ASI Decodes Sanskrit Inscription Found in Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK)

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
An ancient Sanskrit inscription found in Gilgit (PoK) was decoded by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
About the Inscription:
- Location:
- Gilgit (PoK): Written in Brahmi script, dating back to 4th century CE.
- Peshawar (Pakistan): Written in Sharada script, dating to 10th century CE.
- Details of Gilgit Inscription:
- Mentions Pushpasingha, who installed a Mahesvaralinga for the merit of his guru.
- Written in Brahmi script, which was prevalent during the 4th century CE.
- Religious Context: Indicates significant religious connection, particularly with Shaivism.
- Details of Peshawar Inscription:
- Fragmentary: Engraved on a slab.
- Written in Sharada characters (10th century CE).
- Mentions Buddhist Dharini (chants), particularly referring to Da (Dha) rini in line six.
- The inscription is partially damaged, and further details are unclear.
- Earlier Discoveries:
- This is not the first Sanskrit inscription decoded from Pakistan. In the past, Sanskrit inscriptions have been found in various parts of Pakistan.
- Swat Valley: Known for numerous Buddhist rock inscriptions in Sanskrit using Nagari script, which were part of the Gupta Empire (circa 240–550 CE).
- Religious and Cultural Implications:
- The Gilgit inscription provides evidence of Shaivism as a prominent religious practice in the region during the 4th century CE.
- The Peshawar inscription suggests Buddhist influences, particularly related to Buddhist chants and rituals.
- Swat Valley's Role: The inscriptions found here highlight its importance as a center of Buddhist learning and cultural exchange.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
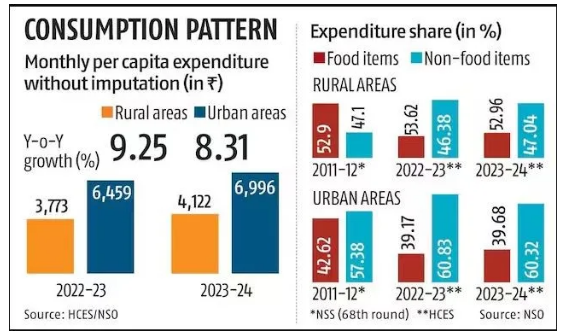
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
One Nation One Subscription (ONOS)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Cabinet approves One Nation One Subscription (ONOS) Scheme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: It is a new initiative to provide unified access to international scholarly research articles and journals for all government-managed higher education institutions and research institutions in India.
- Scheme Overview:ONOS aims to make nearly 13,000 scholarly journals accessible to over 1.8 crore students, faculty, researchers, and scientists in more than 6,300 institutions across India. These journals will cover all academic disciplines, promoting both core and interdisciplinary research, including in tier 2 and tier 3 cities.
- Digital Platform:The scheme will be implemented through a fully digital process, coordinated by the Information and Library Network (INFLIBNET), an autonomous center under the University Grants Commission (UGC). The platform will provide easy access to the journals and facilitate a streamlined subscription process.
- Investment and Coverage:A total of ?6,000 crore has been allocated for ONOS for three years (2025-2027). The scheme will cover major international publishers such as Elsevier, Springer, Wiley, and Oxford University Press. It will enable institutions to access 13,000 journals from 30 global publishers.
Benefits of the Scheme:
- Access to Top-Quality Research:ONOS will provide wide access to top-tier scholarly journals, benefiting institutions, researchers, and students across various fields. It will significantly improve the research environment in the country, especially for institutions that previously lacked the resources to access high-impact journals.
- Fostering Research and Development:The initiative aligns with India's vision of becoming an Atmanirbhar and Viksit Bharat by 2047, supporting the government's goals under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF). It will help foster a culture of research and innovation in Indian institutions.
- Inclusivity:The scheme will particularly benefit institutions in smaller towns and rural areas, helping bridge the knowledge gap between urban and rural academic institutions.
- Simplified Access:The scheme eliminates the need for separate subscriptions to individual journals by different institutions, streamlining access to high-quality content through a single platform.
Implementation Details:
- Platform and Process:The ONOS platform will allow institutions to access journals through a unified portal, providing easy and coordinated access. The Department of Higher Education (DHE)will be responsible for conducting awareness campaigns about the initiative, ensuring widespread utilization among students and faculty.
- Review Mechanism:The ANRF will monitor and periodically review the usage of ONOS and track the contributions of Indian authors in the journals, ensuring that the initiative continues to support India’s research landscape.
- Operational Date:The ONOS platform is set to become operational on January 1, 2025, providing comprehensive access to research materials for government-managed higher education and research institutions.
The One Nation One Subscription scheme is a major step towards enhancing India's position in the global research ecosystem. It will provide unparalleled access to scholarly resources, supporting research excellence and innovation across the country.
Know Your Medicine (KYM) App

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, has launched a nationwide appeal to strengthen the fight against doping in sports, urging athletes, coaches, and the entire sporting community to embrace the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India's ‘Know Your Medicine (KYM)’ app.
Introduction to KYM App
- Launch: The app was launched by Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, to combat doping in sports.
- Developer: National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India.
- Purpose: To prevent inadvertent doping by allowing athletes to check whether a medicine contains substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Key Features of the KYM App
- Medicine Verification: The app enables athletes to verify if any medicine or its ingredients contain banned substances listed by WADA.
- Image and Audio Search: Unique search features help users easily search for specific sport-related information.
- Customizable Search: Users can select their sport category and receive relevant, sport-specific information.
- User-Friendly: Designed for athletes, coaches, and sports professionals to quickly verify medicines and ensure clean competition.
Importance of KYM App
- Supporting Clean Sports: The app promotes a fair and ethical sporting culture by reducing the risk of inadvertent doping.
- Integrity of Sports: Helps athletes avoid penalties or bans due to accidental doping, maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- Accessible Information: Provides easy access to information regarding medicines that may contain banned substances, which is crucial for athletes' health and careers.
NADA India's Mission
- Anti-Doping Awareness: The KYM app is part of NADA India’s broader initiative to educate athletes and raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Goal: To promote dope-free sports and ensure that athletes and coaches are equipped with the tools needed for compliance with anti-doping regulations.
NADA India: Background and Functions
- Established: NADA India was set up in November 2005 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Mission: To serve as the independent Anti-Doping Organization for India, aiming to create a doping-free sporting environment.
- Key Functions:
- Implementing Anti-Doping Code: Ensuring compliance with the World Anti-Doping Code among all sports organizations in India.
- Dope Testing Program: Coordinating a national dope testing program with stakeholders across various sports.
- Promoting Research and Education: Encouraging research on anti-doping and educating athletes on the importance of staying clean.
- Adopting Best Practices: Ensuring the implementation of high-quality standards for anti-doping programs.
Impact and Significance
- Preventing Doping: The KYM app helps prevent inadvertent doping incidents by providing athletes with the necessary tools to check their medicines.
- Supporting Athletes: It provides athletes with a reliable way to avoid banned substances in over-the-counter medications, thus safeguarding their careers.
- National and International Compliance: Supports India’s commitment to complying with international anti-doping norms, contributing to a global effort to maintain fairness in sports.
India’s Vision of ‘Adaptive Defence’

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh introduced the concept of ‘Adaptive Defence’ at the inaugural Delhi Defence Dialogue (DDD).
- Adaptive Defence aims to prepare India's military for the rapidly changing landscape of modern warfare, with evolving threats and technologies shaping global security.
Key Aspects of Adaptive Defence:
- Strategic Approach:
- Adaptive Defence is an evolving strategy where military and defence systems continuously adjust to emerging threats, focusing on proactive preparedness rather than reactive responses.
- It is based on anticipating future threats, fostering flexibility, resilience, and agility in both strategic and tactical responses.
- Core Elements:
- Situational Awareness: The ability to understand and respond to dynamic, often unpredictable environments.
- Flexibility & Agility: At both the strategic and tactical levels to ensure swift and effective responses.
- Resilience: The capacity to recover and adapt quickly to unforeseen circumstances.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Emphasis on adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI, drones, and cybersecurity to stay ahead of adversaries.
The Changing Nature of Warfare:
- Grey Zone & Hybrid Warfare:
- Modern conflicts now often occur in the grey zone and involve hybrid warfare, blending traditional and non-traditional threats like cyber-attacks, terrorism, and psychological warfare.
- These new threats demand continuous adaptation in strategies, doctrines, and military operations.
- Technological Transformation:
- Drones and swarm technologies are reshaping warfare. India aspires to become a global hub for drones, leveraging these technologies for both economic and military growth.
- The increasing significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, and quantum technologies in defence highlights the need for international collaboration in research and innovation.
- Psychological Warfare:
- The rise of information overload and psychological warfare challenges traditional defence paradigms. Manipulation of information to influence public opinion and disrupt decision-making processes is now a key threat.
Government Initiatives for Adaptive Defence:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Establishment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and initiatives to enhance jointness among the three armed services (Army, Navy, Air Force) to create a unified strategic force.
- Reform of training curricula and emphasis on integrated operations to ensure readiness for new-age warfare.
- Focus on Self-Reliance:
- Strengthening the indigenous defence sector through initiatives like Make in India and the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) in defence and promoting defence exports, with India currently exporting to over 100 nations.
- Drone Hub Vision:
- India aims to become the world’s drone hub, supporting R&D and fostering innovation to develop reliable certification mechanisms and enhance Indian intellectual property in the drone sector.
- Programs like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and ADITI are rewarding innovation and driving India's defence sector towards greater self-sufficiency.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Focus on cybersecurity, AI, and quantum technologies to develop solutions that address both national and global security challenges.
- India is also working on Theaterisation, integrating the three services into a unified force structure for enhanced coordination and joint operations.
- Defence Acquisition and Export:
- Introduction of the Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, establishment of Defence Industrial Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, and a Positive Indigenisation List to boost self-reliance.
- India is actively increasing defence exports, aiming for Rs 50,000 crore worth of exports by 2029, with key export destinations including the USA, France, and Armenia.
Strategic Vision for the Future:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Given the interconnectedness of global security, the defence minister emphasized the importance of a collaborative approach in dealing with transnational threats.
- Cross-border issues, cyberspace threats, and the potential of quantum and nanotechnologies demand the sharing of knowledge and strategies across borders.
- Joint Military Vision:
- Jointness in defence strategy should go beyond national borders and should involve international cooperation in response to global security challenges.
- The need for interconnected solutions in the face of transnational threats underscores the importance of multilateral cooperation.
Adoption Awareness Month 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Adoption Awareness Month is an annual event where CARA and all its stakeholders come together to raise awareness about the legal process of adoption.
Context
- Celebrated by: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) and the Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA).
- When: November 2024.
- Theme: “Rehabilitation of Older Children through Foster Care and Foster Adoption.”
- Purpose: To raise awareness about legal adoption, foster care, and the rehabilitation of older children in India.
Objectives
- Promote Legal Adoptions:
- Create awareness about the legal framework and processes for adoption.
- Encourage prospective adoptive parents (PAPs) to adopt older children or children with special needs.
- Foster Care Focus:
- Highlight the importance of foster care as a rehabilitative measure for older children.
- Public Engagement:
- Engage various stakeholders, including adoptive families, PAPs, older adoptees, and the general public, to share experiences and insights.
Key Activities
- Nationwide Campaigns:
- Offline events in states like Ladakh, Assam, Mizoram, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and West Bengal.
- Mega event in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, on November 21, 2024.
- Online Initiatives (via MyGov India):
- Storytelling, poster making, slogan writing, pledges, and online surveys.
- Informative content on adoption and foster care shared via social media.
- Interactive Engagements:
- Cultural programs, competitions, Q&A sessions with PAPs, and discussions with stakeholders.
- Sharing of experiences by older adoptees and adoptive parents.
Significance of Adoption Awareness Month
- Focus on Older Children:
- Addresses challenges faced by older children in finding permanent families.
- Promotes inclusive adoption practices for children with special needs or in foster care.
- Stakeholder Involvement:
- Builds trust and awareness by sharing real-life adoption experiences.
- Encourages societal participation in the rehabilitation of vulnerable children.
- Policy Awareness:
- Educates the public about the legal adoption process under CARA.
- Highlights the benefits and responsibilities of foster care and adoption.
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
- Role: Apex body for regulating adoption in India under the MWCD.
- Key Function: Ensures legal, ethical, and transparent adoption processes for orphaned, abandoned, and surrendered children.
Challenges in Adoption and Foster Care
- Limited awareness about adopting older children or children with special needs.
- Cultural and societal barriers.
- Complexities in the legal adoption process.
Way Forward
- Streamlining Processes: Simplify legal procedures to make adoption and foster care accessible.
- Increased Awareness: Continued campaigns to reduce stigma and misinformation about adoption.
- Policy Support: Strengthen programs for foster care and ensure periodic evaluation of their impact.
Golden trevally Fish

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The golden trevally, a popular marine fish on Tamil Nadu’s coastline, has been successfully bred in captivity by scientists at ICAR-CMFRI’s Visakhapatnam station.
What is Golden trevally Fish?
- The Golden Trevally (Gnathanodon speciosus), also known as the Golden Kingfish or Banded Trevally, is a popular and fascinating marine fish species found in the Indo-Pacific and Eastern Pacific regions.
- It typically inhabits deep lagoons and seaward reefs, often in association with larger fish species.
- This fish is highly sought-after for both consumption and ornamental purposes due to its faster growth rates, good meat quality, and attractive appearance.
- According to fish landing observations in India, golden trevally are primarily landed at reef area fishing grounds in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Kerala, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
About the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI):
- CMFRI was established in 1947 under India's Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It joined the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) in 1967.
The institute's primary objectives include:
- Monitoring exploited marine fisheries resources and assessing under-exploited resources within India's Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Understanding fluctuations in marine fisheries resources in response to environmental changes.
- Developing sustainable mariculture technologies for finfish, shellfish, and other organisms to supplement capture fishery production.
- The CMFRI's notable achievements include developing the "Stratified Multistage Random Sampling Method" for estimating fishery catch and effort along India's 8,000 km coastline.
- Headquartered in Kochi, Kerala, the institute continues to contribute significantly to the growth and development of India's marine fisheries sector.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global trade dynamics are expected to remain sluggish in 2024, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has warned.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- UNCTAD’s latest projections indicate global growth of 2.6 percent in 2024, slightly slower than in 2023.
- This marks the third consecutive year in which the global economy will grow at a slower pace than before the pandemic when the average rate for 2015–2019 was 3.2 percent.
India’s growth is expected to be marginally lower than in 2023:
- Regarding India, the report stated that the economy grew at 6.7 percent in 2023 and is expected to be marginally lower at 6.5 percent in 2024.
- It noted that the expansion in 2023 was influenced by strong public investment and the services sector, which received a boost from robust local demand for consumer services along with assured external demand for business services exports.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to keep interest rates constant in the near term, while strong public investment expenditures will offset restrained public consumption spending.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1964 to promote the interests of developing countries in global trade.
- With its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD has 195 member states and collaborates with numerous nongovernmental organizations worldwide.
- The organization focuses on formulating policies related to various aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance, and technology.
- UNCTAD plays a crucial role in addressing the concerns of developing countries regarding international institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank.
- By providing a platform for these countries to discuss and tackle their unique challenges, UNCTAD contributes to global economic development and reduces inequalities.
- Some notable achievements of UNCTAD include the establishment of the Global System of Trade Preferences (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), which reduces tariffs and removes non-tariff trade barriers, the Common Fund for Commodities, providing financial assistance to countries dependent on commodity exports, and various agreements for debt relief.
- In recent years, UNCTAD has focused on addressing globalization challenges and helping the least developed countries integrate into the global economy.
OptiDrop Platform

- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) in Bengaluru recently announced that it has developed a new platform that makes it easier and cheaper to study single cells.
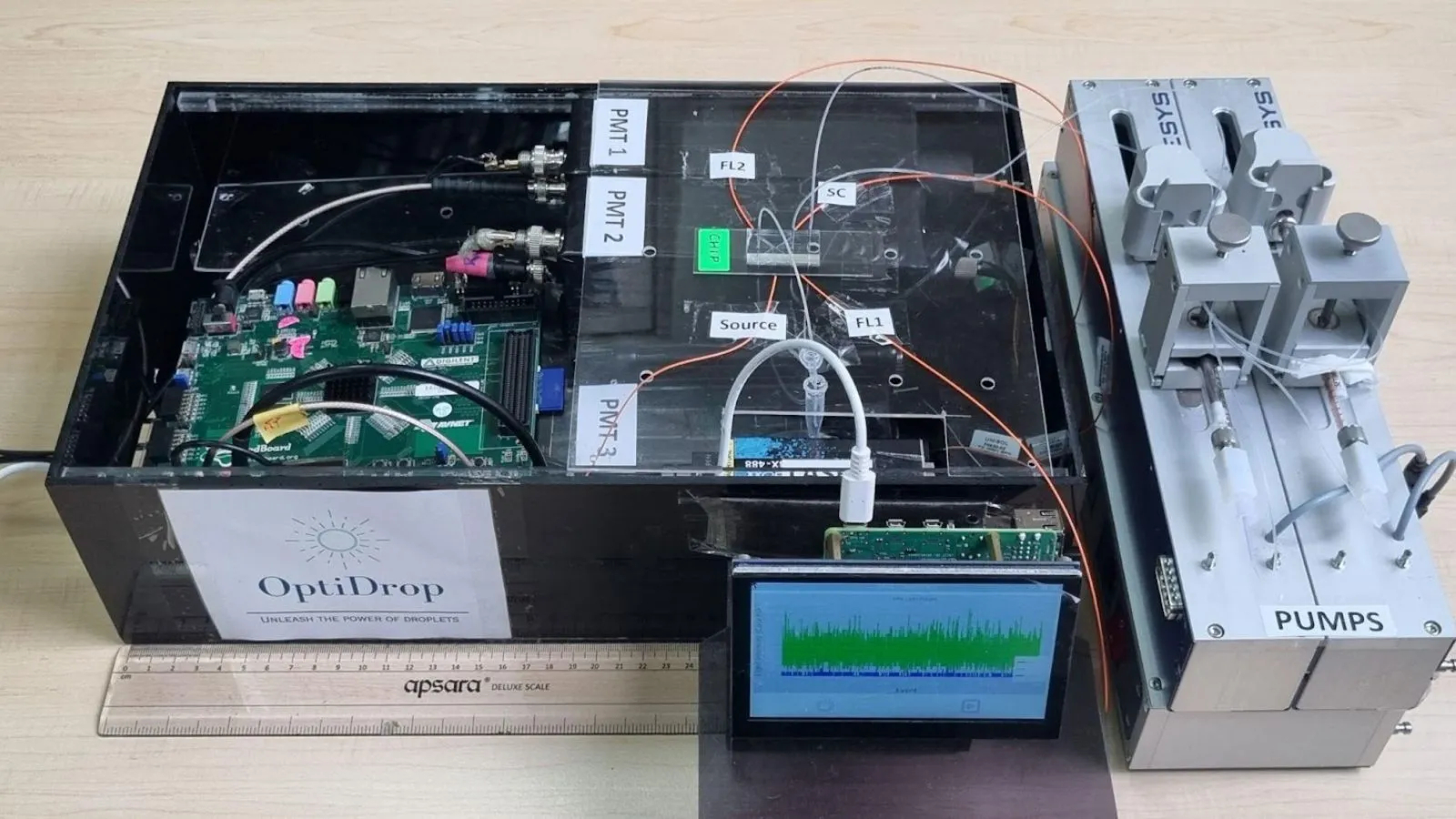
About the OptiDrop Platform:
- The OptiDrop platform is an innovative microfluidic chip-based technology that simplifies and reduces the cost of single-cell analysis.
- Developed by the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) in Bengaluru, India, OptiDrop enables precise and cost-effective analysis of single cells encapsulated in droplets.
- The platform boasts unique features, including live data visualization, a smaller data footprint, and a 'closed' system design that prevents external contamination.
- OptiDrop has potential applications in diagnostics, therapeutics, agriculture, and animal health, making it a versatile tool for various research areas.
Applications:
- This cutting-edge technology holds vast potential across diverse fields including diagnostics, therapeutics, agriculture, and animal health. Its versatility enables:
- Precise examination of individual cells during drug screening processes.
- Environment control for monitoring and addressing water contamination.
- Identification and sorting of CAR-T cells in immuno-oncotherapeutics.
- Selection of CRISPR-modified single cells.
- Identifying high-efficiency clones in single-cell genomics paves the way for advancements in personalized medicine and beyond.
- This platform is a testament to the potential of combining microfluidic technologies with advanced optical sensing techniques, paving the way for more efficient and cost-effective single-cell analysis.
What is the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP)?
- The Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms, or C-CAMP, was conceptualized by the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India in 2009 as an enabler or catalyst of cutting-edge research and innovation in the life sciences.
- C-CAMP has established itself as a major platform technology base, industry-oriented innovation hub, and incubator unit for life science research.
- With state-of-the-art technology platforms, a rich academic environment, and networks of business and industry-related resources, it encourages researchers and entrepreneurs to develop scientific tools and solutions for socially relevant problems.
- It is an institution with the core mandate of enabling cutting-edge life science research and innovation.
India-led ‘Group of Friends’

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a high-level meeting of the India-led 'Group of Friends (GOF), India launched a new database designed to record crimes against UN peacekeepers and monitor progress in holding perpetrators accountable.
About the 'Group of Friends':
- The Group of Friends (GOF) was launched by India in 2022 to promote accountability for crimes against the Blue Helmets during its presidency of the UN Security Council.
- India, Bangladesh, Egypt, France, Morocco, and Nepal are co-chairs of the GOF, which comprises 40 member states.
Key objectives of the group include:
- Engaging and sharing information with the UN Secretary-General to assist member states hosting or having hosted peacekeeping operations in bringing perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers to justice.
- Serving as an informal platform at the UN to exchange information, share best practices, and mobilize resources to facilitate accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- Monitoring progress on bringing accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- The 'Group of Friends' will convene two meetings of its members per year and organize one event annually involving Permanent Missions and other stakeholders, ensuring greater safety and security for peacekeepers.
- This initiative represents the political will of member states, particularly troop and police contributing countries, to champion the implementation of UN Security Council resolution 2589, adopted in August 2021 under India's Presidency of the Council.
- Resolution 2589 called upon member states hosting or having hosted UN peacekeeping operations to take all appropriate measures to bring to justice perpetrators of violence against UN personnel, including their detention and abduction.
- The 'Group of Friends serves as a crucial platform for advancing this resolution, promoting accountability, and enhancing the protection of peacekeepers worldwide.
India's Significant Role in UN Peacekeeping:
- As a longstanding advocate for global peace and stability, India has demonstrated its commitment to United Nations (UN) peacekeeping operations.
- Over the past seven decades, India has contributed more than 260,000 peacekeepers, making it the largest cumulative contributor to UN peacekeeping missions.
- Despite the risks associated with such endeavors, India has remained steadfast in its support of peacekeeping efforts.
- Tragically, 177 Indian peacekeepers have made the ultimate sacrifice in the line of duty, reflecting India's dedication to fostering stability worldwide.
- Presently, India has more than 6,000 peacekeepers deployed in nine out of the twelve UN peacekeeping missions.
- As a strong proponent of accountability for crimes against peacekeepers, India plays a crucial role in advocating for the safety and security of these dedicated personnel.
NITI Aayog launches 'vocal for local' initiative to promote grassroots-level entrepreneurship

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog on Wednesday launched the 'Vocal for Local' initiative under its Aspirational Blocks Programme to bolster local economies and foster grassroots-level entrepreneurship, an official statement said.
What is the ‘Vocal for Local’ Initiative?
- The 'Vocal for Local' initiative, led by NITI Aayog through its Aspirational Blocks Programme, aims to foster self-reliance and sustainable development.
- Under this initiative, products from 500 aspirational blocks have been curated and unified under the Aakanksha brand.
- Aakanksha is an overarching brand, with potential extensions into various sub-brands to tap into global markets.
- A dedicated section has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal under the Aakanksha brand to promote these products.
- Additionally, partners in the initiative offer support in areas such as e-commerce facilitation, establishing market linkages, financial and digital literacy, documentation and certification, and skill enhancement.
About Aspirational Blocks Programme:
- Inspired by the Aspirational District Programme launched in 2018, the Aspirational Blocks Programme extends its reach to 112 districts nationwide.
- This new initiative targets the enhancement of underperforming blocks across various development indicators.
- It aims to foster comprehensive growth in regions requiring additional support.
- Initially encompassing 500 districts across 31 States and Union Territories, the programme focuses on blocks in six key states: Uttar Pradesh (68 blocks), Bihar (61), Madhya Pradesh (42), Jharkhand (34), Odisha (29), and West Bengal (29).
What is the Government e-Marketplace (GeM)?
- Established in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) serves as an online platform for public procurement.
- GeM acts as a centralized portal, streamlining the procurement process for common-use Goods & Services required by various Government Departments, Organizations, and PSUs.
- Purchases made through GeM by Government users are mandated by the Ministry of Finance under the General Financial Rules, 2017.
- GeM is operated by GeM SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle), a 100% Government-owned, non-profit company operating under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Analysis of Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23 Report

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The per capita monthly household expenditure more than doubled in 2022-23 as compared to 2011-12, according to the latest study by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO).
Context:
- As per the 2022-23 report, rising inequality between the top and bottom of the pyramid.
- Urban and rural households register higher expenditure, spending less on food items.
- New methodology and questionnaire used in Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23.
About the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO):
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) comes under the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation headed by a Director General.
- It is responsible for the conduct of large-scale sample surveys in diverse fields on an All-India basis.
- Primarily data are collected through nationwide household surveys on various socio-economic subjects, Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), etc.
- Besides these surveys, NSSO collects data on rural and urban prices and plays a significant role in the improvement of crop statistics through supervision of the area enumeration and crop estimation surveys of the State agencies.
- It also maintains a frame of urban area units for use in sample surveys in urban areas.
The NSSO has four Divisions:
- Survey Design and Research Division (SDRD): This Division, located at Kolkata, is responsible for the technical planning of surveys, formulation of concepts and definitions, sampling design, designing of inquiry schedules, drawing up of tabulation plans, and analysis and presentation of survey results.
- Field Operations Division (FOD): The Division, with its headquarters at Delhi/Faridabad, is responsible for the collection of primary data for the surveys undertaken by NSS.
- Data Processing Division (DPD): The Division, with its headquarters at Kolkata is responsible for sample selection, software development, processing, validation and tabulation of the data collected through surveys.
- Survey Coordination Division (SCD): This Division, located in New Delhi, coordinates all the activities of different Divisions of NSS.
- It also brings out the bi-annual journal of NSS, titled “Sarvekshana”, and organizes National Seminars on the results of various Socio-economic surveys undertaken by NSS.
Key Insights From the 2022-23 Survey:
- Evolution of Food Expenditure: Over the past two decades, there has been a notable shift in spending patterns on food in India.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2022-23, both urban and rural households witnessed a gradual decline in the share of expenditure allocated to food.
- This period marks the first instance where food expenditure has dropped to below 50% in rural India and below 40% in urban India.
- Changing Dietary Preferences: The composition of food consumption has also undergone significant changes.
- Cereals and pulses have seen a reduction in their share of overall food consumption expenditure, while spending on milk has surged, surpassing that on cereals and pulses combined.
- In a noteworthy shift, the average Indian now spends more on fruits and vegetables than on food grains.
- Furthermore, expenditure on animal proteins like eggs, fish, and meat has shown a growing trend, indicating a preference for animal-based proteins over plant-based ones.
- Rise in Processed Food Consumption: There has been an observed increase in the share of expenditure allocated to processed foods, beverages, and purchased cooked meals.
- This trend aligns with the Engel Curve hypothesis, suggesting that as incomes rise, households allocate a smaller proportion of their spending to food and tend to prefer superior items over inferior ones.
- Closing Rural-Urban Consumption Gap: Consumption growth in rural areas has outpaced that in urban areas, leading to a narrowing of the rural-urban consumption divide.
- If this trend continues, it could potentially lead to parity in urban and rural incomes and consumption patterns in the future.
- Challenges in Inflation Calculation: The findings of the latest Household Consumption Expenditure (HCE) Survey underscore the need to review the inflation basket.
- The current Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation calculation, established in 2012, may not accurately reflect contemporary consumption patterns.
- For instance, the disparity between the weightage assigned to cereals in the CPI basket and actual expenditure on cereals by rural households highlights the need for recalibration.
- Insights on Poverty Reduction: According to NITI Aayog CEO B V R Subrahmanyam, the latest survey indicates a reduction in poverty to five per cent nationwide.
- Both rural and urban areas are witnessing increased prosperity, as evidenced by rising per capita monthly expenditure.
- Demand for Legal Guarantee to MSP: While there is a demand for a legal guarantee to Minimum Support Price (MSP) for 23 crops, including food grains and sugarcane, the survey data suggests that the growth in the farm sector is being primarily driven by livestock, fisheries, and horticulture crops.
- This poses a pertinent question regarding the promotion of production: should the focus be on crops outside the MSP purview, such as milk, fish, poultry products, fruits, and vegetables, given their growing consumption trends?
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre on Monday introduced a Bill that would enable it to prescribe the norms for nominating chairpersons of State Pollution Control Boards, exempt certain industrial units from restrictions, and decriminalize “minor offenses” related to water pollution.
News Summary:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 has been introduced in the Rajya Sabha.
- It is applicable to Himachal Pradesh and Rajasthan, with the potential to extend to other states through resolutions under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- The Bill empowers the Centre to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions and issue guidelines related to industry establishment.
About Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024:
- Enacted in 1974, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act aimed to prevent and control water pollution, establishing penal provisions for non-compliance.
Rationale for the Amendment:
- The Amendment Bill underscores the importance of democratic governance, emphasizing trust in people and institutions. It addresses the outdated regulations leading to a trust deficit.
Key Amendments Proposed:
- The Amendment Bill seeks to modernize the existing penal provisions, replacing imprisonment with fines for minor violations. This move aligns with the principles of Ease of Living and Ease of Doing Business.
Major Features of the Amendment Bill:
- The Bill proposes several key changes, including:
- Prescribing the process for nominating the chairman of the State Pollution Control Board by the Central Government.
- Granting the Central government authority to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions on new outlets and discharges.
- Issuing guidelines on matters related to the establishment of industries by the Central government.
- Decriminalizing minor offenses and substituting them with monetary penalties.
- Specifying the adjudication process for penalties by officers of appropriate rank.
- Outlining penalties for non-compliance with regulations regarding new outlets, discharges, and sewage.
- Allocation of penalty amounts to the Environmental Protection Fund established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
India Ranks 93 on Corruption Perceptions Index 2023 (The Hindu)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 as its overall score remained largely unchanged, according to a Transparency International report.
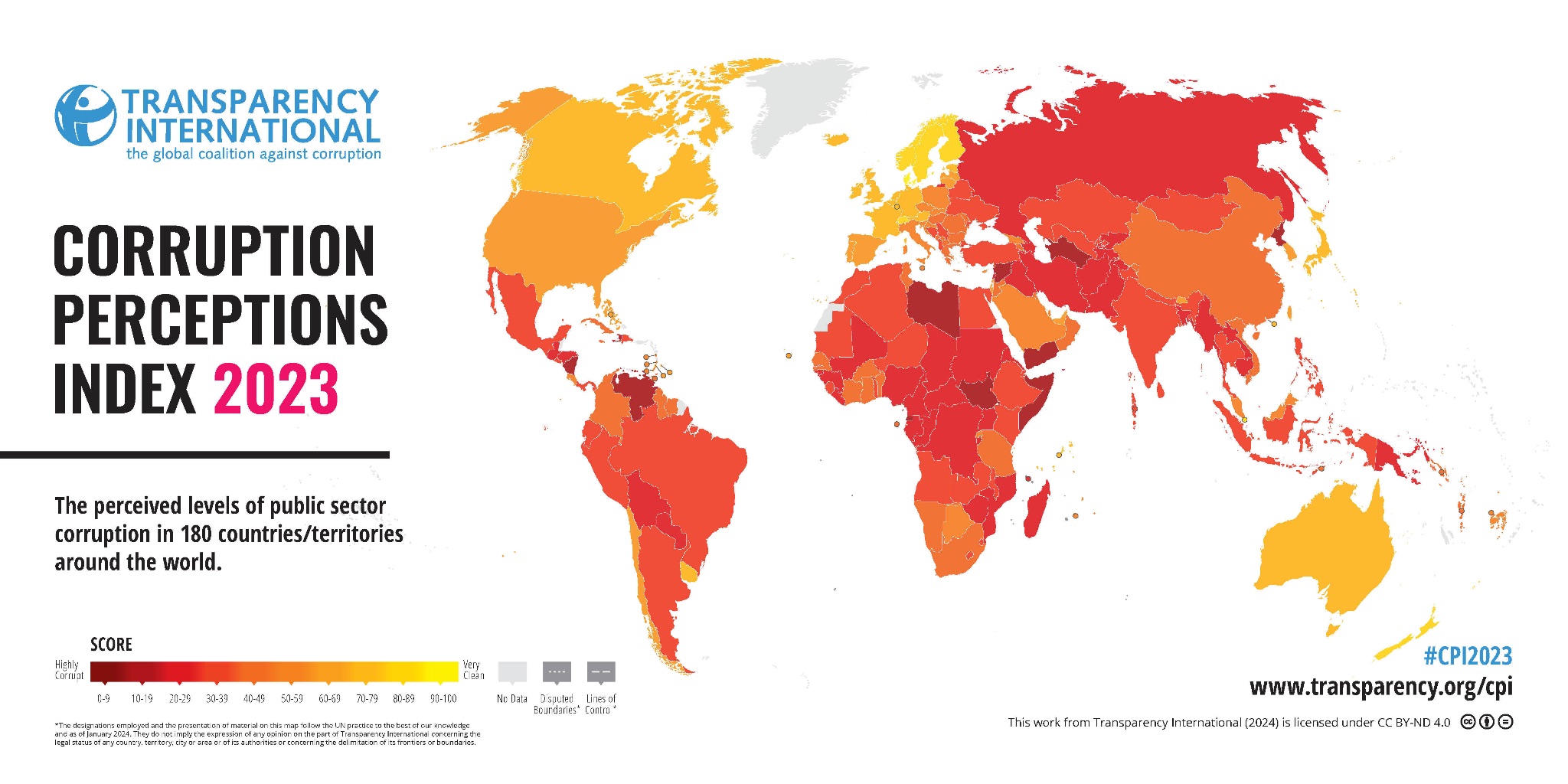
Key Facts About Corruption Perceptions Index 2023:
- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 tied with Maldives, Kazakhstan, and Lesotho also ranking at 93 out of 180 countries.
- In 2023, India's overall score was 39 while in 2022, it was 40.
- India's rank in 2022 was 85.
- Denmark (90) tops the index for the sixth consecutive year, with Finland and New Zealand.
- In South Asia, both Pakistan (133) and Sri Lanka (115) grapple with their respective debt burdens and ensuing political instability.
- Bangladesh (149) emerges from the least developed country (LDC) status, with economic growth supporting a continued reduction in poverty and improving living conditions.
- China (76), with its aggressive anti-corruption crackdown, has punished more than 3.7 million public officials for corruption over the last decade.
- Somalia (11), Venezuela (13), Syria (13), South Sudan (13) and Yemen (16) take the bottom spots in the index.
What is the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)?
- The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) scores and ranks countries/territories based on how corrupt a country’s public sector is perceived to be by experts and business executives.
- It is a composite index, a combination of 13 surveys and assessments of corruption, collected by a variety of reputable institutions including the World Bank, World Economic Forum, private risk and consulting companies, think tanks and others.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and the results are given on a scale of 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- The CPI is released annually by Transparency International, an independent nonprofit organization that aims to fight corruption, especially in the public sector.
- Transparency International is a global independent, nongovernmental nonprofit organization (NPO) that aims to stop corruption by promoting transparency in various sectors of society.
- The organization's international secretariat is located in Berlin and it has national chapters in more than 100 countries.
- The agency is funded through donations from governments, individuals, private donors, and other organizations.
- The organisation conducts research, and advocacy work, and undergoes various projects in its fight against corruption.
- In 1995, the organization created the first Corruption Perceptions Index, ranking 45 countries based on how much corruption they were perceived to have in the public sector.
Economic Impact of Corruption:
- Corruption continues to be a big hurdle to political, economic, and social development.
- Those who are economically challenged are the most affected by the effects of corruption and related fraud.
- That's because they often rely heavily on public services and can't afford to pay bribes.
- The International Finance Corporation also cites increases in the cost of business as a result of corruption.
What is end-to-end encryption? How does it secure information? (The Hindu)
- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
There are several ways to encrypt information depending on the level of secrecy and protection required.
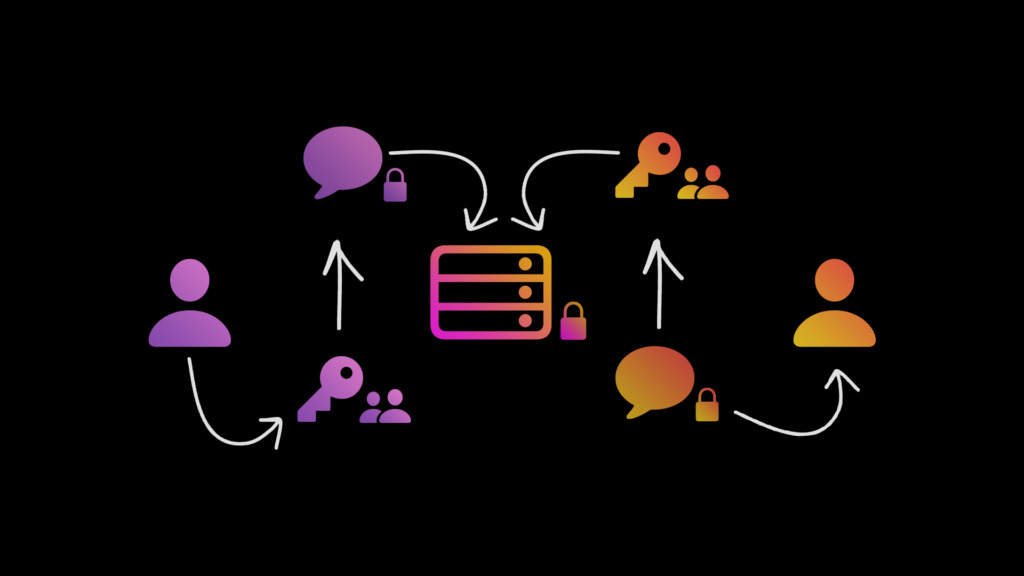
What is End-to-end Encryption (E2EE)?
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a type of messaging that keeps messages private from everyone, including the messaging service.
- When E2EE is used, a message only appears in decrypted form for the person sending the message and the person receiving the message.
- The sender is one "end" of the conversation and the recipient is the other "end"; hence the name "end-to-end."
How Does Encryption Work?
- Encryption works by altering data so that only someone who possesses a specific piece of knowledge — known as the key — can interpret the data.
- Keys can take different forms in different contexts.
- With communications over the Internet, a key is a string of bits that plays a role in the complex mathematical equations used to scramble and unscramble data.
- With E2EE, the key that can encrypt and decrypt messages remains saved on a user's device.
What Kind of Encryption Does E2EE Use?
- End-to-end encryption uses a specialized form of encryption called public key encryption (also sometimes called asymmetric encryption).
- Public key encryption enables two parties to communicate without having to send the secret key over an insecure channel.
- Public key encryption relies on using two keys instead of one: a public key and a private key.
- While anyone, including the messaging service, can view the public key, only one person knows the private key.
- Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key (not the public key).
- This contrasts with symmetric encryption, where only one key is used to both encrypt and decrypt.
How Does End-to-end Encryption Support Privacy?
- E2EE ensures that no one can see messages except for the two people who are communicating with each other.
- When implemented properly, it does not require users to trust that a service will handle their data properly.
- Thus, E2EE gives people total control over who can read their messages, enabling them to keep their messages private.
What are the Limitations of End-to-end Encryption?
- E2EE keeps messages secure in transit (as they pass from one person to another).
- But it does not protect messages once they reach their destination.
- E2EE is not guaranteed to be future-proof. When implemented correctly, modern encryption methods are strong enough to resist encryption-breaking efforts from even the most powerful computers in the world.
- But the more powerful in the future like Quantum computers, if developed, would be able to crack modern encryption algorithms.
- Using E2EE keeps messages secure in the present, but it may not keep them secure permanently.
National Quantum Mission to call for proposals to set up four tech hubs (PTI)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will set up a coordination cell to implement the National Quantum Mission (NQM) with a focus on establishing four technology hubs in the format of consortia of academia, research and development labs and industry.
What is the National Quantum Mission (NQM)?
- The National Quantum Mission (NQM) will assist India take a giant leap into the future of technology.
- India has entered the ranks of the select few nations actively pursuing the advancement of quantum technology by establishing this programme.
- In 2023, the government sanctioned the National Quantum Mission (NQM), spanning from 2023-24 to 2030-31, with the following key features:
- The mission aims to initiate, foster, and amplify scientific and industrial research and development in Quantum Technology (QT), establishing a dynamic and innovative ecosystem.
- Its ultimate goal is to propel quantum technology-led economic growth, foster the QT ecosystem, and position India as a leading nation in the field of Quantum Technologies & Applications.
- It willl be implemented by the Department of Science & Technology (DST) under the Ministry of Science & Technology.
Key Objectives:
- Develop intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 physical qubits across platforms like superconducting and photonic technology within eight years.
- Implement satellite-based secure quantum communications over a 2000-kilometre range within India, ensuring long-distance secure quantum communications with other countries.
- Establish inter-city quantum key distribution over 2000 km and multi-node Quantum networks with quantum memories.
- Develop highly sensitive magnetometers in atomic systems and Atomic Clocks for precision timing, communications, and navigation.
- Support the design and synthesis of quantum materials like superconductors, novel semiconductor structures, and topological materials for quantum device fabrication.
- Develop single photon sources/detectors and entangled photon sources for applications in quantum communications, sensing, and metrology.
Implementation:
- The mission involves the establishment of four Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) in leading academic and National R&D institutes, focusing on Quantum Computing, Quantum Communication, Quantum Sensing & Metrology, and Quantum Materials & Devices.
- These hubs will concentrate on generating new knowledge through basic and applied research and promote R&D in their respective domains.
Significance:
- NQM has the potential to elevate India's Technology Development ecosystem to global competitiveness.
- It is expected to significantly benefit various sectors such as communication, health, finance, and energy, with applications ranging from drug design to space, banking, and security.
- The mission aligns with national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, Skill India, Stand-up India, and Start-up India, and contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
- With the launch of this mission, India will be the seventh country to have a dedicated quantum mission after the US, Austria, Finland, France, Canada and China.
What is Quantum Technology?
- The term "quantum technology" is used to describe the research and development of techniques to build supercomputers with enhanced speed, security, and efficiency in data processing above conventional computers.
- Quantum mechanics, which governs the behaviour of subatomic particles, is used to design these novel systems.
- The peculiar characteristics of subatomic particles are the key to quantum technology's capabilities in processing massive quantities of information concurrently.
10th century Kadamba inscription written in Kannada, Sanskrit found in Goa (The Hindu)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An inscription written in Kannada and Sanskrit and said to be of 10th century A.D. Kadamba period has been discovered in the Mahadeva temple at Cacoda in southern Goa.
About the Kadamba Inscription:
- Discovery and Study of the Inscription: The inscription illuminates the Kadamba period in Goa, commencing with the auspicious phrase 'Be it well' (Swasthi Shri).
- It was discovered between the temples of Mahadev and Sateri-Betal at Cacoda in Goa.
- Epigraphic Details: It chronicles the story of Gundayya, Talara Nevayya's son, who vowed to fulfill his father's desire by capturing a Gopura in the port of Goa.
- The inscription is engraved in Kannada and Nagari characters.
- Its literary style mirrors the Talangre inscription of Jayasimha I from the same period.
- The deciphering of the Kadamba stone inscription has brought to light its historical and socio-cultural importance.
- Historical Narrative: The Kadambas of Goa served as subordinates to the Chalukyas.
- Kadamba Shasthadeva, appointed as Mahamandaleshwara of Goa by Chalukyan emperor Tailapa II, played a key role in overthrowing the Rashtrakutas.
- In 960 A.D., Kadamba Shasthadeva conquered Chandavara and the port of Gopakapattana (present Goa).
- Gundayya, Talara Nevayya's son, actively participated in the battle, successfully securing the port but sacrificing his own life.
- To commemorate his son's heroic fight, Talara Nevayya erected a memorial stone with the inscription in the Mahadev temple at Cacoda.
- Socio-cultural Importance: Cacora village, situated near navigable waterways, establishes connections to the Upper Ghat region through the ancient route of Diggi ghat leading to Karnataka.
- Currently a census town under the Municipality of Curchorem Cacora in Goa, Cacoda hosts the Mahadev temple with its affiliated deities, showcasing the cultural richness and historical significance of the area.
PM inaugurates Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Optical Fibre Connection (PIB)
- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently, in Kavaratti, Lakshadweep, inaugurated the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands submarine optical fibre connection (KLI-SOFC) project including various developmental projects worth more than Rs 1,150 crore.
Background-Kochi-Lakshadweep Submarine OFC (KLI) Project:
- The need for digitally connecting the Lakshadweep Islands through a high-capacity submarine cable link with the mainland has been felt for some time.
- Earlier, the only means of communication with the Islands was through Satellite medium, which had limited bandwidth capacity and was not able to meet the growing bandwidth demand.
- In the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Cable (KLI) project submarine cable connectivity from Mainland (Kochi) to eleven Lakshadweep Islands namely, Kavaratti, Agatti, Amini, Kadmat, Chetlet, Kalpeni, Minicoy, Androth, Kiltan, Bangaram and Bitra has been extended.
- The project is funded by the Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF), Department of Telecommunication.
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) was the Project Executing Agency and the work was awarded to NEC Corporation India Pvt Ltd.
- Major activities related to the project include Marine Route Survey, Submarine Cable laying, Civil Construction of CLS stations, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of End Terminals (SLTE).
- Highlights of the KLI Project:
- Total link distance: 1,868 kilometres.
- Total cost of project: Rs 1072 crore
???????Benefits of the KLI Project:
- The project will play a significant role in achieving the objective of ‘Digital India’ and ‘National Broadband Mission’ and in rolling out various e-governance projects of the Government of India in Lakshadweep Islands.
- E-Governance, Tourism, Education, Health, Commerce and Industries will get a boost
- It will also help in further improvement in the standards of living of the people on the Island and will accelerate overall social and economic development in these areas.
- The population of Lakshadweep Islands will be provided high-speed wireline broadband connectivity.
- High-speed broadband will be provided through FTTH and 5G/4G Mobile networks.
- The bandwidth created under this project will be available to all Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) to strengthen their telecom services in the Lakshadweep Islands.
Oil Producers Water Down Provision on Fossil Fuel Phase-out (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After four days of deadlock, a new draft agreement text emerged at the COP28 climate meeting that severely watered down earlier provisions on fossil fuel elimination but singled out coal for a rapid phase-down, which could be problematic for India.
Context:
- The 28th Conference of the Parties (COP 28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is underway in the United Arab Emirates from November 30 to December 12, 2023.
- During the climate meeting on December 10, negotiators took an initial step toward enhancing action on adapting to climate change.
- A draft text outlining potential "global goals" on adaptation was introduced for the first time, serving as a starting point for further negotiations.
- Negotiators are actively discussing various topics, including the contentious issue of fossil fuel phase-out, in informal sessions to find common ground.
- The draft document is titled 'Global Goal on Adaptation' (GGA) and aims to establish a shared global objective for adaptation, similar to the global goal of limiting temperature rise below the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold for mitigation.
- This initiative addresses a longstanding demand from developing countries, emphasizing the need for increased focus and resource mobilisation for adaptation efforts.
- Notably, the draft removes the term 'phasing out' of fossil fuels but includes stronger language against coal, urging a "rapid phase-down of unabated coal," a point that may face objections from major consumers like India, Indonesia, and China, all developing countries heavily reliant on coal power.
Responses to the Draft Text 'Global Goal on Adaptation':
- The European Union (EU) and certain small island states promptly dismissed the draft agreement text.
- The EU climate commissioner criticized the overall insufficiency of the text, deeming it inadequate in addressing the climate change challenge.
- Primary dissatisfaction arose from the weakening of a provision related to the use of fossil fuels.
- The draft initially urged countries to "reduce both consumption and production of fossil fuels, in a just, orderly, and equitable manner."
- Notably, fossil fuels, responsible for nearly 80 percent of greenhouse gas emissions, have never been explicitly mentioned in prior COP decisions.
- While previous decisions emphasized the need to cut emissions, they avoided specifying actions for emission reduction.
- COP28 marked the first formal discussion of a fossil fuel phase-out but attempts to incorporate a robust provision faced resistance from oil-producing nations like Saudi Arabia and Russia.
- India, while not offering an immediate reaction to the draft agreement, has consistently asserted that singling out coal for accelerated reduction is discriminatory.
India's Ambitious Initiative to Expand Renewable Energy Capacity (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has proposed an exemption for green hydrogen developers from adhering to its list of authorised manufacturers to enable them to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China.
What Does The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) Propose?
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is exploring the option of granting an exemption to green hydrogen developers from its list of authorized manufacturers.
- This proposed exemption would enable these developers to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China, aiming to enhance the competitiveness of green hydrogen exports.
- It's noteworthy that Chinese manufacturers are presently absent from MNRE's Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) and Revised List of Models and Manufacturers (RLLM).
The MNRE’s Proposal Background:
- After the 2020 Galwan Valley skirmishes, the Indian government issued directives to restrict the involvement of Chinese vendors in public procurement.
- Recently, the Indian procurement portal GeM announced the removal of hundreds of Chinese vendors over the past three years.
- At a time when energy companies are intensifying efforts to mass-produce green hydrogen, essential for which are renewable energy equipment and electrolysers, the government has sidelined Chinese manufacturers.
- This aligns with the MNRE's policy to enhance domestic manufacturing of renewable energy equipment.
- While central PSUs may face restrictions on importing electrolysis machinery from China, others continue to do so.
- In FY23, India witnessed a 40% increase, in importing machines and apparatus for electroplating, electrolysis, and electrophoresis, worth $45.61 million, compared to the preceding fiscal year.
What is the Significance of the MNRE’s Proposal?
- ??The proposal to import solar PV modules from China carries significance in bolstering the supply chain and enhancing the global competitiveness of Indian green hydrogen exports.
- Central PSUs such as Indian Oil Corporation Ltd and NTPC Ltd, both actively involved in green hydrogen projects, would benefit by sourcing equipment from Chinese manufacturers.
- This move is poised to strengthen India's position in the global green hydrogen market, aligning with the objectives outlined in the National Green Hydrogen Mission and facilitating the achievement of set targets.
Digital Crop Survey System (Indian Express)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Emphasizing the current manual nature of crop area and production estimation, the Central Government has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to transition to a digital approach by implementing the Digital Crop Survey System starting in July next year.
About the Digital Crop Survey:
- As a part of the Digital Crop Survey initiative, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (MoA&FW) has instructed states to capture data on essential parameters, encompassing:
- Village name, year, season, farmer ID, farm ID,
- Crop name (at the farm plot level),
- Crop variety,
- Crop sown area (at the farm plot level),
- Geotags of crop photos,
- Geotags of the farm boundary where the crop is cultivated,
- Sowing/planting date (at the farm plot level),
- Irrigation type (at the farm plot level), and
- Irrigation source (at the farm plot level).
- This directive follows the introduction of a pilot Digital Crop Survey across multiple states earlier this year.
- In a parallel initiative, the MoA&FW has also revised the release timelines for crop estimates.
- Previously conducted in five phases, the ministry has streamlined the process by eliminating the fourth phase traditionally released in August.
- The ministry now plans to unveil comprehensive final estimates encompassing all states and seasons (kharif, rabi, summer) in September-October, departing from the earlier practice of releasing final estimates in February of the subsequent year.
Guidelines for the Digital Crop Survey:
- According to sources, the Economics, Statistics and Evaluation Division (ESED) under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW), has finalised the guidelines.
- According to the guidelines, all states/ UTs shall automate/digitise the process of area enumeration/girdawari of crops at field level, i.e., Digital Crop Survey, from 2024-25 Agricultural Year.
- In India, the agriculture year begins in July and ends in June, the following year.
- Under the guidelines, states and UTs shall use GPS-enabled mobile applications for collecting crop-sown data of each plot for each season and share the village-level aggregated data with DA&FW through API only.
Need for the Digital Crop Survey:
- The current methodology for gathering and consolidating crop statistics relies entirely on manual processes across most states, leading to delays and human errors in the data compilation.
- Only a handful of states, such as Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh, have embraced a digital approach to data collection through GPS-enabled mobile applications, particularly for the recording of crop area and Collection of Cost of Cultivation and Equipment Survey (CCEs) data directly from the fields.
- While Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh have implemented digital systems, they are primarily focused on recording crop areas.
- India faces a challenge due to the lack of dependable agricultural production estimates, accentuating the necessity for a "real-time assessment estimate" of crops.
- Recognizing this gap, there is a compelling need to modernize the current production estimation system by incorporating technological interventions.
Microalgae are Adapting to Warming Climate (DownToEarth)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study finds microalgae are firing up a light-responsive protein to use sunlight for growth.
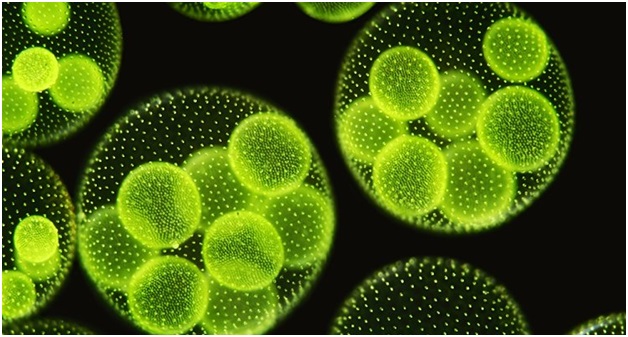
What is the Microalgae?
- Microalgae are microscopic algae prevalent in freshwater and marine environments, consisting of unicellular species that can exist independently or in chains and groups.
- Comprising unicellular algal varieties such as green algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates, these organisms exhibit sizes ranging from a few micrometres to several hundred micrometres.
- Their colour, determined by predominant pigments, categorizes them into groups like green, red, or brown.
- Unlike higher plants, microalgae lack roots, stems, or leaves, and they predominantly engage in photosynthesis, fueled by photosynthetic pigments.
- Heterotrophic microalgae, lacking these pigments, rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Significance:
- Microalgae play a foundational role in the aquatic food chain, offering vital nutrients for zooplankton, small fish, and various aquatic organisms.
- They serve as a primary food source for filter-feeding organisms.
- Moreover, photosynthetic microalgae contribute significantly to global carbon and oxygen cycles, absorbing carbon dioxide and generating oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Approximately half of atmospheric oxygen is produced by these organisms.
- Microalgae can also establish symbiotic relationships, as seen in their association with corals (zooxanthellae), providing nutrients through photosynthesis.
- Certain microalgae, like Nostoc, Anabaena, and Oscillatoria, exhibit nitrogen-fixing capabilities.
- Additionally, microalgae are rich in nutrients and can be consumed by humans. Notable examples like Spirulina and Chlorella are often utilized as dietary supplements.
What are Macroalgae?
- Macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds, are marine plants engaging in photosynthesis but reproducing without flowers.
- Visible to the naked eye, in contrast to microalgae, they typically grow attached to the seabed or reef substrate.
- These macroscopic algae play crucial roles in reef ecosystems, providing both food and habitat for a diverse array of species while contributing significantly to nutrient dynamics.
Phreatomagmatic Eruptions (TOI)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently a new island emerged near Japan's Ogasawara island chain after an undersea volcano erupted.
What is Phreatomagmatic Eruption?
- A phreatomagmatic eruption is a volcanic eruption caused by the interaction of magma and water.
- They differ exclusively from magmatic and phreatic eruptions.
- Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) debris.
- Large explosive eruptions typically contain magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.
- Phreatomagmatic ash is formed by the same mechanism over a wide range of basic and acidic compositions.
- A blocky and uniform crust with low vesicle content is formed.
- Deposits from phreatomagmatic eruptions are thought to be better classified and finer-grained than those from magmatic eruptions.
- This is the result of higher fragmentation of phreatomagmatic eruptions.
About Ogasawara Islands:
- The Ogasawara Islands are a group of more than 30 small subtropical islands in the North-Western Pacific Ocean roughly 1,000 km south of the main Japanese Archipelago.
- It is also known as the Bonin Islands.
- It is one of the famous UNESCO World Heritage sites of Japan.
Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Paris-based International Energy Agency highlighted India’s Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), 2017 as something that sets it apart from other developing economies where “energy efficiency in buildings stands out as a laggard”.
About Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC):
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) Released by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- It was first released in 2007 and again updated in 2017.
- The purpose of ECBE is to set minimum energy standards for commercial buildings, with the objective of enabling energy savings of between 25 and 50% in compliant buildings.
- Commercial buildings include hospitals, hotels, schools, shopping complexes and multiplexes which have a connected load of 100 kW or more, or contract demand of 120 kVA or more.
- Also the code is for both new buildings and retrofitting existing buildings.
- Assessment Parameters: The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) primarily looks at parameters like building design including envelope (walls, roofs, windows), lighting systems, and renewable energy integration among others.
- Tagging of buildings: Compliant buildings are assigned one of three tags in ascending order of efficiency, namely ECBC, ECBC Plus, and Super ECBC.
- 23 out of 28 states have notified ECBC rules. But only 15 states have notified rules based on the latest ECBC,2017.
- Five states — Gujarat, Maharashtra, J&K, Ladakh, and Manipur — are yet to notify ECBC rules.
Himalayan vulture bred (The Hindu)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The first-ever instance of captive breeding of the Himalayan vulture in India has been successfully recorded at the Assam State Zoo in Guwahati by researchers.
About Himalayan Vulture:
- Scientific Name: Gyps himalayensis
- It is a rare and the largest bird species native to the Himalayas.
- Habitat:
- The Himalayan vulture primarily inhabits higher regions of the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, typically found at elevations above 1500 meters.
- This species has a distribution range that extends from western China, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to the eastern part of the Himalayan mountain range, including India, Nepal, and Bhutan, and further to central China and Mongolia.
- Description:
- This vulture is impressively large, featuring a sandy brown plumage with a pale, featherless head. In flight, it displays black primaries and a distinctive small-headed, squared-winged appearance.
- Himalayan vultures are usually spotted alone or in small groups, but they gather in large flocks when feeding on a carcass.
- Conservation status:
- The Himalayan vulture is categorized as "Near Threatened" on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
- To ensure its preservation, the species is covered under the Multi-species Action Plan (MsAP) for the conservation of African-Eurasian vultures and is also included in national Action Plans in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Cambodia.
- Threats:
- The most significant potential threat to this vulture species is believed to be mortality resulting from the ingestion of diclofenac and other vulture-toxic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), commonly used in livestock, particularly in South Asia.
Hematene (PIB)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
A new and remarkably efficient optical limiter has been developed by researchers, utilizing a novel 2D material known as 'hematene.'
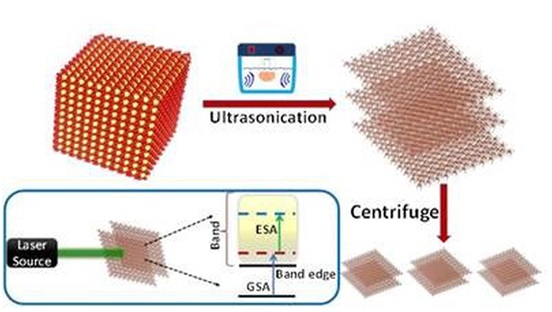
- About Hematene:
- Nanoflakes of a material called hematene extracted from iron ore have been found capable of withstanding and acting as a shield from high laser intensities.
- Hence it could be used to make devices called optical limiters that can protect sensitive optical equipment from light-induced damage.
- Radiation from laser sources is highly concentrated and powerful and can be detrimental to sensitive equipment such as sensors, detectors, and other optical devices.
- When the input intensity increases optical limiters control the amount of light that passes through, thereby preventing damage to the optical component.
- These devices are often useful in laser technologies, military, telecommunications, aircraft, and scientific research in several ways.
- The MESO (Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices) Group of the Department of Physics, Sanatana Dharma College, Alappuzha, in collaboration with the Ultrafast and Nonlinear Optics Lab of the Raman Research Institute, Bangalore, has come up with a new and highly efficient optical limiter using a novel 2D material, ‘hematene’.
- They found that 2D nanoflakes of hematene, a material extracted from iron ore or hematite are capable of withstanding very high laser intensities, and they exhibited excellent optical limiting of green laser light (532 nm) while maintaining a high linear transmission (about 87%) for low-intensity light.
- The nanoflakes of lateral dimensions less than 10 nm, prepared by applying ultrasonic waves to hematite in a liquid medium ( facile exfoliation process) for a definite period to exfoliate the 2D nanoflakes of hematene were also found to be highly stable after year-long storage under ambient conditions, indicating tremendous potential as an optical limiter for futuristic applications.
- This research work carried out at SD College using the instrumentation facility procured through the Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST) programme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) programme, was recently published in ACS Applied Optical Materials.
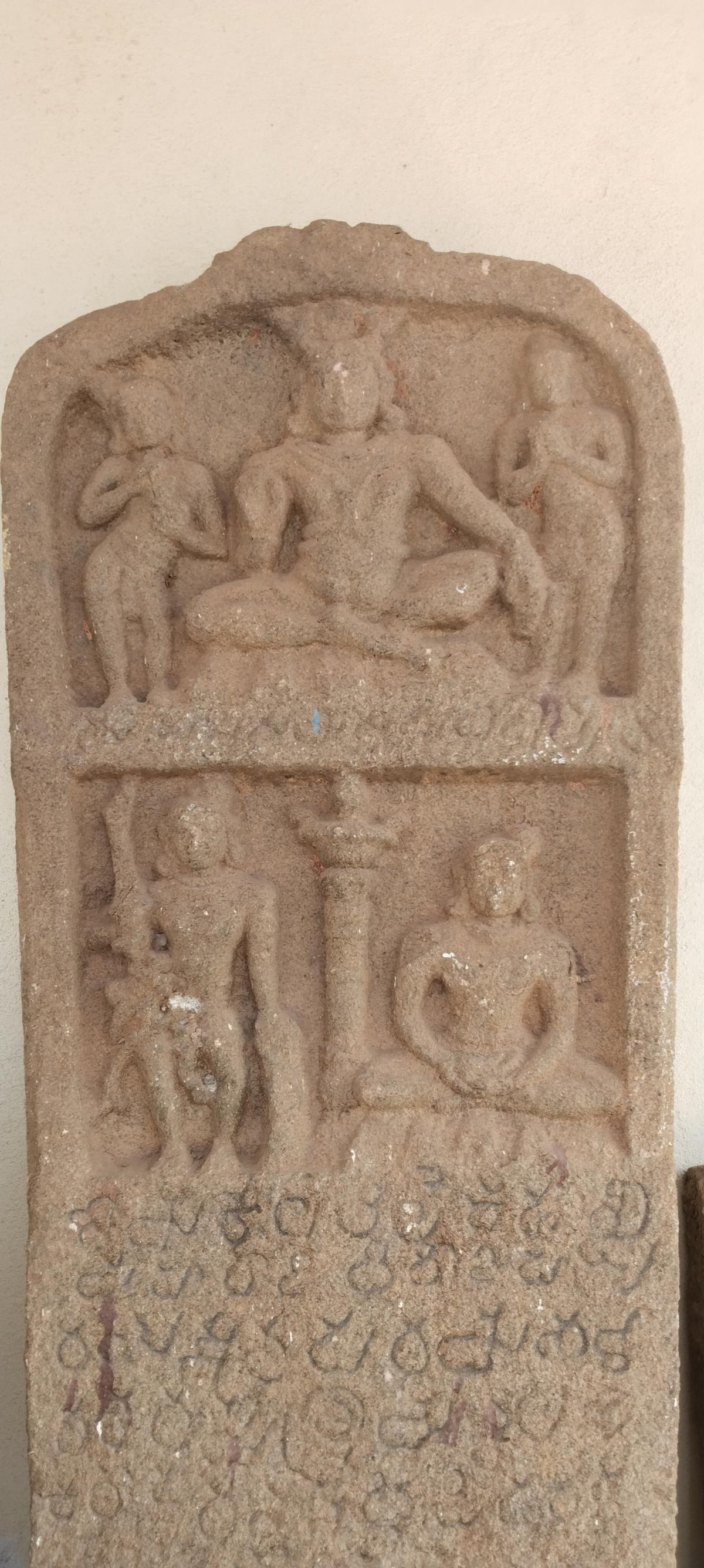
Mangaluru | Archaeologist discovers inscription announcing the death of King KulashekaraAlupendra I at Someshwara (The Hindu)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent archaeological exploration at Someshwara near Mangaluru, Karnataka, archaeologists unearthed a rare inscription related to the Alupa dynasty.
About the Someshwara inscription:
- This inscription holds great importance in understanding Tuluva history and culture.
- It features two panels on top, with the first line carved between them.
- The rest of the inscription, inscribed below the panels in Kannada script and the language of 12th century characters, announces Alupendra I's death.
- The human figures depicted in the inscription are KulashekaraAlupendra.
- He is depicted in the first figure standing in Tribhanga (tri-bent stance).
- He is holding a sword in his right hand and a gurani (shield) in his left.
- The King is represented in a sitting posture on a mound to the left of this panel, separated by a pillar, resting both palms on the center of his legs in dhyana mudra.
About the Alupa dynasty:
- The Alupa dynasty, active from the 2nd to the 15th century CE, ruled over Alvakheda Arusasira in the coastal regions of modern Karnataka.
- Initially independent, they later became vassals to powers like the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and Hoysalas due to shifting politics in Southern India.
- They practiced matrilineal inheritance.
- Their descendants, known as the Bunt, continue to follow this system and bear surnames like Shetty, Rai, Hegde, Alva, and Chowta.
- While most are Hindus, some still follow Jainism.
- The last Alupa king, Kulasekharadeva Alupendradeva, is documented through a 1444 CE inscription in Mudabidri's Jain Basadi.
JAMRANI DAM MULTIPURPOSE PROJECT (PTI)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
Facts About:
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
About the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project:
- According to the project, a dam will be built in the Uttarakhand district of Nainital, close to Jamrani village, across the Gola River, a tributary of the Ram Ganga.
- The neighboring state of Uttar Pradesh would receive a sizable portion of the project's irrigation benefits.
- This is the seventh project to be added to the PMKSY-AIBP list.
Facts about the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana:
It was introduced in 2015–16.
Aim: To improve physical access to water on farms, increase cultivable land under assured irrigation, increase on-farm water use efficiency, and implement sustainable water conservation practices.
Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), ongoing major and medium irrigation projects, including national projects, will be completed more quickly.
Har Khet Ko Pani: It is divided into four smaller components:
- Ground Water (GW) Development component,
- Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI),
- Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies, and
- Command Area Development & Water Management (CAD&WM).
The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, is the nodal ministry.
TRIBAL COOPERATIVE MARKETING DEVELOPMENT FEDERATION (TRIFED) (PTI)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Tribal Affairs Ministry on Saturday declared "null and void" the suspension of the managing director of TRIFED.
Facts About:
The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation (TRIFED) is a national-level organization operating under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Its primary focus is on the development and marketing of tribal handicrafts and natural products.
Established in 1987, it became registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984 (now the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002).
TRIFED's main objectives include enhancing the capabilities of tribal communities, promoting their products, and creating marketing opportunities to ensure better prices for tribal products, ultimately improving their income sustainably.
Some of its key goals are:
- Enhancing the socio-economic welfare of tribal communities.
- Facilitating and providing services to improve production within tribal communities.
- Offering training to enhance artistic skills using modern technology, making tribal products more competitive in the global market.
- Promoting tribal art and crafts to provide a stable livelihood.
- Identifying target groups, monitoring activities, and providing input to the Ministry.
Under retail marketing, TRIFED is responsible for marketing of tribal products under the brand name "TRIBES INDIA."
It promotes and establishes a sustainable market through retail outlets, exhibitions like Aadishilp, Aadichitra, and OCTAVE, international fairs, and e-marketing.
The Government of India has also entrusted TRIFED with the implementation of the Minimum Support Price Scheme for Minor Forest Produce.
Headquarter: New Delhi
It continues to operate a system of Regional Offices throughout India and a collection of TRIBES INDIA Retail Outlets.
Data-driven Innovations in Agriculture (PTI)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (Nabard) has teamed up with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in India to jointly develop data-driven innovations for the benefit of smallholder farmers in agriculture and food systems.
Facts About:
- This partnership aims to improve the well-being of smallholder farmers by jointly using open-source data for product development, technology transfer, and policy formulation.
- It focuses on enhancing climate resilience in agriculture and involves sharing collaborative digital resources like DiCRA (Data in Climate Resilient Agriculture).
- DiCRA offers access to essential geospatial data related to climate-resilient agriculture and is curated by UNDP and partner organizations.
- This collaboration represents a significant opportunity to harness data and present it as a digital public infrastructure for India's rural farming community.
- Such open data innovations can promote best practices, optimize agricultural investments, and bolster the resilience of smallholder farmers, including women, against various challenges.
