India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
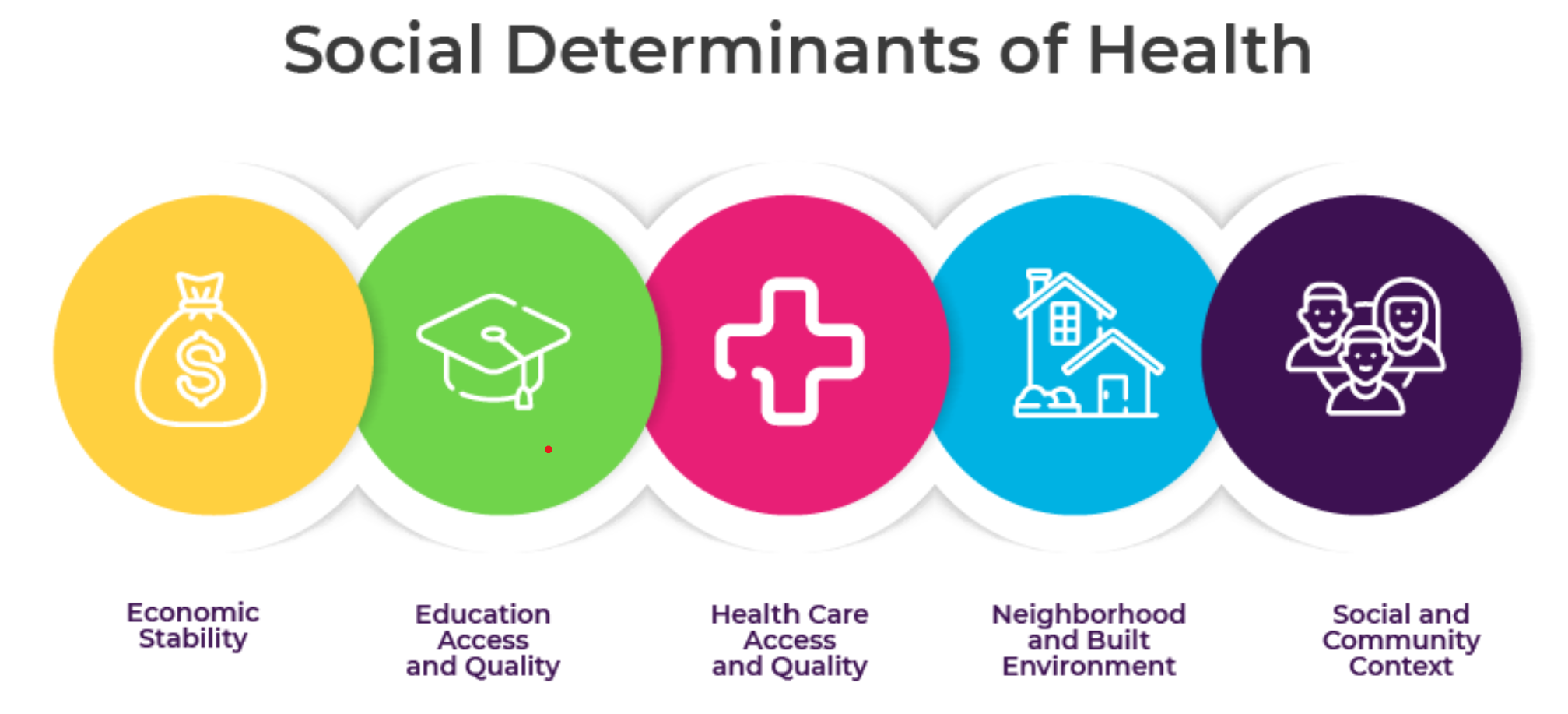
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
