Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Odisha has become the 34th state to implement the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The National Health Authority (NHA) of the Union Ministry of Health signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Odisha to onboard the state under the scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme will be implemented alongside the existing Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana in Odisha.
- It provides health coverage of Rs. 5 lakh per family per annum, with an additional Rs. 5 lakh for women members.
- Approximately 1.03 crore families will be covered under the scheme.
- Shri JP Nadda, Union Health Minister, emphasized that the scheme is the world’s largest and fastest-growing health coverage initiative.
- Shri Mohan Charan Majhi, Chief Minister of Odisha, highlighted that people will now have access to cashless treatment in over 29,000 empaneled hospitals.
About Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY:
- Launched in 2018 under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoH&FW).
- Targets 12 crore families (~55 crore beneficiaries).
- Provides cashless hospital coverage for secondary and tertiary care.
- Fully funded by the government, with cost-sharing between the Centre and states.
- Covers nearly 2,000 medical procedures, including major surgeries.
Since its inception, over 8.19 crore hospital admissions have been recorded, with ?1.13 lakh crore spent on healthcare for marginalized sections.
Cyclone Dikeledi
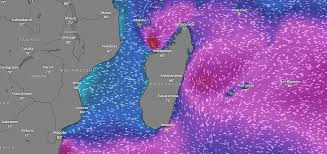
- 15 Jan 2025
Cyclone Dikeledi struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, located in the Mozambique Channel. The cyclone caused severe flooding and damage, following closely after Cyclone Chido, which had hit the region in December 2024.
About Mayotte:
- Comprises two islands from the Comoros archipelago: Mayotte (Grande Terre) and Pamandzi (Petite Terre).
- It is the poorest region in both France and the European Union.
- Colonized by France in 1843 and annexed along with the Comoros in 1904.
- In a 1974 referendum, while 95% of Comoros opted for independence, 63% of Mayotte voted to remain French.
- While Comoros declared independence in 1975, Mayotte continues to be governed by France.
Cyclone Chido, which struck in December 2024, was recorded as the most severe storm to hit Mayotte in 90 years.
Twigstats

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The tracing of genetic ancestry remains a challenging task due to the statistical similarity among populations across geographical regions. However, recent advances in genetic analysis, particularly the development of the Twigstats tool, are significantly enhancing our ability to reconstruct genetic histories at a very high resolution.
Key Insights from Genetic Research:
- Ancient DNA (aDNA): Prehistoric human ceremonial burials, mass grave mounds, and war graves are rich sources of ancient genetic material, offering key insights into population dynamics. These samples help us understand past migrations, cultural transitions, and the genetic legacy of ancient groups.
- Challenges in Ancestry Tracing:
- Populations often share many genetic similarities, complicating the task of tracing ancestry across regions.
- Ancient DNA samples are typically of lower quality compared to modern samples, limiting the precision of past genetic studies.
- The movement of genes across time and space, through processes like gene flow, adds complexity to the understanding of population ancestry.
Traditional Genetic Techniques:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Used to identify natural genetic variations, SNP analysis has been central to reconstructing genetic histories. However, it is limited by its reliance on high-quality samples and struggles with closely related groups.
- Haplotypes and Genealogical Trees: By analyzing shared DNA segments (haplotypes) and rare variants, researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of population structure and ancestry, which can reveal shifts in population over time.
The Emergence of Twigstats:
- What is Twigstats?
- Twigstats is an advanced analytical tool that enhances the precision of ancestry analysis through time-stratified ancestry analysis, a method that allows for a more fine-grained look at genetic data.
- It is designed to address the limitations of traditional methods by integrating SNPs, haplotypes, and rare genetic variants, providing a more holistic view of ancestry.
- The tool is powered by statistical languages R and C++, which help researchers better manage and analyze complex genetic data.
- How It Works: Twigstats builds family trees by analyzing shared genetic mutations, identifying recent mutations that offer a clearer understanding of historical periods and events. It helps trace the evolution of populations and offers insights into their migrations, mixing, and cultural shifts.
Key Features and Impact of Twigstats:
- Time-Stratified Ancestry Analysis: Allows researchers to study how populations evolved over time, with a focus on specific historical periods.
- Enhanced Precision: Reduces statistical errors and enhances the precision of individual-level ancestry reconstruction.
- Higher-Resolution Mapping: Provides high-resolution genetic maps of migration patterns and admixture events across centuries.
Applications of Twigstats:
- Historical Case Studies: The tool has been used to study ancient genomes from Europe, particularly the Iron, Roman, and Viking Ages (500 BC to 1000 AD). It revealed the fine-scale genetic history of populations in regions like northern and central Europe, including the movement of Germanic and Scandinavian peoples.
- Viking Age Insights: Researchers were able to trace the early presence of Scandinavian-like ancestry in regions such as Britain and the Baltic before the traditionally believed start of the Viking Age. This suggests earlier interactions and migrations from Scandinavia, which aligns with historical records of Anglo-Saxon and Viking movements.
- Cultural Transitions: The analysis identified shifts in population genetics corresponding to cultural changes, such as the shift from the Corded Ware culture to the Bronze Age and the influence of the Wielbark culture.
Genetic Methods Used in the Study:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Commonly used to trace ancestry but requires high-quality samples.
- Haplotypes and Rare Variants: Offer more nuanced insights into population movements by considering combinations of genetic markers inherited together.
- Genealogical Tree Inference: Applied to both ancient and modern genomes, it provides detailed demographic and ancestry information, supporting the reconstruction of high-resolution genetic histories.
Case Study: India’s Genetic History (2009 Study)
- Researchers used SNP analysis to trace the genetic history of India, revealing two major ancestral groups:
- Ancestral North Indians (ANI): Genetically closer to Central Asian, European, and Middle Eastern populations.
- Ancestral South Indians (ASI): A distinct genetic group, showcasing India’s diverse population structure.
India’s First Organic Fisheries Cluster

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Minister, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for 50 key projects worth Rs. 50 crores under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) covering all North East Region States Except Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Key Highlights:
- Initiative: India’s first Organic Fisheries Cluster, launched under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY). The cluster focuses on sustainable aquaculture, promoting the production of antibiotic, chemical, and pesticide-free organic fish.
- Target Markets: Eco-conscious domestic and global markets.
Sikkim's Role as India’s First Organic State:
- Sikkim's Organic Commitment: Sikkim is the first Indian state to embrace 100% organic farming, covering 75,000 hectares of land.
- Vision: The Organic Fisheries Cluster aligns with Sikkim’s broader goal of promoting organic, sustainable agricultural practices.
Objective of Organic Fisheries Cluster:
- To prevent pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems by using ecologically healthy practices.
- Promotes sustainable fish farming methods, reducing environmental damage.
- Focus on species like amur carp and other carp varieties, aligning with the state’s success in organic farming.
Support from NABARD:
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) will provide financial and technical assistance.
- Key support includes:
- Infrastructure development.
- Formation of Fisheries-based Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs).
- Capacity building of local fishers and farmers.
PMMSY: A Comprehensive Fisheries Development Scheme:
- Investment: ?20,050 crore under PMMSY.
- Objective: To revolutionize India’s fisheries sector by promoting sustainable growth, enhancing fish production, and improving infrastructure.
- Implementation Period: FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- Key Goals:
- Boosting fish production and exports.
- Enhancing welfare of fishers and farmers.
- Promoting cluster-based development for better efficiency and competitiveness.
Cluster-Based Approach in Fisheries:
- Objective: To bring together geographically connected enterprises to enhance economies of scale.
- Impact: This approach improves financial viability, strengthens the fisheries value chain, and creates new business and livelihood opportunities.
- Types of Clusters: Includes Pearl, Seaweed, Ornamental Fisheries, Cold Water Fisheries, Organic Fisheries, and more.
Fisheries Focus in the North Eastern Region (NER):
- Fisheries Potential: The North Eastern Region (NER) has abundant freshwater resources and is a biodiversity hotspot.
- Growth: Inland fish production in the NER surged from 4.03 lakh tonnes (2014-15) to 6.41 lakh tonnes (2023-24), marking an impressive 5% annual growth.
- Investment in NER: Over ?2,114 crore invested through schemes like Blue Revolution and PMMSY.
- Key Projects:
- 50 projects worth ?50 crore to boost the region’s fisheries infrastructure, generating over 4,500 jobs.
- Projects include hatcheries, cold storage units, aquaculture parks, and fish kiosks.
India’s Global Fisheries Standing:
- India is the second-largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to global fish production.
- Top Rankings:
- Second in aquaculture production.
- Leading in shrimp production and exports.
- Third in capture fisheries.
Government Commitments and Schemes:
- Total Investment: Since 2015, the government has committed ?38,572 crore to fisheries development through key schemes like:
- Blue Revolution.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
- PMMSY.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- These initiatives aim to promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and enhance infrastructure in the fisheries sector.
Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits:
- Economic Impact:
- Higher incomes for fishers and farmers through better production and export.
- Employment generation through infrastructure development.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced pollution and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- Social Impact: Empowerment of local communities, fostering sustainable livelihoods.
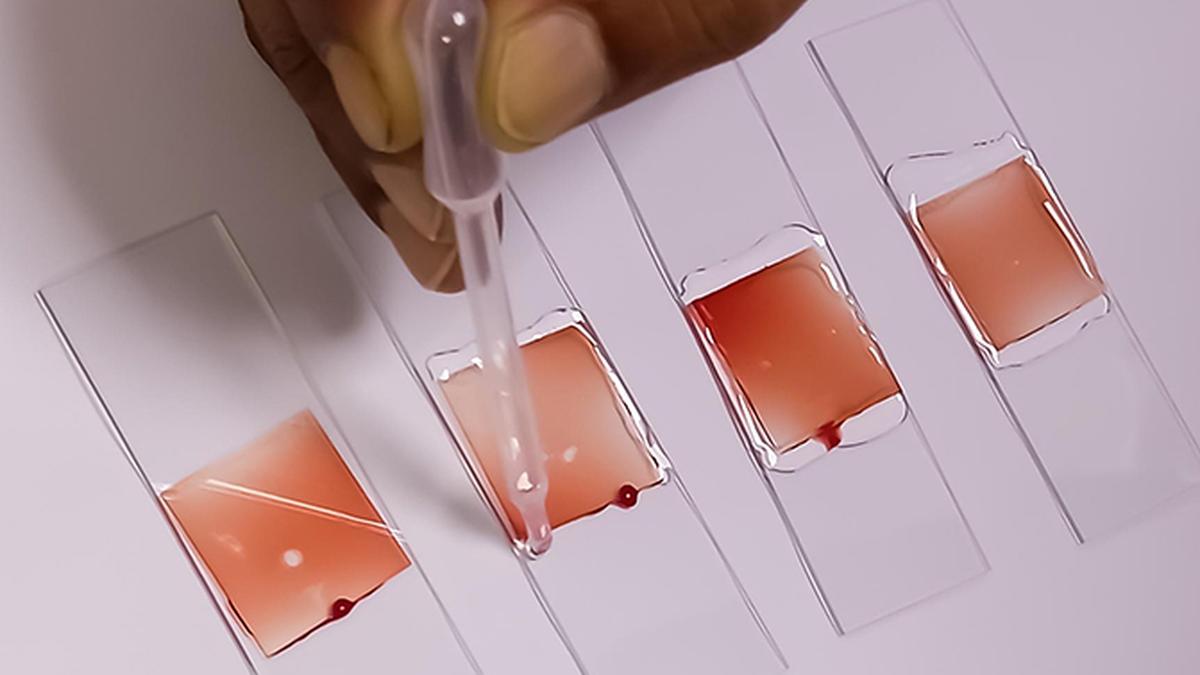
AnemiaPhone

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
AnemiaPhone, a technology developed by Cornell University researchers to accurately, quickly, and cheaply, assess iron deficiency, has been transferred to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for integration into its programmes for anaemia, women’s health, and maternal and child health throughout the country.
Key Highlights:
- Technology Features:
- Portable, Rapid, and Affordable: AnemiaPhone is designed to detect iron deficiency efficiently at low cost.
- Requires a fingerstick (small blood sample).
- Results are available within minutes.
- Wireless: Data uploaded to a clinical database via mobile, tablet, or computer.
- Can be used by healthcare workers to assess iron deficiency on the spot and take action (guidance, triage, referral).
- Working Mechanism:
- A drop of blood is placed on a test strip.
- The reader processes the sample.
- Data is uploaded for immediate diagnosis and action.
- Test results assist in on-the-spot intervention by healthcare workers.
Anaemia and Iron Deficiency:
- Prevalence in India:
- Iron deficiency is a leading cause of anaemia.
- 50%-70% of pregnant women in India suffer from anaemia.
- 59% of women and 47% of children (6-59 months) in India suffer from anaemia (NFHS data).
- Consequences of Anaemia:
- Fatigue, dizziness, organ failure, complications in childbirth, and in severe cases, death.
- Contributes to higher maternal and child mortality rates in India.
- Impact on Health in India:
- India has one of the highest rates of anaemia in the world.
- Iron deficiency is a significant contributor to maternal deaths.
ICMR's Role and Integration into National Programs:
- ICMR and AnemiaPhone:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has integrated AnemiaPhone into its Anaemia Mukt Bharat (Anaemia-Free India) program.
- The program focuses on eliminating anaemia by 2025 through screening, diagnosis, and treatment in women and children, especially in remote areas.
- Transfer of Technology:
- In November 2024, Cornell University transferred the technology to ICMR for free.
- This collaboration aims to improve health outcomes by sharing innovative health technologies.
Advantages of AnemiaPhone:
- Cost-Effective and Portable:
- Low-cost compared to traditional lab tests.
- Portable and can be used in remote and underserved areas.
- Quick Diagnosis: Results are processed in minutes, allowing healthcare workers to act without delay.
- No Need for Expensive Labs:
- Can be used at primary health centers or in door-to-door health surveys.
- Facilitates healthcare in rural or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Wireless and Easy to Use: The device is user-friendly and does not require extensive training.
Impact on Healthcare System:
- Improvement in Accessibility:
- Helps reduce the need for people to travel long distances for diagnosis, especially in rural areas.
- Ensures early diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency and anaemia.
- Enhancing Maternal and Child Health: AnemiaPhone will contribute to reducing maternal and child mortality rates linked to anaemia.
Technology Testing and Development:
- Testing in India:
- AnemiaPhone has been tested in India and has shown accurate results in diagnosing iron deficiency.
- Single-use test strips help ensure accuracy and prevent contamination.
Global Health Context:
- Global Prevalence of Anaemia: More than 2 billion people worldwide suffer from anaemia, particularly pregnant women and young children.
- WHO’s Role: The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies anaemia as a major global health issue.
Sonobuoys

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
India and the U.S. have announced cooperation on the co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy. This technology is vital for tracking submarines and strengthening defense capabilities, particularly in the Indian Ocean region amidst growing Chinese naval presence.
This partnership is a key step in deepening defense cooperation under the U.S.-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), launched in May 2022, and will contribute to strengthening both countries’ defense industrial bases.
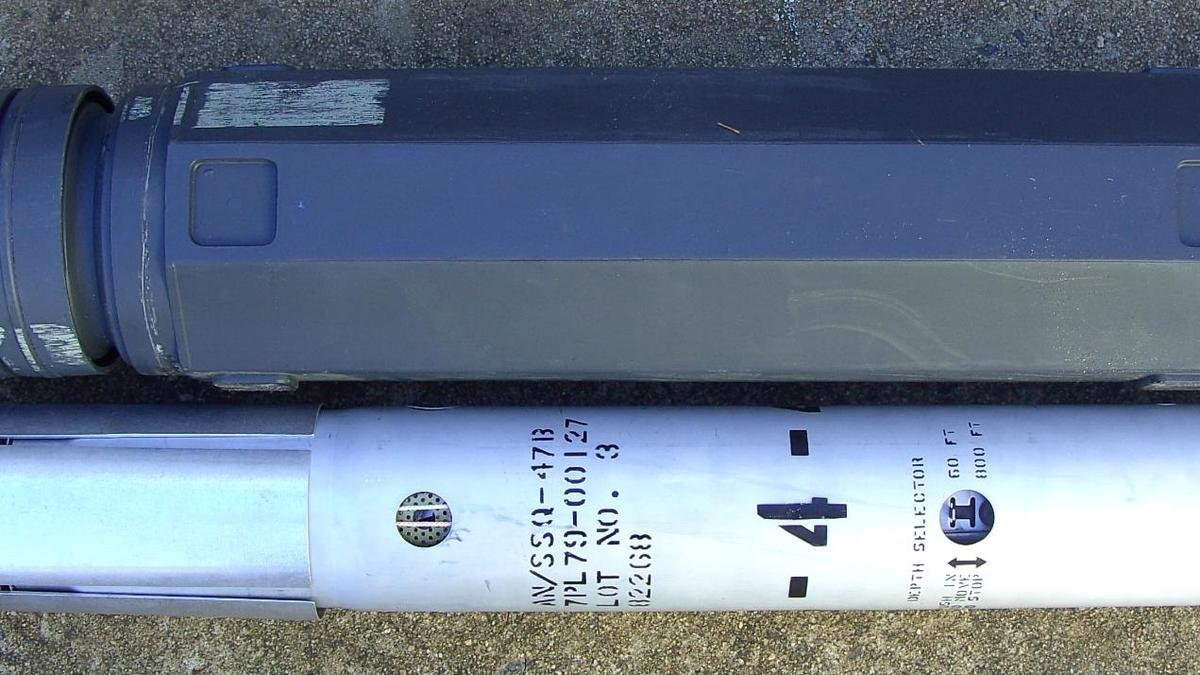
About Sonobuoys
- What They Are:
- Sonobuoys are expendable sonar devices used for anti-submarine warfare and underwater acoustic research.
- Typically, small (13 cm in diameter and 91 cm in length), they are designed for deployment from aircraft or ships to detect submarines in deep waters.
- Working Principles:
- Deployment: Dropped from aircraft or ships, they activate upon water impact.
- Surface Float: Equipped with inflatable floats and radio transmitters to communicate with tracking platforms on the surface.
- Sensors: Hydrophones descend to selected depths, capturing underwater acoustic signals.
- Data Communication: Transmit acoustic data via Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radios to operators on aircraft or ships.
- Types of Sonobuoys:
- Active Sonobuoys: Emit sound energy and receive echoes, transmitting the data back to operators.
- Passive Sonobuoys: Only listen for underwater sounds from submarines or ships and relay the information back.
- Special Purpose Sonobuoys: Measure environmental data like water temperature and ambient noise.
- Other Applications:
- Beyond anti-submarine warfare, sonobuoys are used for environmental research, including studying marine life such as whales.
Co-production of Sonobuoys: India-U.S. Collaboration
- Manufacturing Agreement:
- Ultra Maritime (U.S.) and Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) have entered into discussions to co-produce U.S. sonobuoys, in line with India’s "Make in India" initiative.
- The production will follow U.S. Navy standards, with manufacturing split between the U.S. and India.
- The focus will also be on developing bespoke technologies to optimize sonobuoy performance in the unique acoustic environment of the Indian Ocean.
- Interoperability:
- The sonobuoys co-produced in India will be interoperable between U.S. Navy, Indian Navy, and allied aircraft such as P-8, MH-60R, and MQ-9B Sea Guardian.
- This ensures seamless integration and compatibility with naval assets from the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, especially given the Quad's strategic naval exercises like Malabar.
- Production Location:
- The sonobuoys will be manufactured at BDL's facilities in Visakhapatnam, with a focus on meeting the Indian Navy’s operational demands.
Strategic and Defense Context
- U.S. and Indian Naval Cooperation:
- India has increasingly acquired military platforms from the U.S., such as the P-8I maritime patrol aircraft, MH-60R helicopters, and MQ-9 drones. These assets are also used by other Quad nations like Australia and Japan, highlighting the importance of interoperability and shared defense capabilities in the region.
- Enhanced Maritime Domain Awareness:
- With China’s growing naval presence in the Indian Ocean, the cooperation on sonobuoys aligns with India’s strategic priority of enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA), which are critical for national security.
- Future Plans:
- India has also signed a $3.5 billion contract for 31 MQ-9B drones, enhancing its surveillance capabilities for maritime and other defense applications. Deliveries of these drones will begin in 2029, further boosting India’s defense readiness in the region.
Disposal of Toxic Waste from Union Carbide Factory (Bhopal)

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The Madhya Pradesh government has begun disposing of the 337 tonnes of toxic waste from the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) in Bhopal, 40 years after the gas tragedy.
Key Highlights:
- Packing and Transportation:
- Waste is packed in airtight containers under the supervision of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board (MPPCB).
- 12 specially designed airtight containers are being used for packing, and each container will be loaded onto trucks for transport.
- The waste movement will be escorted with a green corridor of about 250 kilometers.
- Incineration Process:
- The waste will undergo incineration in Pithampur, with residue stored in a two-layer membrane landfill to prevent contamination.
- A trial incineration of 10 tonnes of the waste was done in 2015 with no harmful effects, and results were submitted to the High Court.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy: A Historical Overview
- About the Tragedy:
- In 1984, a chemical leak at the Union Carbide pesticide plant released methyl isocyanate (MIC), leading to one of the worst industrial disasters in history.
- The leak was caused by a failed maintenance attempt and malfunctioning safety systems.
- Immediate effects included respiratory issues, eye problems, and abdominal pain, while long-term effects included chronic lung conditions, genetic abnormalities, and higher infant mortality rates.
- Legal and Government Response:
- In 1985, the Indian government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster Act to represent victims in legal claims.
- UCIL initially offered USD 5 million, while the Indian government demanded USD 3.3 billion. The case was settled in 1989 for USD 470 million.
- In 2010, seven Indian nationals were convicted for causing death by negligence, but were released on bail.
Hazardous Waste Management in India
- Definition and Types:
- Hazardous waste refers to waste that poses significant risks due to toxicity, reactivity, or corrosiveness.
- Common sources include chemical production, outdated technologies, and wastewater treatment.
- Regulations and Disposal Methods:
- The Environment Protection Act (1986) and the Basel Convention (1992) govern hazardous waste management in India.
- India generates about 7.66 million tonnes of hazardous waste annually, with the majority being landfillable (44.3%) and recyclable (47.2%).
- Disposal methods include incineration, co-processing in cement plants, and material/energy recovery.
- Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management:
- Inadequate treatment technologies, especially in small and medium industries.
- The need for stricter compliance with waste management laws and more efficient remediation of hazardous sites like Bhopal.
Great Nicobar Island Development Project
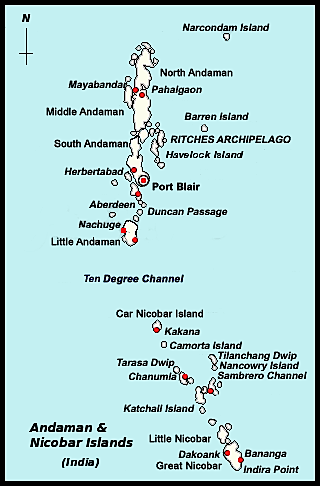
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
An international cruise terminal to facilitate a “global” port-led city, “high-end” tourism infrastructure, and a ship-breaking yard are among the new additions to the ?72,000 crore mega-infrastructure project in Great Nicobar Island proposed by the Union Shipping Ministry.
Overview of the Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island Development Project is a ?72,000-crore initiative to transform the southernmost island of India into a hub for defense, logistics, commerce, eco-tourism, and infrastructure development.
- It is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd (ANIIDCO) over 16,610 hectares of land.
- The project includes multiple components like an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), an international airport, greenfield cities, a mass rapid transport system, and a free trade zone.
Key Proposed Developments:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): To make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: To improve connectivity and serve as a strategic airport.
- Greenfield Cities: New urban settlements to support the infrastructure.
- Coastal Mass Rapid Transport System: An advanced transportation network along the coast.
- Free Trade Zone: To facilitate international trade activities.
- International Cruise Terminal (new addition): To attract global tourists and facilitate cruise tourism.
- Ship Breaking Yard (new addition): To establish a facility for ship building and breaking.
Geographical and Ecological Context:
- Great Nicobar Island is the largest island in the Nicobar group, located at the southern tip of India. It is covered in rainforests and hosts diverse species, including endangered ones like the leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode.
- The island's ecosystem is rich in biodiversity, with extensive mangroves, coral reefs, and rainforests.
Significance of the Project:
- Geo-strategic Importance: The island’s location near the Malacca Strait offers a strategic maritime advantage, enhancing India’s global maritime presence.
- National Security: With increasing Chinese influence in the region, the project aims to strengthen India's maritime security.
- Economic Growth: The ICTT and other infrastructure will boost economic activities, making the region a vital trade hub.
- Job Creation: The development will lead to numerous job opportunities for locals, especially in sectors like tourism, ports, and transport.
- Tourism Development: With eco-tourism at its core, the project is expected to generate substantial income through tourism, improving the local economy.
- Social Infrastructure: It will lead to improvements in healthcare, education, and digital services through initiatives like telemedicine and tele-education.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Donald Trump threatened to take back the Panama Canal, calling the transfer treaty “foolish”.
Why Trump Called the Panama Canal Transfer 'Foolish'?
- Transit Fees:
- Trump expressed frustration over high transit fees imposed by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP) on U.S. vessels.
- In 2023, due to droughts affecting Lakes Gatun and Alhajuela (which are crucial for canal operations), the ACP reduced crossing slots by 36%, leading to an increase in transit fees for ships.
- Chinese Presence:
- Trump is also concerned about the growing Chinese influence in the Panama Canal region.
- In 2017, Panama became the first Latin American country to sign a Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) agreement with China, increasing Chinese investments.
- Hutchison Ports PPC, a subsidiary of a Hong Kong-based company, operates ports near the canal, raising concerns over China's influence on logistical operations and potential surveillance capabilities.
The Torrijos-Carter Treaties and Canal Transfer:
- Panama Canal Treaty (1977):
- The treaty transferred control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by December 31, 1999.
- The U.S. would no longer control the canal, and Panama would assume full responsibility for its operation and defense.
- Permanent Neutrality Treaty (1977):
- Declared the canal to be neutral and open to vessels of all nations.
- U.S. Right to Defense: The U.S. retained the right to defend the neutrality of the canal and had priority passage in case of military emergencies.
Panama’s Response to Trump’s Criticisms:
- Defense of Transit Rates:
- President José Raúl Mulino rejected Trump’s claims, defending the transit fees as being in line with international standards and based on a transparent procedure.
- Sovereignty:
- Mulino emphasized Panama’s sovereignty over the canal, asserting that Panama’s control over the canal was non-negotiable. He categorically denied the presence of Chinese soldiers in the canal, stating that there would never be any.
China’s Response:
- China's Position:
- China's Foreign Ministry responded by emphasizing that the Panama Canal is a neutral passageway, a vital infrastructure for Panama and the global trade system.
- China affirmed its respect for Panama's sovereignty and denied any military presence in the canal area.
Implications and Future:
- Diplomatic Tensions:
- The issue of transit fees and foreign influence, particularly China's presence in the region, is likely to remain a point of diplomatic negotiation.
- Panama is expected to assert its sovereignty and seek international support to prevent any external interference in the canal’s operations.
- U.S. Influence:
- The U.S. might attempt to renegotiate terms related to the Panama Canal's operations, especially concerning transit fees and military rights, although Panama remains firm on maintaining control.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties:
- Significance:
- Panama Canal Treaty and Permanent Neutrality Treaty marked a major shift in U.S.-Latin America relations, ending U.S. control and restoring Panamanian sovereignty.
- The treaties also ensured the neutrality of the canal while maintaining U.S. military access in emergencies.
- Impact:
- The treaties were a symbol of Panama’s regained sovereignty and played a key role in stabilizing relations between the U.S. and Panama, as well as resolving tensions over control of the canal.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
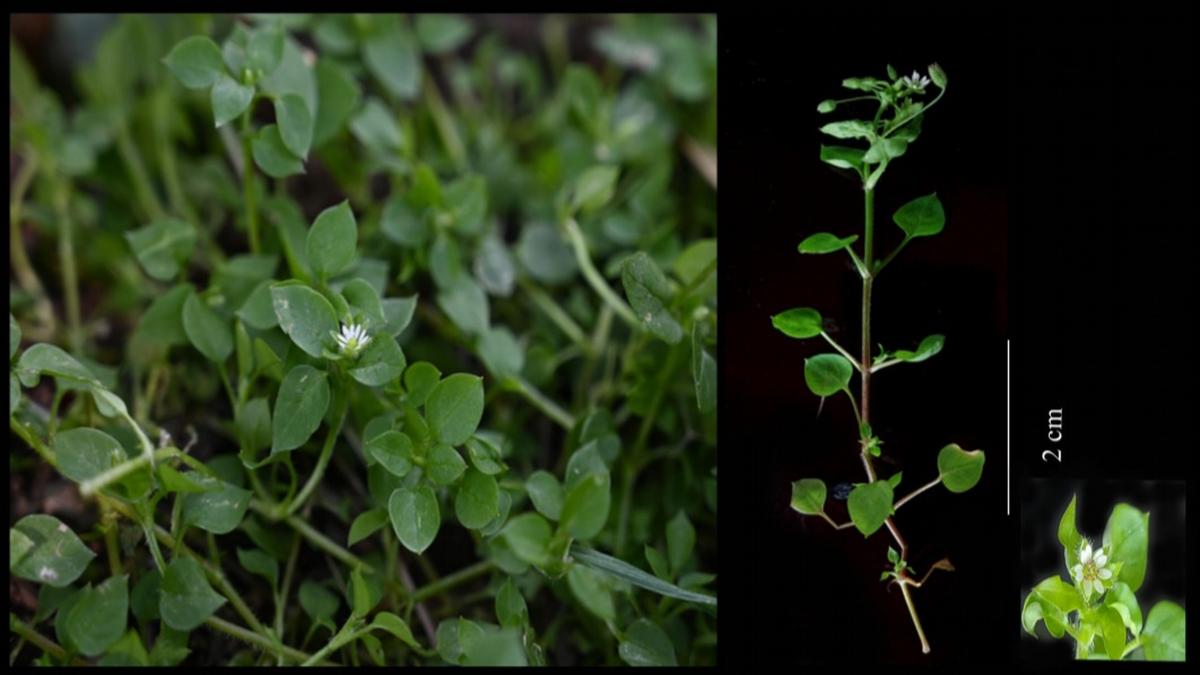
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
ASI Discovery at Srisailam Temple

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) uncovered ancient copper plates and gold coins at the Srisailam Temple in Andhra Pradesh, specifically in the Ghantamandapam area.
- The discovery includes 20 sets of copper plates, totaling 72 leaves, and various gold coins.
- The ASI's Epigraphy Branch in Mysore has completed the documentation of these findings, and the materials are being studied in detail.
Collaboration with Srisailam Devasthanam:
- In collaboration with the Srisailam Devasthanam, ASI plans to publish a book that will detail the findings and their historical significance.
- The book will be printed soon by Pragati Publications in Hyderabad.
Srisailam Temple Overview:
- The Srisailam Temple, also known as the Mallikarjuna Swamy Temple, is a prominent Hindu pilgrimage site in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is located in the Nallamala Hills, overlooking the Krishna River.
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva in the form of Mallikarjuna Swamy and Goddess Parvati as Bhramaramba Devi.
- It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva and one of the Shakti Peethas, making it significant in both Shaivism and Shaktism.
Architectural Significance:
- The temple is built in the Dravidian style, featuring lofty towers and expansive courtyards, and is considered a prime example of Vijayanagara architecture.
- Historical references to the temple date back to the Satavahana period (2nd century AD), and the temple was further endowed by the Kakatiyas and Vijayanagara rulers.
Cultural and Religious Importance:
- The Srisailam Temple is unique for housing both a Jyotirlinga (Lord Shiva) and a Shakti Peetha (Goddess Bhramaramba), a rare combination not found at other temples.
- The great religious figure Adi Shankaracharya is believed to have visited the temple and composed the Sivananda Lahiri there.
Historical Context:
- The copper plates and inscriptions discovered are likely to provide valuable insights into the historical and cultural significance of the temple, as well as the region's ancient religious practices.
Reassessment of Conjugal Visits in Delhi Prisons

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi government is reassessing the proposal to permit conjugal visits for prisoners, following the suspension of a similar initiative in Punjab.
- Delhi Chief Minister has sought further input from the Law Department and explored if similar schemes are implemented in other states.
Conjugal Visits - Definition & Context:
- Conjugal visits involve allowing prisoners to spend private time with their legal partners or spouses, including intimate relations, within prison premises.
- No national policy exists in India for conjugal rights of prisoners, leading to varied implementations across states.
Punjab’s Pilot Project - ‘Parivar Mulakat’:
- Ludhiana Central Jail introduced the 'Parivar Mulakat' programme in September 2022, allowing face-to-face meetings with family in designated rooms.
- The initiative was suspended shortly after its launch due to security concerns, particularly difficulty in conducting thorough body checks on visitors.
Challenges in Delhi:
- Overcrowded prisons in Delhi make it challenging to manage the logistical demands of conjugal visits, especially with up to 1,200 daily visitations.
- The Home Department has received proposals but no progress has been made over the past year.
Legal Precedents on Conjugal Rights:
- Punjab and Haryana High Court (2014) ruled that prisoners have a right to conjugal visits to facilitate procreation.
- Madras High Court (2018) allowed a life convict on parole for conjugal relations, and in 2023, a judge called for similar considerations for Tamil Nadu.
Human Rights Argument:
- Advocates argue that denying conjugal visits to prisoners violates basic human rights of both prisoners and their spouses, particularly those aged 21-50, who are often in sexually active years.
- Amit Sahni, a social activist, filed a PIL highlighting that most prisoners in Delhi are denied conjugal rights despite their eligibility.
Government’s Position:
- Delhi DG (Prisons) had argued that temporary leave such as parole and furlough serve the purpose of family ties, questioning the need for conjugal visits within prison.
Need for Legal Framework:
- Legal experts suggest the creation of a law and policy framework to regulate conjugal visits, ensuring clear guidelines for their implementation.
- S.D. Singh, a Supreme Court advocate, emphasized that conjugal visits should be legally recognized as a right, requiring formal legislation for consistent implementation.
Future Considerations:
- The Delhi government’s reassessment may lead to a policy that considers both human rights and security concerns in its decision on conjugal visits.
Re-emergence of the Dodo in Kashmir’s Papier Mâché Craft
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
Artisans in Srinagar, Kashmir, have revived the extinct dodo bird in papier mâché forms. These figurines are exported worldwide, particularly to Mauritius and Europe, ahead of the Christmas season. Over 50,000 dodo figurines have already been sent to international markets in 2024.
Key Highlights:
The Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus.
- Extinct Since: 1681, approximately 80 years after humans began interacting with them.
- Endemic to Mauritius: A flightless bird from the Indian Ocean island of Mauritius, a national symbol of the country.
- Extinction Causes: Overhunting and the introduction of invasive species like rats, pigs, and cats that preyed on their eggs.
- Physical Traits: Grey or brown plumage, about 3 feet tall, flightless and fearless.
Papier Mâché Craft in Kashmir:
- History: Practiced for over 600 years in Kashmir, introduced during the reign of King Zain-ul-Abidin (15th century).
- Techniques: Involves creating decorative objects using paper pulp, with traditional Persian motifs.
- Recent Addition of Dodo: The dodo was introduced to the papier mâché craft around two decades ago, likely by Mauritian tourists.
International Market and Demand:
- Mauritius: A significant market for the papier mâché dodo, as the bird is a national emblem of Mauritius.
- Europe: Exported to European countries during the Christmas season, contributing to the popularity of Kashmir’s handicrafts.
- Kashmir's Karkhanas: Local craft workshops in Srinagar are producing thousands of dodo figurines each season, with over 3,000 dodos produced this year.
Cultural and Economic Impact:
- Artisans' Contribution: Local artisans are helping keep the memory of the extinct dodo alive, while boosting Kashmir’s handicraft industry.
- Global Recognition: The dodo is now a sought-after item in global markets, linked to the traditional art of Kashmir.
- Kashmir Handicrafts: Several crafts from Kashmir, including papier mâché, have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags for their distinct cultural and regional significance.
Neolithic Age Grooves Discovery Near Boothapandi

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered rock grooves created during the Neolithic age near Boothapandi village, Kanniyakumari district.
- The discovery was made by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan (Archaeological Officer, Tirunelveli and Kanniyakumari districts) and M. Faisal (Sembavalam Research Centre).
Key Highlights:
- Groove Characteristics:
- The grooves are approximately 4,000 years old, formed by Neolithic people for tool sharpening.
- Tools used for activities like hunting, ploughing, and digging were sharpened here.
- The grooves resulted from wear and tear of tools that had broken or worn out during use.
- Groove Dimensions:
- Largest groove: 15 cm in length, 4 cm in width.
- Smallest groove: 8 cm in length, 3 cm in width.
- Similar Discoveries:
- Similar grooves have been found in other parts of Tamil Nadu, including Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram.
- Significance:
- The grooves provide evidence of Neolithic human habitation in the region.
- Ongoing excavations are expected to uncover more about Neolithic culture in the area.The Hindu
Rupee and Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The real effective exchange rate (REER) index of the rupee touched a record 108.14 in November, strengthening by 4.5 per cent during this calendar year, according to the latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data.
Key Highlights:
- Record REER Index:
- The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached an all-time high of 108.14 in November 2024.
- This marks a 4.5% appreciation in REER during the calendar year 2024, according to RBI data.
- What is REER?
- REER is a weighted average of a country’s currency value against the currencies of its major trading partners, adjusted for inflation differentials.
- It considers 40 currencies accounting for about 88% of India's trade.
- REER Calculation:
- Nominal Exchange Rates: The exchange rate between the rupee and each partner's currency.
- Inflation Differentials: Adjusts for inflation differences between India and its trading partners.
- Trade Weights: Based on the trade share with each partner.
- Recent Trends in REER:
- In 2023, REER dropped from 105.32 in January to 99.03 in April.
- It has since been on an appreciating trend, reaching 107.20 in October and 108.14 in November 2024.
- Dollar Strengthening Impact:
- Despite the rupee weakening against the US dollar (from 83.67 to 85.19 between September and December 2024), it has appreciated against the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen.
- The dollar's strengthening was fueled by global economic factors, including inflation expectations in the US and high bond yields, which led to capital outflows from other countries, including India.
- Impact on Exports and Imports:
- Overvaluation: A REER above 100 signals overvaluation, which can harm export competitiveness (exports become costlier) while making imports cheaper.
- Undervaluation: A REER below 100 indicates a currency is undervalued, boosting exports but increasing the cost of imports.
- India's Inflation and REER:
- India's higher inflation relative to trading partners is a key factor behind the rupee’s rising REER, despite its depreciation against major currencies.
- This suggests the rupee is overvalued, which could explain why the RBI may allow the rupee to depreciate further against the dollar.
- Global Context:
- The strengthening of the US dollar, influenced by factors such as tariff policies under the Trump administration and tighter US monetary policies, plays a significant role in the depreciation of the rupee against the dollar.
- This dynamic affects India's trade balance, with potential consequences for export growth.
- Implications for India’s Economy:
- Overvalued currency (as indicated by REER above 100) can lead to a trade deficit, as imports become cheaper and exports less competitive.
- A weaker rupee, particularly against the dollar, could boost Indian exports but raise the cost of imports.
Strengthening Fisheries Extension Services

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
Importance of Fisheries Extension Services:
- Livelihood Support: Fisheries provide livelihoods to over 3 crore fishers and fish farmers in India. The sector's growth is crucial for enhancing sustainable practices and ensuring long-term productivity.
- Growth in Fish Production: India’s fish production has seen an 83% increase since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23, with 75% of production coming from inland fisheries. India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
- Role of Extension Services: Extension services bridge the gap between scientific advancements and fishers, offering guidance on:
- Species lifecycle management
- Water quality management
- Disease control
- Sustainable rearing technologies and business models.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Fisheries Extension:
- Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs):
- Launched under PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) in 2020, MSKs are one-stop centers providing comprehensive extension services.
- Support to Fish Farmers: MSKs offer:
- Disease testing, water, and soil analysis.
- Training on sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Technology infusion in seed/feed management.
- Focus on Inclusivity: Government assistance (up to 60%) is available for women and marginalized communities to set up MSKs.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Equipped with labs for water and microbial analysis.
- Maharashtra (Nasik and Sangli): Capacity-building efforts on seed/feed inputs.
- Collaborations: MSKs mobilize start-ups, cooperatives, and Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) to share best practices, including regenerative and conservation management in the face of climate change.
- Sagar Mitras:
- Role: Deployed in coastal states and union territories, Sagar Mitras act as a vital interface between the government and marine fishers.
- Functions:
- Collection and dissemination of daily marine catch data, price fluctuations, and market insights.
- Dissemination of important information: weather forecasts, fishing zones, local regulations, and hygienic fish handling.
- Provide support on disaster preparedness and natural calamities.
Enhancing Extension Services through Digital Platforms:
- AquaBazaar: A virtual learning platform initiated by the National Fisheries Development Board to provide expert guidance on:
- Seed production and breeding of commercially important fish species.
- Practical demonstrations to improve fishers' knowledge.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding such platforms will improve access to resources for fishers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Institutional Convergence and Capacity Building:
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Fisheries extension services should be integrated with the over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and state-level agricultural extension services for effective outreach.
- Formalizing the Sector: The World Bank-assisted project aims to create work-based digital identities for fishers and fish farmers, enhancing their access to extension services, training, and awareness programs.
Challenges in Fisheries Extension Services:
- Fragmented Initiatives: Multiple government schemes and programs lack institutional convergence, leading to inefficiencies in reaching the grassroots level.
- Digital Divide: Many rural and coastal areas face challenges in terms of digital literacy and internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of online platforms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns and resource depletion due to overfishing demand adaptive strategies and the promotion of climate-resilient practices.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- Institutional Convergence: Combining existing extension machinery like Krishi Vigyan Kendras with fisheries extension services to leverage established networks and knowledge.
- Expand Digital Outreach: Platforms like AquaBazaar should be expanded to ensure wider access to expert knowledge, training, and best practices.
- Private Sector Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can enhance technology dissemination, capacity building, and resource mobilization in the fisheries sector.
- Focus on Sustainability: Developing climate-resilient and sustainable fisheries practices will be essential to address challenges posed by environmental changes and overfishing.
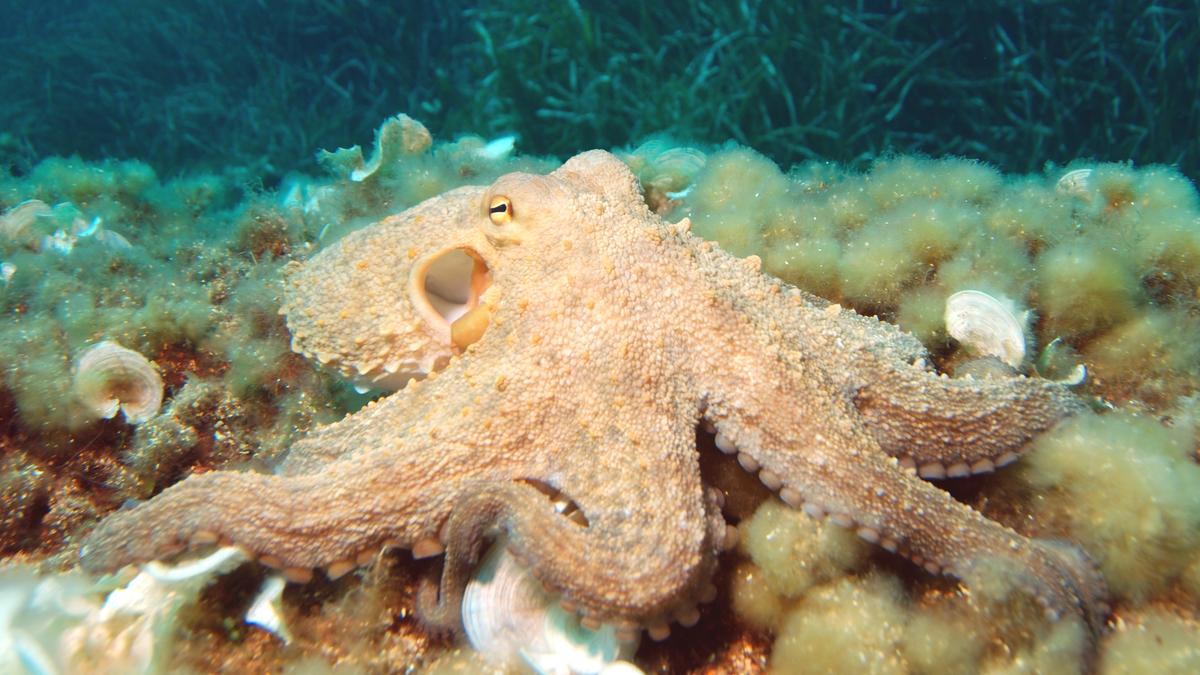
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
Centenary of Belgaum session

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Belagavi Session of 1924, marking its centenary in December 2024, holds significant historical and cultural value in India's freedom struggle. This session, the 39th All-India Congress session, was presided over by Mahatma Gandhi, the only instance he served as the Congress president. It took place in Belagavi, Karnataka, from December 26-27, 1924, amidst a growing momentum for India’s fight against British colonial rule.
Key Aspects of the Belagavi Session:
- Gandhi's Leadership: This was the only Congress session Gandhiji chaired, marking a pivotal moment in the freedom movement. His leadership emphasized non-violence, self-reliance, and unity among diverse groups, setting the stage for future movements like the Salt March and Quit India Movement.
- Focus on Social Change: Gandhi used the session to push for social reforms, including the abolition of untouchability, promotion of khadi (hand-spun cloth), and supporting village industries. These initiatives aimed to make Congress a movement for both political freedom and social upliftment.
- Promoting Hindu-Muslim Unity: Gandhi strongly advocated for Hindu-Muslim unity, recognizing its critical importance in the larger struggle for independence. His stance emphasized communal harmony during a time of social and political divisions.
- Cultural Impact: The session also featured musical performances, including contributions from Hindustani maestros like Vishnu Digambar Paluskar and Gangubai Hangal. The Kannada song “Udayavagali Namma Chaluva Kannada Nadu” became an anthem for the region's unification movement.
- Legacy: The session had a lasting impact, with initiatives such as promoting khadi, reducing Congress membership fees, and creating new avenues for peasant participation in the freedom movement. The Pampa Sarovara well, dug during the event, continues to provide water to parts of Belagavi.
Centenary Celebrations:
The centenary of the Belagavi Session is being celebrated with a range of events, including:
- A Congress Working Committee (CWC) meeting on December 26, 2024.
- A public rally with the theme “Jai Bapu, Jai Bhim, Jai Samvidhan.”
- Cultural events and exhibitions are also planned, including competitions, tableaux, and charkha marathons.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
72% Decline in Bird Species at Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary, Assam

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study has revealed a dramatic decline in the number of bird species at Assam's Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary (BBBS). The sanctuary, once home to a rich diversity of avian species, has experienced a 72% decline in bird species over the past 27 years. The study, published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa, highlights the severe biodiversity crisis facing the sanctuary.
Key Findings:
- Bird Species Count Decline:
- In 1997, the sanctuary recorded 167 bird species.
- Recent surveys (2022-2024) have only recorded 47 species, marking a 71.85% decline in species count.
- Surveys:
- 2011 Survey: Recorded 133 species (86 resident, 23 migratory, 24 local migrants).
- 2017-2018 Survey: Found 120 species, along with a variety of other biodiversity, including macrophytes, fish, and aquatic ferns.
- Impact on Migratory Birds:
- Migratory species like Brown Shrike, Citrine Wagtail, and White Wagtail (winter migrants), and the Lesser Kestrel (summer migrant) were recorded recently.
- Main Causes of Decline:
- Anthropogenic Activities: Overfishing, poaching, excessive harvesting of aquatic plants, and egg collection.
- Land Use Changes: Habitat degradation due to agriculture, machinery noise, and land being used as pasture areas.
- Disruption of Food Chain: Habitat loss and changes in foraging and breeding grounds for both migratory and resident birds.
- Species of Concern:
- Poached Birds: Lesser whistling duck, Fulvous whistling duck, White-breasted waterhen, Indian pond heron, Eastern spotted dove, and Yellow-footed green pigeon.
- Threatened Species: The sanctuary is home to globally threatened species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant.
About Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated between Dhemaji and Lakhimpur districts in Assam, the sanctuary spans 11.25 sq. km at an altitude of 90-95 meters above sea level.
- History: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1996, it was originally part of the Subansiri River which has now shifted 7 km from the wetland.
- Climate & Vegetation:
- Moist tropical climate with an average annual rainfall of around 2,000 mm.
- The vegetation includes flooded valley grasslands and wetland plants, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds.
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Hosts a variety of migratory waterfowl, especially during the winter.
- Home to globally threatened bird species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant, along with resident birds such as the Indian Pond Heron and Fulvous Whistling Duck.
Conservation Efforts:
- The decline in bird species at the sanctuary has raised alarm about the degradation of wetland habitats.
- The study emphasizes that habitat loss can disrupt the food chain, water table, and nutrient cycle, which in turn harms both the ecosystem and human communities.
- The authors of the study advocate for intense conservation efforts to restore and protect the sanctuary’s biodiversity.
Assam's Biodiversity:
- Assam is one of India's most biodiverse states, with around 950 bird species, including 17 endemic species.
- The state also hosts 55 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBA), which are vital hotspots for avian species.
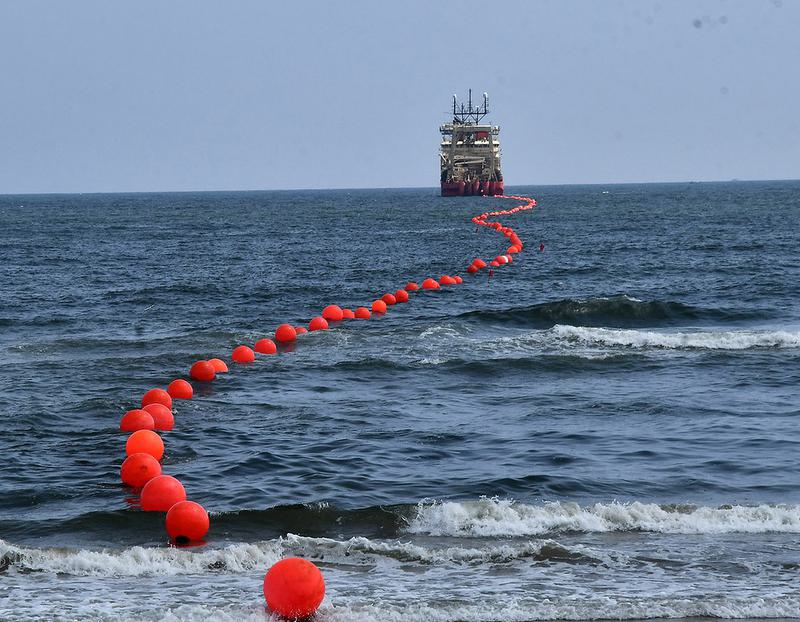
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Dark Comets

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Dark comets are a newly identified class of celestial objects that challenge our traditional understanding of comets and asteroids. Unlike regular comets, these objects exhibit characteristics that blur the lines between comets and asteroids, leading astronomers to closely study their nature, origin, and significance.
Discovery and Background
The first hint of dark comets appeared in 2016, when asteroid 2003 RM exhibited strange orbital deviations that suggested it might be a comet in disguise. NASA further fueled this interest in 2017 when it discovered ‘Oumuamua, an interstellar object that entered our Solar System. Though initially classified as an asteroid, its erratic motion and lack of a visible tail led scientists to consider it a dark comet. Since then, several more objects with similar characteristics have been discovered, and astronomers now identify these objects as a new class—dark comets.
Characteristics of Dark Comets
- Appearance: Dark comets do not exhibit the brilliant, glowing tails typically associated with comets. Instead, they resemble asteroids, appearing as faint points of light in space. Unlike bright comets, they do not have a visible coma (a cloud of gas and dust) or a tail, making them much harder to detect.
- Size: Dark comets are typically small, ranging from a few meters to a few hundred meters in diameter. Due to their small size, there is less surface area for material to escape, preventing the formation of the iconic tails seen in traditional comets.
- Orbital Path: These objects follow elongated, elliptical orbits. While some of them travel close to the Sun, they can also venture to the outer reaches of the Solar System, far beyond Pluto, and even into the Oort Cloud—the distant region where long-period comets are believed to originate.
- Spin and Gas Dispersion: Dark comets often rotate rapidly, dispersing gas and dust in all directions. This rapid spin contributes to their invisibility, as the gas and dust are scattered evenly, making it more difficult for astronomers to detect their presence.
- Composition: The composition of dark comets may also play a role in their lack of visibility. Over time, the materials that form the bright tails of comets may be depleted, especially for older objects. As a result, dark comets may not release enough gas to produce a visible coma or tail.
Types of Dark Comets
There are two main categories of dark comets:
- Inner Dark Comets: These are smaller objects that reside closer to the Sun and typically travel in nearly circular orbits. They are often just a few meters in size, with less surface area for gas and dust to escape.
- Outer Dark Comets: These larger objects, measuring over 100 meters in diameter, travel in highly eccentric orbits, similar to Jupiter-family comets. These dark comets follow elliptical paths that bring them close to the Sun and then send them back toward the outer reaches of the Solar System.
Importance of Studying Dark Comets
Dark comets may hold critical clues about the early Solar System and the formation of Earth. Studying these objects can provide insights into the origins of water on Earth, as well as the ingredients necessary for life. Their unique composition and orbits also offer potential for understanding the processes that led to the formation of planets.
Recent Discoveries and Advancements
Astronomers recently discovered 10 new dark comets with the help of the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) on a large telescope in Chile. The DECam, designed to study distant galaxies and stars, has enabled researchers to detect these faint objects by analyzing images of the night sky. Further progress is expected with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which will feature the largest digital camera ever built. This new instrument will allow astronomers to capture more detailed images of the night sky and detect fainter objects, potentially doubling or even tripling the number of known dark comets in the next decade.
Key Facts:
- Dark comets lack the characteristic glowing tails of typical comets, instead resembling asteroids.
- They exhibit erratic motions and follow elliptical orbits, often extending beyond Pluto and into the Oort Cloud.
- They are typically small (a few meters to hundreds of meters wide) and spin rapidly.
- The first dark comet was identified in 2016, with more discoveries made in the years since.
- The Dark Energy Camera (DECam) in Chile has been instrumental in detecting these elusive objects, with a new Vera C. Rubin Observatory expected to further enhance detection in the future.
- Studies suggest that between 0.5% and 60% of Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) could be dark comets, many originating from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2024

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2024 was released by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI). The report focuses on the theme “Poverty Amid Conflict”, examining the interplay between violent conflict and multidimensional poverty.
Key Findings:
- Global Poverty Levels:
- 1.1 billion people (~18% of the global population) live in acute multidimensional poverty across 112 countries.
- India has the largest number of people living in multidimensional poverty, with 234 million people.
- Multidimensional Poverty Indicators:
- The MPI assesses poverty across three key dimensions:
- Health: Child mortality, malnutrition.
- Education: Years of schooling, school attendance.
- Living Standards: Access to clean water, sanitation, electricity, cooking fuel, housing quality, and ownership of basic assets.
- A person is considered MPI poor if they are deprived in one-third or more of the weighted indicators.
- The MPI assesses poverty across three key dimensions:
- Impact of Conflict:
- Countries experiencing violent conflict exhibit higher deprivations across all 10 MPI indicators when compared to non-conflict nations.
- 40% (455 million people) of those living in poverty are in conflict-affected regions. These regions include active war zones, fragile states, and areas with low peace.
- Child Poverty:
- 584 million children (27.9% of all children globally) are living in extreme poverty, highlighting the disproportionate impact on the younger population.
- In contrast, 13.5% of adults are living in extreme poverty.
- Regional Distribution:
- The regions with the highest poverty rates are Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, which together account for 83.2% of the global poor.
- Rural Poverty: A majority of the poor (83.7%, or 962 million people) live in rural areas, with 70.7% of the poor concentrated in rural parts of Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
- Countries with the Highest Poverty:
- India: 234 million people.
- Pakistan: 93 million people.
- Ethiopia: 86 million people.
- Nigeria: 74 million people.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: 66 million people. These five countries account for 48.1% of the global poor.
- Poverty Amid Conflict:
- The report underscores that 2023 witnessed the highest number of conflicts since World War II, leading to the displacement of 117 million people due to violent conflicts and other factors like natural disasters.
- Conflict zones continue to experience higher poverty, as nearly 40% of the world's poorest people live in these areas.
India's Poverty Situation:
- India's Poor Performance:
- India has 234 million people living in multidimensional poverty, making it the country with the largest share of the global poor.
- Regional Disparities: Poverty rates in rural areas remain high due to poor infrastructure, limited economic opportunities, and underdeveloped services outside of agriculture.
- Poor Nutrition: Malnutrition, especially among children, is a significant concern.
- Education: The quality of education remains subpar, especially in government-run schools, affecting learning outcomes.
- Water and Sanitation: Inadequate access to clean drinking water and sanitation is prevalent, especially in rural areas.
- Economic Setbacks: The COVID-19 pandemic worsened the economic situation, leading to job losses and reduced incomes.
Government Initiatives for Poverty Alleviation:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 67% of India's population, targeting rural areas (75%) and urban areas (50%).
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY): Aims to provide LPG connections to women from Below Poverty Line (BPL) families.
- Ayushman Bharat: Health insurance coverage up to ?5 lakh per family, designed to protect against catastrophic healthcare costs.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan: Focuses on reducing malnutrition, particularly among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- Right to Education Act (RTE): Guarantees free and compulsory education for children between 6 and 14 years.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Works to ensure universal sanitation coverage, including the construction of toilets and promoting cleanliness.
Schengen Zone Membership

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the European Union (EU) cleared Bulgaria and Romania for full membership in the Schengen Zone, effective January 1, 2025. This marks the end of a 13-year wait for these Eastern European nations, which joined the EU in 2007.
Key Highlights:
- Schengen Integration: Until now, Bulgaria and Romania were partially integrated into the Schengen Zone, with air and sea travel without border checks since March 2024. However, land border controls were still in place due to Austria's objections, mainly due to concerns over migration and border security.
- Austria's Shift: Austria had blocked full entry for years but finally lifted its veto on December 9, 2024, after a border protection package was agreed upon. This package includes joint border guard deployment at the Bulgarian-Turkish border and temporary land border controls for six months.
Schengen Zone Details:
- What is the Schengen Zone?
- Created by the Schengen Agreement (1985) and the Schengen Convention (1990), it is the world’s largest area without internal border controls, allowing free movement across most EU countries and some non-EU countries. It currently includes 29 countries (25 EU states and 4 non-EU countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland).
- Key Features:
- Free Movement: Over 425 million people can travel freely within the zone without border checks.
- Uniform Visa Policy: Short-term stays of up to 90 days are allowed for tourists and business travelers from outside the Schengen Area.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: The Schengen Information System (SIS) facilitates security and border management by sharing critical data between countries.
- Temporary Border Controls: Countries can temporarily reintroduce border controls for security reasons, after notifying other member states and the European Commission.
Bulgaria and Romania
- Bulgaria:
- Capital: Sofia
- Location: Southeastern Europe, bordered by the Black Sea, Romania, Turkey, Greece, North Macedonia, and Serbia.
- Political System: Parliamentary Republic
- Romania:
- Capital: Bucharest
- Location: Bounded by Ukraine, Moldova, Black Sea, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Hungary.
- Political System: Semi-Presidential Republic
Implications of Full Schengen Membership:
- Security and Unity: Romania and Bulgaria's full integration into the Schengen Zone is seen as a boost to both EU security and unity. It solidifies the EU's commitment to free movement while enhancing border security across Europe.
- Impact on Migration: With Bulgaria and Romania’s full membership, the EU’s border management system will be more integrated, helping to address ongoing migration challenges.
Cyclone Chido
- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Cyclone Chido makes landfall in Mozambique after leaving trail of destruction in French-administered Mayotte.
About Cyclone Chido:
- Location and Impact:
- Cyclone Chido struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, in December 2024.
- It is the strongest storm to hit Mayotte in at least 90 years.
- Cyclone Characteristics:
- Wind speeds exceeded 200 km/h (124 mph), with gusts surpassing 225 km/h (140 mph).
- The cyclone caused significant devastation to the region, prompting expressions of condolences from global leaders.
- Cyclone Classification:
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), cyclones are classified based on wind speed:
- Depression: 31–49 km/h
- Deep Depression: 50–61 km/h
- Cyclonic Storm: 62–88 km/h
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: 89–117 km/h
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: 118–166 km/h
- Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm: 167–221 km/h
- Super Cyclonic Storm: Above 222 km/h
- Cyclone Chido was classified as a Super Cyclonic Storm, based on its wind speeds exceeding 222 km/h.
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), cyclones are classified based on wind speed:
About Mayotte:
- Geography:
- Mayotte is an archipelago in the Mozambique Channel, between Madagascar and the coast of Mozambique.
- It consists of two main islands: Grande Terre (the larger main island) and Petite Terre (the smaller island of Pamandzi).
- Political and Economic Context:
- Mayotte is an overseas department of France, and it is the poorest territory in both France and the European Union.
- France colonized Mayotte in 1843 and annexed the entire Comoros archipelago in 1904.
- A 1974 referendum showed that 95% of Comoros voters favored independence, but 63% of Mayotte's population voted to remain part of France. Subsequently, Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Moheli declared independence in 1975.
- Mayotte remains administratively under French governance.
- Biodiversity:
- Mayotte is renowned for its rich biodiversity, particularly for having one of the world’s largest enclosed lagoons.
Cyclones
- What is a Cyclone?
- A cyclone is a large-scale, rotating system of air that forms around a low-pressure area, bringing violent storms and extreme weather conditions.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones rotate anticlockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate clockwise due to the Coriolis effect.
- Tropical Cyclone Characteristics:
- Calm Centre (Eye): The cyclone’s center, or "eye," experiences relatively calm weather with low air pressure.
- High Wind Speed: Cyclones generally have average wind speeds around 120 km/h.
- Closed Isobars: Isobars (lines of equal atmospheric pressure) are tightly packed, leading to high wind velocities.
- Formation Over Oceans: Cyclones typically form over warm ocean waters.
- East-to-West Movement: Influenced by trade winds, cyclones usually move from east to west.
- Seasonal Nature: Cyclones occur during specific seasons based on regional climatic conditions.
Kisan Kavach

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
How La Niña Affects India's Climate?
- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
La Niña, a phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), occurs when the Pacific Ocean region between Indonesia and South America is cooler than usual. This phenomenon influences global weather patterns, including those in India. Here’s how La Niña specifically affects India’s climate:
Monsoon Rainfall:
- La Niña typically results in normal to above-normal rainfall during the monsoon season in India. This is due to the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific, which affects atmospheric circulation and strengthens the monsoon winds.
- In contrast, El Niño usually brings below-average rainfall and droughts to India, leading to agricultural stress.
- Recent La Niña years (2020-2022) saw above-normal monsoon rains, which benefited agricultural productivity, while the El Niño year of 2023 resulted in below-normal rains, impacting water availability and agriculture.
Winter Temperatures:
- During La Niña, winter temperatures in India are generally colder in the north, with cooler nights but relatively warmer days compared to El Niño winters. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) tends to be lower, trapping pollutants close to the surface. However, higher wind speeds during La Niña help to disperse air pollution, improving air quality.
- South India may experience colder-than-usual winters during La Niña, but current meteorological data suggests the ongoing winter in India is not strongly influenced by La Niña, as its expected onset has been delayed.
Impact on Summer Heat:
- La Niña generally provides relief from extreme summer heat, as it reduces the frequency and intensity of heatwaves. In contrast, El Niño summers are typically hotter and bring record-breaking heat waves.
- For example, April 2023 saw intense heatwaves across India, attributed to the El Niño phase, but if a La Niña forms and persists into the summer of 2025, it could help moderate the extreme heat.
The "Triple Dip" La Niña Phenomenon:
- A Triple Dip La Niña refers to a rare occurrence where three consecutive La Niña events happen, as was the case from 2020 to 2022. This is significant because these prolonged events can lead to stronger climatic impacts. In contrast, the current El Niño (2023) follows this period, potentially contributing to an irregular transition between La Niña and El Niño phases, which may intensify extreme weather patterns.
Global Climate Changes and La Niña:
- Climate change is believed to be increasing the frequency and intensity of both La Niña and El Niño events. Rising sea and land temperatures are disrupting the balance of the Pacific Ocean and could exacerbate extreme La Niña events, which might lead to harsher winters in India and other regions.
Forecast for 2024-2025:
- As of December 2024, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and global meteorological bodies predict a weak La Niña event to emerge by late 2024 or early 2025. This could lead to colder winters and above-normal rainfall in the 2025 monsoon season, offering some relief from the heatwaves and dry conditions of the previous years.
Conclusion:
If a La Niña forms by the end of 2024, it is likely to bring cooler winters, a relief from extreme summer heat, and above-normal monsoon rainfall in 2025. Given the delayed onset and weakening of the current La Niña, the overall impact on India’s climate in the immediate future might be milder compared to previous La Niña years, but it still holds potential for more favorable conditions for agriculture and air quality.
Search and Rescue Aid Tool (SARAT)

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, has developed SARAT Version 2 to aid Indian Search and Rescue (SAR) agencies like the Indian Coast Guard.
Key Highlights:
Purpose: SARAT is designed to assist in locating missing objects or individuals at sea by simulating the probable search area, considering factors like wind, currents, and waves.
Improvements in Version 2:
- The search area now starts from the last known position of the object, improving the accuracy of the search.
- Enhanced visualizations for better judgment of probable search areas, including colour coding of regions and markers to identify the last known position.
- Optimized search: Reduces the vast search area to a few high-probability regions, allowing for better utilization of limited search resources.
Technical Aspects:
- The tool uses model currents from the Regional Ocean Modelling System run on high-performance computers at INCOIS.
- It accounts for uncertainties in the initial location and the last known time of the missing object using model ensembling.
- Users can select from 60 types of missing objects based on shape and buoyancy.
Interactive Map & Multi-language Support:
- Results are shown on an interactive map, providing the probable search area.
- The tool also sends results as text messages to emails and mobile phones in languages of coastal states, enabling local fishermen to use it effectively during distress situations.
Launched in 2016, Updated in 2024: SARAT was launched in 2016 and the updated version (SARAT Version 2) has been designed with feedback from the Indian Coast Guard and other stakeholders involved in marine search operations.
Access: The updated SARAT Version 2 can be accessed at: https://sarat.incois.gov.in/sarat/home.jsp.
One Nation, One Election Bill
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The One Nation, One Election Bill has made significant progress in India, passing the Lok Sabha with 269 votes in favor and 198 votes against. The bill proposes the synchronization of elections for the Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and local bodies (Panchayats and Municipalities), aiming to streamline the electoral process, reduce costs, and enhance governance.
Key Updates:
- The bill has been approved by the Union Cabinet and will be reviewed by a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC), whose report will be presented for further approval and discussion in Parliament.
- The process will unfold in two phases:
- Phase 1: Simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Synchronizing local body elections (Panchayats and Municipalities) within 100 days of the general elections.
Historical Context:
- 1951-1967: India previously conducted simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies until disruptions, such as premature dissolutions of assemblies, led to staggered elections after 1967.
- The One Nation One Election concept has been revived to address inefficiencies in the current system, especially the high cost of conducting frequent elections.
Advantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Cost Reduction: Synchronizing elections can significantly lower the financial burden by eliminating the need for multiple election cycles, reducing the deployment of resources like security personnel and election staff.
- Long-Term Governance Focus: Politicians can prioritize governance and policy implementation rather than election campaigning, fostering long-term stability.
- Increased Voter Turnout: Voter fatigue, caused by frequent elections, may reduce, leading to higher turnout as elections occur less often.
- Fairer Political Competition: Smaller regional parties could have a better chance to compete with larger national parties by reducing election-related costs.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Security forces and administrative resources can be deployed more effectively, avoiding the redundancy caused by multiple election cycles.
Disadvantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Synchronization Challenges: Aligning elections across a vast and diverse country like India, especially in states with unstable political situations, may prove difficult.
- Federalism Concerns: The implementation may require constitutional changes that could impact India's federal structure, potentially limiting the autonomy of states in election matters.
- Impact on Regional Issues: National issues could overshadow regional concerns, diluting the focus on state-specific matters.
- Challenges for Regional Parties: Larger national parties may dominate the electoral landscape, reducing the influence of regional parties and undermining the federal nature of the political system.
- Accountability Risks: Fixed terms without frequent elections might reduce public scrutiny of elected officials, affecting their accountability.
Constitutional Amendments Required:
The implementation of One Nation, One Election requires amendments to several key constitutional provisions:
- Article 83: Regarding the duration of the Lok Sabha, amendments are needed to synchronize the timing of dissolution.
- Article 85: Deals with the sessions and dissolution of Parliament, which needs to be aligned with the new system.
- Article 172: Pertains to the duration of State Legislatures, requiring amendments for synchronization.
- Article 174: Similar to Article 85, it governs the sessions and dissolution of State Legislatures, needing standardization.
Implementation Challenges:
- Logistical Complexity: Conducting simultaneous elections would require immense logistical coordination, including vast numbers of electronic voting machines and trained personnel.
- Political Accountability: Fixed terms may reduce the accountability that frequent elections bring, potentially leading to governance stagnation.
- Impact on Federalism: Amendments to the Constitution regarding state legislatures might face resistance from states concerned about their autonomy.
India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Journey Hits $1 Trillion Milestone
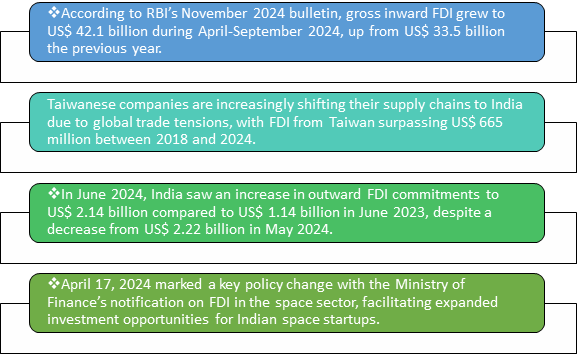
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
India has reached a historic milestone, surpassing $1 trillion in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows since April 2000. This achievement highlights India’s growing status as a major global investment hub and is further validated by a 26% increase in FDI inflows, which reached $42.1 billion during the first half of FY 2024-25.
Key Highlights of India’s FDI Growth:
- $1 Trillion Milestone: India has attracted a total of $1 trillion in FDI from April 2000 to September 2024. This figure includes equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital inflows.
- 26% Growth in FDI: FDI inflows surged by 26% in the first half of FY 2024-25, totaling $42.1 billion.
- Top Investors: Major investors include Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), and the United States (10%). These countries benefit from favorable tax treaties with India, boosting investment.
- Dominant Sectors: FDI has flowed into sectors like services, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications, with significant investments also in pharmaceuticals, automobile, and construction development.
Factors Behind India’s FDI Success:
- Policy Reforms: India’s liberalized FDI policies, such as allowing 100% FDI in most sectors under the automatic route, have attracted foreign capital. Key reforms like abolishing angel tax and reducing corporate tax rates in the Income Tax Act of 2024 have also enhanced investor confidence.
- Business Environment: India’s rise in global competitiveness is evident in its improvement in rankings. It moved from 43rd to 40th in the World Competitiveness Index 2024 and climbed to 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2023, up from 81st in 2015.
- Investor Confidence: The government’s efforts, including initiatives like "Make in India", Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sector-specific incentives, have fostered a conducive environment for investment.
- Global Investment Standing: India has been the third-largest recipient of greenfield projects globally and saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals.
Contribution of Mauritius and Singapore:
- Mauritius and Singapore lead as the primary sources of FDI into India. Their favorable tax treaties with India make them attractive gateways for foreign investments. Mauritius accounted for 25%, and Singapore for 24% of the total FDI inflows.
Key Sectors Attracting FDI:
- Services Sector: Significant growth in services, especially financial services, has attracted substantial foreign investments.
- Manufacturing and Technology: These sectors have benefited from policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, which encourage foreign investments in high-tech manufacturing.
- Telecommunications and Pharmaceuticals: India’s growing digital ecosystem and strong pharmaceutical industry continue to attract international investments.
Importance of FDI for India:
- Infrastructure Development: FDI plays a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects, helping meet the country’s significant infrastructure needs.
- Balance of Payments: FDI helps bridge India’s current account deficit, ensuring stable foreign exchange reserves.
- Technology Transfer and Employment: Foreign investments bring advanced technology and create jobs, boosting productivity across sectors.
- Currency Stability: FDI supports the Indian Rupee in global markets by injecting foreign capital.
Challenges:
Despite the positive trends, India faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions, regulatory issues, global economic uncertainty, and infrastructure bottlenecks that can affect investor sentiment and capital inflows.
Way Ahead:
- Focus on Infrastructure: Continued investment in infrastructure development, including public-private partnerships (PPPs), will be crucial for sustained economic growth.
- Workforce Skilling: Collaborative efforts to upskill the workforce will ensure that India can meet the evolving demands of industries.
- Research and Development: Strengthening R&D and innovation will enhance India’s productivity and global competitiveness.
Disease X
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent outbreak reported in the first week of December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has claimed over 400 lives and remains unclassified, has raised concerns that it could be an instance of Disease X.
What is Disease X?
- Definition: Disease X is a hypothetical, unidentified pathogen that has the potential to cause a global health crisis, either as an epidemic or pandemic.
- Origins: Could arise from zoonotic spillover (animal-to-human transmission), antimicrobial resistance, bioterrorism, or lab accidents.
- Severity: Predicted to be 20 times more lethal than SARS-CoV-2, with rapid transmission and significant mortality.
- Features: Represents unknown threats, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, or prions.
- Emergence Factors: Driven by deforestation, urbanization, climate change, and human-wildlife interactions.
Historical Context
- Conceptualization: The term was coined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018, post the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak, which revealed gaps in global health responses.
- Zoonotic Origins: Around 70% of emerging diseases since 1940 have zoonotic origins, linked to human encroachment on wildlife habitats.
WHO’s Priority Pathogen List
- Purpose: To focus global resources and attention on diseases with high epidemic or pandemic potential but lacking sufficient vaccines or treatments.
- Pathogens Listed: Includes Ebola, Marburg, Lassa fever, Nipah virus, Rift Valley fever, Zika virus, and Disease X.
- Criteria: These diseases have high mortality rates, potential for rapid spread, and inadequate preventive or therapeutic options.
Why Disease X is a Concern
- Unpredictability: Its emergence, transmission, and impact remain uncertain, making preparedness challenging.
- Globalization: Increased global travel and trade facilitate rapid spread of diseases across borders.
- Environmental Drivers: Climate change, urbanization, and deforestation disrupt ecosystems, bringing humans into closer contact with wildlife and pathogens.
Patterns in Emerging Diseases
- Zoonotic Spillover: The majority of emerging diseases originate from animals, with over 1.7 million undiscovered viruses in wildlife that could infect humans.
- Increased Outbreaks: Since the mid-20th century, the frequency of new diseases has risen, reflecting environmental, demographic, and global factors.
Challenges in Predicting Disease X
- Uncertainty: The vast pool of potential pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc.) makes it difficult to predict the exact nature, origin, or timing of Disease X.
- Environmental and Climatic Changes: Climate change reshapes disease transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases like malaria and dengue.
- Technological and Knowledge Gaps: Many pathogens that could cause pandemics are still unidentified. Genomic sequencing and AI are advancing but cannot fully predict Disease X.
Global Preparedness Initiatives
- WHO's Role: WHO’s priority pathogen list and Pandemic Treaty aim to ensure coordinated, global responses to future outbreaks.
- Pandemic Fund: Supports strengthening health systems, especially in low-income countries.
- mRNA Vaccine Hubs: Enhance vaccine production capacity, particularly in developing countries.
- Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI): Works on "prototype pathogen" platforms to create vaccines within 100 days of identifying a new disease.
Indian Initiatives for Disease Surveillance and Preparedness
- Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP): Tracks outbreaks, monitors trends, and strengthens the country’s epidemic preparedness.
- National Institute of Virology (NIV): Focuses on researching viral pathogens and zoonotic diseases.
- Biotech Initiatives: Indigenous vaccine development and diagnostic tools are crucial for combating future outbreaks.
- Emergency Response Fund: Allocates resources to support immediate pandemic response efforts.
Key Challenges in Tackling Disease X
- Prediction Complexity: The interactions between humans, animals, and the environment are too complex to predict the exact nature of Disease X.
- Health Disparities: Low- and middle-income countries often lack the infrastructure to effectively combat pandemics, making them more vulnerable.
- Climate Change: Alters transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases carried by vectors like mosquitoes.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Surveillance: Implementing real-time genomic sequencing and AI-driven tools for early outbreak detection.
- Global Cooperation: Promoting equitable sharing of vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments to ensure timely and efficient responses.
- Public Health Infrastructure: Invest in strengthening healthcare systems, especially in high-risk regions like the Congo Basin.
- Research and Development: Focus on universal vaccines, diagnostic tools, and prototype pathogen platforms that can be quickly adapted to new diseases.
Kala-azar Disease
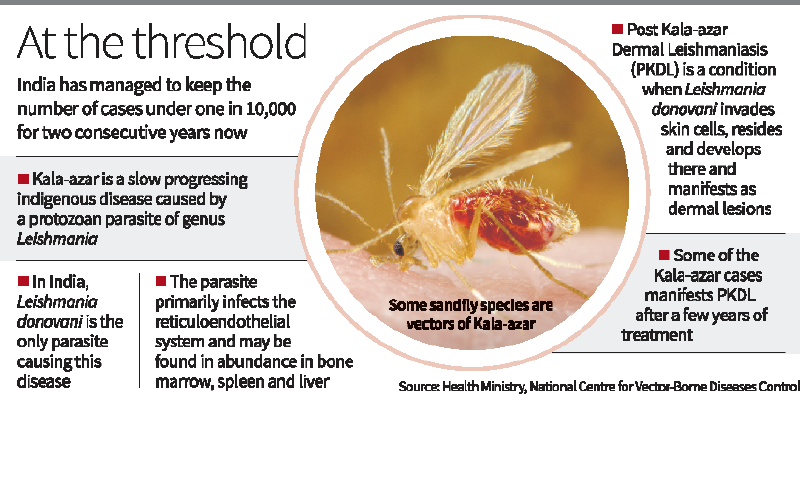
- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
India to seek WHO certification for eliminating disease.
Overview of Kala-Azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
- Cause: Kala-azar is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani, transmitted by the bite of infected female sandflies (Phlebotomus argentipes in India).
- Symptoms: Includes irregular fevers, weight loss, swelling of the spleen and liver, severe anaemia. If untreated, it is fatal in over 95% of cases.
- Affected Areas: Historically, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and parts of Uttar Pradesh report the highest number of cases, with Bihar alone accounting for over 70% of India's cases.
India's Achievement in Kala-Azar Control
- Current Status:
- India has managed to maintain Kala-azar case numbers below 1 per 10,000 population for two consecutive years.
- This meets the WHO's criteria for elimination certification.
- 2023 and 2024 Statistics:
- 2023: 595 cases and 4 deaths.
- 2024 (so far): 339 cases and 1 death.
WHO Certification for Elimination
- WHO's Target: The World Health Organization aims to eliminate Kala-azar as a public health problem by 2030.
- Elimination Criteria: A country can be certified when:
- Local transmission is interrupted for a specified period.
- There is a system in place to prevent re-emergence of the disease.
- Global Context: Bangladesh is the first country to have eliminated Kala-azar, receiving WHO certification in October 2024, after reporting fewer than 1 case per 10,000 people for three consecutive years.
India's Kala-Azar Elimination Strategies
- National Health Policy (2002): Initially set the target to eliminate Kala-azar by 2010, revised multiple times, and is now aiming for 2030.
- Key Strategies:
- Active Case Detection: Identification and treatment of all cases.
- Vector Control: Targeting sandfly breeding grounds through insecticides and environmental management.
- Community Awareness: Educating the public on disease prevention and early diagnosis.
- Improved Surveillance: Ensuring rapid diagnosis and treatment access, including the use of the rK39 diagnostic kit.
- Integrated Vector Management: Combining insecticide spraying with environmental changes to reduce sandfly populations.
Challenges and Areas of Focus
- Root Causes: Persistent issues like poverty, inadequate sanitation, and malnutrition contribute to the spread of Kala-azar, particularly in rural, impoverished areas.
- Long-term Solutions:
- Strengthen vector control and improve sanitation.
- Address socio-economic factors like poverty and displacement.
- Invest in research for vaccines and new treatments.
Public Health Impact and the Way Forward
- Elimination Milestone: If India continues to reduce cases, it will join Bangladesh in eliminating Kala-azar as a public health threat.
- Sustaining Gains:
- Surveillance and quick response to new cases remain critical.
- Expand access to rapid diagnostic tools and effective anti-parasitic treatments.
- Focus on inter-sectoral convergence, integrating efforts from various government sectors, including health, sanitation, and housing.
Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
GE’s LM2500 Marine Engines to Power Indian Navy’s Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)
Key Highlights:
- Engine Selection:
- General Electric’s LM2500 marine gas turbines have been chosen to power the Indian Navy's Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV), currently being built by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Project Details:
- Number of Vessels: Six NGMVs are under construction.
- Contract Value: ?9,805 crore, awarded by the Defence Ministry.
- Delivery Schedule: The first deliveries are expected to commence in March 2027.
- Key Components and Suppliers:
- GE Aerospace will deliver six LM2500 engine kits to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for assembly and testing at their Industrial and Marine Gas Turbine Division in Bengaluru.
- GE will also supply the composite base, enclosure, and a full set of auxiliary systems for the gas turbines.
- LM2500 Marine Gas Turbine:
- The LM2500 turbine is known for its reliability and high power output, making it ideal for the NGMV mission.
- Top Speed: 35 knots (64 km/h).
- It is central to the propulsion system, meeting the stealth and power demands of the new missile vessels.
- Capabilities of NGMVs:
- Role: Designed for offensive missions, the NGMVs will be equipped for anti-surface warfare, maritime strike operations, and sea denial.
- Speed & Stealth: Capable of speeds up to 35 knots while maintaining stealth, these vessels will be difficult for enemy ships to detect.
- Weapons: They will carry a variety of anti-surface weapons, including the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, loitering munitions, unmanned vehicles, and other guided weapons.
- Operational Roles:
- Offensive: The NGMVs will engage in attacking enemy warships, merchant ships, and land-based targets.
- Defensive: They will also be used for local naval defense operations, including the seaward defense of offshore development areas and defending choke points.
- Strategic Importance:
- The NGMVs will significantly enhance India’s maritime strike capability and provide a formidable presence in strategic sea routes, especially in regions like choke points and offshore development areas.
- Cochin Shipyard’s Role:
- After successfully constructing INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, CSL is now focusing on the NGMV project, along with building anti-submarine warfare shallow water crafts for the Indian Navy, currently in various stages of construction.
- Partnerships:
- In 2023, GE Aerospace and HAL signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to expand their collaboration on marine gas turbines, including assembly, inspection, and testing (AIT) of the LM500 turbines.
- To date, GE Aerospace has delivered 24 marine gas turbine kits to HAL, supporting India’s Make-In-India initiative.
- Global Impact:
- The LM2500 gas turbine is used by 714 vessels globally, reinforcing its reputation for reliability and availability in critical maritime defense systems.
First Chief Minister of J&K UT Takes Charge
- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Omar Abdullah sworn in as J&K CM; Surinder Kumar Choudhary is Deputy CM
Key Highlights:
- Omar Abdullah’s Political Context:
- This marks Omar Abdullah's second term as Chief Minister, after his tenure in 2009.
- He becomes the first Chief Minister of Jammu and Kashmir after the region’s special status was revoked and it was reorganized as a Union Territory in 2019.
- Challenges as CM of a Union Territory:
- Omar Abdullah acknowledged the unique challenges of serving as Chief Minister in a Union Territory and expressed hope that J&K’s Union Territory status would be temporary.
- Public Service and Security Measures:
- In his first official instructions, Abdullah asked the Director General of Police (DGP) to avoid creating “green corridors” or traffic halts during his movements. He also requested the minimization of sirens and aggressive security gestures, emphasizing minimal public inconvenience.
- Legal Context:
- Oath of Office: As per Article 164(3) of the Indian Constitution, the Chief Minister and other ministers are sworn in by the Governor or Lieutenant Governor in Union Territories.
- Abdullah is the first CM of the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir post the abrogation of Article 370 and the transition of J&K from a state to a Union Territory in 2019.
- Revocation of President's Rule:
- President’s Rule (under Article 356) was revoked following the election results, signaling the restoration of a functioning elected government after direct central governance in the region.
Haber-Bosch process
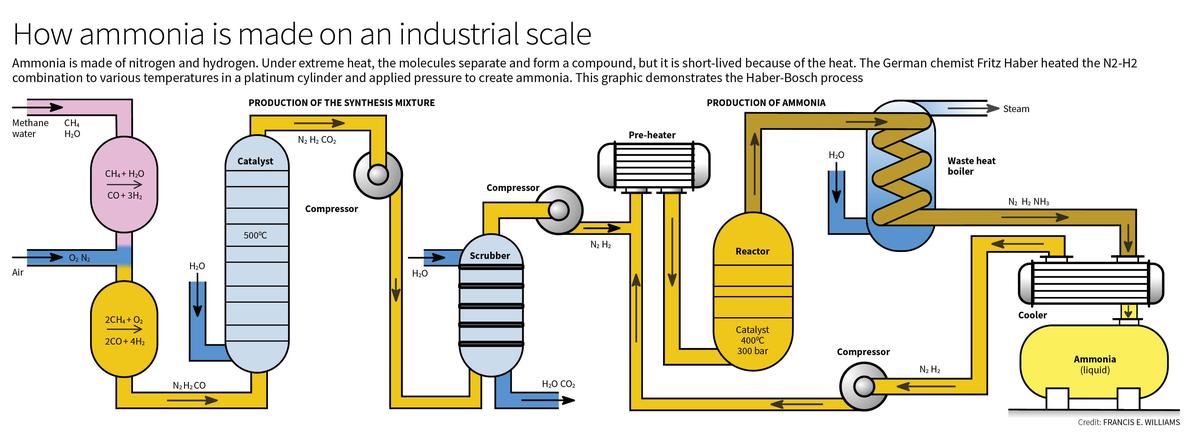
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Haber-Bosch process has fundamentally transformed agricultural practices and global food production, enabling the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is essential for fertilizers.
The Nitrogen Molecule
- Composition: Nitrogen primarily exists as molecular nitrogen (N?) in the atmosphere, where two nitrogen atoms are bonded with a strong triple bond. This bond is very stable and requires significant energy (946 kJ/mol) to break, rendering N? largely inert and unavailable for direct use by plants.
Nitrogen in Nature
- Natural Fixation: In nature, the energy required to break the N? bond is typically provided by phenomena like lightning, which converts nitrogen to reactive forms such as nitrogen oxides (NO and NO?). These can subsequently form nitric acid when they react with water, depositing reactive nitrogen through rainfall.
- Microbial Processes: Certain bacteria, including Azotobacter and Rhizobia, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into reactive forms, supporting plant growth. Azolla, a fern with a symbiotic cyanobacterium, also helps in nitrogen fixation.
The Nitrogen Cycle
- Plant Uptake: Plants absorb reactive nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH??) and nitrate (NO??) from the soil, essential for synthesizing proteins and other vital compounds. Humans and animals rely on plants for their nitrogen intake.
- Cycle Completeness: While nitrogen is returned to the soil through excretion and decomposition, some is lost back to the atmosphere as N?. This loss contributes to the depletion of soil nitrogen, especially in crops that do not fix their own nitrogen.
Ammonia Production
- Haber-Bosch Process: This process synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature, using a catalyst to enhance efficiency. Initially developed by Fritz Haber and scaled by Carl Bosch, this method became the backbone of modern fertilizer production.
Benefits and Downsides of Fertilizers
- Food Security: The Haber-Bosch process has significantly increased food production, contributing to a remarkable rise in global food supply and preventing widespread hunger. It is estimated that one-third of the world’s population relies on fertilizers produced via this process for their food.
- Environmental Impact: The widespread use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to environmental issues:
- Excess Nutrients: Over-application can result in nutrient runoff into water bodies, causing eutrophication, which depletes oxygen and harms aquatic life.
- Acid Rain: Reactive nitrogen can contribute to acid rain, affecting soil health and biodiversity.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous fertilizer use without adequate replenishment of nutrients can degrade soil quality over time.
While the Haber-Bosch process is crucial for modern agriculture and food security, it also presents significant environmental challenges. The balance between using fertilizers effectively and sustainably is essential to ensure that technological advancements do not come at the cost of ecological health. As such, addressing food security requires not just technological innovation, but also thoughtful political and social engagement to manage resources responsibly.
Wayanad’s New X-Band Radar

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Following devastating floods and landslides in July 2024 that resulted in over 200 fatalities in Wayanad, Kerala, the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences approved the installation of an X-band radar to enhance monitoring and early warning systems.
- Impact of Events: The floods were exacerbated by heavy rains, leading to significant debris flows and landslides, highlighting the need for advanced meteorological tools.
What is Radar?
- Definition: Radar stands for "Radio Detection and Ranging." It uses radio waves to determine the distance, velocity, and characteristics of objects.
- Functioning: A transmitter emits radio signals that reflect off objects, returning to a receiver for analysis. This technology is crucial in meteorology for monitoring weather patterns.
X-Band Radar Specifics
- Operating Frequency: X-band radar operates at 8-12 GHz, corresponding to wavelengths of 2-4 cm. This allows it to detect smaller particles, such as raindrops and soil.
- Advantages: The shorter wavelengths provide higher resolution images but have a limited range due to faster signal attenuation.
- Applications: In Wayanad, the radar will monitor particle movements like soil, enabling timely landslide warnings through high temporal sampling.
India’s Radar Network
- Historical Context: India has utilized radar for meteorological purposes since the early 1950s. The first indigenous X-band radar was established in 1970.
- Current Infrastructure: India operates both X-band and S-band radars (2-4 GHz) for various meteorological functions. The X-band network includes storm detection and wind-finding capabilities.
- Future Plans: The Indian government plans to add 56 more Doppler radars under the ?2,000-crore "Mission Mausam," enhancing weather forecasting capabilities across the country.
NISAR Satellite
- Collaboration: NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is a joint satellite project between NASA and ISRO, set to launch in 2025.
- Capabilities: It will feature L-band and S-band radars to monitor Earth’s landmass changes, further supporting environmental monitoring and disaster management.
Jipmer Launches ‘Tele-MANAS’ Mental Health Helpline

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Jipmer (Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) has launched the "Tele-MANAS" (Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States) helpline, a toll-free service (14416) aimed at providing mental health support.
- This initiative is part of the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP), launched by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Purpose and Need:
- With an estimated 1 in 10 people in India suffering from mental illness, and about 1% experiencing severe conditions, the service addresses significant gaps in mental health access, particularly in rural and remote areas.
- The helpline aims to provide immediate support for issues such as anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.
Training and Operations:
- Jipmer will train qualified counsellors who will subsequently train additional counsellors to expand the reach of the service.
- Counselors will be available 24/7, including holidays, to ensure continuous support.
Support Structure:
- Trained counselors will serve as the first point of contact for individuals seeking help, providing responses, suggestions, and necessary referrals to advanced mental health facilities.
- Jipmer will supervise the program, ensuring regular retraining and maintaining service quality.
Integration with National Programs:
- The initiative is coordinated by the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), which acts as the National Apex Centre for the NTMHP.
- It includes a comprehensive information library on mental health and guidance for managing early signs of stress and emotional challenges.
Impact on Mental Health Services:
- The program aims to enhance the overall quality of mental health services across states and union territories in India, making them more accessible to a larger population.
- Emphasizes the importance of mental health as a public health priority.
RBI's Recent Monetary Policy Review
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintained its benchmark interest rate at 6.5% for the 10th consecutive monetary policy review since April 2023. The policy stance was shifted to “neutral,” indicating potential for a future rate cut.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Overview
- The decision to keep interest rates unchanged was supported by a majority of five out of six members of the MPC, which convened for three days starting October 7.
- The change in policy stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral” was unanimously agreed upon.
Focus Areas
- The MPC emphasized the need for a durable alignment of inflation with targets while supporting economic growth.
- Macroeconomic parameters for inflation and growth were described as well balanced.
Inflation Insights
- A moderation in headline inflation is expected to reverse in September, likely remaining elevated due to adverse base effects.
- Retail inflation was below the central bank’s median target of 4% in July and August.
Growth Projections
- The RBI maintained its 7.2% GDP growth projection and a 4.5% average inflation estimate for 2024-25, with risks evenly balanced.
- Second-quarter inflation projection was revised down to 4.1% from 4.4%, while a rise to 4.8% is expected for the October to December quarter.
Domestic Growth and Investment
- Domestic growth remains robust, with private consumption and investment growing together.
- This growth has provided the RBI with the capacity to prioritize inflation control to achieve the 4% target.
Risks to Inflation
The Governor highlighted that unexpected weather events and escalating geopolitical conflicts pose significant upside risks to inflation.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024: MicroRNA Research

- 08 Oct 2024
Overview
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. This award highlights their individual contributions to understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression, significantly advancing the field of molecular biology.
What are MicroRNAs?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules typically 19-24 nucleotides long. They regulate protein production by interacting with messenger RNA (mRNA), ultimately influencing how much protein is synthesized from genetic information.
The Process of Gene Regulation
Gene expression involves two primary steps:
- Transcription: DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into proteins by ribosomes with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA).
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating this process, particularly after transcription, by silencing mRNA and thereby controlling protein production.
Pioneering Research
Background
In the late 1980s, Ambros and Ruvkun utilized the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a small roundworm, to explore developmental processes. They focused on mutant strains, lin-4 and lin-14, which displayed abnormal development.
Key Discoveries
- Victor Ambros: Ambros cloned the lin-4 gene and discovered that it produced a short RNA molecule that did not code for proteins. This finding suggested that lin-4 could inhibit lin-14’s activity.
- Gary Ruvkun: Ruvkun investigated the regulation of the lin-14 gene and determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA. Instead, it inhibited protein production later in the gene expression process. He identified crucial segments in lin-14 mRNA essential for its inhibition by lin-4.
Collaborative Findings
Their subsequent experiments demonstrated that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking the production of lin-14 protein. Their findings were published in 1993 and laid the foundation for the understanding of microRNA.
Impact and Recognition
Initially, the significance of their discoveries was not widely recognized, as it was thought that microRNA regulation was specific to C. elegans. However, Ruvkun’s later identification of the let-7 gene, a microRNA found in various animal species, broadened the understanding of microRNAs' universal role in gene regulation.
Current Understanding
Today, it is known that humans possess over a thousand genes that code for different microRNAs. These molecules are crucial in regulating gene expression across multicellular organisms.
Applications and Future Directions
MicroRNAs can fine-tune gene expression, influencing various cellular functions despite similar genetic backgrounds. Abnormal microRNA regulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. While the Nobel Committee acknowledged that practical applications of miRNA research are still developing, understanding these molecules is vital for future research and therapeutic advancements.
Mpox Diagnostic Test

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
In an important move to improve global access to Mpox testing, the World Health Organization (WHO) has listed the first Mpox in vitro diagnostic under its Emergency Use Listing procedure.
- Context of Mpox Outbreak:
- Since January 2022, mpox has spread to 121 countries.
- By September 2024, there were 103,048 confirmed cases and 229 deaths.
- Diagnostic Test Approval:
- WHO approved Abbott Laboratories’ PCR diagnostic test, Alinity MPXV assay, for emergency use.
- This test detects mpox virus DNA from skin swabs, intended for trained lab personnel.
- Emergency Use Listing (EUL) Procedure:
- Allows WHO to expedite approval of unlicensed vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tests during public health emergencies.
- In August, WHO called for manufacturers to submit diagnostic tools to aid low-income countries.
- Current Testing Landscape:
- Limited testing capacity has hindered response, especially in Africa, where over 30,000 suspected cases were reported in 2024.
- 35 laboratories in India are now equipped to test suspected mpox cases.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early detection facilitates timely treatment and control of the virus, essential in outbreak areas.
- Characteristics of the Alinity MPXV Assay:
- Utilizes real-time PCR to detect mpox virus (clade I/II) DNA from lesion materials.
- Designed for skilled laboratory personnel familiar with PCR techniques.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- WHO is reviewing three additional mpox diagnostic tests and negotiating with more companies to enhance availability.
- Efforts include addressing the spread of a new variant, clade Ib, which is affecting more women and children.
- Public Health Implications:
- Expanding access to diagnostics is vital for managing the mpox outbreak and protecting populations, particularly in underserved regions.
- WHO emphasizes the importance of quality-assured medical products in containing the virus spread.
Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
DRDO completed development trials of the 4th Generation miniaturised Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD).
Key Details:
- Trial Location: Conducted at Pokhran Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Importance: VSHORAD addresses the Indian Army's need to replace legacy Igla systems, with past efforts making little progress.
- Recent Procurement: Army acquired small volumes of Igla-S through emergency procurement.
- Production Collaboration: Two production agencies involved in Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) mode for VSHORAD missiles.
- Trial Dates: Successful tests held on October 3 and 4, 2024.
Key Performance Metrics:
- Maximum Range and Altitude: Interception against high-speed aerial targets.
- Hit-to-Kill Capability: Demonstrated success in engaging targets in various scenarios (approaching, receding, crossing).
System Overview:
- Type: Fourth generation man-portable air defence system (MANPADS).
- Developer: Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
Capabilities:
- Designed to neutralise low altitude aerial threats at short ranges.
- Features include Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System, and integrated avionics.
- More portable and lightweight than existing missile systems in the Army's arsenal.
Pradhan Mantri-Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) Scheme

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister of India is set to announce the 18th installment of the PM-KISAN scheme in Washim, Maharashtra. This will benefit over 9.4 crore farmers nationwide, with the government allocating more than ?20,000 crore for this initiative.
About PM-KISAN
The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) initiative aimed at providing income support to farmers.
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance: The scheme offers ?6,000 annually to small and marginal farmer families, distributed in three equal installments.
- Eligibility: Initially targeted at families with up to 2 hectares of cultivable land, the scope was later broadened to include all farmer families, regardless of land size.
- Family Definition: The definition of a family under this scheme includes the husband, wife, and minor children.
- Identification of Beneficiaries: State governments and Union Territory administrations are responsible for identifying eligible farmer families based on the scheme's guidelines.
- Direct Transfers: The funds are directly credited to the beneficiaries' bank accounts.
Exclusion Criteria
Certain categories of individuals are not eligible for benefits under the PM-KISAN scheme, including:
- Institutional Land-holders: Those who hold land under institutional ownership.
- High-Profile Government Officials: This includes former and current holders of constitutional posts, ministers, members of legislative assemblies, mayors, and district panchayat chairpersons.
- Government Employees: Serving or retired officers and employees of central or state government ministries and departments are excluded.
- Pensioners: Retired pensioners receiving a monthly pension of ?10,000 or more, as well as those in the previously mentioned categories, are also ineligible.
- Income Tax Filers: Individuals who have paid income tax in the last assessment year.
- Registered Professionals: Professionals such as doctors, engineers, lawyers, chartered accountants, and architects who are engaged in practice and registered with professional bodies.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
Indian push needed to end AIDS as a global health threat by 2030: UNAIDS

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The UNAIDS Director recently highlighted the crucial role India plays in the global fight against HIV/AIDS, asserting that without its significant contributions, achieving the Sustainable Development Goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 is unlikely.
Understanding HIV/AIDS
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which diminishes the body's ability to combat infections and diseases.
- When HIV progresses to its most severe form, it is diagnosed as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), characterized by a severely compromised immune system, leading to life-threatening infections and cancers.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids, including blood, semen, and breast milk. While there is currently no cure, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively manage HIV and prevent its progression to AIDS.
India’s Progress in Combating HIV/AIDS
- From 2010 to 2023, India has made significant strides in reducing annual new HIV infections by 44%, surpassing the global average.
- Additionally, AIDS-related deaths in India have decreased by nearly 80% during the same period, also exceeding global trends. However, challenges persist, with approximately 68,000 new infections reported in 2023, translating to around 185 daily.
- The Global AIDS Strategy emphasizes the need for 80% of prevention services to be delivered by community-led organizations, which are essential for reaching key populations but require sufficient resources and support.
About UNAIDS
UNAIDS, established in 1996, coordinates global efforts to combat HIV/AIDS and supports those affected. Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations and works in collaboration with various global and national partners to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Key aspects of UNAIDS include:
- Global Mandate: To coordinate responses, support countries in prevention and treatment, and advocate for human rights and equality in access to services.
- Targets: The "90-90-90" targets aimed for 2020 sought to ensure that 90% of people living with HIV were diagnosed, 90% of those diagnosed were on treatment, and 90% of those on treatment achieved viral suppression.
- Current Strategy: The 2021-2026 Global AIDS Strategy focuses on eliminating inequalities that drive HIV and aims to ensure that 30 million people are on treatment by 2025.
- Funding and Advocacy: Funded by governments, private foundations, and corporations, UNAIDS organizes key campaigns, including World AIDS Day, to raise awareness and promote advocacy.
PM Internship Scheme

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme, announced by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman during her Budget speech on July 23, was launched on October 3. The PM Internship Scheme aims to provide internship opportunities to one crore youth in the top 500 companies over the next five years.
Companies will upload their internship positions, and candidates can submit applications starting October 12.
What is the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme?
The PM Internship Scheme will enhance youth employability in India by offering them hands-on exposure to real-world business environments. The scheme represents a transformative opportunity to bridge the skills gap and drive sustainable growth in India.
A monthly stipend of ?4,500 will be provided to the interns from the central government via DBT (Direct Benefit transfer), with an additional ?500 offset provided by the company’s CSR fund.
Who is eligible for the PM internship scheme?
- Candidates aged between 21 and 24 years who are not engaged in full-time employment are eligible for the one-year internship programme.
- Internships are available to those who have passed class 10 or higher.
- Individuals from families with government jobs are excluded
- The scheme is not open to post-graduates
- A candidate who graduated from premier institutes such as IIT, IIM, or IISER, and those who have CA, or CMA qualification would not be eligible to apply for this internship.
- Anyone from a household that includes a person who earned an income of ?8 lakh or more in 2023-24, will not be eligible.
How to apply for the PM internship scheme?
- Interns can register in the portal and apply for internships. The portal, pminternship.mca.gov.in, is likely to be opened up for youngsters to enroll for consideration by companies on October 12. This window will be open till October 25 for the first batch of internships. Candidates must share and self-certify some data about their educational qualifications and residential pin codes.
- Candidates’ data will be matched with companies’ needs and locations using Artificial Intelligence tools, and a shortlist of candidates will then be generated for companies to consider.
- The portal is designed to streamline the application process and make candidate selection more transparent. Applicants can check the status of their applications in the portal once they have applied to the available posts.
What is the benefit of the scheme?
The scheme is to provide on-job training to youth and an exposure to real-life work environment. The scheme will also benefit the industry by creating a pipeline of skilled, work-ready youth who can be employed post-internship both in large as well as micro, small and medium enterprise.
Little Prespa Lake's Decline
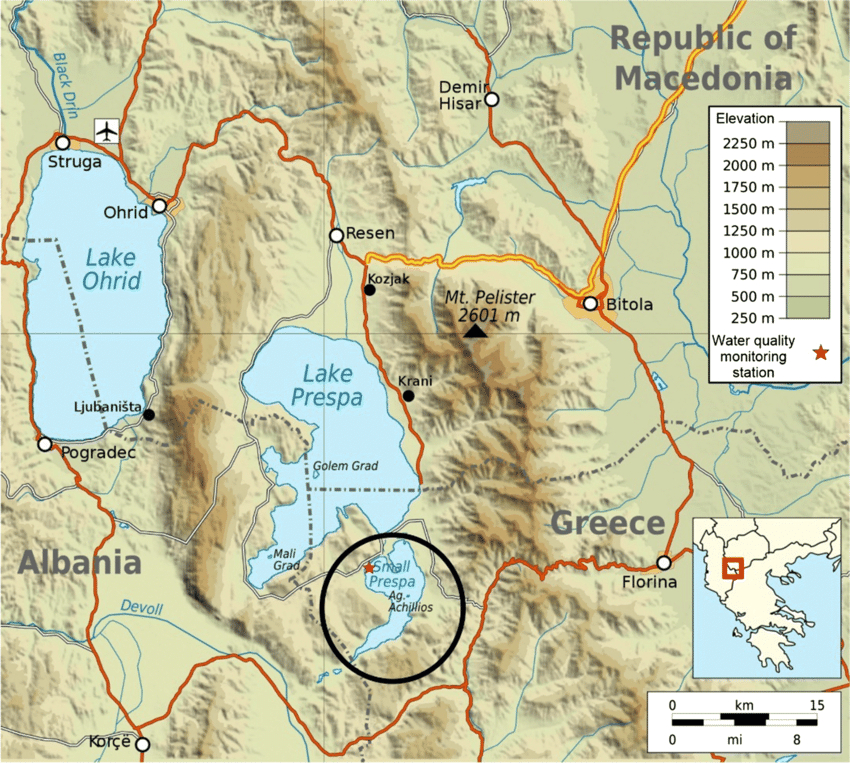
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
Little Prespa Lake on Albanian-Greek border slowly dying.
Overview of Little Prespa Lake's Decline
- Location and Geography:
- Little Prespa Lake is situated on the Albanian-Greek border, primarily in Greece with a southern tip extending into Albania.
- It covers approximately 450 hectares in Albania, now largely transformed into swamps or dry land.
- Ecological Changes:
- Once a crystal-clear lake, it has degraded into a marshy area, with about 430 hectares in Albania suffering from significant drying.
- Local wildlife has shifted; cows now roam where fish once thrived.
- Historical Context:
- The lake's decline began in the 1970s when Albanian authorities diverted the Devoll River to irrigate surrounding agricultural lands, severely limiting water inflow.
- Climate Change Impact:
- Rising temperatures, mild winters, and decreased precipitation have intensified the lake’s ecological crisis.
- Local experts warn that continued dry winters and hot summers could lead to irreversible damage.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India

- 03 Sep 2024
Overview
India’s mental healthcare landscape is evolving, with increasing awareness and decreasing stigma around mental health issues. However, access to mental healthcare remains a significant challenge due to a shortage of professionals. Here are the key points:
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India
- Rising Demand: Shifts in societal attitudes have led to more individuals seeking mental health support. Awareness and willingness to access treatment have notably increased.
- Professional Shortage: Despite the rising demand, there are only 0.75 psychiatrists per one lakh population, far below the World Health Organization’s recommendation of three per lakh. As of the latest data, India has about 9,000 psychiatrists, while an estimated 36,000 are needed to meet the standard.
- Slow Workforce Growth: Approximately 1,000 psychiatrists enter the workforce annually, but with attrition and unemployment, it could take around 27 years to reach the WHO target without intervention.
- Comparative Analysis: India has one of the lowest psychiatrist-to-population ratios among BRICS nations, trailing only Ethiopia. However, it performs better than many South Asian countries.
Limitations of Current Data
- Outdated Survey: The data largely relies on the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted between 2015 and 2016, which is based on a limited sample size of around 40,000 people across 12 states.
- Narrow Focus: The NMHS primarily addressed specific mental illnesses and overlooked milder conditions, emotional issues, and vulnerable populations like prisoners and the homeless.
- Need for Updated Research: A second NMHS is scheduled for release next year, which may provide more comprehensive data and insights.
Improvements in Awareness and Attitudes
- Positive Attitudinal Shift: A study by the LiveLoveLaugh Foundation found significant improvements in how Indians perceive mental health. For instance, the percentage of people believing that individuals with mental illnesses can handle responsibilities rose from 32% in 2018 to 65% in 2021.
- Willingness to Seek Help: Over 90% of respondents in 2021 indicated they would seek treatment for themselves or support others in doing so, a substantial increase from 54% in 2018.
- Increased Awareness: Awareness of mental health issues has grown, with 96% of respondents in 2021 recognizing mental health compared to 87% in 2018.
Conclusion
While India is making strides in reducing stigma and increasing awareness around mental health, the critical shortage of mental health professionals poses a significant barrier to accessing timely care. Addressing this issue requires targeted policy interventions and incentives to boost the supply of mental health professionals and improve the overall infrastructure for mental healthcare in the country.
Queers can open Joint Bank Accounts

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Government issued an advisory that LGBTQIA+ individuals and queer couples can open joint bank accounts. They can nominate each other as beneficiaries.
Key Details:
- Supreme Court Background:
- In October 2023, the Supreme Court of India urged the government to consider equal entitlements for partners in queer relationships.
- This was part of a judgment that did not recognize same-sex marriage but suggested enabling joint bank accounts and beneficiary nominations.
- Clarification from the Department of Financial Services:
- Issued on August 28, 2023, confirming no restrictions on opening joint accounts for the queer community.
- The Reserve Bank of India also clarified this to Scheduled Commercial Banks on August 21.
- Private Banks' Initiatives:
- Some banks, like Axis Bank, have been allowing joint accounts and beneficiary nominations for LGBTQIA+ couples since September 2021.
- Axis Bank expressed support for the Finance Ministry's advisory, noting alignment with its inclusive banking initiative.
- Government Committee Formation:
- In April 2023, a six-member committee was established to define entitlements for queer couples.
- Chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, it includes Secretaries from various ministries.
- The committee can co-opt experts if needed.
New Target for Cancer Treatment Discovered by IACS Scientists

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant breakthrough, scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) in Kolkata have identified a new target for cancer therapy. Their study, recently published in The EMBO Journal, focuses on how cancer cells manage DNA repair during cell division, potentially paving the way for more effective treatments.
Key Findings
The researchers explored how cancer cells respond to topoisomerase 1 (Top1)-targeted chemotherapy. Top1 inhibitors, such as camptothecin, topotecan, and irinotecan, disrupt DNA replication and transcription, causing damage that usually leads to cell death. However, cancer cells can sometimes develop resistance by employing internal DNA repair mechanisms, primarily involving a protein called TDP1.
Mechanism of Action
Top1 is crucial for relaxing DNA supercoils during cell division, a process necessary for accurate chromosome segregation. Drugs targeting Top1 can kill cancer cells by preventing this relaxation. Nonetheless, cancer cells counteract this damage with TDP1, which repairs the DNA and promotes cell survival.
The IACS team discovered that TDP1's function is influenced by its phosphorylation status, which changes during the cell cycle and drug treatment. This modification helps TDP1 detach from chromosomes during cell division, a mechanism that helps cells survive despite the presence of chemotherapy drugs.
Novel Therapeutic Approach
The researchers propose a novel approach that combines inhibitors of two key molecules: CDK1 protein and TDP1 enzyme. CDK1 plays a critical role in regulating the cell cycle, while TDP1 is involved in repairing DNA damage. By inhibiting both, the researchers aim to disrupt the cancer cell's ability to repair DNA damage caused by Top1 inhibitors.
This combinatorial targeting strategy could enhance the effectiveness of cancer treatments. While Top1 inhibitors induce DNA damage, CDK1 inhibitors could prevent the repair of this damage or halt the cell cycle, making it difficult for cancer cells to survive. This dual-target approach may also help overcome resistance mechanisms that cancer cells develop against single-agent therapies.
Clinical Implications
CDK1 inhibitors, including avotaciclib, alvocidib, roniciclib, riviciclib, and dinaciclib, are currently in various stages of clinical trials. These drugs can be used alone or in combination with other DNA-damaging agents. Combining CDK1 inhibitors with Top1 inhibitors holds promise for significantly improving cancer treatment outcomes by targeting different aspects of the cell cycle and DNA replication.
Although the study was conducted using human breast cancer cells, the findings suggest potential benefits for patients with other types of cancer, such as ovarian, colorectal, and small cell lung cancers (SCLC). SCLC, in particular, is associated with tobacco smoking and could potentially benefit from this new combinatorial approach.
Conclusion
The IACS study opens new possibilities for cancer treatment by targeting DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. By combining CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors, the researchers aim to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and overcome resistance. Further research, including clinical trials, will be essential to validate these findings and develop personalized cancer therapies that could improve patient outcomes across various cancer types.
Recent Announcement on Dark Matter Research

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently two representatives from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment, working 1.5 km underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota, announced that they had placed the tightest restrictions yet on the identities of dark matter particles, resulting in a null finding that clarified which identities these particles could not have, leading to a sense of resignation rather than disappointment among the physics community, as similar experiments like XENON-nT in Italy and PandaX-4T in China have yielded empty results for decades despite significant efforts.
Background on Dark Matter
- Definition: Dark matter makes up most of the universe's mass, contributing to its structure.
- Composition: Likely consists of previously unknown particles that:
- Do not interact with photons.
- Remain stable over billions of years.
- Key Question: Can dark matter interact with atomic nuclei and electrons?
Experimental Strategies
- Proposed Method:
- Introduced by physicists Mark Goodman and Ed Witten in 1985.
- Concept: Use a “sail” (a chunk of metal) deep underground to detect dark matter interactions.
- Objective: Measure unknown mass and interaction rate (cross-section) of dark matter particles.
Scattering Cross-Section
- Concept:
- Similar to light interaction with different media (vacuum, glass, rock).
- Cross-sections indicate how readily a particle can scatter.
- Previous Limits: Proposed limits as small as 10−38cm210^{-38} text{cm}^210−38cm2.
- Current Achievements: Recent experiments have ruled out cross-sections as small as 10−44cm210^{-44} text{cm}^210−44cm2.
Challenges Ahead
- Neutrino Interference:
- As detectors increase in size, they also detect more noise from neutrinos, complicating dark matter detection.
- Both PandaX-4T and XENONnT report issues with neutrino signals.
- Resignation in Community:
- Scientists had hoped for clearer results before facing the challenge of distinguishing dark matter from neutrinos.
Alternative Research Avenues
- Focus on Lighter Particles:
- Exploring dark particles lighter than atomic nuclei for easier detection.
- Technological Development:
- Advancing technologies to measure minimal energy transfers using special materials.
Conclusion
- Ongoing Effort: The search for dark matter continues to unite scientific disciplines and require innovative approaches.
- Human Ingenuity: The pursuit reflects a broader effort to understand the universe, drawing on collective expertise and creativity.
NAMASTE programme

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
A recent government survey has shed light on the demographics of workers engaged in the hazardous cleaning of urban sewers and septic tanks across India. This initiative, part of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's NAMASTE programme, highlights significant disparities within this labor sector.
Key Findings
- Community Representation: An overwhelming 91.9% of the 38,000 workers profiled belong to marginalized communities:
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 68.9%
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 14.7%
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 8.3%
- General Category: 8%
- Mortality Rates: Between 2019 and 2023, at least 377 individuals died while performing hazardous cleaning tasks, underscoring the dangers associated with this work.
The NAMASTE Programme
- Objective: The NAMASTE programme aims to mechanize sewer work to prevent fatalities linked to manual cleaning. It seeks to transition workers into safer, more sustainable roles as "sanipreneurs" by providing safety training, equipment, and capital subsidies.
- Background: This programme replaces the earlier Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), focusing on the more technical aspects of hazardous cleaning rather than manual scavenging.
- Namaste is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) as a joint initiative of the MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The Scheme has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 360 crore for four years from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- NAMASTE aims to achieve the following outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
- Strengthened supervisory and monitoring systems at national, state and ULB levels to ensure enforcement and monitoring of safe sanitation work
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered and skilled sanitation workers
Progress and Coverage
- Implementation: Since the scheme's inception, 3,326 urban local bodies (ULBs) have begun profiling workers, with many reporting minimal or no workers engaged in hazardous cleaning.
- Data Collection: The government is gathering data from over 3,000 ULBs across 29 states and union territories to better understand the scope and risks associated with this labor.
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
INDIA TO SUPPORT TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO IN DEVELOPING UPI-LIKE PAYMENT SYSTEM

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- NPCI International Payments Limited (NIPL) has partnered with Trinidad and Tobago's Ministry of Digital Transformation to create a payment platform for person-to-person and person-to-merchant transactions.
- Modeling on UPI: The new digital payments system will be based on India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which is widely recognized as a leading digital payment solution.
- Role of NPCI: NIPL, a quasi-government body under the Reserve Bank of India, manages India’s retail payment systems, including UPI.
Previous Initiatives
- Global Expansion: Earlier in 2024, NIPL also committed to establishing digital payment systems in Peru and Namibia, leveraging the UPI model.
- Ongoing Talks: NIPL is exploring opportunities with additional countries in Africa and South America to assist in building their payment infrastructures.
Significance:
- UPI has emerged as a transformative force in India's financial landscape, registering nearly 15 billion transactions in August 2024, with an estimated value of USD 245 billion.
- This strategic partnership aims to empower Trinidad and Tobago to establish a reliable and efficient real-time payments platform for both person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions, expanding digital payments in the country and fostering financial inclusion.
GST COMPENSATION CESS

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- GST compensation cess likely to continue beyond January 2026, with potential rebranding and new end-use defined.
- Revenue Collection: Estimated Rs 20,000 crore expected from the cess by February 2026, with recent receipts of Rs 12,068 crore in August 2024.
- Cess Nature: The compensation cess, originally intended for revenue shortfall, cannot merge with the 28% GST slab due to regulatory limitations.
Financial Context
- RBI Study Insights: Weighted average GST rate decreased from 14.4% at launch to 11.6%, now even below 11%, raising concerns among states.
- State Concerns: Many states, including Punjab and Kerala, seek a 2-5 year extension for the compensation period to stabilize finances.
Regulatory Framework
- Cess Legislation: GST Compensation Cess is governed by the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act, 2017, initially set for five years.
- Taxpayer Obligations: All suppliers of designated goods/services must collect the cess, except exporters and those under the composition scheme.
Distribution Mechanism
- Calculation of Compensation: Based on projected revenue growth (14%) against actual revenue, with payments distributed bi-monthly.
- Surplus Distribution: Any surplus in the compensation fund post-transition period will be shared between the Centre and states.
Future Considerations
- Ministerial Panel: A panel established by the GST Council will recommend the cess's future and revenue sharing post-compensation.
- Tax Expert Opinions: Some experts argue against pursuing the revenue-neutral rate, suggesting broader tax base expansion instead.
- Revenue Gap Solutions: Options for addressing compensation fund deficits include revising cess formulas, increasing rates, or market borrowing.
GlobE Network

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- India was elected to the 15-member GlobE Steering Committee on September 26, 2024, in a plenary session in Beijing. The election involved a multistage voting process.
- Role and Significance:
- India will play a vital role in shaping the global agenda on corruption and asset recovery.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) highlighted India's expertise in combating corruption as a significant asset for the GlobE Network.
- About the GlobE Network:
- The Global Operational Network of Anti-Corruption Law Enforcement Authorities (GlobE Network) is a G-20 initiative, supported by India since 2020.
- Officially launched on June 3, 2021, during a UN General Assembly session against corruption.
- Currently comprises 121 member countries and 219 member authorities.
- Governance Structure:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) serves as the central authority for India within the GlobE Network.
- Indian member authorities include the CBI and the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
- The Steering Committee consists of one chair, one vice-chair, and 13 members providing leadership and direction.
- Functionality and Objectives:
- The GlobE Network facilitates the sharing of best practices, criminal intelligence, and strategy development among international agencies to combat corruption.
- It is supported by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), which provides secretariat services.
- G-20 Presidency Initiatives:
- During India’s G-20 Presidency in 2023, two high-level principles for combating corruption were adopted, emphasizing the use of the GlobE Network to enhance global cooperation.
China test-fires an intercontinental ballistic missile into the Pacific Ocean

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
China stated that it test-launched an intercontinental ballistic missile, firing it into the Pacific Ocean in its first such exercise in decades.
- Launch Details:
- The missile carried a dummy warhead and fell into a designated area in the high seas.
- The specific flight path and landing location were not disclosed.
- Testing Objectives:
- The launch tested weapon performance and troop training levels, achieving its expected objectives.
- Historical Context:
- This is the first ICBM test over the Pacific Ocean in over 40 years.
- China's first ICBM, the DF-5, was test-fired in 1980.
- ICBM Specifications:
- The latest ICBM, likely the DF-41, has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilometers (7,400 to 9,300 miles), capable of reaching the US mainland.
- Strategic Messaging:
- Analysts interpret the test as a warning to the US, suggesting direct intervention in Taiwan could expose the American homeland.
- The test signals China's ability to engage multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Regional Tensions:
- Recent weeks have seen heightened tensions with Japan, the Philippines, and Taiwan due to military incursions and exercises.
- International Norms:
- There is a global expectation to notify nations of long-range missile launches to avoid miscalculations. China has limited agreements regarding this, primarily with Russia.
- Military Buildup:
- Under Xi Jinping, China has enhanced its nuclear capabilities and revamped the PLA’s Rocket Force.
- Recent satellite imagery indicates the construction of hundreds of ICBM silos in China’s deserts.
- Future Projections:
- As of 2023, China has over 500 operational nuclear warheads, projected to exceed 1,000 by 2030 according to the Pentagon.
- Implications of the Test:
- The ICBM test may be aimed at demonstrating military readiness despite recent corruption scandals within the Rocket Force.
About ICBMs:
- An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range ballistic missile system primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery. They are powerful and destructive weapons, capable of travelling vast distances at incredibly high speeds.
- Key features of ICBMs:
- Range: Range greater than 5,500 kilometres with maximum ranges varying from 7,000 to 16,000 kilometres.
- Speed: ICBMs can travel at speeds exceeding 20,000 kilometres per hour.
- Payload: Typically designed to carry nuclear warheads, though they could potentially be used to deliver other types of weapons, such as chemical or biological weapons.
- Deployment: ICBMs can be launched from silos underground, mobile launchers on land, or submarines at sea.
- Countries having operational ICBMs: Russia, United States, China, France, India, United Kingdom, Israel and North Korea.
KEY FINDINGS ON ATROCITIES AGAINST SCS AND STS (2022)
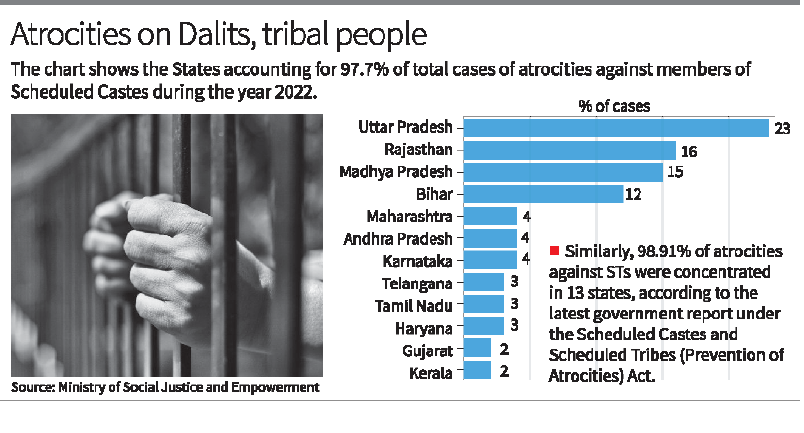
- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
According to the latest report under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act by the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry, the majority of atrocities against Scheduled Tribes (STs) were also concentrated in 13 states, which reported 98.91% of all cases in 2022.
- Case Statistics:
- Total cases of atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SCs): 51,656
- Total cases against Scheduled Tribes (STs): 9,735
- 97.7% of SC cases and 98.91% of ST cases reported from 13 states.
- States with Highest Incidents:
- SCs:
- Uttar Pradesh: 12,287 cases (23.78%)
- Rajasthan: 8,651 cases (16.75%)
- Madhya Pradesh: 7,732 cases (14.97%)
- Other significant states: Bihar (6,799), Odisha (3,576), Maharashtra (2,706)
- STs:
- Madhya Pradesh: 2,979 cases (30.61%)
- Rajasthan: 2,498 cases (25.66%)
- Odisha: 773 cases (7.94%)
- Other significant states: Maharashtra (691), Andhra Pradesh (499)
- SCs:
- Charge Sheets and Investigations:
- SC-related cases: 60.38% resulted in charge sheets; 14.78% ended with final reports (false claims/lack of evidence).
- ST-related cases: 63.32% led to charge sheets; 14.71% concluded similarly.
- Pending investigations by end of 2022: 17,166 SC cases, 2,702 ST cases.
- Conviction Rates:
- Decline from 39.2% in 2020 to 32.4% in 2022.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies:
- Only 194 out of 498 districts in 14 states have established special courts for these cases.
- Lack of identified atrocity-prone areas in states like Uttar Pradesh despite high case numbers.
- Protection Cells:
- SC/ST protection cells established in multiple states and union territories.
Reasons for Atrocities Against SCs and STs
- Caste Prejudice: Deep-rooted hierarchies and social exclusion lead to violence.
- Land Disputes: Conflicts over land access among historically deprived SC/ST communities.
- Economic Marginalization: Limited access to education and resources heightens vulnerability.
- Power Imbalance: Dominant castes wield political and social influence, perpetuating discrimination.
- Inadequate Law Enforcement: Weak implementation of protective laws and bureaucratic bias hinder justice.
- Political Exploitation: Caste tensions are sometimes used for electoral gains.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989
- Objective: Protect SCs and STs from caste-based violence and discrimination.
- Key Provisions:
- Defines various offences against SC/ST members, prescribing stricter punishments.
- Excludes anticipatory bail provisions for accused under the Act.
- Mandates establishment of special courts for speedy trials.
- Investigations must be conducted by senior police officers and completed within stipulated time frames.
- Recent Amendments:
- 2015: Enhanced protections for SC/ST women.
- 2019: Restored original provisions for arrest procedures following a Supreme Court ruling.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Strengthen Legal Framework: Establish more special courts and train personnel in sensitive handling of SC/ST cases.
- Improve Reporting Mechanisms: Enhance systems for victims to report atrocities without fear.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate communities on SC/ST rights and legal protections.
- Targeted Interventions: Identify and address issues in atrocity-prone districts.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement frameworks for accountability and continuous improvement in addressing these issues.
- Collaborate with NGOs: Work with civil society to support victims and advocate for their rights.
TRISHNA MISSION

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
During a recent event, the President of the French Space Agency, Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), addressed various topics, celebrating 60 years of collaboration between France and India in space exploration, alongside discussions on the Gaganyaan and TRISHNA missions.
Overview of the TRISHNA Mission
The Thermal Infrared Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment (TRISHNA) is a joint initiative by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and CNES.
Mission Objectives
TRISHNA aims to provide high-resolution, timely observations of Earth's surface temperature, monitor vegetation health, and analyze water cycle dynamics. It will facilitate:
- Assessment of urban heat islands
- Detection of thermal anomalies related to volcanic activity and geothermal resources
- Monitoring of snowmelt runoff and glacier behavior
- Collection of data on aerosol optical depth, atmospheric water vapor, and cloud cover
Satellite Payloads
TRISHNA is equipped with two main payloads:
- Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) Payload: Supplied by CNES, this payload includes a four-channel long-wave infrared imaging sensor that enables high-resolution mapping of surface temperature and emissivity.
- Visible-Near Infra-Red-ShortWave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) Payload: Developed by ISRO, this payload consists of seven spectral bands aimed at detailed mapping of surface reflectance, which is crucial for calculating biophysical and radiation budget variables.
The data retrieved from both payloads will aid in solving surface energy balance equations to estimate heat fluxes.
Operational Details
- TRISHNA will operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 761 km, with a scheduled overpass time of 12:30 PM at the equator.
- This orbit will achieve a spatial resolution of 57 meters for land and coastal regions, and 1 km for oceanic and polar areas.
- The mission is expected to have an operational lifespan of five years.
PROJECT 200

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
At the Bengaluru Space Expo 2024, Bengaluru-based start-up Bellatrix Aerospace launched Project 200, a pioneering satellite designed to operate in the Ultra-Low Earth Orbit (ULEO) range of 180 km to 250 km.
Revolutionary Capabilities
Bellatrix Aerospace claims that operating in this orbit dramatically enhances satellite capabilities and redefines their connection to Earth. The satellite's launch is part of a technology demonstration mission, showcasing an innovative propulsion system tailored for this low altitude.
Breakthrough Propulsion Technology
Traditionally, satellites are positioned above 450 km to minimize atmospheric interference. However, deploying at 200 km can significantly enhance capabilities, which has been hindered by propulsion technology limitations until now.
Enhanced Performance Metrics
The new propulsion system allows satellites to maintain their orbits for years, avoiding rapid deorbiting due to atmospheric drag. Key benefits of Project 200 include:
- Reduced Communication Latency: Halves the delay in satellite communication.
- Improved Image Resolution: Enhances clarity threefold.
- Cost Efficiency: Significantly lowers overall satellite costs.
Bellatrix's innovative approach not only addresses current limitations but also positions its satellite as a transformative solution for applications in high-resolution Earth observation, telecommunications, and scientific research.
India-Maldives Defence Talks

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
- India and the Maldives held their first defence talks since India withdrew its military personnel early this year.
Significance of Talks:
- The dialogue is notable given recent tensions in bilateral relations. Relations soured after President Mohamed Muizzu's election on an "India Out" platform, leading to the withdrawal of Indian troops. The last defence cooperation dialogue was held in March 2023 under President Ibrahim Solih.
Discussion Topics:
-
- Expediting ongoing defence cooperation projects.
- Planning forthcoming bilateral military exercises.
- Enhancing high-level exchanges and capability development.
Context of Tensions:
-
- Mohamed Muizzu, who took office in November 2023, had called for the removal of Indian military personnel, a significant shift from the previous administration’s stance.
- India agreed to withdraw 80 military personnel between March and May 2024. Indian technical personnel now operate key equipment like helicopters and a Dornier aircraft in the Maldives.
Recent Developments:
-
- Maldives Foreign Minister Moosa Zameer visited India in May.
- President Muizzu attended PM Narendra Modi’s swearing-in ceremony in June.
- In August, Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar visited the Maldives to reaffirm bilateral ties.
Historical Defence Cooperation:
-
- India gifted a Dornier aircraft to the Maldives in 2020 and a patrol vessel in 2019.
- India provided a coastal radar system last year and laid the foundation for the 'Ekatha Harbour' project, enhancing Maldivian Coast Guard capabilities.
Ongoing Projects:
-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) - a $500 million initiative financed by India.
- Building a new Coast Guard base at Uthuru Thilafalhu (UTF) atoll.
- India’s grant for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs).
Strategic Importance:
-
- For Maldives: India is a key security partner and crisis responder, with historical assistance during emergencies (Operation Neer, Vaccine Maitri). Maldives seeks to restore Indian tourist numbers, vital for its economy.
- For India: The Maldives is crucial to India's Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision SAGAR. Its strategic location between major Indian Ocean chokepoints makes it a vital partner for maritime security and countering China's influence.
Recent Changes:
-
- The Muizzu government decided not to renew a 2019 MoU for hydrographic surveying with India, ending joint hydrographic surveys conducted under the pact.
Travel and Trade:
-
- Both countries benefit from an open skies arrangement and visa-free access for tourism, medical, and business purposes
Centre gives clearance for ‘Mission Mausam’

- 13 Sep 2024
The Union Cabinet approved 'Mission Mausam,' a groundbreaking initiative with an investment of ?2,000 crore over the next two years. The mission, spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), aims to significantly advance India's capabilities in atmospheric sciences and climate resilience.
Objectives and Key Focus Areas
Mission Mausam is designed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of weather forecasting and climate management through several critical components:
- Advanced Technology Deployment: The mission will focus on deploying next-generation radars and satellite systems equipped with advanced sensors. These technologies are crucial for enhancing weather surveillance and prediction accuracy.
- Research and Development: A key objective of Mission Mausam is to bolster research and development in atmospheric sciences. This will include the development of enhanced Earth system models and advanced weather forecasting techniques.
- GIS-Based Decision Support System: An automated decision support system based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS) will be developed to facilitate real-time data sharing and improve decision-making processes.
Institutional Framework and Implementation
The Ministry of Earth Sciences will oversee the implementation of Mission Mausam. The following institutions will play central roles in the mission:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
- National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting
Additional support will come from other MoES bodies:
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research
- National Institute of Ocean Technology
Sectoral Benefits
Mission Mausam is expected to bring significant improvements across various sectors:
- Agriculture: Enhanced agromet forecasts will aid farmers in optimizing crop management and increasing resilience to climatic variability.
- Disaster Management: Improved monitoring and early warning systems will enhance disaster preparedness and response, potentially reducing loss of life and property damage.
- Defence: Accurate weather forecasting will support strategic planning and operational efficiency within the defence sector.
- Energy and Water Resources: Better weather predictions will lead to more efficient management of energy and water resources.
- Aviation: Safer aviation will be supported by more reliable weather information, reducing risks and improving travel safety.
- Tourism: Sustainable tourism will benefit from accurate weather forecasting, contributing to safer and more enjoyable travel experiences.
Mission Mausam represents a significant investment in India’s ability to manage and mitigate the impacts of climate change and extreme weather events, ultimately aiming to enhance the resilience of communities and support sustainable development.
Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari Initiative

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently launched the ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative via video conferencing from Surat, Gujarat.
Key Points:
- Campaign and Objectives:
- Objective: The initiative seeks to bolster water conservation through extensive public and governmental collaboration.
- Scope: About 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures will be constructed across Gujarat.
- Approach: Emphasizes a Whole-of-Society and Whole-of-Government approach to water management.
- Significance:
- Cultural Significance: PM Modi highlighted that water conservation is deeply embedded in Indian culture, with water revered as a divine entity and rivers considered Goddesses.
- Policy and Virtue: He stated that water conservation transcends policy and is both an effort and a virtue, reflecting social commitment and cultural consciousness.
- Future Challenges: The Prime Minister acknowledged the exacerbating impact of water scarcity due to climate change, urging a shift to the ‘Reduce, Reuse, Recharge, and Recycle’ mantra for sustainable water management.
- Impact of Drought and Water Scarcity:
- Recent Challenges: The drought affecting the Amazon region and other parts of India has highlighted the urgent need for effective water conservation strategies.
- Water Table Decline: Significant declines in river levels, such as the Rio Negro reaching its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) on record, and the death of endangered species due to low water levels underscore the crisis.
- Government Initiatives:
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Aims to provide piped water to every home, with significant progress noted from 3 crore households to over 15 crore.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Focuses on renovation and construction of water sources with widespread public participation.
- Amrit Sarovar: Over 60,000 Amrit Sarovars have been constructed under this campaign, which began during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- Innovative Solutions and Technological Integration:
- Drip Irrigation: Promotion of water-efficient farming techniques like drip irrigation to ensure sustainable agriculture.
- Support for Farmers: Encouragement for cultivating less water-intensive crops such as pulses and millets.
- Role of Industries:
- CSR Contributions: Industries have played a significant role in water conservation through initiatives like Net Zero Liquid Discharge Standards and the completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
- Future Plans: The ‘Jal Sanchay-Jan Bhagidari Abhiyan’ aims to create an additional 24,000 recharge structures.
- Conclusion and Vision:
- Global Leadership: PM Modi expressed his belief that India can become a global leader in water conservation.
- Public Movement: Stressed the importance of continuing public participation in water conservation to make India a model for global sustainability.
Background: The ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative builds on the success of the earlier Jal Sanchay program by involving citizens, local bodies, and industries in water conservation efforts. The initiative aligns with the vision of water security and aims to mobilize collective action for long-term sustainability.
Key Data:
- Construction of 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures.
- Significant increase in tap water connections from 3 crore to over 15 crore households.
- Creation of more than 60,000 Amrit Sarovars across the country.
- Completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
Climate change drives Amazon rainforest's record drought, study finds
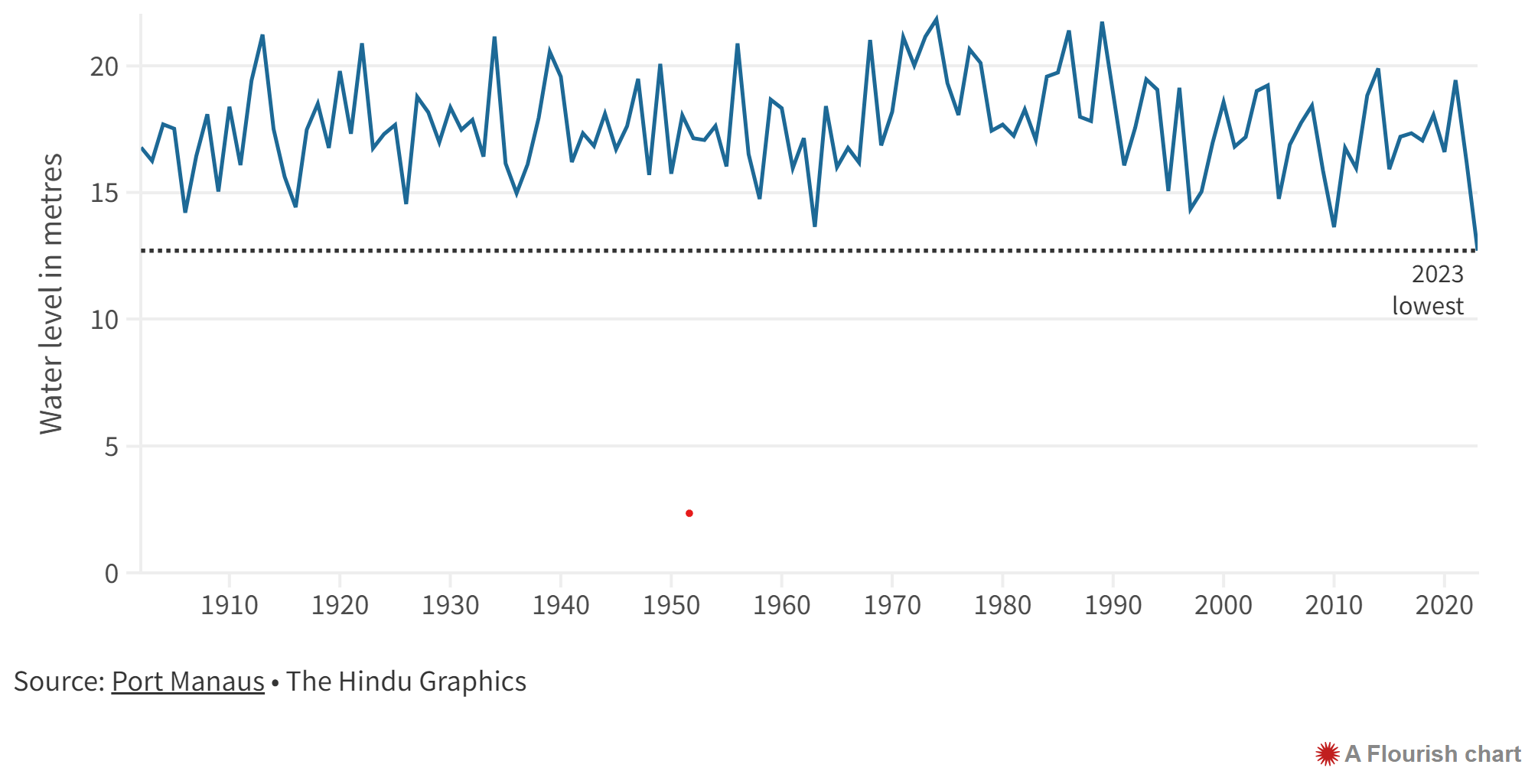
- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
The drought that hit all nine Amazon rainforest countries - including Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Peru - is expected to worsen in 2024
Role of Climate Change:
- Likelihood Increase: Climate change made the drought 30 times more likely.
- Temperature and Rainfall: It drove extreme high temperatures and contributed to lower rainfall.
Future Projections:
- Expected Worsening: The drought is predicted to worsen in 2024, with the rainy season expected to recede in May.
Impact on Ecosystems:
- River Levels: Rivers have reached their lowest levels on record, with the Rio Negro river falling to its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) since records began in 1902.
- Dolphin Deaths: At least 178 endangered pink and gray Amazon river dolphins died due to low water levels and high temperatures.
- Fish Deaths: Thousands of fish died from low oxygen levels in Amazon tributaries.
Impact on Human Life:
- Disruptions: Waterways dried up rapidly, forcing people to undertake long journeys across dried river sections to access essential goods like food and medicine.
Contributing Factors:
- El Niño Influence: Periodic warming in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (El Niño) contributed to decreased rainfall but not to higher temperatures.
Potential Consequences:
- Forest Fires and Biome Health: The drought could exacerbate forest fires, combined with climate change and deforestation, potentially pushing the Amazon toward a point of no return where it ceases to be a lush rainforest.
- Previous Droughts: While the region has experienced at least three intense droughts in the past 20 years, this one’s impact on the entire Amazon basin is unprecedented.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
The NB8 visit to India focuses on cooperation and trust
- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar hosted the India-Nordic-Baltic meeting on the sidelines of the ongoing Raisina Dialogue 2024 recently.
What are the Nordic-Baltic Countries?
- The Nordic-Baltic countries, also known as the NB8, are a group of Northern European countries that share historical, cultural, and geopolitical ties.
- The group includes
- Nordic countries of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, and
- Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- These countries collaborate on various regional issues, such as security, economy, environment, and culture, and often work together within international organisations and forums.
- The term "Nordic-Baltic" highlights the close relationship and cooperation between these neighbouring states in the Baltic Sea region.
India's Relations with NB8 Countries:
- India's collaboration with NB8 nations is broadening, exemplified by initiatives like the India-Denmark Green Strategic Partnership, the India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy, and cooperation on sustainability and ICT with Finland, including the 'LeadIT' (Leadership for Industry Transition) initiative with Sweden.
- Cooperation extends across various sectors, including innovation, green transition, maritime affairs, healthcare, intellectual property rights, emerging technologies, space exploration, and artificial intelligence.
- Trade and investment between the NB8 region and India are on a steady rise, reflecting deepening economic ties.
- Moreover, the security dynamics of the Nordic-Baltic region and the Indo-Pacific are intertwined, underlining the interconnectedness of regional security challenges.
Significance of NB8:
- The NB8 nations embody advanced economies characterised by their outward orientation, emphasis on innovation, complementarity, and seamless integration into the European Common Market, the world's largest single market area.
- The Baltic states, in particular, stand out as pioneers in IT, digitization, cyber technology, and green innovations, showcasing their leadership in these critical domains.
- Moreover, all NB8 members share a steadfast commitment to democracy and human rights, serving as advocates for an international order grounded in principles of multilateralism and adherence to international law.
NB8 Proposals for India:
- In light of the Ukraine conflict and its ripple effects on global food and energy security, supply chains, macro-financial stability, inflation, and growth, the NB8 seeks to collaborate with India in the following ways:
- Recognizing Shared Challenges: In an increasingly interconnected world, challenges such as the Ukraine conflict, global health crises, climate-related events, and geopolitical tensions affect us all.
- Acknowledging these shared challenges underscores the necessity for collaborative efforts to address them effectively.
- Embracing a Positive Agenda: There is an urgent imperative to pivot towards a more positive agenda for global cooperation.
- Leveraging our mutual commitment to the multilateral system, the NB8 proposes to enhance dialogue and cooperation on issues that are paramount to India's priorities and those of other global partners.
Mines Ministry unveils draft rules for offshore minerals auction (The Hindu Business Line)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s Mines Ministry has proposed a new set of rules for the auction of offshore mineral blocks. It is also in the process of identifying such mineral blocks, including those in exclusive economic zones beyond territorial waters.
Context:
- To implement the amended Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act), the ministry has unveiled two draft rules:
- Offshore Areas Mineral Auction Rules: These rules delineate provisions governing the auctioning of production leases.
- Offshore Areas Existence of Mineral Resources Rules: These rules set forth norms for the exploration of minerals and deposits in offshore areas.
Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act):
- The OAMDR Act governs the development and regulation of mineral resources in India's territorial waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zones, and other maritime zones.
About Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
- The Bill proposes amendments to the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, governing mining activities in India's maritime zones.
Key highlights include:
- Empowering the government to reserve offshore areas without operating rights.
- Granting the administering authority the discretion to issue composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Eliminating the provision for renewing production leases and setting a fixed fifty-year period, aligning with the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Mandating the grant of production leases to the private sector through competitive bidding.
- Allowing non-competitive bidding for operating rights in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government for government entities or corporations.
- Restricting the grant of exploration licenses or production leases for atomic minerals to government or government corporations.
- Introducing a four-year timeline for the commencement of production and dispatch after executing a composite license or production lease, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement after discontinuation.
- Authorizing the central government to establish rules for mineral conservation, systematic development, and environmental protection in offshore areas, preventing or controlling pollution from exploration or production operations.
India's Maritime Zone Mineral Resources:
- India's maritime zone hosts diverse mineral resources, including lime mud off the Gujarat and Maharashtra coasts within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Additionally, the region boasts construction-grade sand along the Kerala coast and heavy mineral placers in the inner-shelf and mid-shelf regions off Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra.
- Phosphorite is found in the Eastern and Western continental margins, while the Andaman Sea and Lakshadweep Sea house Polymetallic Ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) nodules and crusts.
ICRISAT Joins One CGIAR Global Initiative (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), a Hyderabad-based international research institute with a focus on tropical dryland agrifood system innovation, has joined the One CGIAR integrated partnership.
What is One CGIAR Global Initiative?
- The One CGIAR global initiative is designed to establish a cohesive approach to transform food, land, and water systems in response to the challenges posed by the climate crisis.
- This collaborative effort involves the CGIAR System Organisation and 12 research centres operating under the umbrella of One CGIAR.
- CGIAR is a publicly-funded network of research centres focused on agrifood systems, operating in over 80 countries.
Key Facts about ICRISAT:
- ICRISAT, a non-profit, non-political international research organization, is dedicated to agricultural research for development in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Its mission is to support farmers by providing improved crop varieties and hybrids, particularly aiding smallholder farmers in arid regions to combat climate change.
- The organization specializes in research on five highly nutritious, drought-tolerant crops: chickpea, pigeonpea, pearl millet, sorghum, and groundnut.
- Recognized for its impactful work, ICRISAT was awarded the 2021 Africa Food Prize for the Tropical Legumes Project, contributing to improved food security across 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
- ICRISAT is headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana State, India, with two regional hubs in Nairobi, Kenya, and Bamako, Mali.
- Through its research and initiatives, ICRISAT plays a crucial role in addressing agricultural challenges and promoting sustainable development in diverse regions.
India to Hold Satellite Spectrum Auctioning (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Elon Musk vs Mukesh Ambani battle on whether to auction or allocate satellite spectrum has attracted intervention from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
What is Satellite Spectrum?
- The satellite spectrum is like a special section of radio waves reserved for satellites when they're up in space.
- It's part of the larger family of radio waves that we use for things like Wi-Fi, TV, and radio.
- This spectrum serves as a vital resource for countries, facilitating satellite broadcasting, communication, and weather services.
Key Points:
- Limited Resource: The satellite spectrum is finite, allocated for activities like satellite broadcasting and communication.
- It plays a crucial role in facilitating services provided by communication satellites and weather satellites.
- Frequency Bands: The spectrum is categorized into different frequency bands, chosen based on diverse applications.
- The frequency assigned during a satellite's construction remains unchanged post-launch.
- Impact on Data Transfer: The frequency of a signal dictates the speed of data transfer.
- Higher frequencies enable faster data transmission, but they also entail shorter wavelengths, leading to signal attenuation over distances and increased interference risks.
- Frequency Range: Satellites typically transmit in the frequency range of 1.5 to 51.5 gigahertz.
- High-speed broadband operations often use the higher end of this spectrum.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Founded in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, later becoming a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Functions:
- Allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordinates and sets technical standards for telecommunication/ICT.
- Strives to enhance ICT access in underserved communities globally.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- India's Association with ITU: India has actively participated in the ITU since 1869, maintaining a consistent presence on the ITU Council since 1952.
Supplementary Grants (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supplementary Demands for Grants (SDG) are likely to see additional allocation for fertliser, food and fuel subsidy along with Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme.
About Supplementary Grants:
- According to Article 115 of the Indian Constitution, there's a provision for additional funds known as supplementary, additional, or excess grants.
- When the funds approved by the Parliament are not enough for the planned expenses, an estimate is submitted to the Parliament for extra grants.
- These additional grants are reviewed and approved by the Parliament before the conclusion of the financial year.
- If the actual spending surpasses the approved grants, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Railways make a request for an Excess Grant after the financial year ends.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India highlight these excesses to the Parliament.
- The Public Accounts Committee then examines these cases and provides recommendations to the Parliament.
- The Demand for Excess Grants is presented to the Parliament after the financial year, once the actual expenditures have been incurred.
Asian Development Bank (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The central government recently signed a USD 400 million policy-based loan with the Manila-based Asian Development Bank (ADB) to support its urban reform agenda to create high-quality urban infrastructure, improve service delivery, and promote efficient governance systems.
About Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
- It was established in 1966 to promote economic development and cooperation in Asia and the Pacific.
- The ADB's primary goal is to reduce poverty in its member countries.
- The bank provides loans, grants, technical assistance, and policy advice to its member countries.
- It also mobilizes private sector investment through its private sector arm, the Asian Development Bank Private Sector Operations.
- It has 68 member countries, including 49 countries in Asia and the Pacific, and 19 non-regional developed countries.
- The ADB's annual lending volume is around $32 billion.
- As of 2022, ADB's five largest shareholders are Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People's Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
- Source of Funding: It relies on member contributions, retained earnings from lending, and the repayment of loans for the funding of the organization.
The bank's strategy is focused on four key areas:
- Promoting sustainable growth: The ADB is committed to supporting its member countries in achieving their sustainable development goals by financing infrastructure, clean energy, and climate change mitigation and adaptation projects.
- Tackling poverty and inequality: The ADB is providing financing for education, health, social protection, and other programs that benefit the poor and vulnerable to reduce poverty and inequality in its member countries.
- Strengthening regional cooperation: The ADB is promoting regional cooperation and integration in Asia and the Pacific.
- The bank is supporting its member countries in developing regional infrastructure, trade, and investment projects.
- Responding to crises and disasters: The ADB is helping its member countries prepare for and respond to crises and disasters by providing finances for disaster risk reduction and resilience projects.
Krishi 24/7 7 (The Hindu Business Line)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Union Agriculture Ministry partnered with the Wadhwani Institute for Artificial Intelligence (Wadhwani AI) to create a solution known as Krishi 24/7.
About Krishi 24/7:
- Krishi 24/7 is a groundbreaking AI-powered solution developed with support from Google.org, designed for automated monitoring and analysis of agricultural news.
- Key Features:
- This tool scans news articles in various languages and translates them into English for easy access.
- It extracts crucial information from news articles, including headlines, crop details, event types, dates, locations, severity, summaries, and source links.
- This ensures that the ministry receives timely updates on relevant events found on the internet.
- Significance:
- Krishi 24/7 addresses the vital need for an efficient system to identify and manage agricultural news articles.
- This aids in making timely decisions.
- It serves the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) by identifying pertinent news, delivering timely alerts, and facilitating swift action to protect the interests of farmers and promote sustainable agricultural growth through informed decision-making.
Strategic Disinvestment (The Hindu Business Line)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The government has recently issued a Request for Proposal (RFP) to hire an asset appraiser for the Strategic Disinvestment of IDBI Bank.
Facts About:
Strategic disinvestment involves the sale of a significant portion of the government's ownership in a central public sector enterprise (CPSE), which can be up to 50% or a higher percentage as decided by the competent authority.
- This process also includes the transfer of management control.
It essentially means transferring both ownership and control of a public sector entity to another entity, which can be either private or public.
Distinguishing Strategic Disinvestment/Sale from Disinvestment:
- Disinvestment refers to the sale of minority shares of public enterprises to another entity, whether it's public or private.
- In this case, the government still maintains ownership of the enterprise.
In contrast, strategic disinvestment/sale occurs when the government sells a majority share in an enterprise, relinquishing not only ownership but also control of the entity.
What are the objectives of Strategic Disinvestment:
- Reduce Government Ownership
- Raise Capital
- Enhance Efficiency
- Foster Competition
- Attract Private Investment
- Focus on Core Functions
- Alleviate Fiscal Burden
