Global Economic Prospects (GEP) Report 2025
- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Bank has released its Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report for 2025, a flagship biannual publication analyzing trends and projections in the global economy, with a focus on emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). The report highlights economic growth forecasts, trade dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Outlook
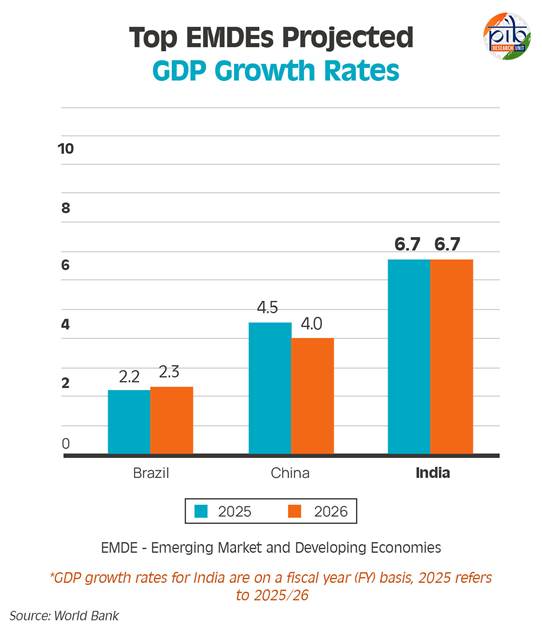
- The world economy is projected to expand at a steady yet subdued rate of 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, maintaining the pace of 2024.
- Inflation, which peaked above 8% in recent years, is expected to stabilize at an average rate of 2.7% in 2025 and 2026, aligning with central bank targets.
- Despite growth, the global economy remains 0.4 percentage points below the 2010-2019 average, raising concerns about its ability to tackle poverty effectively.
Challenges and Risks
- Trade Restrictions: New trade restrictions imposed in 2024 were five times higher than the 2010-19 average, contributing to a slowdown in global trade and economic growth.
- Rising Protectionism: Increased fragmentation in global trade policies is limiting exports and hampering economic integration.
- Policy Uncertainty: Adverse policy shifts, sluggish progress in reducing inflation, and weaker performance in major economies pose downside risks to global recovery.
- Debt and Investment Concerns: Developing economies are experiencing sluggish investment growth and high debt levels, exacerbated by climate change-related costs.
Emerging Markets and Developing Economies (EMDEs)
- EMDEs have significantly evolved since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
- The three largest EMDEs—India, China, and Brazil—have accounted for approximately 60% of annual global growth over the past two decades.
- Growth in low- and middle-income developing countries is expected at 4.1% in 2025 and 4% in 2026, with a notable slowdown compared to the early 2000s.
- Low-income countries are projected to rebound to 5.7% in 2025 and 5.9% in 2026, aided by easing conflicts in some regions.
- The world's poorest nations, with annual per capita incomes below USD 1,145, recorded growth of 3.6% in 2024, impacted by conflicts in regions like Gaza and Sudan, alongside lingering effects of COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions.
India-Specific Highlights
- Fastest-Growing Major Economy: India is expected to maintain its position as the world’s fastest-growing major economy, with a projected growth rate of 6.7% in both 2025 and 2026.
- Sectoral Growth: The services sector will remain robust, while manufacturing activity is expected to strengthen.
- Investment Growth: Supported by rising private investment, improved corporate balance sheets, and favorable financing conditions, investment growth in India is expected to remain steady.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Innovation-driven initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- Expansion of the digital economy and financial inclusion efforts.
- Rural Demand and Consumption: Growth in rural demand and a recovery in farm production have bolstered consumer spending, although urban consumption remains affected by inflation and slow credit growth.
Nine Years of Startup India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 16, 2025, India marks nine years of Startup India, a transformative journey that began in 2016. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion celebrates the nation’s strides in fostering a robust and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Current Status (as of Jan 2025)
Over 1.59 lakh startups recognized by DPIIT, making India the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- More than 100 unicorns (startups valued over $1 billion).
- Key hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi-NCR; growing contribution from smaller cities.
Key Sectors
- Major sectors: Fintech, Edtech, Health-tech, E-commerce.
- Notable companies: Zomato, Nykaa, Ola exemplify India's shift from job seekers to job creators.
Key Milestones (2016–2025)
- Startups grew from around 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- 73,151 startups with at least one-woman director as of 2024, showcasing rise in women entrepreneurship.
- Over 16.6 lakh jobs created by DPIIT-recognized startups by 2024.
Core Features of Startup India
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified compliance, self-certification, and single-window clearances.
- Tax Benefits: Three-year tax exemptions for eligible startups.
- Funding Support: ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) supports early-stage funding.
- Sector-Specific Policies: Policies focusing on sectors like biotechnology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Industry-wise Jobs Created
- IT Services: 2.04 lakh jobs.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: 1.47 lakh jobs.
- Professional & Commercial Services: 94,000 jobs.
- Total direct jobs created: 16.6 lakh (as of Oct 2024).
Flagship Schemes
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
Other Key Initiatives
- Capacity Building & Handholding: Workshops for regional ecosystems, especially in non-metro cities.
- Outreach & Awareness: Initiatives to facilitate funding, incubation, and mentorship opportunities.
- Ecosystem Development: National-level events like Startup Mahakumbh to bring together key stakeholders.
- International Linkages: India’s G20 Presidency institutionalized Startup20 to enhance global collaborations.
BHASKAR Platform (Launched in Sept 2024)
- Objective: Centralize and streamline interactions within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- Networking: Connects startups, investors, mentors, and government bodies.
- Resources: Provides quick access to essential tools and knowledge for scaling startups.
- Global Outreach: Promotes India as a global innovation hub.
Startup Mahakumbh
- 2024 Edition: Hosted 1,300 exhibitors, 48,000 visitors, and 392 speakers, including unicorn founders and policymakers.
- 2025 Edition (3-5 April, New Delhi): Theme - “Startup India @ 2047 – Unfolding the Bharat Story.”
Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Shri Piyush Goyal launches Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform:
- Objective: Strengthen India's cleantech value chains, especially in solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Platform Features:
- Aims to promote collaboration, co-innovation, and knowledge-sharing among Indian firms.
- Focus on scaling up manufacturing, sharing ideas, technologies, and resources.
- Acts as a financing platform for the cleantech sector.
- Designed to position India as a global leader in sustainability and cleantech innovation.
India's Clean Energy Commitment:
- Target: 500 GW of clean energy capacity by 2030.
- India has been a front-runner in fulfilling its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and UNFCCC.
- Early Achievement: India achieved its 2022 renewable energy target of 200 GW, 8 years ahead of schedule.
- Largest Interconnected Grid: India boasts the world’s largest interconnected power grid, enhancing its renewable energy distribution capacity.
- Gujarat is a pioneer in solar power adoption in India.
Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal's Views:
- On Product-Linked Incentives (PLIs):
- PLIs and subsidies are seen as short-term aids; long-term growth of the clean energy sector depends on it becoming self-sustaining.
- Urged Indian firms to innovate and scale up manufacturing within the country.
- On Clean Energy and Sustainability:
- Stressed the importance of innovation and collaboration to achieve sustainability goals.
- India aims to attract international investors by creating a compelling business case for cleantech investments.
- 3S Approach (Speed, Scale, and Skill): Key to implementing India's renewable energy program, emphasizing rapid deployment, large-scale adoption, and skill development in the sector.
Bharat Climate Forum 2025:
- Event Objective: A platform for policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders to discuss climate action, clean energy, and India’s role in global climate goals.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Aligning India’s clean energy initiatives with global climate goals (UNFCCC, Paris Agreement).
- Emphasizing India’s early achievements in clean energy adoption.
- Promoting sustainable development and clean energy solutions.
India's Performance in Renewable Energy:
- India’s progress has been commendable in meeting its climate targets and setting up clean energy capacity ahead of schedule.
- The government’s initiatives, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, have made solar power affordable and scalable through transparency in auctions, competitive bidding, and speed in project implementation.
National Youth Day 2025

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 12, 2025, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated in the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2025, an event aimed at empowering India's youth and charting a roadmap for the nation's development. This occasion also coincided with the celebration of National Youth Day, marking the 163rd birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, a renowned spiritual leader and social reformer who strongly believed in the transformative potential of India's youth.
Significance of National Youth Day
- Purpose:
- National Youth Day is celebrated to honor Swami Vivekananda's contributions, emphasizing the role of youth in nation-building.
- It promotes empowerment, leadership, and innovation among the youth.
- Year of First Celebration: 1985
- Key Theme (2025): "Arise, Awake, and Realize the Power You Hold"
Key Highlights from the Dialogue
- Goal of the Dialogue:
- Engaging youth in the decision-making process for a developed India by 2047.
- Empowering youth through platforms like quizzes, essay competitions, and thematic presentations.
- Ten Key Themes Discussed:
- Technology & Innovation
- Sustainability
- Women Empowerment
- Manufacturing & Agriculture
- Education and Skill Development
India’s Roadmap for 2047 (Viksit Bharat)
- Vision:
- Economic Power: India is moving toward becoming the third-largest economy.
- Strategic and Cultural Strength: India will have a robust economic, strategic, social, and cultural framework.
- Youth's Role: Innovation in technology, digital economy, space, and manufacturing will drive India’s growth.
- Key Projects and Targets:
- Target: Generating 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Net Zero Emissions for Railways: Set for 2030.
- Olympics: India aims to host the Olympics in the next decade.
- Space Power: Plans for a space station by 2035.
Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Challenge
- Objective:
- Engage youth in shaping ideas for a developed India.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is part of the Viksit Bharat Challenge.
- Stages of the Challenge:
- Viksit Bharat Quiz: Participation by 30 lakh youth.
- Essay Writing: Over 2 lakh essays on key developmental themes.
- State Rounds: Rigorous in-person competition to identify the top young leaders.
- Participant Categories:
- 1,500 from Viksit Bharat Challenge Track.
- 1,000 from Traditional Track (cultural and science innovation).
- 500 Pathbreakers (leaders in diverse sectors).
Achievements Under Government Benefiting Youth
- Educational Reforms:
- Increase in IITs, IIITs, IIMs, and AIIMS.
- Growth in the number of higher education institutions and their global rankings.
- Economic Growth:
- India's economy has grown to nearly $4 trillion.
- Infrastructure Investments: More than ?11 lakh crore allocated for infrastructure development.
- Employment Opportunities for Youth:
- Mudra Loans: ?23 lakh crore distributed to youth entrepreneurs.
- Startup Ecosystem: India is among the top three in global startups.
- PM Gati Shakti Mission: Facilitating logistics and infrastructure development, creating employment opportunities.
Future Outlook
- Youth as the Future Leaders of India:
- India’s Youth Power: Vital to achieving a developed nation by 2047.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is a platform for youth to voice their opinions and engage with policymakers.
- Role of Youth in India’s Transformation:
- Collective Responsibility: Every citizen's effort is essential for national goals.
- The vision of a Viksit Bharat hinges on the innovative contributions and ownership by young minds.
EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog, in partnership with New Shop (India’s largest 24/7 convenience retail chain), launched the initiative EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan under the Award to Reward (ATR) program. This program aims to empower women entrepreneurs by providing them with the skills, resources, and mentorship needed to succeed in the organized retail sector. The collaboration seeks to create a robust retail ecosystem that supports women in overcoming barriers such as societal biases, limited access to financing, and a lack of mentorship.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Target Participants: The program will select 50 women aged 18-35 through an online application process. Women from Delhi NCR, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat will be considered.
- Top 20 Participants: The 20 best candidates will receive a 100% waiver on New Shop franchise fees, enabling them to operate their own retail businesses with reduced financial barriers.
- Program Objective: Equip women entrepreneurs with skills such as retail management, digital tools, financial literacy, and business development. Participants will also receive valuable mentorship to help them grow and scale their businesses.
- Focus on Retail: The initiative focuses on empowering women within the organized retail sector, creating a sustainable ecosystem that fosters growth and development for female entrepreneurs.
About Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP):
- Incubation & Transition: Established in 2018, WEP was incubated within NITI Aayog and transitioned into a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in 2022.
- Purpose: WEP aims to empower women entrepreneurs by addressing challenges like information asymmetry and providing essential support in key areas such as:
- Access to Finance
- Market Linkages
- Training & Skilling
- Mentoring & Networking
- Compliance & Legal Assistance
- Business Development Services
- Collaboration: WEP partners with over 30 public and private sector organizations to develop scalable and impactful programs. Since 2023, the Award to Reward initiative offers a framework for stakeholders to create impactful programs for women entrepreneurs.
About New Shop:
- Business Model: New Shop operates over 200 round-the-clock convenience retail stores in high-density areas, including highways and gas stations. The company plans to expand into airports, railway stations, and other mass transit hubs.
- Franchising Vision: By 2030, New Shop aims to empower over 10,000 entrepreneurs in India through its franchising model. The partnership with WEP seeks to help women entrepreneurs access this growth opportunity.
Program Outcomes:
- Mentorship & Training: Participants will be mentored and trained on key aspects such as retail management, business development, and digital tools.
- Franchise Opportunity: Top participants will gain access to New Shop’s franchising ecosystem, providing them a ready-made business opportunity with lower entry barriers.
- Financial Assistance: The program will also provide financial resources to the women, helping them build their businesses with greater ease.
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
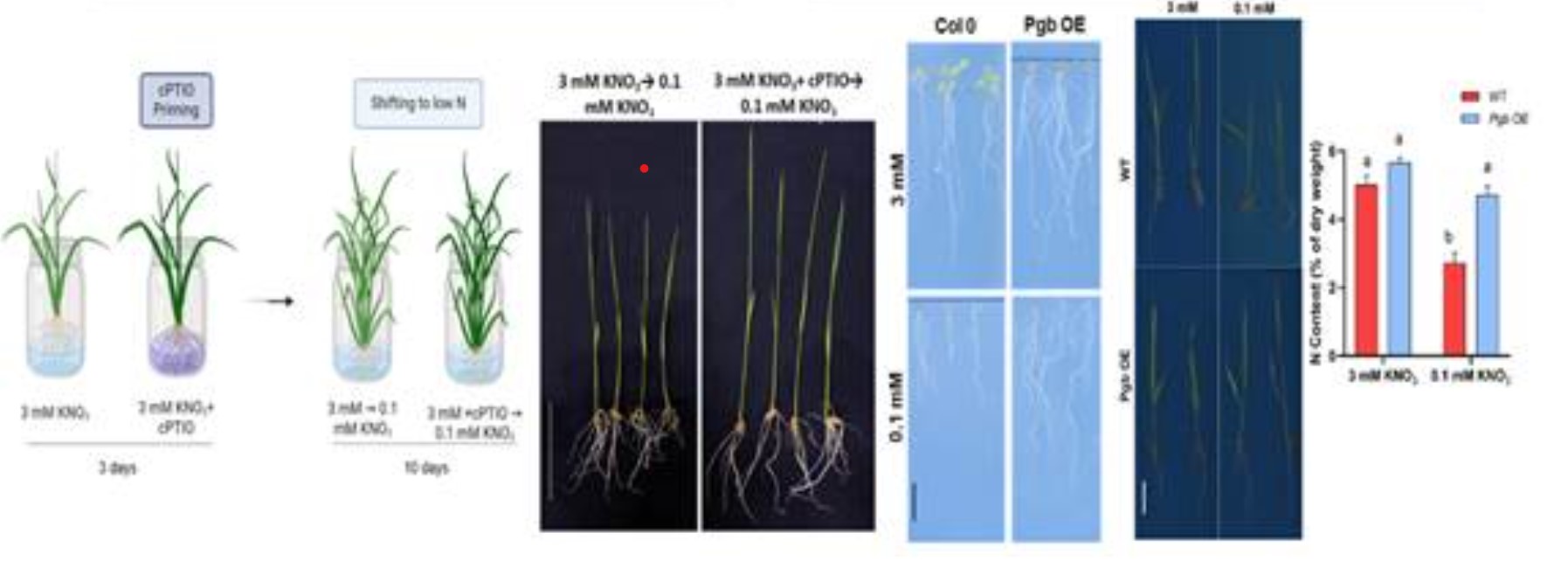
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD)
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) Convention will be held from January 8-10, 2025, in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
Key Highlights:
- Theme 2025:
- The theme is "Diaspora’s Contribution to a Viksit Bharat", highlighting the vital role of the Indian diaspora in India's development into a prosperous and developed nation.
- Exhibitions:
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Vishwaroop Ram – The Universal Legacy of Ramayana: Showcasing the Ramayana’s influence through traditional and contemporary art forms.
- Diaspora’s Contribution to Technology and Viksit Bharat: Highlighting the global technological impact of the Indian diaspora.
- Spread and Evolution of the Indian Diaspora: Focused on the migration of Indians from Mandvi (Gujarat) to Muscat (Oman).
- Heritage and Culture of Odisha: A look into Odisha’s rich cultural traditions.
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Key Initiatives:
- Pravasi Bharatiya Express: PM Modi will flag off this special tourist train for the diaspora, covering key religious and tourist sites in India under the Pravasi Teertha Darshan Yojana.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards (PBSA): Recognizing significant contributions by members of the Indian diaspora in various fields.
About Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD):
- Origins:
- Celebrated on January 9 each year, marking Mahatma Gandhi's return to India from South Africa in 1915, symbolizing the contributions of migrants.
- First held in 2003, the event became biennial in 2015.
- Objectives:
- Recognizes the contributions of the Indian diaspora to India’s growth.
- Fosters engagement between India and its global diaspora.
- Strengthens India’s relations with host countries and promotes understanding of India’s culture and achievements.
Contributions of the Indian Diaspora to a Viksit Bharat:
- Economic Growth:
- The diaspora plays a pivotal role through remittances, investments, and connecting Indian businesses to global markets.
- Example: The development of a thorium-based fuel by a U.S.-based NRI is a significant step toward clean nuclear energy in India.
- Global Trade Linkages:
- Facilitating partnerships, investments, and knowledge exchange to expand India’s trade base and global market presence.
- Supporting Innovation: Diaspora-driven collaborations in emerging markets boost India’s entry into high-growth sectors, enhancing the country's development prospects.
- Cultural Contributions: Indian diaspora members serve as cultural ambassadors, promoting Indian traditions, art, and heritage globally (e.g., Diwali recognized as a public holiday in several U.S. states).
Challenges Faced by the Indian Diaspora:
- Cultural Integration: Struggles with balancing cultural identity and integrating into host societies can lead to alienation.
- Political and Religious Issues: Increasing politicization and religious biases, especially against Hindus and Sikhs, in countries like the USA and Europe.
- Legal and Citizenship Issues: Complicated visa statuses, restrictive immigration laws, and issues like the H-1B visa challenge the diaspora, despite their significant contributions.
- Remittance Challenges: Economic instability, exchange rate fluctuations, and banking hurdles affect the regular flow of remittances to India, impacting families dependent on them.
Government Initiatives for the Diaspora:
- National Pension Scheme for NRIs
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Card Scheme
- Pravasi Bhartiya Kendra
- Indian Community Welfare Fund (ICWF)
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
LEADS 2024 Report

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launch of the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report and the Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield (LEAPS) 2024 awards in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of LEADS 2024 Report:
- Evaluate logistics performance across Indian states and union territories.
- Provide actionable insights for logistics reforms to foster competitive federalism.
- Assess logistics infrastructure, services, regulatory environment, and sustainability efforts.
- Performance Evaluation:
Region Achievers Fast Movers Aspirers
Coastal States Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh, Goa Kerala, West Bengal
Landlocked States Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand
North-Eastern States Assam, Arunachal Pradesh Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura Manipur
Union Territories Chandigarh, Delhi Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Ladakh
Lakshadweep, Puducherry
- Key Remarks:
- Action Plans for Better Logistics: States should develop regional and city-level logistics plans, including for last-mile connectivity, to attract investments.
- Green Logistics: Advocate for sustainable logistics practices to ensure environmentally responsible growth.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encourage PPPs to promote multi-modal hubs and streamline logistics infrastructure.
- Technological Integration: Push for the adoption of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics to enhance efficiency in logistics operations.
- Skill Development & Gender Inclusivity: Focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development to boost sectoral growth. Promote gender diversity in logistics.
- LEAD Framework: Urge logistics sectors to embrace the LEAD framework (Longevity, Efficiency, Accessibility, Digitalisation) for transformation.
- LEAD Framework and Recommendations:
- Longevity, Efficiency, and Effectiveness: Improve long-term logistics strategies.
- Accessibility and Accountability: Ensure better reach and transparent logistics practices.
- Digitalisation: Enhance digital transformation across logistics processes.
- About LEADS:
- Full Form: Logistics Ease Across Different States.
- Launched: 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Purpose: To assess and improve logistics infrastructure and services across Indian states and UTs.
- Methodology: Based on over 7,300 responses from a pan-India survey and inputs from over 750 stakeholder consultations.
- LEAPS 2024 Awards: Recognized excellence in the logistics sector across categories such as air, rail, road, maritime freight service providers, startups, MSMEs, and educational institutions.
- PM GatiShakti Course: Launched a 15-hour online course on “PM GatiShakti Concept for Efficient Infrastructure Planning and National Development”, hosted on iGOT Karmayogi platform and UGC SWAYAM portal.
- Logistics Cost Framework Report: Unveiled a report on the logistics cost framework, aiming to accurately estimate logistics costs in India through a hybrid methodology, incorporating both EXIM and domestic cargo data.
- Significance of LEADS:
- Provides critical insights into logistics performance, helping States and UTs to improve infrastructure, services, and regulatory practices.
- Plays a key role in India's vision of becoming a $32 trillion economy by 2047 by improving logistics efficiency, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
National Sports Awards 2024
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Sports Awards 2024 were recently announced by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports to celebrate excellence in Indian sports.
Key Highlights:
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award
- This is India's highest sporting honor, renamed in 2021 after hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- It’s awarded for exceptional performance in sports over a four-year period.
- 2024 Winners:
- Gukesh D (Chess)
- Harmanpreet Singh (Hockey)
- Praveen Kumar (Para-Athletics)
- Manu Bhaker (Shooting)
- The award includes a cash prize of Rs 25 lakh.
Arjuna Award
- Recognizes outstanding performance in sports over the previous four years and attributes like leadership, discipline, and sportsmanship.
- 2024 Winners: Various athletes across multiple disciplines received this honor.
Arjuna Award (Lifetime)
- Given to retired athletes who have not only excelled during their careers but also contributed to the promotion of sports post-retirement.
- 2024 Winners:
- Shri Sucha Singh (Athletics)
- Shri Murlikant Rajaram Petkar (Para-Swimming)
Dronacharya Award
- Given to coaches who have made a consistent and significant contribution by guiding sportspersons to excel at international events.
- The award includes a bronze statue of Dronacharya, a certificate, and a cash prize.
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy
- Awarded to the top-performing university in the Khelo India University Games.
- 2024 Winner: Chandigarh University.
Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar
- Recognizes individuals or organizations for their contribution to the promotion and development of sports.
- 2024 Winner: Physical Education Foundation of India.
These awards were selected by a committee led by Justice (Retd.) V. Ramasubramanian and include eminent sportspersons, journalists, and sports administrators. The winners will receive their awards from the President of India, marking a prestigious moment in Indian sports.
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completes two years of remarkable success, driving mutual growth and showcasing the complementarity of both economies.
Key Achievements:
- Bilateral Merchandise Trade Surge:
- Trade increased from USD 12.2 billion (2020-21) to USD 26 billion (2022-23).
- Trade moderated slightly in 2023-24 to USD 24 billion, but exports from India to Australia grew by 14%.
- From April-November 2024, bilateral trade reached USD 16.3 billion.
- Preferential Import Utilization:
- Export utilization: 79%
- Import utilization: 84%
- Sectoral Growth:
- Textiles, chemicals, and agriculture sectors have seen significant growth.
- New export products: Gold studded with diamonds, turbojets.
- India’s imports: Metalliferous ores, cotton, wood products that fuel Indian industries.
- Geopolitical Strengthening:
- Enhanced relations in forums like Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI).
Key Features of the Agreement:
- Tariff Reductions:
- Australian goods: 85% tariff-free access to India (rising to 90% by 2026).
- Indian goods: 96% tariff-free access to Australia (rising to 100% by 2026).
- Access to Key Markets:
- India: Access to Australia's fast-growing market.
- Australia: Access to India's labor-intensive sectors like gems, jewelry, textiles, leather, furniture, food, agriculture.
- Services and IT:
- 135 sub-sectors covered in services.
- India gains market access in 103 sub-sectors with Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status in 31.
- Fast-tracked approval of medicines and elimination of double taxation for India's IT sector.
- Job Creation & Skill Exchange:
- Expected creation of 1 million jobs in India.
- Opportunities for Indian yoga teachers, chefs, and 100,000 students with post-study work visas.
Future Prospects:
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): Builds on ECTA to advance bilateral trade, with 10 formal rounds and ongoing inter-sessional discussions.
- Trade Target: Aim to reach AUD 100 billion in trade by 2030.
- Global Economic Impact: Strengthening the partnership will contribute to a more resilient and dynamic global economy, with deeper economic integration between India and Australia.
Exercise SURYA KIRAN

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian Army Contingent Departs for 18th Edition of Exercise SURYA KIRAN (India-Nepal Joint Military Exercise).
Key Highlights:
- Event Overview:
- Name: 18th Edition of Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
- Dates: 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
- Location: Saljhandi, Nepal.
- Participants: Indian Army (334 personnel, led by a Battalion from the 11th Gorkha Rifles) and Nepal Army (Srijung Battalion).
- Objective of Exercise:
- Enhance interoperability in jungle warfare, counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrain, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) under the UN Charter.
- Focus on operational preparedness, aviation training, medical aspects, and environmental conservation.
- Key Features:
- Training Focus: Improving combat skills and coordination to operate together in challenging situations.
- Exchange of Ideas: Soldiers from both nations will share best practices, enhance mutual understanding of operational procedures.
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: Reinforces strong bonds of friendship, cultural linkages, and defense cooperation between India and Nepal.
- Significance:
- Historical Context: Exercise held alternately in India and Nepal since 2011.
- Enhances Combat Readiness: Prepares both armies to address shared security challenges and improve operational capabilities.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Fosters a productive professional environment between India and Nepal.
- Recent Developments:
- The exercise follows visits by General Upendra Dwivedi (Indian Army Chief) to Nepal and General Ashok Raj Sigdel (Nepali Army Chief) to India, strengthening military ties.
- Previous Editions:
- 17th Edition: Conducted in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand (24th Nov - 7th Dec 2023).
Lighthouse Tourism in India

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
Lighthouse tourism in India is rapidly emerging as an exciting and profitable segment of the country's travel and tourism industry. India's coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is home to 204 lighthouses, many of which are being transformed into vibrant tourist destinations, celebrating both India's rich maritime history and its natural beauty.
Key Highlights:
- Historical and Scenic Appeal: Lighthouses in India are often located in breathtaking coastal or island locations, offering panoramic sea views and access to surrounding natural beauty. Some of these structures are centuries old and are situated near significant cultural landmarks or UNESCO World Heritage Sites, adding cultural depth to the visitor experience.
- Economic Growth: As part of the broader Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, the Government of India is keen to transform these historic lighthouses into hubs of economic activity. By developing infrastructure, creating new tourism-related jobs, and fostering local entrepreneurship, lighthouse tourism aims to benefit coastal communities and boost India's tourism economy. As of 2023-24, 75 lighthouses across 10 states have been equipped with modern amenities, attracting 16 lakh visitors—a 400% increase from previous years.
- Government Initiatives:
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- The 1st Indian Lighthouse Festival, “Bharatiya Prakash Stambh Utsav”, was inaugurated on 23rd September, 2023 by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal and Goa Chief Minister, Shri Pramod Sawant at the historic Fort Aguada in Goa.
- The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held in Odisha. Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, was also joined by Odisha Chief Minister, Mohan Charan Majhi. Shri Sonowal dedicated two new lighthouses at Chaumuck (Balasore) and Dhamra (Bhadrak) and emphasized empowering coastal communities to preserve and promote lighthouses as part of India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Sagarmala Programme: This government initiative integrates infrastructure development with sustainable practices, ensuring that the growth of lighthouse tourism benefits local communities while preserving the environment.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The government has invested ?60 crore in enhancing these sites, providing facilities like museums, parks, amphitheaters, and more to enrich the visitor experience.
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- Sustainable Development: The Indian government places a strong emphasis on eco-friendly tourism. This includes integrating lighthouses into broader coastal circuits and launching digital awareness campaigns to attract domestic and international tourists.
- Community Empowerment and Employment: Lighthouse tourism has already created direct and indirect employment, from hospitality to transportation, local handicrafts, and artisan work, with more than 500 jobs being generated. Local communities are being trained to offer skills in hospitality and tourism services.
Future Plans:
- Skill Development: Programs are being introduced to equip local people with the necessary skills to cater to the tourism industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly practices will continue to be emphasized to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Integration with Coastal Circuits: Lighthouses will become key points of interest in broader coastal tourism itineraries, further enhancing their appeal to tourists.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
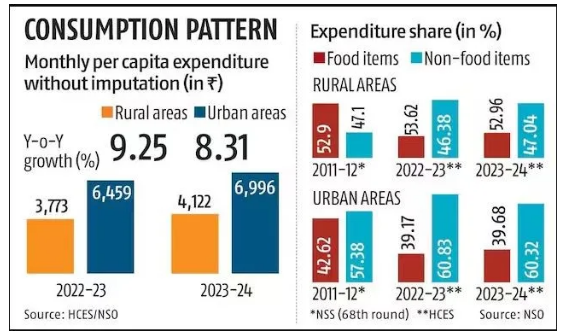
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
72nd North Eastern Council (NEC) Plenary Session

- 23 Dec 2024
Overview:
The 72nd Plenary of the North Eastern Council (NEC), concluded in Agartala, Tripura, marking the second time the city hosted this significant event since 2008. The plenary featured a series of high-level discussions focused on accelerating development and addressing the socio-economic challenges of the North Eastern Region (NER), which includes Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura.
Key Highlights:
- Pre-Plenary Technical Sessions: Central ministries presented their developmental agendas for the NER, charting a path forward for the region's growth and addressing key challenges.
- Main Plenary:
- Presiding Officers: The session was chaired by the Union Home Minister and NEC Chairman, Shri Amit Shah, along with DoNER Minister, Shri Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, and Minister of State, Dr. Sukanta Majumdar.
- Participants: Governors, Chief Ministers, Chief Secretaries, Planning Secretaries, and high-ranking officials from all eight northeastern states will engage in strategic discussions to foster regional development.
- Agartala as Host:
- Agartala's selection as the venue signifies the evolving role of the city in regional development, as plenary sessions are usually held in Shillong and Guwahati.
- Significance of the NEC:
- The North Eastern Council (NEC), established in 1971, plays a pivotal role in the socio-economic development of the region. It was initially an advisory body but has evolved into a regional planning agency with a larger mandate.
- The NEC has contributed significantly to the development of critical infrastructure in the region, such as over 11,500 kilometers of roads, power generation through NEEPCO, and educational institutions like RIMS.
- Prime Minister's Vision for the NER:
- The Prime Minister’s vision for the region revolves around recognizing it as 'Ashta Lakshmi'—symbolizing immense potential and cultural richness. The NEC is central to realizing this vision through initiatives like the PM-DevINE scheme.
Key Achievements of the NEC:
- Over 11,500 kilometers of road construction, improving regional connectivity.
- Increased power generation capacity via projects managed by NEEPCO.
- Established institutions like the Regional Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) and others that cater to regional educational and technical needs.
Recent Focus and Shift in Governance:
- In the 72nd Plenary, the Union Home Minister highlighted a shift in the focus of police forces in northeastern states, urging them to focus not just on insurgency control but on ensuring the constitutional rights of citizens, reflecting a new governance phase in the region.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 INITIATIVE

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, launched by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), aims to enhance the competitiveness of the Indian capital goods sector by promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. This initiative is part of the Scheme for Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
Key Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- Establishment of Smart Manufacturing Hubs: Under this initiative, four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been set up across India:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- Cluster Industry 4.0 Experience Centres: In addition to the above centres, 10 cluster Industry 4.0 experience centres have been approved. These will be established under a Hub and Spoke model, managed by the C4i4 Lab in Pune, and spread across India.
- Key Achievements:
- Model Factories: Development of an Industry 4.0 enabled Model Factory at C4i4, Pune, and a smart production-based factory at CMTI Bengaluru.
- Industry 4.0 Solutions: More than 50 use-cases for Industry 4.0 solutions were compiled to support implementation.
- Maturity Assessment Tool: Creation of the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model (I4MM), specifically designed to assess the readiness of Indian manufacturing companies for Industry 4.0.
- Online Assessment Tool: Launch of a free online assessment tool by C4i4 Lab, Pune, to help MSMEs evaluate their maturity in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Training and Awareness:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular awareness seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events are organized to educate industries about Industry 4.0.
- Workforce Training: The SAMARTH Centres have trained over 5000 professionals on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy Services: The centres offer consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups and MSMEs.
- Impact on MSMEs:
- Digital Maturity Assessments: Over 100 digital maturity assessments have been completed for the auto industry, and more than 500 improvement initiatives have been identified.
- Training and Capacity Building: Over 500 digital champions have been trained on Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Focus on MSMEs: While no direct financial assistance is provided to industries, including MSMEs, under this initiative, the SAMARTH Centres play a key role in helping them adopt Industry 4.0 technologies and build their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative seeks to increase the global competitiveness of India's capital goods and manufacturing sectors.
- It leverages Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, automation, data analytics, and AI to modernize manufacturing processes.
- The initiative involves setting up 4 major Smart Manufacturing Hubs and 10 regional experience centres across the country to facilitate awareness, training, and adoption of Industry 4.0 among manufacturers, especially MSMEs.
- While it does not provide financial aid, it helps industries improve their digital maturity, trains workforce, and guides them through consultancy and workshops.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program

- 21 Dec 2024
On December 20, 2024, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $350 million policy-based loan aimed at expanding India's manufacturing sector and improving the resilience of its supply chains. This loan is part of the Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program.
Key Points:
- Loan Agreement Signatories:
- Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance, Government of India
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- SMILE Program:
- Goal: Strengthen the logistics ecosystem to enhance India's manufacturing sector and improve supply chain resilience.
- Structure: The program includes two subprograms focusing on strategic reforms in logistics and infrastructure development.
- Key Features of the SMILE Program:
- Strengthening Multimodal Infrastructure: Enhances logistics infrastructure at the national, state, and city levels.
- Standardization: Improves warehousing and other logistics assets to attract private sector investment.
- External Trade Logistics: Enhances efficiencies in external trade logistics.
- Smart Systems: Adopts systems for efficient, low-emission logistics to promote sustainability.
- Expected Outcomes:
- Cost Reduction & Efficiency: Strategic reforms will reduce logistics costs and improve efficiency.
- Job Creation: Infrastructure development and reforms are expected to generate substantial employment opportunities.
- Gender Inclusion: The program promotes gender inclusion through economic growth initiatives.
- Impact on India’s Economy:
- The transformation of India’s logistics sector will enhance the competitiveness of the manufacturing sector and drive sustainable economic growth.
About the Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- Established: December 19, 1966.
- Members: 69 countries, including both regional (e.g., India, China) and non-regional (e.g., USA, Japan) members.
- Function: ADB promotes social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific, providing loans, grants, and technical assistance for development projects.
- Key Shareholders:
- Japan: 15.57%
- USA: 15.57%
- India: 6.32%
- China: 6.43%
- Australia: 5.77%
India's First-Ever Ganges River Dolphin Tagging in Assam

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
India conducts the first-ever satellite tagging of the Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica) in Assam, a key step in wildlife conservation.
Key Highlights:
Objective of Tagging: The tagging aims to understand:
- Migratory patterns
- Range and distribution
- Habitat utilization, especially in fragmented river systems.
Key Participants:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
- Assam Forest Department
- Aaranyak (NGO)
- Funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
Significance of the Tagging:
- Technology Used: Lightweight satellite tags compatible with Argos systems were employed, minimizing interference with the dolphin’s movement despite its limited surfacing time (5-30 seconds).
- Insight into Dolphin Ecology: Helps fill knowledge gaps regarding habitat needs and seasonal migration, especially in disturbed river ecosystems.
Ganges River Dolphin – India's National Aquatic Animal:
- Endemic to India with around 90% of the population in India.
- Known for being nearly blind and using echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Plays a crucial role as an apex predator and indicator species for river ecosystem health.
Project Dolphin:
- Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2020, modeled after Project Tiger.
- Focuses on conservation of riverine and marine dolphins.
- A 10-year initiative funded by MoEFCC to safeguard dolphin populations and address ecosystem challenges.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered.
- Protection: Included in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and CITES Appendix I.
- Major Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, bycatch, and water abstraction, compounded by damming and sand mining.
Broader Impact:
- The tagging initiative contributes to evidence-based conservation strategies for Ganges River Dolphins.
- Will aid in the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the species.
- Expands the understanding of critical habitats within river ecosystems, benefiting both biodiversity and the communities dependent on these resources.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
One Nation, One Election
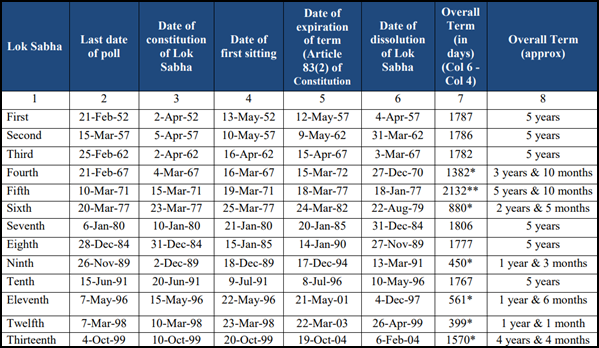
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The government has recently taken steps to implement "One Nation, One Election" by presenting two Constitution Amendment Bills in the Lok Sabha: the One Nation One Election – The Constitution 129th Amendment Bill 2024 and the Union Territories Laws Amendment Bill 2024.
Introduction to the Concept:
- Objective: Proposes synchronizing elections for Lok Sabha (national) and State Legislative Assemblies to be held on the same day.
- Purpose: Aims to reduce costs, minimize logistical challenges, and address governance disruptions caused by frequent elections.
- 2024 Report: The High-Level Committee Report on Simultaneous Elections, released in December 2024, outlines a roadmap for implementing this reform.
Historical Background:
- Previous Practice: From 1951 to 1967, Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections were conducted together.
- Disruptions: The practice was interrupted due to premature dissolutions and emergencies, leading to staggered elections across India.
High-Level Committee on Simultaneous Elections:
- Committee Formation: Headed by former President Ram Nath Kovind, formed on 2nd September 2023.
- Public Response: Over 21,500 responses, with 80% in favor.
- Political Party Responses: 32 political parties supported the idea, while 15 raised concerns about regional party marginalization.
- Expert Consultations: Majority of experts supported the reform, emphasizing resource optimization and reduced disruptions.
Committee Recommendations:
- Constitutional Amendments: Proposals to amend Articles 82A and 324A to enable simultaneous elections.
- Two-Phase Implementation:
- Phase 1: Synchronize elections for Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Include Municipalities and Panchayats within 100 days.
- Single Electoral Roll: Creation of a unified electoral roll and EPIC for all levels of elections, reducing duplication and errors.
Rationale for Simultaneous Elections:
- Governance Consistency: Reduces focus on election preparation, allowing more attention to developmental work.
- Prevents Policy Paralysis: Mitigates disruptions caused by the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) during frequent elections.
- Resource Optimization: Reduces the need for personnel and resources for election duties, allowing better allocation to governance tasks.
- Preserves Regional Party Relevance: Local issues remain prioritized, ensuring regional parties' concerns are heard.
- Equitable Political Opportunities: Encourages diversification and inclusivity within political parties.
- Financial Benefits: Reduces the financial burden of conducting multiple elections, enhancing economic efficiency.
Conclusion:
- The concept of "One Nation, One Election" is a significant reform aimed at streamlining India's electoral processes. With broad public and political support, it promises improved governance, cost savings, and better resource management in the future.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
Vijay Diwas 2024

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 16, 2024, India commemorated Vijay Diwas, marking the 53rd anniversary of its victory in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. This day honors the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers and the Mukti Bahini, whose collective efforts led to the creation of Bangladesh as an independent nation. On this occasion, leaders across India, paid heartfelt tributes to the fallen heroes who contributed to the victory, and to the enduring India-Bangladesh friendship.
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War culminated in the surrender of over 90,000 Pakistani soldiers, and India’s victory is celebrated as a defining moment in South Asian history.
The War’s Historical Context:
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War was a pivotal conflict between East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Pakistan (now Pakistan), leading to Bangladesh’s independence. It was a direct result of decades of social, political, and economic discrimination faced by East Pakistan, despite its larger population and contribution to Pakistan’s economy. Major events leading to the war included:
- Cultural and linguistic marginalization, with East Pakistan's Bengali language and identity being suppressed by the West.
- The 1970 elections that saw the Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, win a decisive victory in East Pakistan, but their demand for greater autonomy was rejected by West Pakistan.
- The violent crackdown by the Pakistani military in Operation Searchlight in March 1971, leading to widespread atrocities and a mass exodus of refugees into India.
India’s Role in the War:
India’s involvement in the conflict was initially cautious, but the refugee crisis—with over 10 million people fleeing to India—forced India to take action. India provided humanitarian aid and supported the Mukti Bahini, a guerrilla force of Bangladeshi fighters. On December 3, 1971, Pakistan’s preemptive airstrike on Indian military bases led to India's retaliation and full-scale military involvement, including air and naval operations.
India’s military, with assistance from the Mukti Bahini, launched a decisive campaign, ultimately leading to Pakistan’s surrender on December 16, 1971, and the creation of Bangladesh.
Vijay Diwas Observances:
- The 53rd Vijay Diwas celebrations at Fort William, Kolkata, saw a Bangladeshi delegation—including Mukti Joddhas (freedom fighters)—reflect on their memories of the war, highlighting India's crucial role in the liberation of Bangladesh.
- The event also featured a wreath-laying ceremony, military tattoo, and a salute to the shared sacrifice and friendship between India and Bangladesh.
The 1971 Surrender Painting and New Symbolism:
In an interesting development, the iconic 1971 surrender painting, depicting the surrender of Pakistani forces in Dhaka, was moved from the Army Chief’s lounge to the Manekshaw Centre. The painting was replaced by Karam Kshetra–Field of Deeds, a new artwork symbolizing India’s strategic and cultural heritage. This new piece incorporates elements like Lord Krishna’s chariot, Chanakya, and modern military assets, reflecting India’s military prowess and heritage.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
India Maritime Heritage Conclave 2024

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The 1st India Maritime Heritage Conclave (IMHC 2024), a landmark event organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) was recently held.
Key Highlights:
Event Overview:
- Organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), held on December 11-12, 2024.
- Theme: "Towards Understanding India's Position in Global Maritime History."
- Celebrated India’s maritime legacy and future vision as a maritime powerhouse.
India’s Maritime Heritage:
- Deeply rooted in ancient traditions; references in Rig Veda, mythology, literature, and archaeology.
- Modern India boasts a 7,500 km coastline, 13 major ports, 200 non-major ports, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Ports handle 1,200 million tonnes of cargo annually, vital for economic growth.
Key Features of IMHC 2024:
- International Participation: Dignitaries from 11 countries, including Greece, Italy, UK.
- Exhibition: Showcased ancient shipbuilding techniques, navigation systems, historical trade routes.
- Cultural Program: Celebrated coastal traditions with performances and festivities.
- Key Focus: Sustainable maritime innovation, skill development, youth engagement, and cultural preservation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC):
- Location: Lothal, Gujarat – an ancient Harappan site (2600 BCE).
- Significance: Home to the world’s oldest dry-dock (2400 BCE).
- Future Vision: NMHC to showcase maritime history with 14 galleries, open aquatic gallery, lighthouses, and a research institute.
Modern Maritime Significance:
- India’s Global Maritime Ranking: 16th largest globally, 3rd largest in ship recycling.
- Trade Backbone: 95% of India's trade by volume, 70% by value handled by maritime sector.
- Port Performance: India ranks 22nd in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2023).
Future Maritime Vision:
- Sustainable Blue Economy: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, green shipping, and maritime tourism.
- Skill Development: Training programs to empower local communities and boost maritime workforce.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading ports and shipping infrastructure under the Sagar Mala Program.
- Policy Framework: Integrated policies for maritime heritage preservation and economic development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Focus on increasing maritime capacity and sustainability.
- SAGAR: Security and Growth for All in the Region initiative.
- Ship Repair & Recycling Mission: Promote India as a global leader in ship recycling.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: Development of eco-friendly maritime infrastructure.
'Jalvahak' Scheme for Inland Waterways Promotion

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
Govt Unveils ‘Jalvahak’ To Boost Inland Waterways, Cargo Movement Incentivised on NW1, NW2 & NW16
Key Highlights:
- Launch of 'Jalvahak' Scheme:
- Launched by: Union Minister for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, on December 15, 2024.
- Objective: The scheme aims to promote the use of inland waterways for long-haul cargo transportation, reduce logistics costs, and alleviate congestion in road and rail networks.
- Targeted Waterways:
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- NW 1: River Ganga
- NW 2: River Brahmaputra
- NW 16: River Barak
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- Incentives:
- The scheme offers up to 35% reimbursement on operating expenses for cargo transported over 300 km via these waterways, particularly using the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Encouraging Private Operators: The scheme also incentivizes the hiring of vessels owned by private operators to promote competition and efficiency.
- Scheduled Cargo Service:
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Kolkata - Patna - Varanasi - Patna - Kolkata (for NW 1)
- Kolkata - Pandu (Guwahati) (for NW 2 via IBPR)
- Transit Times: Predefined and fixed for efficiency:
- Kolkata to Patna: 7 days
- Patna to Varanasi: 5 days
- Kolkata to Varanasi: 14 days
- Kolkata to Pandu: 18 days
- Pandu to Kolkata: 15 days
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Cargo Shift Target: The initiative aims to shift 800 million tonne-kilometres of cargo by 2027.
- Growth Projections:
- 200 million tonnes of cargo by 2030.
- 500 million tonnes by 2047, supporting the Blue Economy and Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- The move to waterways aims to reduce the pressure on India's roads and rail systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system.
- Strategic Goals:
- Modal Shift: The scheme seeks to achieve a shift of 800 million tonne-kilometres by 2027 with an investment of ?95.4 crores.
- Sustainability: Inland waterways are considered an environmentally friendly, efficient, and low-cost transportation mode, with a focus on sustainability.
- Logistics Optimization: This initiative is expected to help optimize supply chains for major shipping companies, freight forwarders, and trade bodies involved in bulk and containerized cargo.
- Implementation Agencies:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): The main body responsible for the development and regulation of inland waterways.
- Inland & Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL): A subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India, responsible for the operation of vessels.
- Broader Impact:
- Economic Growth: The scheme is expected to foster economic growth by improving logistics efficiency.
- Decongestion: The initiative aims to decongest the road and rail transport systems, facilitating smoother movement of cargo.
- Regional Connectivity: Enhances connectivity, particularly in eastern India, benefiting areas along the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak rivers.
- About the National Waterways:
- India has 14,500 km of navigable inland waterways, which include rivers, canals, and backwaters. These waterways are significantly under-utilized compared to other countries.
- The National Waterways Act, 2016 declared 111 waterways (including both existing and newly identified ones) for navigation.
- The Jalvahak scheme is part of India's broader strategy to unlock the potential of its inland waterways, offering an efficient, economical, and environmentally sustainable alternative for cargo transport.
Rajmarg Saathi - Upgraded Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPV) by NHAI
- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
With an aim to enhance road safety and strengthen highway patrolling, NHAI plans to implement the upgraded and forward-looking Incident Management Services. The guidelines on the subject include updated specifications for new Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs) named ‘Rajmarg Saathi’ and outlines design, functions, technology, components and manpower specifications for the RPVs.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Rajmarg Saathi:
- Initiative by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Objective: Enhance highway safety, emergency response, and road maintenance efficiency across India.
- Launched in: December 2024.
What is Rajmarg Saathi?
- Definition: An upgraded version of Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs), designed for effective highway patrolling and incident management.
- Main Aim: Improve highway safety and ensure smooth traffic flow through advanced technology and quick emergency responses.
Key Features:
- Advanced Design:
- Closed Cabinets: For organized storage and easy access to emergency tools and inventory, replacing earlier models with open storage space.
- AI-Powered Technology:
- Dashboard Cameras: Equipped with AI-enabled cameras to capture and analyze road conditions like cracks, potholes, and other distresses.
- Road Monitoring: The system also monitors vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, and other infrastructure elements.
- Integration with NHAI One: Data collected by AI systems is integrated into NHAI’s centralized application for efficient road maintenance.
- Emergency Preparedness: The RPVs are fully equipped with modern communication and safety tools, designed to minimize traffic disruptions during emergencies.
Data Collection and Maintenance:
- Weekly Analytics: The system will collect and analyze road condition data weekly to streamline maintenance activities and monitor highway safety.
Vehicle Usage and Replacement:
- Replacement Guidelines: RPVs will be replaced after 3 years of operation or 3,00,000 km to ensure they remain functional and service-ready.
Visibility and Branding:
- External Branding: RPVs are designed to be highly visible with enhanced branding for easy recognition as highway patrol vehicles.
- Uniform for Personnel: The patrolling personnel will wear updated uniforms, including bright blue colors and reflective jackets with authority logos for better identification.
Role in Incident Management:
- RPVs will play a crucial role in managing traffic incidents, ensuring smooth traffic flow, and enhancing road safety by addressing emergencies quickly.
Commitment to Road Safety:
- NHAI remains committed to improving road safety standards and ensuring a smooth, hassle-free travel experience for all users across the national highway network.
About NHAI:
- Establishment: NHAI was established under the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988, and became operational in 1995.
- Responsibilities: It is responsible for developing, maintaining, and managing national highways in India.
- Objectives:
- Promote transparency in awarding contracts.
- Maintain high standards of project implementation.
- Ensure comfort and convenience for users of the national highway system.
India's Road Network:
- Size: India has the 2nd-largest road network in the world, spanning approximately 63.32 lakh km, which includes national highways, expressways, state highways, and rural roads.
India-Australia CCEA

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The 3-day stocktake meeting took place in New Delhi, marking a significant step in strengthening the India-Australia trade and strategic partnership.
Key Highlights:
- Key Discussion Areas:
- Trade in goods and services.
- Mobility, agri-tech cooperation, and market access.
- Focus on ensuring the CECA delivers balanced benefits for both nations.
- Food security concerns and market access modalities aligned with India’s goals.
- Background on Negotiations:
- The discussions in New Delhi were a continuation of the 10th round of negotiations held in Sydney (August 2024).
- Both sides aimed to outline a path forward for the early conclusion of the CECA.
- Importance of CECA:
- CECA is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) aimed at eliminating tariffs and liberalizing services sectors to enhance business opportunities and cooperation.
- It addresses five key areas: Goods, Services, Digital trade, Government procurement & **Rules of Origin/Product Specific Rules
- New areas under discussion include: Competition policy, MSMEs, Gender, Innovation, Agri-tech, Critical minerals & Sports
- Historical Context:
- CECA negotiations began in May 2011, were suspended in 2016, and resumed in September 2021.
- The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) was signed in 2022, serving as a foundational agreement and a precursor to CECA.
- Trade Statistics (2023-24):
- India's imports from Australia: $16.2 billion.
- India's exports to Australia: $8 billion.
- Trade has grown significantly, with India being Australia’s 5th-largest trading partner.
- Regional Cooperation Initiatives:
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
- Trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) with Japan.
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- India's CECA with Other Countries:
- India has similar CECA agreements with several nations, including: Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand & New Zealand
- Future Prospects:
- The stocktake discussions have paved the way for further cooperation in areas such as agricultural innovation, market access, and supply chain resilience.
- Both nations are optimistic about the early conclusion of the CECA and the broader economic partnership.
This recent stocktake visit represents a significant step in the ongoing efforts to solidify trade ties and deepen economic cooperation between India and Australia under the framework of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement.
100-Day Intensified Nationwide TB Campaign

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
- Union Health Minister Shri JP Nadda launched a 100-day intensified TB campaign in Panchkula, Haryana, aimed at reducing TB incidence and mortality. The campaign will focus on 347 high-risk districts across India.
Key Highlights:
- Campaign Goals:
- Find and treat missing TB cases, especially in high-risk groups.
- Significantly reduce TB-related deaths.
- Focus Areas:
- The campaign is part of India’s larger goal to eliminate TB before the 2030 SDG deadline.
- Strategies include early detection and rapid treatment of TB patients.
- Historical Context:
- TB was once seen as a "slow death" and patients were isolated.
- In 2018, the Prime Minister set the vision to end TB before 2030.
- Recent Government Initiatives:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs network of 1.7 lakh centers helps in early TB detection.
- Increased diagnostic infrastructure: Laboratories increased from 120 in 2014 to 8,293 today.
- Introduction of new drug regimens: Shorter and more effective treatments have increased the treatment success rate to 87%.
- Ni-kshay Support: Rs 3,338 crore transferred to 1.17 crore TB patients via direct benefit transfer.
- Key Achievements:
- TB decline rate in India has increased from 8.3% (2015) to 17.7% today, surpassing the global average.
- TB-related deaths have dropped by 21.4% over the past decade.
- Private Sector Involvement:
- Mandatory notification of TB patients by private practitioners has led to an 8-fold increase in TB case notifications.
- 4Ts Approach for TB Elimination: Test, Track, Treat, and Technology (use of advanced tools for diagnosis and treatment).
- New Initiatives:
- Ni-kshay Vahaan: Mobile vans to detect and treat TB patients in remote areas.
- Launch of national guidelines for a new drug-resistant TB regimen (BPaLM), which is a 4-drug combination therapy for multi-drug-resistant TB.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana:
- Increase in nutritional support: Monthly support raised from Rs 500 to Rs 1000 per TB patient.
- The initiative also includes energy boosters for enhanced patient care.
- Mobile Diagnostics:
- Deployment of AI-enabled portable X-ray units and molecular tests to bring diagnostics closer to people, especially in remote areas.
- Monitoring and Data: Intensified data tracking via the Ni-kshay portal to provide timely updates to TB patients.
- Background of the Campaign:
- Part of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- The 347 districts were selected based on indicators like death rates, presumptive TB examination rates, and incidence rates.
- Campaign Materials:
- Unveiling of Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) resources in regional languages.
- Honoring TB Champions and Ni-kshay Mitras during the event.
- Government’s Strategic Framework:
- India’s National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign and Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- Tuberculosis (TB) Overview:
- TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and primarily affects the lungs, spreading through the air.
- Mortality rate has decreased from 28 per lakh (2015) to 23 per lakh (2022).
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
Indian Military Heritage Festival 2024

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan inaugurated the 2nd edition of the Indian Military Heritage Festival (IMHF) on November 8, 2024, in New Delhi.
- The two-day festival engages global and Indian experts, corporations, academicians, and non-profits focusing on India’s national security, foreign policy, military history, and military heritage.
Launch of Project Shaurya Gatha:
- Project ‘Shaurya Gatha’ was launched to conserve and promote India’s military heritage.
- The initiative, spearheaded by the Department of Military Affairs and USI of India, focuses on education and tourism to highlight India’s military history and valor.
- Publications Released:
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- "Because of this: A History of the Indo-Pak Air War December 1971" by Air Marshal Vikram Singh (Retd).
- "Valour and Honour", a joint publication by the Indian Army and USI of India.
- "War-wounded, Disabled Soldiers, and Cadets", a joint publication by USI and the War Wounded Federation.
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- Festival's Significance:
- The festival addresses the gap in public awareness regarding India’s military heritage and security concerns.
- It aims to enhance understanding of India’s military traditions, security issues, and the country’s efforts toward self-reliance in military capabilities under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held with the aim of promoting lighthouse tourism and celebrating India’s maritime legacy.
Strategic Importance of the Lighthouse Projects
- The Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW) has invested significantly in developing lighthouses as tourist hubs. The festival marks a concerted effort to integrate tourism with the preservation of these iconic structures.
- Lighthouse tourism has witnessed a remarkable increase of over 400% in visitor numbers since 2014, as part of India's broader vision to promote the blue economy.
-
- From just 4 lakh visitors in 2014, the footfall surged to 16 lakh in 2023-24, with over 9 lakh tourists already in the first half of FY 2024-25.
-
Key Projects and Announcements at the Festival
- New Lighthouses: The announcement of the two new lighthouses at Chaumuck and Dhamra along Odisha’s coastline is significant for enhancing coastal infrastructure and promoting maritime tourism in the state.
- Kalwan Reef Lighthouse: Located in Jamnagar, Gujarat, this lighthouse is part of a broader effort to enhance maritime navigation and heritage conservation along India’s western coastline.
- Development of Coastal Communities: Highlighted the importance of empowering coastal communities, particularly those living around lighthouses, to preserve and promote these structures as national cultural icons. These communities are expected to play a crucial role in lighthouse preservation, as well as in tourism and local economic development.
- Paradip Port Initiatives: Additionally, major infrastructure projects at Paradip Port, such as a stacker-cum-reclaimer and a flyover bridge, were inaugurated to further bolster the port’s capabilities and enhance its role in maritime logistics. The Sagarmala Programme also continues to transform Paradip Port into a mega port with a projected handling capacity of 500 MTPA by 2047.
Economic and Employment Impact
The development of 75 iconic lighthouses across 9 coastal states and one Union Territory is not only aimed at tourism development but also focuses on job creation. As of 2024:
- More than 150 direct jobs and 500 indirect jobs have been created in sectors such as hospitality, transportation, and local crafts, driven by the increasing footfall at these tourist destinations.
- The creation of modern amenities at these lighthouses, such as museums, amphitheaters, and children’s parks, has helped in transforming lighthouses into multifaceted tourism hubs that attract both domestic and international tourists.
Collaborative Efforts for Preservation and Promotion
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encouraging collaboration between the government, local communities, and private stakeholders to develop and maintain lighthouses as sustainable tourist destinations.
- National Framework: A central association will be created to manage coastal societies surrounding lighthouses, enabling local communities to actively participate in their preservation, protection, and promotion.
- Cultural Integration: The event also underscored the need for integrating cultural heritage with tourism development, using the lighthouses as platforms to showcase local art, cuisine, and history.
eShram-One Stop Solution

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
- The ‘eShram-One Stop Solution’ will be launched on 21 October 2024 by the Union Minister of Labour & Employment and Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Objective: To provide easy access to various social security and welfare schemes for unorganized workers in India.
Key Features
- Mediator Platform: The eShram-One Stop Solution will act as an intermediary to facilitate the integration of multiple government schemes for unorganized workers, ensuring efficient access to services and support.
- Information Integration: It will integrate data on beneficiaries across various social security and welfare programs meant for unorganized workers, providing a single point of access.
- Target Group: Aimed at unorganized workers, including daily wage earners, migrants, and others who do not have regular formal employment.
Benefits
- Awareness & Accessibility: The platform will make unorganized workers aware of various government schemes tailored to their needs, helping them access benefits more easily.
- Effective Scheme Implementation: The eShram-One Stop Solution will aid in the identification and implementation of welfare schemes for faster saturation and coverage.
Integration with Existing Schemes
- 12 Integrated Schemes: Currently, 12 social security schemes from different ministries/departments have already been mapped with eShram.
eShram’s Progress So Far
- Launch: eShram was launched on 26 August 2021.
- Achievements: Over 30 crore unorganized workers have been enrolled, highlighting the widespread impact and popularity of the initiative among the target population.
Naseem-Al-Bahr 2024

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise Naseem-Al-Bahr was held in Goa from October 2024.
Naseem-Al-Bahr Exercise Overview
- Indian and Omani Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand (warship) and Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft.
- Royal Navy of Oman: Vessel Al Seeb.
- Initiation: Launched in 1993, marking a long-standing strategic partnership between India and Oman.
- Structure: The exercise is conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional Interactions: Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), planning conferences.
- Social & Sports Engagements: Informal activities to foster mutual understanding.
- Sea Phase:
- Naval Operations:
- Gun firings at surface inflatable targets.
- Close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopter Operations: INS Trikand’s helicopter performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- Aircraft Support: Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data to enhance operational coordination.
- Naval Operations:
- Harbour Phase:
Key Highlights of the 2024 Exercise
- Interoperability: The exercise focused on improving operational coordination and enhancing mutual understanding of naval practices.
- Cohesion: The Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb to further strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthening Ties: Naseem-Al-Bahr reaffirms the strong strategic relationship between India and Oman.
- Regional Collaboration: This exercise exemplifies India's growing collaboration with like-minded nations in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Broader Defence Relations:
- Oman is the first GCC country to conduct such bilateral naval exercises with India.
- Both countries also engage in other defence exercises:
- Army: Al Najah.
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge.
Trade Relations Between India and Oman (2022):
- Oil: India is the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil exports, following China.
- Non-oil Exports: India is Oman's fourth-largest market for non-oil exports, after UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia.
- Imports: India is the second-largest source of Oman's imports, following the UAE.
- Ongoing Trade Agreement: Both nations are currently negotiating a trade agreement to further boost bilateral economic cooperation.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
Karmayogi Saptah – National Learning Week

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ‘Karmayogi Saptah’ - National Learning Week on 19th October at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Context:
- The National Learning Week is a key event in the ongoing Mission Karmayogi initiative, aimed at building a civil service rooted in Indian ethos with a global outlook.
- Objective:
- To promote capacity building for civil servants through competency-linked learning.
- To align civil servants with national goals and foster a "One Government" approach.
- About National Learning Week (NLW):
- Largest learning event for civil servants, focused on individual and organizational growth.
- Encourages lifelong learning and continuous professional development.
- Provides fresh impetus to the Mission Karmayogi initiative, launched in September 2020, aimed at a future-ready, citizen-centric civil service.
- Learning Targets for Karmayogis:
- Each civil servant (Karmayogi) must complete at least 4 hours of competency-linked learning during the week.
- Learning opportunities include:
- Role-based modules on iGOT (Integrated Government Online Training platform).
- Webinars, public lectures, and policy masterclasses by prominent experts.
- Focus on improving skills for citizen-centric service delivery.
- Workshops & Seminars:
- Ministries, departments, and organizations organized domain-specific workshops and seminars.
- The goal is to enhance skills and knowledge, fostering better public service delivery.
- Outcomes:
- Strengthened alignment of civil servants with national priorities and goals.
- Enhanced individual competencies to better address citizen needs.
- A stronger commitment to continuous learning within the civil service.
Scam se Bacho Campaign

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Government and Meta join forces for "Scam se Bacho" Campaign to tackle rising online scams.
Key Details
- The "Scam Se Bacho" initiative aims to create a safer, more secure digital India by empowering users to protect themselves against growing cyber threats, contributing to the resilience of India’s digital progress.
- Objective: To combat rising online scams and cyber frauds by promoting digital safety and vigilance across India.
- Partners:
- Meta (formerly Facebook)
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
Purpose and Vision
- Goal: Empower Indian citizens with the knowledge and tools to protect themselves from online scams and cyber threats.
- Strategic Focus:
- Foster a culture of digital safety and vigilance.
- Align with the Digital India initiative, which has seen extraordinary growth in digital services, including 900 million internet users and leadership in UPI transactions.
- The campaign aims to build a national movement to safeguard citizens, emphasizing the importance of cyber literacy and digital security.
Key Points
- Growing Cybersecurity Threats:
- India has seen a surge in cyber frauds, with 1.1 million cases reported in 2023.
- The government is committed to addressing these threats through stronger cybersecurity measures and enhancing digital literacy.
- Meta’s Role:
- Meta’s global expertise in online safety will be leveraged to equip citizens with the knowledge to prevent cyber scams.
- Meta’s collaboration with the government aims to extend the reach of the campaign nationwide.
Features of the "Scam Se Bacho" Campaign
- Nationwide Reach:
- The initiative targets India’s 900 million internet users, making it a comprehensive national effort.
- Government Support:
- Backed by key ministries to ensure alignment with national digital and cybersecurity goals under Digital India.
- Whole-of-government approach to raise awareness on cyber safety.
- Educational Focus:
- The campaign emphasizes educating citizens on how to recognize and prevent online scams and threats.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
The Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, hosted a two-day Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) knowledge sharing workshop in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Event Overview:
- Two-day workshop hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education.
- Focus areas: School-to-Work Transition and Strengthening the Assessment System.
- Key Objectives:
- To enhance school-to-work transitions.
- To discuss strengthening educational assessment systems.
- Align education with future workforce needs as per the National Education Policy 2020.
Day 1: School-to-Work Transition
Panel Discussions:
- Policy Frameworks:
- Role of National Education Policy 2020, National Curriculum Framework (NCF), and National Credit Framework (NCrF) in school-to-work transitions.
- Focus on integrating skill education into school curricula, fostering multidisciplinary learning, and continuous evaluation to meet industry standards.
- Emphasis on internships, apprenticeships, and flexible learning pathways.
- Curriculum Integration:
- Need for integrated efforts across departments and aligning curriculum with industry demands.
- Focus on strengthening 21st-century skills in CBSE schools.
- Career Counselling and Psychometric Analysis:
- Focus on using psychometric assessments for career counselling and preparing students for future work environments.
- Work-Based Learning:
- Discussed partnerships with industry for work-based learning.
- Effective collaborations between schools and industry for internships, placements, and best practices.
Day 2: Strengthening Assessment System
- Psychometric Analysis & Career Counselling:
- Smt. Idzes Angmo Kundan (Principal Secretary, Maharashtra) presented the 3 P approach to career choices: Personal Interest, Parental Approach, and Possible Opportunities.
- Enhancing Student Outcomes:
- Discussed improving student outcomes by strengthening assessment systems.
- Shared innovations in educational assessments.
- Highlighted innovative assessment practices for future education.
- VSK Implementation (Chhattisgarh):
- Discussed VSK modes, data analysis, and strategies for integrating assessment outcomes with learning objectives.
- Strengthening Assessment Cells:
- Advocated for the establishment of assessment cells.
- Discussed best practices and challenges in strengthening assessment cells across states.
SAMARTH Scheme

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
Samarth is a demand-driven and placement-oriented umbrella skilling program of the Ministry of Textiles. Samarth Scheme has been extended for two years (FY 2024-25 and 2025-26) with a budget of Rs. 495 Crore to train 3 lakh persons in textile-related skills.
Key Details:
- Scheme Name: Samarth (Scheme for Capacity Building in Textile Sector)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Extension Period: FY 2024-25 and 2025-26
- Budget: ?495 Crores
- Target: Train 3 lakh individuals in textile-related skills
Objectives
- Skilling Programs: Provide demand-driven, placement-oriented training.
- Industry Support: Encourage job creation in organized textile and related sectors.
- Skill Enhancement: Focus on upskilling and reskilling in traditional sectors (handloom, handicraft, silk, jute).
Implementation
- Implementing Partners:
- Textile Industry/Industry Associations
- Central/State government agencies
- Sectoral Organizations (e.g., DC/Handloom, Central Silk Board)
- Current Achievements:
- Total Trained: 3.27 lakh candidates
- Employment Rate: 2.6 lakh (79.5%) have secured jobs
- Women Empowerment: 2.89 lakh (88.3%) women trained
Scheme Features
- Coverage: Entire textile value chain, excluding spinning and weaving.
- Training Focus:
- Entry-level skilling
- Upskilling/reskilling existing workers in apparel and garmenting
- Beneficiaries: Handicraft artisans and job seekers in the textile sector.
Background
- Cabinet Approval: The scheme is a continuation of the Integrated Skill Development Scheme from the 12th Five Year Plan.
- Implementation Agency: Office of the Development Commissioner (Handicrafts).
Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi is organising its first-ever international conference - Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024.
Key Details:
- Theme: "Advancements in Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda"
- Conference Goals
- Position Ayurveda as a key pillar of global health and wellness.
- Facilitate dynamic exchanges among scholars, industry leaders, and practitioners.
- Explore the integration of traditional Ayurvedic wisdom with modern scientific advancements.
- Agenda Highlights
- Topics Covered:
- Ayurveda and ethnomedicine
- Quality control and standardization
- Diagnosis and drug delivery
- Evidence-based understanding and globalization
- Topics Covered:
- Institute Background
- All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA): Apex institute for Ayurveda with NAAC A++, NABH, and ISO accreditations.
- Facilities: 200-bed referral hospital, 44 specialty departments.
- Global Collaborations: Partnerships with institutions in 17 countries, including London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and Western Sydney University.
- Innovations: Focus on research, drug development, and scientific validation of Ayurvedic practices.
- Participant Benefits
- Networking Opportunities: Engage with experts in Ayurveda and holistic healthcare.
- Learning Experiences: Attend plenary sessions, round table discussions, and exhibitions on medicinal plants and startups in Ayurveda.
- Recognition: Awards for contributions to Ayurveda.
- Research and Innovation Focus: Discussions on technology integration, including AI and bioinformatics.
DigiLocker Partners with UMANG
- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) has announced the integration of the UMANG app with DigiLocker- India’s Digital Wallet. This collaboration aims to provide citizens with seamless access to a wide range of government services bringing greater convenience and allowing users to manage multiple services through a single platform.
UMANG app
- The UMANG app is accessible to all Android users with an expansion to iOS in the pipeline.
- The UMANG mobile app is an all-in-one single, unified, secure, multi-channel, multi-lingual, multi-service mobile app.
- It provides access to high-impact services of various organizations of the Union and States.
Simplified Citizen-Government interaction
This integration makes it easier for citizens to interact with the Government in an efficient, digital-first manner. DigiLocker has always been a pioneer in simplifying access to personal and official documents, and after integration with UMANG, it has expanded the range of services you can access on the go.
About DigiLocker
DigiLocker is a flagship initiative under the Digital India program aimed at providing secure cloud-based storage of essential documents. By integrating with e-governance services such as UMANG, DigiLocker further is committed to further enhance accessibility and ease of living.
World Food Day 2024

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
World Food Day, observed annually on October 16, has its roots in the establishment of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) by the United Nations in 1945.
Significance: World Food Day emphasizes the critical need to address global hunger and promote resilient food systems capable of overcoming challenges like climate change and economic disparities.
Introduction
- Food is vital for life, health, and well-being.
- Despite sufficient global food production, millions lack access to nutritious food.
- World Food Day serves as a reminder of ongoing challenges in achieving food security.
History and Theme
- Origins: Established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 1945, officially recognized in 1979.
- First Celebration: Took place in 1981 with the theme "Food Comes First."
- 2024 Theme: "Right to Food for a Better Life and a Better Future," highlighting that food security is essential for dignity and health. It emphasizes the need for sustainable practices and equitable distribution.
India’s Commitment to Food Security
- India has made significant strides in combating hunger through various programs aimed at malnutrition and poverty alleviation.
- Key initiatives include:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population, benefiting about 81 crore individuals.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): Offers free food grains to approximately 81.35 crore beneficiaries, extending support during the COVID-19 pandemic for an additional five years.
- PM POSHAN Scheme: Aims to improve children's nutritional status in government schools with a budget of ?12,467.39 crores for 2024-25.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY): Focuses on the most vulnerable populations, supporting over 8.92 crore individuals and empowering women.
- Rice Fortification: Distribution of fortified rice through the Public Distribution System has improved nutritional intake for millions.
- Price Stability Initiatives: The government manages price volatility of essential commodities using the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) and ensures affordability through strategic product launches.
Global Recognition of Indian Cuisine
- The Indian Thali has been recognized for its nutritional and sustainable qualities by the WWF Living Planet Report.
- Its plant-based composition contributes to lower resource use and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- If globally adopted, India’s dietary patterns could significantly lessen the environmental burden.
Significance
- India’s comprehensive initiatives reflect its dedication to food security and improving citizens' quality of life.
- By enhancing agricultural productivity and supporting vulnerable populations, India makes strides towards eradicating hunger.
- On World Food Day, these efforts underline India's commitment to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2: Zero Hunger, while serving as a model for global food security initiatives.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Prime Minister commended the completion of three years of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, calling it a transformative initiative for India’s infrastructure development.
- Key Benefits: The plan enhances multimodal connectivity and improves efficiency across various sectors, contributing to logistics, job creation, and innovation.
Overview of PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Launch Date: October 2021
- Objective: A transformative initiative worth ?100 lakh crore aimed at revolutionizing India’s infrastructure over five years.
- Development Tool: Created as a Digital Master Planning tool by the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
- GIS Platform: Utilizes a dynamic Geographic Information System to integrate action plans from various ministries into a comprehensive database.
- Goals: Accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by addressing inter-ministerial challenges.
Key Features
- Digital Integration: A digital platform coordinating the efforts of 16 ministries for seamless infrastructure planning.
- Multi-Sector Collaboration: Incorporates initiatives from major programs like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
- Economic Zones Development: Focuses on key areas such as textile clusters and pharmaceutical hubs to boost productivity.
- Technology Utilization: Employs advanced spatial planning tools and ISRO satellite imagery for data-driven project management.
Core Sectors Driving the Plan
- The National Master Plan is centered around seven primary sectors that enhance economic growth and connectivity, supported by sectors like energy transmission and social infrastructure.
Six Pillars of PM GatiShakti
- Comprehensiveness: Integrates various initiatives through a centralized portal, ensuring efficient planning.
- Prioritisation: Allows ministries to prioritize projects based on national importance and resource allocation.
- Optimisation: Identifies infrastructure gaps and selects the most efficient transportation routes.
- Synchronisation: Ensures coordinated efforts across ministries to avoid delays.
- Analytical Capabilities: Offers extensive data layers for improved spatial planning and decision-making.
- Dynamic Monitoring: Uses satellite imagery for real-time project tracking and adjustments.
Achievements of PM GatiShakti
- District-Level Expansion: Extended to 27 aspirational districts, with plans for 750 in the near future.
- Technological Integration: Enhanced real-time infrastructure planning using geospatial tools.
- Global Outreach: The GatiShakti tool showcased to 30 countries and highlighted at international conferences.
- Social Sector Benefits: Identified areas for new healthcare facilities and improved planning in various districts.
- Rural and Urban Development: Implemented projects for irrigation and city logistics in multiple states.
- Employment Initiatives: Utilized for setting up training institutes near industrial clusters.
Announcement of AI Centres of Excellence

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, announced the establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence (CoE) focused on Healthcare, Agriculture, and Sustainable Cities in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Establishment of Three AI-CoEs:
- Focus Areas:
- Healthcare: Led by AIIMS and IIT Delhi.
- Agriculture: Led by IIT Ropar, Punjab.
- Sustainable Cities: Led by IIT Kanpur.
- Collaboration: CoEs will work with industry partners and start-ups.
- Focus Areas:
- Financial Commitment:
- Total Approved Budget: ?990 crore for FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Purpose: Support the establishment and operation of the CoEs.
- Vision and Impact:
- Pradhan emphasized the CoEs' role as solution providers for global public good.
- Expected to create a new generation of job and wealth creators.
- Aims to strengthen India's credentials in the global AI landscape.
- Leadership and Implementation:
- Apex Committee: Co-chaired by Shri Sridhar Vembu (Zoho CEO).
- Committee includes industry leaders and academic heads.
- Shri K. Sanjay Murthy highlighted the importance of interdisciplinary research and collaboration.
- Future Prospects:
- Dr. Vembu noted the CoEs will enhance the health of villages and cities, nurture talent, and generate opportunities.
- The initiative aligns with India's vision of "Viksit Bharat" (Developed India).
- Presentation and Film:
- Insights into the development of AI-CoEs presented by Smt. Saumya Gupta.
- A short film titled "Make AI in India and Make AI work for India" was showcased.
The establishment of these Centres of Excellence in AI signifies a major step toward fostering an effective AI ecosystem in India, aimed at developing scalable solutions and enhancing human resources in critical sectors.
International Abhidhamma Divas

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, International Abhidhamma Divas was celebrated at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, with PM Narendra Modi.
Key Details:
- India's Spiritual Legacy: Birthplace of Buddhism; site of Gautam Buddha's enlightenment.
- Sacred Sites: Veneration of locations like Bodh Gaya, symbolizing Buddha's journey and teachings.
- Core Teachings: Abhidhamma as a key philosophical component emphasizing mental discipline and self-awareness.
International Abhidhamma Divas
- Global Observation: Celebrates the significance of Abhidhamma in ethical conduct and mindfulness.
- Cultural Connection: Highlights India's role in preserving Buddhism and bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary practices.
Historical Background and Significance
- Commemoration: Marks Buddha’s descent from T?vati?sa to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur).
- Teaching Period: Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to deities for three months; linked to the end of the Rainy Retreat and the Pav?ra?? festival.
Teachings of Abhidhamma
- Systematic Analysis: Provides a detailed exploration of mind and matter, differing from Sutta Pi?aka.
- Specialized Vocabulary: Key terms include "citta" (consciousness), "cetasika" (mental factors), "r?pa" (materiality), and "nibb?na" (liberation).
- Textual Framework: Six core books of Abhidhamma Piñaka cover moral states, aggregates, and causal relationships.
- Key Treatise: The Paññh?na offers in-depth causal analysis, essential for practitioners’ understanding.
Modern Observance and Celebrations
- Significance of Pali: Recognition of Pali as a classical language; promoting India's Buddhist heritage.
- Participants: Gathering of ambassadors, monks, scholars from 14 countries; emphasizes Abhidhamma's relevance today.
- Program Highlights: Dhamma discourse, academic sessions on Abhidhamma’s significance, exhibitions on Pali's evolution and Buddha's teachings.
Classical Status of Pali Language
- Pali's Role: Sacred language for delivering Buddha's teachings; recognized as a Classical Language by India.
- Buddhist Canon: Major texts include the Tipitaka (Vinaya, Sutta, Abhidhamma Pitaka) and commentarial traditions.
- Literary Heritage: Jataka Kathas reflect shared moral values; status enhances Pali studies in education and research.
Significance
- Significance of Celebration: Abhidhamma Divas underscores efforts to preserve and promote Buddhism’s legacy.
- Revitalization of Buddhism: Fosters global engagement and appreciation for Buddha’s teachings, reaffirming India's role in Buddhist studies.
India's Renewable Energy Capacity Hits 200 GW Milestone
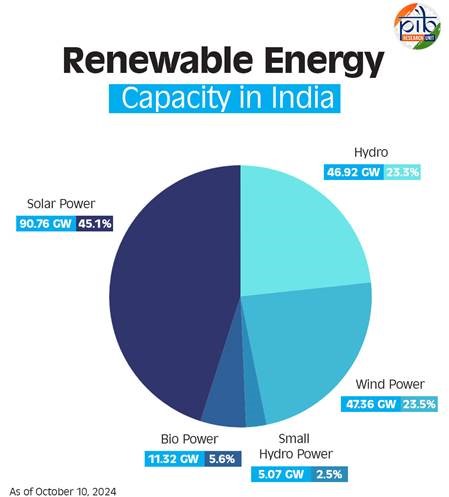
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
India has recently celebrated a landmark achievement in its renewable energy sector, with its total renewable energy capacity surpassing 200 GW as of October 10, 2024. This milestone, reported by the Central Electricity Authority, showcases the country’s growing commitment to clean energy and its strategic shift towards a more sustainable future.
Overview of India’s Renewable Energy Landscape
As of October 2024, India's total electricity generation capacity stands at 452.69 GW, with renewable sources contributing a substantial 201.45 GW, representing 46.3% of the overall capacity. This shift highlights India’s increasing reliance on cleaner, non-fossil fuel energy.
Key contributors to this capacity include:
- Solar Power: Leading with 90.76 GW, capitalizing on India's abundant sunlight.
- Wind Power: Following closely at 47.36 GW, leveraging the country’s vast wind corridors.
- Hydropower: Large hydro projects add 46.92 GW, while small hydro contributes an additional 5.07 GW.
- Biopower: Incorporating biomass and biogas energy, contributing 11.32 GW.
Together, these resources are pivotal in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
Leading States in Renewable Energy Capacity
Certain states are at the forefront of this renewable energy expansion:
- Rajasthan: 29.98 GW, benefiting from ample land and sunlight.
- Gujarat: 29.52 GW, driven by robust solar and wind initiatives.
- Tamil Nadu: 23.70 GW, utilizing favorable wind conditions.
- Karnataka: 22.37 GW, supported by a mix of solar and wind projects.
Key Schemes and Programs
The Indian government has introduced numerous initiatives to accelerate renewable energy capacity, aiming for 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030. Notable programs include:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission
- PM-KUSUM Scheme
- PM Surya Ghar Scheme
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) for solar PV modules
These efforts reflect the government's commitment to fostering a sustainable energy future while addressing the challenges posed by climate change and energy security. Here are some other ongoing key initiatives:
- Notification of a trajectory for renewable energy power bids of 50 GW per annum by Renewable Energy Implementation Agencies (REIAs) from FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Foreign Direct Investment permitted up to 100 percent under the automatic route to attract investments.
- Waiver of Inter-State Transmission System charges for solar and wind power projects commissioned by June 30, 2025; green hydrogen projects until December 2030; and offshore wind projects until December 2032.
- Announced Renewable Purchase Obligation trajectory until 2029-30, including separate RPO for Decentralized Renewable Energy.
- A Project Development Cell has been established to attract and facilitate investments in the renewable sector.
- Standard Bidding Guidelines issued for tariff-based competitive bidding for procurement of power from grid-connected solar, wind, and wind-solar projects.
- Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Parks are being set up to provide land and transmission for large-scale renewable energy projects.
- Cabinet approval for a Viability Gap Funding scheme for offshore wind energy projects, facilitating the installation and commissioning of 1 GW of offshore wind energy capacity along the coasts of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Issued Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020, for net-metering up to 500 kilowatts or the electrical sanctioned load, whichever is lower.
- The “National Repowering and Life Extension Policy for Wind Power Projects, 2023” has been released.
- “Strategy for Establishment of Offshore Wind Energy Projects” outlines a bidding trajectory of 37 GW by 2030.
- Offshore Wind Energy Lease Rules, 2023, notified to regulate the grant of leases for offshore wind energy development.
- Procedure for Uniform Renewable Energy Tariff (URET) has been established.
- Standard & Labelling (S&L) programs for Solar Photovoltaic modules and grid-connected solar inverters have been launched.
- A transmission plan has been prepared to augment transmission infrastructure until 2030.
- The Electricity (Late Payment Surcharge and Related Matters) Rules have been notified.
- Green Energy Open Access Rules 2022 have been issued to promote renewable energy.
- Launched the Green Term Ahead Market (GTAM) to facilitate the sale of renewable energy power through exchanges.
- Orders issued to ensure that power is dispatched against Letters of Credit or advance payment for timely payments to renewable energy generators.
ITU World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly 2024

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated ITU WTSA 2024 and India Mobile Congress 2024, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- First Time in India: WTSA hosted for the first time in India and the Asia-Pacific region.
- Participants: Over 3,000 industry leaders, policy-makers, and tech experts from more than 190 countries expected.
ITU WTSA 2024
- Significance: Governing conference for the standardization work of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), held every four years.
- Focus Areas: Discussion on standards for next-generation technologies including:
- 6G
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Cybersecurity
- Opportunities for India: Enhances India’s role in shaping the global telecom agenda; insights into Intellectual Property Rights and Standard Essential Patents for startups and research institutions.
India Mobile Congress 2024
- Theme: "The Future is Now"
- Technological Focus: Highlight advancements in:
- Quantum Technology
- Circular Economy
- 6G and 5G use cases
- Cloud and Edge Computing
- IoT and Semiconductors
- Cybersecurity
- Green Technology
- Satellite Communication and Electronics Manufacturing
Importance for India
- Showcase of Innovation: A platform for India’s innovation ecosystem, demonstrating advancements in digital technology.
- Global Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between government, industry, and academia to address global telecommunication challenges.
New Cancer Therapy Target
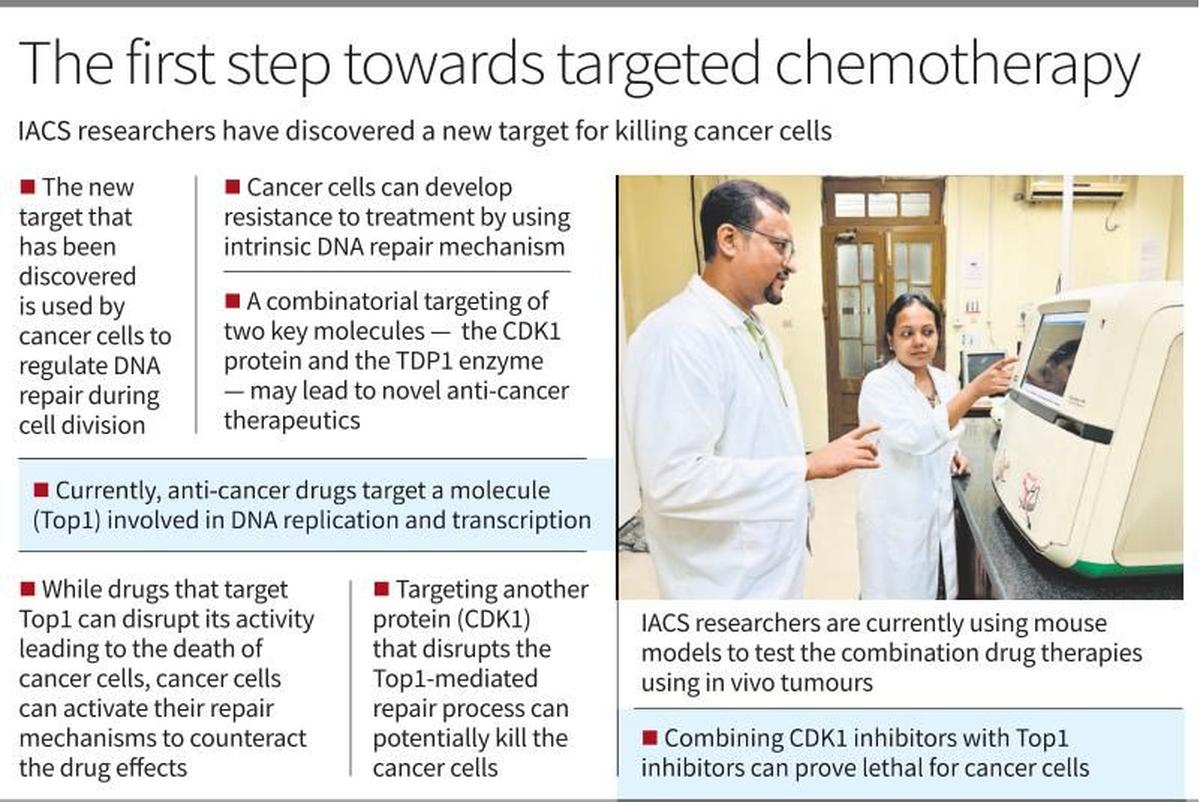
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
NABARD Survey on Rural Financial Inclusion
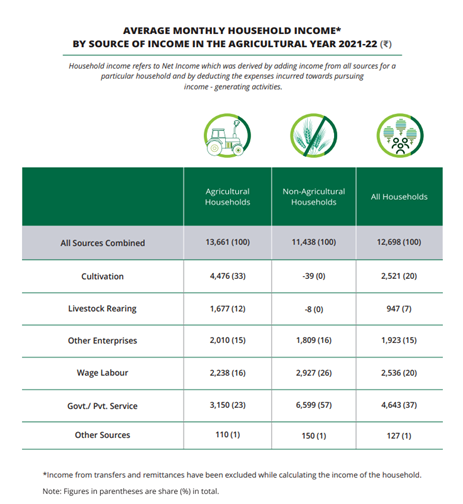
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
NABARD has published the findings from its second All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey (NAFIS) for 2021-22, which offers primary data based on a survey of 1 lakh rural households, covering various economic and financial indicators in the post-COVID period.
Survey Overview:
- Inaugural survey conducted for 2016-17, results released in August 2018.
- Aims to analyze changes in rural economic conditions since 2016-17.
- Included all 28 states and Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Insights from NAFIS 2021-22
- Increase in Average Monthly Income:
- Average monthly income rose by 57.6% from Rs. 8,059 (2016-17) to Rs. 12,698 (2021-22).
- Nominal CAGR of 9.5%, with annual nominal GDP growth at 9%.
- Agricultural households earned Rs. 13,661; non-agricultural households earned Rs. 11,438.
- Salaried employment contributed 37% to total income; cultivation contributed one-third for agricultural households.
- Rise in Average Monthly Expenditure:
- Average monthly expenditure increased from Rs. 6,646 (2016-17) to Rs. 11,262 (2021-22).
- Agricultural households reported higher consumption (Rs. 11,710) compared to non-agricultural households (Rs. 10,675).
- Expenditure exceeded Rs. 17,000 in states like Goa and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Increase in Financial Savings:
- Annual average financial savings grew to Rs. 13,209 in 2021-22 from Rs. 9,104 in 2016-17.
- 66% of households saved in 2021-22, up from 50.6% in 2016-17.
- 71% of agricultural households reported savings, compared to 58% of non-agricultural households.
- States like Uttarakhand (93%) and Uttar Pradesh (84%) had high saving rates, while Goa (29%) and Kerala (35%) had lower rates.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Coverage:
- 44% of agricultural households possessed a valid KCC.
- Among larger landholders and those with recent agricultural loans, 77% reported having a KCC.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Households with at least one insured member increased from 25.5% (2016-17) to 80.3% (2021-22).
- Vehicle insurance was most common (55%), followed by life insurance (24%).
- Pension Coverage:
- Households with at least one member receiving any form of pension rose from 18.9% to 23.5%.
- 54% of households with members over 60 years old reported receiving a pension.
- Financial Literacy:
- Good financial literacy increased by 17 percentage points, from 33.9% to 51.3%.
- Sound financial behavior improved from 56.4% to 72.8%.
Conclusion
- The NAFIS 2021-22 highlights significant advancements in rural financial inclusion since 2016-17.
- Improvements in income, savings, insurance coverage, and financial literacy are notable.
- Government welfare schemes (e.g., PM Kisan, MGNREGS) have positively impacted rural lives.
- Continued support and investment in rural development are essential for economic empowerment and financial security in India's rural population.
Trachoma

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has now recognised that India has successfully eliminated trachoma, a bacterial infection that affects the eyes, as a public health problem.
WHO Declaration:
- India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem (2024).
- Third country in the South-East Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
Trachoma Overview:
- Bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis.
- Contagious; spreads through contact with infected secretions.
- Can lead to irreversible blindness if untreated.
- Considered a neglected tropical disease.
Global Impact:
- WHO estimates 150 million affected worldwide; 6 million at risk of blindness.
- Most prevalent in underprivileged communities with poor living conditions.
Historical Context in India:
- Leading cause of blindness in the 1950s-60s.
- National Trachoma Control Program launched in 1963.
- Control efforts integrated into the National Program for Control of Blindness (NPCB).
Statistics:
- Blindness due to Trachoma was 5% in 1971; now reduced to less than 1%.
- Implementation of the WHO SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial hygiene, Environmental cleanliness).
Milestones:
- India declared free from infective Trachoma in 2017.
- Continued surveillance for cases from 2019 to 2024.
National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT) Survey:
- Conducted in 200 endemic districts (2021-2024) under NPCBVI.
- Mandated by WHO to confirm elimination status.
MACE Observatory

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The MACE Observatory was recently inaugurated by the Secretary of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission in Hanle, Ladakh.
About MACE Observatory
- Name: Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory.
- Significance:
- Largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia.
- Highest imaging Cherenkov observatory in the world.
- Location: Situated at approximately 4,300 meters altitude in Hanle, Ladakh.
- Indigenous Development:
- Built by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- Supported by the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL), Hyderabad, and other Indian industry partners.
Scientific Contributions
- Research Focus:
- Enhances understanding in astrophysics, fundamental physics, and particle acceleration mechanisms.
- Observes high-energy gamma rays to investigate cosmic phenomena like supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts.
- Global Impact:
- Aims to foster international collaborations in space research.
- Strengthens India’s position in the global scientific community.
Socio-Economic Role
- Local Impact: Contributes to the socio-economic development of Ladakh, promoting scientific awareness and opportunities.
Understanding Cherenkov Radiation
- Definition: A blue glow emitted when charged particles (e.g., electrons and protons) travel faster than light in a specific medium.
- Historical Note: Named after Pavel Cherenkov, who, along with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958 for his work in demonstrating and explaining this phenomenon.
44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses

- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
India Participates in 44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses
Key Contributions:
- Nutrient Reference Values:
- Advocated for reference values for ages 6 to 36 months.
- Suggested combining NRV-R values by averaging those for 6-12 months and 12-36 months.
- This proposal was accepted by the committee.
- Probiotic Guidelines:
- Emphasized the need to update FAO/WHO probiotic guidelines, which are two decades old.
- Highlighted the lack of international harmonization in probiotic regulations affecting global trade.
- Committee agreed to revisit guidelines and requested FAO and WHO to conduct a literature review on probiotics.
- Discussion on Sweetness Assessment:
- Disagreed with the EU’s sensory testing proposal for carbohydrate sources in Follow-up Formula, citing lack of scientific validation.
- Supported by USA, Canada, and others; this led to the committee discontinuing the topic for now.
- Noted that ISO 5495 or other methods could be used in the absence of harmonized methods.
- Delegation:
- Included representatives from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Advocated for various food safety, consumer health, and trade-related issues.
- Outcome:
- India’s suggestions were officially incorporated into the final report, significantly influencing global food safety and nutrition standards.
- Additional Announcements:
- FAO/WHO plans for a Joint Statement on Healthy Diet Principles.
- Updates on reviewing benefits and risks of Alternative Animal Source Foods (A-ASFs).
- FAO introduced a new “Food and Diet” domain on its FAOSTAT database.
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024, Commencing at Visakhapatnam on 08 Oct Hosted by India, USA, Australia and Japan in Participation.
Background
- Origins: Initiated in 1992 as a bilateral naval drill between the United States and Indian Navy.
- Evolution: Has grown into a key multilateral exercise aimed at enhancing interoperability and addressing maritime challenges in the Indian Ocean and Indo-Pacific region.
Participating Naval Assets
- India: Various platforms, including:
- Guided missile destroyers
- Multi-purpose frigates
- Submarines
- Fixed-wing maritime reconnaissance aircraft
- Fighter aircraft and helicopters
- Australia:
- HMAS Stuart (Anzac Class Frigate)
- MH-60R helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- United States:
- USS Dewey (Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyer)
- Integral helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- Japan:
- JS Ariake (Murasame-class Destroyer)
Focus Areas of the Exercise
- Operational Enhancements:
- Discussions on special operations
- Surface, air, and anti-submarine warfare
- Subject Matter Expert Exchange (SMEE)
- Maritime Operations:
- Anti-submarine warfare
- Surface warfare
- Air defense exercises
- Emphasis: Improving situational awareness in the maritime domain.
Special Events
- Distinguished Visitors’ Day: Scheduled for October 9, 2024.
- Hosted by Vice Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Eastern Naval Command.
- Joint Press Conference: Co-chaired by heads of delegations from all participating nations during the Harbour Phase.
Significance
- Comprehensive Exercise: Malabar 2024 is expected to be the most detailed edition to date, featuring complex operational scenarios and enhanced cooperation among the naval forces of the participating countries.GS Paper
DefConnect 4.0

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
- DefConnect 4.0 was inaugurated by Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh on October 7, 2024, at Manekshaw Centre, Delhi Cantonment.
- Organizer: Hosted by Innovations for Defence Excellence - Defence Innovation Organisation (iDEX-DIO) under the Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence.
Purpose and Focus
- Advancing Indigenous Innovation: Aims to enhance India’s defense ecosystem by promoting self-reliant defense technologies.
- Participants: Involves Armed Forces, Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), start-ups, MSMEs, academia, incubators, investors, and policymakers.
Technology Showcase
- Exhibitions: iDEX innovators showcased cutting-edge technologies, products, and capabilities.
- Collaboration and Dialogue: Encourages partnerships and discussions to drive defense innovation and long-term collaborations.
Special Sessions
- Budget Insights: Focused on key takeaways from recent budget announcements impacting the defense innovation ecosystem.
- Semiconductor Domain: Highlighted initiatives and opportunities within the semiconductor sector.
Path Forward: Vision for 2047
- Viksit Bharat Goal: Aligns with India’s vision of becoming a global leader in defense innovation by 2047.
- Government Initiatives: Supports local talent and indigenous solutions through programs like iDEX.
iDEX Impact
- Defence India Start-up Challenges: 11 editions launched, garnering over 9,000 applications.
- Collaborations: Engages with over 450 start-ups/MSMEs on significant defense projects.
- Contribution to Self-Reliance: Supports the goal of achieving self-reliance in the defense and aerospace sectors.
Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
DRDO completed development trials of the 4th Generation miniaturised Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD).
Key Details:
- Trial Location: Conducted at Pokhran Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Importance: VSHORAD addresses the Indian Army's need to replace legacy Igla systems, with past efforts making little progress.
- Recent Procurement: Army acquired small volumes of Igla-S through emergency procurement.
- Production Collaboration: Two production agencies involved in Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) mode for VSHORAD missiles.
- Trial Dates: Successful tests held on October 3 and 4, 2024.
Key Performance Metrics:
- Maximum Range and Altitude: Interception against high-speed aerial targets.
- Hit-to-Kill Capability: Demonstrated success in engaging targets in various scenarios (approaching, receding, crossing).
System Overview:
- Type: Fourth generation man-portable air defence system (MANPADS).
- Developer: Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
Capabilities:
- Designed to neutralise low altitude aerial threats at short ranges.
- Features include Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System, and integrated avionics.
- More portable and lightweight than existing missile systems in the Army's arsenal.
National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds)

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
Cabinet Approves National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds) (2024-25 to 2030-31).
Objective:
- Achieve self-reliance in edible oil production in seven years.
Financial Outlay:
- ?10,103 crore for the mission period.
Key Goals:
- Increase primary oilseed production from 39 million tonnes (2022-23) to 69.7 million tonnes by 2030-31.
- Boost domestic edible oil production to 25.45 million tonnes, meeting 72% of projected requirements.
Focus Areas:
- Enhance production of key oilseed crops: Rapeseed-Mustard, Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Sesamum.
- Improve extraction efficiency from secondary sources (e.g., Cottonseed, Rice Bran).
Strategies:
- Promote high-yielding, high oil content seed varieties.
- Extend cultivation to rice fallow areas and encourage intercropping.
- Use advanced technologies like genome editing for seed development.
SATHI Portal:
- Launch of an online 5-year rolling seed plan for timely seed availability.
- Coordination with cooperatives, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and seed corporations.
Infrastructure Development:
- Establish 65 new seed hubs and 50 seed storage units.
- Develop over 600 Value Chain Clusters across 347 districts, covering over 1 million hectares annually.
Support for Farmers:
- Access to high-quality seeds, training on Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), and pest management advisory.
Environmental Benefits:
- Promote low water usage, improve soil health, and utilize crop fallow areas.
Background Context:
- India relies on imports for 57% of its edible oil demand.
- Previous initiatives include the National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) and significant increases in Minimum Support Price (MSP) for oilseeds.
- Imposition of 20% import duty on edible oils to protect local producers.
The NMEO-Oilseeds mission aims to enhance domestic oilseed production, reduce import dependency, and improve farmers' incomes while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Status of Classical Language: An Explainer

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved to confer the status of Classical Language to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali languages.
Why is a language declared as Classical?
Designating a language as classical acknowledges its historical significance and its role in preserving Bharat’s rich cultural heritage. These languages have been crucial in transmitting ancient knowledge, philosophies, and values for millennia. Government recognition emphasizes their deep antiquity and literary traditions, enhancing their status and promoting efforts for their preservation and research, ensuring their relevance in the modern world.
What are the criteria for declaring a language as classical?
In 2004, the Government of India, for the first time, created a new category of languages known as Classical Languages. It set the following as criteria for the status of Classical Language:
- High antiquity of its early texts/ recorded history over a thousand years.
- A body of ancient literature/ texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generation of speakers.
- The literary tradition must be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
This criterion was revised in 2005 and 2024 based on the recommendations of Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under Sahitya Akademi to examine the proposed languages for the status of Classical Language. Later the criteria were revised in 2024 as follows:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500- 2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a heritage by generations of speakers.
- Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence.
- The Classical Languages and literature could be distinct from its current form or could be discontinuous with later forms of its offshoots.
The 2024 Linguistic Expert Committee also recommended the following languages to be fulfilling revised criteria to be considered as a Classical Language: Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, Bengali
How many languages have been declared classical so far?
Languages Date of Recognition Notification by Source/Notification Date
Tamil October 12, 2004 Ministry of Home Affairs October 12, 2004
Ministry of Sanskrit November 25, 2005 Ministry of Home Affairs November 25, 2005
Telugu October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Kannada October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Malayalam August 8, 2013 Ministry of Culture August 8, 2013
Odia March 1, 2014 Ministry of Culture March 1, 2014
Steps Taken by the Ministry of Education for Advancing Classical Languages:
- Establishment of Central Universities (2020): Three universities created to promote Sanskrit through an Act of Parliament.
- Central Institute of Classical Tamil:
- Facilitates translation of ancient Tamil texts.
- Promotes research and offers courses for students and scholars.
- Centres for Excellence:
- Established for Classical Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia under the Central Institute of Indian Languages in Mysuru.
- Awards: Introduction of national and international awards to recognize achievements in Classical Languages.
- Additional Benefits:
- National Awards for Classical Languages.
- Establishment of university chairs.
- Dedicated centers for promoting Classical Languages.
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) Results for 2022-23
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the results of the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for the financial year 2022-23 (April 2022 to March 2023).
- The fieldwork for this survey was conducted from November 2023 to June 2024.
- The ASI provides critical insights into the dynamics of the manufacturing sector, covering aspects such as output, value added, employment, and capital formation.
Key Highlights
- Gross Value Added (GVA): Increased by 7.3% in current prices for 2022-23 compared to the previous year.
- Industrial Output: Grew by over 21% in 2022-23 compared to 2021-22.
- Employment: Estimated employment in the sector rose by 7.4% over the previous year, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
The growth in key economic parameters such as invested capital, input, output, GVA, and wages indicates a robust recovery in the industrial sector. Notably, industries like Basic Metal Manufacturing, Coke & Refined Petroleum Products, Food Products, Chemicals, and Motor Vehicles were significant contributors, accounting for about 58% of total output and showing a 24.5% increase in output and 2.6% in GVA.
State Contributions
- Top GVA Contributors:
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Uttar Pradesh
Together, these states contributed over 54% of the total manufacturing GVA.
- Highest Employment States:
- Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Uttar Pradesh
- Karnataka
Collectively, these states accounted for about 55% of total manufacturing employment in 2022-23.
Survey Details
The ASI encompasses various industrial units, including:
- Factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948.
- Bidi and cigar manufacturing establishments.
- Electricity undertakings not registered with the Central Electricity Authority.
- Units with 100 or more employees registered in the Business Register of Establishments.
The survey employs a comprehensive sampling strategy, dividing units into Central and State Samples to ensure accurate representation. Key components of the data collection include:
- Central Sample: Includes all units in less industrially developed states and specific industrial categories.
- State Sample: Comprises selected units based on employee count and other criteria.
Industrial Classification
Since 1959, the ASI has adopted various classifications to categorize industries. The current classification, NIC 2008, is based on the UN's international standards and has been in use since 2008-09.
Data Collection and Reliability
Data collection is conducted via a dedicated web portal, following the Collection of Statistics Act. Various quality checks ensure reliability, with the Relative Standard Errors (RSE) for important estimates remaining within acceptable limits.
Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
BharatGen Initiative
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
BharatGen is a pioneering generative AI initiative launched in New Delhi, aimed at revolutionizing public service delivery and enhancing citizen engagement, with Dr. Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State, in virtual attendance.
- Significance
- Represents India's commitment to advancing homegrown technologies.
- Positions India as a global leader in generative AI, similar to achievements with UPI and other innovations.
- Marks the world's first government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model project focusing on Indian languages.
- Leadership and Implementation
- Spearheaded by IIT Bombay under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- Collaboration with the TIH Foundation for IoT and various academic partners, including IITs and IIMs.
- Key figures involved include Prof. Shireesh Kedare (Director, IIT Bombay) and Prof. Ganesh Ramakrishnan (consortium leader).
- Core Objectives
- Deliver generative AI models as a public good, prioritizing socio-cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Address broader needs such as social equity, cultural preservation, and inclusivity.
- Make AI accessible for industrial, commercial, and national priorities.
- Key Features
- Multilingual and Multimodal Models: Capable of handling text and speech in multiple languages.
- Bhartiya Data Sets: Focus on India-centric data collection and training.
- Open-Source Platform: Promotes collaboration and innovation in AI research.
- Ecosystem Development: Fosters a robust AI research community.
- Project Timeline and Impact
- Expected completion in two years, with benefits for government, private, educational, and research institutions.
- Ensures coverage of India’s diverse linguistic landscape through multilingual datasets.
- Emphasis on data sovereignty to strengthen control over digital resources.
- Alignment with National Goals
- Supports the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by reducing reliance on foreign technologies.
- Aims to strengthen the domestic AI ecosystem for startups, industries, and government agencies.
- Focuses on democratizing access to AI for innovators and researchers.
- Research and Community Engagement
- Data-efficient learning for languages with limited digital presence.
- Development of effective models with minimal data through research collaborations.
- Initiatives to foster an AI research community, including training programs and hackathons.
- Future Roadmap
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
- Extensive AI model development and experimentation.
- Establishment of AI benchmarks tailored to India’s needs.
- Scaling AI adoption across industries and public initiatives.
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
Joint Military Exercise KAZIND-2024

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The 8th edition of the India-Kazakhstan Joint Military Exercise, KAZIND-2024, has commenced in Auli, Uttarakhand, running from September 30 to October 13, 2024.
Key Details:
- Joint Exercise KAZIND-2024 has been held annually since 2016.
- Last edition of the Joint Exercise was held at Otar, Kazakhstan from 30th October to 11th November 2023.
Participants:
- India:
- 120 personnel from KUMAON Regiment of the Indian Army
- Additional support from other arms and Indian Air Force
- Kazakhstan:
- Personnel primarily from Land Forces and Airborne Assault Troopers
Aim:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations
- Focus on sub-conventional scenarios under Chapter VII of the UN Charter
Focus Areas:
- Operations in semi-urban and mountainous terrains
- High physical fitness levels
- Rehearsal and refinement of tactical drills
- Sharing best practices
Tactical Drills:
- Joint response to terrorist actions
- Establishment of a Joint Command Post
- Creation of an Intelligence and Surveillance Centre
- Securing helipad/landing sites
- Combat free fall and Special Heliborne Operations
- Cordon and Search operations
- Employment of drones and counter-drone systems
Outcomes Expected:
- Sharing of tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations
- Development of interoperability between the two armies
- Strengthening of bonhomie and camaraderie
- Enhancement of defense cooperation and bilateral relations between India and Kazakhstan.
7 New Schemes to Boost Farmer Income
- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, approved seven schemes to improve farmers’ lives and increase their incomes at a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 Crore.
1. Digital Agriculture Mission: based on the structure of Digital Public Infrastructure, Digital Agriculture Mission will use technology for improving farmers’ lives. The Mission has a total outlay of Rs 2,817 crores. It comprises two foundational pillars
1. Agri Stack
- Farmers registry
- Village land maps registry
- Crop Sown Registry
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- Geospatial data
- Drought/flood monitoring
- Weather/satellite data
- Groundwater/water availability data
- Modelling for crop yield and insurance
The Mission has provision for
- Soil profile
- Digital crop estimation
- Digital yield modelling
- Connect for crop loan
- Modern technologies like AI and Big Data
- Connect with buyers
- Bring new knowledge on mobile phones
2. Crop science for food and nutritional security: with a total outlay of Rs 3,979 crore. The initiative will prepare farmers for climate resilience and provide for food security by 2047. It has following pillars:
- Research and education
- Plant genetic resource management
- Genetic improvement for food and fodder crop
- Pulse and oilseed crop improvement
- Improvement of commercial crops
- Research on insects, microbes, pollinators etc.
3. Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management and Social Sciences: with a total outlay of Rs 2,291 Crore the measure will prepare agriculture students and researchers for current challenges and comprises the following
- Under Indian Council of Agri Research
- Modernising agri research and education
- In line with New Education Policy 2020
- Use latest technology … Digital DPI, AI, big data, remote, etc
- Include natural farming and climate resilience
4. Sustainable livestock health and production: with a total outlay of Rs 1,702 crore, the decision aims to Increase farmers income from livestock and dairy. It comprises the following
- Animal health management and veterinary education
- Dairy production and technology development
- Animal genetic resource management, production and improvement
- Animal nutrition and small ruminant production and development
5. Sustainable development of Horticulture: with a total outlay of Rs 1129.30 crore the measure is aimed at increasing farmers’ income from horticulture plants. It comprises the following
- Tropical, sub-tropical and temperate horticulture crops
- Root, tuber, bulbous and arid crops
- Vegetable, floriculture, and mushroom crops
- Plantation, spices, medicinal, and aromatic plants
6. Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra with an outlay of Rs 1,202 crore
7. Natural Resource Management with an outlay of Rs 1,115 crore
Digital Agriculture Mission

- 03 Sep 2024
Introduction
India's digital revolution has significantly transformed governance and service delivery in recent years by creating digital identities, secured payments and transactions. This progress has paved the way for a thriving digital ecosystem across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and retail, positioning India as a leader in citizen-centric digital solutions.
For a similar transformation of the Agriculture Sector, the Union Cabinet Committee, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the 'Digital Agriculture Mission' with a substantial financial outlay of Rs. 2,817 Crore, including a central government share of Rs. 1,940 Crore, on September 2, 2024.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is designed as an umbrella scheme to support various digital agriculture initiatives. These include creating Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), and supporting IT initiatives by the Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
The scheme is built on two foundational pillars:
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System.
Additionally, the mission includes ‘Soil Profile Mapping’ and aims to enable farmer-centric digital services to provide timely and reliable information for the agriculture sector.
AgriStack: Kisan ki Pehchaan
AgriStack is designed as a farmer-centric Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to streamline services and scheme delivery to farmers. It comprises three key components:
1. Farmers' Registry
2. Geo-referenced village maps
3. Crop Sown Registry
- A crucial feature of AgriStack is the introduction of a 'Farmer ID', similar to Aadhaar card, serving as a trusted digital identity for farmers.
- These IDs, created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories, will be linked to various farmer-related data, including land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, and benefits availed.
- The implementation of AgriStack is progressing through partnerships between the Central and State Governments, with 19 states having signed MoUs with the Ministry of Agriculture. Pilot projects have been conducted in six states to test the creation of Farmer IDs and the Digital Crop Survey.
- The six states include Uttar Pradesh (Farrukhabad), Gujarat (Gandhinagar), Maharashtra (Beed), Haryana (Yamuna Nagar), Punjab (Fatehgarh Sahib), and Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar).
Key targets include:
- Creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers over three years (6 crore in FY 2024-25, 3 crore in FY 2025-26, and 2 crore in FY 2026-27)
- Launching the Digital Crop Survey nationwide within two years, covering 400 districts in FY 2024-25 and all districts in FY 2025-26
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- The Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) will integrate remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system.
3. Soil Profile Mapping
Under the mission, detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land have been envisaged, with 29 million hectares of soil profile inventory already being mapped.
- Further under the Digital Agriculture Mission, the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will be used for crop-cutting experiments to provide precise yield estimates, enhancing agricultural production accuracy.
- The mission is expected to create direct and indirect employment in agriculture, providing opportunities for around 2,50,000 trained local youth and Krishi Sakhis.
- By leveraging modern technologies like data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, the mission will improve service delivery for farmers, including streamlined access to government schemes, crop loans, and real-time advisories.
Key Components of the Mission
The Digital Agriculture Mission focuses on grassroots implementation, targeting farmers as the primary beneficiaries. Some of the key benefits of the mission include:
- Digital authentication for accessing services and benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced efficiency and transparency in government schemes, crop insurance, and loan systems through accurate data on crop area and yield.
- Crop map generation and monitoring for better disaster response and insurance claims.
- Development of digital infrastructure to optimize value chains and provide tailored advisory services for crop planning, health, pest management, and irrigation.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 that the Government, in partnership with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture over the next three years.
- This initiative will cover farmers and their lands, with a digital crop survey for Kharif planned for 400 districts this year. The goal is to update registries with details of 6 crore farmers and their lands.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 had previously introduced the DPI for agriculture, which aims to provide comprehensive data on farmers, including demographic details, land holdings, and crops sown. The DPI will integrate with state and central digital infrastructures to offer a range of farmer-centric services, including information on livestock, fisheries, soil health, and available benefits.
Conclusion
- The Union Cabinet also approved six major schemes alongside the Digital Agriculture Mission, with a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 crore.
- These initiatives include Rs 3,979 crore for Crop Science aimed at ensuring food security and climate resilience by 2047, and Rs 2,291 crore for strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences to support students and researchers. Rs 1,702 crore is allocated for Sustainable Livestock Health and Production to boost incomes from livestock and dairy, while Rs 1,129.30 crore is designated for Sustainable Development of Horticulture to increase income from horticulture. Additionally, Rs 1,202 crore will be invested in strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendra, and Rs 1,115 crore towards Natural Resource Management.
- These comprehensive approaches leverage digital technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in India's agricultural sector, potentially transforming the lives of millions of farmers across the country. By extending the digital revolution to agriculture, India aims to further solidify its position as a global leader in innovative, technology-driven solutions for critical sectors of the economy.
Supreme Court of India

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
On August 31, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the National Conference of District Judiciary at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi. This event marked the 75th anniversary of the Supreme Court of India, highlighted by the unveiling of a commemorative stamp and coin.
Supreme Court of India: History and Key Insights
The Origins of the Judiciary
- The concept of law, or Dharma, in ancient India was significantly influenced by the Vedas, which outlined rules of conduct and rituals in the Dharma Sutras. These texts addressed the duties of individuals and the rights of kings, forming the foundation of Hindu Law. The earliest systematic examination of jurisprudence can be found in Kautilya's Artha Sastra (circa 300 B.C.), particularly its third chapter, which discusses legal transactions and disputes.
Establishment of the Supreme Court
- The Regulating Act of 1773, enacted by the British Parliament, initiated the establishment of the Supreme Court of Judicature at Calcutta, with its Letters of Patent issued on March 26, 1774. This court had the authority to hear all complaints and lawsuits involving His Majesty’s subjects in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa. Additional Supreme Courts were later established in Madras (1800) and Bombay (1823).
- The Indian High Courts Act of 1861 replaced these Supreme Courts with High Courts in various provinces, which became the highest judicial authorities until the Federal Court of India was created under the Government of India Act 1935. After India gained independence in 1947, the Supreme Court of India was formally established on January 26, 1950, with its inaugural session held on January 28, 1950.
- The Supreme Court's rulings are binding across India, and it possesses the power of judicial review to ensure that legislative and executive actions align with constitutional provisions and fundamental rights.
Structure and Functioning
- Initially, the Supreme Court operated for only a few hours each day and convened for 28 days a year. Today, it functions extensively, meeting approximately 190 days annually. The court was temporarily housed in the Parliament House before moving to its current location on Tilak Marg, New Delhi, in 1958.
- The court's architecture symbolizes justice, featuring a prominent dome and spacious corridors. It began with a Chief Justice and seven judges, with Parliament later increasing this number as the workload grew. Currently, the Supreme Court includes a Chief Justice and 30 judges.
Appointment and Qualifications of Judges
- Judges are appointed by the President of India, based on recommendations from a committee of senior judges (Collegium System). A candidate must be a citizen of India and have served as a High Court judge for at least five years or as an advocate for ten years. The age of retirement for judges is 65 years.
Judicial Independence and Removal
- Judicial independence is constitutionally protected. A Supreme Court judge can only be removed by the President on grounds of proven misbehavior or incapacity, following a resolution supported by a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Judicial Salaries and Provisions
- Judges’ salaries and pensions are defined by the Supreme Court Judges (Salaries and Conditions of Service) Act, 1958, and are charged to the Consolidated Fund of India.
Acting Chief Justice
- In the absence of the Chief Justice, the President appoints another judge as the Acting Chief Justice, as stipulated in Article 126.
Post-Retirement Opportunities
- While retired judges cannot practice law in India, they often serve in governmental roles, such as leading commissions. There have been calls for a "cool-off" period before such appointments.
Ad Hoc Judges
- Ad hoc judges may be appointed when necessary, and must meet the qualifications for Supreme Court judges. Retired judges can also be called back to serve temporarily.
Courts of Record
- Both the Supreme Court and High Courts are classified as courts of record, with the authority to punish for contempt as per Article 129.
Seat of the Supreme Court
- The Supreme Court is based in Delhi but can convene anywhere in India, with such decisions made by the Chief Justice in consultation with the President.
Samudra Pratap

- 02 Sep 2024
In News
Recently, the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) proudly launched the first indigenously built Pollution Control Vessel, ‘Samudra Pratap’, in Goa.
Key Highlights of the Launch
- Vessel Details:
- Built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL), the vessel is specifically designed to combat oil spills along India’s coastlines.
- Dimensions: Length: 114.5m, Breadth: 16.5m, Displacement: 4170 T.
- The keel laying ceremony took place on November 21, 2022.
- Contract and Construction: GSL signed a contract worth Rs 583 crores for the construction of two Pollution Control Vessels for the ICG. This marks the first instance of such vessels being designed and built entirely in India.
- Significance of the Vessel: ‘Samudra Pratap’ stands as a testament to India's shipbuilding capabilities, showcasing GSL's expertise in producing advanced Pollution Control Vessels and reinforcing India's commitment to indigenization in defense manufacturing.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour & Employment, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme on the occasion of National Sports Day in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
This programme aims to empower retired athletes by equipping them with essential career skills and knowledge, enhancing their employability and enabling them to contribute meaningfully to the sports ecosystem.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Retired athletes aged 20 to 50 years.
- Achievements:
- Must be winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- Alternatively, must have been national or state medallists or participants in competitions recognized by:
- National Sports Federations
- Indian Olympic Association
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
Programme Structure
- Levels: Two tiers based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12th and above
- Class 11th and below
- Learning Mode: A hybrid approach, combining:
- Self-paced online learning through a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training for practical skill development.
Lead Institute
- Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) will oversee the implementation and administration of the programme.
Support and Opportunities
- Placement Assistance: Comprehensive guidance for job placements in relevant sectors.
- Entrepreneurial Guidance: Support for athletes looking to start their own ventures in sports or related fields.
- Internships: Opportunities for hands-on experience in:
- Sports organizations
- Competitions
- Training camps
- Leagues
Implementation and Benefits
- Self-Paced Learning: Flexibility for participants to manage their learning schedules effectively.
- On-Ground Training: Hands-on practical sessions aimed at enhancing skills relevant to various career paths.
- Evaluation and Certification: Participants will be assessed and awarded a certificate upon successful completion, adding value to their career prospects.
The RESET Programme not only recognizes the achievements of retired athletes but also empowers them to leverage their experiences in new and impactful ways, fostering a robust sports ecosystem in India.
Project NAMAN

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the first phase of Project NAMAN, aimed at supporting Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families.
- Key Features of Project NAMAN:
- Implements the SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha) digital pension system.
- Streamlines pension processes and provides accessible facilitation points for Veterans and Next of Kin (NOK).
- Importance:
- Ensures care and support for veterans and their families.
- Services extended to residents of military stations and surrounding localities.
- Establishment of Common Service Centres (CSCs):
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Indian Army’s Directorate of Indian Army Veterans
- CSC e-Governance India Limited
- HDFC Bank Limited
- CSCs provide:
- SPARSH-enabled pension services
- Government to Citizen (G2C) services
- Business to Consumer (B2C) services
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Phase One Deployment:
- 14 CSCs established in key locations: New Delhi, Jalandhar, Leh, Dehradun, Lucknow, Jodhpur, Bengdubi, Gorakhpur, Jhansi, Secunderabad, Saugor, Guntur, Ahmedabad, Bangalore.
- Future expansion plans for approximately 200 centres nationwide in the next 2-3 years.
- Infrastructure Support:
- HDFC Bank provided necessary IT infrastructure.
- Local military stations contributed physical facilities.
- Community Engagement:
- Concept developed based on feedback from the Defence community.
- Promotes camaraderie among serving and retired Armed Forces personnel.
- Management of CSCs:
- Each CSC managed by a Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) selected from veterans or NOKs by Local Military Authorities (LMAs).
- VLEs receive training from CSC e-Governance India Limited.
- HDFC Bank offers monthly grants of ?20,000 for the first 12 months to support VLEs.
- Conclusion:
- Project NAMAN reflects the Indian Army's commitment to veteran welfare.
- Offers SPARSH-centric services and entrepreneurial opportunities for Veterans and NOKs, empowering them to contribute to their communities.
Repairability Index for Mobile and Electronic Sectors

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA), Government of India, has established a committee of experts to create a framework for the Repairability Index.
- Objective:
- Enhance consumer transparency regarding product repairability.
- Promote sustainable practices in the tech industry.
- National Workshop:
- Held on August 29, 2024, focusing on the Right to Repair in the Mobile and Electronics Sector.
- Aimed to gather industry stakeholders to agree on evaluating components for the Repairability Index.
- Key Goals:
- Address the rapid demand and short lifespan of mobile and electronic devices.
- Provide essential repair information and ensure access to spare parts, even for discontinued products.
- Repairability Index:
- A consumer-focused tool that helps in making informed product decisions based on repairability.
- Aims to standardize repairability assessments, enabling easier product comparisons.
- Consumer Empowerment:
- The index fosters mindful consumption and sustainability.
- Ensures affordable repair options and improves overall consumer satisfaction by addressing information gaps.
- Key components of the Repair Ecosystem:
- Comprehensive Repair Information: Access to repair manuals/DIYs, diagnostics, and a list of necessary tools and parts.
- Accessible Spare Parts: Easily identifiable and timely delivery of spare parts.
- Affordable Tools: Inexpensive, widely available, and safe tools for consumers.
- Modular Design: Key components designed for independent access and modularity.
- Economic Feasibility: Ensuring that the cost of repair parts and labor is affordable for consumers.
Taking into account the above necessities the committee is expected to recommend enabling framework for Policies/Rules/Guidelines which support repairability and integration of repairability index with the extant regulatory provisions in mobile and electronics sector to enhance consumer experiences in reusing the mobile and electronics products they own.
The committee will submit a comprehensive report including a framework for repairability index in Indian context by 15th November, 2024.
India's Biotech Revolution

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian Cabinet has recently approved the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) proposal, a significant move to advance the country’s biotechnology sector.
Scheduled to take effect on April 1, 2025, the BioE3 policy aims to capitalize on India's biotechnology potential by focusing on six key areas: bio-based chemicals, functional foods, precision biotherapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, carbon capture, and marine/space research.
Current Status of India’s Biotechnology Sector
India ranks among the top 12 biotechnology destinations globally and is the third-largest in the Asia-Pacific region. As of 2024, India's Bioeconomy is valued at an estimated USD 130 billion. The sector is integral to India’s goal of becoming a USD 5 trillion economy by 2024, with biotechnology contributing about 3% to the global market share.
Biotechnology Categories in India:
- Biopharmaceuticals: India is a major supplier of low-cost drugs and vaccines, leading in biosimilars with the highest number of approvals.
- Bio-Agriculture: India dedicates approximately 55% of its land to agriculture, holding the fifth-largest area of organic agricultural land worldwide. The sector's contribution to the Bioeconomy is expected to grow from USD 10.5 billion to USD 20 billion by 2025.
- Bio-Industrial: Biotechnology is enhancing industrial processes, manufacturing, and waste disposal.
- Bio IT & BioServices: India excels in contract manufacturing, research, and clinical trials, hosting the highest number of US FDA-approved plants outside the US.
Government Initiatives:
- 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) is permitted in greenfield pharma and medical devices.
- The National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2021-25 aims to make India a global leader in biotechnology, targeting a USD 150 billion Bioeconomy by 2025.
- The Department of Biotechnology has established 51 Biotech-KISAN hubs to connect farmers with scientific advancements.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 includes INR 10,000 crore for 500 ‘waste to wealth’ plants under the GOBARdhan scheme.
- The GenomeIndia Project focuses on sequencing and analyzing the Indian population’s genomes to aid public health.
Challenges and Recommendations
Challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complex approval process for GMOs and overlapping regulatory bodies slow down progress.
- Funding Issues: Limited funding and high risks deter investment. The biotechnology sector receives only 0.05% of India's GDP from the Central Government.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate research facilities and cold chain infrastructure hamper progress.
- IP Concerns: Intellectual property protection remains weak, affecting innovation.
- Global Competition: Indian firms face stiff competition from established global players.
- Talent Shortages: A brain drain and skills mismatch impede growth.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical issues related to GMOs and gene editing pose challenges.
Recommendations:
- Regulatory Streamlining: Establish a unified Biotechnology Regulatory Authority and adopt a risk-based assessment approach.
- Innovative Funding: Create a Biotechnology Investment Fund with public-private partnerships.
- Talent Development: Launch skill development programs and integrate biotech training into various disciplines.
- Infrastructure Investment: Develop shared high-end research facilities and upgrade cold chain infrastructure.
- IP Strengthening: Enhance the IPR regime and establish a Biotech Patent Pool.
- Leverage Make in India: Expand the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to cover more biotech products and establish specialized manufacturing corridors.
AVGC: The Future of Media & Entertainment Industry

- 30 Sep 2024
Introduction
- The AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics) sector is set to be the future of the media and entertainment industry.
- According to the FICCI-EY 2024 report, India now boasts the second-largest anime fan base globally and is projected to contribute 60% to the worldwide growth in anime interest in the coming years.
- In a significant step toward making India a global hub for AVGC, the Union Cabinet recently approved the establishment of a National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics, and Extended Reality (AVGC-XR) in Mumbai.
NCoE Background
- NCoE will be set up as a Section 8 Company under the Companies Act, 2013 in India with Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry and Confederation of Indian Industry representing the industry bodies as partners with the Government of India.
- The establishment of the NCoE follows the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs 2022-23 budget announcement, which proposed the creation of an AVGC task force in the country.
- NCoE AVGC aims at creating a world class talent pool in India to cater to the Indian as well as global entertainment industry.
- Provisionally named the Indian Institute for Immersive Creators (IIIC), this center aims to revolutionize the AVGC sector and foster innovation in immersive technologies.
- It will be modeled after renowned institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs).
Objective of NCoE (IIIC)
Boasting a growth rate of 25% and an estimated value of ?46 billion by 2023 (FICCI-EY Report 2023), the animation industry in India is thriving and offers a promising future for passionate young talent.
Below are some of the key objectives of the NCoE (IIIC):
- Focusing of creating Indian IP
- Leveraging our cultural heritage in new age
- Create a multiplier effect in the industry
- An industry led initiative, in partnership with state and academia
- Integrated focus on education, skilling industry, development, innovation
- Hub and spoke model of development to be followed
- IIIC as the hub and several center’s as its spokes dedicated innovation and research fund to promote start-up ecosystem
Conclusion
The Union Cabinet's approval of the National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for AVGC marks a pivotal step in strengthening India’s media and entertainment industry. This initiative is set to boost the economy while creating new job opportunities in the rapidly growing AVGC sector. As a global hub for filmmaking, India's advancements in technology and infrastructure will enable the production of high-quality content, positioning the country as a leader in technological innovation and creativity.
Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Tourism, Government of India, launched the national responsible tourism initiative ‘Paryatan Mitra & Paryatan Didi’ on September 27, 2024, coinciding with World Tourism Day.
- Vision: Aligned with the Prime Minister's vision to use tourism as a tool for social inclusion, employment, and economic development.
Pilot Locations
- Destinations: The initiative is piloted in six tourist destinations:
- Orchha (Madhya Pradesh)
- Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh)
- Bodh Gaya (Bihar)
- Aizawl (Mizoram)
- Jodhpur (Rajasthan)
- Sri Vijaya Puram (Andaman & Nicobar Islands)
Objectives and Training
- Enhancing Tourist Experience: The program aims to connect tourists with ‘tourist-friendly’ individuals who serve as local ambassadors and storytellers.
- Training Focus: Individuals interacting with tourists—such as cab drivers, hotel staff, street vendors, and students—receive training on:
- Importance of tourism and hospitality
- Cleanliness and safety
- Sustainability practices
- Local stories and attractions
Empowering Women and Youth
- Target Groups: Emphasis on training women and youth to develop tourism products such as:
- Heritage walks
- Food and craft tours
- Nature treks and homestays
- Employment Opportunities: Aims to enable locals to secure jobs as homestay owners, cultural guides, and adventure guides.
Digital Literacy
- Training in Digital Tools: Participants are also educated in digital literacy to enhance visibility of their offerings to tourists.
Impact and Recognition
- Training Success: Since the program's pilot in August 2024, approximately 3,000 individuals have been trained.
- Local Enthusiasm: Increased local interest in participating in tourism training programs and contributing to the tourism ecosystem.
- Future Recognition: The Ministry plans to award dedicated badges to Paryatan Mitra and Didi participants, ensuring tourists can identify those committed to providing exceptional experiences.
India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
AYUSHMAN BHARAT DIGITAL MISSION (ABDM)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created in the past three years under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). The digital healthcare mission marked its three-year anniversary.
Key Highlights:
- Launch Date: September 27, 2021.
- Vision: Establish a robust digital health infrastructure to enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and transparency.
- Duration: A transformative three-year journey aimed at revolutionizing India’s digital healthcare ecosystem.
Objectives and Background
- Alignment with National Health Policy: The mission stems from the National Health Policy (2017), emphasizing accessibility and the integration of digital technologies.
- Building Blocks:
- National Health Stack (2018) introduced unique health identifiers and verified registries.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (2019) provided guidance for implementing ABDM.
Key Features of ABDM
- Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Assigns a unique ID to every individual for managing health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): Comprehensive database of healthcare professionals across all systems of medicine.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): Repository of public and private health facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
- Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): Allows secure access and sharing of health records based on informed consent.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services.
- National Health Claims Exchange (HCX): Standardizes the insurance payment process for quicker claims.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensures confidentiality and security of health-related information in compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Interoperability: Enables seamless data exchange among stakeholders, supported by key gateways (HIE-CM, NHCX, UHI).
- Transparency: Offers individuals access to both public and private health services, ensuring transparent pricing and accountability.
Key Initiatives
- Scan and Share: QR-code based OPD registration reduces wait times and improves data accuracy.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Financial incentives to encourage participation in the ABDM ecosystem, launched on January 1, 2023.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: Operationalized 106 microsites to facilitate ABDM adoption among private providers.
- End-to-End ABDM Adoption Pilot: Aimed at digitizing healthcare facilities across India, with 131 selected for participation.
Achievements
- Health Accounts Creation: Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) established, linking 42 crore health records.
- Ecosystem Participation: Involvement of 236 private entities and leading public institutions, enhancing interoperability.
- Healthcare Facility Registration: 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals registered.
Moving Towards Transformation
- Collaborations: Partnerships with IIT Kanpur and Maharashtra University of Health Sciences to drive digital health education and public goods development.
- Training Initiatives: Introduction of a WhatsApp Chatbot for stakeholder training on digital health practices.
- Digital Health Standards: Launched by the National Accreditation Board of Hospitals to promote digital health technology adoption.
- Integration of eSwasthya Dham Portal: Extends ABDM benefits to Char Dham Yatris.
Vision for the Future
ABDM aims to create a seamless digital health ecosystem, ensuring every Indian citizen has access to their health records through a unique ABHA ID. The initiative includes:
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS): Aids healthcare professionals in improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
INDIA WATER WEEK (IWW) 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- The 8th edition of India Water Week (IWW) 2024 was held from September 17-20, 2024, at the Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
- Organized by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, this prestigious international event has established itself as a key platform for collaboration in water resource management.
- With participation from global water experts, government leaders, and private-sector representatives, the event aimed to address the critical challenges of water management, foster innovation, and promote sustainable water practices.
Theme and Focus
The theme for India Water Week 2024 was "Partnerships and Cooperation for Inclusive Water Development and Management." This theme underscored the importance of cross-sectoral and international collaboration to address the 21st-century's growing water challenges and the need for integrated efforts in water conservation, management, and equitable access to water resources.
India Water Week: An International Forum
- Since its inception in 2012, India Water Week has grown into a pivotal event in global water diplomacy, offering a platform for dialogue, innovation, and knowledge sharing.
- Each edition focuses on a specific water-related issue, providing policymakers, experts, and industry leaders the opportunity to present solutions and explore cooperative strategies.
International WASH Conference
- A key highlight of IWW 2024 was the International WASH Conference, organized by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- This conference focused on global collaboration in Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH), aiming to address pressing sanitation challenges and promote hygiene standards.
- The conference was held between 17th-19th September 2024, in New Delhi. This three-day gathering, centered on the theme ‘Sustaining Rural Water Supply’, offered a platform for knowledge exchange, showcasing innovations, and sharing best practices aimed at addressing global WASH challenges, with a special focus on achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6).
Key Takeaways from India Water Week 2024
The India Water Week 2024 concluded with several important takeaways:
- Collaboration and Cooperation: Water security can only be achieved through partnerships across sectors and borders.
- Innovation in Water Management: Startups and technological innovations are key to addressing the future challenges of water resource management.
- Community Participation: Local communities play a crucial role in water conservation efforts, and their involvement is vital to achieving sustainable development.
- Policy Recommendations: The event produced several policy recommendations for sustainable water governance, addressing challenges in climate resilience, infrastructure development, and groundwater management.
Conclusion
India Water Week 2024 was a landmark event that brought together a diverse group of stakeholders to address the complexities of water management in the 21st century. The event paved the way for a more sustainable and inclusive approach to water development through partnership, cooperation, and innovation, ensuring equitable access to water resources for all.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Prime Minister of India launched three Param Rudra Supercomputing Systems and a High-Performance Computing (HPC) system for weather and climate research via a virtual event.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers
- Development: Indigenously developed under the National Supercomputing Mission.
- Deployment Locations:
- Delhi: Inter University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) focuses on material science and atomic physics.
- Pune: Giant Metre Radio Telescope (GMRT) will explore Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) and other astronomical phenomena.
- Kolkata: S N Bose Centre drives advanced research in physics, cosmology, and earth sciences.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) System
- Purpose: Tailored for weather and climate research.
- Location:
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune.
- National Center for Medium Range Weather Forecast (NCMRWF), Noida.
- System Names: 'Arka' and 'Arunika', reflecting their solar connection.
Significance of the HPC System
- Enhanced Predictive Capabilities:
- High-resolution models improve accuracy and lead time for: Tropical cyclones, Heavy precipitation, Thunderstorms, Hailstorms, Heat waves, Droughts and Other critical weather phenomena
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- Launch and Goals
- Launched in 2015 to position India among world-class computing power nations.
- Aims to connect national academic and R&D institutions with a network of over 70 high-performance computing (HPC) facilities.
- Implementation
- Managed by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Government of India.
- Estimated cost: Rs 4,500 crore over 7 years.
- Supports initiatives like 'Digital India' and 'Make in India'.
- Current Status
- India ranks 74th globally in supercomputing, with only 9 supercomputers out of more than 500 worldwide.
- The mission addresses the growing computing demands of the scientific community and aligns with international technology trends.
- Infrastructure and Networking
- Envisions a supercomputing grid with over 70 HPC facilities networked via the National Knowledge Network (NKN).
- NKN connects academic institutions and R&D labs through a high-speed network.
ASIA POWER INDEX

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
In a major shift, India surpassed Japan to become the third-largest power in the Asia Power Index, reflecting its increasing geopolitical stature. This achievement is driven by India's dynamic growth, youthful population, and expanding economy, solidifying its position as a leading force in the region.
Key Factors Behind India’s Rise:
- Economic Growth: India has shown remarkable post-pandemic economic recovery, contributing to a 4.2-point rise in its Economic Capability. India’s massive population and strong GDP growth reinforce its standing as the world’s third-largest economy in PPP terms.
- Future Potential: India’s Future Resources score increased by 8.2 points, signalling a potential demographic dividend. Unlike its regional competitors, particularly China and Japan, India benefits from a youthful population that will continue to drive economic growth and labour force expansion in the coming decades.
- Diplomatic Influence: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership has garnered greater international recognition. India’s non-aligned strategic posture has allowed New Delhi to navigate complex international waters effectively. India ranked 6th in terms of diplomatic dialogues in 2023, reflecting its active engagement in multilateral forums.
- Further, India’s large population and economic capabilities offer it substantial promise. India’s score in Cultural Influence has also remained relatively strong, underpinned by its global diaspora and cultural exports.
- In addition, India’s role in multilateral diplomacy and security cooperation has been a point of emphasis. India's participation in dialogues, as well as its leadership in the Quad, has allowed it to play a significant role in regional security dynamics, albeit outside of formal military alliances.
Asia Power Index
- The Asia Power Index, launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018, is an annual measure of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It evaluates 27 countries across the Asia-Pacific, examining their ability to shape and respond to the external environment.
- The 2024 edition offers one of the most comprehensive assessments of power distribution in the region to date. Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, reflecting its growing importance in Southeast Asia.
- The Index focuses on both the material capabilities of states and the influence they exert on the international stage.
Criteria and Parameters of Power Measurement
Power in the Asia Power Index is divided into resource-based and influence-based determinants:
- Resource-Based Determinants:
- Economic Capability: The core economic strength of a country, measured through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological sophistication, and global economic connectivity.
- Military Capability: Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces, weapon systems, and signature capabilities like long-range power projection.
- Resilience: The internal capacity to deter threats to state stability, including institutional robustness, geopolitical security, and resource security.
- Future Resources: Forecasts the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors projected for 2035.
- Influence-Based Determinants:
- Economic Relationships: The capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks: The strength of alliances and partnerships, measured through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- Diplomatic Influence: The extent of a country's diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and foreign policy ambition.
- Cultural Influence: The ability to shape international public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people ties.
A country's overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight measures, encompassing 131 individual indicators. The results offer a nuanced understanding of how countries convert their resources into influence within the Asia-Pacific.
10 YEARS OF MAKE IN INDIA

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The “Make in India” initiative has completed 10 years. It was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on September 25, 2014.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The ‘Make in India’ campaign aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best in class manufacturing infrastructure.
- “Make in India” was designed to transform India into a global hub for design and manufacturing.
- Seen as an important ‘Vocal for Local’ initiative, its objective is twofold. Firstly, to boost India’s manufacturing capabilities and secondly to showcase its industrial potential on a global stage.
- The “Make in India 2.0” phase encompassing 27 sectors – both manufacturing and service.
4 pillars of “Make in India” initiative:
- New Processes: To enhance the business environment, promote entrepreneurship and startups – ‘ease of doing business’ became a crucial factor.
- New Infrastructure: Development of industrial corridors, smart cities, integrating state-of-the-art technology and high-speed communication to create world-class infrastructure, improving intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure etc.
- New Sectors: Opening of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in sectors like Defence Production, Insurance, Medical Devices, Construction, and Railway infrastructure.
- New Mindset: In order to support industrial growth and innovation – the government embraced a role as a facilitator rather than a regulator. The Government partners with industry in the economic development of the country.
Key Initiatives to enable Make in India initiative
Production linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: The primary goals of the PLI Schemes are to attract substantial investments, incorporate advanced technology, and ensure operational efficiency. These schemes cover 14 key sectors aimed at fostering investment in cutting-edge technology and promoting global competitiveness.
PM GatiShakti: It is a strategic initiative aimed at achieving Aatmanirbhar Bharat and a US $5 trillion economy by 2025 through the creation of multimodal and last-mile connectivity infrastructure. PM GatiShakti is a transformative approach for economic growth and sustainable development. The approach is driven by 7 engines, namely:
- Railways
- Roads
- Ports
- Waterways
- Airports
- Mass Transport
- Logistics Infrastructure
Semiconductor Ecosystem Development: It encompasses four key schemes:
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Semiconductor Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Display Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, Sensors Fabs, and Discrete Semiconductors, along with Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP) / OSAT Facilities in India
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
It aims to foster the development of a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
The Semicon India Programme aims to provide a significant impetus to semiconductor and display manufacturing by facilitating capital support and promoting technological collaborations.
National Logistics Policy: Introduced to complement the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan. It focusses on enhancing the soft infrastructure of India’s logistics sector.
The Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) was rolled out. The key areas which it addresses are logistics systems, standardization, human resource development, state engagement, and logistics parks.
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme: Aims to create “Smart Cities” and advanced industrial hubs.
Startup India: Several programs aimed at supporting entrepreneurs, building a robust startup ecosystem, and transforming India into a country of job creators instead of job seekers were rolled out.
Implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST): As India’s tax reforms, it is seen as crucial in the context of the Make in India initiative.
Unified Payments Interface: For India’s digital economy growth, it is seen as one of the key initiatives to enable ease of doing business.
Ease of Doing Business: The efforts aim to simplify regulations, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and create a more business-friendly environment, significantly boosting investor confidence and supporting the objectives of the Make in India initiative.
NAGAR VAN YOJANA (NVY)

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India achieved a 100-Day Target of 100 Nagar Vans under Nagar Van Yojana (NVY) with the objective to Enhance Urban Greenery.
Key Details:
- Launch: Initiated in 2020 to enhance urban greenery, improve quality of life, and foster social cohesion.
- Financial Support: Offers ?4 lakh per hectare for creation and maintenance of urban forests.
- Area Specification: Nagar Van areas range from 10 to 50 hectares.
- Coverage: Applicable to all cities with Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Achievements
- 100-Day Target: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change achieved a target of 100 Nagar Vans, surpassing it with the approval of 111 Nagar Vans in just 100 days.
- Geographic Spread: These 111 Nagar Vans are distributed across six states and one Union Territory.
Features of Nagar Vans
- Biodiversity Focus: Emphasis on planting fruit-bearing, medicinal, and native species to attract wildlife and maintain ecological balance.
- Community Involvement: Engages citizens, students, and stakeholders through tree planting, educational programs, and sustainable management.
- Design Elements: Each Nagar Van includes two-thirds tree cover and features components like Biodiversity Parks, Smriti Vans, Butterfly Conservatories, Herbal Gardens, and Matri Vans.
Future Goals
- Expansion Plans: Target to develop 1,000 Nagar Vans by 2027, supported by the National Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (National CAMPA).
- Environmental Impact: Aims to protect forest land from degradation and address urban environmental issues such as air pollution and habitat loss.
Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam Campaign
- Launch Date: Introduced on June 5, 2024, during World Environment Day.
- Purpose: Encourages tree planting as a tribute to mothers, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
- Tree Planting Goals: Aims to plant 80 crore trees by September 2024 and 140 crore by March 2025.
- Tracking Efforts: Participants can document their planting through the MeriLiFE portal, where over 75 crore saplings have been recorded.
Recent Initiatives
- Tree Plantation Drive: A recent drive on September 17, 2024, aimed at creating Matri Vans in newly approved Nagar Vans, highlighting community and governmental collaboration for sustainable urban development.
Ideas4LiFE Initiative

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ideas4LiFE portal was launched by Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, at IIT Delhi.
- Purpose: Designed to invite innovative ideas related to products and services that promote environmentally friendly lifestyles.
- Development Partner: Created in collaboration with UNICEF YuWaah.
Key Features of the Ideas4LiFE Portal
- Themes: Aligned with Mission LiFE, focusing on:
- Water Conservation
- Energy Efficiency
- Waste Reduction
- E-Waste Management
- Minimizing Single-Use Plastics
- Embracing Sustainable Food Practices
- Fostering Healthy Lifestyles
- Recognition: Winning ideas will be awarded attractive prizes for both individuals and institutions.
Engagement and Outreach
- Submissions: As of now, the portal has received approximately 3,300 registrations and over 1,000 ideas.
- Social Media Impact: The initiative has garnered 46.5 million impressions and a reach of 13.5 million through social media under the hashtag #Ideas4LiFE.
Collaboration with Educational Institutions
- Partnerships: Collaborations with the University Grants Commission (UGC), All-India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and various educational institutions to promote the Ideathon among students and researchers.
- Objective: Encourage the academic community to contribute innovative, citizen-focused ideas that support sustainable living.
Future Plans
- Evaluation Process: Submitted ideas will be evaluated by a jury, leading to the announcement of shortlisted and winning ideas.
- Implementation: Winning ideas will be included in a national repository, allowing stakeholders, including government bodies and private entities, to nurture and scale these innovations.
Mission LiFE Context
- Definition: Mission LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment) is a campaign initiated at UN Climate Change Conference COP26 in 2021.
- Goals:
- Mobilize at least one billion people for environmental protection.
- Make 80% of villages and urban local bodies environment-friendly by 2028.
- Promote small, everyday actions to combat climate change.
- Philosophy: Emphasizes the P3 model—Pro Planet People—uniting individuals in the commitment to environmental stewardship.
EXERCISE AIKYA

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), in partnership with the Indian Army's Southern Command and the Tamil Nadu State Disaster Management Authority (TNSDMA), recently conducted "EXERCISE AIKYA" in Chennai. This two-day Integrated Symposium and Table Top Exercise (TTEx) aimed to bolster disaster preparedness and response among key stakeholders across Peninsular India.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: "Aikya," meaning "Oneness" in Tamil, sought to unify India’s disaster management community by enhancing collaboration and preparedness.
- Participants: The exercise involved representatives from:
- Six southern states/UTs: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Puducherry.
- Central ministries related to disaster management.
- State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs).
- Armed forces, including the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Response agencies such as the NDRF, Indian Coast Guard, CRPF, CISF, and Railways.
- Early warning agencies including the IMD, NRSC, INCOIS, CWC, and FSI.
- Research institutions like NIDM, NIOT, IIT Madras, and DAE, with Prof. CVR Murty of IIT Madras serving as the Exercise Mentor.
- Focus Areas: The exercise simulated various emergency situations, covering:
- Tsunamis, landslides, floods, cyclones, industrial incidents, and forest fires.
- Recent disaster events in Tamil Nadu, Wayanad, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Discussions: Participants engaged in discussions about:
- Leveraging technology and AI for disaster management.
- Economic impacts of disasters.
- Vulnerabilities specific to the Peninsular region.
- Strategies for improving response times.
Future Plans
"EXERCISE AIKYA" marks a crucial step towards strengthening India’s disaster management framework. The NDMA and the Southern Command plan to conduct similar exercises with other military commands and institutions, including the Army War College and Naval War College, to further enhance national disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
GLOBAL CYBERSECURITY INDEX 2024

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), with an impressive score of 98.49 out of 100.
Role-Modeling Country: This accomplishment places India among ‘role-modeling’ countries, reflecting a strong commitment to cybersecurity practices globally.
Assessment Criteria: The GCI 2024 evaluates national efforts based on five pillars:
-
- Legal Measures
- Technical Measures
- Organizational Measures
- Capacity Development
- Cooperation
- Evaluation Methodology: The index utilized a comprehensive questionnaire comprising 83 questions, which cover 20 indicators, 64 sub-indicators, and 28 micro-indicators, ensuring a thorough assessment of each country's cybersecurity landscape.
- Tier Classification: The GCI 2024 report categorized 46 countries in Tier 1, the highest tier, indicating a strong commitment across all five cybersecurity pillars. Most countries fall into lower tiers, either “establishing” (Tier 3) or “evolving” (Tier 4) their cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Achievements
- Global Standing: India ranks at the top level of global cybersecurity rankings, showcasing its dedication to enhancing cyber resilience and securing its digital infrastructure.
- Government Initiatives:
- Robust Frameworks: Establishment of comprehensive frameworks for cybersecurity and cybercrime laws.
- Sectoral Support: Implementation of Sectoral Computer Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) that provide technical support and incident reporting across various industries.
- Educational Integration: Cybersecurity has been integrated into primary and secondary education curricula to foster informed digital citizens.
- Public Awareness: Targeted campaigns have promoted secure online practices across multiple sectors, including private industry and academia.
- Skill Development and Innovation: The government has provided incentives and grants to enhance skill development and promote research within the cybersecurity sector.
- International Collaborations: India has engaged in numerous bilateral and multilateral partnerships to strengthen its capacity-building and information-sharing efforts.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Overview: Established in 1865, the ITU is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies, becoming a UN agency in 1947.
- Membership: ITU has 193 member countries and over 1,000 associated organizations, including companies and universities.
- Functions: ITU coordinates global radio spectrum allocation, sets technical standards for telecommunication, and works to improve ICT access in underserved communities.
- India's Involvement: India has been an active ITU member since 1869 and a regular participant in the ITU Council since 1952.
PRADHAN MANTRI JANJATIYA UNNAT GRAM ABHIYAN

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan. This mission aims to enhance the socio-economic conditions of tribal communities by saturating more than 63,000 tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts with a total budget of ?79,156 crore.
Budget Breakdown
- Total Outlay: ?79,156 crore
- Central Share: ?56,333 crore
- State Share: ?22,823 crore
Target Beneficiaries
The initiative is expected to benefit over 5 crore tribal people across 549 districts and 2,740 blocks in 30 States/UTs.
Context
- India's Scheduled Tribe (ST) population stands at 10.45 crore, according to the 2011 Census, with more than 705 tribal communities often residing in remote areas. This mission builds upon the successes of the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN), launched on November 15, 2023.
Mission Objectives
- The mission aims to address critical gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood through a comprehensive approach involving 25 interventions across 17 ministries.
Key Goals and Interventions
Goal 1: Developing Enabling Infrastructure
- Housing: Provision of pucca houses under the PMAY (Gramin) for eligible households, along with access to tapped water and electricity.
- Village Infrastructure: Improvement of all-weather road connectivity, mobile connectivity, and educational and health infrastructure.
Goal 2: Promotion of Economic Empowerment
- Skill Development: Enhanced training and self-employment opportunities for ST youth through initiatives like the Skill India Mission and support for tribal marketing.
Goal 3: Universal Access to Good Education
- Education Initiatives: Increase the gross enrollment ratio in schools and higher education, along with setting up tribal hostels for students.
Goal 4: Healthy Lives and Dignified Ageing
- Health Access: Provision of quality health facilities, aiming to meet national standards in maternal and child health indicators through mobile medical units.
Innovative Schemes
- Tribal Home Stay Initiative: Promotion of 1,000 homestays in tribal areas to boost tourism and provide alternate livelihoods. Each household can receive up to ?5 lakh for construction and ?3 lakh for renovations.
- Sustainable Livelihood for FRA Holders: Focus on 22 lakh FRA patta holders, enhancing their rights and providing livelihood support through various government schemes.
- Improving Educational Infrastructure: Upgrading tribal residential schools and hostels to improve local educational resources and retention rates.
- Sickle Cell Disease Management: Establishing Centers of Competence for affordable diagnostic services and prenatal care in regions where the disease is prevalent.
- Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centres (TMMCs): Setting up 100 TMMCs to improve marketing of tribal products and facilitate better prices for producers.
Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP)

- 18 Sep 2024
In News
The recent Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP) Ministerial between the United States and India aimed to enhance collaboration in clean energy innovation, energy security, and the transition to clean energy.
About the Partnership
The meeting reviewed significant achievements and future initiatives across five core pillars:
- Power and Energy Efficiency
- Responsible Oil and Gas
- Renewable Energy
- Emerging Fuels & Technologies
- Sustainable Growth
The SCEP facilitates bilateral cooperation on clean energy, focusing on power, efficiency, renewable resources, emerging technologies, and sustainable practices.
Key Highlights of SCEP
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP)
Launched in August 2023, RETAP aims to create actionable roadmaps for:
- Hydrogen
- Long-duration energy storage
- Offshore wind
- Geothermal technologies
Energy Storage Task Force
This public-private initiative seeks to address:
- Policy
- Safety
- Regulatory challenges
It explores alternatives to lithium-ion technologies, with projects like Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) in Assam and Haryana focusing on grid integration and renewable energy storage.
Modernization of Power Distribution
The meeting underscored India’s advancements in:
- Smart metering
- Power market reforms
- The Indian Railways’ goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2030
India has successfully procured 1.5 GW of round-the-clock renewable energy.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) & Transport Electrification
A comprehensive workshop was launched to enhance R&D, certification, and partnerships for SAF. India’s PM eBus Sewa scheme aims to deploy 10,000 electric buses, promoting electrification in medium and heavy-duty transport.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) & Methane Abatement
Cooperation on CCUS technologies and regulatory frameworks has increased, alongside efforts to reduce methane emissions in the oil and gas sector through collaboration with India’s Directorate General of Hydrocarbons.
Public-Private Collaborations
The importance of public-private dialogues in shaping policies and reducing the costs of clean energy technologies was emphasized.
Initiatives Supporting Clean Energy
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): A global coalition led by India, promoting solar energy collaboration among solar-rich countries.
- Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP): A US-India initiative focusing on hydrogen, energy storage, offshore wind, and geothermal technologies.
- Green Hydrogen Mission (India): Promotes green hydrogen as a clean energy alternative, especially in heavy industries and transportation.
- EU’s Green Deal: A European strategy aimed at achieving climate neutrality by 2050 through clean energy investments and policies.
- PM KUSUM Scheme (India): Supports solar power generation for irrigation, reducing fossil fuel reliance in agriculture.
PM Gram Sadak Yojana-IV

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the proposal of the Department of Rural Development for “Implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana - IV (PMGSY-IV) during FY 2024-25 to 2028-29”.
- The financial assistance is to be provided for the construction of 62,500 Kms road for providing new connectivity to eligible 25,000 unconnected habitations and construction/upgradation of bridges on the new connectivity roads. Total outlay of this scheme will be Rs. 70,125 crore.
Details of the Scheme:
The details of the approval given by the Cabinet are as follows:
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana -IV is launched for financial year 2024-25 to 2028-29. Total outlay of this scheme is Rs. 70,125 crore (Central Share of Rs. 49,087.50 crore and Sate Share of Rs. 21,037.50 crore).
- Under this scheme 25,000 unconnected habitations of population size 500+ in plains, 250+ in NE & Hill Sates/UTs, special category areas (Tribal Schedule V, Aspirational Districts/Blocks, Desert areas) and 100+ in LWE affected districts, as per Census 2011 will be covered.
- Under this scheme 62,500 Km of all-weather roads will be provided to unconnected habitations. Construction of required bridges along the alignment of the all-weather road will also be provided.
Benefits:
- 25,000 unconnected habitations will be provided all weather road connectivity.
- The all-weather roads will play the role of catalysts for the required socio-economic development and transformation of the remote rural areas. While connecting habitations, the nearby government educational, health, market, growth centers will be connected, as far as feasible, with the all-weather road for the benefit of the local people.
- The PMGSY -IV will incorporate international benchmarks and best practices under road constructions such as Cold Mix Technology and Waste Plastic, Panelled Cement concrete, Cell filled concrete, Full Depth Reclamation, use of construction waste and other wastes such as Fly Ash, Steel Slag, etc.
- PMGSY -IV road alignment planning will be undertaken through the PM Gati Shakti portal. The planning tool on PM Gati Shakti portal will also assist in DPR preparation.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- PMGSY is a central government scheme launched in 2000 to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected rural habitations.
- The scheme was originally a 100% centrally-sponsored initiative, but starting from the financial year 2015-16, the funding has been shared between the Central and State governments in a 60:40 ratio.
Exercise AL NAJAH

- 13 Sep 2024
In News:
- Indian Army contingent departed for the 5th edition of the India-Oman Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH on September 12, 2024.
Key Details:
- Location: Rabkoot Training Area, Salalah, Oman.
- Frequency: Exercise AL NAJAH has been held biennially since 2015, alternating between India and Oman. Last edition was conducted at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- Indian Army Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Battalion of the Mechanised Infantry Regiment, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Royal Army of Oman Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Troops of the Frontier Force.
- Objective:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- Focus on operations in a desert environment.
- Tactical Drills:
- Joint Planning
- Cordon and Search Operation
- Fighting in Built-Up Areas
- Establishment of Mobile Vehicle Check Posts
- Counter Drone Operations
- Room Intervention
- Training Exercises:
- Combined field training exercises simulating real-world counter-terrorism missions.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Exchange of best practices in tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations.
- Foster interoperability, goodwill, and camaraderie between the two armies.
- Strengthen defense cooperation and enhance bilateral relations between India and Oman.
4 Years of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)

- 14 Sep 2024
Context:
Celebrating Four Years of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) has marked its fourth anniversary since its launch in 2020. This flagship scheme, managed by the Department of Fisheries under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying, aims to transform India’s fisheries sector into a vibrant and sustainable industry.
About PMMSY
The PMMSY is designed to invigorate the fisheries sector through a comprehensive approach that consolidates various existing schemes and initiatives. It operates as an umbrella scheme with two main components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS)
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS)
The CSS component is divided into:
Non-Beneficiary Oriented Subcomponents:
- Enhancement of Production and Productivity
- Infrastructure and Post-Harvest Management
- Fisheries Management and Regulatory Framework
Fisheries Sector Overview
India stands as the third-largest fish producer globally and the second-largest in aquaculture production. It is also the fourth-largest exporter of fish and fisheries products, experiencing a notable 26.73% growth in exports from FY 2021-22 to FY 2022-23. Andhra Pradesh leads the country in fish production, followed by West Bengal and Gujarat. The sector supports the livelihoods of over 30 million people.
The Department of Fisheries is spearheading the PMMSY to foster a "Blue Revolution" through sustainable and responsible development of the fisheries sector.
Challenges Facing the Fisheries Sector
1. Overfishing: Excessive fishing pressure threatens fish stocks and disrupts ecosystem balance.
2. Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing: Practices such as fishing without proper authorization and using banned gear undermine conservation efforts.
3. Lack of Infrastructure and Technology: Outdated technology and inadequate storage and transportation facilities result in post-harvest losses and reduced productivity.
4. Poor Fisheries Management: Inefficient regulation enforcement and lack of comprehensive data exacerbate overfishing and IUU fishing.
5. Pollution and Habitat Destruction: Industrial pollution and habitat destruction from activities like coastal reclamation impact marine and freshwater ecosystems.
6. Climate Change: Altered oceanic and freshwater environments affect fish distribution and reproductive cycles, disrupting fisheries ecosystems.
7. Socio-Economic Issues: Poverty and limited livelihood options increase the vulnerability of fishing communities.
Government Initiatives for Sector Growth
1. National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB): Established in 2006, the NFDB plans and promotes fisheries development, enhancing production and infrastructure.
2. Blue Revolution: Launched in 2015, this initiative focuses on sustainable development, modern technology adoption, and strengthening fisheries governance.
3. Sagarmala Programme: Also launched in 2015, it aims to boost port-led development and includes projects to develop fishing harbors and cold chain infrastructure.
4. National Fisheries Policy: Introduced in 2020, this policy provides a framework for sustainable fisheries development, focusing on responsible management and socio-economic improvements.
5. Fish Farmers Development Agencies (FFDAs): Established at the district level to provide technical guidance and support to fish farmers.
6. Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Created in 2018-19 with a fund of Rs 7,522.48 crore to address infrastructure needs, resulting in 121 approved projects.
7. Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA): Regulates coastal aquaculture to ensure sustainability and environmental conservation.
Way Forward
The fisheries sector in India holds immense potential due to its extensive coastline and water resources. Key measures to further enhance the sector include:
- Strengthening Monitoring and Enforcement: Combat IUU fishing with better monitoring and regulatory mechanisms.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: Provide financial incentives for adopting modern technologies and sustainable practices.
- Protecting Aquatic Habitats: Ensure the conservation and restoration of vital habitats like mangroves and coral reefs.
- Improving Supply Chain Infrastructure: Develop better market linkages to ensure fair pricing and access to markets.
With these strategies, the PMMSY aims to drive the sustainable growth of India’s fisheries sector and bolster its contribution to the economy and livelihoods.
Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari Initiative

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently launched the ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative via video conferencing from Surat, Gujarat.
Key Points:
- Campaign and Objectives:
- Objective: The initiative seeks to bolster water conservation through extensive public and governmental collaboration.
- Scope: About 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures will be constructed across Gujarat.
- Approach: Emphasizes a Whole-of-Society and Whole-of-Government approach to water management.
- Significance:
- Cultural Significance: PM Modi highlighted that water conservation is deeply embedded in Indian culture, with water revered as a divine entity and rivers considered Goddesses.
- Policy and Virtue: He stated that water conservation transcends policy and is both an effort and a virtue, reflecting social commitment and cultural consciousness.
- Future Challenges: The Prime Minister acknowledged the exacerbating impact of water scarcity due to climate change, urging a shift to the ‘Reduce, Reuse, Recharge, and Recycle’ mantra for sustainable water management.
- Impact of Drought and Water Scarcity:
- Recent Challenges: The drought affecting the Amazon region and other parts of India has highlighted the urgent need for effective water conservation strategies.
- Water Table Decline: Significant declines in river levels, such as the Rio Negro reaching its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) on record, and the death of endangered species due to low water levels underscore the crisis.
- Government Initiatives:
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Aims to provide piped water to every home, with significant progress noted from 3 crore households to over 15 crore.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Focuses on renovation and construction of water sources with widespread public participation.
- Amrit Sarovar: Over 60,000 Amrit Sarovars have been constructed under this campaign, which began during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- Innovative Solutions and Technological Integration:
- Drip Irrigation: Promotion of water-efficient farming techniques like drip irrigation to ensure sustainable agriculture.
- Support for Farmers: Encouragement for cultivating less water-intensive crops such as pulses and millets.
- Role of Industries:
- CSR Contributions: Industries have played a significant role in water conservation through initiatives like Net Zero Liquid Discharge Standards and the completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
- Future Plans: The ‘Jal Sanchay-Jan Bhagidari Abhiyan’ aims to create an additional 24,000 recharge structures.
- Conclusion and Vision:
- Global Leadership: PM Modi expressed his belief that India can become a global leader in water conservation.
- Public Movement: Stressed the importance of continuing public participation in water conservation to make India a model for global sustainability.
Background: The ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative builds on the success of the earlier Jal Sanchay program by involving citizens, local bodies, and industries in water conservation efforts. The initiative aligns with the vision of water security and aims to mobilize collective action for long-term sustainability.
Key Data:
- Construction of 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures.
- Significant increase in tap water connections from 3 crore to over 15 crore households.
- Creation of more than 60,000 Amrit Sarovars across the country.
- Completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
Khelo India Rising Talent Identification will take sports to the doorstep of aspiring champions

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, Shri Anurag Singh Thakur inaugurated the unique Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme amidst much enthusiasm at the Sector 7 sports complex, in Chandigarh recently.
About the KIRTI Programme:
- The KIRTI Programme is an ambitious nationwide initiative aimed at school children between the ages of nine and 18.
- With a dual focus, the scheme strives to uncover hidden talent from every corner of the country while simultaneously utilizing sports as a powerful tool to combat addiction to drugs and digital distractions.
Primary Objectives of KIRTI's Programme:
- Identifying and nurturing talented young athletes from across India, ensuring that no potential goes unnoticed.
- Leveraging sports as a means to steer youth away from harmful addictions and encourage a healthier, more active lifestyle.
- To achieve these goals, KIRTI plans to conduct 20 lakh assessments throughout the year at designated Talent Assessment Centres across the nation.
- The programme launched with a strong start at 50 centers in India, assessing 50,000 applicants in the first phase across 10 sports such as athletics, boxing, wrestling, hockey, and football.
- KIRTI's athlete-centric approach is characterized by its transparent selection methodology, which is grounded in Information Technology.
- The programme employs data analytics based on Artificial Intelligence to predict sporting potential in aspiring athletes, ensuring that talent identification is both objective and data-driven.
- By channeling India's youth towards sports and providing them with the necessary support, KIRTI aims to foster a new generation of athletes and promote a healthier, more active society.
About Khelo India Scheme:
- The Khelo India Scheme is the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India.
- This Central Sector Scheme is designed to instill a sports culture and achieve sporting excellence in the country by leveraging the transformative power of sports and its cross-cutting influence.
- The Khelo India Scheme encompasses multiple verticals, with "Sports Competitions and Talent Development" being a key focus area.
- Within this vertical, the "Talent Identification and Development" component plays a crucial role in identifying and nurturing athletes at both the grassroots and elite levels.
- The primary objective is to strengthen the sports ecosystem in India by cultivating talent and providing athletes with the necessary resources and support to excel in their respective disciplines.
- Through the Khelo India Scheme, the government aims to promote sports as a way of life, encouraging greater participation and creating a robust platform for athletes to showcase their skills.
- By investing in sports infrastructure, training, and competition opportunities, the scheme seeks to establish India as a global sporting powerhouse and inspire future generations to embrace the spirit of sportsmanship and athletic achievement.
River Devika Rejuvenation Project (PIB)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology sheds light on the progress of the River Rejuvenation Project, Devika. This initiative, inspired by the Namami Ganga campaign, aims to safeguard the sacred Devika River’s purity and health.
Facts About:
Comprehensive Waste Management:
- Focus on Liquid Waste Management.
- Creation of a network of pipes and manholes connecting households.
- Objective: Efficient disposal of liquid waste, preventing pollution, and preserving the sanctity of the river.
Complementary Solid Waste Management:
- Encompasses responsible collection, disposal, and management of solid waste.
- Essential to prevent environmental degradation and maintain river and surrounding health.
Financial Allocation Breakdown:
- Project investment exceeds Rs 190 crores.
- Allocation shared between Central and Union Territory (UT) at a 90:10 ratio.
Empowering Communities through PRIs:
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) pivotal for grassroots project success.
- PRIs’ involvement enhances community engagement, fosters ownership, and promotes sustainable development practices.
Devika River:
- Originates from Suddha Mahadev temple in Jammu and Kashmir’s Udhampur district.
- Flows through western Punjab (now Pakistan) where it merges with the Ravi River.
Cultural Significance:
- Revered by Hindus as sister of the Ganga River.
- Devika River believed to be a manifestation of Goddess Parwati, benefiting the people of MaderDesha (areas between river Ravi and Chenab).
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1946187
