IMF's World Economic Outlook (WEO)
- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
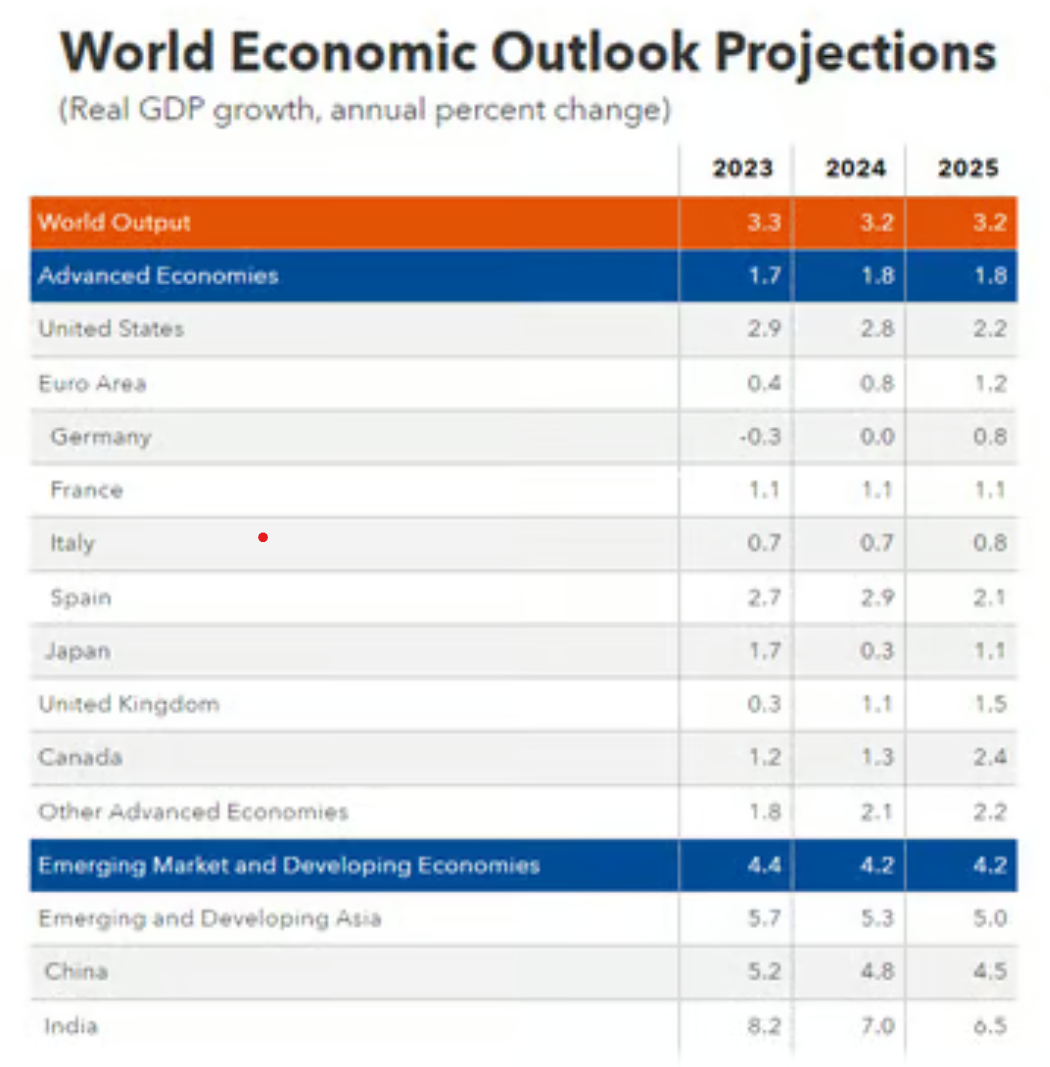
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has maintained India’s GDP growth forecast at 7% for FY2024, marking a moderation from 8.2% in 2023.
- FY2025 Projection: Growth is expected to slow further to 6.5% in FY2025.
- India’s growth is expected to be stronger than most other large economies, yet the downward revision reflects challenges in the global economy and moderation in domestic economic momentum.
Global Economic Growth Projections:
- Global Growth (2024-2025): Global growth is projected at 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, which is stable but modest. This growth rate is largely unchanged from previous IMF forecasts.
- Long-Term Outlook: The IMF's long-term projection for global growth is 3.1%, which is considered subpar compared to pre-pandemic growth rates, signaling a potential era of low growth.
Key Risks and Uncertainties:
- The IMF highlights several downside risks to global growth, including:
-
- Monetary tightening: Central banks' high-interest rate policies to combat inflation could have long-term negative effects on economic growth and financial stability.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, could disrupt global supply chains and trade, exacerbating inflation and slowing growth.
- China’s Economic Slowdown: China, the world’s second-largest economy, is facing a slower growth trajectory, especially in its real estate sector, which is dragging down its overall growth.
- Structural Challenges: The aging population and weak productivity are long-term growth inhibitors in many advanced economies, adding uncertainty to future growth prospects.
-
- Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
- 2023: Global inflation is expected to reach 6.7%.
- 2024: It is forecast to fall to 5.8%, with advanced economies expected to return to inflation targets sooner than emerging markets.
- 2025: A further decline to 4.3%.
- The primary driver of disinflation is not interest rate hikes but the unwinding of pandemic-related shocks, supply chain improvements, and the gradual return of labor supply.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks are likely to ease policies once inflation nears target levels, but risks of further commodity price spikes or geopolitical tensions could delay this.
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
US and Europe Growth:
- Emerging Markets and Developing Economies:
- Growth Outlook: The IMF forecasts growth in emerging markets and developing economies at 4.2% for 2024 and 2025, with a slight moderation to 3.9% by 2026.
- Emerging Asia: Growth in emerging Asia (led by India and China) is expected to slow, from 5.7% in 2023 to 5% in 2025.
- India’s Relative Strength: India’s growth continues to outperform many emerging economies, though the slowdown from 8.2% in 2023 to 7% in 2024 reflects global economic headwinds.
- Income Inequality Risks:
- The IMF warns that low growth over an extended period (4+ years) could exacerbate income inequality within countries, as sluggish growth affects job creation and wage growth.
- Countries with slow economic recovery are likely to see a widening gap between rich and poor, undermining social cohesion and stability.
World Energy Outlook 2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Energy Agency's (IEA) World Energy Outlook 2024 offers an in-depth analysis of global energy trends, emphasizing the shift towards clean energy, growing energy demand, and the effects of geopolitical conflicts.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth:
- India was the fastest-growing major economy in 2023 with a 7.8% growth rate.
- On track to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2028.
- Surpassed China in 2023 to become the most populous country globally, despite a fertility rate below replacement level.
- Energy Demand Surge:
- India is projected to experience the highest increase in energy demand over the next decade.
- By 2035, India’s total energy demand is expected to rise by 35%, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increased living standards.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Growth:
- Over 12,000 cars are expected to be added to Indian roads daily by 2035.
- Built-up space is set to increase by over 1 billion square meters annually, surpassing the total built space of South Africa.
- Industrial Expansion:
- Iron and steel production is expected to grow by 70% by 2035.
- Cement output is set to increase by 55%.
- Air conditioner stock to grow more than 4.5 times, with electricity demand from cooling expected to exceed Mexico’s total consumption in 2035.
- Energy Supply & Coal:
- India’s electricity generation capacity is projected to nearly triple to 1,400 GW by 2035.
- Coal remains a dominant energy source despite growth in renewables:
- Coal-fired power capacity will increase by 60 GW by 2030.
- Coal will continue to account for over 30% of electricity generation even as solar PV expands.
- By 2035, coal use in industries like steel and cement will grow by 50%.
- Renewable Energy & Clean Tech:
- India is on track to become a global leader in renewable energy, with a nearly 3x increase in electricity generation capacity.
- The country is expected to have the world’s third-largest installed battery storage capacity by 2030.
- By 2030, low-emission energy sources (solar, wind, nuclear) are expected to generate over 50% of India’s electricity.
- Electric Vehicles & Oil Demand:
- The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to peak India’s oil demand by the 2030s, reducing reliance on oil for transportation.
- Oil demand for transport will decline as EVs proliferate, though demand for oil in other sectors (e.g., petrochemicals) will continue.
- Net Zero Target:
- India aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
- By 2035, clean energy generation could be 20% higher than current policy projections, thanks to electric mobility, hydrogen use, and improved energy efficiency.
- CO2 emissions are projected to be 25% lower than under the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS).
- Policy Support:
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- PM-KUSUM scheme for solar energy in agriculture.
- National Solar Mission.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme to boost domestic solar PV manufacturing.
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- Global Energy Trends:
- Geopolitical Risks: Global energy security remains affected by geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine conflict, Middle East tensions).
- Energy Transition: Global shift toward clean energy, with solar and wind power investments accelerating.
- Oil & Gas Surplus: Oil and LNG supply expected to increase, putting downward pressure on prices by the late 2020s.
- Electric Mobility: EVs projected to account for 50% of new car sales by 2030.
- Energy Efficiency: Despite efforts, global targets for doubling energy efficiency by 2030 are unlikely to be met with current policies.
IEA Overview:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) provides analysis and policy advice on energy security, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
- Established in 1974, it now includes 31 member countries and 13 association countries, including India.
- Major publications: World Energy Outlook, India Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report.
Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR)

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) released the latest global financial stability.
About Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR):
- The Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) is a semiannual report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- It is released twice per year, in April and October.
- The GFSR provides an assessment of the global financial system and markets and addresses emerging market financing in a global context.
- It focuses on current market conditions, highlighting systemic issues that could pose a risk to financial stability and sustained market access by emerging market borrowers.
Key Points from the Report:
- The report highlights significant risks facing the global financial system, including persistent high inflation, increased lending in unregulated credit markets, and a rise in cyber-attacks targeting financial institutions.
- It underscores geopolitical tensions, such as conflicts in West Asia and Ukraine, as potential factors disrupting aggregate supply and driving up prices, possibly constraining central banks from lowering interest rates.
- India emerged as the second-largest recipient of foreign capital in 2023, following the United States, though this trend could shift rapidly if Western central banks signal prolonged high-interest rates.
- Of concern is the expansion of the unregulated private credit market, where non-bank financial institutions extend credit to corporate borrowers, posing potential threats to the broader financial system.
- Many borrowers in this market lack financial stability, with numerous entities unable to cover interest costs with current earnings, highlighting underlying risks.
Gaia-BH3

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
European astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery by identifying Gaia-BH3, a colossal black hole located just 2,000 light years away from Earth within the Milky Way, revolutionizing our comprehension of star formation.
What Is Gaia-BH3?
- Gaia-BH3, a stellar black hole in the Milky Way galaxy, has been identified as the most massive one discovered to date.
- The European Space Agency's Gaia mission detected Gaia-BH3 due to its distinctive 'wobbling' effect on a companion star orbiting it.
- Through the use of the Very Large Telescope at the European Southern Observatory in Chile's Atacama Desert and other ground-based observatories, researchers confirmed its enormous mass.
- With a mass 33 times greater than our sun, Gaia-BH3 is situated in the Aquila constellation at a distance of 1,926 light-years from Earth, earning it the title of the second-closest known black hole.
- Gaia BH1, located about 1,500 light-years away, remains the closest known black hole to Earth with a mass approximately 10 times that of our sun.
- While Gaia-BH3 holds the distinction of being the most massive stellar black hole in our galaxy, it pales in comparison to Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the Milky Way's center, which boasts a staggering mass of roughly 4 million times that of the sun.
Difference Between Stellar and Supermassive Black Holes:
- Stellar and supermassive black holes are two distinct types of cosmic phenomena, each with unique characteristics and origins.
- Stellar-mass black holes result from the gravitational collapse of a single star or the merger of two neutron stars, resulting in masses comparable to stars.
- Their mass typically ranges from three to fifty times that of our sun.
- In contrast, supermassive black holes boast a mass exceeding 50,000 times the solar mass, often reaching into the millions or billions.
- The formation of supermassive black holes remains a mystery to scientists, as they are too massive to have formed from a single star's collapse.
- Their consistent presence at the center of galaxies suggests a potential connection to galactic formation.
- While our understanding of these cosmic giants continues to evolve, one thing is clear: both stellar and supermassive black holes are awe-inspiring fixtures in our universe.
Revenue-Based Financing

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Revenue-based financing (RBF) is increasingly popular among startups and digital SMEs due to a lack of venture capital and limited access to traditional credit options.
What Is Revenue-Based Financing?
- Revenue-based financing is a method of raising capital for a business from investors who receive a percentage of the enterprise's ongoing gross revenues in exchange for the money they invested.
- In a revenue-based financing investment, investors receive a regular share of the business's income until a predetermined amount has been paid.
- Typically, this predetermined amount is a multiple of the principal investment and usually ranges between three to five times the original amount invested.
How Revenue-Based Financing Works?
- Capital investment: An investor or a group of investors provides capital to a company (but not as a traditional loan nor in exchange for equity in the company).
- Revenue percentage agreement: In return for the capital, the company agrees to give the investor a fixed percentage of its gross revenues each month.
- Repayment structure: The company repays the invested capital through payments based on monthly or annual revenue.
- The amount paid each month varies as it is directly tied to the company’s revenue for that month.
- Repayment cap or term: There is usually a cap on the total amount to be repaid, often set as a multiple of the original investment (e.g., 1.5x or 2x the initial amount).
- Alternatively, the repayment might continue until a specific term is reached, such as a number of years.
Comparing Revenue-based Financing to Debt and Equity-based Models:
- While revenue-based financing shares similarities with debt financing in terms of regular investor repayments, it differs notably as it doesn't involve interest payments.
- Instead, repayments are based on a predetermined multiple, yielding returns higher than the initial investment.
- Moreover, unlike traditional debt arrangements, revenue-based financing doesn't necessitate collateral.
- Additionally, unlike equity-based models, it doesn't entail transferring ownership stakes in the company to investors.
World Energy Outlook 2023 (IEA)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released the World Energy Outlook (WEO) Report 2023.
About World Energy Outlook 2023:
- This flagship publication of the International Energy Agency (IEA) has appeared every year since 1998.
- It provides in-depth analysis and strategic insights into every aspect of the global energy system.
- This year, the report delves into how changes in economies and energy usage are meeting the increasing demand for energy amid geopolitical tensions and fragile energy markets.
- It evaluates the evolution of energy security fifty years after the establishment of the IEA and looks at what's necessary at the COP28 climate conference in Dubai to support the 1.5 °C goal.
- The publication analyzes today's energy trends, covering areas like investment, trade flows, electrification, and energy access.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an independent inter-governmental organization operating within the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Its mission involves collaborating with governments and industry to create a secure and sustainable energy future.
- Established in 1974 to safeguard oil supplies, it was a response to the 1973-1974 oil crisis, which exposed the vulnerability of industrialized nations to oil import dependencies due to an oil embargo.
- Comprising 31 member countries and eleven association countries, IEA candidates must be OECD members.
- India joined as an Associate member in 2017.
- The IEA publishes reports such as the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, World Energy Statistics, and Net Zero by 2050.
INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION OUTLOOK 2023 (Down to Earth)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), published the "International Migration Outlook 2023."
Facts About:
- In 2021 and 2022, India had the largest migration flows to nations that are members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- In terms of citizenship, 0.13 million Indians became citizens of an OECD nation in 2021.
- The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has caused the greatest level of internal displacement and refugee inflows into the OECD, with over 10 million people becoming internally displaced or refugees.
- In terms of workers, migration flows from India (+172 percent), Uzbekistan (+122 percent), and Turkey (+240 percent) increased dramatically, making them the primary countries of origin after Ukraine.
About the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- The OECD is an international group of 38 countries that aims to foster economic development, and cooperation, and combat poverty by promoting economic stability.
- It was founded in 1961, by 18 European nations, the United States, and Canada.
Its headquarters are in Paris, France.
- Primary Goal: The primary goal of the OECD is to create policies that promote prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being for everyone.
- They produce economic reports, data, and predictions about global economic growth.
- The OECD also works to combat bribery and financial crimes worldwide, maintaining a list of uncooperative tax havens.
- India is not a member of the OECD, but a key economic partner.
