National Geospatial Mission
- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the launch of a National Geospatial Mission in the Budget 2025-26.
Key Highlights:
Objective: To modernize land records, enhance urban planning, and create a robust geospatial infrastructure to support India’s broader development goals, including sustainable growth, efficient governance, and improved public service delivery.
Key Features of the Mission:
- Modernization of Land Records:
- Digitization and updation of land records using geospatial technology.
- Aim to reduce land disputes and promote efficient and transparent land use.
- Urban and Infrastructure Planning:
- Provides high-resolution geospatial data for informed urban planning.
- Supports better design and execution of infrastructure through integration with the PM Gati Shakti framework.
- Development of National Geospatial Data Infrastructure (NGDI):
- Integrates geospatial data from multiple departments and ministries.
- Enables seamless access and interoperability for users across sectors.
- Open Geospatial Data Policy:
- Encourages private sector participation by allowing access to non-sensitive, high-resolution data.
- Reduces reliance on foreign geospatial data providers.
- Sectoral Impact:
- Agriculture: Precision farming, resource mapping, and yield optimization.
- Disaster Management: Enhances early warning systems and response planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: Facilitates conservation, deforestation tracking, and ecosystem health analysis.
- Transportation: Improves logistics, routing, and infrastructure placement.
- Climate Monitoring: Aids in data-driven climate action and adaptation planning.
- Technological Integration:
- Utilizes emerging technologies such as AI, drones, and quantum computing for spatial data collection and analysis.
- Promotes research and development in geospatial science to drive innovation.
- Support to Private Sector:
- Anticipated growth in demand for services from geospatial startups, drone companies, and mapping enterprises.
- Strengthens India’s indigenous geospatial capability aligned with the booming global geospatial market (projected to reach $1,064 million by 2030).
Significance and Alignment with National Goals:
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in land governance.
- Contributes to sustainable urban development.
- Aligns with Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing data dependency on foreign sources.
- Acts as a foundational enabler for India’s development agenda, particularly in areas of resource management, climate resilience, and national security.
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) will set up a partial credit enhancement facility to promote corporate bond issuance in the infrastructure sector.
Need for Credit Enhancement:
- Pension and insurance funds in India, as per regulatory norms, can invest only in AA-rated or higher securities.
- Most infrastructure firms issue bonds rated below this threshold (often "A" rated).
- Partial credit enhancement will elevate such bonds to AA ratings, enabling large-scale participation from long-term institutional investors.
Significance:
- Currently, pension and insurance funds prefer government bonds. However, with the government's ongoing fiscal consolidation, sovereign bond issuance is expected to decline.
- This measure provides alternative, long-term investment avenues for these funds.
- Enhances liquidity in the corporate bond market, especially for infrastructure players.
- Helps in reducing infrastructure companies' dependence on banks for funding.
About NaBFID:
- Established: 2021 under The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- Type: Development Finance Institution (DFI).
- Regulator: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI).
- Purpose: Bridge gaps in long-term, non-recourse infrastructure financing and promote bond and derivatives markets in India.
Development Finance Institutions (DFIs):
- Government-owned or public sector-backed institutions that finance large-scale, long-gestation projects.
- Provide medium (1–5 years) and long-term (>5 years) financing.
- Raise funds via sovereign borrowings, insurance companies, pension funds, and sovereign wealth funds.
- Offer both financial support (loans, guarantees) and technical support (project viability, consultancy).
- Do not accept public deposits.
Benefits of Partial Credit Enhancement:
- Democratizes access to the corporate bond market for sub-AA-rated firms.
- Attracts long-term capital into infrastructure through safer, credit-enhanced instruments.
- Promotes diversification and deepening of India's debt markets.
- Makes infrastructure financing more cost-efficient and sustainable over the long term.
Challenges Ahead:
- Regulatory streamlining is essential.
- Guarantee fees need optimization to ensure cost competitiveness against traditional bank lending.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
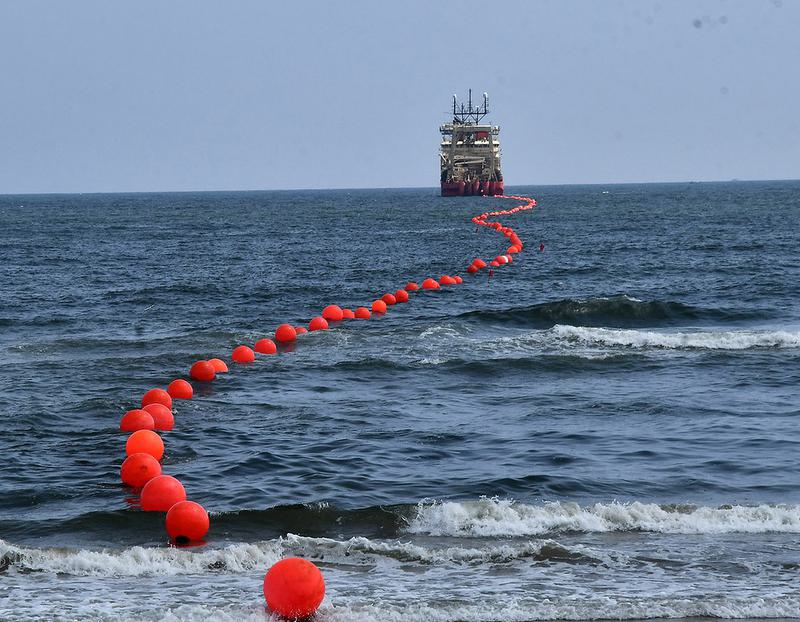
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Good Digital Public Infrastructure
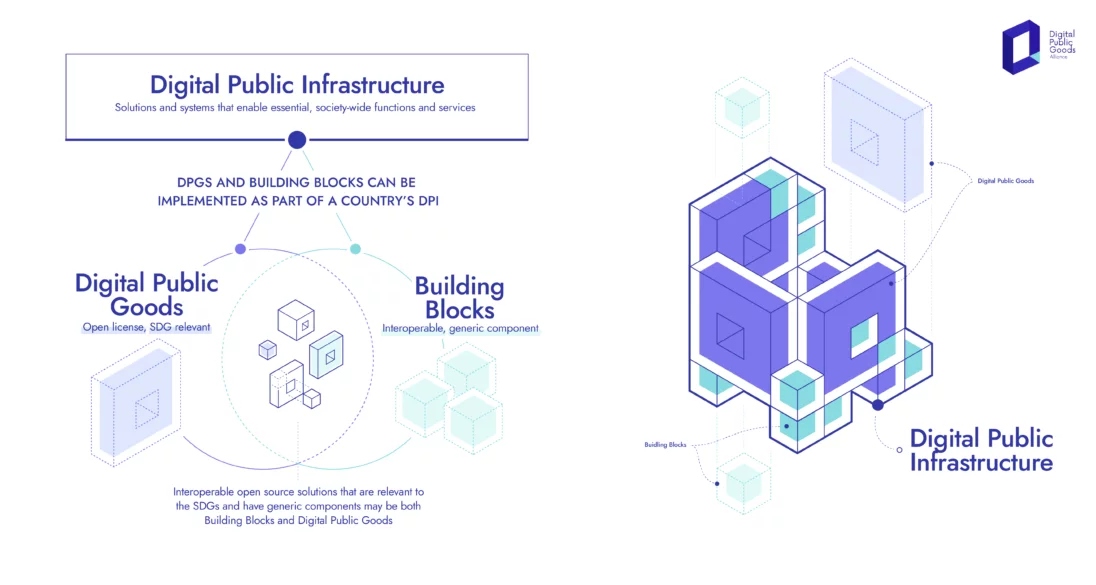
- 08 Sep 2024
Good digital public infrastructure (DPI) integrates technology with societal needs, ensuring that it is secure, scalable, and inclusive.
India’s achievement of over 80% financial inclusion in just six years has drawn international praise, particularly as a model for the Global South. This accomplishment underscores India’s success in achieving both digital and financial inclusion for over a billion people. Consequently, the G20 summit in New Delhi in 2023 highlighted the critical role of digital public infrastructure.
In response, India’s G20 task force has released a comprehensive report outlining a global strategy for DPI development. This positions India to support other nations in achieving digital sovereignty, financial inclusion, and self-reliance.
The evolving digital landscape is marked by a variety of stakeholders—including private enterprises, government bodies, non-profits, and think tanks—each working to advance their DPI solutions. This raises two key questions: How can we identify genuine and reliable DPIs from the plethora available? And what differentiates a “good DPI” from a “bad DPI”?
Identifying effective DPI involves assessing how well technology meets societal needs while ensuring security, scalability, and inclusivity. Authenticity and adherence to core principles are essential for evaluating DPIs.
The Citizen Stack Model
Citizen Stack, built upon the proven success of India Stack, emerges as a trusted ecosystem in digital infrastructure. India Stack, a robust digital platform, has demonstrated its effectiveness and security on a vast scale, serving over a billion citizens. This strong foundation enhances Citizen Stack’s credibility and reliability. Unlike DPI manufacturers, Citizen Stack functions as a regulatory body or auditor, certifying and authenticating DPIs to ensure they meet high standards of quality and security.
Citizen Stack’s approach is comprehensive, focusing on security, scalability, and inclusivity. The DPI platforms approved by Citizen Stack are designed to meet the diverse needs of large populations while maintaining stringent security measures to protect user data and privacy. As an auditor, Citizen Stack ensures that certified DPIs are dependable, secure, and beneficial to the public.
In an era of abundant digital solutions and promises, distinguishing genuinely reliable platforms is essential. Citizen Stack offers assurance as a gold standard for DPI solutions.
Guiding Principles of a “Good DPI”
Citizen Stack has established five core principles—referred to as sutras—that define a good DPI:
- Maintain Citizen Relationships: Ensure that digital infrastructure supports a fair relationship between citizens, the market, and the state, free from undue influence.
- Protect Empowerment and Privacy: Implement consent-based data sharing systems that prioritize individual empowerment and privacy.
- Prevent Monopolistic Lock-In: Ensure interoperability to avoid citizens being restricted by monopolistic entities.
- Combine Techno-Legal Regulation: Integrate technology with legal frameworks to govern ethical tech use, ensuring innovation while safeguarding security and societal rights.
- Foster Public-Private Innovation: Encourage collaboration between public and private sectors, while avoiding corporate dominance. The focus should be on public good rather than corporate monopolies, and technology should prevent exploitation by state or corporate actors.
International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI)

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Countries must build “resilient infrastructure” against natural disasters that are becoming more frequent and severe, said Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently.
About the Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI):
- The Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is a global partnership comprising national governments, UN agencies and programs, multilateral development banks, private sector entities, and academic institutions.
- Established during the United Nations Climate Action Summit in 2019 in New York, CDRI is dedicated to addressing the challenges associated with building resilience in infrastructure systems and development processes.
Objectives:
- CDRI aims to enhance the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks, thereby promoting sustainable development.
- It seeks to expedite the development and retrofitting of resilient infrastructure to meet the imperatives of the Sustainable Development Goals, including universal access to basic services and fostering prosperity and decent work.
- Serving as an inclusive multi-stakeholder platform, CDRI is led and managed by national governments. It facilitates the exchange of knowledge on various aspects of infrastructure resilience.
- CDRI brings together diverse stakeholders to create mechanisms assisting countries in upgrading their capacities, systems, standards, regulations, and practices related to infrastructure development, tailored to their risk contexts and economic needs.
Membership:
- Since its inception, 39 countries, 7 international organizations, and 2 private sector organizations joined as members.
- International organizations include:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- World Bank Group
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
- European Union
- European Investment Bank, and
- The Private Sector Alliance for Disaster-Resilient Societies (ARISE)
- The CDRI is the second major coalition launched by India outside of the UN, the first being the International Solar Alliance.
Secretariat:
- CDRI's secretariat is based in New Delhi, India.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
iBUS, a digital infrastructure solutions company, said recently it has raised $200 million from the government-backed National Investment and Infrastructure Fund Limited (NIIF).
What is the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)?
- The National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) stands as a pioneering fund manager dedicated to investing in India's infrastructure and related sectors.
- Established in 2015, NIIF marks India's inaugural sovereign wealth fund (SWF), embodying a collaborative investment platform for both international and domestic investors.
Key Aspects of NIIF:
- Investment Mandate: NIIF operates with a mandate to deploy equity capital into domestic infrastructure projects, spanning greenfield, brownfield, and stalled ventures.
- Its investment horizon extends across diverse asset classes, including infrastructure, private equity, and other sectors, all aimed at delivering attractive risk-adjusted returns.
- Ownership and Independence: With 49% ownership by the Indian government, NIIF boasts over $4.9 billion in assets under management, solidifying its status as the nation's largest infrastructure fund.
- Despite its close ties with the government, NIIF maintains autonomy in its investment decisions, ensuring a professional and impartial approach to its operations.
- Professional Management: The fund is predominantly owned by institutional investors and managed by a proficient team with expertise in both investments and infrastructure.
- This professional oversight ensures the strategic deployment of capital and efficient management of investments.
- Regulatory Compliance: NIIF operates within the regulatory framework as an Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) registered with the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- It actively raises capital from a spectrum of domestic and international institutional investors, further bolstering its financial resources.
NIIF manages capital through four distinct funds:
- NIIF Master Fund: Focused on infrastructural projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power, it stands as India's largest infrastructure fund.
- NIIF Private Markets Fund: Invests in infrastructure and associated sectors through third-party managed funds.
- NIIF Strategic Opportunities Fund: Devoted to developing large-scale businesses and greenfield projects deemed strategically significant for the nation.
- India-Japan Fund: NIIF's bilateral initiative aimed at environmental preservation in India, with contributions from both the Indian government and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation.
- NIIF catalyzes fostering sustainable infrastructure development in India while facilitating fruitful collaborations between Indian and international stakeholders, exemplifying a robust model for investment-driven growth.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
MeitY signs MoU with Cuba for cooperation on digital public infrastructure (ET)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Cuba have signed an MoU for cooperation in the field of sharing successful digital solutions implemented at the population scale for digital transformation.
India and Cuba Bilateral Relations:
- India and Cuba share a robust and longstanding diplomatic camaraderie, marked by warmth and amity.
- In a gesture of early support, India was among the first nations to acknowledge and establish relations with the new Cuban government post the revolutionary events in January 1959.
- Trade Dynamics: The bilateral trade engagement, while moderate, exhibits a diverse array of commodities.
- India exports pharmaceutical products, organic chemicals, plastic goods, medical equipment, engineering items, textiles, metal products, mineral oil products, and tools to Cuba.
- Conversely, Cuba primarily imports pharmaceuticals and tobacco products from India.
- Energy Partnership: A pivotal facet of India-Cuba relations is their collaboration in the energy sector.
- As a member country and Vice-President of the Latin America & the Caribbean region at the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Cuba plays a significant role in fostering energy cooperation between the two nations.
- Advancements in Science & Technology, Biotechnology, and Health: The bilateral relations in the domains of science, technology, and health have been fortified through ministerial-level visits from both nations.Development Collaboration: Prioritizing development assistance has been a cornerstone of their bilateral ties.
- India has extended disaster relief assistance to Cuba in the aftermath of hurricanes that have afflicted the region over the years.
- Cultural Relations: Cuban appreciation for Indian culture and civilization is evident, with figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Rabindranath Tagore holding a special place in Cuban hearts.
- Indian Diaspora: Although the Indian community in Cuba is relatively small, it includes descendants of Indians who migrated to Cuba in the early twentieth century from Jamaica and other parts of the West Indies to contribute to sugarcane plantations.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- DPI is a digital network that enables countries to safely and efficiently deliver economic opportunities and social services to all residents.
- DPI can be compared to roads, which form a physical network that connects people and provides access to a huge range of goods and services.??
- DPI allows people to open bank accounts and receive wages faster and more easily.
- It allows governments to support citizens more quickly and efficiently, especially during emergencies.
- And it enables entrepreneurs to reach customers far and wide.??
- A strong DPI has three foundational systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—that together can make life easier in important ways.?
- When the three core systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—exist simultaneously and can talk to one another, people, businesses, and governments can reap the full benefits of DPI.
- Over time, safe and inclusive DPI creates vibrant and competitive economies.?
Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (Financial Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister announced the launch of two India-led initiatives: the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository and a Social Impact Fund aimed at promoting the development of Social Impact Fund to advance Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in the Global South during the Virtual G20 Leaders’ Summit on 22nd November 2023.
About the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository:
- It was developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is an extensive resource center that combines knowledge and insights from G20 members and visiting countries.
- Its primary objective is to fill the knowledge gap in the decision-making processes and methodologies necessary for designing, constructing, deploying, and governing Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs).
- The GDPIR presents information in a standardized format from countries and organizations that have successfully implemented DPIs on a large scale.
- This includes elements such as maturity scales, source codes (where available), and governance frameworks.
- Currently, the GDPIR showcases 54 DPIs from 16 countries.
- The DPIs from India featured in the GDPIR include
- Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), eSanjeevani, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DigiLocker, Umang, Co-WIN, Government e-marketplace, API Setu, Diksha, E-Hospital and Poshan Tracker etc.
What about the Social Impact Fund?
- The fund will financially support countries developing DPIs, providing “upstream technical and non-technical assistance”.
- The platform allows other governments, international organisations, and philanthropies to contribute to the fund too.
- India has pledged an initial commitment of $25 million (USD) to the fund.
Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities from the Ministry of Union Housing and Urban Affairs have indicated that the initial installment of loans for supporting ongoing projects in tier-2 and tier-3 cities through the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) is expected to be released shortly.
Facts About:
The UIDF is created by utilizing the priority sector lending shortfall.
Objective:
- This fund serves as a resource for public agencies to develop urban infrastructure in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Emphasis is placed on essential services such as sewage and solid waste management, water supply, sanitation, construction, and improvement of drainage systems, with a priority on projects that have a significant impact.
The National Housing Bank manages this fund.
It initially has a corpus of ?10,000 crore and is modeled after the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF).
States are encouraged to harness resources from the 15th Finance Commission's grants and existing schemes, while also considering user charges when accessing the UIDF.
Currently, it covers 459 tier-2 cities and 580 tier-3 cities.
UIDF Loans:
- nterest rate: Bank Rate minus 1.5%
- The loan principal is repayable in five equal annual installments within seven years from the draw date, including a two-year moratorium period.
- Interest payments are made on a quarterly basis.
