100-Day Intensified Nationwide TB Campaign

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
- Union Health Minister Shri JP Nadda launched a 100-day intensified TB campaign in Panchkula, Haryana, aimed at reducing TB incidence and mortality. The campaign will focus on 347 high-risk districts across India.
Key Highlights:
- Campaign Goals:
- Find and treat missing TB cases, especially in high-risk groups.
- Significantly reduce TB-related deaths.
- Focus Areas:
- The campaign is part of India’s larger goal to eliminate TB before the 2030 SDG deadline.
- Strategies include early detection and rapid treatment of TB patients.
- Historical Context:
- TB was once seen as a "slow death" and patients were isolated.
- In 2018, the Prime Minister set the vision to end TB before 2030.
- Recent Government Initiatives:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs network of 1.7 lakh centers helps in early TB detection.
- Increased diagnostic infrastructure: Laboratories increased from 120 in 2014 to 8,293 today.
- Introduction of new drug regimens: Shorter and more effective treatments have increased the treatment success rate to 87%.
- Ni-kshay Support: Rs 3,338 crore transferred to 1.17 crore TB patients via direct benefit transfer.
- Key Achievements:
- TB decline rate in India has increased from 8.3% (2015) to 17.7% today, surpassing the global average.
- TB-related deaths have dropped by 21.4% over the past decade.
- Private Sector Involvement:
- Mandatory notification of TB patients by private practitioners has led to an 8-fold increase in TB case notifications.
- 4Ts Approach for TB Elimination: Test, Track, Treat, and Technology (use of advanced tools for diagnosis and treatment).
- New Initiatives:
- Ni-kshay Vahaan: Mobile vans to detect and treat TB patients in remote areas.
- Launch of national guidelines for a new drug-resistant TB regimen (BPaLM), which is a 4-drug combination therapy for multi-drug-resistant TB.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana:
- Increase in nutritional support: Monthly support raised from Rs 500 to Rs 1000 per TB patient.
- The initiative also includes energy boosters for enhanced patient care.
- Mobile Diagnostics:
- Deployment of AI-enabled portable X-ray units and molecular tests to bring diagnostics closer to people, especially in remote areas.
- Monitoring and Data: Intensified data tracking via the Ni-kshay portal to provide timely updates to TB patients.
- Background of the Campaign:
- Part of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- The 347 districts were selected based on indicators like death rates, presumptive TB examination rates, and incidence rates.
- Campaign Materials:
- Unveiling of Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) resources in regional languages.
- Honoring TB Champions and Ni-kshay Mitras during the event.
- Government’s Strategic Framework:
- India’s National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign and Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- Tuberculosis (TB) Overview:
- TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and primarily affects the lungs, spreading through the air.
- Mortality rate has decreased from 28 per lakh (2015) to 23 per lakh (2022).
E. coli Outbreak Linked to McDonald's Burgers

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- An E. coli outbreak has been linked to McDonald's burgers in the United States. The infection has affected at least 10 states.
E. coli in India:
- Prevalence: E. coli infections are common in India, especially during the summer and rainy seasons, when there is an increase in gastrointestinal infections.
- Transmission: E. coli spreads mainly through contaminated food and water.
- National statistics: Over 500 outbreaks of diarrhoeal diseases were reported in India in 2023. E. coli is one of the most common pathogens causing gastrointestinal infections in India.
- ICMR data: According to the latest report from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), E. coli was found in 23.19% of patient samples from tertiary care hospitals across India.
- FSSAI's Role: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is establishing a network of 34 microbiology labs to test food for pathogens like E. coli, salmonella, and listeria.
Symptoms of E. coli Infection:
- Common symptoms include:
- High fever (over 102°F)
- Persistent diarrhoea, sometimes bloody
- Vomiting
- Dehydration due to fluid loss
- Severe cases may lead to acute kidney injury.
Treatment of E. coli Infections:
- E. coli is treated with antibiotics, but medical consultation is necessary before taking any medication.
- Antimicrobial resistance is a growing concern, as E. coli's susceptibility to antibiotics, including carbapenem, has declined from 81.4% in 2017 to 62.7% in 2023.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Consult a doctor if:
- Diarrhoea lasts more than a couple of days.
- Frequent visits to the toilet (every half hour to an hour).
- Bloody diarrhoea.
- Vomiting frequently or inability to retain fluids.
Food Safety Measures:
- The FSSAI is working to improve food safety by implementing better testing protocols for microbial contamination in food products across India.
MARBURG VIRUS OUTBREAK IN RWANDA
- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
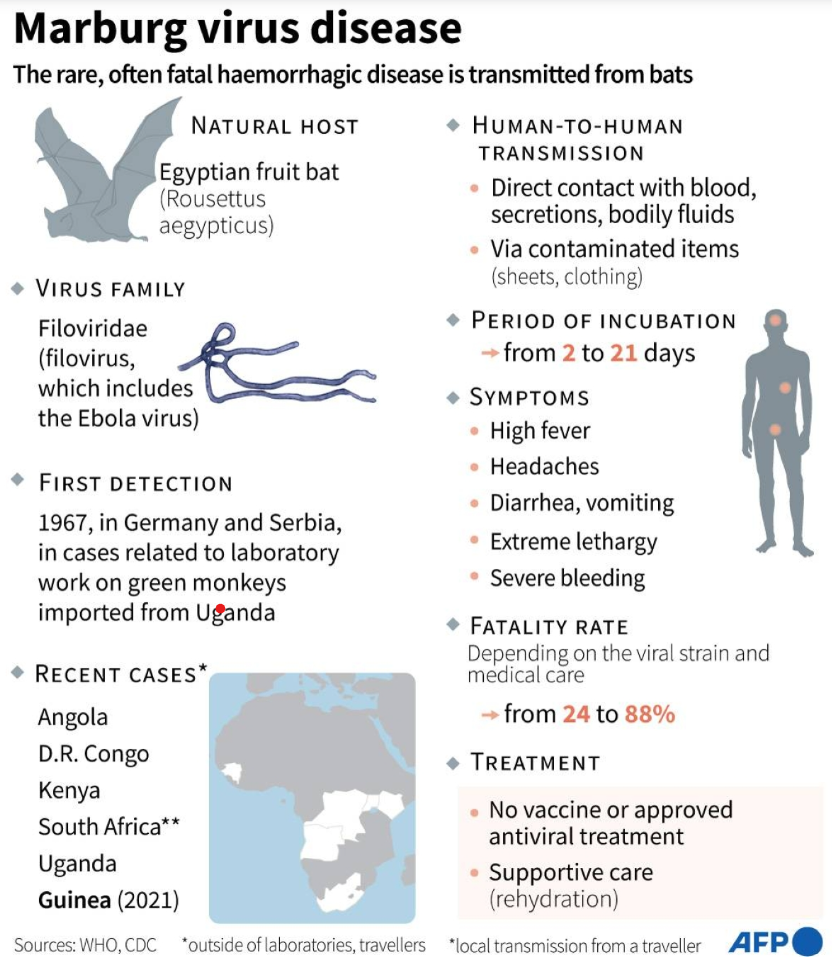
Rwanda is currently facing an outbreak of Marburg virus disease (MVD), leading to six fatalities, primarily among healthcare workers.
What is Marburg Virus Disease?
Marburg virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness first identified in 1967 in Germany. It is caused by the Marburg virus, which is primarily transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, particularly fruit bats.
Current Situation in Rwanda
The ongoing outbreak has claimed six lives, most of whom were healthcare professionals. The Minister of Health has emphasized the need for heightened preventive measures and community vigilance.
Symptoms and Transmission
Common symptoms of MVD include high fever, severe headache, watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. The virus spreads through direct contact with the blood, secretions, and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
Available Treatments and Supportive Care
There is currently no specific treatment for Marburg virus disease. Supportive care, including symptom management and hydration, is critical, and early medical attention is essential for those exhibiting symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To prevent the spread of MVD, individuals should:
- Practice good hygiene.
- Avoid contact with infected persons.
- Ensure thorough cooking of animal products.
- Use protective equipment when caring for sick patients.
Global Context and Pandemic Risk
While Marburg virus disease poses a significant mortality risk and can spread between humans, its pandemic potential is lower than that of more contagious viruses. Rapid containment efforts are essential to prevent wider outbreaks.
Extra-pulmonary TB
- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Approximately 20% of tuberculosis (TB) patients suffer from Extra-pulmonary TB, yet the majority remain undiagnosed. Even among those diagnosed, access to appropriate care is limited to specialized health facilities, posing a challenge to effective treatment.
What is Extra-pulmonary TB?
- Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) is a form of tuberculosis (TB) that affects organs outside the lungs, such as the lymph nodes, pleura, bones, joints, and central nervous system.
- EPTB accounts for a significant portion of active TB cases, ranging from 20% to 40%, and occurs more frequently in immunosuppressed individuals and young children.
- In HIV-positive individuals, EPTB is present in more than 50% of cases.
- EPTB diagnosis remains challenging due to the difficulty in accessing affected sites and the low sensitivity of diagnostic tests.
- A combination of mycobacteriology and histopathologic examinations, along with molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction, can aid in the diagnosis.
- Biochemical markers, like adenosine deaminase or gamma interferon, can be useful adjuncts in diagnosing TB-affected serosal fluids.
Treatments:
- Treatment of EPTB typically involves standard anti-TB drug therapy, but the ideal regimen and duration have not yet been established.
- While the disease usually responds to treatment, complications and paradoxical responses may occur, necessitating the distinction from other causes of clinical deterioration.
- Surgery may be required to obtain diagnostic specimens or manage complications.
Challenges with EPTB:
- EPTB infections may leave disease markers lingering even after treatment, posing concerns about relapse.
- Standardized diagnosis and treatment protocols for various affected organs are lacking, complicating management.
- A lack of awareness among both patients and physicians, along with the absence of precise diagnostic and treatment criteria, adds to the challenge.
- Even after completing anti-TB therapy, some EPTB patients may experience lingering effects of the disease.
- The existing INDEX-TB guidelines, formulated over a decade ago, require updating to incorporate the latest insights and experiences.
Monkeypox (Mpox)
- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is struggling to contain its biggest Mpox outbreak.
What Is Monkeypox (Mpox)?
- Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) is a rare viral infection caused by the mpox virus, a member of the orthopoxvirus genus.
- It was first discovered in 1958 in monkeys but can also infect humans and other animals.
- Mpox typically presents with a range of symptoms and can be transmitted through close contact with infected individuals or animals.
Symptoms:
- Mpox symptoms often begin with fever, muscle aches, and sore throat, followed by a rash that starts on the face and spreads across the body.
- The rash evolves over two to four weeks, forming macules, papules, vesicles, and pustules before crusting over.
- Lesions can also appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
Causes:
- The mpox virus is primarily transmitted through direct contact with the skin lesions, body fluids, or respiratory droplets of infected individuals or animals.
- It can also be contracted through contaminated materials, such as bedding or clothing.
Prevention:
- Preventing mpox involves avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals, practising good hygiene, and disinfecting contaminated surfaces.
- Vaccines are also available for individuals at high risk of contracting the virus.
Treatment:
- There is currently no specific treatment for mpox, but symptoms can be managed with supportive care, such as fever reducers and pain medications. In some cases, antiviral medications may be used.
Expanding Glacial Lakes in the Indian Himalayas: ISRO

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Experts express concern over the ISRO analysis findings, indicating that the expansion of glacial lakes due to warming could result in cascading impacts in lower regions.
Highlights of the ISRO Report:
- The ISRO report said 601 glacial lakes, or 89 percent, have expanded more than twice, and 10 lakes have grown between 15 times and double their size. Sixty-five lakes have expanded 1.5 times.
- Of the 2,431 glacial lakes larger than 10 hectares, 676 have significantly expanded, and at least 130 of these lakes are in India 65 (Indus River basin), 7 (Ganga River basin), and 58 (Brahmaputra River basin).
- Elevation-based analysis shows 314 lakes are located in the 4,000 to 5,000 meters range, and 296 lakes are above 5,000 meters elevation.
What are Glacial Lakes?
- Glacial lakes emerge in hollows or basins shaped by glaciers' erosive force and are prevalent in areas where glaciers once existed or persist.
- They vary widely in size and shape, from tiny pools to expansive bodies of water.
- ISRO classifies them into four main types: moraine-dammed, ice-dammed, erosion-based, and 'others'.
- While vital as freshwater sources for rivers, glacial lakes also pose risks, particularly Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
- GLOFs occur when these lakes discharge large volumes of meltwater, often due to natural dam failures, causing sudden and severe downstream flooding.
Formation Processes:
- Glacial Erosion: Glaciers, moving slowly, sculpt the landscape by eroding bedrock through abrasion and plucking, creating valleys and basins.
- Moraine Deposition: As glaciers move, they transport sediment, depositing it at their edges as moraines, which can act as natural dams, forming lake basins.
- Ice Melting: Rising temperatures or glacier retreat causes ice to melt, filling depressions created by erosion with water, and forming glacial lakes.
- Terminal Moraine Formation: Glaciers may leave behind ridges of sediment at their terminus, creating natural dams that trap water, forming terminal moraine lakes.
Utilization of Remote Sensing for Glacial Lake Monitoring:
- Monitoring glacial lakes in the Himalayan region presents challenges due to rugged terrain, making satellite remote-sensing technology indispensable.
- By analyzing satellite data, changes in glacial lakes can be tracked over time, offering insights into their evolving dynamics.
- This data is vital for understanding their environmental impact and devising strategies to manage risks such as glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) and adapt to climate change in glacier-influenced regions.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Glacial Lakes:
- Research suggests that reducing glacial lake levels by 10 to 30 meters can significantly alleviate downstream impacts, albeit not eliminate GLOF risks.
- One effective method involves siphoning off lake water using extended High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes.
- In 2016, the Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority successfully employed this technique to lower water levels in South Lhonak Lake, showcasing its practicality and efficacy in risk reduction efforts.
Mange Disease
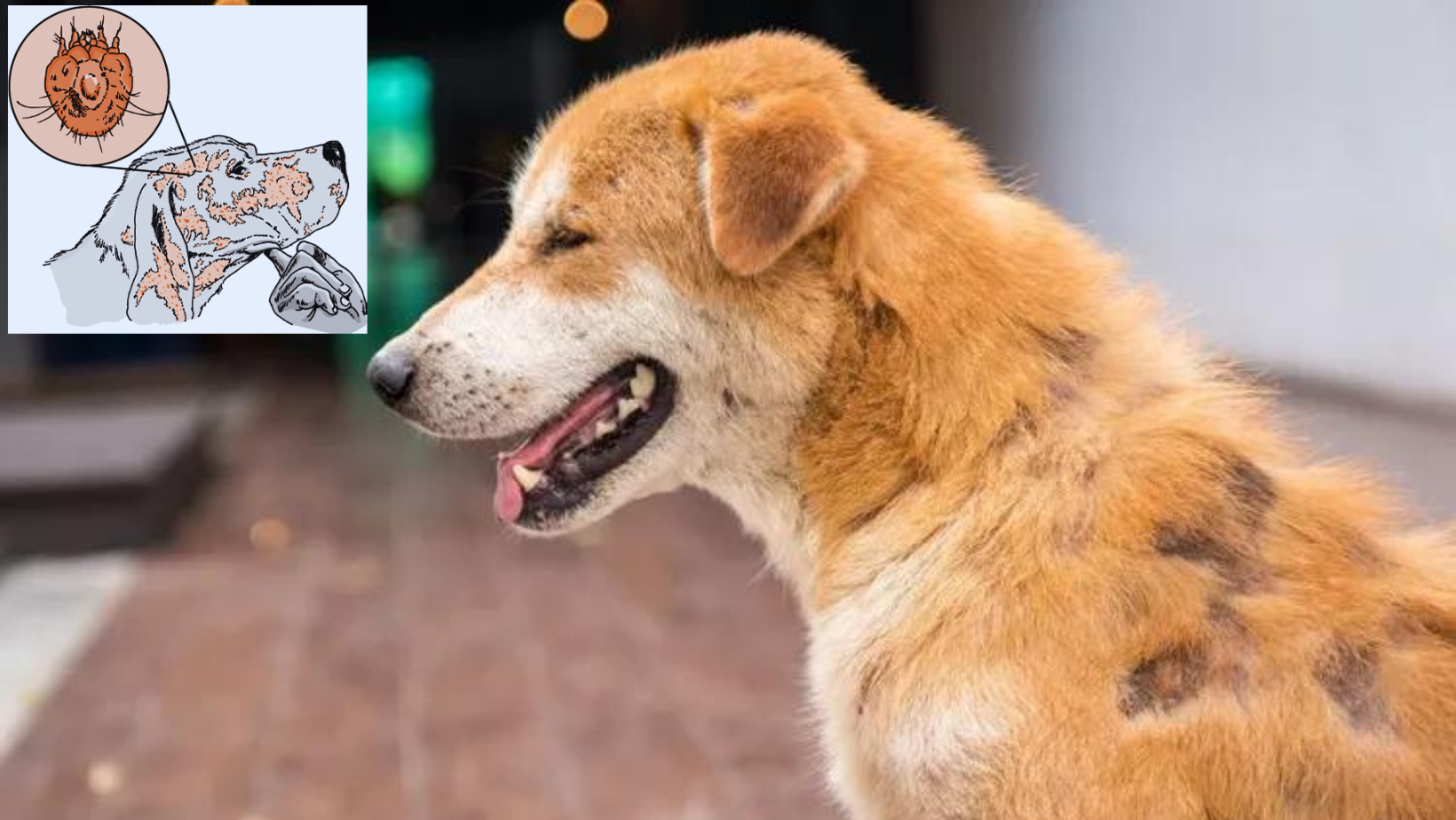

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The forest department is monitoring an outbreak of mange among a pack of Asiatic wild dogs in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR) in the Nilgiris, which they strongly suspect has spread to the animals through the local feral dog population.
What is Mange Disease?
- Mange is a distressing skin condition that affects dogs and is caused by microscopic parasites and different types of mites that infest the dog's skin and coat.
- The two most common forms of mange in dogs are Sarcoptic mange (caused by Sarcoptic scabies mites) and Demodectic mange (caused by Demodex Canis mites).
- Sarcoptic Mange- Scabies: Sarcoptic mange is highly contagious and can spread from dog to dog through direct contact. These microscopic mites burrow into the dog's skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort.
- Demodectic Mange: Demodectic mange, on the other hand, is not usually contagious and often results from an overgrowth of naturally occurring Demodex mites. A weakened immune system or genetic factors can contribute to the development of this form of mange.
- Common Symptoms of Mange in Dogs include:
- Intense Itching
- Skin Infections
- Crusty or Scaly Skin
- Ear Problems
- Mange in dogs is a treatable condition when detected early and managed appropriately.
About Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR):
- The Mudumalai Tiger Reserve, nestled in Tamil Nadu's Nilgiris District at the tri-junction of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, holds ancient significance, dating back 65 million years to the formation of the Western Ghats.
- It shares borders with the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala) to the West and the Bandipur Tiger Reserve (Karnataka) to the.
- The Theppakadu Elephant Camp within the reserve is a popular tourist spot, boasting a rich variety of flora and fauna, including Elephants, Gaurs, Tigers, Panthers, and various deer species.
- This historic elephant camp, established over a century ago, sits on the banks of the Moyar River, serving vital roles in human-wildlife conflict resolution, monsoon patrolling, eco-tourism, elephant conservation, and education.
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Uttarakhand government has constituted two teams of experts to evaluate the risk posed by five potentially hazardous glacial lakes in the region.
What is Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)?
- A GLOF denotes the sudden release of meltwater from a moraine or ice-dammed glacial lake, typically due to dam failure.
- These events pose significant hazards, often resulting in catastrophic flooding downstream, leading to substantial loss of life and property.
- GLOF can be triggered by several factors, including earthquakes, heavy rains, and avalanches.
Key Features of GLOFs:
-
- Sudden water releases.
- Rapid occurrences lasting hours to days.
- Large downstream river discharges.
Threats Posed by GLOFs in the Himalayan Regions:
- Climate Change Impact: Climate change-induced glacier melt accelerates the formation or expansion of glacial lakes, heightening the risk of GLOFs.
- Vulnerability of Moraines and Dams: Glacial lakes situated behind unstable moraines or natural dams are prone to breaching, as evidenced by events like the Kedarnath floods in 2013.
- Immediate Flood Risks: Abrupt water releases trigger massive floods, causing extensive damage to homes, and infrastructure, and triggering landslides and sedimentation.
Mitigation Strategies for GLOFs:
- Risk Assessment and Zonation: Identify high-risk areas and implement necessary mitigation measures, including mapping and modeling, as outlined in the 'Guidelines for Preparation of Disaster Management Plans for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOF)'.
- Early Warning Systems: Establish monitoring networks with sensors to detect changes in glacial lakes and provide timely warnings to vulnerable communities.
- Utilization of Technology: Leverage remote sensing and GIS-based tools for monitoring glacial lakes and surrounding areas.
- Regulation of Construction: Implement construction codes to regulate development in high-risk zones, exemplified by the 'Guidelines for the Construction of Earthquake Resistant Buildings' developed by the NDMA.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Enhance skills and resources through training programs conducted by institutions like the National Centre for Disaster Management, in collaboration with the private sector and NGOs.
- Infrastructure Development: Invest in infrastructure to redirect potential floodwaters away from communities and critical infrastructure.
Lab to monitor seawater quality and testbed to track monsoon systems inaugurated
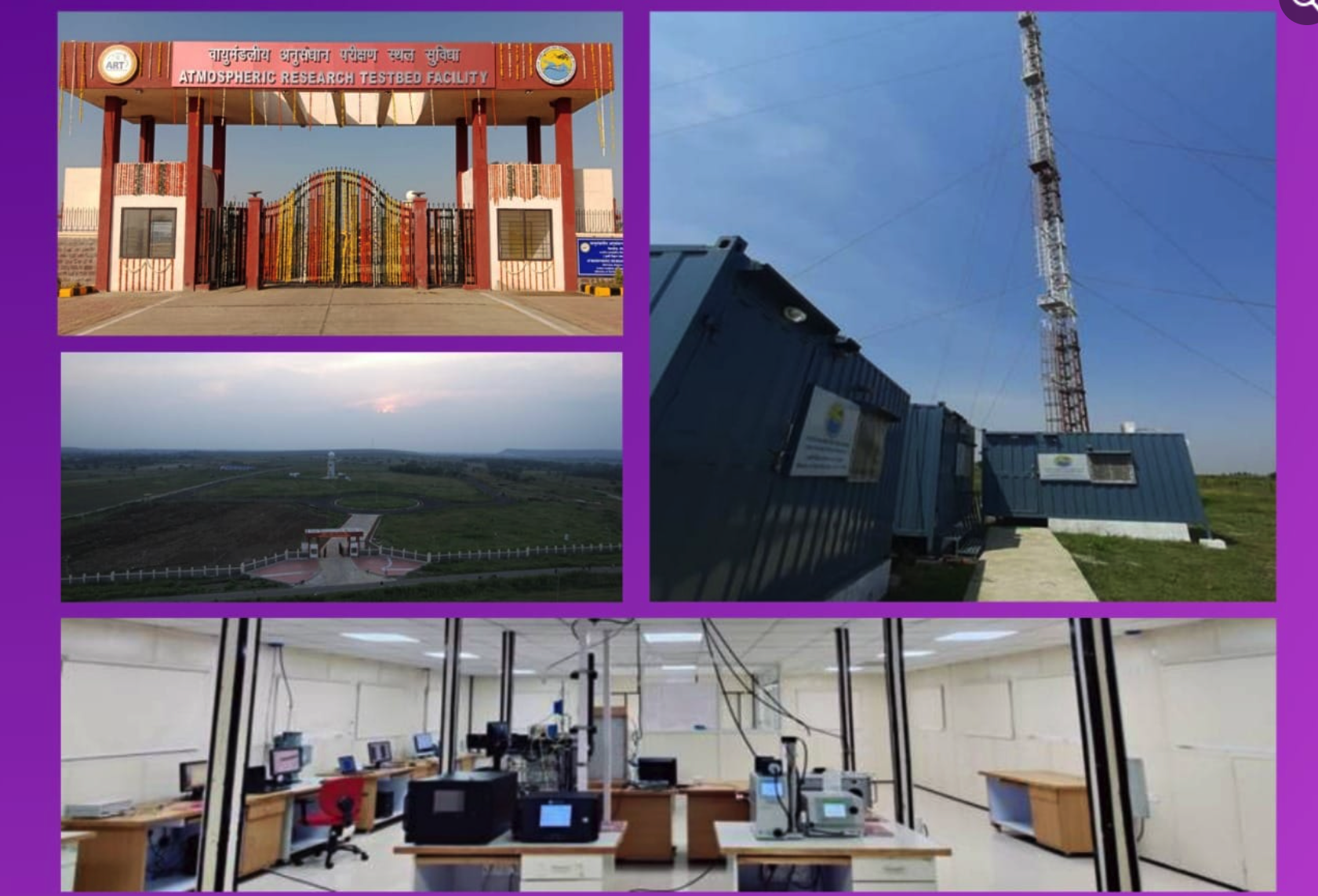

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India commissioned the atmospheric testbed facility near Bhopal, equipped with high-end instruments to record vital parameters for enhancing weather models and conducting advanced studies on the Indian monsoons, with construction commencing in early 2018.
What is the Atmospheric Research Testbed (ART)?
- The ART is an open-field, focused observational and analytical research programme at Silkheda.
- The facility aims to conduct ground-based observations of weather parameters like temperature, wind speeds, etc., and in-situ (on-site) observations of the transient synoptic systems – like low-pressure areas and depressions that form in the Bay of Bengal – during the southwest monsoon season from June to September.
- Studying these systems and their associated cloud parameters will be used to generate high volumes of data over a long period.
- It can then be compared with the existing weather models so that improvements can be made to obtain accurate rainfall predictions.
- The setup at ART will also be used for calibrating and validating various satellite-based observations, part of weather predictions and forecasting.
- Spread over 100 acres, the ART has been developed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences for Rs 125 crore.
- The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, is in charge of the operations.
- Under the first phase, remote sensing-based and in-situ measurements using 25 meteorological instruments have commenced.
- In the second phase, ART will deploy instruments such as a radar wind profiler and balloon-bound radiosonde, and soil moisture and temperature measuring equipment.
What instruments are ART equipped with?
- To obtain continuous observations of convection, clouds, and precipitation, and monitor the major modes of variabilities, the ART is equipped with over two dozen high-end instruments, radars, and more.
- At 72 meters, ART will house India’s tallest meteorological tower.
- Some of the instruments deployed are an aethalometer for performing aerosol studies, a cloud condensation nuclei counter, a laser ceilometer to measure cloud sizes, a micro rain radar to calculate raindrop size and its distribution, and a Ka-band cloud radar and a C-band Doppler weather radar to help track the movement of rain-bearing systems over this zone.
Why is having an Atmospheric Research Testbed important?
- At present, 45% of India’s labor force is employed in the agriculture sector and much of Indian agriculture is rain-fed.
- Cultivation along the Monsoon Core Zone (MCZ), which spans the central India region from Gujarat to West Bengal, is primarily rainfall-fed.
- The southwest monsoon season accounts for 70 percent of the country’s annual average rainfall (880mm).
- Throughout India, the majority of Kharif cultivation is undertaken between July and August, which see an average monthly rainfall of 280.4mm and 254.9mm (1971–2020 average), respectively.
- During this four-month-long season, several rain-bearing synoptic systems, namely the low pressures or depressions, develop in the Bay of Bengal.
- Inherently, these systems move westwards/northwestwards over to the Indian mainland and pass through the MCZ, causing bountiful rainfall.
Why is it important to have data about monsoons over central India?
- Studies have correlated the all-India rainfall performance to the rainfall received over the central India region, highlighting its importance.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issues rainfall forecasts for the country’s four homogeneous regions – north, west, east, and south peninsular India.
- In addition, it issues a special rainfall forecast for the MCZ, which is considered India’s food bowl.
- However, there is still limited understanding of the role of these synoptic systems, their associated cloud physics, cloud properties, and their overall role in enhancing the monsoon rainfall.
- Central India, therefore, acts as a natural laboratory for scientists and meteorologists to perform a hands-on study of the Indian monsoons.
- They can record data and make observations about the allied systems, clouds, and other associated physical and atmospheric parameters.
- Additionally, climate change is driving erratic rainfall patterns in tropical regions, like India.
- It has also strengthened the low-pressure systems, which are aided by high temperatures.
- This results in very heavy rainfall recorded along their trajectory during the monsoons.
- Now, with ART, scientists will be able to generate and obtain long-term observations on cloud microphysics, precipitation, convection, and land-surface properties, among a host of other parameters.
- This information will be assimilated and fed into the numerical weather models to enhance forecast output, especially the rainfall forecasts.
- More accurate forecasts will ultimately help the farming community plan their activities better.
Why Madhya Pradesh?
- The ART has been established at Silkheda, a location that falls directly in line with the path of major rain-bearing synoptic systems.
- This will facilitate direct monitoring and tracking.
- Besides, the locality is pristine and free of anthropogenic and other pollutants, making it the best site in central India for setting up sensitive, high-end meteorological instruments and observatories for recording data.
Inflection AI rolls out new large language model to its Pi chatbot

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Inflection AI launched its latest LLM, Inflection 2.5, an upgrade to its model that powers its friendly chatbot Pi personal assistant.
About Inflection 2.5:
- Inflection-2.5 is an “upgraded in-house model that is competitive with all the world’s leading LLMs like GPT-4 and Gemini.
- The newly upgraded LLM comes with its signature personality and uniquely empathetic fine-tuning.
- Its latest model achieved GPT-4’s performance with only 40 per cent of the OpenAI model’s computation power for training.
- Besides, it seems Inflection 2.5 has made some stellar strides in areas of IQ such as coding and mathematics.
- This means that the model has made substantial improvements on key benchmarks.
- With the new upgrade, Pi has now been endowed with world-class real-time web search capabilities to ensure that users get access to high-quality and up-to-date information in real-time.
What is the Pi chatbot?
- Pi is an advanced chatbot powered by Inflection AI's cutting-edge language model, Inflection 2.5 which allows one to have deep and meaningful conversations.
- To access the chatbot, one needs to log on to Inflection.AI, click on Meet Pi, and simply start talking to the chatbot right away.
- Pi is more humane and has been promoted as a chatbot that has a personality.
- In other words, Inflection AI dubbed it as a chatbot that is “supportive, smart, and there for you anytime”.
- Pi is more like a companion to humans and is free to use.
- The chatbot comes with a voice, in six distinct voices, to choose from adding life to conversations.
Pi chatbot boasts a number of impressive features that make it stand out from other conversational AI systems:
- Real-time web search capabilities: Pi can access and present up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, ensuring that users always have access to accurate and relevant information.
- Empathetic personality: Pi's unique empathetic fine-tuning allows it to understand and respond to the emotional nuances of human communication, making it a more engaging and personable conversational partner.
- Versatile conversation topics: Whether you're discussing current events, asking for local recommendations, studying for an exam, drafting a business plan, coding, or just talking about hobbies, Pi is equipped to handle a wide range of conversational topics.
- User-friendly interface: Designed with accessibility in mind, Pi's intuitive interface makes it easy for users of all technical abilities to engage with the chatbot and get the most out of their conversations.
Bird flu outbreak in Andhra: Could H5N1 spark the next pandemic?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A bird flu outbreak in poultry in Andhra Pradesh’s Nellore district was reported recently. Laboratory tests by the National Institute of High-Security Animal Diseases in Bhopal confirmed that it was caused by the type A strain of the H5N1 variant of the avian influenza virus.
What is Bird Flu/Avian Influenza?
- Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a viral respiratory illness primarily affecting birds.
- It's caused by specific strains of the Influenza A virus.
- Bird flu spreads between both wild and domesticated birds.
- It has also been passed from birds to humans who are in close contact with poultry or other birds.
- There is no clear evidence that the virus can be transmitted from human to human.
- However, this may have happened in rare cases, where a person has become ill after caring for a sick family member.
- While most types don't infect humans, certain strains like H5N1, H7N9, and H5N6 have caused concern due to their ability to transmit to humans in rare cases.
- Transmission:
- Birds: Spreads easily between birds through bodily fluids (saliva, faeces, nasal discharge) and contaminated environments.
- Humans: Primarily occurs through direct contact with infected birds or surfaces, inhaling infected droplets, or consuming undercooked poultry meat from infected birds.
- Symptoms:
- The symptoms of bird flu in humans are similar to those of regular influenza and include:
- Can range from mild (fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches) to severe (pneumonia, respiratory failure, multi-organ failure, death).
- Symptoms usually appear within 3-7 days of exposure.
- Treatment: Antiviral medications like Tamiflu have proven effective in managing human infections caused by avian influenza viruses, reducing both the severity of symptoms and the likelihood of fatalities.
Avian Influenza in India:
- Initial Incidence: The first instance of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) H5N1 in India occurred in 2006 in Navapur, Maharashtra, marking the onset of recurrent annual outbreaks.
- The emergence of H5N8 was documented in India in November 2016, primarily affecting wild birds in five states, with Kerala reporting the highest number of cases.
- This disease has been identified in 24 states and union territories, prompting the culling of over 9 million birds to curb its spread.
- Corresponding Strategy: India's strategy for managing Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) revolves around a "detect and cull" approach, as delineated in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised - 2021).
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia (Indian Express)
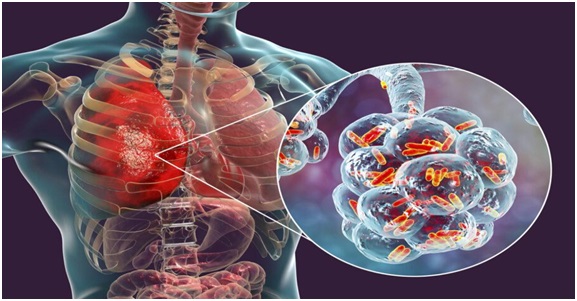
- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
What is Mycoplasma Pneumonia?
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that can cause illness by damaging the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, windpipe).
- It acts more like a virus and spreads faster from person to person.
- It is a common cause of pneumonia in children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Vulnerable groups, who already have respiratory issues, are prone to developing this infection in a severe form.
- Most people with respiratory infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae don’t develop pneumonia.
- For this reason, MP is known as an atypical pneumonia and is sometimes called walking pneumonia.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can include:
- Fever, Cough, Headache, Sore throat, Fatigue, Muscle aches, and Shortness of breath
- In most cases, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is mild and goes away on its own within a few weeks.
- However, some people may develop more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- It spreads through close contact with an infected person, such as through coughing or sneezing.
- It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- There is no vaccine to prevent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection however there are multiple antibiotics that effectively cure this infection.
Mumps outbreak: Worrying symptoms to watch out for, preventive tips (India TV)
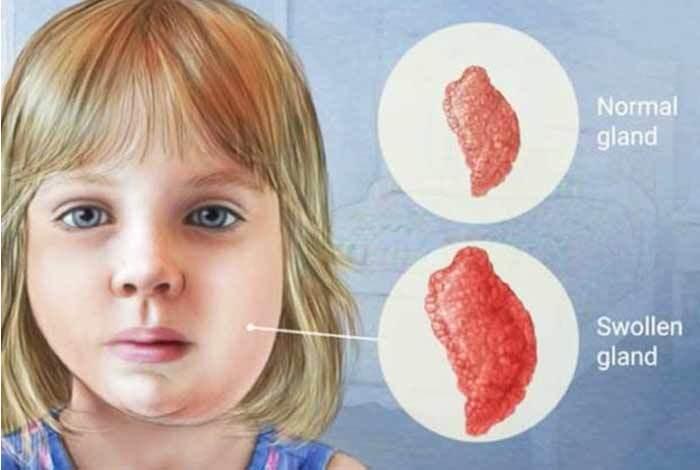
- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A mumps outbreak has recently been reported in several states across the country, causing concern among public health officials.
What is Mumps Disease?
- Mumps is a contagious disease caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family.
- It typically involves painful swelling in the parotid salivary glands, located on the sides of the face below and in front of the ears.
- These swollen glands often give the infected person a characteristic "chipmunk-cheek" appearance.
- Humans are the only known host for the mumps virus, which is spread via direct contact or by airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract of infected individuals.
- Transmission of mumps: Mumps is spread through contact with the saliva or respiratory droplets of an infected person. This can happen through coughing, sneezing, kissing, sharing utensils, or close contact.
- Symptoms:
- Mumps typically manifest after an incubation period of 2 to 4 weeks, starting with nonspecific symptoms like myalgia, headache, malaise, and low-grade fever.
- Within days, these initial symptoms progress to the swelling of the parotid salivary glands, either unilaterally or bilaterally, with other salivary glands affected in 10% of cases.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent mumps is to get vaccinated with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine.
- The MMR vaccine is safe and effective for most people.
- Other preventive measures include practising good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick people, and covering your coughs and sneezes.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for mumps. Most people recover on their own within a few weeks.
- Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as with pain relievers and fever reducers.
- In general, mumps is a mild, self-limiting disease that resolves without lasting effects.
- However, complications can arise, including encephalitis or sensorineural deafness.
- Orchitis, a painful inflammation of the testes, occurs in approximately 20% of young adult males who contract mumps.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (India Today)
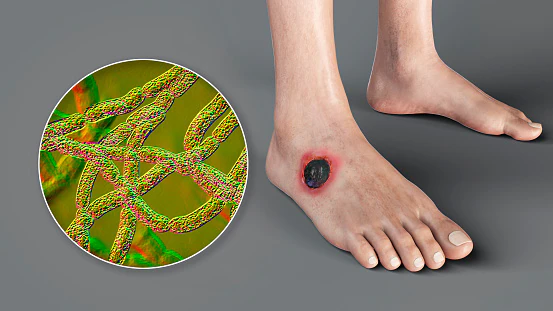
- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has reported a significant anthrax outbreak in Zambia, marking an alarming spread of the disease across nine out of the country's ten provinces.
What is anthrax?
- According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), anthrax is a highly infectious disease that is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- Although it affects animals like cows, sheep, and goats, humans can get sick if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Anthrax is not contagious, which means we can't catch it from another person like the cold or flu.
Symptoms of anthrax:
- The disease manifests in three forms depending on the route of infection: cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and inhalational.
- Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, presents with itchy bumps that develop into black sores, often accompanied by fever and muscle aches.
- Gastrointestinal anthrax resembles food poisoning initially but can escalate to severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhoea.
- Inhalational anthrax, the deadliest form, starts with cold-like symptoms before progressing to severe respiratory distress and shock.
How is anthrax diagnosed?
- Anthrax can be diagnosed by identifying Bacillus anthracis in blood, skin lesions, or respiratory secretions through laboratory culture, PCR, or ELISA tests.
- While there is no specific test to determine exposure to anthrax, public health investigations play a crucial role in identifying potential cases.
Treatment for anthrax:
- Treatment for anthrax is available and includes antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, or levofloxacin.
- If diagnosed early, antibiotic treatment can cure most anthrax infections.
- In severe cases, hospitalisation and treatments like continuous fluid drainage and mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
- Vaccines are also available for both livestock and humans, although human vaccines are typically reserved for those at high occupational risk.
PAINTBRUSH SWIFT BUTTERFLY (The Hindu)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The paintbrush swift was recently photographed and documented for the first time in the Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh.
Facts About:
- The Paintbrush Swift butterfly, a rare species in the western Himalayas, was recently photographed and documented in Himachal Pradesh's Chamba district.
- Himachal Pradesh supports approximately 430 butterfly species, which make up about 25% of all butterfly species found in India.
- The Paintbrush Swift (Baoris farri) belongs to the Hesperiidae family and was discovered during a field survey under the Wild Bhattiyat Project in 2022.
It had never been photographed in Himachal Pradesh since its initial discovery in 1878.
- The project, initiated by the Bhattiyat Forest Range of the Dalhousie Forest Division, has documented 120 butterfly species, including the Paintbrush Swift.
- The butterfly's habitat distribution is common in northeast, central, and south India but rare in Uttarakhand.
- The Paintbrush Swift can be identified by two separated spots in the upper forewing cell.
- Conservation efforts are urgently needed to protect butterflies, including creating butterfly parks, rearing centers, and awareness campaigns, especially for high-altitude species facing habitat destruction and declining numbers.
