Sungrazing Comet
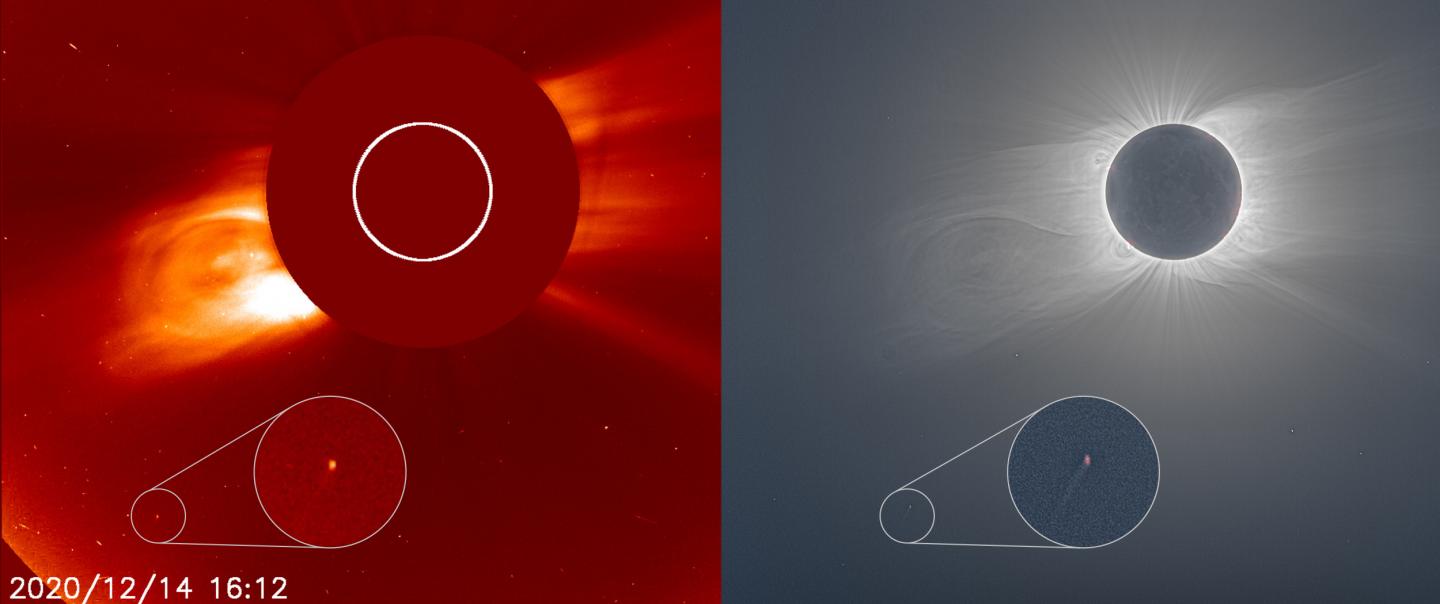
- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A tiny "sungrazer" comet was discovered, photographed, and destroyed during the recent total solar eclipse — all within 24 hours.
What is a Sungrazing Comet?
- Sungrazing comets are a special class of comets that come very close to the sun at their nearest approach, a point called perihelion.
- To be considered a sungrazer, a comet needs to get within about 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion.
- Many come even closer, even to within a few thousand miles.
- Being so close to the sun is very hard on comets for many reasons.
- They are subjected to a lot of solar radiation which boils off their water or other volatiles.
- The physical push of the radiation and the solar wind also help form the tails. As they get closer to the sun, the comets experience extremely strong tidal forces or gravitational stress.
- In this hostile environment, many sungrazers do not survive their trip around the sun.
- Although they don't crash into the solar surface, the sun can destroy them anyway.
- Many sungrazing comets follow a similar orbit, called the Kreutz Path, and collectively belong to a population called the Kreutz Group.
- Close to 85% of the sungrazers seen by the SOHO satellite are on this orbital highway.
- Scientists think one extremely large sungrazing comet broke up hundreds, or even thousands, of years ago, and the current comets on the Kreutz Path are the leftover fragments of it.
- Comet Lovejoy, which reached perihelion on December 15, 2011, is the best-known recent Kreutz-group sungrazer.
- And so far, it is the only one that NASA's solar-observing fleet has seen survive its trip around the sun.
What is a Comet?
- A comet is a small celestial body made primarily of ice, dust, and rocky material that orbits the sun in an elongated path.
- When a comet approaches the sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, releasing dust and gas into a glowing coma, or halo, around the comet's nucleus.
- This glowing coma often forms a tail that stretches away from the sun due to the solar wind and radiation pressure.
- Comets are often referred to as "dirty snowballs" or "icy dirtballs" because of their composition.
- They are believed to be remnants from the early formation of the solar system and carry important information about its history.
- Comets can have highly elliptical orbits, sometimes taking thousands or even millions of years to complete a single orbit around the sun.
