Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya Committee

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has set up an eight-member committee to create a framework for the responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- The committee is chaired by Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya, Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at IIT Bombay.
Key Highlights:
Committee's Objective:
- The primary goal is to develop a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector.
- It will guide the ethical adoption of AI in financial services to enhance operational efficiency, decision-making, and risk management.
Scope of the Committee's Work:
- Assess the current global and domestic adoption of AI in financial services.
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the integration of AI in the sector.
- Recommend a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring AI-related risks.
- Propose compliance requirements for various financial entities (e.g., banks, NBFCs, fintech firms).
- Suggest a governance framework for ethical AI usage.
Key Benefits of AI in Financial Services:
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, process large datasets, and enhance accuracy (e.g., loan application processing).
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics in AI help forecast market trends, aiding in better financial decision-making (e.g., algorithmic trading).
- Customer Relationship Management: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer interaction, offering 24/7 support.
- Improved Risk Management: AI enables proactive fraud detection, improving security and preventing financial losses.
Concerns Associated with AI in Finance:
- Embedded Bias: AI models can replicate biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes and financial exclusion.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI poses risks to personal data security, with potential violations of privacy regulations.
- Operational Challenges: AI systems may exhibit inconsistent responses, leading to challenges in trust and effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased use of AI can heighten vulnerability to cyber-attacks and exploitation.
RBI's Role & Governance:
- The RBI aims to ensure that AI adoption in the financial sector is ethical, transparent, and aligned with global best practices.
- The committee's recommendations will influence policies to prevent misuse and safeguard consumer interests.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)

- 24 Dec 2024
In News
Justice V. Ramasubramanian, a retired Supreme Court judge, has been appointed as the new chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). This decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, and it comes following the completion of Justice Arun Kumar Mishra's tenure as NHRC chairperson in June 2023. After Justice Mishra's retirement, Vijaya Bharathi Sayani served as the acting chairperson. Alongside Justice Ramasubramanian, Priyank Kanoongo and Dr. Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi (Retd.) have also been appointed as members of the commission.
Justice Ramasubramanian had been appointed a judge of the Supreme Court in September 2019 and retired in June 2023. His appointment to the NHRC is seen as a significant development for human rights advocacy and protection in India.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Establishment and Legal Framework
- Formation Date: The NHRC was established on October 12, 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Paris Principles: It was created in alignment with the Paris Principles (1991), which were endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, aimed at setting standards for national human rights institutions.
- Statutory Body: NHRC is a statutory body, meaning it is established by law, with a primary function to safeguard human rights in India.
Objectives
The NHRC's primary objective is to promote and protect human rights as defined in Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA, which include fundamental rights such as:
- Right to Life
- Right to Liberty
- Right to Equality
- Right to Dignity
These rights are guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and are essential to the protection of individuals' freedoms and welfare.
Composition of NHRC
- Chairperson: A former Chief Justice of India or a former Supreme Court judge serves as the chairperson.
- Members:
- One former or sitting Supreme Court judge.
- One former or sitting Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Three members, with at least one woman, who have experience in human rights matters.
- Ex-Officio Members: The chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC/ST, Women, Minorities) and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities are also part of the NHRC.
Functions and Powers
The NHRC has several crucial functions and powers to ensure the protection and promotion of human rights:
- Inquiry into Human Rights Violations: The commission can inquire into violations of human rights by public servants or negligence in protecting rights.
- Recommendations: It can make recommendations on how to protect, promote, and effectively implement human rights within India.
- Review of Laws: NHRC assesses various laws, treaties, and international instruments related to human rights.
- Research and Awareness: It promotes research, publications, and awareness about human rights issues, including educating the public about their rights and safeguards.
- Inspection of Institutions: NHRC has the authority to visit and inspect institutions such as jails, detention centers, and other places of confinement to ensure the humane treatment of individuals.
2023 National Tansen Samman

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
- The prestigious National Tansen Samman for 2023 was conferred upon Pt. Swapan Choudhary, a renowned tabla maestro from Kolkata, at the National Tansen Festival held in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tansen Festival: This festival, renowned for its celebration of classical music, is organized annually in Gwalior, which is considered the music capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Prize Details: As part of the honor, Pt. Swapan Choudhary was presented with an honorarium of five lakh rupees, a citation plaque, and a shawl-shriphal.
- About the Award:
- The National Tansen Samman was established in 1980 by the Madhya Pradesh government to recognize exceptional contributions to Indian classical music.
- It is named after Tansen, one of India's most celebrated classical musicians.
- The award is the highest national honor in the field of Indian classical music.
- Additional Award:
- Raja Mansingh Tomar Samman for 2023 was awarded to Sanand Nyas, an institution from Indore. This institution has been active for 35 years in the promotion of classical music, drama, and cultural festivals.
- Pt. Swapan Choudhary’s Remark: In response to receiving the honor, Pt. Choudhary expressed his gratitude and pride in joining the ranks of distinguished artists awarded the National Tansen Samman.
About Tansen: The Iconic Musician
- Legacy: Tansen, also known as Miyan Tansen, was a prominent Indian classical musician, composer, and vocalist. He is credited with popularizing several ragas and revolutionizing the Indian classical music tradition.
- Role at Akbar’s Court: Tansen was one of the Navaratnas (nine jewels) in the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He held the title of Mian, meaning "learned man," bestowed upon him by Akbar.
- Contributions:
- Tansen is famous for his compositions, including the introduction of notable ragas such as Miyan ki Malhar, Miyan ki Todi, and Darbari.
- He also improved the plucked rabab, which is of Central Asian origin, enhancing its role in Indian classical music.
- Historical Influence: Tansen's life and work are surrounded by extensive legend, and his contributions remain deeply influential in the development of Indian classical music today.
Masali Village in Gujarat

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
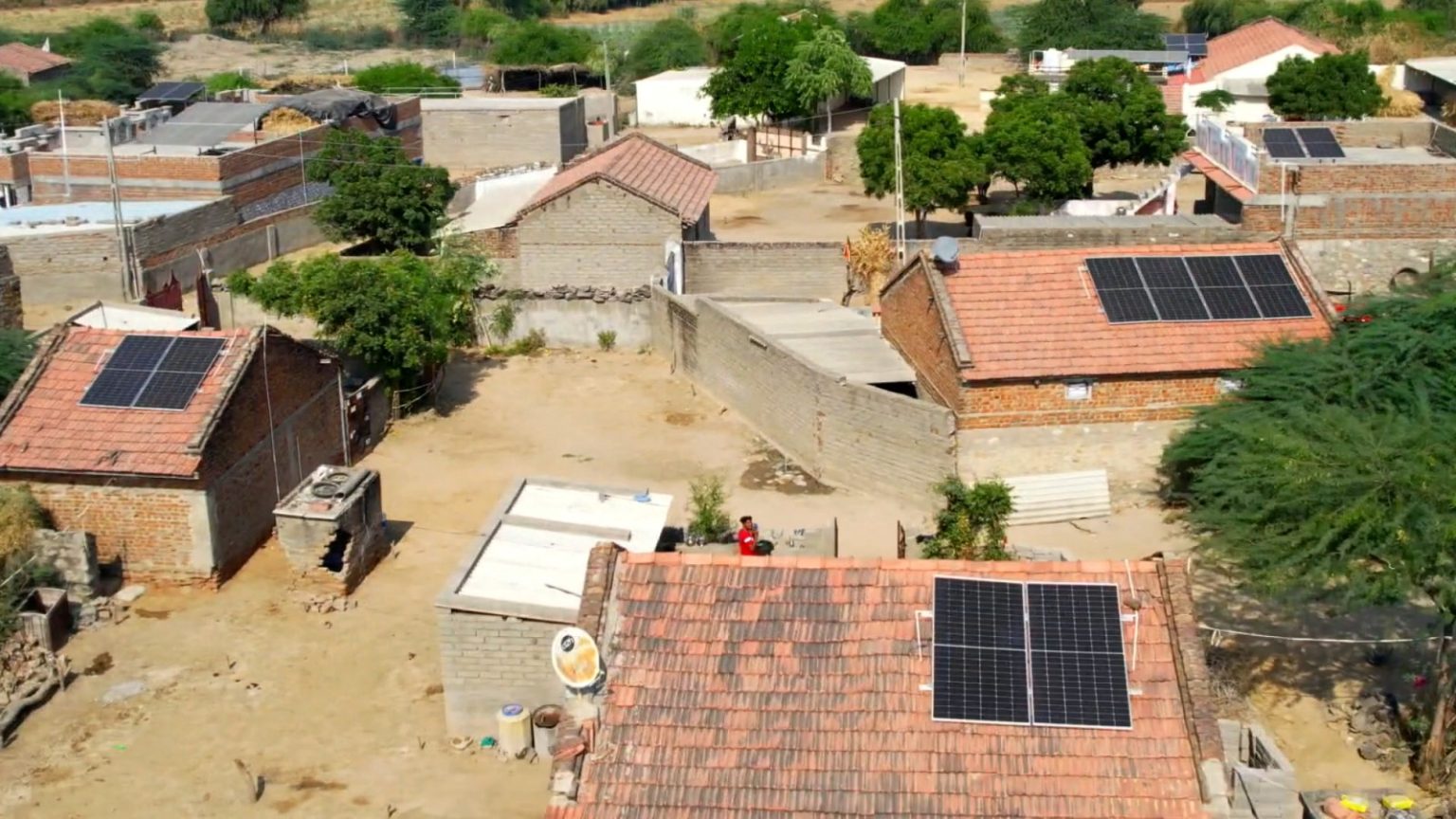
In Gujarat, Masali village in Banaskantha district has become country’s first solar border village.
Key Highlights:
Location:
Masali village is located in Banaskantha district, Gujarat, approximately 40 kilometers from the Pakistan border. The village, with a population of around 800 people, has recently achieved a significant milestone by becoming India’s first fully solar-powered border village.
Solarization Initiative:
Under the PM Suryaghar Yojana, the village has installed solar rooftops on 119 houses. These solar installations collectively generate over 225 kilowatts of electricity, which is more than sufficient to meet the village’s energy needs. This initiative marks a step forward in solarizing border areas of India, promoting sustainability and reducing dependency on conventional energy sources.
Significance of the Initiative:
- India's First Solar-Powered Border Village: Masali village is the first of its kind in India, making it a model for other border regions to adopt renewable energy solutions.
- Promotes Renewable Energy: The transition to solar power encourages sustainability, reduces dependence on traditional fossil fuels, and supports India's renewable energy goals.
- Part of the Border Development Project: Masali is part of a broader government plan that aims to solarize 11 villages in Vav taluka and 6 villages in Suigam taluka, strengthening energy access in these strategically vital areas.
- Energy Security: By harnessing solar energy, the village enhances its energy reliability and self-sufficiency, especially in remote areas with limited access to the national grid.
PM Suryaghar Yojana: Launched in 2024, the PM Suryaghar Yojana aims to provide free electricity to eligible Indian households by subsidizing the installation of rooftop solar panels. Key features of the scheme include:
- A subsidy covering up to 40% of the installation cost of solar panels.
- Eligible families receive 300 free electricity units per month, saving up to Rs. 18,000 annually.
- The scheme is expected to save the government approximately Rs. 75,000 crore annually on electricity costs.
- It encourages the use of renewable energy, lowers carbon emissions, and reduces the electricity expenses for the government.
Eligibility for the Scheme:
- Indian citizens who own a house with a suitable roof for installing solar panels.
- Households must have a valid electricity connection and should not have received any prior subsidy for solar panels.
Broader Implications:
The successful solarization of Masali village is not just an energy achievement but also a significant step toward promoting renewable energy usage, enhancing energy security, and fostering sustainable development in India’s border regions. It is expected that other regions in Gujarat and across the country will follow this example, improving both local living conditions and national energy resilience.
Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
A two-day Mahabodhi Mahotsav is currently being held at the Great Stupa in Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Key Highlights:
- The festival will include religious ceremonies and cultural activities centered around the relics of Lord Buddha’s chief disciples, Sariputra and Maudgalyayana.
- Cultural Significance: The Mahotsav serves as a platform for celebrating and reaffirming the cultural and spiritual heritage of the region, with a focus on the teachings of Lord Buddha.
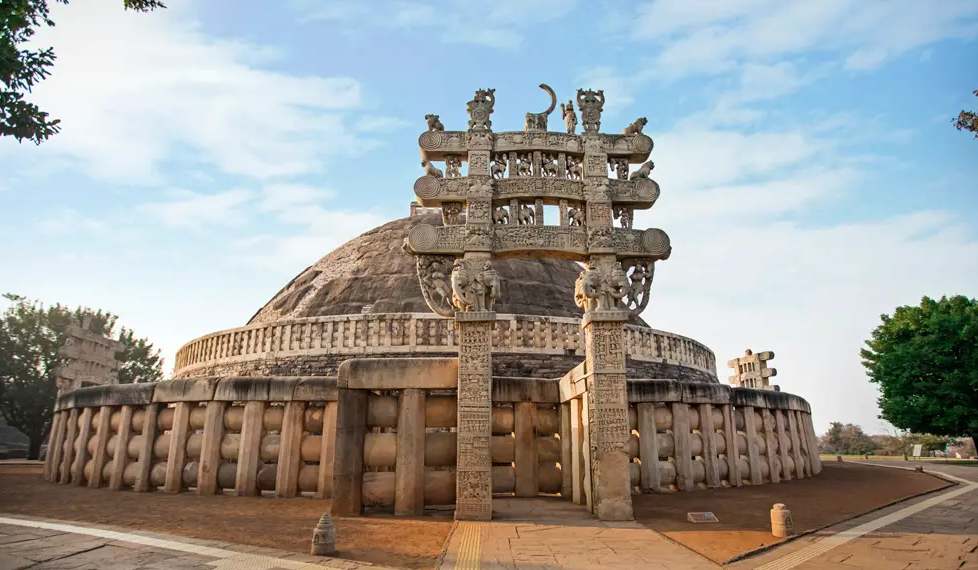
About Sanchi Stupa:
Sanchi Stupa is one of the oldest and most significant monuments of Buddhist architecture in India. It has stood as a symbol of Buddhist history, spirituality, and culture for over two millennia.
- Historical Importance:Commissioned by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, the stupa was later expanded by the Shunga and Satavahana rulers. It stands as a testament to the spread of Buddhism across India and beyond.
- Architectural Features:
- Hemispherical Dome (Anda): The large dome represents the universe, encapsulating the essence of Buddhist cosmology.
- Chatras: The umbrella-like structures on top of the dome symbolize divine protection and royalty.
- Harmika: A small balcony on the dome, which is considered the abode of the gods.
- Medhi: The base of the stupa, which stores sacred relics.
- Toranas: Four intricately carved gateways that depict scenes from the life of Buddha and various Jataka tales. These gateways point to the four cardinal directions, symbolizing the universality of Buddha’s teachings.
- Vedica: The railings surrounding the stupa serve as sacred enclosures.
- Paradakshinapatha: Pathways for circumambulation, allowing devotees to walk around the stupa as a sign of respect.
- Symbolism:The stupa’s architecture is an example of early Buddhist aniconism, where the Buddha is not directly depicted but is represented symbolically through footprints, wheels, or empty thrones.
- Inscriptions:The stupa contains important inscriptions, including the Ashokan Lion Capital and inscriptions in Brahmi and Kharosthi scripts, reflecting the historical significance of the site.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status:In 1989, Sanchi Stupa was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognizing its exceptional historical and cultural importance as a center for Buddhist art, architecture, and philosophy.
Significance of the Mahabodhi Mahotsav:
The Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi not only provides a spiritual experience but also highlights the historical and cultural legacy of Buddhism in India. The event brings attention to the preservation and promotion of Buddhist heritage, reflecting India’s rich diversity and commitment to maintaining its ancient traditions. Through this festival, Sanchi continues to be a center of pilgrimage and learning, attracting visitors from around the world who seek to understand and experience the teachings of Lord Buddha.
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
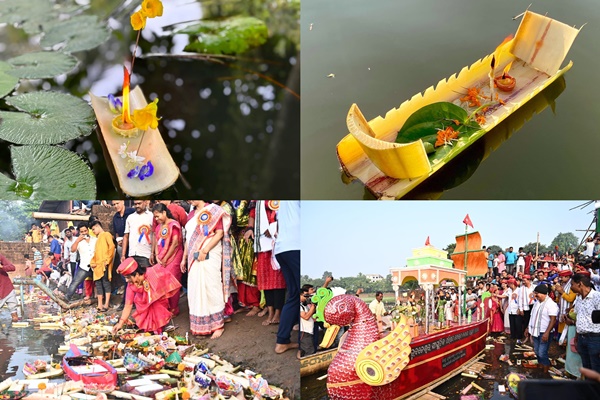
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
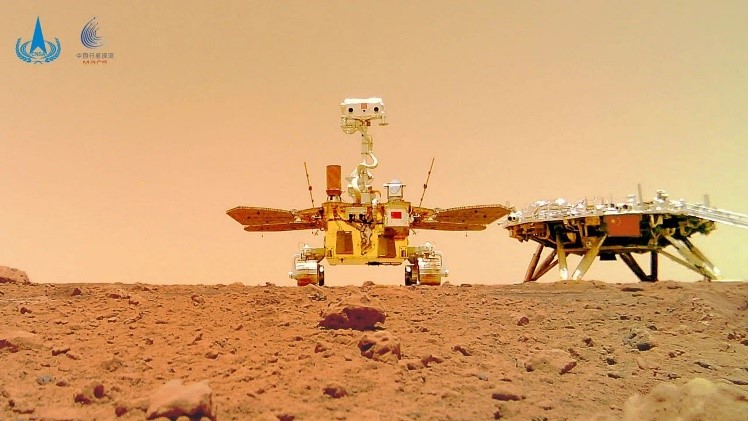
Zhurong Rover

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
PyPIM platform
- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Israeli researchers from the Israel Institute of Technology have developed the PyPIM platform, which allows computers to process data directly in memory, eliminating the need for a central processing unit (CPU). This breakthrough aims to address key challenges in modern computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and processing efficiency.
Key Features of the PyPIM Platform:
- Integration with Python and PIM Technology:
- The PyPIM platform merges Python programming with digital processing-in-memory (PIM) technology, facilitating in-memory computing where computations occur directly within memory instead of transferring data to and from the CPU.
- Functionality and Innovations:
- Direct In-Memory Computations: PyPIM uses specialized instructions that enable computations to take place directly in memory, reducing the need for data movement between the CPU and memory.
- Developer-Friendly: It allows developers to use familiar languages like Python to write software for in-memory computing systems.
- Solving the "Memory Wall" Issue:
- The platform addresses the memory wall problem, where the speed of the CPU and memory exceeds the data transfer rates, creating bottlenecks that lead to inefficiencies.
- By performing calculations directly in memory, PyPIM reduces time and energy spent on data transfer, optimizing performance.
- Performance Improvements:
- Energy and Time Efficiency: By minimizing energy-intensive data transfers, PyPIM leads to significant energy and time savings.
- Simulation Tools: The platform includes tools that allow developers to simulate potential performance improvements from in-memory processing.
- Real-World Benefits:
- Faster Processing: Tasks performed using PyPIM have demonstrated faster processing speeds, with minimal code changes, particularly in mathematical and algorithmic tasks.
- The platform delivers a significant performance boost in areas like data analysis and algorithmic operations.
The PyPIM platform marks a pivotal advancement in computing architecture, providing a more energy-efficient and faster alternative to traditional CPU-dependent systems by reducing reliance on external memory processing and cutting down on data transfer delays.
Critical Minerals Summit

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines today organized a summit to foster collaboration, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical mineral beneficiation and processing in New Delhi.
About Critical Minerals Summit:
- The Critical Minerals Summit was organized by the Ministry of Mines, Government of India, in collaboration with the Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation (Shakti), the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), and the Indian Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD).
- It aims to promote collaboration and innovation in critical mineral beneficiation and processing.
- This event brings together a wide range of stakeholders, including industry leaders, startups, government officials, scientists, academics, and policy experts from both India and abroad.
Key Objectives:
- Tackling Demand: The summit seeks to address the growing demand for Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) needed for renewable energy systems and electric vehicles as part of India's strategic development goals.
- Focus on Key Minerals: The Ministry of Mines has identified eight crucial minerals for focus, including Glauconite (Potash), Lithium – Rare Earth Elements (Laterite), Chromium, Platinum Group, Graphite, Tungsten, Rare Earths (RE), and vanadium-associated with Graphite.
- Diverse Participation: The summit offers a platform for a diverse group of stakeholders to collaborate, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical minerals.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are metallic or non-metallic elements essential for modern technologies, economies, and national security, with potentially vulnerable supply chains.
- Their 'criticality' changes over time due to shifting supply and societal needs.
- Applications: Critical minerals are vital for manufacturing advanced technologies like mobile phones, computers, semiconductors, and renewable energy systems such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels, and batteries.
- They are also used in common products like stainless steel and electronics.
- Examples of Critical Minerals are antimony, beryllium, cobalt, copper, gallium, germanium, lithium, vanadium, and more.
- Top Producers: Countries like Chile, Indonesia, Congo, China, Australia, and South Africa lead in critical mineral production.
- Critical Minerals in India: The Indian government has identified 30 critical minerals, including antimony, beryllium, cobalt, copper, gallium, graphite, hafnium, indium, lithium, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, phosphorous, potash, rare earth elements, rhenium, silicon, strontium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, selenium, and cadmium.
- To meet the rising demand for critical minerals and ensure a stable supply, the Indian government is actively working on auctioning critical mineral blocks and fostering industry partnerships.
- These efforts are crucial for the country's economic development and energy transition goals.
First Pey Jal Survekshan Awards to be conferred by President on 5th March

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
President Droupadi Murmu will present the first Pey Jal Survekshan Awards on the 5th of next month in New Delhi.
About the Pey Jal Survekshan Awards:
- The Pey Jal Survekshan Awards feature a prestigious lineup of 130 accolades, spotlighting outstanding contributions in the realm of water management.
- The awards span various categories, including the Pey Jal Gold, Silver, and Bronze City Awards, with each tier symbolizing excellence in specific population segments (ranging from 1 to 10 Lakh, 10 to 40 Lakh, and more than 40 Lakh).
- In addition to these, commendations are also extended for commendable efforts in areas such as Best Water Body, Sustainability Champion, Reuse Champion, Water Quality, City Saturation, and the prestigious AMRUT 2.0 Rotating Trophy of the Year.
Comprehensive Evaluation Parameters:
- Embracing a multifaceted approach, the evaluation criteria encompass a wide array of parameters, including accessibility, coverage, water quality maintenance at treatment facilities and household levels, sustainability practices ensuring the health of water bodies, adoption of SCADA/flowmeters, and efficient reuse of treated wastewater.
- Cities are meticulously graded using a star rating system, ranging from 5 stars to No star, meticulously reflecting their performance across these pivotal benchmarks.
- Ensuring Water Purity and Transparency: The Pey Jal Survekshan reinforces the assurance of clean water through rigorous independent NABL lab testing at both the source and consumer ends.
- Leveraging advanced technological tools such as GIS-enabled web portals, geo-tagging, and infrastructure mapping, the survey captures precise and transparent data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Enhancing Urban Governance and Citizen Engagement: Anticipated to serve as a catalyst for urban local body (ULB) decision-making processes, the outcomes of the Pey Jal Survekshan are poised to elevate service delivery standards while fostering active citizen participation.
- By nurturing a sense of ownership and disseminating knowledge on water conservation and optimal utilization, the awards endeavor to empower communities toward sustainable water management practices.
What is the AMRUT Mitra initiative?
- The AMRUT Mitra initiative is geared towards active engagement of women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in urban water management, recognizing women as pivotal stakeholders and highlighting their vital role in household water governance.
- Tasked with executing AMRUT 2.0 projects, the Mitras will undertake various responsibilities, including billing, collection, leak detection, plumbing, water quality monitoring, and infrastructure upkeep.
- At its core, AMRUT Mitra seeks to cultivate a sense of ownership among women, fostering inclusivity and diversity in traditionally male-dominated domains while ensuring equitable access to safe drinking water and addressing gender disparities.
- Expected outcomes encompass the empowerment of women SHGs, socio-economic upliftment, alignment with AMRUT 2.0 objectives, heightened community awareness, and the establishment of a blueprint for future endeavors.
