2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held with the aim of promoting lighthouse tourism and celebrating India’s maritime legacy.
Strategic Importance of the Lighthouse Projects
- The Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW) has invested significantly in developing lighthouses as tourist hubs. The festival marks a concerted effort to integrate tourism with the preservation of these iconic structures.
- Lighthouse tourism has witnessed a remarkable increase of over 400% in visitor numbers since 2014, as part of India's broader vision to promote the blue economy.
-
- From just 4 lakh visitors in 2014, the footfall surged to 16 lakh in 2023-24, with over 9 lakh tourists already in the first half of FY 2024-25.
-
Key Projects and Announcements at the Festival
- New Lighthouses: The announcement of the two new lighthouses at Chaumuck and Dhamra along Odisha’s coastline is significant for enhancing coastal infrastructure and promoting maritime tourism in the state.
- Kalwan Reef Lighthouse: Located in Jamnagar, Gujarat, this lighthouse is part of a broader effort to enhance maritime navigation and heritage conservation along India’s western coastline.
- Development of Coastal Communities: Highlighted the importance of empowering coastal communities, particularly those living around lighthouses, to preserve and promote these structures as national cultural icons. These communities are expected to play a crucial role in lighthouse preservation, as well as in tourism and local economic development.
- Paradip Port Initiatives: Additionally, major infrastructure projects at Paradip Port, such as a stacker-cum-reclaimer and a flyover bridge, were inaugurated to further bolster the port’s capabilities and enhance its role in maritime logistics. The Sagarmala Programme also continues to transform Paradip Port into a mega port with a projected handling capacity of 500 MTPA by 2047.
Economic and Employment Impact
The development of 75 iconic lighthouses across 9 coastal states and one Union Territory is not only aimed at tourism development but also focuses on job creation. As of 2024:
- More than 150 direct jobs and 500 indirect jobs have been created in sectors such as hospitality, transportation, and local crafts, driven by the increasing footfall at these tourist destinations.
- The creation of modern amenities at these lighthouses, such as museums, amphitheaters, and children’s parks, has helped in transforming lighthouses into multifaceted tourism hubs that attract both domestic and international tourists.
Collaborative Efforts for Preservation and Promotion
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encouraging collaboration between the government, local communities, and private stakeholders to develop and maintain lighthouses as sustainable tourist destinations.
- National Framework: A central association will be created to manage coastal societies surrounding lighthouses, enabling local communities to actively participate in their preservation, protection, and promotion.
- Cultural Integration: The event also underscored the need for integrating cultural heritage with tourism development, using the lighthouses as platforms to showcase local art, cuisine, and history.
COP16 to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 16th Conference of the Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) will take place in Cali, Colombia, from October 21, 2024. This marks the first gathering since the adoption of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) in 2022.
About Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Adopted in 1992, the CBD is the most comprehensive international treaty focused on biodiversity conservation, the sustainable use of natural resources, and the fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources. It has been ratified by 196 countries, making it a key global instrument for biodiversity governance.
Key Objectives of the CBD
- Conservation of Biodiversity: Protecting genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
- Sustainable Use of Resources: Ensuring resources are used in a way that does not deplete or degrade biodiversity.
- Fair Sharing of Benefits: Ensuring that benefits from genetic resources are shared equitably with countries of origin.
Notable Frameworks within CBD
- Nagoya Protocol (2010): Establishes a framework for the fair and equitable sharing of benefits from the utilization of genetic resources.
- Cartagena Protocol (2000): Regulates the transboundary movement of living modified organisms (LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology.
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)
- Adoption: The KMGBF was adopted at COP15 in 2022, following the Kunming Declaration.
- Targets: The framework includes 23 targets for 2030 and 4 global goals for 2050, aimed at reversing biodiversity loss and promoting sustainability.
- Notably, the 30x30 Target aims for 30% of the world’s land and oceans to be conserved by 2030. This is a key agenda item at COP16.
- The framework also emphasizes equitable access to genetic resources and the sharing of benefits from their use (Target 13).
Challenges and Issues at COP16
- Benefit-Sharing from Digital Sequence Information (DSI):
- A key issue is the fair sharing of benefits from digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources. The adoption of a global mechanism for this issue is still pending, as negotiations between developed and developing countries remain unresolved.
- Developed nations advocate for unrestricted access to genetic materials in exchange for voluntary contributions to a global fund.
- Developing nations seek a more equitable system, aligned with the CBD's principles of fair benefit-sharing.
- A key issue is the fair sharing of benefits from digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources. The adoption of a global mechanism for this issue is still pending, as negotiations between developed and developing countries remain unresolved.
- 30x30 Target Progress:
- The 30x30 target, which aims to conserve 30% of land and oceans by 2030, is far from being met:
- 17.5% of land and 8.4% of oceans are currently under protection.
- Concerns persist about the effectiveness of these protected areas, as studies suggest they may not be sufficient for long-term biodiversity conservation.
- The 30x30 target, which aims to conserve 30% of land and oceans by 2030, is far from being met:
- Financial Commitments (Target 19):
- Developed countries have pledged $20 billion annually for biodiversity financing by 2025. However, progress is slow:
- By September 2024, only $8.2 billion (41% of the target) had been committed.
- COP16 will assess whether this target can be met, with further announcements expected.
- Developed countries have pledged $20 billion annually for biodiversity financing by 2025. However, progress is slow:
- Implementation Gaps:
- Countries are required to set national targets aligned with the KMGBF. As of COP16, only 100 parties have submitted their targets, and 30 countries have updated their National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs).
- A significant implementation gap remains in translating these targets into concrete actions.
Focus Areas for COP16
- Strengthening the 30x30 Target:
- COP16 will push for enhanced efforts to meet the 30x30 conservation goal. There is a need for better management and monitoring of protected areas to ensure they contribute to biodiversity preservation.
- Finalizing Benefit-Sharing Mechanism:
- Countries will focus on finalizing the multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism for genetic resources and DSI. The goal is to ensure that countries benefiting from genetic resources share those benefits with the countries of origin, addressing the issue of biopiracy and ensuring equitable access.
- Financial Commitment and Tracking:
- The financial shortfall for biodiversity conservation will be a critical discussion point. Effective monitoring of the biodiversity finance tracker will be needed to ensure that developed countries meet their $20 billion/year commitment.
- Addressing Implementation Gaps:
- There is a need to enhance monitoring and reporting mechanisms, improve national strategies, and align financial support with on-ground conservation efforts.
eShram-One Stop Solution

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
- The ‘eShram-One Stop Solution’ will be launched on 21 October 2024 by the Union Minister of Labour & Employment and Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Objective: To provide easy access to various social security and welfare schemes for unorganized workers in India.
Key Features
- Mediator Platform: The eShram-One Stop Solution will act as an intermediary to facilitate the integration of multiple government schemes for unorganized workers, ensuring efficient access to services and support.
- Information Integration: It will integrate data on beneficiaries across various social security and welfare programs meant for unorganized workers, providing a single point of access.
- Target Group: Aimed at unorganized workers, including daily wage earners, migrants, and others who do not have regular formal employment.
Benefits
- Awareness & Accessibility: The platform will make unorganized workers aware of various government schemes tailored to their needs, helping them access benefits more easily.
- Effective Scheme Implementation: The eShram-One Stop Solution will aid in the identification and implementation of welfare schemes for faster saturation and coverage.
Integration with Existing Schemes
- 12 Integrated Schemes: Currently, 12 social security schemes from different ministries/departments have already been mapped with eShram.
eShram’s Progress So Far
- Launch: eShram was launched on 26 August 2021.
- Achievements: Over 30 crore unorganized workers have been enrolled, highlighting the widespread impact and popularity of the initiative among the target population.
Kala-azar Disease
- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
India to seek WHO certification for eliminating disease.
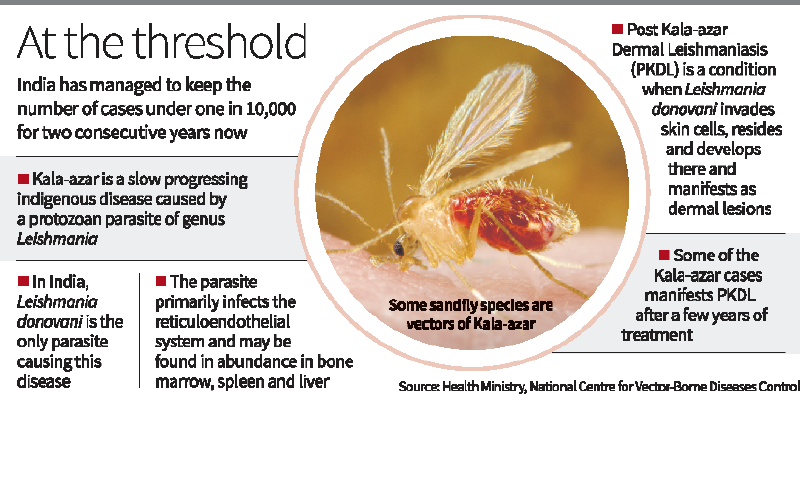
Overview of Kala-Azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
- Cause: Kala-azar is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani, transmitted by the bite of infected female sandflies (Phlebotomus argentipes in India).
- Symptoms: Includes irregular fevers, weight loss, swelling of the spleen and liver, severe anaemia. If untreated, it is fatal in over 95% of cases.
- Affected Areas: Historically, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and parts of Uttar Pradesh report the highest number of cases, with Bihar alone accounting for over 70% of India's cases.
India's Achievement in Kala-Azar Control
- Current Status:
- India has managed to maintain Kala-azar case numbers below 1 per 10,000 population for two consecutive years.
- This meets the WHO's criteria for elimination certification.
- 2023 and 2024 Statistics:
- 2023: 595 cases and 4 deaths.
- 2024 (so far): 339 cases and 1 death.
WHO Certification for Elimination
- WHO's Target: The World Health Organization aims to eliminate Kala-azar as a public health problem by 2030.
- Elimination Criteria: A country can be certified when:
- Local transmission is interrupted for a specified period.
- There is a system in place to prevent re-emergence of the disease.
- Global Context: Bangladesh is the first country to have eliminated Kala-azar, receiving WHO certification in October 2024, after reporting fewer than 1 case per 10,000 people for three consecutive years.
India's Kala-Azar Elimination Strategies
- National Health Policy (2002): Initially set the target to eliminate Kala-azar by 2010, revised multiple times, and is now aiming for 2030.
- Key Strategies:
- Active Case Detection: Identification and treatment of all cases.
- Vector Control: Targeting sandfly breeding grounds through insecticides and environmental management.
- Community Awareness: Educating the public on disease prevention and early diagnosis.
- Improved Surveillance: Ensuring rapid diagnosis and treatment access, including the use of the rK39 diagnostic kit.
- Integrated Vector Management: Combining insecticide spraying with environmental changes to reduce sandfly populations.
Challenges and Areas of Focus
- Root Causes: Persistent issues like poverty, inadequate sanitation, and malnutrition contribute to the spread of Kala-azar, particularly in rural, impoverished areas.
- Long-term Solutions:
- Strengthen vector control and improve sanitation.
- Address socio-economic factors like poverty and displacement.
- Invest in research for vaccines and new treatments.
Public Health Impact and the Way Forward
- Elimination Milestone: If India continues to reduce cases, it will join Bangladesh in eliminating Kala-azar as a public health threat.
- Sustaining Gains:
- Surveillance and quick response to new cases remain critical.
- Expand access to rapid diagnostic tools and effective anti-parasitic treatments.
- Focus on inter-sectoral convergence, integrating efforts from various government sectors, including health, sanitation, and housing.
Naseem-Al-Bahr 2024

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise Naseem-Al-Bahr was held in Goa from October 2024.
Naseem-Al-Bahr Exercise Overview
- Indian and Omani Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand (warship) and Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft.
- Royal Navy of Oman: Vessel Al Seeb.
- Initiation: Launched in 1993, marking a long-standing strategic partnership between India and Oman.
- Structure: The exercise is conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional Interactions: Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), planning conferences.
- Social & Sports Engagements: Informal activities to foster mutual understanding.
- Sea Phase:
- Naval Operations:
- Gun firings at surface inflatable targets.
- Close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopter Operations: INS Trikand’s helicopter performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- Aircraft Support: Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data to enhance operational coordination.
- Naval Operations:
- Harbour Phase:
Key Highlights of the 2024 Exercise
- Interoperability: The exercise focused on improving operational coordination and enhancing mutual understanding of naval practices.
- Cohesion: The Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb to further strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthening Ties: Naseem-Al-Bahr reaffirms the strong strategic relationship between India and Oman.
- Regional Collaboration: This exercise exemplifies India's growing collaboration with like-minded nations in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Broader Defence Relations:
- Oman is the first GCC country to conduct such bilateral naval exercises with India.
- Both countries also engage in other defence exercises:
- Army: Al Najah.
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge.
Trade Relations Between India and Oman (2022):
- Oil: India is the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil exports, following China.
- Non-oil Exports: India is Oman's fourth-largest market for non-oil exports, after UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia.
- Imports: India is the second-largest source of Oman's imports, following the UAE.
- Ongoing Trade Agreement: Both nations are currently negotiating a trade agreement to further boost bilateral economic cooperation.
Musaned Digital Platform

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Saudi Arabia Launches Musaned Digital Platform to Ensure Wage Protection for Foreign Workers.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of Musaned:
- Musaned is a digital platform launched by Saudi Arabia to ensure wage protection and improve working conditions for foreign workers, particularly those in domestic (household) employment.
- The platform aims to safeguard workers' rights, create a stable working environment, and reduce illegal immigration.
- Coverage:
- The platform benefits foreign workers from 10 African countries (including Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya) and 9 Asian countries (including India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Sri Lanka).
- Key Features:
- Employment Contract Access: Workers can check and track their employment contracts and receive updates via the Musaned labour app.
- Financial Transaction Tracking: The platform monitors financial transactions between employers and foreign workers, ensuring employers meet their contractual obligations.
- Integration with Benefits: Musaned can be linked to contract insurance and health benefits, providing additional protection for workers.
- Objectives:
- Wage Protection: Ensures timely and fair wages for foreign workers.
- Human Rights Protection: Promotes human rights by holding employers accountable for fulfilling their obligations.
- Vision 2030 Alignment: Supports Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 by improving the work environment and contributing to legal labor migration.
- Impact:
- The platform is expected to help secure workers’ rights, especially for domestic workers, and provide a more transparent, accountable framework for employment relations in the country.
Musaned is a significant step by Saudi Arabia to enhance the security and welfare of foreign workers, aligning with the Kingdom's broader goals of economic reform and social development under Vision 2030. The platform will provide greater transparency, protect workers’ rights, and contribute to a more regulated and sustainable labor market.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
GE’s LM2500 Marine Engines to Power Indian Navy’s Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)
Key Highlights:
- Engine Selection:
- General Electric’s LM2500 marine gas turbines have been chosen to power the Indian Navy's Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV), currently being built by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Project Details:
- Number of Vessels: Six NGMVs are under construction.
- Contract Value: ?9,805 crore, awarded by the Defence Ministry.
- Delivery Schedule: The first deliveries are expected to commence in March 2027.
- Key Components and Suppliers:
- GE Aerospace will deliver six LM2500 engine kits to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for assembly and testing at their Industrial and Marine Gas Turbine Division in Bengaluru.
- GE will also supply the composite base, enclosure, and a full set of auxiliary systems for the gas turbines.
- LM2500 Marine Gas Turbine:
- The LM2500 turbine is known for its reliability and high power output, making it ideal for the NGMV mission.
- Top Speed: 35 knots (64 km/h).
- It is central to the propulsion system, meeting the stealth and power demands of the new missile vessels.
- Capabilities of NGMVs:
- Role: Designed for offensive missions, the NGMVs will be equipped for anti-surface warfare, maritime strike operations, and sea denial.
- Speed & Stealth: Capable of speeds up to 35 knots while maintaining stealth, these vessels will be difficult for enemy ships to detect.
- Weapons: They will carry a variety of anti-surface weapons, including the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, loitering munitions, unmanned vehicles, and other guided weapons.
- Operational Roles:
- Offensive: The NGMVs will engage in attacking enemy warships, merchant ships, and land-based targets.
- Defensive: They will also be used for local naval defense operations, including the seaward defense of offshore development areas and defending choke points.
- Strategic Importance:
- The NGMVs will significantly enhance India’s maritime strike capability and provide a formidable presence in strategic sea routes, especially in regions like choke points and offshore development areas.
- Cochin Shipyard’s Role:
- After successfully constructing INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, CSL is now focusing on the NGMV project, along with building anti-submarine warfare shallow water crafts for the Indian Navy, currently in various stages of construction.
- Partnerships:
- In 2023, GE Aerospace and HAL signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to expand their collaboration on marine gas turbines, including assembly, inspection, and testing (AIT) of the LM500 turbines.
- To date, GE Aerospace has delivered 24 marine gas turbine kits to HAL, supporting India’s Make-In-India initiative.
- Global Impact:
- The LM2500 gas turbine is used by 714 vessels globally, reinforcing its reputation for reliability and availability in critical maritime defense systems.
First Chief Minister of J&K UT Takes Charge
- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Omar Abdullah sworn in as J&K CM; Surinder Kumar Choudhary is Deputy CM
Key Highlights:
- Omar Abdullah’s Political Context:
- This marks Omar Abdullah's second term as Chief Minister, after his tenure in 2009.
- He becomes the first Chief Minister of Jammu and Kashmir after the region’s special status was revoked and it was reorganized as a Union Territory in 2019.
- Challenges as CM of a Union Territory:
- Omar Abdullah acknowledged the unique challenges of serving as Chief Minister in a Union Territory and expressed hope that J&K’s Union Territory status would be temporary.
- Public Service and Security Measures:
- In his first official instructions, Abdullah asked the Director General of Police (DGP) to avoid creating “green corridors” or traffic halts during his movements. He also requested the minimization of sirens and aggressive security gestures, emphasizing minimal public inconvenience.
- Legal Context:
- Oath of Office: As per Article 164(3) of the Indian Constitution, the Chief Minister and other ministers are sworn in by the Governor or Lieutenant Governor in Union Territories.
- Abdullah is the first CM of the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir post the abrogation of Article 370 and the transition of J&K from a state to a Union Territory in 2019.
- Revocation of President's Rule:
- President’s Rule (under Article 356) was revoked following the election results, signaling the restoration of a functioning elected government after direct central governance in the region.
Karmayogi Saptah – National Learning Week

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ‘Karmayogi Saptah’ - National Learning Week on 19th October at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Context:
- The National Learning Week is a key event in the ongoing Mission Karmayogi initiative, aimed at building a civil service rooted in Indian ethos with a global outlook.
- Objective:
- To promote capacity building for civil servants through competency-linked learning.
- To align civil servants with national goals and foster a "One Government" approach.
- About National Learning Week (NLW):
- Largest learning event for civil servants, focused on individual and organizational growth.
- Encourages lifelong learning and continuous professional development.
- Provides fresh impetus to the Mission Karmayogi initiative, launched in September 2020, aimed at a future-ready, citizen-centric civil service.
- Learning Targets for Karmayogis:
- Each civil servant (Karmayogi) must complete at least 4 hours of competency-linked learning during the week.
- Learning opportunities include:
- Role-based modules on iGOT (Integrated Government Online Training platform).
- Webinars, public lectures, and policy masterclasses by prominent experts.
- Focus on improving skills for citizen-centric service delivery.
- Workshops & Seminars:
- Ministries, departments, and organizations organized domain-specific workshops and seminars.
- The goal is to enhance skills and knowledge, fostering better public service delivery.
- Outcomes:
- Strengthened alignment of civil servants with national priorities and goals.
- Enhanced individual competencies to better address citizen needs.
- A stronger commitment to continuous learning within the civil service.
Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
- India has extended a ?487.60 crore Line of Credit (LoC) to Mauritius for financing a water pipeline replacement project.
- This initiative is part of the Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS), which supports developmental projects in partner countries through concessional loans.
About the IDEAS Scheme
- Origin: Launched in 2003-04 as the India Development Initiative, later renamed as IDEAS Scheme.
- Objective: To promote India’s political, economic, and strategic interests by providing developmental assistance to developing countries.
- Administering Body: The scheme is managed by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) with support from the Exim Bank.
Key Features of the IDEAS Scheme
- Lines of Credit (LoCs):
- Provides LoCs to developing countries for funding projects in various sectors, including:
- Infrastructure
- Water supply
- Education
- Other key developmental areas.
- Provides LoCs to developing countries for funding projects in various sectors, including:
- Project Recommendations:
- Projects funded under the scheme are recommended by MEA and are aimed at bolstering socio-economic development in the partner countries.
- Concessional Financing:
- The scheme offers concessional terms for the financing of these projects, reducing the financial burden on the recipient countries.
- Diplomatic and Strategic Benefits:
- The IDEAS scheme strengthens India’s diplomatic ties and fosters goodwill with countries in the Global South.
- Focus on Development:
- It aims to support key developmental goals in partner countries while advancing India's role as a leader in global development cooperation.
Significance
- The Mauritius water pipeline project is a part of the larger efforts under IDEAS to support infrastructure and socio-economic development in partner nations, helping to improve the quality of life and fostering closer bilateral relations.
Scam se Bacho Campaign

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Government and Meta join forces for "Scam se Bacho" Campaign to tackle rising online scams.
Key Details
- The "Scam Se Bacho" initiative aims to create a safer, more secure digital India by empowering users to protect themselves against growing cyber threats, contributing to the resilience of India’s digital progress.
- Objective: To combat rising online scams and cyber frauds by promoting digital safety and vigilance across India.
- Partners:
- Meta (formerly Facebook)
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
Purpose and Vision
- Goal: Empower Indian citizens with the knowledge and tools to protect themselves from online scams and cyber threats.
- Strategic Focus:
- Foster a culture of digital safety and vigilance.
- Align with the Digital India initiative, which has seen extraordinary growth in digital services, including 900 million internet users and leadership in UPI transactions.
- The campaign aims to build a national movement to safeguard citizens, emphasizing the importance of cyber literacy and digital security.
Key Points
- Growing Cybersecurity Threats:
- India has seen a surge in cyber frauds, with 1.1 million cases reported in 2023.
- The government is committed to addressing these threats through stronger cybersecurity measures and enhancing digital literacy.
- Meta’s Role:
- Meta’s global expertise in online safety will be leveraged to equip citizens with the knowledge to prevent cyber scams.
- Meta’s collaboration with the government aims to extend the reach of the campaign nationwide.
Features of the "Scam Se Bacho" Campaign
- Nationwide Reach:
- The initiative targets India’s 900 million internet users, making it a comprehensive national effort.
- Government Support:
- Backed by key ministries to ensure alignment with national digital and cybersecurity goals under Digital India.
- Whole-of-government approach to raise awareness on cyber safety.
- Educational Focus:
- The campaign emphasizes educating citizens on how to recognize and prevent online scams and threats.
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India, Will Assume Office on November 11
- Appointment:
- Justice Sanjiv Khanna has been appointed as the 51st Chief Justice of India by President Droupadi Murmu.
- He is set to take office on November 11, 2024, succeeding Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, who is retiring on November 10, 2024.
- Tenure:
- Justice Khanna's tenure will be relatively short, lasting only six months, as he is scheduled to retire on March 13, 2025.
Career and Background
- Education and Early Career:
- Justice Khanna is a graduate of Delhi University’s Campus Law Centre.
- He enrolled as an advocate in 1983 and primarily practiced before the Delhi High Court.
- Prior to his elevation to the Delhi High Court in 2005, he served as the Senior Standing Counsel for the Income Tax Department and the standing counsel for civil matters for the Delhi government.
- Judicial Career:
- Supreme Court Appointment: Justice Khanna was appointed to the Supreme Court in January 2019, despite not having served as Chief Justice of a High Court. He was elevated over other senior judges from the Delhi High Court, such as Justices Rajendra Menon and Pradeep Nandrajog, whose names were initially recommended but not forwarded to the government.
- Key Contributions:
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- February 2024: Part of the five-judge bench that struck down the Electoral Bond Scheme as unconstitutional.
- 2023: Contributed to upholding the abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution.
- 2023: Authored a ruling granting the Supreme Court the power to directly grant divorce under Article 142 on the grounds of "irretrievable breakdown of marriage."
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- Administrative Role:
- Justice Khanna currently serves as the Executive Chairman of the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
Process of Appointment of Chief Justice of India (CJI)
- Seniority Principle: The CJI is typically the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court.
- Memorandum of Procedure (MoP): The Law Ministry requests a recommendation from the outgoing CJI for his successor.
- Presidential Appointment: After receiving the recommendation, the President of India formally appoints the new CJI.
- Tenure and Retirement: The CJI serves until the age of 65. Upon retirement, the senior-most judge becomes the next CJI.
- Merit and Integrity Considerations: In addition to seniority, merit and integrity play crucial roles in the selection process for the CJI.
Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Director-General of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) inaugurated the third Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum.
Purpose and Goals
- Objective: To accelerate the transformation of agrifood systems to address global challenges:
- Eradicate poverty (SDG 1)
- End hunger and malnutrition (SDG 2)
- Reduce inequalities (SDG 10)
- Target: Focuses on improving the lives of poor and vulnerable populations by:
- Raising incomes
- Enhancing nutritional status and overall well-being
- Strengthening resilience to climate change
Key Features of the HIH Initiative
- Launched: 2019 as a flagship program by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- Primary Focus Areas:
- Geospatial and analytics-driven approach: Utilizes advanced geospatial modeling, biophysical, socio-economic data, and analytics to identify key territories for intervention.
- Market-based transformation: Aims to create sustainable, market-based solutions for agricultural development and food systems transformation.
- Value Chain Development: Focus on developing value chains for priority commodities to boost incomes and food security.
- Agro-Industry Building: Strengthening agro-industries and introducing efficient water management and precision agriculture systems.
- Digitalization: Introducing digital services for better agricultural planning and productivity.
Key Areas of Intervention
- Agricultural Transformation: Identifying territories with the highest potential for transformation.
- Sustainable Management: Focus on sustainable practices in forestry, fisheries, and land management.
- Climate Resilience: Building systems to mitigate the effects of climate change and reduce vulnerability.
- Food Loss Reduction: Addressing food losses and waste across agricultural value chains.
Global Participation
- Member Countries: 72 countries have joined the initiative, collaborating on shared goals for agrifood systems transformation.
The Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum
- Purpose: A platform to mobilize investments for the successful implementation of agrifood transformation programs under the HIH initiative.
- Event: The third Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum was recently opened by the FAO Director-General to discuss challenges and solutions for global agrifood system transformation.
About the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Established: October 1945, it is the oldest permanent specialized agency of the United Nations.
- Mandate:
- Improve nutrition.
- Increase agricultural productivity.
- Raise the standard of living in rural areas.
- Contribute to global economic growth.
- Headquarters: Rome, Italy.
- Members: 194 Member States and the European Union.
Key Role of FAO:
- FAO leads international efforts to combat hunger and malnutrition worldwide.
- Supports member countries in implementing agricultural and food security programs.
Strategic Importance
- The Hand-in-Hand Initiative is integral to FAO’s mandate, focusing on countries with the most pressing needs due to poverty, hunger, or crises (natural or man-made).
- It enhances cooperation among nations to tackle global food security challenges, with a particular emphasis on countries with limited national capacities.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
The Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, hosted a two-day Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) knowledge sharing workshop in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Event Overview:
- Two-day workshop hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education.
- Focus areas: School-to-Work Transition and Strengthening the Assessment System.
- Key Objectives:
- To enhance school-to-work transitions.
- To discuss strengthening educational assessment systems.
- Align education with future workforce needs as per the National Education Policy 2020.
Day 1: School-to-Work Transition
Panel Discussions:
- Policy Frameworks:
- Role of National Education Policy 2020, National Curriculum Framework (NCF), and National Credit Framework (NCrF) in school-to-work transitions.
- Focus on integrating skill education into school curricula, fostering multidisciplinary learning, and continuous evaluation to meet industry standards.
- Emphasis on internships, apprenticeships, and flexible learning pathways.
- Curriculum Integration:
- Need for integrated efforts across departments and aligning curriculum with industry demands.
- Focus on strengthening 21st-century skills in CBSE schools.
- Career Counselling and Psychometric Analysis:
- Focus on using psychometric assessments for career counselling and preparing students for future work environments.
- Work-Based Learning:
- Discussed partnerships with industry for work-based learning.
- Effective collaborations between schools and industry for internships, placements, and best practices.
Day 2: Strengthening Assessment System
- Psychometric Analysis & Career Counselling:
- Smt. Idzes Angmo Kundan (Principal Secretary, Maharashtra) presented the 3 P approach to career choices: Personal Interest, Parental Approach, and Possible Opportunities.
- Enhancing Student Outcomes:
- Discussed improving student outcomes by strengthening assessment systems.
- Shared innovations in educational assessments.
- Highlighted innovative assessment practices for future education.
- VSK Implementation (Chhattisgarh):
- Discussed VSK modes, data analysis, and strategies for integrating assessment outcomes with learning objectives.
- Strengthening Assessment Cells:
- Advocated for the establishment of assessment cells.
- Discussed best practices and challenges in strengthening assessment cells across states.
World Energy Outlook 2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Energy Agency's (IEA) World Energy Outlook 2024 offers an in-depth analysis of global energy trends, emphasizing the shift towards clean energy, growing energy demand, and the effects of geopolitical conflicts.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth:
- India was the fastest-growing major economy in 2023 with a 7.8% growth rate.
- On track to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2028.
- Surpassed China in 2023 to become the most populous country globally, despite a fertility rate below replacement level.
- Energy Demand Surge:
- India is projected to experience the highest increase in energy demand over the next decade.
- By 2035, India’s total energy demand is expected to rise by 35%, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increased living standards.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Growth:
- Over 12,000 cars are expected to be added to Indian roads daily by 2035.
- Built-up space is set to increase by over 1 billion square meters annually, surpassing the total built space of South Africa.
- Industrial Expansion:
- Iron and steel production is expected to grow by 70% by 2035.
- Cement output is set to increase by 55%.
- Air conditioner stock to grow more than 4.5 times, with electricity demand from cooling expected to exceed Mexico’s total consumption in 2035.
- Energy Supply & Coal:
- India’s electricity generation capacity is projected to nearly triple to 1,400 GW by 2035.
- Coal remains a dominant energy source despite growth in renewables:
- Coal-fired power capacity will increase by 60 GW by 2030.
- Coal will continue to account for over 30% of electricity generation even as solar PV expands.
- By 2035, coal use in industries like steel and cement will grow by 50%.
- Renewable Energy & Clean Tech:
- India is on track to become a global leader in renewable energy, with a nearly 3x increase in electricity generation capacity.
- The country is expected to have the world’s third-largest installed battery storage capacity by 2030.
- By 2030, low-emission energy sources (solar, wind, nuclear) are expected to generate over 50% of India’s electricity.
- Electric Vehicles & Oil Demand:
- The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to peak India’s oil demand by the 2030s, reducing reliance on oil for transportation.
- Oil demand for transport will decline as EVs proliferate, though demand for oil in other sectors (e.g., petrochemicals) will continue.
- Net Zero Target:
- India aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
- By 2035, clean energy generation could be 20% higher than current policy projections, thanks to electric mobility, hydrogen use, and improved energy efficiency.
- CO2 emissions are projected to be 25% lower than under the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS).
- Policy Support:
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- PM-KUSUM scheme for solar energy in agriculture.
- National Solar Mission.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme to boost domestic solar PV manufacturing.
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- Global Energy Trends:
- Geopolitical Risks: Global energy security remains affected by geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine conflict, Middle East tensions).
- Energy Transition: Global shift toward clean energy, with solar and wind power investments accelerating.
- Oil & Gas Surplus: Oil and LNG supply expected to increase, putting downward pressure on prices by the late 2020s.
- Electric Mobility: EVs projected to account for 50% of new car sales by 2030.
- Energy Efficiency: Despite efforts, global targets for doubling energy efficiency by 2030 are unlikely to be met with current policies.
IEA Overview:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) provides analysis and policy advice on energy security, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
- Established in 1974, it now includes 31 member countries and 13 association countries, including India.
- Major publications: World Energy Outlook, India Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report.
India’s Semiconductor Market Projected to Surpass $100 Billion by 2030
- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
India's semiconductor market is poised to exceed $100 billion by 2030, according to a report from the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association and Counterpoint Research. Currently valued at $45 billion in 2023, the market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 13%, driven by demand in mobile handsets and IT sectors, which together account for over 75% of revenues.
Key Highlights:
- Growth Drivers: The growth is supported by strong demand for electronics and government initiatives like the production-linked incentive scheme. Semiconductors are essential for various industries, including electronics, defense, healthcare, and automotive.
- Importance of Semiconductors: These materials, which include silicon and germanium, are crucial for electronic devices. They can conduct electricity under certain conditions, making them fundamental in transistors, integrated circuits, and devices like LEDs and solar cells.
- Global Context: The global semiconductor supply chain has shown vulnerabilities, particularly during the chip shortage of 2021. Major producers include Taiwan (44% market share), China (28%), South Korea (12%), the U.S. (6%), and Japan (2%). Countries are now focusing on building domestic chip industries to reduce dependency on a few key suppliers.
Factors Favoring India's Growth in Semiconductors:
- Skilled Workforce: India has a vast pool of STEM graduates, providing a skilled workforce for semiconductor manufacturing and design.
- Cost Advantage: Lower labor costs and efficient supply chains position India favorably for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Diversification: India is becoming a hub for back-end assembly and testing operations, with potential for front-end manufacturing.
- Government Support: Initiatives like Semicon India and the India Semiconductor Mission aim to create a robust semiconductor ecosystem, offering substantial fiscal incentives for companies.
Government Initiatives:
- Semiconductor Fab Scheme: Provides 50% project cost support for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Display Fab Scheme: Offers similar support for display manufacturing.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: Trains 85,000 engineers across academic and R&D institutions.
- Recent approvals for the establishment of semiconductor plants in Gujarat and Assam further bolster this initiative.
Nobel Prize for Economics 2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
The winners of this year’s Economics Nobel, or the Sveriges Riksbank Prize awarded for economic sciences, Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson and James Robinson (AJR), pioneers in new institutional economics, emphasised the role of institutions in the direction of development.
The Great Divergence
- Definition: Refers to the economic and political development gap between the West and East, particularly during the 17th and 18th centuries.
- Key Factors:
- Industrialization in Western Europe enabled the projection of political power globally.
- Colonial institutions established during this period have long-lasting effects on post-colonial nations.
Role of Institutions in Development
- Nobel Prize Winners: Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson, and James Robinson (AJR) awarded for their work in new institutional economics.
- Institutions Defined: Set of rules constraining human behavior, ensuring law and order, and preventing coercion.
- Types of Institutions:
- Extractive Institutions: Concentrate wealth among elites, historically prevalent in colonized regions (e.g., Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America).
- Inclusive Institutions: Promote broader participation in economic growth, more common in countries like the U.S., Canada, and Australia.
Research Contributions
- Natural Experiments: AJR used historical data to show how differing colonial practices influenced economic outcomes.
- Key Findings:
- Areas with landlord-based colonial systems had lower agricultural investment and productivity.
- Regions under direct colonial rule lagged in infrastructure like schools and health centers.
Implications of AJR's Work
- Economic Institutions: Reflect collective choices shaped by political power, which can be either de jure (formal) or de facto (informal).
- Challenges in Reform: Conflicting interests often hinder agreement on the nature of beneficial institutions.
Critical Perspectives
- Skepticism of AJR's Framework: Some scholars argue that AJR's emphasis on Western liberal institutions overlooks the complexities of historical contexts, including corruption and systemic inequalities in early U.S. history.
- Modern Economic Dynamics: AJR caution against assuming that inclusive institutions will automatically lead to prosperity, as evidenced by concerns regarding China's future growth under extractive political systems.
Insights from Nobel Prize Research
- Key Focus Areas:
- Institutional structures in colonized countries significantly shape economic prosperity.
- Example of Nogales, Arizona, and Nogales, Mexico illustrates the impact of institutions on economic opportunities.
About the Nobel Prize Recipients
- Daron Acemoglu:
- MIT professor and co-author of influential works on power and prosperity.
- Advocates for democracy's role in economic growth while acknowledging its challenges.
- Simon Johnson:
- Former IMF chief economist, current MIT professor.
- Emphasizes the complexity of addressing entrenched poverty due to institutional frameworks.
- James A. Robinson:
- University of Chicago professor, co-author of works on economic disparity.
- Highlights historical transitions toward inclusive societies and their importance in economic development.
Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences
- Established: 1968 by the Swedish central bank.
- Purpose: Complement existing Nobel Prizes, recognizing contributions to economic sciences.
- Notable Previous Laureates: Include Claudia Goldin (2023) for gender pay gap research and Abhijit Banerjee et al. (2019) for poverty alleviation studies.
SAMARTH Scheme

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
Samarth is a demand-driven and placement-oriented umbrella skilling program of the Ministry of Textiles. Samarth Scheme has been extended for two years (FY 2024-25 and 2025-26) with a budget of Rs. 495 Crore to train 3 lakh persons in textile-related skills.
Key Details:
- Scheme Name: Samarth (Scheme for Capacity Building in Textile Sector)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Extension Period: FY 2024-25 and 2025-26
- Budget: ?495 Crores
- Target: Train 3 lakh individuals in textile-related skills
Objectives
- Skilling Programs: Provide demand-driven, placement-oriented training.
- Industry Support: Encourage job creation in organized textile and related sectors.
- Skill Enhancement: Focus on upskilling and reskilling in traditional sectors (handloom, handicraft, silk, jute).
Implementation
- Implementing Partners:
- Textile Industry/Industry Associations
- Central/State government agencies
- Sectoral Organizations (e.g., DC/Handloom, Central Silk Board)
- Current Achievements:
- Total Trained: 3.27 lakh candidates
- Employment Rate: 2.6 lakh (79.5%) have secured jobs
- Women Empowerment: 2.89 lakh (88.3%) women trained
Scheme Features
- Coverage: Entire textile value chain, excluding spinning and weaving.
- Training Focus:
- Entry-level skilling
- Upskilling/reskilling existing workers in apparel and garmenting
- Beneficiaries: Handicraft artisans and job seekers in the textile sector.
Background
- Cabinet Approval: The scheme is a continuation of the Integrated Skill Development Scheme from the 12th Five Year Plan.
- Implementation Agency: Office of the Development Commissioner (Handicrafts).
Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi is organising its first-ever international conference - Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024.
Key Details:
- Theme: "Advancements in Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda"
- Conference Goals
- Position Ayurveda as a key pillar of global health and wellness.
- Facilitate dynamic exchanges among scholars, industry leaders, and practitioners.
- Explore the integration of traditional Ayurvedic wisdom with modern scientific advancements.
- Agenda Highlights
- Topics Covered:
- Ayurveda and ethnomedicine
- Quality control and standardization
- Diagnosis and drug delivery
- Evidence-based understanding and globalization
- Topics Covered:
- Institute Background
- All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA): Apex institute for Ayurveda with NAAC A++, NABH, and ISO accreditations.
- Facilities: 200-bed referral hospital, 44 specialty departments.
- Global Collaborations: Partnerships with institutions in 17 countries, including London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and Western Sydney University.
- Innovations: Focus on research, drug development, and scientific validation of Ayurvedic practices.
- Participant Benefits
- Networking Opportunities: Engage with experts in Ayurveda and holistic healthcare.
- Learning Experiences: Attend plenary sessions, round table discussions, and exhibitions on medicinal plants and startups in Ayurveda.
- Recognition: Awards for contributions to Ayurveda.
- Research and Innovation Focus: Discussions on technology integration, including AI and bioinformatics.
DigiLocker Partners with UMANG
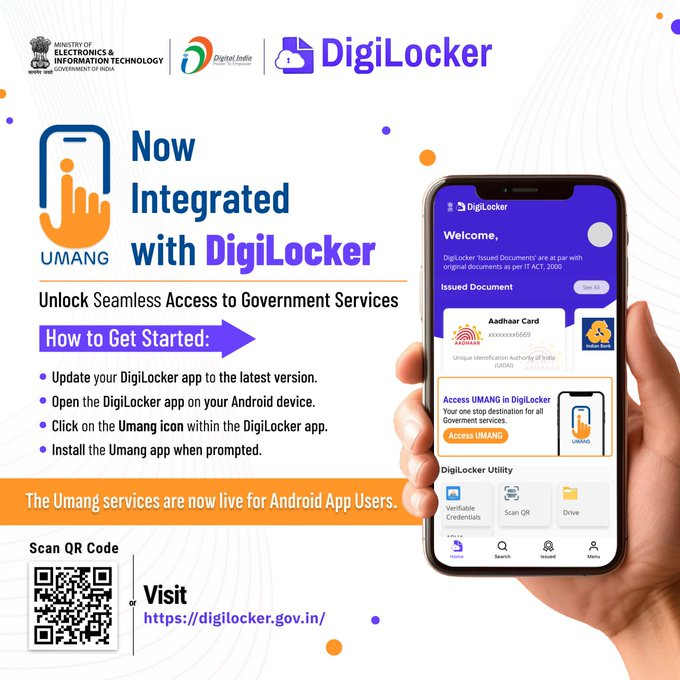
- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) has announced the integration of the UMANG app with DigiLocker- India’s Digital Wallet. This collaboration aims to provide citizens with seamless access to a wide range of government services bringing greater convenience and allowing users to manage multiple services through a single platform.
UMANG app
- The UMANG app is accessible to all Android users with an expansion to iOS in the pipeline.
- The UMANG mobile app is an all-in-one single, unified, secure, multi-channel, multi-lingual, multi-service mobile app.
- It provides access to high-impact services of various organizations of the Union and States.
Simplified Citizen-Government interaction
This integration makes it easier for citizens to interact with the Government in an efficient, digital-first manner. DigiLocker has always been a pioneer in simplifying access to personal and official documents, and after integration with UMANG, it has expanded the range of services you can access on the go.
About DigiLocker
DigiLocker is a flagship initiative under the Digital India program aimed at providing secure cloud-based storage of essential documents. By integrating with e-governance services such as UMANG, DigiLocker further is committed to further enhance accessibility and ease of living.
World Food Day 2024

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
World Food Day, observed annually on October 16, has its roots in the establishment of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) by the United Nations in 1945.
Significance: World Food Day emphasizes the critical need to address global hunger and promote resilient food systems capable of overcoming challenges like climate change and economic disparities.
Introduction
- Food is vital for life, health, and well-being.
- Despite sufficient global food production, millions lack access to nutritious food.
- World Food Day serves as a reminder of ongoing challenges in achieving food security.
History and Theme
- Origins: Established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 1945, officially recognized in 1979.
- First Celebration: Took place in 1981 with the theme "Food Comes First."
- 2024 Theme: "Right to Food for a Better Life and a Better Future," highlighting that food security is essential for dignity and health. It emphasizes the need for sustainable practices and equitable distribution.
India’s Commitment to Food Security
- India has made significant strides in combating hunger through various programs aimed at malnutrition and poverty alleviation.
- Key initiatives include:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population, benefiting about 81 crore individuals.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): Offers free food grains to approximately 81.35 crore beneficiaries, extending support during the COVID-19 pandemic for an additional five years.
- PM POSHAN Scheme: Aims to improve children's nutritional status in government schools with a budget of ?12,467.39 crores for 2024-25.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY): Focuses on the most vulnerable populations, supporting over 8.92 crore individuals and empowering women.
- Rice Fortification: Distribution of fortified rice through the Public Distribution System has improved nutritional intake for millions.
- Price Stability Initiatives: The government manages price volatility of essential commodities using the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) and ensures affordability through strategic product launches.
Global Recognition of Indian Cuisine
- The Indian Thali has been recognized for its nutritional and sustainable qualities by the WWF Living Planet Report.
- Its plant-based composition contributes to lower resource use and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- If globally adopted, India’s dietary patterns could significantly lessen the environmental burden.
Significance
- India’s comprehensive initiatives reflect its dedication to food security and improving citizens' quality of life.
- By enhancing agricultural productivity and supporting vulnerable populations, India makes strides towards eradicating hunger.
- On World Food Day, these efforts underline India's commitment to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2: Zero Hunger, while serving as a model for global food security initiatives.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Prime Minister commended the completion of three years of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, calling it a transformative initiative for India’s infrastructure development.
- Key Benefits: The plan enhances multimodal connectivity and improves efficiency across various sectors, contributing to logistics, job creation, and innovation.
Overview of PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Launch Date: October 2021
- Objective: A transformative initiative worth ?100 lakh crore aimed at revolutionizing India’s infrastructure over five years.
- Development Tool: Created as a Digital Master Planning tool by the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
- GIS Platform: Utilizes a dynamic Geographic Information System to integrate action plans from various ministries into a comprehensive database.
- Goals: Accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by addressing inter-ministerial challenges.
Key Features
- Digital Integration: A digital platform coordinating the efforts of 16 ministries for seamless infrastructure planning.
- Multi-Sector Collaboration: Incorporates initiatives from major programs like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
- Economic Zones Development: Focuses on key areas such as textile clusters and pharmaceutical hubs to boost productivity.
- Technology Utilization: Employs advanced spatial planning tools and ISRO satellite imagery for data-driven project management.
Core Sectors Driving the Plan
- The National Master Plan is centered around seven primary sectors that enhance economic growth and connectivity, supported by sectors like energy transmission and social infrastructure.
Six Pillars of PM GatiShakti
- Comprehensiveness: Integrates various initiatives through a centralized portal, ensuring efficient planning.
- Prioritisation: Allows ministries to prioritize projects based on national importance and resource allocation.
- Optimisation: Identifies infrastructure gaps and selects the most efficient transportation routes.
- Synchronisation: Ensures coordinated efforts across ministries to avoid delays.
- Analytical Capabilities: Offers extensive data layers for improved spatial planning and decision-making.
- Dynamic Monitoring: Uses satellite imagery for real-time project tracking and adjustments.
Achievements of PM GatiShakti
- District-Level Expansion: Extended to 27 aspirational districts, with plans for 750 in the near future.
- Technological Integration: Enhanced real-time infrastructure planning using geospatial tools.
- Global Outreach: The GatiShakti tool showcased to 30 countries and highlighted at international conferences.
- Social Sector Benefits: Identified areas for new healthcare facilities and improved planning in various districts.
- Rural and Urban Development: Implemented projects for irrigation and city logistics in multiple states.
- Employment Initiatives: Utilized for setting up training institutes near industrial clusters.
Announcement of AI Centres of Excellence

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, announced the establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence (CoE) focused on Healthcare, Agriculture, and Sustainable Cities in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Establishment of Three AI-CoEs:
- Focus Areas:
- Healthcare: Led by AIIMS and IIT Delhi.
- Agriculture: Led by IIT Ropar, Punjab.
- Sustainable Cities: Led by IIT Kanpur.
- Collaboration: CoEs will work with industry partners and start-ups.
- Focus Areas:
- Financial Commitment:
- Total Approved Budget: ?990 crore for FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Purpose: Support the establishment and operation of the CoEs.
- Vision and Impact:
- Pradhan emphasized the CoEs' role as solution providers for global public good.
- Expected to create a new generation of job and wealth creators.
- Aims to strengthen India's credentials in the global AI landscape.
- Leadership and Implementation:
- Apex Committee: Co-chaired by Shri Sridhar Vembu (Zoho CEO).
- Committee includes industry leaders and academic heads.
- Shri K. Sanjay Murthy highlighted the importance of interdisciplinary research and collaboration.
- Future Prospects:
- Dr. Vembu noted the CoEs will enhance the health of villages and cities, nurture talent, and generate opportunities.
- The initiative aligns with India's vision of "Viksit Bharat" (Developed India).
- Presentation and Film:
- Insights into the development of AI-CoEs presented by Smt. Saumya Gupta.
- A short film titled "Make AI in India and Make AI work for India" was showcased.
The establishment of these Centres of Excellence in AI signifies a major step toward fostering an effective AI ecosystem in India, aimed at developing scalable solutions and enhancing human resources in critical sectors.
International Abhidhamma Divas

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, International Abhidhamma Divas was celebrated at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, with PM Narendra Modi.
Key Details:
- India's Spiritual Legacy: Birthplace of Buddhism; site of Gautam Buddha's enlightenment.
- Sacred Sites: Veneration of locations like Bodh Gaya, symbolizing Buddha's journey and teachings.
- Core Teachings: Abhidhamma as a key philosophical component emphasizing mental discipline and self-awareness.
International Abhidhamma Divas
- Global Observation: Celebrates the significance of Abhidhamma in ethical conduct and mindfulness.
- Cultural Connection: Highlights India's role in preserving Buddhism and bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary practices.
Historical Background and Significance
- Commemoration: Marks Buddha’s descent from T?vati?sa to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur).
- Teaching Period: Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to deities for three months; linked to the end of the Rainy Retreat and the Pav?ra?? festival.
Teachings of Abhidhamma
- Systematic Analysis: Provides a detailed exploration of mind and matter, differing from Sutta Pi?aka.
- Specialized Vocabulary: Key terms include "citta" (consciousness), "cetasika" (mental factors), "r?pa" (materiality), and "nibb?na" (liberation).
- Textual Framework: Six core books of Abhidhamma Piñaka cover moral states, aggregates, and causal relationships.
- Key Treatise: The Paññh?na offers in-depth causal analysis, essential for practitioners’ understanding.
Modern Observance and Celebrations
- Significance of Pali: Recognition of Pali as a classical language; promoting India's Buddhist heritage.
- Participants: Gathering of ambassadors, monks, scholars from 14 countries; emphasizes Abhidhamma's relevance today.
- Program Highlights: Dhamma discourse, academic sessions on Abhidhamma’s significance, exhibitions on Pali's evolution and Buddha's teachings.
Classical Status of Pali Language
- Pali's Role: Sacred language for delivering Buddha's teachings; recognized as a Classical Language by India.
- Buddhist Canon: Major texts include the Tipitaka (Vinaya, Sutta, Abhidhamma Pitaka) and commentarial traditions.
- Literary Heritage: Jataka Kathas reflect shared moral values; status enhances Pali studies in education and research.
Significance
- Significance of Celebration: Abhidhamma Divas underscores efforts to preserve and promote Buddhism’s legacy.
- Revitalization of Buddhism: Fosters global engagement and appreciation for Buddha’s teachings, reaffirming India's role in Buddhist studies.
e-Migrate Portal

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministers for External Affairs and Labour and Employment launched the upgraded e-Migrate portal and mobile app, aimed at enhancing the migration experience for Indian workers seeking employment abroad. This initiative reflects the Indian government's commitment to ensuring the safety and welfare of its migrant workforce, aligning with global migration goals under the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
About e-Migrate Portal
The e-Migrate portal is an online platform designed to facilitate and manage the migration of Indian workers. It promotes safe and legal mobility channels by providing a transparent framework for migrant workers, including:
- Information Access: Comprehensive resources to help migrants understand the migration process.
- Documentation Support: Tools to assist with necessary paperwork.
- Helpline Support: A 24/7 multilingual helpline that addresses issues faced by workers, particularly in the Gulf region.
- Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to educate workers about their rights and responsibilities abroad.
The upgraded version of the portal, launched in October 2024, features enhanced functionality to better serve Indian migrants.
Key Features of e-Migrate v2.0
- Multilingual Helpline: Offers real-time support in multiple languages, ensuring that urgent issues are resolved efficiently.
- Integration with Digilocker: Facilitates secure, paperless submission of essential documents, such as passports and employment contracts.
- Social Security Net: Enhances social security measures for migrants, including insurance policies and partnerships with the State Bank of India for fee-free digital payment services.
- Mobile App: Introduced for the first time, this app provides easy access to services, including a job search marketplace for overseas employment opportunities.
- Rural Accessibility: Collaboration with Common Service Centres (CSCs) aims to expand immigration services to rural areas in local languages, making the platform more accessible to diverse populations.
Significance
The e-Migrate portal aligns with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 10, which promotes orderly and responsible migration. By fostering safe migration practices, this initiative seeks to empower Indian workers and protect their rights while contributing to the country's international workforce.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has officially launched its first two initiatives: the Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG) and the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission. These initiatives aim to enhance India’s research landscape and support innovation in critical sectors.
Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG)
- Objective: The PMECRG is designed to empower early career researchers by providing flexible funding and support for high-quality innovative research. It aims to foster creativity and drive technological progress, positioning India as a global leader in science and technology (S&T).
- Significance: This grant recognizes the essential role of young researchers in advancing India's scientific agenda. By investing in their development, ANRF aims to cultivate a vibrant research ecosystem that encourages groundbreaking discoveries.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission
- Focus: The MAHA-EV Mission targets the development of key technologies for electric vehicles, specifically in areas such as tropical EV batteries, power electronics, machines and drives (PEMD), and charging infrastructure.
- Goals:
- Reduce Import Dependency: By fostering domestic innovation in EV components.
- Global Leadership: Positioning India as a leader in the electric vehicle sector, aligning with the government's Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- Collaboration: The mission is designed to encourage multi-institutional and multi-disciplinary collaboration to address critical scientific challenges, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of India's EV sector.
Significance of Both Initiatives
- Bridging Gaps: Both initiatives aim to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial applications, a key goal of ANRF. This alignment is crucial for translating research into practical applications that benefit society.
- Strategic Interventions: These programs reflect the discussions held during the ANRF's Governing Board meeting, which emphasized global positioning in key sectors, capacity building, and fostering an innovation ecosystem.
- Long-term Vision: The initiatives contribute to India's goal of achieving a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047, accelerating the country's progress toward a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
The launch of the PMECRG and MAHA-EV Mission marks a significant step in enhancing India's research ecosystem. By supporting early career researchers and advancing electric vehicle technologies, ANRF is poised to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and strengthen India’s position on the global scientific stage. These initiatives reflect a commitment to sustainable development and technological leadership, paving the way for transformative advancements in various sectors.
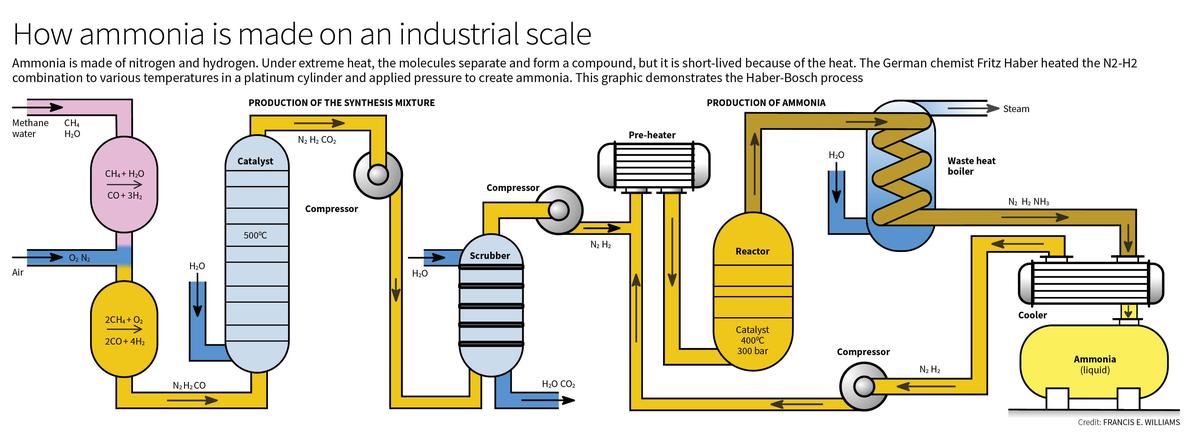
Haber-Bosch process
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Haber-Bosch process has fundamentally transformed agricultural practices and global food production, enabling the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is essential for fertilizers.
The Nitrogen Molecule
- Composition: Nitrogen primarily exists as molecular nitrogen (N?) in the atmosphere, where two nitrogen atoms are bonded with a strong triple bond. This bond is very stable and requires significant energy (946 kJ/mol) to break, rendering N? largely inert and unavailable for direct use by plants.
Nitrogen in Nature
- Natural Fixation: In nature, the energy required to break the N? bond is typically provided by phenomena like lightning, which converts nitrogen to reactive forms such as nitrogen oxides (NO and NO?). These can subsequently form nitric acid when they react with water, depositing reactive nitrogen through rainfall.
- Microbial Processes: Certain bacteria, including Azotobacter and Rhizobia, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into reactive forms, supporting plant growth. Azolla, a fern with a symbiotic cyanobacterium, also helps in nitrogen fixation.
The Nitrogen Cycle
- Plant Uptake: Plants absorb reactive nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH??) and nitrate (NO??) from the soil, essential for synthesizing proteins and other vital compounds. Humans and animals rely on plants for their nitrogen intake.
- Cycle Completeness: While nitrogen is returned to the soil through excretion and decomposition, some is lost back to the atmosphere as N?. This loss contributes to the depletion of soil nitrogen, especially in crops that do not fix their own nitrogen.
Ammonia Production
- Haber-Bosch Process: This process synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature, using a catalyst to enhance efficiency. Initially developed by Fritz Haber and scaled by Carl Bosch, this method became the backbone of modern fertilizer production.
Benefits and Downsides of Fertilizers
- Food Security: The Haber-Bosch process has significantly increased food production, contributing to a remarkable rise in global food supply and preventing widespread hunger. It is estimated that one-third of the world’s population relies on fertilizers produced via this process for their food.
- Environmental Impact: The widespread use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to environmental issues:
- Excess Nutrients: Over-application can result in nutrient runoff into water bodies, causing eutrophication, which depletes oxygen and harms aquatic life.
- Acid Rain: Reactive nitrogen can contribute to acid rain, affecting soil health and biodiversity.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous fertilizer use without adequate replenishment of nutrients can degrade soil quality over time.
While the Haber-Bosch process is crucial for modern agriculture and food security, it also presents significant environmental challenges. The balance between using fertilizers effectively and sustainably is essential to ensure that technological advancements do not come at the cost of ecological health. As such, addressing food security requires not just technological innovation, but also thoughtful political and social engagement to manage resources responsibly.
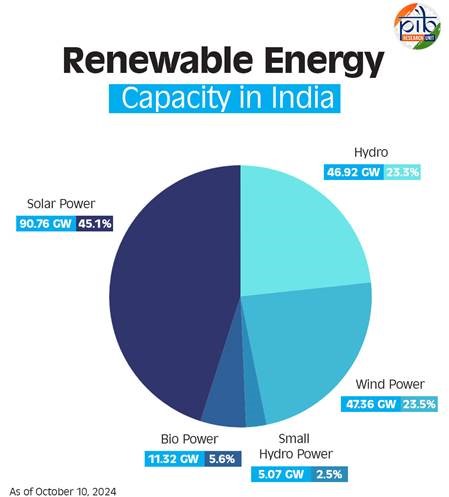
India's Renewable Energy Capacity Hits 200 GW Milestone
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
India has recently celebrated a landmark achievement in its renewable energy sector, with its total renewable energy capacity surpassing 200 GW as of October 10, 2024. This milestone, reported by the Central Electricity Authority, showcases the country’s growing commitment to clean energy and its strategic shift towards a more sustainable future.
Overview of India’s Renewable Energy Landscape
As of October 2024, India's total electricity generation capacity stands at 452.69 GW, with renewable sources contributing a substantial 201.45 GW, representing 46.3% of the overall capacity. This shift highlights India’s increasing reliance on cleaner, non-fossil fuel energy.
Key contributors to this capacity include:
- Solar Power: Leading with 90.76 GW, capitalizing on India's abundant sunlight.
- Wind Power: Following closely at 47.36 GW, leveraging the country’s vast wind corridors.
- Hydropower: Large hydro projects add 46.92 GW, while small hydro contributes an additional 5.07 GW.
- Biopower: Incorporating biomass and biogas energy, contributing 11.32 GW.
Together, these resources are pivotal in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
Leading States in Renewable Energy Capacity
Certain states are at the forefront of this renewable energy expansion:
- Rajasthan: 29.98 GW, benefiting from ample land and sunlight.
- Gujarat: 29.52 GW, driven by robust solar and wind initiatives.
- Tamil Nadu: 23.70 GW, utilizing favorable wind conditions.
- Karnataka: 22.37 GW, supported by a mix of solar and wind projects.
Key Schemes and Programs
The Indian government has introduced numerous initiatives to accelerate renewable energy capacity, aiming for 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030. Notable programs include:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission
- PM-KUSUM Scheme
- PM Surya Ghar Scheme
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) for solar PV modules
These efforts reflect the government's commitment to fostering a sustainable energy future while addressing the challenges posed by climate change and energy security. Here are some other ongoing key initiatives:
- Notification of a trajectory for renewable energy power bids of 50 GW per annum by Renewable Energy Implementation Agencies (REIAs) from FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Foreign Direct Investment permitted up to 100 percent under the automatic route to attract investments.
- Waiver of Inter-State Transmission System charges for solar and wind power projects commissioned by June 30, 2025; green hydrogen projects until December 2030; and offshore wind projects until December 2032.
- Announced Renewable Purchase Obligation trajectory until 2029-30, including separate RPO for Decentralized Renewable Energy.
- A Project Development Cell has been established to attract and facilitate investments in the renewable sector.
- Standard Bidding Guidelines issued for tariff-based competitive bidding for procurement of power from grid-connected solar, wind, and wind-solar projects.
- Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Parks are being set up to provide land and transmission for large-scale renewable energy projects.
- Cabinet approval for a Viability Gap Funding scheme for offshore wind energy projects, facilitating the installation and commissioning of 1 GW of offshore wind energy capacity along the coasts of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Issued Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020, for net-metering up to 500 kilowatts or the electrical sanctioned load, whichever is lower.
- The “National Repowering and Life Extension Policy for Wind Power Projects, 2023” has been released.
- “Strategy for Establishment of Offshore Wind Energy Projects” outlines a bidding trajectory of 37 GW by 2030.
- Offshore Wind Energy Lease Rules, 2023, notified to regulate the grant of leases for offshore wind energy development.
- Procedure for Uniform Renewable Energy Tariff (URET) has been established.
- Standard & Labelling (S&L) programs for Solar Photovoltaic modules and grid-connected solar inverters have been launched.
- A transmission plan has been prepared to augment transmission infrastructure until 2030.
- The Electricity (Late Payment Surcharge and Related Matters) Rules have been notified.
- Green Energy Open Access Rules 2022 have been issued to promote renewable energy.
- Launched the Green Term Ahead Market (GTAM) to facilitate the sale of renewable energy power through exchanges.
- Orders issued to ensure that power is dispatched against Letters of Credit or advance payment for timely payments to renewable energy generators.
ITU World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly 2024

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated ITU WTSA 2024 and India Mobile Congress 2024, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- First Time in India: WTSA hosted for the first time in India and the Asia-Pacific region.
- Participants: Over 3,000 industry leaders, policy-makers, and tech experts from more than 190 countries expected.
ITU WTSA 2024
- Significance: Governing conference for the standardization work of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), held every four years.
- Focus Areas: Discussion on standards for next-generation technologies including:
- 6G
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Cybersecurity
- Opportunities for India: Enhances India’s role in shaping the global telecom agenda; insights into Intellectual Property Rights and Standard Essential Patents for startups and research institutions.
India Mobile Congress 2024
- Theme: "The Future is Now"
- Technological Focus: Highlight advancements in:
- Quantum Technology
- Circular Economy
- 6G and 5G use cases
- Cloud and Edge Computing
- IoT and Semiconductors
- Cybersecurity
- Green Technology
- Satellite Communication and Electronics Manufacturing
Importance for India
- Showcase of Innovation: A platform for India’s innovation ecosystem, demonstrating advancements in digital technology.
- Global Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between government, industry, and academia to address global telecommunication challenges.
THAAD Missile Defence System

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
The US pledged its THAAD missile defence system as well as several troops to Israel after Iran warned the country to not get involved.
In a new boost to Israeli forces, the United States will send a Terminal High Altitude Area Defence battery (THAAD) and troops to Israel amid its ongoing offensive against the Hezbollah.
THAAD battery:
- The Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system (THAAD) is an American anti-ballistic missile defence system. It can shoot down short, medium and intermediate range missiles in it's sphere.
- The THAAD has a “hit to kill” approach which blasts missiles as they before they enter their target zone during their descent.
- The THAAD was developed by the US after their experience of Iraq's Scud missile attacks during the Persian Gulf War in 1991. Out of a total of 88 Scud missiles, Iraq fired 42 into Israel and 46 into Saudi Arabia, killing many American soldiers in barracks as well.
- The first proposal for the THAAD was submitted to the US Defence Ministry in 1987 and a series of tests resulting in failures, finally led to a successful version in 1999.
- In 2008, the US deployed an early missile warning radar, a part of the THAAD system to Israel. Similar deployments were also made in 2012 and 2019, aiding Israel's ability to emerge as a military power in the Middle East.
Ladakh's Aurorae

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
In October 2024, Ladakh witnessed spectacular auroras, typically seen in higher latitudes, indicating increased solar activity. This phenomenon was reported following intense solar storms, with red and green lights observed in the night sky. The auroras were captured by all-sky cameras operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Hanle and Merak.
What Are Auroras?
Auroras are vibrant displays of light caused by interactions between charged particles from the Sun and Earth's magnetosphere. When solar winds—streams of charged particles—collide with atoms in the upper atmosphere, they create visible light, similar to how neon lights function.
Causes of Recent Auroras
The recent auroras in Ladakh were linked to several strong solar storms, particularly coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which are significant bursts of solar wind and magnetic fields rising above the solar corona. The storms, emanating from active solar regions, traveled towards Earth at remarkable speeds, disrupting the normal space weather and allowing auroras to be visible at lower latitudes, including Mexico and Germany.
Implications of Solar Activity
Astrophysicists at the Center of Excellence in Space Sciences India (CESSI) noted that these auroras validate ongoing efforts in space weather monitoring. The increased solar activity is part of the solar cycle, which peaks approximately every 11 years. Current predictions indicate that Solar Cycle 25 may reach its peak in 2024.
Monitoring Space Weather
Organizations like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) closely monitor space weather to provide timely warnings about solar events that could disrupt satellite communications and other services. The CESSI team successfully predicted the occurrence of solar storms, enhancing confidence in their ability to forecast space weather and its potential impacts.
Potential Hazards
While auroras are visually striking, intense solar storms can have detrimental effects, including:
- Satellite Disruption: Increased drag and radiation can damage satellites in low Earth orbit, affecting navigation, communications, and military operations.
- Communication Blackouts: Severe storms can interfere with radio and satellite communications, impacting daily life and services.
Wayanad’s New X-Band Radar

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Following devastating floods and landslides in July 2024 that resulted in over 200 fatalities in Wayanad, Kerala, the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences approved the installation of an X-band radar to enhance monitoring and early warning systems.
- Impact of Events: The floods were exacerbated by heavy rains, leading to significant debris flows and landslides, highlighting the need for advanced meteorological tools.
What is Radar?
- Definition: Radar stands for "Radio Detection and Ranging." It uses radio waves to determine the distance, velocity, and characteristics of objects.
- Functioning: A transmitter emits radio signals that reflect off objects, returning to a receiver for analysis. This technology is crucial in meteorology for monitoring weather patterns.
X-Band Radar Specifics
- Operating Frequency: X-band radar operates at 8-12 GHz, corresponding to wavelengths of 2-4 cm. This allows it to detect smaller particles, such as raindrops and soil.
- Advantages: The shorter wavelengths provide higher resolution images but have a limited range due to faster signal attenuation.
- Applications: In Wayanad, the radar will monitor particle movements like soil, enabling timely landslide warnings through high temporal sampling.
India’s Radar Network
- Historical Context: India has utilized radar for meteorological purposes since the early 1950s. The first indigenous X-band radar was established in 1970.
- Current Infrastructure: India operates both X-band and S-band radars (2-4 GHz) for various meteorological functions. The X-band network includes storm detection and wind-finding capabilities.
- Future Plans: The Indian government plans to add 56 more Doppler radars under the ?2,000-crore "Mission Mausam," enhancing weather forecasting capabilities across the country.
NISAR Satellite
- Collaboration: NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is a joint satellite project between NASA and ISRO, set to launch in 2025.
- Capabilities: It will feature L-band and S-band radars to monitor Earth’s landmass changes, further supporting environmental monitoring and disaster management.
Global Hunger Index 2024
- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 Global Hunger Index (GHI) emphasizes food as a fundamental human right, alongside air and water.
Key Highlights:
- Current Crisis: Despite adequate food production globally, around 350 million people face extreme hunger, with 49 million on the brink of famine.
- Statistics: Over 820 million people are chronically undernourished, and malnutrition claims the lives of five million children under five each year.
Top 10 Countries Most Affected by Hunger (2024)
- Somalia: GHI Score 44.1 (GHI 2000: 63.3)
- Yemen: GHI Score 41.2 (GHI 2000: 41.6)
- Chad: GHI Score 36.4 (GHI 2000: 50.5)
- Madagascar: GHI Score 36.3 (GHI 2000: 42.3)
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: GHI Score 34.9 (GHI 2000: 47.2)
- Haiti: GHI Score 34.3 (GHI 2000: 39.8)
- Niger: GHI Score 34.1 (GHI 2000: 53.1)
- Liberia: GHI Score 31.9 (GHI 2000: 48.0)
- Central African Republic: GHI Score 31.5 (GHI 2000: 48.0)
- Korea (DPR): GHI Score 31.4 (GHI 2000: 43.7)
India's Position
- Ranking: India ranks 105th in the GHI 2024, categorized as having a "serious" hunger situation.
- GHI Score: India’s score stands at 27.3, showing some improvement from a score of 38.4 in 2000 (previously classified as "alarming").
Key Concerns in India
- Undernourishment: 13.7% of the population is undernourished.
- Child Stunting: 35.5% of children under five are stunted.
- Child Wasting: 18.7% of children under five experience wasting.
- Child Mortality: 2.9% of children do not survive to age five.
Global Hunger Index (GHI):
A tool measuring hunger across countries based on four indicators:
-
- Undernourishment
- Child Wasting
- Child Stunting
- Child Mortality
- Data Sources: The GHI is based on data from credible organizations like the FAO, WHO, and UNICEF, as well as government surveys.
Hunger Indicators Explained
- Undernourishment: Reflects the overall food access situation.
- Child Wasting: Indicates acute malnutrition; a critical health issue.
- Child Stunting: Reflects chronic malnutrition; significant public health concern.
- Child Mortality: Represents the most severe consequence of hunger.
The 2024 GHI report reveals that while progress has been made in addressing hunger globally, significant challenges remain, particularly in countries like India and the most affected nations. Addressing these issues is crucial for achieving the goal of zero hunger by 2030.
Jipmer Launches ‘Tele-MANAS’ Mental Health Helpline

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Jipmer (Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) has launched the "Tele-MANAS" (Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States) helpline, a toll-free service (14416) aimed at providing mental health support.
- This initiative is part of the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP), launched by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Purpose and Need:
- With an estimated 1 in 10 people in India suffering from mental illness, and about 1% experiencing severe conditions, the service addresses significant gaps in mental health access, particularly in rural and remote areas.
- The helpline aims to provide immediate support for issues such as anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.
Training and Operations:
- Jipmer will train qualified counsellors who will subsequently train additional counsellors to expand the reach of the service.
- Counselors will be available 24/7, including holidays, to ensure continuous support.
Support Structure:
- Trained counselors will serve as the first point of contact for individuals seeking help, providing responses, suggestions, and necessary referrals to advanced mental health facilities.
- Jipmer will supervise the program, ensuring regular retraining and maintaining service quality.
Integration with National Programs:
- The initiative is coordinated by the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), which acts as the National Apex Centre for the NTMHP.
- It includes a comprehensive information library on mental health and guidance for managing early signs of stress and emotional challenges.
Impact on Mental Health Services:
- The program aims to enhance the overall quality of mental health services across states and union territories in India, making them more accessible to a larger population.
- Emphasizes the importance of mental health as a public health priority.
South Karanpura Coalfield
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research has highlighted significant shale gas generation potential in the eastern region of the South Karanpura coalfield, located in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand, India. Evidence from microscopic palynomorphs and organic remains, combined with geochemical assessments, indicates that the eastern Sirka coalfield demonstrates a higher potential for hydrocarbon generation compared to the Giddi coalfield to the north.
Overview of the South Karanpura Coalfield
- Location and Size: The South Karanpura coalfield is situated along the Chingara fault and covers approximately 195 square kilometers, housing an estimated 5,757.85 million tonnes of coal reserves.
- Composition: This region is rich in coal, carbonaceous shale, and sandstone layers, making it well-established for its substantial coal deposits.
- Emerging Focus: With increasing energy demands and interest in hydrocarbon exploration, there is a growing emphasis on the potential for coal bed methane and shale gas generation in this area, aligning with national energy strategies for greener energy sources.
Research Methodology
Scientists from the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP) conducted a comprehensive study to evaluate hydrocarbon generation potential. The research involved:
- Sample Collection: Sediments were collected from coal, carbonaceous shale, and sandstone layers at the Sirka and Giddi C collieries in Hazaribagh district.
- Analysis Techniques: The study utilized palynological analysis of microscopic remains, alongside Rock-Eval pyrolysis to assess the potential of the rock samples. Key parameters analyzed included:
- Palynofacies
- Free hydrocarbons (S1)
- Heavy hydrocarbons (S2)
- Pyrolyzable carbon (PC)
- Residual hydrocarbon (RC)
The collected samples, which date back to the Permian (Barakar) period, indicate favorable conditions for high hydrocarbon resource potential in the eastern South Karanpura coalfield.
Shale Gas Overview
Shale gas is an unconventional natural resource found at depths of 2,500 to 5,000 meters, deeper than conventional crude oil. Its extraction involves deep vertical drilling followed by horizontal drilling, with hydraulic fracturing (fracking) being the most common method used to access gas trapped in low-permeability rocks.
New Cancer Therapy Target
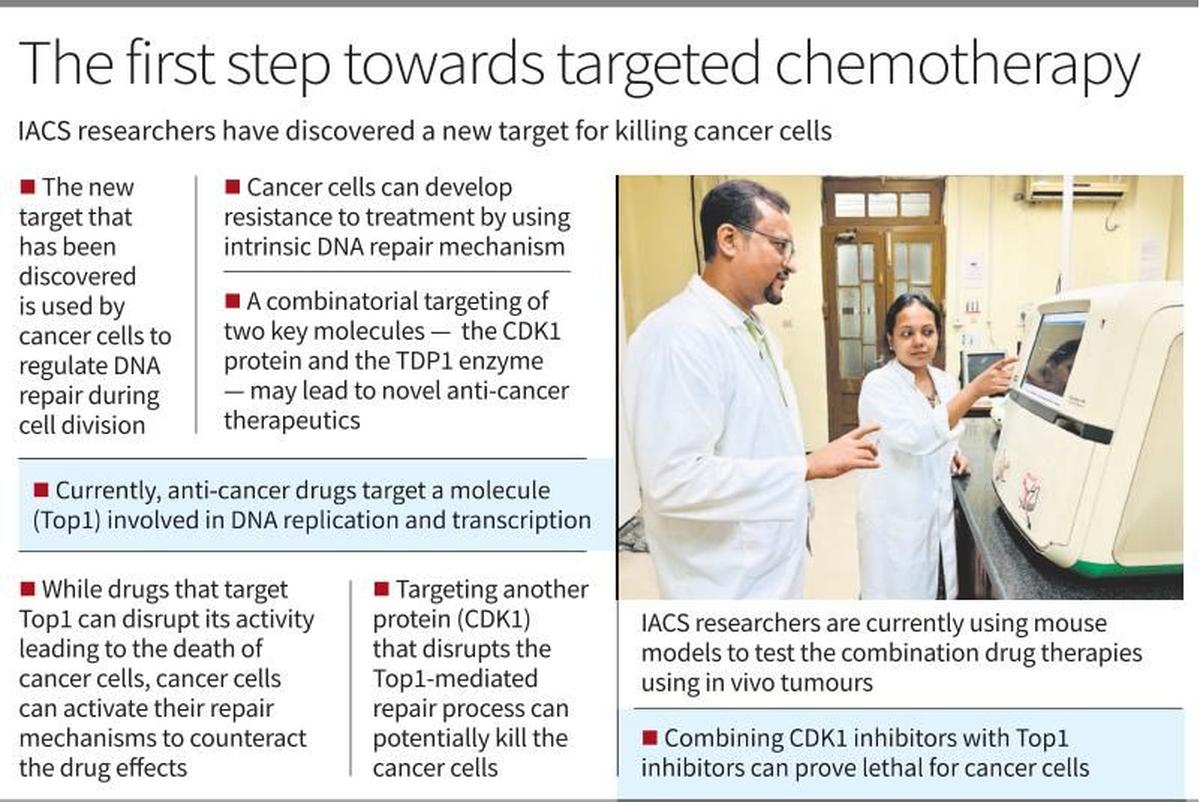
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
NABARD Survey on Rural Financial Inclusion
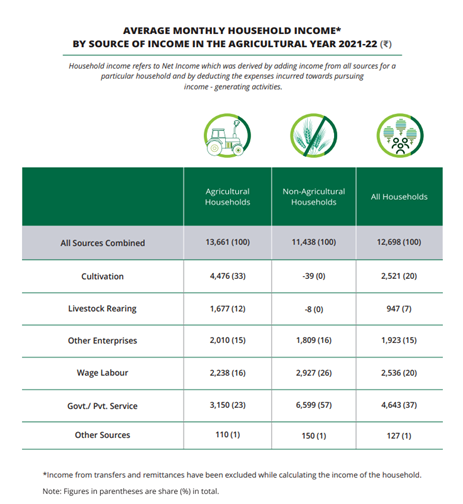
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
NABARD has published the findings from its second All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey (NAFIS) for 2021-22, which offers primary data based on a survey of 1 lakh rural households, covering various economic and financial indicators in the post-COVID period.
Survey Overview:
- Inaugural survey conducted for 2016-17, results released in August 2018.
- Aims to analyze changes in rural economic conditions since 2016-17.
- Included all 28 states and Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Insights from NAFIS 2021-22
- Increase in Average Monthly Income:
- Average monthly income rose by 57.6% from Rs. 8,059 (2016-17) to Rs. 12,698 (2021-22).
- Nominal CAGR of 9.5%, with annual nominal GDP growth at 9%.
- Agricultural households earned Rs. 13,661; non-agricultural households earned Rs. 11,438.
- Salaried employment contributed 37% to total income; cultivation contributed one-third for agricultural households.
- Rise in Average Monthly Expenditure:
- Average monthly expenditure increased from Rs. 6,646 (2016-17) to Rs. 11,262 (2021-22).
- Agricultural households reported higher consumption (Rs. 11,710) compared to non-agricultural households (Rs. 10,675).
- Expenditure exceeded Rs. 17,000 in states like Goa and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Increase in Financial Savings:
- Annual average financial savings grew to Rs. 13,209 in 2021-22 from Rs. 9,104 in 2016-17.
- 66% of households saved in 2021-22, up from 50.6% in 2016-17.
- 71% of agricultural households reported savings, compared to 58% of non-agricultural households.
- States like Uttarakhand (93%) and Uttar Pradesh (84%) had high saving rates, while Goa (29%) and Kerala (35%) had lower rates.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Coverage:
- 44% of agricultural households possessed a valid KCC.
- Among larger landholders and those with recent agricultural loans, 77% reported having a KCC.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Households with at least one insured member increased from 25.5% (2016-17) to 80.3% (2021-22).
- Vehicle insurance was most common (55%), followed by life insurance (24%).
- Pension Coverage:
- Households with at least one member receiving any form of pension rose from 18.9% to 23.5%.
- 54% of households with members over 60 years old reported receiving a pension.
- Financial Literacy:
- Good financial literacy increased by 17 percentage points, from 33.9% to 51.3%.
- Sound financial behavior improved from 56.4% to 72.8%.
Conclusion
- The NAFIS 2021-22 highlights significant advancements in rural financial inclusion since 2016-17.
- Improvements in income, savings, insurance coverage, and financial literacy are notable.
- Government welfare schemes (e.g., PM Kisan, MGNREGS) have positively impacted rural lives.
- Continued support and investment in rural development are essential for economic empowerment and financial security in India's rural population.
Colombo Security Conclave

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) reached a milestone on August 30, 2024 with India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Mauritius signing a Charter and a memorandum of understanding, for the establishment of the CSC secretariat.
Key Facts:
Background of CSC:
- Originally called the NSA Trilateral on Maritime Security, the CSC was established in 2011 among India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. The initiative aimed to bolster maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
Membership:
- The founding members include India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Mauritius joined in 2022, and Bangladesh became a member in 2024. Seychelles participates as an observer state.
Goals of CSC:
The CSC aims to foster cooperation in five main areas:
- Maritime safety and security
- Counterterrorism and prevention of radicalization
- Combating trafficking and transnational organized crime
- Cybersecurity and safeguarding critical infrastructure
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
Defence Exercises:
- In November 2021, India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives held Exercise Dosti XV in the Maldives, marking their first joint military exercise in the Arabian Sea under the CSC framework.
Nobel Prize in Literature 2024

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Prize in Literature 2024 was awarded to South Korean author Han Kang “for her intense poetic prose that confronts historical traumas and exposes the fragility of human life.”
Key Details:
About South Korean author Han Kang
- Literary Style: Known for her physical empathy and metaphorical style; addresses extreme life stories.
- Career Beginnings:
- Started in 1993 with poetry in Literature and Society.
- Prose debut in 1995 with Love of Yeosu.
- Major Work:
- The Vegetarian (2007; English translation 2015).
- Explores violent consequences of protagonist Yeong-hye's refusal to conform to societal norms regarding food.
- Background:
- Born in 1970 in Gwangju, South Korea; later moved to Seoul.
- Comes from a literary family; father is a noted novelist.
- Engaged in art and music, influencing her writing.
- Significance: First South Korean writer to receive the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Previous Nobel Laureate
- 2023 Awardee: Jon Olav Fosse, Norwegian author.
- Contribution: Recognized for "innovative plays and prose which give voice to the unsayable."
Overview of the Nobel Prize
- Definition: Prestigious awards in six fields for those who have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind.
- Fields: Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, Peace, and Economic Sciences.
- Peace Prize: Awarded for advancing international fellowship and promoting peace.
- Establishment: Founded by Alfred Nobel in his will dated 27 November 1895.
- Nobel's Background:
- Born on 21 October 1833 in Stockholm, Sweden.
- Noted for inventing dynamite; had interests in peace, poetry, and drama.
- Died in 1896; allocated his fortune for the prizes.
- First Award: Presented on 10 December 1901.
Prize Money
- Current award amount: $1.1 million per prize.
Note:
Rabindranath Tagore:
- Awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913 for his profound literary contributions.
- Notable works include Manasi, Gitanjali, and Chitra.
Unexpected Transformation of the Sahara Desert
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Sahara Desert, one of the driest regions globally, is undergoing a surprising transformation due to an extratropical cyclone that impacted northwestern Africa on September 7-8, leading to patches of green across Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya.
Key Details:
- Satellite Observations: NASA's satellite images reveal extensive greenery sprouting in areas typically known for drought conditions, as reported by NASA’s Earth Observatory.
- Flourishing Vegetation: Climate researcher Sylwia Trzaska noted that shrubs and trees are thriving in low-lying regions like riverbeds. Peter de Menocal, president of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, highlighted that plant life can quickly respond to significant rainfall, transforming dunes into vibrant landscapes.
- Historical Context: Research indicates that the Sahara was once a lush environment with lakes and vegetation between 11,000 and 5,000 years ago. Recent heavy rains have replenished normally dry lakes.
- Rainfall Dynamics: The unusual rainfall event is attributed to the northward shift of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which has moved further north than usual, resulting in equatorial-like downpours in the Sahara. Some areas experienced over half a foot of rain, surpassing typical annual precipitation levels.
- Impact of Rain Patterns: While the rains primarily affected less populated regions, severe flooding has resulted in over 1,000 fatalities and impacted around four million people across 14 African nations, according to reports from the World Food Programme and Associated Press.
- Climate Change Factors: Experts suggest that the repositioning of the ITCZ may be connected to record-high ocean temperatures and climate change, potentially altering rainfall patterns across Africa.
- Future Projections: As global ocean temperatures stabilize, de Menocal predicts that the rain belt may revert to a more southerly position, potentially crossing the equator.
- Sahara Desert Facts:
o The Sahara is the world's largest hot desert, spanning approximately 4,800 km in length and 1,800 km in width.
o It covers about 31% of the African continent, extending across 11 North African nations, including Algeria, Egypt, Mali, Morocco, Western Sahara, Tunisia, Chad, Libya, Mauritania, Niger, and Sudan
Universal Postal Union

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Universal Postal Union (UPU) is set to assess the integration of the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) with cross-border remittances via the global postal network, according to a recent official announcement.
About the Universal Postal Union
The UPU is a specialized agency of the United Nations and serves as the main platform for international cooperation in the postal sector. Established by the Treaty of Bern in 1874, it stands as the second oldest international organization in the world.
Functions
The UPU coordinates postal policies among its member nations and oversees the global postal system. It establishes the rules for international mail exchanges and makes recommendations aimed at enhancing the volume and quality of mail, parcel, and financial services. Additionally, it plays an advisory, mediating, and liaison role while providing technical assistance when necessary.
Membership
Any member state of the United Nations is eligible to join the UPU. Non-member countries can also become UPU members, subject to approval by at least two-thirds of the existing member nations. Currently, the UPU comprises 192 member countries.
Structure
The UPU consists of four main bodies:
1. The Congress: The highest authority of the UPU, convening every four years.
2. The Council of Administration: Responsible for ensuring the continuity of UPU operations between Congresses and supervising activities related to regulatory, administrative, legislative, and legal matters.
3. The Postal Operations Council: Acts as the technical and operational hub of the UPU, composed of 48 member countries elected during Congress.
4. The International Bureau: Functions as the secretariat, providing logistical and technical support to the other UPU bodies.
The headquarters of the Universal Postal Union is located in Bern, Switzerland.
Caracal

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Gujarat government has recently announced plans to establish a Caracal Breeding and Conservation Center in the Chadva Rakhal area of Kutch, with a budget of ?10 crore.
About the Caracal
- The caracal, known locally as "siya gosh" (meaning "black ear" in Persian), is a reclusive and primarily nocturnal feline celebrated for its agility and remarkable skill in catching birds mid-flight.
- In terms of nesting, caracals typically utilize abandoned porcupine burrows or rock crevices for denning and are often found with their young hidden among dense vegetation. They tend to live in small groups, and their elusive behavior makes them hard to spot in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
Caracals inhabit various environments, including woodlands, savannahs, and scrub forests. In India, suitable habitats are found in regions such as Kutch, the Malwa Plateau, the Aravalli hills, and Bundelkhand. This species is also present in numerous countries across Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia.
Threats to Survival
The caracal faces significant threats from extensive hunting, illegal wildlife trade, and the destruction of its natural habitats.
Conservation Status
According to the IUCN, the caracal is classified as "Least Concern." In India, it is protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
RBI's Recent Monetary Policy Review
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintained its benchmark interest rate at 6.5% for the 10th consecutive monetary policy review since April 2023. The policy stance was shifted to “neutral,” indicating potential for a future rate cut.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Overview
- The decision to keep interest rates unchanged was supported by a majority of five out of six members of the MPC, which convened for three days starting October 7.
- The change in policy stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral” was unanimously agreed upon.
Focus Areas
- The MPC emphasized the need for a durable alignment of inflation with targets while supporting economic growth.
- Macroeconomic parameters for inflation and growth were described as well balanced.
Inflation Insights
- A moderation in headline inflation is expected to reverse in September, likely remaining elevated due to adverse base effects.
- Retail inflation was below the central bank’s median target of 4% in July and August.
Growth Projections
- The RBI maintained its 7.2% GDP growth projection and a 4.5% average inflation estimate for 2024-25, with risks evenly balanced.
- Second-quarter inflation projection was revised down to 4.1% from 4.4%, while a rise to 4.8% is expected for the October to December quarter.
Domestic Growth and Investment
- Domestic growth remains robust, with private consumption and investment growing together.
- This growth has provided the RBI with the capacity to prioritize inflation control to achieve the 4% target.
Risks to Inflation
The Governor highlighted that unexpected weather events and escalating geopolitical conflicts pose significant upside risks to inflation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC)

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the development of NMHC in Lothal, Gujarat, under the Sagarmala programme.
- Purpose and Vision Aimed at showcasing India’s 4,500-year-old maritime heritage using an edutainment approach with modern technology.
Employment Generation
- Expected to create approximately 22,000 jobs: 15,000 direct and 7,000 indirect.
Project Phases
- Phase 1A
- Features a museum with 6 galleries, including:
- A large Indian Navy & Coast Guard gallery with external naval artifacts.
- Replica of Lothal township surrounded by an open aquatic gallery.
- A jetty walkway.
- Phase 1B
- Expansion includes:
- 8 additional galleries.
- The world's tallest Light House Museum.
- Bagicha complex with facilities for 1,500 cars, a food hall, and a medical center.
- Phase 2
- Development of Coastal States Pavilions by respective states and union territories.
- Hospitality zone featuring maritime-themed eco-resorts and museuotels.
- Recreation of ancient Lothal City and establishment of a Maritime Institute with hostel.
- Creation of four theme-based parks:
- Maritime & Naval Theme Park
- Climate Change Theme Park
- Monuments Park
- Adventure & Amusement Park
Governance and Management
- Governing Council
- Chaired by the Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, overseeing project implementation and operation.
- Separate Society
- A dedicated society will manage future phases, governed under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
Benefits and Funding
- Beneficiaries
- Local communities, tourists, researchers, government bodies, educational institutions, cultural organizations, conservation groups, and businesses.
- Funding
- Construction of the Light House Museum in Phase 1B will be financed by the Directorate General of Lighthouses and Lightships (DGLL).
Sagarmala Programme
- Objective
- A flagship initiative aiming to transform India’s maritime sector by enhancing logistics performance and fostering port-led development and coastal community upliftment.
- Background
- Approved in March 2015, the programme focuses on utilizing India’s extensive coastline and waterways for economic growth.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)

- 09 Oct 2024
Recent Initiatives:
- The Indian government has launched a nationwide survey of kutcha houses.
- Introduction of the Awas Sakhi mobile app to streamline housing assistance.
Purpose of the Kutcha House Survey
- Identify Housing Needs: The survey aims to collect data on families living in kutcha (temporary) houses, enabling targeted support for those in need.
- Support for Awas Sakhi App: The survey will enhance the functionality of the Awas Sakhi app, facilitating the application process and providing beneficiaries with vital housing information.
Overview of PMAY-G
- Launch: Initiated in 2016, PMAY-G aims to provide secure housing for the poorest communities.
- Beneficiary Selection Process: A comprehensive three-stage validation, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensures that aid reaches those most deserving.
Benefits for PMAY-G Beneficiaries
- Financial Assistance:
- ?1.20 lakh for families in plain areas.
- ?1.30 lakh for families in hilly regions, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Support for Sanitation:
- An additional ?12,000 for toilet construction, aligned with the Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin or MGNREGS.
- Employment Opportunities:
- Provision of 90/95 days of unskilled wage employment through MGNREGA for house construction.
- Access to Basic Amenities:
- Connections for water, LPG, and electricity facilitated through relevant schemes.
- Cost Sharing Structure:
- Expenses are shared in a 60:40 ratio for plain areas and a 90:10 ratio for northeastern states and selected Himalayan states. The Centre covers 100% of costs for other Union Territories.
Progress Under PMAY-G
- Targets: The government aims to construct 2.95 crore houses.
- Current Status: As of August 2024, 2.94 crore houses have been sanctioned, with 2.64 crore completed, enhancing living conditions for millions in rural areas.
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, the Union Cabinet approved funding for two crore additional houses at existing assistance rates.
- Eligibility Criteria Changes:
- Individuals owning bikes or scooters are now eligible.
- The income limit for eligibility has been raised from ?10,000 to ?15,000 per month.
Future Goals
- This initiative, spanning FY 2024-2029, aims to address ongoing housing demands, benefiting approximately 10 crore individuals by providing safe, hygienic, and socially inclusive housing.
2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
U.S. Scientists David Baker and John Jumper and Britain’s Demis Hassabis won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, for their work on understanding the protein structures.
Prize Distribution
- David Baker: Awarded half of the Prize for pioneering work in computational protein design.
- Demis Hassabis and John Jumper: Jointly awarded the other half for their revolutionary contributions to protein structure prediction using artificial intelligence.
Significance of Achievements
- The advancements in protein science represent a major milestone for healthcare and biotechnology.
- These innovations have unlocked new possibilities for designing proteins, potentially leading to breakthroughs in medicine, agriculture, and more.
David Baker's Innovations
- Baker has achieved the significant feat of creating entirely new types of proteins, enhancing our understanding of protein functionality.
- In 2003, he designed a novel protein using amino acids and custom software methods, which opened avenues for rapid protein creation.
- Applications include pharmaceuticals, vaccines, nanomaterials, and tiny sensors.
AI Contributions by Hassabis and Jumper
- Demis Hassabis and John Jumper employed advanced artificial intelligence to address the challenge of predicting complex protein structures.
- In 2020, they introduced the AI model AlphaFold2, which can predict the structure of nearly all identified proteins (approximately 200 million).
Notable Facts about the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded 116 times to 197 laureates from 1901 to 2024.
- Frederick Sanger and Barry Sharpless are the only recipients to have won the Prize twice.
- The inaugural Prize was awarded in 1901 to Jacobus H. van ‘t Hoff for his work on chemical dynamics and osmotic pressure.
- Marie Curie became the first woman to win the Prize in 1911 for her discovery of radium and polonium.
- Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, a citizen of Indian origin, received the Prize in 2009 for his research on ribosomes.
2024 Nobel Prize in Physics

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton won the 2024 Nobel Prize for physics “for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks”. Their work lies at the roots of a large tree of work, the newest branches of which we see today as artificially intelligent (AI) apps like ChatGPT.
Significance of ANNs
- Definition: ANNs are collections of interconnected nodes that mimic the networks of neurons in animal brains, enabling machines to process data, recognize patterns, and learn.
- Applications: Integral to AI applications such as facial recognition, language translation, and numerous fields including physics, chemistry, and medicine.
Historical Context
- Hopfield Network:
- Developed by John Hopfield in 1983.
- Based on Donald Hebb's neuropsychological theory of learning, emphasizing how connections between neurons strengthen through repeated interactions.
- Capable of storing and reconstructing images by adjusting node connections to achieve a low-energy state, effectively denoising input.
- Boltzmann Machine:
- Geoffrey Hinton's work on deep-learning machines, building on Ludwig Boltzmann's statistical mechanics.
- Introduced the concept of generative AI through networks that differentiate between probable outcomes.
- Developed Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) in the 2000s, enhancing learning efficiency through layered networks.
Evolution and Current State of ANNs
- Technological Progress: ANNs have evolved significantly, transitioning from individual computers to distributed networks like the cloud.
- Current Variants: Innovations include transformers, backpropagation, and long short-term memory techniques, making ANNs more capable and widely accessible.
Concerns and Risks
- Ethical Considerations: Rapid advancements in AI raise concerns about safety, misinformation, and job displacement.
- Expert Opinions: Both Hopfield and Hinton have expressed worries about the implications of AI systems surpassing human intelligence and the potential for misuse.
Trachoma

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has now recognised that India has successfully eliminated trachoma, a bacterial infection that affects the eyes, as a public health problem.
WHO Declaration:
- India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem (2024).
- Third country in the South-East Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
Trachoma Overview:
- Bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis.
- Contagious; spreads through contact with infected secretions.
- Can lead to irreversible blindness if untreated.
- Considered a neglected tropical disease.
Global Impact:
- WHO estimates 150 million affected worldwide; 6 million at risk of blindness.
- Most prevalent in underprivileged communities with poor living conditions.
Historical Context in India:
- Leading cause of blindness in the 1950s-60s.
- National Trachoma Control Program launched in 1963.
- Control efforts integrated into the National Program for Control of Blindness (NPCB).
Statistics:
- Blindness due to Trachoma was 5% in 1971; now reduced to less than 1%.
- Implementation of the WHO SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial hygiene, Environmental cleanliness).
Milestones:
- India declared free from infective Trachoma in 2017.
- Continued surveillance for cases from 2019 to 2024.
National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT) Survey:
- Conducted in 200 endemic districts (2021-2024) under NPCBVI.
- Mandated by WHO to confirm elimination status.
MACE Observatory

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The MACE Observatory was recently inaugurated by the Secretary of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission in Hanle, Ladakh.
About MACE Observatory
- Name: Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory.
- Significance:
- Largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia.
- Highest imaging Cherenkov observatory in the world.
- Location: Situated at approximately 4,300 meters altitude in Hanle, Ladakh.
- Indigenous Development:
- Built by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- Supported by the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL), Hyderabad, and other Indian industry partners.
Scientific Contributions
- Research Focus:
- Enhances understanding in astrophysics, fundamental physics, and particle acceleration mechanisms.
- Observes high-energy gamma rays to investigate cosmic phenomena like supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts.
- Global Impact:
- Aims to foster international collaborations in space research.
- Strengthens India’s position in the global scientific community.
Socio-Economic Role
- Local Impact: Contributes to the socio-economic development of Ladakh, promoting scientific awareness and opportunities.
Understanding Cherenkov Radiation
- Definition: A blue glow emitted when charged particles (e.g., electrons and protons) travel faster than light in a specific medium.
- Historical Note: Named after Pavel Cherenkov, who, along with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958 for his work in demonstrating and explaining this phenomenon.
UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
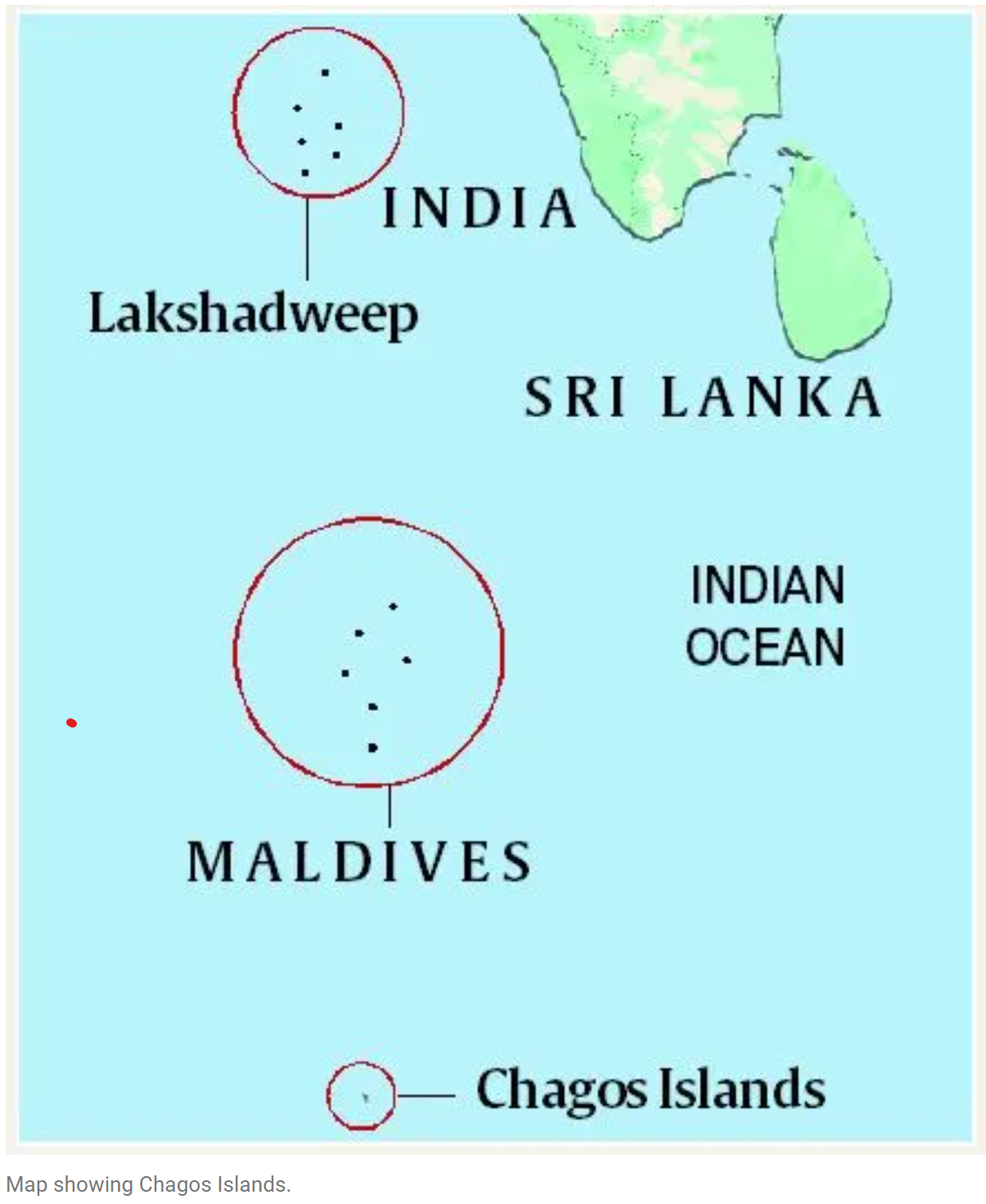
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Kingdom said it would cede sovereignty of the strategically important Chagos Islands to Mauritius, calling it a “historic political agreement”. The UK has long controlled Chagos and the Diego Garcia military base located there, jointly operating it with the United States.
Background of the Chagos Archipelago
Historical Context
- The Chagos archipelago consists of 58 islands located about 500 km south of the Maldives.
- Initially uninhabited, the islands were populated in the late 18th century through the importation of slave labor.
- The islands were ceded to Britain from France in 1814, and in 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which includes Chagos.
Controversy Over Sovereignty
- Mauritius, a former British colony, claims that the detachment of Chagos from its territory during its independence in 1968 was illegal.
- The UK compensated Mauritius with a grant but retained control, establishing a military base on Diego Garcia.
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
Military Significance
- Diego Garcia has been a crucial U.S. military base since its operational status began in 1986.
- It played a key role in U.S. military operations during conflicts in the Gulf, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The base enables rapid response to crises and supports regional security, especially in light of U.S. interests in monitoring key trade routes like the Malacca Strait.
Geopolitical Implications
- The presence of the U.S. military in the Indian Ocean is vital for countering security threats, particularly regarding China's growing influence.
Recent Developments: The UK-Mauritius Agreement
Key Features of the Treaty
- On October 3, 2023, the UK agreed to cede sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, marking a significant political shift.
- The treaty allows Mauritius to resettle Chagossians (excluding Diego Garcia) and establishes a trust fund for their benefit.
- Despite this, the UK retains control over Diego Garcia for an initial period of 99 years.
Implications of the Agreement
- The resolution of the sovereignty issue may strengthen Western commitments to a stable and free Indo-Pacific region.
- If unresolved, tensions could push Mauritius toward seeking alliances with alternative powers like China.
India’s Position and Interests
Support for Mauritius
- India has historically supported Mauritius in its claims over Chagos, reflecting its stance against colonial legacies.
- In 2019, India voted in favor of Mauritius at the UN General Assembly regarding the Chagos dispute.
Strategic Partnerships
- With increasing Chinese assertiveness in the Indian Ocean, India has been strengthening its ties with Mauritius.
- Recent initiatives include the inauguration of an India-built airstrip and jetty in Agaléga, enhancing connectivity and support for Mauritius.
Conclusion
The UK-Mauritius treaty over the Chagos Archipelago marks a significant turning point in colonial legacies and geopolitical alliances in the Indian Ocean. For India, supporting Mauritius aligns with its broader strategic interests and enhances its influence in a region marked by competing global powers. As the dynamics evolve, India's role in fostering regional stability and partnerships will be crucial.
44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses

- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
India Participates in 44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses
Key Contributions:
- Nutrient Reference Values:
- Advocated for reference values for ages 6 to 36 months.
- Suggested combining NRV-R values by averaging those for 6-12 months and 12-36 months.
- This proposal was accepted by the committee.
- Probiotic Guidelines:
- Emphasized the need to update FAO/WHO probiotic guidelines, which are two decades old.
- Highlighted the lack of international harmonization in probiotic regulations affecting global trade.
- Committee agreed to revisit guidelines and requested FAO and WHO to conduct a literature review on probiotics.
- Discussion on Sweetness Assessment:
- Disagreed with the EU’s sensory testing proposal for carbohydrate sources in Follow-up Formula, citing lack of scientific validation.
- Supported by USA, Canada, and others; this led to the committee discontinuing the topic for now.
- Noted that ISO 5495 or other methods could be used in the absence of harmonized methods.
- Delegation:
- Included representatives from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Advocated for various food safety, consumer health, and trade-related issues.
- Outcome:
- India’s suggestions were officially incorporated into the final report, significantly influencing global food safety and nutrition standards.
- Additional Announcements:
- FAO/WHO plans for a Joint Statement on Healthy Diet Principles.
- Updates on reviewing benefits and risks of Alternative Animal Source Foods (A-ASFs).
- FAO introduced a new “Food and Diet” domain on its FAOSTAT database.
Marburg Virus
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
- Definition:
- Marburg virus is one of the deadliest pathogens known to infect humans, causing severe hemorrhagic fever.
- Current Situation in Rwanda:
- Rwanda reported its first Marburg case late last month.
- At least 46 individuals have been infected, with 12 reported deaths.
- Approximately 80% of infections are among medical workers.
- The outbreak poses a significant threat to Rwanda’s fragile healthcare system, which has only 1,500 doctors for over 13 million people.
Characteristics of Marburg Virus
- Deadliness:
- Marburg virus disease (MVD) has case fatality rates ranging from 24% to 88%, depending on the strain and case management.
- The first outbreak occurred in Marburg, Germany, in 1967, with subsequent outbreaks primarily in Africa.
- Family:
- Marburg belongs to the filovirus family, which includes Ebola.
- Both viruses are clinically similar and can cause high-fatality outbreaks.
Transmission
- Initial Infection:
- Human infections initially occurred through prolonged exposure to mines or caves inhabited by Rousettus bats (notably the Egyptian fruit bat).
- Human-to-Human Transmission:
- MVD spreads directly through contact with blood and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
- Indirect transmission can occur via contaminated surfaces and materials (bedding, clothing).
- Risk for Medical Workers:
- Medical workers treating MVD cases are frequently infected, especially when infection control measures are inadequate.
Symptoms of Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)
- Incubation Period: Symptoms can appear 2 to 21 days after infection.
- Initial Symptoms: High fever, Severe headache, Muscle ache, Watery diarrhea, Abdominal pain and cramping, Vomiting
- Hemorrhagic Symptoms:
- Many patients develop bleeding from various sites, including the digestive system (fresh blood in feces and vomit), nose, gums, and vagina.
- Fatalities often occur due to severe blood loss and shock, typically 8 to 9 days after symptom onset.
Prevention and Treatment
- Current Status:
- No approved vaccines or specific treatments exist for MVD.
- Supportive Care:
- Rehydration (oral or intravenous fluids) and symptom management improve survival rates.
- Experimental Treatments:
- Rwanda is seeking experimental vaccines and treatments to address the outbreak.
- The US-based Sabin Vaccine Institute provided 700 doses of an experimental Marburg vaccine for healthcare professionals on the frontlines.
Genome Editing and Hereditary Cancers
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Agency for Research on Cancer’s estimates of the burden of 36 cancers in 185 countries suggest one in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer.
- Impact of CRISPR on Cancer Research:
- CRISPR screens have revolutionized the study of BRCA genes through high-throughput functional genetic analysis.
- Researchers use CRISPR-Cas9 to create specific mutations in BRCA genes, studying their effects on DNA repair and cancer development.
- Cancer Statistics:
- One in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer (International Agency for Research on Cancer).
- In 2022, there were approximately 20 million new cancer cases and 9.74 million cancer-related deaths; projections suggest these could rise to 32 million new cases and 16 million deaths by 2045, with Asia potentially accounting for half of the cases.
- Genetic Mutations and Inheritance:
- All cancers stem from genetic mutations; about 10% of cancer cases may involve inherited mutations.
- Specific inherited mutation prevalence:
- 20% in ovarian cancer patients.
- 10% in breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancers.
- 6% in cervical cancer.
- BRCA Genes Overview:
- The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, discovered in 1994 and 1995, are crucial for understanding hereditary cancer syndromes.
- Mutations in BRCA genes significantly increase the risk of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers.
- BRCA mutations are estimated to occur in 1 in 400 individuals, with higher prevalence (1 in 40) among Ashkenazi Jews due to genetic bottlenecks and founder effects.
- Importance of Genetic Testing:
- Testing for BRCA mutations helps identify individuals at higher risk, enabling personalized prevention strategies such as increased surveillance or preventive surgery.
- The American Society of Clinical Oncology recommends testing for 15 genes related to breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Targeted Therapies:
- PARP inhibitors represent a new class of chemotherapy drugs effective for cancers with BRCA mutations.
- Clinical trials show promising results, especially when combined with platinum-based chemotherapy.
- Advancements in Understanding Cancer Genes:
- CRISPR technology has improved our understanding of cancer-related genes, enabling researchers to study the effects of specific mutations.
- Studies have identified how different mutations influence responses to therapies like PARP inhibitors.
- Recent Research Findings:
- Research from the Wellcome Sanger Institute identified over 3,000 genetic changes in the RAD51C gene that could significantly increase breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Variants disrupting RAD51C function can increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and aggressive breast cancer risk four-fold.
- Risk Spectrum:
- Genetic risk is a spectrum based on how mutations affect protein function.
- Large-scale variant analysis is vital for personalized medicine and cancer prevention.
- Role of Population Studies:
- Population prevalence studies help identify hereditary cancer risks and inform genetic screening for at-risk individuals.
- Early cancer detection allows for better healthcare decisions and potential preventive therapies.
- Goals for Cancer Management:
- The ultimate aim is to reduce cancer morbidity and mortality, leading to healthier lives for individuals and families.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024: MicroRNA Research

- 08 Oct 2024
Overview
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. This award highlights their individual contributions to understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression, significantly advancing the field of molecular biology.
What are MicroRNAs?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules typically 19-24 nucleotides long. They regulate protein production by interacting with messenger RNA (mRNA), ultimately influencing how much protein is synthesized from genetic information.
The Process of Gene Regulation
Gene expression involves two primary steps:
- Transcription: DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into proteins by ribosomes with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA).
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating this process, particularly after transcription, by silencing mRNA and thereby controlling protein production.
Pioneering Research
Background
In the late 1980s, Ambros and Ruvkun utilized the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a small roundworm, to explore developmental processes. They focused on mutant strains, lin-4 and lin-14, which displayed abnormal development.
Key Discoveries
- Victor Ambros: Ambros cloned the lin-4 gene and discovered that it produced a short RNA molecule that did not code for proteins. This finding suggested that lin-4 could inhibit lin-14’s activity.
- Gary Ruvkun: Ruvkun investigated the regulation of the lin-14 gene and determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA. Instead, it inhibited protein production later in the gene expression process. He identified crucial segments in lin-14 mRNA essential for its inhibition by lin-4.
Collaborative Findings
Their subsequent experiments demonstrated that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking the production of lin-14 protein. Their findings were published in 1993 and laid the foundation for the understanding of microRNA.
Impact and Recognition
Initially, the significance of their discoveries was not widely recognized, as it was thought that microRNA regulation was specific to C. elegans. However, Ruvkun’s later identification of the let-7 gene, a microRNA found in various animal species, broadened the understanding of microRNAs' universal role in gene regulation.
Current Understanding
Today, it is known that humans possess over a thousand genes that code for different microRNAs. These molecules are crucial in regulating gene expression across multicellular organisms.
Applications and Future Directions
MicroRNAs can fine-tune gene expression, influencing various cellular functions despite similar genetic backgrounds. Abnormal microRNA regulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. While the Nobel Committee acknowledged that practical applications of miRNA research are still developing, understanding these molecules is vital for future research and therapeutic advancements.
Doddalathur Megalithic Burial Site

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore have embarked on an excavation of megalithic burial sites in Chamarajanagar district.
- Location: Doddalathur village, Hanur taluk, Chamarajanagar district, situated in a valley by the Male Mahadeshwara Hill ranges.
- Team: A group of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore, in collaboration with the Mythic Society, Bengaluru.
- Excavation Focus: Exploration of megalithic burial sites corresponding to the Iron Age (approximately 1200 BC to 300 CE).
- Site Features:
- Burials consist of circles made of large boulders, referred to as "megalithic."
- A small hillock is located to the west of the village.
- Historical Significance:
- The site was discovered by C. Krishnamurti of the Archaeological Survey of India in 1961.
- Originally contained over 1,000 burials, many of which have been lost due to agricultural expansion and development.
- Despite disturbances, many burials remain intact and are considered suitable for excavation.
- Goals of the Project:
- To enhance understanding of megalithic-Iron Age culture in southern Karnataka's hilly regions.
- To provide practical field training for archaeology students.
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024, Commencing at Visakhapatnam on 08 Oct Hosted by India, USA, Australia and Japan in Participation.
Background
- Origins: Initiated in 1992 as a bilateral naval drill between the United States and Indian Navy.
- Evolution: Has grown into a key multilateral exercise aimed at enhancing interoperability and addressing maritime challenges in the Indian Ocean and Indo-Pacific region.
Participating Naval Assets
- India: Various platforms, including:
- Guided missile destroyers
- Multi-purpose frigates
- Submarines
- Fixed-wing maritime reconnaissance aircraft
- Fighter aircraft and helicopters
- Australia:
- HMAS Stuart (Anzac Class Frigate)
- MH-60R helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- United States:
- USS Dewey (Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyer)
- Integral helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- Japan:
- JS Ariake (Murasame-class Destroyer)
Focus Areas of the Exercise
- Operational Enhancements:
- Discussions on special operations
- Surface, air, and anti-submarine warfare
- Subject Matter Expert Exchange (SMEE)
- Maritime Operations:
- Anti-submarine warfare
- Surface warfare
- Air defense exercises
- Emphasis: Improving situational awareness in the maritime domain.
Special Events
- Distinguished Visitors’ Day: Scheduled for October 9, 2024.
- Hosted by Vice Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Eastern Naval Command.
- Joint Press Conference: Co-chaired by heads of delegations from all participating nations during the Harbour Phase.
Significance
- Comprehensive Exercise: Malabar 2024 is expected to be the most detailed edition to date, featuring complex operational scenarios and enhanced cooperation among the naval forces of the participating countries.GS Paper
DefConnect 4.0

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
- DefConnect 4.0 was inaugurated by Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh on October 7, 2024, at Manekshaw Centre, Delhi Cantonment.
- Organizer: Hosted by Innovations for Defence Excellence - Defence Innovation Organisation (iDEX-DIO) under the Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence.
Purpose and Focus
- Advancing Indigenous Innovation: Aims to enhance India’s defense ecosystem by promoting self-reliant defense technologies.
- Participants: Involves Armed Forces, Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), start-ups, MSMEs, academia, incubators, investors, and policymakers.
Technology Showcase
- Exhibitions: iDEX innovators showcased cutting-edge technologies, products, and capabilities.
- Collaboration and Dialogue: Encourages partnerships and discussions to drive defense innovation and long-term collaborations.
Special Sessions
- Budget Insights: Focused on key takeaways from recent budget announcements impacting the defense innovation ecosystem.
- Semiconductor Domain: Highlighted initiatives and opportunities within the semiconductor sector.
Path Forward: Vision for 2047
- Viksit Bharat Goal: Aligns with India’s vision of becoming a global leader in defense innovation by 2047.
- Government Initiatives: Supports local talent and indigenous solutions through programs like iDEX.
iDEX Impact
- Defence India Start-up Challenges: 11 editions launched, garnering over 9,000 applications.
- Collaborations: Engages with over 450 start-ups/MSMEs on significant defense projects.
- Contribution to Self-Reliance: Supports the goal of achieving self-reliance in the defense and aerospace sectors.
India’s Tripartite Agreement

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Nepal, India, and Bangladesh have signed a tripartite agreement to facilitate cross-border electricity trade, enabling Nepal to export surplus electricity to Bangladesh via India.
Key Details of the Agreement
- Export Period: The agreement allows for electricity exports from June 15 to November 15 each year.
- Initial Export Volume: In the first phase, Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Electricity Rate: The fixed rate per unit of electricity is set at 6.4 cents.
- Projected Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn approximately $9.2 million annually from this trade.
This agreement aims to enhance regional cooperation in energy trade and support sustainable development in the participating countries.
Increasing Frequency of Typhoons in Southeast Asia
- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Overview of Typhoons
- Definition: A typhoon is a type of cyclone with wind speeds of 119 km/h or more, forming over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- Mechanism: As warm, moist air rises from the ocean, it creates a low-pressure system, leading to the characteristic circular wind patterns: anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Recent Typhoon Events
- Typhoon Yagi: The most powerful tropical cyclone in Asia in 2024, with peak winds of 260 km/h. It caused significant destruction across Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand, displacing around 631,000 people and resulting in over 500 fatalities.
- Typhoon Bebinca: Reached wind speeds of 151 km/h, classified as a Category 1 storm, impacting eastern China with heavy rainfall and forcing evacuations for over 414,000 residents.
- Typhoon Shanshan: Affected Japan, bringing severe weather conditions.
Why are Typhoons more frequent?
- Rising Sea Surface Temperatures:
- Global warming has raised ocean temperatures, providing more energy for typhoon formation and intensification.
- Atmospheric Circulation Changes:
- Alterations in patterns, such as the weakening of the Walker Circulation, affect the frequency and paths of typhoons.
- El Niño and La Niña Effects:
- The El Niño-Southern Oscillation significantly influences typhoon activity. El Niño years often lead to increased typhoon occurrences in Southeast Asia, while La Niña can enhance cyclone activity in the Western Pacific.
- Increased Atmospheric Moisture:
- Higher global temperatures result in more evaporation, adding moisture to the atmosphere, which fuels stronger storms and increases rainfall intensity.
- Geographical Vulnerability:
- Southeast Asia’s location near warm ocean currents makes it a hotspot for typhoon activity, particularly along its extensive coastlines.
- Marine Heat Waves:
- Climate change has led to more frequent marine heat waves, causing extreme ocean warming, which contributes to intensified storms.
- Weaker Land-Sea Temperature Gradients:
- Changes in temperature differences between land and sea can prolong storm duration and severity.
- Urbanization and Environmental Degradation:
- Rapid urban development and the destruction of coastal ecosystems, like mangroves, diminish natural barriers against storm impacts.
Humanitarian Impact and Response
- The increasing intensity and frequency of typhoons have precipitated severe humanitarian crises in affected regions. The need for international cooperation in disaster response has become critical, involving collaboration among governments, civil societies, and humanitarian organizations to provide aid and support for those affected.
- Understanding the multifaceted reasons behind the rising frequency of typhoons is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts and enhance community resilience in Southeast Asia.
Mpox Diagnostic Test

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
In an important move to improve global access to Mpox testing, the World Health Organization (WHO) has listed the first Mpox in vitro diagnostic under its Emergency Use Listing procedure.
- Context of Mpox Outbreak:
- Since January 2022, mpox has spread to 121 countries.
- By September 2024, there were 103,048 confirmed cases and 229 deaths.
- Diagnostic Test Approval:
- WHO approved Abbott Laboratories’ PCR diagnostic test, Alinity MPXV assay, for emergency use.
- This test detects mpox virus DNA from skin swabs, intended for trained lab personnel.
- Emergency Use Listing (EUL) Procedure:
- Allows WHO to expedite approval of unlicensed vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tests during public health emergencies.
- In August, WHO called for manufacturers to submit diagnostic tools to aid low-income countries.
- Current Testing Landscape:
- Limited testing capacity has hindered response, especially in Africa, where over 30,000 suspected cases were reported in 2024.
- 35 laboratories in India are now equipped to test suspected mpox cases.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early detection facilitates timely treatment and control of the virus, essential in outbreak areas.
- Characteristics of the Alinity MPXV Assay:
- Utilizes real-time PCR to detect mpox virus (clade I/II) DNA from lesion materials.
- Designed for skilled laboratory personnel familiar with PCR techniques.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- WHO is reviewing three additional mpox diagnostic tests and negotiating with more companies to enhance availability.
- Efforts include addressing the spread of a new variant, clade Ib, which is affecting more women and children.
- Public Health Implications:
- Expanding access to diagnostics is vital for managing the mpox outbreak and protecting populations, particularly in underserved regions.
- WHO emphasizes the importance of quality-assured medical products in containing the virus spread.
Discovery of New Hammerhead Shark Species

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of marine biologists led by a Florida International University researcher has described a new species of the shark genus Sphyrna from the Caribbean and the Southwest Atlantic.
- New Species: Named Sphyrna alleni (common name: shovelbill shark).
- Habitat: Found in coastal waters, estuaries, coral reefs, and seagrass beds from Belize to Brazil, with confirmed presence in:
- Caribbean: Belize, Panama, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago.
- Southwestern Atlantic: Brazil.
- Characteristics:
- Small species, less than 1.5 m in length.
- Distinctive flat, shovel-shaped head lacking indentations on the anterior edge.
- Different from Sphyrna tiburo:
- More rounded anterior margin.
- Absence of lobules on the posterior margin.
- Higher precaudal vertebral count (80-83 vs. ~73 in Sphyrna tiburo).
- Evolutionary Insight: Possible sister lineage to Sphyrna vespertina, suggesting Sphyrna tiburo diverged later.
- Conservation Status:
- Hammerhead sharks are highly threatened, primarily due to overfishing.
- Most species, except Sphyrna gilberti, are listed as Vulnerable, Endangered, or Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- Current IUCN assessment of Sphyrna tiburo as Globally Endangered may need reevaluation considering the new findings.
- Management Recommendations:
- Increased management efforts needed for Sphyrna alleni, particularly restrictions on gillnets and trawls, which significantly impact this species.
- Publication: Findings reported in the journal Zootaxa.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar will attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Heads of Government meeting in Islamabad on October 15-16, 2023.
- This marks the first visit by an Indian External Affairs Minister to Pakistan since Sushma Swaraj in 2015.
Context of the Visit:
- The visit is primarily for the SCO meeting, reflecting India's focus on regional cooperation mechanisms.
- No bilateral meetings have been scheduled as of now, although Jaishankar's presence is based on "reciprocity" following Pakistan's participation in an earlier SCO meeting in India.
SCO Overview:
- Established on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai; evolved from the "Shanghai Five" formed in 1996.
- Original members included China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and later Uzbekistan.
- Current members: India, Pakistan, Iran, and others, with Afghanistan and Mongolia holding Observer Status.
Significance of the SCO:
- Focuses on security cooperation, primarily among Asian nations.
- Seen as an alternative to Western international frameworks, especially with heavyweights like Russia and China positioning against US influence.
- India's inclusion alongside Pakistan in 2017 reflects the geopolitical jostling between Russia and China.
Geopolitical Dynamics:
- While SCO promotes cooperation, underlying tensions remain, particularly between India and Pakistan, and India and China.
- The organization has limited tangible outcomes due to member states' rivalries and differing interests.
India's Objectives in SCO:
- Provides a platform for enhancing relations with Central Asian countries, addressing common security concerns.
- Involves participation in the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) to combat terrorism and drug trafficking.
India-Pakistan Relations:
- Jaishankar's visit is seen in light of ongoing tensions; India shares difficult relations with both China and Pakistan.
- India canceled a summit under its presidency last year, opting for a virtual format instead.
Implications for Regional Politics:
- The visit comes shortly after the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections, with potential implications for India-Pakistan ties.
- Despite attending the SCO meeting, there is little expectation of progress in the India-Pakistan peace process.
- Recent statements from the Indian government criticize Pakistan for hosting wanted individuals, reflecting ongoing diplomatic tensions.
Strategic Importance:
- Participation in SCO allows India to engage with key regional players, including Russia, China, and Central Asian leaders.
- The meeting serves as preparation for India's participation in upcoming BRICS discussions, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these groupings.
Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP) to tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:
- Tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses (e.g., Zika, chikungunya).
- Reduce disease burden, suffering, and deaths globally.
- Background:
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Unplanned urbanization.
- Poor water, sanitation, and hygiene practices.
- Climate change.
- Increased international travel.
- An estimated 4 billion people at risk, projected to increase to 5 billion by 2050.
- Significant increase in dengue cases; 12.3 million reported by August 2023, nearly double the total from 2022.
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Global Impact:
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- South-East Asia.
- Western Pacific.
- Americas.
- Africa facing compounded health crises due to conflicts and disasters.
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- Emergency Grade: WHO has graded the global dengue situation as grade 3, the highest emergency level.
- Key Components of SPRP:
- Emergency Coordination: Leadership and coordination activities for outbreak response.
- Collaborative Surveillance: Tools for early detection and control, including strengthened surveillance and epidemiological analysis.
- Community Protection: Engaging communities in local prevention and response measures.
- Safe and Scalable Care: Ensuring resilient health services for adequate patient care.
- Access to Countermeasures: Promoting research for better treatments and vaccines.
- Implementation Timeline: Over one year until September 2025, requiring US$ 55 million for health preparedness and response efforts.
- Alignment with Other Initiatives:
- Supports the Global Vector Control Response 2017-2030.
- Linked to the Global Arbovirus Initiative (2022) targeting mosquito-borne diseases.
- Call to Action:
- Encourages collaboration among government agencies, healthcare providers, and communities.
- Emphasizes the need for innovation and improved vector control strategies.
This plan aims to mobilize a coordinated response to the escalating threat of dengue and related diseases, emphasizing the role of all stakeholders in public health.
Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
DRDO completed development trials of the 4th Generation miniaturised Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD).
Key Details:
- Trial Location: Conducted at Pokhran Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Importance: VSHORAD addresses the Indian Army's need to replace legacy Igla systems, with past efforts making little progress.
- Recent Procurement: Army acquired small volumes of Igla-S through emergency procurement.
- Production Collaboration: Two production agencies involved in Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) mode for VSHORAD missiles.
- Trial Dates: Successful tests held on October 3 and 4, 2024.
Key Performance Metrics:
- Maximum Range and Altitude: Interception against high-speed aerial targets.
- Hit-to-Kill Capability: Demonstrated success in engaging targets in various scenarios (approaching, receding, crossing).
System Overview:
- Type: Fourth generation man-portable air defence system (MANPADS).
- Developer: Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
Capabilities:
- Designed to neutralise low altitude aerial threats at short ranges.
- Features include Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System, and integrated avionics.
- More portable and lightweight than existing missile systems in the Army's arsenal.
Pradhan Mantri-Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) Scheme

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister of India is set to announce the 18th installment of the PM-KISAN scheme in Washim, Maharashtra. This will benefit over 9.4 crore farmers nationwide, with the government allocating more than ?20,000 crore for this initiative.
About PM-KISAN
The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) initiative aimed at providing income support to farmers.
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance: The scheme offers ?6,000 annually to small and marginal farmer families, distributed in three equal installments.
- Eligibility: Initially targeted at families with up to 2 hectares of cultivable land, the scope was later broadened to include all farmer families, regardless of land size.
- Family Definition: The definition of a family under this scheme includes the husband, wife, and minor children.
- Identification of Beneficiaries: State governments and Union Territory administrations are responsible for identifying eligible farmer families based on the scheme's guidelines.
- Direct Transfers: The funds are directly credited to the beneficiaries' bank accounts.
Exclusion Criteria
Certain categories of individuals are not eligible for benefits under the PM-KISAN scheme, including:
- Institutional Land-holders: Those who hold land under institutional ownership.
- High-Profile Government Officials: This includes former and current holders of constitutional posts, ministers, members of legislative assemblies, mayors, and district panchayat chairpersons.
- Government Employees: Serving or retired officers and employees of central or state government ministries and departments are excluded.
- Pensioners: Retired pensioners receiving a monthly pension of ?10,000 or more, as well as those in the previously mentioned categories, are also ineligible.
- Income Tax Filers: Individuals who have paid income tax in the last assessment year.
- Registered Professionals: Professionals such as doctors, engineers, lawyers, chartered accountants, and architects who are engaged in practice and registered with professional bodies.
India's BRAP 2024 Alignment with World Bank's B-READY Index

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian government plans to align indicators of the BRAP 2024 index with the World Bank’s B-READY index to enhance business readiness rankings.
- State Involvement: States have been instructed to address gaps identified in the B-READY evaluations to improve their global rankings.
- Indicators Included: The upcoming 2024 BRAP rankings, prepared by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, will incorporate specific indicators from the B-READY index.
- Enterprise Survey Launch: An enterprise survey for the B-READY index in India is set to start in October, with support from the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- Participation Timeline: Although B-READY rankings will commence in 2024, India’s participation will begin in 2026. The initial rankings will cover 54 countries, expanding to 120 in 2025 and 180 in 2026.
- Successor to Previous Rankings: The B-READY index replaces the Ease of Doing Business rankings, which were discontinued in 2021 due to irregularities. It considers a broader range of factors in its assessments.
- Benchmark for Global Institutions: The B-READY framework will serve as a benchmark for global financial institutions and multinational companies to evaluate a country’s regulatory and policy environment.
- Historical Improvement: India improved its Ease of Doing Business ranking from 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2020.
- Technical Understanding: A team of government officials is tasked with understanding the technical aspects of the B-READY index to formulate strategies for improving India’s score.
- Lifecycle Parameters: The new index tracks ten parameters throughout a firm's lifecycle, including business entry, utility services, and labor, focusing on real-world applications rather than just legal changes.
- Recent BRAP Rankings: The BRAP 2022 rankings were recently announced, with Andhra Pradesh and Kerala achieving the top positions.
Co-district Initiative

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
Assam has launched an innovative administrative initiative by inaugurating 21 'co-districts' as part of its Phase 1 rollout, which began on Friday and will extend into Saturday, ultimately introducing a total of 39 co-districts. This new structure replaces the previous system of 24 civil sub-divisions, aiming to bring governance closer to the citizens.
About the Co-District Initiative
- Structure: Co-districts serve as smaller administrative units within the larger district framework, each headed by an Assistant District Commissioner.
- Objective: This unique initiative, the first of its kind in India, seeks to enhance accessibility to governance and address administrative challenges faced by district administrations.
- Scope: The government plans to establish co-district offices in all 126 assembly constituencies in Assam.
Functions and Powers
The co-districts will handle a variety of important functions, including:
- Land Revenue Matters: Managing land-related issues and revenue collection.
- Development and Welfare Work: Overseeing development projects and welfare programs.
- Excise and Disaster Management: Addressing excise-related matters and coordinating disaster response efforts.
- Administrative Control: Co-districts will have authority over all departmental activities within their jurisdiction.
- Magisterial Powers: Commissioners will be empowered to issue permissions for events and manage other administrative tasks.
- Routine Administrative Tasks: Responsibilities include issuing ration cards, caste certificates, and land sale permissions.
India-U.S. MoU on Critical Minerals Supply Chains

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The sixth Commercial Dialogue took place in Washington on October 4, 2024, led by Indian Union Minister of Commerce Piyush Goyal and U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo.
- MoU Signing: A day prior, the leaders signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) aimed at expanding and diversifying critical minerals supply chains to enhance resilience.
- Focus Areas:
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Exploration
- Extraction
- Processing and refining
- Recycling and recovery
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Context: This agreement follows China's export restrictions on gallium and germanium, critical for the semiconductor industry, and its ban on technology related to rare earth magnets and critical materials extraction.
- Strategic Goals:
- Promote open supply chains, technology development, and investment flows for green energy.
- Explore collaboration with other mineral-rich countries, particularly in Africa and South America.
- Progress on Semiconductor Supply Chains:
- Continued efforts to establish resilient semiconductor supply chains since the previous MoU.
- Completion of a "readiness assessment" by the U.S. Semiconductor Industry Association and India Electronics Semiconductor Association.
- Commitment to foster investments, joint ventures, and technology partnerships.
- Innovation Handshake: Success of roundtables in San Francisco and New Delhi aimed at enhancing innovation ecosystems and startup collaboration.
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership: Discussions from the EIN Roundtable in March 2024 informed the U.S.-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership meeting.
- IPEF Supply Chain Agreement: Significant progress noted in the IPEF ministerial meeting, focusing on semiconductors, chemicals, and critical minerals, particularly batteries and healthcare products.
- Future Collaborations:
- Focus on expanding U.S. Department of Commerce presence in India with approximately 70 Foreign Commercial Service staff.
- Plans for a U.S. trade mission to India in March 2025 aimed at supporting U.S. SMEs owned by underserved communities.
- Domestic Solar Manufacturing Protection: India reinstated the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) order to protect local solar PV module production against cheaper imports from China.
- Economic Context:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights China's expanding manufacturing trade surplus and its restrictive actions affecting India's access to solar equipment.
- India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes have invested over $4.5 billion to bolster clean energy manufacturing but require additional policies to safeguard these investments.
Status of Elephant in India 2022-23

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- Shelved Census Report: The Environment Ministry has delayed the release of the elephant census report, “Status of Elephant in India 2022-23,” due to a lag in the Northeast census, with publication on hold until at least June 2025.
- Population Decline: Preliminary data from the report indicates significant drops in elephant populations across several regions:
- Southern West Bengal: 84% decline
- Jharkhand: 64% decline
- Odisha: 54% decline
- Kerala: 51% decline
- Developmental Threats: The report cites “mushrooming developmental projects,” including unregulated mining and infrastructure development, as major threats to elephant populations.
- Methodological Concerns: The Environment Ministry noted that refined counting methods could explain some discrepancies, suggesting new data may not be directly comparable to previous censuses conducted every five years since the 1990s.
- Old Counting Methods:
- Pre-2002: Elephants were counted using the “total direct count” method, which involved simple head counts but lacked scientific rigor for larger populations.
- 2002: Introduction of the “indirect dung count” method, where dung samples were used to estimate density based on decay rates.
- Sample Block Counts: Modified methods involved surveying limited areas (5 sq km) to improve detection accuracy.
- Elephants vs. Tigers: In 2021, a harmonized approach for estimating elephant and tiger populations was proposed, utilizing a similar block and co-variate methodology for both species.
- Genetic Mark-Recapture: The 2022-23 elephant census employed a genetic mark-recapture model using dung samples to identify individual elephants.
- Impact of Delay: Experts argue that withholding the available data hinders conservation efforts and governance. Delays could exacerbate the plight of elephant populations, particularly in regions facing specific threats, such as mining in Odisha.
Key Findings of the Unreleased Report:
- Overall Decline: The overall elephant population has decreased by 20% since 2017, with some areas reporting reductions of up to 41%.
- Regional Impact:
- Southern West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha have seen losses of nearly 1,700 elephants.
- The Western Ghats region indicates an 18% decline.
- Northeast Region: The census for this area relies on extrapolated data from 2017, with approximately one-third of India's elephants located there.
- Contributing Factors: Habitat fragmentation, poaching, and human-elephant conflicts due to developmental activities are major threats.
- Conservation Recommendations: Strategies to strengthen elephant corridors, restore habitats, and enhance community involvement in conservation are vital.
- Challenges in the Northeast: Urban development, mining, and agriculture significantly threaten elephant movement and survival, underscoring the need for targeted conservation strategies.
- Conservation Status of Elephants in India:
- Leading States: Karnataka, Assam, and Kerala have the highest elephant populations.
- Conservation Status: Elephants are classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and are protected under multiple international conventions.
- Threats to Elephants:
- Habitat Loss: Rapid human population growth is diminishing elephant habitats.
- Fragmentation: Habitat disruption from construction and development projects is prevalent.
- Unlawful Killing: Human-elephant conflict often leads to retaliatory killings.
- Poaching: Targeting of male elephants for tusks continues to threaten genetic diversity.
- Conservation Measures:
- Financial support under various government schemes for habitat conservation and human-elephant conflict resolution.
- Establishment of 33 Elephant Reserves across 14 states.
- Collaborative efforts with railways and power departments to mitigate risks.
- Regular elephant census every five years by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) for monitoring populations.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
Indian push needed to end AIDS as a global health threat by 2030: UNAIDS

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The UNAIDS Director recently highlighted the crucial role India plays in the global fight against HIV/AIDS, asserting that without its significant contributions, achieving the Sustainable Development Goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 is unlikely.
Understanding HIV/AIDS
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which diminishes the body's ability to combat infections and diseases.
- When HIV progresses to its most severe form, it is diagnosed as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), characterized by a severely compromised immune system, leading to life-threatening infections and cancers.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids, including blood, semen, and breast milk. While there is currently no cure, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively manage HIV and prevent its progression to AIDS.
India’s Progress in Combating HIV/AIDS
- From 2010 to 2023, India has made significant strides in reducing annual new HIV infections by 44%, surpassing the global average.
- Additionally, AIDS-related deaths in India have decreased by nearly 80% during the same period, also exceeding global trends. However, challenges persist, with approximately 68,000 new infections reported in 2023, translating to around 185 daily.
- The Global AIDS Strategy emphasizes the need for 80% of prevention services to be delivered by community-led organizations, which are essential for reaching key populations but require sufficient resources and support.
About UNAIDS
UNAIDS, established in 1996, coordinates global efforts to combat HIV/AIDS and supports those affected. Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations and works in collaboration with various global and national partners to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Key aspects of UNAIDS include:
- Global Mandate: To coordinate responses, support countries in prevention and treatment, and advocate for human rights and equality in access to services.
- Targets: The "90-90-90" targets aimed for 2020 sought to ensure that 90% of people living with HIV were diagnosed, 90% of those diagnosed were on treatment, and 90% of those on treatment achieved viral suppression.
- Current Strategy: The 2021-2026 Global AIDS Strategy focuses on eliminating inequalities that drive HIV and aims to ensure that 30 million people are on treatment by 2025.
- Funding and Advocacy: Funded by governments, private foundations, and corporations, UNAIDS organizes key campaigns, including World AIDS Day, to raise awareness and promote advocacy.
PM Internship Scheme

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme, announced by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman during her Budget speech on July 23, was launched on October 3. The PM Internship Scheme aims to provide internship opportunities to one crore youth in the top 500 companies over the next five years.
Companies will upload their internship positions, and candidates can submit applications starting October 12.
What is the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme?
The PM Internship Scheme will enhance youth employability in India by offering them hands-on exposure to real-world business environments. The scheme represents a transformative opportunity to bridge the skills gap and drive sustainable growth in India.
A monthly stipend of ?4,500 will be provided to the interns from the central government via DBT (Direct Benefit transfer), with an additional ?500 offset provided by the company’s CSR fund.
Who is eligible for the PM internship scheme?
- Candidates aged between 21 and 24 years who are not engaged in full-time employment are eligible for the one-year internship programme.
- Internships are available to those who have passed class 10 or higher.
- Individuals from families with government jobs are excluded
- The scheme is not open to post-graduates
- A candidate who graduated from premier institutes such as IIT, IIM, or IISER, and those who have CA, or CMA qualification would not be eligible to apply for this internship.
- Anyone from a household that includes a person who earned an income of ?8 lakh or more in 2023-24, will not be eligible.
How to apply for the PM internship scheme?
- Interns can register in the portal and apply for internships. The portal, pminternship.mca.gov.in, is likely to be opened up for youngsters to enroll for consideration by companies on October 12. This window will be open till October 25 for the first batch of internships. Candidates must share and self-certify some data about their educational qualifications and residential pin codes.
- Candidates’ data will be matched with companies’ needs and locations using Artificial Intelligence tools, and a shortlist of candidates will then be generated for companies to consider.
- The portal is designed to streamline the application process and make candidate selection more transparent. Applicants can check the status of their applications in the portal once they have applied to the available posts.
What is the benefit of the scheme?
The scheme is to provide on-job training to youth and an exposure to real-life work environment. The scheme will also benefit the industry by creating a pipeline of skilled, work-ready youth who can be employed post-internship both in large as well as micro, small and medium enterprise.
National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds)

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
Cabinet Approves National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds) (2024-25 to 2030-31).
Objective:
- Achieve self-reliance in edible oil production in seven years.
Financial Outlay:
- ?10,103 crore for the mission period.
Key Goals:
- Increase primary oilseed production from 39 million tonnes (2022-23) to 69.7 million tonnes by 2030-31.
- Boost domestic edible oil production to 25.45 million tonnes, meeting 72% of projected requirements.
Focus Areas:
- Enhance production of key oilseed crops: Rapeseed-Mustard, Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Sesamum.
- Improve extraction efficiency from secondary sources (e.g., Cottonseed, Rice Bran).
Strategies:
- Promote high-yielding, high oil content seed varieties.
- Extend cultivation to rice fallow areas and encourage intercropping.
- Use advanced technologies like genome editing for seed development.
SATHI Portal:
- Launch of an online 5-year rolling seed plan for timely seed availability.
- Coordination with cooperatives, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and seed corporations.
Infrastructure Development:
- Establish 65 new seed hubs and 50 seed storage units.
- Develop over 600 Value Chain Clusters across 347 districts, covering over 1 million hectares annually.
Support for Farmers:
- Access to high-quality seeds, training on Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), and pest management advisory.
Environmental Benefits:
- Promote low water usage, improve soil health, and utilize crop fallow areas.
Background Context:
- India relies on imports for 57% of its edible oil demand.
- Previous initiatives include the National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) and significant increases in Minimum Support Price (MSP) for oilseeds.
- Imposition of 20% import duty on edible oils to protect local producers.
The NMEO-Oilseeds mission aims to enhance domestic oilseed production, reduce import dependency, and improve farmers' incomes while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Status of Classical Language: An Explainer

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved to confer the status of Classical Language to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali languages.
Why is a language declared as Classical?
Designating a language as classical acknowledges its historical significance and its role in preserving Bharat’s rich cultural heritage. These languages have been crucial in transmitting ancient knowledge, philosophies, and values for millennia. Government recognition emphasizes their deep antiquity and literary traditions, enhancing their status and promoting efforts for their preservation and research, ensuring their relevance in the modern world.
What are the criteria for declaring a language as classical?
In 2004, the Government of India, for the first time, created a new category of languages known as Classical Languages. It set the following as criteria for the status of Classical Language:
- High antiquity of its early texts/ recorded history over a thousand years.
- A body of ancient literature/ texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generation of speakers.
- The literary tradition must be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
This criterion was revised in 2005 and 2024 based on the recommendations of Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under Sahitya Akademi to examine the proposed languages for the status of Classical Language. Later the criteria were revised in 2024 as follows:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500- 2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a heritage by generations of speakers.
- Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence.
- The Classical Languages and literature could be distinct from its current form or could be discontinuous with later forms of its offshoots.
The 2024 Linguistic Expert Committee also recommended the following languages to be fulfilling revised criteria to be considered as a Classical Language: Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, Bengali
How many languages have been declared classical so far?
Languages Date of Recognition Notification by Source/Notification Date
Tamil October 12, 2004 Ministry of Home Affairs October 12, 2004
Ministry of Sanskrit November 25, 2005 Ministry of Home Affairs November 25, 2005
Telugu October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Kannada October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Malayalam August 8, 2013 Ministry of Culture August 8, 2013
Odia March 1, 2014 Ministry of Culture March 1, 2014
Steps Taken by the Ministry of Education for Advancing Classical Languages:
- Establishment of Central Universities (2020): Three universities created to promote Sanskrit through an Act of Parliament.
- Central Institute of Classical Tamil:
- Facilitates translation of ancient Tamil texts.
- Promotes research and offers courses for students and scholars.
- Centres for Excellence:
- Established for Classical Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia under the Central Institute of Indian Languages in Mysuru.
- Awards: Introduction of national and international awards to recognize achievements in Classical Languages.
- Additional Benefits:
- National Awards for Classical Languages.
- Establishment of university chairs.
- Dedicated centers for promoting Classical Languages.
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) Results for 2022-23
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the results of the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for the financial year 2022-23 (April 2022 to March 2023).
- The fieldwork for this survey was conducted from November 2023 to June 2024.
- The ASI provides critical insights into the dynamics of the manufacturing sector, covering aspects such as output, value added, employment, and capital formation.
Key Highlights
- Gross Value Added (GVA): Increased by 7.3% in current prices for 2022-23 compared to the previous year.
- Industrial Output: Grew by over 21% in 2022-23 compared to 2021-22.
- Employment: Estimated employment in the sector rose by 7.4% over the previous year, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
The growth in key economic parameters such as invested capital, input, output, GVA, and wages indicates a robust recovery in the industrial sector. Notably, industries like Basic Metal Manufacturing, Coke & Refined Petroleum Products, Food Products, Chemicals, and Motor Vehicles were significant contributors, accounting for about 58% of total output and showing a 24.5% increase in output and 2.6% in GVA.
State Contributions
- Top GVA Contributors:
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Uttar Pradesh
Together, these states contributed over 54% of the total manufacturing GVA.
- Highest Employment States:
- Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Uttar Pradesh
- Karnataka
Collectively, these states accounted for about 55% of total manufacturing employment in 2022-23.
Survey Details
The ASI encompasses various industrial units, including:
- Factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948.
- Bidi and cigar manufacturing establishments.
- Electricity undertakings not registered with the Central Electricity Authority.
- Units with 100 or more employees registered in the Business Register of Establishments.
The survey employs a comprehensive sampling strategy, dividing units into Central and State Samples to ensure accurate representation. Key components of the data collection include:
- Central Sample: Includes all units in less industrially developed states and specific industrial categories.
- State Sample: Comprises selected units based on employee count and other criteria.
Industrial Classification
Since 1959, the ASI has adopted various classifications to categorize industries. The current classification, NIC 2008, is based on the UN's international standards and has been in use since 2008-09.
Data Collection and Reliability
Data collection is conducted via a dedicated web portal, following the Collection of Statistics Act. Various quality checks ensure reliability, with the Relative Standard Errors (RSE) for important estimates remaining within acceptable limits.
Modified PKC-ERCP project
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan governments signed an agreement for the implementation of the Rs 72,000 crore Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal river linking project.
Modified PKC-ERCP Project Overview
- Signatories: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti signed a MoU for implementation.
- Project Type: Inter-state river linking initiative.
- Integration: Combines the long-standing Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) project with the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) under India's National Perspective Plan for interlinking rivers.
Objectives and Benefits
- Water Supply: Aims to provide drinking and industrial water to 13 districts in eastern Rajasthan and the Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh.
- Irrigation: Expected to irrigate approximately 5.6 lakh hectares across both states.
- Groundwater Management: Focus on improving groundwater levels and enhancing socio-economic conditions in rural Rajasthan.
Project Components
- Detailed Project Report (DPR): Currently under preparation, will outline water sharing, cost distribution, and implementation strategies.
- Historical Context:
- PKC Project: Proposed in 1980 as part of a national plan, initially focused on diverting water from Kalisindh and Newaj rivers to Chambal.
- ERCP: Proposed by Rajasthan in 2019 to optimize water resources by redistributing surplus monsoon water from various sub-basins to deficit areas.
Geographic Focus
- Beneficiary Districts in Rajasthan: Includes Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, and others.
- River Systems Involved:
- Chambal River: Originates in Madhya Pradesh, flows through Rajasthan, and joins the Yamuna.
- Kalisindh and Parbati Rivers: Serve as sources for water diversion.
Implementation Challenges
- Dependable Yield Issues: The original project proposal was based on a 50% dependable yield, contrary to the 75% norm, which was unacceptable to Madhya Pradesh. This led to discussions and revisions.
- Task Force Recommendations: Integrated discussions led to the proposal of the Modified PKC-ERCP, addressing both states' concerns.
Significance of the Project
- National Perspective Plan (NPP): Part of a larger initiative to manage water resources effectively across India, aiming to address water scarcity and improve irrigation.
- Support for Industrial Development: Enhances water availability for the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor, fostering economic growth.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme

- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE) Scheme to promote electric mobility in the country.
Objective:
- Accelerate electric vehicle (EV) adoption
- Establish essential charging infrastructure
- Promote cleaner and sustainable transportation
Key Highlights
- Significant Occasion: Launched on the eve of Mahatma Gandhi's 155th Birth Anniversary, aligning with the vision of ‘Swachh Bharat’ and ‘Swachh Vahan’.
- Financial Commitment: Union Cabinet approved a financial outlay of ?10,900 crore for the scheme over two years (approved on September 11, 2024).
Key Features of the PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Subsidies/Demand Incentives:
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- 24.79 lakh electric two-wheelers (e-2Ws)
- 3.16 lakh electric three-wheelers (e-3Ws)
- 14,028 electric buses (e-buses)
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- E-Voucher Introduction:
- Aadhaar-authenticated e-vouchers for EV customers
- Simplifies access to incentives, with real-time generation for dealers.
- E-Ambulances:
- ?500 crore allocated for deployment
- Standards to be developed with relevant ministries.
- E-Buses:
- ?4,391 crore for 14,028 e-buses in nine major cities
- Focus on replacing scrapped state transport unit buses.
- E-Trucks:
- ?500 crore for incentivizing electric trucks
- Scrapping certificates required for incentives.
- Public Charging Stations:
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- 22,100 fast chargers for electric four-wheelers (e-4Ws)
- 1,800 for e-buses
- 48,400 for e-2Ws/3Ws
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- Test Agency Modernization:
- ?780 crore for upgrading Ministry of Heavy Industries test agencies to accommodate new EV technologies.
India’s Oil Imports from Saudi Arabia and Russia

- 03 Oct 2024
Context
- India’s crude oil imports are influenced by refinery maintenance cycles, which affect demand.
- August saw a dip in oil demand due to pre-maintenance preparations, but September recorded a recovery.
September Oil Import Trends
- Saudi Arabia:
- Imports rose 39.8% month-on-month to 0.73 million barrels per day (bpd), the highest since March.
- Saudi market share increased to 15.5% in September from 11.7% in August.
- Riyadh is reducing prices to regain lost market share, as earlier imports had plummeted to a multi-year low (0.42 million bpd in June).
- Russia:
- Remains India’s largest oil supplier with imports increasing by 6.4% from August to 1.88 million bpd.
- Russian crude constituted 40.2% of India’s total crude imports of 4.68 million bpd in September.
- Iraq:
- Supplied 0.87 million bpd, accounting for 18.7% of total imports.
- UAE:
- Oil imports increased by 18.6% month-on-month to 0.49 million bpd, the highest since June 2022.
Market Dynamics
- Price Sensitivity: Indian refiners are highly price-sensitive, which could lead to increased competition among suppliers.
- Potential for Increased Russian Imports: With Indian refiners expected to secure larger long-term contracts for Russian oil, further increases in imports from Russia are anticipated.
Strategic Implications
- Saudi Arabia is concerned about losing market share to Russia, especially as India’s refiners are currently favoring discounted Russian crude.
- Increased competition may benefit Indian refiners through better pricing from various suppliers.
Economic Context
- India, as the world's third-largest oil consumer with over 85% import dependency, is significantly affected by global oil price fluctuations.
- Although discounts on Russian crude have decreased, the overall savings from purchasing large volumes remain significant for Indian refiners.
The evolving landscape of India’s oil imports highlights the competitive dynamics among major suppliers, particularly Saudi Arabia and Russia, and underscores India’s strategic importance as a key market in the global oil sector.
Little Prespa Lake's Decline
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
Little Prespa Lake on Albanian-Greek border slowly dying.
Overview of Little Prespa Lake's Decline
- Location and Geography:
- Little Prespa Lake is situated on the Albanian-Greek border, primarily in Greece with a southern tip extending into Albania.
- It covers approximately 450 hectares in Albania, now largely transformed into swamps or dry land.
- Ecological Changes:
- Once a crystal-clear lake, it has degraded into a marshy area, with about 430 hectares in Albania suffering from significant drying.
- Local wildlife has shifted; cows now roam where fish once thrived.
- Historical Context:
- The lake's decline began in the 1970s when Albanian authorities diverted the Devoll River to irrigate surrounding agricultural lands, severely limiting water inflow.
- Climate Change Impact:
- Rising temperatures, mild winters, and decreased precipitation have intensified the lake’s ecological crisis.
- Local experts warn that continued dry winters and hot summers could lead to irreversible damage.
Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
BharatGen Initiative
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
BharatGen is a pioneering generative AI initiative launched in New Delhi, aimed at revolutionizing public service delivery and enhancing citizen engagement, with Dr. Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State, in virtual attendance.
- Significance
- Represents India's commitment to advancing homegrown technologies.
- Positions India as a global leader in generative AI, similar to achievements with UPI and other innovations.
- Marks the world's first government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model project focusing on Indian languages.
- Leadership and Implementation
- Spearheaded by IIT Bombay under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- Collaboration with the TIH Foundation for IoT and various academic partners, including IITs and IIMs.
- Key figures involved include Prof. Shireesh Kedare (Director, IIT Bombay) and Prof. Ganesh Ramakrishnan (consortium leader).
- Core Objectives
- Deliver generative AI models as a public good, prioritizing socio-cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Address broader needs such as social equity, cultural preservation, and inclusivity.
- Make AI accessible for industrial, commercial, and national priorities.
- Key Features
- Multilingual and Multimodal Models: Capable of handling text and speech in multiple languages.
- Bhartiya Data Sets: Focus on India-centric data collection and training.
- Open-Source Platform: Promotes collaboration and innovation in AI research.
- Ecosystem Development: Fosters a robust AI research community.
- Project Timeline and Impact
- Expected completion in two years, with benefits for government, private, educational, and research institutions.
- Ensures coverage of India’s diverse linguistic landscape through multilingual datasets.
- Emphasis on data sovereignty to strengthen control over digital resources.
- Alignment with National Goals
- Supports the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by reducing reliance on foreign technologies.
- Aims to strengthen the domestic AI ecosystem for startups, industries, and government agencies.
- Focuses on democratizing access to AI for innovators and researchers.
- Research and Community Engagement
- Data-efficient learning for languages with limited digital presence.
- Development of effective models with minimal data through research collaborations.
- Initiatives to foster an AI research community, including training programs and hackathons.
- Future Roadmap
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
- Extensive AI model development and experimentation.
- Establishment of AI benchmarks tailored to India’s needs.
- Scaling AI adoption across industries and public initiatives.
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
Joint Military Exercise KAZIND-2024

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The 8th edition of the India-Kazakhstan Joint Military Exercise, KAZIND-2024, has commenced in Auli, Uttarakhand, running from September 30 to October 13, 2024.
Key Details:
- Joint Exercise KAZIND-2024 has been held annually since 2016.
- Last edition of the Joint Exercise was held at Otar, Kazakhstan from 30th October to 11th November 2023.
Participants:
- India:
- 120 personnel from KUMAON Regiment of the Indian Army
- Additional support from other arms and Indian Air Force
- Kazakhstan:
- Personnel primarily from Land Forces and Airborne Assault Troopers
Aim:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations
- Focus on sub-conventional scenarios under Chapter VII of the UN Charter
Focus Areas:
- Operations in semi-urban and mountainous terrains
- High physical fitness levels
- Rehearsal and refinement of tactical drills
- Sharing best practices
Tactical Drills:
- Joint response to terrorist actions
- Establishment of a Joint Command Post
- Creation of an Intelligence and Surveillance Centre
- Securing helipad/landing sites
- Combat free fall and Special Heliborne Operations
- Cordon and Search operations
- Employment of drones and counter-drone systems
Outcomes Expected:
- Sharing of tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations
- Development of interoperability between the two armies
- Strengthening of bonhomie and camaraderie
- Enhancement of defense cooperation and bilateral relations between India and Kazakhstan.
La Nina and North India’s pollution
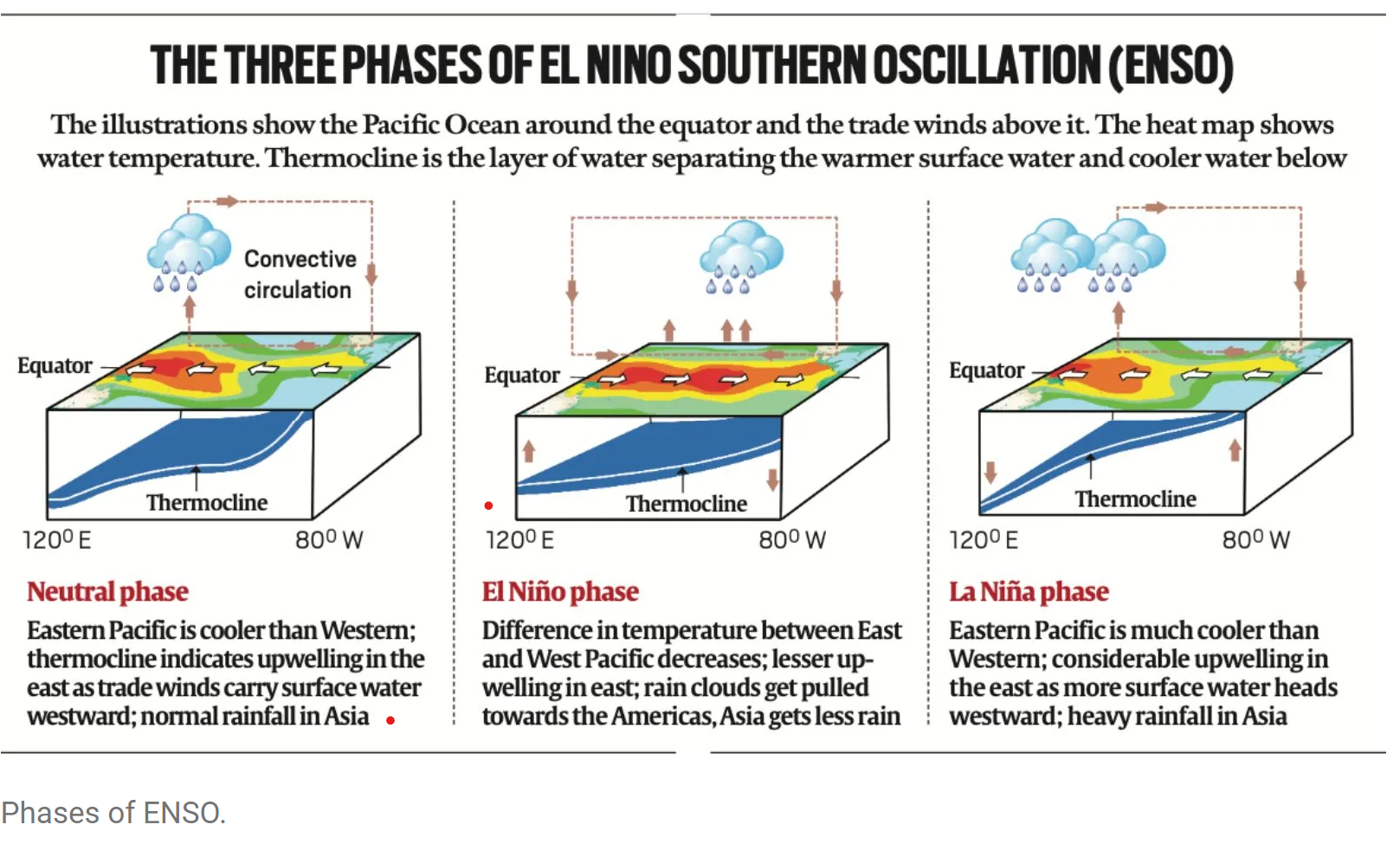
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research by scientists at the National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) has underlined the links between climate change, La Niña and air quality.
Key Points on Air Quality Outlook for Delhi and North India
- Delayed La Niña & Monsoon Retreat:
- Erosion of optimism for improved air quality this winter in Delhi.
- Significant pollution challenges anticipated in early winter months.
- Possible relief in December and January, contingent on La Niña strengthening.
- Impact of Stubble Burning:
- If stubble burning occurs at half the intensity of previous years, November air quality may deteriorate.
- Research Insights:
- Study by National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) links climate change, La Niña, and air quality.
- Notable air quality improvement in winter 2022-23 was linked to La Niña conditions.
- Late onset of La Niña contributes to air quality uncertainty.
- Changing Pollution Dynamics:
- Shift from local emission-centric views to broader climatological factors is necessary.
- Air quality in Delhi worsens during winter due to high humidity, calm winds, and poor pollutant dispersion.
- La Niña Delays:
- Delayed La Niña onset means weak winds and stagnant conditions, worsening pollution.
- Expected development between September and November 2024.
- Effects of Stubble Burning:
- North-north-westerly winds could carry pollution from stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana into Delhi.
- Potential Outcomes of Late La Niña Onset:
- If La Niña develops in December or January, may improve air quality slightly.
- However, a longer, severe winter could exacerbate pollution issues due to lower inversion layers.
- NIAS-SAFAR Model Predictions:
- Early La Niña could have worsened air quality in the peninsular region.
- Early onset might have improved northern air quality.
- Link to Climate Change:
- Evidence suggests extreme air pollution correlates with climate change.
- Emphasizes the need for rigorous mitigation efforts and broader airshed management.
- Call for Rethinking Air Quality Strategies:
- Focus on integrating larger climatic factors into air quality policies.
- Prioritize health-centric measures through collaborative efforts with scientific bodies.
What is La Niña?
- La Niña (or ‘The Little Girl’ in Spanish) is a phase of what climatologists refer to as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a phenomenon that is a key driver of global natural climate variability.
- ENSO is characterised by changes in sea temperatures along the tropical Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric fluctuations overhead. These changes alter and interfere with the global atmospheric circulation, and influence weather worldwide.
- Occurring in irregular cycles of anywhere between two to seven years, ENSO has three phases — warm (El Niño or ‘The Little Boy’ in Spanish), cool (La Niña), and neutral.
- During the neutral phase, the eastern Pacific (off the northwestern coast of South America) is cooler than the western Pacific (around Philippines and Indonesia). This is because prevailing trade winds — caused by Earth’s rotation, between 30 degrees north and south of the equator — move east to west, sweeping warmer surface water along with them. The relatively cool waters from below rise to the surface to replace the displaced water.
- These wind systems weaken in the El Niño phase, leading to lesser displacement of warmer waters off the American coasts. Consequently, the eastern Pacific becomes warmer than usual. The opposite happens in the La Niña phase i.e. trade winds become stronger than usual and push larger quantities of water to the western Pacific.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
