Colombo Security Conclave (CSC)

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) recently marked a significant milestone with the signing of the Charter and the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the establishment of its Secretariat in Colombo. This initiative aims to strengthen regional security collaboration among member states.
Key Features of the Colombo Security Conclave
- Member States: The CSC comprises five member countries:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka
- Maldives
- Mauritius
Additionally, Seychelles participates as an observer nation.
- Core Objectives: The primary goal of the CSC is to enhance regional security by addressing transnational threats and challenges that are common concerns for member states. This includes a collaborative approach to ensure stability and safety in the region.
Origin and Evolution
- The CSC originated as the Trilateral for Maritime Security Cooperation, established through trilateral meetings among National Security Advisors (NSAs) and Deputy NSAs from India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka starting in 2011.
- The initiative faced a setback after 2014 due to heightened tensions between India and the Maldives.
- It was revived and rebranded as the CSC in 2020, expanding its membership to include Mauritius and, more recently, Bangladesh.
Structure and Cooperation
- The conclave facilitates interactions among NSAs and Deputy NSAs of member countries, fostering dialogue and cooperation on security matters.
- Cooperation under the CSC is organized around five key pillars:
- Maritime Safety and Security
- Countering Terrorism and Radicalization
- Combating Trafficking and Transnational Organized Crime
- Cybersecurity and Protection of Critical Infrastructure
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief
Permanent Secretariat
- The establishment of a permanent Secretariat in Colombo is expected to enhance coordination and streamline operations among member states, bolstering the efficacy of the CSC in addressing regional security issues.
Thanjavur Veena

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
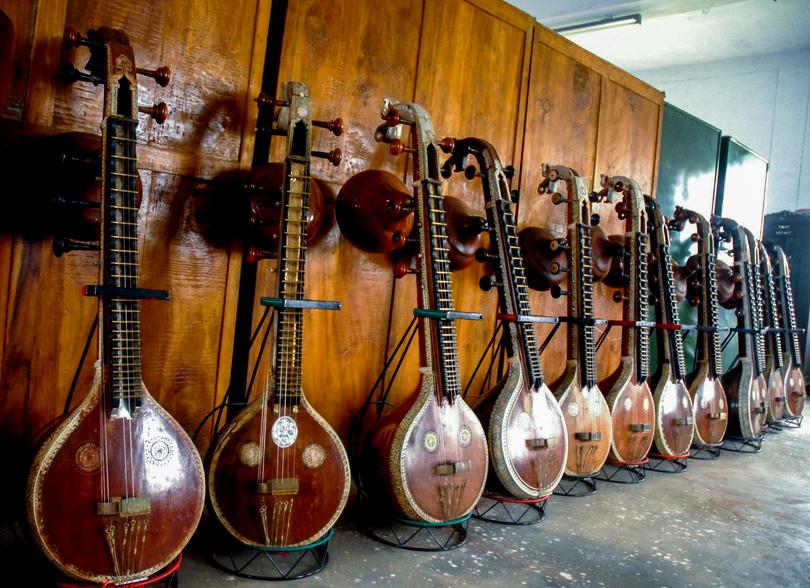
The Thanjavur Veena has the distinction of being the first musical instrument in India to receive the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, highlighting its cultural and artistic significance. Here’s an overview of its features, types, and craftsmanship:
About Thanjavur Veena
- Construction:
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Ekantha Veena: Carved from a single block of wood.
- Sada Veena: Composed of three sections—resonator (kudam), neck (dandi), and head—with joints.
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Design Features:
- The instrument features 24 fixed frets (mettu), enabling musicians to play a wide range of ragas.
- Traditionally made from the bark of the Jackfruit tree, the bark undergoes extensive testing to ensure quality and durability.
- Craftsmanship:
- The process of crafting a Thanjavur Veena can take 15-20 days, involving cutting, intricate carving, shaping, and assembly of the wood to form the integral parts of the instrument.
Types of Veena
The Thanjavur Veena is one of several types of veenas used in Indian classical music:
- Rudra Veena and Vichitra Veena: Predominantly used in Hindustani classical music.
- Saraswati Veena and Chitra Veena: Associated with Carnatic classical music, with the Saraswati Veena being unique to Thanjavur.
Cultural Significance
- The Saraswati Veena is particularly notable as it is often associated with Goddess Saraswati, the deity of learning and arts, who is frequently depicted holding a veena. This connection emphasizes the instrument's importance in Indian culture and music.
7 New Schemes to Boost Farmer Income
- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, approved seven schemes to improve farmers’ lives and increase their incomes at a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 Crore.
1. Digital Agriculture Mission: based on the structure of Digital Public Infrastructure, Digital Agriculture Mission will use technology for improving farmers’ lives. The Mission has a total outlay of Rs 2,817 crores. It comprises two foundational pillars
1. Agri Stack
- Farmers registry
- Village land maps registry
- Crop Sown Registry
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- Geospatial data
- Drought/flood monitoring
- Weather/satellite data
- Groundwater/water availability data
- Modelling for crop yield and insurance
The Mission has provision for
- Soil profile
- Digital crop estimation
- Digital yield modelling
- Connect for crop loan
- Modern technologies like AI and Big Data
- Connect with buyers
- Bring new knowledge on mobile phones
2. Crop science for food and nutritional security: with a total outlay of Rs 3,979 crore. The initiative will prepare farmers for climate resilience and provide for food security by 2047. It has following pillars:
- Research and education
- Plant genetic resource management
- Genetic improvement for food and fodder crop
- Pulse and oilseed crop improvement
- Improvement of commercial crops
- Research on insects, microbes, pollinators etc.
3. Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management and Social Sciences: with a total outlay of Rs 2,291 Crore the measure will prepare agriculture students and researchers for current challenges and comprises the following
- Under Indian Council of Agri Research
- Modernising agri research and education
- In line with New Education Policy 2020
- Use latest technology … Digital DPI, AI, big data, remote, etc
- Include natural farming and climate resilience
4. Sustainable livestock health and production: with a total outlay of Rs 1,702 crore, the decision aims to Increase farmers income from livestock and dairy. It comprises the following
- Animal health management and veterinary education
- Dairy production and technology development
- Animal genetic resource management, production and improvement
- Animal nutrition and small ruminant production and development
5. Sustainable development of Horticulture: with a total outlay of Rs 1129.30 crore the measure is aimed at increasing farmers’ income from horticulture plants. It comprises the following
- Tropical, sub-tropical and temperate horticulture crops
- Root, tuber, bulbous and arid crops
- Vegetable, floriculture, and mushroom crops
- Plantation, spices, medicinal, and aromatic plants
6. Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra with an outlay of Rs 1,202 crore
7. Natural Resource Management with an outlay of Rs 1,115 crore
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India

- 03 Sep 2024
Overview
India’s mental healthcare landscape is evolving, with increasing awareness and decreasing stigma around mental health issues. However, access to mental healthcare remains a significant challenge due to a shortage of professionals. Here are the key points:
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India
- Rising Demand: Shifts in societal attitudes have led to more individuals seeking mental health support. Awareness and willingness to access treatment have notably increased.
- Professional Shortage: Despite the rising demand, there are only 0.75 psychiatrists per one lakh population, far below the World Health Organization’s recommendation of three per lakh. As of the latest data, India has about 9,000 psychiatrists, while an estimated 36,000 are needed to meet the standard.
- Slow Workforce Growth: Approximately 1,000 psychiatrists enter the workforce annually, but with attrition and unemployment, it could take around 27 years to reach the WHO target without intervention.
- Comparative Analysis: India has one of the lowest psychiatrist-to-population ratios among BRICS nations, trailing only Ethiopia. However, it performs better than many South Asian countries.
Limitations of Current Data
- Outdated Survey: The data largely relies on the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted between 2015 and 2016, which is based on a limited sample size of around 40,000 people across 12 states.
- Narrow Focus: The NMHS primarily addressed specific mental illnesses and overlooked milder conditions, emotional issues, and vulnerable populations like prisoners and the homeless.
- Need for Updated Research: A second NMHS is scheduled for release next year, which may provide more comprehensive data and insights.
Improvements in Awareness and Attitudes
- Positive Attitudinal Shift: A study by the LiveLoveLaugh Foundation found significant improvements in how Indians perceive mental health. For instance, the percentage of people believing that individuals with mental illnesses can handle responsibilities rose from 32% in 2018 to 65% in 2021.
- Willingness to Seek Help: Over 90% of respondents in 2021 indicated they would seek treatment for themselves or support others in doing so, a substantial increase from 54% in 2018.
- Increased Awareness: Awareness of mental health issues has grown, with 96% of respondents in 2021 recognizing mental health compared to 87% in 2018.
Conclusion
While India is making strides in reducing stigma and increasing awareness around mental health, the critical shortage of mental health professionals poses a significant barrier to accessing timely care. Addressing this issue requires targeted policy interventions and incentives to boost the supply of mental health professionals and improve the overall infrastructure for mental healthcare in the country.
Digital Agriculture Mission

- 03 Sep 2024
Introduction
India's digital revolution has significantly transformed governance and service delivery in recent years by creating digital identities, secured payments and transactions. This progress has paved the way for a thriving digital ecosystem across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and retail, positioning India as a leader in citizen-centric digital solutions.
For a similar transformation of the Agriculture Sector, the Union Cabinet Committee, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the 'Digital Agriculture Mission' with a substantial financial outlay of Rs. 2,817 Crore, including a central government share of Rs. 1,940 Crore, on September 2, 2024.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is designed as an umbrella scheme to support various digital agriculture initiatives. These include creating Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), and supporting IT initiatives by the Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
The scheme is built on two foundational pillars:
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System.
Additionally, the mission includes ‘Soil Profile Mapping’ and aims to enable farmer-centric digital services to provide timely and reliable information for the agriculture sector.
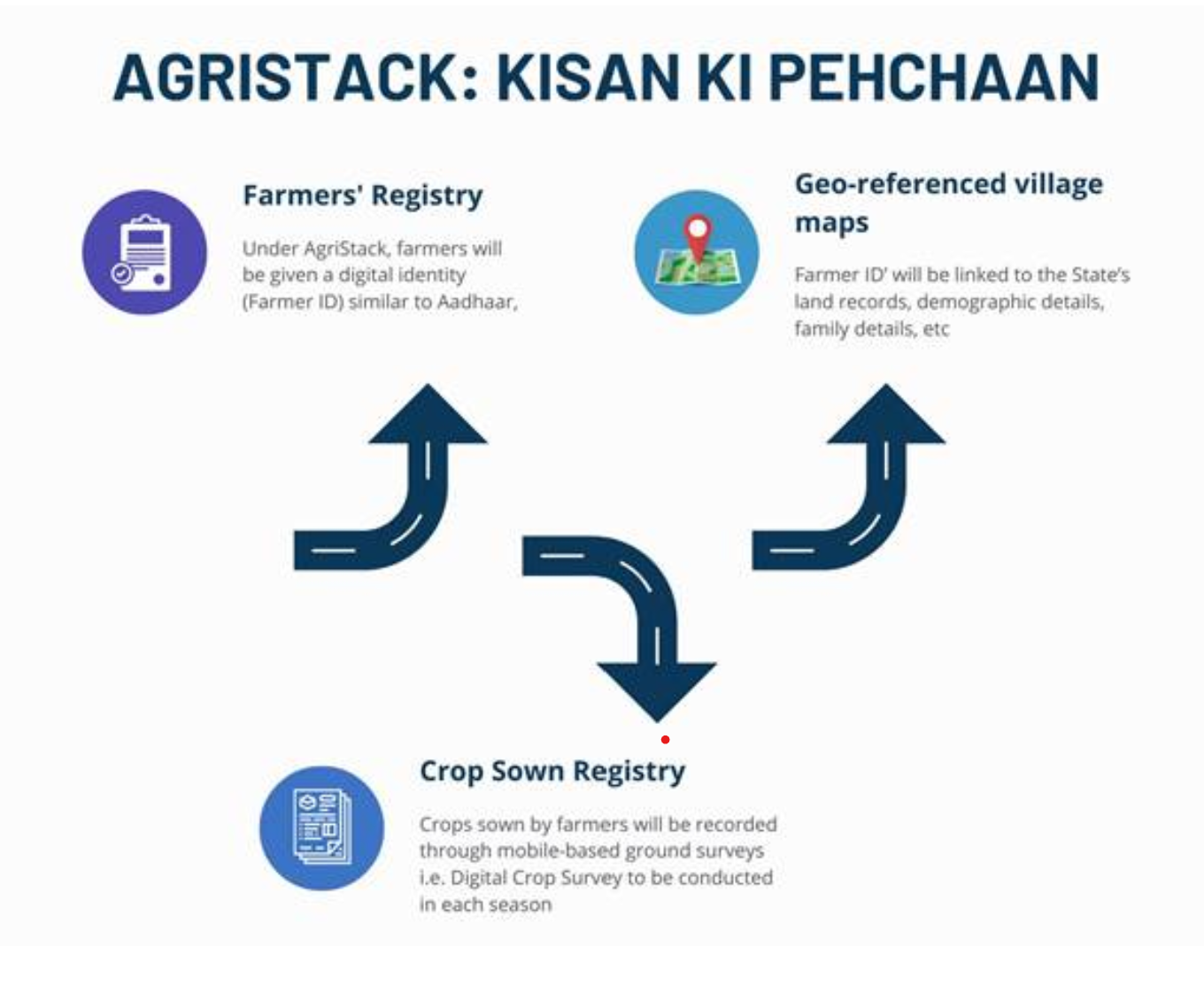
AgriStack: Kisan ki Pehchaan
AgriStack is designed as a farmer-centric Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to streamline services and scheme delivery to farmers. It comprises three key components:
1. Farmers' Registry
2. Geo-referenced village maps
3. Crop Sown Registry
- A crucial feature of AgriStack is the introduction of a 'Farmer ID', similar to Aadhaar card, serving as a trusted digital identity for farmers.
- These IDs, created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories, will be linked to various farmer-related data, including land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, and benefits availed.
- The implementation of AgriStack is progressing through partnerships between the Central and State Governments, with 19 states having signed MoUs with the Ministry of Agriculture. Pilot projects have been conducted in six states to test the creation of Farmer IDs and the Digital Crop Survey.
- The six states include Uttar Pradesh (Farrukhabad), Gujarat (Gandhinagar), Maharashtra (Beed), Haryana (Yamuna Nagar), Punjab (Fatehgarh Sahib), and Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar).
Key targets include:
- Creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers over three years (6 crore in FY 2024-25, 3 crore in FY 2025-26, and 2 crore in FY 2026-27)
- Launching the Digital Crop Survey nationwide within two years, covering 400 districts in FY 2024-25 and all districts in FY 2025-26
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- The Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) will integrate remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system.
3. Soil Profile Mapping
Under the mission, detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land have been envisaged, with 29 million hectares of soil profile inventory already being mapped.
- Further under the Digital Agriculture Mission, the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will be used for crop-cutting experiments to provide precise yield estimates, enhancing agricultural production accuracy.
- The mission is expected to create direct and indirect employment in agriculture, providing opportunities for around 2,50,000 trained local youth and Krishi Sakhis.
- By leveraging modern technologies like data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, the mission will improve service delivery for farmers, including streamlined access to government schemes, crop loans, and real-time advisories.
Key Components of the Mission
The Digital Agriculture Mission focuses on grassroots implementation, targeting farmers as the primary beneficiaries. Some of the key benefits of the mission include:
- Digital authentication for accessing services and benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced efficiency and transparency in government schemes, crop insurance, and loan systems through accurate data on crop area and yield.
- Crop map generation and monitoring for better disaster response and insurance claims.
- Development of digital infrastructure to optimize value chains and provide tailored advisory services for crop planning, health, pest management, and irrigation.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 that the Government, in partnership with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture over the next three years.
- This initiative will cover farmers and their lands, with a digital crop survey for Kharif planned for 400 districts this year. The goal is to update registries with details of 6 crore farmers and their lands.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 had previously introduced the DPI for agriculture, which aims to provide comprehensive data on farmers, including demographic details, land holdings, and crops sown. The DPI will integrate with state and central digital infrastructures to offer a range of farmer-centric services, including information on livestock, fisheries, soil health, and available benefits.
Conclusion
- The Union Cabinet also approved six major schemes alongside the Digital Agriculture Mission, with a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 crore.
- These initiatives include Rs 3,979 crore for Crop Science aimed at ensuring food security and climate resilience by 2047, and Rs 2,291 crore for strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences to support students and researchers. Rs 1,702 crore is allocated for Sustainable Livestock Health and Production to boost incomes from livestock and dairy, while Rs 1,129.30 crore is designated for Sustainable Development of Horticulture to increase income from horticulture. Additionally, Rs 1,202 crore will be invested in strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendra, and Rs 1,115 crore towards Natural Resource Management.
- These comprehensive approaches leverage digital technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in India's agricultural sector, potentially transforming the lives of millions of farmers across the country. By extending the digital revolution to agriculture, India aims to further solidify its position as a global leader in innovative, technology-driven solutions for critical sectors of the economy.
Supreme Court of India

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
On August 31, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the National Conference of District Judiciary at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi. This event marked the 75th anniversary of the Supreme Court of India, highlighted by the unveiling of a commemorative stamp and coin.
Supreme Court of India: History and Key Insights
The Origins of the Judiciary
- The concept of law, or Dharma, in ancient India was significantly influenced by the Vedas, which outlined rules of conduct and rituals in the Dharma Sutras. These texts addressed the duties of individuals and the rights of kings, forming the foundation of Hindu Law. The earliest systematic examination of jurisprudence can be found in Kautilya's Artha Sastra (circa 300 B.C.), particularly its third chapter, which discusses legal transactions and disputes.
Establishment of the Supreme Court
- The Regulating Act of 1773, enacted by the British Parliament, initiated the establishment of the Supreme Court of Judicature at Calcutta, with its Letters of Patent issued on March 26, 1774. This court had the authority to hear all complaints and lawsuits involving His Majesty’s subjects in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa. Additional Supreme Courts were later established in Madras (1800) and Bombay (1823).
- The Indian High Courts Act of 1861 replaced these Supreme Courts with High Courts in various provinces, which became the highest judicial authorities until the Federal Court of India was created under the Government of India Act 1935. After India gained independence in 1947, the Supreme Court of India was formally established on January 26, 1950, with its inaugural session held on January 28, 1950.
- The Supreme Court's rulings are binding across India, and it possesses the power of judicial review to ensure that legislative and executive actions align with constitutional provisions and fundamental rights.
Structure and Functioning
- Initially, the Supreme Court operated for only a few hours each day and convened for 28 days a year. Today, it functions extensively, meeting approximately 190 days annually. The court was temporarily housed in the Parliament House before moving to its current location on Tilak Marg, New Delhi, in 1958.
- The court's architecture symbolizes justice, featuring a prominent dome and spacious corridors. It began with a Chief Justice and seven judges, with Parliament later increasing this number as the workload grew. Currently, the Supreme Court includes a Chief Justice and 30 judges.
Appointment and Qualifications of Judges
- Judges are appointed by the President of India, based on recommendations from a committee of senior judges (Collegium System). A candidate must be a citizen of India and have served as a High Court judge for at least five years or as an advocate for ten years. The age of retirement for judges is 65 years.
Judicial Independence and Removal
- Judicial independence is constitutionally protected. A Supreme Court judge can only be removed by the President on grounds of proven misbehavior or incapacity, following a resolution supported by a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Judicial Salaries and Provisions
- Judges’ salaries and pensions are defined by the Supreme Court Judges (Salaries and Conditions of Service) Act, 1958, and are charged to the Consolidated Fund of India.
Acting Chief Justice
- In the absence of the Chief Justice, the President appoints another judge as the Acting Chief Justice, as stipulated in Article 126.
Post-Retirement Opportunities
- While retired judges cannot practice law in India, they often serve in governmental roles, such as leading commissions. There have been calls for a "cool-off" period before such appointments.
Ad Hoc Judges
- Ad hoc judges may be appointed when necessary, and must meet the qualifications for Supreme Court judges. Retired judges can also be called back to serve temporarily.
Courts of Record
- Both the Supreme Court and High Courts are classified as courts of record, with the authority to punish for contempt as per Article 129.
Seat of the Supreme Court
- The Supreme Court is based in Delhi but can convene anywhere in India, with such decisions made by the Chief Justice in consultation with the President.
Samudra Pratap

- 02 Sep 2024
In News
Recently, the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) proudly launched the first indigenously built Pollution Control Vessel, ‘Samudra Pratap’, in Goa.
Key Highlights of the Launch
- Vessel Details:
- Built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL), the vessel is specifically designed to combat oil spills along India’s coastlines.
- Dimensions: Length: 114.5m, Breadth: 16.5m, Displacement: 4170 T.
- The keel laying ceremony took place on November 21, 2022.
- Contract and Construction: GSL signed a contract worth Rs 583 crores for the construction of two Pollution Control Vessels for the ICG. This marks the first instance of such vessels being designed and built entirely in India.
- Significance of the Vessel: ‘Samudra Pratap’ stands as a testament to India's shipbuilding capabilities, showcasing GSL's expertise in producing advanced Pollution Control Vessels and reinforcing India's commitment to indigenization in defense manufacturing.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour & Employment, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme on the occasion of National Sports Day in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
This programme aims to empower retired athletes by equipping them with essential career skills and knowledge, enhancing their employability and enabling them to contribute meaningfully to the sports ecosystem.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Retired athletes aged 20 to 50 years.
- Achievements:
- Must be winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- Alternatively, must have been national or state medallists or participants in competitions recognized by:
- National Sports Federations
- Indian Olympic Association
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
Programme Structure
- Levels: Two tiers based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12th and above
- Class 11th and below
- Learning Mode: A hybrid approach, combining:
- Self-paced online learning through a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training for practical skill development.
Lead Institute
- Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) will oversee the implementation and administration of the programme.
Support and Opportunities
- Placement Assistance: Comprehensive guidance for job placements in relevant sectors.
- Entrepreneurial Guidance: Support for athletes looking to start their own ventures in sports or related fields.
- Internships: Opportunities for hands-on experience in:
- Sports organizations
- Competitions
- Training camps
- Leagues
Implementation and Benefits
- Self-Paced Learning: Flexibility for participants to manage their learning schedules effectively.
- On-Ground Training: Hands-on practical sessions aimed at enhancing skills relevant to various career paths.
- Evaluation and Certification: Participants will be assessed and awarded a certificate upon successful completion, adding value to their career prospects.
The RESET Programme not only recognizes the achievements of retired athletes but also empowers them to leverage their experiences in new and impactful ways, fostering a robust sports ecosystem in India.
Queers can open Joint Bank Accounts

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Government issued an advisory that LGBTQIA+ individuals and queer couples can open joint bank accounts. They can nominate each other as beneficiaries.
Key Details:
- Supreme Court Background:
- In October 2023, the Supreme Court of India urged the government to consider equal entitlements for partners in queer relationships.
- This was part of a judgment that did not recognize same-sex marriage but suggested enabling joint bank accounts and beneficiary nominations.
- Clarification from the Department of Financial Services:
- Issued on August 28, 2023, confirming no restrictions on opening joint accounts for the queer community.
- The Reserve Bank of India also clarified this to Scheduled Commercial Banks on August 21.
- Private Banks' Initiatives:
- Some banks, like Axis Bank, have been allowing joint accounts and beneficiary nominations for LGBTQIA+ couples since September 2021.
- Axis Bank expressed support for the Finance Ministry's advisory, noting alignment with its inclusive banking initiative.
- Government Committee Formation:
- In April 2023, a six-member committee was established to define entitlements for queer couples.
- Chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, it includes Secretaries from various ministries.
- The committee can co-opt experts if needed.
Project NAMAN

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the first phase of Project NAMAN, aimed at supporting Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families.
- Key Features of Project NAMAN:
- Implements the SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha) digital pension system.
- Streamlines pension processes and provides accessible facilitation points for Veterans and Next of Kin (NOK).
- Importance:
- Ensures care and support for veterans and their families.
- Services extended to residents of military stations and surrounding localities.
- Establishment of Common Service Centres (CSCs):
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Indian Army’s Directorate of Indian Army Veterans
- CSC e-Governance India Limited
- HDFC Bank Limited
- CSCs provide:
- SPARSH-enabled pension services
- Government to Citizen (G2C) services
- Business to Consumer (B2C) services
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Phase One Deployment:
- 14 CSCs established in key locations: New Delhi, Jalandhar, Leh, Dehradun, Lucknow, Jodhpur, Bengdubi, Gorakhpur, Jhansi, Secunderabad, Saugor, Guntur, Ahmedabad, Bangalore.
- Future expansion plans for approximately 200 centres nationwide in the next 2-3 years.
- Infrastructure Support:
- HDFC Bank provided necessary IT infrastructure.
- Local military stations contributed physical facilities.
- Community Engagement:
- Concept developed based on feedback from the Defence community.
- Promotes camaraderie among serving and retired Armed Forces personnel.
- Management of CSCs:
- Each CSC managed by a Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) selected from veterans or NOKs by Local Military Authorities (LMAs).
- VLEs receive training from CSC e-Governance India Limited.
- HDFC Bank offers monthly grants of ?20,000 for the first 12 months to support VLEs.
- Conclusion:
- Project NAMAN reflects the Indian Army's commitment to veteran welfare.
- Offers SPARSH-centric services and entrepreneurial opportunities for Veterans and NOKs, empowering them to contribute to their communities.
Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD)

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- Establishment of Disease-Free Zones:
- The Union government plans to create FMD-free zones in eight states: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Uttarakhand, Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
- Aim: Expand export opportunities for Indian animal products and enhance global market presence.
- Vaccination Efforts:
- Advanced vaccination initiatives are underway in the identified states, as stated by Alka Upadhyaya, Secretary of the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- Collaborative Workshop:
- A workshop on ‘Animal Infectious Disease Prioritisation’ was held in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organisation.
- Focus: Prioritized 20 major animal infectious diseases based on severity, transmissibility, and national importance.
- Action Plan:
- Formulated focusing on five critical areas:
- Coordination
- Communication
- Monitoring and surveillance
- Prevention and control
- Therapeutics and socio-economic planning
- Formulated focusing on five critical areas:
- Regional Disease Prioritization:
- Strengthening regional-level prioritization of animal diseases for tailored control strategies.
- Overview of FMD:
- Highly contagious viral disease affecting cloven-hoofed animals like cattle, swine, sheep, and goats, but not horses or cats.
- Significant economic impact due to its effect on livestock production and trade.
Key Characteristics of FMD:
- Transmission:
- Virus present in excretions and secretions; aerosolized virus can infect other animals via respiratory or oral routes.
- Symptoms:
- Fever, blister-like sores on the tongue, lips, and hooves.
- High mortality in young animals, with production losses noted even post-recovery.
- Vaccination:
- Available vaccines must be matched to specific virus types/subtypes.
Repairability Index for Mobile and Electronic Sectors

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA), Government of India, has established a committee of experts to create a framework for the Repairability Index.
- Objective:
- Enhance consumer transparency regarding product repairability.
- Promote sustainable practices in the tech industry.
- National Workshop:
- Held on August 29, 2024, focusing on the Right to Repair in the Mobile and Electronics Sector.
- Aimed to gather industry stakeholders to agree on evaluating components for the Repairability Index.
- Key Goals:
- Address the rapid demand and short lifespan of mobile and electronic devices.
- Provide essential repair information and ensure access to spare parts, even for discontinued products.
- Repairability Index:
- A consumer-focused tool that helps in making informed product decisions based on repairability.
- Aims to standardize repairability assessments, enabling easier product comparisons.
- Consumer Empowerment:
- The index fosters mindful consumption and sustainability.
- Ensures affordable repair options and improves overall consumer satisfaction by addressing information gaps.
- Key components of the Repair Ecosystem:
- Comprehensive Repair Information: Access to repair manuals/DIYs, diagnostics, and a list of necessary tools and parts.
- Accessible Spare Parts: Easily identifiable and timely delivery of spare parts.
- Affordable Tools: Inexpensive, widely available, and safe tools for consumers.
- Modular Design: Key components designed for independent access and modularity.
- Economic Feasibility: Ensuring that the cost of repair parts and labor is affordable for consumers.
Taking into account the above necessities the committee is expected to recommend enabling framework for Policies/Rules/Guidelines which support repairability and integration of repairability index with the extant regulatory provisions in mobile and electronics sector to enhance consumer experiences in reusing the mobile and electronics products they own.
The committee will submit a comprehensive report including a framework for repairability index in Indian context by 15th November, 2024.
India's Biotech Revolution

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian Cabinet has recently approved the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) proposal, a significant move to advance the country’s biotechnology sector.
Scheduled to take effect on April 1, 2025, the BioE3 policy aims to capitalize on India's biotechnology potential by focusing on six key areas: bio-based chemicals, functional foods, precision biotherapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, carbon capture, and marine/space research.
Current Status of India’s Biotechnology Sector
India ranks among the top 12 biotechnology destinations globally and is the third-largest in the Asia-Pacific region. As of 2024, India's Bioeconomy is valued at an estimated USD 130 billion. The sector is integral to India’s goal of becoming a USD 5 trillion economy by 2024, with biotechnology contributing about 3% to the global market share.
Biotechnology Categories in India:
- Biopharmaceuticals: India is a major supplier of low-cost drugs and vaccines, leading in biosimilars with the highest number of approvals.
- Bio-Agriculture: India dedicates approximately 55% of its land to agriculture, holding the fifth-largest area of organic agricultural land worldwide. The sector's contribution to the Bioeconomy is expected to grow from USD 10.5 billion to USD 20 billion by 2025.
- Bio-Industrial: Biotechnology is enhancing industrial processes, manufacturing, and waste disposal.
- Bio IT & BioServices: India excels in contract manufacturing, research, and clinical trials, hosting the highest number of US FDA-approved plants outside the US.
Government Initiatives:
- 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) is permitted in greenfield pharma and medical devices.
- The National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2021-25 aims to make India a global leader in biotechnology, targeting a USD 150 billion Bioeconomy by 2025.
- The Department of Biotechnology has established 51 Biotech-KISAN hubs to connect farmers with scientific advancements.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 includes INR 10,000 crore for 500 ‘waste to wealth’ plants under the GOBARdhan scheme.
- The GenomeIndia Project focuses on sequencing and analyzing the Indian population’s genomes to aid public health.
Challenges and Recommendations
Challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complex approval process for GMOs and overlapping regulatory bodies slow down progress.
- Funding Issues: Limited funding and high risks deter investment. The biotechnology sector receives only 0.05% of India's GDP from the Central Government.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate research facilities and cold chain infrastructure hamper progress.
- IP Concerns: Intellectual property protection remains weak, affecting innovation.
- Global Competition: Indian firms face stiff competition from established global players.
- Talent Shortages: A brain drain and skills mismatch impede growth.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical issues related to GMOs and gene editing pose challenges.
Recommendations:
- Regulatory Streamlining: Establish a unified Biotechnology Regulatory Authority and adopt a risk-based assessment approach.
- Innovative Funding: Create a Biotechnology Investment Fund with public-private partnerships.
- Talent Development: Launch skill development programs and integrate biotech training into various disciplines.
- Infrastructure Investment: Develop shared high-end research facilities and upgrade cold chain infrastructure.
- IP Strengthening: Enhance the IPR regime and establish a Biotech Patent Pool.
- Leverage Make in India: Expand the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to cover more biotech products and establish specialized manufacturing corridors.
Unified Pension Scheme

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The new Unified Pension Scheme (UPS), set to launch on April 1, 2025, aims to provide improved old age income security. Around 23 lakh Central government employees will benefit from this new scheme, and those currently under the National Pension System (NPS) will have the option to switch to UPS. States can also adopt the UPS for their employees, but they will need to secure funding from their own resources.
Key Components of UPS
The UPS introduces several enhancements to pension benefits:
- Pension Benefits: Employees will receive half of their average basic pay over the final 12 months of service as a monthly pension after completing a minimum of 25 years of service. For those with less than 25 years, the pension will be proportionately reduced, with a minimum pension of ?10,000 for those with at least 10 years of service.
- Family Pension: A family pension equivalent to 60% of the employee's pension will be provided to dependents upon the employee's death.
- Inflation Adjustment: Pension incomes will be adjusted in line with the consumer price trends for industrial workers, similar to the dearness relief provided to current government employees.
- Superannuation Payout: In addition to gratuity, a lumpsum superannuation payout will be given, amounting to 1/10th of the employee’s monthly emoluments for every six months of service.
Differences from the Current System
The new UPS combines features from the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) and NPS:
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS): Employees who joined before January 1, 2004, are covered under OPS, which guarantees a pension of 50% of the last drawn salary, adjusted for dearness allowance. It also offers a family pension of 60% of the last drawn pension, with provisions for commutation and additional increases for pensioners over 80 years of age.
- National Pension System (NPS): Introduced in 2004, NPS replaced OPS for new employees, shifting from a defined benefits system to a defined contribution scheme. Employees and the employer contribute a percentage of the salary to market-linked securities, with no guaranteed pension amount, only a corpus that must be used to buy an annuity upon retirement.
The UPS aims to blend the certainty of OPS with the funded approach of NPS. While employees' contributions will be capped at 10% of their salary, the government will contribute 18.5%, with potential adjustments over time. The government will cover any shortfall between investment returns and pension promises.
Reasons for the Change
The transition to UPS addresses concerns raised by government employees and political pressure regarding the NPS. Employees have criticized NPS for its lack of guaranteed pension benefits compared to OPS. The issue has become politically significant, with opposition parties promising to revert to OPS in various states.
In March 2023, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a review of NPS led by former Finance Secretary T.V. Somanathan. Though the review’s findings are yet to be made public, the introduction of UPS reflects a compromise balancing employee expectations with fiscal prudence.
Reactions and Future Impact
Central government employees generally welcome the UPS, recognizing it as a step toward addressing the shortcomings of NPS. However, there are concerns about the contributory nature of UPS and the absence of a commutation option like in OPS. Economists are analyzing the scheme's financial implications, with an expected additional cost of ?7,050 crore this year for the government. Future pension payouts may increase but are anticipated to be manageable with higher revenue growth.
The UPS marks a significant shift in pension policy, aiming to provide greater financial security for government employees while managing fiscal responsibilities.
New Target for Cancer Treatment Discovered by IACS Scientists

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant breakthrough, scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) in Kolkata have identified a new target for cancer therapy. Their study, recently published in The EMBO Journal, focuses on how cancer cells manage DNA repair during cell division, potentially paving the way for more effective treatments.
Key Findings
The researchers explored how cancer cells respond to topoisomerase 1 (Top1)-targeted chemotherapy. Top1 inhibitors, such as camptothecin, topotecan, and irinotecan, disrupt DNA replication and transcription, causing damage that usually leads to cell death. However, cancer cells can sometimes develop resistance by employing internal DNA repair mechanisms, primarily involving a protein called TDP1.
Mechanism of Action
Top1 is crucial for relaxing DNA supercoils during cell division, a process necessary for accurate chromosome segregation. Drugs targeting Top1 can kill cancer cells by preventing this relaxation. Nonetheless, cancer cells counteract this damage with TDP1, which repairs the DNA and promotes cell survival.
The IACS team discovered that TDP1's function is influenced by its phosphorylation status, which changes during the cell cycle and drug treatment. This modification helps TDP1 detach from chromosomes during cell division, a mechanism that helps cells survive despite the presence of chemotherapy drugs.
Novel Therapeutic Approach
The researchers propose a novel approach that combines inhibitors of two key molecules: CDK1 protein and TDP1 enzyme. CDK1 plays a critical role in regulating the cell cycle, while TDP1 is involved in repairing DNA damage. By inhibiting both, the researchers aim to disrupt the cancer cell's ability to repair DNA damage caused by Top1 inhibitors.
This combinatorial targeting strategy could enhance the effectiveness of cancer treatments. While Top1 inhibitors induce DNA damage, CDK1 inhibitors could prevent the repair of this damage or halt the cell cycle, making it difficult for cancer cells to survive. This dual-target approach may also help overcome resistance mechanisms that cancer cells develop against single-agent therapies.
Clinical Implications
CDK1 inhibitors, including avotaciclib, alvocidib, roniciclib, riviciclib, and dinaciclib, are currently in various stages of clinical trials. These drugs can be used alone or in combination with other DNA-damaging agents. Combining CDK1 inhibitors with Top1 inhibitors holds promise for significantly improving cancer treatment outcomes by targeting different aspects of the cell cycle and DNA replication.
Although the study was conducted using human breast cancer cells, the findings suggest potential benefits for patients with other types of cancer, such as ovarian, colorectal, and small cell lung cancers (SCLC). SCLC, in particular, is associated with tobacco smoking and could potentially benefit from this new combinatorial approach.
Conclusion
The IACS study opens new possibilities for cancer treatment by targeting DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. By combining CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors, the researchers aim to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and overcome resistance. Further research, including clinical trials, will be essential to validate these findings and develop personalized cancer therapies that could improve patient outcomes across various cancer types.
Recent Announcement on Dark Matter Research

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently two representatives from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment, working 1.5 km underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota, announced that they had placed the tightest restrictions yet on the identities of dark matter particles, resulting in a null finding that clarified which identities these particles could not have, leading to a sense of resignation rather than disappointment among the physics community, as similar experiments like XENON-nT in Italy and PandaX-4T in China have yielded empty results for decades despite significant efforts.
Background on Dark Matter
- Definition: Dark matter makes up most of the universe's mass, contributing to its structure.
- Composition: Likely consists of previously unknown particles that:
- Do not interact with photons.
- Remain stable over billions of years.
- Key Question: Can dark matter interact with atomic nuclei and electrons?
Experimental Strategies
- Proposed Method:
- Introduced by physicists Mark Goodman and Ed Witten in 1985.
- Concept: Use a “sail” (a chunk of metal) deep underground to detect dark matter interactions.
- Objective: Measure unknown mass and interaction rate (cross-section) of dark matter particles.
Scattering Cross-Section
- Concept:
- Similar to light interaction with different media (vacuum, glass, rock).
- Cross-sections indicate how readily a particle can scatter.
- Previous Limits: Proposed limits as small as 10−38cm210^{-38} text{cm}^210−38cm2.
- Current Achievements: Recent experiments have ruled out cross-sections as small as 10−44cm210^{-44} text{cm}^210−44cm2.
Challenges Ahead
- Neutrino Interference:
- As detectors increase in size, they also detect more noise from neutrinos, complicating dark matter detection.
- Both PandaX-4T and XENONnT report issues with neutrino signals.
- Resignation in Community:
- Scientists had hoped for clearer results before facing the challenge of distinguishing dark matter from neutrinos.
Alternative Research Avenues
- Focus on Lighter Particles:
- Exploring dark particles lighter than atomic nuclei for easier detection.
- Technological Development:
- Advancing technologies to measure minimal energy transfers using special materials.
Conclusion
- Ongoing Effort: The search for dark matter continues to unite scientific disciplines and require innovative approaches.
- Human Ingenuity: The pursuit reflects a broader effort to understand the universe, drawing on collective expertise and creativity.
NAMASTE programme

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
A recent government survey has shed light on the demographics of workers engaged in the hazardous cleaning of urban sewers and septic tanks across India. This initiative, part of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's NAMASTE programme, highlights significant disparities within this labor sector.
Key Findings
- Community Representation: An overwhelming 91.9% of the 38,000 workers profiled belong to marginalized communities:
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 68.9%
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 14.7%
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 8.3%
- General Category: 8%
- Mortality Rates: Between 2019 and 2023, at least 377 individuals died while performing hazardous cleaning tasks, underscoring the dangers associated with this work.
The NAMASTE Programme
- Objective: The NAMASTE programme aims to mechanize sewer work to prevent fatalities linked to manual cleaning. It seeks to transition workers into safer, more sustainable roles as "sanipreneurs" by providing safety training, equipment, and capital subsidies.
- Background: This programme replaces the earlier Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), focusing on the more technical aspects of hazardous cleaning rather than manual scavenging.
- Namaste is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) as a joint initiative of the MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The Scheme has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 360 crore for four years from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- NAMASTE aims to achieve the following outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
- Strengthened supervisory and monitoring systems at national, state and ULB levels to ensure enforcement and monitoring of safe sanitation work
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered and skilled sanitation workers
Progress and Coverage
- Implementation: Since the scheme's inception, 3,326 urban local bodies (ULBs) have begun profiling workers, with many reporting minimal or no workers engaged in hazardous cleaning.
- Data Collection: The government is gathering data from over 3,000 ULBs across 29 states and union territories to better understand the scope and risks associated with this labor.
AVGC: The Future of Media & Entertainment Industry

- 30 Sep 2024
Introduction
- The AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics) sector is set to be the future of the media and entertainment industry.
- According to the FICCI-EY 2024 report, India now boasts the second-largest anime fan base globally and is projected to contribute 60% to the worldwide growth in anime interest in the coming years.
- In a significant step toward making India a global hub for AVGC, the Union Cabinet recently approved the establishment of a National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics, and Extended Reality (AVGC-XR) in Mumbai.
NCoE Background
- NCoE will be set up as a Section 8 Company under the Companies Act, 2013 in India with Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry and Confederation of Indian Industry representing the industry bodies as partners with the Government of India.
- The establishment of the NCoE follows the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs 2022-23 budget announcement, which proposed the creation of an AVGC task force in the country.
- NCoE AVGC aims at creating a world class talent pool in India to cater to the Indian as well as global entertainment industry.
- Provisionally named the Indian Institute for Immersive Creators (IIIC), this center aims to revolutionize the AVGC sector and foster innovation in immersive technologies.
- It will be modeled after renowned institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs).
Objective of NCoE (IIIC)
Boasting a growth rate of 25% and an estimated value of ?46 billion by 2023 (FICCI-EY Report 2023), the animation industry in India is thriving and offers a promising future for passionate young talent.
Below are some of the key objectives of the NCoE (IIIC):
- Focusing of creating Indian IP
- Leveraging our cultural heritage in new age
- Create a multiplier effect in the industry
- An industry led initiative, in partnership with state and academia
- Integrated focus on education, skilling industry, development, innovation
- Hub and spoke model of development to be followed
- IIIC as the hub and several center’s as its spokes dedicated innovation and research fund to promote start-up ecosystem
Conclusion
The Union Cabinet's approval of the National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for AVGC marks a pivotal step in strengthening India’s media and entertainment industry. This initiative is set to boost the economy while creating new job opportunities in the rapidly growing AVGC sector. As a global hub for filmmaking, India's advancements in technology and infrastructure will enable the production of high-quality content, positioning the country as a leader in technological innovation and creativity.
MARBURG VIRUS OUTBREAK IN RWANDA
- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Rwanda is currently facing an outbreak of Marburg virus disease (MVD), leading to six fatalities, primarily among healthcare workers.
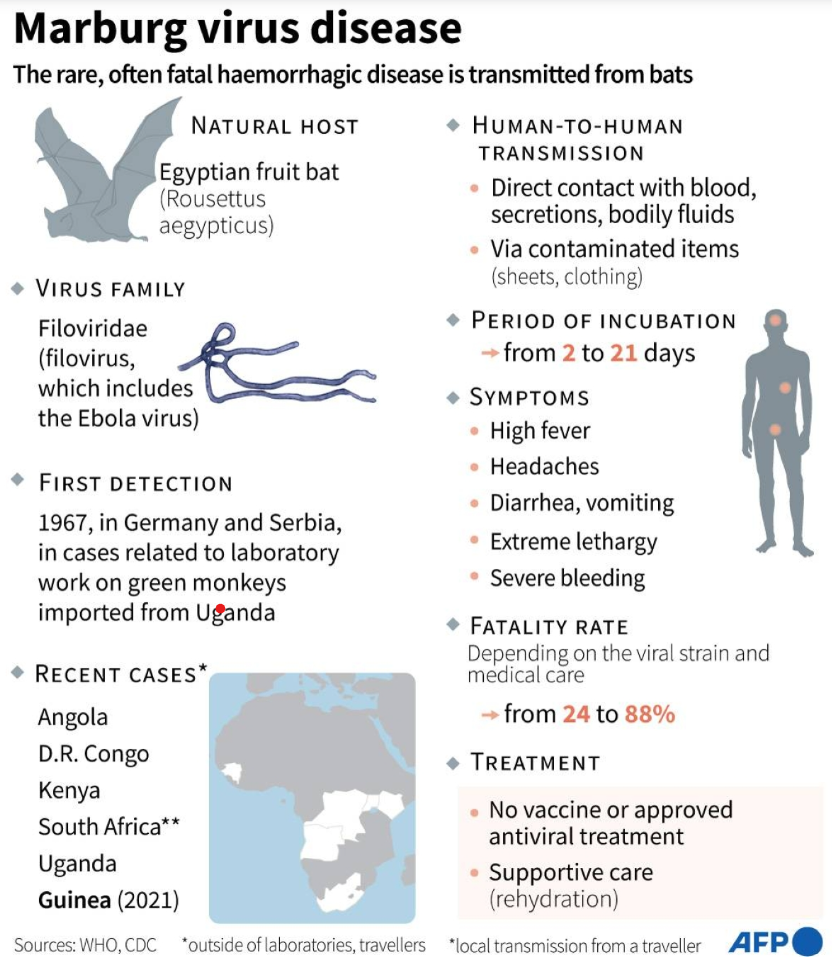
What is Marburg Virus Disease?
Marburg virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness first identified in 1967 in Germany. It is caused by the Marburg virus, which is primarily transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, particularly fruit bats.
Current Situation in Rwanda
The ongoing outbreak has claimed six lives, most of whom were healthcare professionals. The Minister of Health has emphasized the need for heightened preventive measures and community vigilance.
Symptoms and Transmission
Common symptoms of MVD include high fever, severe headache, watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. The virus spreads through direct contact with the blood, secretions, and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
Available Treatments and Supportive Care
There is currently no specific treatment for Marburg virus disease. Supportive care, including symptom management and hydration, is critical, and early medical attention is essential for those exhibiting symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To prevent the spread of MVD, individuals should:
- Practice good hygiene.
- Avoid contact with infected persons.
- Ensure thorough cooking of animal products.
- Use protective equipment when caring for sick patients.
Global Context and Pandemic Risk
While Marburg virus disease poses a significant mortality risk and can spread between humans, its pandemic potential is lower than that of more contagious viruses. Rapid containment efforts are essential to prevent wider outbreaks.
INDIA DESERVES PERMANENT UNSC SEAT: BHUTAN

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
With its significant economic growth and leadership of the Global South, India deserves a permanent seat at the UN Security Council, says Bhutan’s Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth: Highlights India’s significant economic growth and its leadership in the Global South as justifications for this status.
- International Backing: India’s bid gains momentum with support from several UN Member States, including France, the UK, and the U.S.
- Need for Reform: Bhutan emphasized that the UNSC is outdated and must evolve to reflect contemporary geopolitical and economic realities.
- Advocacy for Representation: Bhutan has long called for a more representative and effective Security Council, backing India’s inclusion at the high table.
About UN Security Council (UNSC)
- Composition: Total of 15 member states.
- 5 permanent members (P5): China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States (with veto rights).
- 10 non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- Election of Non-Permanent Members:
- Elected on a regional basis:
- 5 seats for African and Asian states.
- 2 seats for Latin American and Caribbean states.
- 1 seat for Eastern European states.
- 2 seats for Western European and other states.
- Elected on a regional basis:
- Presidency:
- Rotates monthly among members, following the English alphabetical order of country names.
- Primary Functions:
- Maintain international peace and security.
- Investigate and resolve disputes.
- Impose sanctions and authorize the use of force.
- Establish peacekeeping missions.
- Make recommendations to member states.
- Meeting Schedule:
- Regular meetings at UN headquarters in New York.
- Can convene at any time in response to emergencies.
- Decision-Making:
- Requires affirmative votes from at least 9 of the 15 members.
- Any of the P5 can veto resolutions, raising concerns about the Council's effectiveness.
- Subsidiary Bodies:
- Includes committees, working groups, and sanctions committees focused on specific issues like counter-terrorism, nuclear non-proliferation, and peacekeeping operations.
- Reforming the UN Security Council (UNSC)
- Charter Amendments:
- Reforming the UNSC requires amendments to the UN Charter.
- Voting Requirements:
- An amendment must be adopted by a two-thirds majority of the General Assembly.
- It must also be ratified by two-thirds of UN member states, including all permanent members of the UNSC.
- Charter Amendments:
Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Tourism, Government of India, launched the national responsible tourism initiative ‘Paryatan Mitra & Paryatan Didi’ on September 27, 2024, coinciding with World Tourism Day.
- Vision: Aligned with the Prime Minister's vision to use tourism as a tool for social inclusion, employment, and economic development.
Pilot Locations
- Destinations: The initiative is piloted in six tourist destinations:
- Orchha (Madhya Pradesh)
- Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh)
- Bodh Gaya (Bihar)
- Aizawl (Mizoram)
- Jodhpur (Rajasthan)
- Sri Vijaya Puram (Andaman & Nicobar Islands)
Objectives and Training
- Enhancing Tourist Experience: The program aims to connect tourists with ‘tourist-friendly’ individuals who serve as local ambassadors and storytellers.
- Training Focus: Individuals interacting with tourists—such as cab drivers, hotel staff, street vendors, and students—receive training on:
- Importance of tourism and hospitality
- Cleanliness and safety
- Sustainability practices
- Local stories and attractions
Empowering Women and Youth
- Target Groups: Emphasis on training women and youth to develop tourism products such as:
- Heritage walks
- Food and craft tours
- Nature treks and homestays
- Employment Opportunities: Aims to enable locals to secure jobs as homestay owners, cultural guides, and adventure guides.
Digital Literacy
- Training in Digital Tools: Participants are also educated in digital literacy to enhance visibility of their offerings to tourists.
Impact and Recognition
- Training Success: Since the program's pilot in August 2024, approximately 3,000 individuals have been trained.
- Local Enthusiasm: Increased local interest in participating in tourism training programs and contributing to the tourism ecosystem.
- Future Recognition: The Ministry plans to award dedicated badges to Paryatan Mitra and Didi participants, ensuring tourists can identify those committed to providing exceptional experiences.
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
INDIA TO SUPPORT TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO IN DEVELOPING UPI-LIKE PAYMENT SYSTEM

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- NPCI International Payments Limited (NIPL) has partnered with Trinidad and Tobago's Ministry of Digital Transformation to create a payment platform for person-to-person and person-to-merchant transactions.
- Modeling on UPI: The new digital payments system will be based on India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which is widely recognized as a leading digital payment solution.
- Role of NPCI: NIPL, a quasi-government body under the Reserve Bank of India, manages India’s retail payment systems, including UPI.
Previous Initiatives
- Global Expansion: Earlier in 2024, NIPL also committed to establishing digital payment systems in Peru and Namibia, leveraging the UPI model.
- Ongoing Talks: NIPL is exploring opportunities with additional countries in Africa and South America to assist in building their payment infrastructures.
Significance:
- UPI has emerged as a transformative force in India's financial landscape, registering nearly 15 billion transactions in August 2024, with an estimated value of USD 245 billion.
- This strategic partnership aims to empower Trinidad and Tobago to establish a reliable and efficient real-time payments platform for both person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions, expanding digital payments in the country and fostering financial inclusion.
India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
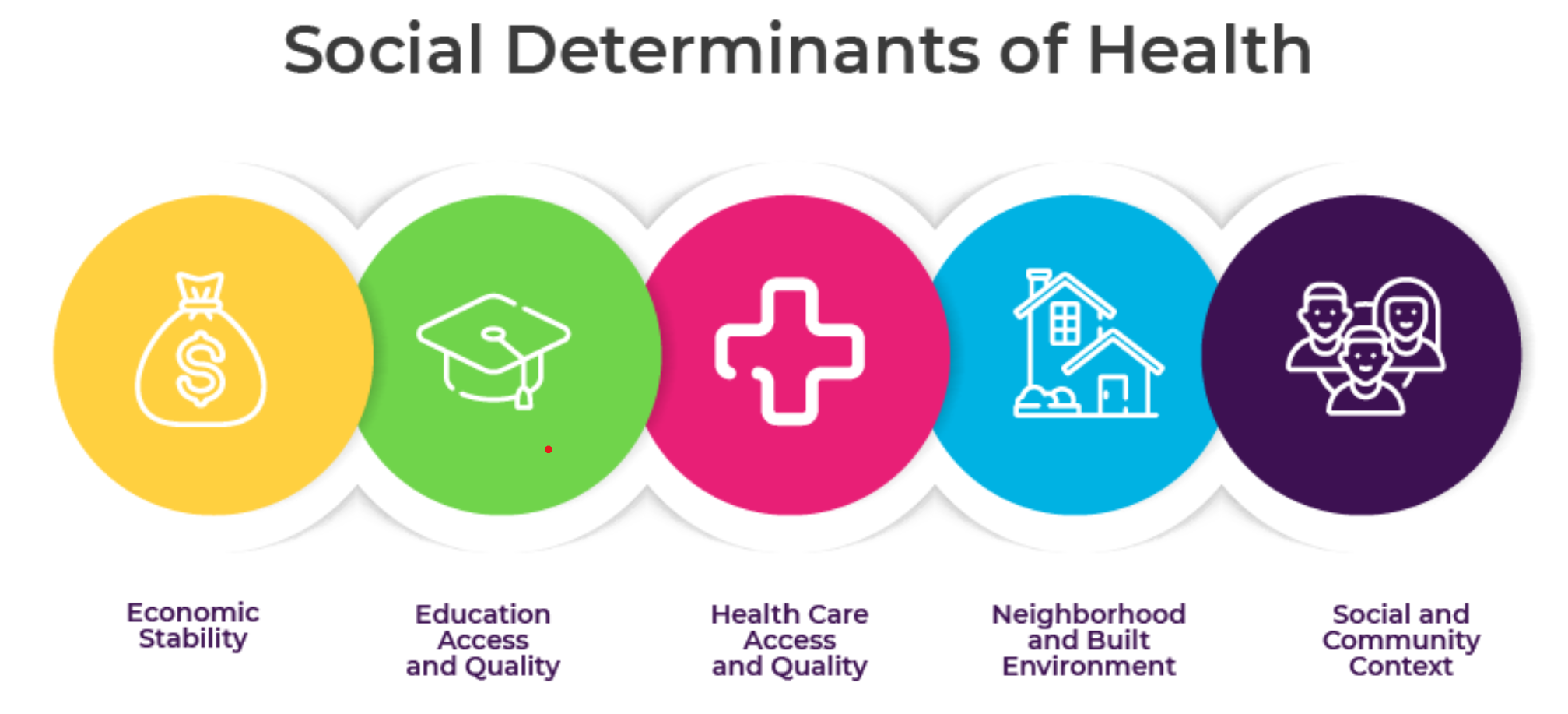
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
GST COMPENSATION CESS

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- GST compensation cess likely to continue beyond January 2026, with potential rebranding and new end-use defined.
- Revenue Collection: Estimated Rs 20,000 crore expected from the cess by February 2026, with recent receipts of Rs 12,068 crore in August 2024.
- Cess Nature: The compensation cess, originally intended for revenue shortfall, cannot merge with the 28% GST slab due to regulatory limitations.
Financial Context
- RBI Study Insights: Weighted average GST rate decreased from 14.4% at launch to 11.6%, now even below 11%, raising concerns among states.
- State Concerns: Many states, including Punjab and Kerala, seek a 2-5 year extension for the compensation period to stabilize finances.
Regulatory Framework
- Cess Legislation: GST Compensation Cess is governed by the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act, 2017, initially set for five years.
- Taxpayer Obligations: All suppliers of designated goods/services must collect the cess, except exporters and those under the composition scheme.
Distribution Mechanism
- Calculation of Compensation: Based on projected revenue growth (14%) against actual revenue, with payments distributed bi-monthly.
- Surplus Distribution: Any surplus in the compensation fund post-transition period will be shared between the Centre and states.
Future Considerations
- Ministerial Panel: A panel established by the GST Council will recommend the cess's future and revenue sharing post-compensation.
- Tax Expert Opinions: Some experts argue against pursuing the revenue-neutral rate, suggesting broader tax base expansion instead.
- Revenue Gap Solutions: Options for addressing compensation fund deficits include revising cess formulas, increasing rates, or market borrowing.
IBSA (INDIA, BRAZIL, SOUTH AFRICA) GROUPING

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant move for global security, the Foreign Ministers of the IBSA (India, Brazil, South Africa) grouping issued a strong declaration against terrorism during the 79th UN General Assembly in New York. This declaration condemned terrorism in all its forms and reaffirmed the collective responsibility of the international community to eliminate terrorist safe havens worldwide.
Key Points from the IBSA Declaration:
- Universal Threat: The ministers stressed that terrorism is a threat that transcends borders, cultures, and governments.
- Rule of Law: They emphasized that counter-terrorism efforts must adhere to international law, particularly the UN Charter and human rights laws, ensuring civil liberties are respected.
- International Framework: A call was made for establishing a comprehensive international counter-terrorism framework, with the United Nations at its core, to coordinate global efforts against terrorism.
- Cross-Border Security: The declaration highlighted the need for stringent actions against the movement of terrorists and the financing of terrorist networks, condemning groups like Al-Qaeda, ISIS/Daesh, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT), and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM).
- Comprehensive Convention: A renewed commitment to accelerate the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism at the UN was emphasized, aiming to create a unified legal framework for combating terrorism.
POLITICAL DECLARATION ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
World leaders have officially adopted the Political Declaration on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) at the UN High-Level Meeting, highlighting the urgent need for coordinated global action to combat AMR, which claims 1.27 million lives annually. This declaration recognizes drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) as a critical component of the global AMR response, marking a significant moment in the fight against antimicrobial resistance.
Key Highlights of the Declaration
- DR-TB Priority: The declaration emphasizes the severe burden that DR-TB imposes on health systems, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), and the potential reversal of progress made against tuberculosis and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Global Death Reduction Target: A target to reduce global deaths associated with AMR by 10% by 2030 and a funding goal of USD 100 million to help at least 60% of countries establish funded AMR plans by 2025.
- Support for Vulnerable Groups: Recognition of the socioeconomic challenges faced by those affected by AMR, affirming the need for integrated, person-centered healthcare, including support to reduce stigma.
- Independent Panel for Action: Agreement to establish an independent panel to provide evidence for actions against AMR by 2025.
Commitment to Action
The Stop TB Partnership applauds this commitment and urges UN Member States to provide necessary funding for implementing the declaration's commitments. The partnership aims to work closely with governments and civil society to translate these commitments into concrete actions.
Challenges of Antimicrobial Resistance
AMR poses a significant threat, particularly in LMICs, where it exacerbates existing healthcare challenges:
- Increased Infections: Medical facilities often become hotspots for treatment-resistant infections, making routine procedures riskier. In LMICs, about 11% of surgical patients experience infections.
- Lack of Resources: Access to clean water, proper diagnostics, and antimicrobial medicines is often limited, increasing vulnerability to drug-resistant infections.
- Impact of Conflicts: AMR complicates treatment in conflict zones, where drug-resistant infections spread rapidly among displaced populations, further emphasizing the need for peaceful resolutions.
Economic Implications of AMR
The economic case for addressing AMR is compelling:
- Without a stronger response, AMR could lead to an additional $412 billion in healthcare expenditures annually over the next decade, along with $443 billion in losses due to workforce participation and productivity declines.
- Implementing critical AMR interventions is considered a “best buy,” with a potential return of $7 to $13 for every dollar invested.
AYUSHMAN BHARAT DIGITAL MISSION (ABDM)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created in the past three years under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). The digital healthcare mission marked its three-year anniversary.
Key Highlights:
- Launch Date: September 27, 2021.
- Vision: Establish a robust digital health infrastructure to enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and transparency.
- Duration: A transformative three-year journey aimed at revolutionizing India’s digital healthcare ecosystem.
Objectives and Background
- Alignment with National Health Policy: The mission stems from the National Health Policy (2017), emphasizing accessibility and the integration of digital technologies.
- Building Blocks:
- National Health Stack (2018) introduced unique health identifiers and verified registries.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (2019) provided guidance for implementing ABDM.
Key Features of ABDM
- Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Assigns a unique ID to every individual for managing health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): Comprehensive database of healthcare professionals across all systems of medicine.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): Repository of public and private health facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
- Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): Allows secure access and sharing of health records based on informed consent.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services.
- National Health Claims Exchange (HCX): Standardizes the insurance payment process for quicker claims.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensures confidentiality and security of health-related information in compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Interoperability: Enables seamless data exchange among stakeholders, supported by key gateways (HIE-CM, NHCX, UHI).
- Transparency: Offers individuals access to both public and private health services, ensuring transparent pricing and accountability.
Key Initiatives
- Scan and Share: QR-code based OPD registration reduces wait times and improves data accuracy.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Financial incentives to encourage participation in the ABDM ecosystem, launched on January 1, 2023.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: Operationalized 106 microsites to facilitate ABDM adoption among private providers.
- End-to-End ABDM Adoption Pilot: Aimed at digitizing healthcare facilities across India, with 131 selected for participation.
Achievements
- Health Accounts Creation: Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) established, linking 42 crore health records.
- Ecosystem Participation: Involvement of 236 private entities and leading public institutions, enhancing interoperability.
- Healthcare Facility Registration: 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals registered.
Moving Towards Transformation
- Collaborations: Partnerships with IIT Kanpur and Maharashtra University of Health Sciences to drive digital health education and public goods development.
- Training Initiatives: Introduction of a WhatsApp Chatbot for stakeholder training on digital health practices.
- Digital Health Standards: Launched by the National Accreditation Board of Hospitals to promote digital health technology adoption.
- Integration of eSwasthya Dham Portal: Extends ABDM benefits to Char Dham Yatris.
Vision for the Future
ABDM aims to create a seamless digital health ecosystem, ensuring every Indian citizen has access to their health records through a unique ABHA ID. The initiative includes:
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS): Aids healthcare professionals in improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
INDIA-UZBEKISTAN BILATERAL INVESTMENT TREATY (BIT)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
India and Uzbekistan signed the Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) aimed at boosting the confidence of investors of both the countries.
Key Highlights:
- Investor Protections:
- Assured Protection: The BIT guarantees protection for investors from both countries, aligning with international standards.
- Minimum Standards: It establishes a minimum standard of treatment and non-discrimination for investors.
- Dispute Resolution: An independent arbitration forum will be available for dispute settlement.
- Investment Safeguards:
- Protection from Expropriation: The treaty safeguards investments from unjust expropriation.
- Transparency and Compensation: Provisions are included for transparency and compensation for losses incurred.
- Regulatory Balance: While protecting investors, the treaty maintains a balance with the state's right to regulate, ensuring adequate policy space for both countries.
Economic Context
- Shared Commitment: The BIT reflects the commitment of both nations to foster economic ties and create a resilient investment environment.
- Expected Outcomes: It is anticipated that the treaty will facilitate increased bilateral investments, benefiting businesses and economies in India and Uzbekistan.
- Current Investment Landscape: As of August 2024, Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) from India to Uzbekistan stands at $20 million, with Indian investments notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, amusement parks, automobile components, and hospitality.
India and Bilateral Investment Treaties
BITs are reciprocal agreements between two countries designed to promote and protect foreign private investments within each other's territories.
- Key Guarantees Established:
- National Treatment: Foreign investors are treated on par with domestic companies.
- Fair and Equitable Treatment: Investors receive treatment aligned with international law.
- Protection from Expropriation: Limits the ability of a country to seize foreign investments without appropriate compensation.
- Status of BITs in India
- Historical Context:
- Until 2015, India had signed BITs with 83 countries, with 74 currently in force. These agreements were based on the Indian Model BIT established in 1993.
- Revisions and Current Approach: In 2015, India revised its Model BIT text. Since then, India has:
- Signed new BITs/Investment Agreements with four countries.
- Entered negotiations with 37 countries/blocks for new agreements.
- Terminated older BITs with 77 countries, with only six remaining in force.
- Historical Context:
- Key Features of the Revised Model BIT
- Investor Protection:
- Provides robust protection for foreign investors in India and Indian investors abroad.
- Balances investor rights with government obligations.
- Investor Confidence:
- Enhances investor confidence by ensuring non-discriminatory treatment and a level playing field.
- Establishes an independent arbitration forum for dispute resolution.
- Investment Definition:
- Adopts an "enterprise"-based definition of investment to encompass various forms of investment.
- Dispute Settlement Provisions:
- Refined Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) provisions require investors to exhaust local remedies before seeking international arbitration.
- Limits arbitration tribunals to awarding monetary compensation only.
- Regulatory Authority Preservation:
- Excludes government procurement, taxation, subsidies, compulsory licenses, and national security from BIT coverage, ensuring the government retains regulatory authority.
- Investor Protection:
- Strategic Impact
- Preferred FDI Destination: The revised BIT aims to position India as a preferred destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Protection of Outbound FDI: It also focuses on safeguarding outbound investments made by Indian entities.
GLOBAL INNOVATION INDEX (GII) 2024

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has moved up to 39th place among 133 economies in the GII 2024, showcasing significant progress from its 81st position in 2015.
Key Details:
- Regional Leadership: India ranks first among the 10 economies in Central and Southern Asia, highlighting its emerging leadership in innovation within the region.
- Lower-Middle-Income Economies: India is also the top-ranked lower-middle-income economy in the GII.
- WIPO Science & Technology Ranking: India holds the 4th position in the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Science & Technology Cluster Ranking, indicating robust innovation capabilities.
- Top Science & Technology Clusters: Major Indian cities—Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru, and Chennai—are recognized among the world’s Top 100 S&T clusters, emphasizing urban centers' roles in fostering innovation.
- Intangible Asset Intensity: India ranks 7th globally in intangible asset intensity, reflecting a strong focus on knowledge-based assets and intellectual property.
Context and Significance of GII
- Purpose of GII: The GII evaluates innovation ecosystems of 133 economies, providing insights into trends that drive economic and social change through innovation.
- Global Leaders: The top five most innovative economies according to the GII 2024 are Switzerland, Sweden, the US, Singapore, and the UK.
- Fastest Climbers: India is among the fastest climbers in the GII over the past decade, alongside China, Turkey, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
Overview of WIPO
- Foundation and Mission: The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), established in 1974 and part of the UN since then, aims to support global innovators and creators, ensuring the safe journey of their ideas to market.
- Membership: WIPO comprises 193 member states, including a diverse range of developing and developed countries, facilitating a broad exchange of intellectual property knowledge.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
WORLD TOURISM DAY 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Tourism celebrated World Tourism Day on September 27, 2024, under the theme “Tourism and Peace.” The focus was on how tourism fosters global peace by encouraging cross-cultural interactions and understanding.
Key Details:
- World Tourism Day, established in 1980 by the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO), celebrates the global impact of tourism and raises awareness about its economic, social, and cultural significance.
- This day celebrates the diverse experiences that tourism offers and commits to making travel more inclusive, sustainable, and beneficial for all; here’s all you need to know about the day.
- The date, September 27, was chosen to commemorate the adoption of UNWTO statutes in 1975
- The theme for World Tourism Day 2024 is “Tourism and Peace,” which will highlight the association between tourism and world peace, with the United Nations emphasising the significance of comprehending diverse cultures and encouraging sustainable tourism.
World Tourism Day: Significance and Celebrations
- World Tourism Day is a global event that celebrates the role of tourism in bridging cultural gaps, enhancing mutual understanding, and driving economic development.
- It focuses on responsible tourism practices, celebrating diverse cultural heritage, and addressing environmental sustainability and fair distribution of benefits.
- Events include seminars, workshops, and conferences on the theme of the year, cultural festivals, exhibitions, and public performances.
- Educational campaigns and community outreach activities raise awareness about responsible travel, supporting local economies, and protecting natural environments.
Note:
- The World Economic Forum, in its recently released Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI), shares the top countries gaining popularity in the travel and tourism industry.
- Notably, in Southeast Asia, India ranks 39th as the TTDI’s top lower-middle-income economy. India’s strong Natural (6th), Cultural (9th) and Non-Leisure (9th) resources drive its travel industry, with the country’s being only one of three to score in the top 10 for all the resources pillars.
- The TTDI measures the set of factors and policies that enable the sustainable and resilient development of the T&T sector, which in turn contributes to the development of a country. Among the 119 countries, here are the top 10 countries for travel and tourism in 2024 attracting travellers from all over the globe.
GlobE Network

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- India was elected to the 15-member GlobE Steering Committee on September 26, 2024, in a plenary session in Beijing. The election involved a multistage voting process.
- Role and Significance:
- India will play a vital role in shaping the global agenda on corruption and asset recovery.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) highlighted India's expertise in combating corruption as a significant asset for the GlobE Network.
- About the GlobE Network:
- The Global Operational Network of Anti-Corruption Law Enforcement Authorities (GlobE Network) is a G-20 initiative, supported by India since 2020.
- Officially launched on June 3, 2021, during a UN General Assembly session against corruption.
- Currently comprises 121 member countries and 219 member authorities.
- Governance Structure:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) serves as the central authority for India within the GlobE Network.
- Indian member authorities include the CBI and the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
- The Steering Committee consists of one chair, one vice-chair, and 13 members providing leadership and direction.
- Functionality and Objectives:
- The GlobE Network facilitates the sharing of best practices, criminal intelligence, and strategy development among international agencies to combat corruption.
- It is supported by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), which provides secretariat services.
- G-20 Presidency Initiatives:
- During India’s G-20 Presidency in 2023, two high-level principles for combating corruption were adopted, emphasizing the use of the GlobE Network to enhance global cooperation.
PLANETARY BOUNDARIES AND OCEAN ACIDIFICATION
- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
A new report from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) indicates that the world's oceans are nearing critical acidity levels.
- Key Findings:
- Nine Crucial Factors: The report identifies nine essential elements for sustaining life on Earth.
- Exceeded Limits: Six of these factors have already surpassed safe limits due to human activities.
- Ocean Acidification: This is poised to become the seventh boundary breached.
- Crossed Boundaries:
- Factors Affected:
- Climate change
- Loss of natural species and habitats
- Depletion of freshwater resources
- Increase in pollutants, including plastics and agricultural chemicals
- Factors Affected:
- Causes of Ocean Acidification:
- Primarily driven by rising carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels (oil, coal, gas).
- Implications of Acidification:
- Damage to corals, shellfish, and phytoplankton, disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Threats to food supplies for billions of people.
- Reduced capacity of oceans to absorb CO2, exacerbating global warming.
- Ozone Layer Status:
- Currently not close to being breached; showing recovery since the banning of harmful chemicals in 1987.
- Air Quality Concerns:
- A ninth boundary related to particulate matter is near danger limits.
- Improvements in air quality are noted, but industrializing nations still face pollution risks.
- Tipping Points:
- Crossing these boundaries could lead to irreversible and catastrophic consequences for humanity and future generations.
- All boundaries are interconnected; breaching one can destabilize the entire system.
- Opportunities for Solutions:
- Addressing critical issues, such as limiting temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, can have widespread benefits across multiple environmental challenges.
Planetary boundaries
- The planetary boundaries were introduced in 2009 to define the global environmental limits within which humans can safely live.
- Johan Rockström, former director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre, led a group of 28 renowned scientists to identify the nine processes that regulate the stability and resilience of the Earth system.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gas concentrations, primarily CO2, are the primary metric here. Exceeding the recommended levels risks amplifying global warming.
- Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorb CO2, leading to decreased pH levels. This boundary measures the carbonate ion concentration, vital for marine life like corals.
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion: The ozone layer protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation. This boundary emphasizes the ozone concentration in the stratosphere.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycles: Excess nitrogen and phosphorus, often from fertilizers, can disrupt ecosystems. Here, the focus is on their flow into the environment.
- Freshwater Use: Freshwater is vital for life. This boundary pinpoints the annual consumption of freshwater resources.
- Land-System Change: As we modify landscapes, particularly through deforestation, we alter habitats and carbon storage capabilities. This threshold concerns the amount of forested land remaining.
- Biodiversity Loss: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem resilience. This metric observes the extinction rate of species.
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading: Aerosols influence climate and human health. This boundary examines their density in the atmosphere.
- Chemical Pollution: Synthetic chemicals can harm ecosystems and human health. This boundary reviews their concentration and spread.
INDIA WATER WEEK (IWW) 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- The 8th edition of India Water Week (IWW) 2024 was held from September 17-20, 2024, at the Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
- Organized by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, this prestigious international event has established itself as a key platform for collaboration in water resource management.
- With participation from global water experts, government leaders, and private-sector representatives, the event aimed to address the critical challenges of water management, foster innovation, and promote sustainable water practices.
Theme and Focus
The theme for India Water Week 2024 was "Partnerships and Cooperation for Inclusive Water Development and Management." This theme underscored the importance of cross-sectoral and international collaboration to address the 21st-century's growing water challenges and the need for integrated efforts in water conservation, management, and equitable access to water resources.
India Water Week: An International Forum
- Since its inception in 2012, India Water Week has grown into a pivotal event in global water diplomacy, offering a platform for dialogue, innovation, and knowledge sharing.
- Each edition focuses on a specific water-related issue, providing policymakers, experts, and industry leaders the opportunity to present solutions and explore cooperative strategies.
International WASH Conference
- A key highlight of IWW 2024 was the International WASH Conference, organized by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- This conference focused on global collaboration in Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH), aiming to address pressing sanitation challenges and promote hygiene standards.
- The conference was held between 17th-19th September 2024, in New Delhi. This three-day gathering, centered on the theme ‘Sustaining Rural Water Supply’, offered a platform for knowledge exchange, showcasing innovations, and sharing best practices aimed at addressing global WASH challenges, with a special focus on achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6).
Key Takeaways from India Water Week 2024
The India Water Week 2024 concluded with several important takeaways:
- Collaboration and Cooperation: Water security can only be achieved through partnerships across sectors and borders.
- Innovation in Water Management: Startups and technological innovations are key to addressing the future challenges of water resource management.
- Community Participation: Local communities play a crucial role in water conservation efforts, and their involvement is vital to achieving sustainable development.
- Policy Recommendations: The event produced several policy recommendations for sustainable water governance, addressing challenges in climate resilience, infrastructure development, and groundwater management.
Conclusion
India Water Week 2024 was a landmark event that brought together a diverse group of stakeholders to address the complexities of water management in the 21st century. The event paved the way for a more sustainable and inclusive approach to water development through partnership, cooperation, and innovation, ensuring equitable access to water resources for all.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Prime Minister of India launched three Param Rudra Supercomputing Systems and a High-Performance Computing (HPC) system for weather and climate research via a virtual event.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers
- Development: Indigenously developed under the National Supercomputing Mission.
- Deployment Locations:
- Delhi: Inter University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) focuses on material science and atomic physics.
- Pune: Giant Metre Radio Telescope (GMRT) will explore Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) and other astronomical phenomena.
- Kolkata: S N Bose Centre drives advanced research in physics, cosmology, and earth sciences.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) System
- Purpose: Tailored for weather and climate research.
- Location:
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune.
- National Center for Medium Range Weather Forecast (NCMRWF), Noida.
- System Names: 'Arka' and 'Arunika', reflecting their solar connection.
Significance of the HPC System
- Enhanced Predictive Capabilities:
- High-resolution models improve accuracy and lead time for: Tropical cyclones, Heavy precipitation, Thunderstorms, Hailstorms, Heat waves, Droughts and Other critical weather phenomena
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- Launch and Goals
- Launched in 2015 to position India among world-class computing power nations.
- Aims to connect national academic and R&D institutions with a network of over 70 high-performance computing (HPC) facilities.
- Implementation
- Managed by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Government of India.
- Estimated cost: Rs 4,500 crore over 7 years.
- Supports initiatives like 'Digital India' and 'Make in India'.
- Current Status
- India ranks 74th globally in supercomputing, with only 9 supercomputers out of more than 500 worldwide.
- The mission addresses the growing computing demands of the scientific community and aligns with international technology trends.
- Infrastructure and Networking
- Envisions a supercomputing grid with over 70 HPC facilities networked via the National Knowledge Network (NKN).
- NKN connects academic institutions and R&D labs through a high-speed network.
ASIA POWER INDEX

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
In a major shift, India surpassed Japan to become the third-largest power in the Asia Power Index, reflecting its increasing geopolitical stature. This achievement is driven by India's dynamic growth, youthful population, and expanding economy, solidifying its position as a leading force in the region.
Key Factors Behind India’s Rise:
- Economic Growth: India has shown remarkable post-pandemic economic recovery, contributing to a 4.2-point rise in its Economic Capability. India’s massive population and strong GDP growth reinforce its standing as the world’s third-largest economy in PPP terms.
- Future Potential: India’s Future Resources score increased by 8.2 points, signalling a potential demographic dividend. Unlike its regional competitors, particularly China and Japan, India benefits from a youthful population that will continue to drive economic growth and labour force expansion in the coming decades.
- Diplomatic Influence: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership has garnered greater international recognition. India’s non-aligned strategic posture has allowed New Delhi to navigate complex international waters effectively. India ranked 6th in terms of diplomatic dialogues in 2023, reflecting its active engagement in multilateral forums.
- Further, India’s large population and economic capabilities offer it substantial promise. India’s score in Cultural Influence has also remained relatively strong, underpinned by its global diaspora and cultural exports.
- In addition, India’s role in multilateral diplomacy and security cooperation has been a point of emphasis. India's participation in dialogues, as well as its leadership in the Quad, has allowed it to play a significant role in regional security dynamics, albeit outside of formal military alliances.
Asia Power Index
- The Asia Power Index, launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018, is an annual measure of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It evaluates 27 countries across the Asia-Pacific, examining their ability to shape and respond to the external environment.
- The 2024 edition offers one of the most comprehensive assessments of power distribution in the region to date. Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, reflecting its growing importance in Southeast Asia.
- The Index focuses on both the material capabilities of states and the influence they exert on the international stage.
Criteria and Parameters of Power Measurement
Power in the Asia Power Index is divided into resource-based and influence-based determinants:
- Resource-Based Determinants:
- Economic Capability: The core economic strength of a country, measured through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological sophistication, and global economic connectivity.
- Military Capability: Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces, weapon systems, and signature capabilities like long-range power projection.
- Resilience: The internal capacity to deter threats to state stability, including institutional robustness, geopolitical security, and resource security.
- Future Resources: Forecasts the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors projected for 2035.
- Influence-Based Determinants:
- Economic Relationships: The capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks: The strength of alliances and partnerships, measured through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- Diplomatic Influence: The extent of a country's diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and foreign policy ambition.
- Cultural Influence: The ability to shape international public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people ties.
A country's overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight measures, encompassing 131 individual indicators. The results offer a nuanced understanding of how countries convert their resources into influence within the Asia-Pacific.
10 YEARS OF MAKE IN INDIA

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The “Make in India” initiative has completed 10 years. It was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on September 25, 2014.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The ‘Make in India’ campaign aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best in class manufacturing infrastructure.
- “Make in India” was designed to transform India into a global hub for design and manufacturing.
- Seen as an important ‘Vocal for Local’ initiative, its objective is twofold. Firstly, to boost India’s manufacturing capabilities and secondly to showcase its industrial potential on a global stage.
- The “Make in India 2.0” phase encompassing 27 sectors – both manufacturing and service.
4 pillars of “Make in India” initiative:
- New Processes: To enhance the business environment, promote entrepreneurship and startups – ‘ease of doing business’ became a crucial factor.
- New Infrastructure: Development of industrial corridors, smart cities, integrating state-of-the-art technology and high-speed communication to create world-class infrastructure, improving intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure etc.
- New Sectors: Opening of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in sectors like Defence Production, Insurance, Medical Devices, Construction, and Railway infrastructure.
- New Mindset: In order to support industrial growth and innovation – the government embraced a role as a facilitator rather than a regulator. The Government partners with industry in the economic development of the country.
Key Initiatives to enable Make in India initiative
Production linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: The primary goals of the PLI Schemes are to attract substantial investments, incorporate advanced technology, and ensure operational efficiency. These schemes cover 14 key sectors aimed at fostering investment in cutting-edge technology and promoting global competitiveness.
PM GatiShakti: It is a strategic initiative aimed at achieving Aatmanirbhar Bharat and a US $5 trillion economy by 2025 through the creation of multimodal and last-mile connectivity infrastructure. PM GatiShakti is a transformative approach for economic growth and sustainable development. The approach is driven by 7 engines, namely:
- Railways
- Roads
- Ports
- Waterways
- Airports
- Mass Transport
- Logistics Infrastructure
Semiconductor Ecosystem Development: It encompasses four key schemes:
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Semiconductor Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Display Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, Sensors Fabs, and Discrete Semiconductors, along with Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP) / OSAT Facilities in India
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
It aims to foster the development of a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
The Semicon India Programme aims to provide a significant impetus to semiconductor and display manufacturing by facilitating capital support and promoting technological collaborations.
National Logistics Policy: Introduced to complement the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan. It focusses on enhancing the soft infrastructure of India’s logistics sector.
The Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) was rolled out. The key areas which it addresses are logistics systems, standardization, human resource development, state engagement, and logistics parks.
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme: Aims to create “Smart Cities” and advanced industrial hubs.
Startup India: Several programs aimed at supporting entrepreneurs, building a robust startup ecosystem, and transforming India into a country of job creators instead of job seekers were rolled out.
Implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST): As India’s tax reforms, it is seen as crucial in the context of the Make in India initiative.
Unified Payments Interface: For India’s digital economy growth, it is seen as one of the key initiatives to enable ease of doing business.
Ease of Doing Business: The efforts aim to simplify regulations, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and create a more business-friendly environment, significantly boosting investor confidence and supporting the objectives of the Make in India initiative.
China test-fires an intercontinental ballistic missile into the Pacific Ocean

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
China stated that it test-launched an intercontinental ballistic missile, firing it into the Pacific Ocean in its first such exercise in decades.
- Launch Details:
- The missile carried a dummy warhead and fell into a designated area in the high seas.
- The specific flight path and landing location were not disclosed.
- Testing Objectives:
- The launch tested weapon performance and troop training levels, achieving its expected objectives.
- Historical Context:
- This is the first ICBM test over the Pacific Ocean in over 40 years.
- China's first ICBM, the DF-5, was test-fired in 1980.
- ICBM Specifications:
- The latest ICBM, likely the DF-41, has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilometers (7,400 to 9,300 miles), capable of reaching the US mainland.
- Strategic Messaging:
- Analysts interpret the test as a warning to the US, suggesting direct intervention in Taiwan could expose the American homeland.
- The test signals China's ability to engage multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Regional Tensions:
- Recent weeks have seen heightened tensions with Japan, the Philippines, and Taiwan due to military incursions and exercises.
- International Norms:
- There is a global expectation to notify nations of long-range missile launches to avoid miscalculations. China has limited agreements regarding this, primarily with Russia.
- Military Buildup:
- Under Xi Jinping, China has enhanced its nuclear capabilities and revamped the PLA’s Rocket Force.
- Recent satellite imagery indicates the construction of hundreds of ICBM silos in China’s deserts.
- Future Projections:
- As of 2023, China has over 500 operational nuclear warheads, projected to exceed 1,000 by 2030 according to the Pentagon.
- Implications of the Test:
- The ICBM test may be aimed at demonstrating military readiness despite recent corruption scandals within the Rocket Force.
About ICBMs:
- An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range ballistic missile system primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery. They are powerful and destructive weapons, capable of travelling vast distances at incredibly high speeds.
- Key features of ICBMs:
- Range: Range greater than 5,500 kilometres with maximum ranges varying from 7,000 to 16,000 kilometres.
- Speed: ICBMs can travel at speeds exceeding 20,000 kilometres per hour.
- Payload: Typically designed to carry nuclear warheads, though they could potentially be used to deliver other types of weapons, such as chemical or biological weapons.
- Deployment: ICBMs can be launched from silos underground, mobile launchers on land, or submarines at sea.
- Countries having operational ICBMs: Russia, United States, China, France, India, United Kingdom, Israel and North Korea.
INDIA'S BIOE3 POLICY AND SMART PROTEINS

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian government recently approved the Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment (Bioe3) Policy, which prioritizes the production of "smart proteins". This initiative aligns with broader national goals of achieving a sustainable, circular bioeconomy and a Net Zero carbon economy.
What Are Smart Proteins?
Smart proteins are alternative proteins derived from unconventional sources such as:
- Algae
- Fungi
- Insects
- Fermentation processes
- Lab-grown cells
This category also includes plant-based proteins, designed to replicate the taste and nutritional value of animal products without the need for livestock farming.
Environmental Benefits
The production of smart proteins offers significant environmental advantages:
- Water Use: 72-99% less water compared to conventional meat.
- Land Use: 47-99% less land required.
- Water Pollution: 51-91% reduction in pollution.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: 30-90% fewer emissions.
Health and Safety
With rising incomes, India's protein consumption has increased, from 9.7% of calories in 1991 to 11% in 2021. Smart proteins:
- Enhance food safety by reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases.
- Foster ethical consumption and align with traditional Indian dietary preferences.
Objectives of the BioE3 Policy
The Bioe3 Policy aims to:
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing.
- Promote sustainable growth and innovation in biotechnology.
- Support the transition towards a Net Zero carbon economy.
By emphasizing the development of smart proteins, the Bioe3 Policy represents a strategic move towards a more sustainable and resilient food system in India.
ACHIEVING GLOBAL NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT

- 26 Sep 2024
Overview
Global nuclear disarmament remains a top priority for the United Nations, initially emphasized in the General Assembly’s first resolution in 1946. Despite historical efforts, approximately 12,100 nuclear weapons still exist today, with ongoing modernization plans in many countries.
Key Historical Milestones
- 1945: Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 213,000 people.
- 1946: First UN resolution identifies nuclear disarmament as a key goal.
- 1959: General Assembly endorses the goal of general and complete disarmament.
- 1963: Opening of the Partial Test Ban Treaty.
- 1978: First Special Session of the General Assembly dedicated to disarmament.
- 1996: Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty opens for signature.
- 2017: Adoption of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Recent Developments
- 2019: U.S. withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty.
- 2023: Russia suspends participation in the New START Treaty, raising concerns over arms control.
The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons
- Established: December 2013, following a high-level meeting on nuclear disarmament.
- Observed: Annually on September 26.
- Purpose: Raise awareness about the dangers of nuclear weapons and promote their total elimination.
Goals of the International Day
- Enhance public education on the humanitarian risks associated with nuclear weapons.
- Mobilize international efforts towards a nuclear-weapon-free world.
Continuing Challenges
- The doctrine of nuclear deterrence remains central to the security policies of nuclear-armed states and their allies.
- No nuclear weapons have been destroyed under a treaty framework, and current disarmament negotiations are stagnant.
- Growing frustration among UN Member States over the slow progress in nuclear disarmament.
NAGAR VAN YOJANA (NVY)

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India achieved a 100-Day Target of 100 Nagar Vans under Nagar Van Yojana (NVY) with the objective to Enhance Urban Greenery.
Key Details:
- Launch: Initiated in 2020 to enhance urban greenery, improve quality of life, and foster social cohesion.
- Financial Support: Offers ?4 lakh per hectare for creation and maintenance of urban forests.
- Area Specification: Nagar Van areas range from 10 to 50 hectares.
- Coverage: Applicable to all cities with Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Achievements
- 100-Day Target: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change achieved a target of 100 Nagar Vans, surpassing it with the approval of 111 Nagar Vans in just 100 days.
- Geographic Spread: These 111 Nagar Vans are distributed across six states and one Union Territory.
Features of Nagar Vans
- Biodiversity Focus: Emphasis on planting fruit-bearing, medicinal, and native species to attract wildlife and maintain ecological balance.
- Community Involvement: Engages citizens, students, and stakeholders through tree planting, educational programs, and sustainable management.
- Design Elements: Each Nagar Van includes two-thirds tree cover and features components like Biodiversity Parks, Smriti Vans, Butterfly Conservatories, Herbal Gardens, and Matri Vans.
Future Goals
- Expansion Plans: Target to develop 1,000 Nagar Vans by 2027, supported by the National Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (National CAMPA).
- Environmental Impact: Aims to protect forest land from degradation and address urban environmental issues such as air pollution and habitat loss.
Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam Campaign
- Launch Date: Introduced on June 5, 2024, during World Environment Day.
- Purpose: Encourages tree planting as a tribute to mothers, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
- Tree Planting Goals: Aims to plant 80 crore trees by September 2024 and 140 crore by March 2025.
- Tracking Efforts: Participants can document their planting through the MeriLiFE portal, where over 75 crore saplings have been recorded.
Recent Initiatives
- Tree Plantation Drive: A recent drive on September 17, 2024, aimed at creating Matri Vans in newly approved Nagar Vans, highlighting community and governmental collaboration for sustainable urban development.
INDIA’s FIRST MISSION TO VENUS

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
India is set to launch its first mission to Venus in March 2028, following the recent approval from the Union Cabinet. This mission, led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), marks India’s second interplanetary endeavor after the successful Mars Orbiter Mission in 2013.
Importance of Studying Venus
- Earth's Twin: Venus is often referred to as Earth’s twin due to its similar mass, density, and size. Understanding Venus can provide insights into Earth’s own evolution.
- Extreme Conditions: The planet has a surface temperature around 462°C and an atmospheric pressure similar to that found deep under Earth’s oceans. Its atmosphere consists primarily of 96.5% carbon dioxide and features clouds of sulfuric acid.
- Historical Water Presence: Venus may have had water in the past, leading scientists to explore how it transitioned to its current hostile environment, likely due to a runaway greenhouse effect.
Mission Overview
- Launch Timeline: The mission will utilize a strategic launch window when Earth and Venus are closest, occurring every 19 months. It was initially planned for 2023 but is now set for 2028.
- Payload: The mission will carry around 100 kg of scientific instruments, including 17 Indian and 7 international experiments.
- Journey to Venus: After exiting Earth's orbit, the spacecraft will take about 140 days to reach Venus.
Aero-Braking Technique
- First-time Use: This mission will employ aero-braking, a technique to adjust the spacecraft’s orbit by skimming through Venus's atmosphere, creating drag that reduces altitude.
- Target Orbit: The satellite will initially be in a highly elliptical orbit of 500 km x 60,000 km and will be gradually lowered to an orbit of either 300 x 300 km or 200 x 600 km over about six months.
Scientific Payloads
- Synthetic Aperture Radar: For imaging the surface of Venus.
- Thermal Camera: To study temperature variations.
- Interplanetary Dust Analysis: Investigating dust particle flow.
- High-Energy Particle Studies: Examining particles entering the atmosphere and their ionization effects.
- Atmospheric Composition Study: Assessing the structure, variability, and thermal state of Venus’s atmosphere.
Which countries are trying to study Venus?
- There have been several missions to Venus in the past by the United States, the erstwhile USSR, Japan, and a collaborative mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) with Japan.
- The US has planned at least two more missions to Venus in the future — DaVinci in 2029 and Veritas in 2031 — and the ESA has planned the EnVision mission for 2030.
INDIA ATTENDS IPEF MINISTERIAL MEETING

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal joined a virtual meeting of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) alongside representatives from 13 other partner countries. This meeting marked the third gathering focused on the framework's key pillars: Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, and Fair Economy.
Key Agreements and Future Steps
- Entry into Force of Agreements:
- The IPEF partners celebrated the upcoming implementation of the Clean Economy Agreement and the Fair Economy Agreement on October 11 and October 12, 2024, respectively. These agreements aim to enhance economic cooperation and deliver tangible benefits to member nations.
- Supply Chain Resilience:
- The ministers discussed the progress in operationalizing the Supply Chain Agreement, emphasizing collaborative efforts to create more competitive and resilient supply chains. Key actions include:
- The formation of action plan teams for critical sectors like semiconductors, critical minerals, and chemicals, addressing vulnerabilities revealed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- India's election as Vice Chair of the Supply Chain Council, which aims to streamline communication and cooperation among member countries.
- The ministers discussed the progress in operationalizing the Supply Chain Agreement, emphasizing collaborative efforts to create more competitive and resilient supply chains. Key actions include:
- Clean Economy Initiatives:
- The Clean Economy Agreement focuses on energy security, climate resilience, and reducing fossil fuel dependence. Ministers acknowledged the advancement of eight Cooperative Work Programs (CWPs) addressing topics such as hydrogen and carbon markets.
- The first IPEF Investor Forum, held in Singapore, facilitated discussions on investment opportunities in climate-friendly technologies.
- Fair Economy Measures:
- The Fair Economy Agreement aims to bolster anti-corruption measures and improve tax administration efficiency. Upcoming workshops will address foreign bribery laws and public procurement oversight.
- India highlighted its own anti-corruption measures and commitment to transparency under Prime Minister Modi's leadership.
About IPEF
Launched on May 23, 2022, in Tokyo, IPEF includes 14 countries: Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, and the USA. The framework seeks to enhance economic engagement, stability, and prosperity across the Indo-Pacific region through its four key pillars: Trade, Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, and Fair Economy.
SPICED SCHEME

- 25 Sep 2024
In the News
The Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry has authorized the SPICED scheme (Sustainability in Spice Sector through Progressive, Innovative, and Collaborative Interventions for Export Development), which will run until 2025-26.
Overview
This initiative aims to expand the cultivation area and enhance the productivity of both small and large cardamom. It will also focus on improving the quality of spices for export through advancements in post-harvest processes and promoting value-added spice exports.
Key Objectives:
- Increase cardamom production and boost export potential.
- Improve post-harvest quality to meet export standards and ensure compliance with safety and quality regulations.
India holds the position of the largest producer, consumer, and exporter of spices globally.
Cardamom
Cardamom is sourced from the seeds of the Elettaria cardamomum plant (commonly known as green or true cardamom) and is a member of the ginger family. It is known for its unique, robust flavor that combines both spicy and sweet notes. There are two primary varieties: Small Cardamom and Large Cardamom.
Small Cardamom:
- Origin: Native to the evergreen forests of South India's Western Ghats.
- Major Producers: Primarily grown in Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Growing Conditions: Thrives in loamy soil with thick shade, requires temperatures between 10°C and 35°C, and needs 1500 to 4000 mm of annual rainfall.
Large Cardamom:
- Distribution: Mainly cultivated in the Sub-Himalayan regions of Northeast India, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Major Producers: Key production areas include Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and the Darjeeling district of West Bengal.
- Growing Conditions: Prefers high altitudes (600 to 2000 meters), with average rainfall of 3000-3500 mm, and temperatures ranging from 6°C to 30°C. Well-drained, loamy soils rich in organic matter are ideal.
About the Spices Board of India
Established in 1987 under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the Spices Board of India serves as the apex organization for the promotion and export of a diverse array of spices, including black pepper, both small and large cardamom, ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, cumin, and fenugreek. The Board was formed by merging the Cardamom Board (1968) and the Spices Export Promotion Council (1960). Its headquarters is located in Kochi, Kerala.
Ideas4LiFE Initiative

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ideas4LiFE portal was launched by Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, at IIT Delhi.
- Purpose: Designed to invite innovative ideas related to products and services that promote environmentally friendly lifestyles.
- Development Partner: Created in collaboration with UNICEF YuWaah.
Key Features of the Ideas4LiFE Portal
- Themes: Aligned with Mission LiFE, focusing on:
- Water Conservation
- Energy Efficiency
- Waste Reduction
- E-Waste Management
- Minimizing Single-Use Plastics
- Embracing Sustainable Food Practices
- Fostering Healthy Lifestyles
- Recognition: Winning ideas will be awarded attractive prizes for both individuals and institutions.
Engagement and Outreach
- Submissions: As of now, the portal has received approximately 3,300 registrations and over 1,000 ideas.
- Social Media Impact: The initiative has garnered 46.5 million impressions and a reach of 13.5 million through social media under the hashtag #Ideas4LiFE.
Collaboration with Educational Institutions
- Partnerships: Collaborations with the University Grants Commission (UGC), All-India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and various educational institutions to promote the Ideathon among students and researchers.
- Objective: Encourage the academic community to contribute innovative, citizen-focused ideas that support sustainable living.
Future Plans
- Evaluation Process: Submitted ideas will be evaluated by a jury, leading to the announcement of shortlisted and winning ideas.
- Implementation: Winning ideas will be included in a national repository, allowing stakeholders, including government bodies and private entities, to nurture and scale these innovations.
Mission LiFE Context
- Definition: Mission LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment) is a campaign initiated at UN Climate Change Conference COP26 in 2021.
- Goals:
- Mobilize at least one billion people for environmental protection.
- Make 80% of villages and urban local bodies environment-friendly by 2028.
- Promote small, everyday actions to combat climate change.
- Philosophy: Emphasizes the P3 model—Pro Planet People—uniting individuals in the commitment to environmental stewardship.
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION 2.0

- 24 Sep 2024
Mission Overview:
- Launched on October 1, 2021, as the second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims for "Garbage-Free Status" in all urban areas by 2026.
- Focuses on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific waste management.
Legacy Waste Issues:
- Legacy waste consists of improperly collected and stored solid waste, often found in landfills and abandoned sites.
- Approximately 15,000 acres of prime land are buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste in India.
- The mission seeks to convert legacy dumpsites into green zones and establish scientific landfills to manage untreated waste.
Current Progress:
- Of 2,424 identified dumpsites (each with over 1,000 tonnes of waste), only 470 have been fully remediated (16% reclaimed).
- 1,224 sites are under ongoing remediation, while 730 remain untouched.
- Out of 28,460 acres of affected land, 4,552 acres have been reclaimed, with 23,908 acres still to be addressed.
State Performance:
- Tamil Nadu: 837 acres reclaimed (42% of its total dumpsite area).
- Gujarat: Leads in percentage, reclaiming 75% of its landfill area (698 out of 938 acres).
Financial Aspects:
- Central assistance of ?3,226 crore has been approved for remediation efforts.
- States and Union Territories must provide a matching share to access these funds.
Challenges:
- Legacy waste management involves complexities such as radiological characterization, leachate management, and fire control.
- Current municipal solid waste generation in India is around 150,000 tonnes per day.
Historical Context:
- The original Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 1.0) launched on October 2, 2014, focused on making urban areas Open Defecation Free (ODF).
GREENLAND LANDSLIDE AND GLOBAL SEISMIC WAVES

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Massive Greenland landslide sent seismic waves around earth for 9 days. One year ago, roughly 25 million cubic metres of ice and rock splashed into the Dickson Fjord in Greenland and displaced the water enough to give rise to a 200-metre high mega-tsunami; in this way, a melting glacier led to a planet-wide tremor, and researchers warn that it may not be the last
Seismic Observations
- Detection: Unusual seismic signals recorded by stations worldwide, characterized by a single frequency, unlike typical earthquake vibrations.
- Classification: Initially termed a "USO" (unidentified seismic object) due to its atypical properties.
- Duration: Waves persisted for nine days, unlike typical aftershock patterns.
Investigation Efforts
- Collaboration: Involved over 68 researchers from 40 universities across 15 countries.
- Data Sources: Combined seismic data, satellite imagery, water level monitors, and a classified bathymetric map from the Danish Navy.
- Conclusion: The seismic waves resulted from a massive landslide caused by the collapse of Hvide Støvhorn peak, which triggered a series of events leading to the tsunami.
Mega-Tsunami and Seiche
- Tsunami Details:
- Created by the avalanche crashing into the fjord, displacing water significantly.
- Resulted in waves that reflected off fjord walls, reaching heights of nearly 110 meters due to the fjord's unique shape.
- Seiche Phenomenon:
- Oscillations in the fjord persisted for over nine days, reflecting the energy from the landslide.
- Maximum amplitude of the seiche recorded at 7.4 meters, with a frequency of 11.45 MHz.
Climate Context
- Global Warming Impact: Thinning glaciers contributed to instability in the region, making such landslides more likely.
- Future Predictions: Researchers warn of increased frequency and scale of similar events as climate change continues to affect Arctic and subarctic regions.
Key Takeaways
- The Greenland landslide serves as a reminder of the unpredictable consequences of climate change, including massive geological events.
- The incident highlights the interconnectedness of natural systems and the potential for localized events to have global repercussions.
ROBOTIC MULES AND HIGH-ALTITUDE INNOVATIONS IN THE ARMY

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
The Army has inducted 100 robotic mules, known as Multi-Utility Legged Equipment (MULE), under the fourth tranche of emergency procurements (EP).
- Purpose: These robotic mules are designed for surveillance and transporting light loads across challenging terrains, especially in high-altitude areas.
- Specifications:
- Endurance: Capable of operating for up to three years.
- Temperature Range: Functions effectively in extreme temperatures from -40°C to +55°C.
- Payload Capacity: Can carry up to 15 kg.
- Mobility: Can climb stairs, steep hills, and traverse obstacles; waterproof and able to cross rivers.
- Sensing Abilities: Equipped with electro-optics and infrared capabilities for object recognition.
- Control Mechanisms: Operable via an easy-to-use remote control, Wi-Fi, or Long-Term Evolution (LTE) connections.
- Mission Programming: Can be programmed for specific missions using waypoints or pre-recorded tasks.
- Combat Integration: Capable of integration with small arms for military applications.
- Logistics Drones: Logistics drones are currently undergoing trials to enhance support and movement in forward areas, particularly in high-altitude conditions.
- High-Altitude Habitat Evaluation: A new tent designed for extreme cold environments (operating at temperatures down to -40°C) is under evaluation. This tent, called Peak Pods, is intended for use in sub-zero conditions.
- Evaluation Locations: The tent has been tested in three high-altitude sites:
- Leh (11,500 feet)
- Daulat Beg Oldie (16,700 feet)
- Durbuk (12,500 feet)
- Significance: These advancements reflect the Army's focus on technological innovations to enhance operational capabilities in high-altitude areas, especially following the 2020 stand-off with China in Eastern Ladakh.
- Funding and Timelines: The EP process allows contracts up to ?300 crore, with a requirement for delivery within one year.
GINGEE FORT PROPOSED FOR UNESCO WORLD HERITAGE SITE

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently nominated for UNESCO’s World Heritage Site status, Gingee Fort is part of the Maratha Military Landscapes of India, which encompasses 12 historical sites, primarily located in Maharashtra, with Gingee being the sole representative from Tamil Nadu. The nomination highlights the fort’s historical importance, unique military architecture, and its integral role in Maratha military history.
Significance of Gingee Fort
Gingee Fort, often referred to as the "Troy of the East," stands as a crucial historical monument in Tamil Nadu. Perched atop three prominent hillocks—Rajagiri, Krishnagiri, and Chandragiri—it has served as a significant stronghold for numerous empires throughout Indian history, including the Vijayanagar Nayaks, Marathas, Mughals, French, and British. This fortification exemplifies India’s rich and diverse historical legacy.
Unique Features
The fort complex spans 11 acres and boasts an array of significant structures, including:
- Kalyana Mahal: An eight-storey royal residence.
- Durbar Hall: A ceremonial hall for gatherings.
- Stepped Well and Cannon: Examples of advanced engineering and military use.
- Clock Tower and Armory: Reflecting its historical military significance.
- Elephant Tank and Stables: Indicating its use for royal elephants.
- Temples and Mosques: Including the Venkataramana Temple with intricate carvings and the Sadathtulla Mosque.
Additionally, the fort features advanced water supply systems from various historical periods, ensuring adequate resources for its inhabitants.
Historical Timeline
The origins of Gingee Fort trace back to 1200 CE when built by Ananta Kon of the Konar Dynasty. The fort underwent significant renovations under the Vijayanagar Empire. Key historical events include:
- 1677: Captured by Chhatrapati Shivaji, it remained under Maratha control until 1698.
- 1698: Came under Mughal possession, later ruled by the Nawabs of Arcot and briefly by the French.
- 1750-1770: Occupied by the French before falling to the British.
This timeline reflects the fort's strategic and cultural significance across different dynasties.
Nomination Process for UNESCO
The process for securing UNESCO World Heritage Site status involves rigorous evaluation. Experts from UNESCO and the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) assess the site's historical significance, conservation state, and management strategies. A visit to Gingee Fort is scheduled as part of this evaluation, with a recommendation expected for the 2025 World Heritage designation.
Preparation of the Nomination Dossier
The Development and Research Organisation for Nature, Arts and Heritage (DRONAH) prepared the nomination dossier, aligning with UNESCO’s operational guidelines. This comprehensive document details the fort's historical context, conservation status, and management strategies, aimed at demonstrating its outstanding value for humanity.
SUPREME COURT RULING ON CHILD SEXUAL EXPLOITATIVE MATERIAL: KEY HIGHLIGHTS

- 24 Sep 2024
Overview of the Ruling
- Date: Recent ruling by the Supreme Court of India.
- Context: Determined that viewing, downloading, storing, or distributing material involving child sexual exploitation constitutes a criminal offense under the POCSO Act and the Information Technology Act.
- Appeal Background: Decision overturned a Madras High Court ruling that deemed private viewing of such material non-criminal.
Terminology and Legislative Recommendations
- Terminology Change: Supreme Court advocates replacing “child pornography” with “Child Sexual Exploitative and Abuse Material” (CSEAM) to avoid trivialization of the crime.
- Amendment Call: Court urged Parliament to amend the POCSO Act and advised promulgating an ordinance for immediate effect.
Key Highlights of the Ruling
- Redefinition of Terminology: Emphasizes that "pornography" may imply consensual acts, misrepresenting the nature of child exploitation.
- Expansion of Section 15 of the POCSO Act:
- Possession Without Reporting: Individuals must delete or report any stored CSEAM; failure results in penalties.
- Intent to Transmit: Possessing CSEAM with intent to share, barring reporting, is punishable.
- Commercial Possession: Storing CSEAM for commercial purposes faces the strictest penalties.
- Concept of Inchoate Offenses: Classifies offenses related to CSEAM as preparatory actions towards further crimes.
- Redefinition of Possession:
- Includes "constructive possession," where individuals can be liable without direct physical possession.
- Watching CSEAM online without downloading can still be deemed possession.
- Educational Reforms:
- Court urged for comprehensive sex education to counter stigma and misconceptions.
- Curriculum should cover consent, healthy relationships, and respect for diversity.
- Awareness of the POCSO Act: Central and state governments are mandated to promote awareness, supported by the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR).
- Formation of Expert Committee: To develop programs for health and sex education while increasing POCSO awareness among children.
- Victim Support and Awareness: Emphasized the need for psychological support, counseling, and educational assistance for victims.
Status of Crimes Against Children
- Increasing Incidents: India leads in online child sexual abuse imagery, with 25,000 uploads reported from April to August 2024.
- Geographical Distribution: Major uploads identified in Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Rising Cases: From 331 cases in 2017 to 781 in 2018, with 1,171 cases of inappropriate content dissemination reported in 2022.
Overview of the POCSO Act
- Purpose: Addresses sexual exploitation and abuse of children, defining a child as anyone under 18.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral: Recognizes that both genders can be victims.
- Victim Confidentiality: Mandates protection of victims’ identities.
- Mandatory Reporting: Requires reporting of suspected abuse.
Gaps in Implementation
- Support Persons: Lack of designated support persons for victims; 96% of cases showed inadequate support during legal processes.
- POCSO Courts: Only 408 designated courts across 28 states as of 2022, leading to access issues.
- Special Prosecutors: Shortage of trained public prosecutors for POCSO cases.
Conclusion
- Call for Collaboration: Emphasizes the need for a coordinated approach involving educators, healthcare providers, and law enforcement to combat child sexual exploitation.
- Societal Responsibility: A shift in societal attitudes is essential for preventing victimization and ensuring recovery for victims.
KEY FINDINGS ON ATROCITIES AGAINST SCS AND STS (2022)
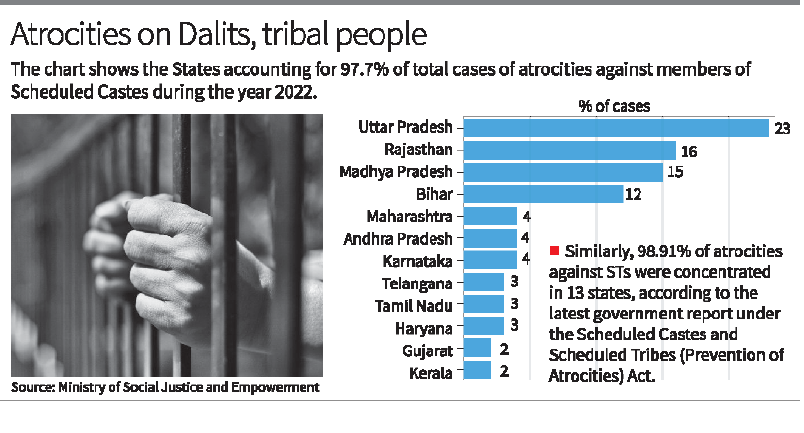
- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
According to the latest report under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act by the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry, the majority of atrocities against Scheduled Tribes (STs) were also concentrated in 13 states, which reported 98.91% of all cases in 2022.
- Case Statistics:
- Total cases of atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SCs): 51,656
- Total cases against Scheduled Tribes (STs): 9,735
- 97.7% of SC cases and 98.91% of ST cases reported from 13 states.
- States with Highest Incidents:
- SCs:
- Uttar Pradesh: 12,287 cases (23.78%)
- Rajasthan: 8,651 cases (16.75%)
- Madhya Pradesh: 7,732 cases (14.97%)
- Other significant states: Bihar (6,799), Odisha (3,576), Maharashtra (2,706)
- STs:
- Madhya Pradesh: 2,979 cases (30.61%)
- Rajasthan: 2,498 cases (25.66%)
- Odisha: 773 cases (7.94%)
- Other significant states: Maharashtra (691), Andhra Pradesh (499)
- SCs:
- Charge Sheets and Investigations:
- SC-related cases: 60.38% resulted in charge sheets; 14.78% ended with final reports (false claims/lack of evidence).
- ST-related cases: 63.32% led to charge sheets; 14.71% concluded similarly.
- Pending investigations by end of 2022: 17,166 SC cases, 2,702 ST cases.
- Conviction Rates:
- Decline from 39.2% in 2020 to 32.4% in 2022.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies:
- Only 194 out of 498 districts in 14 states have established special courts for these cases.
- Lack of identified atrocity-prone areas in states like Uttar Pradesh despite high case numbers.
- Protection Cells:
- SC/ST protection cells established in multiple states and union territories.
Reasons for Atrocities Against SCs and STs
- Caste Prejudice: Deep-rooted hierarchies and social exclusion lead to violence.
- Land Disputes: Conflicts over land access among historically deprived SC/ST communities.
- Economic Marginalization: Limited access to education and resources heightens vulnerability.
- Power Imbalance: Dominant castes wield political and social influence, perpetuating discrimination.
- Inadequate Law Enforcement: Weak implementation of protective laws and bureaucratic bias hinder justice.
- Political Exploitation: Caste tensions are sometimes used for electoral gains.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989
- Objective: Protect SCs and STs from caste-based violence and discrimination.
- Key Provisions:
- Defines various offences against SC/ST members, prescribing stricter punishments.
- Excludes anticipatory bail provisions for accused under the Act.
- Mandates establishment of special courts for speedy trials.
- Investigations must be conducted by senior police officers and completed within stipulated time frames.
- Recent Amendments:
- 2015: Enhanced protections for SC/ST women.
- 2019: Restored original provisions for arrest procedures following a Supreme Court ruling.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Strengthen Legal Framework: Establish more special courts and train personnel in sensitive handling of SC/ST cases.
- Improve Reporting Mechanisms: Enhance systems for victims to report atrocities without fear.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate communities on SC/ST rights and legal protections.
- Targeted Interventions: Identify and address issues in atrocity-prone districts.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement frameworks for accountability and continuous improvement in addressing these issues.
- Collaborate with NGOs: Work with civil society to support victims and advocate for their rights.
100 YEARS OF ICAR-NISA

- 23 Sep 2024
Overview:
The ICAR-National Institute of Secondary Agriculture (NISA), originally established in 1924 as the Indian Institute of Natural Resins and Gums in Ranchi, Jharkhand, marks its centenary this year. Renamed in 2022, it operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, focusing on enhancing the value of agricultural products.
Understanding Secondary Agriculture:
Secondary agriculture encompasses the transformation of primary agricultural products into higher-value commodities and includes activities such as:
- Beekeeping
- Poultry farming
- Agricultural tourism
This sector plays a crucial role in converting agricultural produce, residues, and by-products into valuable goods for various uses, including pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial applications. Examples of secondary agriculture practices include:
- Extracting vitamins from grains
- Producing oil from rice bran
- Making jaggery from sugarcane
- Cottage industries for jams and pickles
Growth Potential: The sector is poised for growth due to:
- Increasing consumer demand for value-added products like ready-to-eat meals.
- The need for innovative uses of renewable agro-bio resources.
- The significant availability of agricultural byproducts.
Significance of Secondary Agriculture:
- Environmental Sustainability: Proper utilization of crop residues can reduce waste and pollution.
- Enhanced Farmer Income: Activities like beekeeping and lac culture provide additional revenue streams for farmers.
- Value Addition: Processing agricultural products increases their shelf life and overall productivity.
- Promotion of Cottage Industries: Supports rural economies and fosters technology adoption.
Challenges Ahead: Despite its potential, secondary agriculture faces several hurdles:
- The industry for high-value products from agricultural byproducts, such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, is still emerging.
- Small landholdings complicate the collection of crop residues.
- Limited research on suitable technologies hampers development.
- There is a lack of awareness among farmers regarding the processing of agricultural waste.
Conclusion
As ICAR-NISA celebrates its 100th anniversary, it remains crucial in shaping the future of secondary agriculture in India, addressing both challenges and opportunities to enhance sustainability and farmer livelihoods.
INDO-PACIFIC ECONOMIC FRAMEWORK (IPEF)

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
India signed agreements within the US-led 14-member IPEF focused on a clean and fair economy.
- Objectives:
- Facilitate development, access, and deployment of clean energy and climate-friendly technologies.
- Strengthen anti-corruption measures and promote tax transparency among member countries.
- Clean Economy Agreement:
- Aims to accelerate energy security and mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Focuses on innovative methods to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote technical cooperation.
- Fair Economy Agreement:
- Seeks to create a transparent and predictable business environment to enhance trade and investment.
- Emphasizes information sharing, asset recovery facilitation, and strengthening cross-border investigations.
- Funding Mechanisms:
- IPEF offers platforms for technical assistance and concessional funding.
- IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund: Initial grant of $33 million aimed to catalyze $3.3 billion in private investments.
- PGI Investment Accelerator: Received $300 million from the US International Development Finance Corporation.
- Concerns Raised:
- Experts highlighted concerns over the secrecy of IPEF negotiations with limited public input.
- Expressed hope that India has not agreed to a non-derogation clause that could limit domestic regulatory flexibility for national projects.
- Potential Risks:
- Most standards discussed in IPEF are aligned with those in the US and OECD countries.
- India risks compliance pressures in future trade deals if it adopts these standards without adequate preparation.
- Strategic Importance of IPEF:
- Involves 14 member countries, focusing on economic cooperation through four key pillars: trade, supply chain resilience, clean economy, and fair economy.
- Represents 40% of the global economy and 28% of world trade, highlighting India's commitment to regional partnerships alongside the US, Japan, Australia, and other Indo-Pacific nations.
COP 29 AT BAKU

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
Azerbaijan is making a significant move in the global climate finance landscape by proposing the Climate Finance Action Fund (CFAF) at the upcoming COP29 conference. This fund aims to gather voluntary contributions from fossil-fuel-producing nations and companies, with Azerbaijan itself making the initial investment. The fund’s goal is to support climate action in developing countries, which often struggle to finance their environmental initiatives.
Key Aspects of the CFAF:
- Voluntary Contributions: The fund seeks donations from fossil fuel entities, allowing them to contribute based on a fixed amount or production volumes.
- Bipartite Allocation: Proposed funds will be split equally—half for climate projects in developing nations and half for supporting those countries in executing their national climate action plans.
- Operational Threshold: The CFAF will only commence operations once it secures a minimum of $1 billion and commitments from at least ten countries to participate.
Context of COP29:
COP29, hosted in Baku from November 11 to 22, centers on finalizing a climate finance agreement, particularly the obligations of developed nations post-2025. This follows the ongoing struggle to meet the $100 billion annual financing target established in the Paris Agreement.
Additional Proposals:
Azerbaijan has also introduced several other initiatives as part of its agenda, including:
- Expanding Global Energy Storage: Aiming to increase capacity sixfold by 2030.
- Green Hydrogen Market: Fostering a global marketplace for green hydrogen.
- Minimizing Emissions from Digital Growth: Ensuring that the environmental impact of increasing digitalization and data centers is mitigated.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite the ambitious plans, there are significant hurdles to overcome, including establishing a robust framework for the CFAF, garnering international support, and ensuring compliance from contributors. As the conference approaches, ongoing negotiations will be crucial to achieving substantial agreements on climate finance that can lead to meaningful progress in combating climate change.
QUAD CANCER MOONSHOT

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
The Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative is a significant collaborative effort among the Quad countries—India, the United States, Australia, and Japan—aimed at combating cancer through innovative strategies. The initiative focuses on key areas such as preventing and detecting cancer, improving treatment, and alleviating the disease's impact on patients and families.
Key Highlights of the Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative:
- Focus Areas:
- Cervical Cancer Screening: Enhancing access to screening programs.
- HPV Vaccination: Increasing vaccination rates against HPV, which is the leading cause of cervical cancer.
- Patient Treatment: Improving treatment protocols and accessibility for cancer patients.
- India’s Contributions:
- Financial Commitment: India has pledged $10 million to support the WHO’s Global Initiative on Digital Health, aimed at enhancing digital health technologies for cancer care in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Material Support: India will provide cervical cancer screening kits, detection tools, and HPV vaccines valued at $7.5 million to bolster healthcare initiatives in the region.
- AI-based Protocols: Development of AI-driven treatment protocols to improve care delivery for cancer patients.
- Capacity Building: India aims to enhance radiotherapy services and overall cancer prevention strategies in the Indo-Pacific.
This initiative represents a strong commitment to fostering international collaboration in healthcare, particularly in the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. By empowering communities with accessible tools and resources, the Quad countries aim to significantly reduce the burden of cancer in the region.
AMUR FALCONS

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
An order issued by the District Magistrate directed the owners of air guns to deposit their hunting weapons at the offices of respective village authorities.
Amur Falcons: An Overview
Scientific Classification:
- Common Name: Amur Falcon
- Scientific Name: Falco amurensis
- Family: Falconidae
Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Small raptors, approximately 28-30 cm in length.
- Distinctive Features: Dark plumage with white wing linings; reddish-orange eyes and feet.
Migration Patterns:
- Breeding Grounds: Southeastern Russia and northern China.
- Migratory Route: They leave their breeding areas in autumn, traveling south to round the Himalayas, stopping in Nagaland, and then heading towards the Western Ghats before crossing the Indian Ocean to reach South Africa.
- Distance: These falcons undertake an incredible journey of around 22,000 kilometers annually, making them one of the most remarkable long-distance migrants among raptors.
Diet:
- Primarily insectivorous, they also consume small vertebrates when available.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- Legal Protection:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix II
Recent Conservation Efforts:
- Ban in Manipur: The Tamenglong district administration has imposed a ban on hunting, catching, killing, and selling Amur falcons in preparation for their migratory arrival.
- Tagging Program: In 2016, radio transmitters were used to monitor their migration routes.
- Awareness Initiatives: An annual ‘Amur Falcon Festival’ in Tamenglong district promotes awareness and celebrates these migratory birds.
Threats:
- Amur falcons face various threats including habitat loss, hunting, and illegal trapping.
Cultural Significance:
- Locally known as ‘Kahuaipuina’ in Manipur and ‘Molulem’ in Nagaland, these birds hold ecological and cultural significance, particularly in regions that serve as critical stopover points during migration.
Summary
The Amur falcon is a small but remarkable migratory raptor known for its long-distance travels from its breeding grounds in Asia to Africa. Conservation efforts in India, particularly in the Tamenglong district of Manipur, aim to protect these birds from hunting and habitat loss, ensuring their continued survival and highlighting their importance in the ecosystem.
WORLD RHINO DAY

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Celebrated annually on September 22, World Rhino Day raises awareness about the critical conservation status of rhinoceroses and the myriad threats they face, such as poaching and habitat loss. This day, first initiated by the World Wildlife Fund South Africa in 2010, aims to highlight the need for the conservation of all five species of rhinos: the Javan, Sumatran, Black, Greater One-Horned, and White rhinos.
The Current Status of Rhino Species
- Among the five rhino species, three are classified as
- Critically Endangered: the Black, Javan, and Sumatran rhinos.
- The White Rhino is considered Near Threatened, with the Northern White Rhino itself critically endangered.
- The Greater One-Horned Rhino, primarily found in India, is listed as Vulnerable.
Notably, Kaziranga National Park in Assam is home to the largest population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos, boasting approximately 3,700 individuals.
Conservation Efforts
In India, initiatives like Project Rhino play a crucial role in safeguarding rhino populations. This project focuses on preventing poaching, enhancing habitat management, and increasing public awareness. It collaborates with various conservation groups and government agencies to strengthen law enforcement against poaching and to relocate rhinos to safer areas.
Another significant program is the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020), aimed at boosting the population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos in Assam, particularly in regions where they had previously become extinct.
Surprising Facts About Rhinos
- Despite their thick skin, rhinos can get sunburned.
- Rhinos are related to zebras, horses, and tapirs.
- All five species are considered endangered.
- A group of rhinos is called a "crash."
- Rhinos' horns are made of keratin, the same protein found in human hair and nails.
- The term "rhinoceros" comes from two Greek words meaning "nose" and "horn."
- Rhinos and elephants are not natural enemies.
- One of the most famous depictions of a rhino is Albrecht Dürer's woodcut from 1515.
- The gestation period for rhinos can last up to 16 months.
- Rhinos have historically been used in traditional Asian medicine.
QUAD GROUPING

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in the United States, where he will participate in the fourth Quad Leaders Summit in Wilmington, Delaware.
What is the Quad Grouping?
The Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is an informal strategic alliance comprising India, the United States, Japan, and Australia. Originally formed in response to the Indian Ocean tsunami in 2004, the Quad aims to foster collaboration in various areas, but its primary focus has become countering the influence of China in the Indo-Pacific region.
Historical Background
- 2004: The Quad began as a response to the Indian Ocean tsunami, facilitating disaster relief.
- 2007: Japanese PM Shinzo Abe formalized the alliance.
- 2017: Amid rising Chinese assertiveness, the Quad was revitalized, expanding its objectives beyond maritime security.
Structure and Characteristics
- The Quad is not a formal organization; it lacks a secretariat or permanent decision-making body like the EU or UN.
- It focuses on strengthening bilateral and multilateral ties among member nations.
- Unlike NATO, the Quad does not include collective defense provisions but conducts joint military exercises to demonstrate unity.
Key Developments
- In 2020, the Malabar naval exercises expanded to include Australia, marking the first joint military exercises of the Quad since its resurgence.
- The first in-person summit took place in Washington, D.C. in 2021.
Objectives of the Quad
The Quad has outlined several primary objectives:
- Maritime Security: Ensuring safe and open sea routes in the Indo-Pacific.
- Climate Change: Addressing environmental challenges collaboratively.
- Investment Ecosystem: Creating opportunities for economic investment in the region.
- Technological Innovation: Promoting advancements and cooperation in technology.
- Public Health: Collaborating on initiatives like vaccine diplomacy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Expansion and Future Directions
The Quad members have discussed expanding the partnership to include countries like South Korea, New Zealand, and Vietnam. In a joint statement, they reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, resilient, and inclusive Indo-Pacific governed by international law.
Challenges and Opposition
China views the Quad as an effort to encircle and contain its influence. Beijing has criticized the grouping, labeling it as a strategy that incites discord among Asian nations.
45TH CHESS OLYMPIAD

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, both the Indian men's and women's chess teams achieved remarkable success by winning gold medals at the Chess Olympiad in Budapest.
- In the final round of the 45th Chess Olympiad, the Indian men's team triumphed over Slovenia with a score of 3.5-0.5.
- At the same time, the Indian women's team showcased their skills by defeating Azerbaijan with the same score of 3.5-0.5.
- With this victory, India joins an elite group, as only China and the former Soviet Union had previously managed to win both men's and women's gold medals in the same Chess Olympiad edition.
- The Indian men's team had previously claimed bronze medals in 2014 and 2022.
- Meanwhile, the Indian women's team secured a bronze medal in the 2022 tournament held in Chennai.
About the Chess Olympiad:
- This prestigious event occurs every two years and features national teams from around the globe. It is organized by FIDE, which also selects the host nation.
- The inaugural Olympiad, which was unofficial, took place in 1924.
100 Years of the Discovery of the Indus Civilization
- 22 Sep 2024
Introduction
The centenary of the announcement of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) by Sir John Marshall on September 20, 1924, marks a significant milestone in archaeological history. This civilization, known for its advanced urban planning, encompasses over 2,000 sites across India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
Historical Context
Discovery of the Indus Civilization
- John Marshall's Role: As the Director-General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), Marshall played a pivotal role in the excavations of Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
- Initial Findings: The civilization was revealed through meticulous work over two decades, beginning with Marshall's initial interest in the antiquities of India.
The Process of Discovery
The Concept of 'The Slow Hunch'
- Definition: Inspired by Steven Johnson's idea of 'the slow hunch,' this concept highlights how insights develop over time, similar to Joseph Priestley's early experiments with oxygen.
- Application to Marshall: Marshall's initial curiosity about the antiquity of India was nurtured through years of observations and explorations, culminating in the excavation of Harappa in 1921.
Key Individuals Involved
- Daya Ram Sahni: Conducted the first excavations at Harappa, uncovering evidence of an ancient culture.
- Rakhaldas Banerji: Excavated Mohenjodaro in 1922, leading to significant discoveries that indicated a widespread civilization.
Institutional Challenges
Limitations within ASI
- Lack of Collaboration: The ASI lacked a platform for archaeologists to share insights, impeding a collaborative approach to discoveries.
- Marshall's Focus: His dedication to ongoing projects, particularly at Taxila, resulted in delays in recognizing the significance of findings at Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
Announcing the Discovery
Marshall's Publication
- Impactful Presentation: In September 1924, Marshall's article vividly described the architectural and cultural features of the Indus Civilization, captivating readers.
- Scholarly Reception: The discovery sparked immediate scholarly interest, leading to further inquiries into the civilization's connections with ancient Mesopotamia.
Characteristics of the Harappan Civilization
Overview
- Timeframe: Flourished around 2500 BCE, classified as a Bronze-age civilization.
- Major Sites: Notable locations include Harappa, Mohenjodaro, and Lothal.
Key Features
- Urban Planning: Cities featured grid layouts, advanced drainage systems, and distinct public and private spaces.
- Agriculture and Economy: The economy thrived on agriculture, trade, and crafts, with evidence of cotton production and extensive trade networks.
Religious Practices
- Deities and Symbols: Terracotta figurines and seals indicate worship of fertility deities and animal figures, suggesting a rich spiritual life.
Reasons for Decline
Theories of Collapse
- Environmental Changes: Shifts in rainfall and tectonic activity may have disrupted agriculture and led to resource scarcity.
- Invasion Theories: While some suggest Indo-European invasions, evidence of cultural continuity challenges this narrative.
Recent Initiatives
Preservation and Promotion
- National Maritime Heritage Complex: Development at Lothal aims to highlight maritime history and attract tourism.
- UNESCO Recognition: Dholavira was added to the World Heritage list in 2021, showcasing the importance of IVC sites.
JORDAN
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
Jordan has made history by becoming the first country in the world to be officially verified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as having eliminated leprosy. This achievement marks a significant advancement in global public health efforts.
Key Highlights:
- WHO Recognition: WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus praised Jordan for this milestone, emphasizing the importance of stopping transmission and alleviating the suffering and stigma associated with leprosy.
- Historic Achievement: This success is not just about disease elimination but also about combating stigma and socio-economic harm.
- No Local Cases: Jordan has not reported any locally transmitted cases of leprosy for over two decades, demonstrating its effective public health strategies and strong political commitment.
- Independent Verification: WHO commissioned an independent team to conduct a thorough assessment, leading to the official recognition of leprosy elimination.
- Ongoing Vigilance: While celebrating this success, both the WHO and the Jordanian Ministry of Health emphasize the need for robust surveillance systems to detect and manage any future cases, including those from abroad.
Additional Context:
Leprosy, or Hansen's disease, is a chronic infectious condition caused by Mycobacterium leprae, primarily affecting the skin and nerves. Although it remains a neglected tropical disease, with over 200,000 new cases reported annually across more than 120 countries, Jordan's success showcases the potential for eradication through dedicated efforts.
This milestone serves as a beacon of hope, illustrating that with strong commitment, collaboration, and strategic planning, even longstanding public health challenges can be addressed effectively.
EXERCISE AIKYA

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), in partnership with the Indian Army's Southern Command and the Tamil Nadu State Disaster Management Authority (TNSDMA), recently conducted "EXERCISE AIKYA" in Chennai. This two-day Integrated Symposium and Table Top Exercise (TTEx) aimed to bolster disaster preparedness and response among key stakeholders across Peninsular India.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: "Aikya," meaning "Oneness" in Tamil, sought to unify India’s disaster management community by enhancing collaboration and preparedness.
- Participants: The exercise involved representatives from:
- Six southern states/UTs: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Puducherry.
- Central ministries related to disaster management.
- State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs).
- Armed forces, including the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Response agencies such as the NDRF, Indian Coast Guard, CRPF, CISF, and Railways.
- Early warning agencies including the IMD, NRSC, INCOIS, CWC, and FSI.
- Research institutions like NIDM, NIOT, IIT Madras, and DAE, with Prof. CVR Murty of IIT Madras serving as the Exercise Mentor.
- Focus Areas: The exercise simulated various emergency situations, covering:
- Tsunamis, landslides, floods, cyclones, industrial incidents, and forest fires.
- Recent disaster events in Tamil Nadu, Wayanad, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Discussions: Participants engaged in discussions about:
- Leveraging technology and AI for disaster management.
- Economic impacts of disasters.
- Vulnerabilities specific to the Peninsular region.
- Strategies for improving response times.
Future Plans
"EXERCISE AIKYA" marks a crucial step towards strengthening India’s disaster management framework. The NDMA and the Southern Command plan to conduct similar exercises with other military commands and institutions, including the Army War College and Naval War College, to further enhance national disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
EUROPA CLIPPER MISSION

- 21 Sep 2024
In news:
NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which aims to investigate Jupiter's icy moon, Europa.
Key Details:
- Objective: This mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a thorough study of Europa, focusing on its potential habitability.
- Significance: Europa Clipper will be NASA's first mission specifically designed to explore an ocean world beyond Earth. Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy surface, which raises the possibility of supporting life.
- Spacecraft Specifications:
- The spacecraft measures 100 feet (30.5 meters) from end to end and 58 feet (17.6 meters) across, making it the largest NASA spacecraft ever built for a planetary mission.
- Mission Plan:
- Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct 49 close flybys of Europa to gather critical data regarding its environment and potential habitability.
- Instrumentation:
- Equipped with nine scientific instruments and a gravity experiment that leverages its telecommunications system, the spacecraft will maximize data collection by operating all instruments simultaneously during each flyby. This approach will allow scientists to compile comprehensive data layers, creating an in-depth understanding of Europa.
- Power Source:
- The spacecraft is outfitted with large solar arrays to harness sunlight for its energy needs while operating in the challenging environment of the Jupiter system.
Solar Array
A solar array is a collection of solar panels interconnected to generate electrical power. When combined with other components like an inverter and battery, it forms a complete solar energy system.
GLOBAL CYBERSECURITY INDEX 2024

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), with an impressive score of 98.49 out of 100.
Role-Modeling Country: This accomplishment places India among ‘role-modeling’ countries, reflecting a strong commitment to cybersecurity practices globally.
Assessment Criteria: The GCI 2024 evaluates national efforts based on five pillars:
-
- Legal Measures
- Technical Measures
- Organizational Measures
- Capacity Development
- Cooperation
- Evaluation Methodology: The index utilized a comprehensive questionnaire comprising 83 questions, which cover 20 indicators, 64 sub-indicators, and 28 micro-indicators, ensuring a thorough assessment of each country's cybersecurity landscape.
- Tier Classification: The GCI 2024 report categorized 46 countries in Tier 1, the highest tier, indicating a strong commitment across all five cybersecurity pillars. Most countries fall into lower tiers, either “establishing” (Tier 3) or “evolving” (Tier 4) their cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Achievements
- Global Standing: India ranks at the top level of global cybersecurity rankings, showcasing its dedication to enhancing cyber resilience and securing its digital infrastructure.
- Government Initiatives:
- Robust Frameworks: Establishment of comprehensive frameworks for cybersecurity and cybercrime laws.
- Sectoral Support: Implementation of Sectoral Computer Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) that provide technical support and incident reporting across various industries.
- Educational Integration: Cybersecurity has been integrated into primary and secondary education curricula to foster informed digital citizens.
- Public Awareness: Targeted campaigns have promoted secure online practices across multiple sectors, including private industry and academia.
- Skill Development and Innovation: The government has provided incentives and grants to enhance skill development and promote research within the cybersecurity sector.
- International Collaborations: India has engaged in numerous bilateral and multilateral partnerships to strengthen its capacity-building and information-sharing efforts.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Overview: Established in 1865, the ITU is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies, becoming a UN agency in 1947.
- Membership: ITU has 193 member countries and over 1,000 associated organizations, including companies and universities.
- Functions: ITU coordinates global radio spectrum allocation, sets technical standards for telecommunication, and works to improve ICT access in underserved communities.
- India's Involvement: India has been an active ITU member since 1869 and a regular participant in the ITU Council since 1952.
INDIA JOINS THE INTERNATIONAL BIG CAT ALLIANCE (IBCA)
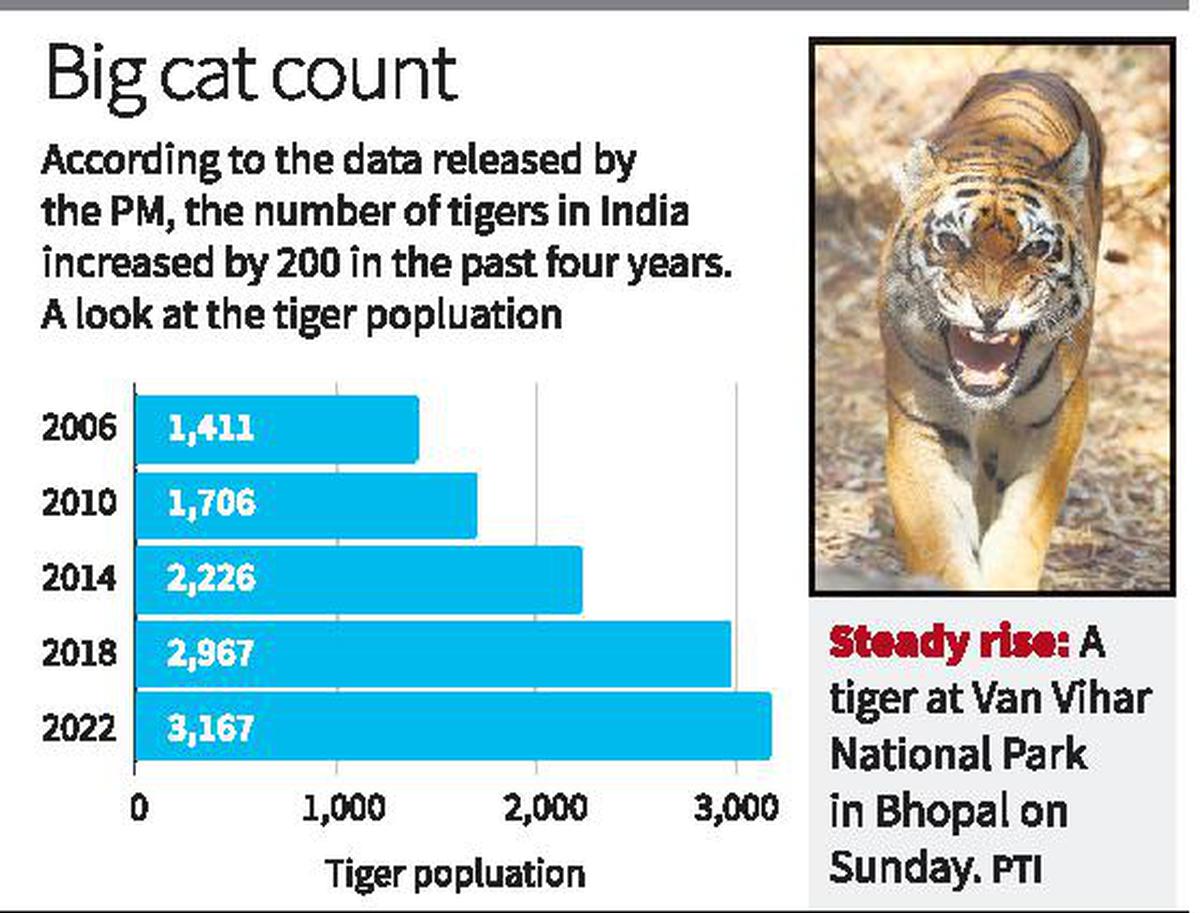
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
India formally joined the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 9, 2023, during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- Objective: The IBCA aims to conserve the world's seven big cat species: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar, and puma, focusing on their protection and natural habitats.
- Founding Members: India joins Nicaragua, Eswatini, and Somalia as founding members of the IBCA, which will collaborate with 24 countries and nine organizations.
- Headquarters: The IBCA will be headquartered in India, facilitating efforts to protect big cats and their ecosystems.
Purpose and Goals of IBCA
- Conservation Focus: The alliance addresses common challenges in the protection of the seven big cats, promoting sustainable resource use and tackling climate change.
- Collaboration and Support: The IBCA will provide a platform for member nations to share knowledge, expertise, and support recovery efforts in potential habitats.
- Mobilization of Resources: The alliance aims to mobilize financial and technical resources for effective conservation strategies based on global experiences.
Background and Evolution
- Inception: PM Modi proposed an international initiative against poaching and illegal wildlife trade in 2019, advocating for collaboration among tiger range countries.
- Extension of Project Tiger: The IBCA serves as an extension of India's long-standing commitment to wildlife protection, initially exemplified by the launch of Project Tiger in 1973.
Big Cat Species Overview
- Tiger (Endangered)
- Population: Approx. 3,167 in India, accounting for over 75% of the global population.
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and climate change impacting their territory.
- Lion (Vulnerable)
- Population: Estimated 700 in India.
- Threats: Habitat reduction and targeted poaching.
- Leopard (Near Threatened)
- Population: Around 13,000 in India, with approximately 250,000 globally.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
- Snow Leopard (Vulnerable)
- Population: 400-700 in India, with global estimates of 4,000-6,500.
- Threats: Poaching, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
- Cheetah (Vulnerable)
- Population: Declined to less than 7,000 globally; declared extinct in India in 1952.
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change, and illegal trafficking.
- Jaguar (Near Threatened)
- Population: Approximately 173,000 globally, primarily in South America.
- Threats: Deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat fragmentation.
- Puma (Near Threatened)
- Population: Estimated 50,000, experiencing a decline.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
Future Initiatives
- Translocation Efforts: Following successful cheetah translocations from Namibia and South Africa, India plans to explore similar initiatives for other big cats.
- Global Cooperation: The IBCA will strengthen conservation efforts by working with a broader network of range countries to combat poaching and promote habitat preservation.
EARTH TO EXPERIENCE A TEMPORARY 'MINI-MOON' IN SEPTEMBER

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
In late September, Earth will temporarily capture a small asteroid known as 2024 PT5. This phenomenon, where an asteroid becomes a "mini-moon," will last for about two months before the asteroid escapes back into space. While Earth has gained mini-moons before, such occurrences are quite rare; most asteroids either miss the planet entirely or burn up upon entering the atmosphere.
What Is a 'Mini-Moon'?
Mini-moons are small asteroids that get temporarily captured by Earth's gravity, orbiting the planet for a limited time. These asteroids are typically small and difficult to detect—only four mini-moons have been identified in Earth's history, and none remain in orbit today. Some objects previously thought to be mini-moons were later determined to be space debris, including rocket stages and satellites.
Details About 2024 PT5
Discovered on August 7 through the NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS), 2024 PT5 measures approximately 33 feet in length, making it invisible to the naked eye and standard amateur telescopes. However, it is detectable by professional astronomical equipment.
According to Carlos de la Fuente Marcos, a professor at the Complutense University of Madrid, 2024 PT5 originates from the Arjuna asteroid belt, which consists of space rocks that share similar orbits with Earth. There is also speculation that it could be a fragment resulting from an impact on the moon, as noted by Paul Chodas from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
However, some experts argue that 2024 PT5 may not fully qualify as a mini-moon. For an asteroid to be classified as such, it must complete at least one full orbit around Earth. Instead, 2024 PT5 will follow a horseshoe-shaped path, leading Lance Benner, a principal investigator at JPL, to express skepticism about its classification as a mini-moon.
Significance of the Event
Studying 2024 PT5 will provide valuable insights into asteroids that pass near Earth and their potential for future collisions. Additionally, many asteroids are believed to contain precious minerals and water, which could be harvested for future space missions and resource utilization. Observing this mini-moon will enhance our understanding of these celestial bodies and their behavior in Earth's vicinity.
TRISHNA MISSION

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
During a recent event, the President of the French Space Agency, Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), addressed various topics, celebrating 60 years of collaboration between France and India in space exploration, alongside discussions on the Gaganyaan and TRISHNA missions.
Overview of the TRISHNA Mission
The Thermal Infrared Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment (TRISHNA) is a joint initiative by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and CNES.
Mission Objectives
TRISHNA aims to provide high-resolution, timely observations of Earth's surface temperature, monitor vegetation health, and analyze water cycle dynamics. It will facilitate:
- Assessment of urban heat islands
- Detection of thermal anomalies related to volcanic activity and geothermal resources
- Monitoring of snowmelt runoff and glacier behavior
- Collection of data on aerosol optical depth, atmospheric water vapor, and cloud cover
Satellite Payloads
TRISHNA is equipped with two main payloads:
- Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) Payload: Supplied by CNES, this payload includes a four-channel long-wave infrared imaging sensor that enables high-resolution mapping of surface temperature and emissivity.
- Visible-Near Infra-Red-ShortWave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) Payload: Developed by ISRO, this payload consists of seven spectral bands aimed at detailed mapping of surface reflectance, which is crucial for calculating biophysical and radiation budget variables.
The data retrieved from both payloads will aid in solving surface energy balance equations to estimate heat fluxes.
Operational Details
- TRISHNA will operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 761 km, with a scheduled overpass time of 12:30 PM at the equator.
- This orbit will achieve a spatial resolution of 57 meters for land and coastal regions, and 1 km for oceanic and polar areas.
- The mission is expected to have an operational lifespan of five years.
PROJECT 200

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
At the Bengaluru Space Expo 2024, Bengaluru-based start-up Bellatrix Aerospace launched Project 200, a pioneering satellite designed to operate in the Ultra-Low Earth Orbit (ULEO) range of 180 km to 250 km.
Revolutionary Capabilities
Bellatrix Aerospace claims that operating in this orbit dramatically enhances satellite capabilities and redefines their connection to Earth. The satellite's launch is part of a technology demonstration mission, showcasing an innovative propulsion system tailored for this low altitude.
Breakthrough Propulsion Technology
Traditionally, satellites are positioned above 450 km to minimize atmospheric interference. However, deploying at 200 km can significantly enhance capabilities, which has been hindered by propulsion technology limitations until now.
Enhanced Performance Metrics
The new propulsion system allows satellites to maintain their orbits for years, avoiding rapid deorbiting due to atmospheric drag. Key benefits of Project 200 include:
- Reduced Communication Latency: Halves the delay in satellite communication.
- Improved Image Resolution: Enhances clarity threefold.
- Cost Efficiency: Significantly lowers overall satellite costs.
Bellatrix's innovative approach not only addresses current limitations but also positions its satellite as a transformative solution for applications in high-resolution Earth observation, telecommunications, and scientific research.
PRADHAN MANTRI JANJATIYA UNNAT GRAM ABHIYAN

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan. This mission aims to enhance the socio-economic conditions of tribal communities by saturating more than 63,000 tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts with a total budget of ?79,156 crore.
Budget Breakdown
- Total Outlay: ?79,156 crore
- Central Share: ?56,333 crore
- State Share: ?22,823 crore
Target Beneficiaries
The initiative is expected to benefit over 5 crore tribal people across 549 districts and 2,740 blocks in 30 States/UTs.
Context
- India's Scheduled Tribe (ST) population stands at 10.45 crore, according to the 2011 Census, with more than 705 tribal communities often residing in remote areas. This mission builds upon the successes of the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN), launched on November 15, 2023.
Mission Objectives
- The mission aims to address critical gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood through a comprehensive approach involving 25 interventions across 17 ministries.
Key Goals and Interventions
Goal 1: Developing Enabling Infrastructure
- Housing: Provision of pucca houses under the PMAY (Gramin) for eligible households, along with access to tapped water and electricity.
- Village Infrastructure: Improvement of all-weather road connectivity, mobile connectivity, and educational and health infrastructure.
Goal 2: Promotion of Economic Empowerment
- Skill Development: Enhanced training and self-employment opportunities for ST youth through initiatives like the Skill India Mission and support for tribal marketing.
Goal 3: Universal Access to Good Education
- Education Initiatives: Increase the gross enrollment ratio in schools and higher education, along with setting up tribal hostels for students.
Goal 4: Healthy Lives and Dignified Ageing
- Health Access: Provision of quality health facilities, aiming to meet national standards in maternal and child health indicators through mobile medical units.
Innovative Schemes
- Tribal Home Stay Initiative: Promotion of 1,000 homestays in tribal areas to boost tourism and provide alternate livelihoods. Each household can receive up to ?5 lakh for construction and ?3 lakh for renovations.
- Sustainable Livelihood for FRA Holders: Focus on 22 lakh FRA patta holders, enhancing their rights and providing livelihood support through various government schemes.
- Improving Educational Infrastructure: Upgrading tribal residential schools and hostels to improve local educational resources and retention rates.
- Sickle Cell Disease Management: Establishing Centers of Competence for affordable diagnostic services and prenatal care in regions where the disease is prevalent.
- Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centres (TMMCs): Setting up 100 TMMCs to improve marketing of tribal products and facilitate better prices for producers.
WHITE REVOLUTION 2.0

- 20 Sep 2024
- Overview:
- India is the world's largest milk producer, with production reaching 230.58 million tonnes in 2022-23.
- White Revolution 2.0 focuses on cooperative societies, similar to the foundation laid by Operation Flood in the 1970s.
- Objectives of White Revolution 2.0:
- Increase daily milk procurement from 660 lakh kg (2023-24) to 1,007 lakh kg by 2028-29.
- Enhance the market access for dairy farmers, especially in uncovered areas.
- Generate employment and empower women through increased dairy cooperative involvement.
- Current Landscape:
- The Ministry of Cooperation has prioritized expanding the cooperative network since its formation in 2021.
- Dairy cooperatives operate in 70% of India’s districts with approximately 1.7 lakh dairy cooperative societies (DCSs).
- These DCSs serve around 2 lakh villages (30% of total villages) and account for 10% of milk production and 16% of marketable surplus.
- Regional Coverage:
- States like Gujarat, Kerala, and Sikkim have over 70% village coverage by dairy cooperatives.
- In contrast, states such as Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Madhya Pradesh have only 10-20% coverage.
- Less than 10% coverage is observed in West Bengal, Assam, and several smaller northeastern states.
- Expansion Plans:
- NDDB plans to establish 56,000 new multipurpose dairy cooperative societies over the next five years and strengthen 46,000 existing DCSs.
- A pilot project initiated in February 2023 aims to set up dairy cooperatives in uncovered gram panchayats in Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Funding Sources:
- The National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) 2.0 will primarily fund White Revolution 2.0.
- Financial assistance will support village-level milk procurement, chilling facilities, and training initiatives.
- Current Production Insights:
- India’s milk production has grown significantly from 17 million tonnes in 1951-52 to 230.58 million tonnes.
- Average yield per animal is 8.55 kg/day for exotic/crossbred and 3.44 kg/day for indigenous animals.
- Per Capita Milk Availability:
- National average: 459 grams/day, higher than the global average of 323 grams/day.
- Significant regional variation: from 329 grams in Maharashtra to 1,283 grams in Punjab.
- Top Milk Producing States:
- Uttar Pradesh (15.72%), Rajasthan (14.44%), Madhya Pradesh (8.73%), Gujarat (7.49%), Andhra Pradesh (6.70%) contribute to 53.08% of total production.
- Indigenous buffaloes contribute 31.94%, while crossbred cattle contribute 29.81%.
- Market Dynamics:
- About 63% of total milk production is marketed; two-thirds of this is in the unorganised sector.
- Cooperatives hold a significant share in the organised sector, providing livelihoods to over 8.5 crore individuals, primarily women.
- Economic Impact:
- The dairy sector represents 40% (?11.16 lakh crore) of the agricultural value output in 2022-23, surpassing cereals.
One Nation, One Election

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union cabinet has recently approved the "One Nation, One Election" proposal, facilitating the conduct of simultaneous elections in India. This initiative follows a report submitted in March by a high-level committee chaired by former President Ram Nath Kovind, which unanimously recommended synchronizing Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, along with local body polls, within 100 days.
What are Simultaneous Polls?
Simultaneous polls aim to align the timing of Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections across all states, thereby reducing the frequency of elections. Historically, simultaneous elections were held during the first four general election cycles (1952, 1957, 1962, and 1967), but this practice ended in 1959 after the dismissal of the Kerala government. Since then, due to premature dissolutions of various Assemblies, elections have been staggered. Currently, only four states—Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim—hold simultaneous elections with the Lok Sabha.
Arguments For and Against
Proponents argue that simultaneous elections can significantly reduce election-related costs, which amounted to approximately ?3,870 crore during the 2014 general elections. They also highlight that the Model Code of Conduct triggers twice in a five-year cycle, leading to extended periods of governance downtime.
Opponents caution that this approach may favor larger political parties with national reach, potentially sidelining smaller regional parties. A 2015 study found that the likelihood of a party winning both Lok Sabha and Assembly elections when held simultaneously is 77%, dropping to 61% if elections are spaced six months apart.
Implementation Process
The committee proposed a two-step implementation:
- Simultaneous Elections: Conduct elections for both the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies together.
- Synchronizing Local Elections: Hold elections for municipalities and panchayats within 100 days following the general elections.
Following the announcement of the "appointed date," the terms of all State Assemblies constituted after that date would end with the Lok Sabha's term. This could lead to most State governments not completing their five-year terms, even if they maintain a majority.
Required Constitutional Changes
Several amendments to the Constitution have been proposed:
- Introduction of Article 82A: This would require all Legislative Assemblies elected after the appointed date to conclude with the Lok Sabha’s term.
- Amendment of Article 327: Expanding Parliament's powers to include the conduct of simultaneous elections.
- Revisions to Articles 83 and 172: Defining the five-year term as the "full term" and any remaining period after premature dissolution as the "unexpired term."
- Introduction of Article 324A: Empowering Parliament to ensure that municipality and panchayat elections occur alongside general elections.
- Amendments for Union Territories: Ensuring that Assembly elections in Union Territories align with simultaneous elections.
- Single Electoral Roll: Proposing a common electoral roll for all elections, to be managed by the Election Commission of India (ECI).
State Ratification
Under Article 368, amending the Constitution may require ratification by state legislatures. The panel believes that syncing Assembly elections with Lok Sabha elections will not need state ratification, but amendments for a common electoral roll and synchronization of local elections will require cooperation from the states. The ruling BJP, currently in power in several states, will need to navigate upcoming Assembly elections in Haryana, Maharashtra, and Jharkhand to secure this support.
Conclusion
The "One Nation, One Election" initiative aims to streamline India's electoral process, potentially enhancing governance and reducing costs. However, its success depends on achieving political consensus and implementing necessary constitutional amendments, which will require collaboration among various political parties and state governments.
Cabinet approves Chandrayaan-4 mission, first module of Bharatiya Antariksh Station, Venus mission, next-gen launcher

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The PM Modi-led Union Cabinet has approved several ambitious space initiatives, marking a significant leap for India's lunar and space exploration programs.
Chandrayaan-4 Mission
- Objective: The fourth lunar mission aims to collect lunar samples, return them safely to Earth, and analyze them.
- Timeline: Expected completion within 36 months post-approval, with a budget of ?2,104 crore.
- Significance: This mission will build foundational technological capabilities for a manned Moon landing planned by 2040.
- Remarks: ISRO Chairman S. Somanath emphasized that the mission's highlight is its low-cost execution and the step-by-step approach to developing the necessary technology.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) and Gaganyaan
- BAS Development: Approval for the first module of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, targeted for launch by 2028, with full completion by 2035.
- Gaganyaan Program: The program’s budget has been revised to ?20,193 crore, with an additional funding of ?11,170 crore to enhance its scope and include precursor missions for BAS.
- Mission Plan: Eight missions are envisaged by 2028, including four under the ongoing Gaganyaan program, development of BAS-1, and four additional missions for technology demonstration and validation.
Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for March 2028, VOM will explore Venus's atmosphere, geology, and generate extensive scientific data.
- Budget: The Cabinet approved ?1,236 crore for VOM, with ?824 crore allocated for the spacecraft.
- Research Focus: The mission will provide insights into Venus's transformation and how different planetary environments evolve.
Next-Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
- Development Approval: A reusable NGLV has been greenlit with a budget of ?8,240 crore.
- Capabilities: The new rocket will have three times the payload lifting capability compared to existing vehicles (10 tonnes to 30 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit) and will be cost-effective and commercially viable.
- Features: The NGLV will include reusability options and modular green propulsion systems, enhancing India's capacity for satellite launches.
Net Direct Tax inflows increase by 16.1%

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
- Advance tax payments from corporates and personal taxpayers have risen by 22.6%, surpassing ?4.36 lakh crore. This increase is driven by a 39.2% rise in Personal Income Tax (PIT) receipts and an 18.2% uptick in corporate taxes.
Key Details:
- Overall net direct tax receipts have reached approximately ?9.96 lakh crore, reflecting a 16.1% increase, though this marks a slowdown from the 22.5% growth recorded as of August 11.
- As of September 17, corporate tax collections grew by 10.5%, while inflows from PIT increased by 18.9%.
- Securities Transaction Tax collections nearly doubled to ?26,154 crore, and refunds surged by 56.5% to ?2.05 lakh crore, according to data from the Income Tax Department.
- Personal taxes continue to outpace corporate taxes, contributing 51.7% of net direct tax receipts for the year.
- Gross tax collections, before accounting for refunds, have risen by 21.5%, totaling ?12.01 lakh crore.
Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA)
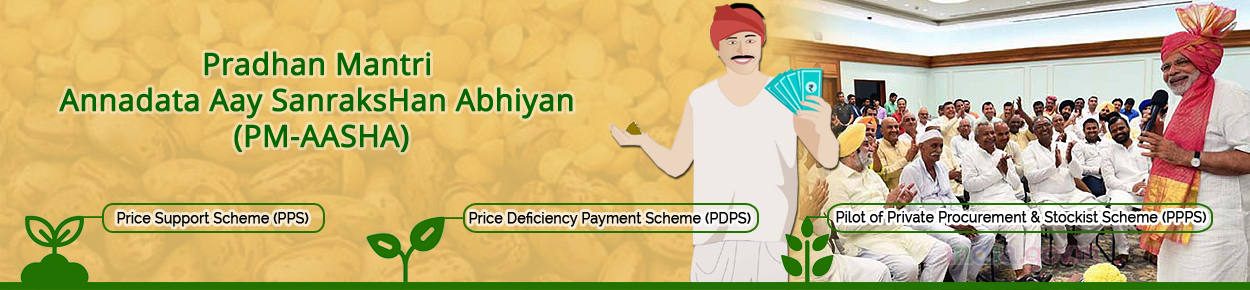
- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the continuation of the PM-AASHA scheme to provide remunerative prices to farmers and control price volatility of essential commodities for consumers.
- Total Financial Outlay: ?35,000 crore during the 15th Finance Commission Cycle, up to 2025-26.
Scheme Integration
- The government has merged the Price Support Scheme (PSS) and Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) into PM-AASHA to enhance efficiency.
- Components of PM-AASHA:
- Price Support Scheme (PSS)
- Price Stabilization Fund (PSF)
- Price Deficit Payment Scheme (PDPS)
- Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
Procurement Details
- MSP Procurement: Starting from the 2024-25 season, procurement of notified pulses, oilseeds, and copra at Minimum Support Price (MSP) will be on 25% of national production.
- Exceptions for 2024-25: 100% procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masur will be implemented.
- Government Guarantee: The existing government guarantee for procurement has been enhanced to ?45,000 crore.
Consumer Protection Measures
- The extension of the PSF scheme will help protect consumers from extreme price volatility by maintaining strategic buffer stocks of pulses and onions.
- Procurement of pulses at market prices will be handled by the Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA) when prices exceed MSP.
Enhanced State Participation
- PDPS Coverage: The coverage for the Price Deficit Payment Scheme for notified oilseeds has been increased from 25% to 40% of state production.
- Implementation Period: Extended from 3 months to 4 months, with compensation limited to 15% of MSP.
Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) Adjustments
- The MIS has been extended to provide remunerative prices for perishable horticultural crops.
- Coverage for MIS has increased from 20% to 25% of production, with an option for direct differential payments to farmers.
- For TOP (Tomato, Onion, Potato) crops, the government will cover transportation and storage costs to ensure price stability.
Fast-track special courts (FTSCs)

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
Fast-track special courts (FTSCs) are much more efficient than other courts in handling rape cases and those related to the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, a report released by the India Child Protection.
Key Details:
West Bengal's Performance
- West Bengal recorded less than a 2% disposal rate for rape and POCSO cases, the lowest in India.
- Only five out of 123 earmarked FTSCs are currently functioning in the state.
Overview of the India Child Protection (ICP)
- Established in 2005, the ICP is dedicated to combatting child sexual abuse and related crimes, including:
- Child trafficking
- Exploitation of children in the digital space
- Child marriage
Efficiency of FTSCs
- The ICP report titled "Fast Tracking Justice" highlighted that FTSCs disposed of 83% of cases in 2022, compared to 10% by conventional courts.
- As of August 2023, 755 out of 1,023 earmarked FTSCs were operational.
- Among these, 410 FTSCs are exclusively for POCSO cases.
Historical Context
- The FTSC scheme was launched by the Centre in October 2019, following a Supreme Court directive for ensuring the swift disposal of cases, related to rape and those coming under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Implemented by the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice.
Case Disposal Statistics
- FTSCs have disposed of 52% of the 4,16,638 rape and POCSO cases since the scheme's inception.
- Disposal rates improved from 83% in 2022 to 94% in 2023.
State-wise Disposal Rates
- Top Performing States:
- Maharashtra: 79.5%
- Punjab: 71.3%
- Kerala (Southern India): 69.5%
- Karnataka: 62.2%
- Tamil Nadu: 58.4%
- Lowest Performing States:
- West Bengal: 1.6%
- Jammu and Kashmir: 25%
- Meghalaya: 26.6%
- Delhi: 28.3%
Note: No data was available for Arunachal Pradesh, Ladakh, and Sikkim.
Need for Additional FTSCs
- The ICP report states that India needs at least 1,000 more FTSCs to manage the backlog effectively.
- The backlog of pending cases rose from 2,81,049 in 2020 to 4,17,673 by the end of 2022.
Advocacy for Reform
- Bhuwan Ribhu, a child rights activist, emphasized the urgent need for FTSCs to ensure justice for victims:
- Investment in the safety and security of women and children is crucial.
- All pending cases should be resolved within the next three years.
- Rehabilitation and compensation for victims should be prioritized.
- Time-bound policies for case disposal across all courts are necessary.
Funding and Resource Utilization
- The ICP report recommends optimizing the Nirbhaya Fund, created after the 2012 Delhi gang rape, to support additional FTSCs.
- There is currently ?1,700 crore unutilized, while the requirement for operationalizing new FTSCs is ?1,302 crore.
Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP)

- 18 Sep 2024
In News
The recent Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP) Ministerial between the United States and India aimed to enhance collaboration in clean energy innovation, energy security, and the transition to clean energy.
About the Partnership
The meeting reviewed significant achievements and future initiatives across five core pillars:
- Power and Energy Efficiency
- Responsible Oil and Gas
- Renewable Energy
- Emerging Fuels & Technologies
- Sustainable Growth
The SCEP facilitates bilateral cooperation on clean energy, focusing on power, efficiency, renewable resources, emerging technologies, and sustainable practices.
Key Highlights of SCEP
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP)
Launched in August 2023, RETAP aims to create actionable roadmaps for:
- Hydrogen
- Long-duration energy storage
- Offshore wind
- Geothermal technologies
Energy Storage Task Force
This public-private initiative seeks to address:
- Policy
- Safety
- Regulatory challenges
It explores alternatives to lithium-ion technologies, with projects like Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) in Assam and Haryana focusing on grid integration and renewable energy storage.
Modernization of Power Distribution
The meeting underscored India’s advancements in:
- Smart metering
- Power market reforms
- The Indian Railways’ goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2030
India has successfully procured 1.5 GW of round-the-clock renewable energy.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) & Transport Electrification
A comprehensive workshop was launched to enhance R&D, certification, and partnerships for SAF. India’s PM eBus Sewa scheme aims to deploy 10,000 electric buses, promoting electrification in medium and heavy-duty transport.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) & Methane Abatement
Cooperation on CCUS technologies and regulatory frameworks has increased, alongside efforts to reduce methane emissions in the oil and gas sector through collaboration with India’s Directorate General of Hydrocarbons.
Public-Private Collaborations
The importance of public-private dialogues in shaping policies and reducing the costs of clean energy technologies was emphasized.
Initiatives Supporting Clean Energy
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): A global coalition led by India, promoting solar energy collaboration among solar-rich countries.
- Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP): A US-India initiative focusing on hydrogen, energy storage, offshore wind, and geothermal technologies.
- Green Hydrogen Mission (India): Promotes green hydrogen as a clean energy alternative, especially in heavy industries and transportation.
- EU’s Green Deal: A European strategy aimed at achieving climate neutrality by 2050 through clean energy investments and policies.
- PM KUSUM Scheme (India): Supports solar power generation for irrigation, reducing fossil fuel reliance in agriculture.
Union Budget 2024-25: Corridor Projects for Bihar's Temples

- 18 Sep 2024
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2024-25 announced plans to develop corridor projects for the Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar. These initiatives aim to enhance both temples as significant pilgrimage and tourist destinations, modeled after the successful Kashi Vishwanath Corridor. The temples are located approximately 10 kilometers apart and hold considerable cultural significance.
Key Facts About the Temples
Vishnupad Temple at Gaya
- Location: Situated on the banks of the Phalgu/Falgu River in Gaya district, Bihar.
- Deity: Dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- Legend: Local mythology recounts that a demon named Gayasur sought the power to help others attain moksha (liberation). After misusing this power, he was subdued by Lord Vishnu, who left a footprint at the temple, symbolizing this event.
- Architectural Features: The temple stands about 100 feet tall and is supported by 44 pillars made from large gray granite blocks (Munger Black stone), joined with iron clamps. The octagonal shrine is oriented towards the east.
- Construction: Built in 1787 under Queen Ahilyabai Holkar's orders.
- Cultural Practices: The temple is especially significant during Pitra Paksha, a time for honoring ancestors, attracting many devotees. The Brahma Kalpit Brahmins, or Gayawal Brahmins, have served as traditional priests since ancient times.
Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya
- Historical Significance: Believed to be the location where Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment under the Mahabodhi Tree.
- Construction: Originally built by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC, with the current structure dating back to the 5th–6th centuries.
- Architectural Features: The temple complex includes the 50-meter-high Vajrasana (the Diamond Throne), the sacred Bodhi Tree, and six other sacred sites associated with Buddha's enlightenment. The site is surrounded by numerous ancient Votive stupas and is protected by circular boundaries.
- Sacred Sites:
- Bodhi Tree: A direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Animeshlochan Chaitya: Where Buddha spent the second week of meditation post-enlightenment.
- Ratnachakrama: Site of Buddha's third week after enlightenment.
- Ratnaghar Chaitya: Site of Buddha's fourth week after enlightenment.
- Ajapala Nigrodh Tree: Site of Buddha’s fifth week after enlightenment.
- Lotus Pond: Site of Buddha’s sixth week after enlightenment.
- Rajyatana Tree: Site of Buddha’s seventh week after enlightenment.
- Recognition: Designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2002, the Mahabodhi Temple attracts numerous national and international pilgrims, emphasizing its spiritual importance.
Other Tourist Attractions in Bihar
Additional notable tourist sites in Bihar include:
- Vishwa Shanti Stupa in Rajgir
- Nalanda
- Ancient city of Patliputra
- Valmiki Nagar Tiger Reserve in West Champaran
What is the Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP)?
The Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP) aims to upgrade religious sites into world-class destinations for spiritual and tourism purposes.
India-China Disengagement Along the LAC
- 18 Sep 2024
Overview of Disengagement Progress
Recently, India’s External Affairs Minister announced that about 75% of the “disengagement problems” with China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in Ladakh have been “sorted out.” However, notable areas such as Demchok and the Depsang plains have seen no progress toward resolution over the past two years.
Recent Developments on India-China Disengagement
Verified Disengagement
India and China have mutually agreed to and verified disengagement from five friction points, including:
- Galwan Valley
- Pangong Tso
- Gogra-Hot Springs
Despite this, issues in Demchok and Depsang remain unresolved.
Diplomatic Efforts
Recent high-level diplomatic interactions have facilitated the disengagement along the LAC. Key meetings include:
- India’s National Security Advisor Ajit Doval meeting Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi at the BRICS NSAs meeting in St Petersburg, Russia.
- Anticipation for further disengagement is linked to the upcoming BRICS Summit in October in Kazan, Russia, where leaders from both nations are expected to meet.
Significance of Disengagement
The 31st meeting of the Working Mechanism for Consultation & Coordination on India-China Border Affairs (WMCC) was described as “frank, constructive, and forward-looking.” Participants urged both parties to “narrow down the differences” and “find early resolution of the outstanding issues.” The phrase "narrow down the differences" marks a hopeful shift in the dialogue surrounding the border standoff.
Strategic Importance of Depsang Plains and Demchok
Depsang Plains
The Depsang Plains hold strategic significance due to the following reasons:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA)’s control threatens India’s position over the Siachen Glacier, potentially encircling the Indian Army between China and Pakistan.
- A coordinated attack from both China and Pakistan would leave India’s military position on the Siachen Glacier vulnerable.
- The Indian Army identifies this region as particularly susceptible to mechanized warfare due to its flat terrain, which also offers direct access to Aksai Chin.
Demchok
Demchok is crucial for several reasons:
- It facilitates effective surveillance of Chinese movements and activities in the Aksai Chin region.
- It supports essential road and communication links that enable rapid military mobilization and logistical support.
Key Areas in the India-China Standoff
Pangong Lake Region
- This area frequently sees patrols from both India and China intersecting.
- The north bank of the lake is divided into eight "fingers," with India claiming territory up to Finger 8 and China disputing it down to Finger 4.
Demchok Region
- Recent reports indicated increased Chinese activity and heavy equipment movement.
Galwan River Basin
- Satellite imagery revealed Chinese tents near the Galwan River basin, suggesting incursions into traditionally held Indian territories.
Gogra Post
- A Chinese military buildup near the Gogra post has escalated tensions.
Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO)
- Chinese encroachments have been reported in the DBO sector, located on the Indian side.
- The DBO airstrip is critical for winter operations and reinforcements, accessible via the 255 km-long Darbuk-Shyok-DBO road.
India Status Report on Road Safety 2024
- 18 Sep 2024
In News:
The "India Status Report on Road Safety 2024," prepared by the TRIP Centre at IIT Delhi, highlights India's slow progress in reducing road accident fatalities and emphasizes the need for a tailored approach to road safety.
Key Findings:
- Road Safety Analysis:
- The report analyzes road safety data from FIRs across six states and evaluates compliance with Supreme Court directives on road safety.
- There are significant disparities in road traffic death rates among states, with motorcyclists and truck-related fatalities being notably high.
- Road traffic injuries remain a critical public health issue, with little progress in reducing fatalities. Many states are unlikely to meet the UN goal of halving traffic deaths by 2030.
- Health Impact:
- In 2021, road traffic injuries ranked as the 13th leading cause of death in India and the 12th leading cause of health loss (measured in Disability-Adjusted Life Years, or DALYs). Six states listed road traffic injuries among their top 10 health loss causes.
- Crash Surveillance Deficiencies:
- India lacks a national crash-level database, relying on police station records, which are often incomplete and inaccurate. This hampers effective public policy and intervention strategies.
- State Performance:
- There is a threefold variation in per capita death rates across states. Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and Chhattisgarh have the highest rates, while West Bengal and Bihar have the lowest.
- Pedestrians, cyclists, and motorized two-wheeler riders are the most common accident victims, with trucks accounting for a large share of accidents.
- Helmet usage is low, especially in rural areas, and basic traffic safety measures are inadequate across many states.
- Global Comparison:
- India's road safety governance is starkly lagging compared to developed nations. By 2021, Indians were 600% more likely to die in road accidents compared to their counterparts in countries like Sweden.
Recommendations for Improvement
- National Database: Establish a comprehensive, publicly accessible database for fatal crashes to enhance understanding of risks and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Scaled Interventions: Prioritize road safety measures at both Central and State levels, tailored to the specific challenges of each region.
- Public Awareness and Safety: Increase public awareness of road safety measures, particularly helmet usage, and improve trauma care facilities.
- Infrastructure Audit: Conduct thorough audits of National and State Highways to identify safety gaps and implement necessary improvements.
By implementing these recommendations, India can take meaningful steps toward improving road safety and reducing fatalities.
Windfall tax on crude oil cut to zero

- 18 Sep 2024
In News:
The windfall tax on domestically produced crude oil will be slashed to ‘zero’ effective September 18. This marks its second reduction to nil since its introduction in July 2022.
Key Details:
- The windfall tax is revised every 15 days based on average oil prices over the previous two weeks, charged as Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED) on profits from domestically produced crude oil.
- The last revision, effective August 31, set the windfall tax at ?1,850 per tonne.
- The SAED on the export of diesel, petrol, and jet fuel (ATF) has been set to ‘nil’ following a major decline in crude oil prices.
- This is the second instance since the tax was imposed that it has been reduced to nil; the first reduction occurred on April 4, 2023.
Crude Oil Prices
- Crude oil prices increased by $1 per barrel due to supply chain issues; traders anticipate demand growth if the US Federal Reserve lowers borrowing costs.
- More than 12% of crude production from the US Gulf of Mexico was offline last week due to Hurricane Francine, contributing to price increases in three of the past four sessions. US crude futures rose by $1.31 (1.9%) to $71.40, while Brent crude futures increased by $1 (1.4%) to $73.75 per barrel.
- The windfall tax on crude oil companies was introduced in July 2022 to control extreme profits from gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuel exports.
What is a Windfall Tax?
- A windfall tax is a surtax imposed by governments on businesses or economic sectors that have benefited from economic expansion.
- The purpose is to redistribute excess profits in one area to raise funds for the greater social good; however, this can be a contentious ideal.
- Some individual taxes—such as inheritance tax or taxes on lottery or game-show winnings—can also be construed as a windfall tax.
Nipah viral infection

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
- The district administration has imposed restrictions on social gatherings and made masks mandatory in Malappuram district after a 24-year-old man from Naduvath, near Wandoor, died from the Nipah viral infection.
- Five wards in Tiruvali and Mampad grama panchayats have been declared containment zones. Schools, colleges, madrasas, anganwadis and cinema halls in these zones will remain closed until further notice.
What is Nipah?
- Nipah is a viral infection that mainly affects animals such as bats, pigs, dogs and horses.
- It is known to cause infection in humans when they come in contact with saliva, urine, or faecal matter of infected animals — by eating fruits that have been bitten into by the animals or scaling trees were the bats live.
- It can also be transmitted human to human through close contact, but this is not the most common route of transmission.
- The case fatality ratio of Nipah can be extremely high at 40 to 75%. To compare, even at the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, the case fatality ratio (CFR) – proportion of people who die among those who test positive – remained at around 3%.
What are the symptoms of Nipah?
People with Nipah start showing symptoms around four to 14 days after getting infected. The infection causes fever, headache, cough, sore throat and difficulty breathing. In later stages, the infection can also lead to brain swelling or encephalitis, leading to confusion, drowsiness, and seizures. With encephalitis, people can go into coma within 24 to 48 hours.
How does the Nipah monoclonal antibody work?
The monoclonal antibody binds with the part of the viral envelope that attaches to the human cells to gain entry. Given early in the disease, it prevents the virus from entering more and more cells, thereby stopping its proliferation and severe disease.
The monoclonal antibody has to be administered in the early stages of the disease, before encephalitis sets in.
India first imported 20 doses of the monoclonal antibodies — enough for ten patients — from a laboratory in Australia’s University of Queensland during the 2018 outbreak. Another 20 doses were requested last year. The monoclonal antibody has so far been used in 14 individuals globally and none of them died.
What can be done to protect yourself?
Usually, Nipah outbreaks are localised, meaning people from the rest of the country are not at risk of the infection at present. People from areas where cases are detected should refrain from coming in close contact with the family members and other contacts of the two case. With the infection transmitted by fruit bats, the government also suggests precautions like washing the fruits and peeling them before consumption. Fruits with signs of bat bites should be discarded. And, palm sap or juice must be boiled before consumption.
All-India Reservoir Status
- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The southwest monsoon has provided significant rainfall across India, with total precipitation at 836.7 mm as of September 12, marking an 8% surplus for this time of year. The Central Water Commission (CWC) reports that reservoir levels are notably higher compared to last year and the 10-year average.
All-India Reservoir Status
- Total Capacity: 180.852 billion cubic metres (BCM) across 155 reservoirs.
- Current Storage: 153.757 BCM, which is 85% of total capacity.
- Last Year Comparison: 119.451 BCM (66%) and 10-year average of 130.594 BCM.
Regional Reservoir Highlights:
- North: 11 reservoirs at 68% capacity (13.468 BCM). Storage is lower than last year (81%) and decadal average (82%). Himachal Pradesh and Punjab saw significant rainfall deficits.
- East: 25 reservoirs at 76% capacity (15.797 BCM), improved from last year's 58%. Despite deficits in Nagaland and Bihar, overall rainfall has supported reservoir levels.
- West: 50 reservoirs at 90% capacity (33.526 BCM), a marked increase from 75% last year. Heavy rainfall, particularly in Gujarat, has led to flooding but boosted water reserves.
- Central: 26 reservoirs at 89% capacity (42.808 BCM), better than last year's 76%. This region has enjoyed normal or above-average rainfall.
- South: 43 reservoirs at 88% capacity (48.158 BCM), significantly higher than 49% last year. Regions traditionally receiving less monsoon rain have also seen improvements.
Comparison to 2023
- Improved Storage: Notable increases in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, and several others.
- Stable: No change in Goa and Telangana.
- Declines: Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Uttarakhand show worse conditions compared to last year.
River Basin Status
Major river basins exhibit normal or above storage levels, including:
- Barak (98.72%)
- Krishna (94.53%)
- Cauvery (93.54%)
- Narmada (92.19%)
- Godavari (91.85%)
- Others range from 83% to 66%.
Overall, the 2024 monsoon has led to improved water storage conditions across much of India, benefiting numerous states while highlighting specific areas of concern.
Precision Farming
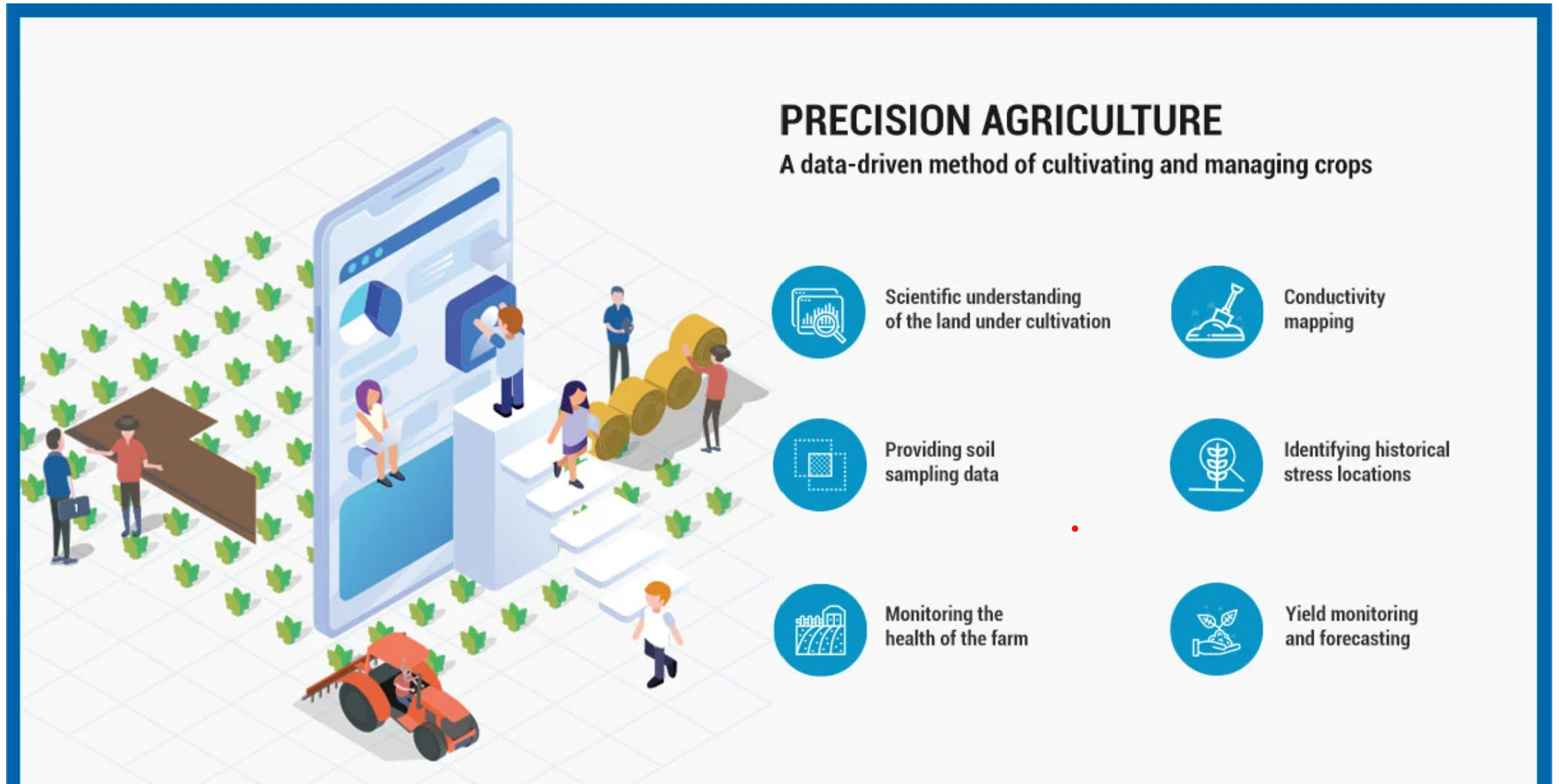
- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The Centre is contemplating to earmark Rs 6,000 crore to promote precision farming, a modern approach that uses smart technology such as Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, drones and data analytics to boost production through maximal use of resources while minimising environmental impact.
Key Details:
- Union Ministry of Agriculture is planning a Smart Precision Horticulture Programme under the existing Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) scheme.
- It will cover 15,000 acres of land in five years from 2024-25 to 2028-29 and is expected to benefit about 60,000 farmers.
- At present, the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), launched during Covid-19, has provisions for financing infrastructure projects for smart and precision agriculture.
- Under AIF, individual farmers as well as farmers’ communities such as Farmer Producer Organization, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies and SHGs are eligible for loans with interest subvention of 3% for using technological solutions in farm practices. These practices include farm/ harvest automation; purchase of drones, putting up specialised sensors on field; use of blockchain and AI in agriculture; remote sensing and Internet of Things (IoT).
Positive impact
- Smart and precision agriculture maximises use of resources like water, fertilisers and pesticides to increase production quality and quantity, all while insulating farmers from vagaries of climate change and other uncertainties, besides ensuring sustainable farming.
Apart from offering financial support, the Centre is also considering collaborating with the Netherlands and Israel, where tech-based modern farming solutions are being used, through Centres of Excellences (CoEs). The number of CoEs is likely to be 100 in the next five years. Under Indo-Israel Agriculture Project, 32 CoEs have already been set up across 14 states.
The Centre has also set up 22 Precision Farming Development Centres (PFDCs) across the country to test new technologies and modify them according to local needs.
According to the Ministry, these 22 PFDCs are located across State/Central Agricultural Universities, ICAR Institutes and IITs in TN, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Haryana, Telangana, West Bengal, Ladakh, UP, Punjab, Gujarat, Uttrakhand, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Manipur and Assam. Besides, funds are released to states/UTs for projects involving use of AI and machine learning, under schemes like the National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture.
What is Precision Agriculture?
- Precision Agriculture is a farm management concept that revolves around the process of observing, measuring, and responding to various inter-and intra-field variability inputs for modern agriculture.
- Popular definitions of Precision Agriculture (PA) or Site-Specific Crop Management (SSCM) describe the term as a technology-enabled approach to farming management that observes, measures, and analyzes the needs of individual fields and crops.
- The goal of precision agriculture is to increase efficiency and productivity, reduce input costs, and improve environmental sustainability.
- Key Advantages:
- A refined set of cultivation practices and choice of crops based on the suitability of land
- Elimination of volatility and risk
- Waste management
- Reduced production costs
- Minimum environmental impact
- Optimized use of fertilizers
- Water management with optimized irrigation practices
- Improved soil health
What is the current status of the introduction of African cheetahs?

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
Project Cheetah has encountered significant setbacks, including prolonged captivity and cheetah fatalities; with long-term success hinging on finding sufficient habitat, scientific management, and community support, the project’s future depends on overcoming these enormous challenges.
Overview of Project Cheetah:
- Cheetah Action Plan (CAP): India’s initiative to reintroduce African cheetahs, aimed at species conservation and ecosystem restoration.
- Long-term Commitment: Requires a minimum of 25 years of financial, technical, and administrative support from various governmental bodies.
Challenges Faced:
- Extended Captivity:
- Cheetahs have been held in captivity longer than planned, with only 12 of the original 20 surviving.
- Delays in the release process raise concerns about the cheetahs' fitness for survival in the wild.
- Health Issues and Fatalities:
- Several cheetahs have died due to pre-existing health conditions or management failures before being released.
- Captivity duration exceeds guidelines set by Namibian policy, rendering the cheetahs unfit for release.
- Environmental Adaptation Problems:
- Some deaths attributed to environmental stressors, such as heat stroke and improper management of conditions leading to health complications.
Location for Introduction:
- Kuno National Park: Chosen for its suitable habitat and prey base. However, many cheetahs remain confined, with release dates now pushed to late 2024 or early 2025.
- Additional Sites: Plans for a captive breeding facility in Gujarat and potential releases in Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary.
Management and Oversight:
- An expert committee, led by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), oversees the project. Responsibilities include negotiating with African countries for cheetah procurement and implementing field activities.
Goals and Measurable Outcomes:
- Short-term Objectives: Achieve a 50% survival rate in the first year, establish home ranges, and generate eco-tourism revenue.
- Long-term Success: Establish a stable cheetah population, improve habitat quality, and support local economies.
Future Considerations:
- The project lacks a definitive sunset clause but will require ongoing management for decades.
- The key question remains whether India has sufficient habitat (4,000 to 8,000 sq. km) to support a viable population of free-ranging cheetahs.
Conclusion: Project Cheetah faces significant challenges in achieving its ambitious conservation goals, raising questions about its long-term viability and management practices.
Why is T.N.’s education funding on hold?

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
Tamil Nadu is yet to receive this year’s funds from the Union government under the flagship education scheme Samagra Shiksha. According to the State government, the Centre has linked these funds to the complete implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which includes provisions that the State has opposed, including the contentious three-language formula.
What is Samagra Shiksha and why has Tamil Nadu not gotten funds under it?
- Samagra Shiksha is an integrated Centrally-sponsored scheme for school education from nursery till Class 12, with components for teacher training and salaries, special education, digital education, school infrastructure, administrative reform, vocational and sports education, with grants for textbooks, uniforms, and libraries, among others.
- The scheme’s estimated outlay between 2021 and 2026 is ?2.94 lakh crore, with the Centre and States contributing funds in a 60:40 ratio. For 2024-25, Tamil Nadu’s allocation under the scheme amounts to ?3,586 crore of which the Central share is ?2,152 crore, with a first quarterly instalment of ?573 crore, which has not yet arrived halfway through the financial year.
- In a letter to Prime Minister Narendra Modi last month, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin accused the Centre of imposing a prerequisite for the fund’s disbursal, namely, the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for another Centrally-sponsored education scheme called PM Schools for Rising India (PM Shri).
- This scheme, being run from 2022-2027, aims to create 14,500 model schools across the country to showcase the implementation of NEP 2020, and has a much smaller project cost of ?27,360 crore. The Centre has sent at least 10 letters to Tamil Nadu from September 2022, asking the State to sign the MoU, which included an agreement to fully implement the NEP.
In March 2024, Tamil Nadu committed to signing the PM Shri MoU due to its link to delayed funding for the larger Samagra Shiksha scheme. However, after signing a modified MoU in July that excluded NEP implementation, the Centre found it unacceptable. In August, Chief Minister M.K. Stalin noted that states signing the MoU received funds, accusing the Centre of “denying funds to the best-performing States” for not complying with NEP. The Union Education Ministry labeled these claims as misleading, but Tamil Nadu has not received Samagra Shiksha funds due to the incomplete MoU.
What is Tamil Nadu’s problem with the NEP 2020?
Tamil Nadu Education Minister highlighted the state's objections to specific NEP elements, such as the three-language formula and curriculum changes. He stated that Tamil Nadu is already implementing many acceptable aspects of the NEP through its own initiatives and warned that linking Samagra Shiksha funds to full NEP compliance infringes on the state's constitutional autonomy in education.
Tamil Nadu’s draft State Education Policy (SEP), submitted in July, clearly indicates that the State wants to stick to the 5+3+2+2 curricular formula, rather than the NEP, which includes the pre-school years. The SEP also proposes five years as the age of entry to Class 1, as against six years in the NEP. The State wants undergraduate college admissions to be based on Class 11 and 12 marks, rather than a common entrance test as proposed by the NEP. The biggest hurdle, however, is the NEP’s three-language formula.
Why does Tamil Nadu oppose the three-language formula?
The NEP 2020 recommends using the mother tongue or local language as the medium of instruction until Class 5, with all students learning at least three languages, including two native to India. This three-language formula has been part of every NEP since 1968 but has faced long-standing opposition in Tamil Nadu, rooted in historical movements against mandatory Hindi.
Tamil Nadu follows a two-language policy, requiring students to study Tamil and English, while allowing the choice of an optional third language, such as Hindi. Education Minister Anbil Mahesh emphasized Tamil's importance in the state's identity alongside English proficiency.
While the NEP offers flexibility and states that no language will be imposed on any state, allowing students to choose Tamil as a third language, all major political parties in Tamil Nadu have rejected the three-language formula. In response to concerns about opposing mother-tongue education, Mahesh affirmed the state prioritizes inclusive learning with Tamil at its core.
Pink Bollworm Attack

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Haryana has seen an overall fall in acreage under cotton cultivation to 4.76 lakh hectares (lh) this kharif season from 6.65 lh in 2023. This has been accompanied by an increase in the area under rice from 15.20 lh to an all-time-high of 16.44 lh in the state.
Key Details:
- The reduction in the cotton area — also reported in neighbouring Rajasthan (from 7.91 lh to 5.13 lh) and Punjab (2.14 lh to 1 lh) — has been attributed mainly to PBW infestation.
- In May-June this year, at the time of sowing, the price of kapas (raw unginned cotton) averaged Rs 6,700-6,800 per quintal in Haryana mandis. This was against the average Rs 11,100-11,200 per quintal two years ago.
Pink Bollworm (PBW) Infestation:
- Impact: The pink bollworm has devastated cotton yields by attacking the bolls, which affects the weight and quality of the cotton. This pest has been particularly damaging since its appearance in 2017-18 and has caused significant losses in Haryana, Rajasthan, and Punjab.
- Spread: PBW spreads through the air and infected crop residues, which harbor larvae and spread to future crops. This infestation has led to a dramatic decrease in cotton acreage.
The spread of pink bollworm
- The pink bollworm first appeared in north India during the 2017-18 season in a few districts in Haryana and Punjab, primarily cultivating Bt cotton, and spread to Rajasthan by 2021.
- PBW primarily spreads through the air. Residue of infected crops, often left by farmers on the field to be used as fuel, can also harbour PBW larvae which can then infect future crops. Infected cotton seeds are another reason behind the pest’s spread.
Economic Impacts:
- Price Decline: The price of kapas (raw cotton) has dropped from Rs 11,100-11,200 per quintal to Rs 6,700-6,800, significantly impacting farmers’ profitability.
- Farmer Losses: Farmers like Shyam Sundar have reported substantial losses due to low yields and poor quality, leading them to switch to more profitable and reliable crops like paddy and guar.
Transition to Paddy
Water Requirements:
- Challenges: Paddy requires much more water compared to cotton. Farmers need to flood their fields, which is challenging in regions where groundwater is saline or limited.
- Current Practices: Despite the increased water requirements, some farmers have transitioned to paddy due to its potentially better economic returns, especially when paddy prices are relatively high.
Monsoon and Irrigation:
- Weather Dependence: The monsoon this year has been favorable, allowing some farmers to successfully grow paddy. However, reliance on monsoon and supplementary irrigation from tubewells is not sustainable in the long term.
Government and Expert Perspectives
Government Incentives:
- Subsidies: The Haryana government is offering incentives for farmers switching to alternative crops and using water-saving techniques like direct seeding of paddy.
- Support: While there is support available, the effectiveness and reach of these measures are mixed, and some farmers have faced issues with insurance claims and financial aid.
Expert Opinions:
- Temporary Solution: Experts caution that while switching to paddy may be a temporary solution, it is not sustainable long-term due to water scarcity and environmental concerns.
- Environmental Impact: Paddy cultivation contributes to higher carbon and methane emissions, which adds to the environmental challenges in the region.
Economic and Industry Implications
Cotton Industry Concerns:
- Reduced Production: Lower cotton production affects the entire supply chain, from textile manufacturers to cottonseed oil and meal producers.
- Potential Recovery: There is hope that reduced PBW infestation this year may lead to a recovery in cotton yields, but the extent of this recovery remains uncertain.
NIDHI Companies

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
The Registrar of Companies has imposed penalties on over two dozen Nidhi companies for breaches of the Companies Act, such as delayed financial filings and share allotment issues. Fines range from ?20,000 to ?12.5 lakh, with Sri Sathuragiri Nidhi receiving the highest penalty.
What is Nidhi Company?
A Nidhi Company is a unique NBFC regulated under the Companies Act, 2013, and the Nidhi Rules, 2014. Nidhi company signifies that these companies promote thrift and savings habits among their members by accepting deposits and providing loans. They primarily cater to their local communities and operate within a defined geographical area.
Requirements for Obtaining Nidhi Company Status:
Within One Year of Registration:
- Minimum Membership: A Nidhi company must have at least 200 members within one year of starting operations.
- Financial Strength: The company's net owned funds (equity share capital + free reserves - accumulated losses - intangible assets) must be ?10 lakh or more.
- Deposit Security: Unencumbered term deposits (deposits not pledged as security) must be at least 10% of the total outstanding deposits.
- Healthy Debt Ratio: The ratio of net owned funds to deposits should not exceed 1:20. This ensures the company has sufficient capital to back its deposit liabilities.
Compliance Filing:
If a Nidhi company meets all the above conditions within the first year, it must file form NDH-1 along with the prescribed fees within 90 days from the end of that financial year. The form needs to be certified by a practicing Chartered Accountant (CA), Company Secretary (CS), or Cost and Works Accountant (CWA).
Extension Option:
Companies that are unable to meet the requirements within the first year can apply for an extension of one additional financial year. To do so, they need to submit form NDH-2 to the Regional Director within 30 days from the end of the first financial year.
Strict Enforcement:
If a Nidhi company fails to meet the requirements even after the second financial year, it will be prohibited from accepting new deposits until it complies with the regulations. Additionally, it may face penalties for non-compliance.
Benefits of Nidhi Company Registration
Nidhi companies offer several advantages for entrepreneurs:
- Tax benefits: They can enjoy tax exemptions on their profits under certain conditions.
- Reduced regulatory burden: Compared to other NBFCs, Nidhi companies face less stringent regulations.
- Local focus: They cater to the specific financial needs of their communities, fostering local economic development.
- Enhanced credibility: Registration brings legitimacy and builds trust among members.
Eligibility for Nidhi Company Registration
For registration of Nidhi company, the following requirements must be met:
- Minimum members: A minimum of seven members are required at the time of incorporation.
- Minimum capital: The minimum paid-up capital must be Rs. 5 lakh.
- Business restrictions: Nidhi companies cannot undertake activities like issuing debentures or underwriting insurance.
- Profit distribution: They can only distribute a maximum of 20% of their net profit as dividend.
BHASKAR Platform

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, is set to launch a groundbreaking digital platform aimed at strengthening India’s startup ecosystem.
Key Details:
- The Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry (BHASKAR) initiative, under the Startup India program, is a platform designed to centralize, streamline, and enhance collaboration among key stakeholders within the entrepreneurial ecosystem, including startups, investors, mentors, service providers, and government bodies.
- This initiative aligns with the Government of India’s vision to transform India into a global leader in innovation and entrepreneurship, reinforcing the country’s commitment to the startup movement.
Empowering Innovation Through a Centralized Platform
- India, home to over 1,46,000 DPIIT-recognized startups, has rapidly become one of the world’s most dynamic startup hubs. BHASKAR seeks to leverage this potential by providing an all-encompassing, one-stop digital platform that addresses the challenges faced by entrepreneurs and investors alike.
- By serving as a centralized registry, BHASKAR will enable seamless access to a wide array of resources, tools, and knowledge that will help fuel the entrepreneurial journey from ideation to execution.
- BHASKAR is designed to foster a conducive environment for networking, collaboration, and growth within the startup ecosystem.
- By providing personalized BHASKAR IDs for each stakeholder, the platform will facilitate easier interaction, enhance searchability, and allow for efficient discovery of relevant opportunities and partnerships.
Key Features of BHASKAR
- The primary goal of BHASKAR is to build the world’s largest digital registry for stakeholders within the startup ecosystem. To achieve this, the platform will offer several key features:
- Networking and Collaboration: BHASKAR will bridge the gap between startups, investors, mentors, and other stakeholders, allowing for seamless interaction across sectors.
- Providing Centralized Access to Resources: By consolidating resources, the platform will provide startups with immediate access to critical tools and knowledge, enabling faster decision-making and more efficient scaling.
- Creating Personalized Identification: Every stakeholder will be assigned a unique BHASKAR ID, ensuring personalized interactions and tailored experiences across the platform.
- Enhancing Discoverability: Through powerful search features, users can easily locate relevant resources, collaborators, and opportunities, ensuring faster decision-making and action.
- Supporting India’s Global Brand: BHASKAR will serve as a vehicle for promoting India’s global reputation as a hub for innovation, making cross-border collaborations more accessible to startups and investors alike.
Driving Forward India’s Startup Ecosystem
- The launch of BHASKAR marks a significant step forward in the government’s ongoing efforts to promote innovation, entrepreneurship, and job creation. It will serve as a central hub where startups, investors, service providers, and government bodies can come together to collaborate, exchange ideas, and accelerate growth.
- By facilitating easy access to knowledge and resources, BHASKAR will help unlock the full potential of India’s startup ecosystem, driving the country’s emergence as a global leader in entrepreneurship. The platform will be pivotal in creating a more resilient, inclusive, and innovation-driven economy, laying the foundation for a prosperous future.
BHASKAR: Shaping the Future of India's Startups
As India’s startup ecosystem continues to grow, BHASKAR will play a critical role in enhancing the country’s global standing in entrepreneurship. By fostering a culture of collaboration, the platform will help startups overcome challenges and build innovative solutions that address the needs of tomorrow.
With the launch of BHASKAR, the Government of India is reinforcing its commitment to making India a leader in global innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
International Day of Democracy

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Karnataka marked the 'International Day of Democracy' by forming a 'historic' 2,500-km-long human chain as a symbol of equality, unity, fraternity, and participative governance. The massive human chain, which according to the Karnataka government will be the "world's longest", is being formed across the state from Bidar to Chamarajanagar, covering all 31 districts.
Key Highlights:
- Democracy Day is an annual celebration observed on September 15.
- The United Nations General Assembly established this day in 2007 to emphasise the global significance of democracy. It serves as a reminder that democracy is not merely a fixed condition, but an ongoing pursuit. It calls for active engagement from international organizations, nation-states, civil society and people to pursue the democratic idea.
International Day of Democracy History
- The International Day of Democracy was accredited by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) on November 8, 2007, by passing a resolution entitled “Support by United Nations system of efforts of governments to promote and consolidate new or restored democracies.”
- September 15 was chosen to coincide with the anniversary of the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s Universal Declaration on Democracy, which was adopted in Geneva on September 15, 1997.
- This declaration outlines the tenets of democracy proclaiming that democracy is “a system of government based on the freely expressed will of the people to determine their own political, economic, social and cultural systems and their full participation, through free and fair periodic elections, in the composition of their representative government.”
- After the Universal Declaration on Democracy, Qatar spearheaded the campaign to observe an International Day of Democracy at the United Nations.
- The first-ever International Day of Democracy was held in 2008.
International Day of Democracy Significance
- The International Day of Democracy evaluates global democracy, emphasising that it requires commitment and engagement from the international community, the national state governments, civil societies and individuals.
- The day also reminds the nations of the need to uphold the principles of democracy such as the freedom of speech enshrined in Article 19 of the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Trilobite fossils from upstate New York reveal extra set of legs
- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
A new study finds that a trilobite species with exceptionally well-preserved fossils from upstate New York has an additional set of legs underneath its head.
Key details:
- The research, led by the American Museum of Natural History and Nanjing University in China, suggests that having a fifth pair of head appendages might be more widespread among trilobites than once thought.
- Published in the journal Palaeontology, the study helps researchers better understand how trilobite heads are segmented.
Trilobites
- Trilobites are a group of extinct arthropods whose living relatives include lobsters and spiders.
- Like other arthropods, the bodies of trilobites are made up of many segments, with the head region comprised of several fused segments.
- As with other parts of the trilobite body (the thorax and tail), these segments were associated with appendages, which ranged in function from sensing to feeding to locomotion.
- Trilobites are a group of extinct marine arthropods that first appeared around 521 million years ago, shortly after the beginning of the Cambrian period, living through the majority of the Palaeozoic Era, for nearly 300 million years. They died out at the end of the Permian, 251 million years ago, killed by the end Permian mass extinction event that removed over 90% of all species on Earth. They were very diverse for much of the Palaeozoic, and today trilobite fossils are found all over the world.
- The name 'trilobite' comes from the distinctive three-fold longitudinal division of the dorsal exoskeleton into a central axis, flanked on either side by lateral (pleural) areas.
Two ways
The segments in the trilobite head can be counted in two different ways: by looking at the grooves (called furrows) on the upper side of the trilobite fossil’s hard exoskeleton, or by counting the pairs of preserved antennae and legs on the underside of the fossil. The soft appendages of trilobites are rarely preserved, though, and when looking at the segments in the trilobite head, researchers regularly find a mismatch between these two methods.
In the new study, researchers examined newly recovered specimens of the exceptionally preserved trilobite Triarthrus eatoni from upstate New York. These fossils, known for the gold shine of the pyrite replacement preserving them, show an additional, previously undescribed leg underneath the head.
Resolving mismatch
By making comparisons with another trilobite species, the exceptionally preserved Olenoides serratusfrom the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, the researchers propose a model for how appendages were attached to the head in relation to the grooves in the exoskeleton.
This model resolves the apparent mismatch and indicates that the trilobite head included six segments: an anterior segment associated with the developmental origin of the eyes and five additional segments, associated with one pair of antennae and four pairs of walking legs, respectively.
PM Gram Sadak Yojana-IV

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the proposal of the Department of Rural Development for “Implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana - IV (PMGSY-IV) during FY 2024-25 to 2028-29”.
- The financial assistance is to be provided for the construction of 62,500 Kms road for providing new connectivity to eligible 25,000 unconnected habitations and construction/upgradation of bridges on the new connectivity roads. Total outlay of this scheme will be Rs. 70,125 crore.
Details of the Scheme:
The details of the approval given by the Cabinet are as follows:
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana -IV is launched for financial year 2024-25 to 2028-29. Total outlay of this scheme is Rs. 70,125 crore (Central Share of Rs. 49,087.50 crore and Sate Share of Rs. 21,037.50 crore).
- Under this scheme 25,000 unconnected habitations of population size 500+ in plains, 250+ in NE & Hill Sates/UTs, special category areas (Tribal Schedule V, Aspirational Districts/Blocks, Desert areas) and 100+ in LWE affected districts, as per Census 2011 will be covered.
- Under this scheme 62,500 Km of all-weather roads will be provided to unconnected habitations. Construction of required bridges along the alignment of the all-weather road will also be provided.
Benefits:
- 25,000 unconnected habitations will be provided all weather road connectivity.
- The all-weather roads will play the role of catalysts for the required socio-economic development and transformation of the remote rural areas. While connecting habitations, the nearby government educational, health, market, growth centers will be connected, as far as feasible, with the all-weather road for the benefit of the local people.
- The PMGSY -IV will incorporate international benchmarks and best practices under road constructions such as Cold Mix Technology and Waste Plastic, Panelled Cement concrete, Cell filled concrete, Full Depth Reclamation, use of construction waste and other wastes such as Fly Ash, Steel Slag, etc.
- PMGSY -IV road alignment planning will be undertaken through the PM Gati Shakti portal. The planning tool on PM Gati Shakti portal will also assist in DPR preparation.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- PMGSY is a central government scheme launched in 2000 to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected rural habitations.
- The scheme was originally a 100% centrally-sponsored initiative, but starting from the financial year 2015-16, the funding has been shared between the Central and State governments in a 60:40 ratio.
National Florence Nightingale Awards 2024

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
President Droupadi Murmu honored 15 exemplary nursing professionals with the National Florence Nightingale Awards 2024, recognizing their extraordinary healthcare service.
Key Details:
- The National Florence Nightingale Award was instituted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India in the year 1973 as a mark of recognition for the meritorious services rendered by the nurses and nursing professionals to the society.
- A total of 15 awards are given in the category of registered auxiliary nurses and midwife, registered nurses and midwife and registered lady visitor, the statement said.
- The award is given to outstanding nursing personnel employed in central, states and Union territories and voluntary organisations.
- The nurse in her/his regular job in the hospital or community settings, educational or administrative setting is eligible for the national award.
- Each award consists of a Certificate of Merit, a cash award of ? 1,00,000 and a medal.
A Legacy of Florence Nightingale
- The National Florence Nightingale Awards, are named in honor of Florence Nightingale, the founder of modern nursing.
- Nightingale’s pioneering work during the Crimean War laid the foundation for professional nursing, and her relentless efforts in promoting hygiene and compassionate care revolutionized healthcare practices worldwide.
- In her honor, International Nurses Day is celebrated every year on May 12, her birthday.
Chamran-1 satellite

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
Iran successfully launched its Chamran-1 research satellite into orbit, utilising the Qaem-100 rocket developed by the paramilitary Revolutionary Guard.
Key Highlights:
- Satellite Details: Chamran-1, a research satellite, was designed and manufactured by Iranian engineers at Iran Electronics Industries (SAIran) in collaboration with the Aerospace Research Institute and private firms. It weighs approximately 60 kilograms.
- Launch Vehicle: The satellite was launched into orbit using the Ghaem-100, Iran's first three-stage solid-fuel space launch vehicle (SLV), developed by the Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- Mission Objectives: The primary mission of Chamran-1 is to test hardware and software systems for validating orbital maneuver technology. Additionally, it aims to assess the performance of cold gas propulsion subsystems and evaluate navigation and attitude control subsystems.
- Orbit Details: The satellite was placed into a 550-kilometer (341 miles) orbit above Earth.
What are Intercontinental ballistic missiles?
- Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are a type of ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometers and are primarily designed to deliver nuclear warheads.
- They can carry conventional, chemical, and biological weapons, although the latter types have rarely been deployed on ICBMs.
- The United States, Russia, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, Israel, and North Korea are known to possess operational ICBMs, with Pakistan being the only nuclear-armed state that does not have them.
Operation Sadbhav

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
India has launched Operation Sadbhav to deliver crucial humanitarian aid to Myanmar, Laos, and Vietnam, all of which have been devastated by Typhoon Yagi. This powerful storm, the most severe in Asia this year, has led to extensive flooding and widespread destruction across the affected countries.
Relief Efforts:
In response to the crisis, India has mobilized a significant amount of aid. The Indian naval ship INS Satpura has transported 10 tonnes of relief supplies, including dry rations, clothing, and medicines, to Myanmar. Concurrently, the Indian Air Force has dispatched a military transport aircraft with 35 tonnes of aid to Vietnam and an additional 10 tonnes to Laos. The aid includes essential items such as generators, water purification systems, hygiene kits, mosquito nets, blankets, and sleeping bags, which are crucial for addressing immediate needs during this emergency.
India's Proactive Approach:
Operation Sadbhav highlights India's proactive approach to humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, emphasizing its role as a leading responder in the region. This initiative reflects India's commitment to providing support to its neighboring countries in times of crisis and aligns with its broader 'Act East Policy,' which aims to strengthen relations with ASEAN member states through practical assistance and cooperation.
Strategic Importance:
The operation also underscores India's strategic goals of enhancing regional stability and reinforcing its position as a reliable partner in disaster management. By providing timely aid, India demonstrates its dedication to supporting regional stability and contributing to international humanitarian efforts.
Global Recognition and Cooperation:
India's response to Typhoon Yagi has received international acknowledgment for its effectiveness and promptness. The coordination of these relief efforts highlights the importance of global solidarity in addressing humanitarian crises and building resilience in disaster-affected regions.
Conclusion:
Operation Sadbhav is a clear demonstration of India's commitment to timely and substantial humanitarian assistance. It not only showcases India's proactive diplomacy but also strengthens its ties with ASEAN nations through meaningful cooperation in times of adversity. The ongoing relief efforts are a testament to India's role as a responsible global stakeholder in disaster response and recovery.
What is Operation Kawach, the new ‘war on drugs’ waged by Delhi Police?

- 05 Sep 2024
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, 'Operation Kawach' is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police.
In a major crackdown on the menace of drugs in the national capital, the Crime Branch of the Delhi Police conducted widespread raids, swooping down on over 100 locations across Delhi. Earlier, raids conducted during the intervening night of May 12 and 13 had led to the arrest of 31 drug offenders in 30 cases under the Narcotic-Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985.
As many as 12 bootleggers were also arrested in six cases of the Excise Act. The operation also saw the seizure of 957.5 grams of heroin, 57.8 kilograms of marijuana and 782 bottles of illicit liquor.
What is Operation Kawach?
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, ‘Operation Kawach’ is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police. The initiative aims to combat the harmful influence of drug addiction on youth and children and underscores the authorities’ commitment to safeguarding the well-being of young individuals and curbing the distribution of illicit substances in educational settings.
Operation Kawach is primarily intended to save the youth from the menace of drugs. Although the focus is to take stringent action on the supply side, it is also appealed to society to create awareness and reduce the demand of drugs. The parents, teachers and the social reformers are specially requested to sensitise the youth about the grave consequences of drug addiction.
Operation Kawach: The story so far
According to the official, the joint operations, which utilised a variety of resources such as undercover officers, surveillance, canine support and intelligence gathering, targetted both street-level dealers and high-level traffickers and have both ‘top-to-bottom’ and ‘bottom-to-top’ approaches to effectively counter drug trafficking in the national capital.
In this year, Delhi Police has arrested 534 narco-offenders in 412 NDPS cases. Around 35 kg of heroin/smack, 15 kg of cocaine, 1,500 kg of ganja, 230 kg of opium, 10 kg of charas and 20 kg of poppy have been recovered during these operations.
Black Coat Syndrome

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
In her recent speech at the National Conference of District Judiciary, President Droupadi Murmu introduced the concept of 'black coat syndrome' to address the persistent issue of case delays in Indian courts. This term is intended to reflect the anxiety and reluctance that people experience when dealing with the judicial system, similar to the 'white coat syndrome' seen in medical settings.
Current Challenges in India's Judicial System
- Case Pendency: As of October 2023, there are over five crore cases pending across various levels of the judiciary in India. The current number of judges—20,580—falls short of effectively managing this caseload.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Many courts lack essential infrastructure and modern technology. For example, as of September 2023, 19.7% of district courts did not have separate toilets for women.
- Judicial Vacancies: There are notable vacancies in the judiciary. High courts have 347 unfilled positions out of a total of 1,114 sanctioned posts. Similarly, 5,300 out of 25,081 district judge positions are vacant.
- Gender Representation: The Supreme Court has three female judges, making up 9.3% of its bench. High courts have 103 female judges, representing 13.42%, while the district judiciary has a more balanced representation with 36.33% female judges.
Ongoing Initiatives to Address Judicial Challenges
- Technological Advancements:
- e-SCR (Electronic Supreme Court Reports): Provides digital access to Supreme Court judgments.
- Virtual Court System: Facilitates court proceedings through videoconferencing.
- eCourts Portal: Serves as a comprehensive platform for interaction among litigants, advocates, government bodies, and the public.
- National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG): Makes case statistics available at various levels for public and research use.
- Legal Reforms and Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR):
- National Mission for Justice Delivery and Legal Reforms (2011): Focuses on improving justice access by tackling delays and arrears.
- ADR Methods: Includes Lok Adalats, Gram Nyayalayas, and Online Dispute Resolution to expedite justice.
- Commercial Courts Act 2015: Enforces pre-institution mediation for commercial disputes.
- Fast Track Courts: Designed to speed up cases involving serious crimes, senior citizens, women, and children.
Strategies for Future Improvement
- Increasing Court Efficiency: The Chief Justice of India has stressed the need for courts to function beyond their current capacity of 71% to better align case disposal with new case inflows.
- Filling Judicial Positions: With 28% of district court positions vacant, a regularized recruitment schedule is suggested to address these gaps. Additionally, integrating judicial recruitment on a national scale is recommended to reduce regional biases.
- Enhancing Case Management: Establish District-Level Case Management Committees to better manage cases by reconstructing records and identifying priority cases. Encouraging pre-litigation dispute resolution can also help manage the case backlog.
- Adjusting Judicial Vacations: The 2003 Malimath Committee report proposed reducing vacation periods to help address the backlog of cases.
- Bridging Judiciary Gaps: Addressing the disparity between district courts and high courts is crucial to create a more cohesive and unified judicial system.
Poshan Tracker Initiative
- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Women and Child Development recently earned the National Award for e-Governance 2024 (Gold) for its Poshan Tracker initiative, which has made significant strides in enhancing child health and nutrition.
About the Poshan Tracker Initiative
The Poshan Tracker initiative focuses on identifying and addressing growth-related issues in children aged 0-6 years. By using real-time monitoring and WHO growth charts, the program ensures that children receive optimal nutrition.
Key components of the initiative include:
- Role of Anganwadi Workers (AWWs): These workers are essential in assessing children's health and implementing necessary interventions when deviations from expected growth are observed.
- Technology Integration: The program employs advanced ICT tools and Growth Measuring Devices (GMD) at Anganwadi Centers (AWCs) to enable precise data collection and regular monitoring.
- Impact: Real-time growth monitoring through the Poshan Tracker has substantially improved child health outcomes in India, benefiting millions of children under the Mission Poshan 2.0 initiative.
Key Features of the Poshan Tracker App
- Comprehensive Overview: The app offers a complete view of Anganwadi Centre activities, including service deliveries and beneficiary management for pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children under six.
- Digitization and Automation: It replaces physical registers used by workers with digital records, thereby enhancing the quality and efficiency of their work.
- Smartphone Provision: Anganwadi workers have been provided with smartphones through the Government e-Market (GeM) to streamline service delivery.
- Technical Support: Each state has a designated nodal person to provide technical assistance and resolve issues related to the Poshan Tracker application.
- Service Accessibility: Migrant workers who registered in their original state can access services at the nearest Anganwadi in their current location.
RHUMI-1

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
India recently celebrated the launch of its first reusable hybrid rocket, RHUMI-1, developed by the Tamil Nadu-based start-up Space Zone India in collaboration with the Martin Group. The launch took place on August 24, 2024, from Thiruvidandhai in Chennai. This innovative rocket was propelled into a suborbital trajectory using a mobile launcher, carrying three Cube Satellites and fifty Pico Satellites designed to gather data on global warming and climate change.
Key Features of RHUMI-1:
- Hybrid Propulsion System: RHUMI-1 utilizes a combination of solid and liquid propellants, which enhances efficiency and lowers operational costs.
- Adjustable Launch Angle: The rocket's engine allows for precise trajectory control with adjustable angles ranging from 0 to 120 degrees.
- Electrically Triggered Parachute System: Equipped with an advanced and eco-friendly descent mechanism, this system ensures safe recovery of rocket components, offering both cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits.
- Environmentally Friendly: RHUMI-1 is entirely free of pyrotechnics and TNT, underlining its commitment to sustainability.
Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLVs):
Reusable Launch Vehicles are spacecraft designed to be launched, recovered, and reused multiple times. They offer several advantages:
- Cost Savings: RLVs can be up to 65% cheaper than constructing a new rocket for every launch.
- Reduced Space Debris: By minimizing discarded rocket components, RLVs help reduce space debris.
- Increased Launch Frequency: Shorter turnaround times allow for more frequent use of the rocket.
Unlike traditional multi-stage rockets, where the first stage is discarded after fuel depletion, RLVs recover and reuse the first stage. After separation, the first stage returns to Earth using engines or parachutes for a controlled landing.
Background on Space Zone India and Recent Missions:
Space Zone India is an aero-technology company based in Chennai, focusing on providing cost-effective, long-term solutions in the space industry. They offer hands-on training in aerodynamic principles, satellite technology, drone technology, and rocket technology while raising awareness about careers in the space sector. In 2023, Space Zone India conducted the "Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam Students Satellite Launch Mission," involving over 2,500 students from various schools across India. This mission resulted in the creation of a student satellite launch vehicle capable of carrying a payload of 150 Pico Satellites for research experiments.
Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
On August 1, 2024, the central government introduced the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill in the Lok Sabha. This Bill, aimed at amending the existing Disaster Management Act of 2005, has been proposed in response to the increasing frequency of climate-induced disasters. However, the Bill’s provisions have raised concerns about further centralisation of disaster management processes, which may complicate and delay disaster response efforts.
Centralisation Concerns
The Bill continues the trend of centralising disaster management, a feature already prevalent in the 2005 Act. It grants statutory status to existing bodies like the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) and the High-Level Committee (HLC), potentially complicating the disaster response process. This centralised approach has previously led to delays, such as the late disbursement of funds to Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, contrary to the Act's intended rapid response.
Proposed Changes
Strengthening NDMA and SDMAs: The Bill aims to bolster the role of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) by having them prepare disaster management plans directly. It also introduces Urban Disaster Management Authorities (UDMAs) for state capitals and major cities, although these bodies may face challenges due to insufficient financial devolution.
Database and Staffing: The Bill mandates the creation of comprehensive disaster databases at national and state levels and allows the NDMA to appoint its own staff, subject to central government approval.
Issues with the Current Definition of ‘Disaster’
Heatwaves Exclusion: On July 25, 2024, the Minister of State for Science, Technology, and Earth Sciences announced that heatwaves will not be classified as a notified disaster under the Act. This decision aligns with the 15th Finance Commission’s view and maintains a restricted list of disasters eligible for assistance, which includes cyclones, droughts, earthquakes, and floods, but excludes climate-induced phenomena like heatwaves.
Inadequate Definition: The existing definition of "disaster" in the Act and the Bill remains narrow, failing to encompass climate-induced events such as heatwaves, which are increasingly recognized globally as significant disasters. Data from the India Meteorological Department shows a record number of heatwave days and related fatalities, highlighting the need for a broader disaster definition.
Critical Issues
Central-State Dynamics: The Bill’s centralisation raises questions about the balance of power between central and state governments. There are concerns that states will remain heavily dependent on central funds, complicating disaster management and response.
Lessons Unlearned: Despite being an update to the 2005 Act, the Bill appears to overlook past shortcomings, including delays in financial preparedness and response. A focus on cooperative federalism and effective disaster management should prioritize practical solutions over a central versus state blame game.
Future Directions: Addressing the challenges of climate-induced disasters and ensuring effective financial and operational preparedness requires revisiting and refining the disaster management framework. Emphasizing cooperative federalism and proactive disaster management strategies will be crucial in improving disaster resilience and response in the face of escalating climate risks.
India-France Bilateral Naval Exercise VARUNA

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
The 22nd edition of the India-France bilateral naval exercise, VARUNA, took place in the Mediterranean Sea from September 2 to 4, 2024. This exercise highlights the strong maritime partnership between the Indian Navy and the French Navy, showcasing their commitment to enhancing interoperability and operational effectiveness.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Vessels and Aircraft:
- Indian Navy:
- INS Tabar: A frontline stealth frigate commanded by Captain MR Harish.
- Ship-borne Helicopter: Provided air support during the exercises.
- LRMR Aircraft P-8I: An advanced long-range maritime reconnaissance aircraft.
- French Navy:
- FS Provence: A French naval ship participating in the exercise.
- Submarine Suffren: A French attack submarine.
- Aircraft F-20: Providing air support.
- Atlantique 2: A French maritime patrol aircraft.
- Fighters MB339: Multi-role fighter aircraft.
- Helicopters NH90 and Dauphin: Providing additional aerial capabilities.
- Indian Navy:
- Exercise Activities:
- Tactical Maneuvers: Advanced maneuvers showcasing the operational capabilities of both navies.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare: Exercises designed to enhance capabilities in detecting and countering submarines.
- FLYEX (Flight Exercises): Coordinated air operations involving various aircraft.
- Air Defence Exercise: Training in defending against aerial threats.
- Live Weapon Firings: Demonstrations of weapon systems in action.
- PHOTO-EX (Photographic Exercise): Exercises designed for documenting and assessing naval operations.
- Steam Past: A ceremonial maneuver showcasing the participating ships.
- Significance of the Exercise:
- Evolution of VARUNA: Since its inception in 2001, VARUNA has become a key component of the India-France naval relationship. The exercise has evolved to improve interoperability and share best practices between the two navies.
- Strategic Importance: Conducting the exercise in the Mediterranean Sea reflects the Indian Navy's capability and commitment to operate far beyond the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). It underscores the strategic depth and outreach of the Indian Navy.
- Enhanced Interoperability: VARUNA demonstrates the mutual commitment of India and France to enhancing naval collaboration and operational effectiveness through joint exercises and shared experiences.
- Future Outlook:
- Commitment to Partnerships: The Indian Navy continues to prioritize building strong partnerships with like-minded navies worldwide. The VARUNA exercise is a testament to this ongoing commitment and the broader strategic goals of both India and France in strengthening maritime security and cooperation.
This bilateral exercise not only enhances the operational capabilities of both navies but also reinforces the strategic partnership between India and France in the maritime domain.
India’s $15 Billion Push for Chipmaking
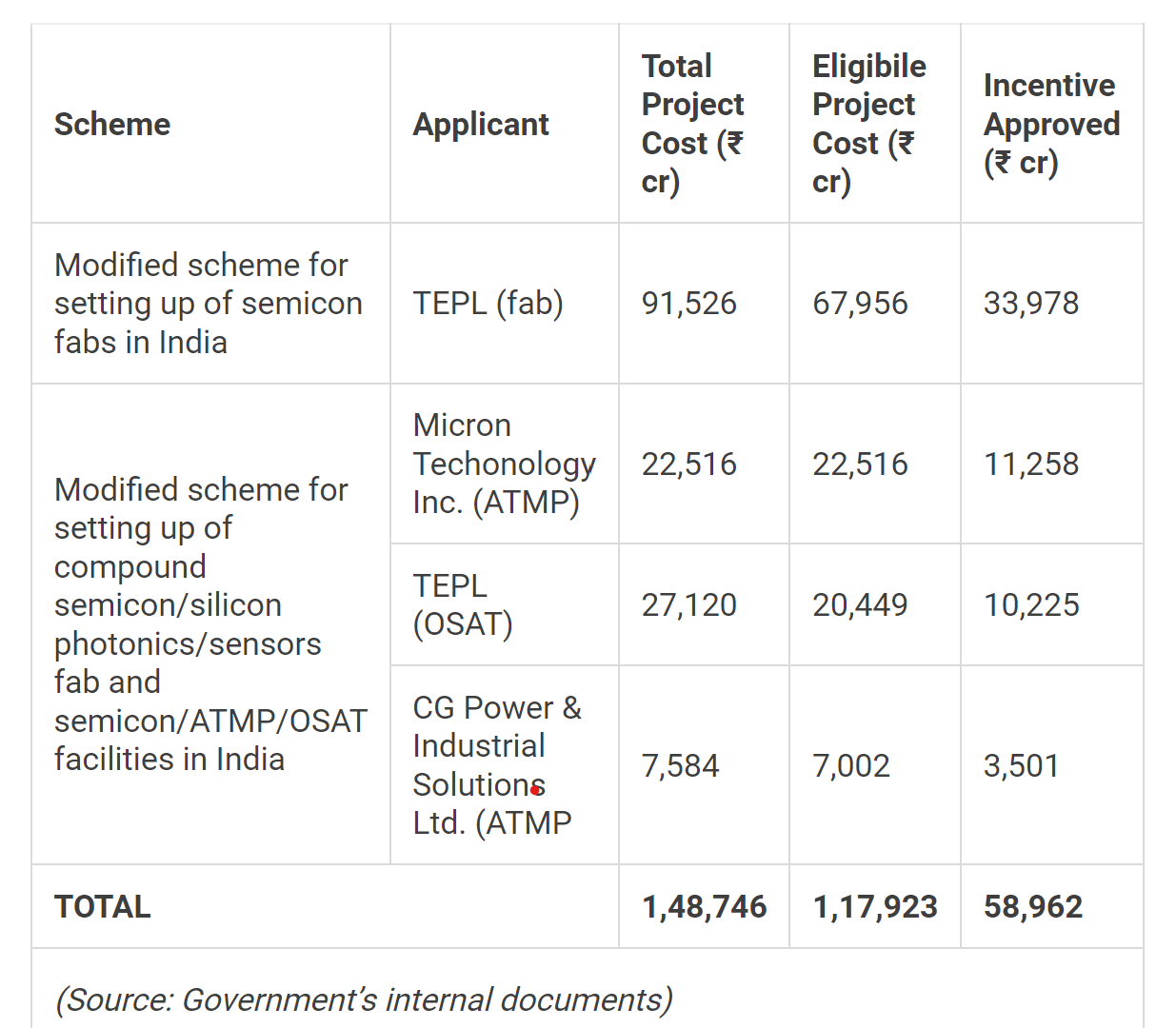
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
India is significantly ramping up its efforts to establish a semiconductor manufacturing industry, with plans to invest $15 billion in the second phase of its chipmaking incentive policy. This move aims to bolster the country's position in the global semiconductor supply chain, where it currently has minimal presence.
Key Points:
- Government Funding and Projects:
- Increased Investment: The Indian government is boosting its funding for chipmaking incentives to $15 billion, up from the $10 billion committed in the first phase.
- Approved Projects: Four major semiconductor projects have been approved, totaling over Rs 1.48 lakh crore ($18 billion). This includes:
- Tata and PSMC Fabrication Plant: India’s first commercial semiconductor fabrication plant, with an investment of more than Rs 91,000 crore ($11 billion), developed in partnership with Taiwan’s Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (PSMC).
- Assembly and Testing Plants (ATMP/OSAT): Three plants:
- Micron Technology is building the first plant, approved in June 2023.
- Tata is constructing an assembly plant in Assam.
- C G Power and Industrial Solutions, in partnership with Japan’s Renesas Electronics, is developing the third plant.
- Government Subsidies:
- Capex Subsidies: The central government will provide nearly Rs 59,000 crore ($7 billion) in capital expenditure subsidies for these projects.
- State Support: State governments are offering incentives such as discounted land and electricity rates.
- Strategic Importance:
- Economic and Strategic Impact: Semiconductor chips are critical to a wide range of industries, including defense, automotive, and consumer electronics. Developing domestic chipmaking capabilities is seen as essential for economic growth and strategic independence.
- Global Competition: India is entering a highly competitive field dominated by Taiwan and the US. The US has a $50 billion chip incentive scheme, while the EU has a similar program. India’s efforts are part of a broader strategy to reduce dependence on global chip supply chains and capitalize on geopolitical shifts.
- Challenges and Realities:
- Technology Barriers: The Tata-PSMC plant will not produce cutting-edge chips, as the technology for advanced nodes is currently beyond their reach. Manufacturing chips with smaller node sizes involves significant technological expertise and innovation, areas where leading companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) excel.
- High Entry Barriers: The chipmaking industry has high entry barriers, and India’s new plants will face challenges in achieving technological and competitive parity with established global leaders.
India's push into semiconductor manufacturing represents a major step in its economic development and strategic planning, aiming to position itself as a significant player in the global tech landscape while addressing critical supply chain vulnerabilities.
India-Maldives Defence Talks

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
- India and the Maldives held their first defence talks since India withdrew its military personnel early this year.
Significance of Talks:
- The dialogue is notable given recent tensions in bilateral relations. Relations soured after President Mohamed Muizzu's election on an "India Out" platform, leading to the withdrawal of Indian troops. The last defence cooperation dialogue was held in March 2023 under President Ibrahim Solih.
Discussion Topics:
-
- Expediting ongoing defence cooperation projects.
- Planning forthcoming bilateral military exercises.
- Enhancing high-level exchanges and capability development.
Context of Tensions:
-
- Mohamed Muizzu, who took office in November 2023, had called for the removal of Indian military personnel, a significant shift from the previous administration’s stance.
- India agreed to withdraw 80 military personnel between March and May 2024. Indian technical personnel now operate key equipment like helicopters and a Dornier aircraft in the Maldives.
Recent Developments:
-
- Maldives Foreign Minister Moosa Zameer visited India in May.
- President Muizzu attended PM Narendra Modi’s swearing-in ceremony in June.
- In August, Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar visited the Maldives to reaffirm bilateral ties.
Historical Defence Cooperation:
-
- India gifted a Dornier aircraft to the Maldives in 2020 and a patrol vessel in 2019.
- India provided a coastal radar system last year and laid the foundation for the 'Ekatha Harbour' project, enhancing Maldivian Coast Guard capabilities.
Ongoing Projects:
-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) - a $500 million initiative financed by India.
- Building a new Coast Guard base at Uthuru Thilafalhu (UTF) atoll.
- India’s grant for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs).
Strategic Importance:
-
- For Maldives: India is a key security partner and crisis responder, with historical assistance during emergencies (Operation Neer, Vaccine Maitri). Maldives seeks to restore Indian tourist numbers, vital for its economy.
- For India: The Maldives is crucial to India's Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision SAGAR. Its strategic location between major Indian Ocean chokepoints makes it a vital partner for maritime security and countering China's influence.
Recent Changes:
-
- The Muizzu government decided not to renew a 2019 MoU for hydrographic surveying with India, ending joint hydrographic surveys conducted under the pact.
Travel and Trade:
-
- Both countries benefit from an open skies arrangement and visa-free access for tourism, medical, and business purposes
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
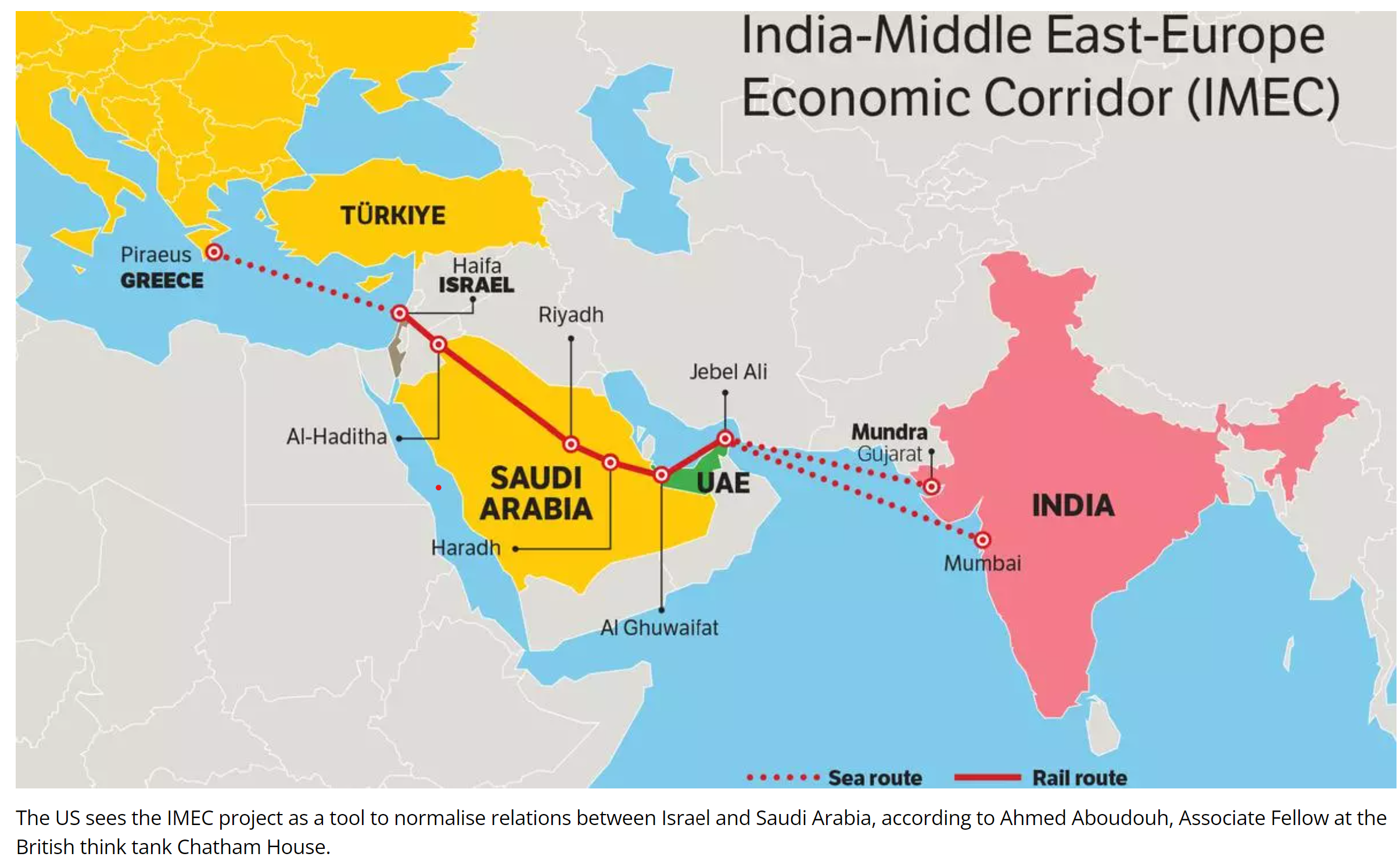
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
IMEC is an important initiative that can add to India's maritime security and faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia, said Union Minister of Commerce & Industry at the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) India-Mediterranean Business Conclave 2024 in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Corridors:
- East Corridor: Connects India to the Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe.
- Components:
- Railroad: Provides a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network.
- Ship-to-Rail Networks: Integrates road, sea, and rail transport routes.
- Road Transport: Complements the overall transport infrastructure.
- Expected Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Enhances transit efficiency and reduces costs.
- Economic Unity: Promotes economic integration and job creation.
- Environmental Impact: Lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transformative Integration: Connects Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Additional Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes laying cables for electricity and digital connectivity, and pipes for clean hydrogen export.
- Implementation:
- MoU Commitments: Participants will collaboratively address technical design, financing, legal, and regulatory aspects.
- Action Plan: A meeting is planned within 60 days to develop an action plan with specific timetables.
Geoeconomic Perspective
- Economic Integration and Interdependence:
- Prosperity Through Integration: IMEC aims to foster trade and investment among India, the Middle East, and Europe, potentially leading to mutual prosperity and regional stability.
- Building Bridges: Aligns with the liberal international order by promoting economic interdependence to reduce tensions and create shared interests.
- Support from Major Powers: Backed by the US, Europe, and India, signaling a strong commitment to economic ties and regional stability.
- Economic Potential:
- Infrastructure and Trade Routes: Enhances infrastructure and trade routes, boosting economic activity, trade volumes, and investment opportunities.
- Regional Development: Promotes job creation and development in economically disadvantaged areas along the corridor.
Geopolitical Perspective
- Strategic Rivalry with China:
- Countering the BRI: IMEC is seen as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering an alternative aligned with US, European, and Indian interests.
- Regional Influence: Aims to limit China’s influence in the Middle East and South Asia by establishing a competing corridor.
- Geopolitical Alliances:
- Aligning Interests: Involves strategic partnerships among the US, Europe, and India, reflecting concerns about China’s global strategy and shifting power dynamics.
- Rivalry and Competition: The IMEC could be viewed as a global positioning move, responding to China’s growing influence and securing strategic interests.
Reasons for Joining the IMEC
- Economic Enhancement:
- Boosts Indo-Gulf Relations: Enhances trade and economic ties with the Arab Gulf, addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Regional Connectivity: Links India with key partners like Israel and Jordan, boosting economic opportunities.
- Strategic Trade Routes:
- Alternative Routes: Complements existing routes like Chabahar Port and INSTC, connecting India to southern Eurasia.
- Bypassing Choke Points: Offers a shorter route to Eastern Mediterranean and Western Europe, avoiding strategic choke points.
- Energy and Trade Opportunities:
- Access to Resources: Provides potential access to Eastern Mediterranean gas fields.
- Trade Bloc Connectivity: Links India with the EU and GCC, opening up growth opportunities.
- Geopolitical Aspirations:
- Global Power Ambitions: Supports India’s goal to enhance global influence and integrate with eastern and western neighbors.
- Economic Growth: Leverages economic integration to support development and influence.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Economic Integration: Facilitates infrastructure creation for increased trade volumes and regional stability.
e-Sankhyiki portal

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has launched e-Sankhyiki portal with the objective to establish a comprehensive data management and sharing system for ease of dissemination of official statistics in the country.
Key Highlights:
- Launched on National Statistics Day 2024, the e-Sankhyiki portal is designed to create a comprehensive system for managing and sharing data, facilitating the easy dissemination of official statistics across the country.
- The portal is also accessible at - https://esankhyiki.mospi.gov.in. It aims to provide timely and valuable data inputs for policymakers, researchers, and the general public.
- It provides time series data for key macroeconomic indicators, with features for filtering and visualising the data. Users can also download customised datasets and visualisations and access them through APIs, enhancing the data's reusability.
- It consists of two modules viz. Data Catalogue and Macro Indicators.
- Data Catalogue Module:
- This module catalogues the Ministry’s major data assets, simplifying users' access. It enables searching within datasets and tables, downloading relevant data, and enhancing its value and reusability.
- The Data Catalogue includes seven core data products:
- Consumer Price Index
- Index of Industrial Production
- National Accounts Statistics
- Periodic Labour Force Survey
- Annual Survey of Industries
- Household Consumption Expenditure Survey
- Multiple Indicator Survey.
- It currently hosts over 2,300 datasets, each accompanied by specific metadata and visualisations for user convenience.
- Macro Indicators module:
- This module provides time series data on key macro indicators, featuring tools for filtering and visualising data.
- It allows users to download custom datasets, generate visualisations, and share data through APIs, promoting greater reusability. The initial phase of this module covering data from the past decade includes four major MoSPI products:
- National Accounts Statistics
- Consumer Price Index
- Index of Industrial Production
- Annual Survey of Industries
- The portal currently features over 1.7 million records, providing access to extensive vital data.
- Data Catalogue Module:
Government Initiatives for Safe Data Dissemination
- In response to the rapid data expansion, the Government of India has instituted robust data safety measures. These include storing data in the cloud facilities provided by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), conducting comprehensive security audits of applications, and implementing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) technology for domain protection.
- Additionally, the government has focused on vulnerability assessments and ensured compliance with guidelines issued by organisations such as NIC and the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In).
- In addition , CERT-In under the Ministry of Electronics and Information technology (MeitY) also undertakes various activities like issuance of advisories and guidelines for cyber/information security, conduct of sensitization programmes/trainings/workshops, operating Cyber Threat exchange platform & Cyber Swachhta Kendra, formulation of a Cyber Crisis Management Plan, setting up of National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) and empanelment of security auditing organisations etc. for data safety.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024

- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of State for Women and Child Development, launched the Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024 in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh on 1st September,2024.
Key Highlights:
- As part of the 7th Rashtriya POSHAN Maah, awareness programs are being organized at various levels.
- Under the ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services) Project, complementary feeding activities were conducted at Anganwadi Centres (AWC) Paduck Bagicha, South Andaman.
- Also, at AWC, Champin Nancowrie, Nicobar district (Andaman & Nicobar) under the ICDS Tribal initiative, local food items and nutrition sources were displayed.
- These efforts aim to further the Prime Minister's vision of a ‘Suposhit Bharat’ by conducting diverse large-scale activities, harnessing the potential of Gram Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah:
- The programme is annually celebrated in the month of September, with a different theme each year, primarily focusing on addressing malnutrition by ensuring convergence of various nutrition-related schemes and programmes.
- The objective of the Poshan Maah is to ensure community mobilisation and bolster people’s participation for addressing malnutrition amongst young children, and women and to ensure health and nutrition for everyone.
Poshan Abhiyaan:
- POSHAN Abhiyan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme For Holistic Nourishment) focuses on advancing nutritional outcomes for children under six years, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- To cultivate widespread awareness about nutrition at each stage of life, it is celebrated annually as Poshan Maah (1st—30th September) and Poshan Pakhwada (fortnight of March).
- POSHAN Abhiyan (National Nutrition Month) aims to strengthen efforts to end hunger and malnutrition.
- It focuses to improving the nutritional outcomes among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers by focusing on prenatal care, diet, and optimal breastfeeding.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development plans month-long activities under Poshan Maah, focusing on issues such as the hygiene and sanitation, anaemia prevention, maternal and infant health, among others.
- There are outreach programmes, identification drives, camps, and fairs with a special focus on pregnant and lactating women, children below six years, and adolescent girls in order to realise the vision of ‘Swasth Bharat’.
SAMRIDH Scheme
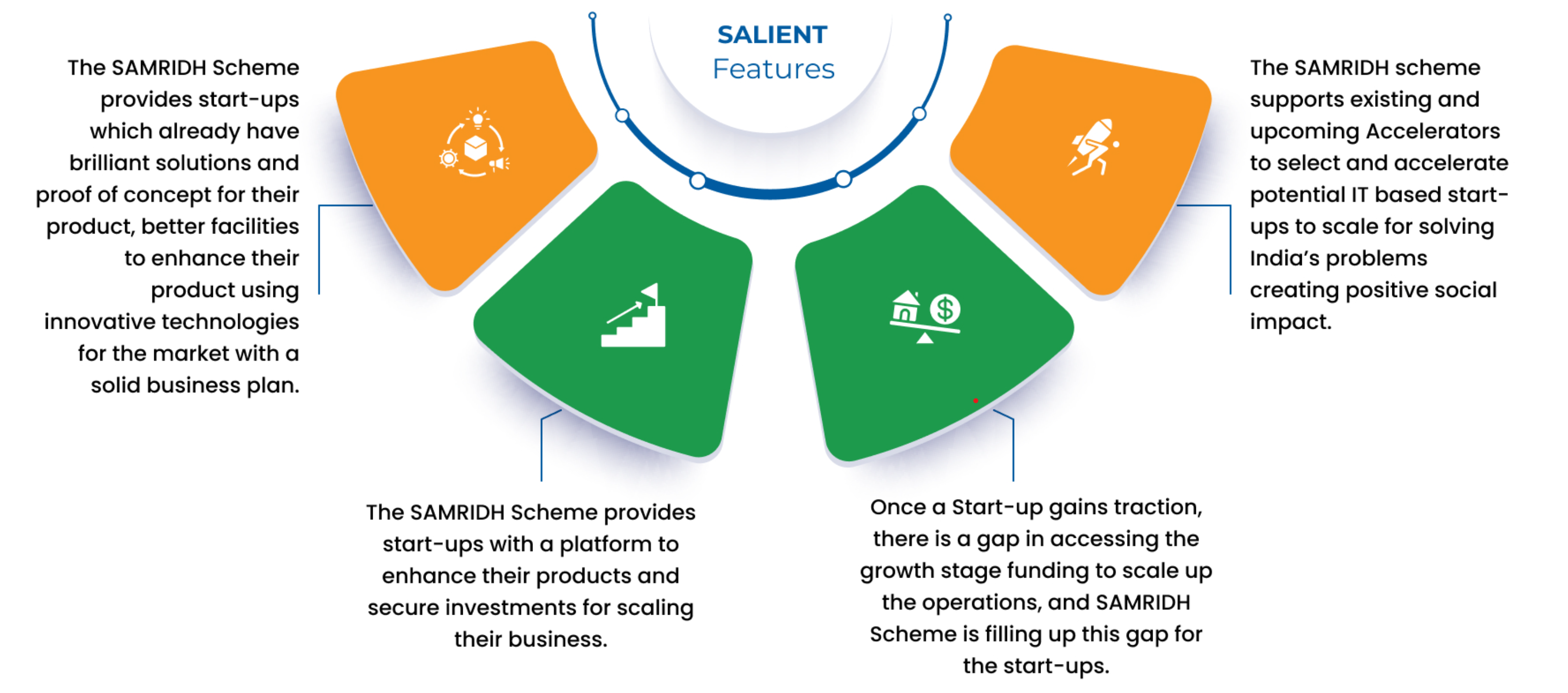
- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launches 2nd Cohort of Startup Accelerators of MeitY for Product Innovation, Development and Growth (SAMRIDH).
About SAMRIDH Scheme:
- SAMRIDH is a flagship programme of MeitY for startups acceleration under National Policy on Software Products – 2019.
- The SAMRIDH programme, launched in August 2021 aims to support 300 software product startups with outlay of ?99 crore over a period of 4 years.
- SAMRIDH is being implemented through potential and established accelerators across India which provide services like making products market fit, business plan, investor connect and international expansion to startups plus matching funding upto ?40 lakh by MeitY.
- The scheme is being implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH), Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- In the first round of cohort, 22 Accelerators spread across 12 states are supporting 175 startups, selected through a multilevel screening process.
- Major Objective:
- The SAMRIDH scheme aims to support existing and upcoming Accelerators to select and accelerate potential IT-based startups to scale.
- Among others, the program focuses on accelerating the startups by providing customer connect, investors connect and connect to international markets
- Eligibility of Accelerator:
- Should be a registered Section-8/Society, [Not-for-Profit Company (eligible to hold equity)] having operations in India.
- The Accelerator and the team are recommended to have more than 3 years of startup experience and should have supported more than 50 start-ups of which at least 10 startups should have received investment from external Investors
- The Accelerator should have an experience of running startup program cohorts with activities listed as desirable under SAMRIDH program.
AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union agriculture minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched two initiatives — a fund aimed at boosting farm-sector startups, and a single-window portal to process investments — as part of a slew of measures being taken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government in its third term to bolster the farm economy.
Key Details:
- AgriSure is a ?750-crore fund established to support agricultural startups.
- Krishi Nivesh Nidhi is a portal designed to expedite the clearance of project proposals.
- Both initiatives aim to enhance farm incomes.
Awards for Credit Disbursal:
- Scheduled banks were recognized for their credit disbursals under the government’s agriculture infrastructure fund.
- First prize: State Bank of India (SBI).
- Second prize: HDFC Bank.
- Third prize: Canara Bank.
Significance of Agriculture Sector:
- Agriculture contributes 16% to India’s GDP.
- Farmers play a crucial role as both producers and consumers in the economy.
PM Modi’s Strategy to Double Farmers’ Incomes:
- The strategy includes:
- Increasing output.
- Reducing input costs.
- Ensuring profitable prices.
- Promoting crop diversification.
- Supporting natural farming.
- Enhancing value addition to crops.
Details of AgriSure Fund:
- Blended capital fund with a total corpus of ?750 crore:
- ?250 crore each from the Department of Agriculture and NABARD.
- ?250 crore to be raised from financial institutions.
- Managed by NabVentures, a subsidiary of NABARD.
- Provides both equity and debt support to startups and agripreneurs.
- Focuses on high-risk, high-impact activities within the agriculture value chain.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:
- Mobilized projects worth ?78,000 crore with ?45,000 crore in financing so far.
- Expanded areas of coverage approved by the Union Cabinet on August 28.
- Aims to create durable farm assets, such as warehouses and processing plants.
- Can be used by agricultural produce marketing committees (APMCs) for market facility improvements.
Funding and Loan Details:
- Part of the ?20-lakh crore stimulus package introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Total funding of ?1 lakh crore over four years:
- ?10,000 crore for 2020-21.
- ?30,000 crore each for the subsequent three financial years.
- Provides medium-to-long term debt financing for rural projects.
- Interest subvention of 3% per annum on loans up to ?2 crore for seven years, with the government covering part of the interest.
eShram portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Labour & Employment (MoLE) stated in a latest update that in the short span of three years since its launch, eShram has registered more than 30 crore unorganised workers, showcasing its rapid and widespread adoption among the unorganised workers.
Key Highlights:
- The Government envisages to establishing the eShram portal as a "One-Stop-Solution" for Country’s unorganised workers.
- During Budget speech 2024-25 it has been announced that, A comprehensive integration of eShram portal with other portals will facilitate such One-Stop-Solution.
- This initiative aims to facilitate access of various social security schemes being implemented by different Ministries/ Departments to unorganised workers through the eShram portal.
- As part of the eShram - One Stop Solution project, Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) has been working to integrate major schemes like Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), Pradhan Mantri Street Vendors Atmanirbhar Nidhi (PM-SVANidhi), Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G), Ration Card scheme etc. for the benefit of the unorganised workers.
What is e-Shram and its purpose?
- e-Shram is a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers (NDUW) launched by the Government of India under the Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- Its primary purpose is to facilitate delivery of welfare benefits and social security measures to unorganised sector workers across the country.
- The platform aims to register and provide identity cards to unorganised workers, enabling them to access various government schemes, benefits, and services more efficiently.
Who are unorganised workers?
Any worker who is a home-based worker, self-employed worker or a wage worker working in the unorganised sector and not a member of ESIC or EPFO, is called an unorganised worker.
What is unorganised sector?
Unorganised sector comprises of establishment/ units which are engaged in the production/ sale of goods/ services and employs less than 10 workers. These units are not covered under ESIC & EPFO.
What is UAN?
UAN or Universal Account Number is a 12 digit number uniquely assigned to each unorganised worker after registration on e-Shram portal. UAN is a permanent number i.e., once assigned, it will remain unchanged for any worker.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the proposal of Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd to setup a semiconductor unit in Sanand, Gujarat, with an investment of Rs 3,300 crore.
Key Highlights:
- The proposed unit, under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), will produce nearly 60 lakh chips per day.
- The chips produced in this unit will cater to a wide variety of applications which include segments such as industrial, automotive, electric vehicles, consumer electronics, telecom and mobile phones, etc.
- The initiative aligns with India’s goal of developing indigenous semiconductor capabilities.
- As per the reports, India’s semiconductor market is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, positioning the country as a major global semiconductor hub.
- The first indigenously-developed chip is set to arrive in the country by the end of this year.
- In March, PM Modi laid the foundation stone of three semiconductor projects worth Rs 1.25 lakh crore.
- Tata Electronics is setting up a semiconductor fab in Dholera, Gujarat and one semiconductor unit in Morigaon, Assam.
- CG Power is setting up one semiconductor unit in Sanand. These units will produce lakhs of direct and indirect jobs.
- These four units will bring an investment of almost Rs 1.5 Lakh crore. The cumulative capacity of these units is about 7 crore chips per day, according to the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- The Programme for Development of Semiconductors and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem in India was notified in 2021 with a total outlay of Rs 76,000 crore.
About India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- It is a specialized and independent Business Division within the Digital India Corporation that aims to build a vibrant semiconductor and display ecosystem to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
- ISM has all the administrative and financial powers and is tasked with the responsibility of catalysing the India Semiconductor ecosystem in manufacturing, packaging, and design.
- ISM has an advisory board consisting of some of the leading global experts in the field of semiconductors.
- ISM has been working as a nodal agency for the schemes approved under the Semicon India Programme.
Semicon India Programme:
- Launched in 2021 with a total budget of Rs. 76,000 crore, the ISM is overseen by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), Government of India. This initiative is part of a broad effort to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem within the country.
- The programme is designed to offer financial support to companies involved in semiconductor and display manufacturing and design. It also aims to foster the creation of domestic Intellectual Property (IP), and to promote and incentivize the Transfer of Technologies (ToT).
- Under this programme, four key schemes have been introduced:
- Scheme for establishing Semiconductor Fabs in India.
- Scheme for establishing Display Fabs in India.
- Scheme for setting up Compound Semiconductors/Silicon Photonics/Sensors Fabs and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP)/OSAT facilities in India.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme.
Centre gives clearance for ‘Mission Mausam’

- 13 Sep 2024
The Union Cabinet approved 'Mission Mausam,' a groundbreaking initiative with an investment of ?2,000 crore over the next two years. The mission, spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), aims to significantly advance India's capabilities in atmospheric sciences and climate resilience.
Objectives and Key Focus Areas
Mission Mausam is designed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of weather forecasting and climate management through several critical components:
- Advanced Technology Deployment: The mission will focus on deploying next-generation radars and satellite systems equipped with advanced sensors. These technologies are crucial for enhancing weather surveillance and prediction accuracy.
- Research and Development: A key objective of Mission Mausam is to bolster research and development in atmospheric sciences. This will include the development of enhanced Earth system models and advanced weather forecasting techniques.
- GIS-Based Decision Support System: An automated decision support system based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS) will be developed to facilitate real-time data sharing and improve decision-making processes.
Institutional Framework and Implementation
The Ministry of Earth Sciences will oversee the implementation of Mission Mausam. The following institutions will play central roles in the mission:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
- National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting
Additional support will come from other MoES bodies:
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research
- National Institute of Ocean Technology
Sectoral Benefits
Mission Mausam is expected to bring significant improvements across various sectors:
- Agriculture: Enhanced agromet forecasts will aid farmers in optimizing crop management and increasing resilience to climatic variability.
- Disaster Management: Improved monitoring and early warning systems will enhance disaster preparedness and response, potentially reducing loss of life and property damage.
- Defence: Accurate weather forecasting will support strategic planning and operational efficiency within the defence sector.
- Energy and Water Resources: Better weather predictions will lead to more efficient management of energy and water resources.
- Aviation: Safer aviation will be supported by more reliable weather information, reducing risks and improving travel safety.
- Tourism: Sustainable tourism will benefit from accurate weather forecasting, contributing to safer and more enjoyable travel experiences.
Mission Mausam represents a significant investment in India’s ability to manage and mitigate the impacts of climate change and extreme weather events, ultimately aiming to enhance the resilience of communities and support sustainable development.
Delhi Declaration on Civil Aviation

- 13 Sep 2024
In the News:
The Prime Minister has announced the adoption of the Delhi Declaration on Civil Aviation.
Overview:
The Delhi Declaration was unanimously accepted following the conclusion of the 2nd Asia Pacific Ministerial Conference held in New Delhi. This Declaration provides a thorough framework designed to boost regional cooperation, tackle emerging challenges, and promote sustainable growth within the civil aviation sector across the Asia-Pacific region. The conference also marks the 80th anniversary of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
Key Announcements:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted significant achievements in Indian aviation, noting that women make up 15% of Indian pilots, a figure that surpasses the global average.
- A proposal for establishing an International Buddhist Circuit was introduced to enhance regional tourism and connectivity.
- India plans to build between 350 and 400 new airports by 2047, aiming to increase its global aviation presence.
- A Pacific Small Island Developing States Liaison Office will be created to help smaller nations manage aviation-related issues.
- The ‘Ek Ped Ma Ke Naam’ campaign was launched, with a goal to plant 80,000 trees in honor of ICAO’s 80 years, emphasizing green aviation and sustainability in future initiatives.
Significance of the Delhi Declaration:
- It marks a significant advancement in enhancing regional cooperation in civil aviation within the rapidly growing Asia-Pacific region.
- The framework tackles crucial issues such as sustainability, green aviation, and safety, which are vital for the current aviation industry.
- Initiatives like the International Buddhist Circuit are in line with broader regional objectives to improve connectivity, tourism, and economic development throughout Asia.
- India aims to assert itself as a major global aviation player with its ambitious plan to construct 350-400 airports by 2047, thereby becoming a key contributor to aviation infrastructure development.
Civil Aviation Sector in India:
- India ranks as the third-largest domestic aviation market globally and is projected to become the third-largest overall by 2025.
- The sector is expanding through significant government programs such as the UDAN Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti Plan, and NCAP 2016.
- With 136 operational airports and plans for an additional 100, the government is focused on modernizing infrastructure, improving regional connectivity, and promoting public-private partnerships for airport development.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO):
- Established in 1947 by the Chicago Convention (1944).
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada.
- Functions:
- Ensures the safety and efficiency of international air transport.
- Sets standards for aviation safety, security, and environmental performance.
- Encourages regional and international agreements to liberalize aviation markets.
- Promotes cooperation and dialogue among its 193 member states.
- Develops legal frameworks for aviation laws and standards.
SAARTHI APP

- 13 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) introduced the Saarthi app in partnership with Bhashini.
About the Saarthi App:
- The Saarthi app is a reference tool designed to help businesses create their own customized buyer-side applications.
- It facilitates network participants in developing buyer apps with multilingual capabilities. Initially, the app supports Hindi, English, Marathi, Bangla, and Tamil, with plans to expand to all 22 languages offered by Bhashini.
- The app features real-time translation, transliteration, and voice recognition, allowing businesses to broaden their market reach and attract customers from new regions.
What is Bhashini?
- Bhashini is India's AI-driven language translation platform. Its goal is to facilitate easy access to the internet and digital services in Indian languages, including through voice-based interactions, and to aid in the creation of content in these languages.
- The platform is designed to provide Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing (NLP) resources to Indian MSMEs, startups, and individual innovators. This support will help developers offer all Indians access to the internet and digital services in their native languages.
- Additionally, Bhashini features a ‘Bhasadaan’ section for crowdsourcing contributions and is available through Android and iOS apps.
Exercise AL NAJAH

- 13 Sep 2024
In News:
- Indian Army contingent departed for the 5th edition of the India-Oman Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH on September 12, 2024.
Key Details:
- Location: Rabkoot Training Area, Salalah, Oman.
- Frequency: Exercise AL NAJAH has been held biennially since 2015, alternating between India and Oman. Last edition was conducted at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- Indian Army Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Battalion of the Mechanised Infantry Regiment, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Royal Army of Oman Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Troops of the Frontier Force.
- Objective:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- Focus on operations in a desert environment.
- Tactical Drills:
- Joint Planning
- Cordon and Search Operation
- Fighting in Built-Up Areas
- Establishment of Mobile Vehicle Check Posts
- Counter Drone Operations
- Room Intervention
- Training Exercises:
- Combined field training exercises simulating real-world counter-terrorism missions.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Exchange of best practices in tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations.
- Foster interoperability, goodwill, and camaraderie between the two armies.
- Strengthen defense cooperation and enhance bilateral relations between India and Oman.
Battle of Saragarhi

- 13 Sep 2024
Why September 12 is Observed as Saragarhi Day:
- Historical Significance: The Battle of Saragarhi is considered one of the finest last stands in military history. On September 12, 1897, 21 soldiers of the 36th Sikh Regiment (now 4 Sikh) defended the fort against 8,000 Orakzai and Afridi tribal militants.
- 127th Anniversary: September 12 marks the 127th anniversary of this battle, which is now regarded as a legendary stand in global military history.
- The Battle: The 21 soldiers held the fort for seven hours despite being heavily outnumbered. They killed 200 militants and injured 600 before they were overwhelmed.
- Capt Amarinder Singh’s Account: In his book, he notes that the soldiers were aware of their certain death but chose to fight valiantly without surrendering, demonstrating unparalleled bravery.
What was Saragarhi and its Importance:
- Location and Role: Saragarhi was a communication tower between Fort Lockhart and Fort Gulistan in the North West Frontier Province (now Pakistan). It was crucial for linking these two forts, which housed a large number of British troops.
- Manning of Saragarhi: On that day, it was manned by only 21 soldiers from the 36th Sikh Regiment and a non-combatant, Daad, who performed odd jobs for the troops.
Details of the Battle:
- Initial Encounter: Around 9 am, the sentry spotted a large tribal army approaching, estimated between 8,000 and 15,000 strong.
- Communication: Sepoy Gurmukh Singh sent a Morse code message to Lt Col Houghton, requesting reinforcements. The response was to hold the position, as the supply route had been cut off.
- Challenges: The soldiers faced being outnumbered, limited ammunition (about 400 rounds per man), and communication issues. Sepoy Gurmukh Singh managed all heliograph communication tasks alone.
Key Figures:
- Havildar Ishar Singh: Leader of the defending troops, known for his bravery and independent nature. He was a respected and loved figure in his regiment.
- Sepoy Gurmukh Singh: The signalman who maintained communication during the battle, despite overwhelming challenges.
- Daad: The non-combatant who fought alongside the soldiers and killed five militants before being killed himself.
Recognition and Legacy:
- British Recognition: Queen Victoria awarded the 21 deceased soldiers the Indian Order of Merit (equivalent to the Victoria Cross), along with two ‘marabas’ (50 acres) and Rs 500 each.
- Current Observance: In 2017, the Punjab government declared September 12 as Saragarhi Day.
- Memorials: The Khyber Scouts regiment of the Pakistani army still mounts a guard at the Saragarhi memorial. The British built an obelisk with bricks from Saragarhi and commissioned gurdwaras at Amritsar and Ferozepur in honor of the martyrs. Shiromani Gurudwara Parbandhak Committee has named a hall after Saragarhi.
- Cultural Impact: The Battle of Saragarhi has inspired various media portrayals, including Akshay Kumar’s film Kesari.
INDUS-X Summit 2024

- 14 Sep 2024
The third edition of the INDUS-X Summit, held on September 9-10, 2024, in California, marked a significant advancement in the collaborative defence innovation ecosystem between India and the USA. Co-organized by the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF) and Stanford University, the summit emphasized the deepening of defence cooperation through innovation, joint research, and investment.
Key Outcomes
A major highlight of the summit was the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India’s Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) and the US Department of Defense’s Defence Innovation Unit (DIU). This agreement aims to enhance collaboration in defence innovation. The summit also saw the release of the INDUS-X Impact Report and the launch of a dedicated webpage for the initiative on both iDEX and DIU platforms.
Technological Showcase and Expert Dialogue
The summit provided a platform for startups and MSMEs to present cutting-edge technologies. Additionally, two advisory forums—the Senior Advisory Group and the Senior Leaders Forum—facilitated in-depth discussions on future technology trends, defence supply chain resilience, and funding opportunities for defence innovation. The discussions included contributions from experts across the defence industry, investment sectors, academia, and think tanks from both countries.
Leadership and Commitment
The Indian delegation was led by Amit Satija, Joint Secretary (Defence Industries Promotion), who underscored the commitment of both India and the USA to advancing defence technology through strategic collaboration. Since its launch in June 2023 during the Indian Prime Minister’s visit to the US, INDUS-X has achieved significant milestones, reinforcing its role in strengthening the US-India defence innovation partnership.
NEUROMORPHIC COMPUTING
- 14 Sep 2024
Indian Researchers Advance Neuromorphic Computing with Innovative Molecular Film
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have made a groundbreaking development in neuromorphic computing, creating an analog computing system that leverages molecular films. This new system can store and process data across 16,500 different states, a significant leap from conventional binary computing methods.
Understanding Neuromorphic Computing
Neuromorphic computing is an advanced computing paradigm designed to emulate the structure and function of the human brain. By using artificial neurons and synapses, this approach marks a departure from traditional binary computing, enabling systems to learn and adapt from their environments.
How Neuromorphic Computing Works
Neuromorphic computing relies on Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), which consist of millions of artificial neurons similar to those found in the human brain. These neurons communicate through electrical spikes or signals, following the principles of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). This setup allows the system to replicate the brain’s neuro-biological networks, performing tasks such as visual recognition and data interpretation with high efficiency.
Key Features of Neuromorphic Systems
- Brain-Inspired Architecture: Neuromorphic systems mimic the brain's structure, particularly the neocortex, which is involved in higher cognitive functions like sensory perception and motor commands.
- Spiking Neural Networks: These networks use spiking neurons that interact through electrical signals, mirroring the behavior of biological neurons. This design facilitates parallel processing and real-time learning.
- Integrated Memory and Processing: Unlike traditional von Neumann architecture, which separates memory and processing functions, neuromorphic systems combine these functions, leading to improved computational efficiency.
Advantages of Neuromorphic Computing
- Enhanced Efficiency: Neuromorphic computing enables faster problem-solving, pattern recognition, and decision-making compared to conventional systems.
- Revolutionizing AI Hardware: It holds the potential to transform AI hardware, allowing for complex tasks, such as training Large Language Models (LLMs), to be performed on personal devices. This advancement addresses current limitations related to hardware resources and energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency: Current AI tools are confined to data centers due to their high energy demands. Neuromorphic computing could overcome these constraints by providing energy-efficient hardware solutions.
Integration with Molecular Films
Molecular films, ultrathin layers engineered with specific electrical and optical properties, are central to this new advancement. These films act as neuromorphic accelerators, enhancing data storage and processing capabilities. They simulate brain-like parallel processing, improving performance in tasks such as matrix multiplication.
The recent development involves a molecular film that supports 16,500 possible states, a significant advancement over traditional binary systems. This film uses molecular and ionic movements to represent memory states, mapped through precise electrical pulses, creating what can be described as a "molecular diary" of states.
Comparison with Traditional Computing
- Parallel Processing: Neuromorphic computers can handle multiple streams of information simultaneously, unlike traditional computers that process data sequentially.
- Energy Efficiency: These systems consume less power by computing only when relevant events occur, making them suitable for real-time data processing applications.
- Analog vs. Binary: Traditional binary computing operates with bits that are either 0 or 1, akin to a light switch being on or off. In contrast, analog computing involves continuous values, similar to a dimmer switch with varying brightness levels.
This breakthrough by IISc researchers signifies a major step forward in neuromorphic computing, potentially transforming the way we approach data processing and artificial intelligence.
4 Years of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)

- 14 Sep 2024
Context:
Celebrating Four Years of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) has marked its fourth anniversary since its launch in 2020. This flagship scheme, managed by the Department of Fisheries under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying, aims to transform India’s fisheries sector into a vibrant and sustainable industry.
About PMMSY
The PMMSY is designed to invigorate the fisheries sector through a comprehensive approach that consolidates various existing schemes and initiatives. It operates as an umbrella scheme with two main components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS)
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS)
The CSS component is divided into:
Non-Beneficiary Oriented Subcomponents:
- Enhancement of Production and Productivity
- Infrastructure and Post-Harvest Management
- Fisheries Management and Regulatory Framework
Fisheries Sector Overview
India stands as the third-largest fish producer globally and the second-largest in aquaculture production. It is also the fourth-largest exporter of fish and fisheries products, experiencing a notable 26.73% growth in exports from FY 2021-22 to FY 2022-23. Andhra Pradesh leads the country in fish production, followed by West Bengal and Gujarat. The sector supports the livelihoods of over 30 million people.
The Department of Fisheries is spearheading the PMMSY to foster a "Blue Revolution" through sustainable and responsible development of the fisheries sector.
Challenges Facing the Fisheries Sector
1. Overfishing: Excessive fishing pressure threatens fish stocks and disrupts ecosystem balance.
2. Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing: Practices such as fishing without proper authorization and using banned gear undermine conservation efforts.
3. Lack of Infrastructure and Technology: Outdated technology and inadequate storage and transportation facilities result in post-harvest losses and reduced productivity.
4. Poor Fisheries Management: Inefficient regulation enforcement and lack of comprehensive data exacerbate overfishing and IUU fishing.
5. Pollution and Habitat Destruction: Industrial pollution and habitat destruction from activities like coastal reclamation impact marine and freshwater ecosystems.
6. Climate Change: Altered oceanic and freshwater environments affect fish distribution and reproductive cycles, disrupting fisheries ecosystems.
7. Socio-Economic Issues: Poverty and limited livelihood options increase the vulnerability of fishing communities.
Government Initiatives for Sector Growth
1. National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB): Established in 2006, the NFDB plans and promotes fisheries development, enhancing production and infrastructure.
2. Blue Revolution: Launched in 2015, this initiative focuses on sustainable development, modern technology adoption, and strengthening fisheries governance.
3. Sagarmala Programme: Also launched in 2015, it aims to boost port-led development and includes projects to develop fishing harbors and cold chain infrastructure.
4. National Fisheries Policy: Introduced in 2020, this policy provides a framework for sustainable fisheries development, focusing on responsible management and socio-economic improvements.
5. Fish Farmers Development Agencies (FFDAs): Established at the district level to provide technical guidance and support to fish farmers.
6. Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Created in 2018-19 with a fund of Rs 7,522.48 crore to address infrastructure needs, resulting in 121 approved projects.
7. Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA): Regulates coastal aquaculture to ensure sustainability and environmental conservation.
Way Forward
The fisheries sector in India holds immense potential due to its extensive coastline and water resources. Key measures to further enhance the sector include:
- Strengthening Monitoring and Enforcement: Combat IUU fishing with better monitoring and regulatory mechanisms.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: Provide financial incentives for adopting modern technologies and sustainable practices.
- Protecting Aquatic Habitats: Ensure the conservation and restoration of vital habitats like mangroves and coral reefs.
- Improving Supply Chain Infrastructure: Develop better market linkages to ensure fair pricing and access to markets.
With these strategies, the PMMSY aims to drive the sustainable growth of India’s fisheries sector and bolster its contribution to the economy and livelihoods.
What is Helium & why is it used in rockets?

- 14 Sep 2024
The Crucial Role of Helium in Space Missions and the Challenges It Presents
Two NASA astronauts aboard Boeing’s Starliner will extend their stay on the International Space Station (ISS) due to issues with the spacecraft’s propulsion system, which includes problematic helium leaks. Meanwhile, SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission, which successfully launched on Tuesday, experienced delays due to similar helium-related issues with ground equipment.
The Importance of Helium in Spacecraft
Helium plays a critical role in space missions for several reasons. As an inert gas, it does not react with other substances or combust, which is crucial for maintaining the safety and stability of rocket systems. With an atomic number of 2, helium is the second lightest element after hydrogen. Its lightweight nature is essential for reducing the overall mass of rockets, which in turn minimizes fuel consumption and the need for more powerful (and costly) engines.
A key property of helium is its extremely low boiling point of –268.9 degrees Celsius. This allows it to remain in a gaseous state even in the super-cold environments where many rocket fuels are stored.
How Helium Is Utilized in Spacecraft
In spacecraft, helium is primarily used for:
- Pressurizing Fuel Tanks: Helium ensures that fuel flows smoothly to the rocket’s engines. As fuel and oxidizer are consumed during launch, helium fills the empty space in the tanks, maintaining consistent pressure.
- Cooling Systems: Helium is also used in cooling systems to manage the temperature of various components, preventing overheating and ensuring the proper functioning of the spacecraft.
Due to its non-reactive nature, helium can safely interact with the residual contents of the tanks without causing adverse reactions.
The Challenge of Helium Leaks
Despite its advantages, helium is prone to leakage. Its small atomic size and low molecular weight allow helium atoms to escape through even minor gaps or seals in storage tanks and fuel systems. This characteristic poses a significant challenge for space missions.
On Earth, helium leaks are easier to detect due to the gas’s rarity in the atmosphere. This makes helium a valuable tool for identifying potential faults in rocket or spacecraft fuel systems. The frequency of these leaks across various space missions, including those by ISRO and ESA, underscores a broader industry need for improved valve designs and more precise tightening mechanisms.
OpenAI’s powerful new AI model o1

- 14 Sep 2024
OpenAI Unveils New AI Model: Key Features and Implications
OpenAI has introduced its latest AI model, a significant advancement that aims to elevate the capabilities of artificial intelligence. This new model, part of the enigmatic ‘Project Strawberry,’ is designed to think more like a human when solving complex problems, offering a glimpse into the future of AI reasoning.
Introduction of OpenAI o1
The new OpenAI o1 model marks the beginning of a series of "reasoning" models intended to address intricate tasks in fields such as science, coding, and mathematics. This model, released as part of a preview in both ChatGPT and the API, represents a major leap forward in AI technology. OpenAI has announced that this is just the start, with regular updates and enhancements expected. Additionally, evaluations for the next model update, currently under development, are included in this release.
How It Works
The o1 model is designed to approach queries with a level of careful consideration similar to human problem-solving processes. It learns to tackle problems from various angles, verify its outputs, and improve through feedback. According to OpenAI, this model performs at a level comparable to PhD students in disciplines such as physics, chemistry, and biology. It is particularly adept in mathematics and coding, solving 83% of problems in a challenging math contest— a notable improvement from previous versions that only managed 13%. In coding, it has outperformed 89% of participants.
Sub-Models and Their Features
Alongside the main o1 model, OpenAI has also launched the o1-Mini. This version is a more cost-effective alternative, being 80% cheaper than the o1-preview. The o1-Mini is designed to offer fast and efficient reasoning, particularly beneficial for developers focused on coding tasks.
Implications for Jobs and Research
The advanced problem-solving capabilities of the o1 model are expected to impact various job sectors, particularly those involving routine coding, data analysis, and mathematical modeling. While this could reduce the need for human intervention in some tasks, it may also create new roles in AI safety and maintenance. For researchers, the model offers a powerful tool for accelerating breakthroughs in fields like physics, chemistry, biology, and healthcare. Its ability to generate formulas and analyze large datasets positions it as a valuable asset for advancing scientific research.
Access and Usage
The OpenAI o1 model is now accessible to ChatGPT Plus and Team users. The o1-preview and o1-mini can be selected using the model picker, with weekly message limits set at 30 for o1-preview and 50 for o1-mini. This rollout marks a new era in AI capabilities, showcasing OpenAI’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence.
Key Points to Note
1. Not Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Despite its advanced capabilities, o1-preview is not a step towards AGI, which aims for AI systems to perform cognitive tasks as well as or better than humans. The o1 models, while more adept at reasoning, still fall short of human-level intelligence.
2. Impact on Competition: While o1 gives OpenAI a temporary edge, it is expected to prompt competitors like Google, Meta, and others to accelerate their development of similar advanced models. These companies have the expertise to quickly develop models that could rival or surpass o1's capabilities.
3. Unknowns About Model Operations: Details on how o1 operates remain limited. It combines various AI techniques, including "chain of thought" reasoning and reinforcement learning, but specifics about its training data and internal mechanisms are not fully disclosed.
4. Cost Considerations: Using o1-preview comes at a higher cost compared to previous models. OpenAI charges $15 per million input tokens and $60 per million output tokens for corporate customers, compared to $5 and $15, respectively, for GPT-4o. The model’s complex reasoning requires more tokens, potentially making it more expensive to use.
5. Chain of Thought Transparency: OpenAI has chosen not to reveal the chain of thought process used by o1, citing safety and competitive reasons. This decision may cause issues for enterprise customers who lack visibility into their usage and billing accuracy.
6. New Scaling Laws: OpenAI's o1 models reveal new "scaling laws" suggesting that longer inference times can improve accuracy. This could increase the computing power and costs required to run these models effectively.
7. Potential Risks: o1 models could enable powerful AI agents, but they also present risks. Instances of “reward hacking” and unintended actions suggest that companies must carefully manage these agents to avoid ethical, legal, or financial issues.
8. Safety Assessments: OpenAI reports that o1 is generally safer than previous models, though it still poses a "medium risk" of assisting in biological attacks. This rating has raised concerns among AI safety and national security experts.
9. Concerns About Persuasion and Deceptive Alignment: AI safety experts are wary of o1’s persuasive capabilities and the potential for “deceptive alignment,” where a model might deceive users to achieve hidden goals. These concerns highlight the ongoing challenges in ensuring AI safety and transparency.
Overall, while the o1 models represent a significant leap forward in AI reasoning and problem-solving, they also introduce new complexities and risks that will need to be managed as they become more integrated into various applications.
Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT)

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
The Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT) has recently unveiled a groundbreaking web portal, ‘shabd.education.gov.in,’ which is set to be a significant resource for technical terminology across all 22 official Indian languages. This initiative, supported by the Union Education Ministry, aims to consolidate and digitize scientific and technical terminologies, making them accessible to users in multiple languages.
Key Features of the Portal:
- Central Repository: The website serves as a central repository for glossaries developed by CSTT and other institutions. It currently hosts 322 glossaries with approximately 2.2 million words, with a goal to expand to 450 glossaries.
- Search Functionality: Users can search for technical terms using various criteria, including language, subject, type of dictionary, or specific language pairs. This comprehensive search capability allows for targeted and efficient access to information.
- Feedback Mechanism: The portal enables users to provide feedback on the terminologies, helping to refine and update the database based on real-world use and expert input.
- Expanding Technical Education: The launch of this platform supports the broader goal of enhancing technical education in Indian languages, which is crucial for fields like medicine and engineering.
Historical Context and Support:
- CSTT's Role: Established in 1961, CSTT is tasked with developing and defining scientific and technical terms in Hindi and other Indian languages. The commission also publishes textbooks, monographs, and journals, and organizes various academic events to promote standardized terminology.
- Process of Compilation: Terminologies are compiled through specialized committees for each subject area, with separate language committees ensuring the standardization of terms. The CSTT has been assisted by the National Translation Mission in this effort.
Impact and Usage:
- Since its launch in March 2024, the portal has seen significant engagement, with over 122,000 hits from both domestic and international users. This reflects the growing interest and need for accessible technical terminology in multiple languages.
- The portal is poised to play a crucial role in standardizing and disseminating technical knowledge across diverse linguistic communities in India, facilitating better understanding and education in various scientific and technical fields.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a major expansion of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) to cover all senior citizens aged 70 years and above.
- This change allows anyone in this age group to be eligible for health insurance, regardless of their income level.
- This expansion aims to address the healthcare needs of the elderly, who often face higher medical expenses as they age.
- By lifting income restrictions, the government is ensuring that more senior citizens can benefit from much-needed health coverage, which will help ease the financial burden of healthcare.
How does the scheme work?
- The AB PM-JAY now covers an additional 6 crore individuals from 4.5 crore families, focusing on seniors aged 70 and above. Each senior citizen will be given a health card, allowing them easy access to healthcare services under the scheme.
- The scheme provides Rs 5 lakh coverage annually per family. If there are multiple senior citizens in the same family, this coverage is shared among them. The scheme is particularly beneficial for nuclear families, where the financial burden on elderly members can be more difficult to manage.
Key details of the scheme for senior citizens above 70
- Eligibility - All senior citizens aged 70 and above are eligible for Rs 5 lakh health coverage, regardless of income or social status.
- Top-up coverage - For families already enrolled in Ayushman Bharat, senior members will receive an extra Rs 5 lakh top-up, which is solely for their use.
- Private insurance - Senior citizens with private health insurance can still take advantage of the scheme without any conflict with their existing coverage.
- Public health schemes - Seniors who are part of other public health schemes like the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or Ayushman Central Armed Police Force (CAPF) will need to choose between their current insurance and the new Ayushman Bharat health coverage.
- New health cards - All eligible senior citizens will receive a separate health card, which will help them access the scheme’s benefits more efficiently.
Who pays for the coverage?
- The cost of this expanded coverage will be Rs 3,437 crore initially. State governments will bear 40% of the expenses, while the Centre will cover the remaining 60%. For states in hilly and northeastern regions, the Centre will fund 90% of the costs.
- As more senior citizens enrol, the costs may increase. Experts point out that covering elderly individuals often costs more than providing insurance for younger, economically weaker sections of society. However, the government is prepared to scale up the coverage based on demand.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
- AB PM-JAY launched in 2018, is a flagship program designed to offer affordable and accessible healthcare to millions of vulnerable families across India.
- The primary aim is to provide health insurance coverage up to ?5 lakhs per family annually for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- The scheme currently supports 55 crore individuals from 12.34 crore families throughout the country.
PM E-Drive replaces FAME India Phase II

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet recently approved a new scheme called PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE) for the promotion of electric vehicles (EV) in India, replacing an earlier flagship scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI) will implement the new scheme with a total outlay of Rs 10,900 crore over a period of two years.
- The PM E-DRIVE will replace Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles in India Phase II (FAME India Phase II).
- The new scheme offers subsidies/demand incentives worth Rs 3,679 crore to incentivise adoption of electric two-wheelers, electric three-wheelers, e-ambulances, e-trucks and other emerging EVs.
- The scheme will support 24.79 lakh electric two-wheelers, 3.16 lakh e-three wheelers, and 14,028 e-buses.
- For e-ambulances, a total of Rs 500 crore has been allocated. In addition, Rs 4,391 crore has been provided for the procurement of 14,028 e-buses by state transport units and public transport agencies.
- To implement this, demand aggregation will be done by Convenience Energy Services Limited (CESL) in nine cities with a population of more than 40 lakh — Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Surat, Bengaluru, Pune, and Hyderabad. Intercity and interstate e-buses will also be supported in consultation with states.
- For availing benefits under the scheme, the ministry will introduce e-vouchers for EV buyers. At the time of purchase, the scheme portal will generate an Aadhaar authenticated e-voucher, which needs to be signed by the buyer and submitted to the dealer.
- Subsequently, the e-voucher will also be signed by the dealer and uploaded on the PM E-DRIVE portal. The signed e-voucher will be sent to the buyer and dealer via SMS, and will be essential for the OEM (original equipment manufacturer) to claim reimbursement of demand incentives under the scheme.
- The primary objective of the PM E-DRIVE scheme is to expedite the adoption of EVs by providing upfront incentives for their purchase, as well as by facilitating the establishment of essential charging infrastructure for EVs.
FAME India Phase II
Launched on April 1, 2019, with a budget of ?10,000 crores for three years. It is an extension of FAME India I, which began on April 1, 2015, with a ?895 crore budget.
Objectives:
- Promote the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Provide upfront incentives for purchasing electric vehicles.
- Develop necessary charging infrastructure.
- Address environmental pollution and fuel security.
Focus Areas:
- Public transportation and shared transport.
- Incentives for electric buses through State/City Transport Corporations.
- For 3W and 4W vehicles, incentives are for public transport and commercial vehicles.
- For e-2Ws, focus is on private vehicles.
Targets:
- 10 lakh e-2Ws
- 5 lakh e-3Ws
- 55,000 e-4Ws
- 7,000 electric buses
Incentives:
- Applied to vehicles with advanced batteries, such as Lithium-ion and other new technologies.
Charging Infrastructure:
- 2,700 charging stations in metros, million-plus cities, smart cities, and hilly areas.
- Charging stations on major highways at 25 km intervals, on both sides of the road.
40% Amazon rainforest unprotected: why is this significant for climate change?

- 12 Sep 2024
In News
- Scientists agree that preserving the Amazon rainforest is critical to combating global warming, but new data published recently, indicate huge swathes of the jungles that are vital to the world’s climate remain unprotected.
- Nearly 40% of the areas of the Amazon rainforest most critical to curbing climate change have not been granted special government protection, as either nature or indigenous reserves, according to an analysis by nonprofit Amazon Conservation.
- The areas lie in the far southwest of the Amazon in Peru and the far northeast in Brazil, French Guiana, and Suriname, the data show.
- Those parts of the Amazon have the biggest, densest trees and the most continuous canopy cover. That means these areas hold the most carbon, which would be released into the atmosphere as climate-warming greenhouse gas if the jungle is destroyed by fire or logging.
What satellite data show
- Amazon Conservation analysed new data from the satellite imaging company Planet that used lasers to get a three-dimensional picture of the forest and combined it with machine-learning models.
- Only aboveground vegetation was considered, and not underground carbon in roots and soils.
- Amazon Conservation’s Monitoring of the Andean Amazon Project (MAAP)’s analysis shows that 61% of the peak carbon areas in the Amazon are protected as indigenous reserves or other protected lands, but the rest generally has no official designation.
- In Brazil, Suriname and French Guiana, only 51% of peak carbon areas are labeled for preservation. Peru protects a higher proportion of its critical areas, but some of the areas that have been left unprotected have been earmarked for logging.
Why the Amazon matters
- MAAP published an analysis last month showing that the Amazon contained 71.5 billion tonnes of carbon, roughly double the global carbon dioxide emissions for 2022. That analysis showed that the Amazon just barely absorbed more carbon than it released in the decade leading up to 2022, a positive signal for the world’s climate.
- But that remains an area of intense debate, with other studies showing the Amazon has flipped to become an emissions source.
- As the effects of anthropogenic climate change become more stark with each passing day, the Amazon becomes one of the most valuable assets for the planet’s health. Scientists say that if the Amazon becomes an emission source instead of a carbon sink — which absorbs carbon from the atmosphere — the impact on the planet may be cataclysmic.
Controversy over Mumbai's salt pans: why do these lands matter?

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
Earlier this month, the Centre approved the transfer of 256 acres of salt pan land in Mumbai to the Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL), a joint venture between Adani Realty Group and the Maharashtra government, for building rental housing for slum dwellers.
What are salt pan lands?
- They comprise parcels of low-lying lands where seawater flows in at certain times, and leaves behind salt and other minerals. Along with Mumbai’s mangroves (also at risk due to development), this ecosystem is instrumental in protecting the city from flooding.
- According to the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) notification of 2011, the ecologically sensitive salt pans fall under CRZ-1B category, where no economic activity is allowed with the exception of salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
- In all, 5,378 acres of land in Mumbai have been designated as salt pan lands, approximately nine times the size of the Dharavi slum. About 31% of this land is located in residential and commercial belts, and roughly 480 acres are encroached upon, a 2014 study by the state government found. The same study found that about 1,672 acres of Mumbai’s more than 5,000 acres of salt pan lands are “developable”.
- Nationally, some 60,000 acres have been demarcated as salt pan lands, spread across Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Karnataka. Andhra Pradesh (20,716 acres) boasts the largest expanse of such land, followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
Why are Mumbai’s salt pan lands at risk?
Development Pressure
- Land Scarcity: Mumbai faces severe land scarcity, with its burgeoning population and high demand for space. Salt pans, being some of the last undeveloped areas, are increasingly targeted for various projects.
- Development Plans: Multiple state governments have eyed salt pan lands for different uses.
Environmental Significance
- Flood Prevention: Salt pans are situated in low-lying areas that naturally collect rainwater and tidal flows, helping to mitigate flooding in Mumbai’s eastern suburbs. They act as natural buffers, absorbing excess water during heavy rains and high tides.
- Historical Context: During the July 2005 deluge, salt pans helped reduce the impact of flooding compared to other areas of Mumbai, highlighting their role in flood management.
- Ecosystems: Salt pans are home to various species of birds and insects and contribute to local biodiversity. The destruction of these lands could lead to loss of habitat and disruption of local ecosystems.
Risks of Development
- Flooding Concerns: Environmentalists argue that constructing on these low-lying areas will lead to increased flooding in areas like Vikhroli, Kanjurmarg, and Bhandup. This is because the land’s natural ability to absorb and manage water will be compromised.
- Quality of Life Issues: Relocating slum-dwellers to these areas raises concerns about their living conditions. Salt pans are prone to flooding, which could undermine the quality of life for new residents. The cost of making these lands habitable, including extensive land filling and waterproofing measures, could negate the benefits of affordable housing.
- Conflict with Climate Goals: There is a contradiction between Mumbai’s Climate Action Plan, which recognizes climate threats, and the push to develop areas critical for flood management.
SEMICON 2024

- 11 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi addressed the SEMICON 2024 conference on the outskirts of the national capital, advocating for increased investment in semiconductor manufacturing and resilient supply chains.
- Significance of Supply Chains: Emphasized the critical need for resilient supply chains, citing the COVID-19 pandemic as a stark reminder of their importance. The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, particularly affecting sectors dependent on chip imports from China.
- Investment in Semiconductors: Modi pitched India as a prime destination for semiconductor investments. He stressed that India aims to have an Indian-made chip in every global device and is committed to becoming a semiconductor powerhouse.
- India's Semiconductor Strategy:
- Reformist Government: Modi highlighted India’s reformist policies and stable business environment as key attractions for semiconductor investments.
- Growing Manufacturing Base: Expanding manufacturing infrastructure in India as a critical factor.
- Aspirational Market: The evolving technology market in India is seen as a strong incentive for semiconductor production.
- Government Commitment: Modi announced that over ?1.5 lakh crore has already been committed to semiconductor manufacturing, with several projects currently in the pipeline.
- Semicon India 2024 Focus:
- Event Goals: SEMICON India 2024 is a three-day conference designed to showcase India’s semiconductor strategies and policies, aiming to position the country as a global hub for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Workforce Development: The government is developing a semiconductor workforce of 85,000 engineers, technicians, and R&D experts.
- Market Growth: India’s semiconductor market, valued at $23.2 billion, is projected to reach $80.3 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.10%.
- Importance of Semiconductors: Semiconductor chips as crucial for fulfilling the aspirations of millions and noted their role in India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), which remained effective during the pandemic when other countries’ banking systems struggled.
- Event Participation: SEMICON India 2024 will feature over 250 exhibitors and 150 speakers, including top executives from global semiconductor companies, industry leaders, businesses, and experts from around the world.
PresVu
- 11 Sep 2024
According to the company, the eye drop PresVu is the first of its kind in India, and that Entod has “applied for a patent for this invention in terms of its formulation and the process”.
Mumbai-based Entod Pharmaceuticals has announced that the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) — the country’s apex drug regulator — has approved its new eye drop, which has been “specifically developed to reduce dependency on reading glasses for individuals affected by presbyopia.”
According to the company, the eye drop PresVu is the first of its kind in India, and that Entod has “applied for a patent for this invention in terms of its formulation and the process”.
What is presbyopia?
Presbyopia is an age-related condition in which the eyes gradually lose the ability to focus on nearby objects. People usually start to develop presbyopia at around the age of 40. According to doctors, spectacles are one of the most effective ways to manage the condition.
How does PresVu work?
- The active ingredient — chemical compounds in medicines that have an effect on the body — in PresVu is pilocarpine. The compound contracts the iris muscles, which control the size of the pupil and help humans see things clearly, thereby enabling one’s eyes to focus better on nearby objects, according to Entod Pharmaceuticals.
- The company also said that PresVu uses “advanced dynamic buffer technology” — essentially, a base solution — to adapt to the pH level (a scale used to measure how acidic or basic a substance is) of tears. This ensures that the eye drop has “consistent efficacy and safety for extended use, keeping in mind that such drops will be used for years at a stretch”.
- PresVu is a prescription-only medicine and, according to doctors, its impact is unlikely to last beyond four to six hours. It should not be used by people who have inflammation of the iris. Regular use of PresVu may lead to itching and redness, eyebrow pain, and muscle spasms in the eyes.
Is this a novel therapy?
- Although Entod’s claims make it seem that PresVu is a new therapy, pilocarpine, the main compound used in the eye drop, has been available in India for decades now.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration approved a pilocarpine eye drop for presbyopia in 2021.
- In India, the government decides on the ceiling price of pilocarpine in 4% and 2% concentrations. PresVu has pilocarpine in 1.25% concentration.
Strengthening India-UAE Relations

- 11 Sep 2024
The bilateral relationship between India and the UAE has flourished in recent years, marked by deepening strategic ties and multifaceted collaboration. The recent visit of Abu Dhabi's Crown Prince to India highlights the growing importance of this partnership. The UAE is now India's second-largest export destination, third-largest trading partner, and fourth-largest investor. The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), effective from May 2022, has been transformative, boosting total trade by nearly 15% and increasing non-oil trade by 20% in the 2023-24 period.
Significance of the UAE for India
- Economic Gateway: The UAE is a crucial entry point for India into the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. As India's third-largest trading partner, bilateral trade reached USD 84.5 billion in FY 2022-23. The CEPA, removing tariffs on 80% of Indian exports to the UAE, has led to a 5.8% increase in non-oil trade early in 2023 and is expected to elevate trade to USD 100 billion by 2030. The UAE’s strategic location and infrastructure make it an ideal hub for re-exporting Indian goods to Africa and Europe.
- Energy Security: The UAE is India's fourth-largest crude oil supplier, with oil imports surging by 81% in January 2024. The partnership extends to renewable energy projects, aligning with India's goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030, underscoring the UAE's role in India's energy transition.
- Investment Catalyst: FDI from the UAE to India has increased more than threefold, reaching USD 3.35 billion from USD 1.03 billion in 2021-22. The UAE-India High-Level Joint Task Force on Investments has played a key role, with significant investments like the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority’s Rs 4,966.80 crore in Reliance Retail Ventures Limited.
- Strategic Partner: The UAE has become a vital strategic ally for India in counterterrorism and maritime security. The bilateral naval exercise "Zayed Talwar" in 2021 and India's access to the UAE’s Al Dhafra air base highlight the expanding defense cooperation between the two nations.
- Remittances and Soft Power: The 3.5 million-strong Indian diaspora in the UAE is a major source of remittances and cultural influence. In 2022, India received nearly USD 111 billion in global remittances, with the UAE as a significant contributor. The diaspora also strengthens cultural ties, as evidenced by the BAPS Hindu Temple in Abu Dhabi, symbolizing the UAE’s commitment to religious tolerance.
- Tech and Innovation Hub: The UAE-India partnership is increasingly focused on technology and innovation. The I2U2 group (India, Israel, UAE, USA) aims to enhance cooperation in clean energy and food security. The UAE’s USD 2 billion investment in food parks in India and the UAE-India Artificial Intelligence Bridge, launched in 2018, facilitate joint research and position both countries at the forefront of technological advancement.
Areas of Friction
- Labor Rights: Persistent labor rights issues for Indian workers in the UAE, including passport confiscation and wage theft, remain a concern.
- Geopolitical Tensions: India’s growing ties with Israel and the UAE’s normalization with Israel complicate the geopolitical landscape, potentially entangling India in regional rivalries, especially with Iran. The UAE’s increasing ties with China also add strategic complexity.
- Energy Transition: Both nations’ commitments to net-zero targets—India by 2070 and the UAE by 2050—pose challenges to their traditional hydrocarbon-based relationship.
- Trade Imbalance: Despite growing trade, India’s trade deficit with the UAE stood at USD 16.78 billion in FY 2022-23. While the CEPA aims to address this, diversifying trade beyond hydrocarbons remains a challenge.
- Maritime Security: Coordinating responses to maritime security threats while respecting strategic autonomy is challenging. The UAE’s expanding naval presence and India’s growing maritime footprint require careful coordination.
Enhancing Relations
- Digital Diplomacy: India could use its IT capabilities to develop digital platforms for collaboration, including a real-time trade portal and a joint innovation hub, and expand cross-border digital payments.
- Green Energy Corridor: Proposing an "India-UAE Green Energy Corridor" could align with both nations’ climate goals through joint investments and research in renewable energy.
- Skill Bridge Program: A "Skill Bridge Program" could upskill Indian workers for the UAE job market, focusing on emerging sectors like AI and sustainable technologies.
- StartUp Synergy Scheme: Developing a "StartUp Synergy Scheme" could foster collaboration between Indian and UAE startups through joint incubation programs and market access facilitation.
- Maritime Cooperation Blueprint: Creating a comprehensive "India-UAE Maritime Cooperation Blueprint" could enhance collaboration in maritime security, blue economy initiatives, and port development, including joint patrols and deep-sea ports.
Polaris Dawn Mission: First Private Spacewalk Attempt

- 11 Sep 2024
Recently, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched from Florida, carrying American billionaire Jared Isaacman and three other astronauts into orbit for the Polaris Dawn mission. This five-day mission marks a milestone as it aims to achieve the world’s first private spacewalk. Polaris Dawn is the inaugural flight of the Polaris Program, a collaborative effort between Isaacman and SpaceX, led by Elon Musk. The program's goal is to develop innovative technologies for future Mars missions.
What is a Spacewalk?
A spacewalk, or “extravehicular activity” (EVA), involves an astronaut conducting activities outside a spacecraft while in space. The concept of a spacewalk dates back to March 18, 1965, when Soviet cosmonaut Alexei Leonov performed the first EVA during the Space Race. Leonov's spacewalk lasted just 10 minutes.
Modern spacewalks typically occur outside the International Space Station (ISS) and can last between five and eight hours. Astronauts conduct spacewalks for various purposes, such as performing scientific experiments, testing new equipment, or repairing satellites and spacecraft.
During a spacewalk, astronauts wear specially designed spacesuits and use safety tethers to prevent floating away into space. These tethers have one end attached to the astronaut and the other secured to the spacecraft. An alternative safety device is the SAFER (Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue), a backpack with small jet thrusters controlled by a joystick, which helps astronauts maneuver in space.
Objectives of the Polaris Dawn Mission
The Polaris Dawn mission, utilizing SpaceX’s Dragon capsule, aims to reach an altitude of approximately 1,400 km from Earth. This altitude exceeds the previous record set by NASA’s Gemini XI mission in 1966, which reached 1,372 km. At this height, the mission will be deep within the Van Allen radiation belts, which start around 1,000 km altitude and are known for their high levels of radiation. The crew will study the effects of spaceflight and radiation on human health.
Following this high-altitude phase, the Dragon capsule will descend to a lower orbit to facilitate the spacewalk scheduled for the third day of the mission, Thursday. During the spacewalk, the capsule will be depressurized, and the hatch will open, exposing the interior to the vacuum of space. Only two crew members, Isaacman and Gillis, will exit the capsule, while Poteet and Menon will remain inside to manage safety tethers and monitor the mission’s status.
The primary objective of the spacewalk is to test SpaceX’s newly developed EVA spacesuits. These suits, designed specifically for this mission, feature built-in cameras and heads-up displays to provide real-time information about the suit's condition. They also incorporate advanced thermal management systems.
After the spacewalk, Isaacman and Gillis will return to the capsule, which will then be repressurized before resuming its mission activities.
Additional Mission Activities
Throughout the mission, the crew will conduct 40 scientific experiments. These include attempting to capture X-ray images using natural space radiation instead of traditional X-ray equipment. The mission will also test SpaceX’s Starlink satellite network for laser-based communication, allowing satellite-to-satellite communication without relying on ground-based infrastructure.
The grave threat from AMR
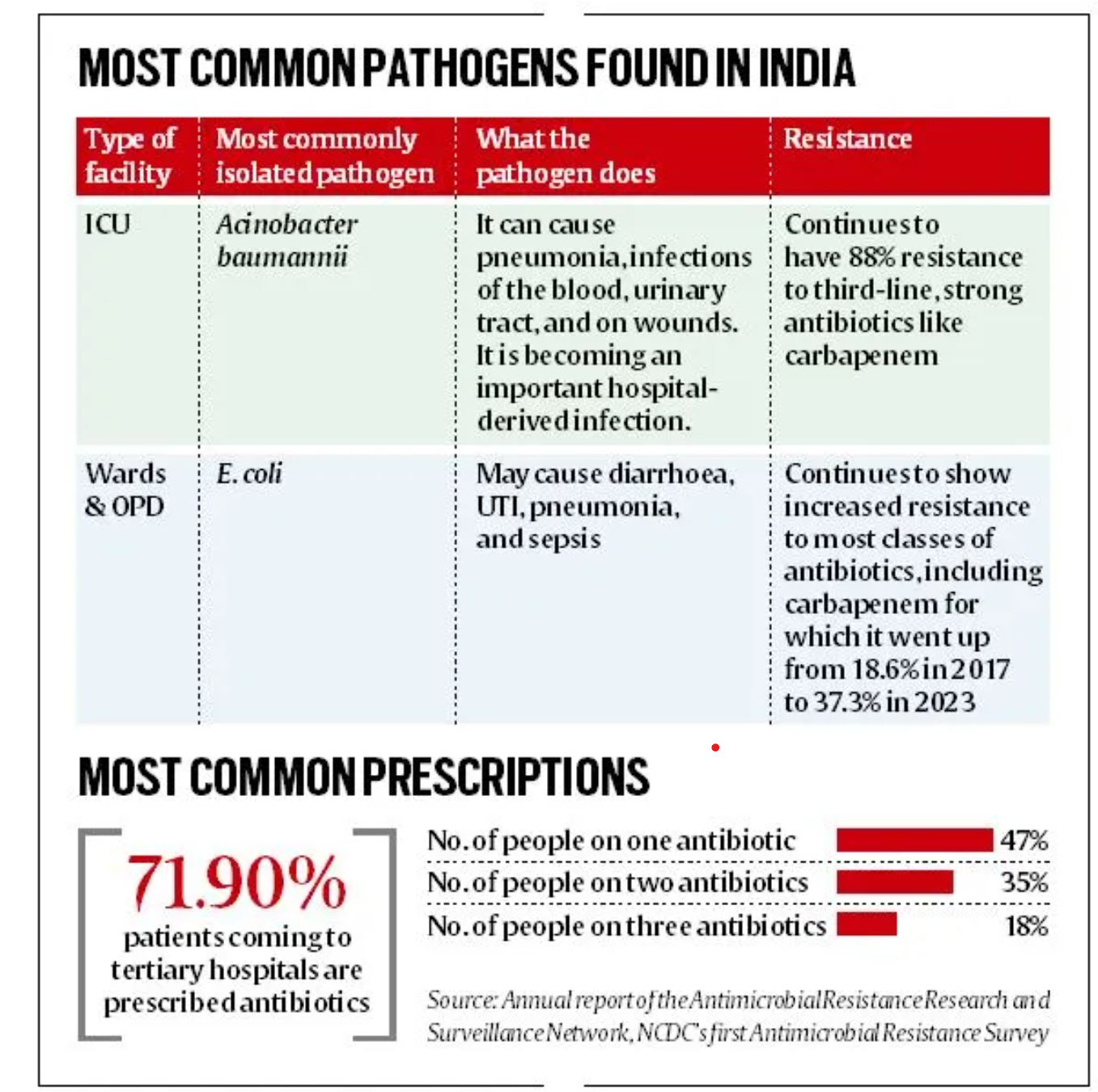
- 11 Sep 2024
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat globally, with escalating concerns in India. AMR arises when microbes evolve into drug-resistant ‘superbugs’ due to the misuse or overuse of antibiotics. This phenomenon is exacerbated by the September 26 UN General Assembly High-Level Meeting on antimicrobial resistance, which highlighted the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recent guidance on antibiotic pollution from manufacturing.
AMR and the emergence of "superbugs" have far-reaching implications for healthcare systems, particularly affecting patients with multiple health conditions. According to a survey by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), AMR is on the rise across India, underscoring the urgency of addressing this issue.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
AMR occurs when pathogens gain the ability to survive and cause infections despite the presence of antimicrobial drugs. This resistance is a result of microbes evolving in response to inappropriate or excessive use of antibiotics. The proliferation of resistant strains can lead to the creation of 'superbugs' that are resistant to commonly prescribed antibiotics. These resistant pathogens can spread through hospitals, drinking water, and sewage systems, complicating the treatment of infections.
Why is AMR Increasing?
- Individual Practices: Many people in India take antibiotics without medical consultation, especially for viral infections like the flu, where antibiotics are ineffective. This misuse contributes to the development of resistance.
- Medical Practices: There is a need for improved education among doctors regarding the use of antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which target a wide range of infections, are more likely to induce resistance. A survey by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) found that 71.9% of patients in hospitals were prescribed antibiotics, often not to treat existing infections but to prevent potential ones. This overprescription has diminished the efficacy of several antibiotics, such as Norfloxacin, and increased resistance to crucial antibiotics like carbapenems.
- Diagnostic Practices: Often, doctors prescribe antibiotics based on symptoms rather than diagnostic tests, leading to empirical treatments with broad-spectrum antibiotics. It is essential for doctors to use diagnostic tests to prescribe targeted antibiotics, minimizing unnecessary resistance development.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: The WHO’s recent guidelines on antibiotic pollution highlight the need for better management of wastewater and solid waste from antibiotic manufacturing facilities. Despite known high levels of antibiotic pollution, regulatory oversight remains limited.
Common Resistant Pathogens in India
In India, the most prevalent resistant pathogens include:
- E. coli: Responsible for gut infections, with susceptibility to carbapenems decreasing from 81.4% in 2017 to 62.7% in 2023.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae: Causes pneumonia and urinary tract infections, showing reduced susceptibility to carbapenems from 58.5% to 35.6% and 48% to 37.6% between 2017 and 2023.
- Acinetobacter baumannii: Primarily associated with hospital-acquired infections, with resistance to carbapenems at 88% in 2023.
Key Actions Required
- Prevention: Enhance infection prevention through better hygiene, sanitation, and vaccination.
- Education: Train doctors on the judicious use of antibiotics, reserving potent antibiotics for severe cases, and ensuring appropriate diagnostic testing.
- Regulation: Implement regulations to control antibiotic pollution from manufacturing processes and investigate resistance pathways.
Good Digital Public Infrastructure
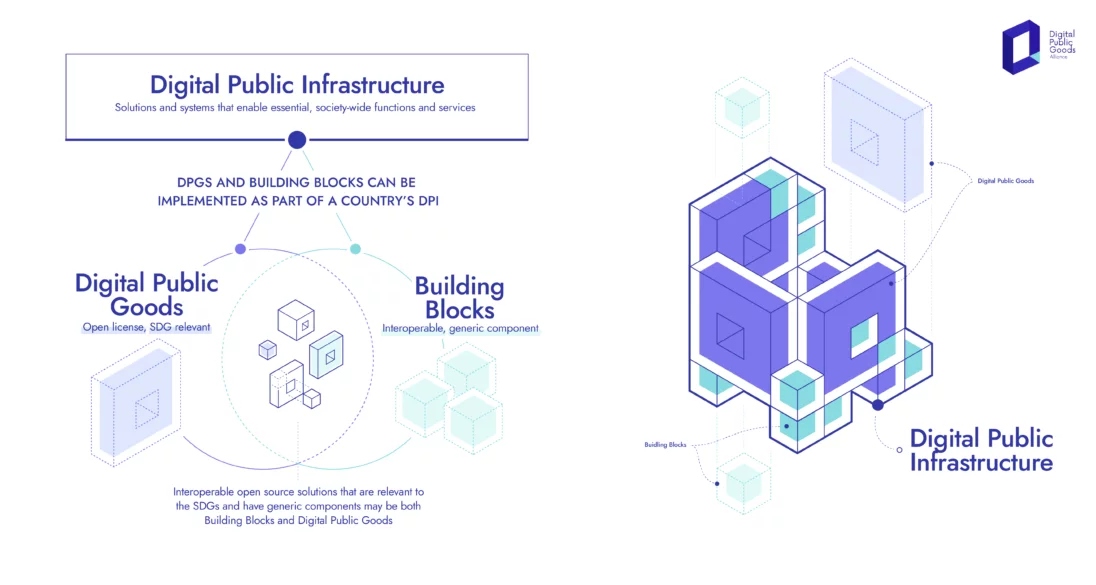
- 08 Sep 2024
Good digital public infrastructure (DPI) integrates technology with societal needs, ensuring that it is secure, scalable, and inclusive.
India’s achievement of over 80% financial inclusion in just six years has drawn international praise, particularly as a model for the Global South. This accomplishment underscores India’s success in achieving both digital and financial inclusion for over a billion people. Consequently, the G20 summit in New Delhi in 2023 highlighted the critical role of digital public infrastructure.
In response, India’s G20 task force has released a comprehensive report outlining a global strategy for DPI development. This positions India to support other nations in achieving digital sovereignty, financial inclusion, and self-reliance.
The evolving digital landscape is marked by a variety of stakeholders—including private enterprises, government bodies, non-profits, and think tanks—each working to advance their DPI solutions. This raises two key questions: How can we identify genuine and reliable DPIs from the plethora available? And what differentiates a “good DPI” from a “bad DPI”?
Identifying effective DPI involves assessing how well technology meets societal needs while ensuring security, scalability, and inclusivity. Authenticity and adherence to core principles are essential for evaluating DPIs.
The Citizen Stack Model
Citizen Stack, built upon the proven success of India Stack, emerges as a trusted ecosystem in digital infrastructure. India Stack, a robust digital platform, has demonstrated its effectiveness and security on a vast scale, serving over a billion citizens. This strong foundation enhances Citizen Stack’s credibility and reliability. Unlike DPI manufacturers, Citizen Stack functions as a regulatory body or auditor, certifying and authenticating DPIs to ensure they meet high standards of quality and security.
Citizen Stack’s approach is comprehensive, focusing on security, scalability, and inclusivity. The DPI platforms approved by Citizen Stack are designed to meet the diverse needs of large populations while maintaining stringent security measures to protect user data and privacy. As an auditor, Citizen Stack ensures that certified DPIs are dependable, secure, and beneficial to the public.
In an era of abundant digital solutions and promises, distinguishing genuinely reliable platforms is essential. Citizen Stack offers assurance as a gold standard for DPI solutions.
Guiding Principles of a “Good DPI”
Citizen Stack has established five core principles—referred to as sutras—that define a good DPI:
- Maintain Citizen Relationships: Ensure that digital infrastructure supports a fair relationship between citizens, the market, and the state, free from undue influence.
- Protect Empowerment and Privacy: Implement consent-based data sharing systems that prioritize individual empowerment and privacy.
- Prevent Monopolistic Lock-In: Ensure interoperability to avoid citizens being restricted by monopolistic entities.
- Combine Techno-Legal Regulation: Integrate technology with legal frameworks to govern ethical tech use, ensuring innovation while safeguarding security and societal rights.
- Foster Public-Private Innovation: Encourage collaboration between public and private sectors, while avoiding corporate dominance. The focus should be on public good rather than corporate monopolies, and technology should prevent exploitation by state or corporate actors.
Barakah Nuclear Energy Plant
- 08 Sep 2024
Location: Situated in Al Dhafra, Emirate of Abu Dhabi.
Specifications:
- Reactor Count: Four nuclear reactors.
- Annual Output: 40 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity.
Objective and Significance:
- Energy Diversification: The plant is a key component of the UAE’s energy diversification efforts, providing clean and efficient power.
- Environmental Impact: It is projected to reduce carbon emissions by up to 22 million tons annually, equivalent to removing 4.8 million cars from the roads.
International Nuclear Energy Agreements
Purpose: Nuclear energy agreements are bilateral or multilateral treaties focused on the peaceful use of nuclear energy. They facilitate international cooperation in areas such as technology transfer, fuel supply, safety standards, and non-proliferation.
India’s Nuclear Energy Agreements:
- General Overview: India has established civil nuclear cooperation agreements with various countries including France, the United States, Russia, Namibia, Canada, Argentina, Kazakhstan, South Korea, Australia, Sri Lanka, and the United Kingdom.
Key Agreements:
- India-Russia: A longstanding partnership since the Cold War, with Russia significantly contributing to the construction of the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant in Tamil Nadu.
- India-US Civil Nuclear Agreement (2008): Known as the 123 Agreement, it marked India’s entry into the global nuclear market despite its non-signatory status to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). This agreement enabled India to engage in nuclear trade with the US and other Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) members.
- India-France Civil Nuclear Agreement (2008): This agreement allows France to supply nuclear technology and fuel to India, including involvement in the proposed Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project in Maharashtra.
- India-Canada Nuclear Cooperation Agreement (2010): This historic deal marked a return to cooperation after a hiatus following Canada's sanctions in 1974, allowing uranium supply for India’s civilian reactors.
- India-Japan Nuclear Agreement (2016): This agreement facilitates the export of nuclear technology from Japan to India, reflecting Japan’s confidence in India's non-proliferation commitments.
- India-Kazakhstan: Agreements with Kazakhstan for uranium supply, given Kazakhstan’s status as a major uranium producer.
- India-Australia Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement: Permits Australia to export uranium for India’s civilian nuclear program. Notably, Australia typically exports uranium only to NPT signatories.
- India-United Kingdom Nuclear Agreement (2015): This agreement promotes collaboration on nuclear technology and research between India and the UK.
- India-UAE Civil Nuclear Energy Cooperation: Recently, India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) formalized their collaboration in civil nuclear energy through an MoU.
National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing innovations (NIDHI) program
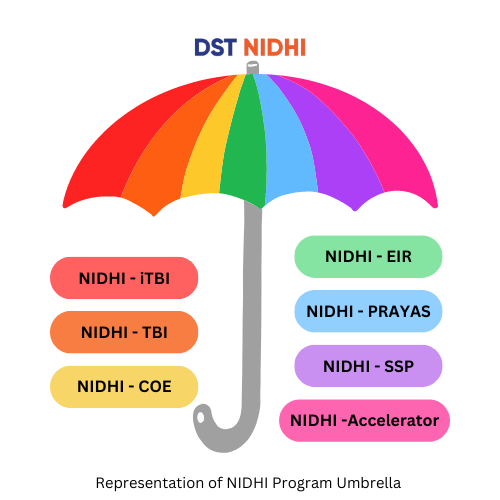
- 08 Sep 2024
- NIDHI is an umbrella programme conceived and developed by the Technology Translation and Innovation (TTI) Division/ National Science and Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board, of Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, for nurturing ideas and innovations (knowledge-based and technology-driven) into successful startups.
- The NIDHI programme works in line with the current national priorities and goals and its focus would be to build an innovation driven entrepreneurial ecosystem with an objective of national development through wealth and job creation.
- NIDHI aims to nurture Startups through scouting, supporting and scaling of innovations by providing them with a series of programme components tailored towards the critical initial phases of the Startup journey.
- The key stakeholders of NIDHI include Science & Technology based entrepreneurs, Startup Incubators, academic and R&D institutions, Startup mentors, financial institutions, angel investors, venture capitalists, relevant government & industry bodies and associations.
- NIDHI has been developed to suit the national aspirations and on the basis of DST’s three-decade long experience in propelling Startup Incubation centres and Science & Technology based entrepreneurs.
- The key components of NIDHI are :-
- NIDHI PRAYAS: Promotion and Acceleration of Young and Aspiring technology entrepreneurs – Support from Idea to Prototype
- NIDHI – EIR: Entrepreneur In Residence – Support system to reduce risk for entrepreneurs.
- NIDHI – TBI : Technology Business Incubator (NIDHI-TBI) – Converting Innovations to start-ups.
- NIDHI – iTBI : Inclusive- Technology Business Incubator – A new variant of the NIDHI-TBI launched in 2022-’23.
- NIDHI – Accelerator : Startup Acceleration Programme – Fast tracking a start-up through focused intervention.
- NIDHI – SSS : Seed Support System – Providing early stage investment
- NIDHI – COE : Centres of Excellence – Globally competitive facilities to help startups go global.
- While NSTEDB is the funding agency, the NIDHI programmes are implemented through Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) available around the country.
- Note: All the NIDHI-Startup funds and offerings are disbursed to eligible startups only through eligible NSTEDB associated incubators across India
Agni-4 ballistic missile successfully test-fired in Odisha

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
India successfully test-fired the Agni-4 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, Odisha. The test, conducted by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) under India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA), demonstrated the missile's operational and technical capabilities.
Key Details:
- Missile Specifications:
- Range: The Agni-4 missile has a maximum range of 4,000 kilometers.
- Payload: It can carry a payload of up to 1,000 kilograms.
- Length: The missile is approximately 20 meters long.
- Launch Platform: It is designed for deployment on a road-mobile launcher, enhancing its flexibility and mobility.
- Historical Context:
- Previous Test (2012): In its earlier test in 2012, Agni-4 successfully covered over 3,000 kilometers within 20 minutes. This was noted as the longest-range mission achieved by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) at that time.
- Name Change: The Agni-4 was previously known as Agni-2 Prime.
- Development and Capabilities:
- Development: The Agni missiles, including the Agni-4, are developed by the DRDO, showcasing India's advancements in missile technology and strategic capabilities.
- Comparison with Agni-5: The Agni-4 is part of a series of Agni missiles that have progressively enhanced India's missile range and strike capabilities. The Agni-5 represents an even more advanced development in this series.
The successful test of Agni-4 underscores India's commitment to strengthening its strategic defense capabilities and maintaining its deterrence posture.
Swachh Bharat Mission averted 60,000-70,000 infant deaths annually: Study
- 09 Sep 2024
- Launched on October 2, 2014, the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) has been pivotal in advancing sanitation infrastructure in India.
- By 2020, the mission had facilitated the construction of over 11 crore household toilets under its Grameen component and over 63 lakh individual and 6.36 lakh community public toilets under its Urban component. This extensive sanitation drive aimed at eradicating open defecation and improving public health.
Impact on Infant Mortality
A recent study published in Nature has highlighted the significant health benefits resulting from SBM. According to the report, titled ‘Toilet Construction under the Swachh Bharat Mission and Infant Mortality in India,’ the initiative may have averted approximately 60,000 to 70,000 infant deaths annually between 2014 and 2020. The study, analyzed data from 35 states and 640 districts from 2011 to 2020, focusing on the infant mortality rate (IMR) and under-five mortality rate (U5MR).
Key Findings
- Decrease in Infant Mortality:
- The study established an inverse relationship between toilet access and infant mortality. It noted that districts with increased toilet coverage saw a marked decline in infant deaths.
- In 2003, the average toilet coverage in districts was below 40%, rising to over 60% by 2020. Correspondingly, infant mortality rates fell from an average of 48.9 per 1,000 live births in 2003 to 23.5 per 1,000 live births in 2020.
- Significant Decline:
- The research observed a substantial decline in infant mortality rates from 40 per 1,000 live births in 2012 to below 30 per 1,000 live births by 2019.
- The mortality rate for children under five also dropped from about 44 per 1,000 live births in 2012 to below 30 by 2019.
- Regional Variations:
- Despite the overall improvement, certain regions like parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh continued to report higher infant mortality rates, ranging between 45-60 per 1,000 live births in 2020.
Conclusion
The SBM has demonstrably improved sanitation in India, with a notable reduction in infant mortality rates attributed to the increased availability of household toilets. While the mission has achieved significant progress, ongoing efforts and investments in broader public health infrastructure are essential to address persistent regional disparities and sustain health gains.
Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari Initiative

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently launched the ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative via video conferencing from Surat, Gujarat.
Key Points:
- Campaign and Objectives:
- Objective: The initiative seeks to bolster water conservation through extensive public and governmental collaboration.
- Scope: About 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures will be constructed across Gujarat.
- Approach: Emphasizes a Whole-of-Society and Whole-of-Government approach to water management.
- Significance:
- Cultural Significance: PM Modi highlighted that water conservation is deeply embedded in Indian culture, with water revered as a divine entity and rivers considered Goddesses.
- Policy and Virtue: He stated that water conservation transcends policy and is both an effort and a virtue, reflecting social commitment and cultural consciousness.
- Future Challenges: The Prime Minister acknowledged the exacerbating impact of water scarcity due to climate change, urging a shift to the ‘Reduce, Reuse, Recharge, and Recycle’ mantra for sustainable water management.
- Impact of Drought and Water Scarcity:
- Recent Challenges: The drought affecting the Amazon region and other parts of India has highlighted the urgent need for effective water conservation strategies.
- Water Table Decline: Significant declines in river levels, such as the Rio Negro reaching its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) on record, and the death of endangered species due to low water levels underscore the crisis.
- Government Initiatives:
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Aims to provide piped water to every home, with significant progress noted from 3 crore households to over 15 crore.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Focuses on renovation and construction of water sources with widespread public participation.
- Amrit Sarovar: Over 60,000 Amrit Sarovars have been constructed under this campaign, which began during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- Innovative Solutions and Technological Integration:
- Drip Irrigation: Promotion of water-efficient farming techniques like drip irrigation to ensure sustainable agriculture.
- Support for Farmers: Encouragement for cultivating less water-intensive crops such as pulses and millets.
- Role of Industries:
- CSR Contributions: Industries have played a significant role in water conservation through initiatives like Net Zero Liquid Discharge Standards and the completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
- Future Plans: The ‘Jal Sanchay-Jan Bhagidari Abhiyan’ aims to create an additional 24,000 recharge structures.
- Conclusion and Vision:
- Global Leadership: PM Modi expressed his belief that India can become a global leader in water conservation.
- Public Movement: Stressed the importance of continuing public participation in water conservation to make India a model for global sustainability.
Background: The ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative builds on the success of the earlier Jal Sanchay program by involving citizens, local bodies, and industries in water conservation efforts. The initiative aligns with the vision of water security and aims to mobilize collective action for long-term sustainability.
Key Data:
- Construction of 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures.
- Significant increase in tap water connections from 3 crore to over 15 crore households.
- Creation of more than 60,000 Amrit Sarovars across the country.
- Completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
Climate change drives Amazon rainforest's record drought, study finds
- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
The drought that hit all nine Amazon rainforest countries - including Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Peru - is expected to worsen in 2024
Role of Climate Change:
- Likelihood Increase: Climate change made the drought 30 times more likely.
- Temperature and Rainfall: It drove extreme high temperatures and contributed to lower rainfall.
Future Projections:
- Expected Worsening: The drought is predicted to worsen in 2024, with the rainy season expected to recede in May.
Impact on Ecosystems:
- River Levels: Rivers have reached their lowest levels on record, with the Rio Negro river falling to its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) since records began in 1902.
- Dolphin Deaths: At least 178 endangered pink and gray Amazon river dolphins died due to low water levels and high temperatures.
- Fish Deaths: Thousands of fish died from low oxygen levels in Amazon tributaries.
Impact on Human Life:
- Disruptions: Waterways dried up rapidly, forcing people to undertake long journeys across dried river sections to access essential goods like food and medicine.
Contributing Factors:
- El Niño Influence: Periodic warming in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (El Niño) contributed to decreased rainfall but not to higher temperatures.
Potential Consequences:
- Forest Fires and Biome Health: The drought could exacerbate forest fires, combined with climate change and deforestation, potentially pushing the Amazon toward a point of no return where it ceases to be a lush rainforest.
- Previous Droughts: While the region has experienced at least three intense droughts in the past 20 years, this one’s impact on the entire Amazon basin is unprecedented.
Uncommon Cyclones in the Arabian Sea
- 09 Sep 2024
Cyclones are intense weather systems with low atmospheric pressure and rotating winds, forming over warm tropical waters. These storms cause severe weather, including heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surges. Cyclones are categorized based on wind speeds, from tropical depressions to severe cyclonic storms. Warm ocean surfaces and high humidity fuel these storms, with atmospheric conditions like wind shear and moisture influencing their strength and formation.
The North Indian Ocean plays a key role in global weather systems, particularly the summer monsoon. Warm waters from the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal are crucial for moisture generation during monsoon seasons. However, despite the warm ocean surfaces that typically promote cyclones, this region has fewer cyclones compared to other tropical oceans. A mix of factors—both promoting and suppressing cyclone formation—makes the North Indian Ocean a unique and less cyclone-prone area.
The Indian Ocean stands out due to its monsoonal circulation, marked by seasonal wind reversals north of the equator. It also has "oceanic tunnels" connecting it to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, which influence its weather. The Pacific tunnel introduces warm water into the upper layers, while the Southern Ocean brings cooler waters into deeper levels. These oceanographic features contribute to distinct weather patterns, including influencing the formation and behavior of cyclones.
As the pre-monsoon season begins and the Sun moves into the northern hemisphere, the Arabian Sea rapidly warms. The Bay of Bengal, typically warmer, heats further, driving atmospheric convection and rainfall. These warming patterns make the Bay of Bengal more prone to cyclones, while the Arabian Sea, with its cooler waters and stronger wind shear, experiences less cyclone activity. These conditions contribute to significant differences in cyclone formation between the two seas.
Impact of Climate Change on Cyclones in the Indian Ocean
Climate change is amplifying the Indian Ocean’s warming, bringing in more heat from the Pacific Ocean while the Southern Ocean pushes warmer waters into deeper layers. These changes, combined with shifts in winds and atmospheric humidity, are causing the Indian Ocean to warm at a rapid pace. This warming is affecting cyclone formation, increasing the frequency and intensity of storms. The Indian Ocean acts as a "clearinghouse" for ocean warming, impacting global weather patterns and intensifying cyclone activity.
Monsoon and Cyclone Seasons in the North Indian Ocean
- The monsoon heavily influences cyclone activity in the region. During the monsoon, strong winds cool the Arabian Sea, reducing the likelihood of cyclone formation. In contrast, the Bay of Bengal sees more low-pressure systems, although many do not become cyclones due to wind shear that weakens their energy.
- The North Indian Ocean experiences two distinct cyclone seasons—pre-monsoon and post-monsoon—unlike other regions that typically have just one. Cooler temperatures and stronger wind shear keep cyclone numbers low in the Arabian Sea, compared to the Bay of Bengal.
- Cyclone Asna, formed in August 2023, was a rare cyclone for this time of year. It developed from a land-based depression that moved over the Arabian Sea, marking the first August cyclone in the region since 1981. This rare occurrence highlights how rapidly warming oceans, influenced by climate change and El Niño, can drive unexpected cyclone formations.
India, UAE ink pact for civil nuclear cooperation

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for civil nuclear cooperation.
- The agreement, established between the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) and the Emirates Nuclear Energy Company (ENEC)-led Barakah Nuclear Power Plant Operations and Maintenance, was formalized during the visit of Sheikh Khalid bin Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi, to New Delhi.
Background:
- This MoU marks the first formal agreement of its kind between NPCIL and ENEC. The collaboration aligns with the broader commitment made during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the UAE in August 2015, which focused on peaceful nuclear energy applications, including safety, health, agriculture, and science and technology.
Trilateral Cooperation:
- The agreement follows a series of discussions on nuclear cooperation between India and the UAE. On September 19, 2022, Foreign Ministers from France, India, and the UAE met in New York during the UN General Assembly and initiated a trilateral cooperation framework. This was further solidified by a phone call on February 4, 2023. The trilateral format aims to promote joint projects in energy, emphasizing solar and nuclear energy.
Additional Agreements:
During the Crown Prince’s visit, several other agreements were also signed:
- LNG Supply MoU: An agreement was reached between Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) and Indian Oil Corporation Limited for long-term LNG supply.
- Production Concession Agreement: Urja Bharat and ADNOC signed an agreement for Abu Dhabi Onshore Block 1.
- Food Parks Development: The Government of Gujarat and Abu Dhabi Developmental Holding Company PJSC (ADQ) signed an MoU for developing food parks in India. This initiative aligns with the I2U2 grouping (including Israel and the United States), which envisions food parks in Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh.
Conclusion:
The visit of the Crown Prince and the signing of these agreements reflect the strengthening ties between India and the UAE. This dynamic development coincides with the first India-Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Foreign Ministers’ meeting held in Riyadh on September 8-9. External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar highlighted India's growing energy demands and its significant role in future global energy markets during his remarks at the meeting.
Govt dissolves Standing Committee on Statistics

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
The recent dissolution of the 14-member Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) by the Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has sparked considerable controversy and debate. The committee, which was chaired by Pronab Sen, a renowned economist and former chief statistician of India, was reportedly disbanded after its members raised concerns about the delay in conducting the decennial census.
Key Points:
- Dissolution of the Committee:
- The SCoS, formed in July 2023, was responsible for advising the Union government on survey methodology and statistical frameworks. According to the experts the decision to dissolve the SCoS was due to an overlap in functions with the newly formed Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys.
- Concerns and Criticism:
- Dr. Pronab Sen and other committee members expressed concerns over the delay in conducting the census, which was due in 2021 but has yet to be carried out. The last census, conducted in 2011, is now outdated, impacting the accuracy of various statistical surveys.
- Members of the SCoS reportedly questioned the delay in census operations during their meetings, leading to speculation that their concerns may have contributed to the committee's dissolution.
- Formation of the New Steering Committee:
- The new Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys, chaired by Rajeeva Laxman Karandikar, was established following a recommendation by the National Statistical Commission (NSC). The roles of this new committee are said to overlap with those of the SCoS, which the Ministry cited as a reason for disbanding the latter.
Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS)
- The Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) was established by renaming and expanding the scope of the Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES), which was originally formed in December 2019.
- The SCES, with 28 members, was tasked with reviewing economic indicators related to the industrial sector, services sector, and labor force statistics, including datasets like the Periodic Labour Force Survey, the Annual Survey of Industries, and the Economic Census.
Current Structure and Members: The newly formed SCoS comprises 14 members, including:
- Four Non-Official Members
- Nine Official Members
- One Member Secretary
The committee's total membership can be extended up to 16 based on requirements.
Functions:
1. Review and Address Issues:
o The SCoS reviews the existing frameworks and addresses issues related to all surveys as presented by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI). This includes evaluating survey results and methodologies.
2. Advisory Role:
o It advises on various aspects of survey methodology, including sampling frames, sampling designs, and survey instruments. The committee is also responsible for finalizing the tabulation plans and results of surveys.
3. Data Collection and Production:
o The SCoS oversees the design and implementation of all data collection and production efforts. It ensures that data collected by MoSPI adheres to high standards of statistical quality and accuracy.
Typhoon Yagi
- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
A devastating series of events unfolded in Vietnam, as a bridge collapsed and a bus was swept away by severe flooding, raising the death toll to at least 65. The fatalities are attributed to Typhoon Yagi and the subsequent heavy rains, which have wreaked havoc across the Southeast Asian country.
In Depth:
- The typhoon made landfall in Vietnam’s northern coastal provinces of Quang Ninh and Haiphong with wind speeds of up to 149 kilometers per hour (92 miles per hour) on Saturday afternoon.
- It raged for roughly 15 hours before gradually weakening into a tropical depression early Sunday morning.
- Vietnam’s meteorological department predicted heavy rain in northern and central provinces and warned of floods in low-lying areas, flash floods in streams and landslides on steep slopes.
What is a cyclone?
- The term 'Cyclone' is derived from the Greek word 'Cyclos' which means 'Coiling of the Snake'.
- Cyclones are created by atmospheric disturbances around a low-pressure area and are usually accompanied by violent storms and severe weather conditions. Basically, a tropical cyclone is a deep low-pressure area.
Sakthan Thampuran

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
Minister of State for Tourism and Thrissur MP Suresh Gopi pledged to replace a statue of Sakthan Thampuran that was knocked over by a state transport bus in June with a new bronze statue if the Kerala government did not do so within 14 days.
Who was Sakthan Thampuran?
- Raja Rama Varma Kunjipillai or Rama Varma IX, better known today as Sakthan Thampuran, ruled over the Cochin kingdom from 1790 to 1805.
- He was born in 1751 to Ambika Thampuran and Chendose Aniyan Namboodiri of the Cochin royal family, but was raised by an aunt who called him Sakthan, meaning ‘powerful’.
- The word thampuran is believed to be an appropriation of the Sanskrit samrat, meaning emperor.
- The Cochin kingdom, which was part of the Late Chera Empire, covered the regions between Ponnani in Malappuram and Thottappally in Alappuzha in today’s Kerala.
Strategist and ruler
- Sakthan Thampuran became heir apparent in 1769 as an 18-year-old. He advised his king to maintain friendly relations with both the Dutch and the English, who were vying for a larger share of trade in the region.
- Sakthan is said to have orchestrated Mysore’s attempt to invade the Travancore kingdom, which had established relations with the English East India Company. This would result in the Powney treaty which freed the Cochin kingdom from its allegiance to Mysore, and helped formalise its relations with the British.
- Sakthan Thampuran put an end to the institution of the Yogiatirippads — the erstwhile spiritual heads of the Vadakkumnathan and Perumanam temples, who had conspired against the previous Cochin king in his wars against the Calicut Zamorin — and entrusted temple management to the government.
- He built a fearsome reputation for himself, and is said to have largely freed his kingdom of crime.
Thrissur and Pooram
- Sakthan Thampuran transferred the seat of the Cochin kingdom from Thrippunithura to modern-day Thrissur.
- The Thekkinkadu Maidanam and the surrounding Swaraj Round became the basis for the city’s elaborate road system and infrastructure.
- The king encouraged merchants of all religions and British officials to relocate to the city. He also overhauled and firmed up the kingdom’s finances, personally overseeing revenue management.
- Sakthan Thampuran started the Thrissur Pooram in 1797 as an alternative to the Arattupuzha Pooram, then the largest temple festival in the state.
- The Thrissur Pooram was conceived as an opportunity for the major temples in Thrissur to come to pay their respects to Lord Shiva, the presiding deity at the Vadakkumnathan Temple.
In a first, critically endangered elongated tortoise spotted in Aravallis

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- A critically endangered species, the elongated tortoise (Indotestudo elongata), was spotted in Haryana’s Damdama area during a research survey in the Aravallis.
Key Features:
- The tortoise is medium-sized with a yellowish brown or olive shell and distinct black blotches at the centre of each scute.
- The tortoise has on its nostril a pink ring, which appears in the breeding season.
- Mature individuals of both sexes develop a distinct pinkish colouration surrounding the nostrils and eyes during the season.
- Habitat:
- The tortoise, found in the Sal deciduous and hilly evergreen forests, is distributed across Southeast Asia from northern India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh in the west, eastward through Myanmar, Thailand, and all of Indochina, north to Guangxi Province of China and south to Peninsular Malaysia.
- A disjunct tortoise population exists in the Chota Nagpur plateau in eastern India. It also inhabits lowlands and foothills of up to 1,000 m above sea level.
- There have not been enough surveys to ascertain its presence in Aravallis, but the tortoise is found in the foothills of the Himalayas.
- It inhabits wetter areas and discovering it here is an aberration than a norm, adding it cannot be ruled out that the tortoise was brought by trade.
Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Status: Critically Endangered, under criteria A2cd.
Threats:
- Currently, I. elongata is heavily exploited for food and traditional medicine throughout its range.
- Local people often opportunistically capture tortoises while farming or extracting other forest resources. However, deliberate hunting also occurs and dogs continue to be widely used for finding tortoises.
India-Singapore Relations

- 04 Sep 2024
- High-Level Inter-Governmental Contacts:
- Frequent and high-level exchanges, including the Prime Minister's upcoming visit.
- Recent second India-Singapore Ministerial Roundtable with senior Indian ministers.
- Key Areas of Cooperation:
- Digitalisation, skills development, sustainability, healthcare, advanced manufacturing, and connectivity.
- Broader contacts include parliamentary and judicial exchanges.
- Economic Ties:
- Singapore is India’s largest trading partner among ASEAN countries and the sixth largest globally.
- Singapore is also the largest source of foreign direct investment (FDI) for India.
- People-to-People Exchanges:
- Large concentration of IIT and IIM alumni in Singapore.
- Historical ties, including the Indian National Army's presence and the contributions of early Indian diaspora in Singapore.
- Regional Policy and Strategic Importance:
- Singapore has supported India’s “Look East” and “Act East” policies.
- Facilitated India’s dialogue partnership with ASEAN.
- Regional implications due to Myanmar’s instability, with India and Singapore both having stakes.
- Defence and Maritime Cooperation:
- Important defence component and maritime collaboration.
- Focus on the Indo-Pacific region amidst growing Chinese influence and new regional architectures like the QUAD.
- Trade and Economic Outlook:
- The visit provides an opportunity to review and expand trade and economic partnerships.
- Potential for increased Chinese FDI into India, with Singaporean entities likely to play a role.
- Complementarities and Challenges:
- Singapore's role as a global trading and investment hub complements India’s economic landscape.
- Highlights India's regulatory and structural inefficiencies, pointing to areas needing improvement for enhanced bilateral cooperation.
World Bank hikes India's economic projection to 7% for FY 2024-25
- 04 Sep 2024
- The World Bank has forecast a growth of 7% for the Indian economy for the current fiscal year, upping its earlier estimate of 6.6%.
- In its report, India Development Update: India’s Trade Opportunities in a Changing Global Context, the World Bank said India’s growth continued to be strong despite a challenging global environment.
- The World Bank growth projection is in line with those of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Asian Development Bank (ADB).
- Both the institutions have raised their forecast to 7% for the financial year ending March 2025.
- The India Development Update [IDU] observes that India remained the fastest-growing major economy and grew at a rapid clip of 8.2% in FY 23/24.
- Growth was boosted by public infrastructure investment and an upswing in household investments in real estate.
- On the supply side, it was supported by a buoyant manufacturing sector, which grew by 9.9%, and resilient services activity, which compensated for underperformance in agriculture.
- Reflecting these trends, urban unemployment has improved gradually since the pandemic, especially for female workers. While female urban unemployment fell to 8.5 % in early FY24/25, the urban youth unemployment remained elevated at 17%.
- India’s robust growth prospects, along with declining inflation rate will help to reduce extreme poverty
- India can boost its growth further by harnessing its global trade potential. In addition to IT, business services and pharma where it excels, India can diversify its export basket with increased exports in textiles, apparel, and footwear sectors, as well as electronics and green technology products.
- A recovery in agriculture will partially offset a marginal moderation in industry and all services will remain robust. The rural private consumption will recover, thanks to the expected recovery in agriculture.
- The report also highlights the critical role of trade for boosting growth. The global trade landscape has witnessed increased protectionism in recent years. The post pandemic reconfiguration of global value chains, triggered by the pandemic, has created opportunities for India.
- The IDU recommends a three-pronged approach towards achieving the $1 trillion merchandise export target by reducing trade costs further, lowering trade barriers, and deepening trade integration.
23rd Law Commission of India

- 06 Sep 2024
Constitution and Tenure:
- Notification and Term:
- The 23rd Law Commission of India was notified by the Union government on September 2, with effect from September 1.
- The commission will have a three-year term, concluding on August 31, 2027.
- The tenure of the previous Law Commission, chaired by former Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, ended on August 31.
Role and Importance of the Law Commission:
- Purpose:
- The Law Commission is a non-statutory body formed by the Union Ministry of Law and Justice through a gazette notification.
- Its role includes reviewing the functioning of laws, recommending the repeal of obsolete legislation, and providing recommendations on issues referred by the government.
- Composition:
- Typically chaired by a retired Supreme Court or High Court judge.
- Includes legal scholars and can also have serving judges.
- Impact:
- Over the years, 22 Law Commissions have submitted 289 reports.
- Their recommendations have influenced significant legislation, such as the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (CrPC), and the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act).
Constitution of the 23rd Law Commission:
- Structure:
- The commission will consist of:
- A full-time chairperson.
- Four full-time members, including a member-secretary.
- Up to five part-time members.
- Ex officio members including the secretaries of the Legal Affairs and Legislative departments.
- The commission will consist of:
- Appointment and Remuneration:
- Chairperson and full-time members can be serving Supreme Court or High Court judges or other experts chosen by the government.
- The chairperson will receive a monthly salary of ?2.50 lakh, while members will receive ?2.25 lakh.
- The member-secretary must be an officer of the Indian Legal Service of the rank of Secretary.
- Serving judges appointed to the commission will serve until retirement or the end of the commission’s term, without additional remuneration.
Terms of Reference:
- Primary Tasks:
- Identify and recommend the repeal of obsolete or irrelevant laws.
- Create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for periodic review and simplification of existing laws.
- Identify laws that are misaligned with current economic needs and suggest amendments.
- Directive Principles and Reforms:
- Examine laws in light of Directive Principles of State Policy and suggest improvements and new legislation to achieve constitutional objectives.
- Address laws affecting the poor, conduct post-enactment audits of socio-economic legislation, and review judicial administration for responsiveness.
Previous Commission's Contributions:
- Reports and Recommendations:
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
- A report in April 2023 recommending retention of Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (sedition law), with suggested amendments for clarity.
- A report recommending a new law to protect trade secrets.
- A report on simultaneous elections, though it was not submitted to the government before the commission’s chairperson assumed office as a Lokpal member.
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
Upcoming Focus:
- The 23rd Law Commission is expected to continue examining key issues, including the implementation of a uniform civil code, which was also considered by the 22nd Commission but whose recommendations remain unpublished.
Addressing Vertical Fiscal Imbalance: The Role of the 16th Finance Commission
- 06 Sep 2024
In India, the financial relationship between the Union government and the States is characterized by vertical fiscal imbalance (VFI), where the Union government holds most of the revenue while States shoulder significant expenditure responsibilities. The 16th Finance Commission has a pivotal role in addressing this imbalance. Here's how it should approach the issue:
Understanding Vertical Fiscal Imbalance (VFI)
- Current Situation:
- States incur 61% of revenue expenditure but collect only 38% of revenue receipts.
- States rely heavily on transfers from the Union government, leading to a pronounced VFI.
- VFI Definition:
- VFI arises when the expenditure responsibilities of States exceed their revenue-raising capabilities, necessitating transfers from the Union.
Reasons to Address VFI
- Constitutional Allocation:
- Revenue duties and expenditure responsibilities are constitutionally divided.
- Union government collects Personal Income Tax, Corporation Tax, and part of indirect taxes for efficiency.
- States are better positioned to deliver publicly provided goods and services effectively.
- Historical Context:
- The 15th Finance Commission highlighted that India has experienced a rising VFI, exacerbated by crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Finance Commission's Role:
- The Commission addresses VFI by determining how to allocate taxes collected by the Union to the States and how to distribute these among States.
Finance Commission Recommendations
- Tax Devolution:
- The Commission recommends devolving a portion of Union taxes to States.
- The 14th and 15th Finance Commissions recommended devolving 42% and 41% of net proceeds, respectively.
- To eliminate VFI, devolution should be around 48.94%.
- Grants and Transfers:
- The Commission also suggests grants under Article 275 for specific purposes.
- Transfers under Article 282, such as centrally sponsored and central sector schemes, are tied and include conditionalities, which are not untied resources.
Calculation and Recommendations for VFI
- Estimating VFI:
- Ratio = (Own Revenue Receipts + Tax Devolution) / Own Revenue Expenditure.
- A ratio less than 1 indicates insufficient revenue to meet expenditure, showing the VFI deficit.
- Empirical Findings:
- To address VFI, the share of net proceeds devolved to States should be around 49%.
- This increase would ensure that States have more untied resources, enhancing their ability to meet local needs and priorities.
Implications of Increased Tax Devolution
- Enhanced State Capacity:
- A higher share of tax devolution would empower States with more resources for untied expenditures.
- It would improve the alignment of State expenditures with local needs and priorities.
- Improved Efficiency:
- Enhanced devolution would lead to better efficiency in expenditure by allowing States to respond more effectively to jurisdictional requirements.
- Strengthened Fiscal Federalism:
- Addressing VFI through increased tax devolution contributes to a more balanced and cooperative fiscal federalism.
Conclusion: The 16th Finance Commission should focus on increasing the share of tax devolution to around 50% to address the vertical fiscal imbalance. This adjustment will provide States with the necessary resources to manage their expenditure responsibilities more effectively and ensure a more equitable distribution of fiscal resources in India’s federal structure.
Can Kerala access funds from the Loss and Damage Fund?

- 06 Sep 2024
In light of the recent landslides in Kerala’s Wayanad district, the question arises whether subnational entities like Kerala can access the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)’s Loss and Damage Fund (LDF). While the need for compensation is clear, the process of accessing climate funds is complex.
What is the Loss and Damage Fund (LDF)?
- Established at COP27 in Egypt, the LDF aims to support regions experiencing economic and non-economic losses from climate change.
- Includes extreme weather events and slow-onset processes like rising sea levels.
- Managed by a Governing Board, with the World Bank as the interim trustee.
- The Board is developing mechanisms for resource access, such as direct access, small grants, and rapid disbursement options.
- Concerns exist about the speed and accessibility of climate funds, which may affect their effectiveness in immediate disaster recovery.
What has been India’s Role?
- India faced over $56 billion in weather-related damages from 2019 to 2023. Despite this, its National Climate Action Policy prioritizes mitigation over adaptation, leading to limited engagement in Loss and Damage dialogues at COP meetings.
- High vulnerability in certain regions could benefit from active participation in these dialogues.
- India needs a clear legal and policy framework for climate finance, focusing on locally led adaptation, which is vital for vulnerable communities.
- The Union Budget 2024’s introduction of a climate finance taxonomy raises hopes for increased international climate finance.
- Without clear guidelines for accessing loss and damage funds, frontline communities remain at risk.
- India should advocate for decentralized fund disbursement methods from the LDF, contrasting with the centralized systems used for other climate funds.
What have been State Interventions?
- State governments, such as Kerala, often bear the financial burden of disaster recovery.
- Example: The Rebuild Kerala Development Programme post-August 2018 floods, funded by World Bank and KfW Development Bank loans.
- Focused on infrastructure reconstruction, including roads and bridges.
- Lack of a standardized method for comprehensive disaster damage assessments, especially for slow-onset events, may mean significant loss and damage needs go unassessed.
- This could hinder India’s ability to access the LDF.
- The Wayanad situation highlights broader challenges in accessing and managing climate finance for loss and damage.
- A clearer domestic policy framework focusing on locally led adaptation and defined guidelines for accessing loss and damage funds is needed for better climate change protection.
Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack
- 08 Sep 2024
The Government of India has recently introduced several significant initiatives to advance blockchain technology and its applications.
1. Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack
- Purpose: The Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack is designed to offer Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) with a geographically distributed infrastructure. This stack supports various permissioned blockchain-based applications, enhancing the security and efficiency of digital services.
2. NBFLite
- Description: NBFLite is a lightweight blockchain platform intended as a sandbox for startups and academic institutions. It allows for rapid prototyping, research, and capacity building, fostering innovation in blockchain applications.
3. Praamaanik
- Purpose: Praamaanik is a blockchain-enabled solution for verifying the origin of mobile apps. This ensures that users can trust the source of their applications, contributing to enhanced digital security.
4. National Blockchain Portal
- Function: The National Blockchain Portal serves as a central hub for accessing blockchain technologies and services developed under the National Blockchain Framework (NBF).
5. National Blockchain Framework (NBF)
- Overview: The NBF is designed to promote secure, transparent, and trusted digital service delivery. It includes:
- Distributed Infrastructure: Hosted across NIC Data Centers in Bhubaneswar, Pune, and Hyderabad.
- Core Framework Functionality: Provides the backbone for various blockchain applications.
- Smart Contracts & API Gateway: Facilitates interactions with blockchain-based systems.
- Security, Privacy & Interoperability: Ensures robust security and privacy while supporting integration with other systems.
- Applications Development: Supports the creation and deployment of blockchain applications.
- Goals: The NBF aims to address challenges such as the need for skilled manpower, vendor lock-in, and issues related to security, interoperability, and performance.
6. Strategic Objectives
- Digital Trust and Service Delivery: The framework is part of the government's effort to create trusted digital platforms and improve service delivery to citizens.
- Global Leadership: The initiative seeks to position India as a global leader in blockchain technology, driving economic growth, social development, and digital empowerment.
- Governance Transformation: Blockchain technology is envisioned to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accountability in public services.
7. Collaborative Efforts
- Development: The technologies have been developed through the collaborative efforts of organizations including C-DAC, NIC, IDRBT Hyderabad, IIT Hyderabad, IIIT Hyderabad, and SETS Chennai, with support from MeitY.
- Research and Patents: The NBF project has already resulted in several patents and research publications, reflecting its innovative and research-driven approach.
8. Future Directions
- Scaling Applications: There is an emphasis on scaling blockchain applications across various states and departments.
- Exploring New Innovations: Efforts will continue to onboard new applications and innovative components on the NBF stack.
Health Ministry approves new treatment regimen for multidrug-resistant TB
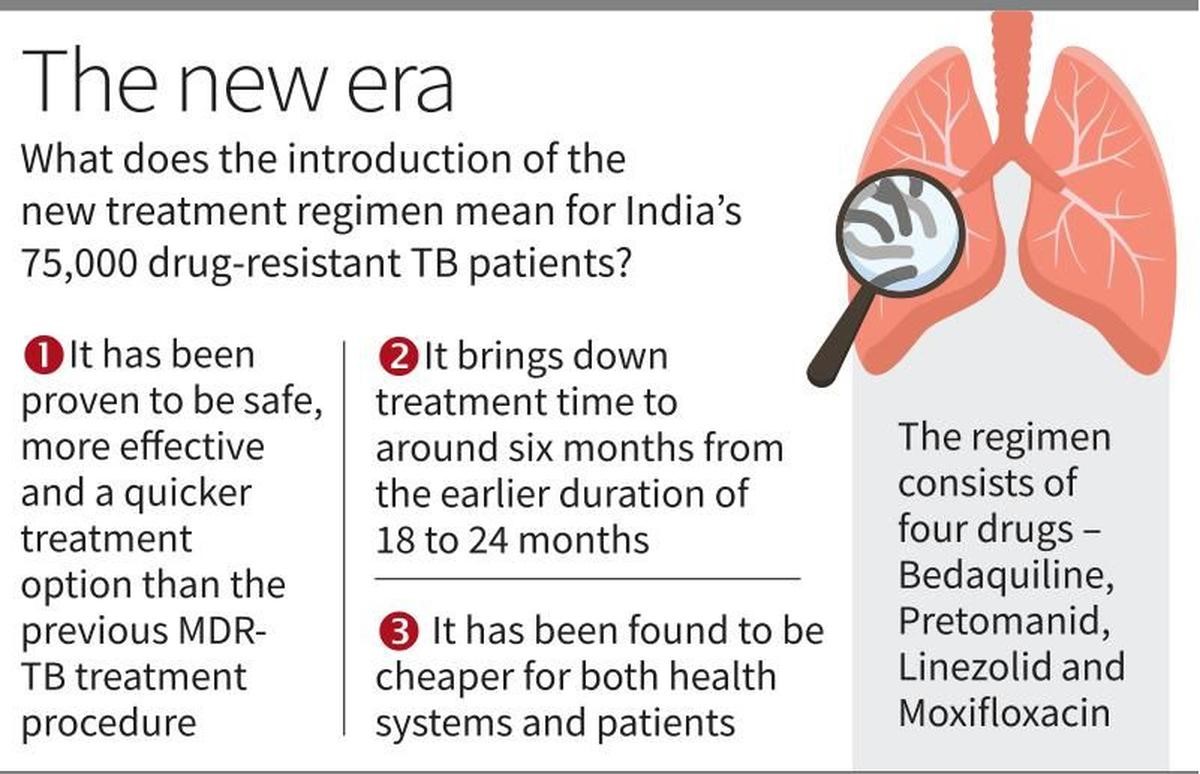
- 08 Sep 2024
The recent approval of the BPaLM regimen by India's Union Health Ministry marks a significant advancement in the fight against multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). This new treatment combines four drugs—Bedaquiline, Pretomanid, Linezolid, and Moxifloxacin—and offers several benefits over traditional treatments.
Key Points:
- Enhanced Effectiveness: The BPaLM regimen has demonstrated a higher efficacy in treating MDR-TB compared to previous methods.
- Shorter Treatment Duration: Unlike traditional treatments, which can take up to 20 months and often come with severe side effects, the BPaLM regimen shortens the treatment period to just six months.
- Improved Safety: The new regimen is noted for its safety profile, potentially reducing the risk of adverse effects compared to older treatments.
- Cost Savings: By shortening the treatment duration and improving outcomes, the BPaLM regimen is expected to lower overall treatment costs.
- Integration into National TB Elimination Programme: This regimen will be incorporated into India’s National TB Elimination Programme, aligning with the country’s ambitious goal to eliminate TB by 2025, which is five years ahead of the global target.
- Infrastructure and Testing Facilities: India boasts a comprehensive TB laboratory network, including 7,767 rapid molecular testing facilities and 87 culture and drug susceptibility testing laboratories, which will support the implementation of the new regimen.
This development represents a significant step forward in TB care and aligns with broader global efforts to combat drug-resistant TB more effectively.
