in cattle.
What is Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD):
- Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a highly infectious viral disease that affects cattle, ranging from acute to chronic in nature.
- It is caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), belonging to the genus Capripoxvirus within the poxviridae family (related to smallpox and monkeypox viruses), but it is not zoonotic, meaning it does not spread to humans.
- Symptoms of LSD include the enlargement of lymph nodes, resulting in lumps on the cattle's skin, primarily appearing on the head, neck, limbs, udder, genitalia, and perineum.
- The cutaneous nodules, usually 2–5 cm in diameter, may develop into ulcers and scabs over time.
- Other signs of infection include high fever, reduced milk yield, nasal and ocular discharge, salivation, loss of appetite, depression, damaged hides, emaciation, infertility, and abortions.
- Transmission occurs through blood-feeding insects such as certain flies, mosquitoes, and ticks, as well as the movement of affected animals and contaminated equipment.
- Direct animal-to-animal transmission can also occur in some cases.
- While no direct antiviral treatment is available for LSD, supportive care is provided to infected animals, including the use of antibiotics, painkillers, and wound care sprays to alleviate symptoms.
- Vaccines are used to control disease transmission, as there is no specific cure.
- LSD is economically significant as it can lead to temporary reductions in milk production, temporary or permanent sterility in bulls, hide damage, and, in some instances, fatalities among the affected cattle population.
ZARTH App (The Hindu)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Center for Data-Driven Discovery at the California Institute of Technology has recently unveiled the ZARTH app, enabling smartphone users to actively search for transients.
What is ZARTH App?
ZARTH (ZTF Augmented Reality Transient Hunter) combines the excitement of an augmented reality mobile game with serious scientific pursuits. This innovative app empowers users to engage in real science while enjoying a gaming experience.
Key Features:
- Leveraging the open-source Sky Map, the ZARTH app integrates daily data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) at California's Palomar Observatory.
- The Palomar Observatory houses the prestigious 200-inch Hale reflector, one of the world's oldest and most powerful telescopes.
- The ZTF conducts bi-daily scans of the entire northern sky, generating crucial large-area sky maps with applications in tracking near-earth asteroids and studying supernovae.
- Each day, the ZARTH app receives real-time data on transients detected by the ZTF, including flaring stars, white dwarf binaries, active galactic nuclei, and other intriguing types.
- Transients are ranked based on rarity and significance, fostering a competitive environment among players who strive to earn points and daily credits displayed on leaderboards.
Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023, has been successfully passed by the Lok Sabha.
The Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
It seeks to amend the existing Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, to regulate mining activities in India's maritime zones.
The key highlights of the Bill include:
- Reservation of Offshore Areas: The government is empowered to reserve offshore areas not under any operating rights.
- Composite Licence and Production Lease: The administering authority can grant composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Fixed Production Lease Period: The provision for renewal of production leases is removed, and a fixed period of fifty years, akin to the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act 1957, is introduced.
- Auction-Based Allocation: Private sector entities can acquire production leases through auction by competitive bidding.
- Operating Rights for Government Entities: Operating rights without competitive bidding can be granted to government or government companies or corporations in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government.
- Atomic Minerals: For atomic minerals, exploration licenses or production leases can only be granted to the government or government corporations.
- Production Commencement Timeline: A four-year timeline for production commencement and dispatch after the execution of composite licenses or production leases is introduced, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement of production and dispatch after discontinuation.
- Framing Rules for Conservation and Environment: The central government is enabled to establish rules for mineral conservation and systematic development in offshore areas, along with measures to protect the environment and control pollution resulting from exploration or production operations.
eSanjeevani (India's Integrated Telemedicine Solution ) (Indian Express)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Health Minister revealed to the Rajya Sabha that the eSanjeevani telemedicine application, introduced by the Centre, has successfully conducted a remarkable 14,17,81,384 teleconsultations.
About eSanjeevani:
- eSanjeevani is an integrated telemedicine solution, hosted on the cloud, developed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- This telemedicine app facilitates seamless communication between doctors and patients as well as doctor-to-doctor interactions.
- The Centre for Development and Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Mohali, is responsible for the design, development, deployment, and maintenance of this platform.
- The eSanjeevani system consists of two essential modules:
- eSanjeevani AB-HWC:
- This module serves as a doctor-to-doctor telemedicine platform, strategically implemented across all Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) in the country under the Ayushman Bharat Scheme.
- It operates on a Hub-and-Spoke model, with zonal hubs comprising MBBS/Specialty/Super-Specialty doctors connected to state-level Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centers.
- eSanjeevani OPD:
- Rolled out in 2020 during the initial Covid-19 lockdown when outpatient departments (OPDs) were closed, this module enables patient-to-doctor remote consultations.
- People can access outpatient services from the comfort of their homes, ensuring healthcare accessibility during challenging times.
- eSanjeevani represents a significant step towards enhancing healthcare accessibility and digital healthcare services across India.
Infrastructure investment trust (InvIT) (Business Standard)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The government is actively developing a proposal to introduce a new Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) dedicated to national highways. This initiative aims to enable domestic retail investors to own units of the trust, expanding opportunities for individual investors to participate in highway infrastructure projects.
What is Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)?
- An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) functions as a Collective Investment Scheme, offering a pathway for both individual and institutional investors to directly invest in diverse infrastructure projects.
- Operating akin to mutual funds, InvITs are established as trusts and undergo registration with Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
- InvITs involve four key parties:
- the Trustee, Sponsor(s), Investment Manager, and Project Manager. The Sebi-certified Trustee assumes the crucial role of overseeing the InvIT's performance. Meanwhile, the Sponsor(s) act as the company's promoters responsible for creating and setting up the InvIT.
- Overall, InvITs present an attractive investment option, as they allow investors to participate in the development of vital infrastructure projects while enjoying the benefits of a collective investment structure similar to mutual funds.
What is NHAI InvIT?
- NHAI InvIT is an infrastructure investment trust proudly sponsored by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) to bolster the government's National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) initiative.
- This Trust has been established by NHAI in accordance with the Indian Trusts Act, of 1882, and adheres to the regulations set forth by SEBI (Security and Exchange Board of India).
- The NHAI InvIT plays a vital role in supporting the nation's infrastructure development by providing a platform for investors to participate in highway projects' growth and monetization.
- Through this innovative investment vehicle, NHAI aims to tap into private and institutional investments to enhance the funding and execution of critical infrastructure projects across the country, ultimately contributing to India's overall economic progress.
TransLunar Injection (TLI) (The Hindu)
- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The TransLunar Injection (TLI) was performed successfully from ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru recently.
What is the TransLunar Injection (TLI)?
- TransLunar Injection (TLI) is a crucial space mission maneuver, propelling spacecraft from Earth's orbit to a trajectory aimed at reaching the Moon.
- An essential step in lunar missions, TLI allows spacecraft to break free from Earth's gravity and commence their journey toward the Moon.
- TLI is executed when the spacecraft reaches the perigee, the closest point to Earth in its orbit.
- During TLI, the spacecraft's propulsion system ignites its engines, accelerating the craft and providing the necessary speed to escape Earth's gravitational pull.
- The thrust and duration of the TLI burn are determined by factors like spacecraft mass, Earth's orbital velocity, and specific mission objectives.
- Following a successful TLI, the spacecraft is directed onto a lunar trajectory, continuing its autonomous journey to the Moon without further reliance on Earth's propulsion.
- Subsequent to TLI, the spacecraft enters a transfer orbit, an elliptical path that intersects with the Moon's orbit.
- The spacecraft traverses this highly eccentric orbit until it reaches the lunar surface.
- As the spacecraft approaches the Moon, additional maneuvers like lunar orbit insertion (LOI) may be executed to enter lunar orbit or facilitate landing, based on the mission's objectives.
- TLI has been effectively utilized in numerous Moon missions, including Apollo, Chang'e, and Artemis missions.
National Digital Nagrik Forum (Indian Express)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The forum by the Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and help build the capacities of citizens to engage with innovation via expert sessions and instructional materials.
About the National Digital Nagrik Forum:
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum is an online platform with the primary goal of advancing the rights of traders, consumers, and various sections of society, while also influencing policy to foster the growth of the digital trade economy.
- Through expert sessions and instructional materials, the forum aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and empower citizens to engage with innovation effectively.
- The main objective is to shape policy discourse around the digital economy trade in India, aligning with the Government of India's vision of establishing a trillion-dollar digital economy.
- Simultaneously, it seeks to maintain an open, safe, trusted, and accountable Internet ecosystem.
- The forum will conduct awareness camps, digital and physical dialogues, and training sessions.
- It will also engage in targeted outreach to stakeholders from the government, private sector, and civil society.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum will concentrate on five core themes:
- The first pillar focuses on consumer protection and online safety, with a central emphasis on efficient grievance redressal mechanisms.
- The second pillar addresses the challenges of digital cartelization, advocating for a level-playing field to discourage discriminatory and anti-competitive practices in the online world.
- The third pillar explores the potential of Indian digital technologies to transform retail and industrial trade, while also contributing to employment growth and expanding investment opportunities.
- The fourth pillar advocates for a first principles-based taxation policy that fosters certainty and productivity, especially for sectors with high growth potential. It simultaneously works to prevent illegal activities like tax evasion and money laundering.
- The fifth pillar conducts research on emerging technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence to assess their impact on retail trade and ensure the protection of consumers' interests.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum aims to make significant contributions towards shaping a vibrant digital economy in India, fostering fair trade practices, and safeguarding the interests of both consumers and traders.
Room-temperature Superconductor (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Korean researchers claim to have developed a superconductor that can operate at room temperature and ambient pressure.
What have the researchers developed?
- The researchers assert that they have created a superconductor named LK-99, which operates at room temperature and under ambient pressure.
- LK-99 is a combination of powdered compounds containing lead, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus.
- Upon heating at extremely high temperatures, it transforms into a dark grey solid.
- The potential significance of this discovery is immense, provided other laboratories can replicate these results.
- Nevertheless, some researchers remain skeptical as this study has not undergone peer review, and the results must be independently reproduced by other scientific groups.
What is a Superconductor?
- A superconductor is a material that exhibits superconductivity, a unique state of matter characterized by the absence of electrical resistance and the exclusion of magnetic fields.
- In a superconductor, an electric current can flow indefinitely without any hindrance.
- Superconductors have significant practical applications in our everyday lives.
- In 1933, Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered that superconductors act as perfect diamagnets, repelling magnetic fields, a phenomenon known as the Meissner effect.
- This property makes them ideal for applications like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- However, achieving superconductivity typically requires extremely low temperatures.
- Currently, researchers are actively exploring and developing superconductors that can operate at room temperature, a groundbreaking advancement that would revolutionize various technologies and industries.
How will the room-temperature superconductors help?
- The use of room-temperature superconductors can offer significant benefits in various applications.
- Typically, the critical temperature of conventional superconductors is below 10 Kelvin (-263 degrees Celsius), whereas room temperature is around 20-22°C.
- By having superconductors that function at room temperature, the cost of electricity grids, computer chips, magnets for maglev trains, energy-storage devices, and fusion reactors can be reduced significantly.
- This is achieved through electricity and cost savings on coolants, as the need for extreme cooling methods is eliminated.
- The widespread adoption of room-temperature superconductors holds the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA) (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
During the Man ki Baat program, the Prime Minister announced that India achieved a remarkable feat by destroying 10 lakh kilograms of drugs worth ?12,000 crore in the previous year.
What is Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA)?
- Launched on: The NMBA was launched on 15th August 2020.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment oversees the implementation of NMBA.
- Aim: The primary objective of NMBA is to raise awareness about the harmful consequences of substance abuse, with a special focus on youth, women, and children.
- It aims to reach out to higher education institutes, university campuses, schools, and the broader community, encouraging community involvement and ownership of the initiative.
- Implementation: NMBA is implemented in 372 vulnerable districts, identified based on the findings of the first Comprehensive National Survey and inputs from the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Significance:
- NMBA targets and engages various stakeholders directly or indirectly affected by substance abuse, as well as those vulnerable to it.
- The major beneficiaries of NMBA include youth, women, children, educational institutions, civil society, and the community at large.
- This approach emphasizes community involvement rather than just organizational participation in addressing the issue of substance abuse.
Cell-free DNA (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Over the past two decades, as genome sequencing technologies have become increasingly accessible, scientists have made significant strides in understanding the applications of Cell-free DNA.
Regarding Cell-free DNA:
- In the human body, a significant portion of the DNA in the genome is safely enclosed within cells, safeguarded by specific proteins to prevent degradation.
- However, in various circumstances, certain DNA fragments are liberated from their confines and can be found outside the cells, circulating in body fluids.
- These minute fragments of nucleic acids are commonly referred to as cell-free DNA (cfDNA).
How Cell-free DNA is generated/released?
- The generation and release of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can occur through various mechanisms.
- One such process is when a cell undergoes cell death, leading to the degradation of nucleic acids and subsequent release of cfDNA.
- The degradation of cfDNA is influenced by a diverse set of processes, resulting in variations in the amount, size, and origin of cfDNA.
- Furthermore, this release of cfDNA can be associated with different biological processes, including those essential for normal development, the progression of certain cancers, and various other diseases.
- The generation and release of cfDNA can be triggered by a range of situations and processes, making it a versatile biomarker with potential implications in various health conditions.
Applications of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA):
- One of the most prevalent uses of cfDNA is in non-invasive prenatal testing, where it aids in screening fetuses for specific chromosomal abnormalities.
- Also, cfDNA serves as a valuable tool for comprehending human diseases and leveraging this knowledge to enhance diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis.
- cfDNA plays a crucial role in understanding the rejection of transplanted organs by the body.
- It shows promise as a potential biomarker for various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, neuronal tumors, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.
Cocos (Keeling) Islands (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A maritime patrol aircraft from the Indian Navy and a transport aircraft from the Indian Air Force (IAF) made a visit to Australia's Cocos (Keeling) Islands (CKI) recently.
About Cocos (Keeling) Islands:
- Location:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are situated in the eastern Indian Ocean, approximately 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) northwest of the Australian city of Perth.
- Geography:
- Comprising coral atolls and islands, the archipelago includes North Keeling Island and the South Keeling Islands.
- Administrative Headquarters:
- The territory's administrative headquarters are located on West Island, situated in the southern atoll.
- Climate:
- The islands experience a warm and humid climate.
- Vegetation:
- The predominant vegetation consists of coconut palms, which were previously cultivated for copra on plantations.
- On North Keeling and Horsburgh islands, coarse grass serves as the primary ground cover.
- National Park:
- The northern atoll is home to Australia's most remote Commonwealth National Park, known as the Pulu Keeling National Park.
- Inhabitants:
- The population of the islands mainly comprises descendants of the original plantation workers, predominantly of Malay origin.
- Administration:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are governed by an administrator appointed by the Australian governor-general. The islands became an Australian territory under the Cocos (Keeling) Islands Act 1955.
Worldcoin Project (The Hindu)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent announcement, the CEO of OpenAI officially reintroduced his Worldcoin project, which had previously taken a backseat to the widespread popularity of ChatGPT.
What is Worldcoin Project?
- The Worldcoin Project aims to establish a digital network that enables everyone to participate and claim some form of stake in the digital economy.
- The project operates on a straightforward model:
- Individuals can prove their uniqueness as humans by allowing their eyes to be scanned, and in return, they receive a cryptocurrency reward and an identification called a "World ID."
- Worldcoin relies on a device called "Orb," which is used by volunteers known as "Orb operators."
- These operators scan a person's iris pattern to collect their biometric data and facilitate the issuance of a World ID through the World app.
- Participants who have been scanned can use the World app to receive the Worldcoin cryptocurrency at regular intervals or engage in transactions using their World ID wherever applicable.
- This process, known as "proof of personhood," ensures that individuals cannot register multiple times to gain more crypto rewards.
Voyager 2 Spacecraft (HT)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
NASA’'s Voyager 2 spacecraft, which is venturing through space between stars, faces communication problems due to antenna misalignment. .
About Voyager 2 Spacecraft:
- Voyager 2 is an iconic interplanetary spacecraft launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, with the primary objective of exploring the outer planets of our solar system.
- It is part of the Voyager program, and along with its twin, Voyager 1, it has provided invaluable insights into the distant regions of our cosmic neighborhood.
- The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study various aspects of the planets it encounters, including their atmospheres, magnetic fields, and planetary surfaces.
- Voyager 2 successfully conducted close flybys of Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986, and Neptune in 1989, becoming the first and only spacecraft to visit these four giant gas planets.
- Beyond its initial mission, Voyager 2 continues to be operational and remains in communication with Earth, traveling at an impressive speed of approximately 34,000 miles per hour (55,000 kilometers per hour).
- It has since left the heliosphere, the region influenced by the Sun's magnetic field, and entered interstellar space, becoming the second human-made object to do so after Voyager 1.
- Throughout its journey, Voyager 2 has provided a wealth of data and discoveries about the outer planets and their moons, as well as valuable information about the space environment outside the solar system.
- It has captured breathtaking images of planetary systems, revealing the beauty and complexity of the outer planets and their fascinating moons.
- The spacecraft continues to be a remarkable testament to human ingenuity and curiosity as it ventures farther into the cosmos, providing us with an enduring legacy of exploration and knowledge about our celestial neighbors.
GOBARdhan Initiative (PIB)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Union Minister for Jal Shakti has launched the Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan.
About GOBARdhan Initiative:
- GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) initiative was launched in 2018.
- Aim:
- The primary goal of the initiative is to convert waste to wealth by promoting a circular economy.
- Nodal Ministry:
- The GOBARdhan Initiative is under the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Gobardhan is an integral part of Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) Phase II, focusing on Solid Waste Management.
- Objectives:
- To assist villages in safely managing their cattle and agricultural waste, leading to cleaner villages.
- To help communities convert cattle and organic waste into wealth using treatment systems.
- To transform organic waste, especially cattle waste, into biogas and organic manure for utilization in rural areas.
- To promote environmental sanitation and control vector-borne diseases by effectively disposing of waste in rural regions.
- To create employment and income-generation opportunities in rural areas by involving entrepreneurs, Self-Help Groups (SHGs), and youth groups in setting up, operating, and managing GOBARdhan units.
- Financial Incentive:
- The Government of India provides technical assistance and financial support of up to 50 lakhs for each district to achieve the safe disposal of cattle and organic waste as part of the initiative.
ULLAS Initiative (PIB)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In New Delhi, the logo, slogan "Jan Jan Sakshar," and mobile application of ULLAS were recently unveiled by Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, the Union Minister of Education and Minister of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
About the ULLAS Initiative:
- The ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society) initiative, holds the potential to revolutionize education and literacy nationwide.
- Its primary objective is to create a learning ecosystem that reaches every individual, bridging the gaps in basic literacy and essential life skills.
- Targeting citizens aged 15 and above who missed the opportunity to attend formal schooling, the initiative imparts basic education, digital and financial literacy, and critical life skills.
- Implementation is driven by volunteerism, emphasizing community participation.
- The slogan of the initiative is "ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram."
- To support its goals, the ULLAS app was launched, designed with user-friendliness and interactivity in mind.
- Available on both Android and iOS platforms, the app serves as a digital gateway for learners to access a diverse range of learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
- The ULLAS app facilitates the registration of learners and volunteers, either through self-registration or with the assistance of surveyors.
- Significance:
- This app plays a crucial role in promoting functional literacy, vocational skills, and vital life skills such as financial literacy, legal literacy, digital literacy, and empowering citizens to actively participate in nation-building efforts.
- Furthermore, the ULLAS Initiative nurtures a culture of continuous learning and knowledge-sharing within communities across India, fostering a brighter future for the nation.
Parkachik Glacier (Indian Express)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
According to a recent study by scientists from the Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, the rapid ice melt of the Parkachik Glacier in Ladakh is anticipated to lead to the formation of three glacial lakes.
Regarding the Parkachik Glacier:
- The Parkachik Glacier, stretching 14 km in length and covering approximately 53 square km, stands as one of the largest glaciers in the Suru River valley.
- This valley is situated within the southern Zanskar Ranges of the western Himalayas.
- The glacier's accelerated melting can be attributed to two primary factors.
- Firstly, the effects of global warming and rising temperatures in the area contribute to this phenomenon.
- Secondly, its lower altitude compared to other glaciers in the Zanskar region also plays a significant role in the rapid melting process.
- Also, its relatively lower altitude compared to other glaciers in the Zanskar region contributes to its vulnerability to melting.
Important details about the Zanskar Ranges:
- Location:
- Zanskar is a high-altitude semi-desert situated on the Northern flank of the Great Himalayan Range.
- Climatic Influence:
- The Zanskar Ranges serve as a climatic barrier, shielding Ladakh and Zanskar from much of the monsoon weather. Consequently, the region experiences a pleasantly warm and dry climate during the summer months.
- Flora:
- The lower reaches of Zanskar's valleys harbor most of its vegetation, primarily consisting of alpine and tundra species.
- Fauna:
- Zanskar is home to diverse wildlife, including marmots, bears, wolves, snow leopards, kiangs (Tibetan wild asses), bharals (Himalayan blue sheep), alpine Ibex, wild sheep and goats, and the impressive lammergeier, also known as the bearded vulture.
National Coal Index (AIR)
- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Coal Index (NCI) has shown a significant decline of 33.8 per cent in May this year at 157.7 points compared to May last when it was at 238.3 points. It indicates a strong supply of coal in the market, with sufficient availability to meet the growing demands.
About National Coal Index:
- Launch Date:
- The National Coal Index was introduced in the year 2020.
- Ministry:
- Developed under the purview of the Ministry of Coal, India.
- The esteemed Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata, played a key role in creating the index as part of India's transition away from coal.
- Price Index:
- It serves as a price index, reflecting changes in the price level of coal during a specific month relative to the fixed base year.
- Objective:
- The primary objective of the National Coal Index is to offer an accurate reflection of the market price of coal.
- Base Year:
- The base year for the index is 2017-18.
- Inclusive Prices:
- The price index amalgamates coal prices from various sales channels, including Notified Prices, Auction Prices, and Import Prices.
- The National Coal Index combines coal prices from all sales channels, including notified prices, auction prices and import prices.
- It serves as a reliable indicator of market dynamics, providing valuable insights into coal price fluctuations.
- The National Coal Index (NCI) has shown a significant decline of 33.8% in May 2023 compared to May 2022, which suggests significant reduction in coal prices.
- This indicates a strong supply of coal in the market, with sufficient availability to meet the growing demands.
Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) (Indian Express)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Union Environment, Forest and Climate Change Minister Bhupender Yadav on Thursday launched a Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC), conceptualised under India’s G20 Presidency, to promote the practices of resource efficiency and circular economy globally.
About Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC):
- RECEIC was launched in 2023 at Chennai, Tamil Nadu, with the honorable presence of Shri Bhupender Yadav, Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- The launch event witnessed the participation of distinguished guests, including the Commissioner on Environment from the European Union and esteemed Ministers from Canada, France, Italy, Denmark, Mauritius, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Industry-Driven Initiative:
- RECEIC is an industry-led initiative with a primary goal of fostering global resource efficiency and circular economy practices.
- Embracing the circular economy model, RECEIC promotes production and consumption practices involving sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to maximize their utility.
- Sustainable Impact:
- The coalition is envisioned to be a self-sustaining entity, committed to lasting environmental sustainability, beyond India's G20 Presidency.
- Founding Members:
- With 39 companies headquartered in 11 different countries, the coalition boasts a diverse group of founding members.
- As a collaborative platform, RECEIC fosters knowledge-sharing, best practice exchange, and the adoption of sustainable approaches among participating industries.
Millipede species (India Today)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent discovery, a previously unknown species of millipede was found dwelling beneath the city of Los Angeles, United States.
About Millipede Species:
- The recently discovered species belongs to the category of thread Millipedes.
- It measures approximately the length of a paperclip but is as slim as pencil lead.
- Scientifically identified as Illacme socal, this millipede is translucent and displays sinuous movements akin to a jellyfish tentacle.
- The creature's habitat lies about four inches beneath the ground, where it burrows and secretes distinctive chemicals, exhibiting unique behavior.
- Remarkably, this millipede is blind and relies on hornlike antennas extending from its head to navigate its surroundings.
What are Millipedes?
- Millipedes belong to the arthropod class Diplopoda, placing them in the same group as centipedes.
- These invertebrates exhibit a cylindrical or slightly flattened body structure.
- Despite their name, "millipede," which translates to "a thousand feet," these creatures do not actually have a thousand feet. However, they possess numerous legs on their bodies.
- The millipede's body is segmented, and each segment carries two sets of legs attached to the underside.
- Diet-wise, millipedes are detritivores, subsisting on dead organic matter found in the earth, such as damp wood pieces, decaying leaves, and other materials that are naturally present in their moist underground habitat.
Rare ‘Ureilite’ Meteorite (Weather Channel)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a team of scientists from Allahabad University and the University of Bern, Switzerland, made an intriguing discovery. They unveiled that the Dhala crater was formed by the impact of an exceedingly uncommon and ancient meteorite called Ureilite.
Key Facts About Ureilite:
- Ureilite is an extraordinary type of meteorite, characterized by its rarity, making up only a minuscule portion of the meteorites found on Earth.
- The name "Ureilite" originates from the location of its first discovery, the Novo Urei village in Russia.
- Composition:
- Ureilites are primarily composed of silicate rock, with olivine and pyroxene being the dominant minerals.
- They also contain a smaller fraction of carbon, which can be in the form of either diamond or graphite, along with metal sulphides and a few fine-grained silicates.
- Elongated cavities are commonly found, typically oriented in the same direction.
- Lack of Chondrules:
- Unlike many other stony meteorites, ureilites do not contain chondrules, which are small, spherical grains that formed in the early solar system.
- Primitive Nature:
- Ureilites are regarded as primitive meteorites because their composition closely resembles the material from which the solar system originated.
- Their unique characteristics offer valuable insights into the early stages of our cosmic environment.
About Dhala Crater:
- Dhala Crater holds significance as India's oldest and largest impact crater, with an estimated formation age of approximately 2500 million years.
- Named after the village Dhala, it remains an eroded remnant of the original impact structure.
- Situated in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, the crater boasts an impressive size, spanning a massive 11 km in diameter, making it the largest impact crater in Asia.
Urea Gold (ET)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent event held in Rajasthan's Sikar, the Prime Minister unveiled "Urea Gold," a novel type of Urea fertilizer.
About Urea Gold:
- Urea Gold is an advanced variety of Urea that features a Sulphur coating.
- Its primary purpose is to address soil Sulphur deficiency while also offering cost-saving benefits to farmers.
- In comparison to the existing Neem-coated urea, Urea Gold stands out due to its superior economic viability and efficiency.
- The gradual release of nitrogen facilitated by its Sulphur coating enhances crop uptake, and the inclusion of humic acid extends its fertilizing lifespan.
- Notably, Urea Gold not only acts as a substitute for traditional urea but also contributes to a reduction in overall fertilizer usage.
- According to a report, using 15 kg of Urea Gold can provide comparable benefits to 20 kg of conventional urea, making it a more efficient and effective choice for farmers.
INDIAai (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, INDIAai and Meta India entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to create a collaborative framework for cooperation and partnership in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies.
About INDIAai:
- INDIAai, the National artificial intelligence Portal of India, was launched on 28th May 2020 as a comprehensive platform.
- It serves as a knowledge portal, research organization, and ecosystem-building initiative.
- Its primary aim is to foster unity and encourage collaborations within India's AI ecosystem by bringing together various entities.
- This joint initiative is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and NASSCOM.
- NeGD, established in 2009 under the Digital India Corporation (a not-for-profit company set up by MeitY), plays a crucial role in this venture.
- NASSCOM, a prominent not-for-profit industry association, serves as the apex body for India's IT and IT-enabled products and services sector.
- INDIAai functions as the central knowledge hub for artificial intelligence and related fields, catering to aspiring entrepreneurs, students, professionals, academics, and all other stakeholders in the domain.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science: It involves the development of intelligent machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
- Machine Learning and Algorithms: AI systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data, learn from it, and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
- Applications in various fields: AI finds applications in diverse domains, including natural language processing, image recognition, robotics, healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles, among others. Its goal is to mimic human cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making.
Hike in US Federal Reserve Interest and Impact on Indian Economy (Live Mint)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The US Federal Reserve is expected to raise benchmark rates by 25 bps to the 5.25-5.50 percent range on Wednesday. Investors will be watching for cues on inflation and rate hike trajectory.
About US Federal Reserve:
- The US Federal Reserve, also known as the Fed, serves as the central banking system of the United States, offering a secure, adaptable, and steady monetary and financial framework.
- It operates through 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, each responsible for a designated U.S. geographic area.
- The Fed's primary functions encompass conducting national monetary policy, overseeing and regulating banks, ensuring financial stability, and delivering banking services.
Impacts of US Federal Reserve Interest Hike:
- The US Fed's Significance: As the world's most powerful central bank, the decisions taken by the US Federal Reserve regarding interest rates have significant implications worldwide. These decisions influence both developed and emerging economies across the globe.
- Global Effects: Changes in US interest rates have a ripple effect that extends beyond the nation's borders. The adjustments impact various economies worldwide, leading to shifts in investment patterns and financial flows.
- Appeal of American Assets: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, American assets become more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Consequently, there is a possibility of capital outflows from emerging and riskier markets to the US.
- Impact on Capital-Intensive Sectors: Sectors heavily reliant on Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of a US interest rate hike. The increased cost of borrowing may affect their growth prospects.
- Global Liquidity Tightening: Higher US interest rates can lead to a tightening of global liquidity. Foreign investors may face challenges in obtaining affordable funds, which could have implications for their investment decisions and overall economic activities.
Potential Impacts on the Indian Economy:
- Interest Rate Differential: Following a rate hike by the US Federal Reserve, the gap between interest rates in the US and India narrows, adversely affecting currency trade and financial flows.
- Foreign Investor Response: With higher returns available in the US due to increased interest rates and attractive Dollar and US Treasury yields, foreign investors may be inclined to withdraw investments from the Indian market, leading to capital outflows.
- Currency and RBI Response: The relative strengthening of the US currency (Dollar) makes the Indian rupee weaker, prompting the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to consider a rate hike domestically.
- RBI's Action to Curb Outflows: To mitigate the outflows of funds from Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and safeguard the rupee's stability, the RBI may find it necessary to increase interest rates within India.
- Forex Reserve Management: In the event of a significant decline in the rupee's value, the RBI might be compelled to sell some of its Dollar reserves to support the domestic currency. This action, however, depletes the country's foreign exchange reserves.
Conjunctivitis (India Today)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
India has been witnessing a sharp increase in eye infections, specifically conjunctivitis. Amid heavy rainfall, Delhi and nearby areas have reported multiple cases of conjunctivitis.
About Conjunctivitis:
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as "pink eye," is an inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, which is the thin, clear tissue that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelids. It can affect one or both eyes and is a highly contagious condition.
Causes of Conjunctivitis:
- Bacterial Infection: Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae, can cause bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Viral Infection: Viruses, including adenoviruses, can lead to viral conjunctivitis. This form of conjunctivitis is highly contagious and is often associated with colds or respiratory infections.
- Allergies: Allergic conjunctivitis occurs due to an allergic reaction to substances like pollen, pet dander, dust mites, or certain medications.
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants like smoke, chemicals, or foreign objects in the eye can cause irritant conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis:
- Redness of the eyes
- Watery or thick, yellowish discharge from the eyes
- Itchiness or burning sensation in the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Crusty eyelids or lashes, especially in the morning (more common in bacterial conjunctivitis)
- Swelling of the conjunctiva
- Blurred vision
Treatment:
- The treatment of conjunctivitis depends on its underlying cause:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial infections.
- Viral conjunctivitis: Since it is caused by a virus, antibiotics won't work. The symptoms are often relieved with supportive measures like artificial tears, cold compresses, and good hygiene practices to prevent spreading.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: Avoiding allergens is essential. Antihistamine eye drops or oral medications can help alleviate symptoms.
- Irritant conjunctivitis: Removing the irritant and using artificial tears can help soothe the eyes.
Prevention:
- To prevent the spread of conjunctivitis, one should follow these measures:
- Frequent handwashing.
- Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes.
- Avoid sharing towels, pillowcases, or eye makeup with an infected person.
- Avoid close contact with individuals showing symptoms of conjunctivitis.
Hematene (PIB)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
A new and remarkably efficient optical limiter has been developed by researchers, utilizing a novel 2D material known as 'hematene.'
- About Hematene:
- Nanoflakes of a material called hematene extracted from iron ore have been found capable of withstanding and acting as a shield from high laser intensities.
- Hence it could be used to make devices called optical limiters that can protect sensitive optical equipment from light-induced damage.
- Radiation from laser sources is highly concentrated and powerful and can be detrimental to sensitive equipment such as sensors, detectors, and other optical devices.
- When the input intensity increases optical limiters control the amount of light that passes through, thereby preventing damage to the optical component.
- These devices are often useful in laser technologies, military, telecommunications, aircraft, and scientific research in several ways.
- The MESO (Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices) Group of the Department of Physics, Sanatana Dharma College, Alappuzha, in collaboration with the Ultrafast and Nonlinear Optics Lab of the Raman Research Institute, Bangalore, has come up with a new and highly efficient optical limiter using a novel 2D material, ‘hematene’.
- They found that 2D nanoflakes of hematene, a material extracted from iron ore or hematite are capable of withstanding very high laser intensities, and they exhibited excellent optical limiting of green laser light (532 nm) while maintaining a high linear transmission (about 87%) for low-intensity light.
- The nanoflakes of lateral dimensions less than 10 nm, prepared by applying ultrasonic waves to hematite in a liquid medium ( facile exfoliation process) for a definite period to exfoliate the 2D nanoflakes of hematene were also found to be highly stable after year-long storage under ambient conditions, indicating tremendous potential as an optical limiter for futuristic applications.
- This research work carried out at SD College using the instrumentation facility procured through the Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST) programme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) programme, was recently published in ACS Applied Optical Materials.
Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The synchronization of the 660-MW unit-2 of the 1,320-MW Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) with the electricity grid in Bangladesh was recently announced by the state-owned engineering firm Bharat Heavy Electricals.
- Location:
- It is situated in Rampal, in the Bagerhat district of Bangladesh's Khulna division.
- It will be one of the biggest coal-fired power plants in Bangladesh, along with the Payra Power Plant in Pataukhali, which commenced test production in January 2020.
- Capacity and Cost:
- The power station has a capacity of 1320 MW (2x660 MW) and is estimated to cost around $2 billion.
- Financing Plan:
- The project is being developed under India's tax concessions finance plan, aiming to enhance Bangladesh's national grid by an additional 1320 MW.
- Financed through a £1.3bn ($1.6bn) loan from the Export-Import (EXIM) Bank of India.
- Implementing Entity:
- India’s Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is responsible for constructing the power plant on behalf of Bangladesh-India Friendship Electricity Company Private Limited (BIFPCL).
- Commercial Operation:
- The first unit of the super thermal power plant is expected to commence commercial operation in early October, representing a significant milestone in the growing cooperation between India and Bangladesh in the power industry.
- Future Expansion:
- In the subsequent year, the power plant's Unit-II, also known as the Rampal coal-fired power project, is scheduled for implementation.
Ichamati River (PIB)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Minister of State for Ports, Shipping, and Waterways recently launched the dredging project on National Waterways 44 in the Ichamati River of West Bengal.
About the Ichamati River:
- The Ichamati River crosses both India and Bangladesh.
- It serves as a natural boundary between the two nations India and Bangladesh.
- It has three main sections.
- The longest part originates from the Mathabhanga River, a branch of the Padma River, flowing for 208 kilometers before merging with the Kalindi River near Hasnabad in North 24 Parganas and Debhata in the Satkhira District of Bangladesh.
- Additionally, the Ichhamati River and its tributaries together create a large oxbow lake complex in the North 24-Paraganas district, near Bangaon.
NanoPtA (The Hindu)
- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science's Materials Research Centre (MRC) have recently created a novel enzyme mimic known as NanoPtA.
About NanoPtA:
- The research team at the Materials Research Centre (MRC), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has created a unique platinum-based nanozyme called NanoPtA.
- This nanozyme can be turned into a powder for use in industries.
- When NanoPtA encounters wastewater, the molecule's benzene rings and long alkyl chains engage in multiple non-covalent interactions.
- Individual NanoPtA molecules link together to form tape-like structures that emit light, which is the source of its oxidizing capability.
- In the presence of sunlight, this nanozyme can break down pollutants in wastewater, reducing its toxicity.
- Remarkably, the nanozyme can rapidly degrade even small amounts of common contaminants like phenols and dyes (micromolar levels) within ten minutes when exposed to sunlight.
- The researchers also observed that the NanoPtA complex remained stable for up to 75 days at room temperature.
Applications:
- Besides wastewater treatment, this nanozyme could find applications in healthcare and serve as a valuable diagnostic tool for neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
BlueWalker 3 Satellite (The Hindu)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international team of scientists has recently published a paper that explains how the prototype BlueWalker 3 satellite has affected the field of astronomy.
About the BlueWalker 3 satellite:
- The BlueWalker 3 satellite is a prototype that's part of a constellation owned by AST SpaceMobile.
- Launched in September 2022, it's notable for being one of the brightest objects in the night sky, even outshining the brightest stars.
- This satellite represents the largest-ever commercial communications array in low-Earth orbit, specifically designed to directly communicate with cellular devices at 5G speeds using 3GPP standard frequencies.
- Interestingly, the satellite operates at wavelengths close to those observed by radio telescopes, which could potentially interfere with radio astronomy.
Yak Churpi (TOI)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Arunachal Pradesh, a northeastern state, achieved a noteworthy milestone as the distinctive and culturally important yak milk product known as 'Yak Churpi' has received the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About 'Yak Churpi':
- Yak Churpi is a special dairy product crafted from the milk of the indigenous Arunachali yak breed.
- It's produced by Brokpas, tribal yak herders who migrate with their yaks to higher altitudes (above 10,000 ft) during summers and return to mid-altitude mountainous areas in winters.
- These exceptional yaks are primarily found in the West Kameng and Tawang districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Churpi is a naturally fermented dairy item with a high protein content.
- It plays a vital role in the diets of tribal communities living in the cold, mountainous regions of the state.
- It's often used as a vegetable substitute and is a common ingredient in vegetable and meat dishes, frequently enjoyed with rice.
- The GI tag for Yak Churpi has significant benefits, including the conservation of yaks and the improvement of the socio-economic status of yak herders.
- Arunachali yaks are unique in terms of their body characteristics, size, strain, and weight, making them the only registered yak breed in India.
National Turmeric Board (NTB) (PIB)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Government of India recently announced the formation of the National Turmeric Board.
About the National Turmeric Board:
- The National Turmeric Board has a specific focus on developing and expanding turmeric and its products in India.
- It's especially dedicated to helping turmeric growers improve their skills and capabilities to add more value to their products.
- The Board also works to ensure high-quality and safe turmeric products.
- The composition of the Board includes a Chairperson appointed by the Central Government, members from various government departments such as AYUSH, Pharmaceuticals, Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Commerce & Industry, as well as senior representatives from three states (on a rotational basis).
- Additionally, it includes representatives from national/state research institutions, turmeric farmers, and exporters.
- The Department of Commerce appoints a Secretary for the Board, and this department provides funds and infrastructure support.
- The NTB's main responsibilities include boosting demand, production, research, market connections, and exports related to turmeric.
PM Modi flags off RRTS: What is this mass transport system, and how it can benefit NCR (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The inauguration of the first segment of India's Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS), the country's inaugural mass rapid transit system designed for regional connectivity, will be officiated by the Prime Minister of India.
About the Regional Rapid Transit System:
- The RRTS is an integrated mass transit network with semi-high-speed rail connectivity at its core.
- It aims to promote "balanced and sustainable urban development" throughout the National Capital Region (NCR) by improving connectivity and access.
- The National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC), a joint venture of the Central government and the governments of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, is building it.
- It is modeled after systems such as Paris' RER, Regional-Express trains in Germany and Austria, and SEPTA Regional Rail in the United States, among others.
- The project will develop eight corridors, three of which are currently under construction:
- the 82-kilometer Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut,
- the 164-kilometer Delhi-Gurugram-SNB-Alwar, and
- the 103-kilometer Delhi-Panipat corridors
- The importance of this system:
- The RRTS network is faster when compared to metros
- It will serve commuters who need to cover relatively longer distances across the NCR in a short amount of time.
- When compared to Indian Railways, the RRTS train will cover shorter distances but at a higher frequency and with greater comfort than the average railway coach.
List Niemann-Pick as a rare disease, parents of young patients (TOI)
- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, parents of children with Niemann-Pick disease urged the Union government to notify the disease under the National Policy for Rare Diseases.
About Niemann-Pick Disease:
Niemann-Pick Disease is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the buildup of harmful substances in the body's cells and organs.
- Genetic Basis: It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that both parents must carry a mutated gene for their child to develop the disease.
- Types: There are several types of Niemann-Pick Disease, with types A and B being more common and types C and D being rarer.
- Lipid Accumulation: The disease is primarily characterized by the abnormal accumulation of lipids, specifically sphingomyelin, in various tissues and organs.
- Symptoms: Symptoms vary depending on the specific type of Niemann-Pick Disease but can include hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen), neurological problems, and lung issues.
- Type A: Niemann-Pick Disease Type A typically presents in infancy and can lead to severe neurological problems, making it a life-limiting condition.
- Type B: Niemann-Pick Disease Type B generally has a later onset and primarily affects the liver and spleen, with milder or absent neurological symptoms.
- Type C and D: Type C and D are characterized by cholesterol metabolism issues and can lead to neurological symptoms.
- Type C, in particular, can present with cognitive decline and movement problems.
- Treatment: There is currently no cure for Niemann-Pick Disease, but treatments aim to manage symptoms and may include enzyme replacement therapy, medications, and supportive care.
Niemann-Pick Disease is a complex condition with various subtypes, and the severity and specific symptoms can differ significantly among affected individuals.
Mangaluru | Archaeologist discovers inscription announcing the death of King KulashekaraAlupendra I at Someshwara (The Hindu)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent archaeological exploration at Someshwara near Mangaluru, Karnataka, archaeologists unearthed a rare inscription related to the Alupa dynasty.
About the Someshwara inscription:
- This inscription holds great importance in understanding Tuluva history and culture.
- It features two panels on top, with the first line carved between them.
- The rest of the inscription, inscribed below the panels in Kannada script and the language of 12th century characters, announces Alupendra I's death.
- The human figures depicted in the inscription are KulashekaraAlupendra.
- He is depicted in the first figure standing in Tribhanga (tri-bent stance).
- He is holding a sword in his right hand and a gurani (shield) in his left.
- The King is represented in a sitting posture on a mound to the left of this panel, separated by a pillar, resting both palms on the center of his legs in dhyana mudra.
About the Alupa dynasty:
- The Alupa dynasty, active from the 2nd to the 15th century CE, ruled over Alvakheda Arusasira in the coastal regions of modern Karnataka.
- Initially independent, they later became vassals to powers like the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and Hoysalas due to shifting politics in Southern India.
- They practiced matrilineal inheritance.
- Their descendants, known as the Bunt, continue to follow this system and bear surnames like Shetty, Rai, Hegde, Alva, and Chowta.
- While most are Hindus, some still follow Jainism.
- The last Alupa king, Kulasekharadeva Alupendradeva, is documented through a 1444 CE inscription in Mudabidri's Jain Basadi.
ISRO’s Gaganyaan TV-D1 test flight tomorrow: Everything you need to know (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is preparing to launch its first-ever test flight, TV-D1, for the Gaganyaan mission, marking a watershed moment in the country's pursuit of human spaceflight.
About the TV-D1 Mission:
- Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) will assess the crew module's readiness for the Gaganyaan mission.
- It is a single-stage liquid rocket designed specifically for this abort mission.
- The payloads include the Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES) with their fast-acting solid motors, as well as the CM fairing (CMF) and Interface Adapters.
- This flight will simulate the abort condition encountered during the Gaganyaan mission's ascent trajectory, which corresponds to a Mach number of 1.2.
- The Crew Escape System is designed to operate automatically at various altitudes if the onboard computer detects any problems.
One nation, one student: Educationists apprehensive of APAAR student ID card scheme (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
In accordance with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, the Union Education Ministry has recently established the concept of 'One Nation, One Student ID,' referred to as APAAR ID.
About Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) ID:
- The Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry, or APAAR ID, is a digital identification system used by students in India.
- Academic qualifications, credit scores, certificates, and other academic data for students from pre-primary to higher education will be digitally stored.
- Students must obtain their parent’s consent to enroll in the APAAR ID system, and states have been directed to begin this process.
- The unique 12-digit APAAR ID will be used for admissions and other academic activities, making it more convenient for students.
- Both new and returning users can register or log in using their mobile number, Aadhar Card, or ID and password.
- This initiative seeks to unify the educational system, improve security, and make academic data more easily accessible to students.
Lok Sabha passes Advocates (Amendment) Bill to weed out touts from court complexes(The Hindu)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently passed a Bill that seeks to regulate the legal profession by targeting “touts”, with Law Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal asserting there should be no role of such persons in courts.
About the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- The Rajya Sabha introduced the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023, in August 2023.
- This bill amends the Advocates Act of 1961, specifically repealing certain sections related to touts under the Legal Practitioners Act of 1879.
- The 1961 Act consolidates laws regarding legal practitioners and establishes Bar Councils and the All-India Bar.
- Having already passed in the Rajya Sabha during the Monsoon Session, the bill aims to regulate the legal profession through a single act with a focus on addressing the issue of touts.
Key Features of the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- Touts: High Courts, district judges, sessions judges, district magistrates, and revenue officers are empowered to create and publish lists of touts.
- A tout is defined as a person who either seeks or secures the employment of a legal practitioner in legal matters for payment or frequents specific locations to obtain such employment.
- The Court or judge has the authority to bar any person listed as a tout from the premises of the Court.
- Preparation of Lists: Authorities with the power to create tout lists may instruct subordinate courts to conduct inquiries into individuals suspected or alleged to be touts.
- If proven, the person's name can be included in the list, ensuring due process is followed before inclusion.
- Penalty: Individuals acting as touts while being listed can face imprisonment up to three months, a fine up to Rs 500, or both.
Will India reassess its position on China-backed Asian trade bloc RCEP? (Business Standard)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is keeping a watchful eye on its neighbour countries’ recent deliberations to join the China-backed Asian trade bloc, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), although the government is yet to “re-evaluate” the position it took four years ago.
What is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)?
- RCEP, or the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, is a proposed agreement involving ASEAN member states and their free trade agreement partners.
- Introduced in 2011, negotiations started in 2012, aiming to finalize the deal by November 2019.
- After the withdrawal of India, there are 15 members of RCEP, which includes 10 ASEAN countries and 5 other countries, namely:
- Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- RCEP's objective is to establish an integrated market, facilitating the availability of products and services across the region.
- The negotiations cover trade, investment, intellectual property, dispute settlement, e-commerce, SMEs, and economic cooperation.
- Initially proposed by Beijing in 2012 to counter the Trans-Pacific Partnership, RCEP became a key tool for China after the U.S. withdrew from the TPP in 2016.
- India chose not to sign the RCEP in 2019 due to concerns about its industries competing with China and potential flooding of Indian markets.
- Despite some sectors anticipating gains, India emphasized the need for a deal favorable to all countries and sectors.
SC pulls up Bhopal municipal corporation for flouting Solid Waste Management Rules (DownToEarth)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
There is non-compliance with the provision of the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 by the Bhopal Municipal Corporation, the Supreme Court observed December 1, 2023 after going through the affidavit filed by the corporation.
What is About Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)?
- The Supreme Court of India, in 2001, mandated the creation of the Compensatory Afforestation Fund and the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- Initially, an ad-hoc CAMPA was established in 2006 to manage the Compensatory Afforestation Fund.
- (CAMPA) are meant to promote afforestation and regeneration activities as a way of compensating for forest land diverted to non-forest uses.
- National CAMPA Advisory Council has been established as per orders of The Hon’ble Supreme Court with the following mandate:
- Lay down broad guidelines for State CAMPA.
- Facilitate scientific, technological and other assistance that may be required by State CAMPA.
- Make recommendations to State CAMPA based on a review of their plans and programmes.
- Provide a mechanism to State CAMPA to resolve issues of an inter-state or Centre-State character.
CAMPA Act:
- To address the loss of forest area and ensure sustainability, the Government of India introduced the CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority) Act.
- This legislation establishes the National Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of India and a State Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of each state.
- These funds receive payments for compensatory afforestation, net present value of forests (NPV), and other project-specific payments.
- The National Fund gets 10% of these funds, while the State Funds receive the remaining 90%.
- As per the Act, companies diverting forest land must provide alternative land for compensatory afforestation.
- For afforestation purposes, companies are required to pay for planting new trees in the alternative land provided to the state.
Houthi attacks on vessels in Red Sea sound alarm for global trade (Financial Times)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Shipowners have called for more military protection on maritime routes in the Middle East after attacks by Iran-backed rebels in the Red Sea sparked fears of new disruptions to global trade, including of energy supplies.
Key Facts the about Red Sea:
- The Red Sea is a semi-enclosed inlet of the Indian Ocean situated between Africa and Asia.
- It stands out as one of the warmest seas globally.
- Connecting to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean through the Gulf of Aden and Bab El-Mandeb strait to the south, it is divided by the Sinai Peninsula into the Gulf of Aqaba and the Gulf of Suez in the north.
- The Gulf of Suez is linked to the Mediterranean Sea via the famous Suez Canal.
- The Red Sea is bordered by Yemen and Saudi Arabia to the east, while Egypt is to the north and west, and Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti are to the west.
- Covering an area of about 438,000 km2, it stretches approximately 2,250 km.
- The sea's maximum width is 355 km, and its deepest point, the central Suakin Trough, reaches 3,040 m, with an estimated average depth of 490 m.
- Notable islands in the Red Sea include Tiran Island near the mouth of the Gulf of Aqaba and Shadwan Island at the entrance of the Gulf of Suez.
Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric gets GI Tag (Northeast Live)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric has received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag from the Registrar of Geographical Indications in Chennai.
About Lakadong Turmeric:
- Lakadong Turmeric is known as one of the best turmerics in the world and is sourced from a village in Meghalaya’s Jaintia Hills.
- Lakadong, a distinct type of turmeric, is exceptionally abundant in curcumin, with levels ranging from 7-8%, a significant contrast to the typical varieties containing only 2-3% curcumin.
- Curcumin has numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Under the “One District One Product” scheme, Lakadong turmeric gained recognition in the West Jaintia Hills district.
- India produces 78% of the world’s turmeric.
What is One District One Product (ODOP)?
- One District One Product (ODOP) initiative is aimed at fostering balanced regional development across all districts of the country.
- The initiative aims to select, brand, and promote at least One Product from each District (One District - One Product) of the country for enabling holistic socioeconomic growth across all regions.
- The ODOP Initiative has identified a total of 1102 products from 761 districts across the country.
- Under the ODOP initiative, all products have been selected by States/UTs by taking into consideration the existing ecosystem on the ground, products identified under Districts as Export Hubs (DEH), and GI-tagged products.
- The finalized list is communicated to DPIIT by the relevant Department of States/UTs.
- All activities including exhibitions, capacity building, etc. are undertaken at the State/UT and district level, in consultation and coordination with the States/UTs.
Quantum Dots (QDs) (The Hindu)
- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Moungi G. Bawendi, Louis E. Brus, and Alexei I. Ekimov were recently honored with the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their remarkable contributions to the discovery and synthesis of quantum dots.
About Quantum Dots (QDs):
- Quantum dots, often referred to as "artificial atoms," are tiny semiconductor nanoparticles that possess unique optical and electronic properties because of their minuscule size.
- The concept of quantum dots was first theorized in the 1970s and later successfully synthesized in the early 1980s.
- Various semiconductor materials, including cadmium selenide, cadmium sulfide, or indium arsenide, can be utilized to create quantum dots. These nanoparticles exhibit quantum dot properties.
- During the synthesis process, scientists can precisely control the size and composition of quantum dots, allowing for tailored properties suitable for diverse applications.
- Optical Properties: A standout characteristic of quantum dots is their adjustable emission properties. Researchers can finely adjust the wavelength of emitted or absorbed light by manipulating the size of the quantum dot.
- Quantum dots can emit light across the entire visible spectrum and even into the infrared and ultraviolet ranges, providing a broad spectrum of colors for numerous applications.
- The smallest quantum dots emit high-energy waves, resulting in blue light, while larger dots emit lower-energy waves, producing red light, with intermediate sizes generating colors in between.
Applications:
- Displays: Quantum dots are employed in display technology to enhance color and efficiency in devices like TVs, monitors, and other electronics.
- Photovoltaics: Quantum dots can enhance light absorption and energy conversion efficiency in solar cells.
- Biomedical Applications: Due to their small size, quantum dots have versatile applications in areas such as medical imaging, biosensors, and targeted drug delivery.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum dots are under investigation for their potential role in quantum computing as they can function as qubits, the fundamental units of quantum information.
Swamp Deer (NewsOnAIR)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Manas National Park & Tiger Reserve recently shared some good news: The number of swamp deer in the park has increased.
About Swamp deer:
- Swamp deer, also known as barasingha (scientifically called Rucervus duvaucelii), is a type of deer found in the Indian subcontinent.
- They belong to the Cervidae family and are typically spotted in open forests and grasslands across India and Nepal.
- These deer primarily feed on wetland plants and the herbs commonly found in their natural habitat.
- Unfortunately, their population is now limited to isolated areas in Nepal, Assam, and the northern regions of India.
- Swamp deer used to exist in Bangladesh and Pakistan, but they are now extinct in both of these countries.
In the Indian Subcontinent, there are three subspecies of swamp deer:
- Western swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii) found in Nepal.
- Southern swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii branderi) found in central and north India.
- Eastern swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii ranjitsinhi) found in the Kaziranga and Dudhwa National Parks.
In terms of conservation, swamp deer are classified as follows:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
Bojjannakonda (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Central government allocated 7.30 crore rupees to undertake landscaping and develop tourist amenities at the Bojjannakonda site.
About Bojjannakonda:
- Bojjannakonda is situated in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- It was excavated by Alexander Rim in 1906.
- Originally known as ‘Buddhuni konda’ (meaning hill of the Buddha), it eventually came to be known as ‘Bojjannakonda’ over time.
- Approximately 2,000 years ago, Buddhist monks used this hill for their practices.
- During excavations, various artifacts were unearthed, including a gold coin from the Samudra Gupta period, copper coins from the Chalukya king Kubja Vishnu Vardhan, coins from the Andhra Satavahanas, and pottery.
- Bojjannakonda is unique as it reflects features of all three phases of Buddhism: Hinayana, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
- Notable discoveries at the site include a figure of ‘Kalabhairava’ with the head of Lord Ganesha adorned with conch shells and the statue of a Buddhist monk named ‘Harati.’
- There is a large double-storeyed cave on the hill with a rectangular doorway flanked by 'dwarapalakas' on both sides.
- At its center stands a rock-cut stupa on a square platform.
- The northern side of the hill features a series of rock-cut caves and monolithic structures on rock platforms.
- The upper cave has a rectangular doorway, with Buddha figures on either side.
- The prominent attractions for tourists at Bojjannakonda are the imposing figures of the Buddha seated in a meditative posture and the stupa.
- At the hill's summit, there are structural buildings and a vihara (monastery), which are now in ruins.
- To the west of Bojjannakonda lies another hillock called Lingalakonda or Lingalametta, where several monolithic and structural stupas can be found.
- Interestingly, the structures on Lingalametta served as inspiration for the Buddhist temple at Barabodur in Java.
- Similarities between the caves at Bojjannakonda and those in Takshasila suggest Buddhist influences, although the word ‘Sangrama’ was used in Takshasila but not in Andhra Pradesh.
Haploclastus Nilgirinus (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists warned that Haploclastus nilgirinus, a tarantula species, may face endangerment due to habitat loss and the effects of climate change.
About Haploclastus Nilgirinus:
- This tarantula species, known as Haploclastus nilgirinus, is a venomous and rarely seen spider that burrows in the Nilgiri hills of the Western Ghats.
- Notably, there is a significant difference in size between males and females of this species, with the males being considerably smaller.
- The primary threats to Haploclastus nilgirinus are illegal wildlife trade and the impact of climate change.
What is a tarantula?
- Tarantulas are a type of large, hairy spider belonging to the Theraphosidae family.
- They are found all around the world, except for Antarctica.
- These spiders move slowly on their eight hairy legs but are skilled nocturnal predators.
- Adult tarantulas typically measure around five inches (13 centimeters) in length, and when their legs are fully extended, their span can reach up to 11 inches (28 centimeters).
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund collaborated with the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) to launch the India-Japan Fund, which amounts to $600 million.
About the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF):
- NIIF is a fund manager owned by investors and anchored by the Government of India (GoI).
- It collaborates with both global and domestic institutional investors.
- Established in 2015, NIIF is India's first sovereign wealth fund (SWF).
- NIIF plays a vital role in financing infrastructure projects, including greenfield (new), brownfield (existing), and stalled projects.
- The primary objective of NIIF is to maximize its economic impact by investing in various infrastructure-related projects.
There are three types of NIIF funds:
- Master Fund: This fund primarily invests in infrastructure projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power generation.
- It also invests in well-established enterprises operating under long-term agreements in regulated environments with a strong track record.
- Fund of Funds: This category focuses on investing in funds managed by renowned fund managers with a proven track record.
- It acts as an anchor investor, which encourages fund managers to attract more investments from institutional investors.
- Strategic Fund: Registered as an Alternative Fund II under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the Strategic Fund primarily invests in equity and equity-linked instruments.
- All these funds are registered as Alternative Investment Funds (AIF) with SEBI.
Basohli Pashmina is Recognized with GI Tag (HT)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Basohli Pashmina, a traditional craft with over a century of history from the Kathua district in Jammu and Kashmir, has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Basohli Pashmina:
- Basohli Pashmina is renowned for its exceptional softness, fineness, lightweight quality, insulation, and durability.
- Pashmina products include shawls, mufflers, blankets, and baskets.
- Pashmina is a premium variety of cashmere, obtained from the fine undercoat of the Changthangi mountain goats.
- These goats are found on the Changthang Plateau in Tibet and parts of Ladakh.
- The Changpa people, who are nomads living on the Changthang plateau of Tibet, are traditional producers of pashmina wool.
United Nations Convention against Transnational Organised Crime (PIB)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Minister of State for Home Affairs Shri Nityanand Rai attends the two-day conference to mark the 20th anniversary of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organised Crimes (UNTOC) at Palermo in Italy.
About the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC):
- NTOC, established by the United Nations in 2000, is a global treaty targeting transnational organized crime.
- It's often referred to as the Palermo Convention.
- It has 147 signatories and 190 parties to the convention.
- The Convention is complemented by three Protocols:
- Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women, and Children
- Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea, and Air
- Protocol against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms, their Parts, and Components, and Ammunition.
- India signed UNTOC and its three Protocols on December 12, 2002.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is the primary agency responsible for all interactions related to UNTOC.
Exercise SAMPRITI (PIB)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
On the 3rd of October 2023, India and Bangladesh kicked off the 11th installment of exercise SAMPRITI in Umroi, Meghalaya.
About Exercise SAMPRITI:
- This is an annual joint military exercise that India and Bangladesh hold together.
- It began in Jorhat, Assam, in 2009 and has successfully completed ten editions up to 2022.
- The exercise is organized alternately by both countries, demonstrating their strong bilateral defense cooperation.
- SAMPRITI-XI, which spans 14 days, will involve around 350 personnel from both sides.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to improve interoperability between the two armies, exchange tactical strategies, and promote best practices.
- A wide range of units, including artillery, engineers, and other supporting arms and services, will participate from both sides.
- The exercise centers on the execution of Sub-Conventional Operations in line with Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
- It includes a Command Post Exercise (CPX) and a Field Training Exercise (FTX), concluding with a Validation Exercise.
- SAMPRITI-XI aims to strengthen defense cooperation between India and Bangladesh, fostering deeper bilateral relations, cultural understanding, and mutual benefits through shared experiences in Sub-Conventional Operations.
International Coral Reef Initiative (NewsOnAIR)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI) announced its commitment to obtain both public and private investments to support the conservation and restoration of coral ecosystems.
About the International Coral Reef Initiative:
- It was established in 1994 with founding members including Australia, France, Japan, Jamaica, the Philippines, Sweden, Britain, and the United States.
- It now boasts a membership of 45 countries, collectively representing three-quarters of the world's coral reefs.
- India is one of these member countries.
- This initiative serves as a global partnership between nations and organizations dedicated to preserving coral reefs and their related ecosystems worldwide.
- It's important to note that the decisions made by ICRI are not legally binding on its members.
- ICRI's work is frequently recognized in United Nations documents, emphasizing its significant role in cooperation, collaboration, and advocacy on the international stage.
Objectives of ICRI include:
- Promoting the adoption of best practices for sustainable management of coral reefs and associated ecosystems.
- Building capacity to effectively manage and protect these ecosystems.
- Raising awareness at all levels about the challenges faced by coral reefs worldwide.
R21/Matrix-M vaccine (The Hindu)
- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The WHO has given its thumbs-up to the R21 vaccine, the second malaria vaccine they've recommended, following the RTS, S/AS01 vaccine, which got their approval in 2021. Right now, the WHO is closely examining this vaccine for prequalification, which is like their gold seal of approval. Once it's prequalified, organizations like GAVI (a global vaccine alliance) and UNICEF can purchase the vaccine from the manufacturers.
About the R21/Matrix-M Vaccine:
- It's a new vaccine designed to protect children from malaria.
- The University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India developed it, with support from the European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP), the Wellcome Trust, and the European Investment Bank (EIB).
- This vaccine is a game-changer as it's the first one to meet the WHO's target of 75% effectiveness.
- Burkina Faso, Ghana, and Nigeria have already given the green light for its use.
- In early 2024, these African countries will start administering the vaccine, and by mid-2024, it will be available in other countries too.
Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS) 2.0 (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science & Technology, MoS Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions introduced the upgraded version of the Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS 2.0).
About the Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS) 2.0:
- IGMS 2.0 is a digital platform and Automated Analysis in Tree Dashboard portal, under the purview of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- Implementation of this system has been entrusted to IIT Kanpur.
Key Objectives:
- The Dashboard provides real-time tabulated analysis of both filed and resolved grievances, offering insights at state, district, and ministry levels.
- It assists in identifying the underlying causes of grievances.
- Additionally, this portal streamlines the creation of draft letters for specific schemes or ministries, expediting the grievance resolution process within the respective ministries and departments.
- IGMS 2.0 is equipped with Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities, enhancing its functionality.
Sanwariya Seth Temple (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister recently visited and paid his respects at the Sanwariya Seth Temple located in Chittorgarh, Rajasthan.
About Sanwariya Seth Temple:
- Sanwariya Seth Temple is a Hindu place of worship dedicated to Lord Krishna, particularly in his cherished child form known as “Sanwariya Seth” or “Shyam Seth."
- Location: Situated in the village of Mandaphia, Chittorgarh district, Rajasthan.
- Historical Origin: The temple dates back to its construction in the year 1840 A.D.
- Architectural Marvel:
- The temple embodies the quintessential Rajasthan architectural style, renowned for its intricate carvings, distinctive domes, and vivid color palette.
- The primary temple structure is crafted from pristine white marble.
- Elaborate carvings grace the walls, pillars, and ceilings, illustrating scenes from Hindu mythology and an array of motifs.
- Multiple ornate domes adorn the temple, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
- The temple boasts a prominent spire, or 'shikhar,' which soars above the central sanctum.
- Sanctum Sanctorum: Inside the temple's innermost chamber rests a black stone idol of Lord Krishna.
- Welcoming Spaces: The temple offers expansive, pillared halls that serve as communal gathering areas for devotees and visitors alike.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (DownToEarth)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
As per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development's Review of Maritime Transport 2023, international shipping witnessed a notable increase of 20 percent in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2023 compared to the previous decade.
Key Highlights from the Review:
- The shipping industry plays a pivotal role, accounting for over 80 percent of global trade volume, yet contributes nearly three percent of total global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Containerized trade, after a 3.7 percent decline in 2022, is projected to grow by 1.2 percent in 2023 and is expected to further expand by three percent from 2024 to 2028.
- Oil and gas trade exhibited robust growth in 2022, with tanker freight rates experiencing a significant resurgence driven by geopolitical developments.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- UNCTAD serves as the United Nations' primary institution addressing trade and development matters.
- Established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly, it functions as a permanent intergovernmental body.
- UNCTAD's mission is to promote equitable and effective access to the benefits of a globalized economy for developing countries.
- It offers economic and trade analysis, fosters consensus-building, and provides technical assistance to assist developing nations in leveraging trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD publishes influential reports, including the Trade and Development Report, the World Investment Report, and The Least Developed Countries Report.
National Service Scheme Awards (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the President of India conferred the National Service Scheme Awards for the period 2021-2022 at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
About the National Service Scheme Awards:
- Established in 1993-1994, the National Service Scheme Awards have been an annual tradition since their inception.
- These awards are bestowed by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Department of Youth Affairs.
- Objectives:
- Acknowledge exceptional contributions of NSS student volunteers, NSS Programme Officers, and Programme Coordinators in community service.
- Encourage young NSS student volunteers to develop their personalities through community engagement.
- Applaud the efforts of Programme Officers and Programme Coordinators in fulfilling the goals of the National Service Scheme through NSS volunteers.
- Motivate NSS Volunteers to continue their selfless service in community work.
What is the National Service Scheme?
- The National Service Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme initiated by the Government of India.
- It provides students in the 11th & 12th grade at the +2 Board level, as well as students at technical institutions, colleges, and universities, the opportunity to participate in government-led community service activities and programs.
- Motto: The guiding motto of the National Service Scheme is 'NOT ME BUT YOU.'
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry responsible for overseeing the National Service Scheme is the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports.
Sastra Ramanujan Prize (The Hindu)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Ruixiang Zhang, an Assistant Professor at the University of California, Berkeley, USA, will receive the prestigious 2023 SASTRA Ramanujan Prize in recognition of his exceptional achievements in the field of mathematics.
About the SASTRA Ramanujan Prize:
- Established in 2005, the SASTRA Ramanujan Prize is an esteemed mathematical award.
- It is annually presented by SASTRA University, located near Kumbakonam in Tamil Nadu, on December 22, Ramanujan's birth anniversary.
- This accolade is reserved for mathematicians worldwide who are under the age of 32 and are engaged in research influenced by the legendary Srinivasa Ramanujan.
- The age limit of 32 is a tribute to Ramanujan's remarkable achievements within a short lifespan.
- The prize includes a cash award of $10,000 along with a citation.
- It has earned global recognition and prestige since its inception.
- Notable past recipients of the prize include mathematicians Manjul Bhargava and Akshay Venkatesh.
Ruixiang Zhang's Contributions:
- Ruixiang Zhang, a young mathematician, has made significant contributions across various mathematical domains, including analytic number theory, combinatorics, and Euclidean Harmonic Analysis, among others.
- Based on his doctoral work at Princeton, Zhang, in collaboration with Shaoming Guo, successfully demonstrated a multivariable extension of Vinogradov's Mean Value Theorem.
- This groundbreaking work, published in Inventiones Mathematicae in 2019, is celebrated as a major milestone in the field.
Sycamore tree (Indian Express)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a 300-year-old sycamore tree in England, renowned for its beauty and exceptional location, was felled by a teenager.
About Sycamore Tree:
- Location: Situated within a hollow between two hills, at a break in the Hadrian Wall, an ancient stone structure near the border of England and Scotland in Northumberland, northern England.
- These 'breaks' are essentially channels that were naturally carved by extensive meltwater flows beneath ancient ice sheets, thousands of years ago.
- As they mature, sycamore trees can grow impressively tall, reaching heights of up to 35 meters.
- They are commonly found in the UK and feature leaves reminiscent of maple trees.
- Initially, the bark is dark pink-grey and smooth when young, but over time, it becomes textured, developing small plates.
- Sycamores have a remarkable lifespan and can survive for as long as 400 years.
- Distribution: Native to central, eastern, and southern Europe, it's believed that the introduction of sycamore trees to the UK occurred either during the Roman era or in the Tudor period around the 1500s.
Greater sand-plover (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A Greater sand-plover (Charadrius leschenaultii), typically found along seashores, was recently observed in an urban reservoir within Coimbatore.
About Greater Sand-Plover:
- Known for its impressive long-distance migrations.
- Physical Characteristics:
- A medium-sized plover featuring a lengthy and robust bill.
- Breeding adults display a dark mask and an orange chest, neck, and forehead, with females being somewhat less vibrant than males.
- Non-breeding birds and juveniles exhibit sandy brown plumage on top and white underneath, including a white throat and 'eyebrows.'
- Notably, unlike some Lesser Sand-Plovers, the Greater Sand-Plover never sports a black boundary around the throat.
- Breeding habitat includes high-elevation regions, favoring arid, open environments, often near water sources.
- During winters, it can be found along coastal mudflats and estuaries.
- Breeding season typically spans from April to May in central Asia, late March to late May in Turkey, and up to late June in Armenia.
- During the non-breeding season, it migrates to the shores of the Indian and Australian Oceans.
- The bird sustains itself on a diet comprising beetles, worms, crustaceans, mollusks, other insects, and their larvae.
- Preferred Habitat: Mudflats and sandy shores.
- Behavior/Ecology: Tends to associate with other shorebirds, particularly the Lesser Sand Plover.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Least Concern
Pygmy hog (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a total of eighteen pygmy hogs, which were bred in captivity, were set free within the Manas National Park and Tiger Reserve located in western Assam.
About Pygmy Hog:
- It holds the distinction of being the world's smallest and rarest wild pig species.
- Remarkably, it's among the few mammals that construct their own dwellings, complete with a 'roof.'
- Considered an indicator species, its presence serves as a barometer for the well-being of its primary habitat, which consists of tall and moist grasslands.
- Habitat: Pygmy hogs thrive in untouched expanses of grassland dominated by early-stage riverine ecosystems.
- These areas typically feature dense tall grass interspersed with a rich variety of herbs, shrubs, and young trees.
- Currently, the only viable population of these hogs in the wild resides in the Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I
Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (Indian Express)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Madurai Bench of the Madras High Court has recently issued a notice to the State regarding a public interest litigation petition. This petition aims to request a directive to limit the access of individuals and vehicles into the Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve.
About Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- Established as a Tiger Reserve in 1988.
- Comprises three primary sanctuaries:
- Kalakad Sanctuary
- Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The core area of the sanctuary is the Agastya Malai Hill Range, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- This range is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- Often referred to as the 'River Sanctuary,' it serves as the source for as many as 14 rivers.
- Terrain: Characterized by undulating landscapes with numerous valleys and porous rock formations.
- Vegetation:
- Varies from thorny shrub jungles to lush evergreen forests.
- Apart from forests, the reserve also includes savannah woodlands, grasslands, and even tea and coffee plantations.
- Flora: Notable species encompass Sarcandra, Paphiopedulum druryi, Hopea parviflora, Hopea utilis, Calophylum elatum, Cullenia exarillata, and more.
- Fauna: Home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, rusty spotted cats, wild dogs, sloth bears, elephants, gaurs, sambar deer, spotted deer, mouse deer, Nilgiri langurs, slender lorises, bonnet macaques, lion-tailed macaques, among others.
Sela Tunnel Project (Times of India)
- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The officials from BRO (Border Roads Organization) recently announced that they have almost finished about 96 percent of the work on the strategically important Sela Tunnel. It's expected to be officially opened by the end of this year.
About Sela Tunnel Project:
- Location: Situated in the West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- When it's finished, the Sela tunnel will be the world's longest two-lane tunnel, located at an altitude above 13,000 feet.
- Its purpose is to provide year-round connectivity between Guwahati in Assam and Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This tunnel is being constructed underneath the Sela Pass as part of NH-13, a segment of the Trans-Arunachal Highway system.
- The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is responsible for its construction under Project Vartak, which began on April 1, 2019.
- Project Details:
- Tunnel 1: This tunnel is 980 meters long and has a single tube.
- Tunnel 2: A two-lane tunnel that spans 1555 meters, equipped with an emergency escape tunnel.
- Roads: The road leading to Tunnel 1 is 7100 meters long, the road connecting the two tunnels is 1340 meters long, and the road leading to Tunnel 2 is 340 meters in length.
FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE (FATF) (Business Standard)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an inter-governmental body that sets anti-money laundering standards, has removed the offshore tax haven Cayman Islands from its ‘grey list’.
Facts About:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an intergovernmental organization that was founded in 1989 as part of the G7's effort to develop laws to combat money laundering.
- Its directive was extended to cover financing of terrorism in 2001.
- Only a few nations are listed in the grey and black lists that the FATF releases.
- To monitor the country's progress in combating money laundering and terrorism financing, a grey list is established.
- Non-cooperative nations are included on a blacklist in an effort to combat money laundering and financing of terrorism.
About the Cayman Islands:
- The Cayman Islands are situated in the Western Caribbean Sea and are a British Overseas Territory.
- Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman are the three islands that make up the territory; they are situated northwest of Jamaica and south of Cuba.
- Its topography is low-lying, with coral reefs.
- Economy: The islands are a thriving offshore financial hub, with a mixed economic system.
ARALAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, individuals suspected to be associated with Maoist groups allegedly engaged in a gunfire exchange with Forest Department watchers in the Aralam Wildlife Sanctuary located in Kannur, Kerala.
Facts About:
- It's situated on the Western Ghats' western slopes.
- Founded in 1984, it is the northernmost wildlife sanctuary in Kerala.
- It shares borders with Wayanad-Brahmagiri, the northern slopes of Wayanad, and the Karnataka State Protected Areas, which include the Coorg forests and the Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Katti Betta is the sanctuary's highest peak.
- In terms of vegetation, West Coast semievergreen forests and tropical evergreen forests predominate here.
It is the only protected area of the West Coast Tropical Evergreen Forest of Dipterocarpus-Mesua- Palaquium type.
- This wildlife sanctuary is traversed by the Cheenkani River.
- Flora: Cinnamomum Zeylanicum, Hopea parviflora, Largestroemia lanceolata, Xyliaxylocarpa, Mallotus, and Philippinensis are common trees in the semievergreen regions.
- Fauna: Bison, deer, boar, and elephants are fairly common. Here, one can see leopards, jungle cats, and a variety of squirrel species.
CRAB PLOVER (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, for the first time, breeding nests of crab plovers were spotted at Great Vedaranyam Swamp near Point Calimere, Tamil Nadu.
Facts About:
The Crab-Plover is a distinctive bird found along the coasts of the Indian Ocean.
- It stands out with its long legs and striking black-and-white colouration.
This bird belongs to the plover family and is closely related to other shorebird species.
Unlike most shorebirds, the Crab-Plover lays white eggs.
- Their chicks stay inside burrows until they are ready to fledge, which sets them apart from other shorebirds.
Distribution: They can spotted in various places around the Indian Ocean, as they are residents in these regions.
- They breed in places like the Arabian Sea in Pakistan, the Gulf of Oman, the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, Somalia, the Andaman Islands, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, and Madagascar.
Habitat: Crab Plovers make their homes in a variety of coastal environments, including sandy coastlines, mudflats, estuaries, lagoons, exposed coral reefs, and rocky shorelines. During the breeding season, they can also be found in sand dunes.
Conservation Status: The Crab-Plover is categorized as 'Least Concern' by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Additionally, it falls under the protection of the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA).
CARBON NANOFLORETS (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Carbon nanoflorets made by IIT Bombay researchers can convert incident sunlight to heat with 87% efficiency.
Facts About:
Carbon nanoflorets (NCFs) are a newly discovered type of carbon nanostructure that resembles tiny marigold flowers.
- They are made up of a network of carbon nanotubes arranged in a conical microcavity structure. NCFs have a number of unusual properties, including:
Broadband absorption: NCFs can absorb sunlight at all wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared.
- This is because their conical microcavity structure traps light for a longer period of time, allowing it to be absorbed by the carbon nanotubes.
- They are also extremely black, absorbing more than 95% of sunlight across a broad spectrum of wavelengths.
High light-heat conversion efficiency: NCFs can convert sunlight to heat with an efficiency of up to 87%.
- This is much higher than the efficiency of other solar-thermal materials, such as photovoltaic cells.
Low thermal conductivity: NCFs have a very low thermal conductivity, which means that they can efficiently convert sunlight to heat without losing much of the energy to conduction.
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) reported that NCFs could convert incident sunlight to heat with an efficiency of 87%.
- This is significantly higher than the efficiency of other solar thermal materials, such as black carbon.
- It effectively absorbs over 97 per cent of sunlight's ultraviolet, visible, and infrared components, converting them into thermal energy.
- The resulting heat can be efficiently transferred to either air or water for practical applications.
- Research reveals that NCFs can raise the temperature of the surrounding air from room temperature to 60 degrees Celsius, providing smoke-free space-heating solutions.
AGARTALA-AKHAURA RAIL LINK PROJECT (Indian Express)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Bangladesh counterpart Sheikh Hasina will jointly inaugurate the Agartala-Akhaura cross-border rail link project on Wednesday.
Facts About:
- The rail line between Agartala in Tripura and Akhaura in Bangladesh would pave the way for the first train to run from the northeastern region of India to Bangladesh.
- The project is significant from an international as well as from a domestic point of view.
- At present, the rail route from Agartala to Kolkata is around 1600 kilometres and takes about 38 hours.
- The footfall of passengers from Agartala to Kolkata is significantly very high due to the linguistic similarity between the two states.
Both states also share age-old cultural and business relations and Agartala depends on Kolkata from the medical tourism point of view as well.
- Upon operationalisation of the Agartala-Akhaura Rail link project the distance will be reduced by around 500 kilometres and the travel time will be 16 hours between Agartala and Kolkata.
- In addition, this rail link will also provide direct access between landlocked northeastern India and the Chittagong port of Bangladesh.
- The Ministry for Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) has funded the railway line from Agartala to Nischintpur;
whereas the Ministry of External Affairs has funded the rail line from Nischintpur to Gangasagar which is in Bangladesh.
- The project is part of India's 'Act East Policy', which aims to promote economic cooperation and develop strategic ties with countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
AMANGARH TIGER RESERVE (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The tiger population at the Amangarh Tiger Reserve has increased from 21 mature tigers and six cubs in 2021 to 28 mature tigers and four cubs now.
Facts About:
Amangarh Tiger Reserve is situated in Amangarh, Bijnor district, Uttar Pradesh, covering an area of approximately 97 square kilometres.
- It shares its boundaries with Uttarakhand's Jim Corbett National Park.
Originally a part of Jim Corbett National Park, Amangarh became a separate reserve in Uttar Pradesh when Uttarakhand was carved out of UP..
- It received the status of a tiger reserve in 2012.
The reserve features diverse ecosystems, including grasslands, wetlands, and dense forests.
Wildlife: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife.
- Among the mammals present are tigers, elephants, swamp deer, sambar, cheetal, hog deer, kakar, langur, sloth bear, porcupine, and otter.
- The bird population includes hornbills, red jungle fowl, pea fowl, Bengal floricans, fishing eagles, serpent eagles, ospreys, woodpeckers, shamas, Indian pittas, paradise flycatchers, orioles, and emerald doves.
- Additionally, the reserve is inhabited by reptiles such as monitor lizards, turtles, pythons, Gangetic dolphins, muggers, and gharial.
BRU REFUGEES (The Hindu)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Bru refugees have been granted permanent settlement in Tripura as part of a centrally sponsored rehabilitation arrangement, which means they won't be taking part in Mizoram elections for the first time.
Facts About:
- The Bru refugees, also known as Reang, are an indigenous community primarily residing in the Northeast of India, particularly in Tripura, Mizoram, and Assam.
In Tripura, they hold the status of a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group, recognized by the government.
- Ethnically, they can be classified into two main clans, Meska and Molsoi, and they belong to the Indo-Mongoloid racial stock.
Their languages are affiliated with the Austro-Asiatic groups within the Tibeto-Burman family.
- They speak a language called "Kaubru," which shares some tonal features with the Kuki language, although it broadly falls under the Kok-Borok dialect.
- Occupation-wise, they continue to maintain their nomadic traditions, with a significant number of them engaged in Hilltop Jhum Cultivation and various food-gathering activities.
- Their beliefs encompass a belief in spirits and the existence of the soul.
- Religiously, they follow Hinduism, with most of their deities being akin to gods and goddesses of the Hindu faith.
Traditionally, they practice endogamy, not marrying outside their community.
- In their cultural tradition, the village council chief, known as "RAI," has the authority to approve divorce and widow marriages.
MAHABALI TUG (PIB)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Navy launches 'Mahabali', a 25-ton BP Tug, showcasing India's self-reliance in shipbuilding.
Facts About:
- ‘Mahabali’ is a 25-ton Bollard Pull (BP) tug.
- It is one of three tugs of its kind that the Ministry of Defence and the Shipyard jointly commissioned.
It was built at the Shoft Shipyard in Bharuch, Gujarat.
- It has been built in compliance with the Indian Register of Shipping's (IRS) classification guidelines.
- It will become indispensable in supporting naval vessels and submarines in berthing and unberthing procedures and in manoeuvring through restricted waters.
- It has the capability to improve a ship's ability to put out fires while anchored and while cruising at port.
- Additionally, it has limited search and rescue capabilities.
THE SUBSURFACE WATER ICE MAPPING (SWIM) PROJECT (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project, funded by NASA, has released its fourth map pinpointing potential subsurface water ice locations on Mars.
Facts About:
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project goal is to find the best locations to access water ice buried beneath the Mars' surface.
Recently, they released their fourth set of maps, which are the most detailed and accurate maps so far since the project began in 2017.
This project is led by the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
- They gather data from various NASA missions like the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), the 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars Global Surveyor.
To create these maps, SWIM utilized two high-resolution cameras on the MRO.
- They used Context Camera data to make better maps of the Northern Hemisphere.
- For the first time, they used HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) data to get the closest, most detailed view of the ice's edge near the equator.
The SWIM project was done in two phases.
- The first phase, finished in 2019, focused on the northern hemisphere, and
- The second phase, completed in 2020, included the southern hemisphere.
One exciting thing about the new map is that it shows 'polygon terrain,' where the ice beneath the surface causes the ground to crack into polygonal shapes.
- This suggests there's more ice hidden below.
EJECTA HALO (Indian Express)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Chandrarayaan-3 Lander Module produced an amazing 'ejecta halo' of lunar material, according to recent information released by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
Facts About:
An ejecta halo is a bright, irregular patch of lunar material that surrounds a lander after it has landed on the Moon.
- It is caused by the thrust from the lander's engines and the impact of the lander on the lunar surface, which displaces and ejects lunar regolith (soil) and dust.
- The ejecta halo can be several meters in diameter and can extend tens of meters from the lander.
The Vikram lander of the Chandrayaan-3 mission created a spectacular ejecta halo when it landed on the Moon in August 2023.
- Scientists from the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) estimate that about 2.06 tonnes of lunar regolith were ejected and displaced over an area of 108.4 square meters around the landing site.
Ejecta halos can be studied to learn more about the composition and structure of the lunar regolith.
- They can also be used to calibrate remote sensing instruments and to develop new methods for landing spacecraft on the Moon.
NATIONAL TIGER CONSERVATION AUTHORITY (NTCA) (PIB)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is holding an art exhibition in New Delhi from November 3–5, 2023, titled "Silent Conversation: From Margins to the Center."
Facts About:
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has been constituted under section 38 L (1) of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It is a statutory body, established in 2006 under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Objectives:
- Providing statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance with its directives becomes legal.
- Fostering Center-State accountability in Tiger Reserve management by providing a foundation for MoUs with states within the federal structure.
- Including a provision for parliamentary oversight.
- Addressing the livelihood interests of local residents in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
- Members of NTCA:
Minister in charge of MoEFCC (as Chairperson),
Minister of State in MoEFCC (as Vice-Chairperson),
Three members of Parliament, the Secretary (MoEFCC), and other members.
LOWER SUBANSIRI HYDROELECTRIC POWER PROJECT (HT)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Lower Subansiri Hydro Electric Power project in Assam encountered a major problem when a significant landslide completely blocked its sole operational diversion tunnel, causing a substantial interruption in water flow through the river.
Facts About:
- This is the country's biggest hydroelectric project to date.
It is a run-of-river project on the Subansiri River.
- The Project is situated close to North Lakhimpur, which marks the boundary between Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Capacity: 2000 MW.
- Up to 7.4 billion kWh of electricity will be produced there each year.
- Along with building a concrete gravity dam rising 116 meters above the riverbed, the project also entails building a surface powerhouse.
The dam will be 284 meters in length.
- The powerhouse is situated in the Subansiri district of Arunachal Pradesh, whereas the dam is situated in the Dhemaji district of Assam.
- It is being developed by the state-owned National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC).
- Finance: A term loan was used to finance 30% of the project's debt in addition to 70% equity.
- The budgetary support provided by the central government is a component of the equity component.
NASA-ISRO SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (NISAR) (TOI)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The 'NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar' (NISAR) is set to enable the investigation of how changes in Earth's forest and wetland ecosystems affect the worldwide carbon cycle and exert an influence on climate change.
Facts About:
- NASA and ISRO collaborated to develop the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory known as NISAR.
It's about the size of an SUV and weighs 2,800 kilograms.
- It is a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite, having both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments.
- The first satellite mission to measure variations in the surface of our planet will be NISAR, which will use two distinct radar frequencies (L-band and S-band).
No matter the weather, SAR can gather data day or night and penetrate clouds to gather information.
- NASA has contributed GPS, an L-band radar, a payload data subsystem, and a high-capacity solid-state recorder for data storage.
ISRO on the other hand supplied the S-band radar, as well as the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Additionally, it has a sizable 39-foot stationary antenna reflector with an upward-facing feed on the instrument structure that will be used to focus "the radar signals emitted and received."
The reflector is constructed of gold-plated wire mesh.
- The mission's objectives are to measure the dynamic surfaces, ice masses, and changing ecosystems of Earth in order to gather data on groundwater, biomass, natural hazards, and sea level rise.
- NISAR is going to perform global 12-day regular observations of Earth's land and ice-covered surfaces during ascending and descending passes.
SEISMIC SWARM/EARTHQUAKE SWARM (The Hindu)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A seismic swarm has hit the Reykjanes peninsula in southwest Iceland with more than 5,500 small earthquakes in the last three days, raising the prospect of a volcanic eruption.
Facts About:
An earthquake swarm is a sequence of earthquakes that occur in a relatively short period, typically days or weeks, with no clear mainshock.
- It can occur anywhere in the world, but they are most common in volcanic regions and areas with active faults.
There are a number of different possible causes of earthquake swarms, but the most common cause is thought to be the movement of fluids through the Earth's crust.
- Fluids can weaken the rocks along faults, making them more likely to slip and generate earthquakes.
- Fluids can also move heat around, which can trigger earthquakes in some cases.
Reasons for swarm sequences:
Fluid migration: When fluids, such as water or magma, move through the Earth's crust, they can lubricate faults and make them more likely to slip.
- This can lead to a swarm of earthquakes as the fault ruptures in multiple places.
Magmatic activity: Earthquake swarms are often associated with volcanic regions.
- This suggests that magma moving underground can also trigger swarms.
Slow fault slip: When a fault slips slowly, the stress on the fault can build up over time until it is released in a series of small earthquakes.
- This can also lead to a swarm.
About the Reykjanes Peninsula:
- The Reykjanes Peninsula, located in southwestern Iceland, is a captivating region known for its dramatic and otherworldly landscapes.
- This geologically active area is characterized by rugged coastlines, extensive lava fields, and numerous geothermal features, including the famous Blue Lagoon.
- As part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, it showcases a bridge between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates, making it a site of significant geological events such as earthquakes and volcanoes.
TALAGIRISVARA TEMPLE (The Hindu)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The ancient Pallava period paintings at Talagirishwara temple in Panamalai, Villupuram district, have suffered greatly due to neglect. The painting that showed Lord Shiva's dance has nearly disappeared, leaving only the face of goddess Parvathi and a few small sections remaining.
Facts About:
Talagirishwara Temple is situated in Panamalai village, Viluppuram district, Tamil Nadu, India.
- It is built on a small hill overlooking Panamalai Lake.
The temple was constructed by Pallava king Narasimhavarman II, also known as Rajasimha, during the Seventh Century.
Notable features of the temple include a Vimana similar to the one at Kailasanatha temple in Kanchipuram.
- The Vimana has three layers, with the highest tier being reconstructed.
Inside the temple's garbhagriha, there's a Dharalingam, and a Somaskanda section on the rear wall.
The temple has an Ardhamandapam (partial Mandapam) with walls featuring depictions of divinities like Brahma with Saraswati and Vishnu with Lakshmi.
- It faces east and is surrounded on three sides by sub-shrines.
- Additional sub-shrines and a large Mandapam called Mahamandapam were added at a later date.
The typical Pallava-style pillars with crouching lions can be found in the temple.
The temple houses paintings that resemble those in Ajantha and Chithannavasal.
- These paintings are on the walls of a sub-temple on the northern side of Talagirishwara (Shiva) temple.
- Notable among the paintings is one of Lord Shiva with eight hands dancing, known as Latathilagabhani, watched by Goddess Parvathi.
These paintings are older than the ones in Chithannavasal and were created by covering the stonewalls with a paste made of limestone and sand.
MELGHAT TIGER RESERVE (TOI)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a tiger was found dead in the Susarda range within the buffer zone of Melghat Tiger Reserve's Paratwada division.
Facts About:
The name "Melghat" signifies the confluence of various 'ghats' or valleys, reflecting the landscape of the reserve.
Location: Melghat Tiger Reserve is situated in the Amaravati district of Maharashtra.
- It's positioned on the southern offshoot of the Satpura Hill Range known as Gavilgarh Hill, approximately 225 km west of Nagpur.
Establishment: It was initially designated as a wildlife sanctuary in 1967 and later declared a tiger reserve in 1974.
- Melghat was one of the first nine tiger reserves established under Project Tiger in 1973-74, an initiative for the conservation of Bengal tigers in India.
- It is one of the largest tiger reserves in India in terms of its area.
Rivers: Melghat Tiger Reserve serves as the catchment area for five significant rivers: Khandu, Khapra, Sipna, Gadga, and Dolar.
Vegetation: The forest primarily consists of tropical dry deciduous trees, with teak being the dominant species.
Wildlife: Apart from Bengal tigers, the reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including Sloth Bears, Indian Gaur, Sambar deer, Leopards, Nilgais, and more.
- Notably, the endangered Forest Owlet, once believed to be extinct, has been found in various areas of Melghat.
Tribal Communities: The largest tribal community in Melghat is the Korkus.
SARAS AAJEEVIKA MELA (PIB)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The popular SARAS Mela Gurugram was recently inaugurated by the Union Minister of State for Rural Development, Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution.
Facts About:
- SARAS Mela is a women empowerment initiative by the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihoods Mission of the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD)
- It’s aim is to bring the rural women self-help group members under one platform where they can showcase their skills, sell their products and build connections with potential market players at fair prices.
- The organisation trains women in different livelihood craftsmanship skills and gives them a platform to market their products.
- Their stalls are entirely free, and all their expenses, including their stay, are borne by the Mela organising committee.
- The SARAS Mela is organised by the National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR).
- Saras Melas are regularly organised across India throughout the year.
RASHTRIYA GOKUL MISSION (Down to Earth)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Rashtriya Gokul Mission is actively supporting the promotion of the Gir indigenous cow breed.
Facts About:
- It is being implemented for the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- With a budget of Rs. 2400 crore, the program is also carried out under the general Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna from 2021 to 2026.
- The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying is the nodal ministry.
Mission Objectives:
- To use cutting-edge technologies to raise milk production and sustainably improve the productivity of cows.
- To spread the practice of breeding bulls with high genetic merit.
- To increase the breeding network's strength and provide farmers with doorstep artificial insemination services to increase the coverage of artificial insemination.
- To encourage the scientific, all-encompassing rearing of native cattle and buffalo as well as conservation.
WHAT IS THALLIUM? (The Hindu)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A woman uses Thallium to seek revenge from in-laws in Gadchiroli, Maharashtra
Facts About:
- Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol "Tl" and atomic number 81 on the periodic table.
- It is a rare and heavy metal that is often considered a post-transition metal.
It is a soft, malleable metal that can easily be cut with a knife.
- Historical Use: In the past, thallium compounds were used in rat poisons and insecticides, but their use has been largely discontinued due to their toxicity.
- Electrical Conductivity: It has good electrical conductivity and is sometimes used in the manufacturing of electrical conductors.
- Radioactive Isotope: Thallium has a radioactive isotope, thallium-201, which is used in medical imaging as a radioactive tracer in cardiac stress tests.
- Chemical Properties: Thallium is chemically similar to lead and is often found in association with lead and zinc ores.
- Applications: Despite its toxicity, thallium has some limited applications in industries, including the manufacture of electronics, optical glasses, and low-melting thermometers.
- It is highly toxic to humans and is sometimes referred to as "the poisoner's poison" due to its extreme toxicity.
Exposure to thallium can cause a variety of health problems, including hair loss, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, peripheral neuropathy, and seizures.
In severe cases, thallium poisoning can be fatal.
- Due to its toxicity, thallium is a highly regulated substance and its use is restricted to a limited number of industrial applications, and it is not available to consumers.
SATELLITE INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (Indian Express)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Reliance Jio recently declared that it had effectively tested the first gigabit internet service in India, based on satellite technology.
Facts About:
- Satellite Internet operates in a way similar to satellite TV.
- It begins with an internet service provider launching satellites into space to orbit the Earth.
These satellites, placed in low- or high-Earth orbit, transmit a signal.
- A receiver dish, positioned in your home or business, captures this signal.
It should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- You connect a modem to this dish to convert the received signal into usable internet connectivity.
- High-speed satellite internet is typically delivered through constellations of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- LEO satellites orbit the planet at altitudes ranging from 250 to 2,000 kilometers.
- Communication between these satellites and Earth occurs using radio waves.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
- Satellite Internet is ideal for users residing in rural or remote areas, far from urban centers or cable/phone offices.
- It relies on a satellite dish for two-way communication and doesn't require telephone cables or lines.
- When compared to other internet options, satellite internet experiences fewer or minimal network outages.
MANAGEMENT & ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND PROFESSIONAL SKILLS COUNCIL (Business Standard)

- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed by the Management & Entrepreneurship and Professional Skills Council (MEPSC) and Magic Bus India Foundation, a prominent non-profit in the education and skilling sector.
Facts About:
MEPSC is a horizontal Sector Skill Council (SSC) that was established using a unique Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model in 2013 and registered as a Section-8 (Not for Profit Company) under the Companies Act.
The Ministry of Skill Development has been providing guidance to the Council during its operations.
The only organization promoting it is the All India Management Association (AIMA), which is the highest authority for the management profession in India.
MEPSC receives support from the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and is acknowledged as an awarding body by the National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET), the skills regulator.
Over the next ten years, MEPSC aims to train and certify about 4.75 lakh trainees, create and develop 50 Qualifications Packs (QPs)/National Occupational Standards (NOS), and train over 550 trainers.
It will take the lead on skill development programs in five major areas, including:
- Assessment and training
- Professional skills (including Security)
- Non-Teaching job roles in the education sector
- Entrepreneurship
The MEPSC Board of Directors is made up of several well-known and experienced business leaders, academics, NSDC, AIMA, and Ministry officials.
HANLE DARK SKY RESERVE (the Hindu)

- 27 Oct 2023
Facts About:
- The Hanle Dark Sky Reserve (HDSR) is India’s first dark sky region, and is centered at Hanle in Eastern Ladakh, around the Indian Astronomical Observatory.
- HDSR preserves the dark skies by reducing light pollution in the surrounding areas, and uses these dark skies to promote astrotourism as a means to further enhance socio-economic development in the area.
What is the Indian Astronomical Observatory?
- The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) is one of the highest observatories in the world.
- It is situated in Hanle, Ladakh, at an elevation of 14.8 kilometers.
- Within the Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary, it will surface.
- Ladakh's vast arid region, high elevation, and sparse population make it an excellent choice for long-term observatories and dark-sky locations.
- The facility is supported by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru and the Department of Science and Technology.
GUDAVI BIRD SANCTUARY (The Hindu)
- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Forest Department officials are concerned about the sudden deaths of multiple birds at the Gudavi Bird Sanctuary in the Shivamogga district of Karnataka.
Facts About:
- Gudavi Bird Sanctuary is located in the state of Karnataka.
It is situated on the banks of Gudavi Lake.
- It covers an area of about 0.74 square kilometers, making it a small but important sanctuary.
- Travelers from all over the world come here because of its rich biodiversity and surrounding natural beauty.
- During the winter months, the sanctuary attracts a large number of migratory birds, such as the beautiful Demoiselle Cranes.
- Fauna: The Bird Sanctuary is proud to be home to over 217 different bird species, including migratory and resident birds such as White-Headed Crane, Grey Heron, Little Cormorant, and Little Grebe.
- Flora: There are patches of grass mixed in with moist deciduous forest.
- The microphyte biota and marshy plants make up this type of wetland vegetation.
PM-SHRI SCHOOL (NDTV)
- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Union Minister for Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, Dharmendra Pradhan, along with Haryana Chief Minister Manohar Lal Khattar, launched 124 PM-Shri schools in the state.
Facts About:
- PM SHRI School is a scheme sponsored by the Government of India.
- Objective: The initiative aims to establish over 14,500 PM SHRI Schools, managed by various government bodies, to provide a welcoming and caring environment for students.
These schools will offer a wide range of learning experiences, have good infrastructure, and ensure that all students have access to appropriate resources.
- National Education Policy 2020: The goal is to nurture students to become engaged, productive, and contributing citizens, in alignment with the vision of the National Education Policy 2020.
- Beneficiaries: More than 20 lakh students are expected to benefit directly from this scheme.
- Quality of School Education: The scheme will promote an understanding of various dimensions of the quality of school education and will inform policy, practice, and implementation in the education sector.
- Scaling Up: The lessons and best practices from these schools will be scaled up and implemented in other schools across the country.
- Implementation Period: The scheme is planned to be executed over a 5-year period from 2022-23 to 2026-27.
- Exemplar Schools: PM SHRI Schools are expected to showcase the implementation of the National Education Policy 2020 and become exemplary schools over time.
- This initiative aims to enhance the quality of education in India and create an inclusive and equitable society as envisioned in the National Education Policy.
REFERENCE FUELS (PIB)
- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Indian Oil's "Reference Gasoline and Diesel Fuels" was introduced for the first time in India by the Union Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas.
Facts About:
- Reference fuels (Gasoline and Diesel) are premium, high-value products used for calibration and testing of vehicles by auto Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and organisations involved in testing and certification in the automotive field.
- These fuels are used for calibration and testing of vehicles by automobile manufacturers and testing agencies like ICAT (International Centre for Automotive Technology) and ARAI (Automotive Research Association of India).
- These indigenously developed products will lead to import substitution at better prices and a shorter lead time for the vehicle manufacturers.
- Reference Gasoline fuels will be available in E0, E5, E10, E20, E85, and E100 from Flagship Paradip Refinery.
Reference diesel fuel shall be available in B7 grade from Panipat Refinery.
- The indigenously developed product by Indian Oil meets Automotive Industry Standard (AIS) specifications, substitutes imports, and is available at better prices with reduced lead time.
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited has established facilities for the production of Reference Gasoline Fuels (E-5, E-10, and E-20) at its Paradip Refinery and Reference Diesel Fuel (B-7) at its Panipat refinery.
- The demand for Reference Fuels in India is currently met by imports from other countries.
- Indian Oil has successfully commenced the production of Reference Gasoline and Diesel Fuels for the first time in India.
UNITED NATIONS FORUM ON FORESTS (PIB)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) will organise a Country-Led Initiative (CLI) event hosted by the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change from October 26–28, 2023, at the Forest Research Institute (FRI), Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
Facts About:
- It encourages the sustainable development, preservation, and management of all kinds of forests.
- The UNEconomic and Social Council of the United Nations (ECOSOC) was founded it in 2000.
- Every year, the Forum gathers at the UN Headquarters in New York to discuss high-level policy issues in even years and technical issues in odd years, bringing together representatives of all member states and agencies with an interest in forests.
- All United Nations members as well as specialized agencies make up the forum, which has universal membership.
- India is one of UNFF's founding members.
JAMRANI DAM MULTIPURPOSE PROJECT (PTI)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
Facts About:
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
About the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project:
- According to the project, a dam will be built in the Uttarakhand district of Nainital, close to Jamrani village, across the Gola River, a tributary of the Ram Ganga.
- The neighboring state of Uttar Pradesh would receive a sizable portion of the project's irrigation benefits.
- This is the seventh project to be added to the PMKSY-AIBP list.
Facts about the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana:
It was introduced in 2015–16.
Aim: To improve physical access to water on farms, increase cultivable land under assured irrigation, increase on-farm water use efficiency, and implement sustainable water conservation practices.
Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), ongoing major and medium irrigation projects, including national projects, will be completed more quickly.
Har Khet Ko Pani: It is divided into four smaller components:
- Ground Water (GW) Development component,
- Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI),
- Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies, and
- Command Area Development & Water Management (CAD&WM).
The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, is the nodal ministry.
NANCY GRACE ROMAN SPACE TELESCOPE (NASA)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
NASA is preparing to use its Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope to take humanity's deepest-ever look into the heart of our Milky Way Galaxy.
Facts About:
- The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will offer one of the deepest views into the heart of the Milky Way galaxy.
Its mission includes monitoring hundreds of millions of stars to detect various celestial objects like planets, distant stars, icy objects in our solar system, black holes, and more.
- It will likely discover the farthest-known exoplanet, opening up new possibilities in the search for other worlds.
- Time-domain astronomy is a significant focus, studying how the universe changes over time, and Roman contributes to this field.
- The Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey will concentrate on the Milky Way, using infrared vision to see through dust clouds in the galaxy's central region.
The survey will involve taking images every 15 minutes around the clock for about two months, repeated six times over Roman's five-year primary mission.
- Astronomers anticipate finding over a thousand planets, including some within their host stars' habitable zones.
- It can detect "rogue" worlds that don't orbit stars, providing insights into planetary system formation.
- The mission will also identify brown dwarfs and help explore the boundary between planet and star formation.
- It is expected to spot neutron stars, stellar-mass black holes, Kuiper belt objects, and conduct stellar seismology studies on a million giant stars.
The telescope's broad view of space allows for a new view of an ever-changing universe.
- The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center with participation from several other institutions and partners.
ANCIENT LANDSCAPE UNEARTHED BENEATH ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET (Space.com)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A new study finds that beneath East Antarctica's undulating ice sheet lies an ancient, river-carved landscape that provides a perfect snapshot of the region before glaciers covered the continent.
Facts About:
- In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have unveiled an ancient, hidden world beneath the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, offering a correction to the traditional perception of a frozen wasteland.
This revelation reshapes our understanding of Antarctica's history and environmental conditions.
- This newly discovered landscape, believed to have been shaped by rivers over 14 million years ago, predates the initial formation of the East Antarctic ice around 34 million years ago.
- This ancient terrain comprises valleys and ridges that are strikingly reminiscent of the glacially-altered landscape in North Wales, UK, signifying the long-term temperature stability of the ice sheet in the studied region.
- The recent discovery builds upon the team's prior work, which revealed concealed mountain ranges, canyons, and lakes beneath the Antarctic ice.
The researchers suggest that additional undiscovered ancient landscapes may remain hidden under the East Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- This discovery underscores the significance of ongoing exploration and research in this largely uncharted territory, emphasizing that there is much more to uncover beneath the ice.
- This revelation prompts a re-evaluation of the conventional perception of Antarctica, demonstrating that it has a rich geological history dating back millions of years.
PRAGATI PLATFORM (News On Air)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi chaired the meeting of the 43rd edition of PRAGATI involving Centre and State governments recently.
Facts About:
- PRAGATI, which stands for Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation, is a multi-purpose and multi-modal platform.
- Its primary purpose is to address public grievances and concurrently oversee significant government programs and projects at both the national and state levels.
- It was officially launched on March 25, 2015.
- Developed in-house by the Prime Minister's Office (PMO) team in collaboration with the National Informatics Center (NIC), it is a robust system.
- This platform promotes e-transparency and e-accountability by facilitating real-time communication among key stakeholders.
- It integrates three cutting-edge technologies, video conferencing, digital data management, and geo-spatial technology.
- It fosters cooperative federalism by uniting Chief Secretaries of states and Government of India Secretaries on a common platform.
- The Prime Minister can engage in ground-level discussions with this platform, enabling communication with state and central officials while having access to up-to-date visuals on the screen.
- The three objectives of PRAGATI are:
Grievance Redressal
Programme Implementation
Project Monitoring
CYCLONE HAMOON (Indian Express)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The severe cyclonic storm “Hamoon” weakened into a deep depression and is likely to weaken further into a depression in the next six hours, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said Wednesday.
Facts About:
- Presently situated over the west-central Bay of Bengal, it is anticipated to intensify shortly and proceed north and northeastward towards the coastal regions of Bangladesh and West Bengal.
- Named by: Iran gave the cyclonic storm its name after it formed.
Inland desert lakes and marshlands are referred to as "hamoon" in Persian.
They developed as yearly natural reservoirs in regions that border the Helmand basin.
- Projected Landfall: After weakening into a deep depression, it is predicted to make landfall between Khepupara and Chittagong on the coast of Bangladesh.
- Potential Effects: Parts of India are predicted to receive rainfall from the Hamoon, despite its decreased intensity.
- The northeastern states of Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, south Assam, and Meghalaya are expected to experience light to moderate rainfall, with isolated heavy rains (64.5 mm-115.5 mm) according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Because of the anticipated effects of the cyclone, the (IMD) has also issued a yellow alert for coastal districts in West Bengal and Odisha.
How are Cyclones Given Their Names?
- Cyclones receive their names through a process managed by regional specialized meteorological centers (RSMCs) and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers (TCWCs).
- There are a total of six RSMCs and five regional Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers responsible for this naming process.
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) serves as an RSMC and is responsible for naming cyclones that form over the north Indian Ocean, encompassing the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
- Additionally, the IMD is tasked with issuing advisories to 12 other countries in the region regarding cyclone and storm development.
NANO DAP FERTILIZER (PIB)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, India's first liquid nano di-ammonia phosphate (DAP) fertilizer plant was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah.
Facts About:
- Established in 2023 by Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO).
- Location: Gandhinagar, Gujarat's Kalol.
- It is the nation's first plant-producing liquid nano-ammonia phosphate (DAP).
What is Nano DAP fertilizer?
- Nano DAP is a nanotechnology-based fertilizer that contains di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) in the form of nanoparticles.
This means that the particles of DAP are much smaller than those in conventional DAP fertilizer.
It is more bioavailable to plants than conventional DAP because the smaller particles have a larger surface area, which allows them to be absorbed more easily by plant roots and leaves.
- It can be applied to crops through a variety of methods, including foliar application, soil application, and seed treatment.
- Nano DAP has been shown to increase crop yields by up to 20%. It can also improve crop quality and reduce the need for pesticides.
- It is more efficient than conventional DAP, meaning that less fertilizer is needed to achieve the same results.
This can save farmers money and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture.
- After urea, DAP is the second most popular fertilizer in the country.
DUST SUPPRESSANT (Indian Express)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Dust suppressants will be used in Delhi to mitigate pollution from dust. This, however, is not the first time it has been used in the Capital and parts of NCR.
Facts About:
- Magnesium or calcium salts with moisture-absorbing properties can act as dust suppressants.
- For longer-lasting dust control, water and dust suppressant powder are combined and sprayed on roads.
- Efficacy: In 2019, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) advised using them, citing a study that discovered a 30% decrease in dust concentration, including PM10, PM2.5, and PM1, when dust suppressants were used in conjunction with water.
- Dust suppressants combined with water are significantly more effective at reducing particulate matter emissions than plain water sprinkling, according to a 2019 advisory from the Delhi Public Works Department (PWD).
- Magnesium chloride and bio-additives have been found to be particularly effective as a dust suppressant.
- To reduce dust emissions, the Delhi Pollution Control Committee and the CPCB both released guidelines recommending the use of dust suppressants during construction and in areas with high levels of dust.
The Central Consumer Protection AuthoRITY (CCPA) (The Hindu)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA), has sent notices to 20 IAS coaching institutes across the country for issuing “misleading” advertisements.
Facts About:
CCPA is a regulatory authority set up under Section 10(1) of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 and came into force on 20th July, 2020.
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs is the nodal ministry.
Composition:
- It will be led by a Chief Commissioner, with only two other commissioners as members, one of whom will deal with goods cases and the other with services cases.
- There will be a Director General in charge of the CCPA's Investigation Wing.
- Additionally, District Collectors will have the authority to look into claims of consumer rights abuses, unfair business practices, and deceptive or false advertising.
The goal is to promote, protect, and enforce the rights of consumers as a group.
- It will be given the authority to: conduct investigations into violations of consumer rights and file complaints/prosecute violators.
- Order the recall of dangerous goods and services, the cessation of unfair trade practices and misleading advertisements, and the imposition of penalties on manufacturers, endorsers, and publishers of misleading advertisements.
INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION OUTLOOK 2023 (Down to Earth)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), published the "International Migration Outlook 2023."
Facts About:
- In 2021 and 2022, India had the largest migration flows to nations that are members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- In terms of citizenship, 0.13 million Indians became citizens of an OECD nation in 2021.
- The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has caused the greatest level of internal displacement and refugee inflows into the OECD, with over 10 million people becoming internally displaced or refugees.
- In terms of workers, migration flows from India (+172 percent), Uzbekistan (+122 percent), and Turkey (+240 percent) increased dramatically, making them the primary countries of origin after Ukraine.
About the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- The OECD is an international group of 38 countries that aims to foster economic development, and cooperation, and combat poverty by promoting economic stability.
- It was founded in 1961, by 18 European nations, the United States, and Canada.
Its headquarters are in Paris, France.
- Primary Goal: The primary goal of the OECD is to create policies that promote prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being for everyone.
- They produce economic reports, data, and predictions about global economic growth.
- The OECD also works to combat bribery and financial crimes worldwide, maintaining a list of uncooperative tax havens.
- India is not a member of the OECD, but a key economic partner.
PRADHAN MANTRI ANUSUCHIT JAATI ABHUYDAY YOJANA (PM-AJAY) (PIB)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities have implemented the Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana (PM-AJAY) since 2021-22.
Facts About:
Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana, or PM-AJAY, is a combination of three government schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY),
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP), and
- Babu Jagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY).
The main goals of PM-AJAY are:
- To reduce poverty among Scheduled Caste (SC) communities by creating more jobs through skill development, income-generating programs, and other initiatives.
- To improve the overall development of SC-dominated villages by providing necessary infrastructure and essential services.
The scheme has three parts:
- Developing SC-dominated villages into model villages with proper infrastructure for socio-economic progress.
- Providing grants for projects at the district or state level that aim to better the socio-economic conditions of SCs, including building infrastructure in SC-dominated villages.
- Implementing comprehensive livelihood projects, including skill development, improving infrastructure, and offering financial assistance for assets needed to generate income.
Additionally, the scheme involves constructing hostels in higher educational institutions that are highly ranked according to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) of the Government of India, and these hostels are funded by the Central, State, or Union Territory governments.
PAINTBRUSH SWIFT BUTTERFLY (The Hindu)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The paintbrush swift was recently photographed and documented for the first time in the Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh.
Facts About:
- The Paintbrush Swift butterfly, a rare species in the western Himalayas, was recently photographed and documented in Himachal Pradesh's Chamba district.
- Himachal Pradesh supports approximately 430 butterfly species, which make up about 25% of all butterfly species found in India.
- The Paintbrush Swift (Baoris farri) belongs to the Hesperiidae family and was discovered during a field survey under the Wild Bhattiyat Project in 2022.
It had never been photographed in Himachal Pradesh since its initial discovery in 1878.
- The project, initiated by the Bhattiyat Forest Range of the Dalhousie Forest Division, has documented 120 butterfly species, including the Paintbrush Swift.
- The butterfly's habitat distribution is common in northeast, central, and south India but rare in Uttarakhand.
- The Paintbrush Swift can be identified by two separated spots in the upper forewing cell.
- Conservation efforts are urgently needed to protect butterflies, including creating butterfly parks, rearing centers, and awareness campaigns, especially for high-altitude species facing habitat destruction and declining numbers.
DOGRA ARCHITECTURE (The Hindu)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Srinagar Smart City Limited and the Kashmir chapter of INTACH have joined hands to conserve vernacular elements of Kashmiri architecture, including colonnaded walkways, decorative pilasters, and exposed moulded brickwork.
Facts About:
- The buildings and structures that were built by the Dogra Hindu kings, who ruled over Jammu and Kashmir from 1846 to 1947, are known as "Dogra architecture."
- Maharaja Gulab Singh, a vassal of the Sikh Empire who later joined the British, established the Dogra dynasty.
- The Dogra kings were patrons of the arts and introduced a new architectural style that blended elements of Hindu, Islamic, and Sikh traditions.
- The interiors are richly decorated with frescoes, stucco work, and intricate wooden carvings that evoke both Rajput and Mughal architectural styles.
- European architectural features like arches, columns, and ornamental brackets were incorporated into Dogra architecture.
During the British colonial era, when interactions between European architects and local builders increased, this influence became more pronounced.
- Dogra architecture frequently uses symbolic elements taken from Hindu mythology and religious texts to express the people's spiritual beliefs.
PROJECT UDBHAV (TOI)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army has launched a new project called 'Udbhav' to integrate ancient strategic knowledge with modern military practices.
Facts About:
- The Indian Army launched the Project Udbhav initiative to re-discover the rich Indian heritage of statecraft and strategic ideas drawn from ancient Indian texts on diplomacy, warcraft, and grand strategy.
It concentrates on a wide range of topics, such as indigenous military systems, historical texts, regional texts and kingdoms, thematic studies, and complex Kautilya studies.
Project Udbhav's main goal is to build a link between the past and the present.
- The project aims to create an indigenous strategic vocabulary that is deeply rooted in India's rich philosophical and cultural heritage, going beyond simply rediscovering historical narratives.
- The ultimate goal is to incorporate traditional knowledge into contemporary military education so that the Indian Army can use age-old principles in the complex strategic environment of today.
AADI MAHOTSAV (PIB)
- 24 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Aadi Mahotsav, the National Tribal Festival will be inaguarted by the Union Minister for Tribal Affairs on 25th October, at Ahmedabad (Gujarat).
Facts About:
- The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED), is organizing this mega event.
- It acts as a one-of-a-kind, mutually beneficial bridge to begin a journey through the tapestry of India's indigenous heritage.
- At this event, more than 100 stalls would present a wide range of Indian tribal culture, handicrafts, culinary artistry, and entrepreneurial endeavors.
- 'Millets grown by Tribals' will be featured at this Aadi Mahotsav in addition to other handicrafts, handloom, pottery, and jewelry attractions.
What is the Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED)?
- It is a national-level apex organization that operates under the administrative control of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
It facilitates and provides services to help tribes sell their products.
- In order for tribal people to carry out their operations in a more organized and scientific way, it aims to equip them with the necessary knowledge, resources, and tools.
- Its goal is to promote the socioeconomic development of the nation's indigenous populations through the sale of products made by them, such as pottery, metalwork, textiles, paintings, and pottery, on which they heavily rely for a significant portion of their income.
OPTOELECTRONICS (PIB)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
For the investigation of opto-electronic properties in a variety of materials, a new Laboratory of Advance Synthesis and Characterization (LASC) in Gujarat is creating LASC probe stations for universities in India and abroad.
Facts About:
Optoelectronics is typically regarded as a sub-field of photonics and is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that source, detect, and control light.
The term "light" in this context frequently refers to both visible light and invisible radiation, such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, and infrared.
For their opto-electronic properties, materials like tungsten diselenide (WSe2) and molybdenum diselenide are being closely examined.
The ability of these materials to absorb light and reemit it as a spectrum is known as photoluminescence.
- Quantum LEDs, which can be used for computation and communication, are one example of a device that can make use of photoluminescence properties.
TRIBAL COOPERATIVE MARKETING DEVELOPMENT FEDERATION (TRIFED) (PTI)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Tribal Affairs Ministry on Saturday declared "null and void" the suspension of the managing director of TRIFED.
Facts About:
The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation (TRIFED) is a national-level organization operating under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Its primary focus is on the development and marketing of tribal handicrafts and natural products.
Established in 1987, it became registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984 (now the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002).
TRIFED's main objectives include enhancing the capabilities of tribal communities, promoting their products, and creating marketing opportunities to ensure better prices for tribal products, ultimately improving their income sustainably.
Some of its key goals are:
- Enhancing the socio-economic welfare of tribal communities.
- Facilitating and providing services to improve production within tribal communities.
- Offering training to enhance artistic skills using modern technology, making tribal products more competitive in the global market.
- Promoting tribal art and crafts to provide a stable livelihood.
- Identifying target groups, monitoring activities, and providing input to the Ministry.
Under retail marketing, TRIFED is responsible for marketing of tribal products under the brand name "TRIBES INDIA."
It promotes and establishes a sustainable market through retail outlets, exhibitions like Aadishilp, Aadichitra, and OCTAVE, international fairs, and e-marketing.
The Government of India has also entrusted TRIFED with the implementation of the Minimum Support Price Scheme for Minor Forest Produce.
Headquarter: New Delhi
It continues to operate a system of Regional Offices throughout India and a collection of TRIBES INDIA Retail Outlets.
GLOBAL COOLING COALITION (The Hindu)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The United Arab Emirates is leading the Global Cooling Pledge alongside the United Nations Environment Programme's (UNEP) Cool Coalition during the COP28 Presidency.
Facts About:
- The Global Cool Coalition is a unified front that connects action across the Kigali Amendment, Paris Agreement, and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The aim is to increase aspiration, find solutions, and mobilize action to hasten the transition to clean and effective cooling.
- In addition to the UN, the Kigali Cooling Efficiency Program, the Climate and Clean Air Coalition, and Sustainable Energy for All (SEforALL) all support it.
- It is composed of leaders from civil society, academia, and government from countries like Chile, Rwanda, and Denmark.
Why is it necessary?
- 2020 was the hottest year on record for the entire planet, after 2019, 2018, 2017, and 2015.
- By 2050, there will be 4.5 billion air conditioning units installed worldwide as a result of rising incomes and urbanization; India may account for one billion of those units.
- India's cooling demand will more than double in the next 20 years, with air conditioners alone consuming more than half of the total energy required for cooling in the country by 2037-38.
- The Union Environment Ministry in India has already launched a national cooling action plan on March 8, 2019.
LITTLE ICE AGE (The Hindu)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
During the Little Ice Age (LIA), the Western Ghats in India bore the hallmark of moist conditions, according to a recent study.
Facts About:
- It revealed significant variations in rainfall patterns during that time period, challenging the conventional view of the Little Ice Age (LIA) as a uniformly cold and dry climate with reduced monsoon rainfall.
- It was proposed that the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone's (ITCZ) northward motion, positive temperature anomalies, an increase in the number of sunspots, and high solar activity may be responsible for climate change and an accelerated South West Monsoon.
- In general, they believed that the southward shift of the ITCZ, which was brought on by increased northward energy flux across the equator during a cold northern hemisphere, was to blame for the weakest phase of the Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM) across the Indian subcontinent during the Little Ice Age.
- The high-resolution palaeoclimatic records produced in the current study may be useful in developing paleoclimatic models for future climatic predictions as well as for scientifically sound policy planning.
- In order to better understand the current Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM)-influenced climatic conditions as well as potential future climatic trends and projections, knowledge and understanding of climate change and Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM) variability during the Holocene could be of immense interest.
About the Little Ice Age:
- The Little Ice Age, which began in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, came after the Mediaeval Warming Period (roughly 900–1300 CE) and came before the current warming period.
- It was one of the coldest times in the last 10,000 years, with the North Atlantic region experiencing the greatest cooling.
- Millions of people suffered and died as a result of this cold spell, whose precise timing scholars debate but which appears to have begun around 600 years ago.
It is thought to have been the cause of crop failures, famines, and pandemics throughout Europe.
EDAKKAL CAVES (The Hindu)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Kerala Tourism has initiated a ?2.9-crore project to enhance civic amenities around Edakkal caves in Wayanad.
Facts About:
- These caves are situated on the magnificent Ambukuthi hills, 3,900 feet above sea level. The name Edakkal translates as "a stone in between."
- The ancient intricate stone carvings that are one-of-a-kind and come from the Neolithic and Mesolithic periods.
- The caves are two naturally occurring structures that are thought to have been created by a significant rock split.
- These include Neolithic-era pictorial writings that are thought to have been created at least 6,000 BCE.
Features:
- The Edakkal Caves are not actually caves, despite their name, as they also feature human and animal figures in addition to symbols and letters.
- They are a piece of a prehistoric rock shelter that naturally developed when one enormous boulder got wedged between two larger ones.
These include human figures, animals, tools, vehicles, everyday objects, and scripts in various language scripts.
- The Muniyaras, or ancient burial sites, that have been discovered in these hills have yielded a rich collection of ancient earthenware and pottery.
- The variety of the engravings suggest that the Edakkal caves were inhabited several times at different points in history.
EXERCISE 'MILAN' (TOI)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Navy will host the Mid Planning Conference (MPC) of the MILAN 24 Exercise in Visakhapatnam from February 19 to February 27, 2024.
Facts About:
- ‘MILAN’ is a multilateral naval exercise held every two years.
- It was established in 1995 by the Indian Navy.
- MILAN was originally conceived in accordance with India's 'Look East Policy,' but has since grown to include participation from other Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs) in conjunction with the Government of India's 'Act East Policy' and Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative.
- The harbor phase of MILAN 24 will include a City Parade at RK Beach, an International Maritime Seminar, a Swavlamban Exhibition, a Subject Matter Expert Exchange, and a Milan of Young Officers.
Friendly foreign country ships, maritime patrol aircraft, and submarines would take part in the sea phase alongside Indian Navy units.
- The operations will include large-force maneuvers, sophisticated air defense operations, anti-submarine warfare, and anti-surface warfare.
- MILAN 22 was held in/around Visakhapatnam from February 25th to March 4th, with 39 countries taking part.
UNITED NATIONS WORLD TOURISM ORGANISATION (UNWTO) (PIB)

- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Dhordo village in Gujarat's Kutch district was recently recognized as the Best Tourism Village by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), which was praised by India's Prime Minister.
Facts About:
- The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting sustainable and responsible tourism on a global scale.
- Its functions include acting as a global forum for tourism policy issues and encouraging the adoption of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism.
It was founded in 1975.
- Members: 159 countries are members of the UNWTO.
- Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish are the UNWTO's official languages.
- Structure of the organization:
The World Tourism Organization's General Assembly is the organization's main meeting.
It is made up of full members and associate members. It convenes every two years.
- The Executive Council serves as the UNWTO's governing body.
It is made up of 35 members, one for every five full members, who are elected by the General Assembly. It holds at least two meetings per year.
- Headquarters are in Madrid, (Spain).
GREEN ENERGY CORRIDOR (GEC) (PIB)

- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The 13 GW Renewable Energy Project in Ladakh's Green Energy Corridor (GEC) Phase-II - Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) has received approval from the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs.
Facts About:
- The Green Energy Corridor (GEC) is an initiative that aims to integrate and evacuate renewable energy into India's power grid, promote sustainable growth, and improve energy security. It is divided into two stages.
- Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (POWERGRID) is the implementation agency.
- Implementation of GEC-1 is already underway in Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan, with the goal of integrating and evacuating 24GW of Renewable Energy (RE).
- For GEC-2, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh will be the first states to implement.
Grid integration and power evacuation of approximately 20 GW of renewable energy projects over a five-year period (FY 2021-22 to 2025-26).
Objectives:
- Synchronize renewable energy sources (wind and solar) with traditional power sources.
- Non-fossil fuel installed capacity should reach 500 GW by 2030..
- 20,000 MW of large-scale renewable energy should be evacuated.
- Importance: Improve India's long-term energy security; Promote environmentally friendly growth by reducing carbon footprint; Create employment opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers.
WHITE PHOSPHOROUS BOMBS (Indian Express)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent reports, Israeli forces have been using white phosphorous against the civilian population of Gaza.
Facts About:
It is a waxy solid that is colorless, white, or yellow.
Occurrence:
- It does not occur naturally. Phosphate rocks are used to make it.
- It is a highly flammable substance that reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
- As little as 10 to 15 degrees above room temperature can cause it to catch fire.
Every country has strict regulations regarding its manufacturing and handling due to its combustible nature.
Applications:
- It is primarily used in the military, but it may also be used as a component in fertilizers, food additives, and cleaning compounds.
- It was originally used in pesticides and fireworks, but many countries have banned its use in a variety of industries.
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), an intergovernmental organization and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention, has not included White Phosphorus in any of the three Chemical Weapons Schedules.
YARD 12706 (IMPHAL) (PIB)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) recently delivered to the Indian Navy the third Stealth Destroyer of the Project 15B Class Guided Missile Destroyer, Yard 12706 (IMPHAL).
Facts About:
- The ship is made of indigenous steel DMR 249A and is one of India's largest destroyers, with an overall length of 164 meters and a displacement of over 7500 tonnes.
- The ship is propelled by a powerful Combined Gas and Gas Propulsion Plant (COGAG), which consists of four reversible Gas Turbines and allows her to reach speeds of more than 30 knots (approximately 55 Kmph).
- The ship is a powerful tool that can be used for a wide range of operations and missions, covering every aspect of maritime warfare.
- It is equipped with medium range Surface to Air Missiles ('Barak-8') and supersonic Surface to Surface Missiles ('Brahmos').
- The Destroyer is equipped with indigenously made anti-submarine weapons and sensors, including the Hull-mounted Sonar Humsa NG, Heavy Weight Torpedo Tube Launchers, and ASW Rocket Launchers.
- Compared to earlier classes of naval destroyers and frigates, it is more adaptable.
- It can operate independently without supporting vessels and can also serve as the flagship of a naval task force thanks to its all-around capability against enemy submarines, surface warships, anti-ship missiles, and fighter aircraft.
Toto language (The Hindu)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a dictionary called Toto Shabda Sangraha has been created with the aim of preserving a language from becoming extinct.
Facts About:
- It belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family and is the native language of the Toto tribal community. Toto is typically written using the Bengali script.
- Remarkably, a script for Toto was developed by a prominent community member named Dhaniram Toto as recently as 2015.
- Toto is spoken by a relatively small population of around 1,600 individuals residing in parts of West Bengal that border Bhutan.
Key Highlights of the Toto Shabda Sangraha:
- This dictionary has been meticulously compiled by Bhakta Toto, who serves as both a bank employee and a poet. It has been jointly published by a trust and Bhasha Samsad.
- The dictionary serves as a significant step towards preserving the Toto language, which has primarily been an oral tradition, by documenting its vocabulary in written form.
- To facilitate wider understanding, Toto words will be translated into Bengali and English and presented using the Bengali script, as the Toto script is still in its early stages of development, and community members are more familiar with the Bengali script.
Naganathaswamy Temple (The Hindu)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Tamil Nadu Department of Archaeology is preparing to initiate the restoration of the ancient Naganathaswamy Temple, which has stood for a millennium in Manambadi, located within the Thanjavur district.
Facts About:
- This temple was commissioned by Rajendra Chola I, reigning from 1012 to 1044 CE.
- In historical inscriptions, it is also known as the Kailasamudaiyar Temple.
- Key Features:
- Renowned for its intricate stone carvings and significant inscriptions.
- Comprises a single-tiered vimana (sanctum) and a mukha mandapa (front hall).
- The walls of both structures are divided into three sections.
- Within the central bays of the vimana, niches are dedicated to Dakshinamurthi in the south, Lingodhbava in the west, and Brahma in the north.
- The mukha mandapa features three niches each on the south and north sides.
- Notable sculptures in the southern niches include Bikshatana, Adavallan, and Ganapathi, while the northern niches feature Gangadarara, Durga, and Ammaiappar.
- All these niches exhibit finely crafted and distinctive makara thoranas (decorative arches) with central relief sculptures.
- Inscriptions: The temple boasts important inscriptions dating back to the reigns of Rajendra Chola I and Kulothunga I (1070-1120 CE).
- A total of nine informative inscriptions have been documented within the temple premises.
- The earliest of these inscriptions dates to the fourth year of Rajendra Chola I's rule and pertains to a tax-free land grant by the nagaratthar of Ilaichikkudi for establishing a flower garden in honor of the king for the temple's benefit.
CRIIIO 4 GOOD Initiative (PIB)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Union Minister for Education, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship unveiled a program called 'CRIIIO 4 GOOD'.
Facts About:
- This is a novel online module designed to impart essential life skills.
- Comprising a series of eight cricket-themed animated films, its primary objectives are to promote gender equality, empower girls with valuable life skills, and foster their active engagement in sports.
- Leveraging the immense popularity and enthusiasm for cricket among young audiences, the ICC (International Cricket Council) and UNICEF collaborated to introduce these modules, aiming to inspire children and youth to embrace crucial life skills and appreciate the significance of gender parity.
- The program is available in three languages: English, Hindi, and Gujarati.
- The eight modules revolve around key themes such as leadership, problem-solving, self-assurance, decision-making, negotiation, empathy, teamwork, and goal-setting, all depicted through cutting-edge animations using cricket-related examples.
- This initiative was launched in partnership with the International Cricket Council, UNICEF, and the Board of Control for Cricket in India.
Sankalp Saptaah (News On Air)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister will launch a special week-long program called 'Sankalp Saptaah' at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- This initiative is closely tied to the successful execution of the Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP).
- In order to implement the ABP effectively and devise a robust strategy for block development, 'chintan shivirs' or brainstorming sessions were conducted at the village and block levels across the nation. The Sankalp Saptah marks the culmination of these brainstorming sessions.
- Sankalp Saptah will be observed in all 500 aspirational blocks.
- Each day during Sankalp Saptah will be dedicated to a specific development theme that all aspirational blocks will focus on.
- The themes for the initial six days include 'Comprehensive Health', 'Nourished Families', 'Cleanliness', 'Agriculture', 'Education', and 'Prosperity Day'.
- The final day of the week will be a celebration of the collective efforts undertaken throughout the week, known as 'Sankalp Saptah – Inclusive Conclave.'
- The inaugural event will see the participation of approximately 3,000 representatives from panchayats and block-level officials from across the country at Bharat Mandapam.
CALIPSO Mission (Indian Express)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, NASA declared the conclusion of the CALIPSO mission, which conducted assessments of climate, weather, and air quality.
Facts About:
- CALIPSO (Cloud-Aerosol LIDAR and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations), is a dedicated mission aimed at understanding the influence of clouds and aerosols on Earth's climate.
- A collaborative endeavor between NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales), the French space agency, CALIPSO took to the skies in 2006 as a satellite-based observatory.
- Scientists have harnessed CALIPSO's data to construct three-dimensional atmospheric models, enhancing our capacity to forecast future climate changes.
- CALIPSO has been an integral part of the "A-Train" constellation of spacecraft, which includes Aqua, Aura, and PARASOL, all dedicated to the study of Earth's weather and environment.
Key Instrumentation:
- The mission is equipped with CALIOP, a lidar system that operates at two wavelengths and is sensitive to polarization.
Additionally, it carries two passive sensors functioning in the visible and thermal infrared spectral ranges.
- CALIOP emits laser pulses and measures the light scattered back by clouds and aerosols, enabling the creation of vertical profiles detailing properties such as height, thickness, and optical depth.
- Notably, CALIOP is the first lidar to provide continuous atmospheric measurements from Earth's orbit.
- This invaluable data aids scientists in generating comprehensive three-dimensional profiles of cloud and aerosol distributions.
- Throughout its 17 years of operation, the mission amassed over 10 billion LIDAR measurements and contributed to the creation of numerous scientific reports.
Global Innovation Index 2023 (PIB)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India maintains its position at the 40th rank among 132 economies in the Global Innovation Index for the year 2023..
Facts About:
- Published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- Serves as a valuable tool for governments worldwide to evaluate the impact of innovation on social and economic development in their nations.
- The India Launch of GII 2023 is being virtually hosted on September 29, 2023, by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and WIPO.
Key Insights:
- The Global Innovation Index relies on a diverse dataset, incorporating 80 indicators from international public and private sources, offering a comprehensive view of innovation beyond conventional measures.
- Top 5 countries in the ranking include Switzerland, Sweden, the United States, the United Kingdom (4th), and Singapore (5th).
- India is recognized among the 21 economies that have consistently outperformed in innovation relative to their level of development for the 13th consecutive year.
- The report highlights India, Iran, the Philippines, Turkey, Vietnam, and Indonesia as economies within the GII top 65 that have made significant ranking improvements over the last decade.
- Within the Central and Southern Asia region, India secures top positions in categories such as Human capital and research (48th), Business sophistication (57th), and Knowledge and technology outputs (22nd).
- Prominent indicators for India encompass ICT services exports (5th), Venture capital received (6th), Graduates in science and engineering (11th), and Global corporate R&D investors (13th).
e-Cabinet System (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Tripura inaugurated an e-cabinet system in Agartala, aimed at advancing digital infrastructure and enhancing the digitization of government services and information.
Facts About:
- The e-Cabinet system is a robust software portal designed for State Governments to facilitate electronic and online Cabinet meetings.
- It has been developed by the National Information Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
- Tripura is now the fourth state, and the second in the Northeast region, to implement the e-cabinet system, following in the footsteps of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Key Features:
- Enhances the utilization of technology in meetings and reduces paper consumption.
- Streamlines workflow activities for meetings, covering pre-meeting, during the meeting, and post-meeting phases.
- Offers a user-friendly interface designed for smart tablets, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Incorporates a secure push and pull mechanism to safeguard sensitive Cabinet matters.
- Establishes an institutional memory and knowledge repository, facilitating quick searches and retrieval of information.
- For virtual meetings, eCabinet seamlessly integrates with the Bharat VC solution of NIC.
Benefits and Impact of eCabinet:
- Substantial savings in paper, fuel, and manpower resources.
- Real-time data updates.
- Enhanced information accessibility, promoting coordinated actions.
- Improved decision-making processes and swift retrieval of meeting decisions and action taken.
- Enables virtual participation of Ministers in Cabinet proceedings.
Five Eyes’ Intelligence Alliance (The Hindu)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The recent claims made by Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, connecting the murder of Hardeep Singh Nijjar on Canadian territory to the Indian government, have drawn attention to the intelligence-sharing coalition known as the 'Five Eyes' (FVEY).
Facts About:
- This multilateral intelligence-sharing network involves more than 20 agencies from five predominantly English-speaking nations:
Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- It encompasses both surveillance-based activities and signals intelligence (SIGINT).
- The intelligence documents shared among member countries are labeled as 'Secret—AUS/CAN/NZ/UK/US Eyes Only,' which gives rise to the group's name, 'Five Eyes.'
Background of the Alliance:
- The origins of this alliance between the U.S. and the U.K. date back to the Second World War when they collaborated to counter the Cold War Soviet threat.
- These two nations, renowned for their code-breaking achievements during World War II, established cooperation in sharing intelligence related to various forms of signals, including radio, satellite, and internet communications.
- Following the war, in 1946, the alliance formalized through an agreement focused on signals intelligence.
This agreement, originally named the British-U.S. Communication Intelligence Agreement (BRUSA) and now known as the UKUSA Agreement, was signed between the U.S. State-Army-Navy Communication Intelligence Board (STANCIB) and the British London Signal Intelligence Board (SIGINT).
- Initially, its scope was limited to 'communication intelligence matters only,' involving the unrestricted exchange of intelligence products across six areas: traffic collection, acquisition of communication documents and equipment, traffic analysis, cryptanalysis, decryption and translation, and the acquisition of information regarding communication organizations, practices, procedures, and equipment.
- Over time, the alliance expanded to include 'second party' countries, with Canada joining in 1948, and Australia and New Zealand becoming part of the alliance in 1956.
Conocarpus Tree (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the government of Gujarat has instituted a prohibition on the planting of Conocarpus trees in both forested and non-forested areas, citing concerns regarding their detrimental effects on the environment and human well-being.
Facts About:
- The Conocarpus tree is a flowering plant belonging to the Combretaceae family.
- It is categorized as an invasive mangrove species.
- These trees bloom during the winter season, releasing pollen into their surroundings.
- In India, public authorities have commonly used Conocarpus for landscaping purposes, including road medians, roadsides, and public gardens.
- In the Arabian Peninsula, it has been employed to combat desert storms and pollution.
- This tree is renowned for its year-round dark green leaves and its ability to thrive in harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures.
- It exhibits adaptability, even in areas with high salinity.
- The Conocarpus tree absorbs a significant amount of water from the soil, posing a threat to groundwater levels.
- Its extensive root system can damage communication cables, drainage lines, and drinking water pipelines.
- This species is native to various regions in North and South America, as well as parts of Africa.
Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) has made a plea to the diamond industry, urging them to halt the importation of rough diamonds.
Facts About:
- GJEPC serves as the apex organization representing India's Gem and Jewellery industry, operating under the sponsorship of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India.
- Primary Role: The Council's primary mission is to introduce Indian gem and jewellery products to global markets and facilitate their exports.
It achieves this by furnishing its members with crucial information on foreign trade inquiries, trade regulations, tariff rates, and updates on jewellery fairs and exhibitions.
- Location: Headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, GJEPC maintains a presence through regional offices nationwide, boasting a membership exceeding 7,500.
Additional Functions:
- Collaborating in international jewellery showcases.
- Encouraging countries to explore opportunities for cooperation in the supply of rough diamonds, colored gemstones, and finished jewellery.
- Identifying potential partners and buyers in international markets through buyer-seller meetings.
- Administering the Kimberly Process Certification Scheme as India's Nodal Agency.
- Advocating for export-related matters with the Government, Ministries, Regulatory Authorities, and Agencies.
- Conducting image-building campaigns via international advertisements, publications, and audio-visuals.
- Establishing training institutes across six cities (Mumbai, Delhi, Surat, Jaipur, Varanasi, and Udupi) to impart manufacturing skills and promote technical and design excellence.
- Initiating the establishment of Jewellery Parks throughout the country.
Balsams (Genus Impatiens) (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Balsams, belonging to the genus Impatiens, are currently putting on a vibrant display of blooms in Munnar, offering a captivating visual treat to tourists.
Facts About:
- Locally referred to as Kasithumba and Onappovu.
- Commonly known as 'touch-me-not' due to its seed dispersal mechanism.
- Various names used for these plants include balsams, touch-me-nots, and jewel weeds.
Distribution:
- Natively found in tropical, sub-tropical, and northern temperate regions worldwide.
- Predominantly present in India, China, Africa, and scattered regions of Europe and North America.
- India boasts 220 balsam species, with 135 of them thriving in the southern Western Ghats.
- The Western Ghats, including Anamudi, its highest peak, host diverse wild balsam varieties.
- Typically, balsams complete their life cycle between June and December.
- These fleshy, herbaceous plants are often found in pockets within forested areas.
- They thrive in humid habitats and complete their life cycle during the rainy season.
- Balsams are recognized as significant indicators of climate change.
Manis Mysteria (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In addition to the eight previously identified pangolin species, researchers have recently found a ninth variety, which is currently given the temporary name "Manis mysteria.
Facts About:
Scientists have recently made a significant discovery in the world of wildlife by identifying a previously unknown ninth species of pangolin.
- This newly found pangolin variety has been tentatively named "Manis mysteria."
Origins from Confiscated Scales: The origins of this remarkable discovery trace back to the examination of pangolin scales that were seized in China's Yunnan province during the years 2015 and 2019.
- These scales provided vital clues leading to the identification of the new species.
Ancient Divergence: Research indicates that "Manis mysteria" took a distinct evolutionary path around five million years ago, separating from its Philippine and Malayan pangolin relatives.
- This long separation in the evolutionary timeline highlights its unique characteristics.
Distinctive Features of Pangolins: Pangolins are known for their distinctive characteristics, including protective keratin scales that cover their bodies and a diet primarily consisting of ants and termites.
- They hold the distinction of being the only mammals with such specialized scales.
Defensive Behavior: One of the most intriguing aspects of pangolins is their ability to curl up into a tight, defensive ball when they feel threatened.
- This remarkable behavior helps protect them from potential predators.
- Grave Threats to Pangolins: Unfortunately, all species of pangolins face severe threats to their survival.
- Each species is currently listed on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, a concerning designation that highlights their vulnerable status.
- For instance, the Indian pangolin is specifically categorized as "Endangered," underlining the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard these unique creatures.
Social Bonds (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) has just released its first-ever social bonds, amounting to a total of Rs 1,040.50 crore.
Facts About:
- Social bonds, or social impact bonds (SIBs), are a type of bond used to raise funds for projects with positive social outcomes.
- These projects tackle various societal issues like healthcare, education, affordable housing, poverty reduction, and environmental sustainability.
Notable Example in India:
- In 2020, the Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation (PCMC) in Pune, Maharashtra, partnered with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to create India's first Social Impact Bond (SIB).
Key Features of NABARD's Social Bonds:
- NABARD's social bonds are the first externally certified AAA-rated Indian Rupee-denominated SIBs. They have received 'AAA' ratings from CRISIL and ICRA.
- The initial bond size was ?1,000 crore, with the option to accept oversubscriptions up to ?2,000 crore, totaling up to ?3,000 crore.
- Each bond has a face value of ?1 lakh.
- Maturity period: 5 years
- Coupon Rate: 7.63 percent
Sustainability Bond Framework:
- NABARD has introduced a Sustainability Bond Framework to finance and refinance green and social projects.
- Eligible social projects include basic infrastructure, essential services, affordable housing, job creation, food security, socioeconomic advancement, and empowerment.
- Projects focused on energy efficiency, such as green buildings, energy storage, and smart grids, are also eligible for funding through these bonds.
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) (Indian Express)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has made changes to the regulations for Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA). They now require these NGOs to furnish information about assets, both movable and immovable, that have been established using foreign funds in their annual returns.
Facts About:
- FCRA is a law governing foreign contributions, especially monetary donations, to NGOs and entities in India.
- Originally passed in 1976 and significantly amended in 2010.
- Aims to prevent foreign organizations from influencing India's politics, society, economy, or religion for harmful purposes.
- Administered by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Defines 'foreign contribution' as donations, currency, or securities from foreign sources.
- Allows individuals, associations, companies, and others to receive foreign contributions with FCRA registration.
- Funds must be used for the intended purpose, with a maximum of 20% for administrative expenses.
- Requires NGOs to open a designated bank account with the State Bank of India, Delhi.
- Registration is mandatory for NGOs and can be renewed if they meet requirements.
- Cancellation is possible for false statements or illegal activities.
- Suspension and fund-freezing authority were also granted to the Ministry.
- Challenges to government orders can be filed in the High Court.
Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (LiveMint)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RoDTEP scheme, which initially lasted until September 30, 2023, will now continue until June 30, 2024, with the same rates for products that are already being exported.
Facts About:
- The RoDTEP Scheme, officially known as the Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products, plays a crucial role in helping Indian exporters.
- It became operational on January 1, 2021, replacing the earlier export incentive program called Merchandise Exports from India (MEIS).
- This change was necessary because the World Trade Organization (WTO) found that the MEIS scheme violated WTO rules by providing export subsidies for a wide range of goods.
- How it Works: Under the RoDTEP Scheme, exporters receive a rebate based on a percentage of the value of their exports (known as FOB or Freight On Board value).
This rebate is given in the form of a transferable duty credit/electronic scrip (e-scrip), and the details of these credits are maintained digitally by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
The RoDTEP Committee, which operates within the Department of Revenue, is responsible for reviewing and recommending the maximum rates for different export sectors under this scheme.
- Main Objective: The primary goal of the RoDTEP Scheme is to offer comprehensive support to exporters by refunding the duties and taxes incurred during the production and distribution of exported products.
Importantly, it covers taxes, duties, and levies imposed at the central, state, and local levels, which are not reimbursed through other existing mechanisms.
- Financial Support: In the fiscal year 2023-24, the Indian Government has allocated a substantial budget of Rs. 15,070 crores to support the RoDTEP Scheme.
- Engaging with Stakeholders: The RoDTEP Committee has recently started its work by collaborating with Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and Chambers of Commerce.
Armed Forces Tribunal (Indian Express)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) Chandigarh Bench Bar Association has taken the step of going on an unlimited strike. This strike is a response to the decision made by the AFT chairperson to move a judicial member from Chandigarh to Kolkata.
Facts About:
- The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) is like a special court in India for military matters, and it started in 2009 under the Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007.
- What it does: It deals with arguments and complaints about things like appointments, jobs, and the rules for people who are part of the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- It handles appeals when someone disagrees with the decisions made by military courts.
- If the military court's decision seems right, the Tribunal can say so.
But if it's not right, the Tribunal can change it.
- If someone doesn't agree with what the Tribunal says, they can only go to the Supreme Court to argue their case.
- The AFT has its main office in New Delhi, and there are eight other offices in different cities.
- Each office has two important people:
A Judicial Member who is a retired High Court Judge and
An Administrative Member who is a retired Armed Forces officer with a high rank.
- Sometimes, a Judge Advocate General (JAG) who has been in the job for at least a year can also be an Administrative Member.
- How it works:
The Tribunal follows certain rules for how they do things, and they use English for all their work.
They usually do things the way High Courts in India do them.
Dadasaheb Phalke Award (PIB)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister of Information & Broadcasting has just revealed some exciting news. The renowned actress, Ms. Waheeda Rehman, is set to receive the Dadasaheb Phalke Lifetime Achievement Award for the year 2021.
Facts About:
- The Dadasaheb Phalke Award is India's top honor in the world of cinema.
- Every year, it's given out at the National Film Awards ceremony, organized by the Directorate of Film Festivals, part of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- This award is for people who have made a really big and important contribution to Indian cinema.
- When someone gets this award, they receive a special Golden Lotus medal, a shawl, and 10 lakh rupees in cash.
- The award was created by the Government of India to remember Dadasaheb Phalke, who's often called "the father of Indian cinema."
- It all began in 1969, and the first person to receive it was the famous actress Devika Rani, known as "the first lady of Indian cinema.
Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary is like a lush oasis in a large, dry area that covers seven districts in the northeastern part of Kalyana Karnataka, Karnataka.
Facts About:
- It's located near the Chandrampalli Dam in Karnataka's Kalaburagi district.
- This sanctuary was officially established in 2011.
- It's special because it's the first dry land Wildlife Sanctuary in South India.
- This area in the Hyderabad Karnataka Region is known for having a lot of different plant species.
- You can find a mix of forests, including dry and moist deciduous areas, with Acacia and Teak trees on the edges.
- Some important plants include medicinal herbs, Red Sanders, and Sandalwood.
- As for animals, it's home to Black Bucks, Common Foxes, Four-horned Antelopes, Hyenas, Indian Wolves, and more.
There are also 35 different types of birds here.
- A special mention goes to the Lambani Tandas, a protected tribal community that lives in harmony with nature in this area.
World Coffee Conference (The Hindu)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 5th World Coffee Conference (WCC) is happening in Bengaluru, and it's a joint effort by the International Coffee Organization (ICO), the Coffee Board of India, and the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, along with the Government of Karnataka.
Facts About:
- This is the first time India is hosting this conference.
- In the past, the conference has been held in London (2001), Brazil (2005), Guatemala (2010), and Ethiopia (2016).
- The event is a collaboration between the Coffee Board, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, and the International Coffee Organization.
- The conference's mascot is Coffee Swami.
- The main theme of the conference is "Sustainability through Circular Economy and Regenerative Agriculture.
About the International Coffee Organization:
- The organization was created in 1963 with support from the United Nations after the first International Coffee Agreement was approved in 1962.
- The ICO is a special international group that brings together countries that export and import coffee.
- Right now, it represents a big part of the world's coffee - 93% of coffee production and 63% of coffee consumption.
- Their mission is to make the coffee business better all around the world in a way that's good for everyone involved.
- There are 49 countries in this group, with 42 of them exporting coffee and 7 of them importing it. India is one of these member countries.
Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma (PRIP) scheme (PIB)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Government, led by the Minister of Chemicals and Fertilizers and the Minister of Health & Family Welfare, has just introduced a new program called PRIP. This program aims to support and encourage research and innovation in the Pharma and MedTech sectors.
Facts About:
- The PRIP scheme has a clear goal: to shift the Indian pharmaceutical sector from being focused on costs to being driven by innovation.
This means we want to encourage more research and new ideas in the country.
- Aim: We want to create stronger connections between industries and educational institutions to do research in important areas.
This will help us build a culture of high-quality research and support our scientists.
- By doing this, we hope India will be more competitive on the global stage, and it will also create better job opportunities.
- How Long It Will Last: This program will run for five years, from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
- The Scheme Has Two Parts:
Part A: We will invest Rs 700 Crores to set up 7 Centers of Excellence (CoEs) at the National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs). These will focus on specific areas of research.
Part B: We will support research in six important areas like new medicines, complex generics, medical devices, stem cell therapy, rare disease drugs, and fighting against drug resistance. This will also include helping industries, small businesses, startups, and academic research.
- Total Budget: The program has a total budget of Rs. 4250 Crores.
- This scheme is all about making pharmaceutical research in India stronger and more innovative.
- It will support researchers and industries working on important health-related projects.
Brent Crude (LiveMint)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Brent crude oil has recently surged to its highest point in 10 months, exceeding $93 per barrel.
Facts About:
- Brent Crude is the primary benchmark used to determine oil prices globally.
- The name "Brent" originates from the Brent oil field, which was discovered in the 1970s and became a major source of oil production.
- Roughly two-thirds of all internationally traded crude oil is priced relative to Brent, making it the most widely recognized benchmark.
- It's a type of light, sweet crude oil extracted from oil fields in the North Sea.
- Brent crude's special characteristics, such as its low density and low sulfur content, make it easier to refine into products like gasoline.
- Since it's transported by sea, it's convenient to move Brent crude oil to distant locations.
- The price of Brent Crude is influenced by several factors, including shifts in supply and demand, geopolitical events, production interruptions, and economic conditions.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Down to Earth)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Bhopal (IISER Bhopal) pinpointed a particular circular RNA (circRNA) named 'ciTRAN.' This circRNA plays a vital role in the replication of the HIV-1 virus, which causes AIDS, inside the human body.
Facts About:
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a molecule found in living cells that carries genetic instructions and aids in protein production.
- Most RNAs have a linear, open-end structure, but circular RNA, known as 'circRNA,' forms a closed loop.
- CircRNA plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and is essential for various biological processes.
- Its involvement in the replication of HIV-1 was not well understood for a long time.
- Identifying circular RNA can be challenging because it is typically present in lower amounts, making it harder to detect in its natural form.
- During viral infections, the abundance of viral genetic material can make it difficult to isolate less common components like circular RNA.
Bolson tortoises (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Biologists are working slowly and steadily to assist North America's biggest and most uncommon tortoise species.
Facts About:
- Bolson tortoises are the biggest and rarest land reptiles in North America.
They are also the rarest among the six Gopherus species that are found on this continent.
- Among Bolson tortoises, adult females are generally larger than males.
- These tortoises are land-dwellers and spend over 95% of their time in burrows they dig using their shovel-like front feet.
- They are most active from around April to October when they do everything like searching for food, nesting, and mating.
- While we don't know their exact lifespan, Bolson tortoises can live for more than a century.
- Currently, Bolson tortoises are found in a small area in north-central Mexico, specifically in the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Durango.
However, they exist in separate groups within this region.
- In terms of conservation, Bolson tortoises are Critically Endangered according to the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
Mukurthi National Park (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Tamil Nadu Forest Department carried out thorough operations in Mukurthi National Park and the nearby forest areas to prevent any unlawful entry of individuals and deter poaching activities.
Facts About:
- Mukurthi National Park is situated in the western part of the Nilgiris Plateau, in the northwest corner of Tamil Nadu.
- This park was established primarily to safeguard its key species, the Nilgiri tahr.
- The park is crossed by the Pykara and Kundah rivers, and it's home to several streams that originate within the park and flow into the Bhavani Puzha River.
- It holds the prestigious status of being a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- In terms of its vegetation, the park features high-altitude montane grasslands and shrublands with shola forests, in an area with ample rainfall.
- You can find various plants in the park, including fragrant shrubs like Gaultheria fragrantissima, Helichrysum, and Berberis. Other notable plants include Rhododendrons, Cinnamon, Mahonia, Satyrium, and Raspberries.
- As for wildlife, Mukurthi National Park is a sanctuary for endangered species such as the Nilgiri tahr, Indian elephants, Nilgiri Langur, Bengal tiger, and bonnet macaque, among others.
Galactic Tides (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Similar to how the oceans on Earth have tides at their shores, galaxies in the universe also go through tides, but on a much grander scale.
Facts About:
- Galactic tides are like gravitational pulls that objects within a galaxy, like our Milky Way, experience due to the galaxy's gravitational field.
- These tidal forces happen because of the gravitational interactions between celestial objects, such as stars and gas clouds, within the galaxy.
- Galactic tides have several effects on a galaxy's evolution.
They can change the shape of a galaxy by creating tidal tails and bridges, encouraging the birth of new stars, and disrupting smaller star systems.
- They also alter the paths that stars follow in their orbits, causing long-term changes in a galaxy's structure.
- Galactic tides even play a role in how nearby galaxies interact or don't interact with each other.
For example, when studying Andromeda, the closest galaxy to the Milky Way, researchers have noticed tidal streams near its edges.
- These streams may be signs of dwarf galaxies that were swallowed by Andromeda over time.
- Galactic tides also impact the supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies, leading to events that change how these cosmic giants interact with nearby stars.
India-UN Capacity Building Initiative (News On Air)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India and the United Nations have introduced a collaborative capacity-building effort known as the 'India-UN Capacity Building Initiative.' Its goal is to promote progress and prosperity in the Global South.
Facts About:
What is the Global South?
- The Global South encompasses countries in regions such as Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia (excluding Israel, Japan, and South Korea), and Oceania (excluding Australia and New Zealand).
- These regions are generally characterized by lower levels of economic and industrial development.
About the India-UN Capacity Building Initiative:
- This initiative aims to enhance the capabilities of countries in the Global South.
- Its objective is to facilitate the sharing of India's development experiences, best practices, and expertise through capacity-building programs and training.
- The initiative extends the achievements of India's G20 Presidency, which emphasized the inclusion of perspectives from the Global South in the G20 agenda.
- It builds upon India's existing bilateral cooperation in development and capacity-building with partner countries.
- As part of this endeavor, the UN India team will collaborate with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to leverage India's Technical and Economic Cooperation platform. This partnership will enable the dissemination of India's development experiences and best practices worldwide.
- Furthermore, it will translate the development objectives outlined during India's G20 Presidency into action.
- This includes the implementation of the G20 Action Plan for advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and enhancing technology and digital infrastructure.
Exercise Yudh Abhyas (PIB)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 19th iteration of 'EXERCISE YUDH ABHYAS' is scheduled to take place from September 25th to October 8th, 2023, at Fort Wainwright, Alaska, USA
Facts About:
- Exercise Yudh Abhyas is an annual collaborative military exercise carried out jointly by the Indian Army and the United States Army.
- In this edition, the Indian Army contingent, consisting of 350 personnel, will participate. The lead battalion from the Indian side is associated with the MARATHA Light Infantry Regiment.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to practice a series of tactical drills aimed at improving the ability to work together effectively during United Nations peacekeeping operations.
- The exercise's theme centers on the 'Employment of an Integrated Battle Group in Mountain/ Extreme Climatic Conditions,' as outlined in Chapter VII of the United Nations mandate.
- The Field Training Exercise will encompass various elements, including the validation of Integrated Battle Groups in confronting hostile forces at the Brigade level, the establishment of an Integrated Surveillance Grid at the Brigade/ Battalion level, and the utilization of Heliborne/ Airborne units and Force Multipliers, among others.
- Additionally, the exercise will facilitate the exchange of ideas and best practices in a wide range of combat skills, encompassing combat engineering, obstruction clearance, and tactics for dealing with mines and Improvised Explosive Devices.
Other Exercises involving India and the USA:
- Army: Vajra Prahar
- Navy: MALABAR (Multilateral)
- Air Force: Cope India, Red Flag (Multilateral)
Free Movement Regime (Indian Express)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chief Minister of Manipur recently stated that his government has requested the Union Home Ministry to discontinue the free movement arrangement along the India-Myanmar border and finalize the border fencing.
Facts About:
- The Free Movement Regime (FMR) allows all hill tribes, whether they hold citizenship in India or Myanmar, to travel within a 16 km radius on either side of the Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB).
- To cross the border, they need to present a border pass with a one-year validity issued by the relevant authority.
Each visit can last for up to two weeks.
- The FMR was put into effect in 2018 as part of the Central government's Act East policy.
- Both governments, India and Myanmar, implement the FMR for the benefit of the people residing along the IMB.
- This arrangement facilitates greater cultural integration among residents of trans-border villages.
They engage in activities like weddings, joint celebrations of festivals, and cross-border trade.
- The FMR underscores the physical, ethnic, linguistic, cultural, and fraternal connections among communities living across the border.
- Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB):
The IMB stretches over 1,643 km, traversing four states: Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
It extends from the northern tripoint with China to the southern tripoint with Bangladesh.
The responsibility of guarding the IMB falls on the Assam Rifles.
I2U2 Group (TOI)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The I2U2 group has just unveiled a new collaborative space project with the goal of developing a one-of-a-kind space tool designed for use by policymakers, organizations, and business innovators.
Facts About:
- The I2U2 Group comprises India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States.
- Formation:
This alliance was originally established in October 2021 with the primary objective of addressing infrastructure, transportation, and maritime security issues in the region.
Originally, it was named the "International Forum for Economic Cooperation" and was also referred to as the "West Asian Quad."
- First Virtual Summit: In July 2022, the group conducted its inaugural virtual summit.
- This unique coalition of nations identifies viable projects and initiatives aimed at addressing significant challenges.
- It places special emphasis on collaborative investments and new endeavors in areas such as water, energy, transportation, space, health, food security, and technology.
- The group's objectives encompass mobilizing private sector resources and expertise to achieve various goals, including the modernization of infrastructure, the promotion of low-carbon development pathways, and enhancements in public health.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Indian Express)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
JP Morgan Chase & Co will add Indian government bonds to its emerging markets bond index starting in June 2024.
Facts About:
- This index serves as a benchmark for measuring how well international government and corporate bonds from emerging market countries perform.
These countries must meet specific liquidity and structural requirements.
- Emerging market bonds are debt instruments issued by developing nations.
They usually offer higher yields compared to bonds from developed countries.
- A total of 23 Indian Government Bonds (IGBs) with a combined notional value of $330 billion are eligible for inclusion.
They are all categorized as "fully accessible" for non-residents.
- Advantages of this inclusion:
This development is expected to lead to higher demand for the Indian rupee, potentially protecting it from depreciation.
Lower borrowing costs could support important infrastructure projects.
Increased liquidity may result in more efficient trading conditions.
- India's local bonds will become part of JP Morgan's Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index.
- They are expected to make up a maximum of 10 percent of the GBI-EM Global Diversified Index (GBI-EM GD).
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (The Hindu)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A recent study has shown that Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is becoming more prevalent among contemporary women in India.
Facts About:
- PCOS is a prevalent hormonal issue that primarily affects women in their childbearing years.
- Symptoms: PCOS is associated with irregular ovulation, elevated androgen (male hormone) levels, and the presence of numerous small ovarian cysts.
It can result in missed or irregular menstrual cycles, excess hair growth, acne, fertility challenges, and weight gain.
- Causes: PCOS often has a genetic component, with a family history of diabetes or obesity being common.
Environmental factors that promote an unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, and high stress levels can also contribute.
- Treatment: Managing PCOS involves lifestyle adjustments, medications, and fertility treatments to address its symptoms and complications.
- PCOS is a concern for one out of every five women in India, and 60% of those seeking infertility treatments are doing so because of issues related to PCOS.
Tasmanian Tiger (The Hindu)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Researchers have recently extracted Ribonucleic acid (RNA) from the desiccated skin and muscle of a Tasmanian tiger that had been stored at a museum in Stockholm since 1891.
Facts About:
- The Tasmanian tiger had a wolf-like appearance, distinguished by tiger-like stripes along its back.
- Regrettably, the last known Tasmanian tiger passed away in a Tasmanian zoo in 1936.
- This large carnivorous marsupial is now considered extinct.
- Among the family Thylacinidae, it stood as the sole survivor into modern times.
- Its habitat once spanned across continental Australia, reaching as far north as New Guinea and as far south as Tasmania.
- As an apex predator, it hunted kangaroos and various other prey.
What is RNA?
- RNA, short for Ribonucleic acid, is a complex compound with a high molecular weight, and it plays a crucial role in cellular protein synthesis.
- In some viruses, RNA takes on the role of carrying genetic codes, replacing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
- RNA is composed of ribose nucleotides, which are nitrogenous bases attached to a ribose sugar via phosphodiester bonds.
- The nitrogenous bases found in RNA include adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
- Unlike DNA, RNA is a single-stranded molecule responsible for carrying genetic information.
- RNA's primary function is to synthesize the diverse array of proteins required by an organism for survival, while also regulating cell metabolism.
World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) (Indian Express)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) of India has recently earned a 10-year recognition status from the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME).
Facts About:
WFME is a worldwide organization dedicated to the training and education of medical doctors.
Their mission is to work towards better healthcare for all people.
WFME's primary goal is to elevate the quality of medical education on a global scale by promoting the highest scientific and ethical standards.
They achieve this goal through several means, including:
- Establishing standards in medical education
- Advocating for the accreditation of medical schools
- Developing databases related to medical education
- Initiating projects focused on the future of medicine and medical education
- Publishing informative materials and forming partnerships
WFME was established in 1972 and has its headquarters in Ferney-Voltaire, France.
Notably, WFME is the organization that officially represents medical teachers and medical teaching institutions on a global scale, serving as their voice before the World Health Organization (WHO).
WFME's accreditation program plays a crucial role in ensuring that medical institutions meet and uphold the highest international standards in education and training.
General Crop Estimation Survey Portal (PIB)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Secretary of the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) recently launched the mobile application and web portal for the General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES).
Facts About:
- This innovative portal and mobile application aim to revolutionize agricultural practices across the nation.
- The Department of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare has developed this technology-driven solution to expand the reach, scope, and effectiveness of government initiatives in the development process.
- Automating the GCES process ensures timely reporting of crop statistics and data accuracy.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Information: The portal and app serve as a complete repository of yield estimates, encompassing village-specific GCES plans, plot details where crop cutting experiments occur, and post-harvest crop and driage weights.
- Geo-referencing: The mobile app offers a crucial feature that allows field workers to define the boundaries of experimental plots and upload photos of both the plots and the crops within them.
- This feature enhances data transparency and accuracy.
Adi Shankaracharya (IndianExpress)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh recently revealed a 108-feet tall statue of Adi Shankaracharya, an ancient Vedic scholar and teacher from the 8th century, in Omkareshwar.
Facts About:
- Adi Shankaracharya, also known as Shankara, was an ancient Indian philosopher and theologian who lived around the 8th century CE.
- Birthplace: He was born in Kalady, a village in what is now Kerala.
His Philosophical Contributions:
- His most famous achievement was his role in developing and spreading Advaita Vedanta, a school of Hindu philosophy that emphasizes non-duality.
- He brought together the ideas of 'Advaita Vedanta' and explained the core concepts of the Upanishads.
- Shankaracharya's significant work involved uniting six sub-sects known as 'Shanmata,' which translates to 'six religions.' This concept recognized six supreme deities, all part of one divine power.
- He also established the 'Dashanami Sampradaya,' which promotes a monastic way of life.
- While he strongly believed in ancient Hinduism, he criticized the 'Mimamsa school of Hinduism,' which focused primarily on rituals.
- Founding of Four Mathas: He founded four important monastic centers in India, each associated with one of the cardinal directions:
Sringeri in the south
Dwarka in the west
Puri in the east, and
Badrinath in the north.
Asia Pacific Forum (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The President of India recently opened the Annual General Meeting and Biennial Conference of the Asia Pacific Forum on Human Rights in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- Established in 1996, the Asia Pacific Forum is a unified platform that brings together National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from across the Asia Pacific.
- It focuses on addressing significant human rights challenges in the region.
- The forum consists of 17 full members and eight associate members, with India being a full member since its inception.
- To become a full member, an NHRI must fully adhere to the international standards outlined in the Paris Principles. NHRI's that partially comply are granted associate membership.
- Decisions regarding new member admissions are made by the Forum Council.
- A primary objective of the APF is to encourage the establishment of independent NHRIs in the Asia Pacific and support its members in their effective work.
Promotion of Tribal Products for North East Region’ (PTP-NER 2.0) scheme (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Ltd. (TRIFED), under the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs, is set to launch the second phase of the 'Promotion of Tribal Products for the North East Region' (PTP-NER 2.0) scheme, running from September 21 to November 10, 2023.
Facts About:
This scheme, launched by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, aims to enhance the livelihoods of tribal artisans by improving the procurement, logistics, and marketing of their products.
It covers the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, and Sikkim.
The scheme has two phases:
- Phase 1 included 8 states and 38 districts, with 64 Tribal Artisans Empanelment Melas (TAeM) organized by TRIFED and NEHHDC.
- Phase 2 will cover 29 districts, continuing the effort to support tribal artisans and showcase their cultural heritage.
Implementing partners include the North Eastern Handicrafts and Handlooms Development Corporation (NEHHDC), India Post, and various North Eastern State Government Departments and Agencies.
India Post will provide logistical support to achieve the scheme's objectives.
SIMBEX 23 (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Naval Ships Ranvijay and Kavaratti, along with the submarine INS Sindhukesari, have reached Singapore to take part in the 30th Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX).
Facts About:
- SIMBEX 23 is an annual naval exercise between the Indian Navy and the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN).
- It's been held every year since 1994 and is the longest continuous naval exercise India has with any country.
- The exercise has two phases: a harbor phase in Singapore from September 21 to 24, 2023, and a sea phase.
- In addition to Indian Naval Ships Ranvijay, Kavaratti, and INS Sindhukesari, the Long-Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft P8I is also participating.
- During the harbor phase, there will be professional interactions, cross-deck visits, knowledge exchanges, and sports events to improve cooperation and understanding between the two navies.
- The sea phase will involve advanced exercises like air defense, gunnery, tactical maneuvers, anti-submarine drills, and other maritime operations.
- Both navies aim to enhance their skills for joint maritime operations.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (The Hindu)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Central Government has announced that companies and entities may have approximately one year to comply with the regulations outlined in the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023. Smaller organizations or startups might be granted even more time for compliance.
Facts About:
The DPDP Act is a legal framework in India designed to protect individuals' personal data and ensure it's only shared with their consent. It governs the processing of digital personal data to safeguard privacy in the digital age.
Applicability:
- It applies to digital personal data processed within India, regardless of its origin (online or offline).
- It also applies to data processing outside India if it involves offering goods or services to Indian data subjects.
Evolution:
- It originates from the recommendations of the Justice BN Srikrishna-led Expert Committee, leading to the introduction of the Personal Data Protection Act in 2019.
- After consultations and revisions, the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, was enacted by both houses of Parliament.
Key Stakeholders:
- Data Principal (DP): The data owner who must give consent for data generation and processing.
- Data Fiduciary: The entity collecting, storing, and sharing data, acting as a "Consent Manager."
- Data Processor: The entity processing data on behalf of a data fiduciary.
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): An individual appointed by a data fiduciary to oversee data protection compliance.
Individuals have rights such as the right to information, correction, erasure, grievance redressal, and the right to nominate someone to exercise these rights in case of incapacity or death.
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Government recently introduced a new set of National Awards for achievements in science, technology, and innovation called the "Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar."
Facts About:
The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is an award that recognizes outstanding contributions in the fields of science, technology, and innovation in India.
It's one of the highest honors in these fields.
Who can receive the awards?
- Scientists, technologists, and innovators, whether in government or private sectors, who have made significant breakthroughs in their respective fields.
- People of Indian origin living abroad who have made exceptional contributions benefiting Indian communities.
The awards are given in four categories:
- Vigyan Ratna (VR): Lifetime achievements in science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri (VS): Distinguished contributions in science and technology.
- Vigyan Yuva-Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY-SSB): Young scientists under 45 years old who've made exceptional contributions.
- Vigyan Team (VT): Teams of three or more scientists, researchers, or innovators who've excelled in their field.
The awards cover 13 domains, including Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics & Computer Science, Earth Science, Medicine, Engineering, Agriculture, Environment, Technology & Innovation, Atomic Energy, Space Science, and more.
Nuakhai Juhar Festival (PIB)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India actively conveyed greetings to the people on the auspicious occasion of Nuakhai Juhar.
Facts About:
- Nuakhai Juhar is a significant social festival celebrated in Western Odisha and parts of Simdega in Jharkhand.
- The term 'Nuakhai' combines 'nua,' meaning 'new,' and 'khai,' signifying 'food.'
- This agricultural festival marks the welcoming of the fresh rice harvest of the season.
- It falls on the fifth day of the lunar fortnight in the month of Bhadrapada or Bhadra (August-September), following the Ganesh Chaturthi festival.
- Rituals:
- Nuakhai is associated with nine colors, leading to nine sets of pre-celebration rituals.
- People offer the newly harvested crop, known as Nabanha, to their respective deities.
- Following the Nabanha offering, individuals savor various delicacies made from the freshly harvested produce.
- A central ritual of the Nuakhai Juhar is a significant highlight of the festival.
Vanadium (TOI)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Vanadium, a critical raw material for many industrial applications, has been found in sediment samples collected from Gulf of Khambhat, which opens into the Arabian Sea off Alang in Gujarat.
Facts About:
- Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol "V" and atomic number 23.
- Vanadium is a naturally occurring element found in minerals and ores.
It was first discovered in the early 19th century.
- It is a transition metal known for its various applications in science and industry.
Applications:
- Strengthens Steel: One of its primary uses is as an alloying agent in steel production.
Vanadium steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
It is commonly used in manufacturing tools, knives, and structural components in construction.
- Aerospace Alloys: Vanadium alloys are utilized in aerospace applications, such as jet engines and rocket frames, due to their high-temperature resistance and lightweight properties.
- Batteries: Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are emerging as a promising energy storage technology.
They offer scalability and long cycle life, making them suitable for grid-level energy storage.
- Catalysts: Vanadium compounds act as catalysts in chemical reactions, particularly in the production of sulfuric acid and maleic anhydride.
- Medical Applications: Vanadium has potential health benefits and is being studied for its role in managing diabetes and its antioxidant properties.
- Dye and Pigment Production: Vanadium compounds are used in the manufacture of dyes, pigments, and ceramics.
- Metallurgy: Vanadium is employed in the refining of certain metals like aluminum and titanium.
- Nuclear Applications: In nuclear reactors, vanadium serves as a structural material due to its neutron-absorbing properties.
- Research and Development: Vanadium's unique properties make it valuable for scientific research, including studies in material science and chemistry.
Vanadium's versatility and strength-enhancing properties find application in various industries, from steel manufacturing to energy storage and even potential health-related uses, making it a vital element in modern technology and innovation.
Bharatkosh Portal (PIB)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Union Minister of Civil Aviation actively launched an e-wallet payment option on the Bharatkosh portal.
Facts About:
- The Bharatkosh portal is an initiative led by the Controller General of Accounts under the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- It serves as a unified platform for depositing various fees, fines, and other payments directly into the government's account.
- The portal integrates all Civil Ministries and Departments of the Government of India for streamlined financial transactions.
- Its primary objective is to offer round-the-clock, year-round electronic payment services, enabling users to deposit funds into the government's account through internet-based payment technologies from the convenience of their location via the web-based portal.
- In doing so, it aligns with the government's commitment to e-Governance, ensuring efficient, effective, and excellent government services accessible anytime and anywhere.
Batillipes Kalami (The Hindu)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, researchers at Cochin University of Science and Technology (Cusat) named a new species of marine tardigrade after the late former President and scientist A.P.J. Abdul Kalam.
Facts About:
- Batillipes Kalami, the newly discovered species found in Mandapam, southeast Tamil Nadu, belongs to the Batillipes genus.
- Notably, it's the second marine tardigrade discovered in Indian waters and the first from the east coast.
- This species is also the first of its kind taxonomically described from India and is the 37th species within the Batillipes genus.
Physical characteristics:
- It typically measures around 170 micrometres (0.17 mm) in length and approximately 50 micrometres (0.05 mm) in width.
- Its head has a trapezoid shape with sharp-tipped filament-like appendages (cirri) extending from it.
- Each of its four pairs of legs features sensory spines of varying lengths.
- Females are slightly larger than males.
Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund For Sportspersons (PDUNWFS) (PIB)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports honored athletes supported by the Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons (PDUNWFS) in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- The Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons (PDUNWFS) was established in March 1982.
- Its primary goal is to support former exceptional athletes who are now facing financial hardship but had previously brought honor to India through their sporting achievements.
- In May 2016, the scheme underwent revisions, enabling it to provide one-time financial assistance to former exceptional athletes.
- This scheme covers athletes across the entire nation and is designed to enhance the well-being of sportspersons and their families by alleviating financial distress.
- The scheme can be applied to individual athletes or groups of active sportspersons.
Red-necked Phalarope (The Hindu)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A Red-necked phalarope (Phalaropus lobatus) was recently spotted by a group of birders who visited Kurichi Tank in Coimbatore.
Facts About:
- This is a relatively small shorebird renowned for its energetic spinning on the water surface to stir up small invertebrates.
- With a circumpolar distribution, it inhabits both boreal and tundra zones within the 60 to 70-degree latitude range.
- These phalaropes are commonly found along the coastlines of the Arctic Ocean, extending southward to the Aleutian Islands and northwestward to Britain.
- During the winter months, they predominantly reside in oceanic environments.
- In their non-breeding season, Red-Necked Phalaropes can be observed in areas ranging from central-west South America to the Arabian Sea, and from central Indonesia to western Melanesia.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Classification: Least Concern
Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysala (The Hindu)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
UNESCO recently included the Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas, consisting of three temples in Karnataka, on its World Heritage List.
Facts About:
The Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas consist of a collection of temples crafted by the Hoysala dynasty in the 12th-13th centuries.
- This ensemble includes three significant components: Belur, Halebid, and Somnathapura.
These three temples are as follows:
- The Chennakeshava Temple: Located at the heart of Belur in the Hassan district, it serves as the main temple in the complex. It is surrounded by the remnants of a mud fort and a moat.
- The Hoysaleswara Temple: Situated on the banks of the Dwarasamudra tank in Halebidu, the Hassan district, this temple is part of a town with numerous protected and unprotected temples, archaeological ruins, and mounds.
- The Keshava Temple: Found in the center of Somanathapura village in the Mysore district.
- These temples are primarily dedicated to Hindu deities like Shiva and Vishnu, with some also honoring the Jain faith.
- The architecture of the Hoysala temples reflects a blend of Dravidian design with influences from the Bhumija style prevalent in Central India, the Nagara traditions of northern and western India, and the Karntata-Dravida styles favored by the Kalyani Chalukyas.
Bima Sugam Platform (Indian Express)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has established a steering committee, which will serve as the highest authority responsible for developing its ambitious Bima Sugam platform.
Facts About:
- This platform will empower individuals to purchase life, health, motor, or property insurance policies online, providing a convenient digital solution.
- It aims to offer a one-stop destination for insurance companies, agents, brokers, banks, and aggregators, streamlining accessibility.
- Serving as a centralized database, it will assist consumers with all their insurance-related needs, ensuring efficiency.
- The platform will facilitate the swift introduction of new or experimental insurance products.
- Cyril Amarchand Mangaldas (CAM) has been appointed as the legal counsel for this project, responsible for establishing a Section 8 not-for-profit company that will own the Bima Sugam platform.
- It will cater to both personal and commercial/business insurance needs, aiding users in identifying and comparing the best-suited products within specified timelines.
- The platform will encompass a comprehensive range of insurance offerings, including life insurance and its various forms such as term plans, savings (Par and Non-Par), annuities, pension plans, and more.
- Furthermore, it will showcase a fully digital onboarding process for all insurance products, eliminating manual interventions.
Operation Sajag (PIB)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Coast Guard has recently carried out 'Operation Sajag,' a Coastal Security Exercise along the Western Coast.
Facts About:
- Operation Sajag is a coastal security exercise conducted by the Indian Coast Guard along the western coastline.
- It involves the participation of all stakeholders responsible for Indian coastal security.
- A total of 118 ships, including vessels from Customs, Marine Police, Ports, and the Indian Navy, took part in this exercise.
- The primary goals of this drill are to reassess and strengthen the coastal security system and raise awareness among fishermen operating at sea.
- During the exercise, there was extensive checking and verification of documents and crew passes for all fishing boats, barges, and crafts at sea.
- Additionally, biometric card readers have been provided to security agencies to enhance security measures.
- Apart from monitoring dhows, the coastal security construct also includes initiatives related to island security and community interaction programs.
Kisan Rin Portal (News On Air)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Finance Minister and Agriculture Minister are going to start the 'Kisan Rin Portal' on September 19.
Facts About:
- This portal assists farmers in obtaining reduced-rate loans through the Kisan Credit Card (KCC).
- Several government departments worked together to create it.
- It provides a clear picture of farmer information, loan distribution details, interest subsidy requests, and progress in scheme usage.
- It seamlessly connects with banks to enhance the accessibility and efficiency of agricultural credit.
Brief Overview About Kisan Credit Card (KCC):
- Introduced in 1998, the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme provides farmers with a convenient way to access loans for buying agricultural supplies like seeds and fertilizers and for cash withdrawals.
- Developed by NABARD (the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development), the scheme was later expanded in 2004 to cover investment needs in farming and related activities.
- In 2012, the scheme was simplified to facilitate Electronic Kisan Credit Cards.
- Applicable to Commercial Banks, RRBs, Small Finance Banks, and Cooperatives.
Anamudi Shola National Park (The Hindu)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Pazhathottam region within Anamudi Shola National Park, close to Munnar in Idukki, has blossomed into a lush paradise bustling with vibrant life.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in Kerala, India.
- Surrounded by Eravikulam National Park, Pampadum Shola National Park, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Mathikettan Shola Park.
- Vegetation: Encompasses southern subtropical hill forests, southern montane wet temperate forests, and moist deciduous forests.
- Unique Features: The dense shola woods here contain stunted trees and are adorned with lush lichen, mosses, and climbers.
- Flora: Houses approximately 174 species of herbs and shrubs, 62 tree species, and around 40 species of climbers, some of which are unique to the region.
- Fauna: Abode to diverse wildlife, including leopards, civet cats, wolves, Indian bison, wild boars, elephants, tigers, panthers, and sloth bears.
Gold Exchange-traded Funds (Indian Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In August, Gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) saw an impressive inflow of Rs 1,028 crore, marking the highest influx in the past 16 months.
Facts About:
- These are investment funds linked to the value of gold.
- Gold ETFs are passive investments that track the price of gold and invest in physical gold bullion.
- They represent gold in a form that can be paper-based or dematerialized.
- Each unit of a Gold ETF is equivalent to 1 gram of highly pure physical gold.
- Gold ETFs are listed and traded on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. (BSE).
- They offer complete transparency regarding their gold holdings, thanks to direct gold pricing.
SHREYAS Scheme (PIB)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Through the comprehensive SHREYAS program, a total of 1,628.89 crore rupees have been disbursed from 2014-15 to 2022-23, benefiting 21,326 recipients.
Facts About:
- The Ministry of Human Resource and Development has introduced the Scheme for Higher Education Youth for Apprenticeship and Skills (SHREYAS) to align educational programs with the needs of industries and service sectors.
- It also encourages students to gain practical experience while studying.
Objectives:
- Enhance Students' Employability: By providing on-the-job work exposure through the National Apprenticeship Promotional Scheme (NAPS) and the National Career Service (NCS), SHREYAS aims to improve students' employability.
- Bridge the Gap Between Education and Industry: The scheme establishes a strong connection between education and industry.
- Dynamic Skill Development: SHREYAS offers students the opportunity to acquire skills in a dynamic manner.
- arn While You Learn": It introduces an "earn while you learn" system into higher education.
- Facilitate Quality Manpower: The scheme assists industries in recruiting high-quality manpower.
- Connect Students with Employment Opportunities: It links students with the government's employment facilitation efforts.
Pralay Ballistic Missiles (Financial Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Defense Ministry has recently approved the purchase of a regiment of Pralay tactical ballistic missiles for the Indian Army.
Facts About:
- Pralay is a quasi-ballistic surface-to-surface missile.
- It can strike targets at distances ranging from 150 to 500 kilometers.
- The missile can carry between 350 and 700 kilograms of high-grade explosives.
- Pralay is developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It uses a solid propellant rocket motor and incorporates advanced technologies.
- The missile features a state-of-the-art navigation and integrated avionics system.
- Pralay can alter its trajectory during mid-flight.
Yashobhoomi (Indian Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister recently opened the first part of the India International Convention and Expo Centre (IICC) called Yashobhoomi in New Delhi's Dwarka.
Facts About:
- YashoBhoomi,' also known as the India International Convention and Expo Centre (IICC), is a modern and advanced convention center located in Dwarka, New Delhi.
- It's one of the largest places in the world for meetings, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions (MICE).
Key features:
- The project covers an area of over 8.9 lakh square meters and costs about Rs 5400 crores.
- The Convention Center is huge, with 15 convention rooms, including the Main Auditorium, the Grand Ballroom, and 13 meeting rooms. It can hold up to 11,000 delegates.
- It has the country's biggest LED media facade.
- The plenary hall in the Convention Center can seat about 6,000 guests.
- There are also large exhibition halls covering over 1.07 lakh square meters for exhibitions, trade fairs, and business events.
- The center is environmentally friendly, with a state-of-the-art wastewater treatment system that recycles 100% of the wastewater and provisions for rainwater harvesting.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Presently, the Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Samudra Prahari is on an international mission covering ASEAN countries.
Facts About:
- Samudra Prahari is an Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) specifically designed for pollution control purposes.
Key Highlights:
- It holds the distinction of being Southeast Asia's pioneering pollution control vessel.
- Equipped with cutting-edge Pollution Response and Control equipment for effectively managing oil spills within the Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Features tanks and inflatable barges for the storage of oil spills.
- Capable of seamless oil recovery operations with a substantial storage capacity of 500 KL.
- Designed to accommodate and operate a twin-engine Advanced Light Helicopter, along with the capability to handle and embark Chetak helicopters.
- Notable features encompass an integrated platform management system, power management system, high-powered external firefighting system, and an indigenous gun mount with firefighting capabilities.
- The vessel possesses unmanned machinery operation capabilities for enhanced efficiency.
TrailGuard AI camera (The Hindu)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The wildlife officials have found the TrailGuard AI camera-alert system very useful in the Kanha-Pench corridor in Madhya Pradesh.
Facts About:
- These cameras are thin and can be discreetly placed in trees.
- They look like a pen, measuring 13.8 cm long and 1.4 cm wide. They are connected to another unit, about the size of a notepad.
- These cameras have special software that can be told to take pictures of specific animals or people.
- They are really small, about the size of a person's index finger when you consider the camera head and the infrared sensor.
- You can set them to capture specific things like humans or certain animals like lions, tigers, or cheetahs.
- If the camera is near a cellphone tower, it can send pictures in just 30 seconds. If it's far from a tower, it might take 3-10 minutes using a longer method.
- The 'AI' part of this system means that it doesn't send every picture it takes. Instead, it only sends pictures that are interesting to the forest officials.
- This camera was created by RESOLVE, a non-profit organization. The brain of this camera is Intel's Myriad chip.
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary (TOI)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India is getting ready to bring in a new group of cheetahs from South Africa and release them into the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated at the northern border of Madhya Pradesh's Mandsaur and Nimach districts, adjacent to Rajasthan.
- Area: Covers 368.62 km2 (142.32 sq mi) and is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forest ecoregion.
- Establishment: Established in 1974 and officially designated as a sanctuary in 1984.
- River Chambal: Divides the sanctuary into two sections and adds to its unique landscape.
- Terrain: Features diverse topography, including hills, plateaus, and the catchment area of the Gandhi Sagar Dam on the Chambal River.
- Cultural Significance: Houses historical, archaeological, and religious sites like Chaurasigarh, Chaturbhujnath temple, Bhadkaji rock paintings, Narsinghjhar Hinglajgarh fort, and Taxakeshwar temple.
- Flora: Dominated by tree species like Khair, Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, and Palash.
- Fauna: Home to herbivores such as Chinkara, Nilgai, and Spotted Deer, as well as carnivores like the Indian Leopard, Striped Hyena, and Jackal. The sanctuary also hosts a variety of aquatic life, including crocodiles, fish, otters, and turtles.
Scrub Typhus and Leptospirosisa (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Scrub Typhus claims 5 lives, while Leptospirosis spreads in Odisha; health authorities remain vigilant.
Facts About:
- Scrub typhus, caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi bacteria, is prevalent in Asia-Pacific regions, including India.
- It spreads via chigger mites in rural areas. Symptoms include high fever, headaches, muscle pain, and a distinctive rash, often leading to swollen lymph nodes.
- If untreated, it can cause severe complications affecting vital organs.
- Diagnosis relies on clinical symptoms and blood tests.
- Timely antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin are effective treatments.
- Preventive measures include protective clothing, insect repellent, and avoiding dense vegetation.
- Recent cases in Odisha, have prompted heightened health alerts and emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment, alongside public awareness efforts.
About Leptospirosis:
- Leptospirosis caused by the bacterium Leptospira interrogans, is a potentially fatal zoonotic disease and is common in warm, humid regions worldwide.
- Humans can contract it from infected animal urine, particularly rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Leptospirosis may occur in two phases, with the second phase being more severe and potentially causing kidney or liver failure, or meningitis.
- Antibiotics are effective in treating the disease, particularly when administered early.
- It's prevalent in both urban and rural areas, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures and public health awareness.
Antlion species in Kerala (The Hindu)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a group of researchers in Kerala found two brand new antlion species. They're called Nemoleon ghoshi and Nemoleon madayiensis.
Facts About:
- These two new antlion species are part of the Myrmeleontidae family in the Neuroptera order.
- Antlions are well-known for their habit of building pits.
- Some antlion types, during their larval stages, create cone-shaped pits in loose, dry soil to catch their prey.
- However, the larvae of Nemoleon don't build pits. They live beneath the surface in loose soil, which provides them protection from sunlight, wind, and rain.
- You can easily recognize antlions by their long, distinct antennae.
- This is the first time that the Nemoleon genus has been spotted in the Oriental region.
- In Kerala, these are the 5th and 6th antlion species to be discovered, and they are the 125th and 126th species found in India.
- Antlions are found all around the world, mainly in dry, sandy areas.
- The research was made possible with financial support from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
Monoclonal Antibodies (The Hindu)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India has made a request to Australia for a replenishment of monoclonal antibody doses to fight against the Nipah virus.
Facts About:
Monoclonal antibodies, often abbreviated as moAbs or mAbs, are artificially created proteins in laboratories that mimic the function of natural antibodies found in our immune system.
- These antibodies play a crucial role in identifying foreign substances called antigens and attaching to them to neutralize or eliminate them.
The term "monoclonal" indicates that these laboratory-made antibodies are exact copies of a single antibody.
- They are produced by replicating a specific type of immune cell known as a B cell, resulting in large quantities of identical antibodies.
This process leads to the development of highly specialized antibodies that can precisely target specific antigens, which might include viruses, bacteria, cancer cells, or other disease-related molecules.
- Their remarkable specificity reduces the risk of unintended side effects.
Monoclonal antibodies find applications in various medical fields, including the treatment of cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics (UPAg) (PIB)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare (DA & FW) recently introduced the Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics, and its launch was attended by members of NITI Aayog.
Facts About:
- This innovative platform is specifically designed to improve the management of data within the agricultural sector.
- It represents a significant stride towards a more efficient and responsive framework for agricultural policies.
- As a vital part of the Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture, it's an initiative led by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare to streamline data management in agriculture.
- The primary goal is to offer real-time, standardized, and verified data about agricultural commodities, simplifying data-driven decision-making for policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders.
- This initiative is in line with the principles of e-governance, introducing intelligence, transparency, and flexibility to India's agricultural sector.
World Spice Congress (WSC) (NewsOnAir)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 14th World Spice Congress (WSC) recently kicked off in Vashi, Navi Mumbai.
Facts About:
- The World Spice Congress (WSC) was originally conceived in 1990 as a platform for discussions and interactions between spice importers and exporters.
Over its three decades of existence, it has evolved into a vital gathering for the global spice industry.
- Since its inception, the Spices Board under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, has organized the WSC.
The theme for WSC 2023 is "VISION 2030: S-P-I-C-E-S," which stands for sustainability, productivity, innovation, collaboration, excellence, and safety.
About the Spices Board of India:
- The Spices Board of India was established on February 26, 1987, through the Spices Board Act of 1986. It was formed by merging the former Cardamom Board (1968) and the Spices Export Promotion Council (1960).
- It operates under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- The board has the responsibility of promoting the export of 52 scheduled spices and facilitating the development of both small and large cardamom.
- It serves as a crucial link connecting Indian exporters with foreign importers.
Main Functions:
- Conducting research, development, and regulation related to the domestic marketing of small and large cardamom.
- Enhancing post-harvest practices for all spices.
- Promoting the production, processing, and certification of organic spices.
- Supporting the development of spices in the North East region.
- Providing quality evaluation services.
Digital birth certificates (The Hindu)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The government has announced that starting from October 1, all births and deaths in the country will be registered digitally on the Centre's portal.
Facts About:
- Digital birth certificates are set to become a single, versatile document thanks to the 2023 Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Act.
- This document will serve various purposes such as admission to schools, applying for driver's licenses, government jobs, passports, Aadhaar, voter registration, and even marriage registration.
- The central database will also keep the National Population Register (NPR), ration cards, property records, and electoral rolls up to date.
- All states will be required to use the Centre's Civil Registration System (CRS) portal to register births and deaths and share this data with the Registrar General of India (RGI).
International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML) (Indian Express)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Secretary of the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs announced that India has achieved the status of being an OIML certificate-issuing authority.
Facts About:
- OIML, short for the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, was established in 1955 as an international body.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents that are used by legal metrology authorities and industry worldwide.
- OIML plays a vital part in aligning national laws and regulations concerning the accuracy of measuring instruments such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring devices, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India joined the OIML in 1956 and simultaneously signed the metric convention.
- Headquartered in Paris, France.
National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) portal (PIB)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Justice of India declared the inclusion of the Supreme Court in the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) during a public court session.
Facts About:
- The National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) portal serves as a comprehensive national database for tracking cases in courts throughout India.
- It provides access to case-related information and statistics, including the number of cases filed, pending, and resolved, as well as case types and year-wise data for the Supreme Court of India.
- The NJDG portal is part of the e-Courts Project and covers 18,735 District & Subordinate Courts and High Courts.
- Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) in collaboration with the Computer Cell, Registry's software development team, the NJDG portal features an interactive interface and analytics dashboard.
- It is regularly updated with current case data and serves as a valuable tool for monitoring and managing case backlogs, supporting policy decisions to expedite case resolution, and improving overall court performance.
- Additionally, it aids in tracking land dispute cases.
Data-driven Innovations in Agriculture (PTI)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (Nabard) has teamed up with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in India to jointly develop data-driven innovations for the benefit of smallholder farmers in agriculture and food systems.
Facts About:
- This partnership aims to improve the well-being of smallholder farmers by jointly using open-source data for product development, technology transfer, and policy formulation.
- It focuses on enhancing climate resilience in agriculture and involves sharing collaborative digital resources like DiCRA (Data in Climate Resilient Agriculture).
- DiCRA offers access to essential geospatial data related to climate-resilient agriculture and is curated by UNDP and partner organizations.
- This collaboration represents a significant opportunity to harness data and present it as a digital public infrastructure for India's rural farming community.
- Such open data innovations can promote best practices, optimize agricultural investments, and bolster the resilience of smallholder farmers, including women, against various challenges.
C-295 MW Aircraft (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Airbus delivered the first C-295MW transport aircraft to the Indian Air Force in Seville, Spain.
Facts About:
- C-295 MW Aircraft a versatile transport aircraft with a capacity of 5-10 tonnes.
- Replacing the 1960s Avro aircraft in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- Suitable for various missions.
- Contract includes 16 fly-away aircraft from Seville and 40 to be jointly manufactured with Tata Advanced Systems Ltd. (TASL).
Key Features:
- Up to 11-hour flight endurance.
- All-weather, day and night operations.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL) capability.
- Rear ramp door for troop and cargo drops.
- Air tanker conversion with a detachable refueling kit.
- Airborne Early Warning (AEW) variant with 360-degree radar coverage.
- Water bomber capability (7,000 liters).
- Close-air support and Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR).
- Suitable for medical evacuation, airdropping, and special missions.
Skill India Digital (SID) Platform (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Skill Development has just introduced the Skill India Digital (SID) platform.
Facts About:
- Skill India Digital (SID) is India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for skill development, education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
- It consolidates various skilling initiatives, offering over 264 courses from 42,623 centers nationwide.
- Developed by the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) in partnership with industry players.
- Part of the World Bank-assisted Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion (SANKALP) program.
- Supports multiple Indian languages and uses Aadhaar-based eKYC for secure access.
- Features user-friendly interface, adaptable to various devices.
- Utilizes AI and facial recognition for personalized course recommendations.
- Integrates government training programs from Central and State governments.
- Introduces Digitally Verified Credentials (DVCs) for secure skill showcasing.
- Offers Digital CVs with personalized QR Codes for easy access to qualifications and skills.
eCourts Project (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Cabinet recently gave the green light to the third phase of the eCourts Projects, allocating a budget of ?7,210 crore for it.
Facts About:
- The eCourts Project is a nationwide initiative aimed at modernizing the Indian judiciary by using technology.
- It all began with the 'National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary – 2005,' proposed by the eCommittee of the Supreme Court of India.
- This committee was formed by the Government of India in response to a suggestion from the Chief Justice of India.
- Its purpose is to develop a national strategy for computerizing the Indian judiciary and advise on technological and management-related improvements.
- This project covers all District Courts across India and is overseen and funded by the Department of Justice under the Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India
The eCourts Project has several key goals:
- Providing efficient and citizen-centric services in a timely manner.
- Implementing decision support systems in courts.
- Automating processes to increase transparency and access to information.
- Boosting judicial productivity to make the justice system affordable, accessible, cost-effective, predictable, reliable, and transparent.
- Phase I of the eCourts Project was completed in 2015, computerizing 14,249 court sites. Phase II expanded this effort, computerizing 18,735 District and Subordinate courts.
Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award (The Hindu)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Rajnish Kumar, professor at the Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT-M) has won the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar prize for science and technology.
Facts About:
- Named after the founder Director of CSIR India, Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar.
- Given annually for outstanding contributions in science and technology.
- Prize amount: Rs 5,00,000.
- Awarded in various disciplines including Biological, Chemical, Earth, Engineering, Mathematical, Medical, and Physical Sciences.
- Eligible for Indian citizens up to age 45, including OCI and PIO working in India.
- Recognizes work primarily conducted in India during the five years prior.
- Awardees selected based on recommendations from CSIR Advisory Committees.
West Coast Refinery Project (Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India and Saudi Arabia have recently decided to accelerate the progress of the $50 billion West Coast refinery project.
Facts About:
- The West Coast refinery project, also known as Ratnagiri Refinery and Petrochemicals Ltd. (RRPCL), was initially conceived in 2014.
It is intended to be India's largest greenfield refinery, boasting a massive capacity of 60 million tonnes per annum.
This project is set to become the world's largest integrated refinery and petrochemical facility.
- Location-wise, the project is planned to be situated on India's western coast, specifically in Ratnagiri, Maharashtra.
- Upon completion, the refinery is anticipated to produce approximately 1.2 million barrels of oil daily, in addition to various petroleum products generated by the attached petrochemical facilities.
- Three prominent government-owned enterprises in the Indian oil and gas sector came together to establish a joint venture named RRPCL.
- RRPCL is a joint venture in which India's three national oil companies, namely Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL), Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL), and Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL), hold stakes of 50%, 25%, and 25%, respectively.
- In 2019, Saudi Aramco and the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) also joined the project by acquiring a collective 50 percent stake.
This investment is estimated to be valued at around Rs 3 lakh crore, covering the setup costs.
Overnight Index Swap )Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Indian overnight index swap (OIS) rates have surged to their highest levels in a span of 10 months. This increase has been attributed to offshore payments and the triggering of stop-loss orders.
Facts About:
- An Overnight Index Swap (OIS) is a financial tool that involves exchanging returns from a fixed-rate asset for a predetermined daily overnight reference rate index for an agreed-upon duration.
- The primary goal of OIS is to mitigate interest rate risk, specifically the risk linked to changes in the overnight lending rate.
- An OIS rate is computed daily, and it is based on the average interest rate that institutions with loans tied to the overnight rate have paid for that particular day.
How does an OIS Operate:
- OIS instruments enable financial institutions to exchange the interest rates they are currently paying, all without the need to refinance or alter the terms of their existing loans.
- In a typical overnight index swap arrangement, one financial institution swaps an overnight (floating) interest rate, while the other swaps a fixed short-term interest rate.
- To initiate the swap, both institutions agree to maintain their loan obligations as usual.
- However, at the end of an agreed-upon timeframe, the institution that ends up paying less interest will compensate the other institution for the difference.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (PIB)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD) recently marked World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Day.
Facts About:
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a rare and severe genetic disorder that primarily affects muscles.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a condition passed down through families, which means it's in your genes.
- It mainly affects the muscles, the body's moving parts, making them weaker and less effective as time goes on.
- DMD often begins in childhood, more commonly in boys than girls.
- Signs typically appear when children are about 3 to 5 years old, with noticeable difficulties in walking and getting around.
- Children with DMD may also struggle with breathing and using their arms and legs.
- Unfortunately, DMD worsens as time passes, making everyday tasks more challenging.
- Although there is no cure, there are treatments and therapies available that can help manage the symptoms and enhance the quality of life for those with DMD.
About World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Day:
- World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Day falls on 7th September annually.
- The aim of this day is to increase awareness about Duchenne muscular dystrophy and to encourage initiatives that enhance the lives of individuals with dystrophinopathies through education, advocacy, and promoting social inclusion.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC) (Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian shipping Minister recently mentioned that India and Russia want to start working on the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC).
Facts About:
- The EMC is like a new sea road that connects the Indian port of Chennai with the Russian port of Vladivostok.
- This new road is expected to make it much faster to move things between Indian and Russian ports in the Far East. It could be up to 40 percent faster, which means instead of taking 40 days, it might only take 24 days.
- Right now, when things are shipped from Mumbai, India, to St. Petersburg, Russia, it's a really long trip of 8,675 nautical miles.
- The EMC, on the other hand, is a shorter route, only about 5,600 nautical miles, which is way quicker than the current path through the Suez Canal.
- So, when the EMC is ready, it will be a faster way to send stuff from India to Far East Russia.
- It's great for India, because it's a quicker and better route to reach places in the Far East like China and Japan.
New Spider Species (HT)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In recent discoveries, two new spider species, named Palpimanus Godawan and Palpimanus Maldhok, were identified within the conservation areas of Rajasthan Desert National Park and Solapur.
Facts About:
- These two spider species, Godawan and Maldhok, have been named in tribute to the local name of the Great Indian Bustard.
Features of these Spiders:
- These spiders are quite reserved and tend to seek shelter under rocks or in crevices when they feel disturbed.
- They exhibit a maroon coloration, a distinctive characteristic shared with the other two recognized species within the Palpimanidae genus.
- Being ground-dwelling creatures, they possess relatively robust bodies, which restricts their ability to disperse in the typical spider fashion through ballooning or shooting webs to move from place to place.
- They tend to remain within a limited area.
Megalithic Dolmen Site Near Moodbidri (The Hindu)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
During recent archaeological excavations at the megalithic dolmen site near Moodbidri in Dakshina Kannada, researchers discovered terracotta figurines in various states of preservation that are quite distinct.
Facts About:
The Megalithic culture in India is renowned for its various burial practices and the use of iron.
- One of these practices involves the construction of dolmens.
Characteristics:
- Dolmens consisted of large stone slabs, known as orthostats, placed in a clockwise arrangement, forming a square chamber.
- This square chamber was sealed by another massive stone slab acting as a capstone.
- Typically, an entrance, often circular or U-shaped, known as a port hole, was created on the Eastern slab.
In South India, it was known by various names such as Kalmane, Pandavara Mane, Moriyara Mane, and Moriyara Betta, highlighting its popularity among the local population.
Significance:
- The presence of cow bovines in these dolmens assists in establishing their historical timeline.
The discovery of terracotta artifacts within megalithic burials provides valuable insights into the Bhoota cult or Daiva Aradhane in coastal Karnataka.
Similarities with cow goddess figures are observed in the megalithic terracotta figurines of Malampuzha in Kerala and even in Egypt.
Kisan Credit Card (KCC) (PIB)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Shri Parshottam Rupala chaired a National KCC Conference in Mumbai on 4th September 2023 to boost Kisan Credit Card (KCC) saturation among animal husbandry and dairy farmers.
Facts About:
Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
Historical Background: Introduced in 1998 to simplify and streamline access to timely credit support for farmers. Expanded in 2004 to include allied and non-farm activities. Extended to fisheries and animal husbandry in the Budget-2018-19.
Objectives:
- Meet short-term credit needs for cultivation.
- Cover post-harvest expenses.
- Fulfill household consumption needs.
- Implementing Agencies: Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks, Cooperatives.
Salient Features:
- Offers an ATM-enabled RuPay Card.
- Requires one-time documentation.
- Allows for cost escalation in the limit.
- Permits multiple withdrawals within the limit.
- Covers post-harvest expenses, produce marketing loans, and household consumption.
- Repayment period aligned with crop harvesting and marketing.
- Maximum short-term loan tenure: 1 year, long-term loan: 5 years.
- Interest subvention scheme of 2% for short-term crop loans up to Rs. 3 lakh.
- Additional 2% interest subvention and 3% prompt repayment incentive.
- Simple interest for prompt payments; compound interest for delays.
Benefits:
- Interest rates as low as 2.00%.
- No security required for loans up to Rs. 1.60 lakh.
- Crop insurance coverage against various calamities.
- Insurance coverage for permanent disability, death, and other risks provided to farmers.
Global Symposium on Farmers' Rights (NewsOnAir)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
President Droupadi Murmu recently launched the First Global Symposium on Farmers' Rights in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- Location: ICAR Convention Centre, National Agricultural Science Centre, New Delhi. from September 12 to 15, 2023.
- Historical Background: The concept of hosting the inaugural GFSR was proposed by the Government of India during the Ninth Session of the Governing Body (GB9) of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (International Treaty) in September 2022.
This proposal received approval from the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization).
- Organized by: The Secretariat of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (International Treaty) under the umbrella of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) based in Rome.
- Hosted by: The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India, in collaboration with the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPVFR) Authority, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), and ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR).
- Objective: The primary aim is to address crucial issues concerning farmers' rights and their pivotal role in global food security and agriculture.
- Distinguished scientists and experts from 59 countries around the world will participate.
- They will engage in discussions on how to acknowledge and compensate the significant contributions made by local and indigenous communities, as well as farmers from all corners of the world, in preserving and advancing plant genetic resources (PGR).
Nipah Virus (The Hindu)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Kerala health department sent out a warning in Kozhikode because they suspected that two individuals who passed away from unusual causes in the district might have contracted the Nipah virus (NiV).
Facts About:
Nipah virus infection is an illness that can be passed from animals to humans.
- The virus responsible for Nipah Virus encephalitis is an RNA virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family and Henipavirus genus.
- It is closely related to the Hendra virus.
This virus first emerged in Malaysia and Singapore in 1998 and 1999.
- Initially, it was detected in domestic pigs but has since been found in various domestic animals, including dogs, cats, goats, horses, and sheep.
Transmission:
The disease is transmitted through fruit bats, often referred to as 'flying foxes,' specifically those belonging to the Pteropus genus.
- These bats are natural hosts for both Nipah and Hendra viruses.
- The virus is present in bat urine and, potentially, in bat feces, saliva, and birthing fluids.
Symptoms:
- Typically, when humans become infected, they experience symptoms resembling encephalitis, which include fever, headaches, drowsiness, confusion, disorientation, coma, and sometimes even death.
Treatment: Currently, there is no specific treatment available for this virus.
Vidya Samiksha Kendra (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
As part of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), the Ministry of Education is encouraging states to establish Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs).
Facts About:
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra, abbreviated as VSKs, serves as a comprehensive data repository housing information from all Ministry of Education (MoE) initiatives.
- These Kendras operate control rooms responsible for collecting data, monitoring key performance indicators, and employing AI and machine learning to analyze data sourced from government schemes.
This repository regularly updates data from various sources, including:
- The PM-POSHAN mid-day meal programs.
- Teacher training data sourced from the National Initiative for School Heads' and Teachers' Holistic Advancement portal.
- Textbook content originating from Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing.
- School attendance and dropout statistics accessible through the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE+).
- Students' learning outcomes as determined by the National Achievement Survey.
- The Performance Grading Index, evaluating the state and union territory-level school education systems.
Funding for this initiative includes a central allocation ranging from 2 to 5 crore rupees to each state for the adoption and establishment of VSKs.
Phanigiri Artefacts (The Hindu)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Phanigiri artefacts, which were found in 1942 and date back to 200 BCE-400 CE, are currently showcased at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Facts About:
- The Phanigiri Buddhist site is a significant discovery in Buddhist iconography in this era.
- Phanigiri, a small village located in Telangana, is where these artefacts were unearthed.
Key Discoveries:
- The thoranas found at Phanigiri hold great importance, especially because they are some of the earliest ones discovered south of Sanchi.
- One particular thorana has a panel that depicts both Mahayana and Hinayana schools of Buddhist thought.
- Evidence from Phanigiri indicates the transformation of Buddha's status, marking a transition from a historical and spiritual figure to canonization and ritualization.
- In the monograph of this discovery, you can find an image of Buddha wearing what appears to be a Roman toga, carved in limestone.
Gene-drive Technology (The Hindu)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Gene-drive technology has been employed in India, Brazil, and Panama under carefully controlled outdoor conditions to genetically modify mosquitoes.
Facts About:
- Gene-drive technology is a form of genetic engineering that involves the modification of genes.
- This groundbreaking technique was conceptualized by Professor Austin Burt from Imperial College London.
- Its potential lies in effectively addressing issues posed by pest species, such as malaria-transmitting mosquitoes.
- Rather than adhering strictly to Mendelian genetics principles, this method ensures the selective inheritance of specific genes by mosquitoes.
Here's how it works:
- A protein precisely cleaves the mosquito's DNA at a specific location that doesn't encode a particular sequence in the genome.
- This action triggers a natural cellular mechanism to repair the DNA, compelling the incorporation of a designated sequence known as the 'drive sequence' into the repaired region.
Self Regulatory Organisation for Fintech (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has requested fintech organizations to establish a Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO).
Facts About:
- A Self-Regulatory Organization is an independent entity, not affiliated with the government, responsible for formulating and enforcing industry-specific rules and standards that govern the behavior of its member entities.
- The primary objectives are safeguarding customers' interests and fostering a culture of ethics, fairness, and professionalism within the industry.
Key Functions of an SRO:
- Facilitating Communication: A recognized SRO serves as a vital bridge for communication between its members and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
This ensures a seamless flow of information and feedback.
- Setting Standards: SROs play a pivotal role in establishing and upholding minimum benchmarks and standards.
This helps in cultivating professional and ethical conduct among their member entities.
- Education and Awareness: SROs contribute to enhancing industry expertise by providing training to the staff of their members and other relevant stakeholders.
They also organize awareness programs to disseminate knowledge.
- Grievance Resolution: An important function of an SRO is to create a uniform framework for addressing grievances and managing disputes across its member organizations, promoting fairness and transparency.
Eastern Economic Forum (PIB)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Eastern Economic Forum, taking place in the Russian port city of Vladivostok, will be graced by the presence of the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways.
Facts About:
The EEF, established in 2015, serves as a catalyst for attracting foreign investments into the Russian Far East (RFE). It effectively showcases the economic potential of the region, favorable business conditions, and enticing investment opportunities.
- The significance of the EEF is underlined by the remarkable increase in agreements signed during the forum, surging from 217 in 2017 to a staggering 380 agreements in 2021, valued at 3.6 trillion roubles.
These agreements span various sectors, including infrastructure, transportation, mineral exploration, construction, industry, and agriculture.
Key Players:
- In the RFE, China, South Korea, Japan, and India emerge as pivotal players, with China leading the pack as the largest investor.
- China recognizes the potential for advancing its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the Polar Sea Route in the RFE, accounting for a substantial 90% of total investments in the region.
Objectives:
- Russia's strategic vision for the RFE involves linking the nation to the bustling Asian trade routes.
- Through rapid modernization efforts in cities such as Vladivostok, Khabarovsk, Ulan-Ude, Chita, and more, Russia aims to attract increased investments to fortify its economic resilience amidst challenges like economic crises and sanctions, with support from China and other Asian powers.
Interbank Call Money Market (ET)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RBI is considering launching a pilot program for a central bank digital currency (CBDC) specifically designed for interbank borrowing or the call money market.
Facts About:
- The Interbank Call Money Market is a short-term financial market where big institutions borrow and lend money to each other at interbank rates, which are the interest rates banks charge when they borrow from one another.
- The loans in this market are very short, typically lasting only a week or less.
- These loans are often used by banks to meet their reserve requirements.
- It's not just banks that use this market; other participants can include financial institutions, mutual funds, large corporations, and insurance companies.
One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG) (PIB)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
New Delhi recently hosted a full-day conference discussing "Transnational Grid Interconnections for One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG).
Facts About:
The OSOWOG initiative was introduced by the Prime Minister of India during the First Assembly of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) in October 2018.
Its goal is to link energy supply across international borders.
Vision:
- The initiative plans to connect various regional power grids using a common grid to transmit renewable energy, especially solar power.
The project is a collaboration between the governments of India and the UK, along with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and the World Bank Group.
It will bring together governments, financial organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts to speed up the development of the infrastructure needed for a world powered by clean energy.
Completion timeline:
- The ISA is expected to establish this grid in the next few years.
- Once operational, it will transmit solar power to different countries.
Global Biofuels Alliance (The Hindu)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of India recently declared the establishment of the Global Biofuels Alliance.
Facts About:
- The Global Biofuels Alliance is an initiative led by India that aims to bring together governments, international organizations, and industry to promote the use of biofuels.
- So far, 19 countries and 12 international organizations, including G20 members and non-members, have joined this alliance.
India, Brazil, and the US are its founding members.
- The alliance's main goal is to encourage the use of sustainable biofuels, especially in transportation.
Why it matters:
- The alliance will focus on strengthening markets, promoting global biofuels trade, sharing practical policy lessons, and providing technical support for national biofuels programs worldwide.
- It will support the development and use of sustainable biofuels through capacity-building, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- The alliance will create a virtual marketplace to connect industries, countries, and technology providers involved in biofuels.
- Additionally, it will work on establishing internationally recognized standards and regulations to promote biofuels adoption and trade.
Konark Temple Wheel (Indian Express)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
At the G20 summit venue, Bharat Mandapam, the Prime Minister of India greeted the leaders with a backdrop featuring a replica of the Konark Wheel from Odisha's Sun Temple in Puri.
Facts About:
- The Konark Wheel was created in the 13th century when King Narasimhadeva-I ruled.
- This wheel, with 24 spokes, is also seen on India's national flag.
- It represents India's ancient knowledge, advanced civilization, and great architecture.
- The spinning motion of the Konark Wheel represents time, Kalachakra, and the idea of constant progress and change.
- It's a strong symbol of democracy, reflecting the endurance of democratic values and dedication to societal progress.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Indian EXpress)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of India recently declared the start of a massive economic corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Facts About:
- The project involves India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, France, Italy, Germany, and the US.
- Its goal is to boost trade between these countries, especially in energy products.
- The IMEC has two parts:
An Eastern Corridor linking India to the Gulf region and
A Northern Corridor connecting the Gulf region to Europe.
- It includes railways, ship-rail transit, and road routes.
- This corridor will have a railway, an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline, and a high-speed data cable.
- In the future, it will play a big role in connecting India, West Asia, and Europe economically.
- This rail and shipping corridor is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII).
- Why is it important?
- It will increase prosperity by enhancing energy and digital communications flow among these nations.
- The project will also address the infrastructure needs of developing countries in terms of growth.
Schizostachyum Andamanicum (The Hindu)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Government of India's patent office recently awarded a patent to the Botanical Survey of India for a reusable straw made from bamboo (Schizostachyum andamanicum).
Facts About:
- This bamboo is pretty rare and can only be found in certain forests in the Andaman Islands.
- It likes to grow in wet tropical areas.
- This type of bamboo has tall, skinny stems that are hollow inside. It's perfect for making straws.
- It has little white flowers that grow together in groups. The seeds are small and black, and the baby plants have thin, light green leaves.
NAVAL EXERCISE ‘VARUNA’ – 2023 (PIB)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian and French Navies recently conducted Phase II of the Varuna naval exercise in the Arabian Sea.
Facts About:
- This is a naval exercise that India and France have been doing together since 1993.
- In this exercise, they use guided missile frigates, tankers, Maritime Patrol Aircraft, and helicopters from both sides.
- The goal is to make their fighting skills better, work together smoothly, and show that they can keep the peace, security, and stability in the region.
- This exercise also helps the two navies work together and cooperate to keep the seas safe and free for everyone around the world.
Central Empowered Committee (Indian Express)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Supreme Court of India has transferred its environmental oversight committee, the Central Empowered Committee, to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Facts About:
- The Supreme Court created this committee in 2002, and it was restructured in 2008.
- Its main job was to keep an eye on environmental issues and make sure everyone followed the rules.
- Now, there have been some changes. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change says the CEC shouldn't be a temporary group anymore; it should become a permanent team that deals with environmental stuff.
Here's how the new CEC will be set up:
- It will have a chairperson who has 25 years of experience in environment, forests, and wildlife or 25 years of big-time government work.
- They can't be older than 66 years and should be at least an additional secretary in rank.
- The member secretary will be a full-time government officer, at least a Deputy Inspector General of forests or a director in the Government of India.
- They need to know a lot about the environment, forests, or wildlife and have 12 years of experience.
- There will be three expert members, one each for environment, forests, and wildlife. They should have 20 years of experience.
- The central government will pick these members for a three-year term.
Dark Patterns (The Hindu)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Central Government recently asked the public to share their thoughts on the draft rules for stopping and controlling deceptive tactics on the Internet.
Facts About:
- Dark patterns are sneaky and tricky design tricks that websites, apps, and digital platforms use to fool or manipulate users into doing things they might not want to do or making choices that aren't good for them.
- The term "dark patterns" was coined back in 2010 by Harry Brignull, a specialist in making sure user experiences are good.
- These tricky tricks are often used to get users to sign up for things, buy stuff, or share their personal info, among other stuff.
- Dark patterns work by using the way our brains work and making us do things we might not mean to do. They can be just a little misleading or really pushy and aggressive.
- There are 12 types of dark patterns including, Friend spam, Forced continuity, Disguised ads, Confirm shaming, Bait and switch, Hidden costs, Roach motel, Privacy zuckering, Misdirection, Price comparison prevention, Trick questions, Sneak into basket
For example, "confirm shaming" is when they use words, videos, sounds, or anything else to make you feel bad or embarrassed so you'll do what they want you to do.
Varicella Zoster Virus (Indian Express)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Scientists from the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology have made a historic discovery in India. They have identified the Clade 9 variant of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) here for the first time.
Facts About:
- Varicella-zoster is a type of herpes virus that gives you chickenpox, which is a common illness when you're a kid.
- This virus only infects humans and belongs to the α-herpesvirus family.
- It's found all over the world and spreads easily.
- When you first get infected with this virus, you get chickenpox, which is also called acute varicella.
- In some cases, this virus can even affect your central nervous system and lead to serious problems.
Zero Draft Plastic Pollution Treaty (Down to Earth)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The second session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC) concluded with member states instructing the INC secretariat to create an initial draft aimed at putting an end to plastic pollution, including in marine ecosystems.
Facts About:
- This is a globally binding agreement designed to put an end to plastic pollution, especially in marine ecosystems.
- The zero draft consists of ten sections covering topics such as the preamble, definitions, principles, scope, institutional arrangements, and final provisions.
- During INC-2, member states like Saudi Arabia, Iran, China, and India emphasized the significance of clearly defining the scope of this legally binding instrument.
Competition Commission of India (CCI) (TOI)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Competition Commission of India has recently unveiled preliminary rules for overseeing mergers and acquisitions involving significant India-based operations, particularly those in the technology sector, thereby extending the authority of the antitrust regulator.
Facts About:
- CCI is a government-established statutory body founded in March 2009 under the Competition Act, 2002.
- The primary objective of CCI is to foster fair competition in the economy, ensuring a level playing field for producers and promoting market dynamics that benefit consumers.
- The Commission's key focus areas include eradicating practices detrimental to competition, fostering and maintaining competitive environments, safeguarding consumer interests, and upholding the freedom of trade in India's markets.
Mandate: CCI enforces the provisions of The Competition Act, 2002, which:
- Prohibits anti-competitive agreements and the abuse of dominant positions by enterprises.
- Regulates mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that could potentially harm competition within India. Hence, deals exceeding certain thresholds require clearance from CCI.
- Monitors the activities of large enterprises to ensure they do not misuse their 'dominant position' by controlling supply, setting high purchase prices, or engaging in unethical practices that may harm emerging businesses.
Composition: CCI functions as a quasi-judicial body, consisting of one chairperson and six additional members, all appointed by the Central Government.
Headquarters: The Commission is headquartered in New Delhi.
Wide Field Survey Telescope (HT)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In September, China plans to launch the Wide Field Survey Telescope (WFST).
Facts About:
This telescope is the largest time-domain survey facility in the Northern Hemisphere.
Its main goals are as follows:
- To explore and continuously monitor dynamic astronomical events and conduct research in the field of time-domain astronomy.
- To detect faint and distant celestial signals, including those from galaxies beyond our Milky Way and galaxy clusters.
- To search for planets or their moons in the Kuiper Belt and beyond.
- To track and study a comprehensive list of one million solar system objects, providing a detailed view of the solar system's history and evolution.
The WFST is positioned at the Lenghu astronomical observation base in Qinghai Province, northwest China.
- This location, with an average altitude of approximately 4,000 meters, offers ideal conditions for observing the night sky, thanks to its clear skies, stable atmosphere, dry climate, and minimal artificial light pollution.
- It's widely recognized as one of the finest observatory sites across the Eurasian continent.
The WFST project commenced in July 2019, a result of collaboration between the University of Science and Technology of China and the Purple Mountain Observatory under the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Sambar Deer (The Hindu)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Researchers recently spotted a rare sambar deer with leucism (partial white coloring) in the Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary.
Facts About:
- Sambar deer, scientifically known as Rusa unicolor, are large deer native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- They prefer to stay hidden and are most active during the evening and night.
- These deer can be found in a wide range of forest environments, including dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- One of their crucial roles in the ecosystem is seed dispersal within their natural habitats.
Distribution:
- They inhabit areas stretching from the foothills of the Himalayan Mountains across southern Asia, extending to the islands of Taiwan, Sumatra, and Borneo.
Threats they face:
- The main threats to Sambar deer are hunting and the encroachment of their natural habitat.
- In response to human hunting, they have adapted by becoming more active at night to avoid being hunted for trade and food.
Conservation status:
- According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), they are classified as 'Vulnerable.'
Under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972, they are listed in Schedule-III for protection.
Nation First Transit Card (The Hindu)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The State Bank of India has introduced the 'Nation First Transit Card.' It's a prepaid RuPay card that falls under the National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) program, allowing you to use it anywhere in the country.
Facts About:
- This card is designed to make your commuting experience smooth and convenient.
- You can use it to pay for tickets on metros, buses, water ferries, and even parking with just one card.
- Plus, it's not just for transportation; you can also use it for shopping online and in stores.
- What makes it work is the technology behind it. It's powered by RuPay and National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) tech.
Important Facts About National Common Mobility Card (NCMC):
- With NCMC, you can use your Bank's Debit Cards as travel cards for Metro Rail and Buses in places where it's available.
- The idea for NCMC came from a committee led by Nandan Nilekani, set up by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- NCMC is an initiative by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in India. Its goal is to promote cashless transactions and provide a single payment platform for commuters. It was launched on March 4, 2019.
- It offers a unified contactless transport solution through the RuPay platform, which is developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- NCMC is like a magic card that can turn your smartphone into a transport card. You can use it to pay for Metro, bus, and suburban railway services.
Malaviya Mission (PIB)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Malaviya Mission - Teachers Training Programme, initiated by the University Grants Commission, was recently unveiled at Kaushal Bhawan in New Delhi by the Union Minister for Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
Facts About:
- The primary objective is to offer customized training programs for educators.
- This initiative is focused on enhancing the capabilities of faculty members in higher education institutions (HEI).
- It is dedicated to achieving continuous professional development and strengthening the skills of 15 lakh HEI teachers across India through 111 Malaviya Mission centers within a specific timeframe.
- The program is designed to elevate the quality of teacher training, foster leadership qualities among educators, and align with the objectives of the National Education Policy (NEP).
- Capacity building activities under this Mission will be aligned with a credit framework to facilitate career advancement opportunities for teachers.
- Notably, the Indian Knowledge System has been incorporated into the program's modules.
- As part of this initiative, Human Resource Development Centers will undergo a transformation and be renamed as Madan Mohan Malaviya Teachers Training Centers.
Satkosia Tiger Reserve (New Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Satkosia Tiger Reserve made a distressing discovery of two elephants' severely decomposed remains.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in the heart of Odisha, this reserve spans across four districts: Angul, Cuttack, Boudh, and Nayagarh. The Mahanadi River flows through the valleys within the reserve.
- Size: Covering an area of 1136.70 sq km, with 523.61 sq km designated as the core area, Satkosia Tiger Reserve is also part of the Mahanadi Elephant Reserve.
- Unique Geography: Satkosia serves as the convergence point of two distinctive bio-geographic regions in India: the Deccan Peninsula and the Eastern Ghats.
- Landscape: The terrain here is characterized by hills, featuring moderate to steep slopes and narrow valleys.
- Vegetation: The forest primarily consists of North Indian tropical moist deciduous forests and moist peninsular low-level sal.
- Flora: The dominant tree species is sal, forming dense stands. Other associated species include Asan (Terminalia alata), Dhaura (Anogeissus latifolia), Bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus), and Simal (Bombax ceiba).
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, elephants, spotted deer, sambar deer, chowsingha, barking deer, bison, wild dogs, sloth bears, jackals, giant squirrels, and porcupines. Additionally, it provides a natural habitat for two endangered species: the freshwater crocodile and the gharial.
One-hour Trade Settlement (Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which previously stated its intention to introduce real-time settlement of trades in July, is now considering implementing one-hour settlement of trades as the initial step.
Facts About:
In a one-hour settlement, when an investor sells a share, the money will be deposited into their account within an hour, and the buyer will have the shares in their demat account within an hour.
Trade settlement is a process that involves the transfer of funds and securities on the settlement date.
- It's considered complete when the purchased securities from a listed company are delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the money.
- Previously, trade settlements followed the T+1 cycle, meaning they occurred within one day or 24 hours of the actual transactions.
This changed in January 2023 when India shifted to the T+1 settlement cycle, making it the second country globally, after China, to adopt this cycle for top-listed securities.
Chitala Fish (TOI)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister for Fisheries, Livestock, and Dairying has just revealed plans to boost the population of the Uttar Pradesh state fish Chitala by introducing it into natural water sources like the Ganga through river ranching.
Facts About:
Chitala Fish is a type of predator fish that primarily hunts at night and preys on smaller fish.
Distribution:
- Although it's often reported to inhabit various parts of southern Asia, this species is mainly found in the Indian subcontinent, including Pakistan, India (particularly in states like Manipur, Uttaranchal, West Bengal, Assam, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar), Nepal, and Bangladesh.
Habitat:
- Chitala Fish is commonly found in major river channels and freshwater lakes but has also been observed in swamps.
- Its primary habitat includes the Indus, Ganges-Brahmaputra, and Mahanadi river basins in India.
Conservation Status:
- According to the IUCN, Chitala Fish is classified as "Near Threatened."
Significance of Chitala’s River Ranching:
- The river ranching initiative has multiple aims, including restoring the aquatic ecosystem's balance, boosting the income of fish farmers, and providing the public with a protein-rich diet.
Additionally, Uttar Pradesh has ongoing projects worth over 1000 crore under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
Indian Green Building Council (The Hindu)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) gave the highest Platinum rating to Vijayawada Railway Station, certifying it as a 'Green Railway Station.
Facts About:
- The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) is part of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and started in 2001.
- It's India's top certification organization.
- They offer various services like creating new green building rating systems, certification services, and green building training programs.
- IGBC also hosts the Green Building Congress, their main yearly event on green buildings.
- Additionally, it's one of the five countries on the board of the World Green Building Council, where global issues are discussed at events like COP.
- The rating is based on six environmental categories: sustainable station facility, health, hygiene, and sanitation, energy efficiency, water efficiency, smart and green initiatives, and innovation and development.
- Their headquarters is in Hyderabad.
Project Naman (India Today)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army has initiated 'Project Naman,' which involves setting up centers to provide support and address concerns for veterans and the families of personnel who have made the ultimate sacrifice.
Facts About:
- Project Naman aims to create centers for veterans and the families of fallen personnel to provide assistance and address their concerns.
- The first center will be located in Delhi Cantonment.
- Named 'Naman,' these centers will include a Common Service Centre, offering various government-to-customer services.
- Additionally, they will assist in updating pensioners' accounts on the SPARSH portal for veterans, next of kin, and dependents.
Gramodyog Vikas Yojana (PIB)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chairman of the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC), a part of the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, provided artisans with tool-kits and machinery as part of the 'Gramodyog Vikas Yojna' program.
Facts About:
- Gramodyog Vikas Yojana is a vital part of the Khadi Gramodyog Vikas Yojana and has a mission to advance and enhance village industries through various means such as shared facilities, technological upgrades, training, and more.
- It encompasses a range of activities associated with different village industries.
Components of the Yojana:
- Research & Development and Product Innovation: This component supports institutions engaged in product development, innovations, design improvements, and diversification processes.
- Capacity Building: It focuses on enhancing the skills and knowledge of staff and artisans through the existing MDTCs (Management Development and Training Centers) and excellence institutions.
- Marketing & Publicity: The Yojana assists village industry institutions in various ways, including preparing product catalogs, industry directories, conducting market research, introducing new marketing techniques, organizing buyer-seller meetings, and arranging exhibitions.
- Target beneficiaries of this program are artisans, unemployed youth, and self-help groups (SHGs).
- To be eligible, individuals must be traditional artisans with skill and experience in art and craft.
Tilapia fish (Down to Earth)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The report about invasive alien species highlighted that the proliferation of water hyacinth (scientifically known as Pontederia crassipes) in Lake Victoria has had a negative impact on the tilapia fish population.
Facts About:
- It is a common name for some fish species in the family Cichlidae (order Perciformes), which includes a large number of predominantly freshwater species endemic to Africa.
- These fish are primarily found in freshwater environments, such as shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes. They are less commonly found in brackish water.
- In some cases, Tilapia can become problematic invasive species in warm-water habitats like Australia, whether introduced intentionally or accidentally.
- However, they generally can't survive in cold temperate climates.
- It has emerged as one of the world's most productive and internationally traded food fish.
- Tilapia culture has become economically successful in many parts of the world, and fishery experts have termed tilapia "aquatic chicken" because to its rapid growth and minimal maintenance cultivation.
Nagarahole Tiger Reserve (The Hindu)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A 10-year-old boy was recently killed by a tiger in Nagarahole Tiger Reserve's Metikuppe wildlife region.
Facts About:
Nagarahole Tiger Reserve is located in the Mysore and Kodagu districts of Karnataka.
- Its name, "Nagarahole," means "snake stream" in Kannada, and it's named after a small river that flows through the area, eventually joining the Kabini River.
The reserve is bordered by the Bandipur Tiger Reserve to the southeast and the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala to the southwest.
- It's also a part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
Its history dates back to the time of the Wodeyar dynasty, the former rulers of the Kingdom of Mysore, who used it as an exclusive hunting ground.
- It was established as a wildlife sanctuary in 1955 by Coorg State, later becoming a national park in 1988.
- In 1999, it was designated as a Tiger Reserve under Project Tiger.
Nagarahole's forests consist mainly of deciduous trees.
The eastern part of the reserve has dry deciduous forests, while the western areas, with higher rainfall, feature tropical moist and semi-evergreen forests.
Throughout the reserve, you'll find swampy areas called 'hadlu,' rich in grasses and sedges, which are favored by herbivores.
The region is known for commercially valuable trees like rosewood, teak, sandalwood, and silver oak.
In terms of wildlife, Nagarahole is home to a diverse range of species, including tigers, leopards, wild dogs, sloth bears, Asiatic elephants, gaurs, sambar deer, chital deer, muntjacs, and four-horned antelopes, among others.
Tharosaurus indicus (The Hindu)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists from IIT Roorkee studied dinosaur fossils from the Middle Jurassic period. These fossils were discovered in the Thar desert near the Jaisalmer Basin by the Geological Survey of India.
Facts About:
- It is a member of the Dicraeosauridae family and the Diplodocoidea superfamily.
- These are the earliest dicraeosaurid sauropod fossils discovered in India.
- It is the world's oldest known diplodocoid fossil, dating back 167 million years.
- The dinosaur was named Tharosaurus indicus, with Tharo originating from the Thar desert, Saurus from the Greek'sauros', meaning lizard, and indicus from its Indian provenance.
- This family was distinct in that its members were smaller and had shorter necks and tails than other long-necked sauropods.
- Sauropods originally arrived on Earth some 200 million years ago, during the Jurassic period.
- They were one of the most dominating dinosaur clades, surviving until the late Cretaceous period 65 million years ago, when dinosaurs became extinct.
- According to the experts, dicraeosaurid dinosaur fossils have previously been discovered in North and South America, Africa, and China, but such fossils were unknown from India.
Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities from the Ministry of Union Housing and Urban Affairs have indicated that the initial installment of loans for supporting ongoing projects in tier-2 and tier-3 cities through the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) is expected to be released shortly.
Facts About:
The UIDF is created by utilizing the priority sector lending shortfall.
Objective:
- This fund serves as a resource for public agencies to develop urban infrastructure in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Emphasis is placed on essential services such as sewage and solid waste management, water supply, sanitation, construction, and improvement of drainage systems, with a priority on projects that have a significant impact.
The National Housing Bank manages this fund.
It initially has a corpus of ?10,000 crore and is modeled after the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF).
States are encouraged to harness resources from the 15th Finance Commission's grants and existing schemes, while also considering user charges when accessing the UIDF.
Currently, it covers 459 tier-2 cities and 580 tier-3 cities.
UIDF Loans:
- nterest rate: Bank Rate minus 1.5%
- The loan principal is repayable in five equal annual installments within seven years from the draw date, including a two-year moratorium period.
- Interest payments are made on a quarterly basis.
Stump-tailed Macaque (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Delhi Zoo has recently welcomed eight stump-tailed macaques, which were transferred from the Aizawl Zoological Park in Mizoram.
Facts About:
The stump-tailed macaque, also known as the bear macaque, is an Old-World monkey species native to South Asia.
Scientific Name: Macaca arctoides
Natural Habitat: These monkeys inhabit tropical and subtropical evergreen forests.
Geographic Range:
- They are indigenous to regions including Cambodia, southwest China, northeast India, Laos, Myanmar, northwest Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- In India, they are predominantly found south of the Brahmaputra River, primarily in the northeastern states.
Their Indian range extends from Assam and Meghalaya to eastern Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule II
Gilbert Hill (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Maharashtra Government has recently put forward a plan to transform Gilbert Hill into a tourist attraction, drawing inspiration from the iconic Burj Khalifa in Dubai.
Facts About:
- Situated in Andheri, Mumbai, Gilbert Hill is a remarkable 200-foot tall monolithic column made of black basalt rock.
- This unique geological formation was created approximately 66 million years ago during the Mesozoic Era when molten lava erupted from the Earth's crevices and solidified.
- In 1952, it received National Park status, and in 2007, the Brihan Mumbai Municipal Corporation recognized it as a Grade II heritage structure.
- Notably, Gilbert Hill is one of only three volcanic rock outcrops worldwide.
- As one of the oldest heritage sites in its original condition, it features a collection of temples and a small garden perched atop, accessible via a steep staircase carved into the rock.
PM-DAKSH Yojana (PIB)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
From 2020 to 2023, the PM-DAKSH Yojana has provided training to a total of 107,156 beneficiaries.
Facts About:
The Pradhan Mantri Dakshata Aur Kushalata Sampanna Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana is a Central Sector Scheme launched in the fiscal year 2020-21.
Its primary goal is to boost the skills and competency of specific target groups, making them capable of finding employment, either through self-employment or wage-employment, to improve their socio-economic status.
This Yojana serves as a National Action Plan for training marginalized individuals, including Scheduled Castes (SCs), Other Backward Classes (OBCs), Economically Backward Classes (EBCs), Denotified Tribes (DNTs), sanitation workers, and waste pickers.
Target Groups:
- Artisans: Those looking to enhance their income within their current vocations.
- Women: Empowering them to engage in self-employment while managing domestic responsibilities.
- Youth: Providing them with long-term training and specialization in employable fields to improve their job prospects.
Eligibility:
- Age range: 18-45 years.
- No income limit for SCs, Safai Karamcharis (sanitation workers), and waste pickers.
- Annual family income below Rs. 3 lakh for OBCs.
- Annual family income below Rs. 1 lakh for EBCs (Economically Backward Classes).
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJ&E).
GRIHA-IV Norms (The Hindu)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army is building a new Thal Sena Bhawan (TSB) using GRIHA-IV (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) standards.
Facts About:
GRIHA stands for Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment, and the word 'GRIHA' means 'Abode' in Sanskrit.
It's a tool that helps us measure how well a building performs compared to national standards.
GRIHA looks at a building's environmental impact throughout its entire life cycle, setting a clear standard for what qualifies as a 'green building.'
This rating system is based on accepted energy and environmental principles, balancing established practices with new ideas, both nationally and internationally.
TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute) developed GRIHA, and it's been adopted by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Criteria:
- GRIHA assesses a building using 34 criteria and awards points on a scale of 100.
- To get GRIHA certification, a project needs at least 50 points.
- Some criteria are mandatory, and the project must meet them to be eligible for any rating.
Project Ratings:
- 50-60 points: 1-star GRIHA rating
- 61-70 points: 2-star GRIHA rating
- 71-80 points: 3-star GRIHA rating
- 81-90 points: 4-star GRIHA rating
- 91-100 points: 5-star GRIHA rating
What is Preeclampsia? (The HIndu)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A recent research study has shown that utilizing a liquid-biopsy method to assess DNA-methylation levels in the blood could enhance the early detection of pregnancies at risk of developing preeclampsia.
Facts About:
Preeclampsia is a severe condition characterized by elevated blood pressure that typically emerges during pregnancy, usually after the 20th week.
- This condition can have adverse effects on multiple organs in the body and poses risks to both the mother and the developing fetus.
Symptoms:
- Individuals with preeclampsia commonly experience high blood pressure (hypertension) and elevated levels of protein in their urine (proteinuria).
- Additional symptoms may include vision changes such as temporary loss of vision, blurred vision, or heightened sensitivity to light.
Prevention:
- The primary clinical recommendation for preventing preeclampsia is the use of low-dose aspirin, supported by strong clinical evidence.
Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle and making prudent choices is advisable, especially for individuals who have previously experienced preeclampsia.
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY) (PIB)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY), an inventive employment incentive scheme introduced by the Central Government, has surpassed its initial objectives for generating employment. This achievement highlights its effectiveness in promoting job creation and supporting economic recovery amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Facts About:
- Launched in 2020, the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY) was created to stimulate the creation of new job opportunities.
- It achieves this by providing financial support to employers who are part of the Employees' Provident Fund Organization (EPFO).
- The primary objective of this scheme is to incentivize the employment of individuals, including those who lost their jobs due to the pandemic.
- It does so by covering both the employee and employer contributions, which amounts to 24% of wages, for establishments with up to 1000 employees.
- For larger establishments with over 1000 employees, the scheme covers only the employee's EPF contributions, which is 12% of wages, in relation to new employees.
- As of July 31, 2023, the ABRY has successfully enrolled more than 7.58 million new employees, surpassing its initial target for employment generation.
- This achievement underscores its significant contribution to revitalizing the job market and supporting economic recovery during these challenging times.
Umiam Lake (ET)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Meghalaya government has just started using advanced AI-powered robots to ensure that Umiam Lake, a popular tourist destination, remains clean and free from pollution.
Facts About:
Umiam Lake, also known as Barapani Lake, is located 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) north of Shillong, the capital of Meghalaya.
- This beautiful lake is surrounded by the lush green hills of East Khasi and covers an expansive 10 square kilometers.
The history of Umiam Lake dates back to 1965 when a dam was built to generate hydroelectric power as part of the Umiam Umtru Hydroelectric Power Project, marking the lake's inception.
The primary source of water for the lake is the confluence of two streams, Umkhrah and Umshvrpi, which merge to form the Wah Ro-ro stream in the northwest of the town.
- This stream then joins the River Umiam, ensuring a steady flow of water into the lake.
The catchment area for the lake and dam extends over 220 square kilometers, encompassing not only Shillong but also its neighboring regions.
- Umiam Lake has gained popularity as a hub for water sports and adventure activities, making it a favorite destination for thrill-seekers and nature enthusiasts alike.
C-TAP initiative (WHO)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the COVID-19 Technology Access Pool (C-TAP) has revealed three fresh licensing agreements obtained via the Medicines Patent Pool (MPP).
Facts About:
- In May 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Costa Rica, in collaboration with 44 Member States, the UN Development Programme, Unitaid, UNAIDS, and implementing partners like the Medicines Patent Pool (MPP), launched C-TAP.
- C-TAP operates based on the principles outlined in the Solidarity call to action.
- Its primary objective is to provide a platform where developers of COVID-19 treatments, diagnostics, vaccines, and other health products can voluntarily share their intellectual property, knowledge, and data.
- This sharing is aimed at expediting technological advancements and increasing global production capabilities in the fight against the pandemic.
DIKSHA Platform (The Hindu)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD) within the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is gearing up to incorporate Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into its established Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform.
Facts About:
DIKSHA is a national education platform initiated by the National Council for Education Research and Training (NCERT) under the Ministry of Education.
- Its primary purpose is to deliver educational content to schools through both an online portal and a mobile application.
The platform was developed with a strong emphasis on key principles such as open architecture, open access, open licensing, choice, and autonomy.
- It relies on open-source technology tailored to India, featuring internet-scale capabilities that accommodate various teaching and learning needs.
Key Features:
- DIKSHA incorporates many essential components of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), enabling successful use-cases like interactive textbooks, online courses, content creation, content sourcing, interactive quizzes, question banks, chatbots, analytics, and dashboards.
To support the learning needs of Children With Special Needs (CWSN), DIKSHA offers a substantial collection of resources, including audiobooks, Indian Sign Language (ISL) videos, and a comprehensive dictionary.
DIKSHA Platform (The Hindu)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD) within the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is gearing up to incorporate Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into its established Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform.
Facts About:
DIKSHA is a national education platform initiated by the National Council for Education Research and Training (NCERT) under the Ministry of Education.
- Its primary purpose is to deliver educational content to schools through both an online portal and a mobile application.
The platform was developed with a strong emphasis on key principles such as open architecture, open access, open licensing, choice, and autonomy.
- It relies on open-source technology tailored to India, featuring internet-scale capabilities that accommodate various teaching and learning needs.
Key Features:
- DIKSHA incorporates many essential components of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), enabling successful use-cases like interactive textbooks, online courses, content creation, content sourcing, interactive quizzes, question banks, chatbots, analytics, and dashboards.
To support the learning needs of Children With Special Needs (CWSN), DIKSHA offers a substantial collection of resources, including audiobooks, Indian Sign Language (ISL) videos, and a comprehensive dictionary.
The Global Fund (The Hindu)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Global Fund unveiled an agreement with generic pharmaceutical companies to substantially reduce the cost of a state-of-the-art HIV medication.
Facts About:
The Global Fund represents a global initiative aimed at conquering HIV, TB, and malaria, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable future for everyone.
Established in 2002, this movement unites governments, civil society, healthcare professionals, and the private sector.
Funding:
- The Global Fund operates on a three-year funding cycle, providing more extended-term stability in the fight against AIDS, TB, and malaria.
Funding primarily originates from the public sector, with 92% of total contributions originating from donor governments.
- Additional funding sources encompass the private sector, foundations, and innovative financial initiatives.
In 2006, India became a donor to the Global Fund, committing $25 million for the Seventh Replenishment period spanning 2023-2025.
Adopt a Heritage 2.0 Scheme (Indian Express)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Archaeological Survey of India is ready to introduce its new and innovative program called "Adopt a Heritage 2.0.
Facts About:
- This initiative is a joint effort of the Ministry of Tourism in partnership with the Ministry of Culture and the Archaeological Survey of India.
- It was inaugurated on World Tourism Day in September 2017.
- Under this program, the government invites various entities, including public and private sector companies, as well as individuals, to undertake the development of selected historical monuments and tourist sites throughout India.
- The primary goal is to encourage these entities to become 'Monument Mitras' and assume the responsibility of enhancing both basic and advanced tourist facilities at these locations.
- The corporate sector is encouraged to utilize corporate social responsibility (CSR) funds for site maintenance.
- In return, Monument Mitras receive limited visibility on-site and on the official Incredible India website.
Meningococcal Disease (HT)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The state of Virginia in the United States has issued a caution regarding a widespread outbreak of meningococcal disease.
Facts About:
Meningococcal disease is a rare but severe bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
The two primary forms are meningitis and septicemia, both potentially life-threatening within hours.
Causes:
- This disease is caused by Neisseria meningitidis bacteria. Approximately 1 in 10 people carry these bacteria in their nose and throat without illness, but sometimes they can cause meningococcal disease.
Transmission:
- Transmission occurs through respiratory and throat secretions, like saliva, but usually requires close or prolonged contact. It's less contagious than the common cold or flu.
Symptoms:
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia (sensitivity to light), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a distinctive rash.
Treatment:
- Meningococcal disease is treated with antibiotics, and additional therapies may be necessary, such as oxygen therapy, medications for low blood pressure, and skin treatments, including surgery.
Strategic Disinvestment (The Hindu Business Line)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The government has recently issued a Request for Proposal (RFP) to hire an asset appraiser for the Strategic Disinvestment of IDBI Bank.
Facts About:
Strategic disinvestment involves the sale of a significant portion of the government's ownership in a central public sector enterprise (CPSE), which can be up to 50% or a higher percentage as decided by the competent authority.
- This process also includes the transfer of management control.
It essentially means transferring both ownership and control of a public sector entity to another entity, which can be either private or public.
Distinguishing Strategic Disinvestment/Sale from Disinvestment:
- Disinvestment refers to the sale of minority shares of public enterprises to another entity, whether it's public or private.
- In this case, the government still maintains ownership of the enterprise.
In contrast, strategic disinvestment/sale occurs when the government sells a majority share in an enterprise, relinquishing not only ownership but also control of the entity.
What are the objectives of Strategic Disinvestment:
- Reduce Government Ownership
- Raise Capital
- Enhance Efficiency
- Foster Competition
- Attract Private Investment
- Focus on Core Functions
- Alleviate Fiscal Burden
Financial Action Task Force (Deccan Herald)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India has suggested to all G20 nations to actively cooperate to deal comprehensively and efficiently with fugitive economic offenders as part of the action against them and recovery of the assets.
Facts About:
- The FATF is an international organization made up of governments that focuses on creating policies and standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Objective: Its main goal is to establish global standards and encourage the development of policies at both national and international levels to prevent money laundering and the financing of terrorism.
- The FATF provides recommendations to combat financial crimes, assesses its member countries' policies and procedures, and strives to promote the adoption of anti-money laundering regulations worldwide.
- Formation: The FATF was established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris with the initial aim of addressing money laundering. In 2001, its scope expanded to include combating terrorism financing.
- Headquarters: Its headquarters are located in Paris, France.
- Membership: The FATF comprises 39 member countries, including the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Britain, Germany, France, and the European Union.
- India became a member in 2010.
- As part of its efforts, the FATF maintains two lists: the blacklist and the greylist.
Black List:
- The blacklist contains countries referred to as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs). These are countries known for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering activities.
- The FATF regularly updates this list, adding or removing countries as needed.
Grey List:
- The grey list includes countries considered to be safe havens for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering. Placement on this list serves as a warning that a country may eventually be placed on the blacklist.
- Currently, three countries on the FATF blacklist are North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar.
Consequences of Being on the FATF Blacklist:
- Countries on the FATF blacklist do not receive financial aid from organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank (ADB), and the European Union (EU).
- Additionally, they face various international economic and financial restrictions and sanctions.
Invasive Alien Species (Down to Earth)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Report on invasive species & their control to be approved at the plenary was developed over four years by 86 leading experts from 49 countries
Facts About:
An alien species is one that has been introduced outside its native habitat.
According to experts, these are whether intentionally or accidentally, find their way outside their natural environments.
- Once there, they often outcompete local species, disrupting the delicate ecological balance.
These invasive species typically possess specific traits that aid their success, including the ability to adapt to new conditions (known as phenotypic plasticity).
- Other characteristics include rapid reproduction, high dispersal capabilities, versatility in diet and environmental adaptation, and a propensity for quick reproduction.
It's crucial to note that invasive alien species are not a natural part of their new ecosystems, and their presence can lead to severe harm to the economy, the environment, and even human health.
In developing countries, where agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and natural systems play a pivotal role in people's livelihoods, invasive alien species exacerbate poverty and pose a significant threat to development.
- This situation is further compounded by factors like climate change, pollution, habitat loss, and human-induced disturbances.
Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) (The Hindu)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In the Aditya-L1 mission, ISRO will utilize a Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) identical to the one employed in previous missions to Mars and the Moon.
Facts About:
- This compact yet potent engine, referred to as 'LAM,' assumes a pivotal role in ISRO's upcoming Aditya-L1 mission, designed for the study of the sun.
- The effective functioning of the LAM holds significant importance as it enables ISRO to position the Aditya spacecraft in a halo orbit at Lagrangian point L1.
- These engines are commonly employed for making precise orbital adjustments to satellites and spacecraft while they are in orbit.
- The Liquid Apogee Motor is the product of the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), an ISRO facility specializing in Liquid and Cryogenic Propulsion, located in Thiruvananthapuram.
Bhoramdev Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) (TOI)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chhattisgarh High Court has recently rejected a public interest litigation (PIL) seeking the designation of the Bhoramdeo Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) as a tiger reserve.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in the Kawardha district of Chhattisgarh, this sanctuary takes its name from the renowned 11th-century Bhoramdeo Temple located nearby.
-
- It shares its boundary with Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, making it a significant tiger habitat in central India.
- Covering an expanse of around 325 square kilometres (125 square miles), it boasts a diverse landscape.
- The sanctuary serves as the origin of the Fen and Sankari rivers.
- Characterized by lush green forests, undulating hills, and the Maikal Range of the Satpura Hills, it presents a picturesque setting.
- Vegetation: Comprising a blend of dense forests and open grasslands, it offers a rich variety of flora.
- Flora Highlights: Notable plant species within the sanctuary include sal, saja, tinsa, kara, and haldu.
- Diverse Fauna: Bhoramdeo Wildlife Sanctuary is home to a wide range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, wild dogs, sloth bears, sambar deer, barking deer, chital (spotted deer), gaur (Indian bison), as well as numerous bird and reptile species.
Third Rail Current Collector (PIB)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Kolkata Metro of Indian Railways intends to substitute the steel third rail with a composite Aluminum third rail Current Collector.
Facts About:
- The third rail system serves as a method of supplying electrical power to trains via a conductor positioned beside the railway tracks.
- Kolkata Metro Railway has relied on steel Third Rails for the past four decades.
- It has now opted for composite Aluminium Third Rails in all forthcoming construction projects, as well as retrofitting existing corridors that currently employ steel Third Rails.
- By making this transition, Kolkata Metro Railway joins a select group of metro systems, including those in London, Moscow, Berlin, Munich, and Istanbul, that have also shifted from steel Third Rails to Aluminium Third Rails.
Advantages of Aluminum Composite Third Rail compared to Steel Third Rail include:
- Reduced resistive current loss leading to improved traction voltage levels.
- Lower maintenance and life cycle costs.
- Enhanced efficiency of train operations.
- Significant improvements in energy efficiency.
- Decreased carbon footprint.
JAIS Language Model (NewsOnAir)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a division of the Abu Dhabi-based AI company G42 has unveiled 'Jais,' the most cutting-edge Arabic large language model globally.
Facts About:
- Jais is a bilingual Arabic-English model meticulously trained on an extensive dataset of text and code.
- Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of tasks, including machine translation, text summarization, and question-answering.
- Trained on the world's largest AI supercomputer, the Condor Galaxy, Jais has been exposed to a vast dataset, encompassing 116 billion Arabic tokens and 279 billion English tokens.
- Being open-source means that Jais is accessible for anyone to use and contribute to its development, and it is available for download on the Hugging Face machine learning platform.
- The introduction of Jais represents a significant milestone in advancing AI within the Arabic-speaking community.
Applications:
- Jais finds potential applications in machine translation, bridging the language gap between Arabic and English, thereby enhancing information accessibility and cross-lingual communication.
- This versatile model excels at condensing extensive text content, from news articles to research papers, into concise and comprehensible summaries, facilitating improved accessibility and comprehension.
- Furthermore, Jais is adept at responding to text-based queries, making it a valuable tool for educational purposes, such as interactive chatbots for students, and enhancing customer service applications for effective client inquiries.
US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (Indian Express)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform under the US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
Facts About:
In August 2023, the U.S.-India Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP) was launched under the Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
RETAP was established to take bilateral collaboration further with a result-oriented, time-bound technology focus.
It is intended to advance new and emerging renewable technologies with a view toward deployment and scaling.
RETAP’s initial focus is to be on green/clean hydrogen, wind energy, long long-duration energy storage, and to explore geothermal energy, ocean/tidal energy and other emerging technologies as mutually determined in the future.
The initial work plan is guided by the following five themes:
- Research & Development
- Piloting & Testing of Innovative Technologies
- Advanced Training & Skill Development
- Policy and Planning for Advancing RET and Enabling Technologies
- Investment, Incubation and Outreach programmes
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1940523
Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) report (Economic Times)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Annual update of the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2023 has been released.
Facts About:
India ranked second among the countries worst hit by air pollution with Bangladesh topping the list.
- Nepal ranked third followed by Pakistan and Mongolia.
PMI in South Asia: Particulate pollution has increased9.7 percent from 2013 to 2021 in South Asia.
- In India, PM2.5 levels rose 9.5 percent; in Pakistan 8.8 percent; and in Bangladesh, levels rose by 12.4 percent over this same time interval.
Life Expectancy: An average Indian citizen loses around 5.3 years of life expectancy due to air pollution.
- While an average citizen in Bangladesh loses 6.8 years of their life to air pollution
- An average Chinese citizen has seen an improvement — from 4.7 years of life expectancy being lost in 2013 to 2.5 now, an improvement of 2.2 years,
Pollution in India: Pollution in India has increased from 56.2 µg/m3 in 2020 to 58.7 µg/m3 in 2021.
- This is more than 10 times the WHO guideline of 5 µg/m3.
Health Risk: Pollution is biggest threat to human health in India in terms of lowering life expectancy, beating cardiovascular diseases and child and maternal malnutrition.
- While particulate pollution takes 5.3 years off the life of the average Indian, cardiovascular diseases reduce life expectancy by about 4.5 years, and child and maternal malnutrition reduces life expectancy by 1.8 years.
Poor AIr in Delhi: It is the most polluted city in the world.
- Delhi’s annual average PM2.5 level in 2021 was found to be 126.5 µg/m3, which is more than 25 times the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 µg/m3.
- Delhi residents are on track to lose 11.9 years of life expectancy on average relative to the WHO limit and 8.5 years relative to the national guideline if the current pollution levels persist.
About Air Quality Life Index (AQLI)
- AQLI measures the impact of particulate pollution on life expectancy.
- It is released by Energy Policy Institute at University of Chicago (EPIC).
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/your-life-is-getting-short-by-5-years-due-to-air-pollution-chicago-university-report-reavels-scary-numbers/articleshow/103198930.cms?from=mdr
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World-2023 (FAO)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A recently published report, ‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023, shows that the cost of a healthy diet has increased in India in recent years, but it is still lowest among the BRICS countries (including the newly added six countries) and India’s neighbours.
Facts About:
- The ‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023 report prepared by FAO and United States agencies has been released with the theme of “Urbanisation, agrifood systems transformation, and healthy diets across the rural-urban continuum”.
- According to a UN agency report 74% of people in India can’t afford a healthy diet because of increasing costs.
‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023 :-
The report is published by the partnership of Food and Agriculture Organisation(FAO) of the United Nations with the United States agencies i.e International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), World Food Programme (WFP) and World Health Organisation (WHO).
The aim of the report is
- ending hunger
- achieving food security
- improving nutrition
- to provide an in-depth analysis for achieving this goal in the context of the SDG.
FAO:-Each year, FAO’s most deeply scrutinised report presents the leading numbers of undernourished people worldwide, while advocating for strategies against hunger and malnutrition.
SOFI 2023 related to India:-
PPP report:-
- The concept of PPP is 1ppp dollar in the United States should be able to buy the same amount of goods in either India or Brazil or in other countries.
- xPPP dollar per day means how much would it cost to buy a very simple healthy diet in every country.
- According to this data India compared to its other countries or other regional countries of the world itself has the lowest PPP dollar for a healthy diet.
According to another data which shows the share of the population that is unable to afford a healthy diet in 2021, for instance 74% of the Indian population cannot afford a healthy diet and the fourth highest share in the country itself .
So when it comes to afford a healthy diet, India comes fourth.
Because of stagnation, poor income levels, General stagnation, people of India are not able to afford the cheapest healthy diet in the world.
According to Above two report
- India doesn’t have to spend too much to get a healthy diet.
- 74% of our population cannot afford a healthy diet.
Conclusion:-
The share of people able to afford such a healthy diet is still low: India is at the bottom of that list because income levels are stagnant or going down.
- For example, while in mumbai the cost of meals have risen by 65% in last 5 years wages and salaries have only risen by 28% to 37% , so it shows that prices are rising but our incomes are not rising therefore though India have the cheapest food in the world there is most of people of india can’t afford it.It is not about the can’t afford food it’s a about a nutritional healthy diet divided by FAO and the UN.
Source: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc3017en
Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh’s Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases (Times now)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister presented Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases to Greek President and Prime Minister.
Facts About:
Meghalaya shawls
Meghalaya shawls were originally woven for Khasi and Jaintia royalty who considered them a symbol of their power and status.
Shawls were worn at formal events and festivals, and their intricate designs and vibrant colors reflected the wealth and prestige of the royal family.
The designs used in Meghalaya shawls were very symbolic.
- For example, the use of animal motifs such as tigers and elephants was a symbol of strength and power, while the use of floral motifs was a symbol of beauty and grace.
- The weavers, mostly women, spend hours weaving intricate designs and patterns using traditional weaving techniques.
- The shawls are made from local wool and natural colors.
- Shawls are highly valued for their fine workmanship and intricate designs.
Dhokra Art of Chhattisgarh
One of the earliest manifestations of this ancient art is the dancing girl object found in the excavations at Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa.
Traditionally, the Gadwads, Gonds and Dhurwas tribes of Chhattisgarh practice the art of Dhokra using the lost wax technique or hollow casting.
It is named after the Dhokar Damar, an Indian tribe in the central and eastern part of the country.
Common themes in Dhokra art revolve around Hindu gods and goddesses and various animal figures.
Dhokra Art is a non-ferrous metal casting art that uses wax casting technology.
This type of metal casting has been used in India for over 4000 years and is still used today.
There are two main processes involved in lost wax casting: solid casting and hollow casting.
Bidri Art vases
It originated from the city of Bidar in Karnataka in the 14th century.
Bidar in Karnataka and Hyderabad in Telangana are the most active centers of the art form.
Bidri Work handicraft is the art of inlaying metal alloys.
The soil of Bidar Fort magically gives black color to the base metals and the art form has been given the prestigious GI status.
Technique: For smelting, a new mold must be made, into which molten metal, an alloy of zinc and copper, is poured.
- Patterns are drawn on them and carved with a chisel and hammer.
- The engravings are attached with silver wire.
- This contrast of shiny silver with black metal is unique in Bidri art.
Source: https://www.timesnownews.com/india/meghalaya-shawl-to-telangana-vase-what-pm-modi-gifted-to-his-greek-counterpart-article-103065689
Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary (The Hindu)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists suggested rerouting the railway track running through the Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary.
Facts About:
The Hoollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary was renamed on 25 May 2004, formerly known as the Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary or Hollongapar Reserve Forest.
It is an isolated protected area of evergreen forest located in the Jorhat district of Assam.
Vegetation: The upper canopy of the forest is dominated by the Hollong tree, while the Nahar dominates the middle canopy. The lower canopy consists of evergreen shrubs and herbs.
Fauna:
- The sanctuary has a rich biodiversity and is home to the only apes in India, the western Hoolock, as well as the only nocturnal primate found in the northeast Indian states, the Bengal slow loris.
- Also it is home to Stump-tailed macaque, northern pig-tailed macaque, eastern Assamese macaque, rhesus macaque, and capped langur etc
Key facts about Hoolock Gibbon
It is the only ape found in India.
It is native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China.
Gibbons, the smallest and fastest of all apes, live in tropical and subtropical forests in the southeastern part of Asia.
The Hoolock gibbon, unique to India’s northeast, is one of 20 species of gibbons on Earth.
It is categorised into Western Hoolock Gibbon and Eastern Hoolock Gibbon.
Like all apes, they are extremely intelligent, with distinct personalities and strong family bonds.
Western Hoolock Gibbon
- It has a much wider range, as it is found in all the states of the northeast, restricted between the south of the Brahmaputra River and east of the Dibang River.
- It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Eastern Hoolock gibbon
- It inhabits specific pockets of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India, and southern China and northeast Myanmar.
- It is listed as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red list.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/reroute-railway-track-running-through-assam-gibbon-sanctuary-suggest-scientists/article67247555.ece
Cauvery Water dispute (Indian Express)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Cauvery Water Authority fixes quantum to be released by Karnataka.
Facts About:
- The current outflow rate into the river is 4,398 cubic feet per second (cusecs), whereas the inflow stands at 2,300 cusecs as of Wednesday.
- The outflow rate was 2,292 cusecs on Tuesday at 8 p.m. but was increased after 11 p.m.
- The Kabini Reservoir in Mysuru district also contributes to the outflow, currently standing at 2,000 cusecs.
- Cumulatively, both reservoirs will release around 6,398 cusecs of water.
Cauvery Water Sharing Dispute: Historical Background
- 1892 Onset: The water dispute originates from 1892 between British-ruled Madras Presidency and the princely state of Mysore (now Karnataka).
- 1924 Agreement: A 50-year agreement mediated by the British aimed to ease tensions but set the stage for future conflicts.
- Post-Independence Battles: Karnataka’s dam constructions in the 1960s-80s triggered Tamil Nadu’s Supreme Court appeal, leading to the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT).
- Interim Measures: The Cauvery River Authority (CRA) implemented interim orders in 1998. Contentious issues persisted despite CWDT’s 2013 award.
- Final Award: CWDT’s 2013 award allocated water quantities for Tamil Nadu (419 TMC), Karnataka (270 TMC), Kerala (30 TMC), and Puducherry (7 TMC).
Water Sharing Criteria
- Monthly Schedule: Karnataka, the upper riparian state, must provide Tamil Nadu a specified monthly water quantity.
- Annual Allocation: In a “normal” year, Karnataka provides 177.25 TMC to Tamil Nadu, with 123.14 TMC during the southwest monsoon.
- Challenges: Monsoon disagreements arise due to varying rainfall during this period.
Constitutional Provisions for Water Sharing
- Article 262: Empowers Parliament to address inter-State river disputes; IRWD Act, 1956 enacted under this article.
- Seventh Schedule: Defines legislative authority over water resources in Entry 17 (State List) and Entry 56 (Union List).
Resolving Cauvery Water Sharing
(A) Supreme Court’s 2018 Verdict:
- Cauvery as National Asset: The Supreme Court declared Cauvery a “national asset,” upholding inter-State river water equality.
- Allocation Adjustments: The Court noted deficiencies in CWDT’s assessment, resulting in marginal relief for Karnataka and reduced allocation for Tamil Nadu.
- Formation of CMB: The Court directed the establishment of the Cauvery Management Board (CMB) for effective implementation.
(B) Cauvery Water Management Scheme:
- CWMA Establishment: Formed to regulate water releases with CWRC’s assistance.
- Permanent and Technical Bodies: CWMA oversees regulation, while CWRC ensures data collection and award implementation.
Current Status and Future Implications:
- Ongoing Challenge: The Cauvery water dispute remains a historical and legal challenge.
- Resource Management: CWMA and CWRC aim to address the dispute through effective water management.
- Continued Struggle: The dispute underscores the complexity of water sharing in a federal system and the need for equitable solutions.
Tamil Nadu’s Contention
- CWMA’s Decision: CWMA sought 10,000 cusecs for 15 days from Karnataka, but Karnataka proposed 8,000 cusecs up to August 22.
- Previous Agreement: Karnataka’s refusal to adhere to the earlier agreement of 15,000 cusecs for 15 days at the CWRC meeting angered Tamil Nadu.
- Distress-sharing Formula: Tamil Nadu supports distress-sharing, but Karnataka hasn’t embraced it.
Karnataka’s Perspective
- Rainfall Deficit: Karnataka claims lower rainfall in Cauvery’s catchment areas, including Kerala, leading to reduced inflow.
- Challenging Situation: Karnataka cites reduced reservoir inflow as the reason for not releasing water this year.
- Lack of Consistency: Despite endorsing distress-sharing, Karnataka declined to accept the formula.
Future Scenario
- Tamil Nadu’s Concerns: Mettur reservoir’s critically low storage affects farmers and upcoming kuruvai crop.
- Water Shortage: Current water availability may last only 10 days, considering dead storage and drinking water needs.
- Awaiting Supreme Court: The case’s outcome depends on the Supreme Court’s interpretation and decision.
- Need for Resolution: The need for a mutually acceptable distress-sharing formula is evident.
Ongoing Challenges and Factors Prolonging the Dispute:
- Erratic Water Levels: Flood-drought cycles, pollution, and groundwater depletion cause unpredictable water levels.
- Idealistic Calculations: SC’s verdict relies on favorable conditions often misaligned with reality.
- Dependency and Population: Both states heavily rely on the river, causing conflicting urban and agricultural water needs.
- Inefficient Water Use: Inefficient irrigation methods lead to low crop productivity per unit of water used.
- Hydropolitics and Delays: Water disputes are used for political mobilization. Prolonged tribunal processes contribute to delays.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/bangalore/cauvery-water-dispute-siddaramaiah-says-tn-causing-unnecessary-nuisance-8934747/
Kampala Declaration (Down to Earth)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A total of 48 African countries have now agreed to adopt the Kampala Ministerial Declarationon Migration, Environment and Climate Change (KDMECC) to address the nexus of human mobility and climate change in the continent.
Facts About:
Background: KDMECC was originally signed and agreed upon by 15 African states in Kampala, Uganda in July 2022.
The Declaration is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
The KDMECC-AFRICA is expected to be signed by Member States during the Africa Climate Summit in Nairobi on September 4, 2023.
Need:
- Africa is one of the world's most vulnerable continents to the impacts of climate change.
- Climate change, which leads to an increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, has a direct impact on migration.
Significance:
- The Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment and Climate Change gives us the unprecedented opportunity to support Member State priorities in addressing the challenges while also leveraging migration for sustainable development.
- It will ensure that all voices, including those of youth, women and persons in vulnerable situations are the priority of the expanded declaration.
Linkage between Climate change and Human Rights:
- Climate change has indisputable long-term consequences on the environment, which, in turn, seriously undermine the enjoyment of human rights.
- The African continent is projected to be one of the hardest hit by the negative effects of climate change.
- The consequences of climate change are not only disproportionately felt by the most vulnerable and poorest populations; there are also disparities along gender lines.
- The connections between climate change, gender equality, and women’s rightsare complicated and multidimensional.
- In contrast, most existing studies on gender and climate change action offer a narrow conception of what gender equality and women’s rights mean in the context of climate change action.
Other similar declarations:
The Maputo Convention on the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources: This Convention shall apply;
- To all areas which are within the limits of national jurisdiction of any Party; and
- To the activities carried out under the jurisdiction or control of any Partywithin the area of its national jurisdiction or beyond the limits of its national jurisdiction.
The Parties shall adopt and implement all measures necessary to achieve the objectives of this Convention, in particular through preventive measures and the application of the precautionary principle, and with due regard to ethical and traditional values as well as scientific knowledge in the interest of present and future generations.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/climate-change/kampala-declaration-on-climate-change-human-mobility-now-has-48-african-countries-as-members-91393
Sequencing the Y Chromosome (The Hindu)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Scientists have fully sequenced the Y chromosome for the first time, uncovering information that could have implications for the study of male infertility and other health problems.
Facts About:
- In the nucleus of a human cell, each DNA molecule is packaged into a long thread like structure called chromosome.
- Most human cells contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. One half of each pair of chromosomes from one parent, while other half comes from other parent.
- The 23rd pair are X and Y chromosomes, often called as sex chromosomes. The other 22 pairs called as autosomes.
- Females have a pair of X chromosomes, whereas males have X and Y chromosome.
- The Y chromosome is male-determining because it bears a gene called SRY, which directs the development of a ridge of cells into a testis in the embryo.
- The embryonic testes make male hormones, and these hormones direct the development of male features in a baby boy.
What is the difficulty in sequencing Y chromosome?
- Repetition - The Y chromosome was a particularly hard nut to crack because it is unusually repetitive.
- While all human chromosomes contain repeats, more than 30 million letters of the Y chromosome — out of 62.5 million — are repetitive sequences, sometimes called satellite DNA or junk DNA.
- Repetitive DNA complicates the assembling of data from genetic sequencing.
- Palindromes - The Y chromosome also contains palindromes — sequences of letters that are the same backward and forward, like radar.
- Degeneration of Proto- Y - The proto-Y is degenerating at a faster pace, losing about 10 active genes per million years, reducing the number from its original 1,000 to just 27.
- There has been great debate about whether this degradation continues, because at this rate the whole human Y would disappear in a few million years
How the scientists unravelled the complex Y chromosome?
- Sequencing - Advanced "long-read" sequencing technology and computational methods enabled researchers to achieve a complete reading of the Y chromosome.
- This accomplishment added over 30 million repetitive base pairs to the human reference genome.
- The new technology has allowed sequencing of bases along individual long DNA molecules, producing long-reads of thousands of bases.
- It effectively dealt with repetitive sequences and transformed raw sequencing data into a usable resource.
- These longer reads are easier to distinguish and can therefore be assembled more easily.
- Findings- Overall, the combined research determined that the Y chromosome has 106 protein-coding genes.
- 42 were found that were new, but many still appear to be repeats.
What is the importance of the study?
- Advanced diagnostics- The study empowers future sequencing endeavours to explore into health and disease aspects through comprehensive Y chromosome inclusion.
- To study whether loss of the Y chromosome is a biomarker of biological aging or has a direct effect on the health of men.
- Infertility- It will help to study conditions and disorders linked to the chromosome, such as lack of sperm production that leads to infertility.
- Health- Genes have been identified on the Y chromosomes that have been shown to be required for the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease.
- Dark matter- It represents the ‘dark matter’ of the genome. This analysis will allow us to better understand the regions of the Y chromosome that have regulatory functions and may encode mRNA and proteins.
- Human evolution- Assembling complete sequences of Y chromosomes across space and time not only helps to investigate sex chromosome evolution but also human evolution.
- Gene therapy- It will open up avenues to treat diseases that may linked to Y chromosomes.
- Future studies- The findings provide a solid base to explore how genes for sex and sperm work, how the Y chromosome evolved, and whether as predicted will disappear in a few million years.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/y-male-chromosome-gene-sequencing-sry-gene-sequencing-evolution/article67230274.ece
Food Inflation & Challenges of Malnutrition (Down to Earth)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent data, the cost of meals rose by 65% in five years, wages by just 37% in the last five years.
Facts About:
- In Mumbai, the cost of a vegetarian thali surged 65% in five years, while income for laborers and salaried workers in urban Maharashtra increased only 37% and 28%, respectively. This discrepancy is making essential food items unaffordable, leading to compromised meals.
What is Thalinomics?
- Thalinomics is a term coined by an Indian economist and former Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India, Arvind Subramanian.
- It refers to a concept that involves analyzing changes in the cost of a vegetarian thali (a meal consisting of a variety of dishes served on a single plate) to gain insights into the trends and dynamics of food inflation and affordability.
- It involves tracking the prices of key ingredients that constitute a thali, such as cereals, pulses, vegetables, and other essential items.
- This concept is particularly relevant in countries like India, where food affordability and inflation are significant concerns for a large population.
Key insights: A case study of Mumbai and urban Maharashtra
- Rising Cost of Thali: The cost of preparing a home-cooked vegetarian thali in Mumbai has increased significantly by 65% over the past five years. This increase is attributed to rising prices of essential ingredients like rice, dal, vegetables, and other items that constitute a thali.
- Income Growth: Over the same five-year period, the average wage earned by casual laborers in urban Maharashtra increased by 37%, while the average salary of regular salaried workers increased by 28%. These income growth rates reflect the changes in earnings for these two categories of workers.
- Disparity Between Costs and Income: While the cost of a thali increased by 65%, income growth for casual laborers and salaried workers was significantly lower, at 37% and 28%, respectively.
- Affordability Challenge: The disparity between rising costs and income growth has resulted in essential food items becoming increasingly unaffordable for households. This affordability challenge can lead to reduced portion sizes or a compromise in the variety and nutritional quality of meals.
- Impact on Budget Share: The study also analyzes the portion of monthly wages or salaries required to afford two thalis every day for a month. This share increased from 22.5% of a casual laborer’s monthly earnings in 2018 to 27.2% in 2023. For salaried employees, it increased from 9.9% to 12.8% over the same period.
- Incomplete Data: Data limitations, particularly regarding the absence of certain ingredients like spices and ghee in the analysis, This suggests that the actual cost of making a thali could be even higher than the calculated figures.
Key aspects of the relationship between thali prices and inflation
- Inflation and Ingredient Prices: The prices of ingredients like rice, dal, vegetables, and oil can be affected by inflation. If the prices of these essential ingredients rise due to inflationary pressures, the overall cost of preparing a thali would increase.
- Food Inflation: The cost of a thali, which is composed of various food items, is directly influenced by food inflation. If there’s high food inflation, it can significantly impact the affordability of thalis and other meals.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: Inflation can be driven by supply and demand imbalances. If there’s a shortage of certain ingredients due to supply disruptions (e.g., poor harvests or transportation issues), prices can rise. Similarly, changes in consumer demand patterns can affect the prices of specific ingredients, further impacting thali costs.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks often use monetary policy tools to control inflation. Interest rate adjustments, money supply regulation, and other measures can impact inflation rates. High inflation rates can lead to increased production costs for farmers and manufacturers, which may trickle down to the prices of thali ingredients.
- Income Effects: Inflation can impact consumers’ purchasing power. When inflation outpaces income growth, households might need to allocate a larger portion of their income to cover basic expenses like food. This can particularly affect lower-income households, leading to affordability challenges for items like thalis.
- Regional Variation: Inflation rates can vary regionally and even locally. Different regions might experience different rates of inflation due to factors like supply chain disruptions, local economic conditions, and government policies.
- Government Policies: Government policies such as subsidies, import/export regulations, and agricultural policies can influence ingredient prices and, consequently, the cost of preparing a thali. These policies can impact the supply and availability of key ingredients.
Implications of the higher cost of a thali
- Nutritional Impact: The rising cost of thali ingredients can lead to compromised nutritional intake as households might cut back on certain items to manage expenses. This can result in inadequate diets and potential health implications.
- Affordability Strain: As thali prices escalate, households may face financial strain by allocating a larger portion of their income to food expenses. This can limit their ability to save, invest, and engage in non-essential expenditures.
- Dietary Diversity: Increased thali costs can potentially lead to reduced dietary diversity as households might opt for cheaper, less nutritious alternatives, affecting overall dietary quality.
- Balanced Meals: Higher thali costs might lead to smaller portions or fewer items in the thali, disrupting the balance of a typical meal and potentially impacting satiety and nutritional completeness.
- Quality of Life: Reduced dietary quality due to affordability challenges can have broader implications for individuals’ quality of life, health, and overall well-being.
- Economic Struggles: For households with limited disposable income, the burden of increased thali costs can exacerbate economic struggles and hinder progress.
Way forward
- Policy Interventions: Implement policies to address the widening gap between thali costs and income growth, ensuring that essential food remains affordable.
- Income Enhancement: Focus on raising wages for casual laborers and salaried workers to match the rising cost of thalis.
- Affordability Measures: Establish measures to mitigate the impact of expensive thalis on households, considering subsidies or targeted assistance.
- Nutrition Awareness: Launch campaigns to educate households about maintaining nutritious diets even when faced with affordability challenges.
- Gender-Inclusive Approach: Address gender disparities by formulating policies that empower women economically.
- Data-Driven Approach: Base policies on accurate and up-to-date data on food prices, wages, and consumption patterns.
- Food Security Initiatives: Strengthen food security programs to ensure access to nutritious food despite thali cost increases.
- Policy Evaluation: Continuously assess the effectiveness of policies in addressing thali affordability and overall well-being.
Conclusion
- The shifting dynamics between escalating costs and relatively stagnant income pose a serious challenge to maintaining a nutritionally balanced diet. As prices continue to rise, a more comprehensive approach is crucial to ensuring that affordable nutrition remains within reach for all strata of society.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/price-of-food-inflation-42483
Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23 (PIB)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent departed to participate in Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23, scheduled to be held at Cairo (West) Air Base, Egypt, from 27 August to 16 September 2023.
Facts About:
- It is a biennial multilateral tri-service exercise.
- This multinational exercise was launched in 1980 as part of the US-brokered peace treaty between Egypt and Israel.
- This is the first time that IAF is participating in Ex BRIGHT STAR-23.
- Participating countries: United States of America, Saudi Arabia, Greece and Qatar.
- The Indian Air Force contingent will consist of five MiG-29, two IL-78, two C-130 and two C-17 aircraft.
- Personnel from the IAF's Garud Special Forces, as well as those from the Numbers 28, 77, 78 and 81 Squadrons, will be participating in the exercise.
- Objective: To practice planning and execution of joint operations. Besides leading to the formation of bonding across borders, such interactions also provide a means to further strategic relations between participating nations.
- India and Egypt have had an exceptional relationship and deep cooperation wherein the two jointly undertook the development of aero-engine and aircraft in the 1960s, and training of Egyptian pilots was done by Indian counterparts.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1955399
LK-99 (The Hindu)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Independent scientists have found that LK-99 is not a superconductor.
Facts About:
- LK-99 has been claimed by South Korean scientists as a superconductor at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. However, currently scientists have discarded their claims.
What are the reasons behind discarding LK-99 as a superconductor?
- First, when superconductors get cold, they push away magnets, causing repulsion below their transition temperature. The South Korean video showed LK-99 partly repelling a magnet. However, independent researchers found that the material was an insulator whose impurities could be magnetized.
- Second, the South Korean scientists saw less resistance in LK-99 around 104°C, which could mean it’s a superconductor. However, researchers found that this drop occurred due to the copper sulphide impurities present in the material.
- Hence, as per the scientists, no formal confirmation aligns with the initial declarationthat this material can conduct electricity without resistance in regular conditions.
What lies ahead?
- The LK-99 case raises concerns over misunderstandings caused in the open science competition. However, this misunderstanding shouldn’t stop open collaboration.
- Moreover, now, the burden lies on South Korean group to show evidence for their claim
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/lk-99-room-temperature-superconductor-hype/article67233834.ece
Moody’s Report on Demographic Dividend (Economic Times)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Alongwith the population growth, strong education and quality infrastructure are key to reap economic gains in India: Moody
Facts About:
Relation between population growth and economic growth:
Population Growth as a Driver of Economic Growth (Early Stages)
- A larger population means a larger labor force, which can lead to increased production, consumption, and innovation. This phenomenon is often referred to as the demographic dividend. When the ratio of working-age individuals to dependents (children and elderly) is high, it can create a favorable environment for economic expansion.
Labor Force and Human Capital:
- A growing population can provide a larger labor force, which, if properly educated and skilled, can contribute to higher productivity and economic growth. However, for population growth to positively impact economic growth, there must be adequate investments in education, healthcare, and skill development to ensure that the workforce is productive and capable of contributing to economic activities.
Consumption and Demand:
- A larger population can lead to increased consumption and demand for goods and services, which can stimulate economic growth. Businesses may expand to meet this increased demand, leading to higher levels of investment and production.
Urbanization and Productivity:
- Population growth often leads to urbanization, as people move from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities. Urbanization can lead to increased productivity due to factors like economies of scale, improved infrastructure, and better access to markets and resources.
Resource Constraints and Negative Impacts:
- Rapid population growth without corresponding economic development and resource management can lead to resource constraints, environmental degradation, and increased competition for limited resources. This can have negative effects on economic growth in the long run.
Demographic Transition:
- As economies develop and standards of living improve, birth rates tend to decline. This results in a shift from high population growth rates to lower ones. During this demographic transition, countries can experience a period of accelerated economic growth due to a relatively smaller dependent population.
Aging Population:
- In more advanced economies, declining birth rates and increased life expectancy can lead to an aging population. While this may result in a decline in the working-age population, it can also create opportunities for innovation and growth in industries related to healthcare, elderly care, and technology.
Quality of Institutions and Policies:
- The relationship between population growth and economic growth is influenced by the quality of institutions and policies in place. Good governance, effective healthcare systems, education policies, and infrastructure development play a crucial role in determining how population growth impacts economic growth.
In summary, the relationship between population growth and economic growth is not deterministic, and its effects can vary widely based on numerous factors. While a growing population can potentially provide a demographic dividend and contribute to economic growth, this positive outcome depends on factors such as investments in human capital, infrastructure, and sound governance.
Additionally, as countries progress in their development, the relationship often becomes more nuanced, with demographic transitions and changingpopulation structures influencing economic dynamics.
Factors responsible for India’s population growth
- Falling mortality: The IMR has decreased from 40.7 in 2015-16 to 35.3 in 2019-21.
- Increasing Life expectancy at birth: It reached to 69.7 years in the 2015-19 period from 31 in 1947.
- Unintended pregnancies: 1 in every 7 unintended pregnancies of world occur in India.
- Lack of female education, child marriage and early marriages, etc.
Challenges caused by growing population
- Pressure on resources: As India has only 2.45% of the global surface area and 4% of the water resources.
- Pandemic outbreaks: Due to increasing urbanization and expansion of humans in wild habitats.
- Disruption and Conflicts: Due to rise in struggle for finite resource.
- Decline in social indicators: Due to suboptimal public expenditures on health and education may not be possible.
- Pressure on economy: Due to low skilled workforce, stagnant economy, unemployment, etc.
- Widening gender gap: If expenditure on health and education decline, women would suffer the most.
Way ahead to harness the benefits of population growth
- Supporting Reproductive Justice: Provisions of safe and effective methods of family planning and freedom to make the best reproductive choice.
- Education for all: Educational attainment, particularly of girls, enhances intergenerational formation of human capital and has a positive impact on demographic behaviour with respect to nuptiality, fertility, health, etc.
- Foster Inclusive Growth developing democratic institutions to facilitate equity in the society.
- Facilitate migration to bridge the demand and supply of the workforce.
- Investment in green technology and social innovations to adapt to and mitigate climate and environmental changes.
- Better geriatric care, health insurance and pension facilities for 65+ age category.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/india-must-focus-on-education-and-infra-for-growth-moodys-report/articleshow/103147127.cms?from=mdr
Care Protocol for Babies in India (The Hindu)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
British nurse was sentenced to life in prison after being found guilty in the worst child serial killer case in the history of the U.K.
Facts About:
What are patient safety provisions in India?
National Patient safety Implementation Framework - It was launched for the period 2018-25 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Patient safety - It is the fundamental element of public healthcare, defined as the freedom for a patient from unnecessary harm.
Hippocratic Oath - It is an oath of ethics historically taken by physician which is one of the most widely known of Greek medical texts.
Consumer Protection Act,1986 - It deals with medical negligence and deficiency of services
Clinical Establishment Act, 2010 - It sets out the legal rights of the patients.
Institutional Mechanism - To see the patients’ rights in terms of medication and devices are protected and that they are not overcharged.
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority
- Drugs Controller General of India
Charter of patients’ rights - It is adopted by the National Human Rights Commission.
It act as a guidance document for the Union Government and State Governments to formulate concrete mechanisms for Patients’ Rights.
Charter of Patients’ Rights and Responsibilities - It is approved by National Council for Clinical Establishments.
Responsibilities of Patients’ -
- Provide all health related information.
- Cooperate with Doctors during examination and treatment.
- Pay hospitals agreed fees on time.
- Respect dignity of doctors and other hospital staff.
- Never resort to violence
How is neonatal safety maintained?
- Rules - There are no exclusive rules for neonatal care and safety, or protection against external harm in Indian hospitals.
- However, there are provisions and checks against issues like inadvertent mix-up of babies at birth and abduction.
- Training - The healthcare staff is also trained to counsel parents and provide emotional support, contributing to the safety and development of neonates.
- Adequate manpower - Trained healthcare is fostered by adequate staffing which can closely monitor each baby’s condition and respond swiftly to any concerns.
- Equipment - Neonates are typically kept in controlled environments to avoid exposure to external infections and temperature fluctuations.
What lies ahead?
- Regular training and continuing medical education for healthcare staff are essential to maintain high-quality neonatal care and uphold safety standards.
- The global organisation has also advised families that prompt medical care should be sought in case of danger signs.
- These include feeding problems, reduced activity, difficult breathing, fever, fits or convulsions, jaundice in the first 24 hours after birth.
- Families are also required to register the birth and bring the baby for timely vaccination, according to national schedules.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/explained-what-is-the-care-protocol-for-babies-in-india/article67239285.ece
Seethakali folk art (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 20-member group is going to perform Seethakali folk art, outside Kerala for the first time as to revive one of the fading dance forms of Kerala.
Facts About:
- In the early times, Seethakali was performed as part of the harvest festival Onam.
- From Atham star till the 28th day after Onam, the performers who belong to the subaltern communities go from one house to another performing this art.
Key Features of Seethakali:
- Folk Dance Drama: Seethakali is a traditional folk dance drama that was once performed during the festival days in erstwhile Desinganad (Kollam, Kerala), primarily during the Onam festivities.
- Dalit Artists: The performance was carried out by Dalit artists belonging to the Veda and Pulaya communities, focusing on presenting episodes from the Ramayana from Sita’s perspective.
- Vanayatra to Andardhanam: Seethakali portrays the journey from “vanayatra” (exile to the forest) to “andardhanam” (descend into the earth) of Sita, featuring a blend of songs, storytelling, and fast movements.
- Instruments: The dance drama is accompanied by instruments such as ganjira, manikatta, chiratta, and kaimani.
- Narrative through Songs: Seethakali’s story is conveyed through songs, with 28 collected over three years, featuring a folk style influenced by Vallappaattu, Kuthirappaattu, and Rakshasappattu.
- Oral Tradition: Seethakali songs were orally transmitted from one generation to the next, which led to a pause in the tradition.
- Basic Movements: The dance involves basic steps, striving to preserve the original essence of the art form.
- Character Ensemble: The performance includes key characters such as Sita, Ram, Lakshman, Ravan, and Hanuman.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/artistes-breathe-a-new-life-into-seethakali-folk-art/article67234768.ece
Terai-Arc Landscape (TAL) (Times of India)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the poop of tigers has helped a team of scientists at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) understand the prey selection patterns of the striped feline in the Indian part of the Terai-Arc Landscape.
Facts About:
- It is an 810km stretch between the river Yamuna in the west and the river Bhagmati in the east.
- It comprises the Shivalik hills, the adjoining bhabhar areas and the Terai flood plains.
- It is spread across the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and the low-lying hills of Nepal.
- About 22% of the wild tiger population in India is found across the TAL, living amidst some of the highest human and livestock densities on the subcontinent.
- The landscape boasts of some of India’s most well-known Tiger Reserves and Protected Areas, such as Corbett Tiger Reserve, Rajaji National Park, Dudhwa Tiger Reserve, Valmiki Tiger Reserve and Nepal’s Bardia Wildlife Sanctuary, Chitwan National Park, Sukhla Phanta Wildlife Sanctuary.
- These forests are home to three flagship species: the Bengal tiger(Panthera tigris), the greater one-hornedrhino (Rhinoceros unicornis) and the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus).
Key Facts about the Wildlife Institute of India
- It is an autonomous Institution of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India.
- It was established in 1982.
- It offers training programs, academic courses and advisory in wildlife research and management.
- The Institute is actively engaged in research across the breadth of the country on biodiversity-related issues.
Source: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/dehradun/10-tiger-corridors-across-india-need-attention-experts/articleshow/95518729.cms
The State of India’s Birds Report (The Hindu)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The State of India’s Birds Report has been released recently.
Facts About:
- The State of India’s Birds (SoIB) report based on data collected from approximately 30,000 birdwatchers has unveiled concerning trends regarding India’s bird population.
- The study highlights a substantial decline in numerous bird species, attributing this decline to a range of factors.
About SoIB Report
- The SoIB report aims to evaluate the conservation status of a wide range of species regularly present in India.
- It is published by a partnership involving 13 governmental and non-governmental organizations, including SACON, WII, and ZSI.
- The report extensively employs data from over 30 million observations on eBird by more than 30,000 birdwatchers.
- The report assesses distribution range size, abundance trends over the long term and since 2015, and information from the IUCN Red List to categorize Indian species into Low, Moderate, and High Conservation Priority tiers.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Widespread Decline: Among the species analyzed, 60% of those assessed for long-term trends show decline, while 40% exhibit a decline in current annual trends.
- Raptors and Vultures: Birds consuming vertebrates and carrion, including raptors and vultures, have significantly declined, possibly due to pollutants or prey availability reduction.
- Endemics and Biodiversity Hotspots: Endemic species in the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspot have experienced rapid declines over the past decades.
- Positive Outlook: Certain generalist species, exemplified by the Indian peafowl, demonstrate remarkable increases in abundance, with a 150% rise observed over the past decades.
- Conservation Priority: The report classifies species into High, Moderate, and Low Conservation Priority, with 178 species as High Priority, 323 as Moderate, and 441 as Low Priority. Noteworthy species include the Ruddy shelduck, Indian courser, Narcondam hornbill, and Nicobar megapode.
Identified Threats to Bird Species
- The report underscores threats encompassing forest degradation, urbanization, energy infrastructure.
- Birds are highly impacted by environmental pollutants like Nimesulide affecting vulture populations, climate change’s impacts on migratory species, avian diseases, and illegal hunting and trade.
Actions and Research Implications
- Targeted Conservation: The report advocates for the conservation of specific groups, such as grassland specialists that have suffered a more than 50% decline, highlighting the importance of protecting and preserving grassland ecosystems.
- Long-Term Monitoring: The significance of continuous, systematic bird population monitoring is emphasized to comprehend subtle fluctuations in bird numbers.
- In-Depth Research: Further research is needed to understand the causes behind both declines and increases in bird populations.
- Synergy among Policies: The report calls for the harmonization of policies related to river, water, and wasteland development, recognizing the multifaceted role of abundant, widespread bird species.
- Citizen Participation: Citizen Engagement plays a pivotal role in biodiversity conservation, warranting an essential role in the action plan for bird population and habitat preservation.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/state-of-indias-birds-report-lists-20-species-of-highest-conservation-priority-for-kerala/article67241741.ece
RIGHT TO REPAIR (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In recent years, several states in the U.S. have enacted ‘right to repair’ laws.
Facts About:
- It refers to government measures that forbid manufacturers to impose barriers that deny consumers the ability to repair consumer products.
- The sectors identified for the right to repair include farming equipment, mobile phones/tablets, consumer durables, and automobiles/automobile equipment.
- Government has launched a unified portal, https://righttorepairindia.gov.in, to onboard leading brands and reliable third-party technicians to provide easy access to overhauling services.
- The portal has on boarded leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Honda, Kent RO Systems, Havells, Hewlett Packard, and Hero MotoCorp.
- The portal seeks to streamline trade between original equipment manufacturers and third-party sellers.
- The right to repair has been recognized in many countries across the globe, including the USA, UK, and European Union.
Significance of Right to repair for India:
- Lowering costs for consumers: By providing access to third-party technicians, the right to repair can reduce costs for consumers who may not be able to afford expensive repairs or replacement devices.
- Reducing electronic waste: India is one of the largest generators of electronic waste in the world, and the right to repair can help reduce e-waste by extending the lifespan of electronic devices and appliances.
- Supporting small businesses: The right to repair can also support small businesses that provide repair services, by creating a level playing field with manufacturers who may have previously had a monopoly on repairs.
- Empowering consumers: By giving consumers the ability to repair their own devices or choose where to have them repaired, the right to repair empowers consumers to make informed choices and take control of their own devices.
- Promoting transparency and collaboration: The right to repair framework aims to build a consumer-centric ecosystem that promotes transparency and collaboration between manufacturers, sellers, and consumers.
Challenges associated with implementing right to repair in India
- Limited Access to Information: Many manufacturers do not provide adequate information to consumers about repair options or how to repair devices, which can make it difficult for consumers to exercise their right to repair.
- Lack of Awareness: Consumers lack awareness about their rights to repair and the benefits of repairing their devices leading to a lack of demand for repair services, limiting the growth of the repair industry.
- Opposition from manufacturers: Some manufacturers may oppose the right to repair, arguing that it could compromise their intellectual property rights or lead to safety concerns making it difficult to pass legislation or regulations to support the right to repair.
- Limited availability of spare parts: The availability of spare parts is often limited in India, particularly for older or less common models of devices makes it difficult for repair technicians to perform repairs or for consumers to find reliable repair services.
- Lack of regulatory mechanism: Currently, there is no comprehensive regulation in India that governs the right to repair which can lead to confusion among consumers and repair technicians about their rights and responsibilities, and may limit the growth of the repair industry.
Way Forward:
Many countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws. But the movement has faced tremendous resistance from tech giants such as Apple and Microsoft over the years.
The New York legislation is a reminder that it is time to not only acknowledge the right to repair of consumers but also respond to the corresponding rights of the manufacturers. This warrants some expedited policy changes to recognise the ‘right to repair’, be it through amendments in the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 or through a separate law.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-the-right-to-repair-movement-7400287/
Scholarship Schemes for Religious Minorities (PIB)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
There is a shift in Centre’s policy towards minority education in the past few years. It has discontinued two key educational schemes for religious minorities and gradually cut down on the expenditure incurred on the programmes of the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
Facts About:
Minority Educational Schemes: Overview
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Initially covering classes 1 to 10, now limited to classes 9 and 10.
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Supports class 11 and above students, with increased funding this fiscal year.
- Merit-cum-Means based Scholarship Scheme: Aided professional and technical courses, underwent significant funding reduction.
- Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF): Provided financial assistance for research scholars but discontinued in 2022.
- Padho Pardesh: Discontinued interest subsidy scheme for higher education abroad.
- Begum Hazrat Mahal National Scholarship: Scholarship for meritorious girls discontinued.
Policy Shift and Consequences
- Change in Focus: Despite acknowledging the importance of education for religious minorities and inclusive growth, the government has discontinued two key educational schemes, narrowed the scope of another, and reduced expenditure on multiple programs by the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- Beneficiary Drop: Between 2019 and 2022, the number of beneficiaries under six educational schemes for religious minorities decreased by 7%, while government spending on these programs declined by around 12.5%.
- Budget Cuts: The Ministry of Minority Affairs faced a budgetary reduction of 38.3% for the fiscal year 2023-24, from Rs 5,020.5 crore in 2022-23 to Rs 3,097 crore. Additionally, a significant portion of funds allocated in the previous year went unutilized.
Importance of Strengthening Educational Aid
- Diverse Religious Minorities: India encompasses over 30 crore people from religious minority communities, including Muslims (14.2%), Christians (2.3%), Sikhs (1.7%), Buddhists (0.7%), Jains (0.4%), and Zoroastrians.
- Challenges Faced by Muslims: Muslims, the largest religious minority, confront challenges in areas like economics, health, and education. Their participation in formal employment remains low, with many working in the informal sector under poor conditions.
- Sachar Committee Report: The Sachar Committee highlighted the deprivation and neglect faced by Muslims across various development dimensions, underscoring the need for affirmative action.
- Formation of Ministry of Minority Affairs: Responding to these challenges, the UPA government established this Ministry in 2006 to ensure focused attention on the issues affecting minority communities.
Challenges and Impact
- Reduction in beneficiaries and funding has impacted the implementation of schemes, resulting in a widening gap in education and economic parameters.
- Poor coverage of beneficiaries and unchanged low unit costs remain hurdles in scheme implementation.
- Muslim students’ enrolment in higher education is lagging behind other communities, worsening the existing disparities.
Way Forward
- Strengthen educational aid through enhancing scholarships, such as pre-matric, post-matric, merit-cum-means, and national overseas scholarships.
- Implement targeted schemes based on the 15-Point Programme to address development gaps in minority-concentrated localities.
- Make scholarships demand-driven and provide additional financial resources to improve unit costs.
- Increase the total budget allocation for the Ministry of Minority Affairs to address the deprivation in educational attainment for minorities.
Source: https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2022/mar/doc202231626301.pdf
G20 ministers agree to map global value chains, link MSMEs (Indian Express)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations agreed recently to map global value chains, integrate small businesses with them and ease trade documentation.
Facts About:
What are important parts of outcome document from Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations?
- Comprehensive framework within the G20 context for the purpose of mapping out global value chains is suggested.
The objective is to comprehend the existing issues and identify the necessary actions to enhance the inclusivity, sustainability, and resilience of these value chains.
- It focuses on MSMEs. The declaration from Jaipur emphasizes the imperative of reinforcing the capabilities of MSMEs.
Due to their small scale, MSMEs face limitations in accessing critical information, financial resources, and market-related data points.
A worldwide trade assistance platform, overseen by theInternational Trade Centre, will be consistently upgraded through consultation with UNCTAD and the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
This evolution aims to make the platform more inclusive and to offer comprehensive data to MSMEs.
- The principles associated with the digitization of trade documents is important part of outcome document. The aim is to minimize the reliance on paper documents and remove obstacles that hinder the seamless movement of goods and services.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/g20-trade-meet-ends-ministers-priority-areas-value-chains-msmes-8909647/
China-Bhutan boundary dispute and its impacts on India (The Hindu)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on the China-Bhutan boundary issues was held recently.
Facts About:
- A joint press release from Beijing and Thimphu said the 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) was held in Beijing
- It described as an “important outcome” the setting up of a Joint Technical Team on the Delimitation of the China-Bhutan Boundary, which held its first meeting along the sidelines of the EGM.
- The two sides had talks on
- continuously implementing the MOU on the Three-Step Road Map for Expediting the China-Bhutan Boundary Negotiations
- agreed to expedite and take simultaneous steps to implement the Three-Step Road Map
- agreed upon keeping the positive momentum of frequent Expert Group Meetings
- holding the 14th Expert Group Meeting on the China-Bhutan Boundary Issues as soon as possible
- maintaining communication on holding the 25th Round of China-Bhutan Boundary Talk
- It did not, however, announce a date for the already much delayed 25th round of boundary talks, which have not been held since 2016.
- In recent months, both sides have portrayed the long-running talks as picking up speed and nearing a possible solution, which would have ramifications for India.
- While there was a two-year gap between the 10th round of the EGM held in April 2021 and the 11th round of the EGM held in January 2023, the last two rounds have been held in relatively quick succession.
Impact on India
- Experts in India have said any deal between Beijing and Thimphu that accedes to a “swap arrangement” between areas to the North (Jamparlung and Pasamlung valleys) with Doklam to the West would be of concern to India, given the proximity to India’s narrow “Siliguri corridor” that connects northeastern States with the rest of India.
- India and China were involved in a stand-off in Doklam near the India-China-Bhutan trijunction in 2017.
- In March, the Bhutanese Prime Minister said in an interview that the process of “demarcating territories” and “drawing a line” could be completed “after one or two more meetings”.
Conclusion
The boundary talks between Bhutan and China began in 1984, and the 24th round was held in 2016.
The talks have largely focused on disputed areas to Bhutan’s north, and to its west, abutting the Doklam plateau.
However, these have been stalled since 2016, especially after the 2017 Doklam stand-off.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/interview/post-covid-necessary-for-neighbours-to-work-together-bhutan-fm-on-china-bhutan-boundary-talks/article65646740.ece
7th Global Environment Facility (GEF) Assembly (Down to Earth)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
As per the chief executive of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) in a plenary session, it will likely to work more closely with civil society organisations in the future.
Facts About:
About: Environmental leaders from 185 countries will gather in Vancouver, Canada for the Seventh Assembly of the Global Environment Facility from August 22-26, 2023.
Global Environment Facility (GEF): The GEF Assembly, which meets every 4 years, is the global body that coordinates financing for international efforts to address climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, and factors inhibiting land and ocean health.
Points of discussion:
- Building on recent diplomatic breakthroughs on biodiversity loss, toxic chemicals, and the high seas, the GEF Assembly will be a critical stocktaking for 2030 goals to end pollution and nature loss, combat climate change, and propel inclusive, locally-led conservation.
- GEF would work directly with non-governmental organisations that work at the convention level.
- It is set to include the launch of the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund, a new source of funding for protecting species and ecosystems globally.
- The fund will open new avenues for private sector and philanthropic support to enable rapid implementation of the historic Global Biodiversity Framework agreed at COP15 in Montreal, December 2022, and of the high seas treaty adopted in New York City, in June 2023.
Need of such an initiative:
- Biodiversity funding needs differ between recipient countries, for example between countries with key areas for biodiversity (often large emerging countries such as Brazil and Indonesia) and the least developed countries (LDCs) or Small Island Developing States (SIDS), for which it is more difficult to access funds.
Global Biodiversity Framework:
- It contains goals to be achieved by 2050 focus on ecosystem and specieshealth including;
- To halt human-induced species extinction,
- The sustainable use of biodiversity,
- Equitable sharing of benefits, and
- On implementation and finance to include closing the biodiversity finance gap of $700 billion per year.
Source: https://update-mac.com/?tid=103&tag_id=1528a5df-4f9e-4046-9232-3361bc5f2c12&cnv_id=e891de8lpg6sc0b4c&placement=20427977&sub1=726006&clickcost=0
India-Iran drop Foreign Arbitration clause in Chabahar Port Issue (The Hindu)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India and Iran have agreed to pursue arbitration under rules framed by the UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) and will not go for commercial arbitration in foreign courts.
Facts About:
UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL):
It is a subsidiary body of the UN General Assembly, established in 1966.
Mandate: To further the progressive harmonisation and unification of the law of international trade.
Membership:
- The Commission is composed of 60 member States elected by the General Assembly.
- The 60 member States include 14 African States, 14 Asian States, 8 Eastern European States, 10 Latin American and Caribbean States and 14 Western European and other States.
- The General Assembly elects members for terms of six years; every three years, the terms of half of the members expire.
- India is a founding member of this organisation.
Key facts about Chabahar Port
- It is a seaport in the Sistan-Balochistan province of Iran, on the Gulf of Oman, at the mouth of the Strait of Hormuz.
- It is a deep-water port with direct access to the Indian Ocean that is outside the Hormuz Strait.
- Its geographic proximity to countries such as Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India, as well as its status as a key transit centre on the burgeoning International North-South Transport Corridor.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-and-iran-drop-foreign-court-arbitration-for-chabahar-port/article67234071.ece
Insurance Surety Bonds (PIB)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)is advocating for the adoption of surety bond insurance products for highway projects
Facts About:
These bonds can be defined in their simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act.
These are instruments where insurance companies act as ‘Surety’ and provide the financial guarantee that the contractor will fulfil its obligation as per the agreed terms.
Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement.
The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal: The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety: The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee: The party who requires and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organisation.
What are the advantages?
- It will act as a security arrangement for infrastructure projects and will insulate the contractor as well as the principal.
- The product will cater to the requirements of a diversified group of contractors, many of whom are operating in today’s increasingly volatile environment.
- The product gives the principal a contract of guarantee that contractual terms and other business deals will be concluded in accordance with the mutually agreed terms.
- In case the contractor doesn’t fulfil the contractual terms, the Principal can raise a claim on the surety bond and recover the losses they have incurred.
- Unlike a bank guarantee, the Surety Bond Insurance does not require large collateral from the contractor, thus freeing up significant funds for the contractor, which they can utilise for the growth of the business.
- The product will also help in reducing the contractors’ debts to a large extent, thus addressing their financial worries.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1951715
National Medical Commission (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has put on hold the regulations that make it mandatory for doctors to prescribe generic drugs.
Facts About:
- In light of the criticism received by the Indian Medical Association (IMA) as well as the as the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA), the National Medical Commission put on hold the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023.
- Even the country’s apex drug regulator, the Central Drugs Standard Drug Control Organisation (CDSCO), questioned the language in the notification.
- The participating bodies suggested that the guidelines be kept in abeyance until the WHO’s good manufacturing practices are implemented.
- The participants said that prescribing only generic drugs will prompt pharmacies to sell generic drugs at high-profit margins, disincentivising firms that manufacture quality branded generics
National Medical Commission:
- The National Medical Commission is a statutory body established under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC replaced the erstwhile Medical Council of India (MCI) which was established in 1934.
Objectives of NMC –
- Improve access to quality and affordable medical education;
- Ensure availability of adequate and high-quality medical professionals in all parts of the country;
- Promote equitable and universal healthcare that encourages community health perspective and makes services of medical professionals accessible to all the citizens;
- Encourages medical professionals to adopt latest medical research in their work and to contribute to research;
- Objectively assess medical institutions periodically in a transparent manner;
- Maintain a medical register for India;
- Enforce high ethical standards in all aspects of medical services;
- Have an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
Composition of NMC –
- NMC is a 25-member body, majority of them being nominated by the Central government.
- Tenure of NMC members is four years (except for part-time members whose tenure is two years).
- The NMC has 11 part-time members representing states or state medical councils.
- The NMC chairpersons and other members, nominated by the Central government, cannot be renominated.
- Any decision requires approval of the majority (minimum 13 out of 25) of the Commission.
Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023:
- On August 2nd, the National Medical Commission had published the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023 aimed at reshaping prescription practices.
- It mandated that registered medical practitioners prescribe medications using “generic”, “non-proprietary”, or “pharmacological” names.
- The guidelines define a generic drug as a “drug product that is comparable to brand/reference listed product in dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality and performance characteristics, and intended use.”
- It says branded generic drug is one which has come off patent and is manufactured by drug companies and sold under different companies’ brand names.
- The guidelines say, “Every RMP (Registered Medical Practitioner) should prescribe drugs using generic names written legibly and prescribe drugs rationally, avoiding unnecessary medications and irrational fixed-dose combination tablets.”
- The guidelines have also talked about punitive measures against those violating the directive.
- Besides the instructions on generic drugs, the NMC guidelines included directives on issues ranging from continued medical education, usage of social media platforms and maintaining a dynamic register of doctors.
- It also barred doctors from attending events sponsored by pharmaceutical companies.
- However, the NMC guidelines have not gone down well with the Indian Medical Association (IMA).
Issued Raised by the Indian Medical Association (IMA):
- The IMA issued a statement in response to the regulations introduced by the NMC.
- The IMA says the biggest impediment to generic drugs is the uncertainty about its quality.
- IMA said that the quality control in the nation being very weak, there’s practically no guarantee of the quality of drugs and prescribing drugs without assured quality would be detrimental to patient health.
- The statement added that less than 0.1% of the drugs manufactured in India are tested for quality.
- The IMA said that step should be deferred till the Government can assure the quality of all the drugs released into the market.
- The statement says patient care and safety are not negotiable.
- The IMA says it has been demanding for long that only good quality drugs should be made available in the country and prices should be uniform and affordable.
- It urges the Government to have ‘one drug, one quality, one price’ system whereby all brands should either be sold at the same price or banned and only generics allowed while ensuring highest quality of these drugs.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/nmc-hold-regulations-mandating-doctors-prescribe-generic-drugs-bar-them-endorsing-drug-brand-8907964/
Gene-Edited Mustard (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian scientists have developed the first ever low-pungent mustard that is pest and disease-resistant. It is based on CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing.
Facts About:
- Among India’s domestically grown oilseeds, rapeseed-mustard stands out.
- However, its pungent oil and unpalatable meal have posed challenges for both consumers and livestock.
- Scientists have undertaken breeding efforts to create Canola-quality (white) mustard with reduced pungency and improved meal quality.
About Rapeseed-Mustard
- Rapeseed-Mustard: India’s significant oilseed is rapeseed-mustard, contributing significantly to vegetable oil production and meal availability.
- Pungency: Mustard seeds contain glucosinolates, compounds that give the oil and meal their pungent flavor and odor.
Quest for Canola-Quality Mustard
- Canola-Quality Pursuit: Scientists aimed to breed mustard lines with low glucosinolate content similar to Canola.
- Reducing Pungency: Efforts to create low-pungency oil and meal have faced challenges due to the necessity of glucosinolates in plant defense.
- Vulnerability to Pests and Diseases: Canola-quality mustard lines have not been cultivated extensively due to their susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Role of Gene Editing
- Innovative Research: Gene editing emerges as a solution to balance glucosinolate levels for improved quality and plant defence.
- CRISPR/Cas9 Approach: Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing tool to target and modify 10 out of 12 GTR genes in Indian mustard.
- Achieving Desired Changes: Editing GTR genes led to lower glucosinolate content in seeds while preserving higher levels in leaves and pod walls.
Benefits of GE Mustard
- Easy Synthesis: Glucosinolates are synthesized in mustard leaves and pod walls before translocation to seeds.
- Dual Benefit of Glucosinolates: The study revealed that edited mustard lines with low-seed glucosinolates exhibited improved defence against pests and diseases.
Distinction between GE and GM
- GE Mustard: The new mustard lines are genome-edited (GE), not genetically modified (GM).
- Transgene-Free Solution: Unlike GM crops with foreign genes, GE lines have no foreign DNA and no residual gene-editing tools.
Regulatory Considerations and Future Prospects
- Regulation Changes: India’s regulatory environment is shifting, exempting GE plants free of exogenous introduced DNA from stringent approval requirements.
- Potential Field Trials: Scientists are preparing for open field trials of GE mustard, with expectations to conduct them in the upcoming planting season.
- Importance of Self-Reliance: With massive edible oil imports, domestic oilseed production through breeding advancements like GE mustard becomes vital for self-reliance.
Economic Implications and Self-Sufficiency
- Importance of Oilseeds: India’s substantial edible oil imports highlight the need for boosting domestic oilseed production.
- Mustard’s Role: Mustard’s high oil content and protein-rich meal position it as a significant oilseed crop.
- Potential Benefits: Both GE mustard and GM hybrid mustard have the potential to reduce dependence on imported vegetable oils.
Conclusion
- The journey of rapeseed mustard from its pungent state to a potentially improved, self-sufficient crop demonstrates the power of innovative breeding techniques.
- The breakthrough in gene editing opens doors to balancing quality and plant defence.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/gene-edited-mustard-less-pungent-more-useful-8901549/
India and the Northern Sea Route (NSR) (The Hindu)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Murmansk, the beginning point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is witnessing the rising trend of Indian involvement in cargo traffic.
Facts About:
What is Northern Sea Route?
- It is the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles four seas of the Arctic Ocean.
- Coverage- It runs around 5,600 km, the Route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
- Save distance- Distance savings along the NSR can be as high as 50% compared to the currently used shipping lanes via Suez or Panama.
- The traditional Suez Canal route is 8000 km longer than Northern Sea passage.
- 2021 blockage- The 2021 blockage of the Suez Canal, which forms part of the widely-used maritime route involving Europe and Asia, has led to greater attention on the NSR.
- Navigability- Arctic Ocean remain icebound during most of the year, the icebreaking assistance is organised to ensure safe navigation along the NSR.
What are the advantages of Northern Sea Route?
- Profitable-It is a strategically important transport artery; it is economically profitable when comapared with Suez Canal.
- Save fuel- It will save fuel due to reduced distance.
- Cost effective- The shorter distance reduces the cost of staff labor and chartering vessels.
- The route does not charge payments for the passage unlike Suez Canal.
- Time saving-There are no queues (unlike, for example, the Suez Canal);
- Safety- There is no risk of a pirate attack.
Why Arctic region is so significant for India?
- Impact on India-The vulnerability of the Arctic region leads to unprecedented changes in the climate.
- This may have an impact on India in terms of economic security, water security and sustainabilit
- Svalbard Treaty- India’s engagement with the Arctic can be traced to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920.
- Conduct studies: Indian conducts studies regarding atmospheric, biological, marine, hydrological, glaciological events.
- Arctic Council- Arctic Council addresses the issues faced by governments in the region and the indigenous people of the Arctic.
- India is an observer state in Arctic Council including China.
- Himadri research station- India's first permanent Arctic research station located at Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Norway.
- It is located at the International Arctic Research base, Ny-Alesund.
- Infrastructural base-
- Multi-sensor moored observatory was inaugurated in 2014
- Northernmost atmospheric lab was launched in 2016
- Successful expeditions- India conducted around 13 successful expeditions to Arctic till 2022.
- Arctic Policy of 2022- It mentions that the country’s approach to economic development of the region is guided by UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Potential for minerals- The region constitutes the largest unexplored prospective area for hydrocarbons remaining on the earth.
- There may be significant reserves of coal, zinc, and silver.
- Institutional support- In 2018 India renamed National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research to National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research.
- It shows India’s refocusing priorities in Arctic region.
What are the driving factors for India to participate in the NSR development?
- Growth in cargo traffic- India engagement in NSR is on the constant rise and during 2018-2022, the growth rate was around 73%.
- Last year, the volume of cargo traffic was 34.117 million tonnes.
- India-Russia trade- India increasingly imports crude oil and coal from Russia in recent years.
- The record supplies of energy resources for the Indian economy are possible due to such a reliable and safe transport artery as the NSR.
- Transit route- NSR assumes importance, given India’s geographical position and the major share of its trade associated with sea transportation.
- East meets East- In 2019 India and Russia signed Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) project.
- It is signed as one linking with another organise international container transit through the NSR.
- Reduce travel time-The 10,500 km-long CVMC, passing through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea and Malacca Strait, will bring down transport time to 12 days.
- This is almost a third of what is taken under the existing St. Petersburg-Mumbai route of 16,000 km.
- Chennai Port Trust study- Fuel and fertilisers are some of the cargo that can be imported from Russia to India through CVMC.
What lies ahead?
- NSR development plan- It is approved until 2035 by Russia, this sets the cargo traffic target as 80 million tonnes and 150 million tonnes for 2024 and 2030.
- The plan approval took place amid economic sanctions imposed by the West against Russia following the latter’s war with Ukraine.
- Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor project-Workshop featuring stakeholders from the two countries, is expected to be held in the second half of October.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/explained-india-and-the-northern-sea-route/article67230900.ece
ASTRA air-to-air Missile (PIB)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Light Combat Aircraft(LCA) Tejas successfully test-fired an ASTRA beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile off the coast of Goa.
Facts About:
- The ASTRA BVR missile is designed to engage and destroy highly maneuvering supersonic aerial targets. It has a range of over 100 kilometers.
BVR missiles are capable of engaging beyond the range of 20 nautical miles or 37 kilometres.
- This missile has all weather day and night capability. The system is being developed to meet specific requirements.
- It is jointly designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Research Centre Imarat (RCI) and other laboratories of DRDO.
- ASTRA missile would significantly enhance the combat prowess of Tejas and reduce the dependency on imported weapons.
Tejas is a single-engine multi-role fighter aircraft capable of operating in high-threat air environments. It has been designed to undertake the air defence, maritime reconnaissance and strike roles.
- The ASTRA Mk-I Weapon System integrated with SU-30 Mk-I aircraft is being inducted into the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Fujiwhara Effect (Indian Express)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, powerful winds tormented the Bay Area and other parts of Central and Southern California, uprooting trees and disrupting the power supply due to Fujiwhara effect.
Facts About:
- It was identified by a Japanese meteorologist Sakuhei Fujiwhara.
- It was observed for the first time over the western Pacific Ocean, when typhoons Marie and Kathy merged in 1964.
What is it?
- When two hurricanes (or cyclones, depending on where you live), spinning in the same direction, are brought close together, they begin ‘an intense dance around their common center’ – this interaction between two cyclones is called the Fujiwhara effect.
When it Occur?
- If one hurricane’s intensity overpowers the other, then the smaller one will orbit it and eventually crash into its vortex to be absorbed.
- On the other hand, if two storms of similar strengths pass by each other, they may gravitate towards each other until they reach a common center and merge, or merely spin each other around for a while before shooting off on their own paths.
- In rare instances, the two ‘dancing’ cyclones, if they are intense enough, may merge with one another, leading to the formation of a mega cyclone capable of wreaking havoc along coastlines.
Experts have noted the rising frequency of this unusual effect, attributing it to a rapidly warming world and the subsequent heating of ocean waters.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwia1b_gj6OBAxXpSmwGHVb_DTQQFnoECBUQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Findianexpress.com%2Farticle%2Fexplained%2Fexplained-climate%2Ffujiwhara-effect-cyclones-dance-8905398%2F&usg=AOvVaw0_moE3dRI3IZbhz8XqmBkl&opi=89978449
CHANDRAYAAN 3 MAKES SOFT LANDING (The Hindu)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Launched on 14 July 2023, Chandrayaan-3 etched its place in history when the lander and rover touched down near the lunar south pole region on 23 August 2023 at 18:02 IST.
Facts About:
- Chandrayaan-3, part of the Indian Space Research Organisation's (ISRO) Chandrayaan program, signifies a remarkable feat in lunar exploration.
- Comprising a lander named Vikram and a rover named Pragyan, akin to the Chandrayaan-2 mission, this mission focuses on achieving a controlled landing and rover mobility on the lunar surface.
- With the propulsion module transporting the lander-rover configuration to lunar orbit, a powered descent by the lander was the critical phase of the operation.
- The mission encompasses a Lander and Rover configuration, propelled by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The propulsion module carries the Lander and Rover until the lunar orbit's 100 km mark.
Origins and Progression: Chandrayaan-2's Influence
- Chandrayaan-2's launch in July 2019, which featured an orbiter, lander, and rover, set the stage for Chandrayaan-3.
- While the initial lander's trajectory went awry during a landing attempt in September 2019, ISRO's spirit remained unbroken, leading to the conception of Chandrayaan-3 and other future lunar missions.
Global Collaboration: ESA's Involvement
- The European Space Tracking network (ESTRACK), operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), provided support for the mission.
- A mutual support agreement emerged, where ESA's tracking assistance for ISRO missions, including Gaganyaan (India's human spaceflight program) and the Aditya-L1 solar research mission, was reciprocated by ISRO's support for future ESA missions.
- This collaboration underlines the global nature of space exploration.
Mission Aims
- ISRO laid out three primary objectives for Chandrayaan-3:
- Achieve a safe and soft lunar landing.
- Demonstrate the rover's mobility capabilities.
- Conduct experiments on lunar surface materials to enhance understanding of lunar composition.
Spacecraft Configuration
Propulsion Module
- Carries the lander-rover to a 100 km lunar orbit.
- Features a solar panel and mounting structure for the lander.
Lander (Vikram)
- Executes the soft landing on the Moon.
- It had four landing legs and four landing thrusters capable of producing 800 newtons of thrust each
- Accommodates the rover and scientific instruments.
Rover (Pragyan)
- A six-wheeled, 26 kg vehicle.
- Conducts diverse measurements, contributing to lunar research.
- Investigates lunar surface composition, presence of water ice, lunar impact history, and atmosphere evolution.
Payloads
Lander Payloads
Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)
- Objective: Measure thermal conductivity and temperature of the lunar surface.
- Information gleaned aids in comprehending lunar surface properties near polar regions.
Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA)
- Objective: Measure seismic activity around the landing site, revealing the lunar crust and mantle's structure.
Langmuir Probe (LP)
- Objective: Estimate plasma density variations in the vicinity of the landing site.
- Langmuir probe plays a crucial role in studying ionosphere and atmospheric phenomena.
Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA)
- Objective: Passive experiment for lunar laser ranging studies.
- LRA aids in comprehending the dynamics of the Moon system.
Additional Payload: Collaboration with NASA
- Passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA contributes to lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover Payloads
Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS)
- Objective: Determine elemental composition (e.g., Mg, Al, Si, K, Ca, Ti, Fe) of lunar soil and rocks around the landing site.
- APXS provides insights into the chemical makeup of lunar materials.
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS)
- Objective: Conduct qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis.
- LIBS aids in deciphering chemical and mineralogical composition for a deeper understanding of the lunar surface.
Propulsion Module Payload
Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE)
- Objective: To make future discoveries of smaller planets through reflected light, potentially identifying habitable exoplanets.
- SHAPE payload enhances India's contribution to the study of exoplanets.
Mission Progress
The mission progressed through several stages, including launch, Earth and lunar orbit maneuvers, and descent. Notable milestones include:
- Launch on 14 July 2023.
- Lunar orbit insertion on 5 August 2023.
- Lander separation from the propulsion module on 17 August 2023.
- Successful soft landing on 23 August 2023, making India the fourth nation to land on the Moon.
Technological Innovations
- Advanced Altimeters: Laser and RF-based altimeters for precise altitude measurements.
- Velocimeters: Laser Doppler Velocimeter and Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera for speed monitoring.
- Inertial Measurement: Laser Gyro-based Inertial referencing and Accelerometer package for navigation.
- Navigation, Guidance & Control (NGC): Software elements for powered descent trajectory design.
- Hazard Detection and Avoidance: Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera and Processing Algorithm.
- Landing Leg Mechanism: Enhanced landing leg design for secure touchdown.
Mission Life
- Propulsion Module: Carried lander and rover to lunar orbit, with operation of experimental payload for up to 6 months.
- Lander Module: 1 Lunar Day (14 Earth Days).
- Rover Module: 1 Lunar Day (14 Earth Days).
Key Team Members and Funding:
- ISRO Chairperson: Somanath.
- Mission Director: Mohanakumar.
- Associate Mission Director: Narayanan.
- Project Director: Veeramuthuvel.
- Deputy Project Director: K.
- Vehicle Director: Biju C. Thomas.
- Estimated cost: Around ?615 crore.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/isro-chandrayaan-3-vikram-lander-touch-down-live-updates/article67219323.ece
National Curriculum Framework for school Education 2023 (PIB)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the final National Curriculum Framework (NCF) has been released by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
Facts About:
- Framed by: The NCF was drafted by the National steering committee headed by former Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), K. Kasturirangan.
- Key points:
- For languages:
- From now, Students in Classes 9 and 10 will need to learn three languages, of which at least two will be native to India.
- Classes 11 and 12, students will learn two languages, including one of Indian origin.
- Board Exams: The NCF states that all students will be allowed to take Board exams on at least two occasions during any given school year, with only the best score being retained.
- New Text books: It follows the lead of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, and gives assent for formulating new textbooks from Grades 3 to 12 under the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
- Number of Subjects: For students from Classes 9 to 12 has to study five mandatory subjects, with an option of adding one more subject.
- Now, the number of mandatory subjects for Classes 9 and 10 is seven and six for Classes 11 and 12.
- Optional subjects have been grouped in three parts in the NCF.
- The first optional group includes art education, physical education and vocational education.
- The second group includes Social Science, the Humanities, and interdisciplinary areas.
- The third group includes Science, Mathematics, and computational thinking.
- Shift to semester-based term: The NCF has recommended that in the long term, all Boards should change to semester or term-based systems.
- Now, there is no hard separation between academic and vocational subjects, or between Science, Social Science, Art, and Physical Education.
- For languages:
NCF from NEP 2020:
The NCF brings the aims and commitments of the NEP:
- This includes the full range of human capacities, values and dispositions that are aimed to be developed in school education.
- Pedagogy, practices, and culture must work in tandem to develop these, and move away from an overemphasis on memorization and content accumulation; in fact, content reduction is required to create space for such development.
- The 5+3+3+4 Curricular and Pedagogical structure of school education is reflected in the learning standards, the content, the pedagogy, and the assessment approaches.
- It is integrative and holistic with equal status to all subjects and learning domains from Math to Sports.
- It integrates vocational education in all schools, and there is integration across subjects while developing rigorous subject understanding and capacities.
National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT):
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an autonomous organisation set up in 1961 by the Government of India to assist and advise the Central and State Governments on policies and programmes for qualitative improvement in school education.
- The major objectives of NCERT and its constituent units are to:
- Undertake, promote and coordinate research in areas related to school education
- Prepare and publish model textbooks, supplementary material, newsletters, and journals and develops educational kits, multimedia digital materials, etc.
- organize pre-service and in-service training of teachers
- develop and disseminate innovative educational techniques and practices
- Collaborate and network with state educational departments, universities, NGOs and other educational institutions
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1951485
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The revised guidelines were issued for the Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for the North East Region (PM-DevINE).
Facts About:
- PM-DevINE, was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 to address development gaps in the North Eastern Region (NER).It was approved by the Cabinet for the remaining four years of the 15th Finance Commission from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The new Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme and will be implemented by the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER).
- The PM-DevINE Scheme will have an outlay of Rs.6,600 crore for the four year period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- An Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC) will be established, tasked with various functions under the scheme.
Objectives of PM-DevINE
- Fund infrastructure convergently, in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti;
- Support social development projects based on felt needs of the NER;
- Enable livelihood activities for youth and women;
- Fill the development gaps in various sectors.
Functions of Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC)
- It assesses initial project proposals based on quality, viability, and socio-economic impact, working alongside representatives from relevant Indian Government Ministries/Departments and State Governments.It then recommends project selection from among these proposals.
- The EIMC proposes effective monitoring and evaluation methods, which may involve on-site inspections through third-party agencies.
- The committee also devises mechanisms for the operation and maintenance of PM-DevINEprojects, aiming to ensure their sustainability.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=194206
Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap (Indian Express)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a new report ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’, was published by the anti-debt campaigners Debt Justice and partners.
Facts About:
Key Takeaways from ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’ report:
- Debt-Reliant Economies and Fossil Fuel Dependence:Poor countries burdened with heavy debts are compelled to rely on fossil fuel revenue to repay loans borrowed from wealthier nations, multilateral creditors like the World Bank and IMF, or private lenders.
For Example: Argentina has been supporting fracking projects in the Vaca Muerta oil and gas field in Northern Patagonia to generate revenues to ease the country’s debt crisis. Notably, the IMF has also backed these projects.
- Surging External Debt Payments in Global South:The external debt payments of Global South countries have surged by 150% between 2011 and 2023, reaching the highest levels in 25 years.
- Debt Crisis and Constrained Public Spending:Around 54 countries are facing a debt crisis, resulting in reduced public spending during the pandemic to meet loan repayment obligations.
- Climate Challenges Amplify Borrowing in Global South:Many of these indebted countries lack adequate resources for climate adaptation, mitigation, and addressing loss and damage, forcing them to borrow more money.
- Natural Disasters Escalate Debt-to-GDP Ratio:After events like natural disasters, countries can see their debt as a percentage of GDP rise significantly, such as Dominica’s experience after Hurricane Maria in 2017.
- Unfulfilled Pledges: Despite promises to discontinue investing in fossil fuels in Global South countries, richer nations and lenders continue to finance fossil fuel projects through loans, perpetuating fossil fuel production.
- Resource Backed Loans (RBLs):Resource backed loans (RBLs) are a mechanism through which repayment is tied to natural resources or future income streams derived from those resources.
Recommendations for a Sustainable Path Forward:
- Implementing ambitious debt cancellation for countries in need without economic conditions
- Rejecting repayments from fossil fuel projects.
- Aligning bilateral and multilateral finance with a 1.5-degree warming scenario while avoiding fossil fuel financing.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/rich-countries-force-poor-nations-rely-fossil-fuels-8904371/
20th ASEAN India Economic Ministers’ Meeting (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India participated in the 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting.
Facts About:
- The 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ meeting was held in Semarang, Indonesia.
- The Economic Ministers or their representatives from all the 10 ASEAN countries viz. Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam participated in the meeting.
- The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste also joined the Meeting as an observer.
- The Ministers reviewed the bilateral trade and investment relations between India and ASEAN and underscored their commitment to strengthen and enhance the economic partnership between India and ASEAN to ensure that the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership delivers meaningful benefits for both sides, particularly in the post-pandemic era.
- The Ministers also interacted with the ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC).
- The main agenda of this year’s meeting was the timely review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) which was signed in 2009.
- India and ASEAN registered a bilateral trade of USD 131.5 billion in 2022-23. The trade with ASEAN accounted for 11.3% of India’s global trade in 2022-23.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- AITIGA is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009. The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and not services trade.
ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
Along with the ASEAN-India Investment Agreement, the three agreements collectively form the ASEAN-India Free Trade Area.
- Under the Agreement, ASEAN and India have committed to progressively eliminating duties on 76.4 percent of goods and to liberalize tariffs on over 90 percent of goods.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1950902#:~:text=Shri%20Rajesh%20Agrawal%2C%20Additional%20Secretary,%2C%20Minister%20of%20Trade%2C%20Indonesia.
Strong case to restore Section 8(4) of the RP Act (The Hindu)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The recent disqualification of Rahul Gandhi, based on his conviction and imprisonment in a defamation case, has brought attention to the legal complexities and implications associated with the disqualification of sitting legislators in India. The focus is on the Supreme Court's decision to strike down Section 8(4) of the Representation of People Act 1951.
Facts About:
Disqualification and Legal Framework:
- Instant Disqualification and Lily Thomas Case: The disqualification of Rahul Gandhi based on his conviction in a defamation case raised questions about the legal basis of instant disqualification for sitting legislators. The Supreme Court's judgment in Lily Thomas vs Union of India (2013) invalidated Section 8(4) of the Representation of People Act 1951, removing the three-month appeal window before disqualification took effect.
- Section 8(3) and Disqualification: With the removal of Section 8(4), only Section 8(3) remains, which stipulates that a person convicted and sentenced to imprisonment for at least two years shall be disqualified from the date of conviction. The wording does not explicitly indicate an immediate disqualification upon the court's pronouncement of guilt.
- Disqualification Authority and Presidential Role: The authority to declare a sitting legislator disqualified might lie with the President of India under Article 103. While the Supreme Court rejected this proposition in Lily Thomas, the Consumer Education & Research ... vs Union Of India & Ors (2009) held that the President's declaration is necessary for disqualification.
Legal Implications and Challenges:
- Staying of Sentence and Conviction: The question arises whether the stay of only sentence or the stay of conviction itself is required to lift the disqualification. Different High Courts have held differing views on this issue, adding complexity to the interpretation of disqualification.
- Quantum of Sentence and Disqualification: Disqualification hinges on the imprisonment term being two years or more. The recent case of Rahul Gandhi emphasized this connection, highlighting that the disqualification's trigger is the sentence length, not just the conviction itself.
- Career Impact and Urgent Attention: Instant disqualification can significantly affect legislators' careers, especially given the slow pace of appeals and legal proceedings. There's a need to address this issue urgently to ensure the stability of legislators' careers and prevent abrupt disqualifications.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/a-strong-case-to-restore-section-84-of-the-rp-act/article67224103.ece
New Scheme Guidelines for North Eastern Region (PIB)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER) releases new Scheme Guidelines for implementing Cabinet-approved Schemes during 15th Finance Commission's balance period (2022-2026).
Facts About:
- The Cabinet approved Continuation of the North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS) with an outlay of Rs.8139.50 crore for the period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The scheme is a central sector scheme.It has two components viz. NESIDS-Road and NESIDS-Other Than Road Infrastructure (OTRI).
- The objective of the NESIDS is to support infrastructure development in identified sectors including connectivity in the North Eastern States.
- The Union Cabinet had also approved continuation of the ‘Schemes of North Eastern Council (NEC)’ for the period from 2022-23 to 2025-26 with a total outlay of Rs.3202.7 crore.
- The MDoNER Schemes help provide gap-filling support to the eight North Eastern States as per their felt needs, by taking up projects – e.g., for developing infrastructure to mitigate connectivity and social sector deficits and enhancing livelihood and employment opportunities in the region.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=195088
ICMR study on post COVID mortality (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) study reported that 17.1% of those hospitalized since September 2020 experience post-Covid conditions.
Facts About:
What were the main findings of the ICMR study?
- The study, encompassing 14,419 Covid-19 patients hospitalized since September 2020, revealed a 6.5% mortality rate within a year after hospitalization. Around 17.1% experienced post-Covid-19 conditions. It also highlighted the increased mortality risk associated with comorbidities, age, and gender.
How did the study define “post-Covid-19 conditions”?
- The study defined “post-Covid-19 conditions” as the persistence or new onset of fatigue, breathlessness, or cognitive abnormalities, due to the lack of established definitions from organizations like the World Health Organization or the CDC during patient enrollment.
What impact did a single vaccine dose have on mortality?
- The study indicated that a single vaccine dose prior to Covid-19 infection reduced one-year mortality by 60%, emphasizing the importance of vaccination even before exposure.
Who faced a higher risk of mortality according to the study?
- The study revealed that individuals with comorbid conditions were at the highest risk of mortality, being more than 9 times likely to die within a year. Men were 1.3 times more likely to die, while those above 60 years were 2.6 times more likely.
What risk did children face in terms of mortality?
- Children between 0 and 18 years had a 5.6-fold higher risk of death in the year following infection, with a 1.7-fold increase in the immediate four weeks post-hospitalization. Severe comorbidities among admitted children were hypothesized as a reason for the higher odds of death.
Can mild Covid-19 variants lead to long Covid?
- The long Covid might occur even in individuals with mild Covid-19. While symptoms improve with therapy, over-diagnosis of long Covid may be occurring, warranting consideration of alternative causes for reported symptoms.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
PLI Scheme for Smartphone Manufacturing Industry & Its Effectiveness (The Hindu)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Over the last few months, former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan and the Minister of State for Electronics Rajeev Chandrasekhar have sparred over how well a Central government scheme to boost electronics manufacturing has been faring.
Facts About:
- Former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan, along with two other economists, had released a brief discussion paper arguing that the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) programme isn’t really pushing India towards becoming a self-sufficient manufacturing powerhouse.
- They argued that the government is using taxpayer money to create an ecosystem of low-level assembly jobs that will still depend heavily on imports.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Programme?
- Around five years ago, the Government of India decided it wanted more companies to make things in India.
- Manufacturing is a key ingredient to economic growth and also comes with what economists call a multiplier effect — every job created and every rupee invested in manufacturing has a positive cascading effect on other sectors in the economy.
- To boost manufacturing in India, the Government introduced the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme.
- Under PLI, the government gives money to foreign or domestic companies that manufacture goods here.
- The annual pay-out is based on a percentage of revenue generated for up to five years.
PLI Programme for Smartphone Manufacturing Industry:
- The industry that has shown the most enthusiasm for the scheme is smartphone manufacturing.
- Companies like Micromax, Samsung, and Foxconn (which makes phones for Apple) can get up to 6% of their incremental sales income through the PLI programme.
- With the scheme, mobile phone exports jumped from $300 million in FY2018 to an astounding $11 billion in FY23.
- Imports – while India imported mobile phones worth $3.6 billion in FY2018, it dropped to $1.6 billion in FY23.
- Central government Ministers, including Mr. Chandrasekhar, have regularly cited this data as proof of the PLI’s scheme’s success.
Former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan’s Argument:
- In his paper, the former Central bank governor argued that while imports of fully put-together mobile phones have come down, the imports of mobile phone components — including display screens, cameras, batteries, printed circuit boards — shot up between FY21 and FY23.
- Incidentally, these are the same two years when mobile phone exports jumped the most.
- He said that manufacturers aren’t really making mobile phones in India in the traditional sense which would involve their supply chain also moving to India and making most of the components here as well.
- All that the companies are doing is importing all of the necessary parts and assembling them in India to create a ‘Made in India’ product.
- Another criticism is that low-level assembly work doesn’t produce well-paying jobs and doesn’t nearly have anywhere the same multiplier effect that actual manufacturing might provide.
Union Government’s Response:
- Minister of State for Electronics Rajeev Chandrasekhar’s argument is two-fold.
- First, he said, Mr. Rajan wrongly assumed that all imports of screens, batteries, etc. are used to make mobile phones.
- It is possible these items are used also for computer monitors, DSLR cameras, electric vehicles etc.
- He also argued that not all mobile phone production in India is supported by the PLI scheme, only around 22% so far.
- The Minister’s overarching point is that the import dependency isn’t as bad as Mr. Rajan says it is.
Conclusion:
- Former RBI Governor argued that even if only 60% of imports are used for production, India’s net exports will still be negative.
- That is, even if only 60% of screens, batteries, etc. are used to make mobile phones, the final import tally would still beat the final export tally.
- The main divide is over whether the PLI programme will be able to create long-lasting jobs and firmly establish India as a manufacturing and supply hub that adds value to the production process.
- The Union Government believes that it will take time for the PLI Scheme’s results to show.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
Marine Heat Waves (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Extreme Heat waves are harming marine life in the Mediterranean Sea.
Facts About:
Why are high sea temperatures a problem?
- Lesser dissolution of gases: Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolve better at colder temperatures, so that means the warmer the water; the less oxygen is available to breathe.
- Higher rate of respiration in marine organism: Higher temperatures also cause an increase in metabolism, which in turn means animals have to breathe even more than usual.
- The rise in temperature accelerates metabolism, and the organisms need more food to maintain this metabolic rate.
- More Algal blooms: They are more common in hotter waters. Such blooms can further deplete oxygen levels and produce toxins harmful for fish, marine mammals and birds.
What species and ecosystems are worst hit by marine heat waves?
- High water temperatures are most harmful for animals living at the bottom of oceans, lakes or rivers.
- These benthic species include corals, mussels, sponges, starfish and plants like sea grasses, and are often attached to rock or solid ground.
- Scientists observed mass deaths of benthic species along thousands of kilometers of Mediterranean coastline between 2015 and 2019.
What does extreme heat in the Mediterranean mean for people?
- Affecting fishing activities in the area: Fishermen are catching fewer familiar species and instead are finding more invasive fish which they have difficulty selling.
- Increase in invasive fishes: Some are even poisonous, like the puffer fish migration is seen in the region.
- Habitat loss: It could also lead to an overall decline in fish populations, while disappearing seagrass.
What is the phenomenon behind heat trap in oceans?
- Ocean Heat Content (OHC): It is the amount of energy absorbed by and stored in the oceans. It is measured in joules.
- When sunlight reaches the earth, oceans absorb this energy and store it as heat.
- While the heat is first absorbed at the surface of the water body, some of it is eventually disbursed throughout.
- Water has a higher heat capacity than air, which means that it can store much larger amounts of heat.
- GHG emissions - These gases trap heat in a blanket around the earth, not allowing it to escape, thus raising the temperature of the earth’s surface and leading to global warming.
Why Mediterranean Sea is significant for global temperatures?
The Mediterranean Sea has significant implications for global temperatures due to its role as a "climate amplifier." This phenomenon is referred to as the "Mediterranean Effect" or "Mediterranean Climate Amplification." Here are the reasons:
- Heat Absorption and Release: The Mediterranean Sea has a lower heat capacity compared to the vast oceans, such as the Atlantic or Pacific.
- As a result, it heats up and cools down more quickly. During the summer months, the Mediterranean Sea absorbs heat from the sun, leading to warming of the surrounding land areas.
- In winter, it releases the stored heat, moderating temperatures in nearby regions.
- Warm and Dry Summers: The Mediterranean region experiences warm and dry summers, which are conducive to high evaporation rates from the sea's surface.
- This process results in the release of latent heat into the atmosphere, contributing to the warming of the air.
- Atmospheric Circulation: The temperature contrast between the relatively warm Mediterranean Sea and the cooler landmasses during summer leads to the development of low-pressure systems over land.
- This creates a pressure gradient that drives winds from the sea to the land, bringing warm, moist air with it. This warm air can further increase temperatures over land areas.
- Feedback Loops: The warming effect of the Mediterranean Sea can lead to feedback loops. Warmer land areas result in higher evaporation rates, which in turn contribute to the amplification of temperature rise.
- This cycle of heat absorption, release, and evaporation intensifies the Mediterranean Climate Amplification.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/extreme-heatwaves-mediterranean-sea-8901948/
Vegetated Canopies (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In a recent development in Spain, tensioned sail-like vegetated awnings or canopies known as “Greenshades” have been strategically installed on the facades of buildings.
Facts About:
- Vegetated canopies are innovative structures designed to reintroduce greenery into urban landscapes.
- Inspired by the natural canopies found in forests and diverse plant ecosystems, these canopies play a crucial role in mitigating the urban heat island effect and enhancing the overall environmental quality of urban areas.
- This installation approach not only adds an aesthetic dimension to the urban architecture but also serves as a practical solution for reintroducing green elements in areas where traditional planting is challenging.
Emulating Nature’s Canopies:
- Mimicking the canopy formations observed in forest ecosystems, these vegetated awnings recreate a semblance of natural green cover.
- By doing so, they provide shade, reduce direct sunlight exposure, and create a more pleasant atmosphere in commercial streets and public spaces.
- This is particularly valuable in areas where the presence of trees and vegetation is limited.
Hydroponic Growth System:
- The vegetation integrated within these awnings grows using a hydroponic growth system.
- This method utilises a water supply point to provide the plants with the necessary moisture and nutrients. Additionally, a water outlet is incorporated into the design to facilitate efficient drainage.
- This innovative approach ensures that the greenery thrives even in non-traditional planting environments.
BENEFITS OF VEGETATED CANOPIES
Cooling Effects via Evapotranspiration
- Singular Green’s innovative canopy design efficiently reduces temperatures in both immediate areas and beneath the awnings.
- Achieved through evapotranspiration, where plants transfer water to the atmosphere, this cooling process enhances comfort.
Air Quality Improvement through Plant Selection
- Carefully chosen plants possess a special ability to absorb gases, including pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide.
- This contributes to better urban air quality and healthier living conditions.
Noise Reduction with Sound Wave Absorption
- Vegetated canopies excel at absorbing sound waves, minimising noise pollution and creating a more serene urban environment.
- Incorporating sound-absorbing substrates enhances the auditory experience.
Oxygen Generation and Gas Filtration
- Surprisingly, a single square metre of these canopies produces a year’s worth of oxygen for an individual.
- Moreover, they serve as natural filters, removing harmful gases from the air and thus improving overall air quality.
Efficient Water and Lighting Integration
- Beyond their green benefits, these canopies facilitate centralised water and lighting installations.
- Integrated lights equipped with motion sensors respond to real-time needs, promoting energy-efficient urban infrastructure.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
- Introducing these canopies into urban spaces fosters biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse wildlife.
- This initiative aligns with the vision of sustainable, nature-friendly cities, nurturing a harmonious urban ecosystem.
In the face of climate change-induced challenges, our response must be proactive, multifaceted, and holistic. The success of vegetated canopies as a means to combat extreme heat waves demonstrates that nature-inspired solutions have the power to transform urban environments into havens of sustainability, resilience, and well-being. By embracing such strategies and embarking on a collective journey, we can build cities that thrive in harmony with the planet.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/vegetated-canopies-green-spaces-urban-spain-8893918/
Concerns about Drilling in the North Sea (The Hindu)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of the U.K. recently backed plans for new fossil fuel drilling off Britain’s coast.
Facts About:
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/explained-drilling-in-the-north-sea-history-and-environmental-concerns/article67204792.ece
Turmeric Supplements (The Hindu)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) issued a medical advisory warning Australians of the risk of liver injury from using medicines and herbal supplements containing turmeric or its active ingredient, curcumin.
Facts About:
Health benefits of turmeric:
- The risk of liver injury did not appear to relate to curcuma longa consumed in typical dietary amounts as a food.
- As a staple ingredient in South and South East Asian cuisine, turmeric is also used in Ayurvedic and Chinese-medicine concoctions.
- Several studies report it to have anti-oxidant properties that can help with inflammation.
- These include arthritis and infections.
- A research have reported that curcumin used along with the drug Artemisininwas effective in treating malaria when tested on mice.
- There have also been studies investigating the drug as an adjuvant in chemotherapy based on results in mice and animal studies.
- However, their effect in human trials have been inconclusive.
Adverse effects of turmeric:
- The French Agency for Food reported various adverse effects, including reports of hepatitis, potentially related to the consumption of food supplements containing turmeric or curcumin.
- The ANSES report underlines that turmeric has “choleretic” properties, which means it stimulates the secretion of bile to improve digestion, and therefore, it is advisable that those with bile duct disease should avoidturmeric.
- Curcumin could also interact with medications such as anticoagulants, cancer drugs and immunosuppressants, reducing their safety and effectiveness.
Why is curcumin being used in supplements?
- One of the challenges of turmeric and by extension curcumin is that very little of it is absorbed, or made ‘bioavailable’, by the body.
- To improve its bioavailability, a popular approach is to use piperine, the major active component of black pepper, which improves bioavailability by 2000.
- However, whether increasing the bioavailability of curcumin and packaging them in supplements makes them effective and safe for use in medicines is still being debated with no conclusive evidence emerging from trials.
Safe limit on consumption of turmeric:
- The European Food Safety Authority has set an acceptable daily intake of 180 mg of curcumin per day for a 60 kg adult as the safe level of consumption.
- A World Health Organization/Food and Agricultural Organisationadvisoryrecommends 3 mg/kg of body weight.
- India’s Food Safety and Standards Authority of India has standards that packaged turmeric must comply with but nothing on the recommended dietary allowance.
- Statistically, on an average about 200 to 500mgs is consumed on a daily basis in Indian households.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/explained-are-turmeric-supplements-advisable/article67214093.ece
Expansion of BRICS (Indian Express)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently there have been internal conflicts about the nature and scope of the potential expansion of BRICS.
Facts About:
- BRICS is an acronym for five regional economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The first four were initially grouped as “BRIC” in 2001 by an economist Jim O’Neill, who coined the term to describe fast-growing economies that would collectively dominate the global economy by 2050.
- Summits: The governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits since 2009.
- India hosted the 13th BRICS summit in 2021 virtually.
- China hosted the 14th BRICS summit in 2022.
- South Africa will host the 15th summit 2023.
- BRICS is an important grouping bringing together the major emerging economies from the world, comprising:
- 41% of the world population,
- 24% of the world GDP
- Over 16% share in world trade.
- Total combined area of 29.3% of the total land surface of the world
- Over a period of time, BRICS countries have come together to deliberate on important issues under the three pillars of:
- political and security,
- economic and financial and
- Cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- New Development Bank and BRICS: Formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.
- The Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.
The need for BRICS expansion
- Economic strength: The economic strength of the five members of the grouping is not as promising as it was when the platform was first announced in 2009.
- Though the BRICS nations certainly represent 43% of the world’s population and around 30% of the global economy, their economic weaknesses are certain.
- China’s anti-western orientation: China is focused on a quick expansion of BRICS with the aim of giving the platform a distinctly anti-western orientation.
- Prevailing Anti-Western sentiment: Many realize that the doors of other groupings are closed to them.
- The clamour reflects prevailing anti-western sentiments and a pervasive desire to create a sizeable forum of the Global South.
- Global challenges: Russia is being marginalised in the global economy, while China is facing a difficult economic environment with the west turning against it.
Challenges with expanding BRICS grouping:
- An increase in membership is likely to weigh the group in favour of Chinabecause some countries waiting to join are also part of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative.
- This raise concerns that an expanded BRICS could be seen as a Chinese-led anti-American bloc.
- India, which has been strengthening its bilateral relationship with the US, has been concerned about expansion.
- India views China’s role in driving these countries for membership of BRICS along with the support of Russia.
- India also raised its concern in last year’s BRICS that any addition of new members must follow the carefully thought-out objective criteria for membership.
- This should be mutually discussed among the present members, so that all are of the same view regarding expansion.
- Further, at the BRICS foreign ministers’ meeting last month, India’s External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar emphasized the need to consider the ways in which existing BRICS countries collaborate with each other and engages with non-BRICS countries.
Way Forward:
The 15th BRICS summit holds multifaceted importance for India, offering a platform for addressing geopolitical concerns, facilitating bilateral talks, and advancing economic collaborations. As the global landscape continues to evolve, BRICS remains a critical forum for emerging economies to engage and collaborate on key global challenges. The outcomes of this summit will not only affect the member nations but also shape the broader trajectory of international relations and cooperation.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/brics-expansion-significance-for-india-8907925/
Megalithic Site In Kerala (The Hindu)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A large number of megalithic hat stones were found during a recent archaeological salvage excavation conducted by the Kerala Archaeology Department at Nagaparamba in Kuttippuram village, near Tirunavaya.
Facts About:
- Hat stones, popularly called Thoppikkallu in Malayalam, are hemispherical laterite stones used as lid on burial urns during the megalithic period.
What is Salvage excavation?
- Salvage excavation also known as rescue archaeology or emergency archaeology, refers to a type of archaeological excavation that is conducted in response to a situation where archaeological remains are threatened by construction, development, or other activities
Megaliths
- Megaliths were constructed either as burial sites or commemorative (non-sepulchral) memorials.
- Origin: As megalithic societies were preliterate, the racial or ethnic origins of the megalithic people are thus difficult to pin down.
- Significance: Megaliths were not built for commoners. They signify the emergence of a ruling class or elite who presided over a surplus economy.
- Time – Period: In India, archaeologists trace the majority of the megaliths to the Iron Age (1500 BC to 500 BC), though some sites precede the Iron Age, extending up to 2000 BC.
Geographical Spread: Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent, though the bulk of them are found in peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Even today, a living megalithic culture endures among some tribes such as the Gonds of central India and the Khasis of Meghalaya.
- Different Types of Megalithic Structure include: Stone Circles, Dolmen, Cist, Monolith and Capstone style.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/hat-stones-in-abundance-at-archaeology-site-near-tirunavaya/article67210231.ece
RBI allows switch from ‘floating to fixed rate’ regime (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) asked all regulated entities (REs), including banks and NBFCs, to give personal loan borrowers an option to switch over from a floating rate to a fixed rate regime at the time of resetting interest rates.
Facts About:
- When a customer takes a loan, the interest rate reset clause in the loan agreement allows the lender to review the interest rate after a certain period, as per the occurrence of a scheduled reset date of the loan.
- The reset rate is the new interest rate that a borrower must pay effective from the scheduled reset date.
- EMI of a floating rate loan changes with periodical changes in reset interest rates.
- These rates and the calculation are not uniform for all the banks as the cost of funds differs from banks.
Changes made by RBI:
The RBI asked banks to implement the following regulations:
- For Regulated entities (RE) :
- At the time of sanction, REs will have to clearly communicate to the borrowers about the possible impact of a change in benchmark interest rate on the loan leading to changes in EMI and/or tenor or both.
- Any increase in the EMI/ tenor or both will have to be communicated to the borrower immediately through appropriate channels.
- At the time of reset of interest rates, REs will have to give the option to borrowers to switch over to a fixed rate as per their board-approved policy.
- The policy will also specify the number of times a borrower will be allowed to switch during the tenor of the loan.
- REs will have to disclose all applicable charges for switching loans from floating to fixed rate and any other service charges/ administrative costs in the sanction letter and also at the time of revision of charges or costs from time to time.
- For EMI or Elongation of tenor:
- The borrowers will also be given the choice to opt for enhancement in EMI or elongation of tenor or for a combination of both options, and to prepay, either in part or in full, at any point during the tenor of the loan, with foreclosure charges.
- The RBI said REs will have to ensure that these instructions are extended to the existing as well as new loans by December 31, 2023.
Why has RBI issued new regulations?
- RBI's Supervisory Reviews: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has conducted supervisory reviews and received feedback from the public.
- Unreasonable Tenor Elongation: Instances of banks significantly extending tenors of floating rate loans without proper borrower consent and communication have been identified.
- Interest Rate Changes: Banks can alter interest rates by adjusting the internal benchmark rate and spread during the loan term, potentially harming borrowers' interests and monetary transmission.
- Arbitrary EMI Resets: Borrowers complain of banks arbitrarily resetting Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) and extending tenors without adequate notification.
- Hidden Foreclosure Charges: Borrowers are often unaware of foreclosure charges, adding to borrower dissatisfaction.
- Stress Concealment: RBI notes that prolonged tenor elongation may obscure underlying stress in banks' financial health.
- Refinancing Challenges: While theoretically possible, refinancing floating rate loans across different banks with distinct internal benchmarks is complex due to varying benchmark adjustment methods.
- Limited Borrower Options: Borrowers might feel compelled to stay with their original bank, paying higher charges, as refinancing is often impractical due to benchmark disparities.
Possible impacts:
- Interest rate of borrowers: Banks can change the interest rate by changing the internal benchmark rate and the spread during the term of the loan which could harm the interest of the borrower and also impair monetary transmission.
Benefits of Fixed rate regime:
- For borrowers:
- Protection from Rate Hikes: Shifting to a fixed rate provides protection against potential future increases in interest rates. This can be particularly beneficial if interest rates are expected to rise in the near future.
- Budgeting and Financial Planning: Fixed payments make it easier for borrowers to budget and plan their finances since they know exactly how much they need to allocate for their loan payments.
- Potential Cost: Fixed interest rates tend to be initially higher than prevailing floating rates. Borrowers opting for a fixed rate might end up paying more initially compared to what they would have paid with a floating rate if rates remain relatively stable or decrease.
- For lenders:
- Interest Rate Risk Mitigation: Lenders are less exposed to interest rate risks when borrowers opt for fixed rates. They can better manage their own interest rate risk since they know the interest income they'll receive remains constant.
- Lending Profitability: Fixed-rate loans typically come with higher initial interest rates compared to floating-rate loans. This can lead to increased lending profitability for lenders, especially if rates remain stable or decline.
- Potential Lower Loan Demand: Higher initial fixed rates might deter some potential borrowers who are attracted to lower initial payments offered by floating rates.
- Limited Flexibility: Lenders might have less flexibility in adjusting loan terms for borrowers with fixed-rate loans, as the interest rate remains constant regardless of market conditions.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/rbi-fixed-rate-regime-personal-loan-8898445/
Bio-Trace Minerals Project (PIB)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Technology Development Board under Department of Science and Technology (TDB-DST) collaborated with M/s Chemlife Innovations pvt ltd. for innovation in the Bio-Trace Minerals Project.
Facts About:
How does the collaboration between TDB and Chemlife Innovations align with India’s strategic framework for livestock development?
- The collaboration between TDB and Chemlife Innovations aligns with India’s strategic framework, including the National Livestock Mission, which seeks to enhance livestock productivity, optimize feed resources, and infuse technology into livestock management. By developing bio-trace minerals for animal feed, the project addresses crucial aspects of animal nutrition, aligning seamlessly with the mission’s objectives.
What innovative technology does Chemlife Innovations employ in their project, and how does it contribute to sustainability?
- Chemlife Innovations employs the “Accelerated Natural Bio Transformation” (ANBioT) technology, which facilitates chelation reactions using a proprietary nutrient medium. This technology operates under milder conditions and is eco-friendly, aligning with principles of sustainability by reducing environmental impact and resource consumption.
How does the use of pupa proteins contribute to the project’s eco-friendly approach?
- Pupa proteins, rich in hydroxy amino acids, are utilized in the project as an alternative to imported ligands. This economical alternative not only enhances the project’s economic viability but also aligns with India’s goal of self-sufficiency, reducing reliance on imported resources and promoting sustainable practices.
What certifications does Chemlife Innovations hold, and how do they attest to the company’s commitment to quality?
- Chemlife Innovations holds Global Certification for Animal Feed Additive Quality and Feed Safety, as well as the esteemed FAMI-QS certification. These certifications validate the company’s commitment to producing high-quality and safe products, maintaining global standards in their operations.
How does the project contribute to the circular economy, and what role does repurposing silk worm pupae meal play?
- The project contributes to the circular economy by repurposing silk worm pupae meal, reducing waste generated by the silk industry. By using locally available by-products, the project aligns with principles of sustainability, economic viability, and import substitution goals.
How does the project’s innovative product “MinBioZen” address livestock health and sustainability?
- “MinBioZen” is an innovative bio-trace mineral product developed by Chemlife Innovations. It integrates bioavailability and stability, optimizing livestock health and growth. This product showcases the company’s dedication to innovation and environmental stewardship, aligning with the goals of sustainable resource utilization.
Source: https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjUsaL43aGBAxVEwjgGHU5XAs8QFnoECBQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fpib.gov.in%2FPressReleaseIframePage.aspx%3FPRID%3D1950125&usg=AOvVaw16iXZ25GRw2ND9aklzZ5ri&opi=89978449
Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket (Economic Times)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Chennai-based start-up AgniKul Cosmos, has commenced the process of integrating its cutting-edge Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket at its private Launchpad in Sriharikota.
Facts About:
- The integration process was initiated on Independence Day on August 15, 2023.
- A successful launch would make AgniKul the second Indian space tech start-up to send its launch vehicle into space after Skyroot Aerospace.
- AgniKul: Established in 2017, by aerospace engineers Srinath Ravichandran and Moin SPM, along with IIT-Madras faculty member Prof. Sathyanarayan R Chakravarthy.
About Agnibaan SOrTeD (SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator):-
Type: single-stage launch vehicle.
Powered by: AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet engine: It is the world’s sole single-piece 3D-printed engine.
- It is a single-piece, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine.
- Initial trial: early 2021.
- Verified at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in Thiruvananthapuram.
- 3D printing: uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
Payloads: up to 100 kg.
Altitude: 700 km
- It can carry payloads in five different configurations. (LVM3-M2 rocket)
Stages: It is a customizable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages.
Unique feature: unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, it will lift off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory to perform a precisely orchestrated set of maneuvers during flight.
The rocket’s first stage could have up to seven Agnilet engines, depending on the mission, which are powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene.
The rocket is also designed for launch from more than 10 different launch ports.
To ensure its compatibility with multiple launch ports, AgniKul has built a launch pedestal named ‘Dhanush’.
- It will support the rocket’s mobility across all its configurations.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/chennai-based-agnikul-prepares-for-maiden-sub-orbital-flight-of-agnibaan-rocket/articleshow/102805834.cms?from=mdr
3D Printing (The Hindu)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India’s first 3D printed Post Office was inaugurated in Bengaluru’s Cambridge Layout.
Facts About:
- India’s pioneering 3D-printed post office located in Bengaluru’s Cambridge Layout was recently inaugurated.
3D Printed Post Office
- Swift Build: The 3D-printed post office was constructed in just 43 days, surpassing the original deadline by two days.
- Construction Team: Larsen & Toubro Limited undertook the project in collaboration with IIT Madras.
Technological Process
- Spatial Dimension: The post office covers an area of 1,021 square feet and was created using advanced 3D concrete printing.
- Automated Procedure: Robotic printers used an automated process to layer concrete according to the approved design.
- Strong Bonding: A specially formulated quick-hardening concrete ensured strong bonding between layers.
- Rapid Construction: With robotic precision and pre-embedded designs, the project was completed in just 43 days, far shorter than the conventional 6 to 8 months.
Advantages of 3D Printing
- Cost-Effective: The project cost ?23 lakhs, indicating a 30-40% cost reduction compared to traditional methods.
- Showcasing Technology: The project highlighted concrete 3D printing technology using indigenous machinery and robots, showcasing its scalability.
Distinctive Features
- Continuous Perimeter: The project boasted continuous perimeter construction without vertical joints.
- Flexibility: The 3D printing accommodated curved surfaces and different site dimensions, overcoming flat wall limitations.
- Structural Innovation: Continuous reinforced concrete footing and three-layer walls were created, enhancing structural integrity.
- Reduced Timeline: The innovative technique drastically reduced the construction timeline to 43 days, minimizing material wastage.
Source: https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwi88OSW3aGBAxVDTWwGHafnBzMQFnoECB8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.thehindu.com%2Fnews%2Fcities%2Fbangalore%2Findia-first-3d-printed-post-office-is-now-open-for-business-in-bengaluru%2Farticle67208897.ece&usg=AOvVaw1xcvOgM9Z66xFGFeSZ-7W_&opi=89978449
Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
New data from the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of World Resources Institute (WRI) has been released.
Facts About:
What does it mean for a country to be exposed to extreme water stress?
- Extreme water stress signifies that a country uses more than 80% of its renewable water supply for activities such as irrigation, livestock, industry, and domestic needs. This reliance makes them vulnerable to water scarcity during periods of drought.
How does the WRI define the term ‘water stress’?
- A region is deemed ‘water stressed’ when the demand for water surpasses the available volume or when water quality limitations restrict its use for various purposes.
Which regions and countries are the most water-stressed according to the report?
- The most water-stressed regions are West Asia, North Africa, and South Asia. Notable water-stressed countries include Bahrain, Cyprus, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, and others.
How is global water demand projected to change by 2050?
- Global water demand is estimated to increase by 20-25% by 2050. Additionally, watersheds facing unpredictable water supplies are expected to rise by 19%. This could result in 100% of West Asia and North Africa’s population facing extreme water stress by 2050.
What are the implications of high water stress beyond immediate concerns?
- The report emphasizes that extreme water stress affects not only consumers and industries but also has far-reaching political implications. Water stress can impact political stability, making it a critical issue to address for global leaders.
What are the economic implications of solving global water challenges?
- According to WRI’s findings, addressing global water challenges would cost around 1% of the global GDP or 29 cents per person per day from 2015 to 2030. Despite the costs, the potential economic benefits and stability improvements make it a worthwhile investment.
Source: https://chinawaterrisk.org/useful-links/aquaduct-water-risk-atlas/
INS Vindhyagiri' (PIB)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
President Droupadi Murmu launched the 'INS Vindhyagiri' in Kolkata at Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE).
Facts About:
- Project 17A – Vindhyagiri, named after the mountain range in Karnataka, is the sixth ship of the Project 17A program, as per PTI reports.
- Vindhyagiri, a technologically advanced Frigate, and a tribute to the erstwhile INS Vindhyagiri, the Leander Class ASW Frigate.
- Old Vindhyagiri – It is nearly 31 years of service from July 1981 to June 2012, had witnessed various challenging operations and multinational exercises.
- Under the Project 17A program, a total of 4 ships by Mazagon Dock Ltd (MDL) and 3 ships by GRSE are under construction.
- The project's first 5 ships have been launched by the MDL and GRSE between 2019 and 2022.
- Project 17A ships have been designed in-house by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau, the pioneer organization for all warship design activities.
- A substantial 75% of the orders for equipment and systems of Project 17A ships are from indigenous firms.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1949974
Artificial Intelligence Index 2023 (Indian Express)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India ranked fifth in Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based investments according to Stanford University’s annual AI Index report 2023.
Facts About:
- AI Index is an independent project at Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI).
Purpose:
- The annual report compiles, analyzes, and visually presents AI-related data to empower responsible and ethical AI advancements in collaboration with human interests
Global AI Investment Rankings
- United States
- China
- United Kingdom
- Israel
- India
India's Remarkable Growth
- India secured the fifth position in AI investments received by startups worldwide in 2022.
- AI startups in India attracted $3.24 billion in funding, surpassing countries like South Korea, Germany, Canada, and Australia.
Investment Revival amidst Recession
- Despite a global AI investment dip since 2021 due to economic challenges, a resurgence in Venture Capital (VC) funding is anticipated this year.
- Enterprises and consumers' heightened interest in generative AI products like Open AI's ChatGPT is expected to drive this revival.
Global Contribution to LLM Development
- 54% of researchers involved in advancing large language models (LLMs) hail from American institutions.
- Significant progress observed as researchers from Canada, Germany, and India joined the LLM development landscape in the past year.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/artificial-intelligence/key-takeaways-from-stanford-ai-index-report-2023-8539812/
PM Vishwakarma (Economic Times)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved a new Scheme named “PM Vishwakarma”
Facts About:
Type: Central Sector Scheme
Aim: To strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishyaparampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
– To improve the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople and to ensure that the Vishwakarmas are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Coverage: The scheme will provide support to artisans and craftspeople of rural and urban areas across India.
– Eighteen traditional trades will be covered under the scheme. These include carpenter, boat maker, armourer, blacksmith, hammer and tool kit maker, locksmith, goldsmith, potter, sculptor, stone breaker, cobbler, mason, basket/mat/broom maker/coir weaver, traditional doll and toy maker, barber, garland maker, washerman, tailor and fishing net maker.
Duration of the scheme: Five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).
Key Features of the scheme: Artisans and craftspeople will be provided a recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
– The scheme has a provision of credit support of up to ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
– It also has a provision to provide skill upgradation, incentive for toolkit as well as digital transactions and marketing support.
– Skilling programmes will take place at both basic and advanced types. Participants will get a stipend of ?500 per day while undergoing training.
– Beneficiaries will also receive up to ?15,000 to buy modern tools.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/pms-vishwakarma-scheme-launch-on-sept-17-70-ministers-to-attend-event-at-70-locations/articleshow/103559849.cms?from=mdr
The first-ever Global Summit on Traditional Medicine (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The first WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit will take place in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Facts About:
First WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit:
Organized by: World Health Organization (WHO) and co-hosted by the Ministry of Ayush.
Aim: To bring together various stakeholders, such as traditional medicine practitioners, policymakers, academics, and others on a common platform to share best practices, evidence and innovation related to how traditional medicine contributes to health and sustainable development.
Significance: Traditional and complementary medicine has been vital for health in communities for centuries and has influenced modern medical knowledge.
– About 40% of today’s medicines have natural origins, including well-known drugs like aspirin and artemisinin.
– Currently, 170 countries have informed WHO about their use of traditional medicine, seeking evidence and data to guide safe, cost-effective, and fair policies and regulations.
About WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicine:
In 2022, WHO with the support of the Government of India established the Global Centre for Traditional Medicine in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
Mandate: The centre provides leadership on all global health matters related to traditional medicine as well as extending support to member countries in shaping various policies related to traditional medicine research, practices and public health.
Significance: It is the first and only global outpost for traditional medicine across the globe.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/who-director-general-to-inaugurate-first-ever-global-summit-on-traditional-medicine/article67193778.ece
Removing gender stereotypes from the law (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Supreme Court has recently launched a ‘Handbook on Combating Gender Stereotypes’.
Facts About:
What is the significance?
- Combats Gender Stereotypes: It aims to combat gender stereotypes in language used within the judiciary and legal community.
- For instance, terms like "career woman," "fallen woman," "faithful or obedient wife," "eve-teasing," and "hermaphrodite" have been identified as gender-unjust terms.
- The Supreme Court suggests using more neutral and respectful terms like "woman," "wife," "street sexual harassment," and "intersex" instead.
- Promoting Equity and Justice: Promoting a more just and equitable society. He mentioned that relying on predetermined stereotypes in judicial decision-making goes against the duty of judges to decide cases impartially, based on their merits.
- Addresses false assumptions: The handbook addresses false assumptions about women's characteristics, such as the stereotype that women are overly emotional, illogical, and unable to make rational decisions.
- It emphasizes that a person's gender should not determine their capacity for rational thought.
- Addresses Prejudices: The handbook discusses assumptions made about a woman's character based on her clothing choices and sexual history.
- These assumptions can influence how the court assesses her actions, particularly in cases involving sexual violence, and may undermine the importance of consent in such cases.
- Significance of language: The Chief Justice pointed out that language used by judges reflects not only their interpretation of the law but also their perception of society.
- The example of changing the term "pauper" to "indigent" in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 was cited to demonstrate how language can impact the dignity and humanity attributed to individuals.
- The handbook aims to raise awareness about the role of language in perpetuating gender stereotypes within the legal system and provides guidance on using more respectful and neutral terms to promote fairness and equality.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/to-remove-gender-stereotypes-from-the-law-a-new-supreme-court-handbook/article67201169.ece
Legalising Cannabis : Good or Bad for India (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Himachal Pradesh CM has announced that the state government is considering legalizing the cultivation of cannabis.
Facts About:
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes.
- The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD).
- It is used by smoking, vaporizing, within the food, or as an extract.
Prospects of legalizing Marijuana
(1) Health benefits
- The cannabinoids found in Cannabis is a great healer and has found mentioned in Ayurveda.
- It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions like multiple sclerosis, arthritis, epilepsy, insomnia, HIV/AIDS treatment, and cancer.
(2) Ecological benefits
- The cannabis plant and seeds apart from being labelled a ‘super-foods’ as per studies is also a super-industrial carbon-negative raw material.
- Each part of the plant can be used for some industry. Hemp currently is also being used to make bio-fuel, bio-plastics and even construction material in certain countries. The cosmetic industry has also embraced Hemp seeds.
(3) Marijuana is addiction-free
- An epidemiological study showed that only 9% of those who use marijuana end up being clinically dependent on it.
- The ‘comparable rates’ for tobacco, alcohol and cocaine stood at 32%, 15% and 16% respectively.
(4) Good source of Revenue
- By legalizing and taxing marijuana, the government will stand to earn huge amounts of revenue that will otherwise go to the Italian and Israeli drug cartels.
- In an open letter to US President George Bush, around 500 economists, led by Nobel Prize winner Milton Friedman, called for marijuana to be “legal but taxed and regulated like other goods”.
(5) A potential cash crop
- The cannabis plant is something natural to India, especially the northern hilly regions. It has the potential of becoming a cash crop for poor marginal farmers.
- If proper research is done and the cultivation of marijuana encouraged at an official level, it can gradually become a source of income for poor people with small landholdings.
(6) Prohibition was ineffective
- In India, the consumption of synthetic drugs like cocaine has increased since marijuana was banned, while it has decreased in the US since it was legalized in certain states.
- Moreover, these days, it is pretty easy to buy marijuana in India and its consumption is widespread among the youth. So it is fair to say that prohibition has failed to curb the ‘problem’.
(7) Marijuana is less harmful
- Marijuana consumption was never regarded as a socially deviant behaviour any more than drinking alcohol was. In fact, keeping it legal was considered as an ‘enlightened view’.
- It is now medically proven that marijuana is less harmful than alcohol.
Risks of Legalizing Cannabis
(1) Health risks continue to persist
- There are many misconceptions about cannabis. First, it is not accurate that cannabis is harmless.
- Its immediate effects include impairments in memory and in mental processes, including ones that are critical for driving.
- Long-term use of cannabis may lead to the development of addiction of the substance, persistent cognitive deficits, and of mental health problems like schizophrenia, depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to cannabis in adolescence can alter brain development.
(2) A new ‘tobacco’ under casualization
- A second myth is that if cannabis is legalized and regulated, its harms can be minimized.
- With legalization comes commercialization. Cannabis is often incorrectly advertised as being “natural” and “healthier than alcohol and tobacco”.
- Tobacco, too, was initially touted as a natural and harmless plant that had been “safely” used in religious ceremonies for centuries.
(3) Unconvincing Advocacy
- Advocates for legalization rarely make a convincing case. To hear some supporters tell it, the drug cures all diseases while promoting creativity, open-mindedness, moral progression.
- Too much trivialization of Cannabis use could lead to its mass cultivation and a silent economy wreaking havoc through a new culture of substance abuse in India.
Legalization status elsewhere in India
- Several states in India have already legalized cannabis cultivation, including neighboring Uttarakhand, which became the first state in the country to do so in 2017.
- Controlled cultivation is being done in some districts of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
Legal Framework for Cannabis Cultivation
- Definition of Cannabis: The Parliament has defined cannabis in the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS), 1985.
- Ban on extracting resin and flowers: While a complete ban has been imposed on extracting the resin and flowers of the cannabis plant, the law determines the method and extent of cultivation of cannabis for medicinal and scientific purposes.
- Authorities to States: Section 10 (a) (iii) of the Act empowers States to make rules regarding the cultivation of any cannabis plant, production, possession, transport, consumption, use, purchase, sale, and consumption of cannabis (except charas).
- Cultivation of hemp: States are also empowered to permit, by general or special order, the cultivation of hemp, only for obtaining fibber or seeds or for horticultural purposes.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-risks-of-legalising-cannabis/article29216035.ece
Talwar-class Stealth Frigates (PIB)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
- Two Krivak- or Talwar-class stealth frigates are now expected to be delivered by May and October in 2024
- The ship is in the final stages of development; in two months time, it will go for sea trials.
Facts About:
The Talwar class of frigates of the Indian Navy have been built in Russia under an Indo-Russian joint production.
The Talwar class guided missile frigates are modifiedKrivak III class frigates from Russia.
- In October 2016, India and Russia signed an Inter-Governmental Agreement for four stealth frigates, after which a $1-billion deal was signed for direct purchase.
The Talwar Class has a displacement of 4,000 tons and speed of 30 knots and is capable of accomplishing a wide variety of naval missions, primarily, finding and eliminating enemy submarines and large surface ships.
Due to the use of stealth technologies and a special hull design, the resulting frigate features reduced radar cross section (RCS) as well as electromagnetic, acoustic and infrared signatures.
Source: https://swarajyamag.com/defence/russia-delays-advanced-talwar-class-stealth-frigates-delivery-yet-again-now-projected-to-join-navy-by-may-and-october-2024
Graphene-Aurora program (PIB)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) Secretary launched the ‘Graphene-Aurora program’ at a function in Maker Village Kochi, Kerala.
Facts About:
- The program shall be implemented by Digital University Kerala with joint funding from Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), and Government of Kerala and Industry partners, Carborundum PvtLimitedjoined as one of the main industry partners.
- It shall nurture the deep/emerging Graphene technology & innovation ecosystem that can guide, develop, implement, and support SMEs and startups to commercialize developed graphene technologies for scale adoption.
- Creation of a commercialization eco-system for graphene as an emerging technology would help India take a pole position in the world’s new material market.
Key facts about Graphene
- Graphene is a material that is extracted from graphite and is made up of pure carbon.
- It is one of the most important elements in nature which we find in daily objects like the lead of a pencil.
- It is the world’s thinnest, strongest, and most conductive material of both electricity and heat.
- It conducts electricity better than copper.
- It is 200 times stronger than steel but six times lighter.
- It is almost perfectly transparent as it absorbs only 2% of light.
- It is impermeable to gases, even those as light as hydrogen and helium.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1948661
Deemed Forest (The Hindu)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Odisha has no ‘deemed forest’ as per the amended Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
Facts About:
What are deemed forests?
Deemed forest refers to land that resembles forests but has not been recognized as such by either the Union or the States.
They account for about 1% of the total forest land in the country.
In 1996, the Supreme Court expanded the remit of the Van (SanrakshanEvamSamvardhan) Act to areas that weren’t notified as forests but conformed to the “dictionary” definition of forests i.e. deemed forests.
- The Godavarman verdict stated that the states must identify and categorize such land.
- The SC directed the states to establish Expert committees to determine deemed forests in order to clarify the area that may be protected under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
According to the Forest Act, land cannot be diverted without the consent of the Centre as well as gram panchayats in the regions.
- It serves as a deterrent to deforestation by directing the parties responsible for diverting forest land to grow trees on a plot of land equivalent to twice the razed area and imposing a significant monetary penalty.
What does the Odisha government directive mention?
All district collectors must ensure that the diversion of forest land for infrastructure projects, particularly state development projects, should follow provisions of the new law.
Any survey or exploration will also not be treated as a non-forestry activity.
Expert Committees
Although all the states were expected to form expert committees to identify deemed forests, not all States submitted their reports.
- This has left states with enough leeway in defining or omitting large parcels of land as forests.
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, the amendments to the 1980 Act were necessary to remove ambiguities and clarify the application of the laws.
According to the amended act, the Forest Conservation Act would not apply to notified forest land that was legally diverted for non-forest uses between 1980 and 1996.
- As a result, forest land that was not specifically notified as such would cease to be protected under the provisions of the Act.
The Union Environment Ministry had earlier stated that deemed forests would continue to be protected.
- The amendments made to the FCA recognized deemed forest lands, which had been identified by the Expert Committee of the State. Therefore the provisions of the Act will be applicable in such lands also.
Future unclear
According to the latest Forest Survey of India, Odisha has approximately 52,156 square km or 130 lakh acres of forest coverage.
- This amounts to 33.50% of the State’s geographical area, which is much higher than the national level of forest cover - 21.71%.
Since 1996, around 66 lakh acres have been identified as deemed forests in Odisha.
- However, a majority of this land has not been officially notified in the government records.
This amounts to about 40-50% of Odisha’s forest land.
In addition, there are several community forests that are managed by tribal and forest-dependent groups while several have land title rights under the provisions of the separate Forest Rights Act.
- The decision of the Odisha government that deemed forests have ceased to exist means that these will face an uncertain future.
One consequence of the new amendments is that there will be no check on forest diversion, making it easier to divert forest land.
- According to data from the Union Coal and Mining Ministry, of the 19,200 hectares of forest land that have been diverted nationally for mining between 2017-2022, around 8,000 hectares was from Odisha.
The reality on the ground is that most of the forest officer bureaucracy isn’t too keen on protecting forest rights
Impact
The Adivasi communities of Odisha depend on the deemed forests for their livelihood.
- These include some of the community-protected forests and bio-cultural habitats of vulnerable tribal groups such as the Dongria Kondhs in Niyamgiri.
- The removal of deemed forest areas from the Act could adversely affect the statutory rights of these communities which have claimed community forest rights and habitat rights on such forests
Around 46% of Odisha’s geographical area is notified as fifth schedule area under the Constitution, where thePanchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act applies.
Boundary disputes: In Karnataka, people have alleged that large amounts of agriculture and non-forest land are “unscientifically” classified as deemed forest land.
- This was found to have caused undue hardship to farmers in the region and restricted industrial development.
Criticism
Deemed forests already identified as forests in records ‘held’ by any department or administration should be considered as ‘forest’ even by the new amendment.
- However, the directive of the Odisha government violates this.
It is uncertain if the amendment is yet to be considered to be law as the date of enforcement is yet to be notified.
- The government has temporarily withdrawn the notification until the Union Government establishes the rules and guidelines of the new act.
The amendment narrows down the definition of forests.
- As a result, vast tracts of forests are excluded which leaves them vulnerable to destruction.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/no-more-deemed-forests-says-odisha-government/article67198187.ece
Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA) (PIB)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
14 States and Union Territories are yet to sign a crucial Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Union Education Ministry.
Facts About:
Higher education Institutions (HEIs) in India
Statistics
As per the AISHE report 2020-21, there are 1,113 Universities, 43,796 Colleges, and 11,296 Stand Alone Institutions.
- There are 422 State Public Universities that have 41,836 affiliated colleges.
- 446 Universities are privately managed and 475 Universities are located in rural areas, 17 are women-centric universities.
Total enrolment in higher education has been estimated to be 4.13 crores with 2.12 crores boys and 2.01 crores females.
- Females constitute 48.7% of the total enrolment.
There are 2,255 students enrolled in Integrated Ph.D. in addition to 2.11 lakh students enrolled in Ph.D. Level.
Major problems currently faced by the higher education system in India – As identified by National Education Policy 2020:
- A severely fragmented higher educational ecosystem; less emphasis on the development of cognitive skills and learning outcomes;
- A rigid separation of disciplines, early specialization, and streaming of students into narrow areas of study;
- Limited access particularly in socio-economically disadvantaged areas, with few HEIs that teach in local languages;
- Limited teacher and institutional autonomy;
- Inadequate mechanisms for merit-based career management and progression of faculty and institutional leaders;
- Lesser emphasis on research at most universities and colleges, and lack of competitive peer-reviewed research funding across disciplines;
- Suboptimal governance and leadership of HEIs;
- An ineffective regulatory system; and large affiliating universities result in low standards of undergraduate education.
- PM-USHA aims to address the key gaps and issues identified by NEP 2020.
What is Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA)?
Background
- Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) was a Centrally Sponsored Scheme to fund States/UTs institutions.
- It was launched with the vision to attain higher levels of access, equity, and excellence in the State higher education system with greater efficiency, transparency, accountability, and responsiveness.
- The first phase of the scheme was launched in 2013 and the second phase was launched in 2018.
- Now, in the light of the National Education Policy, RUSA scheme has been launched as Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA).
About
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme of the Government of India executed through the Ministry of Education.
- The scheme aims to work with over 300 HEIs including the state universities, its affiliated colleges to raise the quality of education.
Key Objectives of Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan
The key objectives of PM-USHA are to improve access, equity and quality in higher education through planned development of higher education at the state level.
The objectives also include:
- creating new academic institutions,
- expanding and upgrading the existing ones,
- developing institutions that are self-reliant in terms of quality education, professionally managed, and characterized by greater inclination towards research.
Funding
- The PM-USHA aims at providing strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions.
- The central funding is based on norms and is outcome dependent.
- Funds flow from the central ministry through the state governments/union territories before reaching the identified institutions.
- Funding to states is made on the basis of the critical appraisal of State Higher Education Plans, which enlist each state’s strategy to address issues of equity, access and excellence in higher education.
Source: https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/upload_document/pm-usha_guidelines.pdf
National Medical Commission’s New Guidelines (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to the National Medical Commission’s Registered Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations or NMC RMP Regulations 2023, doctors can now refuse treatment to the unruly and violent patients.
Facts About:
The National Medical Commission Act, 2019:
- It was introduced to address various issues and challenges in the medical field, including improving the quality of medical education, enhancing access to healthcare services, and ensuring ethical and transparent practices.
- Key Provisions include:
- Ethical and Professional Conduct: The Act emphasizes maintaining ethical and professional conduct among medical practitioners and includes provisions to address any deviations from these standards.
- Community Health Providers: The Act introduces the concept of Community Health Providers who are allowed to practice limited medicine in underserved rural areas to address the shortage of doctors.
- Formation of the National Medical Commission (NMC): NMC is an regulatory body which regulates medical education and medical professionals.
- Establishment of Medical Advisory Council.
- Reforms in Medical Education.
Refusing treatment is a complex issue that involves various stakeholders viz. doctors and healthcare professionals, patients and their families, healthcare institutions, medical associations and regulatory bodies, legal authorities, ethics committees, public opinion and media, religious and cultural communities, etc.
Arguments in Favour of the Regulation:
- Unruly Behaviour
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- For example, a 21-year-old patient attacked a doctor with a knife during consultation at Delhi’s Sir Ganga Ram Hospital.
- Dignity and Integrity: Unruly behaviour can sometimes cross ethical boundaries, leading to disrespectful or abusive treatment of healthcare staff. Doctors have a right to work in an environment that respects their dignity and professional integrity.
- For example, a 40-year-old doctor on duty in a hospital in Faridabad was assaulted by attendants of a patient as the doctor was attending to another patient, he could not immediately attend to the patient.
- Brings Deterrence: Allowing unruly behaviour to go unchecked might enable a cycle of disruptive or non-compliant behaviour, which could negatively impact the patient’s overall health outcomes. By refusing treatment, the doctor may communicate that certain standards of behaviour are expected for a therapeutic relationship to proceed.
- Right to Freedom to practise any profession: The regulations give the doctors the right to choose whom they will serve, except in case of a life-threatening emergency.
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- Financial Constraints
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- If a patient cannot afford the treatment, the doctor might argue that proceeding with treatment without full financial transparency could undermine the patient’s autonomy and informed consent.
- In extreme cases, relatives of patients have been known to hold doctors or hospital staff hostage, demanding treatment.
- Professional Boundaries: Some proponents of this perspective argue that doctors have a professional duty to provide medical care and expertise, but they are not obligated to address broader societal issues such as patients’ financial difficulties.
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- Ethical Boundaries: Doctors have ethical responsibilities not only toward their patients but also toward themselves, their families and the healthcare community.
- For example, potential threats and violence have long-lasting impacts which manifests in the degradation of personal and professional relations.
- Objectivity: Taking decisions which are free from subjectivity caused by emotions, perceptions and individual bias is necessary for long term sustainability.
- For example, Free medical care for a desperate patient may be ethical, but providing it to many patients may not be feasible for one provider.
- Selfless Duty: Medical practitioners often prioritize the well-being of their patients above their own comfort, personal time and space. However, the job can be thankless at times.
- For example, During COVID-19 despite their selfless dedication, medical professionals were subjected to regular assaults and verbal abuse throughout the country.
Arguments against the Regulation
- Dedication and the Duty of Care: Dedication is the sense of deep rooted commitment to devote oneself to a cause.. This includes a duty to provide care to those in need, regardless of their financial status.
-
- In India, out-of-pocket health expenditure accounts for more than half of total health expenditure pushing many households into poverty. This shows the dire need for empathy and compassion towards those in need.For example, Dr Ramanand Singh has been treating his patients for just Rs 50 for the past 35 years in Bihar. He even waives off his fees in cases where the patients cannot afford medical treatment.
- Justice and Equity: The principle of justice requires that healthcare be distributed fairly and equitably.Denying treatment to a patient solely based on their inability to pay could be seen as unjust, perpetuating disparities in healthcare access.
- Hippocratic Oath: Physicians pledge to do what is in the best interest of their patients and to avoid causing harm.
- Physicians promise to treat all patients fairly, regardless of their background, and to provide care to the best of their abilities without bias.
- Unholy Nexuses: Many doctors form nexuses with drugmakers to prescribe specific drugs from their brand instead of generic drugs leads to considerable rise in treatment costs for patients.
- For example, freebies given to doctors including travel expenses, gifts etc. by drugmakers is a common practice.Beneficence: It means kindness or generosity and this principle refers to the moral obligation to act in a manner that will benefit others.The principle of beneficence obligates doctors to act in the best interests of their patients and to promote their well-being.
- Compassion: It is the desire to end someone’s suffering which forms the core principle of a medical practitioner. Refusing treatment to individuals on certain grounds could lead to the possibility of crisis of conscience among several practitioners.
- Loss of Trust and Credibility: The medical profession relies on public trust, and denying treatment to those in need could erode that trust and damage the reputation of the medical community.
- Responsibility: Some argue that healthcare professionals have a broader social responsibility to address systemic issues in healthcare, including affordability and access. Refusing treatment might be seen as abdicating this responsibility.
- Undermining Right to Life: Providing a legal caveat for the registered physicians to refuse treatment is against the fundamental right guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Further, there is no specific definition of “abusive” in law as it is purely a subjective interpretation that may depend on the personal opinion of any individual.
- Subjective interpretation may further lead to exclusion on the basis of race, religion, caste, sex etc.
What Should be Done?
- Persuasion: Influencing patients to follow prescribed norms for behaviour and ensuring smooth functioning.
- For example, during COVID-19 pandemic, voice messages were circulated using caller tune to make people aware of the importance of vaccination and prevent attacks on health workers.
- Emotional Intelligence: Equipping and training medical personnel with necessary skills so that they can manage their emotions and try to avoid escalation of situation and providing practical solutions to the given problems.
- Transparent Approaches: Consider alternative approaches before refusing treatment. This might involve social workers, mental health professionals, or conflict resolution experts to address the underlying issues contributing to the unruly behaviour.
- For example, Doctors in San Diego (USA)refer patients to low-cost family health centersthat provide caring, affordable, high-quality health care and supportive services to everyone.
- Ethical Principles Balancing: Weigh the principles of patient autonomy, duty of care, patient safety, and respect for healthcare personnel’s well-being. Consider how refusing treatment aligns with these principles and what potential consequences might arise from the decision.
- For example, Doctors Without Borders is a Nobel Peace Prize receiver charity that provides humanitarian medical care in conflict zones to all those in need of medical care, irrespective of the role played by them in the conflict.
- Tolerance: Accepting actions and practices which may be considered to be incorrect but still tolerable to some extent that they should not be prohibited or penalised heavily.
- For example, a significant number of the cases of unruly behaviour arises in situations which may not be considered as “common” and even the most well-behaved might behave in a way which is not acceptable in society due to the shock or intensity of the moment which one may not be able to handle.
- Consent: Communicating the decision clearly to the patient, and explaining the reasons behind it thus ensuring that the patient understands the potential consequences of their behaviour on their health and the doctor-patient relationship.
- Offering Continuity of Care: If possible, provide recommendations for alternative sources of care, whether within your healthcare institution or elsewhere. Ensure the patient’s ongoing health needs are addressed.
Conclusion
We must protect those who heal. Ethical decisions in healthcare are rarely black and white. It’s important to approach each situation with sensitivity, professionalism, and a commitment to upholding the well-being of patients, healthcare staff, and the broader community. Consulting with colleagues, supervisors, and ethics committees can provide valuable guidance in making these difficult decisions
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/doctors-new-national-medical-commission-guidelines-8890632/#:~:text=The%20guidelines%20say%20that%20doctors,but%20at%20least%20three%20credits.
Urea Gold (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi officially launched Urea Gold fertiliser.
Facts About:
- In a significant development, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled Urea Gold, a novel fertiliser product, created by Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF), a state-owned entity. This pioneering formulation involves enhancing urea with sulphur to address crucial agricultural challenges.
What is Urea Gold?
- Traditional urea primarily consists of 46% nitrogen (N). Urea Gold represents a leap forward by combining 37% nitrogen and 17% sulphur.
- This innovative composition serves two primary purposes: bolstering soil quality and boosting nitrogen utilization efficiency.
Soil Deficiencies Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE)
- Soil Deficiencies in India
- Indian soils suffer from deficiencies, particularly in key nutrients like sulphur (S).
- This deficiency is particularly crucial for certain crops such as oilseeds and pulses, which play a significant role in India’s agricultural output. These crops require adequate sulphur for healthy growth and optimal yield.
- The deficiency in sulphur can hinder their productivity and affect the overall agricultural landscape.
- Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE) Challenge
- NUE refers to the proportion of applied nitrogen fertilisers that is effectively taken up by crops for growth and yield production.
- Only about 35% of the nitrogen from urea, a commonly used fertiliser, is utilized by crops in India.
- The rest, roughly 65%, is lost through various processes, including ammonia volatilisation into the atmosphere and leaching into the ground as nitrate.
Challenges in Urea Consumption in India
- Import Dependency: India heavily relies on imported urea due to insufficient domestic production. Around 7.6 million tonnes of urea were imported out of the total 35.7 million tonnes sold last fiscal year.
- Feedstock Dependency: The feedstock for domestic urea production, natural gas, is predominantly imported. This adds to the overall import dependence for the fertiliser.
- High Consumption: Urea is India’s most widely used fertiliser, with consumption rising from 26.7 million tonnes to 35.7 million tonnes between 2009-10 and 2022-23.
- Environmental Impact: Excessive urea usage contributes to environmental problems such as air and water pollution. Ammonia emissions and nitrate leaching are associated with these environmental challenges.
- Higher Input Costs: Inefficient fertiliser use due to low NUE leads to higher input costs for farmers. They need to apply more fertiliser to achieve desired yields.
Significance of Urea Gold
- Nutrient Enrichment: Urea Gold is a novel fertiliser fortified with sulphur (S). It contains 37% nitrogen (N) and 17% sulphur, addressing soil deficiencies that are critical for crops like oilseeds and pulses.
- Targeted Improvement: The sulphur content in Urea Gold addresses the specific nutrient requirements of oilseeds and pulses, which are crucial components of Indian agriculture and are significantly import-dependent.
- Packaging and Pricing Shift: Urea Gold’s introduction might entail packaging in 40-kg bags, adapting to the preferences of farmers.While exact pricing remains undisclosed, market trends suggest Urea Gold could be priced between Rs 400 to Rs 500 per 40-kg bag.
- Enhanced NUE: The sulphur-coated urea granules in Urea Gold facilitate a controlled and gradual release of nitrogen. This extended nutrient availability improves NUE, leading to reduced fertiliser application frequency and better crop health.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Urea Gold’s dual focus on addressing soil deficiencies and improving NUE contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices. It reduces excessive fertiliser use and associated environmental impact.
- Economic Benefit: The improved NUE offered by Urea Gold has the potential to reduce input costs for farmers, as they can achieve similar or better yields with lower fertiliser quantities.
- Potential Yield Boost: The sustained nitrogen release mechanism of Urea Gold can potentially lead to increased crop yields due to longer periods of vibrant foliage and enhanced nutrient availability.
Potential Hurdles
- Pricing Uncertainty: Lack of clear pricing details for Urea Gold could impact its adoption among farmers.
- Subsidy Disparity: The current additional rates offered by the government may not sufficiently incentivize companies to promote fortified fertilisers like Urea Gold.
- Limited Farmer Incentives: Farmers might perceive fortified fertilisers as more expensive compared to traditional options, leading to reluctance in adoption.
- Distribution Challenges: Ensuring uniform distribution and application of fortified fertilisers presents logistical complexities.
- Regulatory Influence: Regulatory aspects, such as pricing controls and subsidy structures, can affect the feasibility of fortified fertiliser products.
- Awareness Gap: Limited farmer awareness regarding the benefits and correct usage of fortified fertilisers might hinder their willingness to switch.
- Production Scalability: Scaling up fortified fertiliser production to meet demand and ensure availability poses a significant hurdle.
Way Forward
- Price Rationalization: The government could consider revisiting subsidy rates to make fortified fertilisers economically attractive for both companies and farmers. This would encourage the adoption of innovative products like Urea Gold.
- Subsidy Structure: Tailoring subsidies to reflect the enhanced benefits of fortified fertilisers, such as improved NUE and reduced environmental impact, could encourage their adoption.
- Education Campaigns: Launching awareness campaigns about the advantages of fortified fertilisers, like Urea Gold, can educate farmers and dispel misconceptions about their higher costs.
- Field Demonstrations: Organizing on-field demonstrations of the benefits of fortified fertilisers could provide tangible evidence to farmers, boosting their confidence in making the switch.
- Long-Term Perspective: Encouraging farmers to consider the long-term economic and environmental benefits of fortified fertilisers could shift their focus from initial cost concerns.
- Market Diversification: Exploring partnerships with private sector players and agribusinesses to promote fortified fertilisers could enhance market penetration.
- Gradual Transition: Gradually phasing in fortified fertilisers while continuing to offer traditional options at subsidized rates can ease farmers into adopting the new products.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/how-to-make-urea-more-efficient-as-a-fertiliser-and-why-thats-needed-8891183/
Indian judicial data on bail appeals (The Hindu)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The number of bail appeals filed in India’s High Courts surged post 2020, according to the ‘High Court dashboard’ by DAKSH, a think-tank focussed on law and justice system reforms.
Facts About:
- Bail appeals went up from around 3.2 lakh to 3.5 lakh each year before 2020, to 4 lakh to 4.3 lakh thereafter.
- Consequently, the number of pending bail appeals in High Courts also surged from around 50,000 to 65,000 to between 1.25 lakh to 1.3 lakh.
Reasons for rise in bail appeals post 2020
- One possible reason could be the sharp increase in cases related to the flouting of COVID-19-related lockdown norms during the pandemic.
- At the same time, pending bail cases piled up as the functioning of the courts was compromised during this time.
- The DAKSH ‘High Court dashboard’ explains that in 77% of regular bail cases, it was not possible to ascertain the Act under which the person seeking bail was imprisoned.
- It was not mentioned in the e-courts data of various High Courts. An analysis of 23% of cases in which the Act was mentioned shows that the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897, was ranked fourth, hinting at the possibility of cases surging under this Act as the reason for more bail appeals.
- The database also reveals that the median number of days taken from the filing date to the decision date for regular bail applications was 23. However, for some High Courts, the median days taken for disposal were much higher.
Conclusion
- Delays in resolution have the same effect as denying bail as the accused remains in prison for the duration of their trial,” the DAKSH database argues.
- Finally, data regarding the outcome of bail appeals in High Courts were also missing in many cases. In close to 80% of the disposed bail cases in all High Courts, the outcome of the bail appeal — whether it was granted or rejected — was either unclear, or the outcome was missing.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/data/data-indian-judicial-data-hides-more-than-it-reveals-in-bail-cases/article67198313.ece
What is Luna-25? (The Hindu)
- 12 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Russia is set to launch its first lunar landing spacecraft in nearly half a century on August 11
Facts About:
- It is also designated as the Luna-Glob-Lander which is a Russian lunar lander mission.
- It is targeted to the south polar region of the Moon.
- There are two primary scientific objectives of the mission: to study composition of the polar regolith, and to study the plasma and dust components of the lunar polar exosphere.
- It will take off from the Vostochny cosmodrome.
- Lander structure:
- Luna 25's lander features a four-legged base housing landing rockets and propellant tanks.
- An upper compartment contains solar panels, communication equipment, onboard computers, and scientific instruments.
- Payloads:
- It carries eight science instruments, including gamma-ray and neutron spectrometers, infrared spectrometers, mass spectrometers, and imaging systems.
- Landing Site:
- The primary landing site for Luna 25 is near the lunar south pole, with a reserve site located southwest of the Manzini crater.
- Mission duration:
- It is expected to operate on the lunar surface, studying regolith and exospheric dust and particles, for approximately one year.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/luna-25-failure-roscosmos-implications-moon-base-china/article67218643.ece
MALABAR-2023 (PIB)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Navy's indigenous frontline warships INS Sahyadri and INS Kolkata will participate in Exercise MALABAR 2023.
Facts About:
- The MALABAR series of maritime exercises commenced in 1992 as a bilateral exercise between the Indian Navy and US Navy.
- Japan joined the Naval Exercises in 2015. Malabar 2020 saw the participation of the Australian Navy.
- This year marks the 27th edition of MALABAR which is being hosted by Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and will see participation from the US Navy (USN), Japan Maritime Self Defence Force (JMSDF) and the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).
- INS Sahyadri is the third ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-17 class multi-role stealth frigates.
- INS Kolkata is the first ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-15A class destroyers.
- Both ships have been built at Mazagon Dock Ltd, Mumbai and are fitted with a state-of-the-art array of weapons and sensors to detect and neutralise threats in surface, air and underwater domains.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947436
China’s economy slides into deflation (Economic Times)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Facts About:
China’s recent bout of deflation, marked by a decline in consumer prices for the first time in over two years, has sparked debates about its implications and causes.
- This article delves into the intricacies of deflation, its potential impact on economic growth, and the unique circumstances driving deflation in China.
Understanding Deflation
- Deflation Defined: Deflation refers to a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services within an economy.
- Historical Context: Historically, the terms “inflation” and “deflation” were linked to changes in the money supply, with “inflation” representing a rise and “deflation” a fall in money supply.
Concerns Associated with Deflation
- Economic Slowdown: Many economists view deflation as an indicator of dwindling demand for goods and services, potentially leading to an economic slowdown.
- Demand-Supply Dynamics: Falling prices may prompt consumers to delay purchases, hampering demand and triggering a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Resource Utilization: A certain level of inflation is deemed necessary for optimal resource utilization, ensuring full economic potential is realized.
Varied Perspectives on Deflation
- Positive Instances: Some economies have experienced deflation during periods of robust growth. Japan witnessed increased real income levels despite persistent deflation.
- Economic Crises: Deflation can arise during economic crises when cautious spending and resource reallocation occur.
- Consumer Demand and Prices: Some economists argue that consumer demand dictates prices, rather than the other way around.
China’s Deflation Scenario
- Policy Measures: China’s central bank maintained low interest rates to stimulate demand amid the post-pandemic recovery.
- Property Sector Turmoil: China’s pre-pandemic property sector challenges, affecting GDP contribution, may be a root cause of the current deflationary trend.
- Complex Factors: While liquidity may not be the core issue, comprehensive analysis of money supply and monetary transmission is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Repercussions of Chinese Deflation
[A] Positive Impacts:
- Cheaper Imports: If Chinese goods become cheaper due to deflation, it could lead to lower import costs for India, benefiting consumers and businesses that rely on Chinese imports.
- Lower Input Costs: Reduced prices for raw materials and intermediate goods from China could lower production costs for Indian industries that depend on these inputs.
- Global Supply Chains: If Chinese deflation reduces the cost of production within global supply chains, Indian businesses integrated into these chains might experience cost savings.
- Improved Trade Balance: Cheaper Chinese imports can contribute to a more favorable trade balance for India, especially if it leads to reduced import bills.
[B] Negative Impacts:
- Export Competition: Cheaper Chinese exports due to deflation could increase competition for Indian exports in international markets, potentially affecting certain Indian industries.
- Import Dumping: A flood of cheap Chinese goods into the Indian market could harm domestic producers, leading to job losses and economic strain.
- Investment Flows: A slowdown in China’s economy caused by deflation might lead to reduced investor confidence and affect foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to India.
- Currency Effects: If China’s central bank devalues its currency to boost exports in response to deflation, it could lead to a stronger Indian rupee, impacting India’s export competitiveness.
- Commodity Prices: Reduced demand for commodities from China due to deflation could lead to lower global commodity prices, affecting Indian exporters of raw materials.
Conclusion
- China’s encounter with deflation amidst efforts to boost demand and stabilize its economy presents a multi-faceted challenge.
- Understanding the nuances of deflation, its interaction with demand dynamics, and China’s unique economic landscape are vital.
- As China navigates its path forward, policymakers must consider the interplay of factors, including the property sector’s impact and broader economic goals.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwidya2w1qGBAxVcd2wGHTEWAzQQFnoECC0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fm.economictimes.com%2Fopinion%2Fet-editorial%2Fwhy-chinas-economy-is-down-not-out%2Farticleshow%2F102731901.cms&usg=AOvVaw1udWdqudtF2oR3qve57xGB&opi=89978449
NavIC to link to Aadhaar enrolment devices (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Department of Space (DoS) has told the Parliamentary Committee of Science and Technology that the Navigation with Indian Constellation or (NavIC) is going to be integrated into Aadhaar enrolment devices.
Facts About:
About the merger:
- Need: Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to Global Positioning system (GPS).
- The DoS has conducted successful field trials and is providing technical expertise for the finalisation of procurement specifications for the devices.
- Overall, the integration of NavIC into Aadhaar enrolment devices will enhance navigation accuracy and provide better disaster management capabilities.
- Significance:
- NavIC’s integration will enhance the accuracy and reliability of these devices.
Aadhaar authentication process:
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has been created, with the mandate of providing a Unique Identity (Aadhaar) to all Indian residents.
- The UIDAI provides online authentication using demographic and biometric data.
- Aadhaar authentication is the process involves Aadhaar Number, along with other attributes, including biometrics, is submitted online to the Aadhaar system for its verification on the basis of information or data or documents available with it.
- During the authentication transaction, the resident’s record is first selected using the Aadhaar Number and then the demographic/biometric inputs are matched against the stored data which was provided by the resident during enrolment/update process.
How NavIC will ensure data protection?
- NavIC offers two services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and;
- Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- These two services are provided in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S band (2498.028 MHz).
- NavIC coverage area includes India and a region up to 1,500 km beyond the Indian boundary.
- Newer satellites will have an additional band called L1 that will be compatible with civilian use.
Present NavIC uses:
- The National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) was already utilising NavIC as an alert dissemination system for major natural disasters like landslips, earthquakes, floods, and avalanches.
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information System (INCOIS) relies on NavIC to broadcast cyclones, high waves, and tsunamis alert messages to fishermen venturing into the deep sea.
Organizations working with NavIC data:
- NavIC standards were set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Telecom Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI), Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC), Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), and Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM), International Electrotechnical Committee (IEC), and International Standards Organisation (ISO).
Concerns with GPS or other global systems:
- Threat to data security and sovereignty: System like GPS and GLONASS are operated by defence agencies of the respective nations.
- Breach of personal information: It is possible that the civilian service can be degraded or denied.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/indian-gps-navic-to-link-to-aadhaar-enrolment-devices/article67181022.ece
India, Japan to restart trilateral cooperation with Sri Lanka (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Sri Lanka, India and Japan are studying ways of restarting trilateral cooperation on the East Container Terminal (ECT) project in Colombo.
Facts About:
Exploring New Avenues of Collaboration
- Shared Vision for Indo-Pacific Stability: India and Japan share a vision of a Free Open and Inclusive Indo-Pacific (FOIIP), which they believe benefits all nations in the region. This common vision has provided a basis for renewed cooperation and joint initiatives.
- Potential Areas for Collaboration: The Pathfinder Foundation's paper highlights potential areas of collaboration, including renewable energy projects, grid connectivity, development of Trincomalee as an oil pipeline hub, and people-centric initiatives like tourism and education.
- Joint Economic Vision Statement: Leaders from India and Sri Lanka have issued a Joint Economic Vision Statement, setting the stage for collaborative efforts to catalyze economic growth.
- While governments will play a role in kickstarting projects, they intend to involve the private sector in investment and execution.
- Debt restructuring process:India, Japan, and France's collaborative effort in co-chairing a committee for Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process demonstrates the commitment to stabilizing the country's financial situation. This initiative aims to address debt-related challenges and foster economic recovery.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Balancing Interests and Lessons from the Past: Officials acknowledge the challenges faced in executing joint projects, given past setbacks. The need to align interests and strategies between India, Japan, and Sri Lanka remains a crucial factor in determining the success of future collaborations.
- Toward a Resilient Indo-Pacific Partnership: Japan underscores the significance of Japan's partnership with India and Sri Lanka in realizing a Free and Open Indo-Pacific.
- Japan emphasizes creditor parity, transparency, and debt sustainability in Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process.
- Role of China: China's involvement in Sri Lanka's infrastructure projects and its status as the country's largest bilateral lender add complexity to the trilateral dynamics. China's investments in Sri Lanka have prompted concerns about debt sustainability and transparency.
- While India and Japan aim to include China in the creditors' platform for Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process, China's decision to remain an observer highlights the complexities of fostering inclusive cooperation.
Conclusion
The revival of trilateral cooperation marks a crucial step toward promoting stability and development in the Indo-Pacific region. By overcoming challenges and leveraging their collective strengths, India, Japan, and Sri Lanka have the potential to contribute to a more interconnected and prosperous future for the region.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-japan-look-to-restart-trilateral-cooperation-with-sri-lanka-but-with-caution/article67180586.ece
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Kerala Legislative Assembly has unanimously adopted a resolution expressing its concern over the Union Government move to impose a Uniform civil code (UCC).
Facts About:
- The Kerala Assembly resolution essentially strikes a cautious note that a proposed “UCC could harm the secular nature of the country. “
- The resolution also talks about federalism – that the Centre could make a unilateral move on the contentious issue without consulting states.
- The resolution also argued that, it is critical to note that the Uniform Civil Code was limited to Directive Principles.
What does Constitution say about UCC?
- The Constitution refers to civil code only in its Directive Principles.
- Implementation of Directive Principles is not mandatory.
- The court may order to enforce Fundamental rights. But the Directive Principles of Article 44 of the Constitution cannot be enforced even by the courts.
Can the state legislate on UCC?
- Article 162 of the Constitution:
- The issue of personal laws falls in List III —the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution.
- While subjects in the Union lists fall within the purview of the Parliament, states can legislate on subjects in the State List.
- For entries in the ‘Concurrent List’, Article 162 of the Constitution gives state governments the power to legislate on subjects where a central law does not occupy the field.
- If there is a central law, it automatically gains precedence over the state law on the subject.
- Entry 5 of Concurrent List:
- Also the Entry 5 of the Concurrent lists “Marriage and divorce; infants and minors; adoption; wills, intestacy and succession; joint family and partition; all matters in respect of which parties in judicial proceedings were immediately before the commencement of this Constitution subject to their personal law.
- This allows states the power to legislate on the subject but only in the absence of a central law.
Do states can bring their own personal laws again?
The answer to it is NO, due to following cases;
- State laws on the issues mentioned in Entry 5 of the Concurrent List will not have precedence over central legislation.
- On specific areas not covered by central legislation, states can legislate.
- But central legislation already covers all aspects of marriage, divorce, inheritance and succession.
Supreme Court’s stand:
- The Court mentioned that Article 162 of the Constitution indicates that the executive power of a State extends to matters with respect to which the Legislature of the State has power to make laws.
- In view of the provisions of Entry 5 of the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule, the constitution of a Committee per se cannot be challenged as ultra vires.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/kerala-assembly-resolution-against-uniform-civil-code-8885558/#:~:text=The%20Kerala%20Legislative%20Assembly%20on,a%20common%20personal%20law%20code.
Bill on Election Commission members’ Appointments (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Bill is set to be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with the view of overturning the effect of the Supreme Court’s (SC) verdict on the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
Facts About:
- The Bill seeks to establish a committee of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Current Procedure: Currently, the Law Minister suggests a pool of suitable candidates to the Prime Minister for consideration.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the PM.
- As per the Bill, a Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary and comprising two other members, not below the rank of Secretary to the government, having knowledge and experience in matters relating to elections, shall prepare a panel of five persons who can be considered for appointment.
- Then, as per the Bill, a Selection Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister will appoint the CEC and other ECs.
Present structure to appoint CEC and ECs:
- Under Article 324 (2), the President appoints the CEC and other ECs.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
- The Constitution does not prescribe any qualifications, academic or otherwise, for appointment to these offices.
- Tenure:
- The tenure of office and the conditions of service of all the commissioners is determined by the President.
- The tenure of commissioners is 6 years or up to the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CEC and the two other ECs have the same powers and emoluments, including salaries, which are the same as a Supreme Court judge.
- All three commissioners have the same right of taking a decision. In case of a difference of opinion amongst the three members, the matter is decided by the Commission by a majority.
Process of removal:
- Article 324 of the Constitution of India mentions the provisions to safeguard and ensure the independent and impartial functioning of the Election Commission.
- The CEC is provided with security of tenure. He cannot be removed from his office except in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Any other election commissioner or a regional commissioner cannot be removed from office except on the recommendation of the CEC.
Supreme Courts’ Judgment:
- On March 2, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court unanimously ruled that a high-power committee consisting of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India must pick the CEC and ECs.
- The judgement by a bench came in 2015, challenging the constitutional validity of the practice of the Centre-appointed members of the Election Commission.
- According to the judgement, the SC has now given the Opposition and the judiciary a say in the matter, ruling that the CEC and ECs must be appointed by the President on the advice of a committee comprising the PM, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
- Also, in 2018, a two-judge bench of the SC referred the case to a larger bench since it required a close examination of Article 324 of the Constitution, which deals with the role of a Chief Election Commissioner.
Debate around appointment of CEC and ECs:
- Article 324(2) reads that “The Election Commission shall consist of the Chief Election Commissioner and such number of other Election Commissioners, if any, as the President may from time-to-time fix and the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners shall, subject to the provisions of any law made in that behalf by Parliament, be made by the President.”
- The Parliament has the power to nullify the effect of a Court ruling by addressing the concerns flagged in the judgment.
- In this case, the arrangement prescribed by the Supreme Court was specifically because the Court noted that there was a “legislative vacuum.” Filling that vacuum is well within the purview of the Parliament.
- However, the idea of an independent body that conducts elections permeates through the judgement.
- The Court repeatedly stated that to be the objective of the framers of the Constitution.
- The composition of the Selection Committee in the Bill raises questions on whether the process is now independent or still rigged in favour of the Executive.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/bill-election-commission-members-appointment-process-explained-8885676/#:~:text=The%20Centre%27s%20Bill%20seeks%20to,Commission%20of%20India%20(ECI).
Consultative Committees (PIB)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the government was asked about the constitution of consultative committees for the year 2023-24.
Facts About:
Consultative Committees.
- These committees are constituted by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs. Consultative Committees of different ministries are not constituted year wise.
- As per Guidelines on Constitution, Functions and Procedures of Consultative Committees, Consultative Committees shall be constituted upon constitution of each Lok Sabha.
- For 17th Lok Sabha, 40 Consultative Committees have so far been constituted.
- The maximum membership of a Consultative Committee should be limited to forty. In addition, a maximum of four Members from both Houses can also be nominated as Permanent Special Invitees. The minimum membership of the Consultative Committee shall be ten.
- There is no requirement of presence of a minimum number of Members to constitute the quorum for holding meetings of Consultative Committees.
- The Minister concerned with each Ministry/Department shall preside over the meeting of the Consultative Committee attached to his/her Ministry.
- Functions: Consultative committees provide a forum for informal discussions between the ministers and the members of Parliament on policies and programmes of the government and the manner of their implementation
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947060
Small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs) (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The recent increase in coal consumption, despite the increase in solar and wind power, suggests that reliable and low-carbon electricity resources are critical to ensure the deep decarbonisation of power generation, along with grid stability and energy security.
Small modular reactors – a type of nuclear reactor – can be helpful to India in this regard.
Facts About:
Sources of Energy Production:
- India’s Energy sector is one of the most diversified in the world. Sources of power generation range from conventional sources such as coal, lignite, natural gas, oil, hydro and nuclear power, to viable non-conventional sources such as wind, solar, agricultural and domestic waste.
- India was ranked fourth in wind power, fifth in solar power and fourth in renewable power installed capacity, as of 2020.
- Near-universal household access to electricity was achieved in 2019, meaning that over 900 million citizens have gained an electrical connection in less than two decades.
- But, the per capita electricity consumption in India is only one-third of the global average, even though the demand for energy has doubled.
- So, to catch up with the increasing demand for energy, there is a need to make arrangements for a secure and sustainable form of self-reliance in the energy sector.
What are Small Modular Nuclear reactors (SMRs)?
- Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW (e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- SMRs, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity using:
- Small– physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
Conventional Nuclear power plants vs. Small modular reactors:
- Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs) are efficient users of land and their grid integration costs are lower than those associated with variable renewable energy (VRE) sources because NPPs generate power 24x7 in all kinds of weather.
- As an alternative, several countries are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) – nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW – to complement conventional NPPs.
- SMRs can be installed in decommissioned thermal power plant sites by repurposing existing infrastructure, thus sparing countries from having to acquire more land and/or displace people beyond the existing site boundary.
- SMRs can be safely installed and operated at several brownfield sites that may not meet the more stringent zoning requirements for conventional NPPs.
Need for SMRs:
- According to the International Energy Agency, the demand for critical minerals like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements, required for clean-energy production technologies, is likely to increase by up to 3.5x by 2030.
- This jump poses several global challenges, including the large capital investments to develop new mines and processing facilities.
- The environmental and social impacts of developing several new mines and plants in China, Indonesia, Africa, and South America within a short time span, coupled with the fact that the top three mineral-producing and -processing nations control 50-100% of the current global extraction and processing capacities, pose geopolitical and other risks.
Advantages of SMRs:
- SMRs are designed with a smaller core damage frequency (the likelihood that an accident will damage the nuclear fuel) and source term (a measure of radioactive contamination) compared to conventional NPPs.
- They also include enhanced seismic isolation for more safety.
- SMR designs are also simpler than those of conventional NPPs and include several passive safety features, resulting in a lower potential for the uncontrolled release of radioactive materials into the environment.
How nuclear reactors can lead to sustainable energy generation?
- Accelerating the deployment of SMRs under appropriate international safeguards, by implementing a coal-to-nuclear transition at existing thermal power-plant sites, will take India closer to net-zero and improve energy security because uranium resources are not as concentrated as reserves of critical minerals.
- Most land-based SMR designs require low-enriched uranium, which can be supplied by all countries that possess uranium mines and facilities for such enrichment if the recipient facility is operating according to international standards.
- Further, serial manufacture of SMRs can reduce costs by simplifying plant design to facilitate more efficient regulatory approvals and experiential learning with serial manufacturing.
What are the initiatives to Achieve Self-reliance in the Energy Sector?
- Gas Based Economy
- Blending of Ethanol in Petrol
- Prime Minister UjjwalaYojana
- Renewable Energy Initiatives
- National Hydrogen Mission
Way forward:
- The aspects like investment, infrastructure development, private-public partnership, green financing, policy framework need to be strengthened both at the national level and regional level to cater to inclusiveness in the development process.
- Green energy has tremendous potential in contributing to income, employment, and entrepreneurship and undoubtedly fosters sustainable development.
- In addition to job and income generation, it opens up opportunities/avenues for investment and markets for new products and services. So, India should focus on achieving green energy and self-reliance in the Energy Sector together.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/small-modular-reactors-india-nuclear-power-net-zero/article67175626.ece
Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The number of elephants in Karnataka has increased according to an interim report on Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates, 2023.
Facts About:
- It was reported by “Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates, 2023”.
- The population range for elephants in Karnataka is estimated to bebetween (5,914 - 6,877).
- The report was officially released by Karnataka’s Forest Minister, ahead of World Elephant Day, which is observed on August 12 to raise awareness about the importance of protecting these endangered animals.
- The report was the result of a synchronised elephant census conducted from May 17 to 19, involving the Forest Department of Karnataka and neighbouring states including Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Goa.
- Among the different regions, the Bandipur Tiger Reserve stands out with the highest elephant density of 1,116 elephants and a density of 0.96 elephants per square kilometre.
The Nagarahole Tiger Reserve follows closely with 831 elephants and a density of 0.93 elephants per square kilometre.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/number-of-elephants-in-state-goes-up-by-364-from-last-census-touching-6395/article67176333.ece
Belem Declaration (Down to Earth)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The eight countries that make up the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) signed the Belém Declaration during the Amazon Summit.
Facts About:
- The leaders focused on initiating a dialogue about the sustainability of mining and fossil fuel-related activities but failed to commit to stopping oil drilling in the region.
- This lack of consensus has implications for global biodiversity goals, including those set under the Convention on Biological Diversity’s Global Biodiversity Framework in 2022, where countries agreed to protect 30% of land and sea by 2030.
About Belem Declaration:
The Belem Declaration is a statement released during the Amazon Summit, involving leaders from Amazon countries.
- It emphasizes the importance of Indigenous knowledge for biodiversity conservation and calls for Indigenous Peoples’ participation in decision-making.
- The declaration promotes sustainable forest use and diverse economic solutions, addressing concerns about deforestation and degradation in the Amazon region.
- It also underlines the need to protect land rights to prevent deforestation and preserve biodiversity within Indigenous territories.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/forests/belem-declaration-amazon-countries-fail-to-agree-on-protection-goals-91095
Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India is all set to get its own car crash safety star rating from Oct 1, 2023
Facts About:
What is Bharat NCAP?
- Bharat NCAP is a new car safety assessment programme which proposes a mechanism of awarding ‘Star Ratings’ to automobiles based upon their performance in crash tests.
- BNCAP standard is aligned with global benchmarks and it is beyond minimum regulatory requirements.
- The proposed Bharat NCAP assessment will allocate Star Ratings from 1 to 5 stars.
- The testing of vehicles for this programme will be carried out at testing agencies, with the necessary infrastructure.
Its implementation
- BNCAP will be rolled out from April 1, 2023.
- It will be applicable on type-approved motor vehicles of category M1 with gross vehicle weight less than 3.5 tonnes, manufactured or imported in the country.
- M1 category motor vehicles are used for the carriage of passengers, comprising eight seats, in addition to driver’s seat.
Significance of Bharat NCAP
- BNCAP rating will provide consumers an indication of the level of protection offered to occupants by evaluating the vehicle in the areas of:
- Adult occupant protection
- Child occupant protection
- Safety assist technologies
- It will serve as a consumer-centric platform, allowing customers to opt for safer cars based upon their Star-Ratings.
- It will also promote a healthy competition among original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in India to manufacture safer vehicles.
- It will ensure structural and passenger safety in cars, along with increasing the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
- It will prove to be a critical instrument in making our automobile industry Aatmanirbhar.
Why does India need to crash-test vehicles?
- Indian vehicles have historically not been crash-tested in the country.
- Despite being home to only 1% of the world’s vehicles, India shoulders 11% of the global road crash fatality burden.
What about existing testing standards?
- India’s Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR) mandate a safety and performance assessment, including a basic conformity crash test by agencies like the ARAI and ICAT when vehicles go in for type approvals.
- However, this does not involve a crash test rating.
- Many international automakers have been found to sell products in India which score much lower on safety and structural performance parameters.
- This is done to reduce costs in the price-sensitive Indian market.
- However, safety is moving up nowadays the list of key purchase criteria in India as well.
How will a homegrown NCAP help?
- Global NCAP (GNCAP) crash tests for many best-selling Indian vehicles have dismal ratings, many of them rated zero in a bias.
- The government hopes that by facilitating these tests by in-house agencies, more automakers will voluntarily undergo safety assessments and build vehicles that hold up to global standards.
How will it compare with GNCAP?
- The government wants the two tests to be in congruence with each other.
- It intends to design the?BNCAP?to?resemble?the GNCAP, the global gold standard, as closely as possible, including the speed for crash testing at 64kmph.
- Central Motor Vehicle rules encompass standards with?respect?to pedestrian protection and seat belt reminders among others and will be retained in the testing under the BNCAP.
- The government hopes the move will increase the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/explained-what-is-the-bharat-new-car-assessment-programme/article67228536.ece
India takes first step to remove animals from Drug-testing (Indian Express)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an amendment to the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules (2023) passed by the Government of India, aims to replace the use of animals in research, especially in drug testing.
Facts About:
What is the reason behind shifting to Alternative testing modes?
- The drug development journey involves rigorous testing to assess the efficacy and unintended effects.
- The first step of this process has been to test the candidate molecule in at least two animal species: a rodent (mouse or rat) and a non-rodent, such as canines and primates
- Lack of accuracy: Human response is influenced by factors like genetics and diet, leading to a significant mismatch between animal models and human responses.
- This mismatch contributes to the high failure rate during human clinical trials, highlighting the need for more accurate testing methods.
- Animals cannot consent to their own participation in research.
- Welfare of animals: Critics argue that animal testing can cause suffering and harm to animals. Animals are held in sterile, isolated cages, forced to suffer disease and injury, and typically euthanized at the end of each study.
What are Alternative testing modes?
- Organoids: These technologies encompass three-dimensional cellular structures, known as "organoids" or "mini-organs," which closely replicate the functions of specific body organs at a miniature scale.
- Organ-on-a-chip: The "organ-on-a-chip" technology employs small chips with human cells and microchannels to simulate physiological processes.
- organ-on-a-chip are AA-battery-sized chips lined with human cells connected to microchannels, to mimic blood flow inside the body.
- Additive manufacturing: 3D bioprinters use human cells as 'bio-ink' to build tissues. This could help make personalized drug tests and change how we create drugs.
What are Global regulatory frameworks that have adopted non-animal methods to test the effect and potential side-effects of new drug candidates?
- European Union: In 2021, the European Union adopted a resolution for an action plan promoting non-animal technologies in research, regulatory testing, and education.
- USA: The U.S. passed the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 in December 2022, permitting the use of these methods for drug safety and efficacy testing.
- South Korea: South Korea introduced a Bill for advancing alternatives to animal testing in December 2022.
- Canada: In June 2023, Canada amended its Environmental Protection Act to minimize vertebrate animal use in toxicity testing.
India
- In March 2023, the Indian government incorporated non-animal alternatives for drug testing and development into the drug development process by modifying the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019.
- This step followed public input and consultation with the Drug Technical Advisory Board, which advises governments on drug-related technical issues at both the Central and State levels.
What are the challenges with these alternate methods?
- Multidisciplinary: Developing an organ-on-a-chip system requires multidisciplinary knowledge in the fields of cell biology, materials science, fluid dynamics, electronics, engineering, and pharmacology/toxicology to accurately replicate organ behavior and assess drug effects.
- At present there is a lack of focused training and expertise in India.
- Dependence of Imports: Most of the reagents, cell-culture related materials, and instruments for these technologies are currently imported from the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
- Managing Complexity: Researchers simplify recreating human tissues in the lab by minimizing components for disease simulation.
- No universal approach due to disease-specific variations; for example, a liver-on-a-chip won't fit all liver diseases.
- Variability arises from differences in lab protocols, expertise, and specific research goals. Regulators express concerns about data consistency due to these variations.
Suggestions
- Establishment of specialized institutes: Recently, a meeting organized by the Centre for Predictive Human Model Systems and Humane Society International India called for the need of specialized institutes similar to the Wyss Institute.
- WyssInsitute in Boston is a dedicated center that focuses on innovations that emulate human biology.
- The dedicated institute will facilitate effective communication and collaboration across various fields.
- Promoting innovation: Developing a comprehensive and self-sustaining ecosystem in India to address this gap in the fields of cell culture, material science, and electronics.
- Guidelines: Urgent need for guidelines establishing minimal quality criteria and standards for these systems.
- Existing guidelines on animal testing requirements need re-evaluation and updating to accommodate advancements in cell-based and gene-editing therapies.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/animal-trials-drug-development-india-amendment-2019-rules/article67019288.ece
ECOWAS and Niger Coup: Challenges and Potential Responses (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Context: Recently there was apprehension of intervention by the ECOWAS( Economic Community of West African States) in Niger following a military coup in the country.
Facts About:
- The recent coup in Niger has brought the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) into the spotlight as it grapples with responding to the political crisis in the region.
- As Niger faces economic hardships and military intervention by regional players looms, the role of ECOWAS is under scrutiny.
Understanding ECOWAS
- Formation and Membership: Established in 1975, ECOWAS aims to foster economic integration among its 15 member countries, including Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Nigeria, and more.
- Objective: The organization envisions a borderless region based on democratic principles and good governance.
- Economic Goals: ECOWAS seeks to create a unified trading bloc, single currency, and enhanced cooperation in sectors such as industry, energy, and telecommunications.
ECOWAS in Conflict Resolution
- Regional Peacekeeping: ECOWAS has played a role in resolving conflicts by deploying peacekeeping missions. Notable examples include ECOMOG’s involvement in Liberia and Sierra Leone during the 1990s and early 2000s.
- Gambia Crisis: In 2017, ECOWAS intervened in Gambia, ensuring the peaceful transfer of power after then-President Yahya Jammeh refused to step down following an election defeat.
- Challenges and Successes: While ECOWAS has effectively resolved conflicts in some cases, it faces challenges due to differing interests among member countries and evolving security threats.
ECOWAS’s Response to Niger Coup
- Potential Military Intervention: ECOWAS has hinted at possible military intervention in Niger. However, regional challenges, including shared borders with other military-led nations, could complicate intervention plans.
- Support for Coups: Some military coups in West Africa have been justified by leaders citing terrorism and security challenges, accusing civilian governments of inadequacy.
- Security Situation: The ECOWAS Commission President reported a significant rise in terrorist attacks in the region, with a substantial death toll and refugees fleeing the violence.
Economic Measures and Sanctions
- Economic Sanctions: ECOWAS has previously imposed economic sanctions on countries undergoing political turmoil. However, the efficacy of these measures is questionable, especially when nations are grappling with economic difficulties.
- France’s Role: France’s historical ties to Niger and the presence of foreign troops have fueled local sentiments against foreign involvement, creating complexities for potential interventions.
Challenges and Dilemmas
- Leadership Dynamics: The current chairman of ECOWAS, Nigerian President Bola Ahmed Tinubu, advocates for military intervention in Niger. However, internal opposition and conflicting interests within ECOWAS member states complicate decision-making.
- Complexity of the Situation: The unique circumstances of each nation undergoing turmoil require tailored responses. The Niger coup’s leader, Gen. Abdourahmane Tchiani, has a history with ECOWAS peacekeeping missions.
Conclusion
- ECOWAS’s response to the Niger coup underscores the complexity of regional dynamics, the challenges of military intervention, and the delicate balance between security and democratic governance.
- As the organization grapples with finding an effective solution, its role as a mediator and peacekeeping force in West Africa continues to evolve in response to the changing geopolitical landscape.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/ecowas-west-africa-niger-coup-explained-8882492/
State of Elementary Education in Rural India Report (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan launched the first State of Elementary Education in Rural India report.
Facts About:
Key Highlight of the Report:
Pan-India survey was conducted by the Development Intelligence Unit (DIU), across 6,229 rural households in 20 states, focussing on 6 to 16-year-old children in rural communities.
Equality Among Gender: Parents from rural communities believe that a child’s gender, whether a boy or a girl, should not hinder their educational aspirations.
- Total of 78 percent of parents of girls and 82 per cent of parents of boys wanted to educate their children to graduation and above.
Parental participation: About 84 percent of parentsregularly attend parent-teacher meetings, demonstrating their active involvement in their children’s education.
Role of Parents: Majority of children (62.5 per cent) are under the supervision of their mothers when it comes to their studies, while 49 per cent are supervised by their fathers.
- Over 38 per cent of parents opt for private tutors to further enhance their children’s education.
- About 26 per cent of the children study under the supervision of a private tutor.
Drop Outs: Out of the total dropped-out children, around one-fourth of male children discontinued their education during primary schooling, due tolack of interest in studies.
- Dropout rate for female children is high at 35 per cent, due to the need to contribute to the family’s earnings.
- A higher proportion of both boys and girls dropped out of school after completing the primary school education (75 per cent for boys and 65 per cent for girls).
Increased access to smartphones: Nearly half, 49.3 percent of students in rural India have access to smartphones.
- 76.7 percent of these students primarily use their phones for entertainment purposes, such as playing video games and watching movies.
- Only 34 percent of smartphone-accessible students use their devices for study-related downloads, while 18 percent access online learning through tutorials.
Learning Environment at Home: 40 percent of parents have age-appropriate reading materials available at home, beyond school books.
- Only 40 percent of parents engage in daily conversations with their children about their school learning, while 32 percent have such discussions a few days a week.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/education/78-parents-in-rural-india-want-their-daughters-to-study-till-graduation-and-beyond-report-8885528/#:~:text=in%20family's%20earnings.- ,According%20to%20the%20survey%2C%20one%2Dfourth%20of%20male%20children%20dropped,after%20completing%20primary%20school%20education.
Gita Mittal Committee (The Hindu)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Supreme Court panel flags reconstruction of lost essential documents of victims as the first healing step in Manipur.
Facts About:
The Committee
- The committee was constituted to supervise, intervene and monitor relief and rehabilitation, restoration of homesteads, religious places of worships, better relief work, etc. in Manipur.
- The committee is led by former Jammu & Kashmir High Court Chief Justice Gita Mittal, the committee includes Justices (retd) Shalini P Joshi and Asha Menon.
- This move aims to oversee various aspects beyond the investigation, such as relief, rehabilitation, and compensation for those affected by the violence.
- The committee's role extends beyond investigation, encompassing vital aspects of recovery and rebuilding.
- The primary goal behind the committee is to restore public confidence, reinforce faith in the rule of law, and rebuild trust within the affected community.
- The committee has filed three separate reports in the Supreme Court after meeting stakeholders on August 19.
The Reports
- First report – The first of the three reports submitted by the committee highlights the loss of essential documentation of the residents of Manipur who have been dis-housed.
- The committee suggests the appointment of a nodal officer to take charge of the reconstruction of these documents.
- Second report – The committee’s second report raised concerns on the Manipur Victim Compensation Scheme (MVCS).
- The committee says the MVCS needs to be substantially improved.
- The MVCS should be in the same league as the schemes framed by the National Legal Services Authority (NLSA).
- Third Report – The committee submitted a proposal for appointment of domain experts to facilitate its work.
Manipur Victim Compensation Scheme (MVCS)
- Victim Compensation Scheme (VCS) – Compensation to persons groundlessly arrested is under Section-358.
- The Government introduced the Central Victim Compensation Fund (CVCF) Scheme to enable support to victims of rape, acid attacks, human trafficking, women killed or injured in cross border firing.
- The Manipur scheme – It provides that if a victim of violence has received benefits under any other scheme, then they would not receive any compensation under the state victim compensation scheme.
- NALSA scheme – The benefit received under other schemes would be taken into consideration while determining the extent of benefits that would be additionally provided to the victims of violence.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/manipur-violence-supreme-court-to-pass-orders-on-august-25-to-facilitate-proper-functioning-of-justice-mittal-panel/article67218800.ece#:~:text=A%20Supreme%20Court%2Dappointed%20committee,taken%20to%20nurse%20the%20Stat
Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 (PIB)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Rajya Sabha approved the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation Amendment) Bill, 2023 which seeks larger participation of the private sector in mineral exploration and production, including that for sought-after lithium.
Facts About:
Key-highlights of the Bill
The Bill amends the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957. The Act regulates the mining sector.
Out of restrictions: The reform initiative in the Bill brings lithium out from the list of restrictive atomic minerals where permission to mine could only be granted by the Centre to government companies.
Welcomed private players: The change would allow auction of this critical mineral, used extensively for making batteries for electric vehicles, by the private sector.
Forestry clearance process: The amendment Bill will also dispense with the cumbersome forestry clearance process for mine reconnaissance and prospecting operations, making it easier for the private sector to participate in exploration of the country’s mineral resources.
Auction power: The Bill empowers the central government to exclusively auction mining lease and composite exploration licence for certain critical high value minerals such as gold, silver, platinum and copper.
Exploration licence: One of the major reforms proposed in the Bill is to introduce exploration licence for deep-seated and critical minerals. The exploration licence granted through auction will allow the licencee from private sectors to undertake “reconnaissance” and prospecting operations for critical and deep-seated minerals.
Composite mineral licence: The reform proposals in the amendment legislation also include allowing states to grant composite mineral licence without having to get central nod.
Fixing mineral-wise maximum area: It will also raise and fix mineral-wise maximum area limits for mineral concessions to provide larger and economically viable mines to investors.
- For prime minerals such as iron ore, the maximum area for prospecting licence and mining lease has been doubled to 50 sq. km and 20 sq. km respectively.
- This would allow private entries to get same land area for mining as was earlier being given to government companies and that also by the state governments itself without any need for central approval.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are elements that are the building blocks of essential modern-day technologies, and are at risk of supply chain disruptions.
- These minerals are now used everywhere from making mobile phones, computers to batteries, electric vehicles and green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines.
- Based on their individual needs and strategic considerations, different countries create their own lists.
Recent government interventions
Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): India joined Mineral Security Partnership (MSP),a US-led collaboration that aims to catalyse public and private investment in critical mineral supply chains globally.
- The MSP includes Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, UK, the European Commission, Italy, and now India.
Identification of critical minerals: Recently, the Centre has identified ‘30 critical minerals’, which are essential for the country’s economic development and national security.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947213
The Coastal Aquaculture Authority (Amendment) Bill 2023 (PIB)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Government has recently introduced the Coastal Aquaculture Authority (Amendment) Bill 2023 to promote ease of doing business.
Facts About:
What is Coastal Aquaculture?
- Coastal aquaculture refers to culturing or cultivating, under controlled conditions in ponds, pens and enclosures or in coastal areas of shrimp, prawn, fish or any other aquatic life in saline or brackish water.
- Coastal aquaculture does not include freshwater aquaculture.
What is the Coastal Aquaculture Authority Act 2005?
- Coastal Aquaculture Authority - The Act introduced the Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA).
- The main objective of the Authority is to regulate coastal aquaculture activities in coastal areas in order to endure sustainable development without causing damage to the coastal environment.
- The authority consists of a Chairperson who is a current or former HC judge being an expert in coastal aquaculture.
- The members will be nominated by the
- Central Department of Ocean Development
- Ministry of Environment and Forests
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Commerce
- 4 members representing coastal States on a rotation basis and one member secretary.
- Coastal area - It refers to the area declared as the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ), and includes such other area as the Central Government may notify under Environment Protection Act 1986.
What are the new provisions of the amendment bill 2023?
- Definition - It broadens the definition of coastal to include rearing and cultivation of any life stages of fish including crustacean, mollusc, finfish, seaweed or any other aquatic life.
- Environment friendly - It encourages environment friendly aquaculture such as cage culture, seaweed culture, bi-valve culture, marine ornamental fish culture and pearl oyster culture.
- It has the potential for creating employment opportunitiesfor coastal fisher communities especially fisherwomen.
- Brood stocks - It encourages the establishment of facilities in areas having direct access to seawater to produce genetically improved and disease-free brood stocks and seeds for use in coastal aquaculture.
- Brood stock or brood fish are a group of mature individuals used in aquaculture for breeding purposes.
- Brood Stock Multiplication Centre - The center will be used to rear marine organisms under strict biosecurity and disease surveillance.
- Usage of antibiotics - The Bill seeks to prevent the use of antibiotics and pharmacologically active substances which are harmful to human health in coastal aquaculture.
- Biosecurity - It introduces measures for analyzing and preventing the risk of introducing or spreading harmful organisms like viruses and bacteria within the coastal aquaculture unit.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947213
Mediation Bill, 2023 (Live law)

- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Parliament has passed the Mediation Bill 2023 to reduce pendency of court cases.
Facts About:
The Mediation Bill, 2021
- It was introduced in the Rajya Sabha in December, 2021, with the Parliamentary Standing Committee being tasked with a review of the Bill.
- The Bill aims at institutionalising mediation and establishing the Mediation Council of India.
Key Features of the Bill
Pre-litigation mediation
- Parties must attempt to settle civil or commercial disputes by mediation before approaching any court or certain tribunals.
- Even if they fail to reach a settlement through pre-litigation mediation, the court or tribunal may at any stage refer the parties to mediation if they request for the same.
Disputes not fit for mediation
- The Bill contains a list of disputes which are not fit for mediation.
- These include disputesrelating to claims against minors or persons of unsound mind, involving criminal prosecution, and affecting the rights of third parties. The central government may amend this list.
Applicability
- The Bill will apply to mediations conducted in India:
involving only domestic parties
involving at least one foreign party and relating to a commercial dispute (i.e., international mediation)
if the mediation agreement states that mediation will be as per this Bill.
- If the central or state government is a party, the Bill will apply to commercial disputes, and other disputes as notified.
Mediation process
- Mediation proceedings will be confidential, and must be completed within 180 days (may be extended by 180 days by the parties).
- A party may withdraw from mediation after two sessions.
- Court annexed mediation must be conducted as per the rules framed by the Supreme Court or High Courts.
Mediators
- Mediators may be appointed bythe parties by agreement, a mediation service provider (an institution administering mediation).
- They must disclose any conflict of interest that may raise doubts on their independence.
- Parties may then choose to replace the mediator.
Concerns Highlighted by the Parliamentary Standing Committee
Pre-Litigation
- The panel highlighted many key issues including mandatory and coercive nature of pre-litigation mediation.
- Making pre-litigation mediation necessary may result in case delays and provide another instrument in the hands of truant litigants to prolong case disposition.
Clause 26: The panel was against Clause 26of the draft which gives power to the SC or the High court to make laws of pre-litigation according to them.
Non-Applicability to Non-Commercial Disputes: The members questioned the non-applicability of the provisions of the Bill to disputes/matters of non-commercial nature involving the Government and its agencies.
Appointments: The panel had discussions about the qualifications and appointment of the Chairperson and Members of the proposed Mediation Council.
Recommendations Accepted by the Union Cabinet
Reducing the Time for Concluding a Mediation
- The Union cabinet has accepted the recommendations of the standing committee by reducing the time for concluding a mediation from 180 to 90 days.
Making Pre-Litigation Mediation Voluntary
- The recommendation for making pre-litigation mediation voluntary instead of mandatory was also much needed as voluntariness is an essential principle of mediation.
Recognition and Enforcement of Agreements
- Recognition and enforcement of settlement agreements arising out of mediation is a welcome move.
- This is also in line with India’s commitment as a signatory to the United Nations Convention on International Settlement Agreements Resulting from Mediation (Singapore Convention).
Provisions of the Final Bill that Require a Relook
Limited Grounds to Challenge a Settlement Agreement
- The limited grounds listed to challenge the enforcement of a settlement agreement and the fact that a period of 90 days is given to raise the challenge need a relook.
- The fact that a settlement agreement is essentially a contract between the parties; there are several instances where grounds for challenge such as fraud and impersonation are detected at a later stage.
Technical Flaws in Clause 8
- Clause 8 of the Bill entitles a party to move the Court before the commencement or during mediation for interim relief but only in “exceptional circumstances”.
- The term “exceptional circumstances”is not only undefined in the Bill but is also abnormal to the settled principles of seeking interim relief before the civil courts.
- Moreover, there is no remedy of appeal available against an order passed under this proposed section.
The Concept of Online and Community Mediation
- A recent Niti Aayog report reveals that only 55 per cent of India have access to the internet and only 27 per cent possess compatible devices.
- For online mediation to be a success, the government will have to scale the bandwidth accessibility to remote parts of the country.
- As for community mediation, the Bill makes it mandatory to have a panel of three mediators.This requirement is unnecessary and impinges on the flexibility that mediation brings.
Restricting the Government’s Participation in Mediation to only Commercial Disputes
- The real issue is that the government is the biggest litigant in the country.
- Restricting the ability of the government to participate in mediation proceedings arising only out of commercial disputes goes against the objective of enacting the legislation.
Way Forward
Legal Aid Setup: Setting up legal aid or access to justice clinics with adequate IT infrastructure could address the issue of online mediation.
Inclusion of Government Related Disputes in the Bill
- The standing committee had also recommended that government-related disputes be included in the Bill.
- The common litigant sees the government as an adversary before the court of law. The Bill provided a golden opportunity to the government to change that perception.
- This will inspire confidence amongst all stakeholders but would also help in reducing pendency backlog.
Conclusion
Mediation should be promoted as a preferred and voluntary mode of securing justice.
Although the legislature may have intended to lighten the load on the judiciary, the law needs to be improved because it may cause a delay in the administration of justice and raise the cost of litigation.
Source: https://www.livelaw.in/news-updates/parliament-passes-mediation-bill-234671
River Devika Rejuvenation Project (PIB)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology sheds light on the progress of the River Rejuvenation Project, Devika. This initiative, inspired by the Namami Ganga campaign, aims to safeguard the sacred Devika River’s purity and health.
Facts About:
Comprehensive Waste Management:
- Focus on Liquid Waste Management.
- Creation of a network of pipes and manholes connecting households.
- Objective: Efficient disposal of liquid waste, preventing pollution, and preserving the sanctity of the river.
Complementary Solid Waste Management:
- Encompasses responsible collection, disposal, and management of solid waste.
- Essential to prevent environmental degradation and maintain river and surrounding health.
Financial Allocation Breakdown:
- Project investment exceeds Rs 190 crores.
- Allocation shared between Central and Union Territory (UT) at a 90:10 ratio.
Empowering Communities through PRIs:
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) pivotal for grassroots project success.
- PRIs’ involvement enhances community engagement, fosters ownership, and promotes sustainable development practices.
Devika River:
- Originates from Suddha Mahadev temple in Jammu and Kashmir’s Udhampur district.
- Flows through western Punjab (now Pakistan) where it merges with the Ravi River.
Cultural Significance:
- Revered by Hindus as sister of the Ganga River.
- Devika River believed to be a manifestation of Goddess Parwati, benefiting the people of MaderDesha (areas between river Ravi and Chenab).
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1946187
Revised manufacturing rules for drug firms (Indian Express)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently the center government directed all pharmaceutical companies in the country to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Facts About:
Directions by the Government:
- Larger companies with a turnover of over Rs 250 crore have been asked to implement the changes within six months.
- The medium and small-scale enterprises with turnover of less than Rs 250 crore have been asked to do so within a year.
About Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
- Quality Management: It is a set of guidelines and quality management principles which ensure pharmaceutical products, as well as other products in the food and healthcare industries, are consistently produced and controlled to meet quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
- Aspects Include: It covers all aspects of the manufacturing process, including the premises, equipment, personnel, materials, production, quality control, documentation, and storage of finished products.
Need for the Improved Standards:
- To match up with the Global Standards: Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- Only 2,000 of the 10,500 drug manufacturing units in the country at present meet global standards, being WHO-GMP certified.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- To improve Indian Products Image: There have been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The deaths of 70 children in the Gambia, 18 children in Uzbekistan, three persons in the United States, and six deaths in Cameroon have been linked to these products.
- To rectify the Deficiencies: A risk-based inspection of 162 manufacturing units by the government found several deficiencies — incoming raw materials not being tested before use, product quality not being reviewed , absence of quality failure investigation, infrastructure deficiency to prevent cross-contamination, faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas, missing qualified professionals, and poor documentation.
- To Provide a Structure to the Draft: Implementation of the revised good manufacturing practices (GMP) as listed in the 2018 draft schedule M of the drugs and cosmetics rules.
Major Changes & Significance:
- Standard & Reliable Quality: The revised GMP guidelines focus on quality control measures, proper documentation, and IT backing to maintain quality of medicines produced.
- Review & Validation: It introduces pharmaceutical quality systems, quality risk management, product quality review and validation of equipment.
- Thorough Investigation: Carrying regular quality reviews of all its products, verify consistency of the quality and the processes, thorough investigation of any deviation or suspected defect and implementation of any preventive actions.
- Evaluation of Changes: It also suggests a change control system to evaluate all changes that may affect the production or quality of the product.
- Maintenance of Stability & Required Conditions:The companies will also be needed to mandatorily maintain the drugs in a stability chamber, set the proper temperature and humidity, and carry out an accelerated stability test as well.
- Data Safety & Security: The guidelines also state that companies should have GMP-related computerized systems, which ensure that there is no tampering of data related to the processes.
- In case sensitive data is entered manually to the system, there will be additional checks to validate the accuracy of the data. Backups would also be created to ensure there is no loss of data.
Conclusion:
The step taken is a required and desirable one. Instituting the same quality across the industry will give confidence to regulators from other countries and will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/revised-manufacturing-rules-for-drug-firms-what-changes-and-why-8879305/
5% of birds in India are endemic (The Hindu)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A publication, titled ‘75 Endemic Birds of India’, which was released on the 108th foundation day of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), points out that about 5% of birds found in the country are endemic and are not reported in other parts of the world.
Facts About:
India’s bird species:
- India is home to 1,353 bird species, which represents approximately 40% of global bird diversity.
- Of these 1,353 bird species, 78 species, which is around 5%, are endemic to the country.
About the Publication:
- The publication highlights the importance of endemic bird species in the country.
- The details of endemic bird species contained in the publication include etymology (meanings of scientific names) and their historical relevance along with vital facts such as subspecies’ differences, distinguishing traits, preferred habitats, breeding habits, and food preferences.
- Objective: The publication is aimed at making information about endemic birds of the country available to everyone, and highlighting the efforts to conserve species that are found only in restricted areas.
Highlights from the Publication:
- Around 75 bird species belong to 11 different orders, 31 families, and 55 genera, and exhibit remarkable distribution patterns across various regions in India.
- The highest number of endemic species has been recorded in the Western Ghats, with 28 bird species.
- Some of the rare species recorded in the country’s bio-geographic hotspot are;
- The Malabar Grey Hornbill (Ocycerosgriseus)
- Malabar Parakeet (Psittaculacolumboides
- Ashambu Laughing Thrush (Montecinclameridionalis)
- The White-bellied Sholakili (Sholicolaalbiventris)
- Amongst them 25 bird species are endemic to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Bird species which are only found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are;
- Nicobar Megapode (Megapodiusnicobariensis);
- Nicobar Serpent Eagle (Spilornisklossi);
- Andaman Crake (Rallinacanningi); and
- Andaman Barn Owl (Tytoderoepstorffi).
- Four species of birds are endemic to the Eastern Himalayas, and one each to the Southern Deccan plateau and central Indian forest.
- Of the 78 endemic species, 25 are classified as ‘Threatened’ by the IUCN.
- Three species are listed as ‘Critically Endangered’.
- Five of the endemic birds in India are categorised as ‘Endangered’, and
- 17 as ‘Vulnerable’,
- While 11 are categorised as ‘Near Threatened’ on the IUCN Red List.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/5-of-birds-in-india-are-endemic-reveals-zoological-survey-of-india-publication/article67162268.ece#:~:text=India%20is%20home%20to%201%2C353,are%20endemic%20to%20the%20country
India's Sugar Surplus and its Impact on Agriculture (The Hindu)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India became the world’s top sugar producer in 2021-2022, surpassing Brazil, but the extensive use of resources in sugar production is depleting rapidly, leading to a potential crisis in the future.
Facts About:
The Factors Behind Excessive Sugar Production
- The phenomenon of India's excess sugar production can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including government policies and measures aimed at promoting sugarcane cultivation. At the heart of this lies the fair and remunerative price (FRP) scheme, a government initiative ensuring that sugar mills pay sugarcane farmers a minimum price, thereby ensuring their fair profits
- State governments have further incentivized sugarcane cultivation through substantial subsidies, which some critics argue are aimed at securing the votes of farmers in politically influential rural regions.
- The repercussions of these policies have led to a significant sugar surplus, driving up exports to record levels. However, this expansionary approach has not escaped global scrutiny. Brazil, Australia, and Guatemala raised objections with the World Trade Organization (WTO), alleging that India's excessive export subsidies and domestic support violate international trade rules. The subsequent ruling against India by the WTO underscored the global ramifications of this sugar surplus.
Addressing the Excess Sugar Production: Ethanol as a Solution
- To mitigate the challenges posed by surplus sugar production, the Indian government has explored alternative avenues, with a focus on diverting excess sugar to ethanol production. Ethanol, a versatile organic compound derived from fermenting sugarcane molasses or sugar, has a range of applications in various industries, from alcoholic beverages to chemicals and cosmetics.
- In the realm of transportation, ethanol-blended petrol (EBP) has emerged as an effective strategy to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles, contributing to reduced crude oil imports and greenhouse gas emissions.
- The government's Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program, initiated in 2003, has made significant strides, aiming to achieve a blending rate of 20% by 2025. Reductions in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on ethanol have further supported this transition.
- Efforts to channel a substantial portion of sugar towards ethanol production have yielded positive results, highlighting a potential solution to the problem of excess sugar.
Groundwater Depletion and Environmental Consequences
- While India's EBP program has succeeded in reducing certain imports and emissions, it has also unearthed environmental concerns associated with sugarcane cultivation. The intensive water requirements of sugarcane, coupled with over-cultivation, have significantly impacted groundwater resources. This trend is particularly pronounced in India's top sugarcane-growing states, which rely heavily on groundwater for irrigation.
- With sugarcane demanding approximately 3,000 mm of rainfall for optimal growth, regions that typically receive 1,000-1,200 mm of rainfall resort to excessive groundwater extraction from confined aquifers. A startling statistic emerges – the cultivation of 100 kg of sugar necessitates a staggering two lakh liters of groundwater for irrigation. This alarming scenario has escalated concerns, particularly in drought-prone and groundwater-stressed areas, threatening the availability of this vital resource.
Sustainable Solutions and the Path Forward
- To safeguard India's agricultural sector from a looming crisis and ensure its long-term sustainability, a multifaceted approach is imperative. While the allure of financial gains from sugar surplus and exports is undeniable, a shift towards balanced and sustainable agricultural practices is essential.
Diversified Subsidy Schemes
- A crucial step involves reevaluating incentive structures that disproportionately favor sugarcane cultivation over other crops. By introducing comprehensive and fair subsidy schemes for a variety of crops, farmers can be encouraged to diversify their cultivation practices. Such measures can prevent monocultures, promote equitable income distribution, and contribute to more efficient resource utilization.
Environmentally Responsible Cultivation
- The adoption of environmentally conscious cultivation practices holds the key to mitigating the groundwater depletion crisis. Implementing methods such as drip irrigation, which directs water directly to the roots of sugarcane plants, can significantly reduce water consumption compared to traditional flood irrigation techniques. Government support through subsidies for setting up drip irrigation systems can accelerate this transition.
Integrated Water Management
- India's agricultural landscape requires a comprehensive approach to water management, encompassing rainwater harvesting, wastewater treatment, and improved canal irrigation networks. By minimising stress on groundwater reservoirs and exploring alternative water sources for irrigation, the strain on vital resources can be alleviated.
Investment in Research
- Despite significant strides, gaps remain in understanding groundwater availability and distribution. Investing in comprehensive groundwater research and data collection is essential for informed decision-making and sustainable resource management.
Conclusion:
As India assumes a prominent role in the global agricultural arena, the imperative for sustainability becomes increasingly apparent. While the achievements in sugar production are commendable, the nation must navigate the delicate balance between economic gains and environmental responsibility. By reassessing subsidy structures, promoting diversified cultivation practices, and embracing environmentally conscious techniques, India can pave the way for a resilient agricultural sector that not only based on the article: meets domestic demands but also ensures the well-being of future generations.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/india-excess-sugar-production-guzzling-groundwater/article67157121.ece
Organ shortage continues to cost lives (The Hindu)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent data, around three lakh patients wait for organ donation in the country.
About:
- the number of donors (including cadavers) grew from 6,916 in 2014 to only 16,041 in 2022.
- The country registered 1,589 kidney, 761 liver and 250 heart transplants in the deceased category that year.
- Kidney and pancreas transplants grew from 3 in 2014 to 22 in 2022.
- In contrast, living donor kidney transplants rose from 4,884 in 2014 to 9,834 in 2022.
- Liver transplants in this category grew from 1,002 to 2,957
- one person is added to the waitlist every 10 minutes in the country
Ministry’s steps to enhance organ donations
- doing away with the domicile rule
- removal of age bar for registration of recipients
- removal of fee for registration for transplant
- easing rules on withdrawal of life support (passive euthanasia)
- facilitation of organ transport across the country
- giving special casual leave for employed organ donors
The annual need for 2,00,000 kidney transplants highlights the pressing urgency of the situation.
- However, a mere 10,000 transplants are performed each year, revealing a staggering gap.
- The demand for deceased donors is substantial because many families lack suitable living donors.
- Therefore, relying on deceased donors can help partially meet this demand
- statistics indicate around 70%-75% of donors are women. Wives, mothers, and sisters have emerged as the most prevalent sources of donatio
Organ donation pledges in India need to translate into actual donations and for that, medical staff need to be educated.
- They must be able to recognise, identify, inform, and counsel familiesabout brain death and the importance of organ donation.
- The gap between demand and supply continues to be tremendous. So, there is a need to equip our ICU staff with knowledge and awareness, the sooner the gap will close.
Greater awareness will improve in following way
- One cadaver can save up to eight lives.
- Two donated kidneys can free two patients from dialysis treatment.
- One donated liver can be split among two patients on the waitlist.
- Two donated lungs mean two other patients are given a second chance, and a donated pancreas and donated heart translate to two more patients receiving the gift of life.
- One tissue donor — someone who can donate bone, tendons, cartilage, connective tissue, skin, corneas, sclera, and heart valves and vessels — can save the lives of as many as 75 people.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/indias-poor-organ-donation-record-continues-to-cost-lives/article67161978.ece#:~:text=Three%20lakh%20patients%20wait%20for,donor%20can%20save%20several%20lives
STARFIRE Algorithm (PIB)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers at Raman Research Institute (RRI) have recently successfully created an algorithm named STARFIRE.
Facts About STARFIRE Algorithm:
- The STARFIRE Algorithm, also referred to as the Simulation of TerrestriAl Radio Frequency Interference in oRbits around Earth (STARFIRE) algorithm, is designed for its specific application in modeling and analyzing terrestrial radio frequency interference within Earth's orbits.
- The model possesses several advantages, including its capability to estimate Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) emitted by various sources such as FM radio stations, Wi-Fi networks, mobile towers, radar, satellites, and communication devices.
This estimation aids in designing and fine-tuning antennas for optimal performance.
- The algorithm can effectively estimate and map unwanted RFI signals in space, providing valuable insights for enhancing data quality from future space-based Astronomy missions.
- By facilitating the design of instruments capable of operating optimally in the presence of RFI, the algorithm significantly enriches the data obtained from future space missions.
- Another noteworthy advantage of the STARFIRE Algorithm is its usefulness in orbit selection for upcoming missions, contributing to better planning and execution.
- To develop this model, scientists utilized data from FM transmitter stations in six countries worldwide, including Canada (8,443 stations), USA (28,072 stations), Japan (Tokyo - 21 stations), Australia (2,664 stations), Germany (2,500 stations), and South Africa (1,731 stations), making the model comprehensive and robust.
Biological Diversity Amendment Bill (The Hindu)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently passed the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021, aimed at modifying the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
About Biological Diversity Act, 2002:
The act was enacted in 2002, it aims at the conservation of biological resources, managing its sustainable use and enabling fair and equitable sharing benefits arising out of the use and knowledge of biological resources with the local communities.
Regulatory Structure: The act envisaged a three-tier structure to regulate the access to biological resources:
- The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) at the national level.
- State Biodiversity Boards(SBB) at the state level.
- Biodiversity Management Committees at the local body level.
- Under the Biological Diversity Act of 2002, provisions are made to share benefits with biodiversity conservers, holders, and creators of associated knowledge. These benefits encompass monetary compensation, sharing of Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs), and technology transfer.
Amendments Made in Biodiversity Bill 2021:
- Regarding Access to biological resources and associated knowledge, It amends the classification of entities, list of activities requiring intimation, and adds exemptions.
- Approval for Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) will be required before the grant of IPR instead of before the application itself.
- SBB will determine benefit sharing while granting approvals to domestic entities as per the regulations by NBA.
- The Bill decriminalises the offences and makes offences punishable with a penalty between one lakh rupees and Rs 50 lakh.
Significance of the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill 2021:
The Bill seeks to amend the 2002 Act to:
- Simplify compliance requirements for domestic companies.
- Encourage the Indian system of medicine and cultivation of wild medicinal plants,
- Facilitate fast-tracking of processes for research, patent application, and transfer of research results,
- Decriminalise offences, and
- Encourage foreign investment in the sector.
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam (The Hindu)
- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Due to heavy rainfall in the river's catchment area, the water level in the Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) across the Cauvery recently surpassed the 100-ft mark, although its capacity reaches 124.80 feet.
About Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam:
- Situated in Karnataka's Mandya district, it lies beneath the merging point of the Kaveri river with its tributaries, Hemavati and Lakshmana Tirtha.
- It is a type of gravity dam.
- The dam is named for the then ruler of the Mysore Kingdom, Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV.
- The dam was designed by Sir M. Visvesvaraya, a famous Indian engineer.
- The reservoir is also the main source of drinking water for all of Mysore city and almost the whole of Bangalore.
- The water released from this dam is further used as an important source of water in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- An ornamental garden named “Brindavan Gardens” is attached to the dam.
Kaveri River:
- Kaveri or Cauvery is a sacred river of southern India. It is known as the Ganga of South India.
- It rises on Brahmagiri Hill of the Western Ghats in southwestern Karnataka state.
Drainage Basin:
- It flows in a southeasterly direction through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, and descends the Eastern Ghats in a series of great falls.
- Before emptying into the Bay of Bengal south of Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu, the river breaks into a large number of distributaries forming a wide delta called the “garden of southern India.”
Tributaries of Kaveri:
- Arkavathi, Hemavathi, Lakshmana Theertha, Shimsa, Kabini and Harangi.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) recently addressed the Manipur DGP, urging the filing of an FIR against three individuals.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members of which at least two should be women.
- All of them are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Functions and responsibilities of NCPCR:
- Examine and assess current safeguards for child rights and propose effective implementation strategies.
- Submit periodic reports to the central government on the efficacy of these safeguards.
- Conduct investigations into child rights violations and recommend legal action when appropriate.
- Raise awareness about child rights and available safeguards through diverse channels, such as publications, media, and seminars.
- Conduct inspections of institutions housing children, including juvenile homes, and suggest remedial measures if required.
- Investigate complaints and proactively address issues related to child rights deprivation, violation, and non-implementation of protective laws.
National Dental Commission Bill, 2023 (TIO)
- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently witnessed the introduction of the National Dental Commission Bill, 2023, by the government.
About National Dental Commission Bill, 2023:
- The primary objective of the Bill is to revoke the Dentists Act of 1948, ushering in new regulations and reforms.
- With a focus on affordability, the bill strives to enhance dental education accessibility and ensure quality oral healthcare services.
- In place of the existing Dental Council of India, the Bill proposes the establishment of the National Dental Commission (NDC) to oversee dental education and related matters effectively.
What is National Dental Commission (NDC)?
- The establishment of the new commission entails the formulation of policies and the maintenance of quality standards in dental education and the dental profession.
- A key responsibility of the commission will be to regulate fees for 50% of seats in private dental colleges.
Composition of NDC:
- The structure of the NDC will mirror that of the National Medical Commission (NMC), which replaced the Medical Council of India.
- The head office of the National Dental Commission will be located in New Delhi, consisting of a chairperson, eight ex officio members, and 24 part-time members and the appointment of members will be done by the central government.
- The Bill mandates that all members of the commission must declare their assets and liabilities upon entering and leaving office, along with disclosing any professional and commercial engagements they are involved in.
ISRO's PSLV-C56 (The Hindu)

- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
ISRO recently declared that the launch of the PSLV-C56, carrying Singapore's DS-SAR satellite, is scheduled for July 30th.
Facts About PSLV-C56:
- From the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, the PSLV-C56 is all set to embark on its mission, carrying the DS-SAR satellite and six additional co-passengers.
- Just like C55, the PSLV-C56 will be configured in its core-alone mode, ensuring a streamlined and efficient launch process.
- The primary objective of the mission is to deploy the DS-SAR satellite, weighing 360 kg, into a Near-equatorial Orbit (NEO) with a precise inclination of 5 degrees and an altitude of 535 km.
What is The DS-SAR satellite?
- The DS-SAR satellite is a collaborative effort between DSTA, representing the Government of Singapore, and ST Engineering.
- Its primary purpose is to cater to the satellite imagery needs of diverse governmental agencies within Singapore.
- ST Engineering intends to utilize the satellite for multi-modal and more responsive imagery and geospatial services, serving their commercial clientele effectively.
- The DS-SAR is equipped with a sophisticated Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload, developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI).
- This advanced technology enables the DS-SAR to offer all-weather day and night coverage, providing imaging capabilities at an impressive 1m resolution with full polarimetry.
Silver cockscomb (Down To Earth)

- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The silver cockscomb plant, which is typically thought of as a weed but has been shown to have benefits, is used by the Soliga tribal community.
About Silver cockscomb:
- This plant is a short-lived, reaching a height of 50-60 cm, often considered a weed, displaying simple, spirally arranged leaves with pinkish or silky white flowers.
- In Karnataka's Chamarajanagara district, it is locally known as "anne soppu," while in other regions, it is referred to as "lagos spinach."
- It belongs to the Amaranthaceae family, which includes economically significant plants like spinach (Spinacia oleracea), beetroot, and quinoa.
- Scientifically named Celosia argentea, it goes by the names "kurdu" in Marathi and "pannai keerai" in Tamil.
- The plant thrives even on fallow land and in drought-like conditions, displaying resilience and adaptability.
- Notably, its leaves have lower levels of oxalic acid and phytic acid, making it nutritionally beneficial for consumption.
Soliga Tribe:
- They are an indigenous tribe of Karnataka.
- Their settlements are located in the outskirts of Biligiri Rangana Hills and Male Mahadeshwara in the Chamarajnagar district of Karnataka, amidst the surrounding forest areas.
- Notably, they hold the distinction of being the first tribal community residing within a tiger reserve in India to have their forest rights formally acknowledged and recognized by a court of law.
Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)
- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, the Government of Goa has been directed by the Goa Bench of the Bombay High Court to take action within the next three months. Specifically, they are required to officially designate the 208 sq. km. Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary (WLS) along with its adjoining areas as a tiger reserve, as per the court's decision.
Key Facts About Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary:
Location:
- It is located in the Northern Part of Goa, Sanguem taluka, near Valpoi town.
- The sanctuary is named after the Mhadei River (also known as Mandovi River), which originates from the Sahyadri range of mountains in Karnataka (Belgaum district) and falls in the Arabian Sea at Panaji crossing Goa.
- There are a number of picturesque waterfalls, including Vazra Sakla Falls and Virdi Falls.
- It is known for its nesting grounds of critically endangered Long-billed vultures near Vazra Falls.
Flora and Fauna
- The sanctuary is abundant with lush vegetation, characterized by a dense cover of moist deciduous trees, interspersed with pockets of evergreen species.
- t is particularly well-known for its sacred groves that protect rare and indigenous trees.
- Faunas like Indian gaur, Barking deer, Sambar deer, Asian palm civet, small Indian civet, Wild boar, Indian hare etc. found here.
- The sanctuary holds immense allure for herpetologists due to its impressive diversity of snakes, encompassing all four of India's notorious venomous species - the Indian krait, Russell's viper, Saw-scaled viper, and Spectacled cobra.
Meri Maati Mera Desh campaign

- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The 'Meri Maati Mera Desh' campaign has been recently launched by the Union government of India, as a culminating event of the 'Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav' celebration, commemorating 75 years of Indian Independence.
About Meri Maati Mera Desh campaign:
- Soil collected from various parts of the country during August will be utilized to create a garden along the Kartavya Path in Delhi.
- Events have been planned at different levels including panchayat, village, block, urban local bodies, and state and national levels, respectively.
- The five-point agenda includes the installation of a shilaphalakam (memorial plaque) bearing the names of those who made the supreme sacrifice, following specific specifications.
- Execution of the shilaphalakam project can be undertaken through the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) by leveraging local materials and resources.
- 'Vasudha Vandhan' aims at every gram panchayat or village renewing Mother Earth by planting 75 saplings of indigenous species and creating an Amrit Vatika.
- 'Veeron Ka Vandan' will honor freedom fighters and the families of deceased freedom fighters.
- Young volunteers and others will collect soil from each panchayat/village and bring it to the block, from where the 'Mitti Kalash' will be transported to Delhi.
- Urban areas will organize events at local bodies, notified area councils, Cantonment Boards, and town panchayats from August 9 to 15, and in larger municipalities and municipal corporations from August 16 to 20.
- The 'Mitti Kalash' will be ceremoniously brought to the larger municipalities/corporations and then transported to Kartavya Path.
