Symbol Loading Units (SLUs)

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court rejected the plea for full verification of VVPAT slips against EVM counts and directed the ECI to seal the Symbol Loading Unit (SLU) for 45 days post-election results announcement.
What is a Symbol Loading Unit (SLU) and How Does it Work?
- Symbol Loading Units (SLUs) were introduced around the same time as VVPATs, a little over a decade ago.
- VVPATs help voters verify their votes, they see a slip with a printed image of the party symbol they voted for.
- But for the VVPAT to print a symbol correctly, information pertaining to the list of candidates and their symbols must be loaded onto the VVPAT machine in the correct order.
- This is where the Symbol Loading Unit, or SLU, comes in.
- The introduction of VVPATs necessitated the use of SLUs.
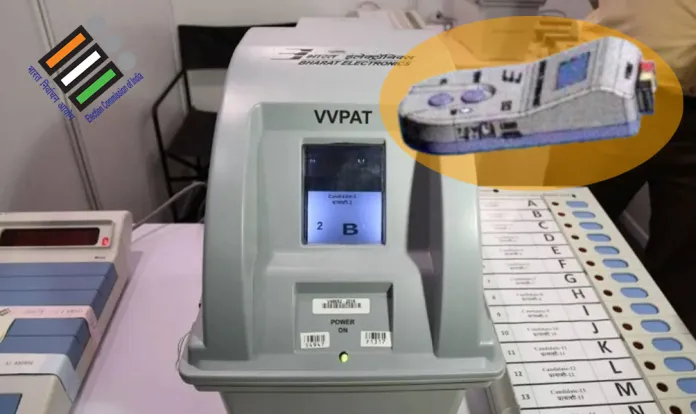
- The SLU is used to load the symbols of the candidates onto the VVPAT.
- It is a matchbox-sized device that is first connected to a laptop or personal computer, from where a symbol-loading application is used to load a bitmap file containing the candidates’ names, serial numbers, and symbols.
- The SLU is then connected to the VVPAT to transfer that file onto the paper audit machine.
- This is done under the supervision of a district election officer.
At Which Point in the Election Process Are SLUs Used?
- The SLUs come into the picture only a few days before polling in a particular seat, when the EVMs are being commissioned and the list/ order of contesting candidates is decided and set on the ballot unit and the VVPAT.
- Candidate-setting can happen at any time from five to two days before voting at a seat.
- Once the SLU is used to load symbols onto the VVPAT, the EVM is ready for use.
- After this, the SLU is of no relevance to the actual voting process.
What Happens to an SLU After Symbols Are Loaded?
- Typically, a small number of SLUs are enough to load symbols onto all VVPATs for a seat.
- According to EC officials, it takes an SLU two to three minutes to load each VVPAT.
- Once the symbol-loading is complete, the SLUs are handed over to the concerned district election officer for safekeeping.
- They remain in the officer’s custody until the day after voting. Afterward, the SLUs are released to the engineers of the two EVM manufacturers, Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) or Electronics Corporation of India Ltd (ECIL), so they can be used to load symbols onto VVPATs for other seats in subsequent phases.
- Thus, in a multi-phase election like the ongoing one for the 18th Lok Sabha, an SLU is typically reused after one phase of polling to load symbols onto VVPATs meant for other seats in subsequent phases.
ZSI names a newly discovered head-shield sea slug after President Droupadi Murmu
- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zoological Survey of India named a new marine species of head-shield sea slug with ruby red spot which was discovered from West Bengal and Odisha coast after President of India Droupadi Murmu.
About Melanochlamys Droupadi:
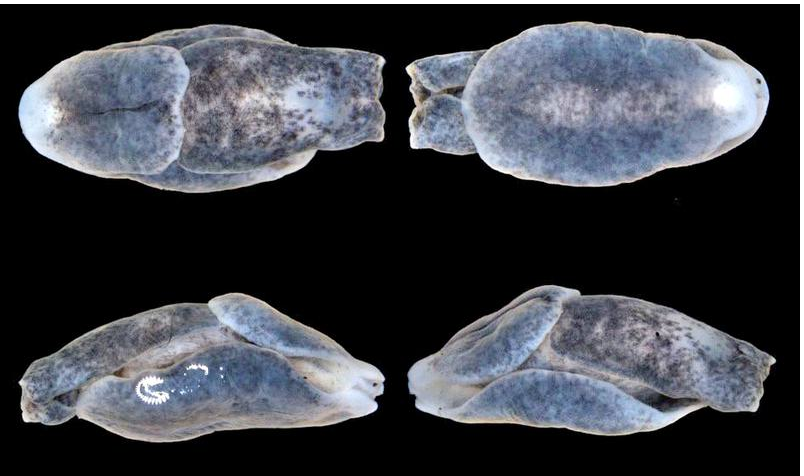
- Melanochlamys Droupadi is a newly discovered marine species of head-shield sea slug distinguished by its striking ruby red spot.
- This species, belonging to the Melanochlamys genus, was first identified along the coasts of Digha in West Bengal and Udaipur in Odisha.
Key Features:
- This small invertebrate typically measures up to 7 mm in length.
- It primarily inhabits wet and soft sandy beaches.
- Adorned in brownish-black hues, it features a distinctive ruby-red spot towards its hind end.
- Melanochlamys Droupadi exhibits hermaphroditic characteristics, possessing both male and female reproductive organs. However, it requires another sea slug for successful reproduction.
- Internally, it possesses a shell and a posterior segment comprising 61 per cent of its body length.
- To safeguard against sand infiltration, it continuously secretes transparent mucus, forming a protective sheath around its body.
- When in motion, it burrows beneath smooth sand, creating a moving capsule where its body remains mostly concealed, akin to a turtle, leaving behind a discernible trail.
What are Sea Slugs?
- Sea slugs are a diverse group of molluscs inhabiting marine environments, characterized by their slug-like appearance.
- They occupy a wide range of habitats, spanning from shallow intertidal zones to the depths of the ocean, and from polar regions to tropical waters.
- As agile predators, sea slugs prey on mobile organisms such as other shelled and unshelled sea slugs, roundworms, marine worms, and small fish.
- Currently, researchers have identified 18 species of sea slugs worldwide.
- While sea slugs predominantly inhabit temperate regions within the Indo-Pacific Oceanic realm, three species exhibit truly tropical distributions: Melanochlamys papillata from the Gulf of Thailand, Melanochlamys bengalensis from the West Bengal and Odisha coast, and the newly discovered species.
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) (HT)
- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A controversy over alleged engineering lapses in the ?1 lakh crore Kaleshwaram lift irrigation project on the Godavari river triggered an electoral slugfest in poll-bound Telangana.
About Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP):
- Location: The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) is situated at Kaleshwaram village in Telangana, along the Godavari River.
- Confluence Point: It is located at the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari Rivers.
- At this confluence, the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers also meet, forming the seventh-largest drainage basin in the subcontinent.
- Originally called Pranahita-Chevella project in erstwhile Andhra Pradesh, it was redesigned, extended and renamed as Kaleshwaram project in Telangana in 2014.
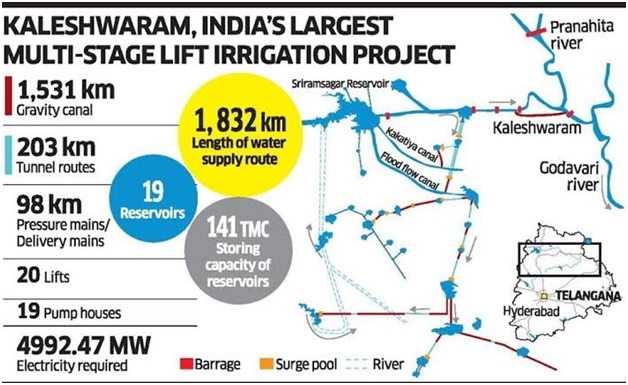
- KLIP is known as the world's largest multi-stage and multi-purpose lift irrigation project.
- A significant feature of KLIP includes a series of underground and surface water pumping stations, claimed to be the world's largest of their kind.
- This lift irrigation system stretches over 300 kilometers and moves large volumes of water from rivers or reservoirs to be distributed through channels and additional reservoirs before reaching the next stations.
- Objective: The project's goal is to provide water to 45 lakh acres of land in Telangana for irrigation and drinking water.
- KLIP started in 2016 and will utilise approximately 283 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) of water from the Godavari River to serve 13 districts in Telangana.
TransLunar Injection (TLI) (The Hindu)
- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The TransLunar Injection (TLI) was performed successfully from ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru recently.
What is the TransLunar Injection (TLI)?
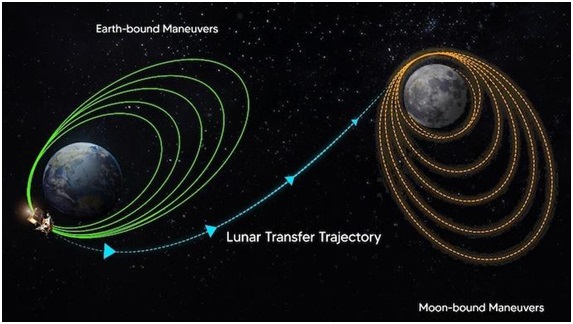
- TransLunar Injection (TLI) is a crucial space mission maneuver, propelling spacecraft from Earth's orbit to a trajectory aimed at reaching the Moon.
- An essential step in lunar missions, TLI allows spacecraft to break free from Earth's gravity and commence their journey toward the Moon.
- TLI is executed when the spacecraft reaches the perigee, the closest point to Earth in its orbit.
- During TLI, the spacecraft's propulsion system ignites its engines, accelerating the craft and providing the necessary speed to escape Earth's gravitational pull.
- The thrust and duration of the TLI burn are determined by factors like spacecraft mass, Earth's orbital velocity, and specific mission objectives.
- Following a successful TLI, the spacecraft is directed onto a lunar trajectory, continuing its autonomous journey to the Moon without further reliance on Earth's propulsion.
- Subsequent to TLI, the spacecraft enters a transfer orbit, an elliptical path that intersects with the Moon's orbit.
- The spacecraft traverses this highly eccentric orbit until it reaches the lunar surface.
- As the spacecraft approaches the Moon, additional maneuvers like lunar orbit insertion (LOI) may be executed to enter lunar orbit or facilitate landing, based on the mission's objectives.
- TLI has been effectively utilized in numerous Moon missions, including Apollo, Chang'e, and Artemis missions.
