Breakthrough in Bacterial Computing
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists at the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics in Kolkatahave successfully engineered bacteria capable of solving mathematical problems, marking a major step forward in the field of synthetic biology and biocomputing. These engineered bacteria can function like artificial neural networks, performing tasks that were traditionally reserved for humans or conventional computers.
Key Highlights:
- Bacterial Computers:
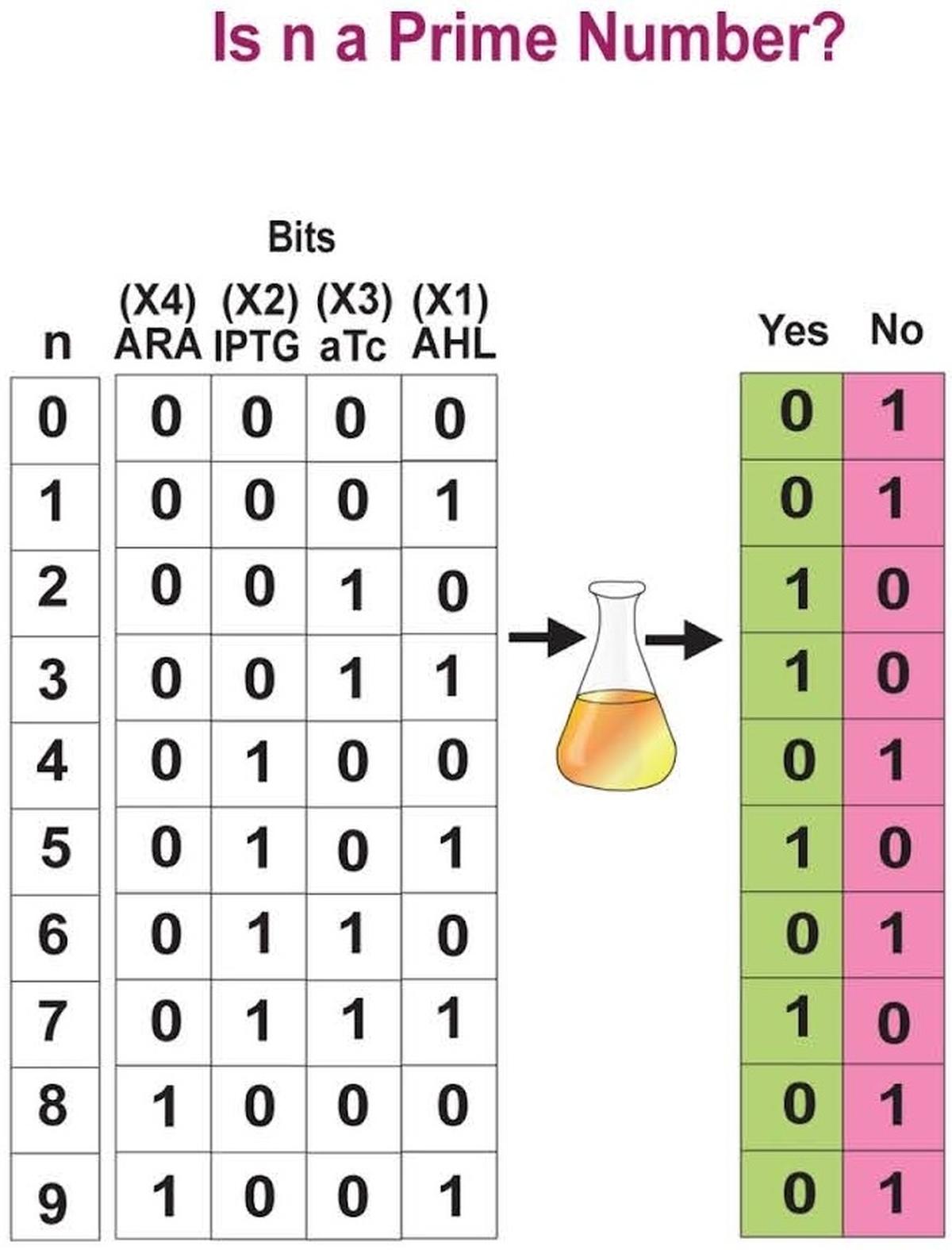
- The research team introduced genetic circuits into bacteria, turning them into computational units capable of tasks like determining whether a number is prime or identifying vowels in an alphabet.
- These bacterial "computers" mimic artificial neural networks (ANNs), where each type of engineered bacterium (called a "bactoneuron") behaves like a node in a network, processing inputs to generate outputs.
- How it Works:
- The bacteria's genetic circuits are activated by chemical inducers, which represent binary 0s and 1s (the fundamental language of computing). The presence or absence of certain chemicals determines whether a bacterium expresses a specific fluorescent protein, representing the binary states.
- For example, when asked if a number between 0-9 is prime, the bacteria can express green fluorescent proteins (1) for "yes" or red fluorescent proteins (0) for "no", providing binary outputs that solve the problem.
- Complex Tasks:
- The team advanced to more complex tasks, such as asking the bacterial computers whether adding a number (like 2 + 3) results in a prime number or if a number's square can be expressed as the sum of factorials.
- In an even more complex test, the bacteria solved an optimization problem—calculating the maximum number of pieces a pie could be cut into with a given number of straight cuts. The bacteria’s fluorescent output represented binary numbers that were converted to decimal for the correct solution.
- Technical Details:
- The researchers used Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, engineered with transcriptional genetic circuits, which recognize specific DNA sequences and trigger the expression of proteins based on the presence of chemical inducers.
- The system is similar to how ANNs work in traditional computing, where nodes (bactoneurons) take inputs, apply weights, and produce outputs based on activation functions.
- Implications and Future Prospects:
- Synthetic Biology & Biomanufacturing: This breakthrough could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals and biomanufacturing by enabling biocomputers that perform specific tasks in a biological environment, potentially reducing reliance on silicon-based computers.
- Medical Applications: The ability of engineered bacteria to process data could lead to biocomputers capable of diagnosing diseases (such as cancer) at an early stage and even administering localized treatments.
- Understanding Intelligence: Bagh and his team hope to explore the biochemical nature of intelligence, pondering how intelligence could emerge from simple, single-celled organisms.
- Groundbreaking Research:
- The research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, has drawn significant attention in the synthetic biology community. Centre for Synthetic Biology highlighting the potential of bacteria programmed to solve complex problems.
This innovative work paves the way for future developments in biocomputing, where living organisms, instead of silicon chips, could be used to perform sophisticated calculations, offering new ways to think about computing, intelligence, and even the future of technology in medicine.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
Bacterial Pathogens Priority List (BPPL)

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently released its updated Bacterial Priority Pathogens List (BPPL) 2024.
What is the Bacterial Pathogens Priority List?
- The Bacterial Pathogens Priority List (BPPL) is a crucial tool in the global effort to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Background:
- In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) created the first BPPL to guide investment in the research and development (R&D) of new antibacterial treatments, listing 13 bacterial pathogens (phenotypes).
- The list was developed using the Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) method, a scientific approach that evaluates and ranks alternatives based on multiple criteria, ensuring systematic and transparent decision-making.
- The 2024 WHO BPPL expands to cover 24 pathogens across 15 families of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, categorizing them into critical, high, and medium priority groups to guide R&D and public health efforts.
Significance:
- The BPPL directs priorities for R&D and investment in AMR, highlighting the necessity for region-specific strategies to combat resistance effectively.
- It is aimed at developers of antibacterial medicines, academic and public research institutions, research funders, public-private partnerships involved in AMR R&D, and policymakers responsible for AMR policies and programs.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the ability of microorganisms to persist or grow in the presence of drugs designed to inhibit or kill them.
- These drugs, called antimicrobials, are used to treat infectious diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoan parasites.
- When microorganisms become resistant to antimicrobials, standard treatments are often ineffective, and in some cases, no drugs provide effective therapy.
- Consequently, treatments fail and this increases illness and mortality in humans, animals and plants.
- For agriculture, this causes production losses, damages livelihoods and jeopardizes food security.
- Moreover, AMR can spread among different hosts and the environment, and antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms can contaminate the food chain.
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major global threat of increasing concern to human and animal health.
- It also has implications for food safety, food security and the economic well-being of millions of farming households.
Materiovigilance Programme of India (MvPI)

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The DCGI recently issued a directive to all medical device license holders and manufacturers, instructing them to report any adverse events associated with life-saving medical equipment on the government's Materiovigilance Programme of India (MvPI) platform.
What is the Materiovigilance Programme of India?
- The Materiovigilance Programme of India was launched on July 6, 2015, that monitors and evaluates the safety of medical devices across the country.
- It aims to systematically collect and scientifically analyze data on adverse events related to medical devices, offering guidance on their safe usage and supporting regulatory decision-making processes.
Objectives and Importance:
- The primary goal of the Materiovigilance Programme is to enhance patient safety in India by carefully recording, assessing, and determining the root causes of adverse events or risks associated with medical devices, including in-vitro diagnostics.
- By coordinating the reporting and analysis of such events, the programme seeks to inform regulatory bodies and healthcare professionals, promoting the appropriate use of medical devices and ultimately improving patient safety.
Governance and Regulation:
- Since 2018, the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has served as the National Coordination Centre (NCC) for the programme.
- The Materiovigilance Programme is regulated by the Central Drugs Standards Control Organization (CDSCO), operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, and Medical Device Rule, 2017, currently govern all medical devices in India.
- Given that the country is 80% dependent on imports for medical devices, the programme's role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these essential healthcare tools is crucial.
About Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI):
- The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) leads the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), ensuring the quality of drug supply nationwide.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
Functions:
- Approving new drugs and overseeing clinical trials.
- Establishing standards for drug manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution in India.
- Granting licenses for specific drug categories such as blood products, IV fluids, vaccines, and sera.
- Ensuring uniform implementation of the Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940, and its associated rules to safeguard patient safety, rights, and well-being.
Fusobacterium nucleatum
- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent study, researchers have discovered a unique subtype of Fusobacterium nucleatum that is more prevalent in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumours.
What is Fusobacterium nucleatum?
- Fusobacterium nucleatum is a species of bacteria commonly found in the human mouth and gastrointestinal tract.
- It is a Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium, meaning it does not require oxygen to survive.
- While it is a normal component of the oral microbiota, Fusobacterium nucleatum can also act as an opportunistic pathogen, potentially causing infections in various parts of the body.
- In recent research, specific subtypes of Fusobacterium nucleatum have been associated with colorectal cancer tumours, highlighting its potential role in certain diseases.
- It plays a role in periodontal disease and is often associated with various human diseases and infections, including preterm births.
- F. nucleatum can aggregate with other bacteria species in the oral cavity and is considered a key component of periodontal plaque due to its abundance.
- Detection of F. nucleatum typically involves surgical tissue retrieval, faecal tests, or blood tests in patients showing symptoms, and early detection is crucial for preventing further disease progression.
Highlights of the Recent Research:
- Researchers examined genomes of F. nucleatum types from colorectal tumour samples and individuals without cancer. Among its subspecies, only one, known as Fusobacterium nucleatum animalis (or Fna), was consistently found in tumour samples.
- Further genetic analysis divided Fna into two distinct groups, with only one group, Fna C2, being prevalent in colorectal tumours.
- Fna C2 showed higher acid resistance, potentially allowing it to travel from the mouth to the intestines via the stomach.
- Additionally, Fna C2 demonstrated the ability to hide within tumour cells, evade the immune system, and utilize nutrients found in the gastrointestinal tract.
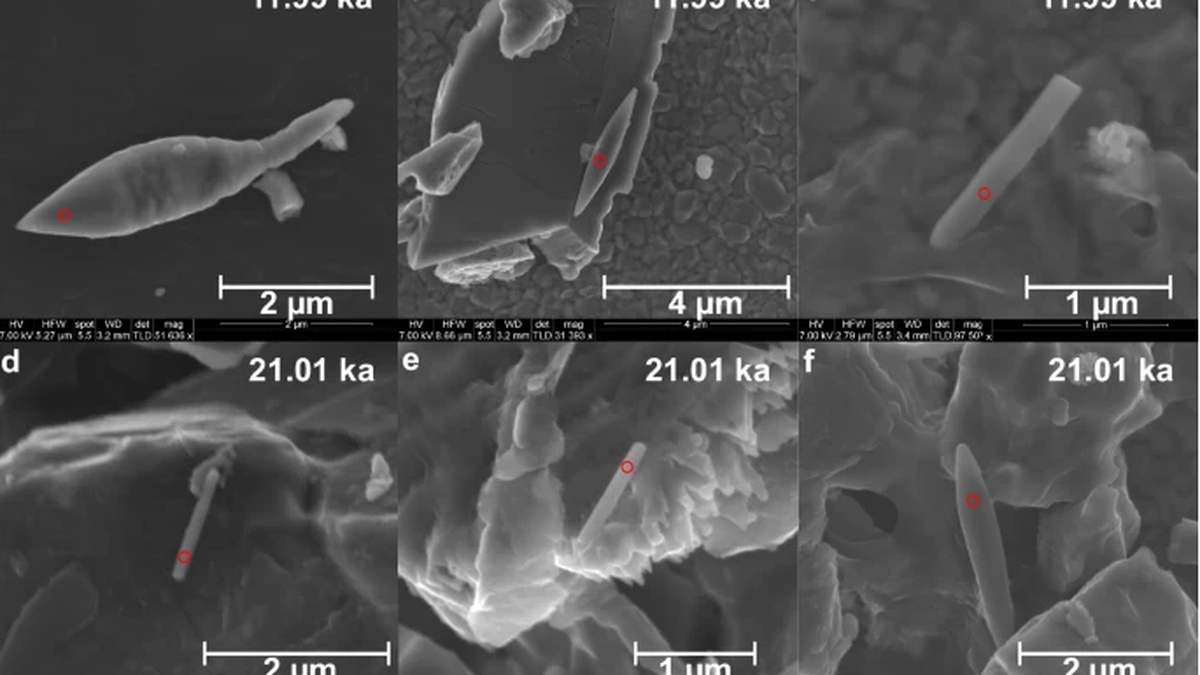
Magnetofossils
- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the depths of the Bay of Bengal, scientists have discovered a 50,000-year-old sediment — a giant magnetofossil and one of the youngest to be found yet.
What are Magnetofossils?
- Magnetofossils represent the fossilized remnants of magnetic particles originated by magnetotactic bacteria, also referred to as magnetobacteria, encapsulated within the geological archives.
About Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria, predominantly prokaryotic microorganisms, possess the unique ability to align themselves in alignment with Earth's magnetic field.
- These organisms were traditionally believed to utilize the Earth's magnetic field as a navigational aid to locate environments with optimal oxygen levels.
- Comprising distinctively structured particles abundant in iron, these bacteria harbor small sacs that function akin to a compass.
- Magnetotactic bacteria synthesize minute crystals composed of iron-rich minerals such as magnetite or greigite, facilitating their navigation amidst fluctuations in oxygen concentrations within their aquatic habitats.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Sediment Composition: The sediment core, measuring three meters in length and extracted from the southwestern Bay of Bengal, primarily comprised "pale green silty clays."
- Foraminifera Abundance: Researchers observed abundant benthic and planktic foraminifera, which are single-celled organisms characterized by shells found near the seabed and freely floating in water.
- Oxygen Concentration: At depths ranging from approximately 1,000 to 1,500 meters, the Bay of Bengal exhibited notably low oxygen levels.
- Analysis of the sediment sample confirmed fluctuations in monsoon activity, as evidenced by the presence of magnetic mineral particles from distinct geological periods.
- Role of Rivers: Rivers such as the Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner, which discharge into the Bay of Bengal, played a pivotal role in magnetofossil formation.
- Nutrient Supply: The nutrient-rich sediment transported by these rivers supplied reactive iron, which, combined with organic carbon in the suboxic conditions of the Bay of Bengal, created a conducive environment for magnetotactic bacteria growth.
- Impact of Oceanographic Processes: Factors such as freshwater discharge from rivers and oceanographic phenomena like eddy formation influenced the oxygen content in these waters, distinguishing them from other low-oxygen zones.
- Persistence of Suboxic Conditions: The presence of magnetofossils indicated the prolonged persistence of suboxic conditions in the Bay of Bengal, fostering an environment conducive to the proliferation of magnetotactic bacteria.
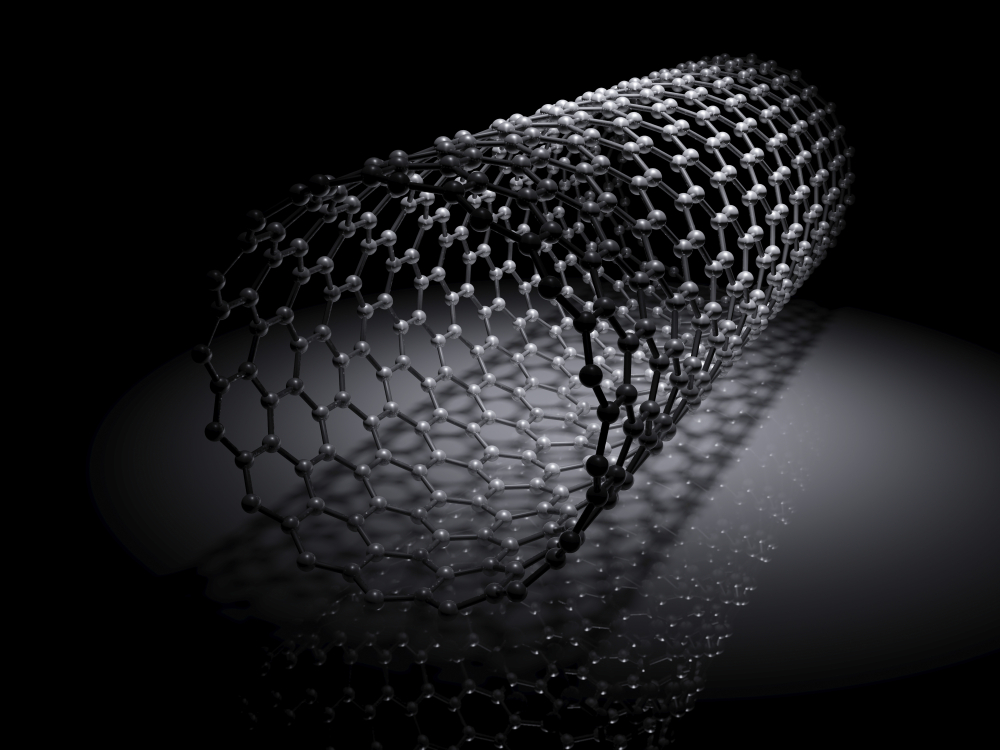
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) (DST)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have pioneered a novel method for directly synthesising CNTs on glass substrates at a temperature of 750 °C.
What are Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)?
- A carbon nanotube is a small cylindrical carbon structure made out of graphene.
- The tube comprises hexagonal structures.
- Despite their very small size, carbon nanotubes are very strong.
- Carbon nanotubes are also known as “Buckytubes” because they resemble R. Buckminster Fuller’s geodesic domes.
- They are pivotal in advancing modern technology by showcasing extraordinary properties.
- Applications: They have found applications in diverse fields, including rechargeable batteries, flexible electronics, aerospace, transparent electrodes, touch screens, supercapacitors, and medicine.
- Recent Developments: The experiment employs the Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition Technique (PECVD), in which a spiral-shaped fused hollow cathode source is specifically constructed to create plasma.
- This novel method avoids the requirement for high temperatures and does not require a transition metal catalyst.
Why is It Necessary?
- Metal catalysts (Fe, Co, and Ni) and high temperatures (~1000 0C) are needed for conventional CNT production procedures.
- Concerns about biocompatibility arise with these catalysts for possible biomedical uses.
- A fascinating area of nanotechnology, the removal of these catalysts from CNTs presents a huge financial hurdle, underscoring the urgent need for cleaner, more sustainable CNT synthesis techniques.
- Clean CNTs that can be used in biomedical settings, optoelectronics, and energy studies may now be produced.
Preamble to the Constitution of India (Indian Express)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently wondered if the Preamble to the Constitution could have been amended while retaining the date when the Constitution was adopted.
Background:
- In historical context, the Preamble underwent a solitary amendment in December 1976 via the 42nd Constitutional Amendment during the Indira Gandhi Government.
- This amendment introduced two modifications: replacing "unity of the nation" with "unity and integrity of the nation," and inserting "socialist" and "secular" between "sovereign" and "democratic."
- Initially, the Preamble described India as a "sovereign, democratic republic."
- Notably, the Supreme Court affirmed in the Kesavananda Bharati case that the Preamble constitutes an integral component of the Constitution, subject to Parliament's amending authority, provided the fundamental structure remains intact.
About the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
- The Preamble to the Constitution of India draws inspiration primarily from the 'Objective Resolution' penned by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1946.
- It serves as a concise introduction, outlining the foundational principles and aspirations of the nation. Key components include:
- Source of Constitutional Authority: It affirms that the Constitution derives its authority from the people of India.
- Nature of the Indian State: It declares India as a Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic, and Republican Polity.
- Objectives of the Constitution: It articulates Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity as the core objectives.
- Adoption Date: It designates November 26, 1949, as the date of adoption.
- Significance:
- Acts as a guiding framework for interpreting the Constitution and formulating laws.
- Defines the national aspirations and goals.
- Highlights the importance of fundamental rights and values for all citizens.
- Fosters a sense of national unity and identity.
Is the Preamble a Part of the Constitution of India?
- In the Berubari Union Case of 1960, the Supreme Court stated that the Preamble is not a formal part of the Constitution.
- However, it acknowledged that the Preamble provides insight into the intentions of the Constitution makers, thus aiding in interpreting any ambiguities within the Constitution.
- The Kesavananda Bharati Case of 1973 marked a reversal of this stance.
- The Supreme Court declared the Preamble as an intrinsic part of the Constitution, attributing it significant interpretive value.
- It emphasized that the Preamble plays a crucial role in understanding the spirit and objectives of the Constitution, guiding the interpretation of its provisions.
- In the LIC of India Case of 1995, the Supreme Court reiterated that the Preamble is indeed an integral component of the Constitution.
- However, it clarified that while the Preamble holds symbolic importance and helps in understanding the Constitution's essence, it cannot be directly enforced as a law in Indian courts.
Can the Preamble be Amended?
- An essential debate revolves around whether the Preamble can undergo amendments under Article 368.
- In the Kesavananda Bharati Case of 1973, the Supreme Court established that the Preamble constitutes a fundamental aspect of the Constitution and is therefore amenable to amendments.
- However, any such amendment must adhere to the principle that the 'Basic Structure' of the Constitution remains untouched.
World Sustainable Development Summit 2024 (TERI)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar inaugurated the World Sustainable Development Summit in New Delhi recently in the presence of Prime Minister of Guyana Mark Phillips.
About the World Sustainable Development (WSDS) Summit:
- The WSDS Summit, organized annually by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), stands as a flagship event in the realm of sustainable development.
- Instituted in 2001, the Summit series boasts a distinguished legacy spanning over two decades, dedicated to advancing 'sustainable development' as a universally embraced objective.
- Distinguished as the sole independently convened international summit on sustainable development and environment originating from the Global South, the WSDS endeavours to forge enduring solutions for the global community.
- It achieves this by convening the world's foremost leaders and intellectuals on a singular platform.
- The upcoming WSDS 2024 marks the 23rd edition of this significant summit, revolving around the theme 'Leadership for Sustainable Development and Climate Justice'.
Key Facts about The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI):
- TERI stands as a premier think tank committed to conducting research aimed at fostering sustainable development in India and across the Global South.
- Established in 1974 as an information centre focusing on energy issues, TERI expanded its scope to encompass multifaceted research, policy analysis, consultancy, and implementation initiatives.
- TERI's research endeavours, commencing in the late 1980s, are rooted in its steadfast belief that the efficient utilization of energy and sustainable management of natural resources are indispensable for developmental progress.
- Across various sectors, TERI concentrates its efforts on:
- Promoting the efficient utilization of resources
- Enhancing access to and adoption of sustainable practices and inputs
- Mitigating environmental and climate impacts
- TERI's headquarters are located in New Delhi, serving as a hub for its diverse activities and initiatives.
Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Lower House of Parliament recently passed the Finance Bill moved by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Context:
- The Lok Sabha passed the Finance Bill, 2024 by voice vote recently.
- Also, the House passed the Appropriation Bill, granting authorization for government expenditures for four months in the upcoming fiscal year.
- The Appropriation Bill is a significant legislative measure that empowers the government to utilize public funds allocated in the annual budget.
- It serves to uphold accountability and transparency by necessitating parliamentary approval for expenditures and prevents unauthorized withdrawals from the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Furthermore, the lower house sanctioned the Rs 1.8 lakh crore budget for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
What is a Finance Bill?
- The Finance Bill, classified as a Money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution, is an annual presentation in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget announcement.
- It encapsulates the government's fiscal proposals concerning taxation, expenditure, and other financial affairs.
- Through this bill, the government submits its proposals for imposing new taxes, altering the existing tax framework, or extending the current tax structure beyond the approved period to Parliament.
- Accompanied by a Memorandum elucidating its provisions, the Finance Bill is exclusively introduced in the Lok Sabha, though amendments can be recommended by the Rajya Sabha.
- Approval from both houses of Parliament is requisite for the bill to become law, with a mandate for passage within 75 days of its introduction.
- While all Money Bills fall under the category of Financial Bills, not all Financial Bills qualify as Money Bills.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely focusing on tax proposals is classified as a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Bill addressing taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects is categorized as a Financial Bill.
- Thus, if a Bill entails government expenditure along with other matters, it is designated as a financial bill.
Highlights of the 2024 Finance Bill:
- Stability in Income Tax: With the impending general elections in April-May 2024, the bill prioritizes continuity by retaining the current tax framework for the fiscal year 2024-2025.
- Targeted Relief Measures: Incorporates slight tax concessions tailored to particular sectors or taxpayer groups.
- Promotion of Economic Expansion: Encompasses provisions aimed at fostering infrastructure enhancement, investment stimulation, and streamlining business operations.
- Fiscal Discipline: Pursues fiscal consolidation objectives through proposed strategies to manage expenditures or enhance revenue generation.
Three New Major Railway Corridors Announced Under PM GatiShakti in the Interim Budget 2024-25 (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget for 2024-25 announcement for implementation of three Economic Railway Corridors identified under the PM GatiShakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity.
Context:
- The Interim Budget for 2024-25 has laid the groundwork for implementing three major Economic Railway Corridors under the PM GatiShakti initiative.
- This will enable multi-modal connectivity, including:
- Energy, mineral, and cement corridors
- Port connectivity corridors and
- High-traffic density corridors
Significance of the Three Corridors:
- Logistics Efficiency Boost: These Corridors serve as catalysts for enhancing logistics efficiency, thereby cutting down on the costs associated with rail transportation.
- By streamlining rail movements, they pave the way for smoother and more cost-effective logistics operations.
- Alleviating Rail Congestion: One of their primary roles is to alleviate congestion on heavily trafficked rail routes.
- By diverting some of the traffic to these designated Corridors, the strain on high-density rail networks is relieved, ensuring smoother and more reliable transportation across the board.
- Promoting Modal Shift: The Corridors play a pivotal role in encouraging a modal shift from road to rail and coastal shipping.
- By providing efficient rail connections and integrating coastal shipping options, they offer viable alternatives to traditional road transport, thereby reducing congestion on highways and minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Sustainability: A key benefit of these Corridors is the reduction of the carbon footprint associated with logistics operations.
- By promoting more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as rail and coastal shipping, they contribute to mitigating the environmental impact of freight movement, fostering sustainability in logistics practices.
About PM GatiShakti National Master Plan:
- The government of India initiated the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan to transform the nation's infrastructure.
- PM Modi launched the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP) on 13th October 2021, on the 75th Independence Day to provide multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- The scheme is expected to smooth out the execution of projects across the nation and foster coordination between different ministries engaged with these projects.
Advantages of PM Gati Shakti:
- It lays out a centralised portal to unite the infrastructural initiatives of 16 central ministries and departments.
- Facilitates these ministries, gives a centralised transportation and logistics grid for smoother data flow and sped up project clearance.
- Large-scale infrastructure projects like UDAAN, expansion of the railway network, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, and Bharat Net will be executed by the Gati Shakti master plan.
- The Gati Shakti master plan aims to create employment potential for a large number of individuals.
- The plan's three primary targets are smooth multimodal connectivity, enhanced prioritisation and optimal usage of resources to create capacities on time, and resolution of issues like standardisation, disjointed planning and clearances.
- The Gati Shakti mission aims to create world-class infrastructure in the country and foster logistical synergy across various modes of movement.
- The general objective of the drive is to increase competitiveness and economic development in India.
CBSE Proposes New Plan For Class 10 & 12 (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
CBSE is reported to have proposed significant changes to the academic framework for secondary and higher secondary education, including a shift from studying two languages to three in Class 10, with the requirement that at least two must be native Indian languages.
Key Highlights of the Proposal:
Proposed Changes for Class 10:
- Transition from studying two languages to three, with a stipulation that at least two must be native Indian languages.
- Potential requirement for students to pass in 10 subjects, contrasting with the current mandate of five.
Proposed Changes for Class 12:
- Shift to studying two languages instead of one, with the condition that at least one must be a native Indian language.
- Introduction of a necessity to clear examinations in six subjects for high school graduation, up from the existing requirement of five.
The objective behind the Proposed Changes:
- These modifications are part of CBSE's broader initiative to implement a national credit framework in school education, addressing the absence of a formalized credit system in the standard curriculum.
Academic Year and National Learning Hours:
- According to the CBSE plan, an academic year will comprise 1200 notional learning hours, equivalent to earning 40 credits.
- Notional learning denotes the specified time required for an average student to achieve set outcomes.
- This encompasses both academic learning at school and non-academic or experiential learning outside of it.
Storage of Earned Credits:
- The scheme of studies has been adjusted to outline teaching hours and credits earned for each subject.
- These earned credits will be digitally stored in the Academic Bank of Credits, accessible through a linked Digilocker account.
What is the National Credit Framework (NCrF)?
- The draft NCrF was introduced by the Union Ministry of Education (MoE) in 2022, based on recommendations from an inter-ministerial committee.
- It serves as a guideline for schools, colleges, and universities to adopt the credit system, marking the inclusion of the entire school education system under its purview.
- Previously, only the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) followed a credit system, but the NCrF extended its coverage to include skill and vocational education.
Proposed Benefits of NCrF for Various Stakeholders:
- Students:
- Facilitates multidisciplinary education with flexible curricula.
- Eliminates distinctions between different streams like arts, science, social sciences, and commerce.
- Rewards students with credits for academic, skill, and experiential learning.
- Expands core learning to encompass both foundational and cognitive aspects.
- Institutions:
- Fosters collaboration between institutions.
- Simplifies and standardizes credit mechanisms.
- Emphasizes research and innovation.
- Utilizes institutional infrastructure efficiently.
- Government:
- Expected to increase student enrollment rates.
- Complements India's demographic dividend, aiming to become the Skill Capital of the World.
- Industry:
- Enables students to acquire NSQF-approved foundational skills from the industry, enhancing employability.
- Allows for quick educational upgradation and up-skilling through micro-credentials.
Significance of NCrF:
- Aligns with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 by integrating academic and vocational domains for flexibility and mobility.
- Facilitates re-entry into the education system for students who have dropped out.
- Promotes Recognition of Prior Learning, acknowledging skills acquired informally through various means.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia (Indian Express)
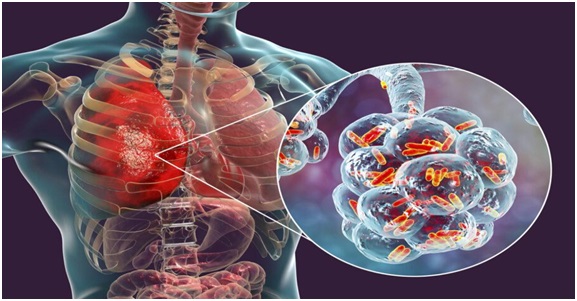
- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
What is Mycoplasma Pneumonia?
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that can cause illness by damaging the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, windpipe).
- It acts more like a virus and spreads faster from person to person.
- It is a common cause of pneumonia in children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Vulnerable groups, who already have respiratory issues, are prone to developing this infection in a severe form.
- Most people with respiratory infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae don’t develop pneumonia.
- For this reason, MP is known as an atypical pneumonia and is sometimes called walking pneumonia.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can include:
- Fever, Cough, Headache, Sore throat, Fatigue, Muscle aches, and Shortness of breath
- In most cases, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is mild and goes away on its own within a few weeks.
- However, some people may develop more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- It spreads through close contact with an infected person, such as through coughing or sneezing.
- It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- There is no vaccine to prevent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection however there are multiple antibiotics that effectively cure this infection.
Coming soon, a ‘Cafeteria’ for oil spill-hit birds at Ennore Creek (The Hindu)
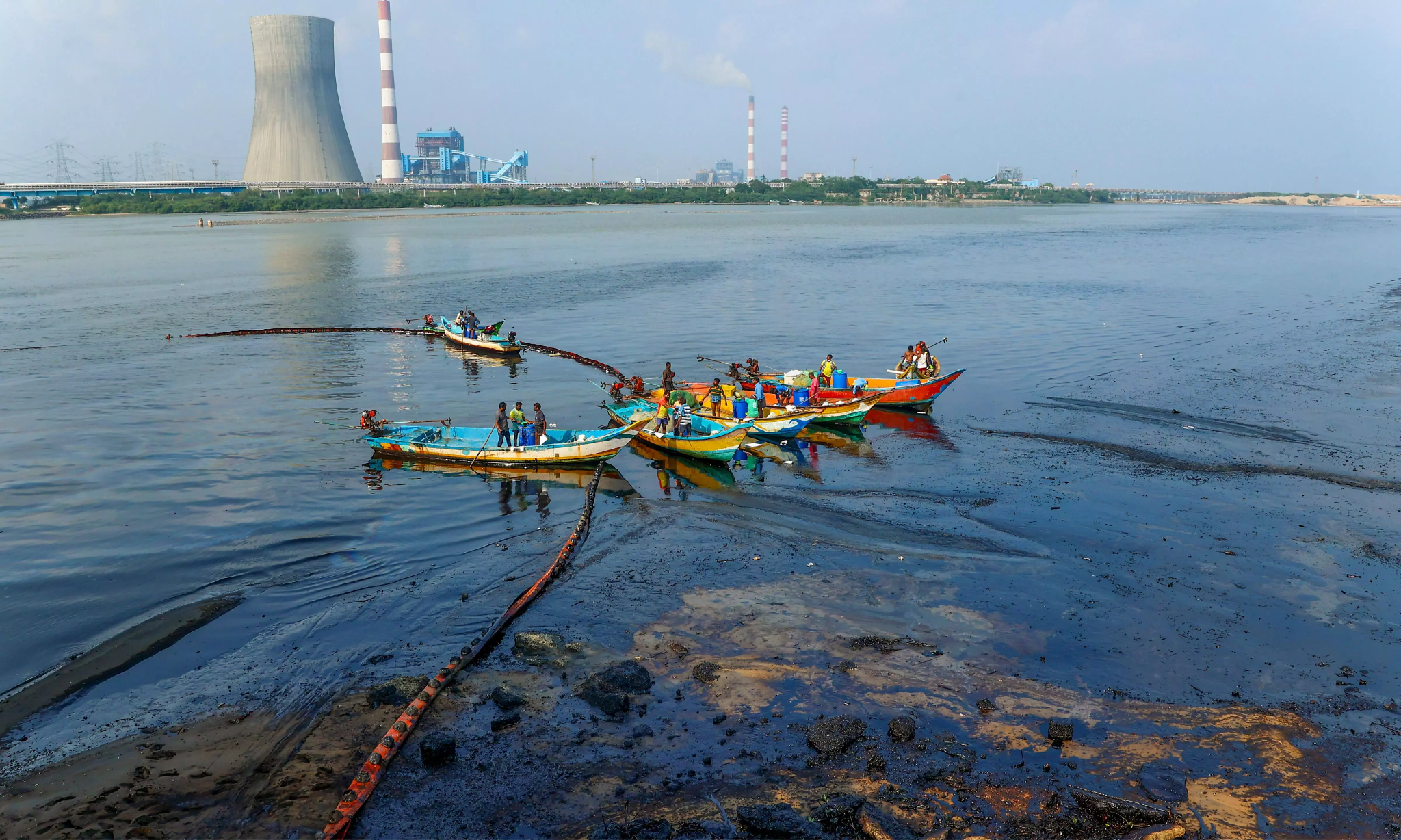

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Experts from the Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) and the Besant Memorial Animal Dispensary (BMAD) are planning to establish feeding stations for birds at the creek, where contamination due to an oil spill from industries in Manali has brought down the bird population drastically.
About Ennore Creek:
- Ennore Creek, situated in Thiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu, is a backwater channel branching off from the Kosathalaiyar River.
- It merges with the Bay of Bengal at Mugathwara Kuppam, while its northern channel links to Pulicat Lake, the country's second-largest brackish water lake.
- For generations, this creek has been a lifeline for communities in the neighbouring villages, designated as CRZ IV (Water Body) in the coastal zone management plan by the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority.
- Its significance is heightened for local fisherfolk, alongside the Buckingham Canal and the broader Pulicat water system.
- The Ennore Creek has historically fostered a robust aquatic ecosystem renowned for its biodiversity.
- This ecologically sensitive area once boasted extensive mangrove swamps, contributing not only to sustainable fish resources but also playing a crucial role in flood mitigation during periods of heavy rainfall, high tides, and cyclones.
About the Wildlife Trust of India:
- Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) is an Indian Non-profit Organisation (NGO) committed to nature conservation.
- Motto: In Service of Nature
- It was formed in November 1998, in response to the rapidly deteriorating condition of the country's wildlife.
- Its mission is to:
- Conserve wildlife and its habitat and
- Work for the welfare of individual wild animals, in partnership with communities and governments.
- WTI has earned recognition for accomplishing significant conservation milestones, including the recovery of populations for critically endangered species, successful species translocation, and the mitigation of human-animal conflicts.
The E Prime Layer (HT)
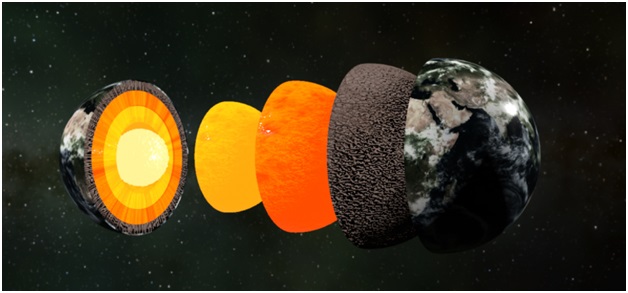
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an international team of scientists found a new mysterious layer called the E prime layer on the outer part of the Earth's core.
About the E Prime Layer:
- Before, it was thought that there's only a small exchange of materials between the Earth's core and mantle.
- However, experiments showed that when water reaches the boundary between the core and mantle, it reacts with silicon in the core and creates silica.
Development of this Layer:
- New research proposes that over billions of years, tectonic plates carrying surface water transported it deep into the Earth.
- When this water reaches about 1,800 miles below the surface at the core-mantle boundary, it triggers significant chemical changes, affecting the core's structure.
- Scientists observed that under high pressure, subducted water chemically reacts with core materials.
- This reaction forms a hydrogen-rich, silicon-depleted layer on the outer core, resembling a film.
- Silica crystals produced in this process rise and mix into the mantle, impacting the overall composition.
- Changes in the liquid metallic layer could potentially lead to reduced density and altered seismic characteristics, consistent with anomalies detected by seismologists.
Importance of this Discovery:
- This finding deepens researchers' understanding of the Earth's internal workings, revealing a more extensive and complex global water cycle than previously known.
- The altered core layer has significant implications for the interconnected geochemical processes that link surface water cycles with the deep metallic core.
Dwarf Planet Eris (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered the inside structure of the enigmatic dwarf planet Eris.
About Dwarf Planet Eris:
- This new dwarf planet is the largest object found in orbit around the sun since the discovery of Neptune and its moon Triton in 1846.
- It was discovered on Jan. 5, 2005, and It is larger than Pluto, discovered in 1930.
- Like Pluto, the new dwarf planet is a member of the Kuiper belt, a swarm of icy bodies beyond Neptune in orbit around the sun.
- Eris is named for the ancient Greek goddess of discord and strife.
- The surface of Eris is extremely cold, so it seems unlikely that life could exist there.
- With a radius of about 1,163 kilometers, Eris is about 1/5 the radius of Earth.
- Eris, like Pluto, is a little smaller than Earth's Moon.
- Eris takes 557 Earth years to make one trip around the Sun.
- As Eris orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 25.9 hours, making its day length similar to ours.
- Moons: Eris has a very small moon called Dysnomia.
- Dysnomia has a nearly circular orbit lasting about 16 days.
- Eris most likely has a rocky surface similar to Pluto.
- Atmosphere: The dwarf planet is often so far from the Sun that its atmosphere collapses and freezes, falling to the surface as snow.
- As it gets closest to the Sun in its faraway orbit, the atmosphere thaws.
5th Annual India- US ‘2+2’ Dialogue (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India and the U.S. on November 10 held extensive deliberations to further expand their global strategic partnership through greater defence industrial ties, enhancing engagement in the Indo-Pacific and boosting cooperation in key areas such as critical minerals and high technology.
Context:
- The fifth annual ‘2+2’ dialogue between India and the United States is underway in New Delhi.
- The U.S. delegation at the 2+2 ministerial talks was led by U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken and U.S. Defence Secretary Lloyd Austin.
- External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar and Defence Minister Rajnath Singh headed the Indian side.
What is the 2+2 Dialogue?
- The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, an annual diplomatic summit being held since 2018, brings together India's foreign and defence ministers with their US counterparts.
- Its purpose is to address and collaborate on common concerns to enhance and strengthen India–United States relations.
- A 2+2 ministerial dialogue enables the partners to better understand and appreciate each other’s strategic concerns and sensitivities taking into account political factors on both sides, in order to build a stronger, more integrated strategic relationship in a rapidly changing global environment.
- India has 2+2 dialogues with four key strategic partners: the US, Australia, Japan, and Russia.
- Besides Russia, the other three countries are also India’s partners in the Quad.
- The US is India’s oldest and most important 2+2 talks partner.
Hematene (PIB)
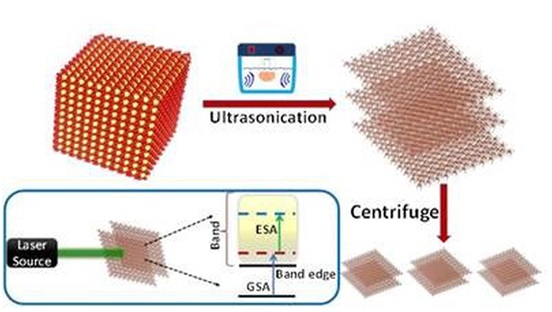
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
A new and remarkably efficient optical limiter has been developed by researchers, utilizing a novel 2D material known as 'hematene.'
- About Hematene:
- Nanoflakes of a material called hematene extracted from iron ore have been found capable of withstanding and acting as a shield from high laser intensities.
- Hence it could be used to make devices called optical limiters that can protect sensitive optical equipment from light-induced damage.
- Radiation from laser sources is highly concentrated and powerful and can be detrimental to sensitive equipment such as sensors, detectors, and other optical devices.
- When the input intensity increases optical limiters control the amount of light that passes through, thereby preventing damage to the optical component.
- These devices are often useful in laser technologies, military, telecommunications, aircraft, and scientific research in several ways.
- The MESO (Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices) Group of the Department of Physics, Sanatana Dharma College, Alappuzha, in collaboration with the Ultrafast and Nonlinear Optics Lab of the Raman Research Institute, Bangalore, has come up with a new and highly efficient optical limiter using a novel 2D material, ‘hematene’.
- They found that 2D nanoflakes of hematene, a material extracted from iron ore or hematite are capable of withstanding very high laser intensities, and they exhibited excellent optical limiting of green laser light (532 nm) while maintaining a high linear transmission (about 87%) for low-intensity light.
- The nanoflakes of lateral dimensions less than 10 nm, prepared by applying ultrasonic waves to hematite in a liquid medium ( facile exfoliation process) for a definite period to exfoliate the 2D nanoflakes of hematene were also found to be highly stable after year-long storage under ambient conditions, indicating tremendous potential as an optical limiter for futuristic applications.
- This research work carried out at SD College using the instrumentation facility procured through the Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST) programme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) programme, was recently published in ACS Applied Optical Materials.
Manis Mysteria (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In addition to the eight previously identified pangolin species, researchers have recently found a ninth variety, which is currently given the temporary name "Manis mysteria.
Facts About:
Scientists have recently made a significant discovery in the world of wildlife by identifying a previously unknown ninth species of pangolin.
- This newly found pangolin variety has been tentatively named "Manis mysteria."
Origins from Confiscated Scales: The origins of this remarkable discovery trace back to the examination of pangolin scales that were seized in China's Yunnan province during the years 2015 and 2019.
- These scales provided vital clues leading to the identification of the new species.
Ancient Divergence: Research indicates that "Manis mysteria" took a distinct evolutionary path around five million years ago, separating from its Philippine and Malayan pangolin relatives.
- This long separation in the evolutionary timeline highlights its unique characteristics.
Distinctive Features of Pangolins: Pangolins are known for their distinctive characteristics, including protective keratin scales that cover their bodies and a diet primarily consisting of ants and termites.
- They hold the distinction of being the only mammals with such specialized scales.
Defensive Behavior: One of the most intriguing aspects of pangolins is their ability to curl up into a tight, defensive ball when they feel threatened.
- This remarkable behavior helps protect them from potential predators.
- Grave Threats to Pangolins: Unfortunately, all species of pangolins face severe threats to their survival.
- Each species is currently listed on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, a concerning designation that highlights their vulnerable status.
- For instance, the Indian pangolin is specifically categorized as "Endangered," underlining the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard these unique creatures.
