Preah Vihear Temple

- 17 Dec 2025
In News:
India has expressed concern and called for the protection of the Preah Vihear Temple amid renewed border tensions between Thailand and Cambodia, which reportedly affected areas near the temple complex.
Location and Setting
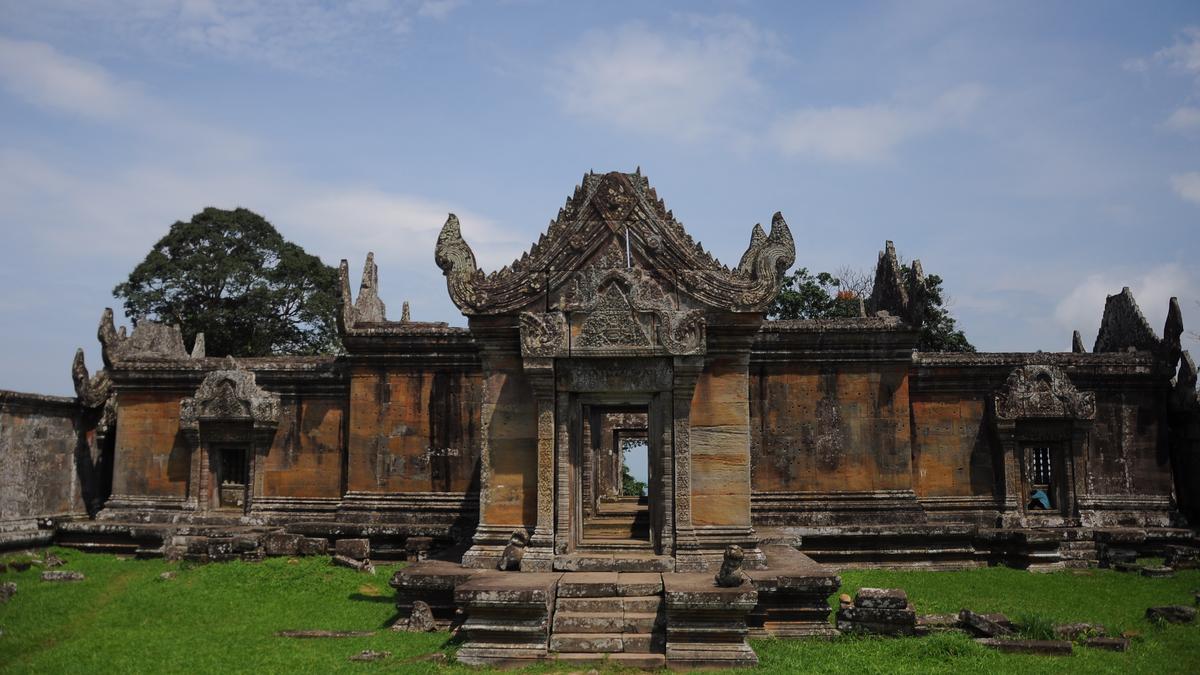
- Preah Vihear Temple is located in Preah Vihear Province in northern Cambodia, dramatically positioned atop a cliff in the Dangrek Mountain range along the Cambodia–Thailand border.
- Its elevated placement provides commanding views over the surrounding plains and has historically contributed to territorial disputes between the two countries.
Religious Significance
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva and is an important example of Hindu religious architecture in mainland Southeast Asia, reflecting the spread of Indian cultural and religious influences across the region during the medieval period.
Historical Background
- The temple was constructed during the height of the Khmer Empire. Its earliest major construction phase is attributed to Suryavarman I (reigned 1002–1050 CE), and it was later expanded and refined under Suryavarman II (reigned 1113–1150 CE), the same ruler associated with major temple-building activity in the region.
- Preah Vihear was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2008, recognizing its outstanding universal value in terms of architecture, history, and cultural significance.
Architectural Features
- Preah Vihear is considered an outstanding masterpiece of Khmer temple architecture. Unlike many other Khmer temples that are arranged concentrically, this complex is laid out along a long north–south axis stretching approximately 800 metres.
- The temple comprises a sequence of sanctuaries connected by pavements and steep staircases that climb the hillside. The approach includes multiple monumental gateways known as gopuras more than five in number which are linked by a long causeway rather than enclosed courtyards.
- Several of these gopuras are topped with multi-tiered platforms, and while some feature stone roofs, others historically had wooden superstructures, highlighting a blend of durable and perishable architectural elements.
Ponduru Khadi

- 17 Dec 2025
In News:
Ponduru Khadi, a traditional handspun and handwoven cotton fabric from Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Geographical Indications Registry under the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
About Ponduru Khadi
- Ponduru Khadi is a heritage textile produced in Ponduru, located in Srikakulam district. Locally, it is known as “Patnulu.” The fabric is widely admired for its extremely fine texture and traditional production techniques that have been preserved for generations.
- The product has also been identified under the One District One Product (ODOP) initiative from Srikakulam district, highlighting its cultural and economic importance.
- During India’s freedom struggle, Mahatma Gandhi praised the fabric’s quality in his journal Young India, recognizing it as an example of self-reliant rural craftsmanship.
Key Characteristics
- Ponduru Khadi stands out due to its fully manual production process. Every step i.e. from cotton cleaning to spinning and weaving is done by hand without the use of mechanised tools.
- The cotton used is locally grown in and around Ponduru and comes from traditional varieties such as hill cotton, punasa cotton, and red cotton. These indigenous varieties contribute to the softness and durability of the fabric.
- The yarn used in Ponduru Khadi is extremely fine, with a yarn count ranging between 100 and 120, making it one of the finest handspun cotton fabrics in India.
Unique features that distinguish Ponduru Khadi
- One of the most distinctive aspects of Ponduru Khadi is the traditional cotton-cleaning method. Artisans use the jawbone of a Valuga fish to separate seeds from cotton — a practice not documented elsewhere in the world.
- Spinning is done using a single-spindle charkha with 24 spokes, popularly referred to as the “Gandhi Charkha.”Ponduru is among the very few places in India where this traditional spinning method is still actively practiced.
Why GI Tag Matters
The GI tag legally recognizes Ponduru Khadi as a product with a specific geographical origin and traditional know-how. This helps:
- Protect it from imitation
- Promote rural artisans
- Enhance export and branding potential
- Preserve intangible cultural heritage
Thaipusam

- 03 Feb 2026
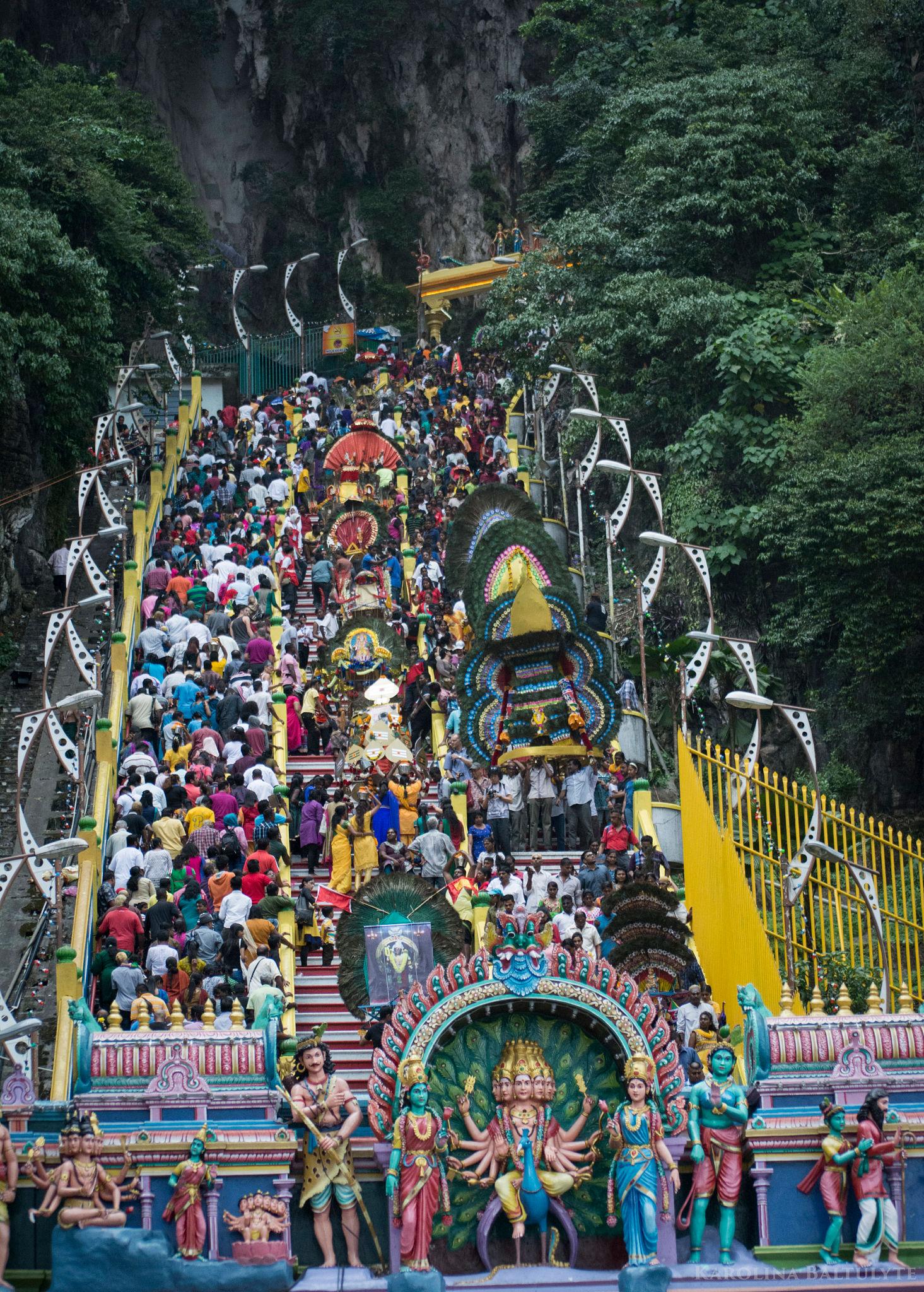
Thaipusam is an important Hindu festival celebrated primarily by the Tamil community to honour Lord Murugan, the deity associated with courage, wisdom, and victory over evil. The festival recently gained attention as the Prime Minister of India extended greetings to devotees, highlighting its cultural and spiritual significance.
Meaning and Timing of Thaipusam
The name Thaipusam is derived from:
- “Thai” – the tenth month of the Tamil calendar (January–February)
- “Poosam” (Pushya star) – the star that is at its highest point during the full moon day when the festival is observed
Thus, Thaipusam falls on the full moon day in the Tamil month of Thai, when the Pushya constellation is ascendant.
Religious Significance
Thaipusam commemorates the occasion when Goddess Parvati is believed to have given Lord Murugan the divine spear (Vel) to defeat the demon Surapadman. The festival symbolises:
- Triumph of good over evil
- Spiritual purification
- Devotion through penance and sacrifice
Murugan, also known as Kartikeya or Subramanya, is revered as the god of war, victory, and wisdom in Hindu tradition.
Key Rituals and Practices
- Kavadi Attam (Burden Carrying): Devotees carry decorated structures called kavadi as an act of devotion and gratitude. The act represents surrendering burdens to the deity.
- Fasting and Penance: Many devotees observe strict fasting, meditation, and celibacy before participating in the festival.
- Body Piercing Rituals: Some devotees pierce their skin, cheeks, or tongue with small spears or hooks as acts of faith and endurance, symbolising spiritual cleansing.
- Pilgrimages: Major processions and temple visits mark the day, especially at prominent Murugan temples.
Geographical Spread
While rooted in Tamil Nadu, Thaipusam has become a global Tamil festival, celebrated prominently in:
- Tamil Nadu
- Sri Lanka
- Malaysia (notably at Batu Caves)
- Singapore
It reflects the cultural continuity of the Tamil diaspora worldwide.
Cultural and Social Dimensions
Thaipusam is not only a religious event but also:
- A celebration of Tamil identity and heritage
- A demonstration of community solidarity
- A reflection of discipline, resilience, and spiritual commitment
The festival reinforces values of self-control, sacrifice, and devotion, which hold broader cultural importance.
Deepavali inscribed on UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage List

- 14 Dec 2025
In News:
Deepavali (Diwali) has been officially inscribed on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO during the 20th Session of the Intergovernmental Committee held in New Delhi. It becomes the 16th Indian element on the list.
About Deepavali
- Also known as Diwali, meaning “row of lights”
- Celebrated on Kartik Amavasya (October–November)
- A multi-regional, multi-faith festival symbolising light over darkness, renewal, hope and harmony
- Observed across India and the global diaspora
Cultural and Mythological Significance
Deepavali is associated with multiple traditions across regions:
- Return of Lord Rama to Ayodhya after exile
- Victory of Lord Krishna over Narakasura (Naraka Chaturdashi)
- Worship of Goddess Lakshmi for prosperity
- Mahavira’s Nirvana for Jains
- Kali Puja in eastern India
- Govardhan Puja linked to Krishna traditions
- King Bali’s return celebrated in parts of western India
These diverse narratives reflect India’s cultural pluralism.
Key Features as Living Heritage
- Social practices: Lighting diyas, rangoli, rituals, gift exchange, sweets, community feasts
- Five-day celebration: Dhanteras - Naraka Chaturdashi - Lakshmi Puja - Govardhan/Bali Pratipada - Bhai Dooj
- Livelihood linkages: Potters, artisans, sweet-makers, florists, farmers, jewellers, textile workers benefit economically
- Diaspora dimension: Celebrated across Southeast Asia, Africa, Europe, Gulf countries, Caribbean
- Values embodied: Inclusivity, unity, generosity, wellbeing, moral ideal of “Tamso Ma Jyotirgamaya” (darkness to light)
Environmental & Social Dimensions
- Promotion of eco-friendly celebrations (e.g., green crackers)
- Cleaning rituals reinforce hygiene and wellbeing
- Strengthens family bonds and community cohesion
- Supports charity, food distribution, and care for vulnerable groups
About Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH)
Definition: ICH includes living traditions, rituals, performing arts, craftsmanship, oral traditions, and knowledge systems that communities recognise as part of their cultural identity.
UNESCO Framework
- Governed by the 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Came into force in 2006
- India ratified in 2005
Five Domains of ICH
- Oral traditions & expressions
- Performing arts
- Social practices, rituals & festivals
- Knowledge concerning nature & the universe
- Traditional craftsmanship
Representative List
Highlights cultural practices that showcase humanity’s diversity and encourage dialogue.
UNESCO Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- 11 Dec 2025
In News:
- India is hosting the 20th session of the UNESCO Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) in New Delhi. This is the first time India is hosting a session of this Committee.
- The session is being held at the Red Fort complex, symbolically bringing together India’s tangible and intangible heritage. The Ministry of Culture and Sangeet Natak Akademi are the nodal agencies organising the event.
What is Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH)?
As defined by UNESCO, Intangible Cultural Heritage includes:Practices, knowledge, skills, expressions, objects, and cultural spaces that communities recognise as part of their cultural identity.
These traditions are:
- Transmitted across generations
- Continuously recreated
- Closely linked to identity, diversity, and creativity
Examples include oral traditions, performing arts, rituals, festivals, traditional craftsmanship, and indigenous knowledge systems.
UNESCO 2003 Convention on ICH
The Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage was adopted by UNESCO in 2003 at its General Conference in Paris.
Objectives of the Convention:
- Safeguard intangible cultural heritage
- Ensure respect for communities and practitioners
- Raise awareness at local, national, and global levels
- Promote international cooperation and assistance
India ratified the Convention in 2005, marking its formal commitment to protecting living traditions.
Intergovernmental Committee for Safeguarding of ICH
The Intergovernmental Committee is the key body that implements the 2003 Convention.
Composition:
- 24 Member States
- Elected for 4-year terms by the General Assembly of States Parties
India is currently a member of the Committee (2022–2026).
Key Functions:
- Monitor implementation of the Convention
- Recommend safeguarding measures and best practices
- Prepare plans for using the Intangible Cultural Heritage Fund
- Examine periodic reports from States Parties
- Decide on:
- Inscription of elements on UNESCO’s ICH Lists
- Granting international assistance
Significance of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Identity & Continuity:ICH strengthens community identity and connects generations.
- Social Cohesion:Shared traditions promote harmony and mutual respect in diverse societies.
- Livelihoods & Economy:Crafts, performing arts, and festivals support artisans, rural economies, and cultural tourism.
- Traditional Knowledge Systems:Indigenous ecological knowledge, healing practices, and agricultural traditions offer sustainable solutions relevant to climate change and biodiversity.
- Education & Intergenerational Learning:ICH carries local histories, values, and skills that enrich learning and cultural literacy.
- Cultural Diplomacy & Soft Power:Elements such as yoga, classical arts, festivals, and crafts enhance India’s global cultural presence.
India’s Role and Contributions
India has played an active role in global ICH safeguarding:
- Served on the Intergovernmental Committee for multiple terms
- Developed national-level documentation, inventories, and safeguarding programmes
- Supports practitioners through schemes under the Ministry of Culture and initiatives of the Sangeet Natak Akademi
India has 15 elements inscribed on UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, covering performing arts, rituals, craftsmanship, and knowledge traditions.
Importance of Hosting the 20th Session
Hosting the session allows India to:
- Showcase its community-based safeguarding model
- Promote international cooperation and joint nominations
- Increase global visibility of lesser-known traditions
- Strengthen cultural diplomacy and soft power
- Link heritage with sustainable development, livelihoods, and tourism
Shani Shingnapur Temple
- 10 Dec 2025
In News:
Two employees of the Shani Shingnapur Temple Trust were recently arrested for allegedly diverting funds by manipulating online applications used for booking pooja services, bringing the temple into the news.
Location
- Situated in Shingnapur village, Ahilyanagar (formerly Ahmednagar) district, Maharashtra
- The village itself is culturally famous for its doorless houses
Deity and Religious Significance
- Dedicated to Lord Shanidev (Shani), the Hindu deity associated with the planet Saturn
- The idol is a five-and-a-half-foot-high black stone slab
- Believed to be Swayambhu (self-manifested), not sculpted by humans
- Devotees worship Shani for relief from malefic planetary effects and life hardships
Unique Traditions of Shingnapur Village
- The village is widely known for houses without doors or locks
- The belief is that Lord Shani protects the village, and theft does not occur due to divine fear
- This tradition has made Shingnapur a symbol of faith-based social trust
Temple Architecture and Features
The Shani Shingnapur Temple is architecturally distinct:
- The idol is placed in the open, under the sky
- There is no enclosed sanctum (garbhagriha) with roof or walls over the main deity
- Devotees traditionally offer mustard oil to Lord Shani, poured over the idol from a suspended copper vessel
Other features within the temple complex include:
- A Trishul (trident) near the idol
- A Nandi statue located to the south of the idol
- Small images of Lord Shiva and Hanuman in front of the Shani idol
- A later-built east-facing multi-deity temple situated west of the Shani stone
- A samadhi (tomb) of Saint Udasi Baba
- A temple dedicated to Lord Dattatreya
Cultural and Pilgrimage Importance
- One of the most important Shani temples in India
- Attracts thousands of devotees, especially on Shani Amavasya and Saturdays
- Reflects a blend of folk belief, astrology, and devotional Hindu practices
Significance
- Represents a unique open-sky form of deity worship
- Illustrates strong links between faith and social customs (doorless homes tradition)
- An important religious and cultural landmark in Maharashtra
Guru Ravidas

- 02 Feb 2026
In News:
The recent inauguration and renaming of Adampur Airport in Punjab after Sri Sant Guru Ravidas Ji highlights the continued relevance of medieval Bhakti saints in India’s socio-cultural landscape. Such recognition goes beyond symbolic tribute and reflects the enduring influence of Guru Ravidas’s teachings on equality, dignity, and spiritual freedom.
Guru Ravidas
- Guru Ravidas (c. 1377–1527 CE) was a prominent saint-poet of the Bhakti Movement, born in Sir Gobardhanpur near Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh). His life coincided with other major Bhakti figures such as Kabir, and he is traditionally regarded as a disciple of Ramananda.
- Guru Ravidas composed devotional poetry in local dialects, making spiritual ideas accessible to common people. His verses emphasised direct devotion to the divine without ritualism or priestly mediation.
Teachings and Philosophy
Guru Ravidas’s philosophy was deeply egalitarian and reformist:
- Rejected the caste hierarchy and social discrimination
- Advocated human dignity and equality
- Promoted spiritual freedom over ritual orthodoxy
- Emphasised Nirguna Bhakti (devotion to a formless divine)
A central idea in his teachings is “Beghumpura” — an ideal city without sorrow, fear, or discrimination, symbolising a just and casteless society. This vision makes him a powerful voice in India’s historical struggle against untouchability and social exclusion.
Literary and Religious Legacy
Guru Ravidas’s influence transcended religious boundaries:
- 41 hymns attributed to him are included in the Guru Granth Sahib, the holy scripture of Sikhism
- His verses also appear in the Panch Vani of the Dadu Panthi tradition
- The Bhakti saint Meera Bai is believed to have regarded him as her spiritual guide
Over time, his teachings became the foundation of the Ravidassia religion, whose followers revere him as their central spiritual authority. The community follows the Amrit Bani Guru Ravidass as its holy book and has developed distinct religious symbols and practices.
Mahad Satyagraha

- 08 Dec 2025
In News:
The Mahad Satyagraha was one of India’s earliest organisedcivil rights movements, led by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar in 1927 in Mahad (present-day Raigad district, Maharashtra). It challenged the practice of untouchability and asserted the right of Dalits to access public water sources, marking a crucial step in the evolution of India’s human rights discourse and later constitutional morality.
Background
- In 1923, the Bombay Legislative Council passed the Bole Resolution, recommending that so-called “untouchable” communities be allowed to use public wells, tanks, schools, and other civic facilities. Despite this legal provision, caste discrimination continued, especially in Mahad, where Dalits were denied access to the Chavdar (Chavadar) Tank, a public water reservoir.
- Mahad was chosen by Ambedkar due to its active social reform environment and presence of anti-caste leaders and organisations advocating equality.
Mahad Satyagraha - Phase I (March 19–20, 1927)
- Thousands of Dalits led by Ambedkar marched to the Chavdar Tank and drank water, symbolically asserting their right to equality and human dignity.
- The act triggered backlash from upper-caste groups, who performed “purification rituals” to “cleanse” the tank, reinforcing caste hierarchies.
- Legal disputes followed, with local elites claiming the tank was privately owned, leading to a court stay on Dalit access.
Mahad Satyagraha - Phase II (December 25–26, 1927)
- A second conference was organised at Mahad.
- As the legal case was pending, Ambedkar refrained from directly accessing the tank again.
- Instead, on December 25, 1927, he led the public burning of the Manusmriti, an ancient text seen as justifying caste hierarchy and gender inequality.
- Ambedkar also addressed women participants, stressing that gender equality was integral to the anti-caste struggle.
Key Features
- Assertion of Civil Rights: Access to public resources framed as a fundamental human right.
- Challenge to Scriptural Authority: Symbolic rejection of texts legitimising caste discrimination.
- Non-violent Protest: Inspired by democratic ideals but rooted in Ambedkar’s ethical vision of liberty, equality, and fraternity.
- Women’s Participation: Marked an early articulation of the link between caste oppression and gender inequality.
Outcomes and Legacy
- In 1937, the Bombay High Court ruled that there was no valid custom barring Dalits from public tanks, affirming equal civic rights.
- The movement strengthened Dalit political consciousness and laid the groundwork for later struggles, including temple entry movements.
- The principles articulated at Mahad later influenced the Fundamental Rights, equality provisions, and constitutional morality embedded in the Constitution of India.
- December 25 is commemorated in some traditions as Indian Women’s Liberation Day, recalling Ambedkar’s emphasis on gender justice.
Hornbill Festival

- 08 Dec 2025
In News:
The 26th edition of the Hornbill Festival (2025) is being celebrated in Nagaland, with vibrant cultural performances held at the Naga Heritage Village, Kisama, near Kohima. The festival, often called the “Festival of Festivals”, brings together diverse Naga tribes to showcase their heritage, traditions, and artistic expressions.
About the Hornbill Festival
- What: A premier cultural festival of Nagaland celebrating the collective identity of Naga tribes
- When: Held annually from 1–10 December
- Where:Kisama Heritage Village, around 12 km from Kohima
- Started in:2000, by the Government of Nagaland
- Named after: The Hornbill bird, revered in Naga folklore as a symbol of valour, beauty, and cultural pride
Cultural Significance
Nagaland is home to 17 major tribes and several sub-tribes, each with unique customs, attire, music, and oral traditions. Over 86% of the state’s population belongs to tribal communities (Census 2011). The Hornbill Festival provides a platform for:
- Preserving and promoting indigenous traditions
- Strengthening inter-tribal unity
- Encouraging interaction between elders and youth
- Showcasing Naga identity at national and international levels
Key Features of the Festival
1. Cultural Performances: Daily events include:
- Traditional dances and folk songs
- War cries and storytelling traditions
- Indigenous sports and martial displays
Examples of performances include youth dances symbolising joy and festivity, women’s folk dances celebrating hospitality, and traditional combat sports practised in village morungs (youth dormitories).
2. Traditional Arts & Crafts: Exhibitions display:
- Wood carving
- Handwoven textiles
- Tribal ornaments and handicrafts
- Paintings and sculptures
3. Food & Lifestyle Exhibitions
- Indigenous Naga cuisine
- Herbal medicine stalls
- Flower shows
- Traditional archery and wrestling competitions
4. Major Events
- Hornbill International Rock Festival
- Morung (traditional youth dormitory) exhibitions
- Fashion shows featuring tribal attire
- Craft bazaars promoting local entrepreneurship
Participation and Outreach
The festival attracts both domestic and international participation. In recent editions, several partner countries and neighbouring Indian states have participated, strengthening cultural diplomacy and tourism links. Such engagement enhances Nagaland’s visibility as a cultural tourism destination.
Economic and Tourism Impact
The Hornbill Festival significantly boosts:
- Tourism revenue
- Local handicraft and handloom markets
- Food and hospitality sectors
- Employment opportunities for local communities
It serves as an important platform for sustainable cultural tourism in Northeast India.
Chaolung Sukapha

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
Assam Day (02nd December) celebrations recently paid tribute to Chaolung Sukapha, the founder of the Ahom kingdom and a key figure in Assam’s historical and cultural identity.
Who was Chaolung Sukapha?
- Chaolung Sukapha was a 13th-century ruler who established the Ahom kingdom in Assam, which went on to rule the region for nearly six centuries. He is widely regarded as the architect of “Bor Asom” (Greater Assam) due to his role in unifying diverse communities.
- Sukapha crossed the Patkai hills and established his first principality at Charaideo, which later became an important political and cultural centre of the Ahom rulers.
Administrative System
- Sukapha developed an organised administrative structure that later evolved into the famous Paik system of the Ahoms.
- The kingdom was divided into territorial units called khels (or phoids). Each unit was supervised by an officer responsible for mobilising paiks, able-bodied adult males who provided labour and military service.
- Every adult male between the ages of 16 and 50 was registered as a paik. They served the state in activities such as agriculture, construction, and warfare for a fixed period each year. In return, they were granted land for cultivation.
- Sukapha also emphasised guerrilla warfare tactics suited to Assam’s geography of rivers, forests, and hills, a strategy that later helped the Ahoms resist external invasions.
Policy of Integration and Assimilation
- One of Sukapha’s most significant contributions was his policy of conciliation and assimilation. Instead of conquering local tribes through force, he built alliances and integrated communities into his kingdom.
- He maintained friendly relations with indigenous groups such as the Sutias, Morans, and Kacharis, laying the foundation for a composite Assamese society. His approach fostered social harmony and cultural blending, which became a defining feature of Assam’s identity.
Why Sukapha is Important Today
- Sukapha’s legacy lies in his vision of unity through diversity. His governance model promoted peace, cooperation, and shared prosperity among different ethnic and cultural groups.
- This inclusive approach is often seen as an early example of nation-building through social integration, making his legacy relevant in discussions on cultural harmony and regional identity.
Charaideo and Historical Legacy
- Charaideo, where Sukapha established his initial base, later became the site of the Charaideo Maidams, the burial mounds of Ahom royalty. These maidams have gained global recognition for their historical and cultural importance.
Ellora Caves

- 03 Dec 2025
In News:
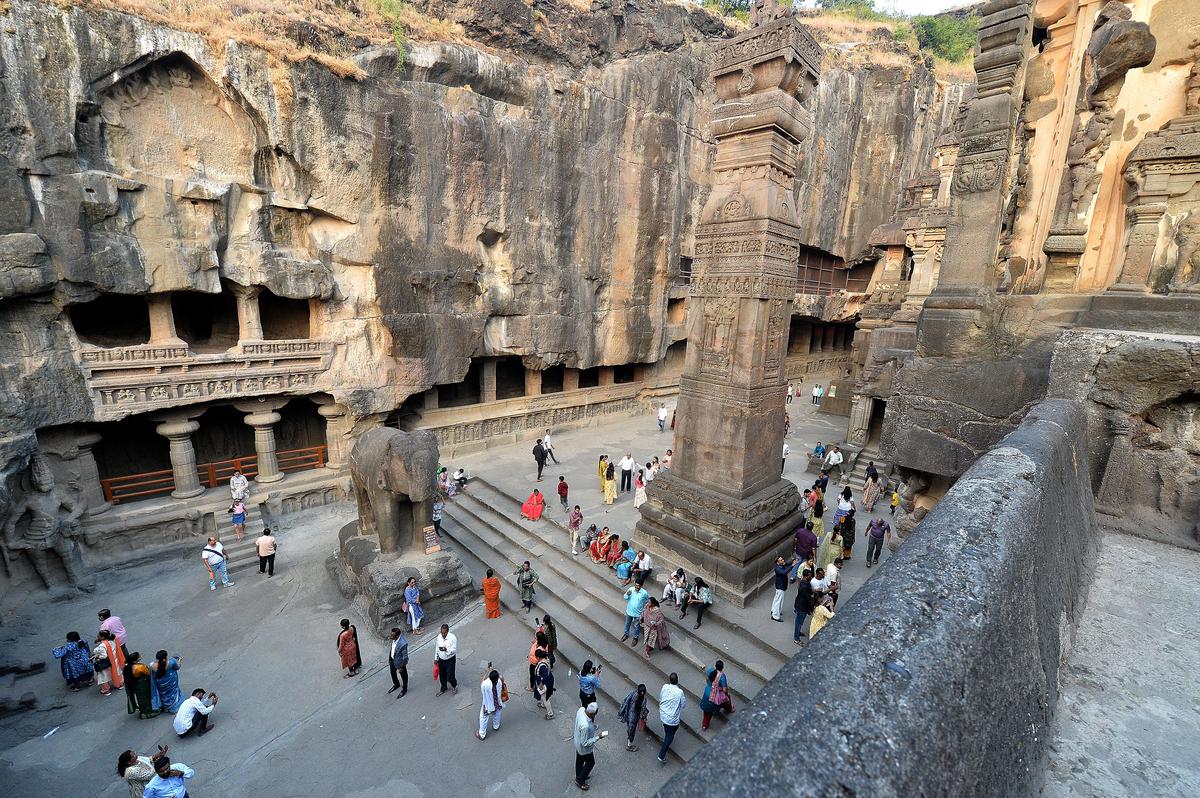
The Ellora Caves, located in Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar (Maharashtra), are among India’s earliest UNESCO World Heritage Sites (inscribed in 1983) and represent one of the largest rock-cut cave complexes in the world. While the caves themselves are globally renowned, the wider Ellora–Khultabad heritage zone contains several historically important but lesser-known monuments that remain under-promoted.
Ellora Caves: Core Facts
Chronology
Constructed between 6th and 10th centuries CE, Ellora reflects continuous religious activity over centuries.
|
Group |
Cave Numbers |
Period |
Features |
|
Buddhist |
1–12 |
c. 600–800 CE |
Viharas (monasteries), chaitya halls, meditation cells |
|
Hindu |
13–29 |
c. 600–900 CE |
Grand sculptural programs, mythological panels |
|
Jain |
30–34 |
c. 800–1000 CE |
Intricate carvings, emphasis on asceticism and detail |
Architectural & Cultural Significance
1. Kailasa Temple (Cave 16)
- Largest monolithic rock-cut structure in the world
- Dedicated to Lord Shiva
- Excavated top-down from a single basalt rock mass
- Estimated 1.5–2 lakh tonnes of rock removed
- Notable features:
- Nandi Mandapa
- Life-size elephant sculptures
- Panels like Ravana shaking Mount Kailasa
- Highly developed Dravidian temple architecture in rock-cut form
2. Multi-Religious Coexistence
- Rare site where Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain monuments coexist
- Demonstrates religious tolerance and artistic continuity in early medieval India
3. Rock-Cut Engineering
- Multi-storeyed structures carved from solid basalt
- Includes pillars, halls, stairways, windows, and elaborate façades
Wider Ellora–Khultabad Heritage Zone
Beyond the caves, the surrounding regionespecially Khultabad, located on the hill above Ellora—contains monuments reflecting layered religious and political history.
1. Malik Ambar’s Tomb
- Mausoleum of Malik Ambar, the Ethiopian-origin military leader and statesman of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate
- Known for administrative reforms and resistance against the Mughals
- Represents Deccan Sultanate architecture
2. Tomb of the First Peshwa
- Refers to an early holder of the Peshwa title (used before and during the Maratha period)
- Highlights the region’s pre-Maratha and Maratha-era political history
3. Empty Tomb of the Last Ottoman Caliph
- Memorial structure linked to the last Ottoman Caliph, Abdulmejid II
- Built by his daughter, who was married into the Hyderabad Nizam’s family
- SymbolisesIndia’s historical connections with West Asia and the Ottoman world
4. Khultabad’s Religious Traditions
- Known for Sufi shrines and long-standing Islamic spiritual traditions
- Also associated with earlier local cults and Naga veneration, indicating continuity of sacred geography
Tourism & Heritage Significance
- Ellora is part of a major heritage circuit including:
- Ajanta Caves
- Daulatabad Fort
- Khultabad monuments
- Together, these sites form a dense cultural landscape spanning:
- Ancient Buddhist heritage
- Early medieval Hindu and Jain architecture
- Deccan Sultanate history
- Maratha-era legacy
- Indo-Islamic and trans-regional Islamic connections
350th Martyrdom Day of Guru Teg Bahadur

- 25 Nov 2025
In News:
The President of India paid tribute to Guru Tegh Bahadur on his 350th Martyrdom Day on 24 November.
About Guru Tegh Bahadur
- Position: 9th Sikh Guru
- Known for: Spiritual depth, courage, and supreme sacrifice for religious freedom.
Early Life and Lineage
- Born: 21 April 1621, Amritsar
- Parents: Guru Hargobind (6th Sikh Guru) and Mata Nanki
- Birth Name: Tyag Mal (reflecting ascetic inclination)
Education and Training
- Scriptural Education: Trained under Bhai Gurdas
- Martial Training: Trained by Baba Budha
- Represents the Sikh tradition of spiritual–temporal synthesis (Miri–Piri).
Contributions and Leadership
- Bani: Composed 116 hymns included in the Guru Granth Sahib
- Preaching: Travelled widely across the Indian subcontinent spreading Sikh teachings
- Town Founded: Chak-Nanki, later developed into Shri Anandpur Sahib (Punjab)
Martyrdom and Legacy
- Year: 1675
- Place: Delhi (near present-day Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib)
- Cause: Executed on the orders of Aurangzeb for opposing forced religious conversions and defending freedom of conscience.
- Title Earned: “Hind di Chadar” (Shield of India)
Significance
- First martyr in world history to sacrifice life for the religious freedom of others.
- His martyrdom strengthened India’s tradition of pluralism, tolerance, and human rights.
Indira Gandhi Peace Prize

- 22 Nov 2025
In News:
Former Chilean President Michelle Bachelet has been awarded the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development for 2024, recognising her global contributions to human rights, social justice and inclusive governance.
About the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
- Instituted:1986, in memory of former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
- Instituted by: Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust
- Official Name:Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development
- Nature: Annual international award
- Eligibility: Individuals or organisationsirrespective of nationality, race or religion
- Award Components:
- ?25 lakh cash prize
- Citation
Objectives of the Award
The prize recognisescreative and sustained efforts towards:
- Promotion of international peace, disarmament, racial equality, and harmony among nations
- Strengthening economic cooperation and a new international economic order
- Accelerating the all-round development of developing countries
- Using science and modern knowledge for the larger good of humanity
- Expanding freedom, human dignity and the human spirit
Why Michelle Bachelet was Awarded
- Political Leadership: Two-time President of Chile (2006–10, 2014–18); first woman to hold the office
- Global Human Rights Role: Former UN High Commissioner for Human Rights and first Director of UN Women
- Domestic Reforms in Chile:
- Education and tax reforms
- Establishment of the Ministry of Women and Gender Equality
- Creation of the National Institute for Human Rights and the Museum of Memory and Human Rights
- Promotion of women’s political participation and LGBTQ rights
- Global Standing: Known for advocacy on civil liberties, democratic values and protection of vulnerable groups
Select Past Recipients
- 1987: Mikhail Gorbachev
- 1989: UNICEF
- 1997: Jimmy Carter
- 2003: United Nations & Kofi Annan
- 2013: Angela Merkel
- 2014: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 2017: Manmohan Singh
- 2019: Sir David Attenborough
- 2021: Pratham NGO
- 2022: Indian Medical Association & Trained Nurses Association of India
- 2023: Daniel Barenboim & Ali Abu Awwad
Meerut Bugle
- 21 Nov 2025
In News:
The Meerut bugle, a brass wind instrument integral to India’s military drills, parades and ceremonies, has received a Geographical Indication (GI) tag, providing legal protection and renewed recognition to a century-old craft rooted in Meerut.
About the Meerut Bugle
- What it is: A handcrafted brass wind instrument used as a command and ceremonial tool in the Army, paramilitary and police forces.
- Cultural Significance: Known for its commanding, clear tone, it occupies a place of honour in regimental bands and national ceremonies.
- Origin & Evolution:
- Bugle-making in Meerut dates back to the late 19th century (British era), when it was central to battlefield communication.
- Over time, it evolved into a specialised local industry, aligning with the growth of India’s military traditions.
- Current Use: Meerut-made bugles continue to be supplied to defence units, paramilitary forces, police organisations and training academies across India.
Key Craft Features
- Material: High-quality brass, ensuring durability and tonal accuracy.
- Process:Handcrafted workmanship, reflecting traditional skills passed down generations.
- Heritage Value: Represents a living military heritage, linking colonial-era communication tools to modern ceremonial functions.
Why the GI Tag Matters
- Authenticity & Protection: Prevents counterfeits and cheap imitations from being sold as “Meerut bugles”.
- Market Value: Enhances brand recognition, encouraging government institutions and buyers to prefer certified instruments.
- Livelihood Support: Offers a pathway to revive traditional workshops affected by rising brass prices, declining orders and imported substitutes.
- Global Exposure: Enables participation in international exhibitions, cultural fairs and heritage showcases.
About the GI Tag
- Definition: A GI tag certifies that a product originates from a specific region and possesses qualities or reputation attributable to that place.
- Legal Framework:Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 (implemented from September 2003).
- Authority:Geographical Indications Registry, under the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs & Trade Marks, Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- Benefits:
- Exclusive rights to authorised producers
- Legal action against misuse
- Boosts rural/artisan livelihoods and preserves traditional knowledge
- India’s GI Landscape:600+ GI-tagged products across agriculture, handicrafts, food and manufactured goods.
VrindavaniVastra

- 19 Nov 2025
In News:
The Government of Assam has initiated formal discussions with the British Museum to facilitate the return of the VrindavaniVastra, a priceless 16th–17th century Assamese textile that holds immense cultural, historical, and religious significance. The move is part of broader efforts to reclaim India’s cultural artefacts preserved abroad.
What is VrindavaniVastra?
- A 400-year-old traditional textile originating from Assam.
- The word Vrindavani refers to Vrindavan, the sacred land of Lord Krishna’s childhood; Vastra means cloth.
- The textile depicts:
- Scenes from Lord Krishna’s childhood.
- His lilas (divine exploits).
- Various events of Vaishnav devotional narratives.
Origin & Patronage
- Created during the rule of Koch King Nara Narayan (16th century).
- Produced under the guidance of SrimantaSankardeva, the founder of Assamese Neo-Vaishnavism.
- Sankardeva took refuge under Nara Narayan after he faced hostility from sections of Ahom-era Brahmin priests.
Weaving Technique
- Made of woven silk using the complex lampas technique.
- Lampas weaving requires:Two weavers working simultaneously, making it a technically demanding process.
- Uses a rich palette of colours:Red, yellow, green, black, white, and others.
- Combines artistic traditions from:
- Assam
- Bengal
- Tibetan and broader Himalayan influences
Historical Journey
- The textile originally consisted of 15 separate silk panels, later stitched into a continuous piece.
- The specimen held in the British Museum is:
- Nine and a half metres long
- Assembled from several draped silk sections
- It travelled from Assam to Tibet through ancient cultural exchanges.
- Acquired by the British Museum in 1904, where it remains one of the most significant exhibits from South Asia.
Cultural Significance
- A masterpiece of Assamese Vaishnavite art and a visual representation of Sankardeva’s devotional philosophy.
- Reflects a synthesis of:
- Textile craftsmanship
- Storytelling
- Religious aesthetics
- Represents the rich heritage of Sattriya tradition, associated with monasteries (sattras) founded by Sankardeva.
World Craft City Programme

- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
The World Craft City (WCC) Programme is a global initiative aimed at recognising and strengthening cities with a rich living craft heritage, while integrating traditional skills into the modern creative economy. Recently, Srinagar was conferred the World Craft City tag, marking a significant milestone for Kashmir’s artisanal legacy and its global cultural linkages.
What is the World Craft City Programme?
- Launched in 2014 by the World Crafts Council (WCC-International).
- Recognises cities where crafts play a pivotal role in cultural identity, livelihoods, and local development.
- Establishes a global network of craft cities, aligned with the principles of the creative economy.
- Emphasises the role of local authorities, artisans, and communities in sustaining traditional crafts.
Indian Cities under the World Craft City Programme
India has several cities recognised under the WCC Programme:
- Jaipur – traditional jewellery, blue pottery, block printing
- Mamallapuram – stone carving and sculpture
- Mysore – silk, wood carving, painting
- Srinagar – diverse and historic handicrafts
The inclusion of Srinagar highlights the global recognition of Kashmir’s craft ecosystem and is expected to revive its traditional links with Central Asia and Iran.
Major Crafts of Srinagar (Kashmir)
- Papier-mâché: Objects made from mashed paper pulp, hand-painted and finished with lacquer or varnish.
- Pashmina: Fine hand-spun and hand-woven shawls originating from Kashmir’s unique geography.
- Sozni embroidery: Delicate needlework (from Persian soz meaning needle); artisans are known as sozankar.
- Kani shawls (associated with pashmina tradition): Intricate weaving using wooden spools.
These crafts are not only cultural symbols but also key sources of artisan livelihoods.
About the World Crafts Council
- Founded in 1964 by Aileen O. Webb, Margaret M. Patch, and Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay.
- A non-governmental, non-profit organisation.
- Objectives:
- Strengthen the status of crafts in cultural and economic life.
- Promote fellowship among craftspeople.
- Facilitate cultural exchange through conferences, workshops, exhibitions, research, and international collaboration.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) was launched in 2004.
- Promotes cooperation among cities that use creativity as a driver of sustainable urban development.
- Includes over 350 cities worldwide across creative fields such as crafts, design, music, and literature.
- While UCCN is a UNESCO initiative, the WCC Programme is led by the World Crafts Council (NGO).
150 Years of Vande Mataram

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
India has commenced a year-long national commemoration marking 150 years of Vande Mataram, with an enthusiastic response across the country and abroad. The celebrations were approved by the Union Cabinet on October 1 and formally inaugurated through a grand national event in New Delhi led by the Prime Minister. The President of India and other constitutional authorities have also extended their greetings, underlining the song’s enduring national significance.
About Vande Mataram
- Author: Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
- First Appearance: Serialized in the Bengali journal Bangadarshan and later included in the novel Anandamath (1882)
- Language: Blend of Sanskrit and Bengali
- Status: National Song of India (adopted on 24 January 1950)
Vande Mataram is not merely a song but a symbolic invocation of the motherland, embodying India’s cultural, spiritual, and national identity.
Historical Significance
- First sung publicly by Rabindranath Tagore at the 1896 Indian National Congress session in Calcutta
- Became a political slogan during the Swadeshi Movement (first used as a slogan on 7 August 1905)
- Madam Bhikaji Cama unfurled India’s tricolour in Stuttgart (1907) with the words Vande Mataram inscribed on it
- Served as a rallying cry for freedom fighters, inspiring mass participation in the national movement
The song played a critical role in forging a shared emotional and cultural identity during colonial resistance.
Baliyatra Festival

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
The President of India, Droupadi Murmu, recently extended greetings to the nation, especially to the people of Odisha, on the occasion of the historic Baliyatra festival and Boita Bandana. She described Baliyatra as a symbol of Odisha’s glorious maritime commercial tradition and rich cultural heritage, inspiring citizens to draw strength from the past to build a developed nation.
About Baliyatra Festival
- Location: Cuttack, Odisha
- Time of Celebration: Annually on Kartika Purnima (full moon day of Kartika month)
- Literal Meaning: Bali Jatra means “Voyage to Bali”
The festival marks the day when ancient Kalingan seafaring traders (Sadhabas) set sail for distant lands across the Bay of Bengal.
Historical Significance
Baliyatra commemorates Odisha’s over 2,000-year-old maritime and trade links between ancient Kalinga (present-day Odisha) and regions of South and Southeast Asia, including:
- Bali
- Java
- Sumatra
- Borneo
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
These voyages played a vital role in spreading Indian culture, language, religion, art, and trade networks, making Kalinga one of the most prosperous maritime powers of ancient India.
Cultural Practices and Celebrations
- Boita Bandana: Women float small boats (boitas) made of paper, banana leaf, or sholapith, with lighted lamps, on rivers—especially the Mahanadi—to honour the ancient sailors.
- Festivities:
- Large fairs and exhibitions
- Folk dance and music
- Traditional food and craft stalls
- Cultural performances reflecting Odisha’s heritage
The festival celebrates the courage, navigational expertise, and commercial acumen of Kalinga’s sailors.
Ramman Festival

- 06 Nov 2025
In News:
During a special session of the Uttarakhand Assembly, President of India Droupadi Murmu was presented with a traditional Ramman mask, bringing national attention to this centuries-old ritual festival practiced in the Garhwal region.
About the Ramman Festival
- Type: Annual religious and cultural festival
- Location: Twin villages of Saloor–Dungra, Chamoli district, Uttarakhand
- Time: Celebrated in late April during Baisakhi
- Deity: Dedicated to the tutelary deity Bhumiyal Devta, worshipped at his temple courtyard where the festival is performed.
- UNESCO Status: Inscribed in 2009 on UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity list.
UNESCO recognises Ramman as a multiform cultural event integrating theatre, music, historical reconstruction, and oral tradition—reinforcing the community’s identity and relationship with nature.
Key Features of the Festival
1. Rituals, Recitations & Divine Storytelling
- Begins with an invocation to Lord Ganesha, followed by the dance of the Sun God, and enactments of the birth of Brahma and Ganesha.
- Includes performances of Bur Deva, dances of Krishna and Radhika, and multiple ritual acts.
- Central attraction: Enactment of the local Ramkatha (episodes from the Ramayana), sung to 324 beats and steps.
2. Theatrical Performances & Masked Dances
- Combines narration, ritual drama, masked dances, music, and local legends.
- 18 different types of masks made from Bhojpatra (Himalayan birch) are used.
- Masks are accompanied by natural make-up materials such as sheep’s wool, honey, vermilion, wheat flour, oil, turmeric, soot, and plant-based dyes.
3. Instruments Used
- Dhol, Damau (percussion)
- Manjira, Jhanjhar (cymbals)
- Bhankora (trumpet)
4. Sacred Space & Community Participation
- Performed in the courtyard of Bhumiyal Devta temple.
- The entire village contributes—roles are caste-based:
- Brahmins: lead rituals
- Bhandaris (Rajputs): allowed to wear the sacred Narasimha mask
- Das drummers (lower caste): play percussion
- Jagaris/Bhallas (Rajput caste): act as bards singing epics and legends
- Funding and organisation are managed by village households collectively.
5. Transmission of Knowledge
- Oral transmission of epic songs, ritual lore, dance forms, mask-making, and traditional practices from elders to the younger generation.
Origin and Evolution
- Exact origins are unclear but believed to date back to medieval times.
- Linked to the arrival of Vaishnavite saints who brought the Ramayana tradition to the Central Himalayas.
- Initially a purely religious tradition centered on Ram bhakti, later expanded to include local folklore, social narratives, and community histories.
Examples of Local Narrative Additions
- Mwar–Mwarin dance: depicts the hardships of buffalo herders attacked by a tiger.
- Baniya–Baniyain Nritya: portrays the struggles of a trader-couple attacked by robbers.
These stories localise the Ramayana tradition, connecting mythic narratives to regional realities.
Cultural Significance
- Reinforces ties between humans, nature, and the divine.
- Ritual offerings include sprouted maize and barley seeds symbolising prosperity and agricultural abundance.
- Embodies the environmental, spiritual, and cultural ethos of the Garhwal Himalayan communities.
UNESCO’s Creative Cities Network

- 03 Nov 2025
In News:
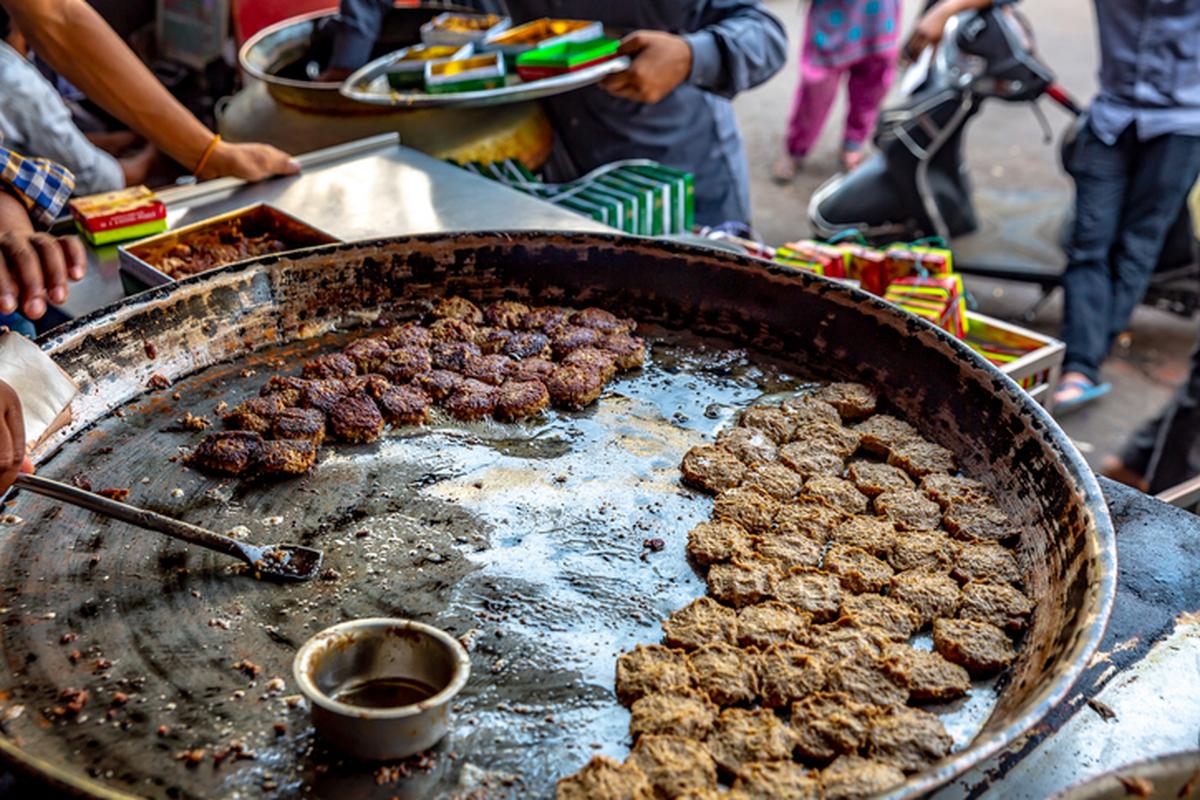
At the 43rd Session of the UNESCO General Conference held in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, Lucknow was officially inducted into the UCCN under the Gastronomy category, recognising its historic culinary heritage—especially Awadhi cuisine.
Cultural Basis of Selection
The nomination emphasised:
- Classical Awadhi dishes: galouti kebab, nihari-kulcha, tokri chaat, puri-kachori.
- Renowned desserts: malai gilori, makhan malai.
- The city’s unique Ganga-Jamuni tehzeeb, reflecting harmonious Hindu-Muslim cultural fusion.
Significance of the Recognition
- Enhances international visibility of Lucknow’s culinary heritage.
- Supports sustainable tourism and preservation of traditional recipes.
- Boosts local livelihoods of chefs, artisans, and food entrepreneurs.
- Strengthens India’s soft-power diplomacy using culture and cuisine.
About UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)
The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN), established in 2004, aims to promote cooperation among cities that identify creativity and cultural industries as drivers of sustainable urban development. The network strengthens cultural diversity and enhances resilience to global challenges such as climate change, inequality, and rapid urbanisation.
UCCN currently includes 350+ cities worldwide, classified into seven creative fields:
- Crafts & Folk Arts
- Media Arts
- Film
- Design
- Gastronomy
- Literature
- Music
Objectives of UCCN
- Mainstream creativity as a strategic component of urban planning and development.
- Foster public-private-civil society partnerships in cultural sectors.
- Promote innovation hubs and expand opportunities for artists, professionals, and cultural enterprises.
- Support cities in advancing the UN Sustainable Development Agenda through culture-led growth.
India and the UCCN
Before 2025, India had eight member cities. With Lucknow’s addition, the total now stands at nine.
Indian Cities in UCCN
|
City |
Category |
Year |
|
Jaipur |
Crafts & Folk Arts |
2015 |
|
Varanasi |
Music |
2015 |
|
Chennai |
Music |
2017 |
|
Mumbai |
Film |
2019 |
|
Hyderabad |
Gastronomy |
2019 |
|
Srinagar |
Crafts & Folk Arts |
2021 |
|
Gwalior |
Music |
2023 |
|
Kozhikode |
Literature |
2023 |
|
Lucknow |
Gastronomy |
2025 |
VandeMataram – 150 Years Celebration

- 30 Oct 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in his October 2025 Mann Ki Baat address, called upon citizens to mark the 150th anniversary of VandeMataram.
Historical Origins and Evolution
- VandeMataram—meaning “I bow to thee, Mother”—was composed by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay in the 1870s in Sanskritised Bengali.
- It was later published in his novel Anandamath (1882), where the motherland was depicted symbolically as a divine, nurturing force.
- The song gained prominence during the freedom struggle. Its first public rendition was by Rabindranath Tagore at the 1896 Indian National Congress session, marking its transition from literary creation to a nationalistic anthem.
- Despite British censorship, it echoed across protest marches, swadeshi gatherings, and revolutionary movements, becoming an enduring symbol of defiance.
Role in National Movement and Political Debates
- During the early 20th century, the song became deeply embedded in anti-colonial resistance, especially during the Swadeshi Movement (1905) and later the Quit India Movement (1942). However, its later stanzas, portraying the motherland as a Hindu goddess, drew objections from the All-India Muslim League and some Muslim leaders.
- To maintain inclusivity, the Indian National Congress in 1937 officially adopted only the first two stanzas, which do not include religious imagery. This selective adoption reflected efforts to preserve unity in a diverse society.
- On 24 January 1950, the Constituent Assembly accorded equal honour to VandeMataram and Jana Gana Mana, defining the former as the national song and the latter as the national anthem.
Cultural, Symbolic and Constitutional Status
Today, VandeMataram holds a unique constitutional and cultural position:
- National Song Status: It enjoys the same respect as the national anthem as per Constituent Assembly resolutions.
- Parliamentary Tradition: An instrumental version is played at the end of every Parliament session.
- Cultural Identity: It continues to symbolise unity, patriotism, and emotional attachment to the motherland.
- Secular Projection: Emphasis remains on the first two stanzas to ensure inclusivity across religious communities.
- Judicial Affirmation: In 2022, the Delhi High Court reaffirmed that citizens should show equal respect to both the national anthem and national song.
Children’s Booker Prize

- 29 Oct 2025
In News:
- The Booker Prize Foundation has announced the establishment of the Children’s Booker Prize, a landmark global award dedicated to fiction written for children aged 8 to 12 years.
- Scheduled to debut in 2027, this prize represents the first major expansion of the Booker brand into children’s literature and carries a purse of £50,000, matching the award value of its established sister prizes.
What the Prize Represents
- The Children’s Booker Prize aims to celebrate and elevate fiction for middle-grade readers, acknowledging the importance of early reading habits in shaping future generations of informed, imaginative, and engaged adults. Books originally written in English or translated into English will be eligible, making the award internationally inclusive.
- The Booker Prize Foundation, in partnership with the AKO Foundation, which supports arts, education, and environmental initiatives, seeks to nurture a global culture of reading and inspire literary excellence in children’s storytelling.
Eligibility and Key Features
- Age Category: Fiction aimed at 8–12-year-old readers.
- Geographic Scope: Open to books published in the UK or Ireland, regardless of the author’s nationality.
- Languages: Both original English works and translated works can be submitted.
- Prize Value: £50,000 (same as the adult Booker and International Booker), funded by the AKO Foundation.
- Selection Process: The first award in 2027 will be decided by a jury of children and adults, chaired by acclaimed British children’s author Frank Cottrell-Boyce, the current children’s laureate.
The submission process begins in early 2026, and the prize hopes to build enthusiasm and visibility around high-quality children’s literature.
Purpose and Vision
- According to Booker Prize Foundation Chief Executive Gaby Wood, the award aims to cultivate an enduring love for reading among younger audiences and to serve as a catalyst for literary engagement across generations. The initiative builds on the Booker’s legacy of recognising works that shape global literary culture.
Position Within the Booker Ecosystem
The Children’s Booker Prize joins two established awards under the Booker umbrella:
1. Booker Prize
- Founded: 1969
- Eligibility: Original novels written in English and published in the UK or Ireland.
- Prize Distribution: Award solely to the author.
- Objective: Celebrates outstanding English-language fiction.
- Indian Winners:
- Salman Rushdie – Midnight’s Children (1981)
- Arundhati Roy – The God of Small Things (1997)
- Kiran Desai – The Inheritance of Loss (2006)
- Aravind Adiga – The White Tiger (2008)
2. International Booker Prize
- Established: 2005; restructured in 2016.
- Eligibility: Translated fiction published in the UK or Ireland.
- Prize Distribution: Shared equally between author and translator.
- Objective: Promotes cross-cultural literary exchange and honours translation.
- Indian-Linked Winners:
- Geetanjali Shree – Tomb of Sand (2022) (Hindi, translated by Daisy Rockwell)
- Banu Mushtaq – Heart Lamp (2025) (Kannada, translated by Deepa Bhasthi)
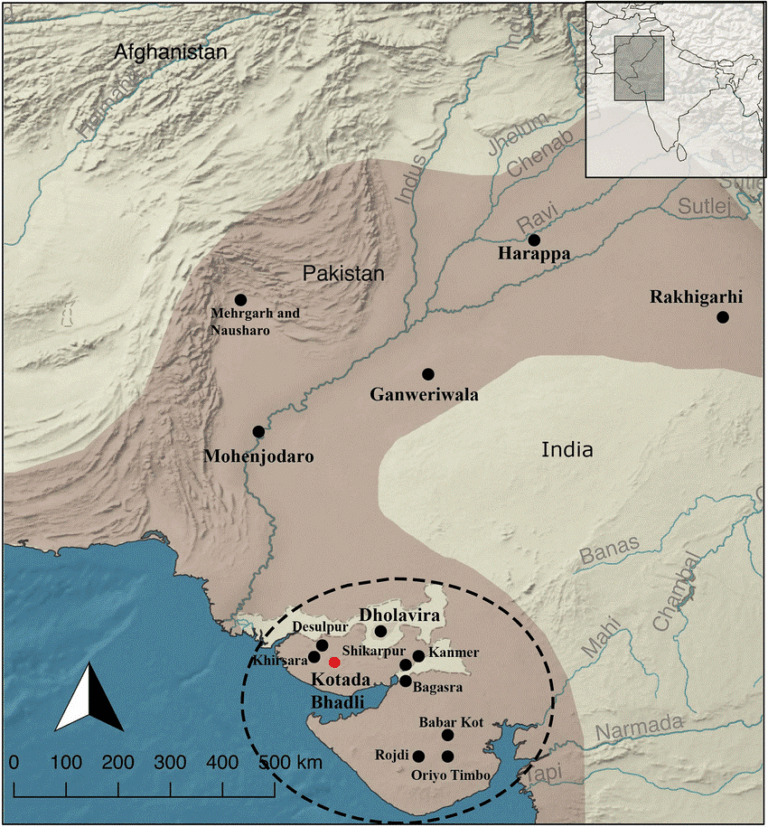
KotadaBhadli
- 29 Oct 2025
In News:
- A recent multidisciplinary research study by Deccan College, Symbiosis School for Liberal Arts, and the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has reinterpreted the Harappan settlement of KotadaBhadli in Kutch, Gujarat, as the earliest known caravanserai, dating to the Mature Harappan phase (2300–1900 BCE).
- The study, published in L’Anthropologie (2025), pushes back the origins of organised trade infrastructure in South Asia by nearly 2,000 years, long before the rise of the Silk Route.
Location and Strategic Significance
- KotadaBhadli lies in the Kutch district of Gujarat, positioned along inland trade corridors linking prominent Harappan centres such as Dholavira, Lothal, and Shikarpur.
- Its placement reveals a purposeful design—serving as a rural logistical stopover facilitating long-distance trade between urban and coastal settlements.
Nature and Function of the Settlement
- Researchers have identified KotadaBhadli as a fortified rural halt, intended not for permanent habitation but for short-term stops by traders and their caravans.
- Its function aligns closely with caravanserai-style establishments known from later historical periods—providing shelter, security, food, and space for pack animals during overland journeys.
- The study clarifies a previously missing link in Harappan commerce: while trade with Mesopotamia and inland India was well documented, the operational mechanism—how traders and goods moved safely across long distances—was not fully understood. KotadaBhadli provides the first archaeological evidence to support this model.
Archaeological and Scientific Evidence
Excavations conducted between 2010 and 2013 and re-analysed through advanced techniques have revealed:
- A multi-roomed central complex, likely functioning as administrative or resting quarters.
- Fortified walls with bastions, confirming its role as a protected stopover.
- Large open courtyards, interpreted as holding areas for animals and storage of goods.
- Remains of food waste and imported material, suggesting active trade activity.
Cutting-edge scientific methods—including ground-penetrating radar, satellite mapping, magnetic surveys, isotopic and lipid analysis, and multiple dating techniques—have improved understanding of the site’s functional layout and confirm its zoning for logistical purposes.
Implications for Harappan Trade Networks
The findings demonstrate that the Harappan economy had a structured overland trade system, supported by a network of small fortified checkpoints rather than solely urban market centres. This reveals an advanced level of planning and coordination within Harappan economic systems.
Key implications include:
- Chronological significance: Organised trade infrastructure existed in South Asia more than two millennia before the Silk Route.
- Economic insight: Harappans displayed sophisticated logistics and administrative planning.
- Civilizational understanding: The Harappan world was not merely dependent on ports like Lothal or trade with Mesopotamia—it also relied on inland support systems that sustained commerce.
Ningol Chakouba Festival

- 24 Oct 2025
In News:
- Manipur recently celebrated the Ningol Chakouba Festival, a unique cultural tradition that reinforces the bond of love between married women and their paternal families.
- As part of the annual celebrations, the Department of Fisheries, Manipur organized the Annual Fish Fair-cum-Fish Crop Competition at Hapta Kangjeibung in Imphal, a day before the festival.
- The event aims to make fish available to the public at affordable prices, as fish curry is an essential part of the festive feast.
About Ningol Chakouba Festival
- Meaning:
- Ningol – married woman (sister or daughter)
- Chakouba – feast or communal meal
Thus, Ningol Chakouba translates to “feast of married women”.
- When Celebrated:Observed annually on the second day of Hiyangei month (October–November) of the Meitei lunar calendar.
- Main Ritual:Married women and their children visit their maternal homes for a grand feast and reunion with their brothers and parents.
- The sons of the family formally invite their married sisters about a week in advance.
- Women arrive in traditional attire, bringing fruits, vegetables, and local delicacies as offerings.
- After a shared meal, brothers present gifts to their sisters as a token of love and respect.
Cultural Essence and Significance
- The festival serves as a symbol of familial unity, respect for women, and continuity of social ties even after marriage.
- It highlights the importance of kinship in Manipuri society and reinforces the bond between daughters and their parental homes.
- Beyond Manipur, the festival is now celebrated by Manipuri communities across India and abroad, preserving cultural identity among the diaspora.
Historical Background
- Origin: Traced back to the reign of King Nongda Lairen Pakhangba, one of Manipur’s earliest rulers.
- At that time, Queen Laisana used to invite her brother Poireiton to the royal palace annually for a feast—originally called “Piba Chakouba” (Piba meaning brother/son).
- Transformation:
The tradition evolved during the reign of King Chandrakirti Singh (1831–1886), who invited his sisters instead of brothers due to logistical challenges in visiting them.- Since then, the celebration became known as “Ningol Chakouba”, centered on the affection between sisters and brothers.
Associated Event: Fish Fair-cum-Fish Crop Competition
- Organized by the Department of Fisheries, Government of Manipur, every year a day before Ningol Chakouba.
- Purpose:
- Ensure easy availability of fresh fish at affordable prices for the festival.
- Promote local fish farmers and aquaculture in the state.
- Venue: Hapta Kangjeibung, Imphal.
- Cultural Link: Fish dishes, especially fish curry, are a mandatory part of the feast, symbolizing prosperity and togetherness.
Sabarimala Temple
- 24 Oct 2025
In News:
President Droupadi Murmu recently made a historic visit to the Sabarimala Sree Dharma Sastha Temple in Kerala, becoming the first woman head of state to offer prayers at the sacred hill shrine dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
She is only the second President of India to visit the temple, after V. V. Giri in the 1970s. The visit holds deep symbolic and constitutional significance, coming in the backdrop of the 2018 Supreme Court judgment on women’s entry to the shrine.
About Sabarimala Temple
- Location: Situated in the Western Ghats, Pathanamthitta District, Kerala.
- Deity: Dedicated to Lord Ayyappa (also known as Dharma Shasta), the son of Lord Shiva and Mohini (the female incarnation of Vishnu).
- Altitude: Located atop a hill at 4,134 ft above sea level, surrounded by dense forests forming part of the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- Access: Pilgrims undertake a challenging trek through forests and hills to reach the sanctum.
- Pilgrimage: Open to devotees mainly during the Mandalam-Makaravilakku season (November–January).
- Scale: Among the largest annual pilgrimages in the world, attracting 40–50 million devotees annually.
Rituals and Traditions
- Vratham (Austerity): Pilgrims observe a 41-day penance before visiting the shrine, maintaining celibacy, vegetarianism, and spiritual discipline.
- Inclusivity: Sabarimala is one of the few Hindu temples that welcomes devotees of all faiths.
- Religious Harmony: Near the temple lies Vavaru Nada, dedicated to Vavar, a Muslim saint believed to be Lord Ayyappa’s companion—symbolizing interfaith harmony.
Architecture
- The temple blends traditional Kerala and Dravidian architectural styles.
- Built on a 40-foot-high plateau, it features:
- A sanctum sanctorum (Sreekovil) with a copper-plated roof and four golden finials (kalasams).
- Two mandapams (halls) for rituals and gatherings.
- A flagstaff symbolizing devotion.
- The iconic 18 sacred steps (Pathinettam Padi), each representing a spiritual or philosophical stage to liberation.
Sabarimala Case: The Women’s Entry Controversy
- Traditional Practice: Women of menstruating age (10–50 years) were historically barred from entering the temple, as the deity is considered a Naishtika Brahmachari (eternal celibate).
- Judicial Intervention:
- In 2018, the Supreme Court of India (in Indian Young Lawyers Association v. State of Kerala) declared the ban unconstitutional, citing gender equality and freedom of religion under Articles14, 15, 25, and 26 of the Constitution.
- The verdict led to widespread protests across Kerala.
- The issue remains under review by a larger constitutional bench, reflecting the ongoing debate between faith and fundamental rights.
Virtual Museum of Stolen Cultural Objects

- 15 Oct 2025
In News:
Recently, UNESCO launched the world’s first Virtual Museum of Stolen Cultural Objects during the MONDIACULT 2025 Conference. This global digital initiative marks a vital step in protecting cultural heritage, raising awareness about illicit trafficking, and facilitating the return of stolen artefacts to their countries of origin.
Key Features and Objectives
The virtual museum serves as an immersive digital platform reconnecting community with cultural treasures lost to theft, smuggling, and colonial-era plundering. Unlike traditional museums, its purpose is not to accumulate artefacts but to systematically empty itself by aiding restitution efforts. Visitors can explore high-resolution 2D and 3D reconstructions of objects, along with contextual history and cultural significance.
The project contributes to the goals of UNESCO’s 1970 Convention on preventing illicit trafficking of cultural property and aligns with a recent UN General Assembly resolution urging stronger international cooperation to restore stolen heritage.
Institutional Framework
- Developed by UNESCO in collaboration with INTERPOL
- Financially supported by Saudi Arabia; additional contribution from the United States
- Announced earlier at MONDIACULT 2022 and launched in September 2025
- Currently displays ~240 missing cultural objects from 46 countries
- Represents diverse cultural forms: manuscripts, sculptures, ritual objects, architectural fragments, artworks, coins, and archaeological finds
The digital experience is designed like a baobab tree, symbolizing resilience and interconnectedness, created by renowned Burkinabe architect Francis Kéré. The platform includes:
- Gallery of Stolen Objects
- Auditorium
- Return & Restitution Room, highlighting successful repatriation stories
India’s Contribution and Significance
Three culturally significant Indian artefacts are showcased:
- 9th-century sandstone sculptures of Nataraja and Brahma from Mahadev Temple, Pali (Chhattisgarh)
- Stone sculpture of Bhairava (undated)
These items reflect India’s rich temple heritage and spiritual aesthetic. Their listing reinforces India’s continuing struggle against antiquities smuggling.
India has intensified its efforts to recover stolen heritage in recent years. Since 2014, over 600 antiquities have been brought back to India. The leadership has repeatedly emphasized ethical cultural restitution, with an official stance that “no museum should hold artefacts acquired unethically.”
Global and Youth Focus
The platform especially targets youth and digital natives, using interactive storytelling to:
- Promote cultural sensitivity
- Highlight community identities tied to artefacts
- Encourage global cooperation on heritage protection
Nobel Prize in Literature 2025
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- The 2025 Nobel Prize in Literature has been conferred on László Krasznahorkai, the Hungarian novelist celebrated for his profoundly philosophical and apocalyptic prose.
- The Swedish Academy recognized him for his ability to capture the “tension between ruin and redemption” and for reaffirming the enduring power of art in an age of crisis.
About the Nobel Prize in Literature
- Established under Alfred Nobel’s will (1895), the Nobel Prize in Literature is awarded annually by the Swedish Academy to an author who has produced “the most outstanding work in an ideal direction.”
- The award, accompanied by a cash prize of 11 million Swedish crowns (≈ USD 1.2 million), represents the highest global recognition in the literary world.
Life and Background
- Born in 1954 in Gyula, Hungary, near the Romanian border, Krasznahorkai grew up amid the tensions of post-war socialism.
- Educated in law and literature in Budapest, his early life in a repressive political climate shaped his preoccupation with decay, faith, and endurance. His Jewish and rural background deepened his sensitivity to questions of identity and moral collapse.
Literary Career and Major Works
Krasznahorkai made his literary debut with Sátántangó (1985), a dark, surreal portrayal of a disintegrating collective farm that has since become a modern classic. Its cinematic adaptation by Béla Tarr as a seven-hour film further cemented its cult status.
His subsequent works expanded his thematic range:
- The Melancholy of Resistance (1989): Explores moral and social decay under authoritarianism in a small Hungarian town.
- War and War (1999): A meditation on history, violence, and transcendence through the story of an archivist.
- Seiobo There Below (2008): Reflects his deep engagement with Asian philosophies and aesthetics, particularly from Japan and China.
- Herscht 07769 (2018): A study of German social unrest and the search for order amid chaos.
Themes and Literary Style
- Krasznahorkai’s fiction fuses metaphysical inquiry with social critique. His narratives depict societies on the brink of collapse, where individuals confront spiritual drift, institutional decay, and existential dread.
- Stylistically, his long, recursive sentences and dense, rhythmic prose challenge readers to engage deeply with the text. His influences range from Franz Kafka and Samuel Beckett to Thomas Bernhard, yet his vision remains uniquely his own — a fusion of absurdism, grotesque realism, and mystical introspection.
International Recognition and Legacy
- Over four decades, Krasznahorkai has emerged as one of Europe’s most formidable literary voices. His earlier accolades include the Kossuth Prize (2004), Hungary’s highest cultural honor, and the Man Booker International Prize (2015).
- His global reach reflects a bridge between Central European existentialism and Eastern contemplative traditions, making his work both regionally grounded and universally resonant.
Erra Matti Dibbalu

- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
Andhra Pradesh has taken a major step towards global heritage recognition with the inclusion of Erra Matti Dibbalu (Red Sand Dunes) near Visakhapatnam and the Natural Heritage of Tirumala Hills in the UNESCO Tentative List of World Heritage Sites. The move reflects India’s growing commitment to protect and preserve sites of geological and ecological importance. Being placed on the Tentative List is a mandatory prerequisite for eventual nomination to the UNESCO World Heritage List, symbolizing international acknowledgment of a site’s Outstanding Universal Value (OUV).
Erra Matti Dibbalu: India’s Rare Coastal Geo-Heritage Site
- Located along the coast near Visakhapatnam, Erra Matti Dibbalu—literally “Red Sand Dunes”—is a unique National Geo-heritage Monument, spread over 1,500 acres.
- The formations consist of sand, silt, and clay, with their deep red hue arising from natural oxidation over thousands of years.
- These dunes exhibit badland topography with striking geomorphic features such as gullies, buried channels, paired terraces, beach ridges, wave-cut terraces, knick points, and waterfalls.
- The site represents the late Quaternary geologic age and provides vital evidence of climatic and sea-level fluctuations over millennia. Dendritic drainage patterns and layered sediments at the site act as a natural archive of environmental changes and coastal evolution.
- First recorded in 1886 by British geologist William King, the site is globally rare — with only two similar formations identified, one in Sri Lanka and another in Tamil Nadu (Teri Sands).
- Additionally, archaeological artefacts discovered here point to Upper Palaeolithic human activity (around 20,000 BCE), making it an important cultural and scientific site.
- Recognizing its geological and historical significance, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) declared Erra Matti Dibbalu a National Geo-heritage Monument in 2016. However, experts warn that unregulated tourism and filming activities pose a threat to its fragile ecosystem, calling for stronger conservation and monitoring mechanisms.
- According to IUCN’s Geological World Heritage (2021) classification, the site may qualify under Theme 2: Tectonic System and Theme 7: Coastal System.
Tirumala Hills: A Geological and Ecological Treasure
- The Tirumala Hills in Tirupati district are celebrated not just for spiritual significance but also for their geological, ecological, and cultural heritage.
- The hills showcase the Eparchaean Unconformity—a rare geological boundary where 2.5-billion-year-old Archean rocks meet younger Proterozoic formations of the Cuddapah Supergroup. This boundary represents a vast time gap in Earth’s geological record, offering critical insights into planetary evolution.
- The site also houses the famous Natural Arch (Silathoranam), a naturally sculpted rock formation estimated to be 1.5 billion years old. The region forms part of the Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve and Venkateswara National Park, both home to rich biodiversity including endangered red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus), Cycas beddomei, and the elusive Jerdon’s Courser.
- With dense forests, seasonal waterfalls, and unique geological formations, Tirumala Hills qualify under multiple UNESCO criteria related to natural beauty, ecological diversity, and geological significance. As per IUCN (2021), the site aligns with Theme 1: History of Planet Earth and Evolution of Life.
Self-Respect Movement
- 09 Sep 2025
In News:
The year 2025 marks the centenary of the Self-Respect Movement, a landmark social reform initiative launched by E.V. Ramasamy “Periyar” in Tamil Nadu. Emerging in 1925 through the Tamil weekly KudiArasu(Republic), the movement fundamentally reshaped Tamil society by questioning caste hierarchies, patriarchy, and religious orthodoxy, and by laying the foundations of modern Dravidian politics.
Origins and Context
- The Justice Party (South Indian Liberal Federation, 1916) had earlier challenged Brahmin dominance but remained largely confined to elite non-Brahmin interests.
- Periyar, after leaving the Indian National Congress in 1925, criticised the Justice Party for lacking a people-centric agenda and warned against creating a new non-Brahmin elite as oppressive as Brahmin oligarchy.
- Through KudiArasu,Periyar articulated a more radical vision — shifting reform efforts towards the common masses and framing an agenda of rationalism, equality, and self-respect.
Core Ideas and Aims
The Self-Respect Movement stood for:
- Abolition of caste hierarchy and Brahmanical dominance.
- Promotion of rationalism over religious superstition and ritualism.
- Assertion of dignity and equality for all individuals, irrespective of caste or gender.
- Social reform over political independence — unlike the Congress-led freedom struggle, which the movement saw as tied to Hindu orthodoxy.
Key Features and Reforms
- Self-Respect Marriages – Conducted without priests or rituals, challenging caste and religious authority.
- Women’s Rights – Advocacy of widow remarriage, right to divorce, property rights, reproductive choice (including abortion), and women’s education.
- Inter-caste Unity – Promotion of inter-caste marriages and solidarity across oppressed groups.
- Critique of Religion and Nationalism – Rejection of Gandhi’s “religion-tinted nationalism” and the Congress as a bastion of caste Hindu interests.
- Dravidian Identity – Assertion of Tamil/Dravidian identity and resistance to Sanskritichomogenisation.
Impact and Legacy
- Mass Awakening: Instilled pride and self-respect among non-Brahmin masses, transforming them from passive subjects of reform to active participants.
- Foundation for Dravidian Politics: Evolved into the DravidarKazhagam (DK) and inspired political parties like DMK and AIADMK, shaping Tamil Nadu’s welfare-driven governance model.
- Gender and Social Justice: Pioneered radical reforms in marriage, family, and gender relations, decades ahead of mainstream Indian discourse.
- Intellectual Tradition: Drew inspiration from earlier reformers such as IyotheeThass, Jyotirao Phule, and B.R. Ambedkar, situating Tamil Nadu in a wider anti-caste, rationalist movement.
Contemporary Relevance
As the movement enters its centenary in 2025, it resonates amid debates over Hindutva, cultural homogenisation, and caste discrimination. Its emphasis on rationalism, social equality, and grassroots empowerment continues to provide a counter-narrative to exclusivist identities and remains vital for advancing social justice and constitutional morality in India.
VrindavaniVastra
- 03 Sep 2025
In News:
The VrindavaniVastra, a 16th-century sacred silk textile of Assam, is set to return temporarily from the British Museum, London, for exhibition in 2027. The decision marks a significant milestone in India’s efforts to reclaim its cultural heritage and present it to the public in its place of origin.
Historical Background
- The VrindavaniVastra was woven in Assam under the guidance of SrimantaSankardeva, the great Vaishnav saint-reformer, at the request of Koch King Nara Narayan.
- It depicts scenes from Lord Krishna’s childhood and divine pastimes in Vrindavan, woven intricately with silk threads.
- Historically, Nara Narayan had sheltered Sankardeva after he faced persecution by the Ahom kingdom under pressure from Brahmin priests, reflecting the socio-political tensions of the time.
Artistic and Cultural Significance
- The textile is regarded as a masterpiece of Assamese Vaishnav art, blending weaving traditions with spiritual themes.
- Originally consisting of 15 separate silk panels, the current exhibit measures around 9.5 metres in length, assembled from multiple fragments.
- It represents not only religious devotion but also the syncretic weaving traditions of Assam, incorporating motifs influenced by diverse artistic cultures.
- As a central artefact of Assamese Vaishnavism, it reinforces Sankardeva’s legacy of devotional bhakti traditions.
Journey to the West
- Fragments of the Vastra were believed to have travelled from Assam to Tibet in the 17th–18th centuries, before being collected by British explorers during the 19th–20th centuries.
- In 1904, the India Museum acquired the textile and later transferred it to the British Museum. Since then, it has been part of their South Asian collection, alongside similar pieces in other European museums.
Mela Patt Festival

- 03 Sep 2025
In News:
The Mela Patt Festival, celebrated annually in Bhaderwah (Doda district, Jammu & Kashmir), is one of the most prominent cultural and religious events of the region. Rooted in Nag culture, the festival honors Lord Vasuki Nag, the presiding deity of Bhaderwah Valley, and reflects the valley’s rich legacy of syncretic traditions and communal harmony.
Historical Background
- The origins of the festival date back to the 16th century, when it was first celebrated by King Nag Pal during the era when Bhaderwah was known as Bhadarkashi.
- The festival commemorates the historic meeting between Mughal Emperor Akbar and King Nag Pal of Bhaderwah, highlighting its integration into broader Indian history.
- Over the centuries, the event has remained a symbol of unity, with no reported communal discord in its nearly 600-year-long history.
Rituals and Celebrations
- Timing: The festival is observed on Nag Panchami, seven days after the conclusion of the sacred Kailash Yatra.
- Cultural Expressions:
- The unique ‘Dikko Dance’ features participation from men and women across communities, symbolizing peace and pride.
- The ‘Dhakku Dance’, a traditional Dogra folk performance, is also showcased, underscoring its importance in the cultural mosaic of India.
- Inclusivity: Devotees and visitors from across Jammu & Kashmir, irrespective of caste or religion, gather to pay homage to Raja Nag Pal’s bravery and spiritual power.
India’s Fossil Heritage
- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
India’s fossil heritage, spanning hundreds of millions of years, holds clues to the evolution of plants, dinosaurs, mammals, and marine life. Yet, the absence of strong protection laws and national repositories leaves this heritage vulnerable to theft, vandalism, and illegal global trade.
India’s Fossil Wealth
- Diverse Record: Fossils in India range from the Precambrian era to the Cenozoic, covering ancient plants, marine life, dinosaurs, and mammals.
- Key Discoveries:
- Vasuki indicus – a 47-million-year-old giant snake (~15 m long) from Kutch.
- Indohyus – an early ancestor of whales, discovered in Central India.
- Dinosaur nests and eggs – particularly in the Narmada Valley and Deccan basalt formations.
- Unique Evolutionary Insights: India’s prolonged isolation after separating from Gondwanaland (~150 million years ago) and later collision with Asia (50–60 million years ago) created unique fossil beds documenting crucial evolutionary transitions.
Sites of Importance
- Kutch, Gujarat – rich in marine fossils and large vertebrates.
- Narmada Valley, Madhya Pradesh – known for dinosaur eggs, nests, and bones.
- Deccan Traps & Himalayan foothills – diverse vertebrate and invertebrate fossils.
- Balasinor, Gujarat – developed as India’s Dinosaur Fossil Park.
Moai Statues
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent study published in the Journal of Cultural Heritage warns that rising sea levels may submerge Easter Island’s iconic Moai statues by 2080, endangering both the island’s cultural heritage and tourism-based economy.
About Moai Statues
- What they are: Massive monolithic statues carved from volcanic rock by the Rapa Nui people, the island’s first Polynesian settlers.
- Time of construction: Approx. 1250–1500 CE (some estimates: 1400–1650 CE).
- Number: Nearly 1,000 statues have been identified.
- Features:
- Tallest statue: ~33 feet high.
- Made primarily of volcanic tuff.
- Carved in the likeness of ancestors.
- Cultural role:
- Built to honor chiefs and important individuals.
- Placed on rectangular stone platforms called ahu, which also served as tombs.
- Each statue has unique traits to represent the person commemorated.
Study Findings
- Researchers used digital twin models and advanced simulations to project flooding risks caused by sea-level rise.
- Results show that by 2080, seasonal waves could reach Ahu Tongariki – the largest ceremonial platform on the island, part of the Rapa Nui National Park (UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1995).
- The flooding could impact 51 cultural assets, including the world-famous Moai statues.
- The study emphasizes the urgency of local community planning to safeguard heritage against climate risks.
Easter Island – Key Facts
- Location: Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- Forms part of the Polynesian Triangle along with Hawaii and New Zealand – the traditional homeland of Polynesian peoples.
- Known globally for its archaeological and cultural significance, particularly the Moai statues.
Nüshu: Revival of the World’s Only Women’s Script

- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
Nüshu, literally meaning “women’s writing” in Chinese, is a unique script originating in the 17th century in Jiangyong, Hunan Province. Developed when women were excluded from formal education, it functioned as a private communication system among women through letters, embroidery, songs, and poetry. With around 500 core characters, it is the only known writing system in the world created and used exclusively by women.
Distinctive Features
- Form: Rhomboid, thread-like characters derived from traditional Chinese script; composed of dots, horizontals, virgules, and arcs.
- Medium of Use: Mothers taught daughters; used among sisters and friends. Content included folk songs, riddles, autobiographies, and translations of Chinese poems.
- Symbolism: Embodied sisterhood, resilience, and empowerment in a patriarchal society.
Historical Transformation and Conservation
- Decline: By the late 20th century, Nüshu faced near extinction with the death of its last native writers such as Yi Nianhua (1988–89).
- Revival Efforts: Since the 21st century, museums, training centers, and manuals have been established to preserve and promote Nüshu.
- National Recognition: Inscribed on China’s National Intangible Cultural Heritage list; efforts are ongoing for UNESCO recognition.
- Community Role: Women inheritors and enthusiasts continue to practice Nüshu as a cultural art form, while scholars study its historical and social value.
Technology and Modern Adaptation
- Digital Archiving: Unicode integration, high-resolution scans, and cloud storage aid global accessibility.
- AI Tools: Machine learning assists in translation and decoding.
- Global Outreach: Social media, e-courses, AR/VR exhibitions, and documentaries such as Hidden Letters have amplified its relevance.
- Cultural Integration: Featured in creative mediums—e.g., WeChat memes celebrating Chinese female athletes during the Paris 2024 Olympics—blending heritage with contemporary culture.
Social and Cultural Impact
- Women’s Empowerment: Nüshu fosters confidence, independence, and identity among modern women, especially Gen Z.
- Dialogue Across Genders: Increasing interest among men reflects its role as a bridge between genders, expanding from women’s private script to a shared cultural heritage.
- Economic Potential: Provides livelihood through digital art, tourism, crafts, and cultural exchanges.
Piprahwa Relics

- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
The recent return of the sacred Piprahwa relics of Lord Buddha to India marks a landmark moment in India’s cultural diplomacy, heritage preservation, and spiritual history. Orchestrated by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with the Godrej Industries Group, this event prevented the relics’ auction in Hong Kong (May 2025) and instead restored them to their rightful home. For India, the land where the Buddha attained enlightenment and preached, this repatriation is more than a matter of archaeology—it reaffirms India’s role as the civilizational custodian of global heritage.
What are the Piprahwa Relics?
- Association: Believed to be the mortal remains of Lord Buddha, enshrined by the Sakya clan (his kinsmen) in the 3rd century BCE.
- Discovery: Excavated in 1898 by William Claxton Peppé, a British civil engineer and estate manager, from a stupa at Piprahwa, Uttar Pradesh, located just south of Lumbini (Buddha’s birthplace, now in Nepal).
- Contents:
- Bone fragments of the Buddha
- Caskets: soapstone, crystal, and sandstone coffer
- Offerings: gold ornaments, gemstones, and other ritual objects
- Inscription: A Brahmi script engraving on one of the caskets confirmed the relics’ identity, noting they were deposited by the Sakya clan.
Historical Journey of the Relics
- Colonial Appropriation (1898–1899)
- Following their discovery, the British Crown claimed the artefacts under the Indian Treasure Trove Act, 1878.
- The bone and ash relics were gifted to King Chulalongkorn of Siam (Thailand), reflecting colonial practices of cultural transfer.
- The majority of the remaining relics were placed in the Indian Museum, Kolkata (1899).
- Legal Protection
- Classified as ‘AA’ antiquities under Indian law, these relics cannot be sold, exported, or removed—underscoring their sacred and national significance.
- Attempted Auction in 2025
- The relics resurfaced in Hong Kong for an intended auction.
- Through timely diplomatic and legal intervention, supported by public-private partnership with the Godrej Group, the Ministry of Culture secured their return.
Significance of the Repatriation
1. Spiritual and Cultural Significance
- Buddhism, which spread from India across Asia, regards relics of the Buddha as sacred embodiments of peace, compassion, and enlightenment.
- The return reaffirms India as the spiritual homeland of Buddhism, strengthening cultural linkages with Buddhist-majority nations like Thailand, Myanmar, Japan, and Sri Lanka.
2. Archaeological and Historical Importance
- Piprahwa is one of the earliest archaeologically verified stupa sites.
- The discovery provides rare material evidence of Buddhist practices of relic veneration, confirming textual accounts in Buddhist scriptures.
3. Diplomatic and Soft Power Dimensions
- The move highlights cultural diplomacy as a tool of India’s foreign policy.
- India positions itself as a global guardian of Buddhist heritage, enhancing ties with Southeast Asian nations where Buddhism is deeply rooted.
4. Model of Public–Private Partnership
- The collaboration between the Government of India and the Godrej Industries Group sets a precedent for safeguarding heritage.
- It reflects how corporate social responsibility (CSR) can extend beyond business to civilizational legacy.
Paithani Sarees
- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister recently highlighted the cultural and artisanal significance of Paithani sarees during the monthly ‘Mann Ki Baat’ radio programme, bringing national attention to this traditional Maharashtrian textile.
Historical Background
- Origin: Paithani sarees derive their name from Paithan, an ancient town on the banks of the Godavari River in Maharashtra.
- Antiquity: The tradition of Paithani weaving dates back over 2,000 years, with its roots in the Satavahana dynasty (2nd century BCE).
- Royal Patronage: These sarees were patronized by several royal courts, including the Satavahanas, Peshwas of Pune, Nizams of Hyderabad, and Mughal emperors.
Key Features
|
Attribute |
Description |
|
Material |
Woven using pure silk and gold/silver zari |
|
Technique |
Crafted using the tapestry weaving method, all handwoven |
|
Designs |
Intricate motifs like peacocks, parrots, lotuses, and floral vines |
|
Border & Pallu |
Known for distinctive kath (border) and padar (pallu) designs |
|
Size |
Typically six- or nine-yard sarees |
|
Cultural Significance |
Regarded as the ‘Mahavastra’ (great garment) of Maharashtra, traditionally worn by Maharashtrian brides |
Recognition and Cultural Value
- Symbol of Heritage: Paithani sarees are considered a symbol of Maharashtrian cultural identity and artisanal excellence.
- GI Tag: Granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2010, acknowledging their unique regional origin and craftsmanship.
- Artistic Value: Among the most exquisite and expensive sarees in India, valued for their aesthetic finesse and traditional techniques.
Gavri Festival
- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
Gavri is a unique 40-day ritualistic folk festival celebrated annually by the Bhil tribal community of the Mewar region in Rajasthan. It is a vibrant blend of dance, drama, music, and oral storytelling rooted deeply in the Bhil worldview, spirituality, and socio-cultural expression.
Key Features:
- Duration: 40 days, usually observed during the Hindu months of Shravana and Bhadrapada (July to September), coinciding with the monsoon and early harvest season.
- Form: A fusion of dance, drama (khel), mime, and dialogues.
- Theme: Enacts mythological battles between good and evil, primarily featuring Goddess Gauri/Amba and demons such as Bhasmasur or Bhiamwal, symbolizing the triumph of good.
- Performance Spaces: Villages where the performers' married sisters and daughters reside, reinforcing familial ties and social cohesion.
- Characters: All roles, including female ones, are portrayed by male performers, due to prevailing patriarchal norms.
- Narration: A storyteller called Kutkadiya introduces each scene, enhancing audience immersion.
- Costumes & Music: Colorful attire, energetic drumming, and folk instruments create a lively, theatrical atmosphere.
Cultural and Social Significance
- Spiritual Identity: The Bhil community considers themselves descendants of Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati, viewing Parvati (Gauri) as their divine sister. Gavri is performed to honour her and ensure the well-being of their married women.
- Oral Heritage: The festival preserves centuries-old oral traditions, possibly dating back to the 3rd or 4th century CE, with references to the era of Siddhraj Jai Singh of Gujarat.
- Carnivalesque Spirit: Gavri subverts caste and class hierarchies through humor, parody, and satire. Authority figures, kings, and even gods may be lampooned in the plays.
- Resistance & Nature Worship: Performances like Badliya Hindwa and Bhilurana reflect themes of nature worship, tribal resistance to invaders (Mughals, British), and warnings against ecological destruction.
- Gender Fluidity: Though patriarchal in nature, the performance of female roles by men adds a layer of gender expression and cultural fluidity during the ritual.
Bhil Tribe: An Overview
- One of India's largest Adivasi groups, found mainly in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Speak the Bhili language and practice a syncretic faith combining animism with Hindu mythology.
- Their cultural identity is closely tied to forests, nature, and community-based rituals like Gavri.
Sohrai Art of Jharkhand

- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
Sohrai Art from Jharkhand was prominently showcased during Kala Utsav 2025 held at Rashtrapati Bhavan, where President Droupadi Murmu hailed it as reflecting the “soul of India.” The event marked a significant national recognition for this traditional tribal art.
About Sohrai Art:
|
Aspect |
Details |
|
Tribal Origins |
Practised by Santhal, Munda, and Oraon tribes in Jharkhand. |
|
Region |
Predominantly in Hazaribagh, Santhal Parganas, and parts of eastern Bihar. |
|
Occasion |
Ritual wall-painting during Diwali and harvest festivals. |
|
Purpose |
Thanksgiving for livestock and land fertility; linked to agrarian rituals and spiritual ecology. |
|
Artists |
Traditionally women; passed down through generations orally and practically. |
Key Features of Sohrai Art:
- Motifs: Stylized animals, birds, trees, and rural life, symbolizing harmony with nature.
- Materials: Uses natural pigments such as red ochre, white kaolin, yellow clay, and black manganese.
- Tools: Made with bamboo twigs, chewed sticks, and cloth instead of synthetic brushes.
- Cultural Essence: Embodies a blend of mythology, agrarian life, womanhood, and sustainability.
Kala Utsav 2025: National Recognition
- Held at Rashtrapati Bhavan as part of the Artists in Residence Programme.
- Ten tribal artists from Hazaribagh showcased their work to a national audience.
- President Murmu lauded the art as a symbol of India’s cultural depth and ecological consciousness.
Institutional Support: IGNCA’s Role
- Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) and its Regional Centre in Ranchi coordinated artist participation.
- IGNCA continues to promote indigenous art forms, ensuring cultural preservation and artist recognition.
Cultural and Policy Relevance:
- Art & Culture: Highlights India’s rich tribal and folk heritage.
- Women Empowerment: Female-centric art practice promoting rural livelihoods.
- Sustainable Development: Use of eco-friendly materials and community-led traditions.
- Tribal Development Schemes: Aligns with objectives of schemes like TRIFED, GI tagging, and cultural promotion under Tribal Affairs Ministry.
Rajendra Chola I
- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
India is commemorating 1,000 years of Rajendra Chola I’s Southeast Asian expedition through cultural events and heritage projects.
Key Highlights:
Rajendra I Chola (r. 1014–1044 CE), son of Rajaraja I, was one of India’s most formidable monarchs, remembered for transforming the Chola Empire into a powerful naval and commercial force that extended influence far beyond the Indian subcontinent.
Background: Rise of the Chola Empire
- Imperial Cholas, based in Thanjavur, rose to prominence after Vijayalaya Chola captured the region around 850 CE.
- Successive rulers like Aditya I and Rajaraja I expanded the empire by defeating the Pallavas, Pandyas, and Rashtrakutas.
- Rajaraja I built the Brihadeeswarar Temple (1010 CE) and initiated overseas campaigns, laying the foundation for maritime expansion.
Rajendra I Chola’s Expansionist Vision
- Ascended the throne in 1014 CE, though anointed in 1012 CE.
- Sought to establish Chola supremacy across land and sea.
- Completed the conquest of Sri Lanka, capturing King Mahinda V and consolidating the southern frontier.
- Defeated the Western Chalukyas, Pandyas, Cheras, and Palas, earning the title Gangaikonda Chola (“the Chola who conquered the Ganges”).
New Capital – Gangaikondacholapuram
- To commemorate northern victories, Rajendra founded Gangaikondacholapuram, an imperial capital that served as a political, administrative, and cultural hub.
Naval Expeditions to Southeast Asia
Motivation:
- Establish maritime supremacy, protect trade routes, and forge strategic alliances.
- Respond to shifting alliances in Southeast Asia (Khmer Empire vs Srivijaya).
The Campaign (c. 1025 CE):
- Launched a massive naval expedition targeting the Srivijaya Empire (modern-day Indonesia, Malaysia).
- Conquered strategic regions like:
- Kadaram (Kedah)
- Pannai (Sumatra)
- Malaiyur (Malay Peninsula)
- Tambralinga, Pegu, and Kalingga
Significance:
- Asserted dominance over key trade routes to Song China.
- Cemented Chola-Khmer alliance.
- Extended Tamil commercial and cultural influence across Southeast Asia.
Commercial and Cultural Legacy
- Promoted merchant guilds such as Manigramam, Ayyavole, and Ainnurruvar, which flourished in overseas ports.
- Tamil inscriptions, artifacts, and temple architecture found across Indonesia, Malaysia, Cambodia, and China.
- Tamil loanwords persist in the Karo language of Sumatra.
- Contributed to a Tamil diaspora that influenced art, architecture, trade, and religion in Southeast Asia.
Military and Administrative Excellence
- Maintained a vast army and navy.
- Efficient administrative system with support from Krishnadeva Kendras (early research and extension centers).
- Built upon the model of divine kingship with Nataraja (Shiva as cosmic dancer) symbolizing spiritual legitimacy.
Global Recognition and Commemoration
- India’s training ship TS Rajendra, commissioned in 1972, honours his naval prowess.
- Chinese accounts from the 11th century describe the Chola court’s wealth, discipline, and grandeur.
- The Coromandel Coast derives its name from Cholamandala ("realm of the Cholas").
Conclusion
Rajendra I Chola stands out in Indian history as a maritime emperor, who not only expanded territorial frontiers but also projected Indian influence across Southeast Asia. His legacy lies in blending military conquests with trade diplomacy, and establishing cultural ties that endured for centuries. His reign marks one of the earliest and most successful examples of Indian soft power abroad.
Paika Rebellion (1817)

- 25 Jul 2025
In News:
The recent exclusion of the Paika Rebellion of 1817 from NCERT’s Class VIII history textbook triggered political backlash in Odisha. Former Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik termed the omission a “huge dishonour” to the Paika warriors, prompting NCERT to clarify that the topic would be included in the second volume of the textbook to be released later in 2025.
Who were the Paikas?
- The Paikas (literally "foot soldiers") were military retainers traditionally employed by the Gajapati kings of Odisha since the 16th century.
- In exchange for military service, they were granted hereditary rent-free lands (nish-kar jagirs), which they cultivated during peacetime.
- Under British rule, their privileges eroded, and they faced land dispossession, economic hardship, and social marginalisation.
Background to the Revolt
- In 1803, the British East India Company annexed Odisha. Colonel Harcourt marched from Madras to Cuttack, defeating feeble Maratha opposition.
- A deal with King Mukunda Deva II of Khurda promised ?1 lakh and four parganas (Lembai, Rahanga, Surai, Chabiskud) for safe passage, but the British defaulted.
- Jayee Rajguru, the king’s adviser, mobilised 2,000 Paikas to confront the British. Though part payment was made, the parganas were not returned.
- Rajguru was arrested and executed on 6 December 1806 for waging war against the British. The king was dethroned and exiled, and the Barunei Fort was demolished.
Causes of the Paika Rebellion
- Loss of Traditional Privileges:
- Confiscation of rent-free lands after British land settlements.
- End of royal patronage.
- Land Alienation & Tax Burden:
- Local Odia landowners were forced to sell land to Bengali absentee landlords.
- Revenue demands shifted to rupee payments, affecting marginal farmers and tribal communities.
- Salt Monopoly & Trade Restrictions: British control over salt trade, particularly after 1814, increased hardship for inland hill populations.
- Cultural and Political Suppression: The decline of local leadership and traditions under colonial authority contributed to growing dissent.
Course of the Rebellion (1817)
- In March 1817, approximately 400 Kondh tribal fighters from Ghumusar marched toward Khurda.
- They were joined by Bakshi Jagabandhu Bidyadhar, the former commander-in-chief of Khurda and ex-holder of the Rodanga estate.
- The rebels:
- Attacked the police station at Banpur
- Burned colonial buildings
- Looted the treasury
- Killed several British officials
- The rebellion spread across southern and central Odisha. Despite initial successes, the British suppressed the revolt.
- Jagabandhu evaded capture for years and surrendered in 1825 under negotiated terms.
Contemporary Significance and Political Debate
- The Paika Rebellion is widely regarded in Odisha as an early expression of anti-colonial resistance.
- In 2017, the Odisha government demanded that the uprising be recognised as the “First War of Independence”, predating the 1857 revolt.
- The Union Government, while not granting this status, acknowledged it as one of the early popular uprisings against colonial rule.
- National Recognition Efforts:
- In 2017, PM Narendra Modi felicitated over 200 descendants of Paika rebels.
- In 2019, President Ram Nath Kovind laid the foundation for a Paika Memorial at Barunei foothills, the rebellion’s epicentre.
- In 2024–25, the new BJP-led government in Odisha announced fast-tracked development of the Paika Academy and Memorial.
Preah Vihear Temple Dispute

- 25 Jul 2025
In News:
Tensions between Thailand and Cambodia have sharply escalated in recent months, marked by armed clashes, airstrikes, and diplomatic fallout, all centering around the Preah Vihear Temple—a centuries-old Hindu monument of immense cultural and geopolitical significance.
About Preah Vihear Temple
- Location: Preah Vihear Province, northern Cambodia, atop a cliff in the Dangrek Mountain range, near the Cambodia–Thailand border.
- Religious Affiliation: Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- Historical Background:
- Constructed during the Khmer Empire, primarily in the 11th and 12th centuries.
- Key patrons: King Suryavarman I (1002–1050) and King Suryavarman II (1113–1150).
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: Inscribed in 2008 for its exceptional architectural and historical value.
Architectural Features
- Exemplifies Khmer temple architecture with a linear arrangement of sanctuaries linked by pavements and staircases over an 800-metre-long axis.
- Contains over five gopuras (monumental gateways) connected by a raised path and tiered platforms.
- Mixture of stone and wooden roofing, though many structures are partially in ruins.
Territorial Dispute Overview
- Historical Basis:
- Dispute stems from differing interpretations of a 1907 French map, which placed the temple inside Cambodian territory.
- Thailand disputes the map, arguing lack of formal acceptance.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ) Rulings:
- 1962: ICJ ruled the temple belongs to Cambodia, citing Thailand’s implicit acceptance of the 1907 map.
- Thailand was ordered to withdraw troops and return artifacts taken since 1954.
- 2013 (Reaffirmation): ICJ clarified that surrounding areas—particularly a 4.6 sq. km. disputed zone—also belong to Cambodia.
Major Flashpoints in the Conflict
- 2008: Cambodia registers Preah Vihear as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, triggering nationalist backlash in Thailand.
- 2008–2011: Border skirmishes escalate, culminating in a 2011 clash that killed at least 15 people.
- 2025 Escalation:
- Renewed violence erupted in July 2025, after a series of provocations:
- May 2025: Cambodian soldier killed.
- July 2025: Two Thai soldiers injured in landmine blasts.
- July 24, 2025: Armed conflict intensifies—Thai airstrikes target Cambodian positions near the temple.
- Casualties: At least 9 civilians killed, 14 injured in Thai provinces bordering Cambodia.
- Both nations expelled ambassadors and blamed each other for violations of sovereignty.
- Renewed violence erupted in July 2025, after a series of provocations:
Significance of the Dispute
- Cultural: Preah Vihear is a sacred site and national symbol for both nations.
- Strategic: Its location atop a cliff offers military advantage and control over surrounding terrain.
- Diplomatic: The temple remains a fault line in bilateral ties, with unresolved territorial claims despite multiple ICJ verdicts.
Marungur Excavation
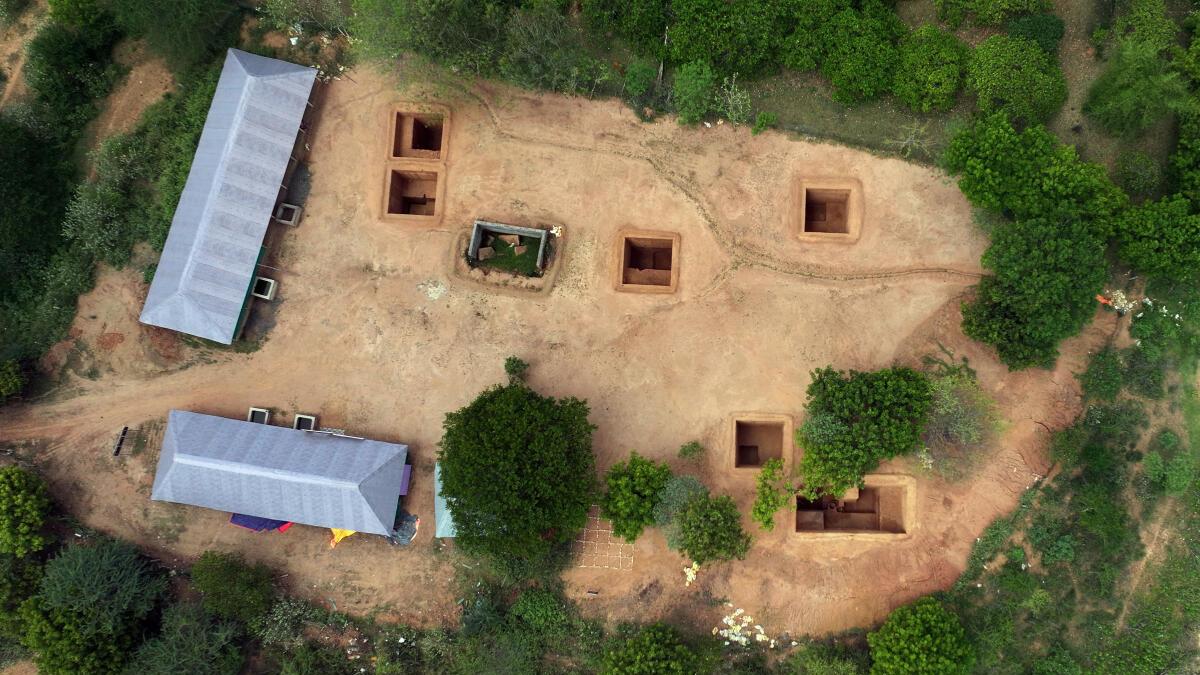

- 21 Jul 2025
In News:
The Tamil Nadu State Department of Archaeology (TNSDA) has completed a landmark archaeological excavation at Marungur village, located in Panruti taluk, Cuddalore district, uncovering a habitation-cum-burial site dating from the Iron Age to the Early Historic period. This multidisciplinary excavation offers significant insights into the cultural evolution of ancient Tamil Nadu’s Naduvil Mandalam (Central Territorial Division), between the Thenpennai and Vada Vellar rivers.
Key Features:
1. Rare Dual Site Discovery
- Both a habitation mound and an associated burial site were found together — a rarity in Tamil Nadu.
- The site is situated at 100 metres above mean sea level, adjacent to a pond and covered by laterite soil.
2. Chronological Context
- Dated tentatively to the transition from late Iron Age to Early Historic Period.
- Radiocarbon dating (AMS) of charcoal samples, phytolith studies, and Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) analysis are underway to confirm dates.
3. Advanced Techniques Used
- UAV Mapping, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), stratigraphic trenching, and archaeo-botanical studies.
- Collaboration with Beta Analytic Laboratory (USA) and the French Institute of Pondicherry for dating and pollen analysis.
Major Discoveries
A. Habitation Mound (8 Trenches Excavated)
- Pottery: Rouletted ware, red-slipped ware, black-and-red ware, grey ware, coarse red ware, and graffiti-inscribed potsherds (some resembling Indus signs).
- Artifacts (95 antiquities): Bone tools (points), burnishing stones, terracotta pipes, and beads (carnelian, agate, quartz, glass, terracotta).
- Iron implements: Crescent-shaped chisels, knives.
- Conch shell cores and antimony rods (ornamental use).
- Copper coin of Raja Raja Chola I from upper layers.
- Large terracotta storage jars (1.25 m), one containing six bone tools.
B. Burial Site (2 Trenches Excavated in Cashew Grove)
- Megalithic Stone Circles (Laterite):
- Two concentric circles (outer and inner), capstone-protected burial urns.
- Total of 10 urns recovered.
- Grave Goods:
- Iron swords, red jasper beads, black-and-red ware, red-slipped ware.
- Offering pots around urns — evidence of complex burial rituals.
C. Tamil-Brahmi Inscribed Potsherds
- Found in urn burials and dated paleographically to 2nd–3rd century BCE.
- Inscriptions include terms like “a-ti-y(a)-ka-n”, “a-ma-?”, and “a-ta”.
- Significance: Among earliest epigraphic evidence of Tamil-Brahmi in burial contexts.
Significance:
|
Aspect |
Significance |
|
Cultural Chronology |
Sheds light on the transition from the Iron Age to Early Historic society. |
|
Urban & Trade Patterns |
Proximity to ancient port cities like Arikamedu and Poompuhar hints at external trade. |
|
Script & Literacy |
Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions expand understanding of early Tamil epigraphy. |
|
Burial Practices |
Megalithic urn burials with grave goods indicate complex socio-religious beliefs. |
|
Scientific Advancement |
Integration of modern remote sensing and dating techniques in Indian archaeology. |
Future Steps
- Radiometric Dating: Charcoal to be analyzed using Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) in the USA.
- Pollen and phytolith analysis to reconstruct ancient diet and environmental conditions.
- Thermoluminescence and petrology studies to date ceramics and sediment exposure.
- TNSDA proposes further surveys at Manikkollai (30 km from Marungur) for 2025–26.
Behdeinkhlam Festival

- 17 Jul 2025
In News:
The Behdeinkhlam Festival, a vibrant cultural and religious celebration of the Pnar community in Jowai, Meghalaya, was recently observed with great enthusiasm. Blending age-old indigenous rituals with contemporary social messages, the festival reflects the rich cultural heritage and evolving societal concerns of the Jaintia Hills region.
Etymology and Meaning
- The term “Behdeinkhlam” comes from the Pnar language:
- “Beh Dien” – to drive away with sticks or prayers.
- “Khlam” – refers to plague, pestilence, or disease.
- Thus, the name signifies a ritual expulsion of illness, evil spirits, and misfortune, historically associated with diseases like cholera.
Cultural and Religious Significance
- Primarily celebrated by the Pnars, a sub-tribe of the Jaintia community, the festival is a symbolic act of:
- Protecting society from disease.
- Invoking blessings for a bountiful harvest.
- Promoting community health, peace, and prosperity.
- It plays a crucial role in preserving the Niamtre faith, the indigenous religion of the Jaintia people, through intergenerational participation in ritual practices.
Timing and Duration
- Held annually in July, right after the sowing season, the festival lasts for three days.
- The timing is agriculturally significant, linking health rituals with hopes for a successful farming cycle.
Key Rituals and Celebrations
- Symbolic Rituals:
- Men go around beating the roofs of houses with bamboo poles to drive away evil spirits and symbolic disease.
- Tree trunks known as Dein Khlam and Khnong—rounded, straight, and polished—are brought from the forest and used in the main rituals.
- Community Processions:
- A sacred wooden post called Symbud Khnong is carried around the town and installed as a spiritual safeguard.
- Gender Roles in Rituals:
- Men perform dances, carry the sacred logs, and lead the processions.
- Women play a vital ceremonial role by preparing sacrificial food for ancestral spirits.
- Dance and Music: On the final day, the community gathers at Aitnar, where both young and old dance to the rhythmic beats of pipes and drums.
- Dad-Lawakor – Traditional Game: A unique football-like game called Dad-lawakor is played at Mynthong, showcasing indigenous sporting traditions and community bonding.
Contemporary Relevance
- In recent years, the festival has evolved to incorporate modern themes such as:
- Awareness against drug abuse
- Prevention of alcoholism
- Climate change consciousness
- These additions reflect a harmonious blending of tradition and modernity, where festivals serve both spiritual and civic functions.
Machilipatnam
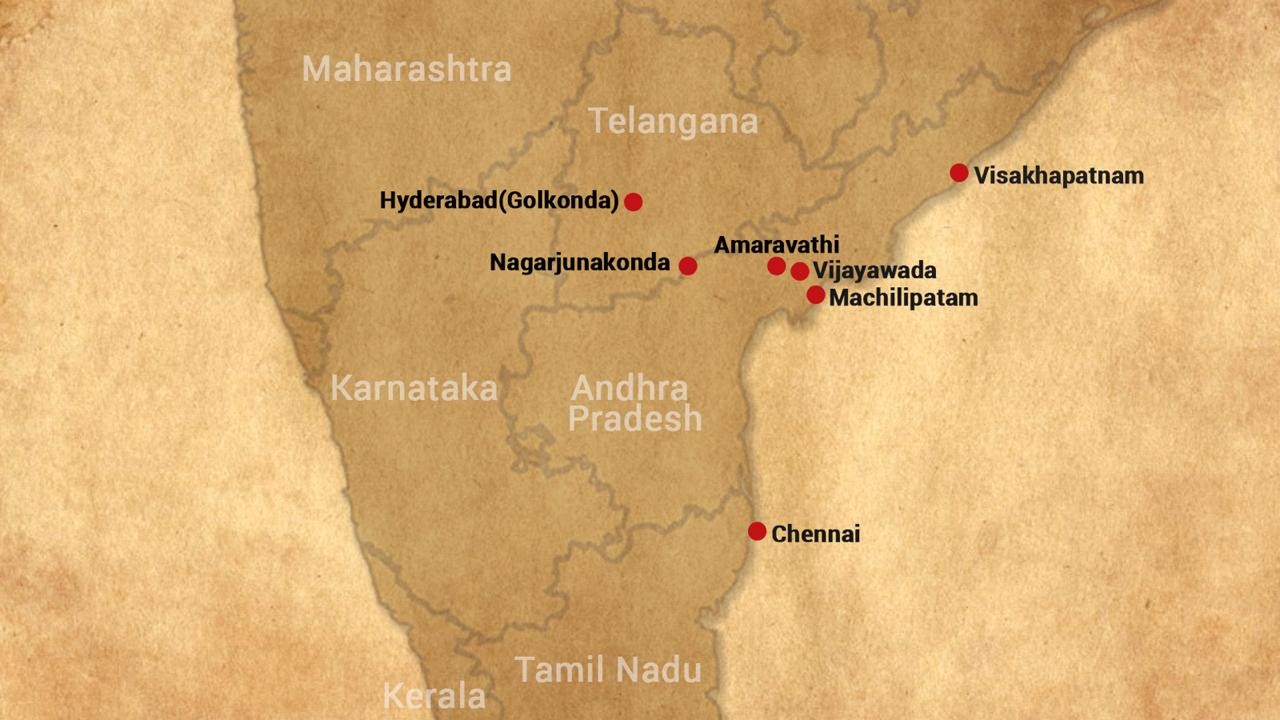
- 17 Jul 2025
In News:
Located at the confluence of the Krishna River and the Bay of Bengal, Machilipatnam—historically known as Masulipatnam—is a port town with a rich maritime legacy. Once a prominent node in ancient and medieval trade networks, the town is now experiencing renewed attention and developmental revival.
Ancient Maritime Significance
- Known in classical sources such as the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea (1st century CE) as Maisolos, Machilipatnam played a crucial role in early Indian Ocean trade.
- Its strategic position on the Coromandel Coast made it a conduit for commercial exchange between the Deccan Plateau and distant civilizations, including Rome, the Arab world, and Southeast Asia.
- Archaeological and literary evidence points to Machilipatnam's role as a trans-shipment point for goods like spices, textiles, and pearls.
Flourishing Under the Satavahanas (1st BCE – 3rd CE)
- During the reign of the Satavahana dynasty, the port witnessed significant expansion.
- It became renowned for the export of fine muslin fabrics, precious stones, and aromatic goods.
- Inland trade links with Amaravati and Dharanikota—important urban and Buddhist centres—further enhanced the port’s economic significance.
Medieval Resurgence and Colonial Trade
- From the 16th to 18th centuries, the port was revitalized under the Golconda Sultanate.
- It emerged as a hub for European maritime powers such as the Dutch, British, and French East India Companies.
- Despite its early importance, Machilipatnam’s influence declined in the 18th century when colonial powers shifted their focus to Madras (now Chennai), which offered better access and facilities for long-distance trade.
Port Cities in Indian Maritime History
The historical prominence of Machilipatnam can be viewed in the broader context of ancient Indian port cities:
|
Port City |
Region/Modern State |
Period/Dynasty |
|
Lothal |
Gujarat |
Indus Valley Civilization |
|
Arikamedu |
Puducherry |
Cholas, Early Tamil Kingdoms |
|
Kaveripattinam |
Tamil Nadu |
Cholas |
|
Sopara |
Maharashtra |
Satavahanas |
|
Tamralipta |
West Bengal |
Mauryas and Guptas |
|
Barygaza |
Bharuch, Gujarat |
Indo-Greek and Kushan Periods |
These ports collectively illustrate India’s extensive maritime interactions across time, with Machilipatnam serving as a significant node in this network during multiple historical phases.
Contemporary Relevance
- Recent efforts to revitalize Machilipatnam’s port infrastructure are aimed at restoring its economic utility and cultural relevance.
- Its historical importance makes it a potential candidate for heritage tourism, as well as a case study in urban renewal based on historical identity.
Sheesh Mahal

- 10 Jul 2025
In News:
The Sheesh Mahal, a 17th-century Mughal-era palace located in Shalimar Bagh, North Delhi, was recently restored and reopened to the public by the Union Culture and Tourism Minister. The restoration was carried out by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and the Delhi Development Authority (DDA).
About Sheesh Mahal
- Built in 1653 by Izz-un-Nisha Begum, wife of Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan.
- Inspired by and a replica of Shalimar Bagh in Kashmir, designed as a royal retreat from Shahjahanabad.
- The garden was originally called Aizzabad Garden, later renamed Shalimar, meaning “abode of pleasure”.
- The palace was the site of Aurangzeb’s first coronation in 1658.
- Declared a monument of national importance in 1983, under ASI protection.
Architectural Features
- Constructed using red sandstone and brick masonry.
- Features archways, three-arched dalans, and a central hall with compartments on each wing.
- A Baradari (pavilion) lies in the main building with a water channel passing through it.
- Houses mirror-worked chambers with paintings in Kangra and Rajasthani qalam, depicting poetic imagery by Keshav, Surdas, and Bihari.
- Adjacent structure served as a Hamam (bathhouse).
Restoration Highlights
- ASI restored the palace’s original heritage features.
- DDA recreated the traditional Mughal Char Bagh-style landscape.
- Traditional materials used: Lime surkhi, lakhori bricks, gud (jaggery), belgiri, and urad dal.
- An old baradari and three heritage cottages were also restored.
New Additions for Public Engagement
- Two heritage cottages repurposed:
- The Readers Café Corner – a literary café.
- Café Shalimar – for general visitors.
Discovery of Penico
- 09 Jul 2025
In News:
Archaeologists have recently uncovered a significant archaeological site in northern Peru—an ancient city named Penico, estimated to be around 3,500 years old. The discovery sheds new light on early urban development, trade networks, and cultural evolution in pre-Inca South America.
Location and Time Period
- Geographic Location: Penico is located in the Barranca Province of northern Peru, approximately 200 km north of Lima, the capital.
- Altitude: The site is situated on a hillside terrace, around 600 metres above sea level.
- Estimated Age: The city is believed to have been founded between 1800 BCE and 1500 BCE, roughly during the same period as early civilizations in Egypt, Sumeria, and the Indus Valley.
Key Features of the Site
Urban and Architectural Highlights:
- The city is laid out around a central circular plaza, encircled by at least 18 identified stone-and-mud structures.
- Structures include:
- Ceremonial temples
- Residential complexes
- Public gathering areas with sculpted wall reliefs
Notable Artifacts:
- Clay figurines depicting human and animal forms
- Pututus (conch shell trumpets), traditionally used for long-distance communication
- Beaded necklaces and ceremonial artifacts crafted from shells and stones
Cultural and Historical Significance
Strategic Importance:
- Penico’s elevated location likely served both practical and symbolic purposes—protecting against natural disasters such as floods or landslides, while also enhancing the visibility and monumentality of its structures.
- The city’s placement made it a vital trading nexus, linking communities across the Pacific coast, Andean highlands, and the Amazon basin.
Link to the Caral Civilization:
- Penico is situated near the ancient city of Caral, considered the oldest known civilization in the Americas (dating back to 3000 BCE in the Supe Valley).
- Researchers suggest that Penico represents a cultural continuation or evolution of the Caral society, which declined due to climatic disruptions.
- The discovery of Penico offers valuable insight into how civilizations adapted and transitioned post-Caral, particularly in terms of urban planning, trade, and ceremonial practices.
Comparative Civilizational Context:
- Despite emerging in geographic isolation, Penico developed contemporaneously with Bronze Age civilizations of Mesopotamia, the Nile Valley, and South Asia, showcasing parallel patterns in complex societal development.
Alluri Sitarama Raju

- 09 Jul 2025
In News:
During the 128th birth anniversary celebration of Alluri Sitarama Raju, the Union Defence Minister lauded his valiant role in India’s freedom movement. The Minister also reiterated the government’s commitment to ending Maoist extremism by August 2026.
Alluri Sitarama Raju
- He was a revolutionary figure revered for leading a tribal resistance against British colonial authority. Although he did not belong to a tribal community himself, he championed the cause of indigenous people, earning their deep respect and admiration.
- He was born on 4 July 1897 in Mogallu village, near Bhimavaram, located in present-day Andhra Pradesh. His revolutionary activities were concentrated in the Eastern Ghats’ Agency areas of the state.
Historical Context
- Early Life and Spiritual Turn: After receiving basic education in his village and later in Visakhapatnam, Alluri chose a life of renunciation around the age of 18. As a sanyasi, he traversed forested and hilly regions, developing a close bond with tribal communities.
- Gandhian Influence and Shift to Armed Struggle: Initially influenced by Mahatma Gandhi’s Non-Cooperation Movement, he urged tribal people to disengage from colonial institutions. However, disillusioned by the ineffectiveness of non-violence in protecting tribal rights, he resorted to armed rebellion.
- Role in the Freedom Struggle
- The Rampa Rebellion (1922–1924): Alluri became the face of the Rampa Rebellion, launched in protest against the Madras Forest Act, 1882, which curtailed traditional tribal practices like Podu cultivation and led to forced displacement. Additionally, tribals were subjected to unpaid labour for constructing colonial infrastructure, fueling widespread anger.
- Guerrilla Tactics and Resistance: Raju organized tribal youth into a guerrilla army that attacked British police outposts, looted weapons, and eliminated British officers, causing considerable concern for the colonial administration.
- Martyrdom: His growing influence and success made him a prime target for the British, who announced a ?10,000 bounty for his capture. He was eventually apprehended through deception and executed on 7 May 1924, reportedly tied to a tree and shot dead.
Legacy
- Revered as “Manyam Veerudu” or the Hero of the Jungle, Alluri’s life epitomizes courage and sacrifice.
- The Government of Andhra Pradesh commemorates July 4 as a state festival in his honour.
- He remains a powerful symbol of tribal resistance and justice in India's freedom narrative.
Chautal

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
During the recent state visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Trinidad and Tobago, a notable cultural highlight was the performance of the traditional Bhojpuri Chautal, reflecting the deep-rooted Indian heritage in the Caribbean diaspora.
Understanding Chautal
- Chautal (also spelled Chartaal or Chowtaal) is a 12-beat rhythmic cycle (taal) integral to Hindustani classical music.
- It is primarily used to accompany vocal forms such as Dhrupad and Dhamar, as well as instrumental music.
- The term “Chautal” can be interpreted as "four claps", hinting at its vibhag (sectional) structure.
Structural Interpretations:
- One tradition describes it as comprising four vibhags of 4, 4, 2, and 2 beats (matras), respectively.
- An alternative view equates its structure with Ektal, dividing the cycle into six segments of 2 beats each.
Musical Characteristics and Cultural Context
- Chautal is closely associated with the pakhawaj, a barrel-shaped percussion instrument, giving it a powerful and resonant character.
- Unlike the subtle and intricate rhythms of the tabla, Chautal emphasizes strength and gravity in performance.
- Beyond classical settings, Chautal holds cultural significance in Bhojpuri folk traditions, especially during festivals and religious gatherings.
Significance in the Indian Diaspora
The inclusion of Chautal in Trinidad and Tobago’s ceremonial welcome reflects the preservation and celebration of Indian classical and folk arts among overseas Indian communities, particularly those with Bhojpuri ancestry.
Sree Narayana Guru

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister recently attended the centenary celebrations of the historic 1925 conversation between Mahatma Gandhi and Sree Narayana Guru, held at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. The event marked the enduring relevance of Guru's message of social equality, spiritual unity, and reform.
Who was Sree Narayana Guru?
- Born: 20 August 1856, in a backward Ezhava community in Kerala
- Died: 20 September 1928
- Role: Spiritual leader, philosopher, poet, yogi, and one of India’s foremost social reformers from Kerala
Historical Context:
- During the 19th century, Kerala society was deeply caste-ridden, and the Ezhava community was subjected to systemic social exclusion.
- Guru revolted against caste oppression, advocating for spiritual liberation without ritual orthodoxy.
Core Philosophy:
- Message of Universal Unity:“OruJathi, OruMatham, OruDaivam, Manushyanu”
(One Caste, One Religion, One God for Mankind) — a powerful call for social harmony, inclusivity, and humanism. - Non-violent transformation:Unlike many radical reform movements, Guru’s approach was inclusive and reformative, rejecting social division without inciting confrontation.
Key Contributions:
- Religious and Spiritual Reforms:
- Aruvippuram Movement (1888):
- Consecrated a Shiva idol at Aruvippuram — a direct challenge to Brahmanical dominance and the exclusion of lower castes from temple worship.
- Established over 40 temples in Kerala, allowing unrestricted worship by the marginalized.
- Promoted yoga and meditation, and spent years in hermitage to attain spiritual depth.
- Aruvippuram Movement (1888):
- Social Reforms:
- Founded the Sivagiri Mutt (1904) near Varkala — a centre for spiritual and social awakening.
- SNDP Yogam (1903):
-
- Full form: Sri Narayana Guru Dharma ParipalanaYogam
- Aimed at securing education, government access, and political rights for the Ezhavas.
- Guru was the permanent chairman; Kumaran Asan, his disciple, became general secretary.
-
- Vaikom Satyagraha:Played a pivotal role in the anti-untouchability movement, alongside leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Periyar.
- Promoted free education, ashrams, and vocational training for underprivileged children and communities.
- Sivagiri Foundation and Pilgrimage:
- Founded in 1924 to promote values like:Cleanliness, education, devotion, agriculture, handicrafts, and trade
- SivagiriTheerthadanam (pilgrimage):Initiated by his followers to reinforce values of purity, education, and organization
Literary Contributions:
- Guru was a Vedantic scholar and philosopher-poet. His notable works include:
- Advaitha Deepika
- Atmavilasam
- DaivaDasakam
- BrahmavidyaPanchakam
These texts reflected Advaita (non-dualist) philosophy, spiritual self-realization, and social ethics.
Legacy and Recognition:
- Revered as “Gurudevan”by his followers
- His birth and death anniversaries are observed as public holidays in Kerala and some other states
- Celebrated as Sri Narayana Jayanthi
Total Revolution
- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
India commemorates the 51st anniversary of Jayaprakash Narayan’s (JP) historic call for “Sampoorna Kranti” or Total Revolution, first proclaimed on June 5, 1974, at Gandhi Maidan, Patna. The movement remains a landmark in India's democratic evolution, reflecting enduring concerns over governance, democracy, and civic empowerment.
What is Total Revolution?
- Concept: A holistic, non-violent movement rooted in Gandhian ideals, aimed at comprehensive transformation—political, economic, social, cultural, and spiritual.
- Vision: Building a just and equitable society through decentralised democracy, moral rejuvenation, and participatory governance.
- Leadership: Spearheaded by Jayaprakash Narayan (JP), advocating a “party-less democracy” blending Gandhian ethics, Sarvodaya ideals, and Marxist critique.
Underlying Causes of the Movement
- Electoral Legitimacy Crisis:The 1975 Allahabad High Court judgment disqualified Prime Minister Indira Gandhi for electoral malpractices, eroding her authority and galvanising mass opposition.
- Youth Unrest:Movements like Navnirman Andolan (Gujarat) and Bihar student protests reflected mounting youth dissatisfaction over unemployment and poor governance.
- Economic Distress:The early 1970s saw inflation exceeding 20%, acute unemployment, and food shortages, leading to widespread discontent.
- Democratic Backsliding:Use of draconian laws like MISA, increased centralisation, and suppression of dissent led to civil society mobilisation.
- Charismatic Mobilisation:JP’s appeal for non-violent civic awakening and his ability to unify diverse ideological streams helped launch a broad-based national movement.
Core Components of the Total Revolution
Domain Focus
Political Advocated bottom-up governance, decentralisation, and accountability
to counter bureaucratic authoritarianism.
Economic Promoted land reforms and people-centric development to address inequality.
Social Called for eradication of casteism, gender bias, and dowry to foster egalitarianism.
Educational Suggested reforms emphasisingethics, rural upliftment, and vocational training.
Cultural-Spiritual Encouraged self-discipline, national unity, and moral regeneration.
Impact of Total Revolution
On Society and Citizenry
- Youth Mobilisation: Inspired a generation of political leaders—Lalu Prasad Yadav, Nitish Kumar, Sushil Modi—who reshaped regional politics.
- Civic Engagement: Fostered a deeper culture of public accountability and democratic participation.
- Non-Violent Resistance: Reinforced the efficacy of peaceful protest, a legacy echoed in later movements like Anna Hazare’s anti-corruption crusade.
On Governance and Policy
- Collapse of Congress Monopoly: Led to the formation of the Janata Party, marking a historic electoral defeat for the Congress in 1977.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Triggered the 44th Constitutional Amendment, curbing emergency powers and restoring judicial oversight.
- Democratic Deepening: Inspired Panchayati Raj reforms through the 73rd and 74th Amendments, enhancing grassroots democracy.
Significance and Contemporary Relevance
- Democratic Dissent: Reinvigorated the right to protest as a fundamental democratic tool.
- Leadership Incubation: Nurtured mass-based political leadership, altering India’s political landscape.
- Institutional Vigilance: Exposed systemic vulnerabilities, prompting long-term institutional reforms.
- Civic Awakening: Broadened the role of civil society in governance beyond electoral cycles.
- Modern-Day Lessons: Offers vital insights for addressing centralisation of power, youth alienation, and democratic backsliding in contemporary India.
Ambubachi Mela 2025
- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
Thousands of devotees have congregated at the Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati, Assam, to participate in the annual Ambubachi Mela—one of the largest and most significant religious gatherings in Northeast India.
About Ambubachi Mela
- Timing: Celebrated annually during the monsoon season, typically in June.
- Location: Held at the Kamakhya Temple, situated atop Nilachal Hill in Guwahati, Assam.
- Religious Significance:
- Marks the menstrual cycle of Goddess Kamakhya, symbolising the fertility of Mother Earth.
- During this period, the sanctum sanctorum is closed for three days, after which it is ceremonially reopened for darshan.
- Cultural Symbolism:
- Reflects ancient beliefs that associate the Earth with feminine fertility.
- The word ‘Ambubachi’ translates to ‘water flowing’, indicative of both the monsoon rains and the goddess’s fertility.
Kamakhya Temple: Key Facts
- Spiritual Importance:
- Dedicated to Goddess Kamakhya, an incarnation of Shakti.
- Considered one of the most revered sites of Tantric Shaktism in India.
- Recognised as one of the 51 Shakti Peethas, where the yoni (womb) of Sati is believed to have fallen.
- Geographical Location:Located on Nilachal Hill, overlooking the southern bank of the Brahmaputra River.
Architectural Features of Kamakhya Temple
- Architectural Style:
- Combines traditional Nagara style with Saracenic (Mughal) architectural elements, known as the Nilachala Style of Architecture.
- Temple Layout:
- Only temple in Assam with a fully developed ground plan.
- Comprises five main sections:
- Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum)
- Antarala (vestibule)
- Jaganmohan (assembly hall)
- Bhogmandir (offering hall)
- Natmandir (performance hall)
- Distinctive Structural Elements:
- Main dome: Modified Saracenic style.
- Antarala: Features a two-roofed structure.
- Bhogmandir: Crowned with five domes, echoing the central shrine.
- Natmandir: Designed with a shell-shaped roof and apsidal end, similar to the namghars (prayer halls) of Assam.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)

- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
Lucknow has officially submitted its nomination to be recognised as a “City of Gastronomy” under the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN), aiming to join Hyderabad as the only other Indian city to hold this title in the gastronomy category.
About the UCCN
- Established: 2004
- Purpose: To promote international cooperation among cities that use creativity as a key element for sustainable urban development.
- Focus Areas: Literature, Music, Crafts & Folk Arts, Design, Film, Media Arts, and Gastronomy.
- Key Goals:
- Leverage the creative economy for sustainable development.
- Encourage cultural diversity and resilience against urban challenges like climate change and inequality.
- Promote collaboration across public, private, and civil society sectors.
UCCN and Sustainable Development
- UCCN supports the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by positioning culture and creativity at the heart of local development policies and planning.
- Member cities are expected to create innovation hubs, support local artists, and preserve cultural heritage.
India and the UCCN
As of 2023, 10 Indian cities are part of the network:
- Hyderabad – Gastronomy
- Jaipur – Crafts and Folk Arts
- Varanasi – Music
- Chennai – Music
- Mumbai – Film
- Srinagar – Crafts and Folk Arts
- Kozhikode – Literature
- Gwalior – Music (Recent entries include Kozhikode and Gwalior)
Lucknow’s Nomination: Highlights
- Nominated Title: City of Gastronomy
- Coordinated by: Department of Tourism and Culture, Lucknow
- Culinary Heritage: Awadhi cuisine, including dishes like nihari, kebabs, biryani, khasta, kulfi, jalebi, and puri-sabzi.
- Cultural Value: The city’s food is not just a tradition but a living culinary ecosystem, passed down through generations and practiced by diverse communities.
- Dossier Preparation: By renowned heritage conservationist Abha Narain Lambah.
- Verification: A field visit by UNESCO is expected as part of the evaluation process.
Global Cities of Gastronomy (Examples)
- Alba (Italy)
- Arequipa (Peru)
- Bergen (Norway)
- Belem (Brazil)
- Bendigo (Australia)
These cities, like Hyderabad, are recognised for their distinctive and sustainable culinary traditions.
Servants of India Society
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
Tensions have resurfaced between Gokhale Institute of Politics and Economics (GIPE) and the Servants of India Society (SIS) over control of a joint bank account and allegations of financial misconduct. This has brought attention back to the legacy and functioning of the historic SIS.
About Servants of India Society (SIS)
- Founded: June 12, 1905
- Founder: Gopal Krishna Gokhale, with G.K. Devadhar, A.V. Patwardhan, and N.A. Dravid
- Location: Fergusson Hill, Pune, Maharashtra
- Headquarters: Pune, with branches in Chennai, Mumbai, Nagpur, Allahabad, etc.
Objectives:
- To train a dedicated cadre of national workers for selfless service to the nation.
- Promote political education, social reform, and public service.
- Work towards upliftment of underprivileged communities, including rural and tribal populations.
- Achieve social change through constitutional and moderate means, not violent agitation.
Membership and Structure:
- Members undergo a five-year training period and vow to serve on modest salaries.
- Considered “young missionaries of Indian nationalism.”
- Notable Members:
- V.S. Srinivasa Sastri (later president after Gokhale’s death in 1915)
- Hriday Nath Kunzru
- A.V. Thakkar
Ideological Basis:
- Strong emphasis on constitutionalism, moderation, and liberalism.
- Aimed to create a disciplined, morally upright civil society to complement political struggle.
About Gopal Krishna Gokhale:
- Born: May 9, 1866 | Died: February 19, 1915
- Moderate leader of the Indian National Congress and a liberal reformer.
- Influenced by Justice M.G. Ranade and Western political thought.
- Advocated for gradual self-governance and saw value in British-initiated modernization.
- Played a pivotal role in the Morley-Minto Reforms (1909).
- Mentor to Mahatma Gandhi and known for his economic insight and powerful oratory.
Sant Kabirdas
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
11th June 2025 marked the 648th birth anniversary of Sant Kabirdas, one of India’s most revered 15th-century Bhakti saints.
Place of Birth: Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
Birth Period: Circa 1440 CE, raised in a Muslim weaver family
Philosophy and Teachings
- Nirguna Bhakti: Kabir rejected idol worship and sectarian divisions, instead preaching devotion to a formless, universal God (Nirguna Brahman).
- Social Reform: He denounced casteism, rituals, and blind faith, stressing ethical conduct, humility, and self-realization.
- Inner Divinity: He believed God resides within and taught seekers to seek truth through introspection (Antar-drishti) rather than temple rituals.
- Language and Style:
- Composed in Sant Bhasha, a blend of local dialects understood across religions.
- Created Ulatbansi verses — paradoxical or "upside-down sayings" — challenging conventional wisdom.
Literary Legacy
- Major Works: Bijak, Sakhi Granth, Kabir Granthavali, Anurag Sagar
- Scriptural Inclusion:
- His verses appear prominently in the Adi Granth Sahib compiled by Guru Arjan Dev.
- Adopted by various traditions:
- Kabir Bijak (Kabirpanth, UP)
- Kabir Granthavali (Dadupanth, Rajasthan)
Impact and Influence
- Kabir Panth: A spiritual sect founded on his teachings, still active in North India.
- Sikhism: Deeply influenced Guru Nanak; Kabir’s dohas are integrated into Guru Granth Sahib.
- Cross-Religious Appeal: Respected by both Hindus and Muslims, he is a symbol of India’s syncretic spiritual culture.
- Other Sects: Influenced Dadu Panthis and Nirguna Bhakti traditions across India.
Contemporary Relevance
- Religious Harmony: In a climate of polarization, Kabir’s teachings offer a path of unity and spiritual inclusivity.
- Social Justice: His resistance to caste hierarchy echoes India’s constitutional values of equality and dignity.
- Sustainable Living: His emphasis on simplicity and contentment aligns with ecological and minimalist principles.
- Spiritual Humanism: He stressed conduct over ritual, making his message resonate across belief systems in today’s pluralistic society.
Bhagwan Birsa Munda

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
On his 125th death anniversary (Balidan Diwas), the Prime Minister of India paid tribute to Bhagwan Birsa Munda, hailing his pioneering role in tribal empowerment and anti-colonial resistance.
Early Life and Identity
- Born: 15 November 1875, Ulihatu, Chotanagpur Plateau (now in Jharkhand).
- Tribe: Munda.
- Title: Revered as “Dharti Aaba” (Father of the Earth).
- Education: Attended Christian missionary schools in Chaibasa; later rejected colonial influence and converted to Vaishnavism, blending it with tribal spirituality.
- Founder of: The Birsait sect, advocating moral reform and cultural awakening among Adivasis.
Role in Freedom Struggle & Tribal Mobilisation
Resistance Against Exploitation:
- Zamindari System: Opposed British-imposed land systems that dismantled the Khuntkatti tribal land tenure, dispossessing tribals and reducing them to bonded labourers.
- Beth Begari: Led resistance against forced labour and revenue policies.
- Forest Rights: Fought against British encroachment and resource extraction in forests.
Cultural and Spiritual Renaissance:
- Condemned social evils like black magic and alcoholism.
- Mobilised tribals using tribal songs, attire, drums, and community gatherings.
- Advocated tribal self-rule and cultural pride against the oppression by Dikus (outsiders).
Ulgulan Movement (1895–1900): The Great Tumult
- Nature: A widespread anti-colonial rebellion across present-day Jharkhand, Odisha, and Bengal.
- Strategy: Guerrilla warfare, targeting British outposts, churches, and police stations.
- Slogan: “Abua Raj setar jana, Maharani Raj tundu jana” (Let the rule of our people begin, let the Queen’s rule end).
- Emphasized a vision of egalitarian tribal raj rooted in indigenous governance systems.
Arrest, Martyrdom, and Legacy
- Arrested: 1895; Died: 9 June 1900 in Ranchi Jail under mysterious circumstances.
- Though the rebellion was crushed, it led to the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act, 1908, securing tribal land rights.
Recognition and Legacy
- Declared as “Bhagwan” (Lord) by tribal communities for his cultural leadership and resistance.
- Institutions named in his honour: Birsa Agricultural University, Birsa Institute of Technology, etc.
- November 15 (birth anniversary) declared Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas (Tribal Pride Day) in 2021 by the Government of India.
- Symbol of tribal assertion, indigenous identity, and early resistance to colonialism in India.
Raja Bhabhut Singh Honoured
- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
In June 2025, the Madhya Pradesh Government held a special Cabinet meeting at Pachmarhi, renaming the Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary after Raja Bhabhut Singh, a lesser-known but formidable tribal freedom fighter of the 1857 revolt.
About Raja Bhabhut Singh
- Lineage: Belonged to the Jagirdar family of Harrakot Raikheri, descended from Thakur Ajit Singh. His grandfather, Thakur Mohan Singh, had allied with Peshwa Appa Saheb Bhonsle of Nagpur during the 1819–20 resistance against the British.
- Role in 1857 Revolt:
- A key Gond tribal leader with control over Jabalpur and the Satpura hills.
- Employed guerrilla warfare tactics in the Satpura forests, using deep geographical knowledge to harass British forces.
- Maintained close ties with Tatya Tope, a prominent national leader.
- Martyrdom:
- British deployed the Madras Infantry to capture him.
- He was executed in 1860, and is remembered in Korku tribal folklore.
- Known as the "Shivaji of Narmadachal" for his resistance strategies.
Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary (Now Raja Bhabhut Singh Sanctuary)
- Located in the Satpura mountain range, central Madhya Pradesh, within the Deccan Peninsula biogeographic zone.
- Highest point: Dhoopgarh (1,352 m).
- Forms part of the Satpura Tiger Reserve, along with:
- Satpura National Park
- Bori Wildlife Sanctuary
- Key Biodiversity Zone in Central India.
Korku Tribe Overview
- Region: Mainly in Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Melghat (Maharashtra).
- Occupation: Traditionally agriculturalists; introduced potato and coffee cultivation.
- Society: Patrilineal communities led by traditional headmen.
- Culture:
- Practice ancestral worship through memorial stones called Munda.
- Rich in oral traditions, which preserve the memory of tribal icons like Raja Bhabhut Singh.
Discovery of 800-Year-Old Pandya-Era Shiva Temple

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
An 800-year-old Shiva temple of the later Pandya period has been unearthed at Udampatti, a village in Melur taluk, Madurai district, Tamil Nadu.
Key Highlights:
- Discovery: Foundation of a later Pandya period Shiva temple (dated to 1217–1218 CE) unearthed accidentally by children.
Architectural Insights:
- Only the stone base of the temple (north and south sides) survives.
- Identified as a Shaivite temple using foundation engravings and reference to Silpa Sastram.
Inscriptions & Historical Significance:
- Inscriptions deciphered by C. Santhalingam (Pandya Nadu Centre for Historical Research).
- Temple identified as Thennavanisvaram, located in ancient Attur (present-day Udampatti).
- “Thennavan” was a Pandya royal title, suggesting direct patronage.
Key Inscriptions (1217–18 CE):
- A sale deed records the transfer of a waterbody named Nagankudi along with wet/dry land.
- Seller: Alagaperumal, chieftain of Kalavalinadu
- Buyer: Nambi Perambala Kuthan alias Kangeyan
- Sale amount: 64 kasu (coins)
- Tax revenue from the land assigned to the temple for daily expenses, indicating its financial independence.
Archaeological Relevance:
- Confirms ancient village name (Attur), showcasing socio-economic practices during the Later Pandya period.
- Highlights temple economy, land-water rights, and administrative structures.
Pandya Dynasty
- One of the Three Crowned Tamil Dynasties (alongside Cholas and Cheras).
- Capital: Initially Korkai, later Madurai.
- Early Pandyas active since 4th century BCE; Later Pandyas (1216–1345 CE) saw a golden age under Maravarman Sundara Pandyan.
- Controlled parts of Sri Lanka, Telugu regions, and had trade links with Rome & Southeast Asia.
- Symbol: Fish
Cultural Contributions:
- Patronage of Sangam literature, Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Jainism.
- Temples: Meenakshi Temple (Madurai), Nellaiappar Temple (Tirunelveli).
- Promoted Tamil arts, Bharatanatyam, and education.
Decline:
- Succumbed to Chola, Hoysala conflicts and Delhi Sultanate invasions.
- Madurai Sultanate (1335) and later Madurai Nayak dynasty (1529) succeeded their rule.
Boothapandi Rock Grooves

- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has recently unearthed one of the first known Neolithic rock grooves in Kanniyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, specifically near Boothapandi village. These grooves—estimated to be around 4,000 years old—were likely created by Neolithic people to sharpen tools and weapons used for hunting, agriculture, and digging.
The discovery was made during a field study conducted by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan, ASI Officer (Tirunelveli &Kanniyakumari), and M. Faisal of the Sembavalam Research Centre. The grooves vary in size:
- Length: 8 cm to 15 cm
- Width: 3 cm to 4 cm
Such grooves have also been previously documented in Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram districts of Tamil Nadu. The find strongly suggests the presence of Neolithic human activity in southernmost India and adds a significant layer to our understanding of prehistoric settlements in the region.
Neolithic Age
The Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) marks the final stage of prehistoric human evolution before the emergence of metal tools. Beginning around 10,000 BCE, it coincides with the Holocene Epoch and follows the Paleolithic Age (chipped-stone tools) and precedes the Bronze Age.
Key Features of the Neolithic Age
- Lifestyle Shift: Transition from hunting-gathering to agriculture and animal domestication.
- Permanent Settlements: Emergence of village communities with mud-and-reed houses, both rectangular and circular in design.
- Toolmaking: Development of polished and ground stone tools.
- Crafts and Culture: Rise of pottery, weaving, alcohol production, and early architecture.
- Burial Practices: Use of status objects (e.g., jade, pottery) in burials indicates belief in afterlife and emerging social hierarchies.
- By the end of the Neolithic era, copper metallurgy began, marking the Chalcolithic (Copper-Stone) Age. Eventually, bronze tools replaced stone ones, signaling the end of the Stone Age and the dawn of early civilizations.
Major Neolithic Sites in India
- Burzahom – Kashmir
- Chirand (Chiron) – Bihar
- Uttarapalli – Andhra Pradesh
- Edakkal Caves – Kerala
- Boothapandi (newly identified) – Tamil Nadu
Ahilyabai Holkar
- 31 May 2025
In News:
On the 300th birth anniversary of Maharani Ahilyabai Holkar, the Prime Minister will participate in the Mahila Sashaktikaran Maha Sammelan in Bhopal to honour her enduring legacy.
Historical Background
- Born: 31 May 1725
- Ruled: Malwa region (1767–1795) as part of the Maratha Confederacy
- Dynasty: Holkar
- Capital: Maheshwar (now in Madhya Pradesh)
Initially serving as a regent, Ahilyabai Holkar became the sovereign ruler after her husband and father-in-law’s deaths. Her rule is widely regarded as the golden age of the Holkar dynasty.
Governance and Administrative Reforms
- Ahilyabai was known for her equitable justice system, exemplified by the sentencing of her own son for a capital crime.
- She abolished discriminatory practices, such as the law confiscating property from childless widows.
- Courts for dispute resolution were established, and she remained accessible to the public, holding daily audiences.
- She broke gender norms by not observing purdah, a rare move for female rulers of the time.
Military Leadership
- Trained under Malhar Rao Holkar, she led her forces in battle.
- Appointed Tukoji Rao Holkar (Malhar Rao’s adopted son) as army commander.
- In 1792, she engaged a French officer, Chevalier Dudrenec, to modernize her army by establishing four battalions.
Cultural and Architectural Contributions
- A patron of literature and arts, she invited scholars like Moropant, Ananta Gandhi, and Khushali Ram to her court.
- Promoted craft and industry, notably founding the Maheshwar textile industry—famous today for Maheshwari sarees.
- Commissioned the construction and restoration of hundreds of Hindu temples and dharamshalas across India.
- Her most iconic act was the renovation of the Kashi Vishwanath Temple in Varanasi in 1780.
- Also contributed to infrastructure development, including roads, wells, forts, and rest houses.
Titles and Recognition
- Referred to as ‘Punyashlok’, meaning one as pure as sacred chants.
- British historian John Keay called her the ‘Philosopher Queen’.
Demise and Succession
Ahilyabai passed away on 13 August 1795 at the age of 70. She was succeeded by Tukoji Rao Holkar, who later abdicated in favour of Jaswant Rao Holkar. Jaswant Rao remained the last Holkar to rule independently until 1804.
Mitathal and Tighrana: Newly Protected Harappan Sites in Haryana

- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
The Haryana Government has declared Mitathal and Tighrana, two historically significant Harappan civilisation sites in Bhiwani district, as protected archaeological sites under the Haryana Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1964.
Location and Legal Status
- Both sites are located in Mitathal and Tighrana villages of Bhiwani district, Haryana.
- The notification was issued on March 13, 2025, designating a 10-acre area at Mitathal for protection.
- The Heritage and Tourism Department will ensure preservation through site fencing and deployment of guards.
Mitathal Site: Key Highlights
- Period: Dates to the Copper-Bronze Age, roughly 3rd to 2nd millennium BCE.
- Archaeological Finds:
- Well-baked red pottery with black painted motifs like pipal leaves and fish scales.
- Beads, copper tools, bangles, terracotta, and bone artefacts.
- Historical Timeline:
- First identified in 1913 through Samudragupta coins.
- Systematic excavations began in 1965–68 and continued post-2016 by the Central University of Haryana.
- Cultural Features:
- Reflects urban planning and craftsmanship typical of the Harappan Civilization.
Tighrana Site: Cultural Significance
- Chronology: Rich in pre-Harappan, Harappan, and post-Harappan layers.
- Inhabitants: Associated with Sothian culture – early Chalcolithic farming communities (~2400 BCE).
- Settlement Traits:
- Mud-brick houses, some possibly fortified.
- Use of bichrome wheel-made pottery (black and white designs).
- Artefacts:Green carnelian bangles, beads, and tools suggest a thriving bead and jewellery industry.
Archaeological and Cultural Importance
- Continuity of Settlement: Offers insight into continuous human occupation from Pre-Siswal to Post-Harappan periods.
- Socio-economic Insights:Demonstrates early agricultural practices, urban planning, and craft traditions in the Indo-Gangetic divide.
Background: Harappan Civilization
- Also known as the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC); flourished around 2500 BCE.
- One of the world’s oldest urban civilizations, alongside Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China.
- Classified as Bronze Age due to artefacts made from copper-based alloys.
- Key excavations:
- Harappa (1921–22) by Daya Ram Sahni.
- Mohenjo-daro (1922) by R.D. Banerji, under supervision of Sir John Marshall (ASI).
Tribhuvandas Patel
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
The Lok Sabha recently approved a bill to establish the Tribhuvan Sahkari University in Anand, Gujarat, named in honour of TribhuvandasKishibhai Patel, a seminal figure in India’s cooperative movement and a founding architect behind Amul.
Who was Tribhuvandas Patel?
- Born in 1903 in a farming family in Gujarat, Tribhuvandas Patel was an Indian freedom fighter, lawyer, and social reformer.
- A dedicated follower of Mahatma Gandhi, he actively participated in the civil disobedience movement, anti-untouchability campaigns, and rural development initiatives.
- He was first arrested during the Salt Satyagraha in 1930 at Nasik and later in Visapur, where he resolved to commit his life to public service.
- Between 1948 and 1983, he served as the President of Harijan Sevak Sangh, an organisation founded by Gandhi to uplift marginalized communities.
Role in India's Cooperative Movement
- In 1946, with encouragement from Morarji Desai and Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Tribhuvandas spearheaded the formation of the Kaira District Cooperative Milk Producers’ Union Ltd. (KDCMPUL) to counter exploitative practices by private dairies such as Polson Dairy.
- His strategy began with organizing village-level milk cooperatives, where membership was inclusive, cutting across caste, class, and religion.
- Recognizing the need for professional management, he brought in Dr. VergheseKurien, who later led India’s White Revolution.
Institution Building and Legacy
Tribhuvandas Patel played a pivotal role in laying the foundations of several key institutions that transformed India’s dairy sector:
- Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF)
- National Dairy Development Board (NDDB)
- Institute of Rural Management, Anand (IRMA)
His lifelong efforts significantly empowered rural milk producers and contributed to India’s emergence as a dairy powerhouse.
Recognitions and Awards
- Ramon Magsaysay Award (1963) for Community Leadership
- Padma Bhushan (1964) from the Government of India for his services to society
Acharya Charaka and Sage Sushruta

- 25 May 2025
In News:
The Vice-President of India recently inaugurated the statues of Acharya Charaka and Sage Sushruta at Raj Bhavan, Goa, to honour India's ancient medical heritage rooted in Ayurveda and surgery.
Acharya Charaka – Father of Indian Medicine
- Period: Circa 100 BCE – 200 CE
- Region: Associated with Taxila, under the Kushan emperor Kanishka.
- Key Contribution:
- Originally based on the Agnivesha Samhita, later revised and compiled by Charaka.
- Focused on internal medicine (Kayachikitsa).
- Discussed physiology, disease pathology, diagnosis, and therapeutic techniques.
- Introduced the concept of three doshas: Vata, Pitta, Kapha—the basis for diagnosis and treatment in Ayurveda.
- Provided early insights into embryology (Garbha Vigyan) and preventive healthcare.
- Stressed medical ethics, such as confidentiality, non-maleficence, and the moral duties of a physician.
- Emphasized the importance of diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors in health.
- The Charaka Samhita is part of the B?hatTrayi (Great Trilogy) of Ayurveda and was expanded by D??habala.
- Translated into Arabic, Latin, and other languages, reflecting its global medical influence.
Sage Sushruta – Father of Surgery
- Period: Circa 600–700 BCE
- Region:Practised in Kashi (Varanasi), likely under King Divodasa.
- Key Contribution:
- A pioneering treatise in surgery and medical science.
- Detailed 300+ surgical procedures and over 100 surgical instruments.
- Innovations include rhinoplasty (nasal reconstruction), skin grafts, cataract surgery, and caesarean sections.
- Explained fractures, dislocations, use of anaesthesia, and surgical training.
- Emphasized dissection-based anatomy, practical education, and simulation for surgical learning.
- Covered areas like public health, toxicology, pediatrics (Kaumarbhritya), and neonatal care.
- Integrated scientific observation, hygiene, and evidence-based methods long before modern systems.
Collective Significance:
- Both are part of the B?hatTrayi (Charaka Samhita, Sushruta Samhita, and Ashtanga Hridaya), forming the backbone of Ayurvedic literature.
- Their work laid the foundation for:
- Holistic medicine and ethical healthcare practice.
- Advanced understanding of human physiology and embryology.
- Scientific surgery, centuries ahead of global developments.
- Contributions to child health (Kaumarbhritya) and public hygiene.
- Their texts influenced Arab and European medicine through translations such as Kitab-i-Susrud.
Keezhadi Excavations

- 24 May 2025
In News:
The Keezhadi archaeological site, located near Madurai along the Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu’s Sivaganga district, is a major site of cultural and historical significance. It offers compelling evidence of an urban, literate, and industrialized Tamil civilization dating back to the Sangam Age.
Background and Discovery
- Discovered: Surveys in 2013–14; Excavations began in 2015.
- Excavating Agencies: Initially conducted by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and later by the Tamil Nadu State Archaeology Department.
- Excavated Area: Only 1 out of 100 acres has been explored; over 4,000 artefacts recovered.
Significant Findings
- Carbon Dating (AMS) of charcoal: Indicates urban habitation existed by 200 BCE.
- Key Discoveries: Brick structures, ring wells, pottery with Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions, beads, graffiti, water storage facilities, and a large decorative pot unique to the region.
- Artefacts suggest links with North India and Western trade networks.
Cultural and Historical Significance
- Suggests early urbanization in South India, independent of northern influence.
- Supports theories of a pre-Sangam urban Tamil culture.
- Establishes Keezhadi as a centre of literacy, trade, and craftsmanship.
- Mention of nearby settlements like Manalur and Konthagai in Tamil classics such as Tiruvilayadal Puranam strengthens the site's literary links.
Sangam Period Context
- Spanned approximately 3rd century BCE to 3rd century CE.
- Tamil academies or ‘Sangams’ under the Pandya dynasty produced extensive literature.
- Notable texts: Tolkappiyam, Ettuthogai, Pattupattu, Padinenkilkanakku, and epics like Silappadikaram, Manimekalai, and CivakaCintamani.
- Literature depicts advanced socio-political systems, agriculture, trade, and maritime activities.
Current Issues and ASI Involvement
- The excavation report prepared by archaeologist Amarnath Ramakrishna (submitted in January 2023) has been returned by ASI for revision to ensure:
- Accurate period classification.
- Better stratigraphic and cartographic details.
- Consistency in scientific dating and layer mapping.
- ASI has flagged the need for clearer mapping, missing illustrations, and precise scientific justification for dating claims, especially for Period I (8th to 5th century BCE).
Controversy and Criticism
- Concerns have been raised over delays in publishing excavation reports.
- Critics highlight a perceived bias in the handling of southern archaeological sites, pointing to similar delays with the Adichanallur site report.
- Experts stress the importance of transparent and timely reporting to enhance historical understanding.
Guttala Inscription

- 24 May 2025
In News:
A rare 16th-century sculptural inscription discovered near the Chandrashekara temple in Guttala village, Haveri district, Karnataka, marks the earliest known epigraphic evidence in India of a large-scale humanitarian disaster caused by a natural calamity—a drought (bara) that claimed 6,307 lives in 1539 CE (Saka 1461, August 18).
Key Features of the Inscription:
- Language and Script: Kannada.
- Medium: Stone slab.
- Depiction: A sculpture showing MarulaihOdeya, the son of NanidevaOdeya, carrying a basket containing dead bodies—representing his act of burying the deceased to earn religious merit for the regional ruler, TimmarasaSvami.
- Religious Context: The burial was conducted after paying homage to Basaveshwara, reflecting the spiritual and ritualistic practices of the time.
- Territorial Reference: Mentions the term "seeme", indicating the existence of local administrative divisions.
Significance:
- First explicit historical record in India of deaths caused by a natural disaster, making it an important source for disaster history and epigraphic heritage.
- Offers textual and visual representation of community response to drought.
- Provides insights into local governance, religious customs, and socio-economic conditions of 16th-century Karnataka.
- Adds depth to the study of historical climate events, with potential to track past climatic patterns and their impact on populations.
Broader Context:
- Inscriptions in India, typically engraved on stone or metal, serve as valuable primary sources for understanding royal decrees, battles, donations, and societal events.
- Other notable Karnataka inscriptions include:
- Maski Edict (3rd Century BCE) – First mention of Emperor Ashoka as "Devanampriya".
- Halmidi Inscription (c. 450 CE) – Oldest Kannada inscription referencing Kadamba king Kakusthavarma.
- Aihole Inscription (634 CE) – Chronicles the military achievements of Pulakeshin II.
Recent Epigraphic Developments:
- The Epigraphy Branch of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered and documented over 1,000 inscriptions across India during 2024–25, including more than 100 new finds this year alone.
- These discoveries reinforce the role of epigraphy in reconstructing Indian history, especially in areas lacking detailed literary sources.
International Booker Prize 2025
- 23 May 2025
In News:
In a historic win, Banu Mushtaq, a prominent Kannada writer, advocate, and activist, became the first Indian author writing in Kannada to win the International Booker Prize 2025 for her short story collection Heart Lamp. The book was translated into English by Deepa Bhasthi, who also became the first Indian translator to win this prestigious award.
About the International Booker Prize
- Established: 2005 by the Booker Prize Foundation, UK.
- Awarded: Annually.
- Purpose: To honour the best work of fiction translated into English, regardless of the original language or nationality of the author.
- Prize Amount: £50,000, shared equally between the author and the translator.
- Shortlisted nominees (authors and translators) receive £2,500 each.
- Focus: Unlike the Booker Prize, which honours original English-language works, the International Booker Prize exclusively celebrates translated fiction, highlighting the importance of translators in global literature.
Key Features
- Celebrates literary excellence, cultural richness, and the art of translation.
- Initially biennial (2005–2015), it became an annual award in 2016.
- Books must be translated into English and published in the UK or Ireland.
India and the International Booker Prize
Year Author Work Language Translator
2022 Geetanjali Shree Tomb of Sand Hindi Daisy Rockwell
2025 Banu Mushtaq Heart Lamp Kannada Deepa Bhasthi
About Banu Mushtaq
- Born: April 3, 1948, in Hassan, Karnataka.
- Professions: Advocate, journalist, feminist writer, women’s rights activist, and former municipal councillor.
- Affiliation: Prominent figure in the Bandaya movement, known for protest literature in Kannada addressing social injustices.
- Journalistic Background: Reported for LankeshPatrike (1981–1990) under the mentorship of P. Lankesh.
Literary Contributions
- Started writing: In 1974; first story published in Prajamatha.
- Themes: Focuses on gender justice, religious identity, caste oppression, and female autonomy.
Heart Lamp: The 2025 Winning Work
- Genre: Short story collection comprising 12 stories written between 1990 and 2023.
- Content: Explores the lives of ordinary South Indian Muslim women, addressing themes like patriarchy, faith, family roles, and self-determination.
- Significance:
- First short story collection to win the International Booker Prize.
- First Kannada-language work to win.
- First win for Indian translator Deepa Bhasthi.
Other Notable Works by Banu Mushtaq
- Benki Male (1999): Awarded the Karnataka Sahitya Academy Award.
- HaseenaMattuItaraKathegalu (2015): Translated into English as Haseena and Other Stories.
- Black Cobra (Short Story): Adapted into the award-winning film Hasina by Girish Kasaravalli.
Shirui Lily Festival
- 21 May 2025
In News:
The 5th State-Level Shirui Lily Festival resumed in Ukhrul district, Manipur from May 20–24, 2025, after a two-year pause due to ethnic unrest. It marks a symbolic step towards peace, as it involved significant movement through previously restricted areas with heightened security.
About the Shirui Lily Festival:
- Organised by: Manipur Tourism Department
- First Held: 2017
- Venue:Shirui Village, Ukhrul District
- Objective: Promote eco-tourism and create awareness about the endangered Shirui Lily
- Special 2025 Edition: Commemorates the 75th anniversary of the discovery of the Shirui Lily
Key Features (2025 Edition):
- Cultural Events: Traditional dances, gospel rock shows, and live performances at the ShiRock music festival
- Eco-Initiatives: Trash collection drives and conservation awareness campaigns
- Competitions:
- SheChef Cooking Contest (vegetarian & childhood memory dishes)
- Miss Shirui Lily 2025 beauty pageant
- Sports (football, wrestling, tug of war, mini-marathon)
- Adventure Activities: Ziplining, camping, biking
- Special Ceremonies: Unveiling of the 75th Anniversary Memorial and a drone show
- Closing Function: Hosted by senior officials from the Ministry of Tourism
About Shirui Lily (Lilium mackliniae):
- Botanical Name:Lilium mackliniae
- Discovered by: Botanist Frank Kingdon-Ward in 1946, named after his wife Jean Macklin
- Local Name:KashongTimrawon
- Geographic Range: Exclusively found in the Shirui Hills (2,673 m altitude) of Ukhrul district
- State Flower of Manipur
Ecological and Cultural Significance:
- Endemic Habitat: The species is not viable for transplantation outside its native micro-climate
- Flowering Season: April to June, marked by a breathtaking bloom of pinkish-white bell-shaped flowers
- Cultural Reverence: Associated with the local deity Philava, symbolising spiritual and ecological identity of the Tangkhul Naga tribe
- Global Recognition: Awarded by the Royal Horticultural Society at the London Flower Show in 1950
Conservation Status and Efforts:
- Threats: Habitat loss, invasive species, and climate change
- Conservation Status:Endangered
- Scientific Interventions: ICAR-NEH, under Dr. Manas Sahoo, has developed micropropagation techniques for in-situ conservation
58thJnanpith Award Conferred

- 20 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the President of India, presented the 58thJnanpith Award to renowned Sanskrit scholar Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Ji at a function held at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi. She also extended congratulations to celebrated writer Gulzar, a fellow recipient who could not attend due to health reasons.
About Jagadguru Rambhadracharya
- A prominent Sanskrit scholar, spiritual leader, poet, and educationist.
- Despite being visually challenged, he has made significant literary and social contributions.
- Recognized for his multi-faceted excellence in Sanskrit literature and devotion to nation-building through literary and cultural service.
Highlights from the President’s Address
- Emphasized that literature unites and awakens society, playing a key role in movements from 19th-century social reform to the freedom struggle.
- Referenced the literary legacy of figures like Valmiki, Vyas, Kalidas, and Rabindranath Tagore as embodiments of India’s civilizational essence.
- Praised the BharatiyaJnanpith Trust for honoring literary excellence since 1965 across various Indian languages.
- Celebrated the contributions of women Jnanpith awardees such as Ashapurna Devi, Amrita Pritam, Mahasweta Devi, and Pratibha Ray, urging young women to draw inspiration from their works.
About the Jnanpith Award
Feature Details
Established 1961
First Awarded 1965 to Malayalam poet G. SankaraKurup for Odakkuzhal
OrganisedBy BharatiyaJnanpith, a literary and cultural organization founded in 1944
Eligibility Indian citizens writing in Schedule VIII languages of the Constitution or
in English
Award Components Cash prize, citation, and a bronze replica of Vagdevi (Saraswati)
Nature Annual, but may be withheld if no suitable candidate is found
One-Time Recognition A writer can receive the award only once
Language Rotation Rule A language that has received the award is ineligible for the next two years
Gyan Bharatam Mission

- 19 May 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will launch the revamped National Manuscripts Mission, which was announced in the Union Budget earlier this year, on June 9.
Key Highlights:
- Implementing Body: Ministry of Culture, Government of India
- Earlier Version: National Manuscripts Mission (est. 2003), under Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA)
- Objective:To survey, document, conserve, and digitize over one crore (10 million) Indian manuscripts located in academic institutions, libraries, museums, and private collections.
Key Features
- Massive Coverage: Targets over 1 crore manuscripts, making it India’s largest manuscript preservation project.
- Digital Repository: Creation of a National Digital Repository of Indian Knowledge Systems to ensure accessibility for researchers and the public. Includes AI-powered tools for metadata tagging, translation, and archiving.
- Modern Techniques: Uses advanced scientific conservation methods, including AI and 3D imaging.
- Collaborative Model: Engages academic institutions, libraries, museums, private collectors, and international bodies.
- Budgetary Support: Budget raised from ?3.5 crore to ?60 crore, with a total outlay of ?482.85 crore for 2024–31.
Background and Need
- The earlier NMM (2003) made limited progress. Out of 52 lakh manuscripts surveyed, only 3 lakh titles were digitized, and only 70,000 are currently viewable due to lack of access policy.
- 80% of manuscripts in India are privately owned, underscoring the need for public-private collaboration.
- Over 9 crore folios have been conserved (preventive and curative) in the last two decades.
What is a Manuscript?
A manuscript is a handwritten document (on paper, palm leaf, birch bark, etc.), at least 75 years old, and of historical, scientific, or artistic significance.
Example: The Bakhshali Manuscript (3rd–4th century BCE) is a key Indian text on mathematics, featuring the earliest known use of the symbol for zero.
JenuKuruba Tribe
- 15 May 2025
In News:
In a significant move, families from the JenuKuruba tribe have begun returning to their ancestral lands located within Nagarhole National Park. This reoccupation marks an important step in their decades-long struggle to reclaim traditional forest habitats.
Who are the JenuKurubas?
The JenuKuruba are an indigenous tribal community classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in India. They are primarily concentrated in the Kodagu and Mysuru districts of Karnataka.
- Etymology:The term "JenuKuruba" derives from Kannada—“jenu” means honey, reflecting their age-old practice of honey collection. Traditionally, they depend on forest produce, minor agriculture, and gathering activities for their livelihood.
- Alternate Names:They are also known as Then Kurumba or KattuNaikar in various local contexts.
Settlement and Lifestyle
- Habitat:The community resides in compact settlements known as “Hadi.”
- Living Style:They follow a semi-nomadic lifestyle, shaped by their deep relationship with forest ecosystems rather than external authorities like the state, police, or religious institutions.
Community Structure
- Governance:
The JenuKurubas follow a traditional leadership hierarchy that includes:- Yajamana (Headman) – responsible for social matters
- Gudda (Ritual Head) – oversees religious ceremonies
While the Gudda handles spiritual issues, all other community functions are managed locally under the guidance of the Yajamana.
Belief System and Culture
- Spiritual Beliefs:Their religion is rooted in the worship of supernatural spirits and deities unique to their tradition. These spiritual entities have distinct identities and are central to their worldview.
- Cultural Expressions:Music, dance, and oral storytelling are vital cultural practices. Their traditional songs and dances revolve around themes of agriculture, marriage, mythology, and faith.
Significance of the return to Nagarhole
The recent return of JenuKuruba families to Nagarhole represents not just a physical homecoming, but a cultural revival. For the tribe, the forest is not just a resource—it is sacred ground tied to their identity, heritage, and spiritual life.
Their reoccupation reopens long-standing debates about conservation, indigenous rights, and forest governance in India.
Piprahwa Gems Controversy
- 15 May 2025
In News:
A group of international Buddhist scholars and monastics has voiced strong objections to the proposed auction of the Piprahwa Gems. These jewels, long venerated as relics intimately linked to the historical Buddha, are at the center of a heated debate over their sale.
Background of the Piprahwa Gems
- Discovery Site: The gems were unearthed in 1898 at Piprahwa, in present-day Uttar Pradesh, where a stupa (Buddhist burial monument) once stood.
- Historical Significance: An inscription on one of the reliquaries claims the stupa housed the physical remains of the Buddha, who passed away circa 480 BCE.
- Excavation: The find was made by William Claxton Peppé, a British colonial engineer, during work on his estate. It marked the first scientifically credible recovery of Buddha’s relics in modern times.
Composition and Distribution
- Material Variety: The collection comprises roughly 1,800 pieces, including amethysts, coral, garnets, pearls, rock crystal, shells, and gold, fashioned into beads, pendants, and other ornaments, as well as unworked specimens.
- Custodial History: Under the 1878 Indian Treasure Trove Act, the British Crown claimed the entire hoard. Most of these gems were subsequently transferred to the Indian Museum in Kolkata. Peppé retained around one-fifth of the collection—items colonial officials deemed “duplicates”—which later entered private hands.
- International Gift: The British gifted the stupa’s bone and ash fragments to King Chulalongkorn of Siam (modern-day Thailand), further dispersing relics tied to the find.
Contemporary Concerns
Many in the Buddhist community argue that auctioning these gems violates their sacred status and severs the spiritual connection believers feel to the Buddha’s remains. They call for the jewels to remain in public or religious trust, rather than being treated as collectors’ items in the art market.
Rare 7th-Century Old Kannada Inscription unearthed at Madapura Lake, Karnataka

- 07 May 2025
In News:
A rare 7th-century Old Kannada inscription from the reign of Vikramaditya I of the Badami Chalukyas has been discovered at Madapura Lake in Davangere, Karnataka. The inscription sheds light on taxation, land grants, and regional governance during his rule.
About the Badami Chalukyas
- Origins: Emerged as a regional Kannada power claiming descent from Ayodhya to establish legitimacy.
- Capital:Vatapi (present-day Badami, Karnataka).
- Notable Rulers and Political History:
- Pulakesin I (543–566 CE): Founder of the dynasty; fortified Badami.
- Pulakesin II (609–642 CE): Most celebrated ruler; defeated Harshavardhana at the Narmada river; established diplomatic contacts with Persia (depicted in Ajanta caves).
- Vikramaditya I (644–681 CE): Son of Pulakesin II; reclaimed Badami from Pallavas and expanded influence over southern kingdoms like the Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas.
- Administration:
- Centralised monarchy with limited autonomy granted to villages.
- Economy relied on land revenue and military conquests.
- Maintained a naval fleet—Pulakesin II had around 100 ships.
- Religion:Patronised Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism, and Jainism. Vikramaditya I and others made donations to Jain institutions; Pulakesin I performed Ashvamedha Yajna.
- Art and Architecture:
- Developed the Vesara style, a fusion of northern Nagara and southern Dravida temple architecture.
- Constructed rock-cut and structural temples in Aihole, Badami, and Pattadakal.
About Vikramaditya I
- Background: Son of Pulakesin II; ascended the throne during a period of political turmoil following his father's death and Pallava invasion.
- Military Achievements:
- Defeated Narasimhavarman I of the Pallavas, who had earlier seized Badami.
- Reunited the fractured Chalukya empire, restoring its former prestige.
- Subdued southern powers including the Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas, consolidating control over the southern Deccan.
- Political Consolidation:
- Re-established central authority across Karnataka and surrounding regions.
- Appointed loyal feudatories, such as Singhavenna (mentioned in the new Davangere inscription), to manage local governance.
- Legacy:
- Known by titles such as Rajamalla (King of Kings) and Yuddhamalla (Warrior King).
- His reign marked a revival of Chalukya power and paved the way for cultural and architectural achievements under his successors Vikramaditya II and Kirtivarman II.
Neanderthal Spear Tip Discovery
- 06 May 2025
In News:
Ancient bone spear tip found in Russia is oldest in Europe and made by Neanderthals.
What Was Discovered?
- Oldest known spear tip in Europe, crafted by Neanderthals, not Homo sapiens.
- Found in a cave in the North Caucasus region, Russia.
- Dated to 70,000–80,000 years ago, prior to modern human arrival in Europe (~45,000 years ago).
- Study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
Artefact Features
- Length: ~9 cm
- Material: Bone (likely from bison)
- Construction:
- Shaped using stone tools
- Attached to a wooden shaft with natural tar (early adhesive use)
- Function:
- Micro-cracks indicate impact with a hard target – used in hunting or combat
- Minimal wear, suggesting it was used shortly after construction
Excavation Details
- Excavated in 2003, thoroughly analyzed recently.
- Found with animal bones and campfire remains – evidence of Neanderthal habitation.
- Analytical techniques used: Spectroscopy, CT scans, Microscopy
Revival of Vikramshila University

- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
Following the revival of Nalanda University, another historic centre of learning—Vikramshila University in Bihar—is now set for rejuvenation. The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) began developing the site in December 2023 to boost heritage tourism. Simultaneously, the Bihar government has earmarked 202.14 acres of land in Antichak village, Bhagalpur district, for setting up a Central University at the ancient site.
The revival project was approved by the Central Government in 2015 with a sanctioned budget of ?500 crore. However, work was delayed due to issues in land acquisition. With recent approval of ?87.99 crore for land procurement and the identification of suitable land, the project has regained momentum. The site is located about 3 km from the ancient ruins of the original university.
Historical Background:
- Vikramshila University was founded in the late 8th or early 9th century AD by King Dharmapala of the Pala Dynasty as a response to declining academic standards at Nalanda.
- Situated along the banks of the Ganges in eastern India, Vikramshila emerged as a major hub of Tantric Buddhism (Vajrayana) and occult studies, distinguishing itself from the broader curriculum of Nalanda.
- During its peak, Vikramshila housed over 1,000 students and 100 teachers, many of whom came from other parts of India and abroad.
- The university became renowned for its scholarship in theology, logic, metaphysics, grammar, philosophy, and especially tantric studies, which were popular in both Buddhism and Hinduism during that era. Among its most prominent scholars was AtisaDipankara, who played a key role in the spread of Buddhism to Tibet.
- The university featured a central cruciform brick stupa surrounded by 208 monk cells, arranged symmetrically on all four sides. A major architectural marvel of the site is its library, which had an innovative cooling system where water from a nearby reservoir was used to preserve manuscripts. This reflects the advanced engineering and scholarly focus of the institution.
- Although Nalanda and Vikramshila were separate entities, they often collaborated and shared scholars under the patronage of King Dharmapala. At one point, Vikramshila even held administrative authority over Nalanda.
Decline:
Vikramshila flourished for nearly four centuries before being destroyed around 1203 AD during the invasions of Muhammad Bin Bakhtiyar Khalji, the same event that marked the end of Nalanda University. The decline was also contributed to by the waning influence of Buddhism in India and the rise of Hinduism.
Recent Initiatives:
The ASI has divided the Vikramshila ruins into grids for careful excavation and preservation. A museum at the site displays several important antiquities, including sculptures of Buddhist and Hindu deities like Avalokiteshvara, Loknath, Surya, Vishnu, Ganesh, and more. Restoration work is also underway on NH-80, which connects Vikramshila to Bhagalpur city, about 50 km away.
Shaheed Diwas

- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
On Shaheed Diwas (23rd March), the nation commemorates the supreme sacrifice of three iconic freedom fighters—Bhagat Singh, Shivaram Rajguru, and Sukhdev Thapar. Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid tribute to these martyrs, remembering their unwavering resolve and courageous efforts in the struggle for India's independence. This day marks the execution of these three revolutionaries by British colonial authorities in Lahore Jail in 1931.
Background of the Martyrs
The trio was convicted for their involvement in the 1928 Lahore Conspiracy Case, which revolved around the killing of J.P. Saunders, a British officer. The incident occurred after Saunders was mistakenly identified as Superintendent James Scott, who was blamed for the death of Lala Lajpat Rai during a protest against the Simon Commission. The execution of these freedom fighters on 23rd March 1931 became a symbol of their sacrifice for the cause of India’s freedom.
The three were members of the Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA), a revolutionary group that sought to overthrow British rule through armed struggle. Their fearless actions continue to inspire the nation to this day.
Brief Profiles of the Martyrs
- Bhagat Singh (1907–1931): Born in Punjab, Bhagat Singh was a prominent revolutionary who played a key role in the fight against British rule. He is remembered for his bold actions, such as the bombing of the Central Legislative Assembly in 1929, and his fearless stand against colonial oppression. His execution at the age of 23 became a catalyst for the freedom struggle.
- Shivaram Rajguru (1908–1931): Born in Maharashtra, Rajguru was a committed revolutionary who, along with Bhagat Singh, was involved in the assassination of J.P. Saunders. He was known for his dedication to the cause of armed resistance and his determination to fight colonial oppression. Rajguru was executed at the age of 23.
- Sukhdev Thapar (1907–1931): A key figure in mobilizing youth for the freedom struggle, Sukhdev was born in Punjab. He played a significant role in the activities of the HSRA and was instrumental in organizing protests and revolutionary activities. His execution, like that of his fellow revolutionaries, became a symbol of the ultimate sacrifice for India's freedom.
Financial Assistance for Promotion of Art and Culture
- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Culture has implemented several schemes aimed at supporting the growth and preservation of India's rich art and cultural heritage. One of the key initiatives is the ‘Financial Assistance for Promotion of Art and Culture’ Scheme, a Central Sector Scheme that provides financial support to eligible cultural organizations across the country. Below is an overview of the scheme, its components, and eligibility criteria.
Eligibility Criteria for Organizations
To be eligible for assistance under this scheme, cultural organizations must meet the following criteria:
- Registered as a society, trust, or not-for-profit company for at least three years.
- Registered on the NGO Darpan Portal of NITI Aayog.
- Have a primary focus on cultural activities.
- Submit audited financial statements for the last three years.
- Have filed Income Tax returns during the last three years.
Sub-Components of the Scheme
The scheme consists of eight sub-components, each designed to support different aspects of art and culture across India.
- Financial Assistance to Cultural Organizations with National Presence
- Objective: To support large cultural organizations with a nationwide presence.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 1 crore (may increase to Rs. 5 crore in exceptional cases).
- Cultural Function & Production Grant (CFPG)
- Objective: Provides financial aid for cultural events like seminars, conferences, research, workshops, festivals, exhibitions, and productions of dance, drama, and music.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 5 lakh (may increase to Rs. 20 lakh in exceptional cases).
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Cultural Heritage of the Himalayas
- Objective: To promote and preserve the cultural heritage of the Himalayan region, including Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 10 lakh per year (may increase to Rs. 30 lakh in exceptional cases).
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Buddhist/Tibetan Organizations
- Objective: To support Buddhist/Tibetan organizations, including monasteries, in preserving and developing Buddhist/Tibetan culture and traditions.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 30 lakh per year (may increase to Rs. 1 crore in exceptional cases).
- Financial Assistance for Building Grants including Studio Theatres
- Objective: To provide financial support for creating cultural infrastructure, such as studio theatres, auditoriums, and rehearsal halls, along with providing essential facilities like lighting, acoustics, and sound systems.
- Grant Amount: Up to Rs. 50 lakh in metro cities and Rs. 25 lakh in non-metro cities.
- Financial Assistance for Allied Cultural Activities
- Objective: To assist in the creation of assets that enhance the audio-visual spectacle for live performances and cultural activities.
- Grant Amount:
- Audio: Up to Rs. 1 crore.
- Audio + Video: Up to Rs. 1.5 crore (includes 5 years of operation and maintenance costs).
- Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Objective: To safeguard and promote India’s intangible cultural heritage, supporting institutions, groups, and NGOs involved in relevant activities.
- Grant Amount: Varies based on specific activities.
- Domestic Festivals and Fairs
- Objective: To assist in organizing RashtriyaSanskritiMahotsavs (National Culture Festivals) across India, engaging artists and showcasing various cultural traditions.
- Grant Amount: Event-based assistance; Rs. 38.67 crore was released in the last three years for these events.
Implementation and Monitoring
The Ministry of Culture closely monitors the effective utilization of funds under this scheme through:
- Utilization Certificates and audited financial statements.
- On-site physical inspections to assess the progress and impact of the funded projects.
- Regular oversight ensures that the assistance is used for its intended purpose and meets the objectives of cultural promotion and preservation.
Support for Individual Artists and Cultural Research
In addition to the above schemes, the Ministry of Culture also supports individual artists and cultural researchers through the ‘Scheme of Scholarship and Fellowship for Promotion of Art and Culture’. This scheme includes the following components:
- Award of Scholarships to Young Artists (SYA)
- Objective: To support young artists aged 18-25 years in various cultural fields.
- Duration: 2 years.
- Eligibility: Applicants should have undergone at least 5 years of training under a recognized guru or institution.
- Award of Senior/Junior Fellowships
- Senior Fellowship: For individuals 40 years and above to support cultural research.
- Junior Fellowship: For individuals 25-40 years for cultural research.
- Up to 400 Fellowships are awarded annually.
- Tagore National Fellowship for Cultural Research
- Objective: To provide funding for cultural research under two categories: Tagore National Fellowship and Tagore Research Scholarship.
- Selection: Fellows and scholars are selected by the National Selection Committee.
- Project Grants for Research in Performing Arts
- Objective: To provide financial assistance to individuals conducting research in performing arts.
PEPSU Muzhara Movement

- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
The PEPSU Muzhara Movement, commemorated annually on March 19, was a significant agrarian uprising by landless tenant farmers (muzharas) in Punjab demanding ownership rights over the land they cultivated. It stands as a historic resistance against feudal and colonial exploitation.
Background & Region
- Initiation: Started in the 1930s in the Patiala princely state.
- Expanded Across: 784 villages in present-day Patiala, Barnala, Mansa, Sangrur, Bathinda, Mohali, Fatehgarh Sahib, Faridkot (Punjab), and Jind (now in Haryana).
- After independence, the region was reorganized into the Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU), where the movement intensified.
Who Were the Muzharas?
- Muzharas were landless tenant farmers who cultivated land owned by biswedars (feudal landlords).
- They were forced to give one-third of their produce to landlords, who further paid a share to princely rulers, who in turn paid the British.
- Even after Independence (1947), landlords continued this exploitative practice, leading to widespread unrest.
Causes of the Movement
- Feudal oppression and loss of ancestral land.
- Colonial revenue structure perpetuated peasant poverty.
- Post-independence continuation of feudal demands.
- Denial of land ownership despite generations of cultivation.
Key Leaders
- Jagir Singh Joga – Organised and united tenant farmers.
- Buta Singh – Advocate for land redistribution.
- Teja Singh Sutantar – Linked the struggle with broader peasant movements.
- Sewa Singh Thikriwala – Anti-feudal ideologue and early inspiration.
- Bhai Jodh Singh – Strengthened the movement through grassroots mobilisation.
Phases and Nature of the Movement
- Peaceful Protests: Initial petitions and mobilisations.
- Armed Resistance: Tenant farmers took up arms for self-defense as repression increased.
- Mass Mobilisation: Conferences, rallies, and united action across villages.
Significance of March 19
- In March 1949, landlords attempted to reclaim cultivated lands in Kishangarh (Mansa district).
- The muzharas resisted by harvesting crops themselves, leading to a violent standoff.
- On March 17, a police officer was killed, resulting in the arrest of 35 muzharas—all acquitted by 1950.
- On March 19, 1949, the army surrounded the village, and four muzharas were killed.
- Since 1953, March 19 has been observed as “Muzhara Shaheedi Diwas”, honouring martyrs of the movement.
Outcome
- Land Reforms (1952): The movement culminated in reforms granting ownership rights to tenant farmers.
- Became a symbol of peasant resistance against exploitation and injustice.
Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs

- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
The Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs of Narayanpet district, Telangana have been included in India’s UNESCO Tentative World Heritage Sites list in 2025, highlighting their archaeological, cultural, and astronomical significance. Telangana now has two tentative UNESCO heritage sites, the first being the Ramappa Temple (inscribed in 2021).
What are Menhirs and Megaliths?
- Menhirs are large, upright standing stones, often tapered at the top, used by prehistoric communities.
- They served ritual, memorial, or astronomical purposes and are found globally, with prominent examples in Europe such as Stonehenge (UK) and Carnac (France).
- Megaliths refer broadly to prehistoric stone structures, used for burials (like dolmens, cairns, cists) or as commemorative monuments (like menhirs).
- In India, megalithic culture thrived during the Iron Age (c. 1500 BCE–500 BCE), especially in the Deccan Plateau (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana).
Significance of the MudumalMenhirs
- Age: Estimated to date back 3,500–4,000 years (1000 BCE–300 BCE).
- Site extent: Spread across 80 acres near the Krishna River, the site comprises:
- Around 80 large menhirs (10–14 feet tall).
- Nearly 3,000 alignment stones set in rows, believed to represent funerary rites and astronomical alignments.
- Astronomical importance: The alignments correspond with solar events such as solstices and equinoxes.
- A unique cup-marked stone represents the Ursa Major (Saptarshi) constellation—South Asia’s earliest known star depiction.
- Suggests advanced prehistoric knowledge of celestial navigation and calendar calculation.
Cultural and Living Traditions
- The site continues to hold spiritual value among locals.
- Menhirs are revered as "NilurallaThimmappa" (Thimmappa of the Standing Stones).
- One stone is worshipped as Goddess Yellamma, blending ancient heritage with living cultural practices.
Path Toward UNESCO World Heritage Status
- The MudumalMenhirs are among six sites added to India’s Tentative List in 2025, alongside:
- Kanger Valley National Park (Chhattisgarh)
- Ashokan Edict Sites (Multiple States)
- Chausath Yogini Temples (MP & Odisha)
- Gupta Temples (Multiple States)
- Palace-Fortresses of the Bundelas (MP & UP)
- India now has 62 sites on the Tentative List, a prerequisite for UNESCO nomination.
Recent ASI Discoveries in Sri Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary

- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) recently made significant archaeological findings in the Sri Lankamalleswara Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kadapa district of Andhra Pradesh. During an epigraphical survey, ASI discovered three rock shelters, rock paintings, and 30 inscriptions, highlighting the region’s historical and cultural significance.
Key Facts:
- Location: Kadapa district, Andhra Pradesh.
- Water bodies:
- The sanctuary forms the catchment area of the Pennar River.
- The Telugu Ganga Canal flows through the eastern part and drains into the Pennar.
Biodiversity:
- Vegetation types:
- Southern tropical dry deciduous forests (hills)
- Scrub forests (plains)
- Southern dry mixed deciduous forests
- Tropical thorn forests
- Tropical dry evergreen forests
- Flora:
- Rare and endangered species: Red Sanders, Sandalwood
- Riparian vegetation: Terminalia spp., Syzygium spp. (Jamun), Wild Mangoes, Anogeissuslatifolia, Phoenix spp., Bamboo, Hardwickiabinata
- Fauna:
- Notable species: Common toad, Bullfrog, Common Indian skink, Green vine snake
- Critically endangered species: Jerdon’s Courser — this sanctuary is the only known habitat of this bird.
Dramatic Performances Act, 1876

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi, at the NXT Conclave, highlighted the Dramatic Performances Act, 1876, as an example of outdated colonial legislation that continued in India long after independence. Though declared unconstitutional in 1956, the Act was formally repealed in 2017 as part of the government's initiative to eliminate obsolete laws and improve ease of doing business.
About the Dramatic Performances Act, 1876
Purpose and Background:
- Enacted by the British colonial government to suppress nationalist sentiments expressed through theatre and performance arts.
- Followed the 1875–76 visit of Prince of Wales (Albert Edward) to India, a period that saw increased resistance against colonial rule.
- Part of a broader strategy alongside other repressive laws such as the Vernacular Press Act (1878) and the Sedition Law (1870).
Key Provisions:
- Wide Banning Powers: Authorities could prohibit any play, pantomime, or public performance deemed seditious, defamatory, scandalous, or obscene.
- Search and Seizure: Magistrates had the authority to raid venues, seize performance materials, and cancel licenses.
- Punishment: Violations could lead to up to 3 months' imprisonment, fines, or both.
- Covered theatre groups, performers, and venues hosting dramatic works.
Post-Independence Status:
Continued Operation:
- Article 372 of the Indian Constitution allowed pre-existing colonial laws to remain valid until repealed or declared unconstitutional.
- The Act was adopted in some states like Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
Judicial Rejection:
- In 1956, the Allahabad High Court, in State vs. Baboo Lal &Ors., ruled the Act unconstitutional, citing violation of Article 19(1)(a) (Freedom of Speech and Expression).
- The Court found the Act’s procedural provisions ultra vires and beyond the permissible limits under Article 19(2).
Notable Case:
- In 1953, the Indian People’s Theatre Association (IPTA) attempted to stage ‘Idgah’, based on Munshi Premchand's story.
- The performance was abruptly banned mid-show by the local magistrate. The theatre group defied the order, leading to the court case that triggered the judicial review.
Final Repeal:
- Although unused since 1956, the law remained on the statute books until its formal repeal through the Repealing and Amending (Second) Act, 2017.
- This repeal was part of a larger reform initiative launched by the Modi government in 2014, which has repealed over 2,000 obsolete laws to streamline the legal system and boost administrative efficiency.
Dholavira
- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
President DroupadiMurmu recently visited Dholavira, a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Gujarat, India. She expressed appreciation for the Archaeological Survey of India’s (ASI) meticulous conservation efforts to preserve this ancient site, despite its remote location.
Location and Significance:
Dholavira is situated on Khadir Bet Island in the Great Rann of Kutch, Gujarat, within the Kutch Desert Wildlife Sanctuary and along the Tropic of Cancer. It was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2021 due to its remarkable contributions to understanding the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization, one of the world's earliest urban cultures.
Key Features:
- City Layout and Construction:Dholavira is distinct from other Harappan sites in its layout, divided into three main sections: the Citadel, the Middle Town, and the Lower Town. The city is unique for its extensive use of stone in construction, unlike the brick-built cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro. It also featured multi-purpose grounds, including a marketplace and a festive area.
- Water Conservation System:The site is renowned for its sophisticated water management techniques, which included 16 massive reservoirs, stepwells, check dams, and underground water storage systems. This advanced water conservation system earned it the name "Jal Durga" or "Water Fort." The engineering skills of the Harappans, especially in water harvesting, were far ahead of their time and continue to be admired today.
- Trade and Cultural Exchange:Dholavira was a significant trade hub, connected to regions such as Magan (modern Oman) and Mesopotamia. It is believed to have been involved in the trade of copper, jewelry, and timber. The site yielded a variety of artifacts, including terracotta pottery, seals, ornaments, and evidence of metallurgy, along with inscriptions in the Indus Valley script.
- Archaeological Discoveries:The site was first discovered by Jagat Pati Joshi in 1967 and excavated systematically between 1990 and 2005 under Dr. Ravindra Singh Bisht of ASI. It is the fifth-largest site of the Indus Valley Civilization and provides evidence of habitation over seven cultural phases from 3000 to 1500 BCE. Notably, no human remains have been found, but the presence of architectural structures, artifacts, and inscriptions gives a rich understanding of the ancient civilization's culture and economy.
- Technological Advancements:The President, during her visit, highlighted the technological advancements of the Harappans, particularly in urban planning and water management, which were superior in many respects to the technology of modern times.
Historical Context:
The Harappan Civilization, flourishing from around 3300 to 1300 BCE along the Indus River, was an urban society known for its advanced city planning, sanitation systems, and trade networks. Dholavira stands out as a crucial link in understanding the broader scope of this civilization. Other key Harappan sites include Harappa, Mohenjo-Daro, Banawali, Lothal, and Ropar.
Amir Khusrau

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
In his address to the 25th edition of Jahan-e-Khusrau at New Delhi’s Sunder Nursery, Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the annual music festival that commemorates the Sufi poet-musician Amir Khusrau as imbued with the “fragrance of the soil of Hindustan”.
Introduction
- Amir Khusrau, a 13th-century poet, musician, and scholar, is a prominent figure in India’s cultural history.
- Known as Tuti-yi-Hind (the Parrot of India), Khusrau’s contributions spanned literature, music, and the Sufi spiritual tradition.
- Revered for his role in shaping India’s syncretic culture, blending Persian, Turkic, and Indian elements.
Early Life and Background
- Born in 1253 in Patiyali, Uttar Pradesh, to a Turkic father and Indian Muslim mother.
- His family migrated to India due to Mongol invasions of Transoxiana.
- Grew up under the patronage of the Delhi Sultanate, serving five rulers: MuizuddinQaiqabad, JalaluddinKhalji, AlauddinKhalji, Qutbuddin Mubarak Shah, and GhiyasuddinTughlaq.
Literary Contributions
- Wrote in Persian and Hindavi, blending Turkic, Persian, and Indian traditions.
- Contributed significantly to the development of Hindavi, the precursor to modern Hindi and Urdu.
- Works include Divans (poetry collections), Mathnawis (narrative poems), and treatises.
- Advocated for Hindu-Muslim unity, promoting syncretic culture (Ganga-JamuniTehzeeb).
- Known for writing riddles, proverbs, and playful verses, which made literature accessible to the common people.
- Praised Hindu philosophical thought in his works, such as MasnaviNuhSiphir.
Musical Contributions
- Credited with creating several ragas, developing khayal (a classical Hindustani music form), and tarana (rhythmic vocal composition).
- Played a significant role in popularizing qawwali, a devotional Sufi music genre, by blending Persian, Arabic, and Indian musical traditions.
- Believed to have invented the sitar and tabla, though evidence is debated.
- Famous qawwalis include ChhaapTilak, Zehal-e-Maskeen, and Sakal Ban PhoolRahiSarson.
Role in the Delhi Sultanate
- Served as a court poet for at least five Delhi Sultans over five decades, a testament to his literary excellence.
- His compositions were vital in enhancing the Sultan’s political and cultural legitimacy.
- Sultan JalaluddinKhalji bestowed upon him the title Amir in recognition of his contributions to poetry.
Spiritual and Sufi Influence
- A devoted disciple of the Chishti Sufi saint NizamuddinAuliya, whose teachings on love and devotion to God deeply influenced Khusrau’s poetry and music.
- Balanced his role as a court poet with devotion to the Sufi order, bridging the worlds of royal courts and spiritual practices.
- His deep spiritual connection to NizamuddinAuliya is immortalized by their shared burial site in Delhi.
Sufism in India
- Sufism is the mystical and spiritual dimension of Islam, emphasizing love, devotion, and inner purification.
- Sufism emerged as a reaction to the rigidity of institutionalized religion and developed alongside India’s Bhakti movement.
- Key Sufi Orders in India:
- Chishti Order: The most influential in India, founded by KhwajaMoinuddin Chishti, focusing on love, devotion, and harmony.
- Suhrawardi Order: Focused on combining religious knowledge with mysticism.
- Naqshbandi Order: Opposed innovations like musical recitals and pilgrimages.
- Rishi Order: Based in Kashmir, drawing from the Shaivite bhakti tradition.
Impact of Sufism in India
- Sufism promoted religious tolerance, social reform, and a deep connection to spirituality.
- It attracted marginalized communities and weakened caste hierarchies.
- Sufi shrines and dargahs became pilgrimage sites for spiritual blessings.
- Influenced Indian music (especially qawwali) and literature, with poets like Bulleh Shah and Sultan Bahu.
- Promoted Sulh-e-Kul (peace with all), a concept that influenced Akbar’s religious tolerance policies.
Khusrau’s Lasting Legacy
- Amir Khusrau’s influence extends across literature, music, and spirituality in India.
- His poetry and music are celebrated today in both sacred and secular contexts.
- His works laid the foundation for the development of Urdu and Hindi literature.
- Khusrau’s teachings on Hindu-Muslim unity and cultural synthesis remain relevant in contemporary India.
Jhumoir Binandini (Jhumur) Dance

- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India is set to attend the Jhumoir Binandini (Mega Jhumoir) 2025, a grand cultural event featuring around 8,600 performers showcasing the traditional Jhumur dance. This event highlights the rich cultural contributions of the tea tribe community of Assam.
About Jhumoir (Jhumur) Dance
- Jhumur, also known as Jhumoir, is a traditional folk dance performed predominantly by the Adivasi tea tribes of Assam.
- It is typically showcased during the harvest season, as well as on occasions like weddings and community festivals.
- The dance was introduced to Assam by the tea garden workers, who originally migrated from regions like Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal in the 19th century under British colonial rule.
Cultural Origins and Community
- The dance traces its roots to the Sadan ethnolinguistic group from the Chotanagpur plateau (present-day Jharkhand).
- The tea tribe community is a multi-ethnic group comprising descendants of migrant tea garden laborers.
- These communities have significantly shaped Assam’s socio-cultural landscape.
Performance Style and Attire
- Jhumur is performed in a circular formation, with dancers often holding each other's waists.
- The performance features rhythmic footwork, swaying movements, and energetic music.
- Women typically wear colorful sarees, often in red and white, while men dress in dhotis and kurtas.
- The musical accompaniment includes traditional instruments like the Madal, Dhol, Dhak, Taal (cymbals), and Flute.
Themes and Social Significance
- Jhumur songs blend liveliness with social commentary, often highlighting the struggles, exploitation, and migration experiences of the tea plantation workers.
- Major tea garden festivals where Jhumur is performed include Tushu Puja and Karam Puja, both celebrating the harvest.
- The dance fosters community bonding, promotes cultural pride, and represents Assam’s syncretic cultural heritage.
- It stands as a symbol of inclusivity, unity, and the resilience of the tea tribe community.
Ali Ai Ligang Festival and the Mising Tribe

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
The Mising tribe, Assam’s largest tribal community, celebrated Ali Ai Ligang in Shankarpur, Jorhat, on the first Wednesday of the Fagun month.
About the Mising Tribe
- Region: Indigenous tribe from Northeast India; primarily reside in Upper Assam and parts of Arunachal Pradesh, with some presence in South Tibet (China).
- Population: As per Census 2011, there are 6,80,424 Mising people in Assam.
- Ethnolinguistic Group: Belong to the Tani group, speak Tibeto-Burmese languages.
- Referred as: Called “Lhobhas” (southerners) by Tibetans.
- Unique Feature: Known as the only riparian tribe of Northeast India, with livelihoods closely linked to rivers like the Brahmaputra.
- Habitat: Construct stilt houses known as Chang Ghar to withstand seasonal floods.
Cultural and Religious Practices
- Religion: Practice Donyi-Poloism – worship of the Sun (Donyi) and the Moon (Polo) as supreme deities.
- Traditional Economy:
- Traditionally practiced Jhum (slash and burn) cultivation.
- Now settled cultivators skilled in wet paddy cultivation.
- Engage in fishing, weaving, and vegetable farming.
- Women are proficient in weaving traditional Mising textiles.
Ali Ai Ligang Festival
- Main Festival of the Mising community.
- Timing: Celebrated in February, on the first Wednesday of Fagun month (as per the Assamese calendar).
- Name Meaning:
- Ali – edible root
- Ai – seed
- Ligang – sowing
Signifies the beginning of the agricultural cycle – first sowing of seeds and roots.
Significance and Rituals
- Purpose: Marks the start of cultivation, invokes blessings from Donyi-Polo to protect crops from pests and natural calamities.
- Community Importance: Strengthens communal ties and preserves agrarian traditions.
- Ritual Practices:
- Morung Okum (Morung Ghar) – youth dormitory where offerings like Apong (rice beer), dry meat, and fish are made.
- Gumrag Dance – performed by men and women to signify joy, unity, and prosperity.
- Feast and Dress – Traditional Mising delicacies are prepared, and people wear colorful ethnic attire.
Modern Celebrations
- Originally village-based, now also celebrated in urban centers like Jorhat.
- Includes stage performances, cultural competitions, and large community gatherings.
- In Jorhat, it has been celebrated for the past 40 years, organized annually by Mising Agom Kebang (Mising apex literary and cultural body).
Dokra Artwork

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
During a recent diplomatic visit, Prime Minister Narendra Modi gifted French President Emmanuel Macron and the First Lady symbolic Indian artifacts — a Dokra artwork and a silver hand-engraved mirror — showcasing India’s rich heritage of tribal and fine metal craftsmanship.
Key Highlights:
Dokra Art: A Living Tradition
- Dokra, also known as Dhokra, is a non-ferrous metal casting craft that employs the lost-wax technique, practiced for over 4,000 years.
- It is predominantly practiced by Ojha metalsmiths and DhokraDamar tribes, across Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, and Telangana.
- Notable for its seamless brass sculptures, each Dokra artifact is cast using a single-use clay and wax mould, ensuring that no two pieces are identical.
- Dokra items include figurines, utensils, jewelry, and religious motifs, often reflecting tribal life and nature.
Historical Significance:
- The “Dancing Girl” of Mohenjo-Daro (from the Harappan Civilization) is considered one of the earliest examples of Dokra-style metal casting, underlining its archaeological and civilizational importance.
Craftsmanship Features:
- The casting process takes nearly a month per piece, reflecting the labour-intensive and skilled nature of the art.
- Dokra is globally recognized for its sustainability, aesthetic uniqueness, and its ability to merge function with folklore.
Fort William Renamed Vijay Durg

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards decolonising the Indian Armed Forces and aligning with indigenous historical consciousness, Fort William, the headquarters of the Eastern Command of the Indian Army in Kolkata, has been renamed Vijay Durg. This renaming is part of a broader initiative to remove colonial-era symbols and practices and restore Indian military heritage.
Historical Background of Fort William
- Construction: The original Fort William was constructed in 1696 by the English East India Company. It was later attacked and captured by Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, in 1756.
- The Black Hole Incident: The original fort had an inner bastion used for imprisoning captives, leading to the infamous “Black Hole of Calcutta” narrative.
- Reconstruction: After the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the defeat of Siraj-ud-Daulah, Robert Clive initiated the construction of a new fort, which was completed in 1773 or 1781 (sources differ).
- Naming: It was named Fort William in honour of King William III of England.
Architectural Features
- Design: The fort is octagonal in shape with a massive structure made of brick and mortar.
- Area: Spread across 70.9 acres on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, it features hundreds of arched windows and lush green surroundings.
- Aesthetics: Its walls are adorned with intricate stonework, reflecting colonial military architecture.
Recent Changes and Renaming
- New Name: Vijay Durg – Inspired by Vijaydurg Fort in Maharashtra, a prominent naval base of the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Other Changes:
- Kitchener House has been renamed Manekshaw House, after Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw.
- St. George’s Gate has been renamed Shivaji Gate.
- Implementation: According to the Defence Public Relations Office in Kolkata, the name change was decided in mid-December 2024, and internal communications have already adopted the new nomenclature, though an official notification is awaited.
Broader De-Colonisation Drive in Indian Defence
The renaming of Fort William is part of a larger movement initiated by the Government of India to eliminate colonial vestiges in the armed forces. Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a 2022 speech at Kevadia, Gujarat, urged the forces to discard “legacy systems” and move towards “freedom from the mentality of slavery (gulami ki mansikta se mukti)”.
Key Initiatives:
- Indianisation of military music during the Beating Retreat ceremony.
- Adoption of a new naval ensign (2022) inspired by the seal of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, moving away from British colonial symbols.
- Renaming of military establishments and symbols rooted in colonial heritage.
- Review publication (2024) titled “Colonial Practices and the Armed Forces – A Review”, released at the Joint Commanders’ Conference in Lucknow by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
Dhimsa Dance

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant development, tribal families from Neelabandha, a remote hilltop hamlet in Anakapalli district, Andhra Pradesh, received electricity for the first time since Independence. In celebration, they performed the Dhimsa dance, a vibrant expression of tribal culture.
About Dhimsa Dance:
- Origin & Region:
- Dhimsa is a traditional tribal dance predominantly performed in Andhra Pradesh, especially in the tribal belts of the Eastern Ghats.
- Its origin can be traced to the Koraput region (present-day Odisha and bordering Andhra Pradesh), primarily home to the Gond tribe.
- Communities Performing Dhimsa:
- Tribes such as Bagata, Valmiki, Poraja, Khond, Gadaba, Kondadora, Mukadora, and Kotia actively perform this dance.
- Occasions:
- Commonly performed during festivals, weddings, and the hunting festival in April.
- Celebratory, spiritual, and social in nature, symbolizing unity and joy.
- Dance Formation and Movements:
- Performed in circular formations with dancers holding each other's arms.
- Emphasis on synchronized hand and leg movements.
- Troupes usually consist of 20 or more dancers.
- Themes:
- Dhimsa is a narrative dance that expresses tribal mythologies, folktales, cultural mores, economic activities, kinship, and marital life.
- Musical Instruments Used:
- Dappu, Tudumu, Mori, Kidgi, Gilka, and Jodukommulu.
- A combination of percussion and wind instruments drives the rhythm and variation in the dance.
- Varieties:
- There are 12 known types of Dhimsa dances, each varying in pace, rhythm, and purpose.
Rural Electrification of Neelabandha Village:
- Background:
- Neelabandha is located in Arla Panchayat of Rolugunta Mandal in Anakapalli district.
- Consists of four households (approximately 20 individuals) who had been living without electricity since Independence.
- Implementation:
- The electrification was part of the Andhra Pradesh government’s rural development drive to provide basic infrastructure to underdeveloped tribal villages.
- Under the directions of District Collector Vijaya Krishnan, and CMD of APEPDCL, Prithvi Tej, the Eastern Power Distribution Company of Andhra Pradesh (EPDCL) carried out the electrification.
- Challenges Overcome:
- The hamlet lacked motorable roads, making it difficult to transport materials.
- Electricity poles had to be carried manually for over 6 km to reach the village.
- Outcome:
- Free electricity was provided to the villagers, marking a major milestone in tribal welfare.
- In a heartfelt celebration, the villagers performed Dhimsa under electric lights for the first time.
Issues Still Persisting:
- Infrastructure Deficits:
- The village still lacks road connectivity, educational access, and healthcare facilities.
- These gaps hinder children's ability to attend school and access essential services.
- Community Response:
- Local leaders, including CPI(M) district committee member K. Govind, welcomed the electrification but urged the government to address remaining developmental needs.
Gyan Bharatam Mission

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 announced the launch of the Gyan Bharatam Mission, a significant cultural initiative aimed at the survey, documentation, digitization, and conservation of over one crore manuscripts across India.
Key Details:
- A special national mission focusing on India’s manuscript heritage preserved in:
- Academic institutions
- Libraries
- Museums
- Private collections
- Objective:
To document and conserve more than one crore manuscripts, centralize them into a national digital repository, and make them accessible to researchers, students, and institutions globally. - Significance:
- Facilitates knowledge-sharing through digitization.
- Promotes India's traditional knowledge systems.
- Enhances academic and historical research in the Indian knowledge domain.
What is a Manuscript?
- A manuscript is a handwritten composition on materials such as:
- Palm leaf, paper, cloth, bark, or metal.
- Must be at least 75 years old and possess scientific, historical, or aesthetic value.
- Printed texts and lithographs are not considered manuscripts.
- Manuscripts may exist in hundreds of languages and scripts, e.g.:
- Sanskrit manuscripts written in Devanagari, Grantha, Oriya, and other scripts.
- Unlike epigraphs or official records (firmans, revenue documents), manuscripts hold knowledge content, not just historical data.
National Manuscripts Mission (NMM)
- Launched in 2003 under the Ministry of Culture, operated through the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
- Mandate: Identify, preserve, and make accessible India's manuscript wealth.
- Revival: The 2025–26 Budget seeks to rejuvenate NMM to implement the Gyan Bharatam Mission effectively.
Budgetary Provisions
- NMM allocation increased from ?3.5 crore to ?60 crore for FY 2025–26.
- Culture Ministry overall allocation:
- ?3,360.96 crore, up from a revised estimate of ?3,260.93 crore.
- Other Key Allocations:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI): ?1,278.49 crore
- National Libraries and Archives: ?156.55 crore
- Museums (National Museum, NGMA): ?126.63 crore
- Note: Allocations for centenary events, cultural collaborations have been reduced.
Libia Lobo Sardesai

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, at the age of 100, Libia Lobo Sardesai was awarded the Padma Shri for her pivotal role in Goa’s liberation struggle from Portuguese colonial rule.
About Libia Lobo Sardesai
- Born: 25 May 1924, in Portuguese-ruled Goa; raised in Mumbai.
- Profession: Freedom fighter, broadcaster, and Goa’s first Director of Tourism post-liberation.
- Legacy: Symbol of courage and resistance, known as the “voice of Goa’s liberation.”
Role in Goa’s Liberation Movement
- Involvement: Joined the Goan nationalist movement during her college years.
- Underground Radio:
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Goenche Sodvonecho Awaz (Voice of Freedom of Goa) – Konkani
- Voz de Liberdade – Portuguese
- Operated from Amboli (Maharashtra) and Castle Rock (Karnataka) in the Western Ghats.
- Purpose: Counter Portuguese censorship and propaganda; broadcast news, updates, and morale-boosting messages to Goans.
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Final Broadcast:
- On 19 December 1961, Libia flew over Panaji in an IAF plane, announcing Goa’s liberation with the message:
“Rejoice brothers and sisters, Rejoice! Today, after 451 years of alien rule, Goa is free and united with the Motherland.”
Goa Liberation Movement: Background
- Colonial Rule: Goa was under Portuguese rule for over 451 years (from 1510 to 1961).
- Key Phases:
- 1954: India imposed an economic blockade after Portuguese crackdown on satyagrahis.
- August 1955: Mass satyagraha met with violent repression by Portuguese forces.
- Censorship: Portuguese regime enforced total censorship; only official Portuguese narratives were allowed.
- 1961 – Operation Vijay:
- Initiated on 17 December 1961 by the Indian Army under Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri.
- Portuguese forces surrendered by 19 December 1961, marking Goa’s official liberation.
Notable Leaders of the Movement
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia: Sparked initial resistance against Portuguese rule.
- Libia Lobo Sardesai: Voice of the resistance via underground broadcasting.
- Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri: Led military operations during Operation Vijay.
Significance
- Libia Lobo Sardesai represents the unsung contributions of civil resistance and communication warfare in India’s decolonization.
- Her work sustained nationalist morale, informed citizens under censorship, and shaped the narrative of a liberated Goa.
Ratnagiri Buddhist Site

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has resumed excavations at the ancient Buddhist site of Ratnagiri in Odisha’s Jajpur district, unveiling monumental discoveries that underline its rich religious, cultural, and maritime legacy. This renewed effort comes more than 60 years after the site was first excavated between 1958 and 1961.
About Ratnagiri
- Meaning: Ratnagiri translates to “Hill of Jewels.”
- Location: Situated on a hill between the Brahmani and Birupa rivers, northeast of Bhubaneswar.
- Part of the Diamond Triangle: Along with Lalitgiri and Udaygiri, Ratnagiri forms Odisha’s famed “Diamond Triangle” of Buddhist heritage sites.
- Historical Period: Flourished between the 5th and 13th centuries CE, peaking under the Bhauma-Kara dynasty (8th–10th century CE).
- Buddhist School: An important centre for Mahayana and especially Vajrayana (Tantrayana) Buddhism.
- It possibly rivalled Nalanda in prominence as a Buddhist learning centre.
- The monastery complex at Ratnagiri is the only one in India with a curvilinear roof, once housing about 500 monks.
Recent Discoveries by ASI
- Three colossal Buddha heads, each measuring 3–4 feet.
- A massive palm sculpture, 5 feet in size.
- Hundreds of votive stupas, sculptures of Buddhist deities.
- A monolithic elephant statue, 5 feet long and 3.5 feet tall.
- Pottery, inscribed stones, beads, stone pillars, and a brick wall believed to be part of a larger structure.
- Rich ceramic assemblages, which may shed light on the region’s cultural and technological evolution.
These artefacts are estimated to date back to the 8th and 9th centuries CE and are believed to enhance understanding of Buddhism’s evolution in Odisha and its linkages with other cultures.
Buddhism in Odisha & Southeast Asian Links
- Buddhism gained a strong foothold in Odisha after Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) in 261 BCE, a turning point that led him to embrace Buddhism.
- Though Buddha never visited Odisha, the region became instrumental in spreading Buddhism to Southeast Asia, especially during the Bhauma-Kara period.
- The state maintained robust maritime trade and cultural links with regions like Java, Bali, Sumatra, Borneo, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
- Baliyatra Festival: A vibrant annual event held in Cuttack, commemorating Odisha’s ancient seafaring ties with Bali and other Southeast Asian regions.
- According to some studies, Chinese monk Hiuen Tsang may have visited Ratnagiri during his travels in India (638–639 CE).
Significance of the Renewed Excavations
- The ASI aims to uncover partially visible structures, complete the site’s mapping, and contextualize the findings within the broader Buddhist history of India and Southeast Asia.
- Researchers hope to discover signs of foreign architectural or cultural influences, further confirming ancient Odisha’s global Buddhist and trade connections.
- The discoveries reaffirm Ratnagiri’s importance as a cornerstone of Buddhist learning and art, potentially on par with other renowned ancient centres like Nalanda and Vikramashila.
Kuka Rebellion and Namdhari Sect

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 17, Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann paid tribute at the Namdhari Shaheed Smarak in Malerkotla to commemorate Kuka Martyrs’ Day. The event marks the execution of 66 Namdhari Sikhs by the British in January 1872.
Kuka Rebellion: An Overview
The Kuka Rebellion was an anti-British movement led by the Namdhari sect in Punjab. It combined religious reform with resistance to colonial rule, reaching its peak in January 1872.
Key Events:
- January 13, 1872: Kukas, led by Hira Singh and Lehna Singh, protested against cow slaughter in Malerkotla.
- January 15, 1872: Clashes occurred between Kukas and government officials. A contingent attacked Malaudh Fort but was repulsed.
- January 17-18, 1872: 66 Kukas were executed by being blown up with cannons under orders of British official John Lambert Cowan.
Reasons Behind the Movement:
- Religious Reform: Opposed meat consumption, alcohol, and social vices.
- Colonial Oppression: Protested against British rule and native collaborators.
- Cow Protection: Strongly opposed cow slaughter, leading to confrontations with British authorities.
Impact and Aftermath:
- Suppression: The British crushed the movement with extreme brutality.
- Exile of Leaders: Satguru Ram Singh and other key leaders were exiled to Rangoon, Burma.
- Legacy of Martyrdom: The sacrifice of young Namdharis like 12-year-old Bishan Singh and Waryam Singh inspired future resistance movements in India.
Who are the Namdharis?
The Namdharis, also called Kukas, are a Sikh sect founded by Satguru Ram Singh in 1857 in Ludhiana. Their distinctive practices include:
- High-pitched recitation of Gurbani (hence the name ‘Kuka’ meaning ‘crying’ or ‘screaming’ in Punjabi).
- Wearing white attire as a sign of mourning for their exiled leader.
- Early adoption of Swadeshi principles, boycotting British goods and services.
Current Status of Namdhari Sect:
- The Namdharis, numbering around 2 lakh in Punjab today, have faced internal divisions since the death of Satguru Jagjit Singh in 2012.
- Two major factions exist:
- One led by Thakur Dilip Singh, headquartered in Sirsa, Haryana.
- Another led by Sangrur Uday Singh, headquartered at Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana.
- A core belief remains that Satguru Ram Singh is still alive and will return one day.
Significance:
The Kuka Rebellion, though localized, was an important precursor to later national movements against British rule. It showcased the early spirit of resistance, long before organized freedom movements gained momentum in the 20th century.
Makaravilakku festival

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Kerala police deploy 5,000 personnel at Sabarimala ahead of Makaravilakku festival.
Key Highlights:
- Makaravilakku is a prominent annual Hindu festival held at the Sabarimala Temple in Kerala, dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
- It marks the celestial event of the Sun entering Capricorn (Makaram Rashi) on Makara Sankranti.
- The festival is a culmination of the 41-day pilgrimage to Sabarimala, celebrated with devotion, discipline, and spiritual purification.
- Sabarimala is one of the largest pilgrimage sites globally, drawing 10-15 million devotees annually.
Location:
- The Sabarimala Temple is located on the Sabarimala hill in Pathanamthitta, Kerala, within the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- It is surrounded by 18 hills and is located along the banks of the Pamba River.
Key Rituals:
- 41-Day Pilgrimage (Vratham): Devotees observe strict practices like celibacy, fasting, and wearing black or saffron attire to purify the body and soul.
- Makaravilakku (Makara Jyothi): A celestial light appears on Makara Sankranti, believed to be a divine manifestation of Lord Ayyappa.
- Thiruvabharanam Procession: On Makaravilakku day, sacred royal ornaments (Thiruvabharanam) are carried in a procession from the Pandalam Palace to the temple.
- Aarti at Ponnambalamedu: The Makaravilakku light is believed to emanate from camphor lit during the Aarti ritual at Ponnambalamedu, viewed three times from Sabarimala.
Festival Duration:
- The Makaravilakku festival lasts for seven days, starting on Makara Sankranti and concluding with the Guruthi offering, which propitiates the gods of the wilderness.
Significance of Makaravilakku:
- The festival symbolizes the merging of celestial and spiritual energies, highlighting devotion, purity, and self-discipline.
- Devotees chant the mantra "Swamiye Saranam Ayyappa," seeking blessings and protection from Lord Ayyappa.
- The event promotes equality, as all devotees wear simple black or blue attire and carry the sacred bundle, “Irumudi Kettu.”
Cultural and Religious Aspects:
- The festival is an important cultural and religious observance for millions of Hindus.
- Though previously believed to be a supernatural event, Makaravilakku now involves a ritual performed by the Malayaraya tribe, overseen by the Travancore Devaswom Board.
Prohibition on Women:
- The temple traditionally restricts women aged 10-50 from entering. This was challenged in 2018 when the Supreme Court ruled to lift the prohibition, although it remains a contentious issue.
National Youth Day 2025

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 12, 2025, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated in the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2025, an event aimed at empowering India's youth and charting a roadmap for the nation's development. This occasion also coincided with the celebration of National Youth Day, marking the 163rd birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, a renowned spiritual leader and social reformer who strongly believed in the transformative potential of India's youth.
Significance of National Youth Day
- Purpose:
- National Youth Day is celebrated to honor Swami Vivekananda's contributions, emphasizing the role of youth in nation-building.
- It promotes empowerment, leadership, and innovation among the youth.
- Year of First Celebration: 1985
- Key Theme (2025): "Arise, Awake, and Realize the Power You Hold"
Key Highlights from the Dialogue
- Goal of the Dialogue:
- Engaging youth in the decision-making process for a developed India by 2047.
- Empowering youth through platforms like quizzes, essay competitions, and thematic presentations.
- Ten Key Themes Discussed:
- Technology & Innovation
- Sustainability
- Women Empowerment
- Manufacturing & Agriculture
- Education and Skill Development
India’s Roadmap for 2047 (Viksit Bharat)
- Vision:
- Economic Power: India is moving toward becoming the third-largest economy.
- Strategic and Cultural Strength: India will have a robust economic, strategic, social, and cultural framework.
- Youth's Role: Innovation in technology, digital economy, space, and manufacturing will drive India’s growth.
- Key Projects and Targets:
- Target: Generating 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Net Zero Emissions for Railways: Set for 2030.
- Olympics: India aims to host the Olympics in the next decade.
- Space Power: Plans for a space station by 2035.
Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Challenge
- Objective:
- Engage youth in shaping ideas for a developed India.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is part of the Viksit Bharat Challenge.
- Stages of the Challenge:
- Viksit Bharat Quiz: Participation by 30 lakh youth.
- Essay Writing: Over 2 lakh essays on key developmental themes.
- State Rounds: Rigorous in-person competition to identify the top young leaders.
- Participant Categories:
- 1,500 from Viksit Bharat Challenge Track.
- 1,000 from Traditional Track (cultural and science innovation).
- 500 Pathbreakers (leaders in diverse sectors).
Achievements Under Government Benefiting Youth
- Educational Reforms:
- Increase in IITs, IIITs, IIMs, and AIIMS.
- Growth in the number of higher education institutions and their global rankings.
- Economic Growth:
- India's economy has grown to nearly $4 trillion.
- Infrastructure Investments: More than ?11 lakh crore allocated for infrastructure development.
- Employment Opportunities for Youth:
- Mudra Loans: ?23 lakh crore distributed to youth entrepreneurs.
- Startup Ecosystem: India is among the top three in global startups.
- PM Gati Shakti Mission: Facilitating logistics and infrastructure development, creating employment opportunities.
Future Outlook
- Youth as the Future Leaders of India:
- India’s Youth Power: Vital to achieving a developed nation by 2047.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is a platform for youth to voice their opinions and engage with policymakers.
- Role of Youth in India’s Transformation:
- Collective Responsibility: Every citizen's effort is essential for national goals.
- The vision of a Viksit Bharat hinges on the innovative contributions and ownership by young minds.
Flamingo Festival 2025

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Flamingo Festival 2025 took place at Sullurpeta, in Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. It celebrates the arrival of migratory birds, with a focus on flamingos, to the region's key bird habitats, including Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary.
Key Highlights:
- Birdwatching: Over 200 bird species, including flamingos, are expected to flock to the region during this festival.
- Locations: The event spans across five locations:
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary
- B.V. Palem (Pulicat Lake)
- Atakanithippa
- Sri City
- Sullurpeta (site for cultural programs and stalls)
- Collaborations: In association with organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society.
- Focus on Local Community: Local residents of the eco-sensitive zone will be prioritized and supported.
Key Facts on Local Wildlife and Significance:
- Pulicat Lake:
- Location: On the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, with 96% of the lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The second-largest brackish water lake in India (after Chilika Lake in Odisha).
- Biodiversity: Critical habitat for migratory birds, including flamingos, and home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Importance: Supports local fisheries and provides livelihood to nearby communities.
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: 20 km north of Pulicat Lake.
- Ecological Role: Largest breeding site in Southeast Asia for spot-billed pelicans.
- Biodiversity: 189 bird species, including painted storks and glossy ibises.
- Flora and Fauna: Features Barringtonia swamp forests and southern dry evergreen scrub, critical for biodiversity conservation.
- Symbiotic Relationship with Locals: Guano (bird droppings) from pelicans serves as a natural fertilizer for local agriculture, benefiting the farmers.
Flamingo Facts:
- Species: India hosts two flamingo species:
- Greater Flamingo (larger size, pale pink)
- Lesser Flamingo (smaller size, bright pink)
- Behavior: Nomadic and social birds, found in large flocks.
- Coloration: Flamingos' pink color comes from carotenoids in their diet, which are broken down and absorbed into their bodies.
Environmental & Economic Impact: The festival, apart from being a celebration of migratory birds, plays a vital role in:
- Eco-tourism development
- Biodiversity conservation
Local community engagement by highlighting sustainable tourism practices and supporting local livelihoods through eco-friendly initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
Bhashini Initiative
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
e-Shram Portal, which aims to provide social security benefits to unorganised workers, has been upgraded with multilingual functionality for all 22 scheduled languages of India. This development, supported by the Bhashini Initiative, ensures that unorganised workers from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access the portal more easily and benefit from government welfare schemes.
About Bhashini Initiative:
- Launched in: July 2022
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Aim: To eliminate language barriers in accessing digital services by making AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools publicly available.
Key Features:
- Local Language Translation: Bhashini offers AI-powered translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages to ensure that digital platforms like e-Shram are accessible to everyone in their native languages.
- Open AI and NLP Resources: These tools are made available to Indian MSMEs, startups, and innovators to create a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
- Crowdsourcing Platform (Bhashadaan): A platform for people to contribute to building linguistic datasets through initiatives like Suno India, Likho India, Bolo India, and Dekho India, furthering language diversity in digital services.
- National Digital Public Platform: Aimed at providing universal access to digital content in all Indian languages, facilitating smoother communication across regions.
e-Shram Portal: A One-Stop Solution for Unorganised Workers
- Purpose: The e-Shram portal was created to provide unorganised workers with access to social security benefits and welfare schemes.
Recent Upgrade:
- Multilingual Functionality: The portal has now been upgraded to support 22 scheduled languages, making it more inclusive and user-friendly for workers who speak various regional languages.
- Previous Version: Previously, the portal was only available in English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi. The integration of 22 languages is a significant improvement, enabling broader participation.
Importance of the e-Shram Portal for Unorganised Workers:
- Welfare Access: The portal provides access to government schemes designed for the welfare, livelihood, and well-being of unorganised workers, including gig and platform workers and building and construction workers.
- Integration of Social Security Schemes:
- As of now, the portal facilitates access to 12 government schemes, with plans to integrate even more, including state-level programs.
- Future plans include launching a mobile app, a single application form, and the integration of payment gateways for faster disbursement of benefits.
Saint Narahari Tirtha
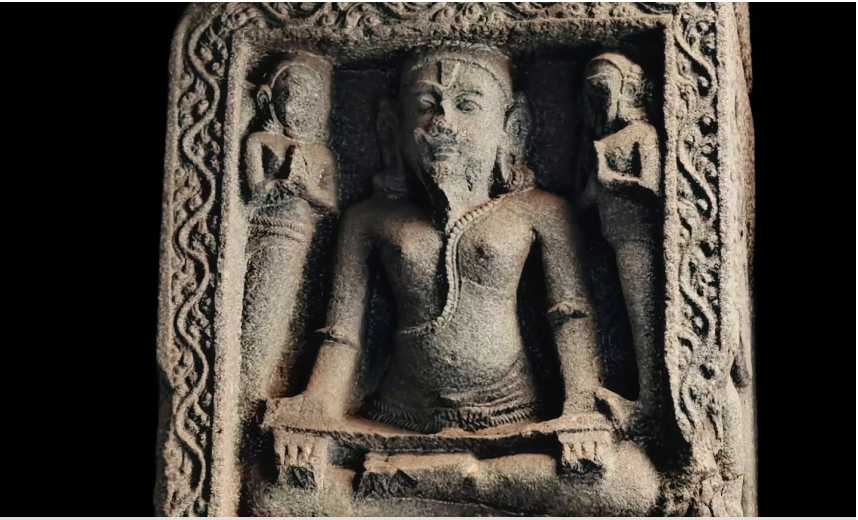

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a remarkable discovery, a member of the Team of Research on Culture and Heritage (TORCH) has hit upon a three-foot idol of the 13th Century saint, Narahari T?rtha recently.
Key Highlights:
Birth and Early Life:
- Born circa 1243 CE in Chikakolu (modern-day Srikakulam, Andhra Pradesh).
- Hailing from an aristocratic family in the Gajapati Empire of Odisha.
Philosophical Influence:
- A prominent disciple of Madhvacharya, the founder of Dvaita philosophy (dualism).
- Narahari Tirtha played a key role in propagating Madhva's Vaishnavism in Eastern India, particularly in the Kalinga region (modern-day Odisha and Andhra Pradesh).
Role in Eastern Ganga Dynasty:
- Served as a minister in the Eastern Ganga Dynasty for over 30 years.
- Guided kings to align their governance with Sanatana Dharma and reformed temple administration.
- His contributions are documented in inscriptions at the Simhachalam and Srikurmam temples.
Religious and Cultural Contributions:
- Played a key role in spreading Vaishnavism and Dvaita philosophy.
- First to compose Devaranamas in Kannada, marking a significant cultural contribution.
- Contributed to the development of Yakshagana Bayalata (a dance-drama) and the classical dance form that evolved into Kuchipudi.
Writings and Intellectual Legacy:
- Authored 15 works, with two surviving texts: Gita Bhasya and Bhavaprakasika.
- His teachings and writings significantly impacted the Madhva tradition and regional literature.
Discovery of the Idol:
- A three-foot idol of Narahari Tirtha was discovered at Simhachalam Temple in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- The idol depicts Narahari Tirtha holding a script on palm leaves, flanked by devotees.
Contributions to Temple and Education:
- Transformed the Simhachalam Temple into a renowned center for Vaishnavism.
- Played a crucial role in safeguarding sacred idols like Moolarama and Moola Sita for Madhvacharya.
Cultural and Artistic Legacy:
- Promoted regional art forms, helping establish Kuchipudi as a classical dance style in Andhra Pradesh.
- Advocated for Yakshagana Bayalata, a form of dance-drama popular in coastal Karnataka.
Honors and Recognition:
- Bestowed titles such as "Loka Surak?a?a Ati Nipu?a?" and "Yo Avati Kalinga Bhu Sambhav?n" for his contributions to philosophy and governance.
Final Resting Place:
- Narahari Tirtha was consecrated near Chakratirtha at Hampi on the banks of the Tungabhadra River after his death.
- His legacy continues to influence the temple traditions, especially in Puri Jagannath, strengthening the Madhva influence in Odisha.
Thanthai Periyar Memorial

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a significant event for both Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan and Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin are set to reunite at Vaikom, to inaugurate the extensively renovated memorial dedicated to Tamil reformist E.V. Ramasami Naicker, popularly known as Thanthai Periyar. This marks a historic occasion over a year and a half after they jointly inaugurated the centenary celebrations of the Vaikom Satyagraha.
Key Highlights:
Memorial History and Significance:
- Established: January 1994
- Location: 70-cent property near Valiyakavala Junction, Vaikom
- Ownership: Tamil Nadu Government
- Periyar Statue: Installed in 1985 on 84 cents of land provided by Kerala government; remains the centerpiece.
- Historical Neglect: The memorial suffered from years of neglect before the renovation.
Role of Periyar in Vaikom Satyagraha:
- Vaikom Satyagraha (1924–1925):
- First organized movement for the rights of the ‘untouchable’ communities in India.
- Led by prominent leaders like T.K. Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon, and K. Kelappan.
- Periyar, alongside his wife Nagamma, joined the movement, seeking access to public roads leading to the Sri Mahadeva Temple in Vaikom.
- Periyar’s Contribution:
- Was imprisoned twice for his participation in the movement.
- Honored with the title Vaikom Veeran for his leadership.
- Impact: The movement played a crucial role in securing social equality for all sections of society.
Periyar’s Legacy:
- Self-Respect Movement: Founded by Periyar to promote social equality and eliminate caste-based discrimination.
- Dravidar Kazhagam: A political and social organization founded by Periyar, advocating for the rights of the Dravidian people.
- Father of the Dravidian Movement: Periyar’s philosophy and activism laid the foundation for the Dravidian political ideology and social reforms in Tamil Nadu.
Tamil Nadu's First Glass Bridge in Kanyakumari
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu inaugurated India’s first glass bridge over the sea in Kanyakumari, connecting the Thiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial.
- The bridge provides a safe and scenic walking route between these two iconic landmarks, eliminating the need for ferry trips.
Key Highlights:
- Dimensions and Design
- The bridge is 77 meters long and 10 meters wide, offering uninterrupted views of the sea from a unique vantage point.
- Designed to withstand marine conditions like corrosion and strong winds, ensuring durability and safety for visitors.
- Tourism Investment
- The bridge was built at a cost of ?37 crore, marking a significant investment in tourism infrastructure for Kanyakumari.
- This project aligns with the state’s vision to boost tourism and modernize amenities in the region.
- Significance as a Tourist Attraction
- The bridge is set to become a landmark tourist attraction, enhancing the visitor experience by providing a direct, scenic route between the two monuments.
- It is expected to play a pivotal role in boosting tourist footfall and the local economy.
About Thiruvalluvar Statue
- Location and Design
- The Thiruvalluvar Statue stands on a rock near the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari.
- It is a symbol of wisdom, officially named the Statue of Wisdom by the Tamil Nadu government.
- Physical Specifications
- The statue stands at a total height of 133 feet (41 meters), with the statue itself measuring 95 feet (29 meters) and the pedestal adding 38 feet (12 meters).
- Weight: The statue weighs approximately 7000 tonnes and is designed in a hollow structure.
About Vivekananda Rock Memorial
- Location and Significance
- Situated on a rock in the Laccadive Sea, around 500 meters from the mainland in Kanyakumari.
- The memorial commemorates Swami Vivekananda, who represented India’s spiritual legacy at the 1893 Parliament of World’s Religions in Chicago.
- Historical and Religious Importance
- The rock is believed to be the site where Swami Vivekananda attained enlightenment.
- It is also associated with goddess Kanyakumari, who is said to have prayed to Lord Shiva on this rock, with an imprint of her feet preserved there.
- Architectural Features
- The memorial incorporates diverse architectural styles, including the Sripada Mandapam and the Vivekananda Mandapam.
- A life-sized bronze statue of Swami Vivekananda is located at the memorial.
- The rock is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea, where these three water bodies converge.
ASI Discovery at Srisailam Temple

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) uncovered ancient copper plates and gold coins at the Srisailam Temple in Andhra Pradesh, specifically in the Ghantamandapam area.
- The discovery includes 20 sets of copper plates, totaling 72 leaves, and various gold coins.
- The ASI's Epigraphy Branch in Mysore has completed the documentation of these findings, and the materials are being studied in detail.
Collaboration with Srisailam Devasthanam:
- In collaboration with the Srisailam Devasthanam, ASI plans to publish a book that will detail the findings and their historical significance.
- The book will be printed soon by Pragati Publications in Hyderabad.
Srisailam Temple Overview:
- The Srisailam Temple, also known as the Mallikarjuna Swamy Temple, is a prominent Hindu pilgrimage site in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is located in the Nallamala Hills, overlooking the Krishna River.
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva in the form of Mallikarjuna Swamy and Goddess Parvati as Bhramaramba Devi.
- It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva and one of the Shakti Peethas, making it significant in both Shaivism and Shaktism.
Architectural Significance:
- The temple is built in the Dravidian style, featuring lofty towers and expansive courtyards, and is considered a prime example of Vijayanagara architecture.
- Historical references to the temple date back to the Satavahana period (2nd century AD), and the temple was further endowed by the Kakatiyas and Vijayanagara rulers.
Cultural and Religious Importance:
- The Srisailam Temple is unique for housing both a Jyotirlinga (Lord Shiva) and a Shakti Peetha (Goddess Bhramaramba), a rare combination not found at other temples.
- The great religious figure Adi Shankaracharya is believed to have visited the temple and composed the Sivananda Lahiri there.
Historical Context:
- The copper plates and inscriptions discovered are likely to provide valuable insights into the historical and cultural significance of the temple, as well as the region's ancient religious practices.
Re-emergence of the Dodo in Kashmir’s Papier Mâché Craft
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
Artisans in Srinagar, Kashmir, have revived the extinct dodo bird in papier mâché forms. These figurines are exported worldwide, particularly to Mauritius and Europe, ahead of the Christmas season. Over 50,000 dodo figurines have already been sent to international markets in 2024.
Key Highlights:
The Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus.
- Extinct Since: 1681, approximately 80 years after humans began interacting with them.
- Endemic to Mauritius: A flightless bird from the Indian Ocean island of Mauritius, a national symbol of the country.
- Extinction Causes: Overhunting and the introduction of invasive species like rats, pigs, and cats that preyed on their eggs.
- Physical Traits: Grey or brown plumage, about 3 feet tall, flightless and fearless.
Papier Mâché Craft in Kashmir:
- History: Practiced for over 600 years in Kashmir, introduced during the reign of King Zain-ul-Abidin (15th century).
- Techniques: Involves creating decorative objects using paper pulp, with traditional Persian motifs.
- Recent Addition of Dodo: The dodo was introduced to the papier mâché craft around two decades ago, likely by Mauritian tourists.
International Market and Demand:
- Mauritius: A significant market for the papier mâché dodo, as the bird is a national emblem of Mauritius.
- Europe: Exported to European countries during the Christmas season, contributing to the popularity of Kashmir’s handicrafts.
- Kashmir's Karkhanas: Local craft workshops in Srinagar are producing thousands of dodo figurines each season, with over 3,000 dodos produced this year.
Cultural and Economic Impact:
- Artisans' Contribution: Local artisans are helping keep the memory of the extinct dodo alive, while boosting Kashmir’s handicraft industry.
- Global Recognition: The dodo is now a sought-after item in global markets, linked to the traditional art of Kashmir.
- Kashmir Handicrafts: Several crafts from Kashmir, including papier mâché, have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags for their distinct cultural and regional significance.
ASI Decodes Sanskrit Inscription Found in Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK)

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
An ancient Sanskrit inscription found in Gilgit (PoK) was decoded by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
About the Inscription:
- Location:
- Gilgit (PoK): Written in Brahmi script, dating back to 4th century CE.
- Peshawar (Pakistan): Written in Sharada script, dating to 10th century CE.
- Details of Gilgit Inscription:
- Mentions Pushpasingha, who installed a Mahesvaralinga for the merit of his guru.
- Written in Brahmi script, which was prevalent during the 4th century CE.
- Religious Context: Indicates significant religious connection, particularly with Shaivism.
- Details of Peshawar Inscription:
- Fragmentary: Engraved on a slab.
- Written in Sharada characters (10th century CE).
- Mentions Buddhist Dharini (chants), particularly referring to Da (Dha) rini in line six.
- The inscription is partially damaged, and further details are unclear.
- Earlier Discoveries:
- This is not the first Sanskrit inscription decoded from Pakistan. In the past, Sanskrit inscriptions have been found in various parts of Pakistan.
- Swat Valley: Known for numerous Buddhist rock inscriptions in Sanskrit using Nagari script, which were part of the Gupta Empire (circa 240–550 CE).
- Religious and Cultural Implications:
- The Gilgit inscription provides evidence of Shaivism as a prominent religious practice in the region during the 4th century CE.
- The Peshawar inscription suggests Buddhist influences, particularly related to Buddhist chants and rituals.
- Swat Valley's Role: The inscriptions found here highlight its importance as a center of Buddhist learning and cultural exchange.
Neolithic Age Grooves Discovery Near Boothapandi

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered rock grooves created during the Neolithic age near Boothapandi village, Kanniyakumari district.
- The discovery was made by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan (Archaeological Officer, Tirunelveli and Kanniyakumari districts) and M. Faisal (Sembavalam Research Centre).
Key Highlights:
- Groove Characteristics:
- The grooves are approximately 4,000 years old, formed by Neolithic people for tool sharpening.
- Tools used for activities like hunting, ploughing, and digging were sharpened here.
- The grooves resulted from wear and tear of tools that had broken or worn out during use.
- Groove Dimensions:
- Largest groove: 15 cm in length, 4 cm in width.
- Smallest groove: 8 cm in length, 3 cm in width.
- Similar Discoveries:
- Similar grooves have been found in other parts of Tamil Nadu, including Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram.
- Significance:
- The grooves provide evidence of Neolithic human habitation in the region.
- Ongoing excavations are expected to uncover more about Neolithic culture in the area.The Hindu
2023 National Tansen Samman

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
- The prestigious National Tansen Samman for 2023 was conferred upon Pt. Swapan Choudhary, a renowned tabla maestro from Kolkata, at the National Tansen Festival held in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tansen Festival: This festival, renowned for its celebration of classical music, is organized annually in Gwalior, which is considered the music capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Prize Details: As part of the honor, Pt. Swapan Choudhary was presented with an honorarium of five lakh rupees, a citation plaque, and a shawl-shriphal.
- About the Award:
- The National Tansen Samman was established in 1980 by the Madhya Pradesh government to recognize exceptional contributions to Indian classical music.
- It is named after Tansen, one of India's most celebrated classical musicians.
- The award is the highest national honor in the field of Indian classical music.
- Additional Award:
- Raja Mansingh Tomar Samman for 2023 was awarded to Sanand Nyas, an institution from Indore. This institution has been active for 35 years in the promotion of classical music, drama, and cultural festivals.
- Pt. Swapan Choudhary’s Remark: In response to receiving the honor, Pt. Choudhary expressed his gratitude and pride in joining the ranks of distinguished artists awarded the National Tansen Samman.
About Tansen: The Iconic Musician
- Legacy: Tansen, also known as Miyan Tansen, was a prominent Indian classical musician, composer, and vocalist. He is credited with popularizing several ragas and revolutionizing the Indian classical music tradition.
- Role at Akbar’s Court: Tansen was one of the Navaratnas (nine jewels) in the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He held the title of Mian, meaning "learned man," bestowed upon him by Akbar.
- Contributions:
- Tansen is famous for his compositions, including the introduction of notable ragas such as Miyan ki Malhar, Miyan ki Todi, and Darbari.
- He also improved the plucked rabab, which is of Central Asian origin, enhancing its role in Indian classical music.
- Historical Influence: Tansen's life and work are surrounded by extensive legend, and his contributions remain deeply influential in the development of Indian classical music today.
Vijay Diwas 2024

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 16, 2024, India commemorated Vijay Diwas, marking the 53rd anniversary of its victory in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. This day honors the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers and the Mukti Bahini, whose collective efforts led to the creation of Bangladesh as an independent nation. On this occasion, leaders across India, paid heartfelt tributes to the fallen heroes who contributed to the victory, and to the enduring India-Bangladesh friendship.
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War culminated in the surrender of over 90,000 Pakistani soldiers, and India’s victory is celebrated as a defining moment in South Asian history.
The War’s Historical Context:
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War was a pivotal conflict between East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Pakistan (now Pakistan), leading to Bangladesh’s independence. It was a direct result of decades of social, political, and economic discrimination faced by East Pakistan, despite its larger population and contribution to Pakistan’s economy. Major events leading to the war included:
- Cultural and linguistic marginalization, with East Pakistan's Bengali language and identity being suppressed by the West.
- The 1970 elections that saw the Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, win a decisive victory in East Pakistan, but their demand for greater autonomy was rejected by West Pakistan.
- The violent crackdown by the Pakistani military in Operation Searchlight in March 1971, leading to widespread atrocities and a mass exodus of refugees into India.
India’s Role in the War:
India’s involvement in the conflict was initially cautious, but the refugee crisis—with over 10 million people fleeing to India—forced India to take action. India provided humanitarian aid and supported the Mukti Bahini, a guerrilla force of Bangladeshi fighters. On December 3, 1971, Pakistan’s preemptive airstrike on Indian military bases led to India's retaliation and full-scale military involvement, including air and naval operations.
India’s military, with assistance from the Mukti Bahini, launched a decisive campaign, ultimately leading to Pakistan’s surrender on December 16, 1971, and the creation of Bangladesh.
Vijay Diwas Observances:
- The 53rd Vijay Diwas celebrations at Fort William, Kolkata, saw a Bangladeshi delegation—including Mukti Joddhas (freedom fighters)—reflect on their memories of the war, highlighting India's crucial role in the liberation of Bangladesh.
- The event also featured a wreath-laying ceremony, military tattoo, and a salute to the shared sacrifice and friendship between India and Bangladesh.
The 1971 Surrender Painting and New Symbolism:
In an interesting development, the iconic 1971 surrender painting, depicting the surrender of Pakistani forces in Dhaka, was moved from the Army Chief’s lounge to the Manekshaw Centre. The painting was replaced by Karam Kshetra–Field of Deeds, a new artwork symbolizing India’s strategic and cultural heritage. This new piece incorporates elements like Lord Krishna’s chariot, Chanakya, and modern military assets, reflecting India’s military prowess and heritage.
Zakir Hussain

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Ustad Zakir Hussain, the legendary tabla virtuoso, passed away at the age of 73 due to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).
Key Highlights:
- Career Highlights:
- Born on March 9, 1951, to Ustad Alla Rakha, a renowned tabla maestro.
- Began tabla training at age 7, with early guidance from his father.
- Co-founded Shakti in 1973 with John McLaughlin, blending Indian classical music with Western influences, pioneering world music.
- Worked with global artists, including George Harrison, John McLaughlin, and Mickey Hart.
- Awarded four Grammy Awards, including three at the 66th Grammy Awards (2024), and honored with the Padma Vibhushan in 2023.
- A visiting professor at Stanford and Princeton universities.
- Musical Style:
- Transformed the tabla from a background instrument into a dynamic, expressive solo performance.
- Known for his complex rhythms and spontaneous performances, making tabla accessible and glamorous.
- Emphasized the concept of "hazri" (attendance) in the court of music, seeing his music as an offering to a higher power.
- Cultural Influence:
- His music was a bridge between traditional Indian classical and contemporary global sounds, impacting audiences worldwide.
- Played a pivotal role in the cultural exchange of Indian classical music, gaining fans and respect across the globe.
- Participated in projects such as the Taj Mahal tea commercials and "Desh Raag", symbolizing unity and diversity in India.
What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)?
- IPF is a chronic lung disease causing scarring of the lung tissue, leading to difficulty in breathing.
- Cause: The exact cause is unknown, hence termed "idiopathic" (unexplained).
- Risk Factors: Most common in older adults (over 50), men, and those with a history of smoking or viral infections.
About the Tabla:
- Structure: Composed of two drums—Tabla (right) and Bayan (left)—used primarily in Hindustani classical music.
- Material: Tabla has a wooden body, while Bayan can be made of clay or metal, both covered with animal skin and syahi paste.
- Role: Primarily accompanies vocal and instrumental performances, and is essential in various classical dance forms in northern India.
- Historical Note: Believed to have been invented by Amir Khusrau.
Prominent Tabla Players:
- Ustad Alla Rakha (father of Zakir Hussain).
- Zakir Hussain (himself).
- Shafat Ahmed and Samta Prasad.
Under the Sal Tree Theatre Festival

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
“Under the Sal Tree” Theatre Festival, held annually in Rampur, Assam, promotes eco-friendly and sustainable practices in theatre while showcasing rich cultural diversity.
Overview:
- Location: Rampur village, Goalpara district, Assam
- Organizer: Badungduppa Kalakendra, a social and cultural organization
- Founded: 1998 by Sukracharjya Rabha
- Festival Focus: Eco-friendly theatre practices, cultural diversity, and sustainability
Key Features
- Unique Setting: Open-air festival under Sal trees, with no artificial lighting or electric sound systems.
- Sustainability:
- No use of plastic.
- Carbon-neutral, with eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, straw, and cane.
- Performances in natural daylight, avoiding electric lights.
- International Participation: Theatre groups from countries like Poland, South Korea, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, North Korea, Bolivia, and Holland have performed.
- Cultural Celebration: Highlights indigenous art forms, languages, and traditions, e.g., Rabha and Bodo plays.
Festival Activities
- Performances:
- Includes plays like “Dadan Raja” (Rabha language play), “Kindhan Charithiram” (Tamil), and “Kisan Raj” (Hindi).
- Focus on themes such as societal change and resilience of farmers.
- Workshops & Community Projects: For performing artists, promoting artistic innovation and social impact.
- Anniversary Celebrations:
- 25th anniversary celebrated with special events and book releases, e.g., “Resonance: Echoing the Spirit of Badungduppa” and “Sukracharjya Rabha on the Back Stage”.
Impact & Legacy
- Theatre Movement: Celebrates art amidst nature, breaking geographical barriers despite the remote location.
- Founder’s Vision: Sukracharjya Rabha believed in the synergy between art and nature, aiming to bring social change through theatre.
- Local Involvement:
- 20 resident artists contribute to the festival’s success.
- Festival has become a major cultural attraction in Assam, drawing thousands of theatre enthusiasts.
Turner Prize

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
Jasleen Kaur, a 38-year-old Indian-origin Scottish artist, has won the prestigious Turner Prize 2024 for her exhibition "Alter Altar". This win highlights Kaur’s unique ability to weave together personal, political, and spiritual elements into a cohesive artistic expression. The exhibition explores themes such as plurality, migration, and cultural identity, drawing from Kaur’s own family history and experiences.
Exhibition Overview:
"Alter Altar," which was first showcased in Glasgow, features an array of everyday objects and cultural symbols, including:
- A vintage red Ford Escort covered in a large crocheted doily, symbolizing her father’s migrant aspirations.
- Worship bells, Irn-Bru orange resin, an Axminster carpet, and family photographs.
- Soundtracks, including music from Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan and Bob Marley, which reflect Kaur’s multicultural upbringing.
The exhibition blends these elements to examine migration, identity, and belonging. The jury, chaired by Alex Farquharson, Director of Tate Britain, praised Kaur’s ability to combine different voices through unexpected and playful material combinations, creating a visual and aural experience that evokes both solidarity and joy.
Personal and Political Reflection:
Kaur’s work reflects on the Sikh concept of Miri Piri, which represents the balance between the political and the spiritual. This duality is central to her exploration of cultural practices and the effects of violence, colonialism, and empire on these traditions. In her acceptance speech, Kaur also addressed political issues, calling for a ceasefire in Gaza and an end to institutional complicity in Israel's actions.
About the Turner Prize:
The Turner Prize, established in 1984, is one of the most prestigious awards in contemporary British art. It aims to recognize recent developments in British art. Kaur’s win is particularly significant as it marks the 40th anniversary of the award. Previous winners include renowned Indian-origin artists such as Anish Kapoor (1991).
Hornbill Festival

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The Hornbill Festival, a vibrant celebration of Nagaland's culture and tourism, is an annual event that takes place from December 1 to 10.
About the Hornbill Festival:
- Origin: First held in the year 2000.
- Purpose: The festival aims to foster inter-tribal communication, preserve the cultural heritage of Nagaland, and showcase the harmonious blending of traditional and modern elements.
- Significance: Referred to as the “festival of festivals,” it has become an essential part of the state’s cultural calendar.
- Organizers: It is organized by the Tourism and Art & Culture Departments of the Government of Nagaland.
- Location: The festival takes place annually at the Naga Heritage Village in Kisama, located about 12 kilometers from Kohima.
- Cultural Showcase: Over the years, it has evolved into a significant celebration that highlights the vibrant and diverse cultural traditions of the various tribes in Nagaland.
- Name Origin: The festival is named after the Hornbill bird, which holds cultural importance among the Naga tribes.
- Theme of the 2024 Hornbill Festival:The 2024 edition is themed “Cultural Connect,” celebrating the rich heritage and cultural diversity of Nagaland. The festival continues to merge modernity and tradition through a variety of activities, including Naga wrestling, traditional archery, food stalls, fashion shows, beauty contests, and musical performances. Additionally, the Archives Branch is presenting a special exhibition titled “Naga-Land & People in Archival Mirror” in partnership with the National Archives of India, offering a deeper look at the region's history and cultural practices.
- Recent Milestone:This year marks the 25th anniversary of the Hornbill Festival.
Festival Highlights:
- Annual Event: Held each year since its inception in 2000, it serves as a major cultural event for Nagaland.
- Symbolism: Named after the Hornbill bird, which represents boldness and grandeur in Naga folklore.
- Location: The festival is hosted at Kisama Heritage Village, a cultural center that preserves Naga traditions with 17 indigenous houses (Morungs) that represent each of the tribes.
- Cultural Diversity: Nagaland, known as the “Land of Festivals,” is home to 17 major tribes, each with its distinct festivals and cultural practices. The Hornbill Festival promotes inter-tribal interaction and celebrates the state’s rich heritage.
- National Significance: Reflecting India’s unity in diversity, the festival serves as a platform for different cultural practices to coexist, strengthening the nation’s collective identity.
Notre-Dame Cathedral

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
The Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, a landmark symbol of French Gothic architecture, is set to reopen on after undergoing extensive renovations following a devastating fire in April 2019.
Historical and Architectural Significance:
- Location: Situated on Île de la Cité in the Seine River, Paris.
- Construction: Began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and completed in 1260, showcasing a blend of early Gothic to Rayonnant Gothic styles.
- Key Features: The cathedral is renowned for its rib vaults, flying buttresses, stained-glass windows, and sculpted gargoyles.
- Cultural Importance: It has been a stage for significant historical events, including Napoleon Bonaparte's coronation in 1804. It also houses the Holy Crown of Thorns and relics from the crucifixion of Jesus.
- Literary Legacy: Featured in Victor Hugo's "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831), which drew attention to its architectural and historical significance.
Modern History and Renovation:
- The cathedral endured historical events such as the French Revolution, World War II, and attacks during the Protestant Reformation.
- In April 2019, a fire severely damaged the roof and spire, sparking an international outpouring of support for its restoration.
- Renovation efforts began soon after, involving more than 1,000 craftspeople, with President Emmanuel Macron calling it “the project of the century.”
Construction and Modifications Over Centuries:
- The Notre-Dame was a model for early Gothic architecture and has undergone multiple renovations, including the addition of flying buttresses and other structural changes during the 13th and 14th centuries.
- Modifications continued through the Renaissance and Classical periods, reflecting changing artistic styles and the political moods of the time.
Significance in French History:
- Witness to History: The cathedral has been central to 800 years of French history, serving as a backdrop for both brilliant and tumultuous events.
- Religious and Political Symbolism: It was the heart of Paris' religious and political life, acting as a symbol of the intertwined relationship between the church and the monarchy.
MahaKumbh Mela 2025

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- On December 1, 2024, the Uttar Pradesh government declared the MahaKumbh Mela area as a temporary district for four months.
- The new district will be known as the MahaKumbh Mela District, to streamline management for the 2025 MahaKumbh.
- Over 5,000 hectares of land will be part of this district, including 66 revenue villages from four tehsils: Sadar, Sorav, Phulpur, and Karchana.
Key Administrative Changes:
- Mela Adhikari (Kumbh Mela Officer) will act as the District Magistrate (DM) and will hold powers of Executive Magistrate, District Magistrate, and Additional District Magistrate.
- The Mela Adhikari will have authority under the Indian Civil Defense Code, 2023, and the Uttar Pradesh Revenue Code, 2006.
- The Mela Adhikari can appoint an Additional Collector for the district.
MahaKumbh Mela Overview:
- The Kumbh Mela is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims, with participants bathing in sacred rivers at locations including Prayagraj, Haridwar, Ujjain, and Nashik.
- The PrayagrajKumbh takes place at the Sangam, the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati rivers.
- The event spans over a month and includes religious, cultural, and social activities, along with massive infrastructural setup including tented townships, civic facilities, and security measures.
Global Engagement Scheme
- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Culture plays a pivotal role in promoting India’s rich cultural heritage across the globe through its Global Engagement Scheme.
- The scheme is designed to enhance India's cultural image internationally while fostering people-to-people connections and strengthening bilateral cultural ties with other nations.
- The scheme has three key components: Festival of India, Grant-in-aid to Indo-Foreign Friendship Cultural Societies, and Contribution Grants.
Key Components of the Global Engagement Scheme:
- Festival of India (FoI):
- Purpose: The Festival of India is organized abroad to celebrate and promote India's diverse culture. It provides a platform for artists from various cultural fields, including Folk Art (folk music, dance, theatre, puppetry), Classical and Traditional Dance, Classical and Semi-Classical Music, Experimental/Contemporary Dance, and Theatre.
- Impact: Since 2013-14, 62 Festivals of India have been held in different countries, with over 2,348 artists, including folk artists, participating. These festivals serve as a means to promote Indian folk art, culture, and music internationally.
- Artist Participation: Folk artists are remunerated with a performance fee of ?35,000 for the leader/main artist and ?7,000 for accompanying artists per performance.
- Grant-in-aid to Indo-Foreign Friendship Cultural Societies:
- Objective: This scheme supports cultural societies abroad that aim to strengthen cultural exchanges and promote Indian art forms. Grants are provided to these societies to organize various cultural programs and activities, fostering closer cultural ties between India and the host countries.
- Support to Folk Artists: This scheme also aids in bringing folk art to the global stage, showcasing India's traditional performances.
- Contribution Grant:
- Objective: The contribution grant is used for India’s membership in international organizations like UNESCO, ICOM, and the World Heritage Fund. This component also facilitates Indian participation in international meetings and helps host global events, further showcasing India’s cultural wealth.
Support for Veteran Artists:
In addition to promoting folk culture globally, the Ministry of Culture supports veteran artists through the Financial Assistance for Veteran Artists scheme. This initiative is aimed at supporting elderly and economically disadvantaged artists (aged 60 and above) who have made significant contributions to their respective art forms, including folk art.
- Financial Support: Artists selected under this scheme receive up to ?6,000 per month, adjusted for any state pension they may already receive.
Regional Contributions:
- The Ministry has empaneled folk artists and groups across India for participation in these international cultural exchanges. For instance, two folk artists/groups and one Kathak artist from Uttarakhand are currently empaneled.
- Notably, a troupe from Uttarakhand participated in the Freedom 70 Cultural Event in Cuba and the Dominican Republic in August 2017, showcasing the diversity of Indian folk art.
- The Financial Assistance for Veteran Artists has also benefitted several artists from Uttarakhand, with four artists from the state receiving support over the past two years.
Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
A two-day Mahabodhi Mahotsav is currently being held at the Great Stupa in Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Key Highlights:
- The festival will include religious ceremonies and cultural activities centered around the relics of Lord Buddha’s chief disciples, Sariputra and Maudgalyayana.
- Cultural Significance: The Mahotsav serves as a platform for celebrating and reaffirming the cultural and spiritual heritage of the region, with a focus on the teachings of Lord Buddha.
About Sanchi Stupa:
Sanchi Stupa is one of the oldest and most significant monuments of Buddhist architecture in India. It has stood as a symbol of Buddhist history, spirituality, and culture for over two millennia.
- Historical Importance:Commissioned by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, the stupa was later expanded by the Shunga and Satavahana rulers. It stands as a testament to the spread of Buddhism across India and beyond.
- Architectural Features:
- Hemispherical Dome (Anda): The large dome represents the universe, encapsulating the essence of Buddhist cosmology.
- Chatras: The umbrella-like structures on top of the dome symbolize divine protection and royalty.
- Harmika: A small balcony on the dome, which is considered the abode of the gods.
- Medhi: The base of the stupa, which stores sacred relics.
- Toranas: Four intricately carved gateways that depict scenes from the life of Buddha and various Jataka tales. These gateways point to the four cardinal directions, symbolizing the universality of Buddha’s teachings.
- Vedica: The railings surrounding the stupa serve as sacred enclosures.
- Paradakshinapatha: Pathways for circumambulation, allowing devotees to walk around the stupa as a sign of respect.
- Symbolism:The stupa’s architecture is an example of early Buddhist aniconism, where the Buddha is not directly depicted but is represented symbolically through footprints, wheels, or empty thrones.
- Inscriptions:The stupa contains important inscriptions, including the Ashokan Lion Capital and inscriptions in Brahmi and Kharosthi scripts, reflecting the historical significance of the site.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status:In 1989, Sanchi Stupa was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognizing its exceptional historical and cultural importance as a center for Buddhist art, architecture, and philosophy.
Significance of the Mahabodhi Mahotsav:
The Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi not only provides a spiritual experience but also highlights the historical and cultural legacy of Buddhism in India. The event brings attention to the preservation and promotion of Buddhist heritage, reflecting India’s rich diversity and commitment to maintaining its ancient traditions. Through this festival, Sanchi continues to be a center of pilgrimage and learning, attracting visitors from around the world who seek to understand and experience the teachings of Lord Buddha.
Ngada Festival

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Rengma Naga tribe concluded a two-day celebration of the Ngada festival-cum-Mini Hornbill Festival at the Tseminyu RSA ground in Nagaland.
Ngada Festival Overview:
- Celebration: It is an annual celebration observed by the Rengma Naga tribe, marking the end of the agricultural cycle.
- Duration: Typically, an eight-day festival, it is celebrated towards the end of November.
- Significance: It is a festival of thanksgiving, joy, and cultural unity, with a focus on gratitude for the harvest and remembrance of departed souls.
Cultural and Ritual Aspects:
- Rituals: The festival involves rituals for protection from misfortunes, such as fire and evil spirits, as well as prayers for peace and prosperity in the community.
- Agricultural Link: The festival is celebrated after the harvest season, symbolizing the end of the agricultural cycle and the beginning of the storage of crops.
- Official Announcement: The village priest announces the start of the festival, and preparations begin shortly after.
Importance of Ngada:
- Gratitude for the Harvest: The festival is a celebration of the hard work of the agricultural year and the bountiful harvest.
- Cultural Identity: The festival serves as a vital reminder of the Rengma Naga’s cultural heritage and traditions, helping to preserve them for future generations.
- Symbol of Unity: It fosters cultural unity and strengthens community bonds within the tribe.
Tribal Demographics:
- Population: The Rengma Naga tribe has a population of around 62,951 in Nagaland and 22,000 in Assam (according to the 2011 Census of India).
- Ethnic Identity: The Rengmas belong to the Tibeto-Burman ethnic group and identify themselves as Njong or Injang.
Historical and Cultural Background:
- Migration: It is believed that the Rengmas, along with other Naga tribes, migrated from Southeast Asia, crossing the Yunnan Mountain ranges, and eventually settled in the upper Burma region.
- Slavery: Historically, slavery was practiced among the Rengmas, with slaves known as menugetenyu and it sakesa. However, by the time the British arrived, slavery was in decline, and no Rengma tribespeople were known to be slaves.
Economy:
- Agricultural Lifestyle: The Rengma Naga are primarily agriculturalists, relying on Jhum cultivation (shifting cultivation) and wet rice cultivation.
- Crops Grown: They grow staple crops like paddy, along with seasonal crops and fruits.
Religion:
- Traditional Beliefs: Traditionally, the Rengma Naga worship supernatural beings.
- Christianity: Today, most of the Rengma tribe has converted to Christianity.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024
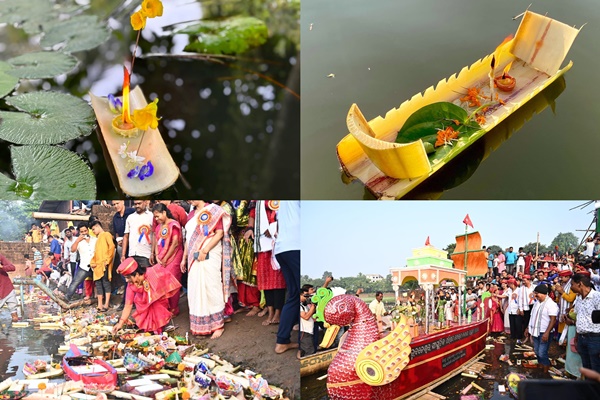

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
Commemoration of Birsa Munda’s 150th Birth Anniversary

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
On November 15, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a commemorative stamp and coin to mark the 150th birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, a prominent tribal freedom fighter and leader from Jharkhand.
Key Points about Birsa Munda:
- Iconic Tribal Leader: Birsa Munda, born in 1875, is often referred to as ‘Bhagwan’ (God) and ‘DhartiAaba’ (Father of the Earth) by the tribal communities. He is celebrated for his leadership in the fight against the exploitation of tribal people by both the British and non-tribal settlers.
- Ulgulan Movement: Birsa Munda led the Ulgulan (Great Tumult) against the alienation of land, forced labour, and the illegal appropriation of tribal land in the Chotanagpur Plateau. His efforts were critical in mobilizing tribal communities and challenging the colonial order.
- Religious and Social Reformer: He founded the Birsait faith, focusing on spiritual practices that emphasized prayer, worship of God, and abstaining from alcohol, fostering unity and resilience among tribal communities.
- Death and Legacy: Birsa Munda died in 1900 in British custody at the young age of 25. Despite his early death, his legacy lives on as a symbol of tribal pride and resistance.
- Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas: Since 2021, the Government of India observes November 15 as Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas (Tribal Pride Day) in honor of Birsa Munda's birth anniversary, recognizing the contributions of tribal communities and their role in India's history.
- Highlights of the 2024 Commemoration:
- Commemorative Stamp and Coin: To mark the 150th birth anniversary, the Prime Minister unveiled a commemorative stamp and coin in Bihar's Jamui district. This serves as a tribute to Munda's sacrifices for the country.
- Year-Long Celebrations: The 2024 event marks the beginning of year-long celebrations to commemorate Birsa Munda’s legacy, with a focus on tribal welfare and recognition of their historical contributions.
- Welfare Projects and Initiatives:
- Prime Minister Modi inaugurated and laid the foundation for tribal welfare projects worth over ?6,640 crore.
- The PM launched two tribal freedom fighter museums and tribal research institutes.
- 1.16 lakh homes were sanctioned under the Dharti Aba Janjati Gram Utkarsh Yojana.
- 25,000 homes for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) were approved under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) scheme.
- The launch of 50 mobile medical units aims to improve healthcare access in tribal regions.
- 10 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) were inaugurated to promote education for tribal students.
- DhartiAabaJanjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan:
- The DhartiAabaJanjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan aims to address gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood in tribal-majority villages.
- The initiative is being implemented across 63,000 villages with the involvement of 17 ministries and departments.
- PM-JANMAN Scheme for PVTGs:
- Launched in November 2023, the PM-JANMAN initiative aims to uplift Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) through various interventions like safe housing, clean drinking water, healthcare, education, and sustainable livelihoods. The scheme also supports Van Dhan Vikas Kendras for the trade of forest produce and solar-powered systems for households in tribal areas.
1st Bodoland Mohotsav

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the 1st Bodoland Mohotsava two-day event focused on language, literature, and culture.
- Objective: Aims to promote peace, unity, and a vibrant Bodo society through cultural integration. The festival celebrates the rich Bodo culture and heritage.
Historical Context and Peace Initiatives:
- End of Violence: The event marks the end of 50 years of violence, following the Bodo Peace Accord (2020), which ended conflict in Bodoland and led to a path of peace and development.
- Peace Agreements: The Bodo Peace Accord served as a catalyst for other peace settlements, such as the KarbiAnglong Accord, Bru-Reang Accord, and NLFT-Tripura Accord.
Development in Bodoland Post-Peace Accord:
- Impact of the Peace Accord:
- Over 10,000 youth in Assam have renounced violence and joined the mainstream of development.
- Increased mutual trust between the people and the government.
- Economic Assistance:
- Rs 1,500 crore special package by the central government.
- Rs 700 crore spent on infrastructure development in education, health, and culture in Bodoland.
- Rs 5 lakh assistance for families affected by the Bodo conflict.
Government Support for Socio-Economic Development:
- Skill Development & SEED Mission:Focus on skilling, entrepreneurship, employment, and development through the SEED Mission for youth empowerment.
- Rehabilitation of Former Cadres:
- Over 4,000 former cadres of the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) have been rehabilitated.
- Many youths have been recruited into Assam Police.
- Tourism & Employment:Growing tourism in Bodoland, with parks like Manas National Park and Raimona National Park, creating employment opportunities for youth.
Cultural Promotion:
- Bodo Culture and GI Tags:Promoting Bodo crafts like Aronnaye, Dokhona, Gamsa, etc., that have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags to preserve cultural identity.
- Bodoland Handloom Mission & Sericulture:Government efforts to promote sericulture and the Bodoland Handloom Mission to sustain Bodo weaving traditions.
- Literary Celebrations:
- Continuous Bodoland Literary Festival in Kokrajhar, enhancing the importance of Bodo literature and language.
- Celebration of Bodo Sahitya Sabha’s 73rd foundation day.
Key Government Initiatives for Development:
- Infrastructure Development:
- Rs 800 crore annually being spent by the Assam government for the development of Bodoland.
- Focus on healthcare, education, and employment.
- Medical Education:Expansion of medical colleges in Assam from 6 to 12, with plans for 12 more new colleges.
PM Vishwakarma Yojana

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The PM Vishwakarma Yojana is a landmark initiative by the Indian government aimed at revitalizing traditional craftsmanship and empowering artisans and craftspeople, often referred to as Vishwakarmas. Launched on September 17, 2023, during Vishwakarma Jayanti, the scheme highlights the government's commitment to preserving India's rich cultural heritage and supporting the unorganized sector.
Key Highlights
- Objective:
- To strengthen the Guru-Shishya tradition and improve the quality, reach, and marketability of products and services by artisans.
- To integrate Vishwakarmas into domestic and global value chains, making them self-reliant.
- To alleviate poverty by supporting rural and urban artisans across India.
- Financial Outlay:,Fully funded by the Union Government with a ?13,000 crore budget spanning five years (2023–2028).
- Eligibility:
- Open to rural and urban artisans and craftspeople involved in 18 traditional crafts, such as blacksmithing, goldsmithing, pottery, boat making, and carpentry.
- Covers 5 lakh families in the first year and aims to reach 30 lakh families over five years.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Support:
- Collateral-free credit of ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) at a concessional 5% interest rate.
- Government provides 8% interest subvention upfront to banks.
- Toolkit Incentive: ?15,000 via e-vouchers for acquiring modern tools.
- Training and Skill Development: Basic and advanced skill training to create industry-ready manpower.
- Digital and Marketing Incentives: Encourages digital transactions and provides marketing support.
- Recognition: Beneficiaries receive a PM Vishwakarma Certificate and ID Card.
- Market Linkage: Facilitates better market access for artisan products.
- Financial Support:
- Achievements (as of Nov 4, 2024):
- 25.8 million applications received.
- 2.37 million artisans registered after verification.
- Over 1 million artisans benefited from toolkit incentives.
Significance
- Promotes inclusive development by supporting an underserved segment of the workforce.
- Recognizes and supports traditional skills passed down through generations, preserving India’s cultural diversity.
- Enhances productivity and competitiveness by integrating artisans into MSME sectors.
- Encourages sustainability through the promotion of handmade, eco-friendly crafts.
Key Institutions Involved
- Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME): Oversees implementation.
- Common Services Centres (CSC): Facilitates registration through biometric-based PM Vishwakarma Portal.
Challenges Addressed
- Lack of access to modern tools and financial support.
- Insufficient market linkages and exposure for traditional crafts.
- Limited opportunities for skill enhancement and product development.
Maha Kumbh Mela 2025

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela 2025 will be held in Prayagraj from January 13 to February 26.
- The event is a sacred pilgrimage that draws millions of pilgrims to bathe in the holy waters of the Triveni Sangam (the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and Sarasvati rivers) for spiritual purification and liberation.
Significance and Spiritual Importance
- Sacred Rituals:
- The central ritual is the act of bathing in the holy waters of the confluence, believed to cleanse one’s sins and bring spiritual liberation (Moksha).
- Pilgrims also engage in worship, spiritual discourses, and seek blessings from revered sadhus and saints.
- Auspicious Dates:
- The event includes Shahi Snan (Royal Bath), where prominent saints and their followers bathe on specific dates, marking the beginning of the Mela.
- Paush Purnima marks the start of the auspicious bathing period.
- Cultural Ceremonies:
- The Mela features a grand procession (Peshwai) with Akharas (spiritual orders) on elephants, horses, and chariots.
- Cultural performances, traditional music, dance, and art are also part of the festivities, showcasing India’s vibrant cultural diversity.
Mythological and Historical Roots
- Mythology:
- The Kumbh Mela is deeply embedded in Hindu mythology, symbolizing humanity’s quest for spiritual unity and enlightenment.
- The timing of the event is based on astrological positions of celestial bodies, particularly the Sun, Moon, and Jupiter.
- Historical Significance:
- The origins of the Kumbh Mela trace back over 2,000 years, with references found in the Maurya and Gupta periods.
- Royal Patronage: Emperors like Akbar supported the Mela, symbolizing unity among different religions and cultures.
- British Colonial Era: British officials documented the Mela, fascinated by its scale and ritualistic practices.
- Modern Recognition:
- In 2017, the UNESCO recognized the Kumbh Mela as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, underscoring its global significance.
Cultural Celebration and Unity
- Cultural Diversity:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela is a celebration of India's rich cultural heritage, where pilgrims experience traditional crafts, art, music, and dance, alongside spiritual practices.
- International Participation:
- Pilgrims from across the globe attend the Mela, drawn by its message of unity, tolerance, and the universal quest for spiritual growth and peace.
- Message of Unity:
- The Mela serves as a reminder of humanity’s shared desire for self-realization and spiritual fulfillment, transcending national, cultural, and religious boundaries.
First Asian Buddhist Summit in New Delhi
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Government of India, in partnership with the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), is hosting the First Asian Buddhist Summit in New Delhi.
- Theme: "Role of Buddha Dhamma in Strengthening Asia."
- Significance: The summit aligns with India’s Act East Policy, focusing on collective, inclusive, and spiritual development across Asia.
- Inauguration: The two-day event will be inaugurated by President Droupadi Murmu on November 5, 2024.
- Participants: Buddhist Sangha leaders, scholars, and practitioners from various Asian Buddhist traditions will gather to promote dialogue, understanding, and address contemporary challenges within the Buddhist community.
Key Themes of the Summit
- Buddhist Art, Architecture, and Heritage
- Focus on preserving and celebrating Buddhist landmarks in India (e.g., Sanchi Stupa, Ajanta Caves).
- Emphasizes the role of Buddhist art in fostering cross-cultural understanding.
- Buddha C?rik? and Dissemination of Buddha Dhamma
- Discusses Buddha’s journeys and how his teachings spread across India and beyond.
- Role of Buddhist Relics in Society
- Relics serve as symbols of Buddha's teachings, promoting devotion, mindfulness, and economic benefits through tourism and pilgrimages.
- Buddha Dhamma in Scientific Research and Well-Being
- Exploration of Buddhist teachings on mindfulness and compassion, and their integration into contemporary scientific practices to enhance well-being.
- Buddhist Literature and Philosophy in the 21st Century
- Delving into timeless Buddhist wisdom that continues to address the human condition, the nature of reality, and paths to enlightenment.
- Exhibition: "India as the Dhamma Setu (Bridge) Connecting Asia," showcasing India's role in the spread of Buddhism and its significance in fostering unity.
India’s Role in Promoting Buddhist Heritage
- Cultural Identity: Buddhism is integral to India's cultural fabric, influencing its national identity and foreign policy.
- Buddhist Tourism Circuit: The Indian government has developed a Buddhist Circuit covering key sites such as Bodh Gaya, Sarnath, and Kapilvastu.
- International Conferences and Symposia: India has hosted several events, including the First Global Buddhist Summit (2023), International Abhidhamma Diwas (2024), and Symposiums on Vipassana Meditation.
- Pali Language Recognition: On October 4, 2024, Pali was granted classical status, recognizing its significance in conveying Buddha’s teachings.
Buddhism’s Influence in Asia
- Historical Context: Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama in the 6th century BCE, spread across Asia with the support of figures like Emperor Ashoka (268-232 BCE), who promoted peace and harmony through Buddhist teachings.
- Spread of Buddhism: From its origins in India, Buddhism spread to Central Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia, adapting to local cultures and creating diverse schools: Theravada, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
Ningol Chakkouba Festival

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
Ningol Chakkouba is one of the biggest festivals of Manipur, primarily celebrated by the Meitei community, but over the years, it has seen participation from various communities.
Key Highlights:
- Date: The festival is celebrated annually on the second day of the lunar month of Hiyangei in the Meitei calendar.
- Main Celebration: The central tradition involves married sisters visiting their maternal homes for a grand feast, joyous reunion, and the exchange of gifts.
- Customary Invitation: A week before the festival, the son of the family formally invites his married sisters to join the celebration.
- Expansion of Celebration: While traditionally celebrated in Manipur, Ningol Chakkouba is now observed in other states and even outside India, where Manipuris are settled.
- Meaning of Ningol Chakkouba:
- Ningol means ‘married woman’.
- Chakouba means ‘invitation for feast’.
- Thus, the festival is a celebration where married women are invited to their parents' home for a special meal.
- Inclusion of Other Communities: Although originally a Meitei tradition, Ningol Chakkouba is now celebrated by various communities due to its emphasis on family reunion, happiness, and promoting peace and harmony in society.
- Cancellation in 2023: The festival was not held in the previous year due to ethnic violence in the state.
Replicas of Konark Wheels at Rashtrapati Bhavan

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Four replicas of the Konark wheels, made of sandstone, have been installed at the Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre and Amrit Udyan.
- This initiative is aimed at showcasing India’s rich cultural heritage and promoting traditional historical elements among visitors to Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Significance of the Konark Sun Temple:
- Historical Background: The Konark Sun Temple was built in the 13th century under King Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty in Konark, Odisha.
- Architectural Design: The temple is a colossal stone chariot with twelve pairs of intricately carved wheels, symbolizing the chariot of the Sun God.
- Materials Used: Constructed using Khondalite stones, the temple features detailed carvings that depict mythology and cultural life.
- Astronomical Significance: The temple's orientation is designed to capture the first light of the sun, reflecting ancient Indian knowledge of astronomy.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status: The Konark Sun Temple was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1984, recognizing its architectural and historical importance.
Symbolism of the Konark Wheel:
- Time and Progression: The Konark wheel represents time (Kalachakra), progression, and democracy. Its 24 spokes symbolize ancient Indian wisdom and the passage of time.
- Sundial Function: The wheel was historically used as a sundial in the temple, marking the passage of time and symbolizing India’s commitment to progress and resilience.
- National Emblem: The Konark wheel's design is also reflected in the Ashoka Chakra, the wheel on the national flag of India, symbolizing the nation’s resolve towards progress.
Cultural Heritage at Rashtrapati Bhavan:
- The installation of these replicas is part of a broader effort to introduce and promote traditional cultural and historical elements at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- The Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre and Amrit Udyan serve as platforms to exhibit India’s diverse artistic legacy to visitors, allowing them to experience the grandeur of ancient Indian architecture and its cultural significance.
National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Ministry of Culture plans to revive and relaunch the National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) to enhance the preservation and accessibility of India’s ancient texts.
- The mission’s objective is to document, conserve, digitize, and disseminate India’s rich manuscript heritage, ensuring their protection and public access.
Formation of a New Autonomous Body:
- The National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) is likely to be restructured into an autonomous body called the National Manuscripts Authority, which will be under the Ministry of Tourism and Culture.
- The new body will address the challenges and gaps in manuscript preservation and management, offering more focused and flexible governance.
Background and Achievements:
- Established in 2003, the NMM has been part of the Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts (IGNCA).
- Key achievements:
- 52 lakh manuscripts have had metadata prepared.
- Over 3 lakh manuscripts have been digitized, though only one-third have been uploaded for public access.
- Preventive and curative conservation of over 9 crore folios of manuscripts has been undertaken over the last 21 years.
- The NMM has set up 100 Manuscripts Resource Centres and Manuscripts Conservation Centres across India.
Current Challenges and Gaps:
- Data Uploading and Access:
- Of the 130,000 digitized manuscripts, only 70,000 are accessible online due to the absence of a comprehensive access policy.
- A significant portion (around 80%) of manuscripts areprivately owned, restricting public access and usage.
- Digitization Mismatch:
- There have been concerns about discrepancies between the digitized data and the original manuscripts, which requires correction to ensure authenticity and accuracy.
- Lack of Comprehensive Access Policy:
- Limited public access to manuscripts due to policy restrictions hinders further research and public engagement with this rich heritage.
Scope and Future of NMM:
- India's Manuscript Heritage: India is believed to have around 10 million manuscripts, spread across various regions, languages, scripts, and topics.
- Digitization and Accessibility: Moving forward, the key challenge will be ensuring that a larger proportion of the manuscripts are digitized, uploaded, and made publicly available, particularly from private collections.
- The establishment of the National Manuscripts Authority is expected to streamline efforts and enhance coordination between government bodies, private institutions, and scholars.
International Abhidhamma Divas

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, International Abhidhamma Divas was celebrated at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, with PM Narendra Modi.
Key Details:
- India's Spiritual Legacy: Birthplace of Buddhism; site of Gautam Buddha's enlightenment.
- Sacred Sites: Veneration of locations like Bodh Gaya, symbolizing Buddha's journey and teachings.
- Core Teachings: Abhidhamma as a key philosophical component emphasizing mental discipline and self-awareness.
International Abhidhamma Divas
- Global Observation: Celebrates the significance of Abhidhamma in ethical conduct and mindfulness.
- Cultural Connection: Highlights India's role in preserving Buddhism and bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary practices.
Historical Background and Significance
- Commemoration: Marks Buddha’s descent from T?vati?sa to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur).
- Teaching Period: Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to deities for three months; linked to the end of the Rainy Retreat and the Pav?ra?? festival.
Teachings of Abhidhamma
- Systematic Analysis: Provides a detailed exploration of mind and matter, differing from Sutta Pi?aka.
- Specialized Vocabulary: Key terms include "citta" (consciousness), "cetasika" (mental factors), "r?pa" (materiality), and "nibb?na" (liberation).
- Textual Framework: Six core books of Abhidhamma Piñaka cover moral states, aggregates, and causal relationships.
- Key Treatise: The Paññh?na offers in-depth causal analysis, essential for practitioners’ understanding.
Modern Observance and Celebrations
- Significance of Pali: Recognition of Pali as a classical language; promoting India's Buddhist heritage.
- Participants: Gathering of ambassadors, monks, scholars from 14 countries; emphasizes Abhidhamma's relevance today.
- Program Highlights: Dhamma discourse, academic sessions on Abhidhamma’s significance, exhibitions on Pali's evolution and Buddha's teachings.
Classical Status of Pali Language
- Pali's Role: Sacred language for delivering Buddha's teachings; recognized as a Classical Language by India.
- Buddhist Canon: Major texts include the Tipitaka (Vinaya, Sutta, Abhidhamma Pitaka) and commentarial traditions.
- Literary Heritage: Jataka Kathas reflect shared moral values; status enhances Pali studies in education and research.
Significance
- Significance of Celebration: Abhidhamma Divas underscores efforts to preserve and promote Buddhism’s legacy.
- Revitalization of Buddhism: Fosters global engagement and appreciation for Buddha’s teachings, reaffirming India's role in Buddhist studies.
Doddalathur Megalithic Burial Site
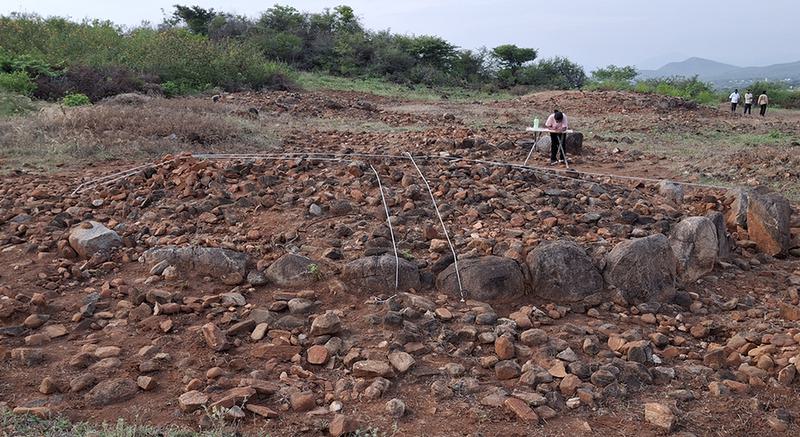

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore have embarked on an excavation of megalithic burial sites in Chamarajanagar district.
- Location: Doddalathur village, Hanur taluk, Chamarajanagar district, situated in a valley by the Male Mahadeshwara Hill ranges.
- Team: A group of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore, in collaboration with the Mythic Society, Bengaluru.
- Excavation Focus: Exploration of megalithic burial sites corresponding to the Iron Age (approximately 1200 BC to 300 CE).
- Site Features:
- Burials consist of circles made of large boulders, referred to as "megalithic."
- A small hillock is located to the west of the village.
- Historical Significance:
- The site was discovered by C. Krishnamurti of the Archaeological Survey of India in 1961.
- Originally contained over 1,000 burials, many of which have been lost due to agricultural expansion and development.
- Despite disturbances, many burials remain intact and are considered suitable for excavation.
- Goals of the Project:
- To enhance understanding of megalithic-Iron Age culture in southern Karnataka's hilly regions.
- To provide practical field training for archaeology students.
Status of Classical Language: An Explainer

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved to confer the status of Classical Language to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali languages.
Why is a language declared as Classical?
Designating a language as classical acknowledges its historical significance and its role in preserving Bharat’s rich cultural heritage. These languages have been crucial in transmitting ancient knowledge, philosophies, and values for millennia. Government recognition emphasizes their deep antiquity and literary traditions, enhancing their status and promoting efforts for their preservation and research, ensuring their relevance in the modern world.
What are the criteria for declaring a language as classical?
In 2004, the Government of India, for the first time, created a new category of languages known as Classical Languages. It set the following as criteria for the status of Classical Language:
- High antiquity of its early texts/ recorded history over a thousand years.
- A body of ancient literature/ texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generation of speakers.
- The literary tradition must be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
This criterion was revised in 2005 and 2024 based on the recommendations of Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under Sahitya Akademi to examine the proposed languages for the status of Classical Language. Later the criteria were revised in 2024 as follows:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500- 2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a heritage by generations of speakers.
- Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence.
- The Classical Languages and literature could be distinct from its current form or could be discontinuous with later forms of its offshoots.
The 2024 Linguistic Expert Committee also recommended the following languages to be fulfilling revised criteria to be considered as a Classical Language: Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, Bengali
How many languages have been declared classical so far?
Languages Date of Recognition Notification by Source/Notification Date
Tamil October 12, 2004 Ministry of Home Affairs October 12, 2004
Ministry of Sanskrit November 25, 2005 Ministry of Home Affairs November 25, 2005
Telugu October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Kannada October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Malayalam August 8, 2013 Ministry of Culture August 8, 2013
Odia March 1, 2014 Ministry of Culture March 1, 2014
Steps Taken by the Ministry of Education for Advancing Classical Languages:
- Establishment of Central Universities (2020): Three universities created to promote Sanskrit through an Act of Parliament.
- Central Institute of Classical Tamil:
- Facilitates translation of ancient Tamil texts.
- Promotes research and offers courses for students and scholars.
- Centres for Excellence:
- Established for Classical Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia under the Central Institute of Indian Languages in Mysuru.
- Awards: Introduction of national and international awards to recognize achievements in Classical Languages.
- Additional Benefits:
- National Awards for Classical Languages.
- Establishment of university chairs.
- Dedicated centers for promoting Classical Languages.
Thanjavur Veena

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Thanjavur Veena has the distinction of being the first musical instrument in India to receive the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, highlighting its cultural and artistic significance. Here’s an overview of its features, types, and craftsmanship:
About Thanjavur Veena
- Construction:
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Ekantha Veena: Carved from a single block of wood.
- Sada Veena: Composed of three sections—resonator (kudam), neck (dandi), and head—with joints.
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Design Features:
- The instrument features 24 fixed frets (mettu), enabling musicians to play a wide range of ragas.
- Traditionally made from the bark of the Jackfruit tree, the bark undergoes extensive testing to ensure quality and durability.
- Craftsmanship:
- The process of crafting a Thanjavur Veena can take 15-20 days, involving cutting, intricate carving, shaping, and assembly of the wood to form the integral parts of the instrument.
Types of Veena
The Thanjavur Veena is one of several types of veenas used in Indian classical music:
- Rudra Veena and Vichitra Veena: Predominantly used in Hindustani classical music.
- Saraswati Veena and Chitra Veena: Associated with Carnatic classical music, with the Saraswati Veena being unique to Thanjavur.
Cultural Significance
- The Saraswati Veena is particularly notable as it is often associated with Goddess Saraswati, the deity of learning and arts, who is frequently depicted holding a veena. This connection emphasizes the instrument's importance in Indian culture and music.
GINGEE FORT PROPOSED FOR UNESCO WORLD HERITAGE SITE

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently nominated for UNESCO’s World Heritage Site status, Gingee Fort is part of the Maratha Military Landscapes of India, which encompasses 12 historical sites, primarily located in Maharashtra, with Gingee being the sole representative from Tamil Nadu. The nomination highlights the fort’s historical importance, unique military architecture, and its integral role in Maratha military history.
Significance of Gingee Fort
Gingee Fort, often referred to as the "Troy of the East," stands as a crucial historical monument in Tamil Nadu. Perched atop three prominent hillocks—Rajagiri, Krishnagiri, and Chandragiri—it has served as a significant stronghold for numerous empires throughout Indian history, including the Vijayanagar Nayaks, Marathas, Mughals, French, and British. This fortification exemplifies India’s rich and diverse historical legacy.
Unique Features
The fort complex spans 11 acres and boasts an array of significant structures, including:
- Kalyana Mahal: An eight-storey royal residence.
- Durbar Hall: A ceremonial hall for gatherings.
- Stepped Well and Cannon: Examples of advanced engineering and military use.
- Clock Tower and Armory: Reflecting its historical military significance.
- Elephant Tank and Stables: Indicating its use for royal elephants.
- Temples and Mosques: Including the Venkataramana Temple with intricate carvings and the Sadathtulla Mosque.
Additionally, the fort features advanced water supply systems from various historical periods, ensuring adequate resources for its inhabitants.
Historical Timeline
The origins of Gingee Fort trace back to 1200 CE when built by Ananta Kon of the Konar Dynasty. The fort underwent significant renovations under the Vijayanagar Empire. Key historical events include:
- 1677: Captured by Chhatrapati Shivaji, it remained under Maratha control until 1698.
- 1698: Came under Mughal possession, later ruled by the Nawabs of Arcot and briefly by the French.
- 1750-1770: Occupied by the French before falling to the British.
This timeline reflects the fort's strategic and cultural significance across different dynasties.
Nomination Process for UNESCO
The process for securing UNESCO World Heritage Site status involves rigorous evaluation. Experts from UNESCO and the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) assess the site's historical significance, conservation state, and management strategies. A visit to Gingee Fort is scheduled as part of this evaluation, with a recommendation expected for the 2025 World Heritage designation.
Preparation of the Nomination Dossier
The Development and Research Organisation for Nature, Arts and Heritage (DRONAH) prepared the nomination dossier, aligning with UNESCO’s operational guidelines. This comprehensive document details the fort's historical context, conservation status, and management strategies, aimed at demonstrating its outstanding value for humanity.
Union Budget 2024-25: Corridor Projects for Bihar's Temples

- 18 Sep 2024
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2024-25 announced plans to develop corridor projects for the Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar. These initiatives aim to enhance both temples as significant pilgrimage and tourist destinations, modeled after the successful Kashi Vishwanath Corridor. The temples are located approximately 10 kilometers apart and hold considerable cultural significance.
Key Facts About the Temples
Vishnupad Temple at Gaya
- Location: Situated on the banks of the Phalgu/Falgu River in Gaya district, Bihar.
- Deity: Dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- Legend: Local mythology recounts that a demon named Gayasur sought the power to help others attain moksha (liberation). After misusing this power, he was subdued by Lord Vishnu, who left a footprint at the temple, symbolizing this event.
- Architectural Features: The temple stands about 100 feet tall and is supported by 44 pillars made from large gray granite blocks (Munger Black stone), joined with iron clamps. The octagonal shrine is oriented towards the east.
- Construction: Built in 1787 under Queen Ahilyabai Holkar's orders.
- Cultural Practices: The temple is especially significant during Pitra Paksha, a time for honoring ancestors, attracting many devotees. The Brahma Kalpit Brahmins, or Gayawal Brahmins, have served as traditional priests since ancient times.
Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya
- Historical Significance: Believed to be the location where Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment under the Mahabodhi Tree.
- Construction: Originally built by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC, with the current structure dating back to the 5th–6th centuries.
- Architectural Features: The temple complex includes the 50-meter-high Vajrasana (the Diamond Throne), the sacred Bodhi Tree, and six other sacred sites associated with Buddha's enlightenment. The site is surrounded by numerous ancient Votive stupas and is protected by circular boundaries.
- Sacred Sites:
- Bodhi Tree: A direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Animeshlochan Chaitya: Where Buddha spent the second week of meditation post-enlightenment.
- Ratnachakrama: Site of Buddha's third week after enlightenment.
- Ratnaghar Chaitya: Site of Buddha's fourth week after enlightenment.
- Ajapala Nigrodh Tree: Site of Buddha’s fifth week after enlightenment.
- Lotus Pond: Site of Buddha’s sixth week after enlightenment.
- Rajyatana Tree: Site of Buddha’s seventh week after enlightenment.
- Recognition: Designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2002, the Mahabodhi Temple attracts numerous national and international pilgrims, emphasizing its spiritual importance.
Other Tourist Attractions in Bihar
Additional notable tourist sites in Bihar include:
- Vishwa Shanti Stupa in Rajgir
- Nalanda
- Ancient city of Patliputra
- Valmiki Nagar Tiger Reserve in West Champaran
What is the Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP)?
The Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP) aims to upgrade religious sites into world-class destinations for spiritual and tourism purposes.
Iron Age Archaeological Sites Discovered in Telangana

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A team of archaeologists claimed to have discovered a unique Iron Age megalithic site at Ooragutta near Bandala village in SS Tadvai mandal of Mulugu district, Telangana.
Recent Archaeological Discoveries in Telangana:
Ooragutta Iron Age Megalithic Site:
- Situated near Bandala village, SS Tadvai Mandal, Mulugu district, and boasts over 200 megalithic structures dating back to 1,000 BCE.
- Notable for its 'Dolmenoid Cists' featuring cap-stone-shaped side slabs, a rarity in India.
- Resembles European 'Passage Chambers', possibly influencing the design of squarish and rectangular monuments.
Rock Art Sites at Damaratogu:
- Two new sites were discovered in Gundala mandal of Bhadradri Kothagudem district.
- 'Devarlabanda Mula' site contains animal depictions, possibly dating back to the Mesolithic Age (8,000 - 3,000 BCE).
- No weapons or domestic animals are shown, suggesting the paintings may be from a pre-agricultural era.
About the Iron Age:
Timeframe:
- Began between 1200 BCE and 600 BCE, following the Stone Age and Bronze Age.
- Spanned across Africa, Europe, and Asia during prehistoric times in the Old World.
Discovery and Use of Iron:
- Iron replaced bronze as the preferred choice of metal in metalworking.
- First discovered in Turkey before spreading to other European countries.
- Used for making strong tools, enhancing agriculture through the development of the iron plow, and creating powerful weapons for armies.
Technological Advancements:
- Construction of large forts, bridges, and deep mines to extract valuable minerals.
- Improvements in pottery and weaving techniques.
Social and Political Impacts:
- Rulers gained significant power through the use of iron weapons and the ability to conquer other lands.
- The transition from prehistory to history as writing became widespread, marking the end of the Iron Age.
- Iron remains popular for various applications today, such as tools, building materials, and machinery.
- The Iron Age was a transformative period in human history, characterized by the discovery of iron, advancements in technology, and shifts in social and political structures. The use of iron revolutionized agriculture, warfare, and everyday life, leaving a lasting impact on human civilization.
Ahobilam Temple
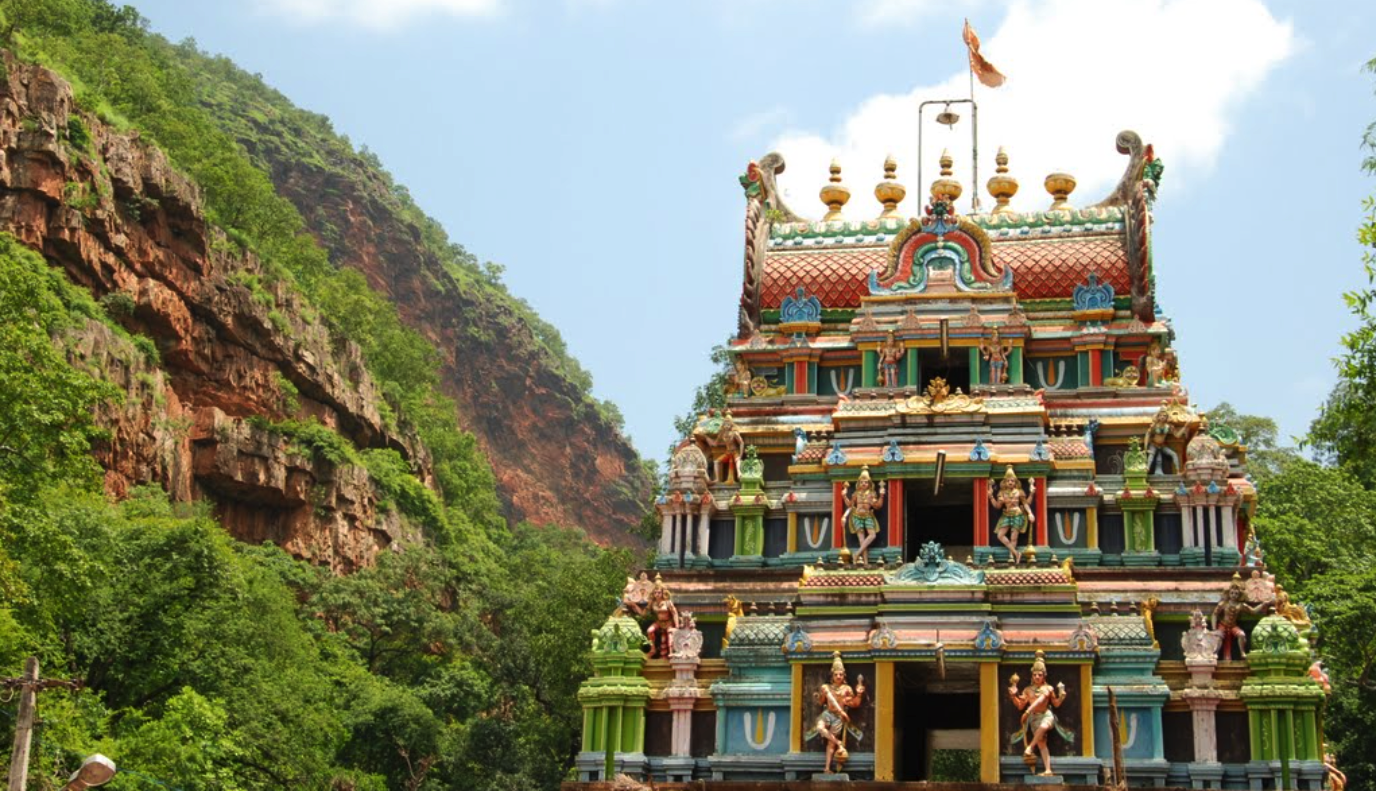

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Forest Department and Sri Lakshmi Narasimha Swamy Devasthanam (SLNSD) at Ahobilam have imposed certain restrictions on visitors arriving at the shrine, which is composed of nine different temples, situated within the Nallamala forest.
About Ahobilam Temple:
- The Ahobilam is a famous temple situated on the Nallamalai ranges in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The Nallamalai ranges south of river Krishna, down to Tirupati, and are called `Sesha Parvatha`.
- Sesha is the name of the king of serpents.
- The hood of the sesha is at Tirupati, the tail is at Srisailam, and the middle is situated at Ahobilam.
- Nallamalais at the tail are called Sringiri
- In the middle are called Vedagiri and
- Garudagiri referred to as the hood
- The shrine of the Ahobilam temple is situated on the top of the first range and is referred to as Upper Ahobilam and down below is called Lower Ahobilam.
- A huge temple surrounded by several buildings can be seen at the Upper Ahobilam.
- The main shrine or the "sacro sanctum" at Upper Ahobilam was carved out of a big egg-like rock with mandapams.
- There is a tank here, which supplies water to the residents of the Upper Ahobliam temple.
- There is a Lower Ahobilam in the below with a big temple and enclosures, It was built according to the South Indian style (Dravidian architecture).
Significance:
- Ahobilam is traditionally regarded as the place where Vishnu in the form of Narasimha killed the Rakshasa Hiranyakashipu to save his devotee Prahlada.
- The legend says that Narasimha emerged from a rock pillar to slay the Rakshasa.
- The moment is represented in several murtis in the various temples.
- Also, Garuda prayed for a vision of Narasimha in the form of Avathara, to fulfill his wish, and settled in nine forms across the hills in Ahobilam.
About Nallamala Forest:
- Nallamala Forest is among South India's largest expanses of untouched woodland, besides the Western Ghats.
Location:
- Situated across five districts in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, it sprawls across the Nallamala Hills, a segment of the Eastern Ghats, south of the Krishna River.
- Part of the forest falls within the Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, the nation's largest tiger reserve, boasting a significant tiger population.
Climate:
- Experiencing warm to hot conditions year-round, with scorching summers and mostly cool, dry winters.
- The majority of rainfall occurs during the southwest monsoon.
Vegetation:
- Tropical dry deciduous.
Flora:
- Nallamala Forest is rich in endemic species like Andrographis nallamalayana, Eriolaena lushingtonii, Crotalaria madurensis var, Dicliptera beddomei, and premna hamitonii.
Fauna:
- Home to over 700 animal species, including tigers, leopards, black bucks, wild hogs, peacocks, pangolins, Indian Pythons, King Cobras, and numerous rare bird species.
Archaeological Survey of India will ‘Delist’ Some ‘Lost’ Monuments

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has decided to delist 18 “centrally protected monuments” because it has assessed that they do not have national importance.
Context:
- ASI has decided to delist 18 protected monuments
- ASI says the monuments have ceased to be of 'national importance'
- The 18 'lost' monuments include eleven in Uttar Pradesh
Significance of Delisting Monuments:
- Several monuments are currently facing the prospect of delisting, including historical landmarks such as a medieval highway milestone in Mujessar village, Barakhamba Cemetery in Delhi, Gunner Burkill’s tomb in Jhansi district, a cemetery at Gaughat in Lucknow, and Telia Nala Buddhist ruins in Varanasi.
- The exact whereabouts or condition of these monuments remain uncertain.
Meaning of Delisting:
- Delisting a monument entails its removal from the roster of protected sites, thereby relinquishing its conservation, protection, and maintenance responsibilities by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, delisted monuments no longer enjoy protection against construction-related activities in their vicinity, enabling regular urbanization and development activities to proceed uninhibited.
Status of Protected Monuments:
- The inventory of protected monuments is subject to change through additions and removals. Presently, the ASI oversees 3,693 monuments, a number set to decrease to 3,675 following the ongoing delisting initiative.
- This marks the first extensive delisting endeavor in several decades.
Procedures for Monument Delisting:
- The regulations governing the List of Protected Monuments are stipulated under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Rules, 1959.
- This legislation safeguards structures and sites aged over a century, encompassing a diverse array of architectural and historical marvels.
- The government possesses the authority to eliminate certain monuments from the protected list via official notification in the Gazette.
- Through such notifications, the government can declare that certain ancient monuments, archaeological sites, or relics no longer hold national significance under the purview of the AMASR Act (Section 35 of the AMASR Act).
Lost Monuments:
- The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act safeguards monuments and sites aged over a century.
- Nevertheless, numerous structures, particularly smaller or lesser-known ones, have gradually disappeared over time due to factors like urbanization, encroachments, dam and reservoir construction, or neglect.
- In some instances, the lack of public memory hampers efforts to locate these monuments.
Extent of Loss:
- According to a submission by the Ministry of Culture to the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism, and Culture in December 2022, 50 out of India's 3,693 centrally protected monuments were unaccounted for.
- Among these, 14 succumbed to rapid urbanization, 12 were submerged by reservoirs or dams, and the remaining 24 remain untraceable.
- The Committee noted that budget constraints limited the provision of security guards to historical sites, with only 2,578 guards assigned to 248 sites out of the required 7,000.
- Additionally, a 2013 report by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India highlighted the disappearance of at least 92 centrally protected monuments nationwide.
About the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI):
- Founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) was later formalized as a statutory body under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act) following India's independence.
- ASI's primary mandate encompasses archaeological research and the safeguarding, conservation, and preservation of cultural monuments across the nation.
- Its operational scope includes conducting surveys of antiquarian remains, exploring and excavating archaeological sites, and overseeing the conservation and maintenance of protected monuments, among other responsibilities.
- The ASI operates under the purview of the Ministry of Culture.
Chausath Khamba

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Characterized by its marble pillars and intricate latticework, Chausath Khamba (64 pillars) stands adjacent to the Nizamuddin dargah, a 14th-century shrine erected in honor of the revered Sufi saint Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
About the Chausath Khamba:
- Chausath Khamba was built in AD 1623 - 24 to serve as a tomb for Mirza Aziz Koka, the foster brother of Mughal Emperor Akbar.
- It is so called on account of the 64 (chausath) monolithic marble pillars (khamba) and stands close to his father, Atgah Khan’s tomb, at the edge of the Dargah of Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
- The tomb enclosure is entered through a lofty arched gateway and has a large sunken forecourt.
- The mausoleum is unique on account of it being built entirely of marble, with 25 marble domes supporting the flat roof of the structure.
- The plan for Chausath Khamba could have been inspired by the wooden garden pavilions from Persia - such as the Chihil Sutun, and in turn, the Chausath Khamba seems to have inspired the architectural design for Emperor Shahjahan’s Diwan-i-Aam, Hall of Audience.
- Each facade of the square structure has five marble arches inset with marble jaallis or lattice screens and a doorway in the central arch providing access to the tomb.
- The column capitals are intricately carved with simple yet striking pendentives bridging the square floor plan to the circular dome above.
- The structure also finds mention in Sir Gordon Risley Hearn’s book The Seven Cities of Delhi.
- As per author and historian Sam Dalrymple, the edifice embodies the architectural style of Gujarat and Ahmedabad within Delhi, serving as the Urs Mahal for hosting festivities during the commemoration of Nizamuddin's passing.
- This illustrates the historical dissemination of regional architectural influences across India over centuries.
Majuli Island's Mask Craft Celebrated With Geographical Indication Tag

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Adding to their growing national and international recognition, the traditional Majuli masks in Assam were given a Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Centre recently.
What are Majuli Masks?
- These handmade masks are traditionally used to depict characters in bhaonas, or theatrical performances with devotional messages under the neo-Vaishnavite tradition.
- Majuli, the largest river island in the world and the seat of Assam’s neo-Vaishnavite tradition, has been home to the art of mask-making since the 16th century.
- It was introduced by the 15th-16th century reformer saint Srimanta Sankardeva.
- The masks can depict gods, goddesses, demons, animals and birds — Ravana, Garuda, Narasimha, Hanuman, Varaha Surpanakha all feature among the masks.
- They can range in size from those covering just the face (mukh mukha), which take around five days to make, to those covering the whole head and body of the performer (cho mukha), which can take up to one-and-a-half months to make.
- According to the application made for the patent, the masks are made of bamboo, clay, dung, cloth, cotton, wood and other materials available in the riverine surroundings of their makers.
Why is This Art Practiced in Monasteries?
- Sattras are monastic institutions established by Srimanta Sankardev and his disciples as centers of religious, social and cultural reform.
- Today, they are also centers of traditional performing arts such as borgeet (songs), sattriya (dance) and bhaona (theater), which are an integral part of the Sankardev tradition.
- Majuli has 22 sattras, and the patent application states that the mask-making tradition is by and large concentrated in four of them:
- Samaguri Sattra
- Natun Samaguri Sattra
- Bihimpur Sattra and
- Alengi Narasimha Sattra
What is Majuli Manuscript Painting?
- It is a form of painting which also received the GI tag.
- It originated in the 16th century done on sanchi pat, or manuscripts made of the bark of the sanchi or agar tree, using homemade ink.
- The earliest example of an illustrated manuscript is said to be a rendering of the Adya Dasama of the Bhagwat Purana in Assamese by Srimanta Sankardev.
- This art was patronized by the Ahom kings.
- It continues to be practiced in every sattra in Majuli.
IGNCA’s ‘language atlas’ to shine a light on India’s linguistic diversity

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts, an autonomous body under the Union Culture Ministry, proposes to conduct a linguistic survey across the country to create a ‘Language Atlas’ of India.
About the Language Atlas of India:
- The Language Atlas of India traces its roots back to the seminal Linguistic Survey of India (LSI) conducted by Sir George Abraham Grierson, which was first published in 1928.
- Since its inception, the linguistic landscape of India has undergone significant transformations, necessitating a comprehensive reevaluation.
- The proposed linguistic survey aims to capture the myriad languages and dialects prevalent across the country, acknowledging the dynamic nature of linguistic diversity.
- It seeks to document not only the languages and dialects actively spoken but also those that have faced extinction or are teetering on the brink of disappearance.
- Engaging a wide array of stakeholders, including the Ministries of Culture, Education, Tribal Affairs, Home, Social Justice and Empowerment, and Development of the North East Region, the survey endeavours to be inclusive and representative of diverse language communities.
- Phased Approach: The Detailed Project Report (DPR) advocates for a structured approach, commencing with state-wise data collection followed by regional assessments.
- Furthermore, the proposal advocates for the preservation of linguistic heritage through the digital archiving of audio recordings encompassing the linguistic richness of the nation.
- Significance: Languages serve as conduits of communication and repositories of cultural heritage, encapsulating local wisdom, traditions, narratives, and medicinal knowledge.
- For instance, many indigenous communities possess indigenous knowledge of medicinal plants and herbs, which are transmitted through generations via their native languages, emphasizing the intrinsic link between language and cultural preservation.
About the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA):
- Established in 1987 as an autonomous institution under the aegis of the Ministry of Culture, the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) serves as a pivotal hub for research, academic endeavours, and dissemination within the realm of the arts.
- Governance Structure: Operating with a Board of Trustees, the IGNCA convenes regularly to provide overarching guidance and direction for its multifaceted activities.
- Under the stewardship of a Chairman, the Executive Committee, composed of select Trustees, oversees the operational facets of the centre.
- Integral Role in Project Mausam: Embracing its role as a research unit, the IGNCA actively contributes to Project Mausam, a collaborative initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), New Delhi.
- Project Mausam endeavours to explore the intricate tapestry of cultural routes and maritime landscapes that historically linked diverse regions along the Indian Ocean littoral, fostering connections between coastal centres and their hinterlands.
- Engagement in the Vedic Heritage Portal: In alignment with its commitment to cultural heritage preservation, the IGNCA embarks on a project dedicated to designing and developing a Vedic Heritage Portal, under the auspices of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- This portal serves as a digital platform aimed at elucidating the profound messages encapsulated within the Vedas, contributing to the dissemination of ancient wisdom and knowledge.
PM Modi unveils of Sant Ravidas statue in Varanasi on 647th birth anniversary

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently said that the present government is taking forward the teachings and ideals of Sant Ravidas while following the mantra of ‘Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas aur Sabka Prayas’.
Who is Guru Ravidas?
- Guru Ravidass (also Ravidas, Rohidas and Ruhidas in eastern India) was a North Indian Guru mystic of the bhakti movement who was active in the 15th century CE.
- Venerated in the region of Uttar Pradesh as well as the Indian state of Maharashtra, his devotional songs and verses made a lasting impact upon the bhakti movement.
- He is often given the honorific Guru.
- He was a socio-religious reformer, a thinker, a theosophist, a humanist, a poet, a traveller, a pacifist and a spiritual figure before whom even head-priests of Benaras lay prostrate to pay homage.
- His birthday comes every year at Puran Mashi in the month of Magh.
- His mother’s name was Mata Kalsi and his father’s name was Baba Santokh Dass.
- Guru Ravidass was born into a humble family which was considered untouchable as per the social order prevailing at that time in Hindu society.
- He spearheaded the fight against man-made discrimination based on caste, colour or creed and preached the lofty ideas of socialism, secularism, equality and fraternity.
- He taught the lessons of universal brotherhood, tolerance, and the message of loving your neighbour, which got more importance in today’s world.
- Guru Ravidass fulfilled Guru Nanak Dev’s request by donating old manuscripts, which contained a collection of Guru Ravidass’s verses and poems.
- The earliest collection of these poems is available in Sri Guru Granth Sahib.
- It was compiled by Guru Arjan Dev, the fifth Guru of the Sikhs.
- There are 41 verses of Guru Ravidass in the Sikh Holy Book, Guru Granth Sahib.
- Meera Bai, a revered figure in Hindu spiritualism, is said to have considered Guru Ravidas as her spiritual Guru.
- It is said that Guru Ravidass disappeared from the world, leaving behind only his footprints.
- Some believe that Guru Ravidass lived in Banaras during his last days, dying a natural death at the age of 126 years.
Will the ‘Paruveta Festival’ celebrated in Andhra’s Ahobilam get UNESCO recognition?

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
INTACH is striving to obtain UNESCO recognition for the yearly 'Paruveta' festival, emphasising its cultural significance.
About the Paruveta Festival:
- Paruveta Festival, also known as the 'mock hunting festival', is a celebrated tradition at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- It stands out as a symbol of communal harmony, where devotees from various religious backgrounds, including Muslims, come together to offer prayers.
Origin and Significance:
- According to folklore, the festival commemorates Lord Vishnu's incarnation as Narasimha, who married Chenchulakshmi, a tribal girl, symbolising unity across different communities.
- The festival's rituals, typically observed during Vijayadashami or Sankranti, extend for a 'mandala' period of forty days in Ahobilam.
Activities and Customs:
- During the festival, the temple deity is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal villages surrounding Ahobilam for forty days.
- The journey begins with a symbolic act where tribals shoot arrows at the deity's palanquin, signifying protection and reverence.
- Chenchus participated by undertaking 'Narasimha Deeksha', wearing yellow robes and Tulasi Mala, while observing celibacy.
- The temple staff reside in these villages throughout the festival, showcasing the tradition of a casteless society with no traces of untouchability.
Key Points about Chenchu Tribes:
- Geographic Distribution: Chenchu tribes primarily inhabit the hills of southern India, particularly in Andhra Pradesh.
- Additionally, Chenchu communities can be found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Orissa.
- Language and Communication: Their native language, known as Chenchu, belongs to the Dravidian language family.
- While many Chenchu individuals speak Telugu, their traditional language holds cultural significance.
- Livelihood and Occupation: Historically, Chenchu people pursued a nomadic lifestyle, relying on food gathering.
- However, due to factors such as agricultural expansion, many have transitioned to working as farmers or forest labourers.
- Housing and Settlements: Chenchu dwellings are typically hive-shaped structures constructed from wattle thatch, composed of interwoven poles, twigs, reeds, or branches.
- These houses reflect their traditional architectural style and are adapted to their environment.
- Social Structure: Chenchu society is organised into clans, which are extended family units, as well as local groups and individual families.
- They adhere to exogamous marriage practices, prohibiting unions within the same clan.
- Additionally, Chenchu kinship is patrilineal, tracing descent through male lineage.
After 30 years, Buddha relics travel to Thailand

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Four of the 20 relics of Lord Buddha preserved at the National Museum are being taken to Thailand for a month-long exposition beginning recently, in a rare trip abroad for the delicate antiquities recovered more than a century ago.
About the Relics of Lord Buddha:
- The relics of Lord Buddha and his disciples Arahata Sariputra and Arahata Maudgalayana are known as the ‘Kapilvastu Relics.’
- The relics date back to around the 4th or 5th Century BC.
- They were found in Bihar’s Piprahwa — a site that is believed to be the ancient city of Kapilvastu.
- Piprahwa today is located in Uttar Pradesh’s Siddharthnagar district.
- The relics were discovered by a team of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) officials in the 1970s.
- The ASI conducted excavations at Piprahwa from 1971-77 under the supervision of the archaeology director KM Srivastava.
History:
- Lord Buddha achieved Mahaparinirvana at the age of 80 in Kushinagar.
- The Mallas of Kushinagara cremated his body with ceremonies befitting a ‘Universal King’ (‘cakravartin’).
- His holy relics, from the funeral pyre, were collected, divided and given by Brahmin priest Dhona of Kushinagar to kings and priests.
- The eight shares were distributed among Ajatashatru of Magadha, the Licchavis of Vaishali, the Sakyas of Kapilavastu, Mallas of Kushinagar, Bullies of Allakappa, the Mallas of Pava, the Koliyas of Ramagrama and a Brahmana of Vethadipa.
- The sacred relics were commemorated in eight different stupas.
- Two more stupas came into existence, one over the urn in which the relics had been collected and one over the embers.
- Thus, stupas erected over the bodily relics of Buddha (Saririka-stupas) are the earliest surviving Buddhist shrines.
- It is stated that Ashoka (circa 272-232 BC), being an ardent follower of Buddhism, opened up seven of these eight stupas, and collected a major portion of the relics for enshrinement within innumerable stupas built by him to popularise Buddhism and spread dharma.
- In 1898, the discovery of an inscribed casket by William Claxton Peppé, a British colonial engineer and an estate manager at a Buddhist stupa site at Piprahwa, was an epoch-making incident.
- The inscription on the lid referred to the relics of Buddha and his community.
- The bone relics present in the stone coffer were presented to King Rama V of Thailand.
- The relics were further divided into three shares and gifted to Thailand, Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
- In Thailand, the holy relic has been enshrined in a chedi on the top of Suwanbanphot, Bangkok.
- Every year, during the Loi Krathong Festival, there is a seven-day and seven-night celebration, which has become a tradition to worship the Buddha’s relics.
Gold Hunt by Villagers Reveals Ancient Harappan Settlement in Gujarat

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The newly discovered Harappan settlement at Lodrani village in the Kutch region of Gujarat has sparked widespread interest in the fascinating remains of this ancient civilisation, making it an important site for archaeological exploration and research.
Features of Harappan site Morodharo:
- Morodharo is a fortified settlement of the Harappan era, with the fortification measuring 102 m to the west and 58 m north to the south.
- The thickness of the wall is 3.3 m on average.
- Morodhara has a 10x10 m platform on the southwest side and a well on the northeast side.
- Burial cairns have been found at Morodharo.
- A cairn is an intentionally constructed mound of stones, typically created for marking a location or serving as a burial mound.
- Harappan pottery with perforated jar sherds, reserved slipware and terracotta cakes have also been unearthed.
- All these items have a striking resemblance to those found in Dholavira.
About Harappan Civilization:
- The Harappan civilization, also known as the Indus Valley civilization was South Asia's first urban civilization, flourishing concurrently with Mesopotamia and Egypt.
- It encompassed the most extensive territory, covering approximately 800,000 square kilometres, compared to its contemporaries.
- Prominent cities during the Harappan period included Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in present-day Pakistan, along with Dholavira, Lothal, and Surkotada in Gujarat, India, among others.
- Urban planning in Harappan cities followed a meticulous grid layout, with streets intersecting at right angles, dividing the cities into neat rectangular blocks.
- The streets and alleys were deliberately designed for efficient movement, accommodating carts and pedestrians, often featuring covered drains alongside.
- For defence and security, the cities were enclosed by sturdy walls made of mud bricks, shielding against intruders and natural calamities.
- Each city was structured into an elevated citadel and a lower town, with the former housing monumental structures like granaries and administrative buildings.
- Residential areas comprised multi-story brick houses clustered around courtyards, some equipped with private wells and well-ventilated bathrooms.
- A sophisticated drainage system ensured efficient waste disposal, with individual house drains connected to street-level drainage networks.
- Granaries and storage facilities were strategically positioned to manage surplus agricultural yields, reflecting advanced urban planning and resource management.
First Prehistoric Pictorial Cave Art Found in Madagascar Offers Clues Regarding Ancient Connections Between Borneo, Egypt (The Hindu)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, distinctive prehistoric rock art depictions were unearthed within the Andriamamelo Cave in western Madagascar.
Key Discoveries:
- Within this cave's truly pictorial art, human-like and animal-like figures depicting scenes from nature have been revealed.
- The remarkable findings unveiled surprising cultural connections, with some scenes directly linking to Egyptian religious motifs from the Ptolemaic period (300-30 BCE).
- Additionally, symbols and inscriptions on the cave walls indicated connections to the Ethiopian and Afro-Arab regions.
- Furthermore, the prevalent symbology and motifs echoed a cave art style from Borneo dating back two millennia.
- Notably, depictions within the cave may include three extinct animals of Madagascar — a giant sloth lemur, an elephant bird, and a giant tortoise.
- The potential connection to Egypt is suggested by eight significant images, including representations of a falcon (Horus), the bird-headed god Thoth, the ostrich goddess Ma`at, and two human-animal figures resembling Anubis, the ancient Egyptian god typically portrayed with a canine head.
About Andriamamelo Cave:
- The Andriamamelo Cave is situated in western Madagascar, nestled within the karstified limestone of the Paysage Harmonieux Protege de Beanka.
- This cave is a component of a vast karst region that encompasses the UNESCO World Heritage site, Parc National de Bemaraha, to the south, and the less-explored Antsingimavo karst area to the north.
Tamil Lambadi Embroidery (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For almost 60 years, the Porgai Artisan Association Society has been producing and distributing embroidered clothing in an effort to raise awareness of the art form and ensure that it is passed down to future generations.
About Tamil Lambadi Embroidery:
- The Lambadi community has a long-standing tradition of practising Lambadi embroidery.
- This craft is used to embellish their clothing and household items and it holds significant cultural and identity value for the Lambadis.
- Traditionally, Lambadi women use colourful cotton threads to create intricate embroidery on cotton and silk fabrics.
- Embroidery Designs: The traditional Lambadi embroidery designs are characterized by geometrical patterns, including squares, rectangles, and circles.
- These designs have also been influenced by elements from the local environment, such as forests, birds, fruits, and flowers.
Facts About the Lambadi Community:
- They are also known as Lambadis or Banjaras.
- Historically they are nomadic tribes, originating from Afghanistan and settling in regions including Rajasthan, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- They also assisted Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in transporting goods in the 17th century.
- Speak 'Gor Boli' or 'Lambadi,' which is often written in Devanagari or local languages.
- Many members of the Lambani community are bilingual or multilingual to communicate in the predominant language of their region in India.
- The elderly women within the Lambadi community continue to wear the Petia, a traditional five-piece dress.
- The Petia is made using Mushru silk from Kutch, showcasing the enduring connection to their heritage and craftsmanship.
Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh’s Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases (Times now)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister presented Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases to Greek President and Prime Minister.
Facts About:
Meghalaya shawls
Meghalaya shawls were originally woven for Khasi and Jaintia royalty who considered them a symbol of their power and status.
Shawls were worn at formal events and festivals, and their intricate designs and vibrant colors reflected the wealth and prestige of the royal family.
The designs used in Meghalaya shawls were very symbolic.
- For example, the use of animal motifs such as tigers and elephants was a symbol of strength and power, while the use of floral motifs was a symbol of beauty and grace.
- The weavers, mostly women, spend hours weaving intricate designs and patterns using traditional weaving techniques.
- The shawls are made from local wool and natural colors.
- Shawls are highly valued for their fine workmanship and intricate designs.
Dhokra Art of Chhattisgarh
One of the earliest manifestations of this ancient art is the dancing girl object found in the excavations at Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa.
Traditionally, the Gadwads, Gonds and Dhurwas tribes of Chhattisgarh practice the art of Dhokra using the lost wax technique or hollow casting.
It is named after the Dhokar Damar, an Indian tribe in the central and eastern part of the country.
Common themes in Dhokra art revolve around Hindu gods and goddesses and various animal figures.
Dhokra Art is a non-ferrous metal casting art that uses wax casting technology.
This type of metal casting has been used in India for over 4000 years and is still used today.
There are two main processes involved in lost wax casting: solid casting and hollow casting.
Bidri Art vases
It originated from the city of Bidar in Karnataka in the 14th century.
Bidar in Karnataka and Hyderabad in Telangana are the most active centers of the art form.
Bidri Work handicraft is the art of inlaying metal alloys.
The soil of Bidar Fort magically gives black color to the base metals and the art form has been given the prestigious GI status.
Technique: For smelting, a new mold must be made, into which molten metal, an alloy of zinc and copper, is poured.
- Patterns are drawn on them and carved with a chisel and hammer.
- The engravings are attached with silver wire.
- This contrast of shiny silver with black metal is unique in Bidri art.
Source: https://www.timesnownews.com/india/meghalaya-shawl-to-telangana-vase-what-pm-modi-gifted-to-his-greek-counterpart-article-103065689
