New Cancer Therapy Target
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
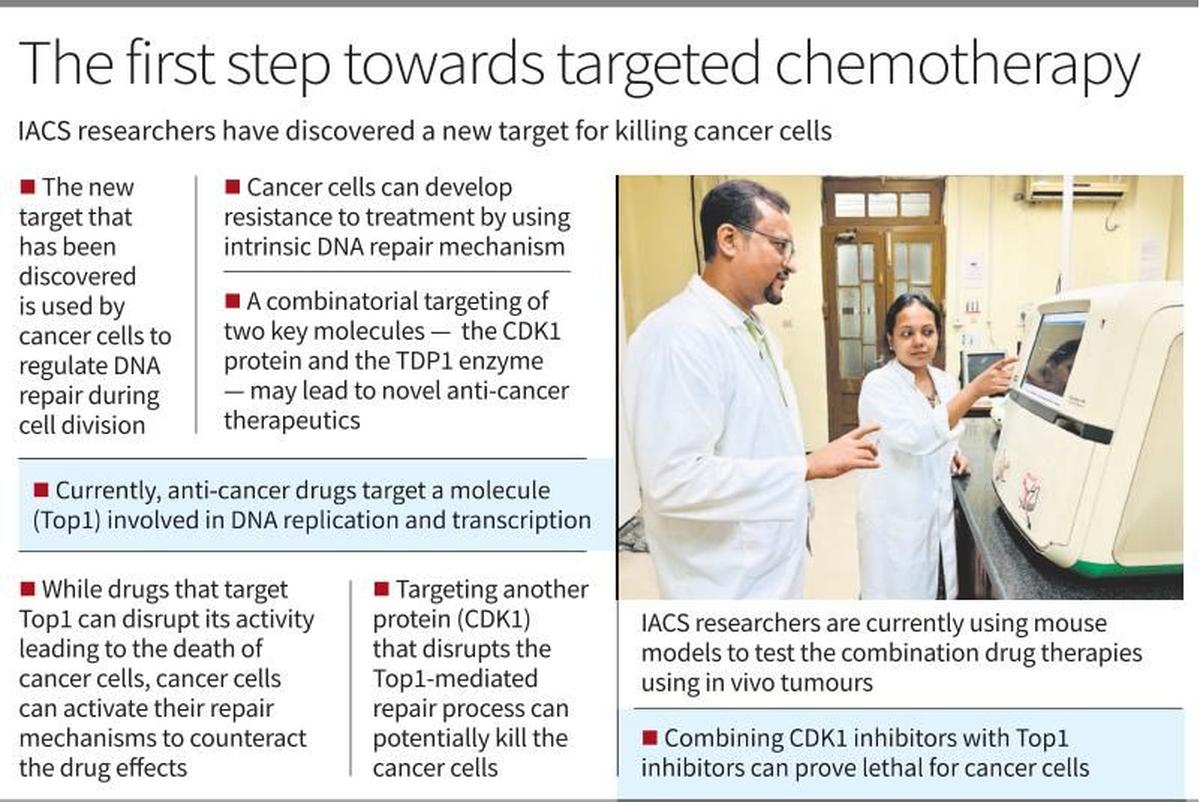
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
