SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
Discovery of New Hammerhead Shark Species

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of marine biologists led by a Florida International University researcher has described a new species of the shark genus Sphyrna from the Caribbean and the Southwest Atlantic.
- New Species: Named Sphyrna alleni (common name: shovelbill shark).
- Habitat: Found in coastal waters, estuaries, coral reefs, and seagrass beds from Belize to Brazil, with confirmed presence in:
- Caribbean: Belize, Panama, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago.
- Southwestern Atlantic: Brazil.
- Characteristics:
- Small species, less than 1.5 m in length.
- Distinctive flat, shovel-shaped head lacking indentations on the anterior edge.
- Different from Sphyrna tiburo:
- More rounded anterior margin.
- Absence of lobules on the posterior margin.
- Higher precaudal vertebral count (80-83 vs. ~73 in Sphyrna tiburo).
- Evolutionary Insight: Possible sister lineage to Sphyrna vespertina, suggesting Sphyrna tiburo diverged later.
- Conservation Status:
- Hammerhead sharks are highly threatened, primarily due to overfishing.
- Most species, except Sphyrna gilberti, are listed as Vulnerable, Endangered, or Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- Current IUCN assessment of Sphyrna tiburo as Globally Endangered may need reevaluation considering the new findings.
- Management Recommendations:
- Increased management efforts needed for Sphyrna alleni, particularly restrictions on gillnets and trawls, which significantly impact this species.
- Publication: Findings reported in the journal Zootaxa.
Planetary Alignment

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Next month, on June 3, there will be a planetary alignment that may actually allow you to witness six planets align in the sky.
What is a Planetary Alignment?
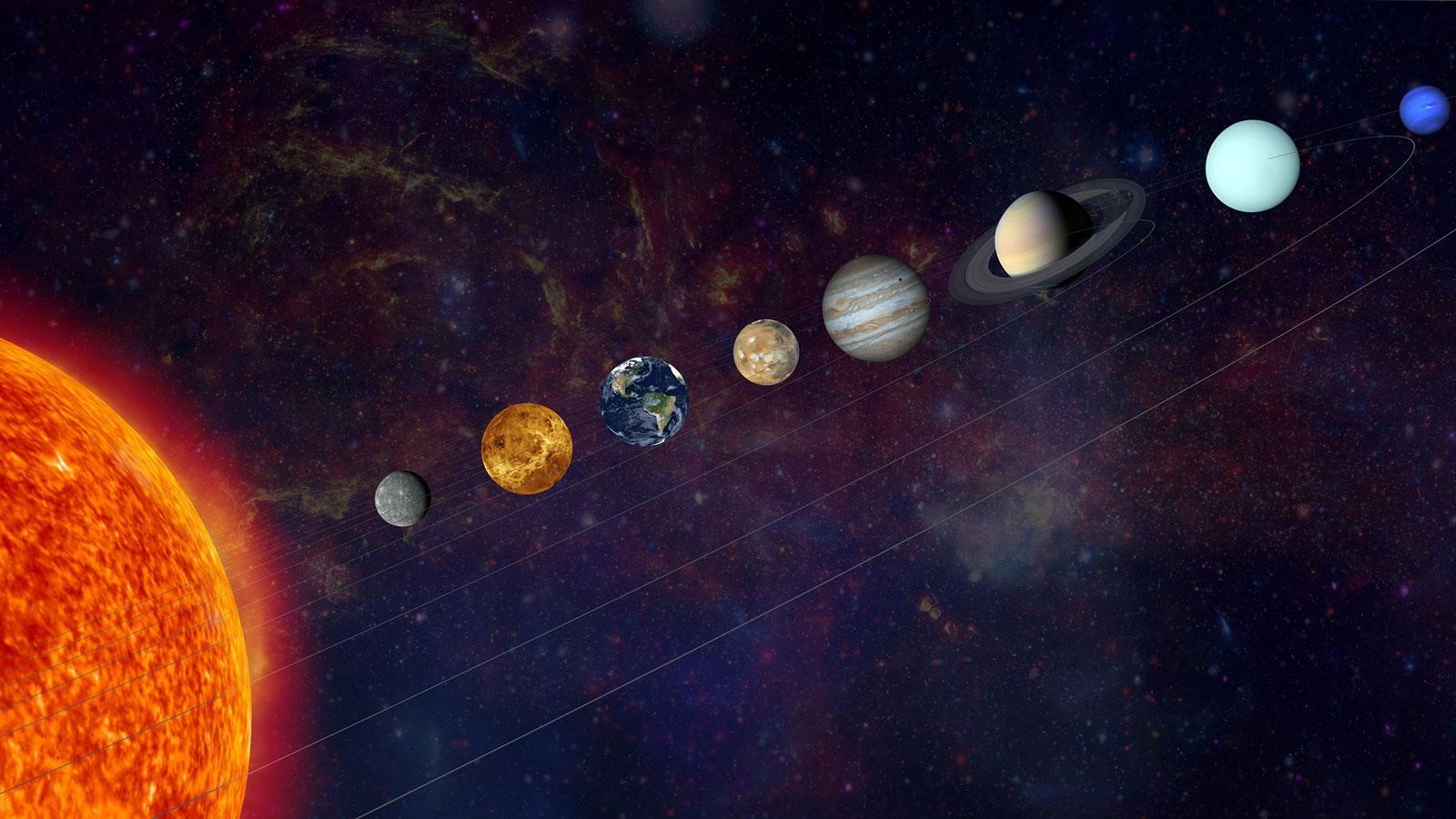
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that's Earth.
- It is an astronomical event that happens when, by coincidence, the orbits of several of the planets of the Solar System bring them to roughly the same side of the Sun at the same time.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- It’s important to emphasise that the planets aren’t forming a straight line in space – that’s a much rarer astronomical event called a syzygy.
- However, because all the planets, including the Earth, orbit around the Sun in roughly the same orientation (moving in which we call the “Plane of the Ecliptic”), when they’re on the same side of the Sun as each other, they appear to form a line in the sky when we view them from Earth.”
- Planetary alignments are rather common within themselves, especially when two, three, or even four planets align in the sky.
- Five or more planets aligning, however, is less common.
- April 8, 2024, was the last time the planets were all in alignment.
Which planets will align?
- Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will form a near-straight line, offering an extraordinary opportunity to witness this cosmic phenomenon.
Which planets will be visible?
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Nucleosynthesis
- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the process by which stars forge elements inside their cores.
What is Nucleosynthesis?
- Nucleosynthesis is the process by which atomic nuclei undergo nuclear reactions and decay to form new nuclei.
- It is responsible for the production of new elements in the universe.
- Nucleosynthesis occurs in various environments, such as during the Big Bang, in the cores of stars through nuclear fusion, and in black hole accretion disks through nuclear burning.
- The process is temperature-dependent, and the rates of nuclear reactions are influenced by the temperature of the environment.
- The Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN) model is a fundamental theory that explains the evolution of the early universe and predicts the abundance of light elements.
- Nucleosynthesis plays a crucial role in understanding the composition of the universe and can provide insights into physics beyond the standard model.
Types of nucleosynthesis:
- Nucleosynthesis occurs in several different environments and phases of the universe's evolution, including:
- Stellar Nucleosynthesis: This occurs within stars and is responsible for producing most of the chemical elements heavier than hydrogen and helium.
- As stars age and undergo various stages of nuclear fusion, they synthesize elements up to iron in their cores, and heavier elements during supernova explosions at the end of their life cycles.
- Big Bang Nucleosynthesis: This took place during the early moments of the universe's existence, shortly after the Big Bang.
- t primarily produced the lightest elements, hydrogen, and helium, along with trace amounts of lithium, beryllium, and boron.
- Cosmic Ray Spallation: High-energy cosmic rays interacting with interstellar matter can cause fragmentation of atomic nuclei, resulting in the production of lighter elements and isotopes.
Project Astra

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, during the company's annual developer conference, Google unveiled an early version of Project Astra.
What is Project Astra?
- Project Astra is an experimental “multimodal” AI assistant developed by Google DeepMind.
- It's designed to be a versatile tool that can understand and respond to information from the real world through various means, like text, voice, images, and even videos.
- This makes it different from current AI assistants that mostly rely on internet searches and user input.
- Building on Google’s Gemini language model, Astra has multimodal capabilities to perceive visuals, sounds, and other real-world inputs.
- The aim is to create a universal AI helper that seamlessly assists us in daily life by comprehending the actual environment through sight and sound, not just text.
- Astra represents Google’s vision for next-gen AI assistants.
Key Features of Google's Project Astra:
- Visual Understanding: Astra can interpret and analyze visual input from its camera feed.
- It identifies objects, reads text, and describes scenes and environments in detail, allowing users to show Astra something and ask questions about it.
- Voice Interaction: Astra supports natural conversation without the need to repeatedly use wake words.
- It comprehends context and facilitates back-and-forth dialogue, even allowing users to interrupt its responses.
- Remembering Context: Astra retains memory of previous conversation parts, objects it has seen, and information provided by the user.
- This contextual awareness enhances the fluidity of interactions.
- Multimodal Integration: Astra integrates visual and auditory inputs to form a comprehensive understanding of the current situation, correlating what it sees and hears to fully grasp the context.
- Real-Time Assistance: Astra delivers real-time assistance by rapidly processing sensor data and queries, ensuring a responsive and interactive user experience.
What are Multimodal AI Models?
- Multimodal AI models are advanced artificial intelligence systems that process and integrate multiple types of data inputs, such as text, images, audio, and video, to develop a comprehensive understanding of context.
- By combining these different modalities, these models enhance their ability to interpret complex scenarios more accurately than unimodal systems.
- For instance, in autonomous vehicles, multimodal AI uses data from cameras, lidar, radar, and GPS for better navigation.
- In healthcare, these models integrate medical images with patient history for improved diagnostics.
- Applications also include virtual assistants, which understand and respond to spoken commands while recognizing objects in images, and educational tools that combine text, video, and interactive content for richer learning experiences.
- Multimodal AI models are often implemented using deep learning techniques, which allow the model to learn complex representations of the different data modalities and their interactions.
- As a result, these models can capture the rich, diverse information present in real-world scenarios, where data often comes in multiple forms.
Plunging Region of a Black Hole

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
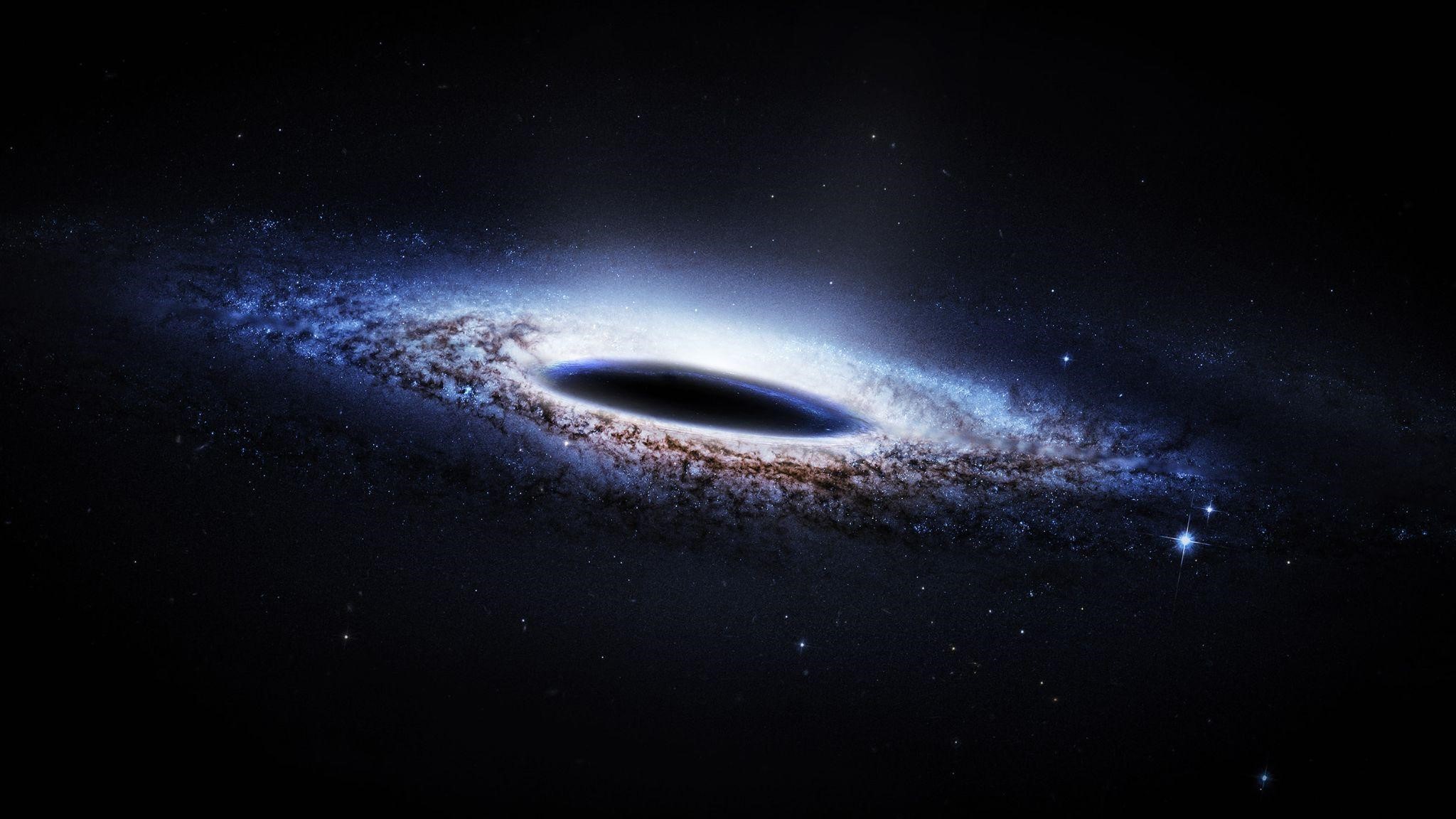
For the first time, astronomers have observed the area right at the edge of a black hole where matter stops orbiting and plunges straight in at near-light speed.
What is the Plunging Region of a Black Hole?
- The plunging region of a black hole is an area where matter ceases to orbit the celestial object and instead falls directly into its incalculable depths.
- This phenomenon was initially predicted by Albert Einstein's groundbreaking theory of general relativity, which continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos.
- As matter approaches a black hole, it is torn apart and forms a rotating ring known as an accretion disc.
- According to general relativity, there exists an inner boundary within this disc, beyond which nothing can maintain its orbit around the black hole.
- Instead, the material is drawn towards the black hole at nearly the speed of light, marking the beginning of the plunging region.
- This region, situated just outside the event horizon, represents the point of no return for matter falling into a black hole.
- Despite the challenges posed by studying these enigmatic structures, researchers believe that investigating plunging regions could unveil new insights into the formation and evolution of black holes.
- Additionally, these studies may offer valuable information about the fundamental properties of space-time, potentially transforming our understanding of the universe and its most mysterious inhabitants.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a celestial phenomenon that arises from the remnants of a massive star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse.
- It is characterized by an unfathomably dense core, known as a singularity, which is enveloped by a boundary called the event horizon.
- The event horizon serves as a point of no return; any matter or light that crosses this boundary is irrevocably drawn towards the singularity, making it impossible to escape the immense gravitational pull.
Black holes are classified into three categories based on their size and formation process:
- Stellar-mass black holes: These form when a massive star collapses at the end of its life cycle. They typically have masses ranging from approximately five to several dozen times that of our Sun.
- Supermassive black holes: Found at the centre of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, these colossal structures boast masses that can reach billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate-mass black holes: With masses between those of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, these entities are thought to form through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of dense clusters of stars.
- Due to their extreme nature, black holes have been the subject of extensive research and fascination in the scientific community.
- The study of these enigmatic structures continues to yield invaluable insights into the fundamental principles governing our universe.
Mitogenome
- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found South African leopards originated from two unique clades in southern and central Africa approximately 0.8 million years ago.
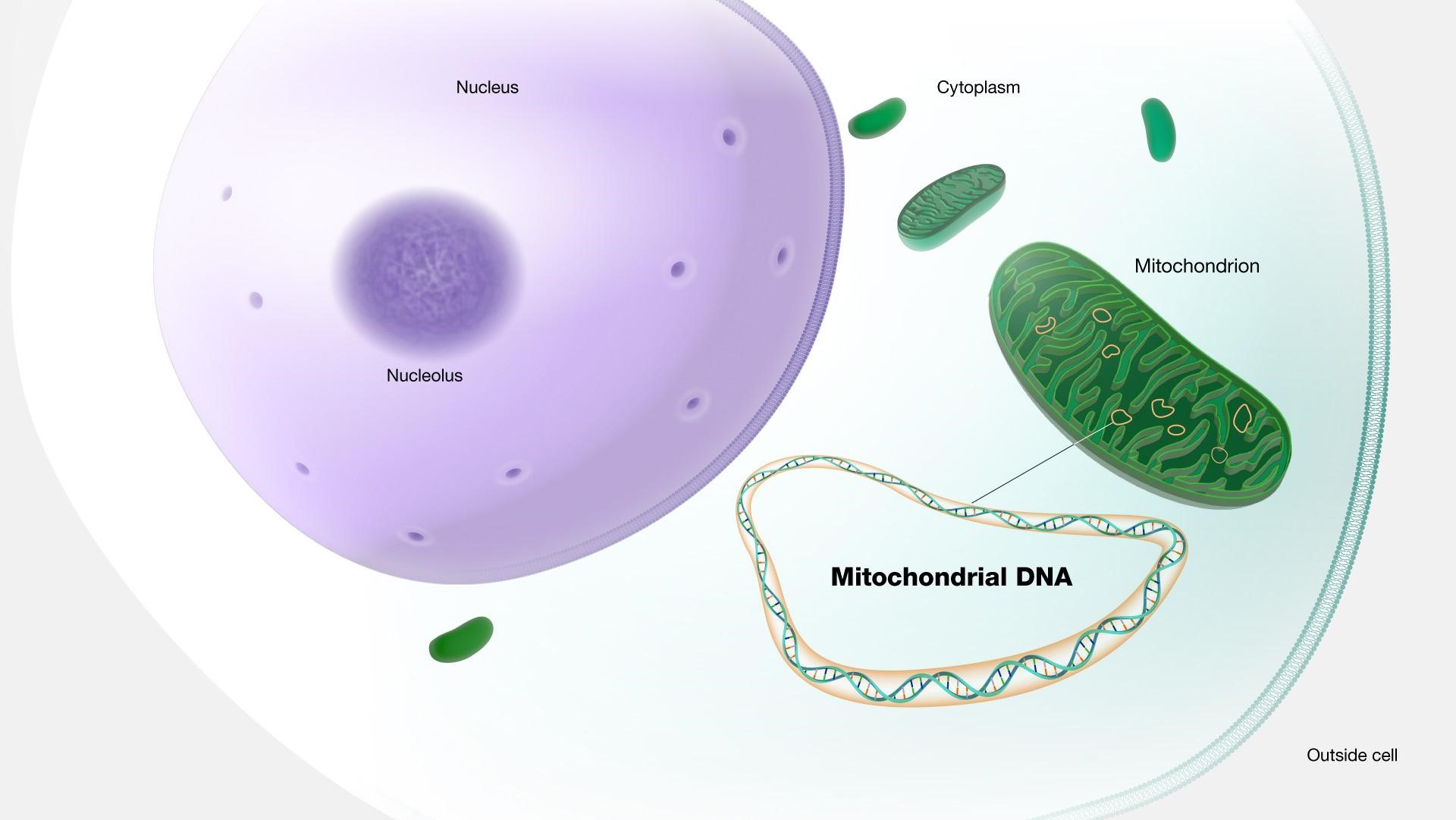
What is a Mitogenome?
- DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and also in the mitochondrial genome, or mitogenome.
- Mitogenomes are DNA molecules that float around outside the nucleus of a cell.
- They store their own set of genetic information and are maternally inherited, which means they are only passed on from mother to offspring.
- Mitogenomes are a “genomic by-catch” when sequencing the whole genome.
- They are so abundant in cells that it is very easy to extract them.
- Studying mitogenomes is a reliable way to track the ancestry of a species.
- This is because genes mutate (change) at a regular rate over time.
- The changes in the mitogenome provide a picture of any species' evolution over hundreds of thousands of years.
What is DNA?
- DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid is the genetic material that codes the information for all the different processes that make an organism living like growth, replication, metabolism, etc.
- DNA is present in each cell (except for some viral species, RBCs, sieve cells, etc.) and is passed down from parents to their offspring. DNA is comprised of units called nucleotides.
- DNA is self-replicating, a long stretch of nucleotides.
- DNA is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four major macromolecules that make up the living system.
- In eukaryotic cells, it is found in the nucleus of the cell whereas in prokaryotes it is found free-floating in the cell cytoplasm.
- Other than the nucleus DNA is also found in mitochondria, chloroplast, and in smaller forms called plasmid in certain bacterial species.
Synchrotron
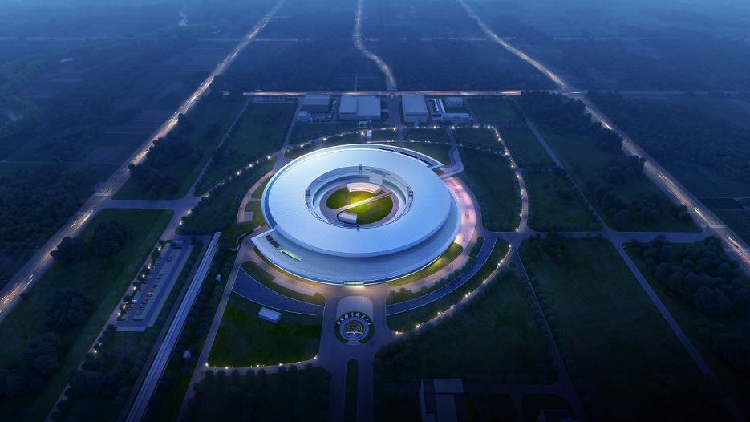

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
China's latest scientific achievement, the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS), is poised to become Asia's first fourth-generation synchrotron light source which is scheduled to commence operations by the end of this year.
What is a Synchrotron?
- A synchrotron is a type of circular particle accelerator where particles travel in a loop.
- It functions by accelerating charged particles, typically electrons, through sequences of magnets until they approach the speed of light.
How Does It Work?
- Acceleration: Charged particles are accelerated through magnets.
- Production of Light: These high-speed electrons generate extremely bright light, known as synchrotron light.
- This light, predominantly in the X-ray region, is millions of times brighter than conventional sources and 10 billion times brighter than the sun.
- Beamlines and Workstations: The intense light is directed down beamlines to experimental workstations for research purposes.
Applications:
- Research: Scientists use synchrotron light to study tiny matter such as atoms and molecules.
- By examining how a sample scatters, diffracts, absorbs, or reemits the synchrotron light, they can uncover details about its structure and chemical composition.
Global Presence:
- There are approximately 70 synchrotrons worldwide in various stages of development.
- They have varying technical specifications and uses, ranging from practical applications to fundamental theoretical research.
In India:
- India has a synchrotron facility known as the "Indus Synchrotron."
- It is located at the Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology (RRCAT) in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- The Indus Synchrotron is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source that is used for various research applications in fields such as materials science, biology, and environmental science.
What is the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS)?
- HEPS (High Energy Photon Source) is recognized as the brightest synchrotron X-ray source in Asia.
- Location: The HEPS facility is situated in Huairou, China, approximately 50 kilometres from Beijing.
- Acceleration Capabilities: HEPS is designed to accelerate electrons up to energies of 6 gigaelectron volts within its 36-kilometer circumference storage ring, producing high-energy X-rays for research purposes.
- Nanoscale Investigations: The high-energy X-rays generated by HEPS can penetrate deep into samples, allowing researchers to study intricate details at the nanometer scale.
- Diverse Research Applications: HEPS will cater to various research fields, including energy, condensed matter physics, materials innovation, and biomedicine, by providing access to 14 specialized beamlines.
- Superiority to Existing Synchrotrons: Compared to China's current most advanced synchrotron, the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (with a circumference of 432 meters), HEPS will offer a time resolution 10,000 times better.
PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) Mission

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
NASA is set to launch the two small satellites of the PREFIRE mission from New Zealand on May 22 aimed at filling in critical gaps in data from Earth's polar regions.
What is the PREFIRE Mission?
- PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) is a NASA mission that involves sending two tiny twin spacecraft, known as CubeSats, to the Earth's polar regions to gather data on the heat energy radiated out to space and its impact on our climate.
- PREFIRE consists of two, 6U CubeSats with a baseline mission length of 10 months.
- These shoebox-sized satellites will orbit at altitudes between 292 and 403 miles, crossing paths in the atmosphere.
Objectives:
- The mission will help close a gap in understanding how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space, especially from the Arctic and Antarctica.
- Analysis of PREFIRE’s measurements will inform climate and ice models, providing better projections of how a warming world will affect sea ice loss, ice sheet melt, and sea level rise.
- Improving climate models can ultimately help to provide more accurate projections on the impacts of storm severity and frequency, as well as coastal erosion and flooding.
- By studying the far-infrared radiation emitted from these regions, PREFIRE will help improve the accuracy of climate models, enhancing our understanding of phenomena such as Arctic warming, sea ice loss, and ice-sheet melting.
The mission will help in:
- Uncover the reasons behind the Arctic warming more than 2½ times faster than the global average since the 1970s.
- Provide scientists with a clearer understanding of how efficiently far-infrared heat is emitted by materials such as snow and sea ice, and how clouds affect the amount of far-infrared radiation that escapes to space.
- Enhance predictions about future changes in the heat exchange between Earth and space, and how these changes will impact phenomena like ice sheet melting, atmospheric temperatures, and global weather patterns.
How will the Satellites Work?
- The mission with cube satellites about the size of a shoebox will be launched aboard an Electron launch vehicle.
- It is equipped with technology proven on Mars and will measure a “little-studied portion” of the radiant energy emitted by Earth.
- Two satellites carrying a thermal infrared spectrometer will be in asynchronous near-polar orbits and will be passing over a given spot on Earth at different times. To maximize coverage, they will be overlapping every few hours near the poles.
- The instruments weighing less than 6 pounds (3 kilograms) each will make readings using a device called a thermocouple, similar to the sensors found in many household thermostats.
Why is it Important to Study the Polar Regions?
- According to NASA, Earth's climate balance hinges on the equilibrium between the heat energy the planet receives from the Sun and the amount it radiates back into space.
- The difference between incoming and outgoing energy determines Earth's temperature and climate.
- The polar regions are crucial in this balance.
- Changes in the polar regions can significantly impact global weather patterns.
- Extreme storms, flooding, coastal erosion – all of these phenomena are influenced by what’s happening in the Arctic and Antarctic.
- This underscores the importance of understanding polar dynamics to predict and mitigate global climate effects.
C-Dome Defense System
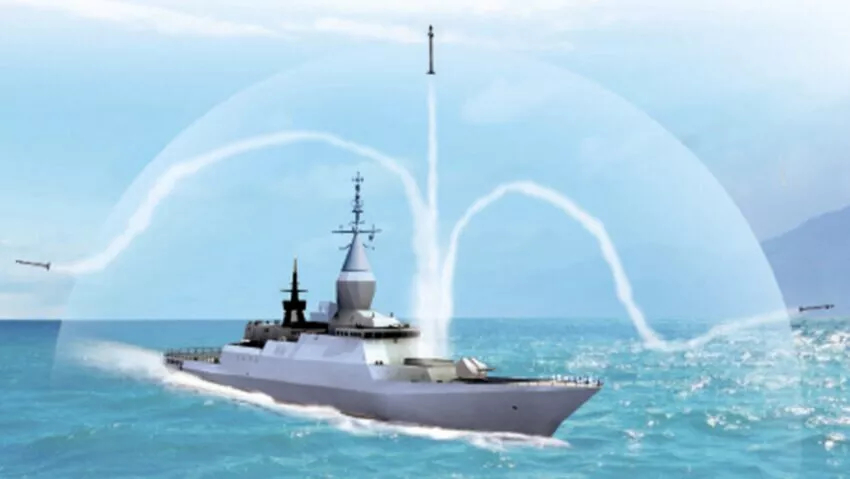

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Israel for the first time used a seaborne missile defense system to shoot down a drone approaching from the Red Sea that had set off sirens in the port city of Eilat.
What is the C-Dome Defense System?
- The C-Dome is a naval version of Israel's Iron Dome air defense system, designed to protect against rocket and missile attacks.
- Drawing from Iron Dome's technology, C-Dome shares its 90% effectiveness rate and utilizes radars to detect and destroy short-range rockets with its missiles.
Operational Deployment and Integration:
- First unveiled in 2014 and declared operational in 2022, the C-Dome is mounted on Sa'ar 6-class corvettes and German-made warships.
- It employs the same interceptor as the Iron Dome but differs in its integration with the ship's radar for target detection, ensuring full-circular vessel protection.
Combatting Modern Threats:
- C-Dome's primary objective is to counter a wide range of modern maritime and coastal threats with high kill probability.
- Its successful deployment and performance underscore its pivotal role in safeguarding Israel's naval interests and assets against evolving security challenges.
About Iron Dome:
- Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Israel Aerospace Industries, the Iron Dome is a cutting-edge air missile defense system that offers protection against short-range rockets by intercepting them above Israeli territory.
- With its multi-rocket handling capacity, Iron Dome became operational in 2011 and features:
- All-weather capabilities for day and night functionality
- Launching versatility with various interceptor missiles
- A range of approximately 40 miles
- Portable design for deployment on ships or land
- Adaptive defense through reloadable interceptors
Iron Dome consists of three key elements:
-
- Radar system for detecting incoming rockets
- Command-and-control mechanism to evaluate threat levels
- Interceptors are designed to neutralize incoming rockets before impact
- These components work in tandem to provide Israel with a robust and reliable defense against aerial threats.
India Imposed Import Restrictions on Solar PV Cells

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recent government orders on attempts to increase local sourcing of solar modules to support India’s renewables manufacturing ecosystem have been widely reported in the media as ‘import restrictions’.
What is the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) List?
- The Approved List of Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules (ALMM) comprises government-approved manufacturers eligible for use in government projects, government-assisted projects, and schemes.
- ALMM aims to boost the domestic solar industry and reduce dependence on imports, particularly from China.
ALMM's Suspension and Reinstatement:
- The ALMM was kept in abeyance for two years to address concerns raised by renewable energy producers with pre-existing government contracts.
- During this period, India's domestic solar industry struggled to compete with cheap Chinese imports.
- To support local manufacturers, the government launched initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme under the Atmanirbhar Bharat ('Self-Reliant India') Programme.
- With the PLI scheme enhancing the competitiveness of Indian manufacturers, the ALMM was reinstated in March 2024.
- The government believes that domestic companies can now meet India's solar equipment demand, making the ALMM an essential tool for promoting import substitution and self-reliance in the renewable energy sector.
Solar PV Imports:
- India heavily relies on solar cell and module imports, with China and Vietnam being the primary suppliers.
- Government data reveals that India imported approximately $11.17 billion worth of solar cells and modules over the past five years.
- As of 2023-24, China accounted for 53% of solar cell imports and 63% of solar PV modules.
China's Competitive Edge:
- Several factors contribute to China's dominance in solar PV exports:
- Cost-effective manufacturing due to lower power costs
- Government policies prioritizing the solar PV sector
- Economies of scale and continuous innovation driven by growing domestic demand
- These advantages have made China the most cost-competitive location for producing solar PV components, making it challenging for other countries to match their production capabilities.
What is the Scope of Solar Energy in India?
- India's solar sector holds immense potential, driven by the government's target of achieving 500 GW of installed non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- Moreover, the country's rapid growth in electricity demand, fueled by economic activities and climate adaptation measures, positions solar power as a critical resource.
- Solar energy accounted for one-third of renewable energy generation from April 2023 to February 2024, showcasing its significance in India's energy mix.
- Despite an estimated solar power potential of 748.99 GW, the country has yet to fully exploit this resource.
- To harness this potential, the government is implementing various schemes and programs, paving the way for a sustainable and prosperous solar future.
Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the US White House has officially instructed NASA to create a lunar time standard for international and private sector coordination on the Moon.
What is Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)?
- Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC) is a lunar-based time system being developed by NASA in collaboration with other government agencies to establish a standardized time zone for the Moon.
- LTC aims to provide a precise timekeeping benchmark for lunar spacecraft and satellites, synchronizing communication between astronauts, bases, and Earth.
Importance of LTC:
- As lunar exploration and commerce expand, a unified time standard becomes essential for managing operations, ensuring transaction reliability, and coordinating logistics.
- Furthermore, LTC addresses the discrepancy in timekeeping between Earth and the Moon due to differences in gravity, as time ticks faster on the Moon, causing Earth-based clocks to lose an average of 58.7 microseconds per day.
- Establishing LTC will prevent potential problems in spacecraft docking, data transfer, communication, and navigation.
How Will a Lunar Time Standard Be Established?
- Like on Earth, atomic clocks can be deployed on the lunar surface to set a time standard.
- These clocks have to be placed on the Moon at different locations since the Moon’s rotation and even local lumps of mass, called mascons, beneath the crust of the Moon affect the flow of time ever so slightly.
- Mascons or mass concentrations are so dense that they alter the Moon’s local gravity field.
- These effects are minor but the output from these clocks can be synthesized to give the Moon its own independent time, which can be tied back to UTC for seamless operations from Earth as well.
How Does Earth’s Time Standard Work?
- Most of the clocks and time zones of the world are based on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), set by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Paris, France.
- UTC is essentially an internationally agreed-upon standard for world time.
- It is tracked by a weighted average of more than 400 atomic clocks placed in different parts of the globe.
- Atomic clocks measure time in terms of the resonant frequencies — the natural frequency of an object where it tends to vibrate at a higher amplitude — of atoms such as cesium-133.
- In atomic time, a second is defined as the period in which a cesium atom vibrates 9,192,631,770 times.
- As the vibration rates at which atoms absorb energy are highly stable and ultra-accurate, atomic clocks make for an excellent device for gauging the passage of time.
- To obtain their local time, countries must subtract or add a certain number of hours from UTC depending on how many time zones they are away from 0 degree longitude meridian, also known as the Greenwich meridian.
- If a country lies on the west of the Greenwich meridian, it has to subtract from the UTC, and if a country is located on the east of the meridian, it has to add.
Imposition of Anti-Dumping Duty on Sodium Cyanide

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) has now recommended the imposition of anti-dumping duty on sodium cyanide (NaCN) imported from China, the European Union, Japan, and Korea.
Key Facts About Sodium Cyanide:
- Sodium cyanide (NaCN) is a highly toxic, inorganic compound with a white, crystalline appearance.
- It is a solid at room temperature and has a high affinity for metals, making it useful in various industrial processes.
- Due to its toxic nature, proper handling and safety protocols must be followed when working with sodium cyanide.
Applications of Sodium Cyanide:
- Mining and Metallurgy: Sodium cyanide is widely used in the extraction of gold and silver from ores. It is employed in a technique called "cyanide heap leaching," where a dilute sodium cyanide solution is sprayed onto crushed ore.
- The cyanide forms a water-soluble complex with the precious metals, enabling their recovery from the ore.
- Electroplating: NaCN is utilized as an electrolyte in electroplating processes, particularly for the deposition of silver, gold, and other metals on various surfaces to improve their appearance, durability, or conductivity.
- Synthetic Fiber Production: Sodium cyanide is used in the manufacturing of synthetic fibers such as acrylic and nylon.
- It serves as a catalyst in the polymerization process, promoting the formation of long-chain polymers that make up the fibers.
- Pesticides: Due to its toxicity, sodium cyanide has been used as a fumigant to control pests and rodents.
- However, its use in this field has been largely phased out in many countries due to safety concerns and the development of safer alternatives.
- Dye and Pigment Production: NaCN can be used in the production of certain dyes and pigments, particularly those containing nitrogen.
- It acts as a precursor for the synthesis of these compounds.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed by a domestic government on foreign imports suspected of being sold at prices lower than those in the exporter's domestic market.
- This measure aims to prevent these products from undercutting local businesses and harming the local economy.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) oversees a framework of international trade rules governing anti-dumping measures.
- Under this agreement, governments are permitted to address dumping practices if they pose a threat of significant harm to a domestic industry.
Calculation of Anti-Dumping Duty:
- The calculation of anti-dumping duty involves determining the difference between the normal value and the export value of the product.
- The normal value represents the market value of the product in the exporter's domestic market, while the export value denotes the price at which the product is sold when exported to India.
- The anti-dumping duty is levied to neutralize this price disparity and safeguard the domestic industry from the adverse effects of inexpensive imports.
Anti-Dumping Mechanism in India:
- India's anti-dumping mechanism is overseen by the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping and Allied Duties (DGAD) under the Ministry of Finance.
- The legal framework for anti-dumping in India is established by the Customs Tariff Act of 1975 and the Customs Tariff Rules of 1995.
- The DGAD conducts investigations to assess whether a surge in below-cost imports has negatively impacted the domestic industry.
Presence of Ozone on Jupiter's Moon Callisto

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of scientists, including from India, has discovered strong evidence indicating the presence of ozone on Jupiter’s moon Callisto, shedding light on the complex chemical processes taking place on icy celestial bodies in the Solar System.
Study on the Formation of Ozone in Callisto's Icy Environment:
- A recent study examined the chemical evolution of sulfur dioxide (SO2)-rich astrochemical ice found on Callisto's surface when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
- The investigation revealed a unique signature indicating the formation of ozone, which could have implications for the potential habitability of the Jovian moon.
- Callisto is Jupiter's second-largest moon and the third-largest moon in our solar system.
- It has a relatively stable surface, which could play a vital role in preserving subsurface oceans or potential habitats beneath its icy crust.
- The study analyzed UV absorption spectra data from ice samples containing SO2, a primary component of Callisto's surface ice, and observed the generation of ozone under UV irradiation.
- Ozone formation on Callisto could have implications for the moon's astrobiological potential, as ozone can protect the surface from harmful radiation.
- Further research is needed to better understand the implications of this discovery on Callisto's habitability and the potential for future exploration missions.
Callisto's Distinctive Environment:
- Following Saturn, Jupiter boasts the second-highest number of moons in the Solar System, with Callisto ranking among its largest moons and holding the position of the third-largest moon overall, after Ganymede and Titan.
- Comprised predominantly of water ice, rocky elements, sulfur dioxide, and traces of organic compounds, Callisto presents a compelling potential for harboring life beyond Earth within the Solar System.
- The moon's extensively cratered surface bears witness to a lengthy history of impacts from asteroids and comets.
Importance of the Research:
- The identification of ozone on Callisto hints at the existence of oxygen, a crucial component essential for the development of intricate molecules vital for life, including amino acids, thus prompting inquiries into the moon's potential for sustaining life.
- This finding also has implications for other icy moons within our Solar System, offering insights that could broaden our comprehension of habitable environments beyond Earth.
Significance of Ozone:
- Consisting of three oxygen atoms bonded together, the ozone molecule plays a pivotal role in shielding life on Earth.
- Situated in the lower region of the Earth's stratosphere, approximately 15-35 kilometers above the surface, the ozone layer acts as a protective barrier.
- Without this layer, ultraviolet radiation would intensify, posing significant threats to various species and disrupting ecosystems.
- Ultraviolet-B and ultraviolet-C, with wavelengths ranging from 290 to 320 nanometers and 100 to 280 nanometers respectively, can cause DNA damage, and mutations, and elevate the risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Furthermore, ultraviolet light can impede plant growth and adversely affect diverse organisms.
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
X-Class Solar Flares

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Earth was hit by an X-class solar flare that was strong enough to ionize part of the planet's atmosphere.
What are Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are large explosions from the surface of the sun that emit intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation.
- The intensity of the explosion determines what classification the flare belongs to.
- The most powerful are X-class flares, followed by M-, C-, and B-class; A-class flares are the smallest.
- These flares can be visible as bright flashes in a particular region of the sun and can last several minutes.
- Solar flares occur when magnetic energy builds up in the solar atmosphere and is released suddenly.
- These outbursts are intrinsically linked to the solar cycle — an approximately 11-year cycle of solar activity driven by the sun's magnetic field.
What Causes Solar Flares?
- The sun's surface is a magnetically mixed-up place.
- Magnetic fields are created from electrically charged gases generating electrical currents that act as a magnetic dynamo inside the sun.
- These magnetic fields twist, tangle, and reorganize themselves due to the turbulent nature of the gases that create them.
- This unsettled magnetic field behavior — also known as solar activity — can trigger solar flare eruptions from the surface that release vast amounts of electromagnetic radiation — a form of energy that includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays, gamma rays, and visible light.
- Solar flares tend to originate from regions of the solar surface that contain sunspots — darker, cooler portions of the solar surface where magnetic fields are particularly strong.
- As such, the number of sunspots can indicate the likelihood of a solar flare eruption.
- Solar activity follows an approximately 11-year cycle with the peak of sunspot activity coinciding with the solar maximum and a sunspot hiatus coinciding with the solar minimum.
- During periods of low solar activity when no sunspots are present, it is unlikely that a solar flare will occur.
What are X-Class Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are categorized into five classes based on the intensity of emitted X-rays, with each class letter denoting a 10-fold increase in energy output, akin to the Richter scale for earthquake strength assessment.
- X-class flares are the most powerful solar flares.
- Then there are M-class flares that are 10 times smaller than X-class flares, then C-class, B-class, and finally A-class flares which are too weak to significantly affect Earth.
- Within each letter class, a finer scale from 1 to 9 gives the flare assessment greater precision with larger numbers representing more powerful flares within the class.
- However, X-class flares can break this nine-point rating mold with higher ratings, since there is no class more powerful than X-class.
- Fortunately, X-class flares occur on average about 10 times per year.
How do Solar Flares Affect the Earth?
- Disruption of Satellite Communications: Solar flares can interfere with satellite communications, GPS signals, and radio transmissions, causing disruptions or blackouts in telecommunications and navigation systems.
- Auroral Displays: Intense solar flares can trigger colorful auroras, or Northern and Southern Lights, as charged particles interact with Earth's magnetic field, creating stunning light displays in the polar regions.
- Power Grid Disturbances: Severe solar flares have the potential to induce geomagnetic storms that can overload power grids, leading to widespread power outages and damage to electrical infrastructure.
- Radiation Hazards: Solar flares emit harmful radiation, particularly in the form of ultraviolet and X-rays, which can pose risks to astronauts in space and airline passengers at high altitudes.
- Impact on Electronics: The influx of charged particles during solar flares can induce currents in electrical circuits, potentially damaging or disrupting sensitive electronic devices, such as computers, satellites, and spacecraft.
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
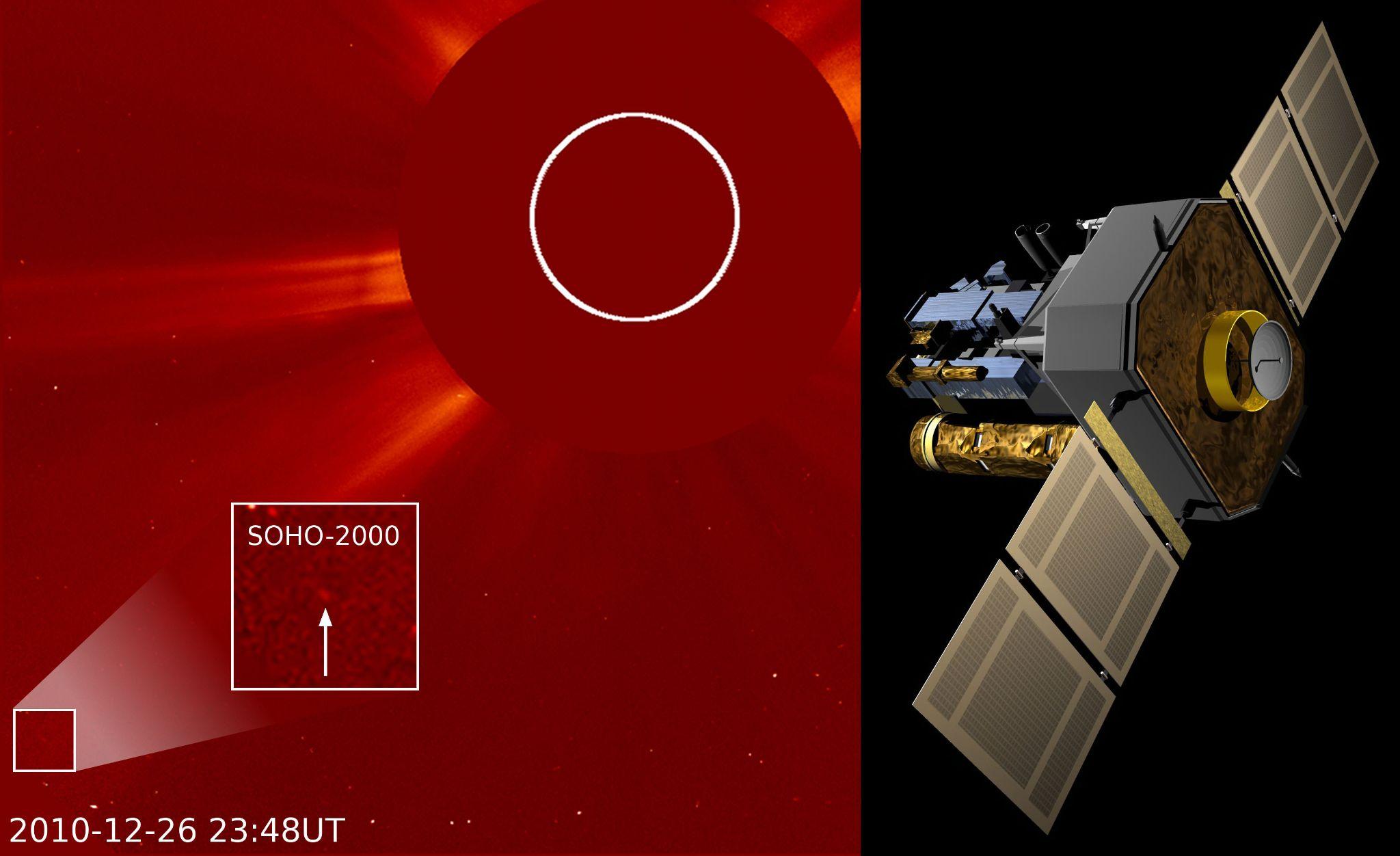
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP)

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kerala's shift towards an alternative approach for the implementation of smart electricity meters, sidelining the Central government's Rs 3 lakh crore project, poses a challenge to the Union Government's initiative of replacing 250 million traditional meters with smart meters in all households by March 2025.
About the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP):
- The Indian government has initiated the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) to revolutionize the country's energy sector through the implementation of smart meters.
- By replacing 25 crore conventional meters, the SMNP aims to enhance the operational efficiency and revenue management of distribution companies (DISCOMs).
- Under the leadership of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of four National Public Sector Enterprises, the scheme is set to make waves in the energy sector.
- EESL, comprised of NTPC Limited, PFC, REC, and POWERGRID, operates under the Ministry of Power and is committed to undertaking the necessary capital and operational expenditures with zero upfront investment from states and utilities.
- The Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) model facilitates the recovery of smart meter costs via the monetization of energy savings resulting from improved billing accuracy, reduced meter reading costs, and increased efficiency.
- In accordance with guidelines set forth by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), the strategic deployment of these smart meters adheres to industry standards.
Smart meters offer a multitude of advantages:
-
- Consumers can monitor their electricity usage and make informed decisions to reduce their bills.
- Utilities benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, enabling better power demand management.
- Web-based Monitoring: The interconnected smart meter network can mitigate utilities' commercial losses, enhance revenue generation, and propel power sector reforms.
- The Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) paves the way for a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape in India, revolutionizing the way utilities operate and consumers engage with their electricity usage.
What are Smart Meters?
- A smart meter serves as an advanced tool for recording electricity consumption and voltage levels, offering a significant upgrade over traditional metering systems.
- While conventional meters simply measure power usage, smart meters take it a step further by transmitting real-time data to utility providers at intervals of 15 minutes or hourly.
- Smart meters truly live up to their name by utilizing internet connectivity to facilitate two-way communication.
- On one hand, they empower consumers with up-to-date information on energy usage patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions and manage consumption more efficiently.
- On the other hand, utility providers gain valuable insights for monitoring purposes and ensuring accurate billing.
- In essence, smart meters pave the way for improved energy management, increased transparency, and enhanced efficiency, catering to the evolving needs of both consumers and utility providers in today's digital era.
ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 Landing Experiment
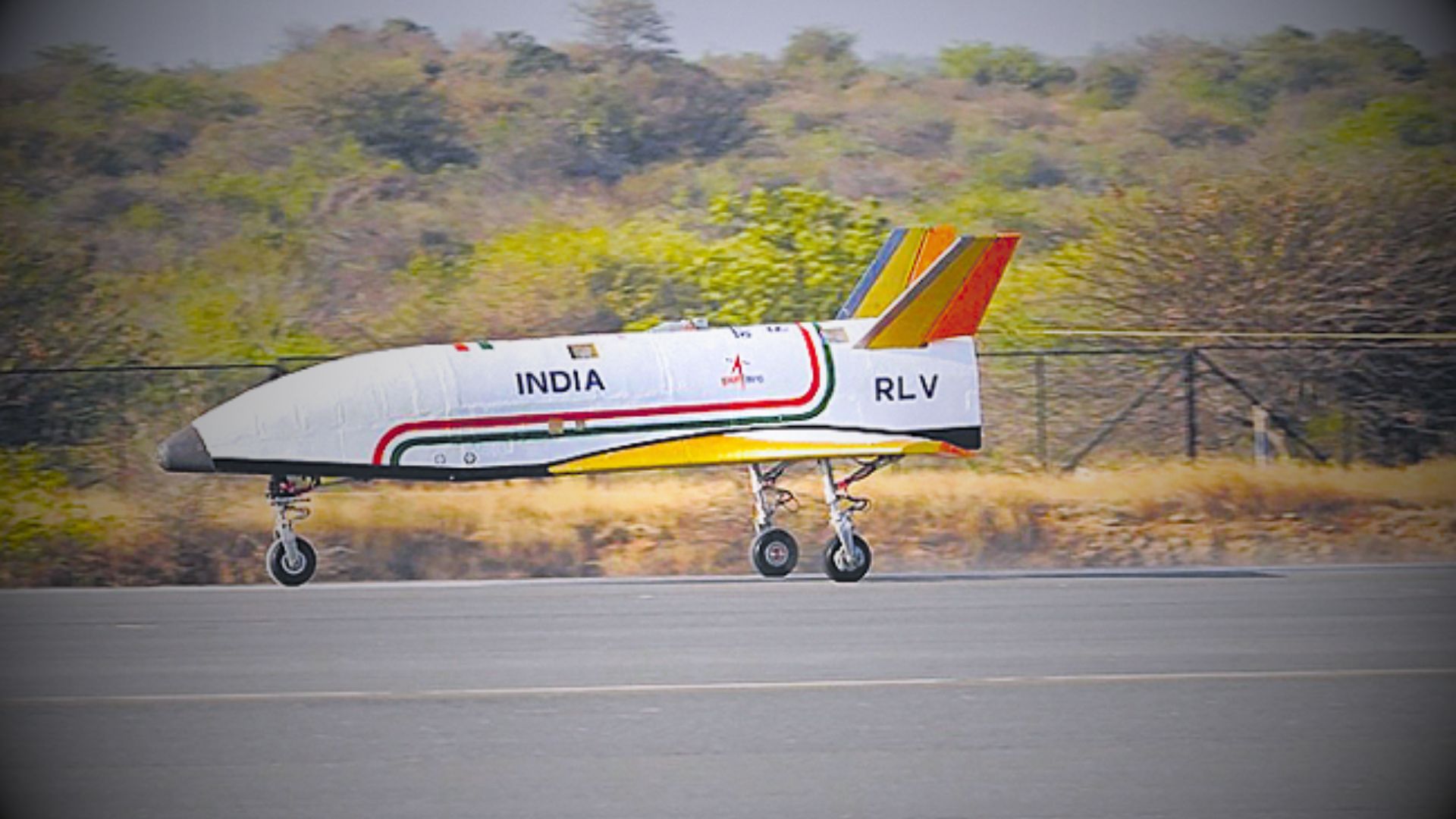

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully conducted the Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 landing experiment at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga recently.
What is a Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02?
- Continuing our exploration into reusable landing vehicles, RLV-LEX-02 marks the second mission in our series conducted at the Aeronautical Test Range.
- Following the success of RLV-LEX-01 last year, this latest endeavor showcases the remarkable autonomous landing capability of our reusable launch vehicle (RLV).
- Notably, RLV-LEX-02 demonstrates the vehicle's ability to navigate and safely land from off-nominal initial conditions immediately upon release from a helicopter.
Methodology of the Experiment:
- The RLV LEX-02 mission showcased the autonomous landing prowess of our reusable launch vehicle under demanding circumstances following its release from a helicopter.
- Dubbed 'Pushpak', this winged vehicle was airlifted by an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter and released from a height of 4.5 km.
- Navigating autonomously, it adeptly approached the runway, making precise cross-range corrections before executing a flawless landing.
- Utilizing a combination of its brake parachute, landing gear brakes, and nose wheel steering system, it safely came to a stop.
- Notably, the winged body and all flight systems previously employed in RLV-LEX-01 were repurposed for RLV-LEX-02 after undergoing necessary certification and clearances.
- This remarkable mission was executed collaboratively by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Liquid Propulsion System Centre (LPSC), and the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU).
What is the Reusable Launch Vehicle?
- The reusable launch vehicle represents a pioneering space plane design characterized by a low lift-to-drag ratio, which mandates high glide angles during approach and consequently requires landing at velocities reaching 350 kmph.
- Integral to its innovation are a multitude of indigenous systems developed meticulously. These encompass sophisticated navigation systems, leveraging pseudolite technology for precise localization, as well as instrumentation and sensor arrays, among other advancements, all spearheaded by ISRO.
Project GR00T

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI chip leader Nvidia on Tuesday (March 19) announced Project GR00T or Generalist Robot 00 Technology, which promises to revolutionize the evolution of humanoid robots.
What is Project GR00T?
- Project GR00T stands for Generalist Robot 00 Technology.
- It is essentially a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots.
- This ambitious project aims to create a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots, enabling them to understand natural language, learn new skills from observing humans, and solve various tasks in real-time.
- Robots built on this platform are designed to understand natural language and emulate movements by observing human actions, such as instantly learning coordination, dexterity, and other skills.
- This can help the robots navigate and engage with the real world around them.
- The goal of Project GR00T is to advance the field of embodied artificial general intelligence (AGI) and drive breakthroughs in robotics.
- NVIDIA intends to leverage its expertise in AI and its technological resources to develop this foundational model, which would provide humanoid robots with human-like abilities, such as emotion, reaction, and movement.
The Potential Consequences of Project GR00T and Humanoid Robots in the Workforce:
- As humanoid robots, such as those envisioned by NVIDIA's Project GR00T, become more advanced and capable of handling various hazardous or repetitive tasks, concerns arise over potential job displacement.
- For instance, Nvidia's partnership with Hippocratic AI to develop AI-powered healthcare agents may lead to a reduction in the demand for nurses.
- However, proponents argue that these robots can serve as valuable aids for humans, enhancing their quality of life and complementing their skills rather than supplanting them entirely.
- Consequently, the impact of humanoid robots on the workforce may ultimately depend on their successful integration into existing labor structures, as well as the willingness and ability of society to adapt to this transformative technology.
Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's largest gas utility GAIL (India) Ltd commissioned the country's first SSLNG unit at its Vijaipur complex in Madhya Pradesh recently.
India Unveils Its First Small-Scale LNG Plant:
- In a significant step towards a cleaner energy mix, GAIL (India) Ltd. has commissioned India's first Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) plant in Vijaipur, Madhya Pradesh.
- This plant will produce 36 tonnes of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) daily, utilizing cutting-edge technology like treatment skids and liquefaction skids to convert natural gas into LNG.
- As part of India's commitment to increasing the proportion of natural gas in its primary energy mix from 6% to 15% by 2030, the SSLNG plant will play a pivotal role in reducing pollution emissions while catering to the nation's growing energy demands.
- This milestone achievement paves the way for a greener future and positions India as a significant player in the global LNG landscape.
What is Small-Scale LNG?
- Small-scale LNG (SSLNG) is an emerging industry that offers a novel approach to natural gas distribution.
- While there is no standard international definition, SSLNG typically involves the liquefaction and transportation of natural gas in smaller quantities using specialized trucks and vessels.
- This allows for the supply of LNG to industrial and commercial consumers in regions without pipeline connectivity.
- SSLNG can be sourced from existing large-scale LNG import terminals or small liquefaction plants in gas-rich locations.
- End-users regasify the LNG using small vaporizers for traditional use cases like supplying Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles and piped gas for households and industries.
- Alternatively, LNG can be supplied in its liquid form for direct use.
Benefits of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG):
- Expanded Accessibility: SSLNG overcomes the constraints of traditional pipeline infrastructure, enabling natural gas delivery to regions previously lacking access.
- This opens new avenues for cleaner fuel alternatives and widespread energy availability.
- Operational Flexibility: SSLNG's modular design allows for rapid deployment in response to local demand fluctuations, making it an ideal solution for remote locations, industrial environments, and diverse transportation requirements.
- Sustainability Promotion: By fostering the adoption of cleaner fuels, SSLNG significantly reduces emissions in various transportation sectors, including trucks, buses, and marine vessels. This contributes to a greener future and combats climate change.
- Strengthened Energy Security: Decentralized SSLNG distribution systems diversify fuel sources and bolster energy security, ensuring reliable and stable energy supply amid global fluctuations and uncertainties.
Challenges of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) Implementation:
- Vehicle Availability Constraints: Limited options for LNG-powered vehicles impede the widespread adoption of LNG as a fuel source, underscoring the need for increased production and diversification of vehicle models.
- Insufficient Retail Infrastructure: The lack of a well-established LNG retail network hinders convenient consumer access to LNG fuel, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure expansion and enhancement.
- Higher Upfront Investment: The comparatively higher initial costs of LNG vehicles compared to traditional diesel options may deter potential buyers, necessitating innovative financial solutions and incentives.
- Financing Barriers: The absence of dedicated financing options for LNG vehicles poses obstacles for interested buyers, requiring tailored financial instruments to support SSLNG uptake.
- Restricted Pipeline Coverage: SSLNG faces logistical challenges in areas without existing natural gas pipeline networks, highlighting the need for infrastructure development to extend its reach to remote regions.
- Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: SSLNG projects may encounter regulatory and permitting setbacks, including environmental and safety concerns, potentially prolonging project timelines and inflating costs.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for expediting SSLNG implementation and fostering its growth.
SAKHI App To Assist Gaganyaan Crew

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) facility at Thumba in Thiruvananthapuram, has developed a multi-purpose app that will help astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission carry out a range of tasks such as looking up vital technical information or communicating with one another.
About SAKHI App:
- The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), an ISRO facility in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, has created the versatile 'SAKHI' app for astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission.
- SAKHI stands for 'Space-borne Assistant and Knowledge Hub for Crew Interaction'.
Purpose:
- During the mission, the app will assist Gaganyaan crew members in various tasks such as accessing vital technical information and communicating with each other.
Utility:
- Health Monitoring: It will monitor key health parameters like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, providing crucial insights into the crew's physical condition during the mission.
- Additionally, it will remind them of hydration, dietary schedules, and sleep patterns.
- Connectivity:
- Astronauts can use the app to maintain mission logs in various formats, including voice recordings, texts, and images.
- It will ensure seamless communication between the crew, the onboard computer, and ground-based stations.
- Current Status: An engineering model of the custom-built hand-held smart device featuring SAKHI has been tested, with the development of a flight model underway.
About the Gaganyaan Mission:
- The primary objective of the mission is to demonstrate the capability to launch and safely return three crew members to low Earth orbit.
- The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) is designated as the launch vehicle for the Gaganyaan mission.
- Crew Escape System (CES): A vital component of the mission, CES is powered by quick-acting, high-burn rate solid motors.
- It ensures the safe evacuation of the Crew Module and crew in case of emergencies during launch or ascent.
- Orbital Module: Comprising the Crew Module (CM) and Service Module (SM), the Orbital Module orbits the Earth, providing safety and support throughout the mission phases.
- Crew Module (CM): Designed to offer a habitable space with Earth-like conditions for the crew during their time in space.
- Service Module (SM): This module supports the CM during orbit, containing essential systems such as thermal, propulsion, power, avionics, and deployment mechanisms.
- This will mark ISRO's inaugural manned spaceflight mission, joining the ranks of the US, Russia, and China, which have previously conducted human spaceflights.
Predictive AI: Its Applications and Advantages

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Predictive AI is revolutionizing data analysis, decision-making, and industry leadership, offering businesses unprecedented insights and strategic advantages.
What is Predictive Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Predictive artificial intelligence (AI) utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and forecast future events, distinguishing it from traditional AI focused solely on retrospective analysis.
- This cutting-edge technology employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to sift through extensive datasets, identifying subtle patterns and trends.
- Unlike conventional approaches, Predictive AI doesn't just analyze data; it transforms it into actionable insights, enabling organizations to:
- Anticipate future outcomes,
- Predict market shifts, and
- Make strategic decisions with unprecedented foresight.
- By continuously learning from past data and adapting to changing trends, Predictive AI becomes an invaluable tool, guiding businesses through uncertain landscapes.
How Predictive AI Work?
- Leveraging Big Data: Predictive AI relies on access to extensive datasets, often referred to as "big data," as larger datasets typically lead to more accurate analyses.
- Utilizing Machine Learning (ML): As a subset of AI, ML involves training computer programs to analyze data autonomously, without human intervention.
- In the realm of predictive AI, ML algorithms are applied to vast datasets to extract valuable insights.
- Autonomous Processing: Predictive AI models are capable of autonomously processing massive datasets, eliminating the need for human oversight.
- Pattern Recognition: Through ML techniques, predictive AI learns to recognize patterns within datasets, associating specific data points or occurrences with potential future events.
- By examining numerous factors, predictive AI can identify intricate patterns indicative of recurring events, enabling organizations to anticipate future outcomes effectively.
Difference Between Predictive AI and Generative AI:
- Predictive AI and generative AI both employ machine learning techniques and leverage extensive datasets to generate their outputs.
- However, while predictive AI utilizes machine learning to forecast future outcomes, generative AI employs machine learning to produce original content.
- For instance, a predictive AI model may inform fishermen about impending storms, whereas a generative AI model may craft a fictional narrative depicting various scenarios involving weather and fishing expeditions.
- While both types of AI rely on statistical analysis to discern patterns, their objectives, machine learning methodologies, and applications differ significantly.
Various Applications of Predictive AI:
- Assessing the Impact of Natural Disasters: With the recent eruption of a volcano in Iceland, the potential repercussions on air travel echo concerns from a similar event in 2010, which disrupted flights across Europe.
- Predictive AI leverages data analysis to identify patterns and anticipate the impact of such extreme weather events on air travel. Platforms like Yandex offer interactive maps for real-time monitoring of ash clouds post-eruption.
- Enhancing Oil and Gas Exploration: In the realm of oil and gas exploration, companies possess extensive historical geological data that can inform predictive AI systems.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- For instance, Saudi Aramco utilizes its meta-brain generative AI to optimize drilling plans, analyze geological data, and forecast drilling outcomes accurately.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- Inventory and Supply chain management: Predictive AI aids in inventory and supply chain management by identifying peak consumer demand periods, facilitating proactive stock adjustments, and optimizing resource allocation to address fluctuations in road congestion and meet increased user demands.
- Marketing campaigns: Just as predictive AI can anticipate user or customer behavior, it can help prognosticate what kinds of content or products prospective customers may be interested in.
- Advancing Medical Research: Predictive AI plays a pivotal role in drug discovery, a cornerstone of contemporary medical research.
- Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating to leverage predictive AI models for analyzing vast datasets and identifying potential drug candidates. Initiatives like the 'MELLODDY Project', supported by the EU Innovative
- Medicines Initiative and multiple pharmaceutical firms, exemplify this collaborative effort in pooling data and leveraging predictive AI for drug discovery.
NHAI to start rolling out satellite-based tolling on national highways soon

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said in Parliament in February that the government plans to implement a new highway toll collection system based on the global navigation satellite system before the model code of conduct for the 2024 election kicks in.
What is the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)?
- GNSS refers to a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers.
- The receivers then use this data to determine location.
- Examples of GNSS include Europe’s Galileo, the USA’s GPS, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou
How will the GNSS-Based Toll System work?
- The system will use an automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) system through cameras installed on highways and deduct tolls based on the distance traveled by a vehicle.
- The device monitors the movements while driving, accurately marking the entry and exit points on tolled segments. By analyzing travel distance, it computes the charges accordingly.
- This eliminates the uniformity of fixed tolls at booths, ensuring fairness for drivers traversing shorter distances.
Difference between FASTags and ANPR technology:
- FASTags streamline electronic toll payments at toll plazas equipped with scanners, enabling vehicles to pass through without stopping.
- Conversely, GNSS-based systems utilize ANPR technology to deduct tolls based on distance traveled, rendering traditional toll plazas unnecessary.
What are the Challenges?
- Detection of Non-Compliance: Without physical barriers, detecting non-compliant vehicles, such as those without an On-Board Unit (OBU) or engaging in fraudulent activities, poses a challenge.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying gantry-mounted Automatic Number-Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems along highways is essential for capturing violations and enforcing toll payments.
- License Plate Quality: The effectiveness of ANPR systems relies on the quality of license plates; subpar plates hinder accurate recognition and enforcement efforts.
- Data Privacy and Security: GNSS-based toll systems entail collecting and processing sensitive location data, necessitating robust privacy and security measures.
Inflection AI rolls out new large language model to its Pi chatbot

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Inflection AI launched its latest LLM, Inflection 2.5, an upgrade to its model that powers its friendly chatbot Pi personal assistant.
About Inflection 2.5:
- Inflection-2.5 is an “upgraded in-house model that is competitive with all the world’s leading LLMs like GPT-4 and Gemini.
- The newly upgraded LLM comes with its signature personality and uniquely empathetic fine-tuning.
- Its latest model achieved GPT-4’s performance with only 40 per cent of the OpenAI model’s computation power for training.
- Besides, it seems Inflection 2.5 has made some stellar strides in areas of IQ such as coding and mathematics.
- This means that the model has made substantial improvements on key benchmarks.
- With the new upgrade, Pi has now been endowed with world-class real-time web search capabilities to ensure that users get access to high-quality and up-to-date information in real-time.
What is the Pi chatbot?
- Pi is an advanced chatbot powered by Inflection AI's cutting-edge language model, Inflection 2.5 which allows one to have deep and meaningful conversations.
- To access the chatbot, one needs to log on to Inflection.AI, click on Meet Pi, and simply start talking to the chatbot right away.
- Pi is more humane and has been promoted as a chatbot that has a personality.
- In other words, Inflection AI dubbed it as a chatbot that is “supportive, smart, and there for you anytime”.
- Pi is more like a companion to humans and is free to use.
- The chatbot comes with a voice, in six distinct voices, to choose from adding life to conversations.
Pi chatbot boasts a number of impressive features that make it stand out from other conversational AI systems:
- Real-time web search capabilities: Pi can access and present up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, ensuring that users always have access to accurate and relevant information.
- Empathetic personality: Pi's unique empathetic fine-tuning allows it to understand and respond to the emotional nuances of human communication, making it a more engaging and personable conversational partner.
- Versatile conversation topics: Whether you're discussing current events, asking for local recommendations, studying for an exam, drafting a business plan, coding, or just talking about hobbies, Pi is equipped to handle a wide range of conversational topics.
- User-friendly interface: Designed with accessibility in mind, Pi's intuitive interface makes it easy for users of all technical abilities to engage with the chatbot and get the most out of their conversations.
India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA
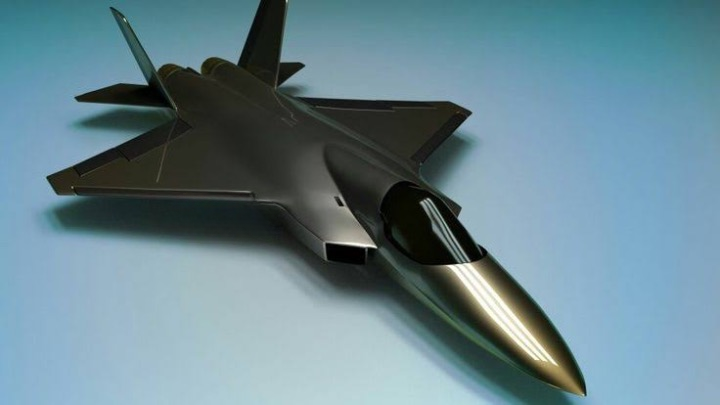

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
India to restart Penicillin G manufacture
- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will start manufacturing the common antibiotic Penicillin G later this year, three decades after the country’s last plant shut down, Union health minister Mansukh Mandaviya announced last week.
What is Penicillin G?
- Penicillin G serves as a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) utilized in the production of various common antibiotics.
- Its molecular formula is C16H18N2O4S.
- Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an FDA-approved antibacterial medication primarily indicated for treating severe bacterial infections like pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, among others.
- This natural penicillin antibiotic is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly due to limited oral absorption.
- Additionally, Penicillin G may be employed in certain instances as prophylaxis against susceptible organisms.
Why did Penicillin Manufacturing Stopped in India?
- The discontinuation of Penicillin G production in India, along with numerous other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), resulted from the influx of cheaper Chinese products driven by subsidies.
- Torrent Pharma in Ahmedabad was the final plant to halt Penicillin G production, with at least five companies, including Torrent, manufacturing the antibiotic in the country during the 1990s.
- In the early 1990s, India boasted nearly 2,000 API manufacturers, while approximately 10,000 units produced formulations. However, the allure of cheaper Chinese alternatives grew, particularly with the relaxation of customs rules during the country's economic liberalization.
- The Drug Prices Control Order, which imposed price caps on essential medicines, further incentivized companies to opt for cheaper imported products.
- While India previously sold Penicillin G for around Rs 800 per kg, China drastically reduced prices to nearly Rs 400 per kg, rendering domestic manufacturing economically unviable.
Why the Delay in Restarting Production?
- Lack of Urgency: Despite awareness within the industry and government about the decline in API production in India due to the availability of cheaper alternatives globally, there was limited emphasis on restarting domestic production.
- The supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic highlighted the need for self-reliance, prompting the government to launch initiatives like the PLI scheme to bolster domestic manufacturing.
- High Initial Investment: API manufacturing, particularly for fermented compounds like Penicillin G, entails significant upfront costs.
- Establishing a production facility requires substantial capital investment, with companies often needing several years to break even.
- Dominance of China: China has emerged as a dominant supplier, significantly expanding its manufacturing capacity over the past three decades.
- Competing with Chinese prices would necessitate substantial investments in larger facilities.
What's the Impact of PLI Schemes?
- Reduction in API Imports: Since the implementation of the PLI scheme, there has been a notable decrease in API imports.
- For instance, the import dependency for paracetamol, which was previously two-thirds of the required volume, has now halved.
- Incentive Structure: The PLI scheme offers incentives structured as follows:
- 20% support for the first four years, gradually reducing to 15% in the fifth year and 5% in the sixth year for eligible sales of fermentation-based bulk drugs like antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones such as insulin.
- Chemically synthesized drugs receive a 10% incentive for six years on eligible sales.
Union Cabinet approves India AI Mission with 10,372 cr outlay

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
India has made its first move to address a key shortcoming it currently has in unlocking opportunities around generative artificial intelligence (AI) – that of computing hardware.
What is IndiaAI Mission?
- India's AI Mission entails the launch of an artificial intelligence (AI) initiative, announced by the Prime Minister at the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi, with implementation overseen by the 'IndiaAI' Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- Led by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the mission aims to establish a computing capacity exceeding 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and develop foundational models trained on datasets encompassing major Indian languages, focusing on priority sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Additionally, the mission will involve the establishment of AI Curation Units (ACUs) in 50-line ministries and the creation of an AI marketplace to provide AI services and pre-trained models to AI application developers.
- Implementation of the AI computer infrastructure will follow a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding, with Rs 4,564 crore allocated from the total outlay of Rs 10,372 crore for building computing infrastructure.
Key Features of the IndiaAI Mission:
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Establishing a scalable AI computing ecosystem to meet the growing demands of India's burgeoning AI start-ups and research community.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Focusing on the development and deployment of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and domain-specific foundational models in critical sectors.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: Streamlining access to high-quality non-personal datasets to fuel AI innovation.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promoting the adoption of AI applications in critical sectors, addressing problem statements sourced from Central Ministries, State Departments, and other entities.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Mitigating barriers to entry into AI programs by expanding AI courses at undergraduate, master's, and Ph.D. levels.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Supporting and accelerating deep-tech AI startups by providing streamlined access to funding for futuristic AI projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Ensuring the responsible implementation of AI projects through the development of indigenous tools and frameworks to foster trust and safety in AI applications.
The Significance of the IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission aligns with the vision of fostering indigenous AI development and leveraging AI technology for the benefit of India.
- It aims to demonstrate to the international community the positive impact of AI technology on society, thereby enhancing India's global competitiveness.
- By establishing a comprehensive ecosystem for AI innovation through strategic partnerships across public and private sectors, the mission will catalyze AI-driven advancements.
- It will foster creativity and bolster internal capabilities, ensuring India's technological sovereignty.
- Furthermore, the mission is poised to create employment opportunities that demand advanced skills, leveraging India's demographic advantage.
ISRO’s second rocket launchport in Tamil Nadu’s Kulasekarapattinam

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the second rocket launchport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at Kulasekarapattinam on February 28.
Why does India need a new launchport?
- With the Union government’s recent policy announcing the opening of the space sector to private players, a sharp rise in the number of commercial launches is certain.
- To ensure that ISRO’s first launchport, the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota, is not overburdened with a high number of launches, the space agency has decided to build another facility.
- While SHAR will be only used for launching bigger and heavy-lift-off missions, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport will be used to launch smaller payloads.
- SHAR will also be available for India’s big ticket missions to the Moon, Venus, and much touted human-flight mission, the Gaganyaan.
- Private players could develop space-qualified sub-systems, build satellites, and even launch vehicles using the new launchport.
- It will also facilitate dedicated launch infrastructure for all the on-demand commercial launches.
Why is the new ISRO launchport located in Tamil Nadu?
- Geographically, scientifically, and strategically, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport provides a natural advantage to ISRO’s future launches pertaining to the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
- Allowing a direct southward and smaller launch trajectory for the light weight SSLVs carrying less fuel, the Kulasekarapattinam facility will boost ISRO’s attempts to enhance payload capacities.
- Currently, the trajectory followed by all launches from SHAR are longer as they follow a path which requires the vehicle to skirt eastwards around Sri Lanka before taking the actual southward flight.
- This consumes additional fuel. However, the same would not be required for future launches from Kulasekarapattinam, which is geographically located several kilometers to the west of Colombo, thereby allowing a straight southward flight and simultaneously saving the already limited fuel available onboard SSLV.
- Notably, both the launch ports are located in Southern India, near the equator.
- For a launch site close to equator the magnitude of the velocity imparted due to Earth’s rotation is about 450 m/s, which can lead to substantial increase in the payload for a given launch vehicle.
- Geostationary satellites must necessarily be in the equatorial plane.
- So, for such satellites, the closer the launch site is to the equator the better it is.
What are SSLVs?
- SSLV is the new small satellite launch vehicle developed by ISRO to cater for the launch of small satellites.
- It has a three-stage launch vehicle, having a lift-off weight of about 120 tonnes and is 34 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter.
- SSLV is designed with a three-stage solid propulsion and a liquid propulsion stage, which is the terminal stage.
- The SSLV missions are useful to launch small-sized satellites weighing anywhere between 10 to 500kg into the Low Earth Orbit.
- Going by their size and weight, these are typically referred to as mini, micro or nano satellites.
- They are low on cost and intended satellite insertion into orbits takes a shorter flight time.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
- Previously, satellite projects built by college students and private players involved in the space sector have benefitted from SSLV missions.
What are the features of SHAR?
- SHAR is situated along the east coast of Andhra Pradesh and is located 80 km off Chennai.
- It currently provides launch infrastructure to all ISRO missions.
- It is equipped with a solid propellant processing setup, static testing, and launch vehicle integration facilities, telemetry services — tracking and command network to oversee the launch — and a mission control center.
- SHAR has two launch complexes that are routinely used to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the Geosynchronous Space Launch Vehicles (GSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III, now renamed as LVM3.
Haiper, the text-to-video model created by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a company founded by former members of Google DeepMind, TikTok, and top labs from research academia — introduced an eponymous new text-to-video model Haiper.
What is Haiper?
- Haiper is an all-in-one visual foundation model that allows everyone, with or without technical training, to generate high-quality video content with ease.
- The founders claim that Haiper brings forward cutting-edge machine learning with the belief that creativity should be “fun, surprising, and shareable”.
- The company has built Haiper as a powerful, industry-agnostic creativity tool.
- It was released by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni.
What does Haiper do?
- Haiper offers tools such as text-to-video, animated static images, video repainting tools, etc.
- Users can go on to the website, log in with their email addresses, and start generating videos for free by typing in text prompts.
- At present, users can only generate HD video spanning 2 seconds, and a slightly lower-quality video could go up to four seconds.
Strengths and limitations:
- While the short length is a limitation, the company is working towards extending the video outputs.
- Presently, the tool is free to use, with an aim to build a community.
- While OpenAI’s Sora is still not available for the public, Haiper is offering users to try its tool for free on its website.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
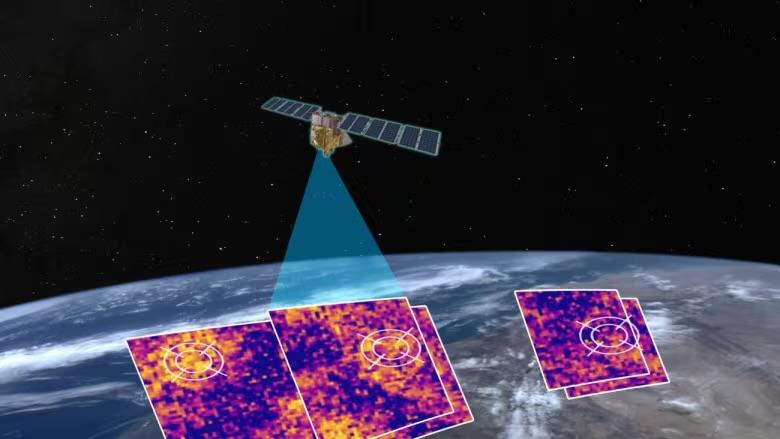
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi witnessed the start of the process of core-loading the indigenous prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) at the Madras Atomic Power Station in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
What is the PFBR?
- The PFBR, or Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, is a nuclear reactor designed to produce more nuclear fuel than it consumes.
- In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom absorbs a neutron, becomes unstable, and splits into two, releasing energy.
- If the unstable nucleus releases additional neutrons, the reactor’s facilities can utilize them to initiate more fission reactions.
How does the PFBR work?
- PHWRs use natural or low-enriched U-238 as the fissile material and produce Pu-239 as a byproduct.
- This Pu-239 is combined with more U-238 into a mixed oxide and loaded into the core of a new reactor together with a blanket.
- This is a material the fission products in the core react with to produce more Pu-239.
- A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor that produces more fissile material than it consumes.
- In a ‘fast’ breeder reactor, the neutrons aren’t slowed, allowing them to trigger specific fission reactions.
- The PFBR is designed to produce more Pu-239 than it consumes.
- It uses liquid sodium, a highly reactive substance, as coolant in two circuits. Coolant in the first circuit enters the reactor and leaves with (heat) energy and radioactivity.
- Via heat-exchangers, it transfers only the heat to the coolant in a secondary circuit.
- The latter transfers the heat to generators to produce electricity.
How India’s first semiconductor fabrication plant can help plug into the global value chain

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved the country's first semiconductor fab to be made by the Tata Group in collaboration with Powerchip Taiwan.
What is Semiconductor Fabrication?
- The semiconductor fabrication process is a complex and highly specialized series of steps that transform raw materials into functional electronic components.
- This process involves a multitude of techniques and technologies, with each stage requiring precise control and attention to detail.
- A semiconductor fab -- short for fabrication -- is a manufacturing plant in which raw silicon wafers are turned into integrated circuits (ICs).
- A fab lab features a clean room where ICs are etched onto wafers.
- The completed chips are sent to a back-end assembly and test facility before they are packaged and sold.
- A semiconductor fab facility always includes a clean room -- so known because its environment is carefully controlled to eliminate dust and vibrations and to keep the temperature and humidity within a specific narrow range.
- Contamination can enter the fab environment through external sources, resulting in damage to products that can affect overall yield.
- To minimize the losses, all potential sources of contamination are thoroughly analysed and cleaned.
- For example, the tools used in the chip manufacturing process have low levels of particulates and fibres.
- The goal is to ensure that extraneous contamination is not introduced into the semiconductor fab to ensure the highest quality of the final products.
Technology Used in Semiconductor Fab Labs:
- Photolithography: Photolithography is a crucial optical process in the fabrication process, as it is used to create intricate circuit patterns on a single wafer's surface.
- This is achieved by coating the wafer with a photosensitive material, called a photoresist, and then exposing it to high-wavelength deep ultraviolet (DUV) or extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light through a mask containing the desired pattern.
- The exposed photoresist undergoes a chemical change, which allows it to be selectively removed.
- It leaves behind a patterned layer that serves as a protective layer for subsequent processing steps, such as etching and deposition.
Scientists are closer to creating a reference genome for Indians; 10,000 samples sequenced already

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Government’s ambitious Genome India initiative achieved a significant milestone Tuesday as researchers completed sequencing 10,000 healthy genomes from different regions of the country, representing 99 distinct populations.
News Summary:
- The Department of Biotechnology has announced the successful completion of India's '10,000 genome' project, aimed at establishing a comprehensive reference database of whole-genome sequences within the country.
- This milestone marks the creation of a detailed genetic map of India, offering significant potential for both clinicians and researchers in diverse fields.
- With India emerging as the largest genetic laboratory globally, this rich dataset is poised to catalyze advancements in the country's biology sector.
- Notably, India's bio-economy has witnessed remarkable growth, expanding from $10 billion in 2014 to over $130 billion in 2024, signaling a promising trajectory for future development.
- The entirety of the genomic dataset will be housed at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC), serving as a valuable digital resource for research purposes.
- Established in 2022, the IBDC represents India's sole indigenous databank, eliminating the need for Indian researchers to rely on foreign servers for hosting biological datasets.
What is Genome Sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the exact order of the building blocks (nucleotides) that make up an organism's entire DNA, or genome.
- It's like reading the complete instruction manual for life, containing the information needed to create and maintain an organism.
Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Healthcare: Doctors can diagnose diseases with greater accuracy, personalize treatments, and uncover the causes of rare conditions.
- Agriculture: Scientists can engineer crops with desired traits like disease resistance and improved yield, while breeders select animals with specific characteristics.
- Forensics: DNA profiling aids criminal investigations and paternity testing.
- Conservation: Studying the genetic diversity of endangered species helps with conservation efforts while analyzing invasive species' origins aids in controlling their spread.
What is the Human Genome Project (HGP)?
- Initiated in 1990, the Human Genome Project aimed to elucidate the entire sequence of the human genome.
- In 2023, the project culminated in the release of the latest version of the complete human genome, boasting a mere 0.3% error margin.
- Enabled by the Human Genome Project, whole-genome sequencing facilitates the examination of an individual's genome to uncover deviations from the average human genome.
- These deviations, or mutations, offer insights into an individual's susceptibility to diseases, their responsiveness to specific stimuli, and other pertinent genetic attributes.
About the Genome India Project:
- The Genome India Project stands as a pioneering initiative approved by the Department of Biotechnology, geared towards gene mapping.
- This project sets out with the ambitious objective of compiling an exhaustive repository documenting genetic diversity across the Indian populace.
- At its core, the endeavor seeks to conduct genome sequencing for more than 10,000 individuals spanning various geographic and ethnic backgrounds within India, ultimately laying the groundwork for a standardized reference genome specific to the Indian demographic.
Significance of the Genome India Project:
- Unveiling Unique Genetic Variants: The Genome India Project holds the key to unraveling genetic variants exclusive to India’s diverse population, enabling tailored drug formulations and therapeutic interventions.
- For instance, mutations like MYBPC3, linked to premature cardiac arrest and prevalent in 4.5% of Indians, underscore the necessity of region-specific genetic insights, contrasting with global rarity.
- Similarly, the discovery of the LAMB3 mutation, causing a severe skin disorder and impacting nearly 4% of the population around Madurai, emphasizes the localized genetic complexities absent in global databases.
- Comprehensive Database for India's Population: With a colossal population exceeding 1.3 billion, India boasts a mosaic of over 4,600 distinct population groups, many practicing endogamy.
- This vast demographic diversity underscores the need for a comprehensive genetic database tailored to India's populace, crucial for identifying and addressing disease-causing mutations prevalent within specific groups.
- Unlike extrapolating findings from global datasets, the Genome India Project provides precise genetic insights essential for Indian-centric healthcare strategies.
Google unveils Genie AI which can create video games from text and image prompts

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Google DeepMind unveiled Genie, a novel model capable of creating interactive video games based solely on textual or image prompts.
What is Genie AI?
- Genie is a foundation world model that is trained on videos sourced from the Internet.
- The model can “generate an endless variety of playable (action-controllable) worlds from synthetic images, photographs, and even sketches.”
- It is the first generative interactive environment that has been trained in an unsupervised manner from unlabelled internet videos.
- When it comes to size, Genie stands at 11B parameters and consists of a spatiotemporal video tokenizer, an autoregressive dynamics model, and a simple and scalable latent action model.
- These technical specifications let Genie act in generated environments on a frame-by-frame basis even in the absence of training, labels, or any other domain-specific requirements.
What does Genie do?
- Genie is a new kind of generative AI that enables anyone – even children – to dream up and step into generated worlds similar to human-designed simulated environments.
- It can be prompted to generate a diverse set of interactive and controllable environments although it is trained on video-only data.
- It is a breakthrough as it makes playable environments from a single image prompt.
- According to Google DeepMind, Genie can be prompted with images it has never seen.
- This includes real-world photographs, and sketches, allowing people to interact with their imagined virtual worlds.
- When it comes to training, they focus more on videos of 2D platformer games and robotics.
- Genie is trained on a general method, allowing it to function on any type of domain, and it is scalable to even larger Internet datasets.
Why is it Important?
- The standout aspect of Genie is its ability to learn and reproduce controls for in-game characters exclusively from internet videos.
- This is noteworthy because internet videos do not have labels about the action that is performed in the video, or even which part of the image should be controlled.
- It allows you to create an entirely new interactive environment from a single image.
- This opens up many possibilities, especially new ways to create and step into virtual worlds.
- With Genie, anyone will be able to create their own entirely imagined virtual worlds.
India gets desi Garbhini GA2 for evaluation of foetal growth
- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Specifically tailored to address the unique characteristics of foetal growth within the Indian population, India has finally got its locally made ‘Garbhini-GA2’, a groundbreaking Artificial Intelligence model.
What is Garbhini-GA2?
- The Garbhini-GA2 model, developed as part of the DBT India initiative (GARBH-Ini) program by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad, addresses the challenge of accurately estimating foetal age (gestational age, GA) in the Indian population, particularly in the second and third trimesters.
- Unlike existing formulas designed for Western populations, Garbhini-GA2 accounts for variations in foetal growth specific to the Indian context, significantly reducing estimation errors by nearly threefold.
- This innovative model is crucial for ensuring precise prenatal care and determining accurate delivery dates, thereby enhancing maternal and foetal health outcomes.
- Garbhini-GA2 marks a milestone as the first late-trimester GA estimation model validated using Indian population data, offering a tailored approach to foetal age determination that is essential for effective maternal healthcare."
About Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI):
- THSTI, an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Science and Technology, was founded in 2009 in Faridabad, Haryana, with a core commitment to advancing research beyond mere discovery.
- By fostering collaboration among diverse teams in medicine, science, and technology, THSTI leverages translational expertise to drive clinical research and innovation.
- In addition to its core mission, THSTI plays a pivotal role in fostering social innovation and entrepreneurial endeavors, particularly in the domain of maternal and child healthcare.
BharatGPT Unveils Hanooman, a New Suite of Indic Generative AI Models

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the BharatGPT group, led by IIT Bombay along with seven other elite Indian engineering institutes announced that it would launch its first ChatGPT-like service next month.
What is Hanooman?
- Hanooman is a series of large language models (LLMs) that can respond in 11 Indian languages like Hindi, Tamil, and Marathi, with plans to expand to more than 20 languages.
- It is unveiled by Seetha Mahalaxmi Healthcare (SML) in partnership with the IIT Bombay-led BharatGPT ecosystem.
- The BharatGPT group, which is backed by Reliance Industries.
- Hanooman has been designed to work in four fields, including health care, governance, financial services, and education.
- According to BharatGPT, the series isn’t just a chatbot but It is a multimodal AI tool, which can generate text, speech, videos and more in multiple Indian languages.
- One of the first customised versions is VizzhyGPT, an AI model fine-tuned for healthcare using reams of medical data.
- The size of these AI models ranges from 1.5 billion to a whopping 40 billion parameters.
Are There Any Other Indian Language Models?
- Apart from BharatGPT, a host of different startups like Sarvam and Krutrim, backed by prominent VC investors such as Lightspeed Venture Partners and billionaire Vinod Khosla’s fund, are also building AI models customised for India
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
- Large language models use deep learning techniques to process large amounts of text.
- They work by processing vast amounts of text, understanding the structure and meaning, and learning from it.
- LLMs are ‘trained’ to identify meanings and relationships between words.
- The greater the amount of training data a model is fed, the smarter it gets at understanding and producing text.
- The training data is usually large datasets, such as Wikipedia, OpenWebText, and the Common Crawl Corpus.
- These contain large amounts of text data, which the models use to understand and generate natural language.
First moon-landing by private company

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fifty-two years after the last successful Apollo mission, a US-made spacecraft landed on the Moon recently which also marks the arrival of private space companies on the lunar surface.
What is Odysseus Lunar Exploration?
- Odysseus is a spacecraft built by Intuitive Machines, embarked on its journey from Earth aboard a Falcon 9 rocket by SpaceX recently.
- Intuitive Machines, headquartered in Houston, USA, boasts a decade-long legacy in space exploration endeavours.
- Loaded with six NASA payloads, Odysseus set its course for the Moon.
- Its lander module, Nova-C, achieved the milestone of landing in the Moon's south pole region, following Chandrayaan-3's similar feat last year.
- This marks the third successful moon-landing event in under a year, alongside Chandrayaan-3 and Japan's SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon).
Mission Objectives:
- The primary aim of the lunar lander is to assess the environmental conditions at the Moon's south pole.
- This assessment holds significant importance as NASA gears up for a crewed mission in September 2026 with Artemis III.
- Before sending astronauts to this area, NASA seeks to gather crucial data, including insights into water presence and accessibility, to inform mission planning.
Funding:
- Under the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, NASA allocated $118 million to Intuitive Machines for this mission.
- CLPS has engaged at least 14 private companies to ferry NASA payloads to the Moon, fostering a collaborative environment aimed at nurturing the private space industry's capabilities in lunar exploration technology and science.
The Significance of Odysseus:
- Advancing Long-Term Lunar Presence: Odysseus' successful landing heralds a transformative phase in lunar exploration, aiming to establish infrastructure and a technological ecosystem capable of sustaining extended human presence.
- Diverging from Past Lunar Missions: In contrast to the moon landings of the 1960s and 1970s spearheaded by the US and the Soviet Union, Odysseus' mission focuses on leveraging lunar resources for sustained exploration.
- While historic moon landings were remarkable feats, technological limitations of the time hindered the immediate utilisation of lunar resources such as mining.
- Supporting US Commitment to Moon Exploration via Artemis Program: Odysseus' touchdown aligns with the US commitment to rekindle lunar exploration through the ambitious Artemis program.
- This endeavour transcends mere lunar landing missions, aiming to establish essential infrastructure and a thriving lunar economy conducive to comprehensive exploration.
- Unlocking Lunar Potential as a Gateway to Deep Space: By laying the groundwork for lunar infrastructure and economic activity, missions like Odysseus pave the way for leveraging the Moon as a springboard for deeper space exploration, offering nations unprecedented opportunities for cosmic discovery.
Race to the global eradication of Guinea worm disease nears the finish line
- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease. There were more than 3.5 million cases of this disease in the 1980s, but according to the WHO, they dwindled to 14 cases in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just six in 2023.
What is Guinea Worm Disease?
- Dracunculiasis is also called guinea worm disease (GWD).
- It is an infection caused by a parasite called Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm).
- This parasite is an organism that survives by deriving nutrients and feeding off another organism.
- GWD spreads through drinking contaminated water.
- It is presently eradicated in most parts of the world but is still seen in remote parts of Africa and some remote rural areas in the world where there is no access to clean drinking water.
- GWD is considered endemic in three African countries, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Mali.
- In recent years, a few cases of GWD in animals, especially dogs, have been reported in developed countries as well.
- GWD is a serious condition, that causes debilitating pain and complications, affecting the quality of life
Symptoms:
- People infected with Guinea worm don’t typically have any symptoms until about a year after they're first infected.
- It’s not until the worm is about to erupt from the skin that people start to feel sick.
- What that happens, the symptoms of Guinea worm disease can include Fever, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhoea, Shortness of breath, Burning, itching, pain, and swelling where the worm is in the body (often the legs and feet) and Blister where the worm breaks through the skin.
Impact:
- Guinea worm disease isn’t often deadly, but it can cause serious complications, lifelong disabilities, and financial hardship for those involved.
- The pain involved is often so intense that it’s difficult for people to work, go to school, or care for themselves or others.
- This lasts an average of 8.5 weeks, though lifelong disability is common.
Dracunculiasis Treatment:
- There is no vaccine or drug developed to prevent or treat this disease.
- The only means available is the management of the disease which is removing the whole worm and caring for the wound caused by it and avoiding infection in the process or exposure to the guinea worm larvae at all costs, especially by avoiding contaminated drinking water and stagnant water sources.
- Without proper treatment, wounds caused by the worm can become infected by bacteria, leading to sepsis, septic arthritis, and contractures (when joints lock and deform).
- In some cases, these infections become life-threatening.
In a first, CERN scientists carry out laser cooling of Positronium

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a first, an international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
About Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS):
- AEgIS is an experiment at the Antiproton Decelerator facility at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- It is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- In 2018, AEgIS demonstrated the first pulsed production of antihydrogen atoms, by interacting pulse-produced positronium (an atom consisting of only an electron and a positron) with cold, trapped antiprotons.
- The primary scientific goal of the Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) is the direct measurement of the Earth's gravitational acceleration, g, on antihydrogen.
What is Positronium?
- Positronium is a bound state system of a positron and an electron, similar to the hydrogen atom, where an electron orbits around a proton.
- In the case of positronium, the positron and the electron orbit around their common centre of mass.
- The system is unstable, and the two particles eventually annihilate each other, releasing two or more gamma ray photons.
- Positronium has two possible states:
- The singlet state (para-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are antiparallel and the system has a shorter lifetime, and
- The triplet state (ortho-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are parallel, and the system has a longer lifetime.
- Positronium has been studied extensively in experimental and theoretical physics because it provides a simple system for testing quantum electrodynamics (QED) and for studying the properties of matter and antimatter.
- It also has potential applications in fields such as material science, plasma physics, and astrophysics.
What is Antimatter?
- Antimatter shares similarities with ordinary matter, except for its opposite electric charge.
- Often referred to as "mirror" matter, antimatter pairs with ordinary matter particles.
- For example, while an electron possesses a negative charge, its antimatter counterpart is a positron, which carries a positive charge and has the same mass as an electron.
- Positrons, antiprotons, and antineutrons are the antimatter counterparts of electrons, protons, and neutrons, respectively, collectively known as antiparticles.
- These antiparticles can combine to form anti-atoms and theoretically could lead to the formation of antimatter regions within our universe.
- However, the coexistence of matter and antimatter is short-lived due to their tendency to annihilate upon contact, resulting in the release of substantial energy in the form of gamma rays or elementary particles.
- Antimatter, like matter, emerged during the Big Bang.
- Scientists have produced antimatter particles through high-speed collisions in large particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider operated by CERN outside Geneva.
- Additionally, antiparticles are sporadically generated throughout the universe through natural processes.
Hundred years ago, Satyendra Nath Bose changed physics forever
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2024, we commemorate the centenary of Bose's pivotal discovery of the precise equations governing the behaviour of collections of photons, fundamental particles of light.
About Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Satyendra Nath Bose (1894-1974) was an eminent Indian physicist renowned for his pioneering contributions to theoretical physics, notably in the realms of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics.
- His groundbreaking research laid the groundwork for Bose-Einstein statistics and the theoretical elucidation of Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Bose's profound insights not only advanced the understanding of fundamental physics but also played a pivotal role in refining the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
- His visionary work eventually paved the way for significant discoveries in particle physics, including the identification of the Higgs Boson, colloquially referred to as the "God Particle."
Major Contributions of Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Foundation of Bose-Einstein Statistics and Bosons: In 1924, Bose formulated a revolutionary explanation for Planck's law of black-body radiation using quantum mechanics principles, introducing the concept of "Bose-Einstein statistics."
- This theory delineates the behaviour of particles known as "bosons," characterized by integer spin.
- Bose-Einstein statistics elucidate how bosons, such as photons and atoms, preferentially occupy the same quantum state, a behaviour distinct from fermions governed by the Pauli exclusion principle.
- This groundbreaking work laid the groundwork for understanding particle behaviour at low temperatures and foretold the existence of the Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Prediction of Bose-Einstein Condensate: Bose's collaboration with Einstein in statistical mechanics led to the theoretical prediction of the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), a revolutionary concept in quantum physics.
- According to Bose-Einstein statistics, at ultra-low temperatures approaching absolute zero, bosons can congregate in the lowest energy state, forming a condensed state.
- Often dubbed the "fifth state of matter," BEC occurs when bosons lose sufficient energy to coalesce into a single quantum state, creating a cohesive "super-particle" cloud.
- Experimental confirmation of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, decades after Bose's theoretical proposal, garnered Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001.
- Together with Meghnad Saha, he published the first English translation of Einstein’s papers on general relativity.
- His dedication to research and scientific integrity earned him numerous accolades, including the Padma Vibhushan and the Fellowship of the Royal Society.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
