NABARD Survey on Rural Financial Inclusion
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
NABARD has published the findings from its second All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey (NAFIS) for 2021-22, which offers primary data based on a survey of 1 lakh rural households, covering various economic and financial indicators in the post-COVID period.
Survey Overview:
- Inaugural survey conducted for 2016-17, results released in August 2018.
- Aims to analyze changes in rural economic conditions since 2016-17.
- Included all 28 states and Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Insights from NAFIS 2021-22
- Increase in Average Monthly Income:
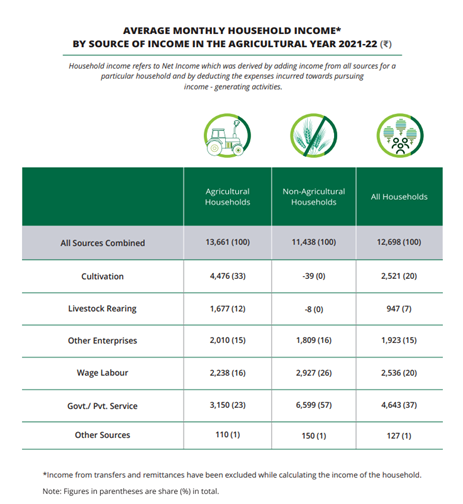
- Average monthly income rose by 57.6% from Rs. 8,059 (2016-17) to Rs. 12,698 (2021-22).
- Nominal CAGR of 9.5%, with annual nominal GDP growth at 9%.
- Agricultural households earned Rs. 13,661; non-agricultural households earned Rs. 11,438.
- Salaried employment contributed 37% to total income; cultivation contributed one-third for agricultural households.
- Rise in Average Monthly Expenditure:
- Average monthly expenditure increased from Rs. 6,646 (2016-17) to Rs. 11,262 (2021-22).
- Agricultural households reported higher consumption (Rs. 11,710) compared to non-agricultural households (Rs. 10,675).
- Expenditure exceeded Rs. 17,000 in states like Goa and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Increase in Financial Savings:
- Annual average financial savings grew to Rs. 13,209 in 2021-22 from Rs. 9,104 in 2016-17.
- 66% of households saved in 2021-22, up from 50.6% in 2016-17.
- 71% of agricultural households reported savings, compared to 58% of non-agricultural households.
- States like Uttarakhand (93%) and Uttar Pradesh (84%) had high saving rates, while Goa (29%) and Kerala (35%) had lower rates.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Coverage:
- 44% of agricultural households possessed a valid KCC.
- Among larger landholders and those with recent agricultural loans, 77% reported having a KCC.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Households with at least one insured member increased from 25.5% (2016-17) to 80.3% (2021-22).
- Vehicle insurance was most common (55%), followed by life insurance (24%).
- Pension Coverage:
- Households with at least one member receiving any form of pension rose from 18.9% to 23.5%.
- 54% of households with members over 60 years old reported receiving a pension.
- Financial Literacy:
- Good financial literacy increased by 17 percentage points, from 33.9% to 51.3%.
- Sound financial behavior improved from 56.4% to 72.8%.
Conclusion
- The NAFIS 2021-22 highlights significant advancements in rural financial inclusion since 2016-17.
- Improvements in income, savings, insurance coverage, and financial literacy are notable.
- Government welfare schemes (e.g., PM Kisan, MGNREGS) have positively impacted rural lives.
- Continued support and investment in rural development are essential for economic empowerment and financial security in India's rural population.
