Fast Track Immigration FTI-TTP

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India is launching the Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Program (FTI-TTP) to streamline immigration at seven major airports.
Key Highlights:
- The initiative, inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, aims to enhance the travel experience for Indian nationals and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cardholders.
- This comes seven months after the programme was first introduced at Indira Gandhi International (IGI) Airport, New Delhi. The airports included in this initial phase are: Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin and Ahmedabad
Objectives of FTI-TTP
- Provide seamless and secure immigration services.
- Reduce human intervention using automated e-gates.
- Align with the Viksit Bharat@2047 vision for modern infrastructure.
How the Programme Works
The FTI-TTP simplifies immigration with automated e-gates. Travellers must complete a one-time online registration to enroll. The process involves:
- Online Registration: Submit personal details and upload necessary documents via the official portal (https://ftittp.mha.gov.in).
- Biometric Submission: Fingerprints and facial images must be submitted at an airport or Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- Immigration Clearance via E-Gates:
- Passengers scan their boarding passes and passports at e-gates.
- Biometrics are automatically verified.
- Upon authentication, the e-gate opens, granting clearance.
Validity: Registration is valid for five years or until the registered passport expires, whichever comes first.
Who is Eligible?
The first phase of the FTI-TTP is open to:
- Indian nationals.
- OCI cardholders aged between 12 and 70 years.
- Children aged 12-18 can register using their parents’ email/phone number.
- ECR (Emigration Check Required) passport holders are not eligible.
Documents Required for Registration
- Passport-sized photograph (as per Indian passport specifications).
- Scanned copy of passport (front and back pages).
- Proof of current address.
- OCI card details (if applicable).
Key Points to Note
- Registration may take up to a month due to verification by field agencies.
- Applications with incorrect or outdated information may be rejected.
- In case of passport loss or expiry, travellers must reapply and submit fresh biometrics.
- Passports must have at least six months’ validity at the time of applying.
- For support, travellers can reach out via email at india.ftittp-boi@mha.gov.in.
Implementation Phases
The FTI-TTP will be implemented in two phases:
- Phase 1: Covers Indian citizens and OCI cardholders.
- Phase 2: Will extend to foreign travellers.
- The programme will be expanded to 21 major airports across the country.
Comparison with Similar Global Programmes
Several countries have implemented similar fast-track immigration systems:
United States: Global Entry
- Introduced in 2008.
- Offers self-service kiosks for pre-approved travellers.
- Requires background checks and in-person interviews.
United Kingdom: Registered Traveller Service
- Launched in 2015.
- Allows frequent visitors from select countries, including India, to use e-gates.
- Requires visa eligibility or multiple prior visits.
European Union: Smart Borders Initiative
- Implemented in 2016, with full deployment expected by 2024.
- Pre-registers biometric data for faster processing at Schengen Area borders.
Australia: SmartGate
- Started in 2007 for Australian and New Zealand passport holders.
- Uses automated kiosks for identity verification via passport scans and photos.
Saudi Arabia: Smart Travel System
- Launched in 2019.
- Uses automated e-gates for faster immigration clearance.
- Expanding as part of Vision 2030 to improve travel experience, particularly for Hajj pilgrims.
Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
US AI Hardware Export Restrictions and Impact on India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
Days before demitting office, the Joe Biden administration has released an expansive regulatory framework on the export of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs), which could have far-reaching consequences for India’s AI ambitions.
Three-Tier Framework for AI Hardware Export Restrictions
- Tier 1: Closest US Allies
- Countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, South Korea, UK, etc.
- No restrictions on computing power deployment.
- Minimal security requirements.
- Impact: Free access to AI technology for these nations.
- Tier 2: Majority of Countries (Including India)
- Countries: India, Brazil, South Africa, etc.
- Restrictions: Limited to importing approximately 50,000 advanced AI chips (around $1 billion) through 2027.
- Potential to Double Cap: If countries sign agreements to uphold strict security standards.
- Impact on India:
- Short-Term: Likely to fulfill current demand for 10,000 GPUs for the IndiaAI Mission.
- Long-Term: Challenges in scaling AI infrastructure, with possible delays in large AI data centers and difficulty acquiring large-scale GPUs.
- Tier 3: Countries of Concern (Restricted Nations)
- Countries: Russia, China, North Korea, Iran, etc.
- No Access to US AI Technology: Nearly total prohibition of AI tech exports.
Special Provisions for India and China
- General Validated End User (GVEU) status for India and China:
- India: Authorisation for civilian and military use, excluding nuclear applications.
- China: Only civilian use permitted under similar conditions.
Why the US Imposed These Restrictions?
- National Security: Prevent adversaries (China, Iran, Russia) from acquiring advanced AI technologies.
- US Technological Leadership: To protect US AI leadership and prevent loss of competitive edge.
- Trusted Ecosystem: Build secure and trusted AI environments for allied nations.
Impact on India
- Short-Term:
- IndiaAI Mission: Current procurement of 10,000 GPUs unlikely to be affected.
- Subsidized GPUs: Available for startups, academia, and researchers.
- Long-Term Concerns:
- Licensing Uncertainties: Possible delays in large-scale AI deployments and AI data centers.
- Impact on Large Firms: Companies like Reliance and Yotta may face challenges scaling up AI compute infrastructure.
- National AI Mission Challenges: Difficulty in acquiring enough GPUs for large-scale AI projects beyond 2027.
- Strategic Leverage: US could use AI export restrictions to negotiate trade deals or tariff adjustments.
Nvidia’s Criticism of the AI Diffusion Rules
- Overreach and Bureaucratic: Nvidia criticized the 200+ page regulatory framework as excessive, secretive, and bureaucratic.
- Harming US Competitiveness: Claims that the rules would hinder US innovation and global leadership, weakening the competitiveness of the US semiconductor and software industries.
- Contrast with Trump’s Approach: Praises the earlier Trump administration for fostering AI growth through industry competition without compromising national security.
Enforcement of the Rules
- Regulatory Control: Managed by the US Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) under the Department of Commerce.
- Technology Access: Ensures AI chips and models do not reach adversaries or nations posing security risks.
Potential Impact on India’s AI Strategy
- AI Hardware Infrastructure: Challenges in large-scale AI hardware deployment.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Potential delays or downsizing of AI data centers could affect India’s competitiveness in AI technology.
- Strategic Partnerships: India may need to secure General National Validated End User authorizations to ensure uninterrupted access to advanced chips.
- AI Market Growth: India’s AI market projected to grow to $17 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 25%-35%.
Commissioning of Three Indian Naval Combatants

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
In a major boost to India’s maritime defense capabilities, three frontline warships—INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer—were commissioned into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai. This marks a significant step in India's self-reliance in defense manufacturing and strengthens its presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
INS Nilgiri: Project 17A Stealth Frigate
INS Nilgiri is the lead ship of the Project 17A class, an advanced version of the Shivalik-class frigates, designed for multi-mission capabilities in blue-water operations.
Key Features:
- Advanced stealth technology reducing radar and infrared signatures.
- Equipped with supersonic surface-to-surface missiles, Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missiles (MRSAM), upgraded 76 mm guns, and rapid-fire close-in weapon systems.
- Versatile roles in anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Constructed using integrated modular design for faster assembly.
- Other ships in this class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, and Vindhyagiri—are under construction at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
INS Surat: Project 15B Stealth Destroyer
INS Surat is the fourth and final guided missile destroyer under Project 15B, following INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal. It represents an upgraded version of the Kolkata-class destroyers.
Key Features:
- AI-Enabled Operations: First Indian warship integrated with artificial intelligence solutions for enhanced combat efficiency.
- High-Speed Capability: Can exceed speeds of 30 knots (56 km/h).
- Advanced Armament: Equipped with modern surface-to-air and anti-ship missiles, torpedoes, and sophisticated network-centric warfare sensors.
- Strategic Role: Acts as a high-speed, maneuverable warship with increased strike capability and endurance.
Project 15B was initiated in 2011, with ships named after major Indian cities to symbolize national unity. These destroyers serve as critical assets in naval operations, ensuring dominance in maritime warfare.
INS Vaghsheer: Project 75 Scorpene-Class Submarine
INS Vaghsheer is the sixth and final Kalvari-class submarine built under Project 75, designed for stealth and versatile naval operations.
Key Features:
- Scorpene-Class Design: Developed in collaboration with the French Naval Group.
- Diesel-Electric Propulsion: Silent and highly maneuverable, making it one of the world’s most advanced attack submarines.
- Mission Capabilities: Specializes in anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
- Weapons Systems: Armed with wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and state-of-the-art sonar systems.
The Kalvari-class submarines continue India's legacy of submarine warfare, named after decommissioned Soviet-origin Foxtrot-class submarines post-Independence.
Iran's Capital Relocation

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Iran has announced plans to relocate its capital from Tehran to the Makran coastal region due to economic and environmental concerns.
Reasons Behind Relocation
- Overcrowding and Resource Constraints: Tehran, the capital for over 200 years since the Qajar dynasty (1794-1925), faces overpopulation, air pollution, water scarcity, and energy shortages.
- Strategic Importance of Makran: Located in Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Makran’s proximity to the Gulf of Oman enhances its potential for economic development.
- Economic and Maritime Significance: Home to key ports like Chabahar, Makran is vital for Iran’s petroleum reserves and coastal trade.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The development of Makran as an international trade hub could strengthen Iran’s economic ties with Central Asia and the Indian Ocean region.
About Makran
- Geographical Overview: A semi-desert coastal plateau shared by Pakistan and Iran, bordered by the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman.
- Key Ports and Trade Routes: Gwadar (Pakistan) and Chabahar (Iran) serve as critical gateways to the Strait of Hormuz, a global oil supply route.
Alexander’s Invasion and Makran’s Historical Significance
Background of Alexander’s Invasion (327–325 BCE)
- Entry into India: Alexander, King of Macedonia (336-323 BCE), entered India via the Khyber Pass after conquering Kabul.
- Key Battles:
- Battle of Hydaspes (Jhelum): Faced and defeated King Porus, later reinstating him as an ally.
- Retreat at Hyphasis (Beas River): His army, exhausted and wary of the Nanda Empire’s strength, refused to march further east.
The Gedrosian Desert March
- Extreme Hardships: While retreating through the Makran Desert, Alexander lost a third of his army to dehydration, starvation, and exhaustion.
- Comparison with Cyrus the Great: Unlike Cyrus II, who failed to cross the desert, Alexander’s army endured the harsh terrain, albeit with heavy casualties.
Impact of Alexander’s Invasion on India
- Cultural and Trade Exchanges: Facilitated early Indo-Greek interactions and opened key trade routes linking South Asia and Europe.
- Greek Settlements: Established cities like Alexandria (Kabul) and Boukephala (Jhelum), influencing local governance and trade.
- Mauryan Expansion: Weakened regional rulers enabled Chandragupta Maurya to establish the Mauryan Empire.
- Influence on Art and Culture: Indo-Greek fusion led to the Gandhara School of Art, integrating Greek and Indian artistic traditions.
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire and Hostage Release Deal
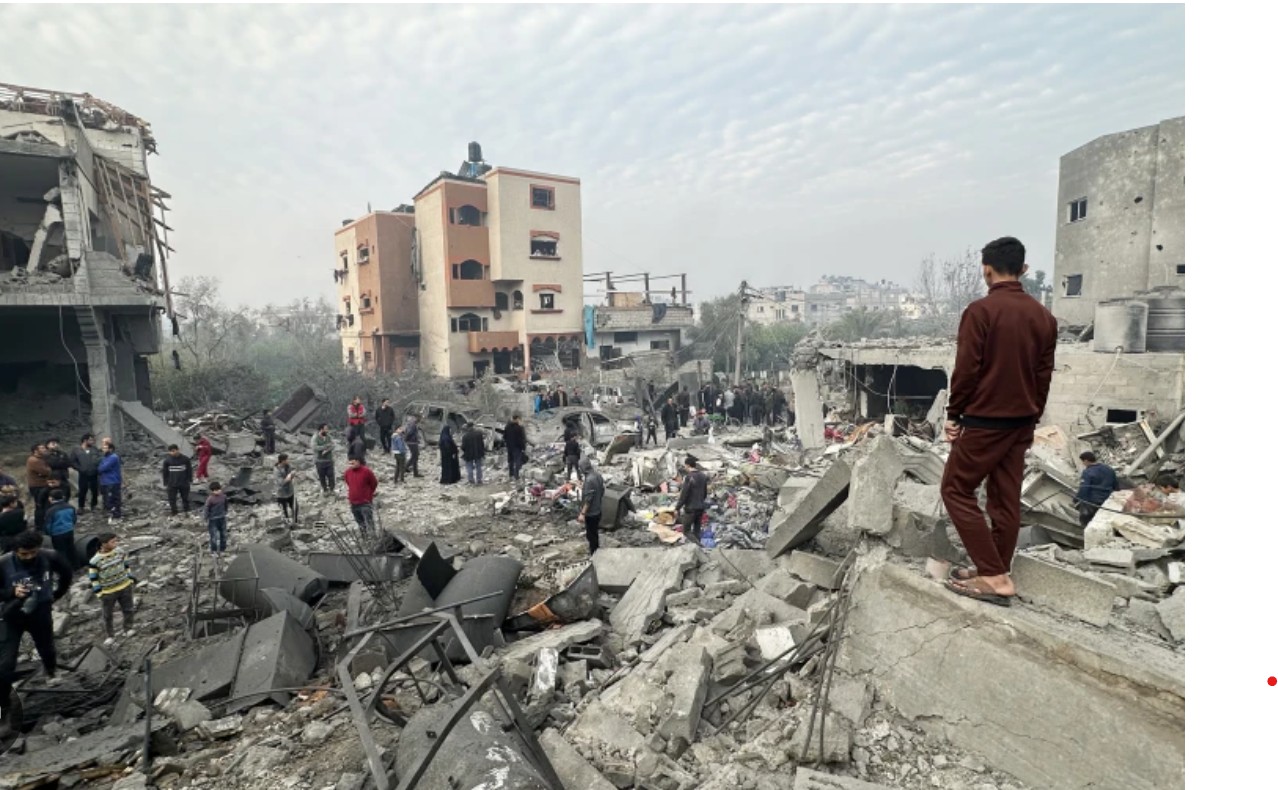

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Israel and Hamas have agreed on a Gaza ceasefire and hostage release deal after 15 months of war.
Key Highlights:
Ceasefire Agreement Details:
- Location: The deal was brokered in Doha, Qatar.
- Approval Process: The deal must be approved by Israel’s Cabinet to take effect.
- Mediators: The agreement was negotiated by Qatar, Egypt, and the United States, with their involvement ensuring the implementation of the deal.
Phases of the Deal:
- First Phase (42 Days):
- Release of 33 hostages by Hamas, including women, children, and elderly people.
- Hostage Exchange: Hostages will be exchanged for Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails.
- Gaza Ceasefire and Withdrawal: Israeli forces will gradually withdraw from Central Gaza and move to the borders.
- Return of Displaced Palestinians: Displaced Palestinians will be allowed to return to Northern Gaza.
- Humanitarian Aid: 600 humanitarian aid trucks will be allowed into Gaza daily.
- Second Phase:
- Hostage Release: Negotiations will begin for the release of remaining hostages.
- Full Israeli Troop Withdrawal: Israel will fully withdraw its forces.
- Third Phase:
- Reconstruction of Gaza: Overseen by Egypt, Qatar, and the United Nations.
- Reopening of Border Crossings: For movement in and out of Gaza.
- Return of Hostage Bodies: Return of any bodies of hostages who died.
Background of the Israel-Hamas Conflict:
- Start: On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched an attack on Israel, called Operation Al-Aqsa Flood, causing significant casualties.
- Israeli Response: Israel launched Operation Iron Sword in retaliation.
- Casualties: The conflict resulted in 46,707 Palestinian deaths, mostly civilians, and 1,210 Israeli deaths.
About Gaza Strip:
- Location: A Palestinian enclave on the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Israel and Egypt.
- Administration: The Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas since 2006.
- Movement Restrictions: Israel controls air space and shoreline, imposing restrictions. Egypt controls one border and also restricts movement.
Gaza Truce Deal:
- Nature: A proposed ceasefire to end the ongoing conflict.
- Primary Parties: Israel and Hamas.
- Supporting Nations: United States, Qatar, and Egypt.
- Significance:
- Aims to stop fighting and address the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- Potential to influence regional stability and Israeli politics.
- Marks an important moment in U.S. diplomacy under the Biden administration.
EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog, in partnership with New Shop (India’s largest 24/7 convenience retail chain), launched the initiative EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan under the Award to Reward (ATR) program. This program aims to empower women entrepreneurs by providing them with the skills, resources, and mentorship needed to succeed in the organized retail sector. The collaboration seeks to create a robust retail ecosystem that supports women in overcoming barriers such as societal biases, limited access to financing, and a lack of mentorship.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Target Participants: The program will select 50 women aged 18-35 through an online application process. Women from Delhi NCR, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat will be considered.
- Top 20 Participants: The 20 best candidates will receive a 100% waiver on New Shop franchise fees, enabling them to operate their own retail businesses with reduced financial barriers.
- Program Objective: Equip women entrepreneurs with skills such as retail management, digital tools, financial literacy, and business development. Participants will also receive valuable mentorship to help them grow and scale their businesses.
- Focus on Retail: The initiative focuses on empowering women within the organized retail sector, creating a sustainable ecosystem that fosters growth and development for female entrepreneurs.
About Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP):
- Incubation & Transition: Established in 2018, WEP was incubated within NITI Aayog and transitioned into a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in 2022.
- Purpose: WEP aims to empower women entrepreneurs by addressing challenges like information asymmetry and providing essential support in key areas such as:
- Access to Finance
- Market Linkages
- Training & Skilling
- Mentoring & Networking
- Compliance & Legal Assistance
- Business Development Services
- Collaboration: WEP partners with over 30 public and private sector organizations to develop scalable and impactful programs. Since 2023, the Award to Reward initiative offers a framework for stakeholders to create impactful programs for women entrepreneurs.
About New Shop:
- Business Model: New Shop operates over 200 round-the-clock convenience retail stores in high-density areas, including highways and gas stations. The company plans to expand into airports, railway stations, and other mass transit hubs.
- Franchising Vision: By 2030, New Shop aims to empower over 10,000 entrepreneurs in India through its franchising model. The partnership with WEP seeks to help women entrepreneurs access this growth opportunity.
Program Outcomes:
- Mentorship & Training: Participants will be mentored and trained on key aspects such as retail management, business development, and digital tools.
- Franchise Opportunity: Top participants will gain access to New Shop’s franchising ecosystem, providing them a ready-made business opportunity with lower entry barriers.
- Financial Assistance: The program will also provide financial resources to the women, helping them build their businesses with greater ease.
Indonesia Becomes 10th Member of BRICS
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, Indonesia officially joined the BRICS group as its 10th member, signaling the expansion of this influential coalition of emerging economies. The addition of Indonesia, a Southeast Asian powerhouse, strengthens BRICS' global position and highlights the group's evolving dynamics.
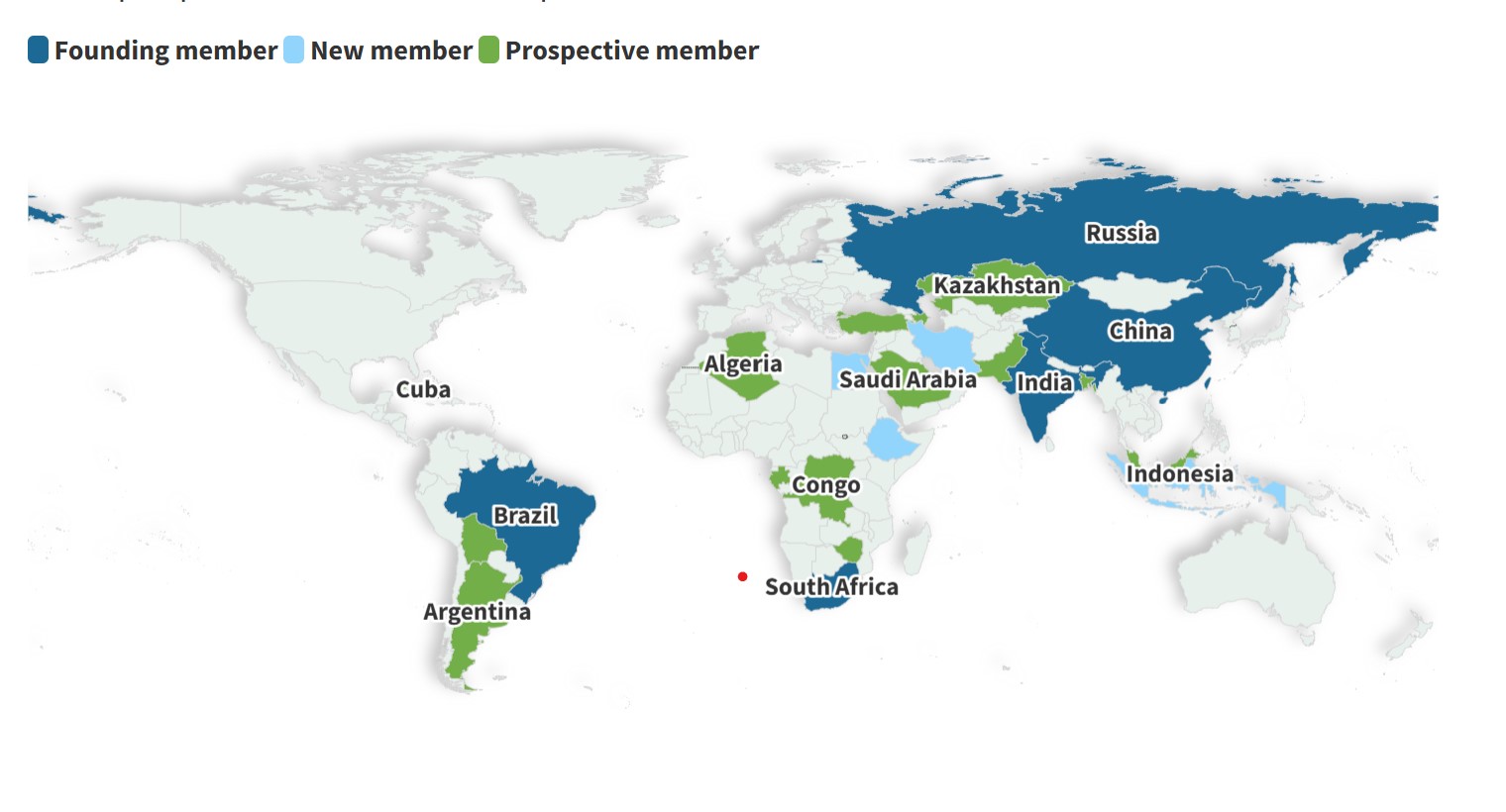
BRICS Overview:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) is an informal intergovernmental group that fosters cooperation among major emerging economies. Initially coined as BRIC by economist Jim O'Neill in 2001, the group became BRICS in 2010 with the inclusion of South Africa. The bloc has grown steadily, with Indonesia now joining as its 10th member.
Recent Expansion:
- In 2023, invitations were extended to Saudi Arabia, Iran, UAE, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Argentina.
- By 2024, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and UAE had joined as permanent members.
- Indonesia's membership was finalized in 2025, following its presidential elections and government formation.
Key Objectives of BRICS:
- Economic Growth: Promote trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Global Governance Reform: Advocate for equitable representation in global institutions like the UN and IMF.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthen people-to-people connections and cultural ties.
- South-South Cooperation: Foster collaboration among developing nations.
BRICS Structure and Mechanisms:
- New Development Bank (NDB): Established in 2014, the NDB finances sustainable development projects in BRICS countries.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA): A $100 billion safety net for financial crises.
- BRICS Academic Forum: Encourages academic collaboration across member states.
Global Influence and Economic Impact:
- Global Share: BRICS+ represents over 45% of the world’s population and 35% of global GDP (PPP-based).
- Strategic Position: The group acts as a counterbalance to the G7, challenging Western-dominated global financial systems.
- Financial Independence: BRICS aims to reduce dependence on the US dollar by facilitating local currency transactions and exploring a common currency.
- Technology Collaboration: Member countries, such as India and China, collaborate on digital payments and renewable energy technologies.
Indonesia’s Entry into BRICS:
Indonesia, the world’s fourth-most populous nation, strengthens BRICS’ representation in Southeast Asia. The country brings a robust economy and extensive trade networks, boosting the group's negotiating power. Indonesia’s membership was approved during the 2023 BRICS Summit and finalized in January 2025.
- Strategic Importance for Indonesia: The membership aligns with Indonesia's goals to enhance global cooperation, particularly with the Global South. It also reflects Indonesia's growing influence in international trade and geopolitics.
BRICS Challenges:
- Diverse Interests: Differences in economic priorities, such as India's ties with the US and Russia-China’s geopolitical rivalry, complicate consensus-building.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Disputes like the China-India border issue and Russia’s sanctions limit BRICS' ability to present a unified stance.
- Economic Sanctions and Internal Challenges: Countries like Russia face Western sanctions, while domestic issues in Brazil and South Africa divert attention from regional collaboration.
Significance of BRICS’ Expansion:
The expansion of BRICS marks a pivotal shift in global power dynamics, with a focus on South-South cooperation and equitable global governance. Indonesia’s membership further solidifies the group’s influence in Southeast Asia and adds to its efforts to challenge the dominance of Western-led financial institutions.
- Local Currency Use: The group promotes the use of local currencies for trade to reduce reliance on the US dollar.
- Global South Advocacy: BRICS champions the cause of developing nations, ensuring that emerging economies have a voice in global governance.
Recent and Upcoming BRICS Summits:
- 16th BRICS Summit (2024): Held in Kazan, Russia, with a focus on strengthening local currencies and promoting non-dollar transactions.
- 17th BRICS Summit (2025): Scheduled for July 2025 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, under the theme "Global South," with an emphasis on payment gateways to facilitate intra-BRICS trade.
Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Trinidad and Tobago declared a state of emergency, in response to a surge in gang violence, which raised the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
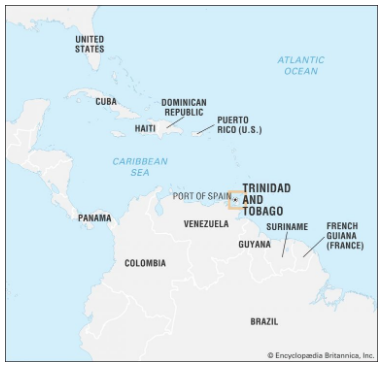
Trinidad and Tobago:
- Location: An island nation in the southern Caribbean, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Population: Approximately 1.5 million.
- Ethnic Composition: African (36.3%), Indian (35.4%), Mixed (22.8%), and others.
- Religions: Christianity (64%), Hinduism (18%), Islam (5%), and others.
- Independence: Gained from the UK on August 31, 1962, and became a republic in 1976.
- Member of: Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Geography:
- Total Land Area: 5,128 sq. km (Trinidad: 4,768 sq. km, Tobago: 300 sq. km).
- Climate: Tropical, with dry and rainy seasons.
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Exports: Major exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and petrochemicals.
- Culture: Known for Carnival, Calypso music, Soca, and the Steelpan (the only musical instrument invented in the 20th century).
- Infrastructure:
- Ports: Port of Spain, Point Lisas, Scarborough.
- Airports: Piarco International Airport (Trinidad) and A.N.R. Robinson International Airport (Tobago).
Engagement with India
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in 1997.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian diaspora constitutes about 42% of the population.
Past Emergency Declarations:
- 2014: State of emergency declared in response to gang violence.
- 2021: Emergency declared for Covid-19 restrictions.
- 2011: Limited state of emergency for drug-related crimes.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
India-Malaysia Cooperation in Critical Minerals and Rare Earth Elements

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
- On January 7, 2025, during the inaugural India-Malaysia Security Dialogue in New Delhi, both countries agreed to enhance cooperation in critical minerals and rare earth elements (REEs).
- The meeting was co-chaired by India's National Security Adviser, Ajit Doval, and Malaysia’s Director General of the National Security Council, Raja Dato Nushirwan Bin Zainal Abidin.
- The agreement follows the upgrade of bilateral relations to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership during Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim’s visit to India in August 2024.
- The dialogue also focused on other security aspects such as counter-terrorism, cyber security, and maritime security.
Importance of Critical Minerals and REEs:
-
- Critical Minerals: These are essential for a variety of industries like IT, energy, and defense. They are integral to manufacturing electric vehicle batteries, solar cells, and advanced electronics.
-
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs): Used in high-tech applications such as wind turbines, electric vehicle engines, and high-powered magnets. While their extraction is not rare, it is technically difficult due to their complex nature.
Strategic Relevance:
-
- Global Demand: The global demand for critical minerals is rising, and both countries see it as a strategic necessity to ensure a stable supply of these materials.
- Malaysia's Resources: Malaysia possesses significant deposits of non-rare radioactive earth ores, including essential REEs like Neodymium (Nd), Dysprosium (Dy), and Praseodymium (Pr). These elements are crucial in today’s technological innovations.
- India’s Dependence on Imports: India, which currently imports a substantial portion of its critical minerals, aims to diversify its supply chain by collaborating with Malaysia.
Sustainability and Ecological Accountability:
-
- Both countries recognize the environmental challenges of mining these critical resources. Malaysia aims to adopt responsible mining practices that minimize ecological harm.
- India seeks to ensure a supply chain that aligns with sustainable development goals, balancing economic needs with environmental responsibilities.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience:
-
- Diversification of Supply Chain: This partnership aims to reduce India’s dependency on a limited number of countries for critical minerals, enhancing resilience against global supply chain disruptions.
- Collaboration in Extraction and Processing: Both nations are exploring joint ventures in the exploration, extraction, and processing of critical minerals to boost their technological and economic standing globally.
Future Prospects:
-
- The institutionalization of this dialogue through annual meetings is expected to strengthen bilateral cooperation in the critical minerals sector.
- Increased cooperation is likely to enhance economic growth for both countries, aligning them strategically in the global minerals market as demand for these resources continues to soar.
Broader Security Cooperation:
-
- Beyond critical minerals, the India-Malaysia Security Dialogue explored enhanced collaboration in areas like counter-terrorism, cyber security, maritime security, and defense industries.
- This broadening of security cooperation complements the strategic minerals partnership, further solidifying the bilateral ties between the two nations.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
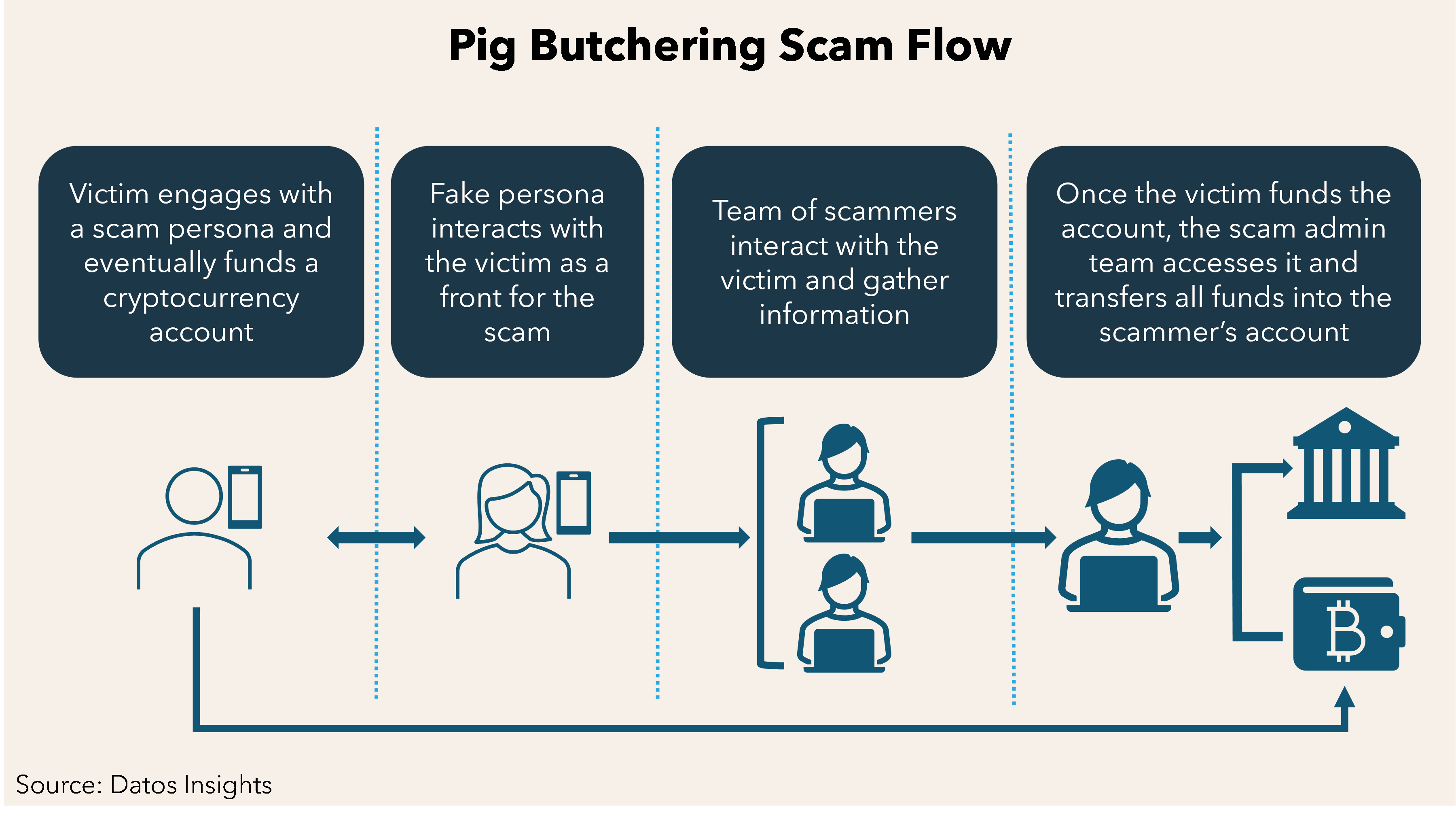
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
National Sports Awards 2024
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Sports Awards 2024 were recently announced by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports to celebrate excellence in Indian sports.
Key Highlights:
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award
- This is India's highest sporting honor, renamed in 2021 after hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- It’s awarded for exceptional performance in sports over a four-year period.
- 2024 Winners:
- Gukesh D (Chess)
- Harmanpreet Singh (Hockey)
- Praveen Kumar (Para-Athletics)
- Manu Bhaker (Shooting)
- The award includes a cash prize of Rs 25 lakh.
Arjuna Award
- Recognizes outstanding performance in sports over the previous four years and attributes like leadership, discipline, and sportsmanship.
- 2024 Winners: Various athletes across multiple disciplines received this honor.
Arjuna Award (Lifetime)
- Given to retired athletes who have not only excelled during their careers but also contributed to the promotion of sports post-retirement.
- 2024 Winners:
- Shri Sucha Singh (Athletics)
- Shri Murlikant Rajaram Petkar (Para-Swimming)
Dronacharya Award
- Given to coaches who have made a consistent and significant contribution by guiding sportspersons to excel at international events.
- The award includes a bronze statue of Dronacharya, a certificate, and a cash prize.
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy
- Awarded to the top-performing university in the Khelo India University Games.
- 2024 Winner: Chandigarh University.
Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar
- Recognizes individuals or organizations for their contribution to the promotion and development of sports.
- 2024 Winner: Physical Education Foundation of India.
These awards were selected by a committee led by Justice (Retd.) V. Ramasubramanian and include eminent sportspersons, journalists, and sports administrators. The winners will receive their awards from the President of India, marking a prestigious moment in Indian sports.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Donald Trump threatened to take back the Panama Canal, calling the transfer treaty “foolish”.
Why Trump Called the Panama Canal Transfer 'Foolish'?
- Transit Fees:
- Trump expressed frustration over high transit fees imposed by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP) on U.S. vessels.
- In 2023, due to droughts affecting Lakes Gatun and Alhajuela (which are crucial for canal operations), the ACP reduced crossing slots by 36%, leading to an increase in transit fees for ships.
- Chinese Presence:
- Trump is also concerned about the growing Chinese influence in the Panama Canal region.
- In 2017, Panama became the first Latin American country to sign a Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) agreement with China, increasing Chinese investments.
- Hutchison Ports PPC, a subsidiary of a Hong Kong-based company, operates ports near the canal, raising concerns over China's influence on logistical operations and potential surveillance capabilities.
The Torrijos-Carter Treaties and Canal Transfer:
- Panama Canal Treaty (1977):
- The treaty transferred control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by December 31, 1999.
- The U.S. would no longer control the canal, and Panama would assume full responsibility for its operation and defense.
- Permanent Neutrality Treaty (1977):
- Declared the canal to be neutral and open to vessels of all nations.
- U.S. Right to Defense: The U.S. retained the right to defend the neutrality of the canal and had priority passage in case of military emergencies.
Panama’s Response to Trump’s Criticisms:
- Defense of Transit Rates:
- President José Raúl Mulino rejected Trump’s claims, defending the transit fees as being in line with international standards and based on a transparent procedure.
- Sovereignty:
- Mulino emphasized Panama’s sovereignty over the canal, asserting that Panama’s control over the canal was non-negotiable. He categorically denied the presence of Chinese soldiers in the canal, stating that there would never be any.
China’s Response:
- China's Position:
- China's Foreign Ministry responded by emphasizing that the Panama Canal is a neutral passageway, a vital infrastructure for Panama and the global trade system.
- China affirmed its respect for Panama's sovereignty and denied any military presence in the canal area.
Implications and Future:
- Diplomatic Tensions:
- The issue of transit fees and foreign influence, particularly China's presence in the region, is likely to remain a point of diplomatic negotiation.
- Panama is expected to assert its sovereignty and seek international support to prevent any external interference in the canal’s operations.
- U.S. Influence:
- The U.S. might attempt to renegotiate terms related to the Panama Canal's operations, especially concerning transit fees and military rights, although Panama remains firm on maintaining control.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties:
- Significance:
- Panama Canal Treaty and Permanent Neutrality Treaty marked a major shift in U.S.-Latin America relations, ending U.S. control and restoring Panamanian sovereignty.
- The treaties also ensured the neutrality of the canal while maintaining U.S. military access in emergencies.
- Impact:
- The treaties were a symbol of Panama’s regained sovereignty and played a key role in stabilizing relations between the U.S. and Panama, as well as resolving tensions over control of the canal.
Open Data Kit (ODK) Toolkit

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has deployed the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform to enhance transparency in government spending and improve accountability in the delivery of government schemes.
- The toolkit is being used for designing, collecting, and managing data relevant to audits.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Enhance transparency in public spending.
- Improve accountability in government schemes and projects.
- Collect real-time beneficiary feedback to aid audit planning and identify areas needing additional review.
Key Features:
- End-to-end encryption: Ensures secure data management.
- Integration with CAG’s Operating System (OIOS): Facilitates seamless analysis and management of data.
- Multi-language support: Allows for surveys in multiple languages, making it more accessible to diverse beneficiaries.
- User-friendly interface: Simplifies the design and management of data collection processes for auditors.
Usage and Applications:
- Beneficiary surveys are a key tool for gathering data, helping CAG identify problem areas in government schemes.
- The ODK toolkit was recently deployed in audits of AIIMS institutions in Mangalagiri (Guntur) and Bibinagar (Hyderabad) to assess patient satisfaction and gather evidence for performance reviews.
Working Process:
- Surveys are designed on the ODK platform and deployed to beneficiaries.
- Data is collected in real-time and analyzed using the OIOS system to generate actionable insights for audits.
- Beneficiary feedback is used to evaluate scheme delivery and improve efficiency.
Significance:
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making in audits, ensuring that audits are more transparent and evidence-based.
- Improves the citizen-centric evaluation of government schemes by gathering direct feedback from beneficiaries.
- Enhances the performance review of key institutions like AIIMS, contributing to better service delivery.
- The introduction of the ODK toolkit is part of the CAG’s efforts to use digital tools for better governance and accountability in the public sector. This also aligns with the growing trend of using technology for governance and auditing.
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
Quad 20th Anniversary
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Quad Foreign Ministers reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific. Marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, originally formed to respond to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
Key Highlights:
- What is the Quad?
- A strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Founded on shared principles of democracy, human rights, rule of law, and countering China's influence.
- Origins:
- Quad traces its origins to the 2004 Tsunami relief efforts.
- Formed formally in 2007, but Australia withdrew in 2008 due to regional tensions. It rejoined in 2017 following strengthened US-Australia ties.
- Commitment to Regional Security:
- Focus on countering China’s assertive behavior in the Indo-Pacific.
- Ensuring maritime security, countering illegal fishing, promoting infrastructure, and advancing economic cooperation.
- Key Initiatives:
- IPMDA: Real-time monitoring of maritime activities.
- MAITRI: Capacity-building for maritime security.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate-level STEM education in member countries.
- Open RAN: Promoting secure 5G infrastructure.
- Cancer Moonshot: Focus on cervical cancer prevention.
- Military and Naval Cooperation:
- Malabar Exercises: Joint naval drills between India, Japan, the US, and Australia.
- ASEAN and Regional Cooperation:
- Emphasis on ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Support for the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Future Developments:
- India to host the next Quad Summit in 2025.
- Continued focus on sustainable regional development, scientific collaboration, and disaster relief efforts.
- Significance of the Quad for India:
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides a platform to counter China's assertive policies, especially in the South China Sea and the "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Maritime Security: Ensures freedom of navigation and counters illegal activities like piracy and illegal fishing in India’s maritime domain.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Strengthens cooperation on infrastructure projects and trade initiatives, such as the Blue Dot Network.
- Post-COVID, Quad may aid India in attracting manufacturing units shifting from China.
- Scientific and People-to-People Collaboration: Supports STEM education and enhances soft power diplomacy through academic and cultural exchanges.
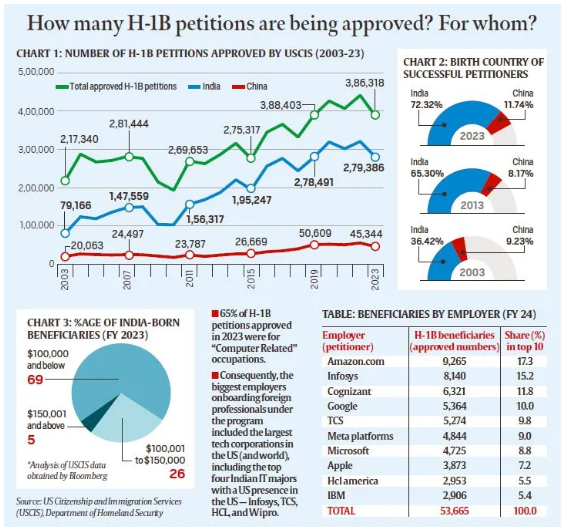
H-1B Visa
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
Pegasus Spyware

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
For the first time, a court in the US has held Israel’s NSO Group liable for its intrusive spyware Pegasus, which could set up a measure of accountability for the company that it has, for long, allegedly downplayed.
Overview:
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
- It has been used for surveillance, allegedly targeting journalists, activists, politicians, and government officials across the world, including India.
Recent Legal Developments:
- US Court Ruling (2024):
- A US court held NSO Group liable for using Pegasus to surveil 1,400 WhatsApp users, including 300 from India.
- NSO Group violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the California Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA).
- The ruling may revive debates on the accountability of spyware use and its implications on privacy.
Use of Pegasus in India:
- Targeted Individuals (2021):
- 300 Indian numbers allegedly targeted, including journalists, politicians, Union Ministers, and civil society members.
- High-profile targets included opposition leaders, constitutional authorities, and activists.
- Government Denial:
- The Indian government denied involvement, stating allegations lacked substance.
- In Parliament, IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw rejected claims, asserting India’s surveillance laws prevent unauthorized surveillance.
- NSO Group Response:
- NSO Group denied the allegations, calling them “false and misleading” and citing doubts about the sources.
Investigations and Legal Actions:
- Supreme Court Inquiry:
- The Supreme Court appointed a committee of technical experts in 2021 to investigate claims.
- August 2022 Report: Found no conclusive evidence of spyware use on examined devices but noted lack of cooperation from the government.
- State-Level Investigations:
- West Bengal: Set up a Commission of Inquiry into Pegasus surveillance, later halted by the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh: The issue became political, with allegations that the previous government used Pegasus to monitor opposition figures.
Pegasus Spyware Features:
- Capability: Can hack iOS and Android devices to collect data, record conversations, capture photos, and access app data.
- Exploitation Method: Uses zero-day vulnerabilities to exploit iOS and Android devices covertly.
- Invisibility: Operates without user knowledge, often only detected through signs like browser closings after phishing links are clicked.
Controversial Use of Pegasus:
- Global Use: Though intended for fighting terrorism and crime, Pegasus has been misused for spying on journalists, politicians, human rights activists, and opposition leaders.
- India Specifics:
- Pegasus Project: Targeted Indian citizens, including activists, journalists, and politicians.
- Amnesty International: Confirmed use of Pegasus to target Indian phones.
India's Legal Framework for Surveillance:
- Telecommunications Act (2023): Empowers the government to control telecom services during emergencies, but requires authorization for lawful interceptions.
- IT Act (2000): Allows the government to monitor, intercept, or decrypt information through computer resources under certain conditions.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act (2023): Aims to protect personal data, including provisions on surveillance, data breaches, and rights of individuals over their data.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns:
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Surveillance infringes on the right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Freedom of speech and expression (Article 19) may be curtailed, with surveillance being used to suppress dissent.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Surveillance often occurs without judicial or parliamentary oversight, leading to potential executive overreach.
- Inability to Seek Legal Remedies:
- Citizens targeted by surveillance cannot challenge it due to lack of awareness, undermining constitutional rights.
- Executive Overreach and Suppression of Free Expression:
- Pegasus revelations have raised concerns about surveillance targeting constitutional functionaries, suppressing free speech, and stifling open discourse.
India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completes two years of remarkable success, driving mutual growth and showcasing the complementarity of both economies.
Key Achievements:
- Bilateral Merchandise Trade Surge:
- Trade increased from USD 12.2 billion (2020-21) to USD 26 billion (2022-23).
- Trade moderated slightly in 2023-24 to USD 24 billion, but exports from India to Australia grew by 14%.
- From April-November 2024, bilateral trade reached USD 16.3 billion.
- Preferential Import Utilization:
- Export utilization: 79%
- Import utilization: 84%
- Sectoral Growth:
- Textiles, chemicals, and agriculture sectors have seen significant growth.
- New export products: Gold studded with diamonds, turbojets.
- India’s imports: Metalliferous ores, cotton, wood products that fuel Indian industries.
- Geopolitical Strengthening:
- Enhanced relations in forums like Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI).
Key Features of the Agreement:
- Tariff Reductions:
- Australian goods: 85% tariff-free access to India (rising to 90% by 2026).
- Indian goods: 96% tariff-free access to Australia (rising to 100% by 2026).
- Access to Key Markets:
- India: Access to Australia's fast-growing market.
- Australia: Access to India's labor-intensive sectors like gems, jewelry, textiles, leather, furniture, food, agriculture.
- Services and IT:
- 135 sub-sectors covered in services.
- India gains market access in 103 sub-sectors with Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status in 31.
- Fast-tracked approval of medicines and elimination of double taxation for India's IT sector.
- Job Creation & Skill Exchange:
- Expected creation of 1 million jobs in India.
- Opportunities for Indian yoga teachers, chefs, and 100,000 students with post-study work visas.
Future Prospects:
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): Builds on ECTA to advance bilateral trade, with 10 formal rounds and ongoing inter-sessional discussions.
- Trade Target: Aim to reach AUD 100 billion in trade by 2030.
- Global Economic Impact: Strengthening the partnership will contribute to a more resilient and dynamic global economy, with deeper economic integration between India and Australia.
PM CARES Fund Contributions and Utilization (2022-23)
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund) received Rs 912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23 as donations continued to pour in even after the Covid pandemic.
Key Highlights:
Contributions Received:
- Total contributions in 2022-23: Rs 912 crore.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 909.64 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 2.57 crore.
Interest Income:
- Total interest income for 2022-23: Rs 170.38 crore.
- From regular accounts: Rs 154 crore.
- From foreign contributions account: Rs 16.07 crore.
Refunds and Additional Inflows:
- Rs 225 crore in refunds, including:
- Rs 202 crore refund from procurement of 50,000 ventilators for government hospitals.
Disbursements:
- Total disbursed in 2022-23: Rs 439 crore:
- Rs 346 crore for PM CARES for Children.
- Rs 91.87 crore for procurement of 99,986 oxygen concentrators.
- Rs 1.51 crore for refunds.
- Rs 24,000 for legal charges, and Rs 278 for bank and SMS charges.
Cumulative Contributions (2019-23):
- Rs 13,605 crore received from 2019-20 to 2022-23.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 13,067 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 538 crore.
- Interest income over these years: Rs 565 crore.
About PM CARES Fund:
Formation and Purpose:
- Established: March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust under the Registration Act, 1908.
- Purpose: To address emergencies like COVID-19, natural disasters, and man-made calamities. It also supports healthcare infrastructure and essential facilities.
Governance and Structure:
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister (ex-officio).
- Trustees: Defence, Home, and Finance Ministers (ex-officio).
- Additional Trustees: Appointed by the PM, serving on a non-profit basis (e.g., Justice K T Thomas (retd.) and Kariya Munda).
Tax Exemptions:
- Donations are eligible for 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Donations qualify as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The fund is exempt under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), allowing it to receive foreign donations.
UN Approves New AU Force to Combat Al-Shabaab in Somalia
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- On January 19, 2024, the UN Security Council approved a new African Union (AU) force in Somalia to counter the Al-Shabaab terrorist group.
- The resolution was supported by 14 of 15 members, with the US abstaining due to concerns about funding.
- The new force will replace the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) after its mandate ends on December 31, 2024.
New Mission - AUSSOM:
- The new mission is named African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
- AUSSOM will continue supporting Somali forces in stabilizing the nation and combating terrorism.
- The mission's objective is to enhance security and stability in Somalia, addressing the challenges posed by Al-Shabaab and ISIL.
Mandate and Operations:
- AUSSOM allows for the deployment of up to 12,626 personnel, including 1,040 police officers, until June 2025.
- The force will focus on counterterrorism, maintaining security, and assisting the Somali government in stabilizing the country.
Financing:
- A hybrid funding approach will be used:
- 75% of the mission’s costs will be covered by the UN, and 25% will come from African Union and partner countries.
- The US raised concerns about the UN's disproportionate funding of the mission, which led to its abstention from voting.
Contributing Countries:
- Egypt has announced its participation in the new force.
- Burundi and Ethiopia will not be contributing troops to AUSSOM.
- Ethiopia has its own ongoing disputes with Somalia, particularly regarding its maritime deal with the breakaway Somaliland region.
Background on Somalia's Challenges:
- Somalia has faced decades of civil war, an insurgency by Al-Shabaab, and recurring climate disasters.
- The country is one of the poorest in the world, and its internal conflicts are exacerbated by clannism, which has fragmented its political and social structure.
Historical Context of Peace Missions in Somalia:
- Previous UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia (1992-1995) faced significant failures, notably the Battle of Mogadishu and the failure to prevent the 1993 massacre.
- The rise of Al-Shabaab in the mid-2000s has further escalated the conflict, and the mission of AUSSOM aims to address these continuing threats.
The Role of Clannism:
- Clannism has hindered the establishment of a unified government in Somalia, with clan rivalries leading to a lack of national cohesion.
- Clannism refers to the prevalence of clan-centric politics, where allegiance to clan and sub-clan interests often takes precedence over national cohesion. In Somalia, the major clans are Darod, Hawiye, Dir, and Rahanweyn.
Importance of AUSSOM:
- AUSSOM represents a strategic shift in the international approach to stabilizing Somalia, relying more on African-led initiatives for peace and security in the region.
Global Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN peacekeeping mission has been active globally, with over 1 million personnel deployed across 70+ operations.
- Success stories like Sierra Leone (1999-2005) and Liberia (2003-2018) demonstrate the potential impact of well-executed peace missions, but past failures like in Somalia (1992-1995) and Rwanda (1994) underline the challenges faced.
India’s Contribution:
- India has contributed significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, deploying over 253,000 personnel in 49 operations since 1948.
- India’s contributions to missions in Somalia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Sudan reflect its active role in global peacekeeping efforts.
China approves construction of World’s Largest Hydropower Dam on the Brahmaputra River

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
China approved the construction of the world's largest dam, stated to be the planet's biggest infra project, on the Brahmaputra river in Tibet close to the Indian border, raising concerns in India and Bangladesh.
Key highlights:
Overview of the Project:
- Location: Lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River (Tibetan name for Brahmaputra), where the river makes a U-turn in the Himalayan region before flowing into Arunachal Pradesh, India.
- Purpose:
- To support China’s carbon neutrality goals.
- To boost industrial growth and create jobs in Tibet.
- Expected to generate 300 billion kWh of electricity annually, over three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam in central China.
Significance:
- Scale: The dam is poised to be the world’s largest hydropower project, surpassing the Three Gorges Dam, and becoming the biggest infrastructure project globally, with an estimated cost of USD 137 billion.
- Engineering Challenges: The site is located in a seismic zone on the Tibetan plateau, prone to earthquakes, making construction and operational stability a major engineering challenge.
Concerns:
- Environmental Impact:
- Potential disruption to the local ecosystem and biodiversity.
- Risk of altering the river’s flow and course, which could impact agriculture and water resources downstream, particularly in India and Bangladesh.
- Geopolitical Risks:
- Water control: India and Bangladesh are concerned about China’s ability to control the water flow, with fears of China manipulating the flow to release excess water during conflicts, causing potential flooding in border areas.
- The project could also disrupt the hydrological cycle, affecting the region’s water availability, especially in Assam and Bangladesh.
Background:
- The Brahmaputra River is a trans-boundary river, flowing through China, India, and Bangladesh. Known by different names in these countries, it plays a vital role in the livelihoods of millions of people.
- China has already initiated hydropower generation on the upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo, with plans for additional projects upstream.
India-China Cooperation:
- China and India have an Expert Level Mechanism (ELM) in place since 2006 to manage trans-boundary river issues, under which China shares hydrological data with India, especially during the flood season.
- India is also constructing its own hydropower projects on the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh.
Potential Outcomes:
- Energy Generation: The dam could significantly contribute to China’s energy needs, providing a substantial amount of renewable energy.
- Regional Tensions: The dam’s construction may escalate tensions between China, India, and Bangladesh due to the control over water resources and environmental impact concerns.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
In mid-2024, India surpassed China as the largest importer of Russian oil. This milestone has been accompanied by the operationalization of a new maritime route, the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC), which connects Chennai in India to Vladivostok in Russia. The new sea route is significantly reducing both shipping times and costs, facilitating smoother commodity trade between the two countries, particularly crude oil shipments.
The Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
The EMC, covering a distance of about 5,600 nautical miles, has reduced the shipping time between India and Russia’s Far East by up to 16 days. The Chennai-Vladivostok route now takes just 24 days, compared to over 40 days using the traditional St. Petersburg-Mumbai route. This reduction in transit time makes it a highly efficient route for transporting goods such as crude oil, coal, LNG, fertilizers, and other commodities. Additionally, this new corridor supports India’s maritime sector and aligns with the country’s broader vision for maritime growth and regional strategic engagement.
Key Features of the EMC:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: The route cuts shipping time and distance, reducing costs associated with longer transit periods. For example, a ship traveling between Vladivostok and Chennai now takes only about 12 days at cruising speed, compared to the traditional route's 40+ days.
- Strategic Importance: Vladivostok is Russia’s largest Pacific port, and the corridor strengthens India's strategic presence in the region. This maritime route bypasses traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal, offering faster, more direct access to key markets.
- Diversification of Trade: Besides crude oil, the EMC facilitates the transportation of coal, LNG, fertilizers, and metals, diversifying India's trade portfolio with Russia. It also helps maintain supply chains for essential goods.
- Boosting India’s Maritime Sector: The corridor supports India’s Maritime Vision 2030, which aims to enhance the efficiency and reach of India's maritime trade, a sector responsible for over 70% of the country’s trade value.
Economic and Strategic Impact:
- The new Eastern Maritime Corridor is particularly significant for India’s energy needs. As the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, India imports over 85% of its crude oil demand. The growing imports of Russian crude, especially the Urals grade, are crucial for securing India’s energy future. Additionally, Russia’s competitive pricing on crude, coupled with the savings on shipping costs through the EMC, makes Russian oil even more attractive.
- Beyond the economic benefits, the EMC also supports India’s broader strategic goals, including strengthening ties with Russia, a key partner in defense, nuclear cooperation, and regional geopolitics. The closer maritime links also help counterbalance China's growing dominance in the Pacific region, aligning with India's Act Far East Policy and enhancing trade and diplomatic engagement with East Asia and Russia.
Other Key Maritime Corridors Relevant to India:
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC): A 7,200 km multimodal route linking the Indian Ocean with Russia, offering alternative trade routes to Europe and Central Asia.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A recent project announced at the G20 Summit, which connects India, the Middle East, and Europe via rail, road, and maritime links, fostering greater regional integration.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR): A 5,600 km Arctic route offering shorter transit times between the Barents and Kara Seas and the Bering Strait, gaining importance due to growing imports of Russian energy resources.
In conclusion, the Eastern Maritime Corridor is reshaping India-Russia trade dynamics, boosting economic ties and strategic cooperation between the two nations. By facilitating faster and cheaper transportation, the EMC is not only beneficial for trade in crude oil but also for a range of other commodities, positioning India as a key player in the evolving global trade network.
Schengen Zone Membership

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the European Union (EU) cleared Bulgaria and Romania for full membership in the Schengen Zone, effective January 1, 2025. This marks the end of a 13-year wait for these Eastern European nations, which joined the EU in 2007.
Key Highlights:
- Schengen Integration: Until now, Bulgaria and Romania were partially integrated into the Schengen Zone, with air and sea travel without border checks since March 2024. However, land border controls were still in place due to Austria's objections, mainly due to concerns over migration and border security.
- Austria's Shift: Austria had blocked full entry for years but finally lifted its veto on December 9, 2024, after a border protection package was agreed upon. This package includes joint border guard deployment at the Bulgarian-Turkish border and temporary land border controls for six months.
Schengen Zone Details:
- What is the Schengen Zone?
- Created by the Schengen Agreement (1985) and the Schengen Convention (1990), it is the world’s largest area without internal border controls, allowing free movement across most EU countries and some non-EU countries. It currently includes 29 countries (25 EU states and 4 non-EU countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland).
- Key Features:
- Free Movement: Over 425 million people can travel freely within the zone without border checks.
- Uniform Visa Policy: Short-term stays of up to 90 days are allowed for tourists and business travelers from outside the Schengen Area.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: The Schengen Information System (SIS) facilitates security and border management by sharing critical data between countries.
- Temporary Border Controls: Countries can temporarily reintroduce border controls for security reasons, after notifying other member states and the European Commission.
Bulgaria and Romania
- Bulgaria:
- Capital: Sofia
- Location: Southeastern Europe, bordered by the Black Sea, Romania, Turkey, Greece, North Macedonia, and Serbia.
- Political System: Parliamentary Republic
- Romania:
- Capital: Bucharest
- Location: Bounded by Ukraine, Moldova, Black Sea, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Hungary.
- Political System: Semi-Presidential Republic
Implications of Full Schengen Membership:
- Security and Unity: Romania and Bulgaria's full integration into the Schengen Zone is seen as a boost to both EU security and unity. It solidifies the EU's commitment to free movement while enhancing border security across Europe.
- Impact on Migration: With Bulgaria and Romania’s full membership, the EU’s border management system will be more integrated, helping to address ongoing migration challenges.
Exercise Agni Warrior

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Agni Warrior (XAW-2024), a joint military drill between the Indian Army and the Singapore Armed Forces (SAF), concluded successfully at the Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra. The exercise focused on enhancing mutual understanding and interoperability between the two nations’ artillery units.
Key Facts:
- Participating Nations: India and Singapore
- Location: Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra
- Participants:
- 182 personnel from the Singapore Artillery
- 114 personnel from the Indian Army's Regiment of Artillery
- Objective: To maximize mutual understanding of drills and procedures for joint operations under the UN Charter, particularly in firepower planning and execution, utilizing advanced artillery technologies.
- Historical Context: The exercise began in 2004 under a bilateral agreement between India and Singapore and has evolved over the years, now marking 20 years of cooperation.
Purpose and Highlights:
The exercise aimed to reinforce the long-standing defense relationship between India and Singapore, focusing on:
- Joint Firepower Planning and Execution: Both forces demonstrated the use of New Generation Artillery Equipment, enhancing their firepower coordination.
- Enhancing Interoperability: The exercise emphasized seamless coordination between the two armies to operate as a multinational force under the UN Charter, addressing global security challenges.
- Knowledge Sharing: Personnel from both armies exchanged expertise on advanced artillery tactics, fostering a deeper understanding of each other's military capabilities.
- Technological Integration: Both sides integrated cutting-edge technologies, allowing the exchange of best practices in the use of artillery systems.
Key Objectives of XAW-2024:
- Enhanced Interoperability: To ensure smooth coordination in joint operations, fostering the ability to respond to regional security threats.
- Firepower and Coordination Techniques: Sharing expertise on artillery planning, coordination, and execution.
- Advanced Equipment Use: Testing and demonstrating modern artillery systems in joint operations, ensuring both forces are prepared for contemporary warfare.
Structure and Execution:
The exercise was structured to include pre-exercise training, field operations, and a post-exercise evaluation:
- Pre-Exercise: Both armies engaged in interactive sessions to familiarize themselves with each other's artillery tactics and advanced systems.
- Field Operations: Simulated combat scenarios tested joint firepower execution, emphasizing real-time problem-solving and decision-making under pressure.
- Post-Exercise Review: A thorough analysis identified areas for improving joint operations and coordination.
Strategic Significance:
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Agni Warrior reinforces the defense partnership, facilitating joint operations that support regional security.
- Regional Stability: The exercise underscores the commitment of both nations to peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Capacity Building: Both Indian and Singaporean forces gained exposure to sophisticated firepower planning and gained operational readiness for future deployments.
India-Australia CCEA

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The 3-day stocktake meeting took place in New Delhi, marking a significant step in strengthening the India-Australia trade and strategic partnership.
Key Highlights:
- Key Discussion Areas:
- Trade in goods and services.
- Mobility, agri-tech cooperation, and market access.
- Focus on ensuring the CECA delivers balanced benefits for both nations.
- Food security concerns and market access modalities aligned with India’s goals.
- Background on Negotiations:
- The discussions in New Delhi were a continuation of the 10th round of negotiations held in Sydney (August 2024).
- Both sides aimed to outline a path forward for the early conclusion of the CECA.
- Importance of CECA:
- CECA is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) aimed at eliminating tariffs and liberalizing services sectors to enhance business opportunities and cooperation.
- It addresses five key areas: Goods, Services, Digital trade, Government procurement & **Rules of Origin/Product Specific Rules
- New areas under discussion include: Competition policy, MSMEs, Gender, Innovation, Agri-tech, Critical minerals & Sports
- Historical Context:
- CECA negotiations began in May 2011, were suspended in 2016, and resumed in September 2021.
- The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) was signed in 2022, serving as a foundational agreement and a precursor to CECA.
- Trade Statistics (2023-24):
- India's imports from Australia: $16.2 billion.
- India's exports to Australia: $8 billion.
- Trade has grown significantly, with India being Australia’s 5th-largest trading partner.
- Regional Cooperation Initiatives:
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
- Trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) with Japan.
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- India's CECA with Other Countries:
- India has similar CECA agreements with several nations, including: Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand & New Zealand
- Future Prospects:
- The stocktake discussions have paved the way for further cooperation in areas such as agricultural innovation, market access, and supply chain resilience.
- Both nations are optimistic about the early conclusion of the CECA and the broader economic partnership.
This recent stocktake visit represents a significant step in the ongoing efforts to solidify trade ties and deepen economic cooperation between India and Australia under the framework of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement.
Desert Knight Air Combat Exercise

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
India, France and UAE recently kicked off a major air combat exercise called “Desert Knight” over the Arabian Sea, strengthening trilateral defence cooperation and enhancing military interoperability amid the ongoing geopolitical churn.
Key Highlights:
- What It Is: A trilateral air combat exercise aimed at improving military interoperability and enhancing combat readiness among the participating nations.
- Nations Involved: India, France, and the UAE.
- Location: Conducted over the Arabian Sea, approximately 350-400 km southwest of Karachi.
- Aim of the Exercise:
- To strengthen trilateral defence cooperation among the three nations.
- To enhance combat skills and military interoperability of the air forces involved.
- Details of the Exercise:
- Duration: The exercise lasts for three days.
- The exercise involves large force engagement and intensive combat maneuvers in a realistic operational environment.
- Aircraft Involved:
- India: Deployed Sukhoi-30MKIs, Jaguars, IL-78 mid-air refuellers, and AEW&C (Airborne Early Warning and Control) aircraft from bases like Jamnagar.
- France: Deployed Rafale jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
- UAE: Deployed F-16 jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
Strategic Significance:
- The exercise is part of India’s efforts to build military interoperability with nations in the Persian Gulf region and strengthen defence ties with France and the UAE.
- Enhances combat readiness and strengthens cooperation against both traditional and non-traditional threats.
- Reflects the geopolitical shift and growing military cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, especially in the context of China’s expansionist activities.
- Trilateral Framework: India, France, and the UAE launched a trilateral framework in 2022, focusing on areas like defence, technology, energy, and environment.
- Previous Exercises: In addition to Desert Knight, the countries also conducted their first trilateral maritime exercise in June 2023 to enhance cooperation in maritime security.
Broader Defence Relations:
- India-France: Long-standing strategic partnership with regular joint exercises like Shakti (army), Varuna (navy), and Garuda (air force).
- India-UAE: The defence relationship has grown significantly in recent years, with regular professional exchanges, combat exercises, and staff talks. India participates in the Desert Flag exercise at Al Dhafra airbase annually.
Switzerland Suspends MFN Clause in Tax Treaty with India

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
Switzerland scraps MFN status to India, dividend income to face higher tax
Key Highlights:
- Reason for Suspension:
- The suspension follows a 2023 Supreme Court ruling in India, which clarified that the MFN clause in tax treaties is not automatically triggered when a country joins the OECD if the tax treaty with that country was signed before its OECD membership.
- The Court ruled that the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) cannot be enforced unless it is notified under the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
- Details of the Suspension:
- Starting January 1, 2025, Switzerland will suspend the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) clause in its DTAA with India.
- The MFN clause was part of the India-Switzerland DTAA signed in 1994.
Impact of the Suspension:
- Higher Tax Liabilities for Indian Companies: Withholding tax on dividends from Switzerland will increase from 5% to 10% for Indian companies.
- Effects on Swiss Investments in India: Swiss companies will continue to face a 10% withholding tax on dividends from India, as per the India-Switzerland DTAA.
- Potential Re-evaluation of MFN Clauses by Other Countries: Other countries may reconsider how the MFN clause is applied in their tax treaties with India, following this development.
- No Change for Other Benefits: Other DTAA benefits and investments related to the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) will remain unaffected.
Most Favoured Nation (MFN) Clause Overview:
- Definition: The MFN principle ensures that favorable trading terms given by one WTO member country to another are extended to all other WTO members, promoting non-discrimination.
- Purpose: To ensure equal treatment among trading nations by preventing discrimination, and to promote fair trade and equitable market access.
- Key Features:
- Equal treatment in tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers.
- Members must extend the best terms to all other WTO members.
- Origin: The MFN principle was established after World War II as a cornerstone of the multilateral trading system under the WTO.
- Exceptions:
- Bilateral or regional trade agreements.
- Special access granted to developing countries.
- Non-WTO members (e.g., Iran, North Korea) are not bound by MFN rules.
- Removal of MFN:
- There is no formal procedure under the WTO to suspend MFN status.
- Countries are not obligated to notify the WTO when suspending or removing MFN treatment.
Recent Development:
- From January 1, 2025, Indian companies will face higher withholding tax (10%) on income sourced from Switzerland, as a result of the MFN clause suspension.
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024 was passed in the Lok Sabha on December 20, 2024, aiming to enhance the functioning and autonomy of Indian Railways.
Key Provisions:
- Repeal of the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905: The Bill repeals the 1905 Act and incorporates its provisions into the Railways Act, 1989, simplifying the legal framework by reducing the need to refer to two separate laws.
- Statutory Backing for Railway Board: The Bill provides statutory backing to the Railway Board, which previously lacked such a legal mandate. It grants the Union government the authority to determine the number of members, their qualifications, terms, and conditions of service.
- Decentralization of Power: The Bill aims to decentralize decision-making, granting greater autonomy to regional railway zones. This shift will allow more independence in budgeting, infrastructure projects, and recruitment, addressing long-standing calls for improved regional empowerment.
- Independent Regulator: The Bill proposes the creation of an independent regulator for overseeing tariffs, safety, and private sector participation. This idea has been supported by previous expert committees to encourage greater competition and transparency in the sector.
- Fast-Tracking Infrastructure and Services: The Bill will streamline approvals for new train services and infrastructure projects, helping meet demands from underserved regions, particularly in states like Bihar.
Objectives:
- Modernization of the Legal Framework: By incorporating the provisions of the 1905 Act into the 1989 Act, the Bill aims to simplify and modernize the legal architecture governing the railways.
- Empowerment of Railway Zones: Autonomy for railway zones is seen as a key step towards improving efficiency and accountability in operations.
- Private Sector Participation: The establishment of an independent regulator is expected to promote private participation in the railway sector, aligning with international standards.
Historical Context:
- The Indian Railways Act, 1890 established the foundations for Indian Railways as a government entity, which was further refined with the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905.
- This Bill aligns with recommendations from previous committees, including the Sreedharan Committee (2014) and the Committee on Restructuring Railways (2015), which have called for greater decentralization and autonomy for railway zones, as well as an independent regulatory body.
Challenges and Proposed Reforms:
- Financial Sustainability: The railways face challenges such as high operating costs, particularly from salaries and pensions, and losses in the passenger segment. Suggestions to improve finances include rationalizing passenger fares, enhancing freight revenue, and attracting private investment in infrastructure.
- Efficient Freight Operations: The Bill also addresses concerns about network congestion, especially for freight operations, and aims to increase the competitiveness of freight transport by improving infrastructure and reducing cross-subsidies from passenger fares.
Recommendations of various Committees on reforming the Railways
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Reforms in Merchant Shipping

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The Government is preparing to introduce several significant bills aimed at driving much-needed reforms in the shipping industry. Key among them are the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 and the Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024, both of which promise to bring transformative changes to boost the sector.
Context and Need for Reforms:
- Outdated Framework: The Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, and the Coasting Vessels Act, 1838, fail to address the current needs of the shipping sector, particularly offshore vessels.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate regulation of offshore vessels, maritime training institutions, and welfare provisions for seafarers on foreign-flagged ships.
- Global Alignment: Need to align with international maritime conventions and modernize administration for competitiveness and better governance.
- Investment and Growth: Outdated laws hinder foreign investment and ease of doing business, necessitating a regulatory overhaul.
Key Features of the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Ease of Vessel Registration:
- Reduces ownership threshold for Indian entities from 100% to 51%, enabling NRIs, OCIs, and foreign entities to invest.
- Facilitates registration of vessels chartered by Indian entities under the "bareboat charter-cum-demise" system, promoting capital-deficient entrepreneurs.
- Temporary registration provisions for vessels destined for demolition, boosting India's ship recycling industry.
- Expansion of Vessel Scope:
- Broadens the definition of "vessel" to include all types of mechanized and non-mechanized crafts, such as submersibles, hydrofoils, and Mobile Offshore Units (MOUs).
- Ensures comprehensive regulatory oversight, particularly in the offshore sector, enhancing transparency and safety.
- Coastal Security:
- Strengthens coastal security by empowering authorities to issue instructions to all types of vessels, addressing vulnerabilities highlighted by incidents like the 26/11 Mumbai attacks.
- Marine Pollution Measures:
- Incorporates global standards like the MARPOL convention to address marine pollution.
- Introduces measures such as reducing sulphur content in marine fuel and banning single-use plastics on Indian ships.
- Launch of the ‘Swachh Sagar’ portal to ensure proper disposal of ship-generated waste.
- Seafarer Welfare:
- Expands welfare provisions to include Indian seafarers working on foreign-flagged ships, offering protections under the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC).
- Ensures better working conditions and safety standards for a growing workforce of Indian seafarers abroad.
- Maritime Training Regulations:
- Establishes a legal framework to regulate maritime training institutions, addressing the rise of unauthorized institutes post-liberalization.
- Ensures standardized, high-quality education and eliminates fraudulent practices.
Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Focus on Commercial Utilization of Coastal Waters:
- Distinguishes between the technical regulation of ships and the commercial utilization of Indian coastal waters.
- Aims to streamline licensing, operations, and coastal planning, enhancing the integration of inland and coastal shipping.
- Alignment with ‘Sagarmala’ Program: Supports the promotion of coastal shipping through better infrastructure and connectivity, in line with the government's ‘Sagarmala’ initiative, which boosts port connectivity and coastal trade.
International Conventions India Has Ratified:
- MARPOL: Focuses on preventing ship-based pollution.
- Maritime Labour Convention (MLC): Protects seafarers' rights and ensures fair working conditions.
- Bunker Convention: Addresses liability for oil pollution damage.
- Wreck Removal Convention: Mandates safe removal of shipwrecks.
- Civil Liability Convention: Establishes liability for oil pollution incidents.
Significance of the Reforms:
- Modernized Framework: Aligns India’s maritime laws with global standards for enhanced competitiveness.
- Economic Growth: Encourages foreign investment and entry into the shipping sector by removing regulatory barriers.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focus on combating marine pollution and ensuring sustainable shipping practices.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Strengthens coastal security and ensures stringent safety regulations for vessels.
- Seafarers’ Welfare: Extends benefits and protections to Indian seafarers working globally, ensuring better working conditions.
- Maritime Education: Provides a robust regulatory framework to ensure high-quality, standardized maritime training.
Development Initiatives for North East Region (NER)

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced as a new Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding in the Union Budget 2022-23 with initial outlay of Rs.1500 crore.
PM-DevINE Scheme:
- Launched in 2022 as a Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding.
- Initial outlay: Rs. 1500 crore in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Total outlay: Rs. 6600 crore for the period from FY 2022-23 to FY 2025-2026, approved by the Union Cabinet on 12 October 2022.
- Objectives:
- Fund infrastructure projects in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti.
- Support social development projects tailored to the felt needs of the NER.
- Enable livelihood opportunities for youth and women.
- Address development gaps in various sectors.
- 35 projects worth Rs. 4857.11 crore have been sanctioned under the scheme up to 30 November 2024, including 7 projects from the Union Budget 2022-23.
Industrialization Initiatives:
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS):
- Launched on 1 April 2017, ended on 31 March 2022.
- Aimed at promoting industrialization in the NER.
- UNNATI Scheme:
- Launched on 9 March 2024 for enhancing regional infrastructure and promoting industrial growth.
- Provides specific incentives to industries, including:
- Capital Investment Incentive.
- Capital Interest Subvention.
- Manufacturing & Services Linked Incentive.
Budgetary Allocation for NER Development:
- Non-exempt Union Ministries/Departments are mandated to allocate at least 10% of their annual Gross Budgetary Allocation towards NER development.
- Between 2019-20 and 2023-24, these Ministries/Departments have incurred Rs. 3,53,412 crore towards the development of NER.
Role of State Governments and Central Support:The Government of India supplements state efforts with various schemes to promote industrialization and infrastructure development in the NER.
The PM-DevINE scheme, along with initiatives like UNNATI and the allocation of substantial funds by the central government, aims to accelerate the holistic development of NER. These efforts focus on infrastructure, social development, and industrialization, with specific emphasis on youth and women empowerment, ensuring long-term growth and prosperity for the region.
China Plus OneStrategy

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India had ‘limited success’ in capturing ‘China Plus One’ opportunity.
Limited Success in ‘China Plus One’ Strategy:
- India has had limited success in attracting multinational companies looking to diversify their supply chains under the ‘China Plus One’ strategy, aimed at reducing dependence on China.
- Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia have been more successful in benefiting from this shift due to factors like lower labor costs, simplified tax laws, and proactive Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Geopolitical Context - US-China Trade Conflict:
- The fresh US-China trade conflict involves tit-for-tat restrictions, with the US imposing export controls on Chinese high-tech goods and China retaliating by banning key materials.
- India's Position: As a "connecting economy" not directly aligned with the US or China, India stands to benefit from trade diversions arising from this conflict.
Opportunities for India Amid Trade Diversion:
- NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam highlighted opportunities arising from trade diversion, particularly due to US trade policies under President-elect Donald Trump, which could potentially create an economic boom for India.
- India has opportunities to capture a larger share of the global trade, especially in sectors where it currently holds a small market share (less than 1% of world trade in many areas).
Trade Policy Challenges:
- Steel Import Duty Proposal: NITI Aayog Vice Chairperson cautioned against imposing high duties on steel imports, arguing that it could reduce India’s competitiveness and lead to negative consequences for domestic industries reliant on steel.
- The global steel market has been affected by oversupply from China, with India’s iron and steel exports experiencing a sharp decline in Q1 FY25 due to weak domestic demand.
Impact of US Tariffs:
- A general 10% tariff on all imports by the US would not have a major negative impact on India.
- However, a 60% tariff on China could open significant opportunities for India, especially in sectors where it competes directly with China. There might be short-term shocks but long-term benefits.
Ongoing Trade Fragmentation:
- The report noted that trade fragmentation is driven by strict export controls on Chinese goods, implemented by the US to curb China’s growth, particularly in high-tech sectors.
Sectoral Competitiveness:
- While China remains India's key competitor across most export sectors, countries like Brazil, Indonesia, and South Africa generally lag behind India.
- Malaysia and Thailand outperform India in select sectors such as electrical machinery.
Challenges in the EU Market - Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- Iron and steel industry facehigh exposure under the CBAM for EU exports, with tariffs potentially rising by 20-35% due to carbon emissions-related regulations.
- Indian firms could experience higher compliance costs due to the requirement for detailed emissions reporting, impacting competitiveness in the European market.
PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, launched the PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31 dedicated to Indian Sign Language (ISL) on December 6, 2024, in New Delhi.
Channel Purpose and Vision:
- Objective: To bridge the communication gap between the hearing-impaired and hearing populations by promoting ISL.
- Significance: Channel 31 aims to unlock talent and ensure equal opportunities for all, making society more inclusive and progressive.
- ISL's Role: Pradhan emphasized the importance of alternative communication methods like ISL, which ensures that individuals with hearing impairments have equal access to education, employment, and societal participation.
Government's Focus on Inclusivity:
- Legal Framework: Pradhan highlighted the expansion of recognized disabilities from 7 to 21, making the legal framework more comprehensive.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The policy focuses on inclusive education, with particular attention to Children with Special Needs (CwSN). The NEP promotes the standardization of ISL and its inclusion in educational curricula.
- Employment and Cultural Expression: ISL is not only essential for communication but also contributes to cultural expressions like dance and drama. Pradhan emphasized that learning ISL would open employment opportunities and allow individuals to express themselves fully.
Importance of Channel 31:
- The launch of Channel 31 aligns with India’s commitment to ensuring equal rights and access to education, as enshrined in the Constitution.
- Pradhan urged for widespread adoption of ISL, ensuring that more people learn the language to better support the hearing-impaired community.
PM e-Vidya Initiative:
- Launch Date: PM e-Vidya was launched as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan on May 17, 2020, to bridge the digital divide and ensure inclusive education.
- Key Components:
- DIKSHA: A national platform providing e-content for all grades.
- DTH TV Channels: Initially started with 12 channels, now expanded to 200, offering supplementary education in multiple languages.
- SWAYAM: A platform for online courses and MOOCs for both school and higher education.
- Community Radio & Podcasts: These platforms are used for wider educational outreach, especially in rural and remote areas.
- e-Content for Teachers: Interactive videos and resources aimed at enhancing teacher education.
Channel Content:
- Channel 31 will provide 24x7 educational content for children with hearing impairments, teachers, and other stakeholders.
- The content will include school curricula, career guidance, skill training, mental health support, and promotion of ISL as a subject.
- The content will be available on YouTube, increasing its reach and accessibility.
India and Slovenia Announce Five-Year Collaboration Plan
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
India and Slovenia have announced a five-year scientific collaboration plan (2024-2029) to deepen ties in research and technology. The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) was finalized during a meeting between Dr. Jitendra Singh (Indian Minister for Science and Technology) and Dr. Igor Papi? (Slovenian Minister for Higher Education, Science, and Innovation) on December 5, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Joint Research Focus: The collaboration will focus on hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, AI, renewable energy, and smart cities.
- Over 20 Successful Projects: More than 20 joint initiatives in sectors like health, AI, and energy have already been implemented.
- Future Areas of Collaboration: New research projects will be launched, further strengthening academic exchanges and scientific networks between the countries.
- Hydrogen Technologies: Both ministers emphasized hydrogen's role in global energy sustainability, marking it as a critical area for future research.
- Historical Partnership: This builds on a partnership dating back to a 1995 agreement, with initiatives like the Joint Working Group on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
What is the Programme of Cooperation (PoC)?
- The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) is a formal agreement between two countries designed to enhance collaboration in specific sectors, such as science, technology, and innovation.
- In the case of India and Slovenia, the PoC for the period 2024–2029 aims to promote joint research efforts, academic exchanges, and partnerships in emerging fields like hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, and other transformative areas.
- The PoC serves as a structured framework for long-term cooperation, enabling both nations to develop networks among scientists and researchers while addressing global challenges through collaborative innovation.
Donald Trump's Threat on BRICS and US Dollar

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
- US President-elect Donald Trump threatens BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) with 100% import tariffs if they create a new currency or support an alternative to the US dollar as the global reserve currency.
- Trump emphasizes that attempts to undermine the US dollar’s dominance will face economic retaliation, asserting the US economy won’t tolerate such moves.
Background
- Weaponization of the Dollar: The US has increasingly used its financial influence to impose sanctions (e.g., Russia, Iran) and cut off countries from systems like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
- Concerns: Countries are concerned about their vulnerability to US monetary policies, which can have global impacts (e.g., rising US interest rates causing economic instability in other countries).
Efforts to Reduce Dependence on the US Dollar
- BRICS Countries’ Initiatives:
- Russian President Putin criticizes the weaponization of the dollar.
- Brazil's President Lula advocates for a new BRICS currency to increase payment options and reduce vulnerabilities.
- India's Steps:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows invoicing and payments in Indian rupees for international trade (since 2022), particularly with Russia.
- Prime Minister Modi supports increasing financial integration and cross-border trade in local currencies within BRICS.
- External Affairs Minister Jaishankar emphasizes the importance of mutual trade settlements in national currencies.
- China-Russia Trade: Over 90% of trade between Russia and China is settled in rubles and yuan due to their more balanced trade relations.
Internationalization of the Indian Rupee
- RBI's Role:
- In July 2022, RBI allowed export/import settlements in rupees, starting with Russia in December 2022.
- More than 19 countries, including the UK and UAE, have agreed to settle trade in rupees.
- Challenges:
- The Indian rupee currently accounts for only 1.6% of global forex turnover.
- India’s trade imbalance with Russia limits the effective use of rupee reserves.
- Indian banks are cautious due to the risk of US sanctions.
Global Trends in Currency Diversification
- Multipolarity in Finance: Emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil are advocating for a more decentralized financial system, moving away from US dominance.
- Declining Dollar Share: The US dollar’s share of global reserves is gradually decreasing, with non-traditional currencies like the Chinese yuan gaining ground.
Risks of Moving Away from the US Dollar
- Chinese Dominance: Concerns about increasing Chinese economic influence, especially within BRICS, as China pushes for more use of the yuan in trade.
- Liquidity and Volatility Issues: Alternatives to the dollar may face challenges like lower liquidity and increased exchange rate volatility.
- Implementation Challenges: Countries, especially those with trade imbalances, find it difficult to adopt local currencies for international trade.
Potential Impact of 100% US Tariff on BRICS Imports
- Global Trade Dynamics: A blanket tariff would likely encourage deeper intra-BRICS trade and accelerate the move towards de-dollarization.
- Impact on the US: Higher import costs for American consumers and potential trade diversification to third countries could hurt the US economy without revitalizing domestic manufacturing.
- Retaliation: BRICS countries might retaliate with tariffs on US goods, escalating trade tensions.
India’s Strategic Approach
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should clarify to the US that diversifying trade mechanisms is not anti-American but seeks financial stability and multipolarity.
- Leadership Role in BRICS: India should support financial reforms within BRICS that align with its interests while maintaining strong ties with the US.
- Promotion of Digital Currency: India should accelerate its Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and strengthen international platforms like UPI to enhance its global financial presence.
International Debt Report 2024
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently released, World Bank’s "International Debt Report 2024" highlights a worsening debt crisis for developing nations, with 2023 marking the highest debt servicing levels in two decades, driven by rising interest rates and economic challenges.
Key Highlights:
Rising Debt Levels:
- Total external debt of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) reached $8.8 trillion by the end of 2023, an 8% increase since 2020.
- For IDA-eligible countries (those receiving concessional loans from the World Bank), external debt rose by 18%, reaching $1.1 trillion.
Debt Servicing Costs:
- Developing nations paid a record $1.4 trillion in debt servicing costs (principal and interest) in 2023.
- Interest payments surged by 33%, totaling $406 billion, putting immense pressure on national budgets, especially in critical sectors like health, education, and environmental sustainability.
Interest Rate Increases:
- Interest rates on loans from official creditors doubled to 4% in 2023.
- Rates from private creditors rose to 6%, the highest in 15 years, exacerbating the financial burden on developing countries.
Impact on IDA-Eligible Countries:
- IDA countries faced severe financial strain, paying $96.2 billion in debt servicing, including $34.6 billion in record-high interest costs (four times higher than a decade ago).
- On average, 6% of their export earnings were allocated to debt payments, with some countries dedicating up to 38%.
Role of Creditors:
- Private creditors reduced lending, leading to more debt-servicing payments than new loans.
- In contrast, multilateral lenders like the World Bank provided additional support, with the World Bank contributing $28.1 billion.
- Multilateral institutions have emerged as crucial support systems, becoming "lenders of last resort" for poor economies.
Debt Data Transparency:
- Efforts to improve debt transparency led to nearly 70% of IDA-eligible economies publishing accessible public-debt data in 2023, a 20-point increase since 2020.
- Accurate debt data can reduce corruption and promote sustainable investment.
Global Financial Reforms:
- There is a growing call for global financial reforms to address the systemic challenges of developing nations facing rising debt burdens.
- Proposed measures include increased concessional financing, improved restructuring mechanisms, and the establishment of a Global Debt Authority for better debt management.
Impact on Climate and Development Goals:
- Debt servicing has become a larger financial burden than climate initiatives in many countries, with developing nations spending more on debt servicing than climate goals (2.4% of GDP vs. 2.1% for climate investments).
- To meet climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, climate investments would need to rise to 6.9% of GDP by 2030.
Debt Relief Initiatives:
- Programs like the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative and the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) provide debt relief to the world’s poorest nations, helping them meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- For instance, Somalia saved $4.5 billion in debt service after completing the HIPC program in December 2023.
Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable (GSDR):
- The GSDR brings together debtor nations and creditors (both official and private) to improve debt sustainability and address restructuring challenges.
- Co-chaired by the IMF, World Bank, and G20, the forum aims to find coordinated solutions for sovereign debt issues.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
At an event celebrating the National Sports Day, The Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour& Employment launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Empower retired athletes through career development.
- Provide tailored education, internships, and skill enhancement.
- Address the human resource gap in the sports sector.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Retired athletes aged 20-50 years.
- Winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- National/state-level medalists or participants in recognized competitions (e.g., National Sports Federations, Indian Olympic Association).
- Courses Offered (16 Courses):
-
- Strength & Conditioning Trainer
- Sports Nutritionist
- Sports Event Management
- Corporate Wellness Trainer
- Sports Masseur
- Sports Entrepreneurship
- Store Manager
- Fitness Centre Manager
- Physical Education Trainer
- Fitness Trainer
- Yoga Trainer
- Venue Supervisor
- Self-Defence Trainer
- Community Sports Trainer
- Camping & Trekking Guide
- Facility Caretaker
- Program Structure:
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12 and above
- Class 11 and below
- Hybrid learning mode:
- Self-paced learning via a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training and internships.
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Internship and Placement:
- Internships offered in sports organizations, competitions, training camps, and leagues.
- Post-course placement assistance and entrepreneurial guidance.
- Implementing Agency:Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) for the pilot phase.
- Importance:
- Provides sustainable career pathways for retired athletes.
- Utilizes the experience and skills of retired athletes to benefit future generations of athletes.
- Contributes to the growth of sports and nation-building.
- National Sports Day (29th August):
- Celebrated in honor of Major Dhyan Chand's birth anniversary.
- Promotes sports and physical fitness in India.
- Awards like Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna presented to honor excellence in sports.
International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities (IDPD), observed annually on December 3, celebrates the resilience, contributions, and leadership of persons with disabilities (PwDs) worldwide.
- Theme: “Amplifying the leadership of persons with disabilities for an inclusive and sustainable future”
History
- Proclamation: Established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1992 to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): Adopted in 2006, further advanced the rights and well-being of PwDs and supports the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Initiatives
Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities
- In order to give focused attention to policy issues and meaningful thrust to the activities aimed at the welfare and empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), a separate Department of Disability Affairs was carved out of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment on May 12, 2012.
- The Department was renamed the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities on December 8, 2014.
- The Department acts as a nodal agency for matters pertaining to disability and persons with disabilities, including effecting closer coordination among different stakeholders: related Central Ministries, State/UT Governments, NGOs, etc., in matters pertaining to disability.
Accessible India Campaign
- The Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan), launched on December 3, 2015 aims to achieve universal accessibility for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) across India.
- The key focus areas include improving Built Environment Accessibility in public spaces, enhancing Transportation Accessibility for independent mobility, creating an accessible Information and Communication ecosystem, and expanding Sign Language Access through interpreter training and better media support.
Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS)
- DDRS is a central sector scheme to provide grant-in-aid to non-governmental organizations (NGOs) for projects relating to the rehabilitation of persons with disabilities aimed at enabling persons with disabilities to reach and maintain their optimal, physical, sensory, intellectual, psychiatric, or socio-functional levels.
District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC)
- The District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC) aims to address the needs of persons with disabilities through a multifaceted approach.
- Its objectives include early identification and intervention, raising awareness, and assessing the need for assistive devices along with their provision and fitment, arrangement of loans for self-employment and more. Additionally, it acts as an outreach center for services provided by National Institutes and works to promote a barrier-free environment for individuals with disabilities.
Assistance to Persons with Disabilities for Purchase/Fitting of Aids/ Appliances (ADIP) Scheme.
- The main objective of the Scheme is to provide grants-in-aid to the various implementing agencies (National Institutes/Composite Regional Centers/Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India.
Schemes For Implementation Of Rights of Persons With Disabilities Act 2016 (SIPDA)
- The Scheme for Implementation of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (SIPDA) is a comprehensive "Central Sector Scheme" that encompasses 10 sub-schemes following its revision during the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) meeting on 11th August 2021.
- This revised scheme, approved by the Hon'ble Finance Minister, is designed to operate from 2021–22 to 2025–26.
Divya Kala Mela
- The Divya Kala Mela is a national-level fair dedicated to Divyangjan and represents a significant milestone in India’s journey toward inclusivity and empowerment of the Divyangjan, or differently-abled individuals.
PM-DAKSH
- PM-DAKSH (Pradhan Mantri DakshtaAurKushaltaSampannHitgrahi) Yojana is a one-stop destination for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), skill training organizations, and employers across India to be a part of the National Action Plan for Skill Development of Persons with Disabilities implemented by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD). Under this portal, there are two modules:
- Divyangjan Kaushal Vikas: Skill training is conducted for PwDs through the portal across the country.
- Divyangjan Rozgar Setu: The platform aims to act as a bridge between PwDs and employers having jobs for PwDs. The platform provides geo-tagged based information on employment/earning opportunities within private companies as well as PwDs across India.
Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The controversy surrounding the Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has intensified following claims that the mosque, built during the Mughal Emperor Babur's reign (1526–1530), was constructed over a Hindu temple, the Hari Har Mandir. This claim has led to legal battles and violent clashes, making it part of a broader series of disputes involving mosques built during the Mughal era, such as the Gyanvapi mosque in Varanasi and the Eidgah Masjid in Mathura.
Background and Legal Context:
The dispute began when a petition was filed in Sambhal's district court on November 19, 2024, claiming the Jama Masjid was built on the site of an ancient temple. The petitioners, led by Hari Shanker Jain, demanded a survey to ascertain the religious character of the site. This petition follows a pattern seen in similar cases in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have raised similar claims about mosque sites. The court ordered a photographic and videographic survey of the mosque, which, initially carried out peacefully, later sparked violence on November 24 when the survey was accompanied by chanting crowds. This led to protests, stone pelting, and allegations of police firing, resulting in several deaths.
The Jama Masjid is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and is listed as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). This gives the case legal and cultural sensitivity, as it involves both national heritage and religious sentiments.
Historical and Architectural Context:
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal was constructed by Mir Hindu Beg, a general under Babur, in the early 16th century. It is one of three mosques commissioned by Babur, alongside those in Panipat and Ayodhya. The mosque is noted for its architectural style, which includes a large square mihrab hall, a dome, and arches, constructed using stone masonry and plaster. Some historians argue that the mosque might be a Tughlaq-era structure modified during Babur's reign. Locally, Hindu tradition holds that the mosque incorporates elements of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
The dispute has reignited debates about the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, which mandates that the religious character of any place of worship as it existed on August 15, 1947, should be maintained, with the exception of the ongoing Babri Masjid dispute. The Act aims to prevent any further contests regarding religious sites, and Section 3 of the Act explicitly prohibits converting a place of worship into a site of a different religious denomination.
The petition filed in Sambhal seeks to alter the religious character of the mosque, directly contravening the Places of Worship Act. The petitioners have cited remarks by Supreme Court Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that a survey to ascertain the religious character of a place might not violate the Act. This has led to petitions challenging the Act in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
The Legal and Social Implications:
The ongoing dispute over the Shahi Jama Masjid highlights the tension between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and communal harmony. The Supreme Court has intervened in the matter, temporarily halting further proceedings in the trial court, urging that the mosque's management committee approach the Allahabad High Court. The Court emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and harmony and cautioned against any actions that could escalate tensions.
The case underscores the challenges of balancing India's rich historical heritage with its diverse religious communities. As the legal process unfolds, the outcome of the Sambhal dispute could set significant precedents for how similar cases are handled in the future.
Conclusion:
The Sambhal mosque dispute, much like the Gyanvapi and Ayodhya cases, brings to the forefront the complex intersections of history, religion, and law. It also raises critical questions about the application of the Places of Worship Act and its implications for preserving India's pluralistic society. The outcome of this case, alongside the pending petitions in other states, will be crucial in shaping the future of religious site disputes in India.
India-Cambodia Joint Military Exercise CINBAX

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The first edition of CINBAX (Counter-Terrorism Counter-Bio-Terrorism and Intelligence Operations Exercise) was launched on December 1, 2024, at the Foreign Training Node, Pune.
Key Details:
- Participants: 20 personnel from each side – the Indian Army and the Cambodian Army – focusing on enhancing cooperation for UN peacekeeping operations.
- Objective:
- Enhancing Trust and Interoperability: CINBAX aims to foster mutual trust, build camaraderie, and improve operational efficiency between the two armies in conducting peacekeeping operations under UN guidelines.
- Focus Areas: Joint Counter-Terrorism (CT) operations, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), cyber warfare, logistics, casualty management, and disaster relief operations.
- Phases of the Exercise:
- Phase I: Orientation for Counter-Terrorism operations in the context of UN peacekeeping missions.
- Phase II: Conduct of tabletop exercises to simulate and plan response scenarios.
- Phase III: Finalization of plans and review of lessons learned, focusing on operational strategies and tactical decision-making.
- Key Topics Covered:
- Discussions on setting up a Joint Training Task Force for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
- Exploring cyber warfare, hybrid warfare, and unconventional tactics.
- Strategies for managing logistics, casualties, and coordination during Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- Promotion of Indigenous Defence Equipment:
- The exercise will showcase Indian-made weapons and defence equipment, supporting India’s commitment to Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance in defence production).
- Objective: To highlight India's advanced military technology and indigenous defence capabilities.
- Significance for India-Cambodia Relations:
- The exercise strengthens military ties between India and Cambodia, contributing to improved cooperation in regional peacekeeping efforts.
- CINBAX marks a significant milestone in India-Cambodiadefence collaboration and sets the stage for future joint operations.
India-Cambodia Bilateral Relations
- Historical Context:
- India and Cambodia share strong religious, cultural, and linguistic ties, with Hindu rituals influencing Cambodian culture and Sanskrit and Khmer sharing common words.
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1952, even before Cambodia's independence from France.
- Key Developments:
- 1954: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited Cambodia, initiating strong diplomatic ties, particularly during the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Post-1970s: India played a pivotal role in Cambodia's recovery from the Khmer Rouge regime. India was the first democratic country to recognize the Heng Samrin regime in 1981 and contributed to Cambodia's political reconciliation.
- 1980s: India facilitated dialogue for the Paris Peace Accord and contributed to the success of UNTAC elections in 1993.
- Strategic and Economic Cooperation:
- Defence: Enhanced cooperation in defence capacity building, military training, and infrastructure development.
- Trade: India exports pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, automobiles, and leather products to Cambodia. In return, Cambodia exports organic chemicals, apparel, and footwear to India.
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC): Established in 2000, MGC includes Cambodia and aims to enhance cooperation in sectors like trade, education, tourism, and cultural exchanges.
- Recent Collaboration:
- India has extended financial assistance for infrastructure projects in Cambodia, especially in restoring and conserving cultural heritage sites like Angkor Wat.
- MoUs signed in bilateral cooperation, cultural exchanges, and development projects highlight the growing India-Cambodia strategic partnership.
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
- It was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences, PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy, and Space, along with Shri V. Srinivas, the Secretary of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- This initiative, conceptualized by DARPG, aims to evaluate and rank central Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal mechanisms.
Key Aspects of GRAI 2023:
- Objective: GRAI 2023 was designed to provide a comparative assessment of Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal systems. It was created based on recommendations from the Parliamentary Standing Committee of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Assessment Method: The index evaluates 89 Central Ministries and Departments across four dimensions:efficiency, feedback, domain&organisational Commitment
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Group A: Ministries/Departments with more than 10,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Group B: Ministries/Departments with 2,000 to 9,999 grievances (33 Ministries/Departments)
- Group C: Ministries/Departments with fewer than 2,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Top Performers:
- Group A: The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare topped the rankings.
- Group B: The Office of the Comptroller & Auditor General of India led.
- Group C: The Department of Investment & Public Asset Management ranked first.
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Analysis: GRAI 2023 includes an in-depth analysis of the root causes of effective grievance redressal for each Ministry/Department, presented in a color-coded, easily understandable format.
- Advancements: The report outlines a roadmap for improving grievance redressal, emphasizing:
- Utilization of advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analytics and data analysis.
- The introduction of features like IGMS 2.0 and TreeDashboard within CPGRAMS.
- Improved training for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) and more rigorous audits to increase accountability.
- Expansion of CPGRAMS integration to local governments, enhancing the grievance redressal system across all levels of governance.
Commonwealth Secretariat recognized CPGRAMS as a best practice in grievance redressal at its meeting in April 2024.
U.N. Peacebuilding Commission

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
India has been re-elected to the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) for the term 2025–2026, continuing its strong commitment to global peace and stability.
UN Peacebuilding Commission (PBC)
It is an advisory body established by the UN General Assembly and UN Security Council in 2005. It is tasked with supporting peace efforts in conflict-affected countries by advising and recommending strategies for post-conflict recovery and long-term peacebuilding.
Composition of PBC:
- The PBC is composed of 31 member states, elected from the General Assembly, Security Council, and Economic and Social Council.
- It includes key financial and troop-contributing countries, which play a central role in shaping global peacebuilding initiatives.
Key Mandates of the PBC
- Coordination of Resources and Strategies:The Commission brings together all relevant actors to propose integrated strategies for post-conflict recovery and peacebuilding.
- Reconstruction and Development:It focuses on rebuilding conflict-affected countries through institution-building and supporting sustainable development efforts.
- Improving Coordination:The PBC ensures better coordination within and outside the UN, develops best practices, and secures predictable financing for early recovery initiatives.
- Sustaining Peace:The Commission promotes sustained international attention to peacebuilding efforts and offers political support to countries emerging from conflict, with their consent.
- Integrated Approach:The PBC advocates for an integrated approach that links security, development, and human rights as interrelated and mutually reinforcing.
- Bridging Role:It serves as a platform to connect UN bodies, Member States, national authorities, civil society, and other stakeholders, sharing good practices in peacebuilding.
India’s Contributions to UN Peacebuilding and Peacekeeping
India has been at the forefront of UN peacebuilding initiatives due to its long-standing commitment to international peace and stability.
- Largest Contributor of Personnel:India is one of the largest contributors of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping. Currently, around 6,000 Indian military and police personnel are deployed across multiple missions in Abyei, Central African Republic, Cyprus, Democratic Republic of Congo, Lebanon, Middle East, Somalia, South Sudan, and Western Sahara.
- Sacrifices in Service:India holds the tragic distinction of having lost over 180 peacekeepers, the highest number from any troop-contributing nation. These sacrifices reflect India's enduring commitment to global peace.
- Financial Support:India contributes to the Peacebuilding Fund, the primary financial instrument for conflict prevention and peacebuilding, which supports countries transitioning from conflict to peace.
- Championing South-South Cooperation:India has actively promoted South-South cooperation, a model for post-conflict recovery that emphasizes shared learning and capacity-building among developing nations.
- Women in UN Peacekeeping:India has led efforts for gender parity in UN peacekeeping. In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN peacekeeping mission. It has since deployed Female Engagement Teams (FETs) and Female Formed Police Units (FFPUs) in Lebanon and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Training and Capacity Building:India has invested in capacity development for both the UN and host nations. The Centre for UN Peacekeeping (CUNPK) in New Delhi, established by the Indian Army, trains over 12,000 troops annually in peacekeeping operations. India also deploys Mobile Training Teams to share best practices with other countries.
India’s Pledges at the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial (2023)
At the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial held in Accra, Ghana (December 2023), India made significant pledges:
- To contribute an Infantry Battalion Group, along with various sub-groups and pre-deployment training courses, for the next two years.
- India’s ongoing commitment to strengthening peacekeeping efforts and supporting the UN’s peacebuilding agenda was reaffirmed.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
E-Daakhil Portal
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- The E-Daakhil portal was launched by the Department of Consumer Affairs to promote consumer rights and ensure timely justice.
- The portal was launched nationwide with its final rollout in Ladakh on 22nd November 2024, making it operational across all states and union territories of India.
Background and Purpose:
- Introduced in September 2020, the portal was developed in response to the Consumer Protection Act 2019, which aims to address emerging consumer concerns.
- Aimed at providing a hassle-free, inexpensive, and speedy mechanism for filing consumer complaints, especially post the COVID-19 pandemic.
- E-Daakhil is an online platform that simplifies the grievance redressal process, allowing consumers to file complaints remotely, without the need for physical presence.
Portal Features:
- User-friendly interface: Simple and intuitive, allowing consumers to file and track complaints online.
- Registration process: Users can register through OTP on their mobile or an activation link via email.
- Paperless and transparent: The entire process, from filing complaints to tracking the case status, is digital and transparent.
- Consumers can file complaints, pay fees, and monitor the progress of their cases from the comfort of their homes.
Success and Impact:
- By the end of 2023, E-Daakhil was available in 35 states and union territories; with Ladakh being the latest addition in November 2024.
- Over 2.81 lakh users have registered, and 1.98 lakh cases have been filed, of which 38,453 cases have been disposed of.
Future Developments:
- E-Jagriti: A new initiative that will further streamline the case filing, tracking, and management process, reducing delays and paperwork.
- E-Jagriti aims to improve communication between parties, ensuring faster dispute resolution.
6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee Meeting
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings for discussions on the review of the AITIGA were held recently in Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Key Negotiation Areas
- 8 Sub-Committees under the AITIGA Joint Committee discussed:
- Market access, rules of origin, SPS measures, standards and technical regulations.
- Customs procedures, economic and technical cooperation, trade remedies, and legal and institutional provisions.
- 5 Sub-Committees met physically during this round of negotiations.
Progress in Discussions
- Textual Discussions: Sub-Committees made progress in discussions on various provisions.
- Tariff Negotiations: Initial steps towards initiating tariff negotiations were covered.
High-Level Meetings Leading to AITIGA Review
- 21st ASEAN-India Economic Ministers Meeting: Held in September 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
- 21st ASEAN-India Summit: Held in October 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
Both meetings urged the Joint Committee to expedite negotiations and aim for the conclusion of the review in 2025.
Bilateral Meetings
- ASEAN delegates held separate bilateral meetings with Thailand and Indonesia to discuss bilateral trade issues.
- Indian and ASEAN Chief Negotiators met to align on the ongoing issues and future steps.
India's Review Demands
- Request for Review: India sought a review of AITIGA (implemented in 2010), citing disproportionate trade benefits favoring ASEAN countries.
- India’s Objectives:
- Enhanced Market Access: India pushed for ASEAN countries, especially Vietnam, to commit to greater market-opening for Indian goods.
- Stricter Rules of Origin (ROO): India requested more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from entering India via ASEAN countries at preferential rates.
Trade Relationship and Economic Impact
- Bilateral Trade:
- Total trade with ASEAN reached USD 121 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Trade during April-October 2024 was USD 73 billion, marking a 5.2% growth.
- Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with ASEAN widened from USD 4.98 billion in FY 2010-11 to USD 38.4 billion in 2023-24.
- ASEAN accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
Future Outlook
- The next meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee is scheduled for February 2025 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The review process aims to further enhance sustainable trade between India and ASEAN countries.
11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
The 11th ADMM-Plus held in Vientiane, Laos saw Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh engage in discussions with his counterparts from the United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Focus: The talks centered on strengthening defence partnerships, regional security, and enhancing cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations.
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- Platform for Dialogue: The ADMM-Plus is a key platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners—Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was held in HàN?i, Vietnam on 12 October 2010.
- Annual Meetings: Since 2017, the ADMM-Plus has met annually to enhance dialogue and cooperation amidst an increasingly complex regional security environment.
Objectives:
- Capacity Building: To aid ASEAN members in addressing shared security challenges.
- Promote Trust and Transparency: Enhance mutual trust and confidence between ASEAN and partner nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Focus on cooperation in defence and security to counter transnational security challenges.
- ASEAN Security Community: Contribute to realizing the ASEAN Security Community, as per the Bali Concord II, aiming for peace, stability, democracy, and prosperity in the region.
- Vientiane Action Programme: Facilitate ASEAN's efforts towards a peaceful, secure, and prosperous ASEAN with outward-looking relations with Dialogue Partners.
India’s First AI Data Bank

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Science and Technologyrecently launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank that is aimed at propelling innovation and boosting the country’s national securityat the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
-
- The event theme: “AI for India: Advancing India’s AI Development – Innovation, Ethics, and Governance”.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Propel innovation and enhance national security.
- Provide access to diverse, high-quality datasets for creating scalable and inclusive AI solutions.
- Key Features of the AI Data Bank:
- Target Audience: Researchers, startups, and developers.
- Data Types: Satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- Purpose:
- To enhance national security through real-time analytics.
- Enable predictive analytics for disaster management and cybersecurity.
Strategic Importance of AI in India:
- National Security: AI to strengthen national security by providing real-time analytics from satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- AI for Development:
- AI’s role in reshaping sectors like governance, business, healthcare, education, and space exploration.
- AI as a tool for economic growth, addressing climate change, improving public service delivery, and ensuring national security.
- Ethics and Governance:
- Ensuring responsible AI use with optimal handling.
- Addressing algorithmic bias and data privacy through robust governance frameworks.
- Commitment to transparent and fair AI systems that empower people rather than replace them.
- AI in Disaster Management and Cybersecurity:
- Aligning with India’s goals to use AI for predictive analytics in disaster management.
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI technologies.
Government’s Vision on AI:
- Empowering Citizens: AI must bridge divides and ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- AI as Backbone for Future Development: India’s focus on making AI an integral part of its future economic and technological growth.
Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Daniel Barenboim (Classical Pianist and Conductor) and Ali Abu Awwad (Palestinian Peace Activist) were jointly awarded the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development for 2023.
- Daniel Barenboim was recognized for fostering peace through musical and cultural dialogue initiatives.
- Ali Abu Awwad was honored for his advocacy of peace through dialogue via his organization Roots, which he founded after serving time in Israeli prison.
Significance of the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- The award is given to individuals or organizations who have made outstanding contributions to international peace, disarmament, and development.
- It includes a monetary award of ?25 lakh and a citation.
About the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- Established: 1986 by the Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust in memory of former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
- Objective: To honor sustained efforts towards international peace, the development of humanity, and the promotion of disarmament.
- Past recipients: Includes prominent figures and organizations such as Mikhail Gorbachev, UNICEF, Jimmy Carter, Angela Merkel, ISRO, and Sir David Attenborough.
2022 Awardees:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize for 2022 was awarded to the Indian Medical Association and the Trained Nurses Association of India, in recognition of their contribution as COVID-19 warriors.
Key Takeaways:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize is regarded as one of the most prestigious awards for promoting peace, disarmament, and development worldwide.
- Daniel Barenboim's musical initiatives and Ali Abu Awwad's work through dialogue exemplify efforts to bridge divides and promote peaceful resolutions to conflict.
Bhu-Neer Portal
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Minister of Jal Shakti, digitally launched the “Bhu-Neer” portal during the India Water Week 2024.
- Developed by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with the National Informatics Centre (NIC).
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Portal:
- Centralized platform for managing and regulating groundwater resources across India.
- Aims to ensure transparency, efficiency, and sustainability in groundwater usage, facilitating easier access to groundwater withdrawal permits.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplified interface to streamline the application process for groundwater withdrawal.
- PAN-Based Single ID System: Allows seamless user registration, providing a unique identification for all stakeholders.
- NOC with QR Code: Enables verifiable and trackable compliance documents, ensuring authenticity.
- Improved Version: An enhanced version compared to the previous NOCAP system, with improved efficiency and features.
- Streamlined Process Flow: Simplifies the process for obtaining groundwater withdrawal permits.
Goals and Benefits:
- Promotes the sustainable use of groundwater and ensures compliance with legal frameworks at state and national levels.
- Supports Ease of Doing Business: Aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision by making the groundwater regulation process seamless and faceless, reducing bureaucratic delays.
Public Accessibility:
- The portal is now live and accessible to both project proponents and the general public.
- It offers services such as groundwater withdrawal related queries, tracking applications, and payment of statutory charges.
Impact on Groundwater Management:
- The platform is expected to bring improved groundwater regulation by providing centralized access to policies, compliance details, and sustainable practices related to groundwater use.
- It will contribute significantly to monitoring and sustainable management of India’s groundwater resources, crucial in light of increasing water scarcity.
Vision of the Portal:
- In line with the government’s broader goals of digitalization, transparency, and environmental sustainability, the “Bhu-Neer” portal marks a significant step in efficient water resource management.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
PM Modi receives Nigeria’s second-highest national award.
Key Events and Achievements
- Award Conferred:
- Award Name: Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger (GCON).
- Significance: Nigeria’s second-highest national award, conferred on Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Historical Context: Modi becomes the second foreign dignitary to receive this award, after Queen Elizabeth in 1969.
Strategic and Developmental Ties Between India and Nigeria
- First Visit in 17 Years: Modi’s visit is the first by an Indian PM to Nigeria in 17 years, underscoring the significance of strengthening bilateral ties.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Over 200 Indian companies have invested around $27 billion in Nigeria across key sectors, making India a major economic partner.
- India has provided $100 million in development assistance through concessional loans and is actively involved in capacity-building training programs in Nigeria.
- MoUs Signed:
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Cultural Exchange.
- Customs Cooperation.
- Survey Cooperation.
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Relief Aid: Modi announced the dispatch of 20 tonnes of relief supplies to help Nigeria recover from the devastating floods that affected the country last month.
Diplomatic Discussions and Initiatives
- Strategic Partnership: Modi described the India-Nigeria partnership as one with immense potential in sectors like defence, energy, technology, trade, health, and education.
- Indian Expatriate Community: Modi acknowledged the 60,000-strong Indian diaspora in Nigeria, recognizing their role as a pillar of bilateral ties.
- Support for Africa:
- Modi highlighted India’s support for the African Union’s membership in the G20, an outcome of the India-hosted G20 summit in 2023.
- Nigeria’s Role: He noted Nigeria’s positive influence on Africa and its importance as a key partner in India’s Africa engagement.
Broader Implications for International Relations
- India-Nigeria Security Cooperation:
- The National Security Advisors (NSA) of India and Nigeria held in-depth discussions on counter-terrorism, extremism, and cybersecurity challenges.
- India and Nigeria are committed to jointly addressing global threats such as arms smuggling and international crime.
- India's Role as a Development Partner:
- India’s growing role as a development partner for African nations is becoming increasingly important, exemplified by Nigeria’s close ties with India.
- Global Diplomacy and Soft Power:
- Modi’s award and visit reflect India’s growing influence in Africa and its emphasis on fostering ties with resource-rich and strategically located nations like Nigeria.
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger is also a reflection of the soft power India is wielding globally.
Key Facts about Nigeria:
- Location: Nigeria is located in West Africa, bordering Niger, Chad, Cameroon, and Benin, with access to the Atlantic Ocean.
- Significance:
- Known as the “Giant of Africa” due to its large population and economic power.
- It has the largest economy in Africa, largely driven by its oil reserves.
Nepal-Bangladesh Power Transfer via India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
Nepal starts exporting energy to Bangladesh with Indian grid support.
Significance of the Power Transfer:
- Energy Cooperation:
- A major step in regional energy cooperation among Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Strengthens sub-regional connectivity in the power sector.
- Nepal’s Hydropower Potential:
- Nepal, a Himalayan nation, possesses untapped hydropower resources, and this agreement opens the door for future cross-border electricity cooperation.
- Nepal’s energy exports are a green energy initiative, supporting sustainable industrial growth in Bangladesh and regional prosperity.
- Electricity Crisis in Bangladesh:
- Bangladesh is facing an ongoing electricity shortage, worsened by the suspension of power supply from Adani’s Godda plant and the maintenance of the Payra thermal unit.
- The addition of 40 MW of Nepalese hydroelectric power aims to alleviate the energy shortfall in Bangladesh.
Tripartite Power Sales Agreement:
- Agreement Details:
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) (India)
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (Nepal)
- Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) (Bangladesh).
- Power Export: Nepal has started exporting 40 MW of electricity, which marks a significant milestone in trilateral power cooperation.
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
Key Entities Involved:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN):
- A wholly owned subsidiary of NTPC Ltd. (National Thermal Power Corporation), created to facilitate power trading.
- NVVN is diversifying into renewables, e-mobility, and green fuel solutions.
- NTPC Ltd.:
- A Maharatna PSU under India’s Ministry of Power, established to develop power resources in India.
- Involved in large-scale power generation and clean energy initiatives
Unified Complex Radio Antenna
- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- India and Japan recently signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) to co-develop the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) mast for deployment on Indian Navy ships. This pact marks a significant milestone as it is India's first military technology transfer agreement with Japan.
- The deal follows a 2015 agreement on the transfer of defense equipment and technology, further strengthening defense ties between the two countries.
- The UNICORN mast is a cutting-edge communication and radar system designed to enhance the stealth characteristics of naval vessels. This agreement is seen as an important step towards deepening India-Japan defense cooperation.
What is UNICORN?
The UNICORN mast is an advanced, integrated antenna system that combines several communication and radar components into a single conical structure or radome (a radar-absorbing dome). It is designed to reduce the radar cross-section (RCS) of ships, improving their stealth capabilities.
Key features of the UNICORN mast include:
- Integration of multiple antennas: It consolidates various antennas used for tactical data links, communications, and navigation systems (e.g., TACAN - Tactical Air Navigation System).
- Stealth enhancement: By reducing the number of exposed components and consolidating them into a single radome, the mast significantly lowers the ship’s radar signature, making it harder to detect.
- Improved performance: The mast design minimizes mutual interference between antennas, enhances maintainability, and increases lightning resistance.
- Space efficiency: It saves valuable below-deck space and reduces ship-building time by integrating multiple systems into one mast.
The UNICORN system is currently deployed on Mogami-class frigates of the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force.
India-Japan Defense Cooperation
- 2015 Defense Technology Transfer Agreement: This pact established a framework for defense cooperation between India and Japan, paving the way for joint projects like the UNICORN mast.
- Bilateral Military Exercises:
- Veer Guardian 2023: A bilateral exercise conducted between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF), which deepened defense interoperability between the two nations.
- Tarang Shakti 2024: The first multilateral air exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force, with Japanese fighter aircraft participating.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands Development: Japan has also provided financial aid for infrastructure development in India’s strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands, contributing to enhancing India’s maritime security in the region.
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
TarunerSwapno Scheme

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has ordered an inquiry after some intended beneficiaries of the ‘Taruner Swapna’ scheme, an initiative of the TMC government, alleged that they did not receive Rs 10,000 meant for the purchase of tablets (mobile device with a touchscreen display, rechargeable battery, and mobile operating system).
Overview:
- Aimed at bridging the digital divide by providing ?10,000 to Class 11 and 12 students in West Bengal for purchasing smartphones/tablets.
- In FY 2024-25, ?900 crore allocated for the scheme, targeting 16 lakh students.
- The main objective of the scheme is to provide scholarship to the students. So that the student can use their scholarship to buy a smartphone and tablet and can get education through online medium.
- This scheme will prove to be effective in making the future of the students bright and will also prove to be effective in strengthening them technically.
- Eligibility criteria for the scheme:
- Applicant must be a permanent resident of West Bengal State.
- The applicant should be a student.
- Students of 11th and 12th will be eligible for this scheme.
- The annual income of the family of the applicant student should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- Students with backlog are not eligible as this grant is for one-time only.
- This scheme will make the students technically strong and they will be able to improve their future with technology.
- Students of government/government-aided/sponsored schools and madrassas can avail assistance.
- TarunerSwapno Yojana will bridge the digital divide among students and facilitate modern education.
Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR)

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched the Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) program to significantly boost research and innovation across Indian universities, especially those with limited research infrastructure. The program is designed to bring about a transformative change in India's academic research ecosystem, aligning with the broader goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Details:
- Launch Date: November 2024
- Ministry/Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Objective:
- To elevate research capabilities in universities that have limited resources by pairing them with well-established, top-tier institutions.
- To foster collaborations that can help these emerging universities enhance their research quality, drive innovation, and make significant, globally competitive research contributions.
- Operational Model: Hub-and-Spoke Framework
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- The top 25 institutions in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Institutions of National Importance ranked in the top 50 NIRF.
- Spoke Institutions: These are emerging universities or institutions with limited research infrastructure. These will include:
- Central and State Public Universities ranked within the top 200 NIRF Overall.
- Top 100 NIRF University/State Public Universities.
- Select NITs and IIITs.
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- Funding:
- The program has a budget allocation of up to ?100 crore per PAIR network.
- Distribution of Funds:
- 30% for the Hub institution.
- 70% for the Spoke institutions.
- Private Institutions serving as hubs will need to contribute 25% of their allocated budget.
- Mentorship & Research Focus:
- Hubs will provide mentorship to spoke institutions, guiding them in various aspects of research such as access to resources, advanced infrastructure, and best practices.
- The collaboration is expected to enhance research capabilities, foster innovation, and encourage the development of collaborative networks across institutions.
- Regional Diversity & Inclusion:
- The program ensures regional diversity, with at least one spoke institution located outside the hub's state.
- It also allows the inclusion of one promising university from Category III institutions that may not meet the eligibility criteria but show potential for growth in research.
- Phase-wise Rollout:
- The first phase will focus on institutions ranked within the top 25 NIRF and Institutions of National Importance.
- Future phases will expand the scope, allowing more universities and institutions to participate.
- Goals Aligned with NEP 2020:
- Fostering Research Excellence: By partnering top institutions with emerging ones, PAIR seeks to improve the quality of research in India’s higher education sector.
- Promoting Regional Diversity: Ensuring a geographically diverse set of institutions participate in the research ecosystem.
- Strengthening Innovation: Helping universities in less-researched areas to compete on an international level, particularly in cutting-edge and impactful research.
- Program Implementation:
- Prospective Program Directors from eligible Hub institutions are invited to apply online for the program at ANRF PAIR Application Portal.
About ANRF:
- ANRF was established under the ANRF Act 2023 as an apex body to provide strategic direction for scientific research in India.
- With the formation of ANRF, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), previously established under an act of Parliament in 2008, has been subsumed into ANRF.
Operation Dronagiri

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Operation Dronagiri, launched under the National Geospatial Policy 2022 by the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Objective: It is a pilot project under India’s National Geospatial Policy 2022 aimed at showcasing the potential of geospatial technologies in sectors such as Agriculture, Livelihoods, and Logistics & Transport to improve quality of life and ease of doing business.
- Implementation:
- The first phase will cover five states: Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Sectors Targeted: The focus will be on demonstrating the integration of geospatial data to solve real-world challenges in agriculture, transportation, and livelihoods.
National Geospatial Policy 2022
- Context: The National Geospatial Policy 2022 is aimed at liberalizing geospatial data and enabling widespread access and use of geospatial technologies across various sectors of governance, business, and development.
- Goals:
- Development of Geospatial Infrastructure: Promoting the creation of a robust infrastructure to make spatial data more accessible and usable.
- Geospatial Skill Development: Focus on creating a workforce proficient in geospatial technologies.
- Implementation of Standards: Establishing clear standards for geospatial data to ensure consistency and interoperability.
Role of Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI)
- Launch: Alongside Operation Dronagiri, the Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI) was also unveiled.
- Purpose: GDI is designed to facilitate seamless data sharing, access, and analysis of geospatial data.
- Key Features:
- Data Exchange: Enables smooth sharing of geospatial data for urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
- Privacy and Security: Built with advanced data exchange protocols and privacy-preserving features to ensure secure data sharing.
- Collaboration: It will promote collaboration among stakeholders, including government agencies, industry, and startups, to unlock actionable insights for decision-making.
- Key Features:
Potential Applications of Geospatial Data
- Urban Planning: Assisting cities in designing efficient infrastructure.
- Disaster Management: Providing real-time data for better disaster response.
- Environmental Monitoring: Supporting initiatives for environmental protection and sustainability.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, crop monitoring, and improving supply chains.
- Logistics & Transport: Streamlining transportation networks, reducing traffic, and improving delivery systems.
Grand Challenge for Startups
- Objective: A Grand Challenge was announced as part of the initiative to support startups in developing Proofs of Concept (POCs) targeting specific problems in the focus sectors.
- Role of Startups: The challenge encourages innovation by early-stage and growth-stage startups in geospatial technology, offering mentorship, resources, and access to datasets.
- Geospatial Innovation Accelerators:
- The Geospatial Innovation Accelerators (GIAs) at prestigious institutions like IIT Kanpur, IIT Bombay, IIM Calcutta, and IIT Ropar will support this effort.
- Mentorship and Resources: These accelerators will provide the necessary support for startups to turn their innovations into scalable solutions.
Key Stakeholders and Operational Arms
- Geospatial Innovation Cell (DST): Responsible for overseeing the project’s implementation and execution.
- Navavishkar I-Hub Foundation (IITTNiF): Will manage the operational activities of Operation Dronagiri.
- Partnering Institutions: GIAs at IIT Kanpur, IIT Bombay, IIM Calcutta, and IIT Ropar will be the operational arms.
- Private Sector Involvement: Significant involvement of private sector companies, including startups, is crucial to ensuring the success and scalability of the project.
Impact and Significance
- Socioeconomic Benefits: The integration of geospatial data into agriculture, transport, and logistics will improve efficiency, reduce costs, and boost economic activity in critical sectors.
- Geospatial Innovation: The initiative marks a significant step towards making India a global leader in geospatial technology and positioning the country as a hub for innovative solutions using geospatial data.
- Government Engagement: The project will involve various government departments and corporates in a public-private partnership (PPP) model, similar to the successful implementation of the UPI payment system.
Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES)
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Australia has come up with a new scheme that allows talented young people from India to work in the country for some time.
What is the MATES Scheme?
- Full Name: Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES).
- Objective: To provide Indian university graduates and early-career professionals with an opportunity to live and work in Australia for up to two years.
- Establishment: The scheme is part of the Migration and Mobility Partnership Arrangement (MMPA) between Australia and India, signed on May 23, 2023.
- Launch Date: MATES will open for applicants in December 2024.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Applicants must be 30 years or younger at the time of application.
- Educational Qualifications: Must have graduated within the last two years from an eligible institution with a Bachelor’s degree or higher in one of the following fields:
- Renewable Energy
- Mining
- Engineering
- Information Communications Technology (ICT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Financial Technology (FinTech)
- Agricultural Technology (AgriTech)
- English Proficiency: A minimum score of 6 overall in IELTS (or equivalent), with at least 5 in each module.
- Institutional Criteria: Graduates must be from the top 100 Indian universities as per the NIRF Ranking 2024 (e.g., Panjab University, Chandigarh University, Thapar Institute of Engineering, Lovely Professional University).
- Previous Participation: Applicants must not have previously participated in the MATES scheme.
Key Features of the MATES Scheme
- No Employer Sponsorship Required: Applicants are not required to have sponsorship from an Australian employer.
- Visa Duration: The visa allows a stay of up to 2 years in Australia, with multiple entries permitted.
- Dependents: Visa holders can bring dependents (spouse and children). Dependents will have work rights in Australia but will not count towards the annual cap.
- Visa Application Process:
- The visa will be granted through a ballot system (random selection).
- Application Fee: AUD 25.
- Shortlisted candidates will proceed to further formalities.
Program Features
- Targeted Sectors: MATES focuses on key sectors such as renewable energy, mining, engineering, ICT, AI, FinTech, and AgriTech, aligning with Australia’s demand for skilled professionals in these areas.
- Pilot Program: Initially, the scheme will offer 3,000 places per year for primary applicants.
- Work Flexibility: While the visa does not require applicants to work in their nominated field, it is designed to help young professionals expand their skills and network in Australia’s key industries.
Additional Benefits
- Career Development: Participants will gain international work experience, expanding their professional network and skills.
- Cultural Exchange: The scheme also promotes cultural exchange between India and Australia, fostering stronger bilateral relations.
- Pathway for Future Opportunities: Participants may apply for further temporary or permanent residence in Australia, provided they meet the eligibility requirements.
Impact and Significance
- Bilateral Cooperation: The MMPA, under which MATES is established, enhances migration and mobility between India and Australia while addressing concerns related to illegal migration.
- Youth Empowerment: The scheme offers young professionals a platform to develop their careers internationally, particularly in sectors of global relevance like AI, FinTech, and renewable energy.
- Skill Development: MATES aims to bridge skill gaps in Australia by attracting Indian professionals to key sectors where expertise is in high demand.
- Global Talent Mobility: This scheme supports the global mobility of young talent and strengthens the India-Australia economic and educational partnership.
Know Your Medicine (KYM) App

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, has launched a nationwide appeal to strengthen the fight against doping in sports, urging athletes, coaches, and the entire sporting community to embrace the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India's ‘Know Your Medicine (KYM)’ app.
Introduction to KYM App
- Launch: The app was launched by Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, to combat doping in sports.
- Developer: National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India.
- Purpose: To prevent inadvertent doping by allowing athletes to check whether a medicine contains substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Key Features of the KYM App
- Medicine Verification: The app enables athletes to verify if any medicine or its ingredients contain banned substances listed by WADA.
- Image and Audio Search: Unique search features help users easily search for specific sport-related information.
- Customizable Search: Users can select their sport category and receive relevant, sport-specific information.
- User-Friendly: Designed for athletes, coaches, and sports professionals to quickly verify medicines and ensure clean competition.
Importance of KYM App
- Supporting Clean Sports: The app promotes a fair and ethical sporting culture by reducing the risk of inadvertent doping.
- Integrity of Sports: Helps athletes avoid penalties or bans due to accidental doping, maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- Accessible Information: Provides easy access to information regarding medicines that may contain banned substances, which is crucial for athletes' health and careers.
NADA India's Mission
- Anti-Doping Awareness: The KYM app is part of NADA India’s broader initiative to educate athletes and raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Goal: To promote dope-free sports and ensure that athletes and coaches are equipped with the tools needed for compliance with anti-doping regulations.
NADA India: Background and Functions
- Established: NADA India was set up in November 2005 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Mission: To serve as the independent Anti-Doping Organization for India, aiming to create a doping-free sporting environment.
- Key Functions:
- Implementing Anti-Doping Code: Ensuring compliance with the World Anti-Doping Code among all sports organizations in India.
- Dope Testing Program: Coordinating a national dope testing program with stakeholders across various sports.
- Promoting Research and Education: Encouraging research on anti-doping and educating athletes on the importance of staying clean.
- Adopting Best Practices: Ensuring the implementation of high-quality standards for anti-doping programs.
Impact and Significance
- Preventing Doping: The KYM app helps prevent inadvertent doping incidents by providing athletes with the necessary tools to check their medicines.
- Supporting Athletes: It provides athletes with a reliable way to avoid banned substances in over-the-counter medications, thus safeguarding their careers.
- National and International Compliance: Supports India’s commitment to complying with international anti-doping norms, contributing to a global effort to maintain fairness in sports.
Operation Kawach

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Delhi Police recently initiated Operation Kawach, arresting and detaining around 1,000 people in an attempt to crack down on various gangs and their operations in the wake of the recent incidents of shootings reported in the city.
Overview of Operation Kawach
- Objective: A crackdown on gang-related violence, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities like possession of firearms, banned drugs, and liquor.
- Agencies Involved:Delhi Police (Local Police, Special Cell, and Crime Branch)
- Duration: Initiated on November 12, 2024 (5 PM) and continued until November 13, 2024 (5 PM).
Key Details of the Operation
- Arrests and Detentions:
- Around 1,000 people detained.
- 486 people apprehended in Outer North Delhi (20% juveniles).
- Arrests made in Dwarka, Southwest, and North Delhi.
- Key Gangs Targeted:
- Associated with notorious gangs led by Lawrence Bishnoi, Neeraj Bawana, Kaushal Chaudhary, TilluTajpuria, Kala Jatheri, Manjeet Mahal, and Nandu gangs.
- Charges: Involvement in activities like:
- Possession of illegal firearms.
- Trafficking of liquor and banned drugs (NDPS Act).
- Theft and other criminal activities.
Significance of Operation Kawach
- Public Safety: Aimed at dismantling organized crime networks to enhance safety and reduce violence in Delhi.
- Impact on Gangs: Directly targets high-profile criminals, including those involved in gang wars and drug trafficking.
- Strategic Law Enforcement: Strengthens law enforcement capabilities, working in coordination across multiple police units.
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund (JNMF)

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund to launch ‘Nehru Archive’ next year.
Nehru Archive Initiative
- Launch Date: The Nehru Archive will go online on November 14, 2025, coinciding with Jawaharlal Nehru's birth anniversary.
- Purpose: The archive will showcase less-known published and unpublished works of India’s first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, including his speeches, letters to Chief Ministers, and other writings.
Archive Content
- Key Features:
- 100 volumes of The Selected Works of Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Letters to Chief Ministers (1947-1964), documenting Nehru's communication with state leadership.
- Nehru’s iconic books like:
-
-
- The Discovery of India
- Glimpses of World History
- Letters from a Father to His Daughter
- An Autobiography
- The Unity of India
- A Bunch of Old Letters
-
-
- Speeches from 1917 to 1964.
- Writings on Nehru by his contemporaries.
- Global archival material from international sources.
- Objective: The goal is to provide dynamic, continuously updated, open-ended access to Nehru’s work, making it the most important research source on Nehru.
Significance
- Educational and Intellectual Contribution: The archive will serve as a comprehensive, accessible source of information for students, scholars, and the general public to understand Nehru’s contributions to the making of modern India.
- Preservation of Legacy: It will preserve and promote Nehru’s intellectual legacy and his vision for India's development post-independence.
- Historical Importance: The archive will help contextualize Nehru’s leadership during critical periods of Indian history, including India’s independence, partition, and post-independence challenges.
Governance and Establishment of JNMF
- Founded: The Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund (JNMF) was established in 1964 through a Deed of Declaration of Trust following a National Committee chaired by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, then President of India.
- Purpose: To preserve and promote Nehru's legacy, especially his role in shaping modern India.
- Governance: The JNMF is governed by 14 trustees and is currently headed by Sonia Gandhi, the Chairperson of the Congress Parliamentary Party.
Accessibility for Disabled Persons

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India delivered a significant ruling affirming that the right of persons with disabilities (PwDs) to access environments, services, and opportunities is a fundamental human right. The judgment was made in the case of RajiveRaturi vs. Union of India &Ors. and is based on a report submitted by the Centre for Disability Studies (CDS) at NALSAR University of Law.
Key Points of the Judgment:
- Social Model of Disability:
- The Court upheld the social model of disability, which focuses on societal changes to ensure the full inclusion and participation of PwDs.
- The model emphasizes removing social barriers and creating an inclusive environment that accommodates all disabilities.
- Challenges Faced by PwDs: The ruling highlighted various challenges faced by PwDs, as identified in the CDS NALSAR report:
- Accessibility Barriers: Significant gaps exist in accessibility measures across public spaces such as courts, prisons, schools, and public transport.
- Intersectionality & Compounded Discrimination: PwDs often face multiple layers of discrimination, such as caste, gender, and socio-economic status, which compound their marginalization.
- Inconsistent Legal Framework: The RPwD Act (2016) mandates mandatory compliance for accessibility standards, but Rule 15 under RPwD Rules (2017) only offers self-regulatory guidelines, which the Court found insufficient.
- Court's Analysis of Rule 15:
- The Court declared Rule 15(1) of the RPwD Rules, 2017, as ultra vires, meaning it is inconsistent with the mandatory compliance intended by the RPwD Act.
- The Court stressed the need for stronger legal and regulatory enforcement to ensure access for PwDs.
- Principles of Accessibility: The Court outlined several essential principles for achieving accessibility:
- Universal Design: Environments and services should be universally accessible to all, including PwDs.
- Comprehensive Inclusion: All types of disabilities, both visible and invisible, should be addressed.
- Assistive Technology Integration: Using technology to support PwDs in daily activities.
- Stakeholder Consultation: PwDs and disability advocacy groups must be consulted in planning and designing accessible spaces.
- Two-Pronged Approach:
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
- Ensure accessibility in existing infrastructure: Modify and update current institutions and services to become accessible.
- Design future infrastructure with accessibility in mind: Plan and build new spaces and services that are inclusive from the start.
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
Legal and Policy Framework:
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016:
- The RPwD Act mandates various accessibility standards and provisions to protect and promote the rights of PwDs, in alignment with India’s obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), which India ratified in 2007.
- The Act defines a person with a benchmark disability as someone with at least 40% of a specified disability.
- International Obligations:
- The ruling reaffirmed the importance of Article 9 of the UNCRPD, which emphasizes the right of PwDs to access the physical environment, transport, and information and communication technologies.
- Government Initiatives: The judgment highlights several initiatives aimed at improving accessibility:
- Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan): A nationwide effort to make public spaces and services accessible to PwDs.
- Assistance for Aids and Appliances: Government schemes to provide PwDs with necessary aids and appliances.
- Unique Disability Identification Portal: A platform for PwDs to register and obtain a disability certificate.
Notable Judicial Precedents:
The Court referred to several previous rulings that recognized the right to accessibility:
- State of Himachal Pradesh v. Umed Ram Sharma (1986): The Court included the right to accessibility under the Right to Life (Article 21) of the Constitution.
- Disabled Rights Group v. Union of India (2017): The Court directed that educational institutions ensure reserved seats for PwDs.
EV as a Service Programme

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 'EV as a Service'programme was launched by Shri Manohar Lal, Union Minister of Power and Housing & Urban Affairs, at the Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium.
- The initiative is spearheaded by Convergence Energy Services Limited (CESL), a subsidiary of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), to promote electric vehicles (EVs) in government offices.
Objective:
- The 'EV as a Service'programme aims to boost e-mobility within the government sector by deploying 5,000 electric cars in central and state government ministries, public sector enterprises (CPSEs), and various institutions over the next two years.
- The programme is designed to support India’s net-zero emissions goal by 2070 and advance the country's environmental sustainability vision.
Flexible Procurement Model:
- The programme utilizes a flexible procurement model, allowing government offices to choose from a range of E-Cars based on operational needs, making it adaptable for different government departments.
- It will help in reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, cutting carbon emissions, and contributing to energy security.
CESL’s Contribution:
- CESL has already deployed 2000 electric cars across India and is working on deploying around 17,000 electric buses.
- The 'EV as a Service'programme is a key step in helping India transition to clean mobility and reducing emissions from government fleets.
Alignment with National Initiatives:
- The launch complements the PM E-DRIVE Scheme, which aims to accelerate India’s transition to electric mobility.
- Vishal Kapoor, MD & CEO of CESL, emphasized that the initiative is helping to create a collaborative ecosystem involving manufacturers, fleet operators, policymakers, and users to scale up electric mobility in India.
Comics Commandos in Assam

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- "Comics Commandos" is an innovative initiative launched in Goalpara district, Assam, aimed at combating child labour and child marriage through the creative medium of comics.
- The initiative trains 30 local youths to create comic strips that use humour and minimal text for effective communication and public engagement.
Purpose and Objectives:
- Primary Goal: To raise awareness about child labour and child marriage, two major social issues prevalent in the region, by using visual storytelling.
- The initiative aims to resonate with the local community, focusing on everyday struggles like economic hardship, child abuse, and the social norms that perpetuate these issues.
- Rising Dropout Rates: Assam has witnessed an increase in school dropout rates, from 3.3% in 2020-21 to 6.02% in 2021-22, exacerbated by economic pressures like poverty, which force children to work or marry early.
Execution and Approach:
- Training: Thirty local youths are trained to design caricatures and doodles for the comics, ensuring the messages are both simple and engaging for a broader audience.
- Visual Storytelling: The use of visuals over text helps overcome literacy barriers and makes the message more impactful and accessible.
- Community Involvement: The program collaborates with teachers and school committees to facilitate wider participation and support in creating social awareness.
Government Support:
- Chief Minister HimantaBiswaSarma initiated a state-wide campaign in 2023 against child marriage, with the ambitious goal of eradicating it by 2026. This initiative aligns with the state's broader efforts to address social issues.
Impact of the Initiative:
- Comics Commandos is being seen as an effective tool for community empowerment and awareness generation in a region that faces persistent social challenges.
- By involving local youths in the campaign, the initiative ensures community participation and ensures that the message is communicated in a culturally relevant manner.
- The program also empowers young people to use their creativity for social change, thus helping build leadership and social responsibility among the youth.
Parliamentary Panel's Review on Mechanism to Curb Fake News

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology is reviewing mechanisms to curb fake news, following the Bombay High Court striking down a provision of the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules, 2021.
- The controversial provision allowed the government to identify and flag "fake news" on social media through its Fact Check Unit (FCU).
- The panel, led by BJP MP Nishikant Dubey, has summoned representatives from News Broadcasters and Digital Association and the Editors Guild of India to discuss the issue on November 21, 2024.
Issue with the Amended IT Rules:
- The IT Rules, 2021 were amended in April 2022 to include “government business” under the definition of fake news, expanding the scope of content flagged by the FCU.
- This amendment was challenged by media bodies and individuals like comedian Kunal Kamra, leading to the Bombay High Court striking it down in 2024.
- The court deemed the provisions unconstitutional, citing concerns about transparency and the potential misuse of power.
Types of Fake News:
- Misinformation: False information spread unintentionally.
- Disinformation: Deliberately false information meant to deceive and cause harm.
Status of Fake News in India:
- India as a major spreader of misinformation: The World Economic Forum's Global Risks 2024 report identifies disinformation as a significant short-term risk, with India as one of the largest consumers and producers of false information.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, and YouTube are widely used in India for news dissemination, making them a breeding ground for fake news.
- Spread of Political and Religious Misinformation: Fake news often serves political or religious agendas, leading to societal polarization and conflict.
Government Efforts to Combat Fake News:
- IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023: This amendment expanded the scope of "fake news" to include “government business” and gave the FCU the authority to flag misleading content.
- Press Information Bureau (PIB) Fact Check Unit: The PIB continues to run a fact-checking initiative, but it lacks the authority to remove flagged content from social media platforms.
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Programs like Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) aim to improve digital literacy, especially in rural areas, to help citizens identify and avoid fake news.
AUSTRAHIND 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd edition of Exercise AUSTRAHIND started on 8th November 2024 at the Foreign Training Node in Pune, Maharashtra. The exercise will run until 21st November 2024.
Participating Forces:
- Indian Contingent: 140 personnel, primarily from the DOGRA Regiment and Indian Air Force (14 personnel).
- Australian Contingent: 120 personnel from the 13th Light Horse Regiment of the 10th Brigade of the 2nd Division.
Purpose of the Exercise:
- Enhance Military Cooperation between India and Australia.
- Promote Interoperability in conducting joint sub-conventional operations in semi-urban and semi-desert terrain.
- Focus on operations under Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
Key Objectives:
- Joint Tactical Drills and Planning to improve coordination between the forces.
- Training in counter-terrorism operations, special heli-borne operations, and drone countermeasures.
Phases of the Exercise:
Combat Conditioning and Tactical Training Phase:
- Includes drills such as terrorist response, territory capture, and Raid and Search & Destroy Missions.
- Establishment of Joint Operations Centre and securing critical infrastructure like helipads.
- Training on drone operations and counter-drone measures.
Validation Phase: Practical application and testing of skills learned in the previous phase.
Significance:
Best Practices Sharing: Both sides will exchange tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting effective tactical operations.
Camaraderie Building: The exercise will foster a strong bond between soldiers from both countries.
Background: AUSTRAHIND is an annual exercise held alternately in India and Australia. The last edition took place in Australia in December 2023.
Digital Population Clock

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bengaluru's first digital population clock was inaugurated at the Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC) on November 8, 2024.
- The initiative is collaboration between ISEC and the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Purpose:
- The clock provides real-time population estimates for Karnataka and India.
- It aims to enhance awareness about population dynamics and provide accurate demographic data for research and policy analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-time Updates:
- Karnataka’s population is updated every 1 minute and 10 seconds.
- India’s population updates every 2 seconds.
- Precision:
- The clock operates with satellite connections for real-time, accurate data updates.
- It functions autonomously with integrated components, ensuring continuous and precise tracking.
- Location: The clock is prominently displayed at the entrance of ISEC.
- National Expansion: Similar digital population clocks are being installed in 18 Population Research Centres across India by MoHFW.
Significance:
- Awareness: The clock serves as a visual tool to highlight the rapid pace of population growth and its implications for sustainable development.
- Research and Analysis: The clock is part of a broader effort to improve demographic studies and inform policy-making.
- Census Data Research Workstation:
- ISEC has introduced a new research workstation, supported by MoHFW, for in-depth demographic analysis.
- The facility is equipped with advanced software for studying population trends and supporting academic research.
RNA Editing

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Wave Life Sciences became the first biotechnology company to treat a genetic condition by editing RNA at the clinical level.
- What is RNA Editing?
- Definition: RNA editing is the modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) after it’s synthesized from DNA but before it is translated into proteins.
- Process: mRNA consists of exons (coding regions) and introns (non-coding regions). Exons code for proteins, while introns are removed before protein synthesis.
- Types of RNA Modifications:
- Addition: Insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
- Mechanism of RNA Editing:
- Involves Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADAR) enzymes.
- ADAR enzymes modify adenosine to inosine, which is recognized as guanosine, allowing mRNA to be corrected.
- Guide RNA (gRNA) directs ADAR enzymes to the specific mRNA region for editing.
- Clinical Use of RNA Editing:
- Wave Life Sciences used RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a genetic disorder.
- Other potential applications include treating diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, and neurological disorders.
- Challenges in RNA Editing:
- Temporary Effects: RNA editing provides temporary changes, requiring repeated treatments for sustained effects.
- Delivery Issues: Current delivery methods, like lipid nanoparticles and adeno-associated virus vectors, have limitations in carrying large molecules.
- Specificity: ADARs may cause unintended changes in non-target regions of mRNA, leading to potential side effects.
- Comparison: RNA Editing vs. DNA Editing:
- Safety: RNA editing causes temporary changes and presents fewer risks than DNA editing, which makes permanent alterations to the genome.
- Immune Response: RNA editing uses enzymes naturally found in the body (ADAR), which reduces the risk of immune reactions, unlike DNA editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 that can trigger immune responses.
- Significance of RNA:
- Structure: RNA is a nucleic acid, similar to DNA but typically single-stranded. It consists of a backbone of ribose sugars and phosphate groups, with bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Regulate gene expression.
- α-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD):
- A genetic disorder where the protein α-1 antitrypsin accumulates in the liver, damaging both the liver and lungs.
- Treatments include weekly intravenous therapy or, in severe cases, liver transplants.
- RNA editing offers a potential new treatment approach.
- Global Impact:
- RNA editing is still in its early stages but shows promise for treating a wide range of genetic and chronic conditions.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials suggest RNA editing could become a key part of future gene-editing therapies.
One Rank One Pension (OROP) Scheme

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
As OROP completes the 10 years in 2024, it is essential to reflect on the immense benefits the scheme has brought to the armed forces community.
Overview:
- Implemented on: November 7, 2015.
- Announced in: Union Budget 2014, allocation of ?1,000 crore.
- Aim: To ensure uniform pension for military personnel retiring at the same rank with equal service duration, irrespective of retirement date.
- Significance: A landmark reform addressing a four-decade-long demand of ex-servicemen.
- Origin: Longstanding demand since the 1970s; first highlighted by the 3rd Central Pay Commission.
- Key Committees: K.P. Singh Dev Committee (1984) and Sharad Pawar Committee (1991) recommended reforms but faced financial and administrative hurdles.
Key Features:
The policy’s primary elements include:
- Re-fixation of Pensions: The pension of all past pensioners is re-fixed based on the pensions of personnel who retired in 2013, starting from July 1, 2014. This created a new benchmark for pensions, with all retirees getting equal benefits for their service.
- Periodic Revision: The pension is to be re-fixed every five years, ensuring that it continues to reflect changes in the pay and pension structure.
- Arrears Payments: Arrears of pension were to be paid in equal half-yearly installments, although the arrears for family pensioners and gallantry awardees were paid in a single installment.
- Safeguarding Above-Average Pension: For personnel drawing pensions higher than the average, their pensions are protected, ensuring that they do not lose out on the benefits of OROP.
- Inclusive of All Ex-Servicemen: The order covered all personnel who retired up to June 30, 2014, and provided a robust framework for revising pensions for all ranks, including family pensioners.
Impact:
- Veterans and Families:
- Benefited over 25 lakh ex-servicemen and families.
- Enhanced financial security, standard of living, and dignity.
- Emotional and Social Value:
- Strengthened trust between veterans and the government.
- Recognized sacrifices of armed forces personnel.
21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) Meeting

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) meeting was held from November 5 to 6, 2024, at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- The meeting focused on strengthening defence ties between India and the US, covering a wide range of topics aimed at improving military cooperation.
Key Areas of Discussion
- Capacity Building: The meeting discussed initiatives for enhancing defence capacity through training exchanges, joint exercises, and sharing best practices.
- Defence Industrial Cooperation: Both countries explored opportunities for collaborative defence industrial ventures and technology sharing.
- Joint Exercises: The advancement of joint military exercises was highlighted to boost readiness against both conventional and hybrid threats.
- Strategic Objectives: The meeting aimed to enhance interoperability between the two countries' armed forces, enabling more effective joint operations.
Commitment to Strengthen Indo-US Defence Ties
- Strategic Partnership: Both nations reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening the Indo-US defence partnership, recognizing the shared challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Focus on Regional Security: The discussions underscored the importance of ensuring regional security and global stability in the face of emerging threats.
The Role of the MCG
- Purpose: The MCG forum serves as a key platform for enhancing strategic and operational defence collaboration between India and the US.
- Long-term Goals: The MCG aims to build mutual defence capabilities, counter emerging threats, and ensure the security of both nations and the wider region.
PM-Vidyalaxmi Scheme
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the PM Vidyalaxmi scheme to provide financial assistance to meritorious students for higher education.
- Objective: The scheme aims to ensure that financial constraints do not hinder students from pursuing quality higher education.
Key Features of the scheme:
- Eligibility:
- Students admitted to top 860 Quality Higher Education Institutions (QHEIs) are eligible.
- Includes both government and private institutions, as per the NIRF (National Institutional Ranking Framework) rankings.
- Loan Provision:
- Collateral-free and guarantor-free education loans for tuition fees and other course-related expenses.
- Loans up to ?7.5 lakhs will have a 75% credit guarantee from the government to encourage banks to offer loans.
- Interest Subvention:
- For students with an annual family income of up to ?8 lakhs (and not eligible for other scholarships or schemes), a 3% interest subvention will be provided on loans up to ?10 lakhs.
- This subvention applies during the moratorium period (when repayment is deferred).
- Preference for interest subvention is given to students in technical/professional courses and those from government institutions.
- Target Beneficiaries:
- Around 22 lakh students are expected to benefit from the scheme annually.
- The government has allocated ?3,600 crore for the period 2024-2025 to 2030-2031, with 7 lakh fresh students anticipated to receive the benefit each year.
- Digital Process:
- A unified “PM-Vidyalaxmi” portal will allow students to apply for loans and interest subvention in a simplified, transparent, and digital manner.
- Payment Method:
- Interest subvention will be paid via E-vouchers or Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) wallets.
Loan Product Features
- Collateral-free & Guarantor-free: Loans will be accessible without the need for collateral or a guarantor.
- Loan Coverage:
- The scheme will cover full tuition fees and other related expenses.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Students enrolled in NIRF top 100 HEIs, state institutions ranked 101-200, and central government institutions are eligible.
- The list of eligible institutions will be updated annually based on the latest NIRF rankings.
Government's Commitment
- The scheme is a part of the National Education Policy 2020’s vision to enhance access to quality education through financial support.
- Additional Support:
- It complements the existing Central Sector Interest Subsidy (CSIS) and Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Education Loans (CGFSEL) under PM-USP.
- The CSIS scheme provides full interest subvention for students with an annual family income of up to ?4.5 lakhs, pursuing technical/professional courses.
India-Algeria Strengthen Defence Ties

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of India recently visited Algeria, culminating in the signing of a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defence cooperation.
- Objective: The MoU aims to strengthen the strategic and military ties between India and Algeria.
Recent Developments in India-Algeria Relations
- Important Visit: The CDS’s visit coincided with Algeria’s 70th anniversary of its revolution, celebrated on November 1st, with military parades and ceremonies highlighting Algeria’s historical and political legacy.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India re-established its defence wing in Algeria, and Algeria reciprocated by considering the establishment of its defence wing in India.
- India emphasized its role as a “Vishwa Bandhu” (global partner) and offered to share defence expertise and experiences with Algeria.
- Strategic Discussion: The MoU aims to enhance mutual understanding, laying the foundation for long-term defence collaboration across multiple sectors, including manufacturing under India’s 'Make in India' and 'Make for the World' initiatives.
- Global Peace Support: CDS reiterated India’s commitment to peaceful conflict resolution and expressed support for Algeria’s defence interests.
Significant Areas of India-Algeria Relationship
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India and Algeria established diplomatic ties in July 1962, the same year Algeria gained independence from French colonial rule.
- India supported Algeria's liberation movement and both countries have maintained close ties as part of the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Trade peaked at USD 2.9 billion in 2018 but dropped to USD 1.5 billion by 2021 due to COVID-19 and Algeria’s import restrictions.
- Trade rebounded in 2022, increasing by 24% to USD 2.1 billion.
- Exports from India (2023-24): Rice, pharmaceuticals, granite.
- Imports from Algeria: Petroleum oils, LNG, calcium phosphates.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- 2015 MoU: Between All India Radio (AIR) and Algerian National Radio for cooperation in broadcasting.
- 2018 Space Cooperation Agreement: Focuses on satellite technology for applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Visa Waiver Agreement (2021): Diplomatic and official passport holders are exempt from visa requirements.
- Cultural Engagement:
- International Day of Yoga (2024): Celebrated in Algeria at the Jardin d’Essai du Hamma, attracting over 300 participants.
- Space Cooperation:
- The 2018 India-Algeria Space Cooperation Agreement focuses on joint space science, technology, and applications.
- India has launched four Algerian satellites (2016), and the 2022 Joint Committee Meeting expanded satellite capacity building efforts.
- Algeria’s space agency has engaged with ISRO on satellite applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Indian Community in Algeria:
- Approximately 3,800 Indians live in Algeria, working in various sectors, including technical and semi-skilled roles.
- The community includes 13 Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), 10 Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and 15 Indian students.
Minuteman III ICBM

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The U.S. Army is scheduled to test launch a Minuteman III ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile) after the closure of voting on Election Day.
Missile Features
- Speed: Hypersonic, capable of reaching speeds up to 15,000 mph (Mach 23).
- Range: 13,000 km.
- Payload: Currently carries one nuclear warhead (as per arms control agreements with Russia), but originally designed for multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs).
- Launch Time: Extremely fast, enabling near-instant global retaliation capabilities.
- Testing Reliability: Nearly 100% success rate in tests, with backup airborne launch controllers to ensure continuity of the retaliatory strike capability.
- Length: 18.2 meters.
- Diameter: 1.85 meters.
- Launch Weight: 34,467 kg.
- Type: Three-stage, solid-fuel missile.
Strategic Significance
- Land-Based Nuclear Deterrent: The Minuteman III is a key component of the U.S. nuclear triad, which includes land-based missiles, submarine-launched missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The Sentinel weapon system (modernized Minuteman III) is viewed as the most cost-effective option for maintaining the land-based leg of U.S. nuclear deterrence until the planned Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD) system replaces it in 2029.
- Global Reach: The missile can strike any target worldwide within minutes, demonstrating U.S. nuclear reach and power projection.
Tumaini Festival

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Tumaini Festival is held annually in the Dzaleka Refugee Camp in Malawi, one of the world’s few music festivals hosted within a refugee camp. It brings together refugees and locals for cultural exchange, showcasing music, art, and crafts.
- Dates: The festival runs from Thursday to Saturday each year, typically in November.
- Founded: In 2014 by Congolese poet Menes La Plume.
Festival Highlights:
- The festival features performances from a diverse range of artists, including refugees and local Malawians, as well as artists from South Africa, Zimbabwe, and beyond.
- In 2024, performances included Jetu, a 72-year-old singer, and Vankson Boy V, a Congolese refugee, alongside other acts like Maveriq Mavo from South Africa.
- The festival aims to:
- Celebrate cultural exchange and community solidarity between refugees and locals.
- Humanize the refugee experience by allowing refugees and locals to share common experiences and celebrate cultural diversity.
- Challenge stereotypes by showing refugees as people with the same aspirations, talents, and desires as locals.
Significance of Dzaleka Refugee Camp:
- Location: Situated near Lilongwe, Malawi, Dzaleka was originally a prison before becoming a refugee camp in 1994.
- Capacity: Initially designed for 10,000 refugees, the camp now hosts over 60,000 individuals from countries like Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- Role: Dzaleka has evolved into a hub for humanitarian aid, cultural exchange, and empowerment of its residents.
PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
The National Achievement Survey (NAS), a nationwide survey meant to assess students’ learning progress, will be held on December 4 this year under a new name – PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024. This year’s assessment involves a few changes from the last round in 2021.
Overview of PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024:
- New Name: The National Achievement Survey (NAS) is now rebranded as the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024.
- Date: The survey will be held on December 4, 2024.
- Purpose: To assess students’ learning achievements across India.
- Organizing Bodies: Spearheaded by NCERT and CBSE.
What Does the Survey Assess?
- Assessment Focus: Evaluates students’ learning outcomes in various subjects.
- Survey Methodology: Uses multiple-choice questions to assess a sample of students.
- Target Groups: Students from government, government-aided, and private schools across every district in India.
History of NAS and PARAKH:
- NAS History: Conducted every three years since 2001 to capture learning progress.
- Involvement of Classes:
- 2001-2014: Included Classes 3, 5, and 8.
- 2014-15: Class 10 was introduced.
- 2017 and 2021: Covered Classes 3, 5, 8, and 10.
- Report Cards: Provides national, state, and district-level performance data.
Changes in 2024 Survey (PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan):
- Targeted Classes:
- Class 3 (End of foundational stage)
- Class 6 (End of preparatory stage)
- Class 9 (End of middle stage)
- Exclusion of Class 10: Unlike previous years, Class 10 students are not part of this year's assessment.
- Subjects Assessed:
- Class 3 & 6: Language, Mathematics, and The World Around Us (Concepts of Science, Social Science, and Environmental Education).
- Class 9: Language, Mathematics, Science, and Social Science.
Alignment with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
- NEP Structure: Aligns with the NEP 2020 framework, categorizing educational stages:
- Class 1-2: Foundational stage
- Class 3-5: Preparatory stage
- Class 6-8: Middle stage
- Class 9-12: Secondary stage
- The shift to Class 6 and 9 for this year’s survey matches the NEP's stage-wise educational framework.
Key Differences in 2024 Assessment:
- Survey Scale: In 2024, 75,565 schools and 22.9 lakh students from 782 districts will participate.
- 2021 Assessment Data:
- The 2021 survey revealed a drop in learning outcomes post-COVID-19.
- Class 3 students showed a performance below the national average in all states.
- Class 5: Only Punjab and Rajasthan had scores above the national average.
PARAKH's Role:
- PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) was established in 2023 as the National Assessment Centre to oversee such achievement surveys.
- Mandate: One of PARAKH’s primary roles is to organize national surveys like the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan.
Significance of the Survey:
- Data Utilization: The survey helps in shaping educational policies based on real-time data on student learning levels.
- Competency-Based Assessment: This year’s survey is focused on competency-based assessments, aligning with the goals of NEP 2020.
- Policy and Planning: The data helps in designing interventions to address regional or subject-wise disparities in education quality.
Hwasong-19

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- North Korea recently announced the successful test-firing of its latest intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), the ‘Hwasong-19’.
- Claims by North Korea: The missile was described as ‘the world’s strongest strategic missile’ and a ‘perfected weapon system’ by North Korean state media.
Key Features of the Hwasong-19:
- Solid-Fuel Propulsion: The Hwasong-19 reportedly uses solid-fuel propulsion, which enables quicker launches and greater secrecy. This contrasts with liquid-fuel missiles, which take longer to prepare and are more visible.
- Enhanced Performance: The missile is said to have improved altitude and flight duration compared to previous North Korean ICBMs, marking significant progress in missile technology.
- Size: The Hwasong-19 is estimated to be 28 meters long (92 feet), which is notably larger than many other ICBMs, including those from the U.S. and Russia, which are typically under 20 meters (66 feet).
Strategic Implications:
- Reach and Targeting: The Hwasong-19 is believed to have a range of over 13,000 kilometers, which is sufficient to target the U.S. mainland, signaling a significant advancement in North Korea’s missile capabilities.
- Nuclear Capability: While specific details on the missile’s payload remain undisclosed, the Hwasong-19 could potentially be equipped with a nuclear warhead, enhancing North Korea's strategic deterrence.
Impact on Regional and Global Security:
- US-North Korea Tensions: The launch occurred against the backdrop of ongoing U.S.-North Korea tensions, particularly over North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs. The missile could potentially alter the regional security dynamics, especially in East Asia.
What is an ICBM?
- ICBM Definition: An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range missile capable of carrying nuclear warheads (or other payloads) across continents.
- Range and Speed: ICBMs typically have a minimum range of 5,500 km (3,400 miles), with some capable of reaching up to 16,000 km or more, making them far faster and more capable than other ballistic missiles.
- Launch Mechanism: ICBMs are launched from land or submarine platforms, traveling through space before re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere and targeting distant objectives.
- Comparison with India's Agni-V: India’s Agni-V ICBM, which has a range of over 5,000 km, is often compared to North Korea’s missile systems.
Asset Recovery Interagency Network–Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP)

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- India, represented by the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), has joined the Steering Committee of the Asset Recovery Interagency Network-Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP).
- Leadership Role: India will assume the presidency of ARIN-AP and host the Annual General Meeting (AGM) in 2026, providing a platform for global cooperation in asset recovery and tackling economic crimes.
ARIN-AP Overview:
- Establishment: ARIN-AP is a multi-agency network formed to address the proceeds of crime across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Network Goals: Its mission is to facilitate cross-border collaboration in the areas of asset tracing, freezing, and confiscation.
- Membership: ARIN-AP includes 28 member jurisdictions and 9 observers, and operates as a key component of the Global CARIN Network (Camden Asset Recovery Inter-Agency Network).
- Functioning: ARIN-AP operates through a network of contact points that enable intelligence exchange among member agencies, promoting effective communication and coordination for asset recovery.
Significance of ARIN-AP's Work:
- Combating Economic Crimes: ARIN-AP enhances the efforts of law enforcement agencies in tracing and recovering assets linked to criminal activities, including both movable and immovable assets.
- Informal Exchange of Intelligence: The network allows for the informal exchange of intelligence between agencies, which often accelerates the identification and recovery of proceeds of crime. This can later lead to formal actions through bilateral or multilateral agreements.
- Global Impact: With over 100 jurisdictions in the broader CARIN Network, ARIN-AP plays a key role in global efforts to combat fugitive economic offenders and illicit financial flows.
India’s Contribution and Alignment with G-20 Priorities:
- India’s Leadership: India’s presidency in ARIN-AP will enhance its leadership in asset recovery, facilitating closer cooperation with regional and international law enforcement agencies.
- G-20 Alignment: This role aligns with India’s priorities under the G-20 framework, particularly focusing on the Nine-Point Agenda aimed at tackling fugitive economic offenders and improving asset recovery mechanisms.
CRS Mobile App
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union Home Minister Amit Shah launched the Civil Registration System (CRS) mobile app.
- The app aims to integrate technology with governance by making the registration of births and deaths more accessible, seamless, and hassle-free.
Key Features of the App:
- Anytime, Anywhere Registration: Citizens can register births and deaths from anywhere and at any time, in their State’s official language.
- The app is designed to significantly reduce the time required for registration, making it more efficient and convenient for users.
Legal and Policy Background:
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Act, 2023 mandates that all births and deaths in India, occurring from October 1, 2023, must be digitally registered through the Centre’s portal: dc.crsorgi.gov.in.
- This move is part of the broader effort to digitize civil records and create a centralized database.
Benefits of Digital Registration:
- Digital Birth Certificates: The new system will issue digital birth certificates which will serve as a single document to prove the date of birth for various services, such as:
- Admission to educational institutions
- Applying for government jobs
- Marriage registration
- Centralized Database: The integration of birth and death data into a centralized database will help update critical records such as:
- National Population Register (NPR)
- Ration cards
- Property registration
- Electoral rolls
National Population Register (NPR) Integration:
- The data collected through the CRS app will assist in updating the National Population Register (NPR), which was first collected in 2010 and updated in 2015 through door-to-door enumeration.
- The NPR serves as the first step toward the creation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) under the Citizenship Act, aimed at identifying Indian citizens.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Brazilhas opted not to join China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), becoming the second BRICS country after India to reject the multi-billion-dollar infrastructure project.
- Brazil prefers to explore alternative ways to collaborate with Chinese investors without signing a formal treaty, aiming to avoid the perceived risks of the BRI.
BRICS and India’s Role:
- Brazil’s decision follows India’s long-standing opposition to the BRI, particularly due to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passing through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which India views as a violation of its sovereignty.
- India has consistently argued that BRI projects should adhere to international norms, good governance, and transparency, emphasizing that such initiatives should be financially sustainable and not lead to debt traps.
Brazil’s Broader Economic Strategy:
- Brazil aims to balance its relationship with China, which is a major economic partner, but without being bound by the BRI. This decision reflects broader concerns within Brazil about the long-term financial sustainability of BRI projects, especially after witnessing debt crises in other countries like Sri Lanka.
Global Context and the BRI's Impact:
- The BRI, launched by China in 2013, spans several infrastructure sectors and has expanded globally, but it has faced criticism for its potential to trap smaller nations in unsustainable debt.
- India and Brazil’s resistance to the BRI highlights growing skepticism among emerging economies about the long-term implications of joining China's flagship project.
New Disability Certificate Rules (RPwD Rules, 2024)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Rules, 2024, were amended by the Union Government in the wake of the Puja Khedkar controversy, where an IAS probationer was dismissed for alleged forgery in her disability and caste certificates.
- National Platform for the Rights of the Disabled (NPRD) has called for a rollback of the new rules, citing that they make the process of obtaining disability certificates more stringent and cumbersome.
Key Changes Under the New RPwD Rules, 2024
- Authority for Issuing Disability Certificates:
- Only a designated medical authority or a notified competent medical authority at the district level can issue disability certificates.
- NPRD had proposed that experts from non-profits also be authorized to carry out checks, but this suggestion was not accepted.
- Colour-Coded UDID Cards:
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- White (general disability)
- Yellow (moderate disability)
- Blue (severe disability with 80% or higher).
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- Mandatory Online Applications:
- Applicants are now required to apply for disability certificates online, which could be problematic for individuals who lack access to the internet, smartphones, or are digitally illiterate.
- The NPRD has urged the government to retain the option for in-person applications.
- Extended Time for Certificate Issuance:
- The new rules extend the time for issuing disability certificates from one month to three months.
- Reapplication Requirement:
- If there is no action taken on an application for two years, the applicant will have to reapply, which the NPRD considers unacceptable, as it punishes disabled individuals for system failures.
NPRD's Concerns
- Regressive and Burdensome:NPRD believes the amendments are regressive, adding more hurdles for genuine persons with disabilities to access certificates, which are crucial for identification and entitlement to services.
- Lack of Accountability:The NPRD argues that the rules do not address the systemic issues highlighted by the Puja Khedkar case, such as the lack of accountability at various levels in the certification process.
- Online Application Issues:Many people from the disabled community may struggle with technical jargon used in online applications and may not have the resources to complete the process digitally.
- Delay in Issuance:Extending the time for issuing certificates to three months could create delays for those in urgent need of certification for services or entitlements.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
United Nations Day 2024

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
United Nations Day is celebrated each year on October 24 to mark the anniversary of the UN Charter's entry into force, aiming to raise awareness about the goals and achievements of the international body.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Celebrates the anniversary of the UN Charter coming into effect on October 24, 1945, after World War II.
- Goal: Raise awareness about the UN’s objectives and accomplishments.
UN Charter Overview
- Signing & Implementation:
- Signed on June 26, 1945, in San Francisco.
- Came into effect on October 24, 1945.
- India ratified the UN Charter on October 30, 1945.
- Predecessor: The League of Nations, created in 1919 after WWI, aimed at promoting international cooperation and peace.
- Content:
- Foundational document of the UN, binding all member states.
- Establishes principles of international relations, including equality of nations and the prohibition of force between countries.
- Amended three times: 1963, 1965, and 1973.
UN's Core Objectives
- Peace and Security: Maintaining global peace and preventing conflicts.
- Humanitarian Aid: Providing assistance to those in need.
- Human Rights: Protecting and promoting human rights globally.
- International Law: Upholding the rule of law on the global stage.
Main Organs of the UN
- General Assembly (UNGA):
- Comprises all 193 Member States, each with one vote.
- Main policy-making body, addressing international issues covered by the UN Charter.
- Security Council (UNSC):
- Consists of 15 members (5 permanent, 10 elected for two-year terms).
- Permanent members: China, France, Russia, UK, USA.
- India has been elected to the UNSC eight times.
- Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC):
- Composed of 54 members elected by the General Assembly.
- Coordinates policy and addresses economic, social, and environmental issues.
- Trusteeship Council:
- Established to oversee trust territories transitioning to independence.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The only international court resolving disputes between UN member states.
- Handles contentious cases and provides advisory opinions.
- Secretariat:
- Led by the Secretary-General, appointed by the General Assembly based on Security Council recommendations.
- Acts as the chief administrative body of the UN.
Note: Most UN organs, including the UNGA, UNSC, ECOSOC, Trusteeship Council, and Secretariat, are based in New York, while the ICJ is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
Nobel Peace Prize 2024

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to Nihon Hidankyo, an organisation of survivors of the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings. In doing so, the Nobel Committee has highlighted the power of their testimonies and the need for disarmament.
Key Points about Nihon Hidankyo and the Hibakusha Movement
- Nihon Hidankyo:
- Established on August 10, 1956, as the nation-wide organization for survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings.
- Focuses on the welfare of Hibakusha (A-bomb survivors), promoting nuclear disarmament, and advocating for compensation for victims.
- Works to share the stories and experiences of Hibakusha, both within Japan and globally.
- Hibakusha (Bomb-affected People):
- Survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- Played a pivotal role in the global nuclear disarmament movement.
- Their testimonies have helped create the "nuclear taboo," ensuring nuclear weapons have not been used since 1945.
Role of Hibakusha in Nuclear Disarmament
- Global Impact:
- The bombings ignited a global movement for nuclear disarmament.
- Hibakusha's advocacy has highlighted the human cost of nuclear weapons, shaping international policy and promoting the nuclear taboo.
- Nihon Hidankyo’s Advocacy:
- The organization has been instrumental in documenting the effects of nuclear weapons and advocating for their abolition.
- Testimonies from Hibakusha have been key in raising awareness about the catastrophic humanitarian consequences of nuclear warfare.
Nobel Committee's Recognition and Current Nuclear Challenges
- Recognition of Hibakusha's Work:
- The Nobel Committee awarded the Peace Prize to Nihon Hidankyo for its role in promoting nuclear disarmament and for contributing to the nuclear taboo.
- The nuclear taboo is under increasing pressure as new countries seek nuclear weapons and existing powers modernize their arsenals.
- Current Nuclear Landscape:
- The US and Russia continue to maintain large nuclear stockpiles, with the US planning to spend over $1 trillion on upgrading its nuclear capabilities by the 2040s.
- New Threats: Geopolitical tensions, including regional conflicts, raise concerns about the resurgence of nuclear arms races.
Previous Nobel Peace Prizes for Disarmament
- Past Laureates:
- 1974: Former Japanese Prime Minister Eisaku Sato awarded for Japan's commitment to non-nuclear weapons policy.
- 2017: International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN) awarded for its efforts to draw attention to the humanitarian consequences of nuclear weapons and push for a nuclear ban treaty.
- Link with Alfred Nobel’s Vision:
- Alfred Nobel, the founder of the Peace Prize, made his fortune with the invention of dynamite and sought to use his wealth to promote peace, especially through disarmament.
PM Young Achievers’ Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM YASASVI)

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
With a vision of "Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas", the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has implemented the PM Young Achievers Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM-YASASVI).
- Objective of PM-YASASVI:
- The scheme aims to provide financial support and educational opportunities to students from Other Backward Classes (OBC), Economically Backward Classes (EBC), and Denotified Tribes (DNT).
- The goal is to help these students overcome financial barriers and pursue quality education, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
- Consolidation of Earlier Schemes:
- PM-YASASVI integrates multiple previous scholarship schemes:
- Dr. Ambedkar Post-Matric Scholarship for EBCs.
- Dr. Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs.
- This consolidation aims to streamline the process and increase the impact on vulnerable groups.
- Key Components of the Scheme:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: For students in Class 9-10 with annual family income below ?2.5 lakh. Provides ?4,000 annually.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: For students pursuing higher education, with academic allowances ranging from ?5,000 to ?20,000 based on course type.
- Top Class School Education: For meritorious students, offering ?1.25 lakh annually for students from OBC, EBC, and DNT categories in Classes 9-12.
- Top Class College Education: Covers tuition, living expenses, and educational materials for students in top institutions.
- Construction of Hostels for OBC Boys and Girls: Provides hostel facilities to socially and educationally backward students near government institutions.
- Scope and Financial Allocation (2023-24):
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: ?32.44 crore allocated to states and UTs for the year 2023-24, benefiting 19.86 lakh students.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: ?387.27 crore allocated for the year, benefiting 27.97 lakh students.
- Top Class School Education: ?6.55 crore for 2,602 students.
- Top Class College Education: ?111.18 crore for 4,762 students.
- Hostel Construction: ?14.30 crore allocated for the construction of hostels, accommodating 1,146 students.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Assistance: Reduces the financial burden on students from marginalized communities, enabling them to continue their education without financial stress.
- Inclusive Education: Supports students from disadvantaged backgrounds, ensuring that they can access quality education from school through to higher education.
- Promotion of Merit: Focuses on meritorious students, ensuring that academic excellence is supported at all levels, from school to top-class institutions.
- Selection Process:
- The YASASVI Entrance Test (YET) is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for candidate selection under the scheme.
- Eligible students must appear for this test, and the results determine scholarship awards.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The scheme is open to OBC, EBC, and DNT students with a family income not exceeding ?2.5 lakh annually.
- Additional specific eligibility criteria may apply for different scholarships under the scheme.
- Application Process:
- Interested students can apply for scholarships via the National Scholarship Portal (scholarships.gov.in), which is the official platform for application submission.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
India-Pakistan Kartarpur Corridor Agreement Renewal
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- India and Pakistan have extended the Sri Kartarpur Sahib Corridor Agreement for another five years (until 2029).
- Purpose: The extension ensures uninterrupted operation of the corridor, allowing Indian pilgrims to visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan.
- Significance: The extension reflects continued cooperation between India and Pakistan, with potential implications for improving bilateral relations.
Background of Kartarpur Corridor:
- Inception: The agreement was first signed on October 24, 2019, to allow visa-free access for Indian pilgrims to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur near Narowal in Pakistan.
- Pilgrimage Details:
- Eligibility: Indian nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders can visit the gurdwara on a daily basis.
- Return on Same Day: Pilgrims must return on the same day.
- No Religious Restrictions: Pilgrims of any faith can use the corridor.
- Capacity: Up to 5,000 pilgrims per day can visit the gurdwara.
- Historical Importance: The corridor facilitates the Sikh community's access to a key religious site, located just 4.7 km from the India-Pakistan border.
- Service Charge Dispute:
- Pakistan's Service Fee: Pakistan continues to charge a $20 service fee (approx. ?1,680) per pilgrim, which India has consistently urged Pakistan to waive.
- Pakistan’s Justification: Pakistan maintains the fee to cover the $17 million spent on refurbishing the gurdwara and developing infrastructure for the corridor.
- Geopolitical Context and Timing:
- Recent Developments: The agreement renewal follows External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to Pakistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Government meeting.
- Improved Bilateral Relations: Jaishankar’s visit marked the first visit by an Indian foreign minister to Pakistan in nearly nine years, signaling potential thaw in relations, despite the lack of formal bilateral dialogue.
- Strategic and Religious Importance:
- Religious Diplomacy: The Kartarpur Corridor is viewed as a confidence-building measure and a symbol of religious diplomacy, particularly for the Sikh community.
- Historical Legacy: The corridor links Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan to Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak in India, facilitating access to a site of immense religious significance for Sikhs.
- Implications for India-Pakistan Relations:
- No Formal Bilateral Talks: Despite the successful renewal of the agreement, formal talks between India and Pakistan remain suspended, particularly after India’s revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir in 2019, which led to a diplomatic freeze.
- Pakistan's Diplomatic Stance: Pakistan had recalled its high commissioner from India in August 2019, and tensions have remained high since then.
- Potential for Future Engagement:
- Diplomatic Channels Opened: The renewal of the Kartarpur agreement and Jaishankar’s visit suggest that diplomatic channels are still open, and there may be scope for further engagement if both sides take steps to address outstanding issues.
Z-Morh Tunnel Project in Kashmir

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Seven people were killed in Jammu and Kashmir when suspected militants targeted the workers of infrastructure company APCO Infratech, which is constructing the Z-Morh tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway. This is the first militant attack on a key infrastructure project in Jammu and Kashmir. In the past, militants have not targeted such infrastructure projects in the region.
What is the Z-Morh Tunnel?
- Length: 6.4 kilometers
- Connection: Links Sonamarg (a popular tourist destination) with Kangan town in central Kashmir’s Ganderbal district.
- Construction Site: Located near Gagangir village, ahead of Sonamarg.
- Naming: The tunnel gets its name from the Z-shaped road near the construction site.
Importance of the Z-Morh Tunnel
- All-Weather Connectivity: The tunnel is crucial for year-round access to Sonamarg, particularly in the winter when the road is often blocked by snow avalanches.
- Location: Situated at 8,500 feet above sea level, the tunnel provides a safe, all-weather route for tourists and locals, especially during winter months when access to Sonamarg is typically limited.
Strategic Importance
- Part of Zojila Tunnel Project:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is integral to the larger Zojila tunnel project, which aims to provide all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh.
- The Zojila Tunnel, under construction at an altitude of around 12,000 feet, will connect Sonamarg (Kashmir) to Drass (Ladakh) and is expected to be completed by December 2026.
- Military and Strategic Significance:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is crucial for rapid military mobilization between Srinagar, Kargil, Leh, and Drass regions.
- It ensures quick access for military personnel to the Ladakh border, particularly in areas of heightened security like Siachen Glacier and the Turtuk sub-sector (on the Pakistan border).
- The tunnel will reduce dependence on air transport for troop and supply movements to forward areas, leading to cost savings and extended aircraft lifespan.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
Russia's Izdeliye 305 (LMUR) Missile

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
Russian state corporation Rostec has claimed that its Light Multipurpose Guided Rocket, also known as Izdeliye 305 or “Product 305,” has demonstrated remarkable resistance to jamming and interference on the battlefield in Ukraine.
Missile Overview
- Name: Izdeliye 305 (Product 305), also known as LMUR (Light Multipurpose Guided Rocket)
- Primary Use: Deployed by Russia’s Mi-28NM and Ka-52M attack helicopters.
- Function: Designed to target and destroy armored vehicles, fortifications, pillboxes, and watercraft with high precision.
Key Features
- Sniper-Like Accuracy: The missile is touted for its exceptional precision in targeting, making it one of Russia’s most successful guided weapons.
- Resistance to Jamming: The missile’s control channel has shown remarkable resistance to enemy electronic warfare (EW) systems, making it effective even in contested environments.
- No instances of the missile's control channel being suppressed during the ongoing Ukraine conflict.
- Versatile Guidance Systems: The missile operates in several modes:
- Fire-and-Forget: The missile locks onto the target before launch and operates autonomously post-launch.
- Remote Control Mode: The operator guides the missile to the target after it locks onto coordinates and transmits live imagery to the operator’s screen.
- Inertial + Homing Mode: The missile initially flies inertially toward target coordinates, then activates its homing system for final target guidance.
- High Explosive Warhead: Equipped with a 25-kg high-explosive fragmentation warhead, the LMUR is effective against a variety of targets.
Technical Specifications
- Weight: 105 kg (231 lbs)
- Range: Up to 9 miles, double the range of traditional Russian anti-tank missiles, providing the tactical advantage of engaging from beyond line-of-sight.
- Warhead: 25 kg high-explosive fragmentation for effective target destruction.
- Guidance: A combination of inertial navigation, satellite positioning, thermal imaging, and a two-way communication channel for real-time control.
Deployment and Use
- Helicopter Integration: Primarily used on Mi-28NM and Ka-52M attack helicopters, and also on the Mi-8MNP-2 for special operations.
- Combat Experience:
- The missile was actively used in Ukraine where it played a key role in countering Ukraine’s NATO-backed counteroffensive operations.
- It was previously tested in Syria against various targets, showcasing its capabilities before full operational deployment in 2022.
Significance in Ukraine Conflict
- Impact on Ukrainian Forces: The missile’s long range and resistance to EW have made it a critical component of Russia’s aerial operations, hampering Ukraine’s battlefield progress, particularly against heavily fortified positions and NATO-backed counteroffensive efforts.
Strategic Advantage: The missile’s ability to engage targets from a distance while evading jamming attempts gives it a significant edge in modern warfare.
National Water Awards 2023

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
The Hon’ble President of India Smt. Droupadi Murmu will confer the 5th National Water Awards 2023 on October 22nd 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
Organizing Body:
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Department: Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR)
- Purpose: To recognize and honor individuals, organizations, and bodies that have made significant contributions to water conservation and management.
Award Categories
- Best State
- Best District
- Best Village Panchayat
- Best Urban Local Body
- Best School or College
- Best Industry
- Best Water User Association
- Best Institution (other than school or college)
- Best Civil Society Organization
Winners
- Best State:
- 1st Prize: Odisha
- 2nd Prize: Uttar Pradesh
- 3rd Prize (joint): Gujarat & Puducherry
- Other Awards: Winners in the remaining categories have been recognized, with citations, trophies, and cash prizes provided in certain categories.
Objectives of the National Water Awards
- Promote Water Conservation: Raise awareness about the importance of water and encourage effective water usage practices.
- Recognize Efforts: Celebrate the work of individuals, institutions, and organizations contributing to the government’s vision of a ‘Jal Samridh Bharat’ (Water-rich India).
- National Campaign: Under the guidance of Hon’ble Prime Minister, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has been working to spread awareness on water management and conservation through extensive national campaigns.
History and Background
- The National Water Awards (NWAs) were launched in 2018 by the DoWR, RD & GR to foster awareness and action on water-related issues.
- Awards were given for 2019, 2020, and 2022, but there were no awards in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The awards aim to inspire best practices in water usage, conservation, and management across India, involving government bodies, industries, communities, and civil society.
Significance
- The National Water Awards serve as a platform to recognize the innovative initiatives taken by various stakeholders in addressing water challenges.
The awards contribute to furthering the government’s mission of achieving sustainable water management practices across the nation.
eShram-One Stop Solution

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
- The ‘eShram-One Stop Solution’ will be launched on 21 October 2024 by the Union Minister of Labour & Employment and Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Objective: To provide easy access to various social security and welfare schemes for unorganized workers in India.
Key Features
- Mediator Platform: The eShram-One Stop Solution will act as an intermediary to facilitate the integration of multiple government schemes for unorganized workers, ensuring efficient access to services and support.
- Information Integration: It will integrate data on beneficiaries across various social security and welfare programs meant for unorganized workers, providing a single point of access.
- Target Group: Aimed at unorganized workers, including daily wage earners, migrants, and others who do not have regular formal employment.
Benefits
- Awareness & Accessibility: The platform will make unorganized workers aware of various government schemes tailored to their needs, helping them access benefits more easily.
- Effective Scheme Implementation: The eShram-One Stop Solution will aid in the identification and implementation of welfare schemes for faster saturation and coverage.
Integration with Existing Schemes
- 12 Integrated Schemes: Currently, 12 social security schemes from different ministries/departments have already been mapped with eShram.
eShram’s Progress So Far
- Launch: eShram was launched on 26 August 2021.
- Achievements: Over 30 crore unorganized workers have been enrolled, highlighting the widespread impact and popularity of the initiative among the target population.
Naseem-Al-Bahr 2024

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise Naseem-Al-Bahr was held in Goa from October 2024.
Naseem-Al-Bahr Exercise Overview
- Indian and Omani Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand (warship) and Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft.
- Royal Navy of Oman: Vessel Al Seeb.
- Initiation: Launched in 1993, marking a long-standing strategic partnership between India and Oman.
- Structure: The exercise is conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional Interactions: Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), planning conferences.
- Social & Sports Engagements: Informal activities to foster mutual understanding.
- Sea Phase:
- Naval Operations:
- Gun firings at surface inflatable targets.
- Close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopter Operations: INS Trikand’s helicopter performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- Aircraft Support: Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data to enhance operational coordination.
- Naval Operations:
- Harbour Phase:
Key Highlights of the 2024 Exercise
- Interoperability: The exercise focused on improving operational coordination and enhancing mutual understanding of naval practices.
- Cohesion: The Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb to further strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthening Ties: Naseem-Al-Bahr reaffirms the strong strategic relationship between India and Oman.
- Regional Collaboration: This exercise exemplifies India's growing collaboration with like-minded nations in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Broader Defence Relations:
- Oman is the first GCC country to conduct such bilateral naval exercises with India.
- Both countries also engage in other defence exercises:
- Army: Al Najah.
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge.
Trade Relations Between India and Oman (2022):
- Oil: India is the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil exports, following China.
- Non-oil Exports: India is Oman's fourth-largest market for non-oil exports, after UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia.
- Imports: India is the second-largest source of Oman's imports, following the UAE.
- Ongoing Trade Agreement: Both nations are currently negotiating a trade agreement to further boost bilateral economic cooperation.
Musaned Digital Platform

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Saudi Arabia Launches Musaned Digital Platform to Ensure Wage Protection for Foreign Workers.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of Musaned:
- Musaned is a digital platform launched by Saudi Arabia to ensure wage protection and improve working conditions for foreign workers, particularly those in domestic (household) employment.
- The platform aims to safeguard workers' rights, create a stable working environment, and reduce illegal immigration.
- Coverage:
- The platform benefits foreign workers from 10 African countries (including Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya) and 9 Asian countries (including India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Sri Lanka).
- Key Features:
- Employment Contract Access: Workers can check and track their employment contracts and receive updates via the Musaned labour app.
- Financial Transaction Tracking: The platform monitors financial transactions between employers and foreign workers, ensuring employers meet their contractual obligations.
- Integration with Benefits: Musaned can be linked to contract insurance and health benefits, providing additional protection for workers.
- Objectives:
- Wage Protection: Ensures timely and fair wages for foreign workers.
- Human Rights Protection: Promotes human rights by holding employers accountable for fulfilling their obligations.
- Vision 2030 Alignment: Supports Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 by improving the work environment and contributing to legal labor migration.
- Impact:
- The platform is expected to help secure workers’ rights, especially for domestic workers, and provide a more transparent, accountable framework for employment relations in the country.
Musaned is a significant step by Saudi Arabia to enhance the security and welfare of foreign workers, aligning with the Kingdom's broader goals of economic reform and social development under Vision 2030. The platform will provide greater transparency, protect workers’ rights, and contribute to a more regulated and sustainable labor market.
Karmayogi Saptah – National Learning Week

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ‘Karmayogi Saptah’ - National Learning Week on 19th October at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Context:
- The National Learning Week is a key event in the ongoing Mission Karmayogi initiative, aimed at building a civil service rooted in Indian ethos with a global outlook.
- Objective:
- To promote capacity building for civil servants through competency-linked learning.
- To align civil servants with national goals and foster a "One Government" approach.
- About National Learning Week (NLW):
- Largest learning event for civil servants, focused on individual and organizational growth.
- Encourages lifelong learning and continuous professional development.
- Provides fresh impetus to the Mission Karmayogi initiative, launched in September 2020, aimed at a future-ready, citizen-centric civil service.
- Learning Targets for Karmayogis:
- Each civil servant (Karmayogi) must complete at least 4 hours of competency-linked learning during the week.
- Learning opportunities include:
- Role-based modules on iGOT (Integrated Government Online Training platform).
- Webinars, public lectures, and policy masterclasses by prominent experts.
- Focus on improving skills for citizen-centric service delivery.
- Workshops & Seminars:
- Ministries, departments, and organizations organized domain-specific workshops and seminars.
- The goal is to enhance skills and knowledge, fostering better public service delivery.
- Outcomes:
- Strengthened alignment of civil servants with national priorities and goals.
- Enhanced individual competencies to better address citizen needs.
- A stronger commitment to continuous learning within the civil service.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
The Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, hosted a two-day Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) knowledge sharing workshop in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Event Overview:
- Two-day workshop hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education.
- Focus areas: School-to-Work Transition and Strengthening the Assessment System.
- Key Objectives:
- To enhance school-to-work transitions.
- To discuss strengthening educational assessment systems.
- Align education with future workforce needs as per the National Education Policy 2020.
Day 1: School-to-Work Transition
Panel Discussions:
- Policy Frameworks:
- Role of National Education Policy 2020, National Curriculum Framework (NCF), and National Credit Framework (NCrF) in school-to-work transitions.
- Focus on integrating skill education into school curricula, fostering multidisciplinary learning, and continuous evaluation to meet industry standards.
- Emphasis on internships, apprenticeships, and flexible learning pathways.
- Curriculum Integration:
- Need for integrated efforts across departments and aligning curriculum with industry demands.
- Focus on strengthening 21st-century skills in CBSE schools.
- Career Counselling and Psychometric Analysis:
- Focus on using psychometric assessments for career counselling and preparing students for future work environments.
- Work-Based Learning:
- Discussed partnerships with industry for work-based learning.
- Effective collaborations between schools and industry for internships, placements, and best practices.
Day 2: Strengthening Assessment System
- Psychometric Analysis & Career Counselling:
- Smt. Idzes Angmo Kundan (Principal Secretary, Maharashtra) presented the 3 P approach to career choices: Personal Interest, Parental Approach, and Possible Opportunities.
- Enhancing Student Outcomes:
- Discussed improving student outcomes by strengthening assessment systems.
- Shared innovations in educational assessments.
- Highlighted innovative assessment practices for future education.
- VSK Implementation (Chhattisgarh):
- Discussed VSK modes, data analysis, and strategies for integrating assessment outcomes with learning objectives.
- Strengthening Assessment Cells:
- Advocated for the establishment of assessment cells.
- Discussed best practices and challenges in strengthening assessment cells across states.
International Abhidhamma Divas

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, International Abhidhamma Divas was celebrated at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, with PM Narendra Modi.
Key Details:
- India's Spiritual Legacy: Birthplace of Buddhism; site of Gautam Buddha's enlightenment.
- Sacred Sites: Veneration of locations like Bodh Gaya, symbolizing Buddha's journey and teachings.
- Core Teachings: Abhidhamma as a key philosophical component emphasizing mental discipline and self-awareness.
International Abhidhamma Divas
- Global Observation: Celebrates the significance of Abhidhamma in ethical conduct and mindfulness.
- Cultural Connection: Highlights India's role in preserving Buddhism and bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary practices.
Historical Background and Significance
- Commemoration: Marks Buddha’s descent from T?vati?sa to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur).
- Teaching Period: Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to deities for three months; linked to the end of the Rainy Retreat and the Pav?ra?? festival.
Teachings of Abhidhamma
- Systematic Analysis: Provides a detailed exploration of mind and matter, differing from Sutta Pi?aka.
- Specialized Vocabulary: Key terms include "citta" (consciousness), "cetasika" (mental factors), "r?pa" (materiality), and "nibb?na" (liberation).
- Textual Framework: Six core books of Abhidhamma Piñaka cover moral states, aggregates, and causal relationships.
- Key Treatise: The Paññh?na offers in-depth causal analysis, essential for practitioners’ understanding.
Modern Observance and Celebrations
- Significance of Pali: Recognition of Pali as a classical language; promoting India's Buddhist heritage.
- Participants: Gathering of ambassadors, monks, scholars from 14 countries; emphasizes Abhidhamma's relevance today.
- Program Highlights: Dhamma discourse, academic sessions on Abhidhamma’s significance, exhibitions on Pali's evolution and Buddha's teachings.
Classical Status of Pali Language
- Pali's Role: Sacred language for delivering Buddha's teachings; recognized as a Classical Language by India.
- Buddhist Canon: Major texts include the Tipitaka (Vinaya, Sutta, Abhidhamma Pitaka) and commentarial traditions.
- Literary Heritage: Jataka Kathas reflect shared moral values; status enhances Pali studies in education and research.
Significance
- Significance of Celebration: Abhidhamma Divas underscores efforts to preserve and promote Buddhism’s legacy.
- Revitalization of Buddhism: Fosters global engagement and appreciation for Buddha’s teachings, reaffirming India's role in Buddhist studies.
Colombo Security Conclave

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) reached a milestone on August 30, 2024 with India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Mauritius signing a Charter and a memorandum of understanding, for the establishment of the CSC secretariat.
Key Facts:
Background of CSC:
- Originally called the NSA Trilateral on Maritime Security, the CSC was established in 2011 among India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. The initiative aimed to bolster maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
Membership:
- The founding members include India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Mauritius joined in 2022, and Bangladesh became a member in 2024. Seychelles participates as an observer state.
Goals of CSC:
The CSC aims to foster cooperation in five main areas:
- Maritime safety and security
- Counterterrorism and prevention of radicalization
- Combating trafficking and transnational organized crime
- Cybersecurity and safeguarding critical infrastructure
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
Defence Exercises:
- In November 2021, India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives held Exercise Dosti XV in the Maldives, marking their first joint military exercise in the Arabian Sea under the CSC framework.
UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Kingdom said it would cede sovereignty of the strategically important Chagos Islands to Mauritius, calling it a “historic political agreement”. The UK has long controlled Chagos and the Diego Garcia military base located there, jointly operating it with the United States.
Background of the Chagos Archipelago
Historical Context
- The Chagos archipelago consists of 58 islands located about 500 km south of the Maldives.
- Initially uninhabited, the islands were populated in the late 18th century through the importation of slave labor.
- The islands were ceded to Britain from France in 1814, and in 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which includes Chagos.
Controversy Over Sovereignty
- Mauritius, a former British colony, claims that the detachment of Chagos from its territory during its independence in 1968 was illegal.
- The UK compensated Mauritius with a grant but retained control, establishing a military base on Diego Garcia.
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
Military Significance
- Diego Garcia has been a crucial U.S. military base since its operational status began in 1986.
- It played a key role in U.S. military operations during conflicts in the Gulf, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The base enables rapid response to crises and supports regional security, especially in light of U.S. interests in monitoring key trade routes like the Malacca Strait.
Geopolitical Implications
- The presence of the U.S. military in the Indian Ocean is vital for countering security threats, particularly regarding China's growing influence.
Recent Developments: The UK-Mauritius Agreement
Key Features of the Treaty
- On October 3, 2023, the UK agreed to cede sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, marking a significant political shift.
- The treaty allows Mauritius to resettle Chagossians (excluding Diego Garcia) and establishes a trust fund for their benefit.
- Despite this, the UK retains control over Diego Garcia for an initial period of 99 years.
Implications of the Agreement
- The resolution of the sovereignty issue may strengthen Western commitments to a stable and free Indo-Pacific region.
- If unresolved, tensions could push Mauritius toward seeking alliances with alternative powers like China.
India’s Position and Interests
Support for Mauritius
- India has historically supported Mauritius in its claims over Chagos, reflecting its stance against colonial legacies.
- In 2019, India voted in favor of Mauritius at the UN General Assembly regarding the Chagos dispute.
Strategic Partnerships
- With increasing Chinese assertiveness in the Indian Ocean, India has been strengthening its ties with Mauritius.
- Recent initiatives include the inauguration of an India-built airstrip and jetty in Agaléga, enhancing connectivity and support for Mauritius.
Conclusion
The UK-Mauritius treaty over the Chagos Archipelago marks a significant turning point in colonial legacies and geopolitical alliances in the Indian Ocean. For India, supporting Mauritius aligns with its broader strategic interests and enhances its influence in a region marked by competing global powers. As the dynamics evolve, India's role in fostering regional stability and partnerships will be crucial.
India’s Tripartite Agreement

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Nepal, India, and Bangladesh have signed a tripartite agreement to facilitate cross-border electricity trade, enabling Nepal to export surplus electricity to Bangladesh via India.
Key Details of the Agreement
- Export Period: The agreement allows for electricity exports from June 15 to November 15 each year.
- Initial Export Volume: In the first phase, Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Electricity Rate: The fixed rate per unit of electricity is set at 6.4 cents.
- Projected Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn approximately $9.2 million annually from this trade.
This agreement aims to enhance regional cooperation in energy trade and support sustainable development in the participating countries.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar will attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Heads of Government meeting in Islamabad on October 15-16, 2023.
- This marks the first visit by an Indian External Affairs Minister to Pakistan since Sushma Swaraj in 2015.
Context of the Visit:
- The visit is primarily for the SCO meeting, reflecting India's focus on regional cooperation mechanisms.
- No bilateral meetings have been scheduled as of now, although Jaishankar's presence is based on "reciprocity" following Pakistan's participation in an earlier SCO meeting in India.
SCO Overview:
- Established on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai; evolved from the "Shanghai Five" formed in 1996.
- Original members included China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and later Uzbekistan.
- Current members: India, Pakistan, Iran, and others, with Afghanistan and Mongolia holding Observer Status.
Significance of the SCO:
- Focuses on security cooperation, primarily among Asian nations.
- Seen as an alternative to Western international frameworks, especially with heavyweights like Russia and China positioning against US influence.
- India's inclusion alongside Pakistan in 2017 reflects the geopolitical jostling between Russia and China.
Geopolitical Dynamics:
- While SCO promotes cooperation, underlying tensions remain, particularly between India and Pakistan, and India and China.
- The organization has limited tangible outcomes due to member states' rivalries and differing interests.
India's Objectives in SCO:
- Provides a platform for enhancing relations with Central Asian countries, addressing common security concerns.
- Involves participation in the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) to combat terrorism and drug trafficking.
India-Pakistan Relations:
- Jaishankar's visit is seen in light of ongoing tensions; India shares difficult relations with both China and Pakistan.
- India canceled a summit under its presidency last year, opting for a virtual format instead.
Implications for Regional Politics:
- The visit comes shortly after the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections, with potential implications for India-Pakistan ties.
- Despite attending the SCO meeting, there is little expectation of progress in the India-Pakistan peace process.
- Recent statements from the Indian government criticize Pakistan for hosting wanted individuals, reflecting ongoing diplomatic tensions.
Strategic Importance:
- Participation in SCO allows India to engage with key regional players, including Russia, China, and Central Asian leaders.
- The meeting serves as preparation for India's participation in upcoming BRICS discussions, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these groupings.
Co-district Initiative

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
Assam has launched an innovative administrative initiative by inaugurating 21 'co-districts' as part of its Phase 1 rollout, which began on Friday and will extend into Saturday, ultimately introducing a total of 39 co-districts. This new structure replaces the previous system of 24 civil sub-divisions, aiming to bring governance closer to the citizens.
About the Co-District Initiative
- Structure: Co-districts serve as smaller administrative units within the larger district framework, each headed by an Assistant District Commissioner.
- Objective: This unique initiative, the first of its kind in India, seeks to enhance accessibility to governance and address administrative challenges faced by district administrations.
- Scope: The government plans to establish co-district offices in all 126 assembly constituencies in Assam.
Functions and Powers
The co-districts will handle a variety of important functions, including:
- Land Revenue Matters: Managing land-related issues and revenue collection.
- Development and Welfare Work: Overseeing development projects and welfare programs.
- Excise and Disaster Management: Addressing excise-related matters and coordinating disaster response efforts.
- Administrative Control: Co-districts will have authority over all departmental activities within their jurisdiction.
- Magisterial Powers: Commissioners will be empowered to issue permissions for events and manage other administrative tasks.
- Routine Administrative Tasks: Responsibilities include issuing ration cards, caste certificates, and land sale permissions.
India-U.S. MoU on Critical Minerals Supply Chains

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The sixth Commercial Dialogue took place in Washington on October 4, 2024, led by Indian Union Minister of Commerce Piyush Goyal and U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo.
- MoU Signing: A day prior, the leaders signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) aimed at expanding and diversifying critical minerals supply chains to enhance resilience.
- Focus Areas:
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Exploration
- Extraction
- Processing and refining
- Recycling and recovery
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Context: This agreement follows China's export restrictions on gallium and germanium, critical for the semiconductor industry, and its ban on technology related to rare earth magnets and critical materials extraction.
- Strategic Goals:
- Promote open supply chains, technology development, and investment flows for green energy.
- Explore collaboration with other mineral-rich countries, particularly in Africa and South America.
- Progress on Semiconductor Supply Chains:
- Continued efforts to establish resilient semiconductor supply chains since the previous MoU.
- Completion of a "readiness assessment" by the U.S. Semiconductor Industry Association and India Electronics Semiconductor Association.
- Commitment to foster investments, joint ventures, and technology partnerships.
- Innovation Handshake: Success of roundtables in San Francisco and New Delhi aimed at enhancing innovation ecosystems and startup collaboration.
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership: Discussions from the EIN Roundtable in March 2024 informed the U.S.-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership meeting.
- IPEF Supply Chain Agreement: Significant progress noted in the IPEF ministerial meeting, focusing on semiconductors, chemicals, and critical minerals, particularly batteries and healthcare products.
- Future Collaborations:
- Focus on expanding U.S. Department of Commerce presence in India with approximately 70 Foreign Commercial Service staff.
- Plans for a U.S. trade mission to India in March 2025 aimed at supporting U.S. SMEs owned by underserved communities.
- Domestic Solar Manufacturing Protection: India reinstated the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) order to protect local solar PV module production against cheaper imports from China.
- Economic Context:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights China's expanding manufacturing trade surplus and its restrictive actions affecting India's access to solar equipment.
- India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes have invested over $4.5 billion to bolster clean energy manufacturing but require additional policies to safeguard these investments.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
Colombo Security Conclave (CSC)

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) recently marked a significant milestone with the signing of the Charter and the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the establishment of its Secretariat in Colombo. This initiative aims to strengthen regional security collaboration among member states.
Key Features of the Colombo Security Conclave
- Member States: The CSC comprises five member countries:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka
- Maldives
- Mauritius
Additionally, Seychelles participates as an observer nation.
- Core Objectives: The primary goal of the CSC is to enhance regional security by addressing transnational threats and challenges that are common concerns for member states. This includes a collaborative approach to ensure stability and safety in the region.
Origin and Evolution
- The CSC originated as the Trilateral for Maritime Security Cooperation, established through trilateral meetings among National Security Advisors (NSAs) and Deputy NSAs from India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka starting in 2011.
- The initiative faced a setback after 2014 due to heightened tensions between India and the Maldives.
- It was revived and rebranded as the CSC in 2020, expanding its membership to include Mauritius and, more recently, Bangladesh.
Structure and Cooperation
- The conclave facilitates interactions among NSAs and Deputy NSAs of member countries, fostering dialogue and cooperation on security matters.
- Cooperation under the CSC is organized around five key pillars:
- Maritime Safety and Security
- Countering Terrorism and Radicalization
- Combating Trafficking and Transnational Organized Crime
- Cybersecurity and Protection of Critical Infrastructure
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief
Permanent Secretariat
- The establishment of a permanent Secretariat in Colombo is expected to enhance coordination and streamline operations among member states, bolstering the efficacy of the CSC in addressing regional security issues.
Queers can open Joint Bank Accounts

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Government issued an advisory that LGBTQIA+ individuals and queer couples can open joint bank accounts. They can nominate each other as beneficiaries.
Key Details:
- Supreme Court Background:
- In October 2023, the Supreme Court of India urged the government to consider equal entitlements for partners in queer relationships.
- This was part of a judgment that did not recognize same-sex marriage but suggested enabling joint bank accounts and beneficiary nominations.
- Clarification from the Department of Financial Services:
- Issued on August 28, 2023, confirming no restrictions on opening joint accounts for the queer community.
- The Reserve Bank of India also clarified this to Scheduled Commercial Banks on August 21.
- Private Banks' Initiatives:
- Some banks, like Axis Bank, have been allowing joint accounts and beneficiary nominations for LGBTQIA+ couples since September 2021.
- Axis Bank expressed support for the Finance Ministry's advisory, noting alignment with its inclusive banking initiative.
- Government Committee Formation:
- In April 2023, a six-member committee was established to define entitlements for queer couples.
- Chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, it includes Secretaries from various ministries.
- The committee can co-opt experts if needed.
Unified Pension Scheme

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The new Unified Pension Scheme (UPS), set to launch on April 1, 2025, aims to provide improved old age income security. Around 23 lakh Central government employees will benefit from this new scheme, and those currently under the National Pension System (NPS) will have the option to switch to UPS. States can also adopt the UPS for their employees, but they will need to secure funding from their own resources.
Key Components of UPS
The UPS introduces several enhancements to pension benefits:
- Pension Benefits: Employees will receive half of their average basic pay over the final 12 months of service as a monthly pension after completing a minimum of 25 years of service. For those with less than 25 years, the pension will be proportionately reduced, with a minimum pension of ?10,000 for those with at least 10 years of service.
- Family Pension: A family pension equivalent to 60% of the employee's pension will be provided to dependents upon the employee's death.
- Inflation Adjustment: Pension incomes will be adjusted in line with the consumer price trends for industrial workers, similar to the dearness relief provided to current government employees.
- Superannuation Payout: In addition to gratuity, a lumpsum superannuation payout will be given, amounting to 1/10th of the employee’s monthly emoluments for every six months of service.
Differences from the Current System
The new UPS combines features from the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) and NPS:
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS): Employees who joined before January 1, 2004, are covered under OPS, which guarantees a pension of 50% of the last drawn salary, adjusted for dearness allowance. It also offers a family pension of 60% of the last drawn pension, with provisions for commutation and additional increases for pensioners over 80 years of age.
- National Pension System (NPS): Introduced in 2004, NPS replaced OPS for new employees, shifting from a defined benefits system to a defined contribution scheme. Employees and the employer contribute a percentage of the salary to market-linked securities, with no guaranteed pension amount, only a corpus that must be used to buy an annuity upon retirement.
The UPS aims to blend the certainty of OPS with the funded approach of NPS. While employees' contributions will be capped at 10% of their salary, the government will contribute 18.5%, with potential adjustments over time. The government will cover any shortfall between investment returns and pension promises.
Reasons for the Change
The transition to UPS addresses concerns raised by government employees and political pressure regarding the NPS. Employees have criticized NPS for its lack of guaranteed pension benefits compared to OPS. The issue has become politically significant, with opposition parties promising to revert to OPS in various states.
In March 2023, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a review of NPS led by former Finance Secretary T.V. Somanathan. Though the review’s findings are yet to be made public, the introduction of UPS reflects a compromise balancing employee expectations with fiscal prudence.
Reactions and Future Impact
Central government employees generally welcome the UPS, recognizing it as a step toward addressing the shortcomings of NPS. However, there are concerns about the contributory nature of UPS and the absence of a commutation option like in OPS. Economists are analyzing the scheme's financial implications, with an expected additional cost of ?7,050 crore this year for the government. Future pension payouts may increase but are anticipated to be manageable with higher revenue growth.
The UPS marks a significant shift in pension policy, aiming to provide greater financial security for government employees while managing fiscal responsibilities.
NAMASTE programme

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
A recent government survey has shed light on the demographics of workers engaged in the hazardous cleaning of urban sewers and septic tanks across India. This initiative, part of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's NAMASTE programme, highlights significant disparities within this labor sector.
Key Findings
- Community Representation: An overwhelming 91.9% of the 38,000 workers profiled belong to marginalized communities:
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 68.9%
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 14.7%
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 8.3%
- General Category: 8%
- Mortality Rates: Between 2019 and 2023, at least 377 individuals died while performing hazardous cleaning tasks, underscoring the dangers associated with this work.
The NAMASTE Programme
- Objective: The NAMASTE programme aims to mechanize sewer work to prevent fatalities linked to manual cleaning. It seeks to transition workers into safer, more sustainable roles as "sanipreneurs" by providing safety training, equipment, and capital subsidies.
- Background: This programme replaces the earlier Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), focusing on the more technical aspects of hazardous cleaning rather than manual scavenging.
- Namaste is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) as a joint initiative of the MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The Scheme has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 360 crore for four years from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- NAMASTE aims to achieve the following outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
- Strengthened supervisory and monitoring systems at national, state and ULB levels to ensure enforcement and monitoring of safe sanitation work
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered and skilled sanitation workers
Progress and Coverage
- Implementation: Since the scheme's inception, 3,326 urban local bodies (ULBs) have begun profiling workers, with many reporting minimal or no workers engaged in hazardous cleaning.
- Data Collection: The government is gathering data from over 3,000 ULBs across 29 states and union territories to better understand the scope and risks associated with this labor.
INDIA DESERVES PERMANENT UNSC SEAT: BHUTAN

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
With its significant economic growth and leadership of the Global South, India deserves a permanent seat at the UN Security Council, says Bhutan’s Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth: Highlights India’s significant economic growth and its leadership in the Global South as justifications for this status.
- International Backing: India’s bid gains momentum with support from several UN Member States, including France, the UK, and the U.S.
- Need for Reform: Bhutan emphasized that the UNSC is outdated and must evolve to reflect contemporary geopolitical and economic realities.
- Advocacy for Representation: Bhutan has long called for a more representative and effective Security Council, backing India’s inclusion at the high table.
About UN Security Council (UNSC)
- Composition: Total of 15 member states.
- 5 permanent members (P5): China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States (with veto rights).
- 10 non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- Election of Non-Permanent Members:
- Elected on a regional basis:
- 5 seats for African and Asian states.
- 2 seats for Latin American and Caribbean states.
- 1 seat for Eastern European states.
- 2 seats for Western European and other states.
- Elected on a regional basis:
- Presidency:
- Rotates monthly among members, following the English alphabetical order of country names.
- Primary Functions:
- Maintain international peace and security.
- Investigate and resolve disputes.
- Impose sanctions and authorize the use of force.
- Establish peacekeeping missions.
- Make recommendations to member states.
- Meeting Schedule:
- Regular meetings at UN headquarters in New York.
- Can convene at any time in response to emergencies.
- Decision-Making:
- Requires affirmative votes from at least 9 of the 15 members.
- Any of the P5 can veto resolutions, raising concerns about the Council's effectiveness.
- Subsidiary Bodies:
- Includes committees, working groups, and sanctions committees focused on specific issues like counter-terrorism, nuclear non-proliferation, and peacekeeping operations.
- Reforming the UN Security Council (UNSC)
- Charter Amendments:
- Reforming the UNSC requires amendments to the UN Charter.
- Voting Requirements:
- An amendment must be adopted by a two-thirds majority of the General Assembly.
- It must also be ratified by two-thirds of UN member states, including all permanent members of the UNSC.
- Charter Amendments:
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
INDIA TO SUPPORT TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO IN DEVELOPING UPI-LIKE PAYMENT SYSTEM

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- NPCI International Payments Limited (NIPL) has partnered with Trinidad and Tobago's Ministry of Digital Transformation to create a payment platform for person-to-person and person-to-merchant transactions.
- Modeling on UPI: The new digital payments system will be based on India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which is widely recognized as a leading digital payment solution.
- Role of NPCI: NIPL, a quasi-government body under the Reserve Bank of India, manages India’s retail payment systems, including UPI.
Previous Initiatives
- Global Expansion: Earlier in 2024, NIPL also committed to establishing digital payment systems in Peru and Namibia, leveraging the UPI model.
- Ongoing Talks: NIPL is exploring opportunities with additional countries in Africa and South America to assist in building their payment infrastructures.
Significance:
- UPI has emerged as a transformative force in India's financial landscape, registering nearly 15 billion transactions in August 2024, with an estimated value of USD 245 billion.
- This strategic partnership aims to empower Trinidad and Tobago to establish a reliable and efficient real-time payments platform for both person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions, expanding digital payments in the country and fostering financial inclusion.
IBSA (INDIA, BRAZIL, SOUTH AFRICA) GROUPING

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant move for global security, the Foreign Ministers of the IBSA (India, Brazil, South Africa) grouping issued a strong declaration against terrorism during the 79th UN General Assembly in New York. This declaration condemned terrorism in all its forms and reaffirmed the collective responsibility of the international community to eliminate terrorist safe havens worldwide.
Key Points from the IBSA Declaration:
- Universal Threat: The ministers stressed that terrorism is a threat that transcends borders, cultures, and governments.
- Rule of Law: They emphasized that counter-terrorism efforts must adhere to international law, particularly the UN Charter and human rights laws, ensuring civil liberties are respected.
- International Framework: A call was made for establishing a comprehensive international counter-terrorism framework, with the United Nations at its core, to coordinate global efforts against terrorism.
- Cross-Border Security: The declaration highlighted the need for stringent actions against the movement of terrorists and the financing of terrorist networks, condemning groups like Al-Qaeda, ISIS/Daesh, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT), and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM).
- Comprehensive Convention: A renewed commitment to accelerate the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism at the UN was emphasized, aiming to create a unified legal framework for combating terrorism.
INDIA-UZBEKISTAN BILATERAL INVESTMENT TREATY (BIT)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
India and Uzbekistan signed the Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) aimed at boosting the confidence of investors of both the countries.
Key Highlights:
- Investor Protections:
- Assured Protection: The BIT guarantees protection for investors from both countries, aligning with international standards.
- Minimum Standards: It establishes a minimum standard of treatment and non-discrimination for investors.
- Dispute Resolution: An independent arbitration forum will be available for dispute settlement.
- Investment Safeguards:
- Protection from Expropriation: The treaty safeguards investments from unjust expropriation.
- Transparency and Compensation: Provisions are included for transparency and compensation for losses incurred.
- Regulatory Balance: While protecting investors, the treaty maintains a balance with the state's right to regulate, ensuring adequate policy space for both countries.
Economic Context
- Shared Commitment: The BIT reflects the commitment of both nations to foster economic ties and create a resilient investment environment.
- Expected Outcomes: It is anticipated that the treaty will facilitate increased bilateral investments, benefiting businesses and economies in India and Uzbekistan.
- Current Investment Landscape: As of August 2024, Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) from India to Uzbekistan stands at $20 million, with Indian investments notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, amusement parks, automobile components, and hospitality.
India and Bilateral Investment Treaties
BITs are reciprocal agreements between two countries designed to promote and protect foreign private investments within each other's territories.
- Key Guarantees Established:
- National Treatment: Foreign investors are treated on par with domestic companies.
- Fair and Equitable Treatment: Investors receive treatment aligned with international law.
- Protection from Expropriation: Limits the ability of a country to seize foreign investments without appropriate compensation.
- Status of BITs in India
- Historical Context:
- Until 2015, India had signed BITs with 83 countries, with 74 currently in force. These agreements were based on the Indian Model BIT established in 1993.
- Revisions and Current Approach: In 2015, India revised its Model BIT text. Since then, India has:
- Signed new BITs/Investment Agreements with four countries.
- Entered negotiations with 37 countries/blocks for new agreements.
- Terminated older BITs with 77 countries, with only six remaining in force.
- Historical Context:
- Key Features of the Revised Model BIT
- Investor Protection:
- Provides robust protection for foreign investors in India and Indian investors abroad.
- Balances investor rights with government obligations.
- Investor Confidence:
- Enhances investor confidence by ensuring non-discriminatory treatment and a level playing field.
- Establishes an independent arbitration forum for dispute resolution.
- Investment Definition:
- Adopts an "enterprise"-based definition of investment to encompass various forms of investment.
- Dispute Settlement Provisions:
- Refined Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) provisions require investors to exhaust local remedies before seeking international arbitration.
- Limits arbitration tribunals to awarding monetary compensation only.
- Regulatory Authority Preservation:
- Excludes government procurement, taxation, subsidies, compulsory licenses, and national security from BIT coverage, ensuring the government retains regulatory authority.
- Investor Protection:
- Strategic Impact
- Preferred FDI Destination: The revised BIT aims to position India as a preferred destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Protection of Outbound FDI: It also focuses on safeguarding outbound investments made by Indian entities.
ASIA POWER INDEX

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
In a major shift, India surpassed Japan to become the third-largest power in the Asia Power Index, reflecting its increasing geopolitical stature. This achievement is driven by India's dynamic growth, youthful population, and expanding economy, solidifying its position as a leading force in the region.
Key Factors Behind India’s Rise:
- Economic Growth: India has shown remarkable post-pandemic economic recovery, contributing to a 4.2-point rise in its Economic Capability. India’s massive population and strong GDP growth reinforce its standing as the world’s third-largest economy in PPP terms.
- Future Potential: India’s Future Resources score increased by 8.2 points, signalling a potential demographic dividend. Unlike its regional competitors, particularly China and Japan, India benefits from a youthful population that will continue to drive economic growth and labour force expansion in the coming decades.
- Diplomatic Influence: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership has garnered greater international recognition. India’s non-aligned strategic posture has allowed New Delhi to navigate complex international waters effectively. India ranked 6th in terms of diplomatic dialogues in 2023, reflecting its active engagement in multilateral forums.
- Further, India’s large population and economic capabilities offer it substantial promise. India’s score in Cultural Influence has also remained relatively strong, underpinned by its global diaspora and cultural exports.
- In addition, India’s role in multilateral diplomacy and security cooperation has been a point of emphasis. India's participation in dialogues, as well as its leadership in the Quad, has allowed it to play a significant role in regional security dynamics, albeit outside of formal military alliances.
Asia Power Index
- The Asia Power Index, launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018, is an annual measure of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It evaluates 27 countries across the Asia-Pacific, examining their ability to shape and respond to the external environment.
- The 2024 edition offers one of the most comprehensive assessments of power distribution in the region to date. Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, reflecting its growing importance in Southeast Asia.
- The Index focuses on both the material capabilities of states and the influence they exert on the international stage.
Criteria and Parameters of Power Measurement
Power in the Asia Power Index is divided into resource-based and influence-based determinants:
- Resource-Based Determinants:
- Economic Capability: The core economic strength of a country, measured through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological sophistication, and global economic connectivity.
- Military Capability: Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces, weapon systems, and signature capabilities like long-range power projection.
- Resilience: The internal capacity to deter threats to state stability, including institutional robustness, geopolitical security, and resource security.
- Future Resources: Forecasts the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors projected for 2035.
- Influence-Based Determinants:
- Economic Relationships: The capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks: The strength of alliances and partnerships, measured through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- Diplomatic Influence: The extent of a country's diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and foreign policy ambition.
- Cultural Influence: The ability to shape international public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people ties.
A country's overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight measures, encompassing 131 individual indicators. The results offer a nuanced understanding of how countries convert their resources into influence within the Asia-Pacific.
China test-fires an intercontinental ballistic missile into the Pacific Ocean

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
China stated that it test-launched an intercontinental ballistic missile, firing it into the Pacific Ocean in its first such exercise in decades.
- Launch Details:
- The missile carried a dummy warhead and fell into a designated area in the high seas.
- The specific flight path and landing location were not disclosed.
- Testing Objectives:
- The launch tested weapon performance and troop training levels, achieving its expected objectives.
- Historical Context:
- This is the first ICBM test over the Pacific Ocean in over 40 years.
- China's first ICBM, the DF-5, was test-fired in 1980.
- ICBM Specifications:
- The latest ICBM, likely the DF-41, has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilometers (7,400 to 9,300 miles), capable of reaching the US mainland.
- Strategic Messaging:
- Analysts interpret the test as a warning to the US, suggesting direct intervention in Taiwan could expose the American homeland.
- The test signals China's ability to engage multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Regional Tensions:
- Recent weeks have seen heightened tensions with Japan, the Philippines, and Taiwan due to military incursions and exercises.
- International Norms:
- There is a global expectation to notify nations of long-range missile launches to avoid miscalculations. China has limited agreements regarding this, primarily with Russia.
- Military Buildup:
- Under Xi Jinping, China has enhanced its nuclear capabilities and revamped the PLA’s Rocket Force.
- Recent satellite imagery indicates the construction of hundreds of ICBM silos in China’s deserts.
- Future Projections:
- As of 2023, China has over 500 operational nuclear warheads, projected to exceed 1,000 by 2030 according to the Pentagon.
- Implications of the Test:
- The ICBM test may be aimed at demonstrating military readiness despite recent corruption scandals within the Rocket Force.
About ICBMs:
- An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range ballistic missile system primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery. They are powerful and destructive weapons, capable of travelling vast distances at incredibly high speeds.
- Key features of ICBMs:
- Range: Range greater than 5,500 kilometres with maximum ranges varying from 7,000 to 16,000 kilometres.
- Speed: ICBMs can travel at speeds exceeding 20,000 kilometres per hour.
- Payload: Typically designed to carry nuclear warheads, though they could potentially be used to deliver other types of weapons, such as chemical or biological weapons.
- Deployment: ICBMs can be launched from silos underground, mobile launchers on land, or submarines at sea.
- Countries having operational ICBMs: Russia, United States, China, France, India, United Kingdom, Israel and North Korea.
ACHIEVING GLOBAL NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT

- 26 Sep 2024
Overview
Global nuclear disarmament remains a top priority for the United Nations, initially emphasized in the General Assembly’s first resolution in 1946. Despite historical efforts, approximately 12,100 nuclear weapons still exist today, with ongoing modernization plans in many countries.
Key Historical Milestones
- 1945: Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 213,000 people.
- 1946: First UN resolution identifies nuclear disarmament as a key goal.
- 1959: General Assembly endorses the goal of general and complete disarmament.
- 1963: Opening of the Partial Test Ban Treaty.
- 1978: First Special Session of the General Assembly dedicated to disarmament.
- 1996: Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty opens for signature.
- 2017: Adoption of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Recent Developments
- 2019: U.S. withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty.
- 2023: Russia suspends participation in the New START Treaty, raising concerns over arms control.
The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons
- Established: December 2013, following a high-level meeting on nuclear disarmament.
- Observed: Annually on September 26.
- Purpose: Raise awareness about the dangers of nuclear weapons and promote their total elimination.
Goals of the International Day
- Enhance public education on the humanitarian risks associated with nuclear weapons.
- Mobilize international efforts towards a nuclear-weapon-free world.
Continuing Challenges
- The doctrine of nuclear deterrence remains central to the security policies of nuclear-armed states and their allies.
- No nuclear weapons have been destroyed under a treaty framework, and current disarmament negotiations are stagnant.
- Growing frustration among UN Member States over the slow progress in nuclear disarmament.
INDIA ATTENDS IPEF MINISTERIAL MEETING

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal joined a virtual meeting of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) alongside representatives from 13 other partner countries. This meeting marked the third gathering focused on the framework's key pillars: Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, and Fair Economy.
Key Agreements and Future Steps
- Entry into Force of Agreements:
- The IPEF partners celebrated the upcoming implementation of the Clean Economy Agreement and the Fair Economy Agreement on October 11 and October 12, 2024, respectively. These agreements aim to enhance economic cooperation and deliver tangible benefits to member nations.
- Supply Chain Resilience:
- The ministers discussed the progress in operationalizing the Supply Chain Agreement, emphasizing collaborative efforts to create more competitive and resilient supply chains. Key actions include:
- The formation of action plan teams for critical sectors like semiconductors, critical minerals, and chemicals, addressing vulnerabilities revealed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- India's election as Vice Chair of the Supply Chain Council, which aims to streamline communication and cooperation among member countries.
- The ministers discussed the progress in operationalizing the Supply Chain Agreement, emphasizing collaborative efforts to create more competitive and resilient supply chains. Key actions include:
- Clean Economy Initiatives:
- The Clean Economy Agreement focuses on energy security, climate resilience, and reducing fossil fuel dependence. Ministers acknowledged the advancement of eight Cooperative Work Programs (CWPs) addressing topics such as hydrogen and carbon markets.
- The first IPEF Investor Forum, held in Singapore, facilitated discussions on investment opportunities in climate-friendly technologies.
- Fair Economy Measures:
- The Fair Economy Agreement aims to bolster anti-corruption measures and improve tax administration efficiency. Upcoming workshops will address foreign bribery laws and public procurement oversight.
- India highlighted its own anti-corruption measures and commitment to transparency under Prime Minister Modi's leadership.
About IPEF
Launched on May 23, 2022, in Tokyo, IPEF includes 14 countries: Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, and the USA. The framework seeks to enhance economic engagement, stability, and prosperity across the Indo-Pacific region through its four key pillars: Trade, Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, and Fair Economy.
SUPREME COURT RULING ON CHILD SEXUAL EXPLOITATIVE MATERIAL: KEY HIGHLIGHTS

- 24 Sep 2024
Overview of the Ruling
- Date: Recent ruling by the Supreme Court of India.
- Context: Determined that viewing, downloading, storing, or distributing material involving child sexual exploitation constitutes a criminal offense under the POCSO Act and the Information Technology Act.
- Appeal Background: Decision overturned a Madras High Court ruling that deemed private viewing of such material non-criminal.
Terminology and Legislative Recommendations
- Terminology Change: Supreme Court advocates replacing “child pornography” with “Child Sexual Exploitative and Abuse Material” (CSEAM) to avoid trivialization of the crime.
- Amendment Call: Court urged Parliament to amend the POCSO Act and advised promulgating an ordinance for immediate effect.
Key Highlights of the Ruling
- Redefinition of Terminology: Emphasizes that "pornography" may imply consensual acts, misrepresenting the nature of child exploitation.
- Expansion of Section 15 of the POCSO Act:
- Possession Without Reporting: Individuals must delete or report any stored CSEAM; failure results in penalties.
- Intent to Transmit: Possessing CSEAM with intent to share, barring reporting, is punishable.
- Commercial Possession: Storing CSEAM for commercial purposes faces the strictest penalties.
- Concept of Inchoate Offenses: Classifies offenses related to CSEAM as preparatory actions towards further crimes.
- Redefinition of Possession:
- Includes "constructive possession," where individuals can be liable without direct physical possession.
- Watching CSEAM online without downloading can still be deemed possession.
- Educational Reforms:
- Court urged for comprehensive sex education to counter stigma and misconceptions.
- Curriculum should cover consent, healthy relationships, and respect for diversity.
- Awareness of the POCSO Act: Central and state governments are mandated to promote awareness, supported by the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR).
- Formation of Expert Committee: To develop programs for health and sex education while increasing POCSO awareness among children.
- Victim Support and Awareness: Emphasized the need for psychological support, counseling, and educational assistance for victims.
Status of Crimes Against Children
- Increasing Incidents: India leads in online child sexual abuse imagery, with 25,000 uploads reported from April to August 2024.
- Geographical Distribution: Major uploads identified in Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Rising Cases: From 331 cases in 2017 to 781 in 2018, with 1,171 cases of inappropriate content dissemination reported in 2022.
Overview of the POCSO Act
- Purpose: Addresses sexual exploitation and abuse of children, defining a child as anyone under 18.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral: Recognizes that both genders can be victims.
- Victim Confidentiality: Mandates protection of victims’ identities.
- Mandatory Reporting: Requires reporting of suspected abuse.
Gaps in Implementation
- Support Persons: Lack of designated support persons for victims; 96% of cases showed inadequate support during legal processes.
- POCSO Courts: Only 408 designated courts across 28 states as of 2022, leading to access issues.
- Special Prosecutors: Shortage of trained public prosecutors for POCSO cases.
Conclusion
- Call for Collaboration: Emphasizes the need for a coordinated approach involving educators, healthcare providers, and law enforcement to combat child sexual exploitation.
- Societal Responsibility: A shift in societal attitudes is essential for preventing victimization and ensuring recovery for victims.
INDO-PACIFIC ECONOMIC FRAMEWORK (IPEF)
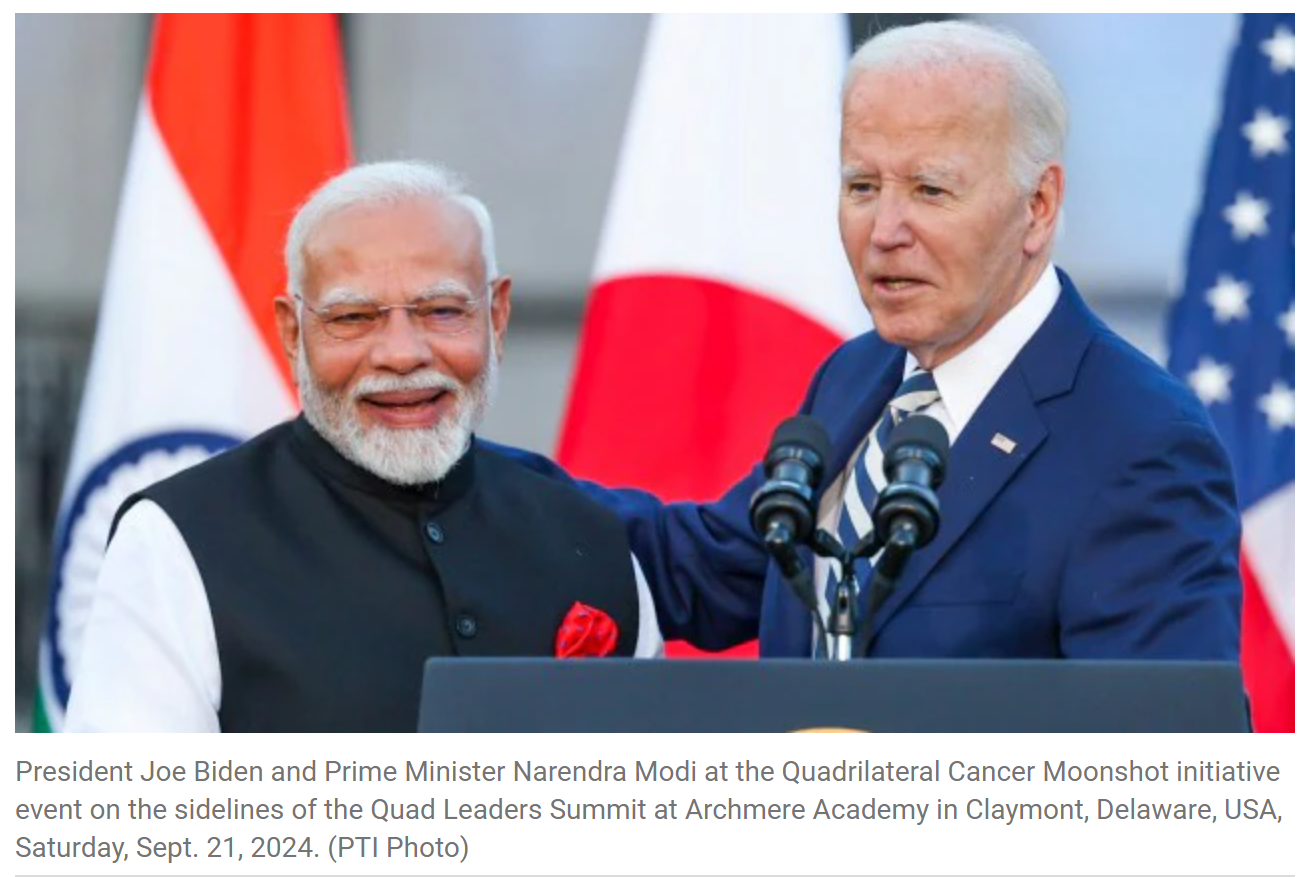

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
India signed agreements within the US-led 14-member IPEF focused on a clean and fair economy.
- Objectives:
- Facilitate development, access, and deployment of clean energy and climate-friendly technologies.
- Strengthen anti-corruption measures and promote tax transparency among member countries.
- Clean Economy Agreement:
- Aims to accelerate energy security and mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Focuses on innovative methods to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote technical cooperation.
- Fair Economy Agreement:
- Seeks to create a transparent and predictable business environment to enhance trade and investment.
- Emphasizes information sharing, asset recovery facilitation, and strengthening cross-border investigations.
- Funding Mechanisms:
- IPEF offers platforms for technical assistance and concessional funding.
- IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund: Initial grant of $33 million aimed to catalyze $3.3 billion in private investments.
- PGI Investment Accelerator: Received $300 million from the US International Development Finance Corporation.
- Concerns Raised:
- Experts highlighted concerns over the secrecy of IPEF negotiations with limited public input.
- Expressed hope that India has not agreed to a non-derogation clause that could limit domestic regulatory flexibility for national projects.
- Potential Risks:
- Most standards discussed in IPEF are aligned with those in the US and OECD countries.
- India risks compliance pressures in future trade deals if it adopts these standards without adequate preparation.
- Strategic Importance of IPEF:
- Involves 14 member countries, focusing on economic cooperation through four key pillars: trade, supply chain resilience, clean economy, and fair economy.
- Represents 40% of the global economy and 28% of world trade, highlighting India's commitment to regional partnerships alongside the US, Japan, Australia, and other Indo-Pacific nations.
QUAD CANCER MOONSHOT

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
The Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative is a significant collaborative effort among the Quad countries—India, the United States, Australia, and Japan—aimed at combating cancer through innovative strategies. The initiative focuses on key areas such as preventing and detecting cancer, improving treatment, and alleviating the disease's impact on patients and families.
Key Highlights of the Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative:
- Focus Areas:
- Cervical Cancer Screening: Enhancing access to screening programs.
- HPV Vaccination: Increasing vaccination rates against HPV, which is the leading cause of cervical cancer.
- Patient Treatment: Improving treatment protocols and accessibility for cancer patients.
- India’s Contributions:
- Financial Commitment: India has pledged $10 million to support the WHO’s Global Initiative on Digital Health, aimed at enhancing digital health technologies for cancer care in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Material Support: India will provide cervical cancer screening kits, detection tools, and HPV vaccines valued at $7.5 million to bolster healthcare initiatives in the region.
- AI-based Protocols: Development of AI-driven treatment protocols to improve care delivery for cancer patients.
- Capacity Building: India aims to enhance radiotherapy services and overall cancer prevention strategies in the Indo-Pacific.
This initiative represents a strong commitment to fostering international collaboration in healthcare, particularly in the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. By empowering communities with accessible tools and resources, the Quad countries aim to significantly reduce the burden of cancer in the region.
QUAD GROUPING
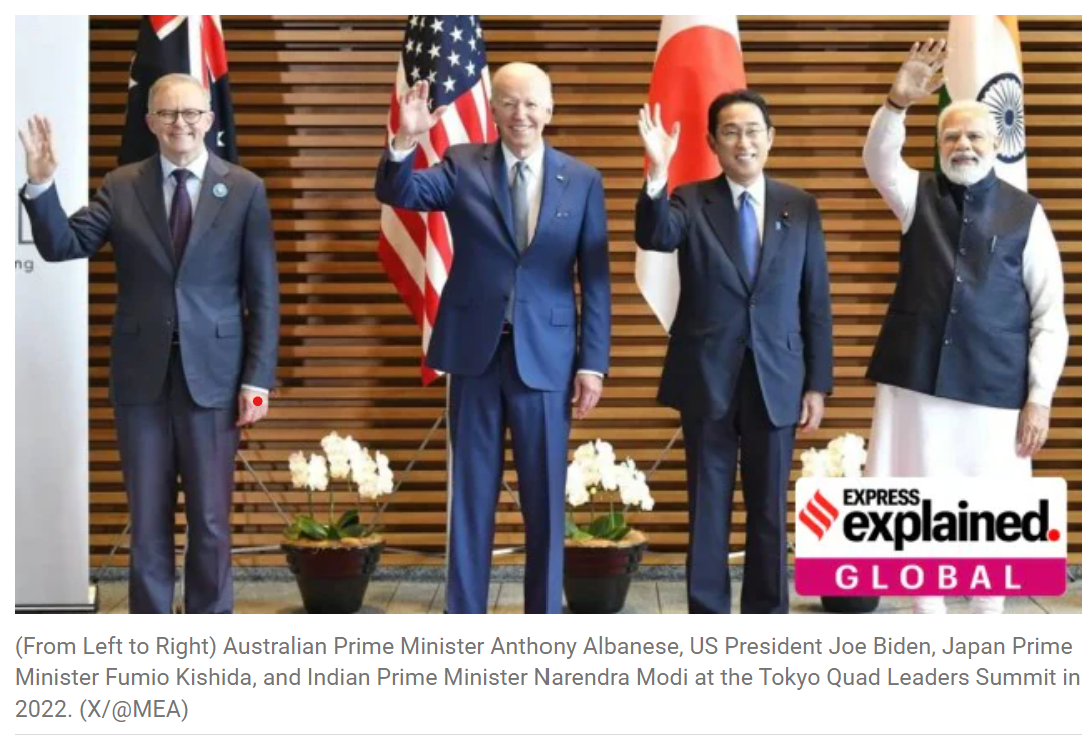

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in the United States, where he will participate in the fourth Quad Leaders Summit in Wilmington, Delaware.
What is the Quad Grouping?
The Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is an informal strategic alliance comprising India, the United States, Japan, and Australia. Originally formed in response to the Indian Ocean tsunami in 2004, the Quad aims to foster collaboration in various areas, but its primary focus has become countering the influence of China in the Indo-Pacific region.
Historical Background
- 2004: The Quad began as a response to the Indian Ocean tsunami, facilitating disaster relief.
- 2007: Japanese PM Shinzo Abe formalized the alliance.
- 2017: Amid rising Chinese assertiveness, the Quad was revitalized, expanding its objectives beyond maritime security.
Structure and Characteristics
- The Quad is not a formal organization; it lacks a secretariat or permanent decision-making body like the EU or UN.
- It focuses on strengthening bilateral and multilateral ties among member nations.
- Unlike NATO, the Quad does not include collective defense provisions but conducts joint military exercises to demonstrate unity.
Key Developments
- In 2020, the Malabar naval exercises expanded to include Australia, marking the first joint military exercises of the Quad since its resurgence.
- The first in-person summit took place in Washington, D.C. in 2021.
Objectives of the Quad
The Quad has outlined several primary objectives:
- Maritime Security: Ensuring safe and open sea routes in the Indo-Pacific.
- Climate Change: Addressing environmental challenges collaboratively.
- Investment Ecosystem: Creating opportunities for economic investment in the region.
- Technological Innovation: Promoting advancements and cooperation in technology.
- Public Health: Collaborating on initiatives like vaccine diplomacy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Expansion and Future Directions
The Quad members have discussed expanding the partnership to include countries like South Korea, New Zealand, and Vietnam. In a joint statement, they reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, resilient, and inclusive Indo-Pacific governed by international law.
Challenges and Opposition
China views the Quad as an effort to encircle and contain its influence. Beijing has criticized the grouping, labeling it as a strategy that incites discord among Asian nations.
INDIA JOINS THE INTERNATIONAL BIG CAT ALLIANCE (IBCA)
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
India formally joined the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 9, 2023, during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- Objective: The IBCA aims to conserve the world's seven big cat species: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar, and puma, focusing on their protection and natural habitats.
- Founding Members: India joins Nicaragua, Eswatini, and Somalia as founding members of the IBCA, which will collaborate with 24 countries and nine organizations.
- Headquarters: The IBCA will be headquartered in India, facilitating efforts to protect big cats and their ecosystems.
Purpose and Goals of IBCA
- Conservation Focus: The alliance addresses common challenges in the protection of the seven big cats, promoting sustainable resource use and tackling climate change.
- Collaboration and Support: The IBCA will provide a platform for member nations to share knowledge, expertise, and support recovery efforts in potential habitats.
- Mobilization of Resources: The alliance aims to mobilize financial and technical resources for effective conservation strategies based on global experiences.
Background and Evolution
- Inception: PM Modi proposed an international initiative against poaching and illegal wildlife trade in 2019, advocating for collaboration among tiger range countries.
- Extension of Project Tiger: The IBCA serves as an extension of India's long-standing commitment to wildlife protection, initially exemplified by the launch of Project Tiger in 1973.
Big Cat Species Overview
- Tiger (Endangered)
- Population: Approx. 3,167 in India, accounting for over 75% of the global population.
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and climate change impacting their territory.
- Lion (Vulnerable)
- Population: Estimated 700 in India.
- Threats: Habitat reduction and targeted poaching.
- Leopard (Near Threatened)
- Population: Around 13,000 in India, with approximately 250,000 globally.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
- Snow Leopard (Vulnerable)
- Population: 400-700 in India, with global estimates of 4,000-6,500.
- Threats: Poaching, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
- Cheetah (Vulnerable)
- Population: Declined to less than 7,000 globally; declared extinct in India in 1952.
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change, and illegal trafficking.
- Jaguar (Near Threatened)
- Population: Approximately 173,000 globally, primarily in South America.
- Threats: Deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat fragmentation.
- Puma (Near Threatened)
- Population: Estimated 50,000, experiencing a decline.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
Future Initiatives
- Translocation Efforts: Following successful cheetah translocations from Namibia and South Africa, India plans to explore similar initiatives for other big cats.
- Global Cooperation: The IBCA will strengthen conservation efforts by working with a broader network of range countries to combat poaching and promote habitat preservation.
PRADHAN MANTRI JANJATIYA UNNAT GRAM ABHIYAN

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan. This mission aims to enhance the socio-economic conditions of tribal communities by saturating more than 63,000 tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts with a total budget of ?79,156 crore.
Budget Breakdown
- Total Outlay: ?79,156 crore
- Central Share: ?56,333 crore
- State Share: ?22,823 crore
Target Beneficiaries
The initiative is expected to benefit over 5 crore tribal people across 549 districts and 2,740 blocks in 30 States/UTs.
Context
- India's Scheduled Tribe (ST) population stands at 10.45 crore, according to the 2011 Census, with more than 705 tribal communities often residing in remote areas. This mission builds upon the successes of the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN), launched on November 15, 2023.
Mission Objectives
- The mission aims to address critical gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood through a comprehensive approach involving 25 interventions across 17 ministries.
Key Goals and Interventions
Goal 1: Developing Enabling Infrastructure
- Housing: Provision of pucca houses under the PMAY (Gramin) for eligible households, along with access to tapped water and electricity.
- Village Infrastructure: Improvement of all-weather road connectivity, mobile connectivity, and educational and health infrastructure.
Goal 2: Promotion of Economic Empowerment
- Skill Development: Enhanced training and self-employment opportunities for ST youth through initiatives like the Skill India Mission and support for tribal marketing.
Goal 3: Universal Access to Good Education
- Education Initiatives: Increase the gross enrollment ratio in schools and higher education, along with setting up tribal hostels for students.
Goal 4: Healthy Lives and Dignified Ageing
- Health Access: Provision of quality health facilities, aiming to meet national standards in maternal and child health indicators through mobile medical units.
Innovative Schemes
- Tribal Home Stay Initiative: Promotion of 1,000 homestays in tribal areas to boost tourism and provide alternate livelihoods. Each household can receive up to ?5 lakh for construction and ?3 lakh for renovations.
- Sustainable Livelihood for FRA Holders: Focus on 22 lakh FRA patta holders, enhancing their rights and providing livelihood support through various government schemes.
- Improving Educational Infrastructure: Upgrading tribal residential schools and hostels to improve local educational resources and retention rates.
- Sickle Cell Disease Management: Establishing Centers of Competence for affordable diagnostic services and prenatal care in regions where the disease is prevalent.
- Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centres (TMMCs): Setting up 100 TMMCs to improve marketing of tribal products and facilitate better prices for producers.
India-China Disengagement Along the LAC
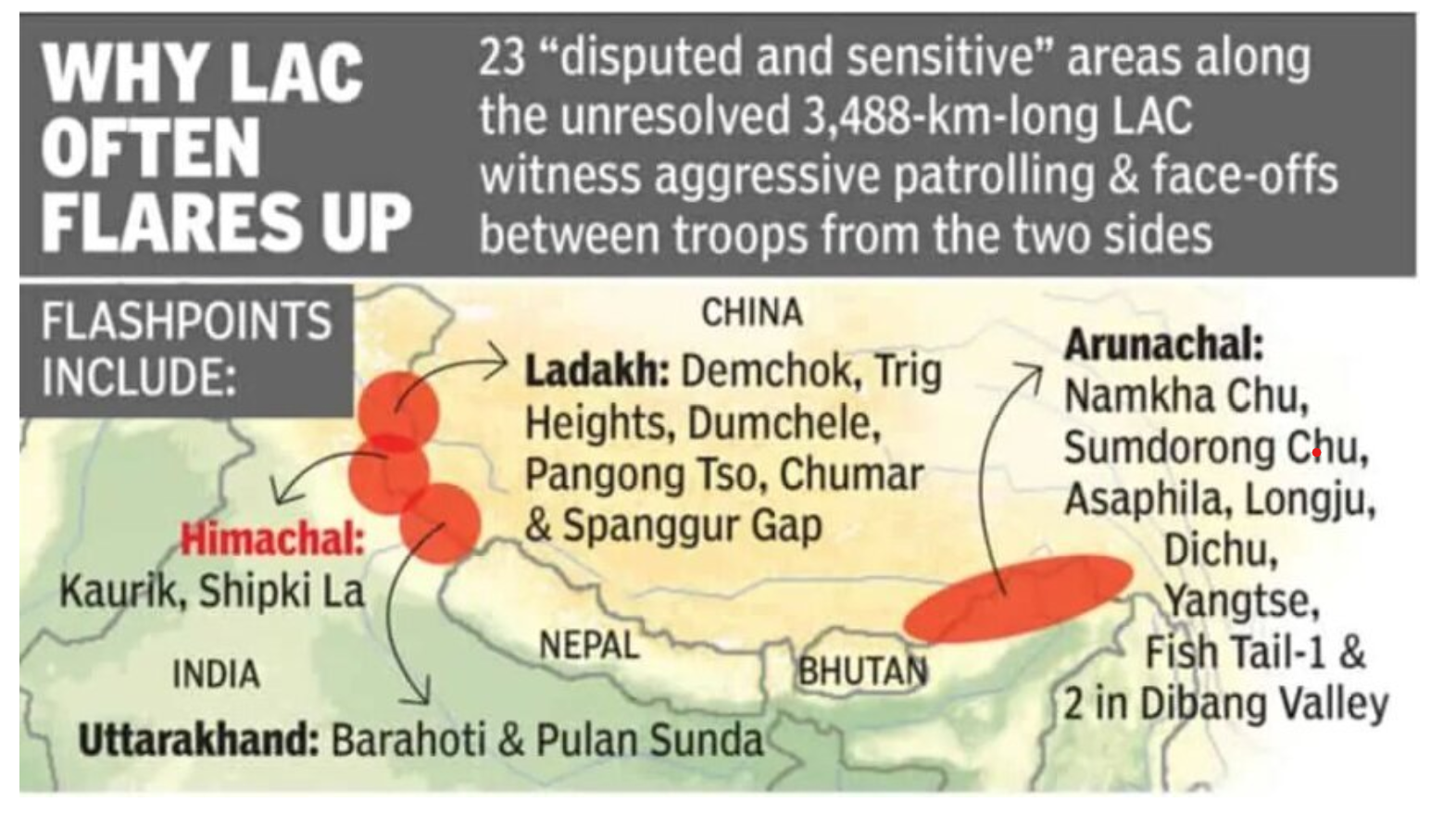
- 18 Sep 2024
Overview of Disengagement Progress
Recently, India’s External Affairs Minister announced that about 75% of the “disengagement problems” with China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in Ladakh have been “sorted out.” However, notable areas such as Demchok and the Depsang plains have seen no progress toward resolution over the past two years.
Recent Developments on India-China Disengagement
Verified Disengagement
India and China have mutually agreed to and verified disengagement from five friction points, including:
- Galwan Valley
- Pangong Tso
- Gogra-Hot Springs
Despite this, issues in Demchok and Depsang remain unresolved.
Diplomatic Efforts
Recent high-level diplomatic interactions have facilitated the disengagement along the LAC. Key meetings include:
- India’s National Security Advisor Ajit Doval meeting Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi at the BRICS NSAs meeting in St Petersburg, Russia.
- Anticipation for further disengagement is linked to the upcoming BRICS Summit in October in Kazan, Russia, where leaders from both nations are expected to meet.
Significance of Disengagement
The 31st meeting of the Working Mechanism for Consultation & Coordination on India-China Border Affairs (WMCC) was described as “frank, constructive, and forward-looking.” Participants urged both parties to “narrow down the differences” and “find early resolution of the outstanding issues.” The phrase "narrow down the differences" marks a hopeful shift in the dialogue surrounding the border standoff.
Strategic Importance of Depsang Plains and Demchok
Depsang Plains
The Depsang Plains hold strategic significance due to the following reasons:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA)’s control threatens India’s position over the Siachen Glacier, potentially encircling the Indian Army between China and Pakistan.
- A coordinated attack from both China and Pakistan would leave India’s military position on the Siachen Glacier vulnerable.
- The Indian Army identifies this region as particularly susceptible to mechanized warfare due to its flat terrain, which also offers direct access to Aksai Chin.
Demchok
Demchok is crucial for several reasons:
- It facilitates effective surveillance of Chinese movements and activities in the Aksai Chin region.
- It supports essential road and communication links that enable rapid military mobilization and logistical support.
Key Areas in the India-China Standoff
Pangong Lake Region
- This area frequently sees patrols from both India and China intersecting.
- The north bank of the lake is divided into eight "fingers," with India claiming territory up to Finger 8 and China disputing it down to Finger 4.
Demchok Region
- Recent reports indicated increased Chinese activity and heavy equipment movement.
Galwan River Basin
- Satellite imagery revealed Chinese tents near the Galwan River basin, suggesting incursions into traditionally held Indian territories.
Gogra Post
- A Chinese military buildup near the Gogra post has escalated tensions.
Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO)
- Chinese encroachments have been reported in the DBO sector, located on the Indian side.
- The DBO airstrip is critical for winter operations and reinforcements, accessible via the 255 km-long Darbuk-Shyok-DBO road.
International Day of Democracy

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Karnataka marked the 'International Day of Democracy' by forming a 'historic' 2,500-km-long human chain as a symbol of equality, unity, fraternity, and participative governance. The massive human chain, which according to the Karnataka government will be the "world's longest", is being formed across the state from Bidar to Chamarajanagar, covering all 31 districts.
Key Highlights:
- Democracy Day is an annual celebration observed on September 15.
- The United Nations General Assembly established this day in 2007 to emphasise the global significance of democracy. It serves as a reminder that democracy is not merely a fixed condition, but an ongoing pursuit. It calls for active engagement from international organizations, nation-states, civil society and people to pursue the democratic idea.
International Day of Democracy History
- The International Day of Democracy was accredited by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) on November 8, 2007, by passing a resolution entitled “Support by United Nations system of efforts of governments to promote and consolidate new or restored democracies.”
- September 15 was chosen to coincide with the anniversary of the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s Universal Declaration on Democracy, which was adopted in Geneva on September 15, 1997.
- This declaration outlines the tenets of democracy proclaiming that democracy is “a system of government based on the freely expressed will of the people to determine their own political, economic, social and cultural systems and their full participation, through free and fair periodic elections, in the composition of their representative government.”
- After the Universal Declaration on Democracy, Qatar spearheaded the campaign to observe an International Day of Democracy at the United Nations.
- The first-ever International Day of Democracy was held in 2008.
International Day of Democracy Significance
- The International Day of Democracy evaluates global democracy, emphasising that it requires commitment and engagement from the international community, the national state governments, civil societies and individuals.
- The day also reminds the nations of the need to uphold the principles of democracy such as the freedom of speech enshrined in Article 19 of the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
What is Operation Kawach, the new ‘war on drugs’ waged by Delhi Police?

- 05 Sep 2024
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, 'Operation Kawach' is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police.
In a major crackdown on the menace of drugs in the national capital, the Crime Branch of the Delhi Police conducted widespread raids, swooping down on over 100 locations across Delhi. Earlier, raids conducted during the intervening night of May 12 and 13 had led to the arrest of 31 drug offenders in 30 cases under the Narcotic-Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985.
As many as 12 bootleggers were also arrested in six cases of the Excise Act. The operation also saw the seizure of 957.5 grams of heroin, 57.8 kilograms of marijuana and 782 bottles of illicit liquor.
What is Operation Kawach?
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, ‘Operation Kawach’ is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police. The initiative aims to combat the harmful influence of drug addiction on youth and children and underscores the authorities’ commitment to safeguarding the well-being of young individuals and curbing the distribution of illicit substances in educational settings.
Operation Kawach is primarily intended to save the youth from the menace of drugs. Although the focus is to take stringent action on the supply side, it is also appealed to society to create awareness and reduce the demand of drugs. The parents, teachers and the social reformers are specially requested to sensitise the youth about the grave consequences of drug addiction.
Operation Kawach: The story so far
According to the official, the joint operations, which utilised a variety of resources such as undercover officers, surveillance, canine support and intelligence gathering, targetted both street-level dealers and high-level traffickers and have both ‘top-to-bottom’ and ‘bottom-to-top’ approaches to effectively counter drug trafficking in the national capital.
In this year, Delhi Police has arrested 534 narco-offenders in 412 NDPS cases. Around 35 kg of heroin/smack, 15 kg of cocaine, 1,500 kg of ganja, 230 kg of opium, 10 kg of charas and 20 kg of poppy have been recovered during these operations.
India-France Bilateral Naval Exercise VARUNA

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
The 22nd edition of the India-France bilateral naval exercise, VARUNA, took place in the Mediterranean Sea from September 2 to 4, 2024. This exercise highlights the strong maritime partnership between the Indian Navy and the French Navy, showcasing their commitment to enhancing interoperability and operational effectiveness.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Vessels and Aircraft:
- Indian Navy:
- INS Tabar: A frontline stealth frigate commanded by Captain MR Harish.
- Ship-borne Helicopter: Provided air support during the exercises.
- LRMR Aircraft P-8I: An advanced long-range maritime reconnaissance aircraft.
- French Navy:
- FS Provence: A French naval ship participating in the exercise.
- Submarine Suffren: A French attack submarine.
- Aircraft F-20: Providing air support.
- Atlantique 2: A French maritime patrol aircraft.
- Fighters MB339: Multi-role fighter aircraft.
- Helicopters NH90 and Dauphin: Providing additional aerial capabilities.
- Indian Navy:
- Exercise Activities:
- Tactical Maneuvers: Advanced maneuvers showcasing the operational capabilities of both navies.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare: Exercises designed to enhance capabilities in detecting and countering submarines.
- FLYEX (Flight Exercises): Coordinated air operations involving various aircraft.
- Air Defence Exercise: Training in defending against aerial threats.
- Live Weapon Firings: Demonstrations of weapon systems in action.
- PHOTO-EX (Photographic Exercise): Exercises designed for documenting and assessing naval operations.
- Steam Past: A ceremonial maneuver showcasing the participating ships.
- Significance of the Exercise:
- Evolution of VARUNA: Since its inception in 2001, VARUNA has become a key component of the India-France naval relationship. The exercise has evolved to improve interoperability and share best practices between the two navies.
- Strategic Importance: Conducting the exercise in the Mediterranean Sea reflects the Indian Navy's capability and commitment to operate far beyond the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). It underscores the strategic depth and outreach of the Indian Navy.
- Enhanced Interoperability: VARUNA demonstrates the mutual commitment of India and France to enhancing naval collaboration and operational effectiveness through joint exercises and shared experiences.
- Future Outlook:
- Commitment to Partnerships: The Indian Navy continues to prioritize building strong partnerships with like-minded navies worldwide. The VARUNA exercise is a testament to this ongoing commitment and the broader strategic goals of both India and France in strengthening maritime security and cooperation.
This bilateral exercise not only enhances the operational capabilities of both navies but also reinforces the strategic partnership between India and France in the maritime domain.
India-Maldives Defence Talks

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
- India and the Maldives held their first defence talks since India withdrew its military personnel early this year.
Significance of Talks:
- The dialogue is notable given recent tensions in bilateral relations. Relations soured after President Mohamed Muizzu's election on an "India Out" platform, leading to the withdrawal of Indian troops. The last defence cooperation dialogue was held in March 2023 under President Ibrahim Solih.
Discussion Topics:
-
- Expediting ongoing defence cooperation projects.
- Planning forthcoming bilateral military exercises.
- Enhancing high-level exchanges and capability development.
Context of Tensions:
-
- Mohamed Muizzu, who took office in November 2023, had called for the removal of Indian military personnel, a significant shift from the previous administration’s stance.
- India agreed to withdraw 80 military personnel between March and May 2024. Indian technical personnel now operate key equipment like helicopters and a Dornier aircraft in the Maldives.
Recent Developments:
-
- Maldives Foreign Minister Moosa Zameer visited India in May.
- President Muizzu attended PM Narendra Modi’s swearing-in ceremony in June.
- In August, Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar visited the Maldives to reaffirm bilateral ties.
Historical Defence Cooperation:
-
- India gifted a Dornier aircraft to the Maldives in 2020 and a patrol vessel in 2019.
- India provided a coastal radar system last year and laid the foundation for the 'Ekatha Harbour' project, enhancing Maldivian Coast Guard capabilities.
Ongoing Projects:
-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) - a $500 million initiative financed by India.
- Building a new Coast Guard base at Uthuru Thilafalhu (UTF) atoll.
- India’s grant for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs).
Strategic Importance:
-
- For Maldives: India is a key security partner and crisis responder, with historical assistance during emergencies (Operation Neer, Vaccine Maitri). Maldives seeks to restore Indian tourist numbers, vital for its economy.
- For India: The Maldives is crucial to India's Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision SAGAR. Its strategic location between major Indian Ocean chokepoints makes it a vital partner for maritime security and countering China's influence.
Recent Changes:
-
- The Muizzu government decided not to renew a 2019 MoU for hydrographic surveying with India, ending joint hydrographic surveys conducted under the pact.
Travel and Trade:
-
- Both countries benefit from an open skies arrangement and visa-free access for tourism, medical, and business purposes
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
IMEC is an important initiative that can add to India's maritime security and faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia, said Union Minister of Commerce & Industry at the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) India-Mediterranean Business Conclave 2024 in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Corridors:
- East Corridor: Connects India to the Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe.
- Components:
- Railroad: Provides a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network.
- Ship-to-Rail Networks: Integrates road, sea, and rail transport routes.
- Road Transport: Complements the overall transport infrastructure.
- Expected Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Enhances transit efficiency and reduces costs.
- Economic Unity: Promotes economic integration and job creation.
- Environmental Impact: Lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transformative Integration: Connects Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Additional Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes laying cables for electricity and digital connectivity, and pipes for clean hydrogen export.
- Implementation:
- MoU Commitments: Participants will collaboratively address technical design, financing, legal, and regulatory aspects.
- Action Plan: A meeting is planned within 60 days to develop an action plan with specific timetables.
Geoeconomic Perspective
- Economic Integration and Interdependence:
- Prosperity Through Integration: IMEC aims to foster trade and investment among India, the Middle East, and Europe, potentially leading to mutual prosperity and regional stability.
- Building Bridges: Aligns with the liberal international order by promoting economic interdependence to reduce tensions and create shared interests.
- Support from Major Powers: Backed by the US, Europe, and India, signaling a strong commitment to economic ties and regional stability.
- Economic Potential:
- Infrastructure and Trade Routes: Enhances infrastructure and trade routes, boosting economic activity, trade volumes, and investment opportunities.
- Regional Development: Promotes job creation and development in economically disadvantaged areas along the corridor.
Geopolitical Perspective
- Strategic Rivalry with China:
- Countering the BRI: IMEC is seen as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering an alternative aligned with US, European, and Indian interests.
- Regional Influence: Aims to limit China’s influence in the Middle East and South Asia by establishing a competing corridor.
- Geopolitical Alliances:
- Aligning Interests: Involves strategic partnerships among the US, Europe, and India, reflecting concerns about China’s global strategy and shifting power dynamics.
- Rivalry and Competition: The IMEC could be viewed as a global positioning move, responding to China’s growing influence and securing strategic interests.
Reasons for Joining the IMEC
- Economic Enhancement:
- Boosts Indo-Gulf Relations: Enhances trade and economic ties with the Arab Gulf, addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Regional Connectivity: Links India with key partners like Israel and Jordan, boosting economic opportunities.
- Strategic Trade Routes:
- Alternative Routes: Complements existing routes like Chabahar Port and INSTC, connecting India to southern Eurasia.
- Bypassing Choke Points: Offers a shorter route to Eastern Mediterranean and Western Europe, avoiding strategic choke points.
- Energy and Trade Opportunities:
- Access to Resources: Provides potential access to Eastern Mediterranean gas fields.
- Trade Bloc Connectivity: Links India with the EU and GCC, opening up growth opportunities.
- Geopolitical Aspirations:
- Global Power Ambitions: Supports India’s goal to enhance global influence and integrate with eastern and western neighbors.
- Economic Growth: Leverages economic integration to support development and influence.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Economic Integration: Facilitates infrastructure creation for increased trade volumes and regional stability.
e-Sankhyiki portal

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has launched e-Sankhyiki portal with the objective to establish a comprehensive data management and sharing system for ease of dissemination of official statistics in the country.
Key Highlights:
- Launched on National Statistics Day 2024, the e-Sankhyiki portal is designed to create a comprehensive system for managing and sharing data, facilitating the easy dissemination of official statistics across the country.
- The portal is also accessible at - https://esankhyiki.mospi.gov.in. It aims to provide timely and valuable data inputs for policymakers, researchers, and the general public.
- It provides time series data for key macroeconomic indicators, with features for filtering and visualising the data. Users can also download customised datasets and visualisations and access them through APIs, enhancing the data's reusability.
- It consists of two modules viz. Data Catalogue and Macro Indicators.
- Data Catalogue Module:
- This module catalogues the Ministry’s major data assets, simplifying users' access. It enables searching within datasets and tables, downloading relevant data, and enhancing its value and reusability.
- The Data Catalogue includes seven core data products:
- Consumer Price Index
- Index of Industrial Production
- National Accounts Statistics
- Periodic Labour Force Survey
- Annual Survey of Industries
- Household Consumption Expenditure Survey
- Multiple Indicator Survey.
- It currently hosts over 2,300 datasets, each accompanied by specific metadata and visualisations for user convenience.
- Macro Indicators module:
- This module provides time series data on key macro indicators, featuring tools for filtering and visualising data.
- It allows users to download custom datasets, generate visualisations, and share data through APIs, promoting greater reusability. The initial phase of this module covering data from the past decade includes four major MoSPI products:
- National Accounts Statistics
- Consumer Price Index
- Index of Industrial Production
- Annual Survey of Industries
- The portal currently features over 1.7 million records, providing access to extensive vital data.
- Data Catalogue Module:
Government Initiatives for Safe Data Dissemination
- In response to the rapid data expansion, the Government of India has instituted robust data safety measures. These include storing data in the cloud facilities provided by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), conducting comprehensive security audits of applications, and implementing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) technology for domain protection.
- Additionally, the government has focused on vulnerability assessments and ensured compliance with guidelines issued by organisations such as NIC and the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In).
- In addition , CERT-In under the Ministry of Electronics and Information technology (MeitY) also undertakes various activities like issuance of advisories and guidelines for cyber/information security, conduct of sensitization programmes/trainings/workshops, operating Cyber Threat exchange platform & Cyber Swachhta Kendra, formulation of a Cyber Crisis Management Plan, setting up of National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) and empanelment of security auditing organisations etc. for data safety.
Centre gives clearance for ‘Mission Mausam’

- 13 Sep 2024
The Union Cabinet approved 'Mission Mausam,' a groundbreaking initiative with an investment of ?2,000 crore over the next two years. The mission, spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), aims to significantly advance India's capabilities in atmospheric sciences and climate resilience.
Objectives and Key Focus Areas
Mission Mausam is designed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of weather forecasting and climate management through several critical components:
- Advanced Technology Deployment: The mission will focus on deploying next-generation radars and satellite systems equipped with advanced sensors. These technologies are crucial for enhancing weather surveillance and prediction accuracy.
- Research and Development: A key objective of Mission Mausam is to bolster research and development in atmospheric sciences. This will include the development of enhanced Earth system models and advanced weather forecasting techniques.
- GIS-Based Decision Support System: An automated decision support system based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS) will be developed to facilitate real-time data sharing and improve decision-making processes.
Institutional Framework and Implementation
The Ministry of Earth Sciences will oversee the implementation of Mission Mausam. The following institutions will play central roles in the mission:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
- National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting
Additional support will come from other MoES bodies:
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research
- National Institute of Ocean Technology
Sectoral Benefits
Mission Mausam is expected to bring significant improvements across various sectors:
- Agriculture: Enhanced agromet forecasts will aid farmers in optimizing crop management and increasing resilience to climatic variability.
- Disaster Management: Improved monitoring and early warning systems will enhance disaster preparedness and response, potentially reducing loss of life and property damage.
- Defence: Accurate weather forecasting will support strategic planning and operational efficiency within the defence sector.
- Energy and Water Resources: Better weather predictions will lead to more efficient management of energy and water resources.
- Aviation: Safer aviation will be supported by more reliable weather information, reducing risks and improving travel safety.
- Tourism: Sustainable tourism will benefit from accurate weather forecasting, contributing to safer and more enjoyable travel experiences.
Mission Mausam represents a significant investment in India’s ability to manage and mitigate the impacts of climate change and extreme weather events, ultimately aiming to enhance the resilience of communities and support sustainable development.
Strengthening India-UAE Relations

- 11 Sep 2024
The bilateral relationship between India and the UAE has flourished in recent years, marked by deepening strategic ties and multifaceted collaboration. The recent visit of Abu Dhabi's Crown Prince to India highlights the growing importance of this partnership. The UAE is now India's second-largest export destination, third-largest trading partner, and fourth-largest investor. The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), effective from May 2022, has been transformative, boosting total trade by nearly 15% and increasing non-oil trade by 20% in the 2023-24 period.
Significance of the UAE for India
- Economic Gateway: The UAE is a crucial entry point for India into the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. As India's third-largest trading partner, bilateral trade reached USD 84.5 billion in FY 2022-23. The CEPA, removing tariffs on 80% of Indian exports to the UAE, has led to a 5.8% increase in non-oil trade early in 2023 and is expected to elevate trade to USD 100 billion by 2030. The UAE’s strategic location and infrastructure make it an ideal hub for re-exporting Indian goods to Africa and Europe.
- Energy Security: The UAE is India's fourth-largest crude oil supplier, with oil imports surging by 81% in January 2024. The partnership extends to renewable energy projects, aligning with India's goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030, underscoring the UAE's role in India's energy transition.
- Investment Catalyst: FDI from the UAE to India has increased more than threefold, reaching USD 3.35 billion from USD 1.03 billion in 2021-22. The UAE-India High-Level Joint Task Force on Investments has played a key role, with significant investments like the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority’s Rs 4,966.80 crore in Reliance Retail Ventures Limited.
- Strategic Partner: The UAE has become a vital strategic ally for India in counterterrorism and maritime security. The bilateral naval exercise "Zayed Talwar" in 2021 and India's access to the UAE’s Al Dhafra air base highlight the expanding defense cooperation between the two nations.
- Remittances and Soft Power: The 3.5 million-strong Indian diaspora in the UAE is a major source of remittances and cultural influence. In 2022, India received nearly USD 111 billion in global remittances, with the UAE as a significant contributor. The diaspora also strengthens cultural ties, as evidenced by the BAPS Hindu Temple in Abu Dhabi, symbolizing the UAE’s commitment to religious tolerance.
- Tech and Innovation Hub: The UAE-India partnership is increasingly focused on technology and innovation. The I2U2 group (India, Israel, UAE, USA) aims to enhance cooperation in clean energy and food security. The UAE’s USD 2 billion investment in food parks in India and the UAE-India Artificial Intelligence Bridge, launched in 2018, facilitate joint research and position both countries at the forefront of technological advancement.
Areas of Friction
- Labor Rights: Persistent labor rights issues for Indian workers in the UAE, including passport confiscation and wage theft, remain a concern.
- Geopolitical Tensions: India’s growing ties with Israel and the UAE’s normalization with Israel complicate the geopolitical landscape, potentially entangling India in regional rivalries, especially with Iran. The UAE’s increasing ties with China also add strategic complexity.
- Energy Transition: Both nations’ commitments to net-zero targets—India by 2070 and the UAE by 2050—pose challenges to their traditional hydrocarbon-based relationship.
- Trade Imbalance: Despite growing trade, India’s trade deficit with the UAE stood at USD 16.78 billion in FY 2022-23. While the CEPA aims to address this, diversifying trade beyond hydrocarbons remains a challenge.
- Maritime Security: Coordinating responses to maritime security threats while respecting strategic autonomy is challenging. The UAE’s expanding naval presence and India’s growing maritime footprint require careful coordination.
Enhancing Relations
- Digital Diplomacy: India could use its IT capabilities to develop digital platforms for collaboration, including a real-time trade portal and a joint innovation hub, and expand cross-border digital payments.
- Green Energy Corridor: Proposing an "India-UAE Green Energy Corridor" could align with both nations’ climate goals through joint investments and research in renewable energy.
- Skill Bridge Program: A "Skill Bridge Program" could upskill Indian workers for the UAE job market, focusing on emerging sectors like AI and sustainable technologies.
- StartUp Synergy Scheme: Developing a "StartUp Synergy Scheme" could foster collaboration between Indian and UAE startups through joint incubation programs and market access facilitation.
- Maritime Cooperation Blueprint: Creating a comprehensive "India-UAE Maritime Cooperation Blueprint" could enhance collaboration in maritime security, blue economy initiatives, and port development, including joint patrols and deep-sea ports.
Good Digital Public Infrastructure
- 08 Sep 2024
Good digital public infrastructure (DPI) integrates technology with societal needs, ensuring that it is secure, scalable, and inclusive.
India’s achievement of over 80% financial inclusion in just six years has drawn international praise, particularly as a model for the Global South. This accomplishment underscores India’s success in achieving both digital and financial inclusion for over a billion people. Consequently, the G20 summit in New Delhi in 2023 highlighted the critical role of digital public infrastructure.
In response, India’s G20 task force has released a comprehensive report outlining a global strategy for DPI development. This positions India to support other nations in achieving digital sovereignty, financial inclusion, and self-reliance.
The evolving digital landscape is marked by a variety of stakeholders—including private enterprises, government bodies, non-profits, and think tanks—each working to advance their DPI solutions. This raises two key questions: How can we identify genuine and reliable DPIs from the plethora available? And what differentiates a “good DPI” from a “bad DPI”?
Identifying effective DPI involves assessing how well technology meets societal needs while ensuring security, scalability, and inclusivity. Authenticity and adherence to core principles are essential for evaluating DPIs.
The Citizen Stack Model
Citizen Stack, built upon the proven success of India Stack, emerges as a trusted ecosystem in digital infrastructure. India Stack, a robust digital platform, has demonstrated its effectiveness and security on a vast scale, serving over a billion citizens. This strong foundation enhances Citizen Stack’s credibility and reliability. Unlike DPI manufacturers, Citizen Stack functions as a regulatory body or auditor, certifying and authenticating DPIs to ensure they meet high standards of quality and security.
Citizen Stack’s approach is comprehensive, focusing on security, scalability, and inclusivity. The DPI platforms approved by Citizen Stack are designed to meet the diverse needs of large populations while maintaining stringent security measures to protect user data and privacy. As an auditor, Citizen Stack ensures that certified DPIs are dependable, secure, and beneficial to the public.
In an era of abundant digital solutions and promises, distinguishing genuinely reliable platforms is essential. Citizen Stack offers assurance as a gold standard for DPI solutions.
Guiding Principles of a “Good DPI”
Citizen Stack has established five core principles—referred to as sutras—that define a good DPI:
- Maintain Citizen Relationships: Ensure that digital infrastructure supports a fair relationship between citizens, the market, and the state, free from undue influence.
- Protect Empowerment and Privacy: Implement consent-based data sharing systems that prioritize individual empowerment and privacy.
- Prevent Monopolistic Lock-In: Ensure interoperability to avoid citizens being restricted by monopolistic entities.
- Combine Techno-Legal Regulation: Integrate technology with legal frameworks to govern ethical tech use, ensuring innovation while safeguarding security and societal rights.
- Foster Public-Private Innovation: Encourage collaboration between public and private sectors, while avoiding corporate dominance. The focus should be on public good rather than corporate monopolies, and technology should prevent exploitation by state or corporate actors.
India, UAE ink pact for civil nuclear cooperation

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for civil nuclear cooperation.
- The agreement, established between the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) and the Emirates Nuclear Energy Company (ENEC)-led Barakah Nuclear Power Plant Operations and Maintenance, was formalized during the visit of Sheikh Khalid bin Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi, to New Delhi.
Background:
- This MoU marks the first formal agreement of its kind between NPCIL and ENEC. The collaboration aligns with the broader commitment made during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the UAE in August 2015, which focused on peaceful nuclear energy applications, including safety, health, agriculture, and science and technology.
Trilateral Cooperation:
- The agreement follows a series of discussions on nuclear cooperation between India and the UAE. On September 19, 2022, Foreign Ministers from France, India, and the UAE met in New York during the UN General Assembly and initiated a trilateral cooperation framework. This was further solidified by a phone call on February 4, 2023. The trilateral format aims to promote joint projects in energy, emphasizing solar and nuclear energy.
Additional Agreements:
During the Crown Prince’s visit, several other agreements were also signed:
- LNG Supply MoU: An agreement was reached between Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) and Indian Oil Corporation Limited for long-term LNG supply.
- Production Concession Agreement: Urja Bharat and ADNOC signed an agreement for Abu Dhabi Onshore Block 1.
- Food Parks Development: The Government of Gujarat and Abu Dhabi Developmental Holding Company PJSC (ADQ) signed an MoU for developing food parks in India. This initiative aligns with the I2U2 grouping (including Israel and the United States), which envisions food parks in Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh.
Conclusion:
The visit of the Crown Prince and the signing of these agreements reflect the strengthening ties between India and the UAE. This dynamic development coincides with the first India-Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Foreign Ministers’ meeting held in Riyadh on September 8-9. External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar highlighted India's growing energy demands and its significant role in future global energy markets during his remarks at the meeting.
India-Singapore Relations

- 04 Sep 2024
- High-Level Inter-Governmental Contacts:
- Frequent and high-level exchanges, including the Prime Minister's upcoming visit.
- Recent second India-Singapore Ministerial Roundtable with senior Indian ministers.
- Key Areas of Cooperation:
- Digitalisation, skills development, sustainability, healthcare, advanced manufacturing, and connectivity.
- Broader contacts include parliamentary and judicial exchanges.
- Economic Ties:
- Singapore is India’s largest trading partner among ASEAN countries and the sixth largest globally.
- Singapore is also the largest source of foreign direct investment (FDI) for India.
- People-to-People Exchanges:
- Large concentration of IIT and IIM alumni in Singapore.
- Historical ties, including the Indian National Army's presence and the contributions of early Indian diaspora in Singapore.
- Regional Policy and Strategic Importance:
- Singapore has supported India’s “Look East” and “Act East” policies.
- Facilitated India’s dialogue partnership with ASEAN.
- Regional implications due to Myanmar’s instability, with India and Singapore both having stakes.
- Defence and Maritime Cooperation:
- Important defence component and maritime collaboration.
- Focus on the Indo-Pacific region amidst growing Chinese influence and new regional architectures like the QUAD.
- Trade and Economic Outlook:
- The visit provides an opportunity to review and expand trade and economic partnerships.
- Potential for increased Chinese FDI into India, with Singaporean entities likely to play a role.
- Complementarities and Challenges:
- Singapore's role as a global trading and investment hub complements India’s economic landscape.
- Highlights India's regulatory and structural inefficiencies, pointing to areas needing improvement for enhanced bilateral cooperation.
World Health Assembly 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Assembly will convene from May 27 to June 1 to discuss amendments to the International Health Regulations, aimed at improving the ability of countries to respond to public health emergencies and prepare a potential new pandemic agreement.
What is the World Health Assembly?
- The World Health Assembly is the decision-making body of the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations (UN) agency dedicated to promoting the global population's health and access to the highest levels of healthcare provision.
- Its main functions are to determine WHO's policies, elect the Organization's Director-General, supervise financial policies, and review and approve the proposed WHO budget.
- Delegates from WHO member states come together at an annual assembly held at the UN headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, to focus on a specific healthcare agenda created by the organization's Executive Board.
- The Executive Board comprises 34 technically qualified members, each elected for a three-year term.
- They meet every year in January to agree on the agenda and any resolutions that will be put before the World Health Assembly for consideration.
- Now in its 76th session, the theme for this year’s event is “Health For All: 75 Years of Improving Public Health”.
What does the Assembly do?
- Delegates at the annual World Health Assembly discuss the Executive Board's policy agenda for the coming year and decide which health goals and strategies will guide the WHO's public health work.
- Other functions include voting to appoint the organization's Director-General to serve a five-year term.
- Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus holds the post currently, having been re-elected in 2022 to serve a second term as head of the world's leading public health agency.
Why is it important?
- Since its inauguration, the Assembly has presided over WHO policies that have helped eradicate deadly diseases like smallpox and the poliovirus and helped foster international collaborations to develop and distribute vaccines for diseases like malaria and COVID-19.
About International Health Regulations (IHR):
- First adopted by the World Health Assembly (WHA) in 1969, the IHR was last revised in 2005. These regulations aim to maximize collective efforts in managing public health events while minimizing disruptions to travel and trade.
- The IHR has 196 State Parties, including all 194 WHO Member States, plus Liechtenstein and the Holy See.
- The IHR provide a comprehensive legal framework that outlines countries' rights and obligations in managing public health events and emergencies with the potential to cross borders.
- The regulations introduce crucial safeguards to protect the rights of travellers and others, covering the treatment of personal data, informed consent, and non-discrimination in the application of health measures.
- Legally Binding Instrument: As an instrument of international law, the IHR is legally binding on 196 countries.
The League of Arab States (LAS)/Arab League
- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Arab League called recently for a UN peacekeeping force in the "occupied Palestinian territories" at an international summit dominated by the war between Israel and Hamas.
What is the Arab League?
- The League of Arab States was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan (later renamed Jordan), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia and Syria, with Yemen joining on 5 May 1945.
- It currently has 22 member states; Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordon, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
- Four countries have been admitted as observers: Brazil, Eritrea, India and Venezuela.
- Each member state has one vote in the League Council, while decisions are binding only on those states that have voted for them.
- The official language of the Arab League and its 22 member states is Arabic.
- The league seeks to promote the political, social, and military interests of its members.
- The head of the league is known as the secretary-general.
- The secretary-general is appointed to a five-year term by a two-thirds majority of league members.
- Headquarters: Cairo, Egypt.
Goals:
- The overall aim of the league is to promote Arab interests.
- Its main goals are to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic, and social programs of its members and to try to settle disputes among them or between them and third parties.
- In 1950 the members also agreed to provide military support to help defend each other.
The Arab League Council:
- The League Council is the highest body of the Arab League and is composed of representatives of member states, typically foreign ministers, their representatives, or permanent delegates.
- Each member state has one vote.
- The Council meets twice a year, in March and September. Two or more members may request a special session if they desire.
- The general secretariat manages the daily operations of the league and is headed by the secretary-general.
- The general secretariat is the administrative body of the league, the executive body of the council, and the specialized ministerial councils.
Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) will now be open to new members and observers after a historic first charter of the grouping came into force on 20 May.
What is BIMSTEC?
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a multilateral regional organization that brings together seven member states located in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal, forming a contiguous regional unity.
- Aims: The primary aim of BIMSTEC is to accelerate shared growth and cooperation among littoral and adjacent countries in the Bay of Bengal region.
- Formation: The organization was initially founded as BIST-EC in June 1997, following the adoption of the Bangkok Declaration.
- The founding members included Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- With Myanmar's entry in late 1997, the organization evolved into BIMST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- In 2004, the inclusion of Nepal and Bhutan led to the formation of BIMSTEC, as we know it today.
- The current member states comprise five South Asian nations: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, and two Southeast Asian nations: Myanmar and Thailand.
- BIMSTEC's Permanent Secretariat is situated in Dhaka, Bangladesh, serving as a hub for regional cooperation and coordination among member states.
Areas of cooperation:
- BIMSTEC functions as a sector-driven cooperative organization, initially focusing on six key sectors: Trade, Technology, Energy, Transport, Tourism, and Fisheries.
- Over time, the scope of cooperation has expanded, and as of now, BIMSTEC has identified 14 priority areas of cooperation.
- The inclusion of Climate Change in 2008 marked the 14th priority area.
- Within these priority areas, each member country takes responsibility for leading specific sectors.
- This allows for focused efforts and utilization of regional expertise.
- India, for example, is the leading country in several crucial areas, including Transport & Communication, Tourism, Environment & Disaster Management, and Counter-Terrorism & Transnational Crime.
- This leadership role involves coordinating initiatives, sharing best practices, and driving collaborative efforts within these sectors to enhance regional development and cooperation.
International Criminal Court (ICC)

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
International Criminal Court (ICC) Chief Prosecutor recently announced that he has applied for arrest warrants against Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Defence Minister Yoav Gallant for crimes against humanity in the ongoing Gaza war.
What is the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
- The International Criminal Court (ICC) in The Hague (Netherlands) is a permanent global court established in 2002.
- The ICC was created as a result of the Rome Statute, a treaty established at a United Nations conference in Italy and signed in 1998 by 120 countries — giving the ICC its power.
- The ICC is independent of the United Nations (UN) but is endorsed by the UN General Assembly.
- It also maintains a cooperation agreement with the UN.
- It has the power to prosecute individuals and leaders for genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes.
- Unlike the International Court of Justice (ICJ), which is an organ of the UN, the ICC does not prosecute states.
The Court does not have universal jurisdiction:
- Its jurisdiction only applies to crimes committed by nationals of States Parties or Non-States Parties that have recognized its jurisdiction through declaration and crimes committed in such States.
- The Court may also exercise its jurisdiction for crimes that have been referred to it by the United Nations Security Council, in accordance with a resolution adopted under Chapter VII of the Charter of the United Nations.
The Court’s jurisdiction is governed by the principle of complementarity:
- It does not relieve States of their primary responsibility and only intervenes when the States have been unable or did not wish, to try crimes under their jurisdiction.
- The Court is not a United Nations body. However, it is part of the international system to fight against impunity and prevent and handle crises.
How is the ICC governed?
- The Rome Statute created three bodies:
- The International Criminal Court
- The Assembly of States Parties
- The Trust Fund for Victims
- The Assembly of States Parties (ASP) is made up of representatives of States Parties.
- It provides general guidelines while respecting the independence of the Court and makes decisions relating to how it operates (in particular by electing judges and the Prosecutor and by approving the ICC’s budget).
- The Trust Fund for Victims was created by the ASP to grant individual reparations to victims by executing reparations orders handed down by the Court.
- It also contributes to their rehabilitation through psychological and physical recovery and material support.
- The Fund has financed projects in Uganda, the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The International Criminal Court is made up of four bodies:
- The Presidency (made up of three judges) is responsible for external relations with States, organizes the Divisions’ judicial work and supervises the administrative work of the Registry;
- The Judicial Divisions – the Pre-Trial Division, the Trial Division and the Appeals Division – carry out judicial proceedings;
- The Office of the Prosecutor carries out preliminary analyses, investigations and prosecutions;
- The Registry carries out non-judicial activities related to safety, interpretation, information and outreach or support to lawyers for the defence and victims.
The recruitment process for judges at the ICC:
- Every three years, the ASP elects six new judges, a third of the 18 ICC judges, for a term of nine years.
- The candidates for the position of judge at the ICC are presented by the States Parties.
- The election of judges is governed by a unique procedure that aims to ensure, insofar as possible, that there is a balanced bench with regard to legal expertise, geographical representation and gender.
How does the International Criminal Court differ from the International Court of Justice?
International Criminal Court:
1. Part of the United Nations (UN)?
Ans. No, The International Criminal Court is independent but co-operates closely with the UN.
2. What is its aim?
Ans. To try individuals who are suspected of the crime of genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity or the crime of aggression.
3. Where is it located?
Ans. The Hague
International Court of Justice:
1. Part of the United Nations (UN)?
Ans. No, The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations.
2. What is its aim?
Ans. To settle legal disputes between states,and to advise the UN on legal questions.
3. Where is it located?
Ans. The Hague
World Telecommunication and Information Society Day

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To commemorate the World Telecommunication and Information Society Day, C-DOT, the premier Telecom R&D Centre of the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) celebrates and announces special Initiatives “NIDHI” & “STAR Program” for the development of indigenous telecom solutions & technologies.
What is World Telecommunication and Information Society Day?
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is celebrated every year in May to honour the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) on May 17, 1969.
- The day can be traced back to commemoration of the two significant events in the history of global communication.
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) commemorates two significant events in the history of global communication.
- Firstly, it marks the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1865, when the first International Telegraph Convention was signed.
- Followed by, in November 2005, the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) called upon the United Nations General Assembly to also declare May 17th as World Information Society Day.
- And then in 2006, the ITU Plenipotentiary Conference in Antalya, Turkey, agreed to combine the two events as World Telecommunication and Information Society Day.
- This year’s World Telecommunications and Information Society Day 2024 focuses on the theme, “Digital Innovation for Sustainable Development,” underlying how digital innovation may help link everyone and create sustainable prosperity for all.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- Established in 1865, it is the oldest among the UN’s 15 specialized agencies.
- ITU is responsible for allocating global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, developing technical standards to ensure network interconnectivity, and improving ICT access for underserved communities.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, ITU is part of the UN Development Group and operates 12 regional offices worldwide.
- It functions as an intergovernmental public-private partnership with 193 member states and around 800 sector members. India, a member since 1952, was re-elected to the ITU Council for the 2019-2022 term.
International Bullion Exchange (IIBX)

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The State Bank of India (SBI) recently announced that it has secured the distinction of being the first bank to become a trading-cum-clearing (TCM) Member of the India International Bullion Exchange at the GIFT City in Gujarat.
What is the International Bullion Exchange (IIBX)?
- India International Bullion Exchange (IIBX) is India's first International Bullion Exchange.
- It is situated within the Gujarat International Finance Tech City (GIFT City) IFSC in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Conceptualized to serve as a premier platform for importing bullion into India, IIBX aims to establish a world-class ecosystem for bullion trading, fostering investment in bullion financial products, and providing top-tier vaulting facilities.
What is Bullion?
- Bullion refers to high-purity physical gold and silver, typically stored in the form of bars, ingots, or coins.
- While sometimes recognized as legal tender, bullion primarily serves as a reserve for central banks and institutional investors.
Key Features:
- Transparent Price Discovery: IIBX prioritizes transparent price discovery mechanisms, ensuring fair and equitable transactions.
- Responsible Sourcing and Supply Chain Integrity: Emphasizing ethical practices, IIBX upholds responsible sourcing and supply chain integrity standards.
- Quality Assurance and Standardization: IIBX maintains rigorous quality assurance protocols and standardized practices to uphold the integrity of traded bullion.
Regulation and Oversight:
- Under the governance of the International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA), IIBX operates under a unified regulatory framework dedicated to the development and oversight of financial products, services, and institutions within IFSCs.
Competitive Advantage:
- Offering a diverse array of products and cutting-edge technology, IIBX provides cost-effective solutions unparalleled by Indian exchanges and global counterparts in major financial hubs like Hong Kong, Singapore, Dubai, London, and New York.
What is the International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA)?
- The International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA) is a regulatory body established in India to oversee and regulate financial products, services, and institutions operating within International Financial Services Centers (IFSCs).
- IFSCA was formed to develop and promote the financial ecosystem within IFSCs, ensuring compliance with international standards and best practices.
- It regulates various entities such as banking, insurance, securities markets, and other financial intermediaries to foster growth and innovation in the financial sector within IFSCs.
- IFSCA's jurisdiction includes Gujarat International Finance Tech City (GIFT City) IFSC in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, which serves as a hub for international financial activities in India.
World Migration Report 2024

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the recently released World Migration Report 2024, which is published by the International Organization for Migration (IOM), India has consistently been the top recipient of remittances globally.
Key Highlights of the World Migration Report 2024:
- Resilience Amidst COVID-19: Despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, international migration remains a vital driver of human development and economic progress.
- Notably, there has been a remarkable over 650 per cent surge in international remittances from 2000 to 2022, soaring from USD 128 billion to USD 831 billion.
- This growth defied predictions of a substantial decrease in remittances due to COVID-19.
- Remittances to Low and Middle-income Countries: Out of the total remittances, which amounted to USD 831 billion, a significant portion of USD 647 billion was sent by migrants to low and middle-income countries.
- These remittances play a crucial role in the GDPs of these nations, surpassing foreign direct investment globally.
- Persistent Challenges: While international migration continues to foster human development, the report underscores enduring challenges.
- The global population of international migrants has reached approximately 281 million, while the number of individuals displaced by conflict, violence, disasters, and other factors has surged to a record high of 117 million.
- Urgent action is imperative to address displacement crises effectively.
- Misinformation and Politicization: Despite the fact that most migration is regular, safe, and regionally focused, public discourse has been clouded by misinformation and politicization.
- It is essential to provide a clear and accurate depiction of migration dynamics to counteract this trend.
About the International Organization for Migration (IOM):
- Established in 1951, IOM, the UN Migration Agency, is the leading inter-governmental organization in the field of migration and works closely with governmental, intergovernmental and non-governmental partners.
- IOM works to help ensure the orderly and humane management of migration, promote international cooperation on migration issues, assist in the search for practical solutions to migration problems and provide humanitarian assistance to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced people.
- Membership: Currently, IOM counts 175 Member States and 8 states with Observer status.
- India joined as an IOM Member State on June 18, 2008.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, IOM's headquarters serves as a hub for its global operations.
AlphaFold 3

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google Deepmind has unveiled the third major version of its “AlphaFold” artificial intelligence model, designed to help scientists design drugs and target diseases more effectively.
About AlphaFold 3:
- AlphaFold 3 is a major advancement in artificial intelligence created by Google's DeepMind in collaboration with Isomorphic Labs.
- It's essentially a powerful tool that can predict the structures and interactions of various biological molecules such as:
- Predict structures of biomolecules: Unlike previous versions that focused on proteins, AlphaFold 3 can predict the 3D structure of a wide range of molecules, including DNA, RNA, and even small molecules like drugs (ligands).
- This is a significant leap in understanding how these molecules function.
- Model molecular interactions: AlphaFold 3 goes beyond just structure prediction.
- It can also model how these molecules interact with each other, providing valuable insights into cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
The potential applications of AlphaFold 3 are vast. It has the potential to revolutionize fields like:
- Drug discovery: By understanding how drugs interact with their targets, researchers can design more effective medications.
- Genomics research: AlphaFold 3 can help scientists understand the function of genes and how mutations can lead to disease.
- Materials science: By modelling the interactions between molecules, scientists can design new materials with specific properties.
- AlphaFold 3 is a significant breakthrough and is freely available for non-commercial use through AlphaFold Server.
- This makes this powerful tool accessible to researchers around the world, potentially accelerating scientific advancements.
Diplomatic Passport

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
After allegations of sexual abuse by Janata Dal (Secular) MP Prajwal Revanna came to light, the politician fled to Germany on a diplomatic passport.
What is a Diplomatic Passport?
- Diplomatic passports are issued to people holding diplomatic status or deputed by the Government of India for official duty abroad.
- Unlike normal passports, which are valid for 10 years and have a dark blue cover, diplomatic passports are valid for five years or less and have maroon covers.
- Diplomatic passports, also known as 'Type D' passports.
- A diplomatic passport has 28 pages.
- Holders of such passports are entitled to certain privileges and immunities as per international law, including immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country.
Issuing Authority:
- The Ministry of External Affairs’s (MEA) Consular, Passport & Visa Division issues diplomatic passports (‘Type D’ passports) to people falling in broadly five categories:
- Those with diplomatic status;
- Government-appointed individuals travelling abroad for official business;
- Officers working under the branches A and B of the Indian Foreign Service (IFS), normally at the rank of Joint Secretary and above; and
- Relatives and immediate family of officers employed in IFS and MEA.
- Select individuals who are authorised to undertake official travel on behalf of the government”.
- The MEA issues visa notes to government officials going abroad for an official assignment or visit.
What are the Benefits of Having a Diplomatic Passport?
- Official identification: The diplomatic passport serves as an official identification document for individuals representing the Indian government on diplomatic missions.
- It helps in establishing their identity and official status.
- Diplomatic immunity: Diplomatic passport holders are typically entitled to certain privileges and immunities as per international law.
- This includes immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country, safeguarding their ability to perform official duties without hindrance.
- Visa facilitation: Diplomatic passports often enjoy certain privileges when it comes to visa facilitation.
- Many countries offer expedited visa processing or waive visa requirements altogether for diplomatic passport holders, simplifying travel arrangements for official purposes.
- Access to diplomatic channels: The diplomatic passport grants access to diplomatic channels and services provided by Indian embassies, consulates, and other diplomatic missions worldwide.
- This includes assistance with consular services, protection, and support while abroad.
- Priority services: Diplomatic passport holders may receive priority services at airports and during immigration procedures.
- This can include dedicated immigration counters or expedited security and customs clearance, saving time during travel.
- Official representation: The diplomatic passport signifies the official representation of the Indian government and confers a sense of authority and credibility while dealing with international counterparts, foreign officials, and diplomatic communities.
Can Diplomatic Passports be Revoked?
- According to The Passports Act, 1967, the passport authority may cancel a passport or travel document, with the previous approval of the Central government.
- The passport authority can impound or revoke a passport if the authority believes that:
- The passport holder or travel document is in wrongful possession
- If the passport was obtained by the suppression of material information or based on wrong information provided by the individual
- If it is brought to the notice of the passport authority that the individual has been issued a court order prohibiting his departure from India or has been summoned by the court.
- A diplomatic passport can be revoked upon orders from a court during proceedings with respect to an offence allegedly carried out by the passport holder before a criminal court.
Booker Prize

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Booker Prize, one of the most prestigious awards in the literary world, has recently come under fire for the historical links to slavery of its original sponsor, Booker Group.
What is the Booker Prize?
- The Booker Prize was founded in 1969, initially just for writers from the Commonwealth, but later opened to writers globally.
- Each year, the prize is awarded to a single work of fiction in the English language.
- In 2004, a separate International Booker Prize was instituted for translated works.
- The prize was co-founded by publishers Tom Maschler and Graham C Greene, and from 1969 to 2001, it was sponsored by, and named after Booker Group Ltd, a British wholesale foods company, established in 1835 as a shipping and trading company, and now owned by Tesco.
- In 2002, British investment management firm Man Group became the prize’s sponsor, and thus it came to be known as The Man Booker Prize.
- After Man Group ended its sponsorship in 2019, American charity Crankstart took over, and reverted the award’s name to its original ‘Booker Prize’.
- Irish author Paul Lynch wins the 2023 Booker Prize for his novel 'Prophet Song'.
About the International Booker Prize:
- The International Booker Prize (formerly known as the Man Booker International Prize) was launched in 2005.
- It was originally awarded every two years to a living author who has published fiction either originally in English or whose work is generally available in translation in the English language.
- It was an award for the body of work of the author, rather than awarded for an individual novel.
- Beginning in 2016, the award changed. It is now given annually to a single book in English translation, with a £50,000 prize for the winning title, shared equally between author and translator.
- Georgi Gospodinov and Angela Rodel have won the International Booker Prize 2023 for the novel ‘Time Shelter’.
- ‘Tomb of Sand’ Geetanjali Shree, translated by Daisy Rockwell Winner 2022 winner.
National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG)

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A central government delegation is on a three-day visit to Bangladesh beginning Sunday to further boost bilateral ties on governance matters, according to an official statement.
About the National Centre for Good Governance:
- The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) was set up in 2014 by the Government of India as an apex–level autonomous institution under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- The Centre traces its origin to the National Institute of Administrative Research (NIAR), which was set up in 1995 by the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), the Government of India's topmost training institute for civil services.
- NIAR was subsequently rechristened and subsumed into NCGG.
- NCGG deals with a gamut of governance issues from local, state to national levels, across all sectors.
- The Centre is mandated to work in the areas of governance, policy reforms, capacity building, and training of civil servants and technocrats of India and other developing countries.
- It also works as a think tank.
- Since its inception, the Centre has been extensively working in areas such as primary and elementary education, decentralized planning at district and block levels, capacity building of Panchayat Raj Institutions (PRIs), participatory models of learning and action, rural development, cooperatives, and public sector management, etc.
- In addition, it focuses on issues related to good governance, social accountability, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH), among other sectors.
- The Centre encapsulates the essence of good governance and weighs on the importance of the rule of law, bringing in transparency, working to promote public participation in governance, service delivery, and reforms, as well as in developing accountable institutions, access to information, etc.
Carnation Revolution

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Portugal commemorated its 50th anniversary of Portugal's Carnation Revolution – the peaceful uprising that toppled a dictatorship and ended a decade of colonial war.
About the Carnation Revolution:
- The Carnation Revolution, also known as the 25th of April, was a pivotal event in Portugal's history that marked the transition from an authoritarian regime to a democratic government.
- On April 25, 1974, a group of military officers orchestrated a nearly bloodless military coup, overthrowing the Estado Novo dictatorship that had ruled Portugal for over four decades.
- The revolution aimed to accelerate decolonization, end ongoing wars through negotiations, and improve socio-economic conditions within Portugal.
- This event not only transformed Portugal's political landscape but also had significant implications for the nation's African colonies.
- Several factors contributed to the success of the Carnation Revolution, including widespread discontent with the authoritarian regime, a costly and unpopular colonial war, and the growing desire for democracy and improved living conditions.
- The coup leaders, known as the Armed Forces Movement (MFA), garnered support from various factions, including the Communist Party, socialists, and moderate democrats.
- The Carnation Revolution was named after a Lisbon flower seller who offered red carnations to soldiers, which were then placed in the barrels of their rifles.
- This iconic gesture symbolized the peaceful nature of the coup and solidified the carnation as a symbol of Portugal's democratic movement.
- The 50th anniversary of the Carnation Revolution celebrated on April 25, 2024, signifies the enduring impact of this historic event on Portugal's political trajectory and its relationship with its former colonies.
World Craft Council International

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Crafts Council International (WCCI), a Kuwait-based organization working on the recognition and preservation of traditional crafts across the globe, has picked Srinagar for mapping its craft clusters before its final nomination as the World Craft City (WCC) from India this year.
About World Crafts Council:
- World Crafts Council AISBL is an international non-profit organization dedicated to fostering the preservation, promotion, and advancement of global craftsmanship and traditional crafts.
- It was founded by Ms. Aileen Osborn Vanderbilt Webb, Ms. Margaret M. Patch, and Smt Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay at the 1st World Crafts Council General Assembly in New York on June 12, 1964.
- Since its inception, the World Crafts Council AISBL has been affiliated with UNESCO under Consultative Status for many years.
- Its mission is to empower artisans, celebrate cultural diversity, and contribute to sustainable development by supporting the rich tapestry of global craftsmanship and preserving languishing crafts from extinction.
- Headquarters: The current headquarters for the term (2021-2024) is located in Kuwait.
Objectives:
- The main objective of the World Crafts Council AISBL is to strengthen the status of crafts in cultural and economic life.
- The Council aims to promote fellowship among craftspersons by offering them encouragement, help, and advice.
- It fosters and assists cultural exchange through conferences, international visits, research studies, lectures, workshops, exhibitions, and other activities.
- The WCC also seeks to foster wider knowledge and recognition of the craftspeople's work with due regard to the diversified cultural and national backgrounds and traditions of its members.
- In carrying out these principles, the Council shall consult with governments, national and international institutions, societies, and individuals.?
India has only 3 cities designated as World Craft City:
- Mysuru (Kinnal paintings, Sandalwood carvings, Rosewood Inlay, etc.)
- Mamallapuram (Stone Carving continuing since the Pallava dynasty (275 CE to 897 CE)
- Jaipur (Kundan Jadai (Gem setting), Meenakari Jewellery, Lac-based craft, Gotta Patti Work, etc.)
About the World Craft City Programme:
- The World Craft City Programme, initiated in 2014 by the World Crafts Council AISBL (WCC-International), recognizes the significance of local authorities, artisans, and communities in global cultural, economic, and social advancement.
- By establishing a vibrant network of craft cities worldwide, it embraces the ideals of the creative economy and acknowledges the valuable contributions of local entities to comprehensive development.
- Notably, Jaipur (Rajasthan), Mamallapuram (Tamil Nadu), and Mysore have already been designated as craft cities under this initiative in India.
Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA)

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) Asia Pacific, in collaboration with other environmental organizations, has called on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to take decisive action in response to plastic pollution.
About Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA):
- The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) is an alliance of over 1,000 grassroots groups, NGOs, and individuals working towards a transition from a linear, extractive economy to a circular system.
- GAIA's primary objective is to create a world that prioritizes people's right to a safe and healthy environment, free from toxic pollution and resource depletion.
- GAIA envisions a just, zero-waste world where communities' rights are respected, and ecological limits are acknowledged. To achieve this vision, the alliance focuses on:
- Eliminating Incineration: GAIA advocates for alternatives to incineration and promotes waste management practices that protect the environment and public health.
- Promoting Zero Waste: The alliance supports the adoption of zero-waste strategies, emphasizing waste reduction, reuse, and recycling to conserve resources and reduce pollution.
- Addressing Plastic Pollution: GAIA recognizes the global plastic pollution crisis and works on initiatives to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable alternatives.
- Mitigating Climate Change: GAIA advocates for climate-friendly waste management practices, emphasizing the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions from waste disposal.
What is Incineration?
- Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves burning hazardous materials at high temperatures to destroy contaminants.
- This process takes place in an "incinerator," a furnace specifically designed to safely burn hazardous materials within a combustion chamber.
- Various types of hazardous materials can be treated through incineration, including soil, sludge, liquids, and gases.
- While incineration effectively destroys many harmful chemicals such as solvents, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pesticides, it does not destroy metals like lead and chromium.
- Modern incinerators are equipped with air pollution control mechanisms, such as fabric filters, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators.
- These technologies help remove fly ash and gaseous contaminants generated during the incineration process, mitigating its environmental impact.
- Despite its benefits in waste treatment, incineration remains a topic of debate due to concerns about residual pollutants and the potential for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
India Abstains from UNHRC Resolution on Gaza Ceasefire

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently abstained on a resolution at the Human Rights Council that called on Israel for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza.
India's Voting Pattern on Israel-Palestine Issues at the UNHRC:
- India's stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict has been reflected in its voting behavior at the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
- While India has voted in favor of resolutions criticizing Israel for human rights violations, occupation of the Syrian Golan, and affirming Palestinian self-determination, it has also abstained from certain resolutions.
- In a significant development, India abstained from a resolution calling for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and an arms embargo on Israel.
- This decision followed instances of violence, including the killing of aid workers and airstrikes.
- India's abstention is believed to be in line with its previous votes on resolutions involving "accountability."
- India's approach indicates its belief that both parties should be held accountable for their actions.
- As a result, it refrains from supporting resolutions that single out one side for condemnation.
- By taking a balanced stance, India aims to promote peace and stability in the region while advocating for the rights of all parties involved.
About the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is an inter-governmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2006.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, the council serves as a key platform for addressing human rights issues globally.
- The High Commissioner for Human Rights serves as the principal human rights official within the UN system.
- The council convenes three times annually to address human rights violations worldwide.
Membership:
- Comprising 47 member states, the council is responsible for promoting and safeguarding human rights across the globe.
- Member states are elected individually via secret ballot by a majority vote of the General Assembly.
- The election of members occurs within geographical groups to ensure equitable representation.
Tenure:
- Council members serve for a term of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after two consecutive terms.
The UNHRC's primary functions include:
- Promoting universal respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- Addressing violations of human rights, including gross and systematic violations.
- Developing international human rights law and making recommendations to the UN General Assembly.
- Conducting investigations into alleged human rights abuses through special rapporteurs and working groups.
- Reviewing the human rights records of all UN member states through the Universal Periodic Review process.
Sannati: Ancient Buddhist Site

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Left neglected for many years after it came to light through the ASI excavations in the 1990s, the ancient Buddhist site of Sannati on the bank of the Bhima River got a restoration project in 2022.
About Ancient Sannati Buddhist site:
- This ancient Sannati Buddhist site, situated alongside the Bhima River near Kanaganahalli in Karnataka's Kalaburagi district, offers a rich historical and cultural experience.
- Notably, it also boasts the Chandrala Parameshwari Temple, a popular attraction among tourists.
Key discoveries at this site include evidence of development across three distinct phases:
- Maurya, Early Satavahana, and Later Satavahana periods, span from the 3rd Century B.C. to the 3rd Century A.D.
- The Ranamandala area of Sannati presents a unique chronological timeline from prehistoric to early historic eras.
- Among the remarkable findings is an inscription in the Prakrit language, inscribed using Brahmi script.
- Noteworthy is the recovery of a significant stone sculpture portraying Mauryan Emperor Ashoka, surrounded by his queens and attendants, with the inscription "Raya Asoko" in Brahmi script, leaving no doubt about the identity of the depicted figure.
- The excavation also yielded around 60 dome slabs featuring sculptural depictions of Jataka stories, significant events in the life of Buddha, portraits of Shatavahana monarchs, and unique representations of Buddhist missionaries dispatched by Ashoka to various regions.
- Moreover, the ancient Nagavi Ghatikasthana, often dubbed as the Takshashila of the South, lies approximately 40 km from Sannati.
- Functioning as a prominent educational center akin to a modern-day university during the Rashtrakuta and Kalyana Chalukya dynasties from the 10th to 12th Centuries, it held great historical significance.
Wadge Bank
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
While India 'gave away' rights to Katchatheevu, in a subsequent pact, it secured sovereign rights in Wadge Bank near Kanyakumari.
What is Wadge Bank?
- Wadge Bank is a 10,000 square kilometer submarine plateau, of the sea south of Kanyakumari that is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- Wadge Bank, located near Cape Comorin, is home to more than 60 species of ornamental fish and other oceanic animals.
- It is a productive coastal area where three seas meet and tides create a rich fishing ground from May to October.
- Moreover, it is an invaluable treasure that indigenous people and communities depend on for food and resources, and is important to their culture.
How did India get control of the Wadge Bank?
- Wadge Bank came to India as part of the second of the two accords signed with Sri Lanka in the 1970s.
- Following the 1974 agreement under which Prime Minister Indira Gandhi ‘gave away’ Katchatheevu island to Sri Lanka, New Delhi, and Colombo signed another pact in 1976 under which the former bought Wadge Bank.
- On March 23, 1976, India and Sri Lanka signed the agreement on the maritime boundary in the Gulf of Mannar and the Bay of Bengal as part of which it was agreed that the Wadge Bank “lies within the exclusive economic zone of India, and India shall have sovereign rights over the area and its resources”.
- In the general description of Wadge Bank annexed with the treaty shared with the United Nations, it is described as “outside the territorial waters of India”.
- The Wadge Bank near Kanyakumari is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- As per the 1976 pact, Sri Lankan fishermen can’t engage in activities here.
- ??But at the request of Sri Lanka and as a gesture of goodwill, India agreed that Lankan fishing vessels licensed by the Government of India could fish in Wadge Bank for three years from its establishment as an exclusive economic zone of India with the stipulation that only six such vessels can fish and their catch cannot exceed 2,000 tonnes in a year.
- And, again at the request of the Sri Lankan government, India agreed to provide Colombo with 2,000 tonnes of fish of the quality, species, and at the price mutually agreed by the two sides for five years after the Lankans stopped fishing at the Wadge Bank.
BIMSTEC Charter

- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a significant majority in Nepal's Lower House backed the proposal to endorse the BIMSTEC Charter.
About the BIMSTEC Charter:
- The BIMSTEC Charter, officially signed and adopted during the Fifth BIMSTEC Summit in Colombo, Sri Lanka in 2022, serves as a cornerstone legal and institutional framework for the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC).
- This charter aims to establish a structured environment conducive to rapid economic development by delineating specific cooperation projects within the agreed areas of collaboration, along with potential expansions into additional areas as mutually agreed upon by Member States.
- Furthermore, the charter reaffirms the enduring commitment to the foundational principles and objectives of BIMSTEC, as articulated in the Bangkok Declaration of 1997.
The Importance of the BIMSTEC Charter:
- By officially adopting the BIMSTEC Charter, the organization transforms into a structured institution comprising member states situated along the Bay of Bengal, thereby formalizing their cooperation and dependence on this vital maritime region.
- The Charter grants BIMSTEC the authority to establish external relations with non-member states, developmental partners, as well as regional, UN, and international organizations, facilitating broader collaboration and engagement.
- Moreover, it underscores the imperative for a fair, just, equitable, and transparent global order while reiterating the commitment to multilateralism, with the United Nations at its core, and advocating for a rule-based international trading system.
About the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC):
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a regional organization comprising seven Member States lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal constituting a contiguous regional unity.
- This sub-regional organization came into being on 6 June 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration.
- It constitutes seven Member States:
- Five derive from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, and
- Two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- Initially, the economic bloc was formed with four Member States with the acronym ‘BIST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- Following the inclusion of Myanmar on 22 December 1997 during a special Ministerial Meeting in Bangkok, the Group was renamed ‘BIMST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- With the admission of Nepal and Bhutan at the 6th Ministerial Meeting (February 2004, Thailand), the name of the grouping was changed to ‘Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation’ (BIMSTEC).
Katchatheevu Island
- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi once again attacked the Congress about its decision to “callously give away” the island of Katchatheevu.
About the Island of Katchatheevu:
- Katchatheevu is an uninhabited area located between India and Sri Lanka in the Palk Strait.
- It measures around 1.6 km in length and slightly over 300 m wide at its broadest point.
- Situated northeast of Rameswaram, it is approximately 33 km away from the Indian coast.
- Moreover, it is positioned about 62 km southwest of Jaffna, at the northern tip of Sri Lanka, and 24 km from the inhabited Delft Island, which is a part of Sri Lanka.
- Katchatheevu is not suited for permanent settlement as there is no source of drinking water on the island.
History of the island:
- Being the product of a 14-century volcanic eruption, Katchatheevu is relatively new in the geological timescale.
- In the early medieval period, it was controlled by the Jaffna kingdom of Sri Lanka.
- In the 17th century, control passed to the Ramnad zamindari based out of Ramanathapuram, about 55 km northwest of Rameswaram.
What is the dispute?
- The island became part of the Madras Presidency during the British Raj.
- But in 1921, both India and Sri Lanka, at the time British colonies, claimed Katchatheevu to determine fishing boundaries.
- A survey marked Katchatheevu in Sri Lanka, but a British delegation from India challenged this, citing ownership of the island by the Ramnad kingdom.
- This dispute was not settled until 1974.
What is the Agreement on Katchatheevu Island?
- In 1974, Indira Gandhi made attempts to settle the maritime border between India and Sri Lanka, once and for all.
- As a part of this settlement, known as the ‘Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime Agreement’, Indira Gandhi ‘ceded’ Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka.
- At the time, she thought the island had little strategic value and that ceasing India’s claim over the island would deepen its ties with its southern neighbor.
- Moreover, as per the agreement, Indian fishermen were still allowed to access Katchatheevu “hitherto”.
- Unfortunately, the issue of fishing rights was not ironed out by the agreement.
- Sri Lanka interpreted Indian fishermen’s right to access Katchatheevu to be limited to “rest, drying nets and for visit to the Catholic shrine without a visa”.
- Another agreement in 1976, during the period of Emergency in India, barred either country from fishing in the other’s Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Again, Katchatheevu lay right at the edge of the EEZs of either country, retaining a degree of uncertainty about fishing rights.
How did the Sri Lankan Civil War Impact Katchatheevu?
- Between 1983 and 2009, the border dispute remained on the back burner as a bloody civil war raged in Sri Lanka.
- With the Sri Lankan naval forces preoccupied with their task of cutting off supply lines of the LTTE based out of Jaffna, incursions by Indian fishermen well into Sri Lankan waters were commonplace.
- Bigger Indian trawlers were especially resented as they would not only tend to overfish but also damage Sri Lankan fishing nets and boats.
- In 2009, the war with the LTTE ended, and things dramatically changed. Colombo beefed up its maritime defenses and turned its focus to Indian fishermen.
- Facing a depletion of marine resources on the Indian side, they would frequently enter Sri Lankan waters as they had been doing for years, but finally began facing consequences.
- To date, the Sri Lankan navy routinely arrests Indian fishermen and there have been many allegations of custodial torture and death.
- The demand for Katchatheevu is revived each time such an incident happens.
Indian Government Stance on Katchatheevu Island:
- The Union government’s position on Katchatheevu has largely remained unchanged.
- It has argued that since the island had always been under dispute, “no territory belonging to India was ceded nor sovereignty relinquished.”
India-led ‘Group of Friends’

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a high-level meeting of the India-led 'Group of Friends (GOF), India launched a new database designed to record crimes against UN peacekeepers and monitor progress in holding perpetrators accountable.
About the 'Group of Friends':
- The Group of Friends (GOF) was launched by India in 2022 to promote accountability for crimes against the Blue Helmets during its presidency of the UN Security Council.
- India, Bangladesh, Egypt, France, Morocco, and Nepal are co-chairs of the GOF, which comprises 40 member states.
Key objectives of the group include:
- Engaging and sharing information with the UN Secretary-General to assist member states hosting or having hosted peacekeeping operations in bringing perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers to justice.
- Serving as an informal platform at the UN to exchange information, share best practices, and mobilize resources to facilitate accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- Monitoring progress on bringing accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- The 'Group of Friends' will convene two meetings of its members per year and organize one event annually involving Permanent Missions and other stakeholders, ensuring greater safety and security for peacekeepers.
- This initiative represents the political will of member states, particularly troop and police contributing countries, to champion the implementation of UN Security Council resolution 2589, adopted in August 2021 under India's Presidency of the Council.
- Resolution 2589 called upon member states hosting or having hosted UN peacekeeping operations to take all appropriate measures to bring to justice perpetrators of violence against UN personnel, including their detention and abduction.
- The 'Group of Friends serves as a crucial platform for advancing this resolution, promoting accountability, and enhancing the protection of peacekeepers worldwide.
India's Significant Role in UN Peacekeeping:
- As a longstanding advocate for global peace and stability, India has demonstrated its commitment to United Nations (UN) peacekeeping operations.
- Over the past seven decades, India has contributed more than 260,000 peacekeepers, making it the largest cumulative contributor to UN peacekeeping missions.
- Despite the risks associated with such endeavors, India has remained steadfast in its support of peacekeeping efforts.
- Tragically, 177 Indian peacekeepers have made the ultimate sacrifice in the line of duty, reflecting India's dedication to fostering stability worldwide.
- Presently, India has more than 6,000 peacekeepers deployed in nine out of the twelve UN peacekeeping missions.
- As a strong proponent of accountability for crimes against peacekeepers, India plays a crucial role in advocating for the safety and security of these dedicated personnel.
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), in 2023, more than 4,500 Rohingya refugees embarked on a perilous journey across the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
About the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR):
- UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency, is a global organization dedicated to saving lives, protecting rights, and building a better future for people forced to flee their homes because of conflict and persecution.
- It leads international action to protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people.
- Formally known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Refugees, UNHCR was established by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1950 in the aftermath of the Second World War to help the millions of people who had lost their homes.
- Today, UNHCR operates in 137 countries and provides life-saving assistance, including shelter, food, water, and medical care for people forced to flee conflict and persecution, many of whom have nobody left to turn to.
- UNHCR defends their right to reach safety and helps them find a place to call home so they can rebuild their lives.
- UNHCR also collaborates with countries to improve and monitor refugee and asylum laws and policies, ensuring that human rights are upheld.
- UNHCR considers refugees and those forced to flee as partners, putting those most affected at the center of planning and decision-making.
Who are the Rohingya Refugees?
- Rohingya are an ethnic group, largely comprising Muslims, who predominantly live in the Western Myanmar province of Rakhine.
- They speak a dialect of Bengali, as opposed to the commonly spoken Burmese language.
- Though they have been living in the South East Asian country for generations, Myanmar considers them as persons who migrated to their land during Colonial rule so, it has not granted Rohingyas full citizenship.
- According to the 1982 Burmese citizenship law, a Rohingya (or any ethnic minority) is eligible for citizenship only if he/she provides proof that his/her ancestors have lived in the country before 1823. Otherwise, they are classified as “resident foreigners” or as “associate citizens” (even if one of the parent is a Myanmar citizen).
- Since they are not citizens, they are not entitled to be part of civil service. Their movements are also restricted within the Rakhine state.
Order of the Druk Gyalpo

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently received Bhutan’s highest civilian award, the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’, during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
What is the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’ Award?
- The Order of the Druk Gyalpo, Bhutan's most prestigious civilian award, was recently conferred upon Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
- As the first foreign Head of Government to receive this esteemed accolade, Prime Minister Modi joins a select group of individuals honored for their exceptional contributions to Bhutanese society, service, integrity, and leadership.
- According to the ranking and precedence established within Bhutan's honor system, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo represents the pinnacle of lifetime achievement, taking precedence over all other orders, decorations, and medals.
- Prime Minister Modi received the award in recognition of his outstanding contributions to strengthening India-Bhutan relations and his dedicated service to the Bhutanese nation and its people.
- Past recipients of the Order of the Druk Gyalpo include:
- Her Majesty The Royal Queen Grandmother Ashi Kesang Choden Wangchuck in 2008
- His Holiness Je Thrizur Tenzin Dendup in 2008, and
- His Holiness Je Khenpo Trulku Ngawang Jigme Choedra in 2018.
- With Prime Minister Modi's recent addition to this esteemed list, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo continues to symbolize Bhutan's appreciation for remarkable individuals who significantly impact the country and its people.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will host the fifth meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation startup forum in January next year according to the commerce and industry ministry.
About the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Startup Forum:
- The SCO Startup Forum is a platform for the stakeholders from the startup ecosystems from all SCO Member States to interact and collaborate.
- The entrepreneurial activities aim to empower the local startup communities in the SCO Member States.
- The SCO Startup Forum aims to create multilateral cooperation and engagement for startups among the SCO Member States.
- This engagement will empower the local startup ecosystems in the SCO Member States.
The following are the objectives of the engagement:
- Sharing of best practices to promote entrepreneurship and innovation to build knowledge-exchange systems
- Bringing Corporations and Investors across to work closely with startups and provide local entrepreneurs with much-needed support and market access
- Increasing scaling opportunities for startups by providing solutions in the field of social innovation and providing Governments with a plethora of innovative solutions
- Creating open procurement channels to enable matchmaking for procuring innovative solutions from startups
- Facilitating cross-border incubation and acceleration programs that will enable the startups to explore international markets and get focused mentorship.
Upcoming Events:
- India is set to host the second meeting of the Special Working Group for Startups and Innovation (SWG) in November 2024 and the SCO Startup Forum 5.0 in January 2025.
Past Initiatives:
- SCO Startup Forum 1.0: Established in 2020, laying the groundwork for multilateral cooperation among SCO Member States' startups.
- SCO Startup Forum 2.0: Held virtually in 2021, introducing the SCO Startup Hub, a centralized platform for the SCO startup ecosystem.
- SCO Startup Forum 3.0: Organized physically in 2023 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), marking a significant milestone for SCO Member States' startup collaboration.
- 1st Meeting of the SWG: Led by India, the first meeting of the SCO Special Working Group on Startups and Innovation in 2023 focused on the theme 'Growing from Roots', emphasizing foundational growth within the startup ecosystem.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Dr. Neeraj Mittal's unanimously elected as co-chair of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s digital innovation board recently.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Established in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, the ITU has evolved into the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICT).
- Recognized as a vital intergovernmental organization, the ITU facilitates collaboration between governments and private sector entities to advance global telecommunication and ICT services.
Key Points:
- Status: Designated as a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Membership: Boasting a diverse membership of 193 countries and over 1000 companies, universities, and international and regional organizations.
Functions:
- Allocation of global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordination and establishment of technical standards about telecommunication/ICT.
- Initiatives to enhance ICT accessibility in underserved communities worldwide.
- India's Engagement: India has maintained an active presence within the ITU since 1869, consistently participating in its endeavors.
- Notably, India has been a regular member of the ITU Council since 1952.
- Headquarters: Located in Geneva, Switzerland, the ITU serves as the global epicenter for fostering collaboration and innovation in the realm of ICT.
What is the Digital Innovation Board?
- The Digital Innovation Board is a pivotal component of the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development, aimed at addressing pressing needs within the realm of innovation as outlined in the Kigali Action Plan, which was adopted at the World Telecommunication Development Conference 2022.
- Comprised of Ministers and Vice Ministers of Telecom/ICT from 23 Member Countries of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), spanning across Asia, Europe, Africa, and North, and South America, this board serves as a strategic advisory body.
- ITU initiated the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development to tackle significant challenges and opportunities in innovation.
- This alliance operates through three key mechanisms:
- The Digital Transformation Lab
- The Network of Acceleration Centers, and
- The Digital Innovation Board.
- The Digital Innovation Board's primary objective is to offer strategic guidance, expertise, and advocacy in promoting local capacity building, fostering innovation, and encouraging entrepreneurship in digital development.
- Its overarching mission is to cultivate a more inclusive and equitable digital future for all stakeholders.
International Day of Forests 2024

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On March 21, 2024, people around the world celebrate World Forest Day. It's a day to remind everyone about how important forests are and all the good things they do for us.
About World Forest Day:
- World Forestry Day, also known as International Day of Forests, is celebrated on March 21 each year.
- The day aims to promote the sustainable management, conservation, and development of all types of forests for the benefit of current and future generations.
The theme for International Day of Forests 2024:
- This year's theme, "Forests and Innovation: New Solutions for a Better World" highlights the critical role of innovation and technology in protecting our forests.
- From advanced monitoring systems that track deforestation to sustainable forestry practices, innovation is key to overcoming the challenges threatening our forests.
History of International Day of Forests:
- The United Nations General Assembly announced March 21 to be the International Day of Forests in 2012.
- The day aims to respect and promote the value of a wide range of forests. Countries are encouraged to take part in regional, global, and local drives to set up a scope of forest and tree-related campaigns, like planting campaigns.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the United Nations Forum on Forests are the coordinators of the International Day of Forests.
Importance of International Day of Forests:
- As per the UNGA, "The United Nations Forum on Forests and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), in collaboration with Governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests and other relevant organizations in the field are responsible for organizing the events and campaigns related to the World Forestry Day."
- The importance of the International Day of Forests is to spread awareness and give instruction at all levels to guarantee feasible forest management and biodiversity preservation.
The Enduring Significance of Forests:
- Forests are often referred to as the "lungs of the planet" for a reason.
They play a vital role in:
- Combating Climate Change: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Protecting Biodiversity: Forests provide habitats for countless species of plants and animals, ensuring the health and balance of ecosystems.
- Providing Clean Air and Water: Forests filter air and water, regulating our climate and providing us with essential resources.
- Supporting Livelihoods: Millions of people around the world depend on forests for food, medicine, and income generation.
Celebrating and Taking Action:
- World Forestry Day is a springboard for action and we can get involved by:
- Support Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working towards forest conservation and sustainable forestry practices.
- Reduce Consumption: Make conscious choices to reduce consumption of paper and wood products, minimizing environmental footprint.
- Plant a Tree: Plant a tree in our community or support tree-planting initiatives.
- Spread Awareness: Educate ourselves and others about the importance of forests and the threats they face.
- By taking action, big or small, we can all contribute to a future where our forests continue to thrive, ensuring a healthier planet for generations to come.
World Pi Day 2024: International Day Of Mathematics And Worldwide Celebrations

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
About International Day of Mathematics:
- Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the International Day of Mathematics at the 40th General Conference on November 19, 2019.
- This day also sheds light on Mathematics' importance in different areas like climate change, energy, artificial intelligence, and sustainable development.
- International Day of Mathematics coincides with International Pi Day.
- Pi is one of the most widely known mathematical constants and it is rounded to 3.14, which is why it is observed on March 14.
- IDM is an opportunity to educate students about the role and importance of mathematics in improving quality of life.
- It also empowers women and girls to contribute to achieving sustainable development goals for the 2030 agenda.
History:
- The 205th session of UNESCO’s Executive Council adopted the International Day of Mathematics.
- The 40th session of UNESCO's General Conference adopted March 14 as the International Day of Mathematics, which was the first official celebration with the theme 'Mathematics is Everywhere'.
- It is an opportunity to understand the importance of mathematics in daily life promoting mathematics use for the advancement of society.
Significance:
- International Day of Mathematics is celebrated to promote Mathematics in different fields highlighting the role of mathematics in solving the real-life world and addressing social concerns.
- IDM shows the application of mathematics in different fields of life including science, technology, engineering, and economics.
- IDM promotes mathematics at different levels encouraging educators, policymakers, parents and to stress the importance of mathematics and inspire students to pursue careers in STEM fields.
- STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It is an opportunity to share research, discoveries, and insights with the general public and demystify the subject to make it more accessible.
- International Day of Mathematics is a global initiative to foster collaboration and exchange ideas across borders, cultures, and disciplines.
- The day aims to promote mathematics and help address global challenges through it.
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024:
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024 is 'Playing With Math.'
Methane emissions from fossil fuels remain high despite progress, US tops list of emitters: IEA

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Global Methane Tracker 2024, methane emissions from fuel consumption in 2023 approached record levels, nearing their highest point in history.
About the Global Methane Tracker:
- The Global Methane Tracker is an annual publication issued by the International Energy Agency (IEA), presenting the latest data on methane emissions primarily from the energy sector. It integrates recent scientific research, measurement campaigns, and satellite data.
Key Highlights from the Global Methane Tracker 2024:
- Methane emissions from fuel usage in 2023 approached record levels, reaching approximately 120 million tonnes (Mt), marking a slight increase from the previous year.
- Bioenergy, derived from plant and animal waste, contributed an additional 10 million tons of emissions.
- Out of the total methane emissions, around 80 million tons originated from ten countries, with the United States and Russia leading in emissions from oil and gas operations, and China leading in emissions from coal operations.
- Despite indications of declining emissions in certain regions, the overall methane emissions remain alarmingly high, posing a significant challenge to achieving global climate objectives.
- To align with the Paris Agreement goal of limiting warming to 1.5°C, there is a critical need to reduce methane emissions from fossil fuels by 75 percent by 2030.
- Achieving this target would require an estimated investment of approximately $170 billion, representing less than 5 percent of the revenue generated by the fossil fuel industry in 2023.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Paris, established in 1974.
- Its primary mandate is to ensure stability in the international oil supply, a response to the oil crisis of 1973, which led to temporary disruptions in the global oil supply chain.
- Operational Framework: The IEA functions within the broader scope of the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership: As of 2022, the IEA comprises 31 member nations, with India joining as an associate member in 2017.
- Key Requirement: Member countries are obligated to maintain reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net oil imports.
- These reserves must be readily accessible by the government to address potential disruptions in the global oil supply chain, even if the reserves are not owned directly by the government.
India world’s top arms importer between 2019-23: SIPRI

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India was the world’s top arms importer for the period 2019-23 with imports having gone up by 4.7% compared to the period 2014-18, according to the SIPRI.
Highlights from the SIPRI Report 2023:
- The report highlights that India continues as the world’s largest arms importer, maintaining this position despite ongoing efforts to enhance its defense-industrial base, accounting for a significant 9.8% of global arms imports between 2019 and 2023.
- There has been a steady increase in India's arms imports, with a 4.7% rise observed between 2014-18 and 2019-23, attributed in part to emergency procurements prompted by the prolonged military standoff with China.
- The dynamics of arms suppliers are changing, with Russia historically serving as India's primary weapons supplier, still accounting for 36% of its arms imports, although there is a shift towards diversification, with India increasingly turning to Western countries and domestic manufacturers.
- Notably, between 2019-23, Russian deliveries constituted less than half of India's arms imports for the first time since 1960-64.
- Western suppliers like France and the United States are emerging as key players, collectively accounting for 46% of India's arms imports, with significant contracts in progress, such as India's procurement of 31 armed MQ-9B Sky Guardian drones from the US and 26 Rafale-M fighters from France.
- In the global arms trade landscape, India ranks as the top importer, followed by Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Ukraine, Pakistan, Japan, Egypt, Australia, South Korea, and China, while the United States leads among exporters with a 42% share, followed by France and Russia.
- India's role as a major arms customer is underscored by its position as the largest arms customer for France, Russia, and Israel, highlighting its significance in global arms procurement.
- Meanwhile, China remains a dominant supplier to Pakistan, accounting for 61% of its exports, and also exports 11% of its arms to Bangladesh, consolidating its influence in the region.
Challenges Encountered by India in Indigenous Production of Defense Equipment:
- Efforts to promote indigenous defense production, exemplified by initiatives like 'Make in India', have encountered persistent challenges, notably the failure to materialize any projects under the Strategic Partnership (SP) model, which was introduced to foster collaboration between the public and private sectors within the defense industry.
- The SP model, designed to facilitate joint endeavors between government-owned defense entities and private companies, has yet to yield tangible results, necessitating a thorough review of the policy framework.
- Key areas for improvement include a reevaluation of pricing methodologies, ensuring long-term orders to sustain production, and addressing bottlenecks that impede project implementation.
- Furthermore, India's defense sector has seen minimal Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), amounting to only Rs 5,077 crore since the sector was opened to private companies in 2001.
- Despite efforts to liberalize FDI regulations, such as allowing up to 74% through the automatic route and up to 100% through the government route in 2020, investment inflows remain disproportionately low.
About Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI):
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) is a renowned independent international institute committed to investigating various aspects of conflict, armaments, arms control, and disarmament.
- Founded in 1966 and headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, SIPRI consistently ranks among the world's most respected think tanks.
SIPRI's mission is multi-faceted and encompasses the following key objectives:
- Conducting in-depth research and activities related to security, conflict, and peace, with the aim of developing a deeper understanding of the complex factors that influence global stability.
- Providing insightful policy analysis and recommendations to policymakers, international organizations, and civil society actors, helping them make informed decisions and develop strategies to address security challenges.
- Facilitating dialogue and building capacities among various stakeholders, including governments, academia, and non-governmental organizations, to foster cooperation and promote mutual understanding on peace and security issues.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in the field of international security by maintaining comprehensive databases on arms transfers, military expenditure, and other relevant data, which contribute to a more accurate assessment of global security trends.
- By adhering to these core principles and objectives, SIPRI plays a vital role in advancing the global discourse on peace and security, while supporting efforts to mitigate conflict and promote stability worldwide.
After 10 years struggle, Mendha gets separate Panchayat status under Gramdan Act

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Maharashtra government recently notified Mendha, a village deep inside the forests of the state’s Gadchiroli district, as a separate Gram Panchayat under The Maharashtra Gramdan Act, 1964.
What is Gramdan?
- Gramdan is an expansion of the Bhoodan Movement started in 1951 by Aacharya Vinoba Bhave.
- ‘Bhoodan’ meant redistribution of land from bigger landowners to the landless.
- Under Gramdan, the entire village will put its land under a common trust.
- This way, the land will not be sold outside the village or to one who has not joined Gramdan in the village.
- But the landowners can continue to cultivate it and reap the benefits.
- The Movement paved the way for the protection of natural resources by giving equal rights and responsibilities to everyone in the community and empowering communities to move towards self-governance.
- Under the Act, at least 75 percent of landowners in the village should surrender land ownership to the village community for it to be declared as ‘gramdan’.
- Such land should at least be 60 percent of the village land. Five per cent of the surrendered land is distributed to the landless in the village for cultivation.
- Recipients of such land cannot transfer the same without the permission of the community.
- The rest remains with the donors.
- They and their descendants can work on it and reap the benefits.
- But they cannot sell it outside the village or to a village resident who has not joined Gramdan.
- Today, seven states in India have 3,660 Gramdan villages, the highest being in Odisha (1,309).
- The states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- In September 2022, the Assam government repealed the Assam Gramdan Act, 1961 and Assam Bhoodan Act, 1965, bypassing The Assam Land and Revenue Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
- This, it said, was done to counter encroachment on donated lands in the state.
- Till that time, Assam had 312 Gramdan villages.
About Mendha’s Village Struggle:
- The village, comprising around 500 Gond Adivasis, has fought for its forests for years.
- It is popular as the first village in India to secure community forest rights (CFR), following the passing of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- Some 80 per cent of the area in the village is covered with dense forest.
- People here believe that land is not a private property but a collective resource that provides food and livelihood and should be saved and passed on to the next generation.
- All villagers in Mendha have surrendered their land, which is unique. In all other villages, only about 75-80 per cent of landowners had agreed to do so.
- The village fulfilled these conditions of the Act in 2013 and notified the district collector about its decision to implement the Act.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
Countries hope to bring BBNJ or High Seas treaty into force by 2025

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Blue Leaders High-Level Event on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction was held in Belgium on March 7, 2024, to urge nations to ratify a new treaty to protect the high seas from pollution, climate change and overfishing.
What is the BBNJ Treaty?
- The BBNJ Treaty, also referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas, is an international agreement aimed at conserving and sustainably managing marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, operating within the framework of the UNCLOS.
- These areas encompass the high seas beyond exclusive economic zones or national waters.
- It represents nearly half of the Earth's surface and is characterized by minimal regulation and understanding of their biodiversity, with only 1% currently under protection.
- Launched at the One Ocean Summit in February 2022, the High Ambition Coalition on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction seeks to unite various delegations involved in BBNJ negotiations toward a comprehensive and ambitious outcome.
- The negotiations focus on key elements agreed upon in 2015, including the conservation and sustainable use of marine genetic resources, area-based management tools such as marine protected areas, environmental impact assessments, and initiatives for capacity-building and technology transfer in marine science and management.
- India is yet to sign the treaty. However, it called on efforts for entry into force and implementation of the treaty at the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration held in September 2023.
The Importance of a Legally Binding Instrument for BBNJ:
- Biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction is crucial for ocean health, coastal communities' welfare, and global sustainability, constituting 95% of the ocean and offering essential ecological, economic, social, cultural, scientific, and food-security benefits.
- Despite their significance, these areas face escalating threats such as pollution, overexploitation, and the impacts of climate change, compounded by the anticipated rise in demand for marine resources in the future.
- Even the deep seafloors, considered one of the most inhospitable habitats, are experiencing the onset of extinction processes, with alarming statistics showing that 62% of assessed mollusc species are threatened, including critically endangered, endangered, and vulnerable species, while the International Seabed Authority permits deep sea mining contracts.
- It is imperative to establish a legally binding framework for managing and regulating biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, as over 60% of this resource in the global seas remains unmanaged and unprotected, necessitating comprehensive conservation measures.
Vaishnaw bats for further simplification of economic laws at ‘NITI for States’ platform launch

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union IT, Communications, and Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw Thursday stressed on the need to further simplify economic laws in a modern and relevant way at the launch of NITI Aayog’s ‘NITI for States’ platform.
About “NITI For States” Platform:
- It serves as a cross-sectoral knowledge hub envisioned to be a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Policy and Good Governance.
Key features include:
- A comprehensive repository comprising Best Practices, Policy documents, datasets, data profiles, and NITI publications across various sectors.
- Knowledge products spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes (Gender and Climate Change), such as Agriculture, Education, Energy, Health, Manufacturing, MSME, Tourism, Urban, and Water resources & WASH.
- An intuitive and user-friendly interface accessible via multiple devices, including mobile phones.
- The platform aims to catalyze digital governance transformation by providing government officials with contextualized, actionable knowledge and insights, thereby enhancing decision-making quality.
- It supports district collectors and block-level functionaries by granting access to innovative best practices from various States and Union Territories.
What is the Viksit Bharat Strategy Room?
- It serves as an interactive platform enabling users to visualize data, trends, best practices, and policies in an immersive manner, facilitating a comprehensive assessment of any problem statement.
- The platform features voice-enabled AI for user interaction and facilitates connectivity with multiple stakeholders through video conferencing.
- Designed as a plug-and-play model, it enables replication by states, districts, and blocks for widespread adoption.
- Collaboration with various government organizations by NITI Aayog includes:
- iGOT Karmayogi's "SAMARTH" online training modules accessible through the platform.
- Integration of NITI Aayog’s National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) to provide access to government datasets.
- Support from the National E-Governance Division (NeGD) in developing the innovative Viksit Bharat Strategy Room.
- Multi-lingual support provided by Bhashini.
- Integration of PM Gatishakti BISAG-N team, with DPIIT support, to offer geospatial tools for Area Based Planning.
Grey-zone Warfare Latest Entry in Lexicon of Warfare

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the last day of the 2024 Raisina Dialogue (February 24), India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan said that “grey zone warfare” is the latest in informal warfare.
What is the Grey Zone Warfare?
- Grey zone warfare refers to a strategic approach where a nation seeks to gain advantages over others without engaging in overt conflict.
- It involves a series of tactics, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and economic pressures, aimed at subtly undermining or destabilizing adversaries.
- China has notably employed this strategy against India and neighboring countries.
What are the China's Grey Zone Tactics Against India?
- South China Sea Activities: China asserts its dominance in the South China Sea using naval and civilian vessels, raising tensions with neighboring countries like India.
- Infrastructure Near Borders: China constructs infrastructure and settlements near India's borders, bolstering territorial claims and strategic positioning.
- Digital Investments: China invests in Indian digital platforms and media, influencing public narratives and perceptions.
India's Counter-Measures:
- Inter-Agency Collaboration: India promotes collaboration among defense, intelligence, and law enforcement agencies to devise comprehensive strategies to counter grey zone threats.
- Enhanced Vigilance: India increases surveillance and presence in border areas and strategic locations to detect and respond to covert Chinese activities.
- Regulating Foreign Investments: India scrutinizes foreign investments in critical sectors, particularly technology, to safeguard national security interests.
Long-Term Implications for India:
- Information Warfare: Grey zone conflicts often involve digital misinformation, influencing public opinion and perceptions.
- Economic Leverage: Dependency on foreign investments poses vulnerabilities if used as leverage by investing nations.
- Technology Dependency: Heavy reliance on foreign technology exposes India to risks, emphasizing the need to bolster indigenous technological capabilities.
Conclusion
Grey zone warfare encompasses a multifaceted strategic landscape, blending digital, economic, and geopolitical tactics. India recognizes these challenges and is actively devising strategies to navigate this complex terrain.
PM Modi hails those supporting wildlife conservation efforts on World Wildlife Day

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of World Wildlife Day on March 3, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded those at the forefront of sustainable practices and supporting wildlife conservation efforts.
About the World Wildlife Day:
- World Wildlife Day is observed to advocate for sustainable practices that contribute to biodiversity conservation and to enhance public consciousness about the importance of safeguarding and nurturing animals.
- It endeavors to underscore the interconnectedness of all life forms on Earth and to foster harmonious coexistence between humans and animals through activism, advocacy, and education.
Origins:
- Initially proposed by Thailand to the UN General Assembly in 2013, World Wildlife Day aimed to dedicate a day to spotlight the significance of wild animals and plants worldwide.
- On December 20, 2013, the General Assembly adopted a resolution, designating March 3 as World Wildlife Day from 2014 onwards.
- Coinciding with the day, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) was signed in 1973, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding species from the threats of international trade.
The theme of WWD 2024:
- The theme, "Connecting People and Planet: Exploring Digital Innovation in Wildlife Conservation," underscores the potential of technological advancements to revolutionize conservation efforts.
- In today's digital era, technological breakthroughs offer novel solutions to persistent conservation challenges, making this theme particularly relevant.
Significance:
- World Wildlife Day serves as a vital global awareness platform for animal protection and conservation.
- It reinforces the intrinsic value of animals and advocates for treating them with compassion, integrity, and reverence.
About the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- CITES is an international treaty that aims to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered plants and animals, including their parts and derivatives, to ensure their survival in the wild.
- Under CITES, member countries are required to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered species through a system of permits and quotas.
- They must also report regularly on their implementation of the treaty and collaborate with other countries to ensure its effectiveness.
- Currently, CITES has 184 parties.
Several OPEC+ nations extend oil cuts to boost prices

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Moscow, Riyadh, and several other OPEC+ members announced extensions to oil production cuts first announced in 2023 as part of an agreement among oil producers to boost prices following economic uncertainty.
What is the OPEC+ Oil Alliance?
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-exporting nations that convenes regularly to determine the quantity of crude oil to offer on the global market.
- Origin: This alliance was established in late 2016 to formalize a framework for collaboration between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations on a consistent and sustainable basis.
- The primary objective of these nations is to collaborate on regulating crude oil production to stabilize the oil market.
- OPEC+ collectively controls approximately 40% of global oil supplies and holds over 80% of proven oil reserves.
- At its core, OPEC+ consists of OPEC member states, predominantly comprising nations from the Middle East and Africa.
- Membership: It includes OPEC member states along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- OPEC, short for the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent intergovernmental organization comprised of oil-exporting nations.
Mission:
- To coordinate and harmonize the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- To ensure the stability of oil prices in global oil markets, aiming to eliminate detrimental and unnecessary fluctuations.
- Formation: Founded in 1960 by the five original members - Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Presently, it consists of 13 member countries, which include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Headquarters: Located in Vienna, Austria.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Indian security agencies have intercepted a Pakistan-bound ship from China at Mumbai's Nhava Sheva port.
What are CNC Machines and Wassenaar Arrangements?
- CNC machines are controlled by a computer and offer efficiency, consistency, and accuracy not possible manually.
- These machines have been included in the Wassenaar Arrangement since 1996.
- This international arms control regime aims to stop the proliferation of equipment with both civilian and military uses, with India being among the 42 member countries exchanging information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies.
About the Wassenaar Arrangement:
- The Wassenaar Arrangement is a voluntary export control framework established in July 1996.
- Comprising 42 member nations, it facilitates the exchange of information regarding transfers of conventional weaponry and dual-use goods and technologies.
- Dual-use items possess the capacity for both civilian and military applications.
- The arrangement's secretariat is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
Membership:
- The arrangement boasts 42 member states, predominantly consisting of NATO and EU nations.
- Members are obligated to report arms transfers and dual-use goods and technology transfers or denials to destinations beyond the arrangement biannually.
- India became a member of the Arrangement in 2017.
Objectives:
- Central to its operation is the continual exchange of technology-related information, encompassing both conventional and nuclear-capable technologies, among member states.
- This information exchange involves the maintenance and refinement of comprehensive lists of materials, technologies, processes, and products deemed militarily significant.
- The primary goal is to regulate the movement of technology, materials, or components to entities or nations that could jeopardize global security and stability.
Wassenaar Arrangement Plenary:
- The WA Plenary is the decision-making and governing body of the Arrangement.
- It is composed of representatives of all Participating States who normally meet once a year, usually in December.
- Chairmanship of the Plenary is subject to annual rotation among Participating States.
- In 2018, the United Kingdom held the Plenary Chair, while Greece assumed the position in 2019.
- Decisions within the Plenary are made through consensus.
Bengaluru's Rameshwaram cafe blast puts the spotlight on IEDs

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least nine people were injured after an explosion at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area recently, possibly by an improvised explosive device (IED).
What is Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)?
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) refers to a makeshift explosive device constructed and deployed unorthodoxly or improvised.
- These devices are typically crafted using commonly available materials, including explosives, triggers, and containers, often to cause destruction, injury, or death.
- IEDs can vary widely in design and complexity, ranging from simple pipe bombs to more intricate devices incorporating timers, remote controls, or even cellular communication for activation.
- IEDs can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- Due to their adaptable nature, IEDs are commonly used by insurgents, terrorists, and other malicious actors to carry out attacks against both military and civilian targets.
- Their unpredictable nature and often concealed placement make them particularly challenging for security forces to detect and mitigate.
- Efforts to counter IED threats involve a combination of technological advancements, intelligence gathering, and counterinsurgency strategies aimed at identifying and neutralizing these devices before they can cause harm.
Types of IEDs:
- Vehicle-Borne IEDs: Among the most destructive forms of IEDs are those concealed within vehicles. These can be driven to specific locations and detonated, causing massive explosions capable of levelling buildings.
- Suicide Bombings: Suicide bombings involve individuals strapping IEDs to their bodies, becoming human carriers of destruction. This method inflicts maximum damage in densely populated areas.
- Package IEDs: Package IEDs are small devices hidden in innocuous-looking packages. They are often placed in public spaces, targeting unsuspecting victims.
Methods of IED Initiation:
- Remote Control: IEDs can be remotely triggered using various methods, such as cell phones or radio signals, allowing attackers to maintain a safe distance from the explosion.
- Pressure Activation: Pressure-sensitive IEDs detonate when a certain amount of pressure is applied, making them lethal traps for those who inadvertently trigger them.
- Timers: IEDs can also be equipped with timers, which delay the explosion to occur at a specific time, further complicating detection and prevention.
The Devastating Impact of IEDs:
- The aftermath of IED explosions is often catastrophic, leading to loss of life, severe injuries, and widespread damage to infrastructure.
- The psychological impact on survivors and affected communities can be long-lasting.
Detection Technologies and Challenges:
- Detection technologies such as (Metal Detectors, X-ray and Imaging Scanners, Explosive Trace Detection (ETD), and Sniffer Dogs) play a critical role in countering the threat of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), but they also face numerous challenges due to the evolving nature of these devices.
How the development of Agaléga figures in India’s vision for its maritime neighbourhood
- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Ministers Narendra Modi and Pravind Jugnauth jointly inaugurated an airstrip and the St James Jetty on North Agaléga Island in the Indian Ocean.
About Agalega Islands:
- Agaléga Island comprises two islets, a long and thin northern island and a shorter, round southern island.
- It is slightly over 3,000 kilometres from the nearest mainland Indian coast, deep in the Indian Ocean near Madagascar.
- Despite its pristine appeal, Agaléga remains largely undiscovered by tourists and there are no hotels, water bungalows, or bustling tourist shops.
- Instead, approximately 300 islanders sustain themselves through coconut cultivation and fishing, maintaining a way of life passed down through generations.
Importance of Agalega Islands:
- The development of the Agalega Islands holds significant socio-economic and national security implications for Mauritius, aligning closely with India's maritime vision.
- Despite being a dependency of Mauritius, the islands have long remained underdeveloped, posing challenges to the sustainability and well-being of their inhabitants.
- Necessities often required referral to Mauritius due to the lack of infrastructure.
- Moreover, the absence of an official government or security presence posed a serious vulnerability, necessitating urgent attention.
- Recognizing the potential to transform this vulnerability into a strategic asset, Mauritius prioritized the development of the islands and the establishment of facilities capable of accommodating ships and aircraft.
- In this regard, the construction of a jetty and an airstrip emerged as imperative steps to bolster the islands' infrastructure.
- Given the shared interests and cooperation between Mauritius and India, the government of Mauritius selected India as its preferred development partner for this ambitious initiative.
Why did Mauritians Choose India?
- Ties between India and Mauritius go back to 1948, 20 years before the country’s independence from Britain.
- Seventy percent of the inhabitants of Mauritius are of Indian origin, and the two countries share deep historical, social, and cultural bonds.
- The consistent feature in the history of bilateral relations has been friendship and trust at all levels — the political leadership, the diplomatic and military communities, as well as between the peoples of the two countries.
- The development of these strategically located islands required trust more than anything else. India was the obvious choice.
Significance for India:
- The goodwill and trust between the two countries will be further enhanced. India will welcome opportunities to further develop these islands in collaboration with Mauritius as the latter deems appropriate.
- The joint development of Agaléga underscores India’s commitment to the vision of Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), and its willingness to assist smaller maritime nations in building capacity and developing capability.
- It will indicate to other maritime neighbours that India is a benign and friendly country that respects the sovereignty of independent nations.
- India would like to emerge as the preferred development and security partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
India to set up International Big Cat Alliance

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Environment Ministry plans to set up and coordinate an International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), along the lines of the International Solar Alliance, an India-headquartered initiative to promote solar installations globally.
About the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- The idea of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was first given by Prime Minister Modi during his speech on the occasion of Global Tiger Day in 2019.
- He called for developing an alliance of global leaders to curb poaching in Asia.
- The alliance was formally announced on April 9, 202, in Mysuru, as India commemorated the completion of 50 years of Project Tiger.
- The alliance will focus on the conservation of seven big cats, which include Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah. Out of these, five are found in India.
- Membership to the IBCA is open to 97 'range' countries, encompassing the natural habitats of these big cats, as well as other interested nations and international organizations.
- The alliance aims to facilitate cooperation among countries to advance the conservation agenda for mutual benefit.
- Operating with a multifaceted approach, the IBCA endeavours to establish robust linkages across various domains, including knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, financial and resource support, research, technical assistance, education, and awareness.
- Governance of the alliance consists of a General Assembly comprising all member countries, a Council comprised of seven to fifteen member countries elected by the General Assembly for a five-year term, and a Secretariat.
- The IBCA Secretary General, appointed by the General Assembly upon the Council's recommendation, serves a specific term.
- To support its initiatives, the IBCA has secured initial funding of Rs. 150 crore from the Government of India for the period spanning from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
The NB8 visit to India focuses on cooperation and trust
- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar hosted the India-Nordic-Baltic meeting on the sidelines of the ongoing Raisina Dialogue 2024 recently.
What are the Nordic-Baltic Countries?
- The Nordic-Baltic countries, also known as the NB8, are a group of Northern European countries that share historical, cultural, and geopolitical ties.
- The group includes
- Nordic countries of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, and
- Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- These countries collaborate on various regional issues, such as security, economy, environment, and culture, and often work together within international organisations and forums.
- The term "Nordic-Baltic" highlights the close relationship and cooperation between these neighbouring states in the Baltic Sea region.
India's Relations with NB8 Countries:
- India's collaboration with NB8 nations is broadening, exemplified by initiatives like the India-Denmark Green Strategic Partnership, the India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy, and cooperation on sustainability and ICT with Finland, including the 'LeadIT' (Leadership for Industry Transition) initiative with Sweden.
- Cooperation extends across various sectors, including innovation, green transition, maritime affairs, healthcare, intellectual property rights, emerging technologies, space exploration, and artificial intelligence.
- Trade and investment between the NB8 region and India are on a steady rise, reflecting deepening economic ties.
- Moreover, the security dynamics of the Nordic-Baltic region and the Indo-Pacific are intertwined, underlining the interconnectedness of regional security challenges.
Significance of NB8:
- The NB8 nations embody advanced economies characterised by their outward orientation, emphasis on innovation, complementarity, and seamless integration into the European Common Market, the world's largest single market area.
- The Baltic states, in particular, stand out as pioneers in IT, digitization, cyber technology, and green innovations, showcasing their leadership in these critical domains.
- Moreover, all NB8 members share a steadfast commitment to democracy and human rights, serving as advocates for an international order grounded in principles of multilateralism and adherence to international law.
NB8 Proposals for India:
- In light of the Ukraine conflict and its ripple effects on global food and energy security, supply chains, macro-financial stability, inflation, and growth, the NB8 seeks to collaborate with India in the following ways:
- Recognizing Shared Challenges: In an increasingly interconnected world, challenges such as the Ukraine conflict, global health crises, climate-related events, and geopolitical tensions affect us all.
- Acknowledging these shared challenges underscores the necessity for collaborative efforts to address them effectively.
- Embracing a Positive Agenda: There is an urgent imperative to pivot towards a more positive agenda for global cooperation.
- Leveraging our mutual commitment to the multilateral system, the NB8 proposes to enhance dialogue and cooperation on issues that are paramount to India's priorities and those of other global partners.
Cabinet approves Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-26

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of “Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)” with a total outlay of Rs. 4,100 crore for a period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
About the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP):
- The FMBAP Scheme is being implemented throughout the country for effective flood management, erosion control and anti-sea erosion and to help in maintaining peace along the border.
- The scheme benefits towns, villages, industrial establishments, communication links, agricultural fields, infrastructure etc. from floods and erosion in the country.
- The catchment area treatment works will help in the reduction of sediment load into rivers.
- The Scheme aims at the completion of the ongoing projects already approved under FMP.
The Scheme has two components:
- Under the Flood Management Programme (FMP) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 2940 crore, central assistance will be provided to State Governments for taking up critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- The pattern of funding to be followed is 90% (Centre): 10% (State) for Special Category States (8 North-Eastern States and Hilly States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and UT of Jammu & Kashmir) and 60% (Centre):40% (State) for General/ Non-Special Category States.
- Under the River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 1160 crore, flood control and anti-erosion work on common border rivers with neighbouring countries including hydrological observations and flood forecasting, and investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers will be taken up with 100% central assistance.
- The Scheme has the provision of incentivizing the States which implement flood plain zoning, recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Importance:
- While the primary duty of flood management lies with the State Governments, the Union Government actively promotes and advocates for the adoption of modern technology and innovative approaches.
- Additionally, projects executed under the RMBA component serve to safeguard critical installations of security agencies and border outposts situated along border rivers from the perils of floods and erosion.
- Furthermore, the scheme includes provisions for incentivizing states that implement flood plain zoning, a recognized and effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Malta becomes the 119th member of the International Solar Alliance

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Malta became the 119th country to join the International Solar Alliance recently.
About the International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an alliance of more than 120 signatory countries that aims to reduce the dependence on non-renewable sources of energy like fossil fuels.
- Currently, 118 countries are signatories to the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- The platform strives to develop and deploy cost-effective and transformational energy solutions powered by the sun to help member countries develop low-carbon growth trajectories, with a particular focus on delivering impact in countries categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and the Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was conceptualised on the sidelines of the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
Role of India:
- As a founding member, India holds a pivotal position within the alliance, serving both as a host nation and a major contributor to achieving its objectives.
- The ISA marks a historic milestone as the first international organisation to establish its secretariat in India.
- With a target of generating 100 GW of solar energy by 2022, India's commitment represents a significant portion of the ISA's overall goal.
Recent Developments:
- The ISA was granted Observer Status by the UN General Assembly, fostering closer collaboration between the alliance and the United Nations to advance global energy growth and development.
- The approval of the 'Solar Facility' by the ISA introduces a payment guarantee mechanism aimed at incentivizing investments in solar projects, further driving progress towards sustainable energy initiatives.
India contributes $1 million to fund combating poverty and hunger

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India has contributed 1 million US Dollars to the Poverty and Hunger Alleviation Fund established by India, Brazil, and South Africa, IBSA.
What is the IBSA Fund?
- Established in 2004 and operational since 2006, the IBSA Fund embodies the collaborative efforts of India, Brazil, and South Africa.
- Contributing one million dollars annually each, the IBSA countries unite in a spirit of partnership to champion Southern-led, demand-driven projects in developing nations.
- With a focus on identifying replicable and scalable initiatives, the fund aims to address pressing development challenges in recipient countries.
- Supported projects align with partner countries' national priorities and international development agendas, including the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The fund's objectives encompass diverse areas such as promoting food security, combating HIV/AIDS, and expanding access to safe drinking water, among others, to advance sustainable development.
- To date, the IBSA Fund has allocated USD 50.6 million, funding 45 projects across 37 countries in the Global South.
- The United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) fulfils the roles of Fund Manager and Secretariat for the IBSA Fund.
What is IBSA?
- IBSA stands for the India, Brazil, and South Africa Dialogue Forum, a unique platform that unites three major democracies and significant economies from diverse continents, collectively addressing common challenges.
- Formally established as the IBSA Dialogue Forum during a historic meeting of the Foreign Ministers from India, Brazil, and South Africa in Brasilia on June 6, 2003, the forum's inception was marked by the issuance of the Brasilia Declaration.
- To date, five IBSA Leadership Summits have been convened, with the 5th Summit held in Pretoria on October 18, 2011.
- In 2021, India held the chairmanship of IBSA under the theme "Democracy for Demography and Development."
- On March 2, 2023, Brazil assumed the rotating presidency of the India, Brazil, South Africa Dialogue Forum (IBSA), further advancing the forum's collaborative agenda.
Global leaders converge in Delhi for Raisina Dialogue 2024

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ninth edition of the Raisina Dialogue will be held from today till Friday (February 23) in New Delhi.
What is the Raisina Dialogue?
- The Raisina Dialogue is India’s premier conference on geopolitics and geoeconomics committed to addressing the most challenging issues facing the global community.
- Every year, leaders in politics, business, media, and civil society converge in New Delhi to discuss the state of the world and explore opportunities for cooperation on a wide range of contemporary matters.
- The Dialogue is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussion, involving heads of state, cabinet ministers and local government officials, who are joined by thought leaders from the private sector, media and academia.
- The conference is hosted by the Observer Research Foundation in partnership with the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India.
- This effort is supported by a number of institutions, organisations and individuals, who are committed to the mission of the conference.
- The theme of the 2024 edition is “Chaturanga: Conflict, Contest, Cooperate, Create”.
- During the three-day conference, the participants will engage with each other over six “thematic pillars”. These include:
- Tech Frontiers: Regulations & Realities
- Peace with the Planet: Invest & Innovate
- War & Peace: Armouries & Asymmetries
- Decolonising Multilateralism: Institutions & Inclusion
- The Post 2030 Agenda: People & Progress; and
- Defending Democracy: Society & Sovereignty.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
NAL Successfully Tested High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) at Challakere, Karnataka (TOI)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from city-based National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab, achieved a breakthrough by successfully testing an unmanned aerial vehicle called High-Altitude Pseudo Satellite (HAPS) at Chitradurga's Challakere in Karnataka.
News Summary:
- National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has achieved a milestone with the successful testing of an unmanned aerial vehicle known as the High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) in Challakere, Karnataka.
- This innovative system, measuring 5 meters in length with an impressive 11-meter wingspan and weighing 23 kg, soared to an altitude of approximately 3 km and maintained its position for an impressive duration of eight hours.
- A comprehensive series of tests is slated, with the ultimate goal of developing a full-fledged aircraft boasting a remarkable 30-meter wingspan comparable to a Boeing 737 by the year 2027.
- This advanced craft is anticipated to ascend to an impressive altitude of 23 km and remain airborne for a remarkable period of at least 90 days.
- NAL's ambitious agenda includes the design and construction of various components essential for the HAPS, including propellers, battery management systems, carbon-composite airframes, flight-control systems, and high-powered electric motors capable of withstanding extreme temperature variations.
- Additionally, in a separate endeavour, a Bengaluru-based private company recently conducted the inaugural test flight of a solar-powered, long-endurance drone, achieving an impressive flight duration of 21 hours.
About High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS):
- Since the 1990s, numerous global initiatives have been undertaken to explore the potential applications of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites, also known as High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS).
- Positioned above 20 km altitude in the stratosphere, these unmanned aircraft are designed for exceptionally long-duration flights, spanning months or even years.
- HAPS encompass various aircraft types, including airplanes, airships, and balloons.
Benefits/Advantages of HAPS:
- These solar-powered vehicles bridge the gap between unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) operating in lower altitudes and traditional satellites in space.
- They offer a wide array of applications, including telecommunications, emergency/public safety communications, intelligent transportation systems, maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and land border control.
- Compared to ground-based communication networks, HAPS can cover larger areas with minimal interference and facilitate data transfer between satellites and ground-based telecom networks.
- Unlike traditional satellites, which are costly to construct and launch, HAPS are more cost-effective and easier to deploy.
- It has both military and civilian applications, including intelligence, surveillance, telecommunication, and disaster response.
- The technology offers lower latency and can connect to multiple ground stations.
Significance for India:
- In India, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) announced in 2022 its collaboration with a startup company to develop a "futuristic" high-altitude pseudo satellite.
- Given India's extensive land borders stretching approximately 15,000 km and a coastline spanning 7,500 km, securing these borders is paramount, necessitating diverse solutions.
- Hovering at the Earth's atmospheric edge, HAPS offer valuable services for efficient border surveillance, tracking enemy movements deep into territories or seas, and conducting round-the-clock missions.
- Equipped with advanced optical and infrared cameras, state-of-the-art sensors, and other sophisticated technology, these aerial platforms are ideal for border patrolling, target tracking, maritime surveillance, navigation, and even missile detection.
- China's Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), a state-owned aerospace and defense conglomerate, has been actively developing various HAPS platforms for surveillance purposes.
- In 2018, it successfully tested the solar-powered Morning Star drone, renowned for its prolonged airborne endurance.
Digital Detox for Responsible Gaming (TOI)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka government recently said it would launch a 'Digital Detox' initiative in collaboration with the All India Game Developers Forum (AIGDF), with special emphasis on gaming and social media.
What is Digital Detox?
- A digital detox entails voluntarily refraining from using digital devices like smartphones, computers, and social media platforms for a defined period.
- This period can range from a few hours to as long as a week or even a month.
- Research indicates that approximately 25% of smartphone owners aged 18 to 44 cannot recall the last time they were separated from their phones.
Benefits:
- Overcoming Technology Addiction: Studies reveal that around 61% of individuals acknowledge their addiction to the internet and digital screens.
- A digital detox aids in combating this addiction.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Disconnecting from technology can alleviate stress and anxiety, thereby fostering improved mental health and overall well-being.
- Increased Productivity and Creativity: Taking a break from continuous digital engagement bolsters focus and concentration, leading to heightened productivity and creativity.
- Improved Sleep: Excessive screen time has been linked to poor sleep quality. A digital detox helps in promoting better sleep by reducing exposure to blue light and stimulating content.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Reducing online time allows for more face-to-face interactions, nurturing better communication skills and social connections.
Challenges:
- Feelings of Disconnection: Detox participants may feel disconnected from friends and family members.
- Fear of Missing Out: Participants may experience FOMO (fear of missing out) or anxiety about missing important information.
- Boredom or Restlessness: Detoxes may lead to feelings of boredom or restlessness.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety or boredom.
Way forward:
- Start Small: Initiate the detox with shorter periods and gradually extend the duration.
- Inform Others: Notify friends and family about the detox to avoid misinterpretations.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Utilize detox time for activities like reading, spending time outdoors, or exercising.
- Minimize Notifications: Turn off device notifications and store them out of sight.
- Reward Progress: Offer yourself incentives for achieving detox goals.
Conclusion
Digital dependence can contribute to mental health issues, shorter attention spans, and strained interpersonal relationships. While technology offers convenience and connectivity, excessive screen time exacts a toll. A digital detox presents an opportunity to enhance mental and physical well-being, as well as nurture healthier relationships. With proper planning and commitment, a successful and fulfilling detox experience is achievable.
Launch of the Traditional Medicine Morbidity codes of Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani Chapter in International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11 as Module 2 (PIB)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The launch event for Module 2 of the World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11 TM Morbidity Codes is scheduled to take place in New Delhi on January 10, 2024.
What is the International Classification of Diseases?
- Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) serves as a global standard for classifying diseases.
- The existing global data on diseases is primarily rooted in modern biomedicine practices, guiding diagnoses within healthcare systems worldwide.
- ICD plays a significant role on a global scale, offering crucial insights into the prevalence, causes, and consequences of human diseases and mortality.
- It achieves this by incorporating reported and coded data, forming the basis for clinical terms in health records and disease statistics across primary, secondary, and tertiary care, as well as cause-of-death certificates.
- The data and statistics derived from ICD coding contribute to various essential functions, including supporting payment systems, aiding in service planning, facilitating quality and safety administration, and driving health services research.
- Moreover, the standardized data collection associated with ICD categories allows for large-scale research initiatives.
- It's important to note that the WHO ICD series currently does not include the classification of data and terminology related to diseases based on Ayush systems such as Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, etc.
- The Central Bureau of Health Intelligence (CBHI), operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, serves as the WHO Collaboration Centre for ICD-related activities.
- The CBHI plays a crucial role in collecting and disseminating data on various diseases and mortality.
What is the TM2 module of ICD11?
- The Ministry of Ayush has introduced the Code for Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani Medicine, utilizing the National Ayush Morbidity and Standardised Electronic Portal (NAMASTE).
- In partnership with the World Health Organization (WHO), the Ministry of Ayush has collaboratively developed a comprehensive categorization of data and terminology about diseases based on Ayush systems, namely Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani, within the TM2 module of the ICD11 series.
- Furthermore, the Ministry of Ayush has formalized this collaboration by signing a Donor Agreement with the World Health Organization for the implementation of these initiatives.
Is Pegasus spyware targeting journalists in India? (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amnesty International and Washington Post recently announced that it has found the presence of Pegasus spyware, sold only to governments, on two Indian journalists’ phones.
What is Pegasus Spyware, and How Does it Infiltrate Devices?
- Pegasus is a sophisticated form of malware, covertly designed to gather information without the user's knowledge.
- Developer: Developed by the Israeli security firm NSO Group.
- Objectives: Pegasus serves three primary purposes:
- Collecting historical data on a device discreetly.
- Continuously monitoring user activities and gathering personal information.
- Transmitting the collected data to third parties.
Infiltration Mechanisms:
- Pegasus utilizes "zero-click exploits," exploiting vulnerabilities in popular apps like iMessage and WhatsApp.
- Notably, zero-click exploits require no user interaction, differentiating them from typical cyberattacks.
- Network injection attacks are another method employed by Pegasus, where unsecured websites are used to infiltrate devices within milliseconds of the user's visit.
What is a Zero-click exploit?
- A zero-click exploit involves the installation of malicious software on a device without the device owner's consent.
- Notably, it does not require any action from the device owner to initiate or complete the installation.
Specific Exploit in the Recent Case with Indian Journalists:
- The particular exploit reportedly used in the incidents is known as BLASTPAST (previously identified as BLASTPASS), unfolding in two phases.
- Initial Phase: The attack aims to establish a connection with Apple HomeKit, a platform enabling users to control various smart devices on their network.
- The primary objective of this phase might be to assess how the device could be vulnerable to exploitation or to maintain visibility for potential future attacks.
- Second Phase: Malicious content is sent through the iMessage app to the target device.
- This stage is pivotal as it delivers the complete spyware payload, enabling extensive surveillance and data collection.
Kambala (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the weekend of November 25 and 26, 160 pairs of buffaloes and their jockeys will race on specially made slush tracks for Kambala races at City Palace Grounds in Bengaluru.
What is Kambala?
- Kambala is a folk sport rooted in coastal Karnataka, particularly in areas where Tulu speakers are predominant.
- In the past, families and groups used to organize races in the muddy paddy fields after the harvest season.
- For many families, especially those from the Bunt community in coastal regions, Kambala holds significant prestige.
- Throughout the year, they groom pairs of buffaloes with the aim of winning major Kambala events and other races.
Kambala consists of four main categories:
- Negilu (plough): Lighter ploughs are used to tie buffaloes for the race.
- This category is for entry-level buffalo pairs participating in their first Kambala race.
- Hagga (rope): Buffaloes are raced by jockeys with just a rope tied to both buffaloes.
- Adda Halage: Participants stand over a horizontal plank dragged by buffaloes.
- Unlike Hagga and Negilu, where jockeys run behind the animals, buffaloes drag the jockeys in Adda Halage.
- Kane Halage: A wooden plank is tied to buffaloes.
- The plank, on which jockeys stand, has two holes through which water gushes out as it is dragged along the slush tracks.
- The height of water splashes determines the winner of the event.
Dwarf Planet Eris (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered the inside structure of the enigmatic dwarf planet Eris.
About Dwarf Planet Eris:
- This new dwarf planet is the largest object found in orbit around the sun since the discovery of Neptune and its moon Triton in 1846.
- It was discovered on Jan. 5, 2005, and It is larger than Pluto, discovered in 1930.
- Like Pluto, the new dwarf planet is a member of the Kuiper belt, a swarm of icy bodies beyond Neptune in orbit around the sun.
- Eris is named for the ancient Greek goddess of discord and strife.
- The surface of Eris is extremely cold, so it seems unlikely that life could exist there.
- With a radius of about 1,163 kilometers, Eris is about 1/5 the radius of Earth.
- Eris, like Pluto, is a little smaller than Earth's Moon.
- Eris takes 557 Earth years to make one trip around the Sun.
- As Eris orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 25.9 hours, making its day length similar to ours.
- Moons: Eris has a very small moon called Dysnomia.
- Dysnomia has a nearly circular orbit lasting about 16 days.
- Eris most likely has a rocky surface similar to Pluto.
- Atmosphere: The dwarf planet is often so far from the Sun that its atmosphere collapses and freezes, falling to the surface as snow.
- As it gets closest to the Sun in its faraway orbit, the atmosphere thaws.
Worldwide Governance Indicators (Indian Express)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Chief Economic Adviser recently expressed worry about credit rating agencies using the World Bank's Worldwide Governance Indicators to assess ratings, particularly for developing countries.
About Worldwide Governance Indicators:
- The Worldwide Governance Indicators is based on a long-standing research programme of The World Bank.
- It was first established in 1996 to measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries.
- These aggregate indicators are derived from over 30 individual data sources produced by a variety of survey institutes, think tanks, non-governmental organizations, international organizations, and private sector firms.
- The indicators capture six key dimensions of governance including:
- Voice and Accountability
- Political Stability and Absence of Violence
- Government Effectiveness
- Regulatory Quality
- Rule of Law
- Control of Corruption
- According to The World Bank, corruption is the single greatest obstacle to economic and social development.
About The World Bank:
- The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries around the world.
- Its goals are to reduce poverty and support development.
- It helps by offering a growing range of free tools, research, and knowledge to help people address the world’s development challenges, for instance, comprehensive, downloadable indicators about development in countries around the globe.
India International Science Festival (PIB)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 9th edition of the India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023 will be held at Faridabad, Haryana from January 17th-20th, 2024.
About the India International Science Festival (IISF):
- The India International Science Festival (IISF) is an annual science festival organized by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Earth Science, and Vijnana Bharati in India.
- The festival aims to promote science and technology in India and to showcase the latest advancements in these fields.
- The IISF has been held every year since 2007.
- The festival typically lasts for four days and features a variety of events, including exhibitions, seminars, workshops, and competitions.
- The exhibitions feature displays of scientific and technological innovations from India and around the world.
- The seminars and workshops provide opportunities for scientists and technologists to share their knowledge with the public.
- The competitions encourage students to participate in science and technology.
- The IISF is a major event in the Indian scientific community and has been praised for its role in promoting science education and public awareness of science.
- The festival has also been successful in attracting international participation, with scientists and technologists from around the world attending the event.
- The 2022 IISF was held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, from January 21 to 24.
India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023:
- It will be held at the Campus of Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) and Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB) of the Department of Biotechnology in Faridabad.
- Theme: 'Science and Technology Public Outreach in Amrit Kaal'.
- IISF 2023 will have a total of 17 themes to showcase scientific achievements, offering diverse benefits to participants and the general public.
World Energy Outlook 2023 (IEA)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released the World Energy Outlook (WEO) Report 2023.
About World Energy Outlook 2023:
- This flagship publication of the International Energy Agency (IEA) has appeared every year since 1998.
- It provides in-depth analysis and strategic insights into every aspect of the global energy system.
- This year, the report delves into how changes in economies and energy usage are meeting the increasing demand for energy amid geopolitical tensions and fragile energy markets.
- It evaluates the evolution of energy security fifty years after the establishment of the IEA and looks at what's necessary at the COP28 climate conference in Dubai to support the 1.5 °C goal.
- The publication analyzes today's energy trends, covering areas like investment, trade flows, electrification, and energy access.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an independent inter-governmental organization operating within the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Its mission involves collaborating with governments and industry to create a secure and sustainable energy future.
- Established in 1974 to safeguard oil supplies, it was a response to the 1973-1974 oil crisis, which exposed the vulnerability of industrialized nations to oil import dependencies due to an oil embargo.
- Comprising 31 member countries and eleven association countries, IEA candidates must be OECD members.
- India joined as an Associate member in 2017.
- The IEA publishes reports such as the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, World Energy Statistics, and Net Zero by 2050.
mRNA, easy to customise, is the next frontier for personalised medicine (The Hindu)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The therapeutic use of messenger RNA (mRNA) has fueled great hope to combat a wide range of incurable diseases.
What is mRNA?
- mRNA, or messenger RNA, represents a type of nucleic acid responsible for conveying genetic instructions.
- Within cells, mRNA serves as a messenger, transporting codes from the DNA located in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, where ribosomes are situated.
- The genetic information in DNA undergoes transcription, or copying, into mRNA before proteins can be synthesized.
- Each mRNA molecule encodes information for a specific protein, with every sequence of three nitrogen-containing bases dictating the inclusion of a particular amino acid in the protein.
Advantages of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Scalability: The production of mRNA in the laboratory is highly scalable, as the method for generating mRNA remains consistent across different types.
- This contrasts with traditional drugs, where each compound has distinct chemistry, requiring varied manufacturing methods.
- Patient-Centric: mRNA, being naturally degradable by cells when no longer needed, allows for flexible dosage adjustments to cater to changing patient requirements.
- Broad Therapeutic Potential: mRNA-based medicine holds promise for addressing a wide range of diseases rooted in cellular errors, such as the production of incorrect proteins, mutant protein versions, or insufficient normal protein levels.
- By delivering corrected mRNA to affected cells, scientists aim to facilitate the production of the correct proteins.
Prospects of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Diverse Treatment Applications: The future of mRNA-based medicine extends to addressing conditions like heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and bone loss, among others.
- Enhanced Wound Healing: mRNA drugs exhibit the potential to stimulate the formation of new blood vessels.
- This capability is particularly beneficial for diabetic patients with compromised blood circulation, reducing the risk of amputation.
- Treatment for Rare Conditions: mRNA-based medicine holds promise in treating rare disorders like propionic acidaemia, characterized by insufficient levels of liver proteins crucial for preventing the accumulation of toxic by-products in the body, especially in children.
Way Forward
- The capacity to tailor and manufacture mRNA easily enhances its prospects as a potent and personalized therapy, offering the potential for reduced side effects and widespread applicability.
- Despite these advancements, mRNA-based therapeutics are in the early stages of development, facing challenges such as the short lifespan of mRNA in cells and limited protein production duration.
- Addressing these hurdles is crucial to optimizing mRNA effectiveness and minimizing the quantity of mRNA needed.
Study in India (SII) portal (Indian Express)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Study In India (SII) portal was recently introduced by the Education Ministry, aiming to promote Indian education among international students.
About the Study in India (SII) portal:
- The Study in India (SII) portal serves as a dedicated website offering comprehensive information about higher education institutions (HEIs) in India.
- The main objective of the portal is to establish India as a global education hub and attract students from diverse backgrounds.
- The portal showcases a wide range of academic programs available in the HEIs, including undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral courses, along with courses related to the Indian Knowledge System (IKS), such as Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical arts.
- Detailed information about the academic facilities, research support, and other related offerings in the institutes is provided on the portal.
- It acts as a convenient one-stop platform for students, enabling them to register, apply for a visa, select desired courses, and receive offer letters from their chosen institutes.
- The portal allows students to apply to multiple institutes or courses of their preference, simplifying the application process.
- Study in India (SII) offers a streamlined and well-organized application process, providing international students with easy access to higher education opportunities in India.
What is Study in India (SII) Programme?
- The Study in India (SII) program is a prominent initiative initiated by the education ministry in 2018 with the aim of positioning India as a premier education destination for international students.
- The program seeks to attract foreign students to pursue higher education in India, providing them with valuable educational opportunities offered by renowned Indian universities.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (DownToEarth)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
As per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development's Review of Maritime Transport 2023, international shipping witnessed a notable increase of 20 percent in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2023 compared to the previous decade.
Key Highlights from the Review:
- The shipping industry plays a pivotal role, accounting for over 80 percent of global trade volume, yet contributes nearly three percent of total global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Containerized trade, after a 3.7 percent decline in 2022, is projected to grow by 1.2 percent in 2023 and is expected to further expand by three percent from 2024 to 2028.
- Oil and gas trade exhibited robust growth in 2022, with tanker freight rates experiencing a significant resurgence driven by geopolitical developments.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- UNCTAD serves as the United Nations' primary institution addressing trade and development matters.
- Established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly, it functions as a permanent intergovernmental body.
- UNCTAD's mission is to promote equitable and effective access to the benefits of a globalized economy for developing countries.
- It offers economic and trade analysis, fosters consensus-building, and provides technical assistance to assist developing nations in leveraging trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD publishes influential reports, including the Trade and Development Report, the World Investment Report, and The Least Developed Countries Report.
INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION OUTLOOK 2023 (Down to Earth)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), published the "International Migration Outlook 2023."
Facts About:
- In 2021 and 2022, India had the largest migration flows to nations that are members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- In terms of citizenship, 0.13 million Indians became citizens of an OECD nation in 2021.
- The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has caused the greatest level of internal displacement and refugee inflows into the OECD, with over 10 million people becoming internally displaced or refugees.
- In terms of workers, migration flows from India (+172 percent), Uzbekistan (+122 percent), and Turkey (+240 percent) increased dramatically, making them the primary countries of origin after Ukraine.
About the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- The OECD is an international group of 38 countries that aims to foster economic development, and cooperation, and combat poverty by promoting economic stability.
- It was founded in 1961, by 18 European nations, the United States, and Canada.
Its headquarters are in Paris, France.
- Primary Goal: The primary goal of the OECD is to create policies that promote prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being for everyone.
- They produce economic reports, data, and predictions about global economic growth.
- The OECD also works to combat bribery and financial crimes worldwide, maintaining a list of uncooperative tax havens.
- India is not a member of the OECD, but a key economic partner.
International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML) (Indian Express)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Secretary of the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs announced that India has achieved the status of being an OIML certificate-issuing authority.
Facts About:
- OIML, short for the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, was established in 1955 as an international body.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents that are used by legal metrology authorities and industry worldwide.
- OIML plays a vital part in aligning national laws and regulations concerning the accuracy of measuring instruments such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring devices, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India joined the OIML in 1956 and simultaneously signed the metric convention.
- Headquartered in Paris, France.
