X-Class Solar Flares

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Earth was hit by an X-class solar flare that was strong enough to ionize part of the planet's atmosphere.
What are Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are large explosions from the surface of the sun that emit intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation.
- The intensity of the explosion determines what classification the flare belongs to.
- The most powerful are X-class flares, followed by M-, C-, and B-class; A-class flares are the smallest.
- These flares can be visible as bright flashes in a particular region of the sun and can last several minutes.
- Solar flares occur when magnetic energy builds up in the solar atmosphere and is released suddenly.
- These outbursts are intrinsically linked to the solar cycle — an approximately 11-year cycle of solar activity driven by the sun's magnetic field.
What Causes Solar Flares?
- The sun's surface is a magnetically mixed-up place.
- Magnetic fields are created from electrically charged gases generating electrical currents that act as a magnetic dynamo inside the sun.
- These magnetic fields twist, tangle, and reorganize themselves due to the turbulent nature of the gases that create them.
- This unsettled magnetic field behavior — also known as solar activity — can trigger solar flare eruptions from the surface that release vast amounts of electromagnetic radiation — a form of energy that includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays, gamma rays, and visible light.
- Solar flares tend to originate from regions of the solar surface that contain sunspots — darker, cooler portions of the solar surface where magnetic fields are particularly strong.
- As such, the number of sunspots can indicate the likelihood of a solar flare eruption.
- Solar activity follows an approximately 11-year cycle with the peak of sunspot activity coinciding with the solar maximum and a sunspot hiatus coinciding with the solar minimum.
- During periods of low solar activity when no sunspots are present, it is unlikely that a solar flare will occur.
What are X-Class Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are categorized into five classes based on the intensity of emitted X-rays, with each class letter denoting a 10-fold increase in energy output, akin to the Richter scale for earthquake strength assessment.
- X-class flares are the most powerful solar flares.
- Then there are M-class flares that are 10 times smaller than X-class flares, then C-class, B-class, and finally A-class flares which are too weak to significantly affect Earth.
- Within each letter class, a finer scale from 1 to 9 gives the flare assessment greater precision with larger numbers representing more powerful flares within the class.
- However, X-class flares can break this nine-point rating mold with higher ratings, since there is no class more powerful than X-class.
- Fortunately, X-class flares occur on average about 10 times per year.
How do Solar Flares Affect the Earth?
- Disruption of Satellite Communications: Solar flares can interfere with satellite communications, GPS signals, and radio transmissions, causing disruptions or blackouts in telecommunications and navigation systems.
- Auroral Displays: Intense solar flares can trigger colorful auroras, or Northern and Southern Lights, as charged particles interact with Earth's magnetic field, creating stunning light displays in the polar regions.
- Power Grid Disturbances: Severe solar flares have the potential to induce geomagnetic storms that can overload power grids, leading to widespread power outages and damage to electrical infrastructure.
- Radiation Hazards: Solar flares emit harmful radiation, particularly in the form of ultraviolet and X-rays, which can pose risks to astronauts in space and airline passengers at high altitudes.
- Impact on Electronics: The influx of charged particles during solar flares can induce currents in electrical circuits, potentially damaging or disrupting sensitive electronic devices, such as computers, satellites, and spacecraft.
Vaikom Satyagraha

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vaikom, a temple town in the princely state of Travancore, saw the start of a non-violent agitation on March 30, 1924 — the first among temple entry movements that would soon sweep across the country.
What is Vaikom Satyagraha?
- Vaikom Satyagraha was a significant non-violent protest against the caste-based discrimination prevalent in the princely state of Travancore, characterized by a feudal, militaristic governance system entrenched with rigid social norms and customs.
- Discriminatory practices, such as the prohibition of lower castes like the Ezhavas and Pulayas from temple entry and even walking on roads near temples, were pervasive.
Contribution of Leaders:
- In 1923, the issue was brought to attention as a resolution by Madhavan during the Kakinada meeting of the All India Congress Committee.
- Subsequently, the Kerala Pradesh Congress Committee formed the Congress Untouchability Committee in January 1924 to address the matter.
- Pioneers of the Vaikom Satyagraha movement include Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon, then secretary of the Kerala Pradesh Congress Committee, and K. Kelappan, a prominent Congress leader and educationist known as Kerala Gandhi.
Factors Leading to Satyagraha:
- The expansion of Christian missionaries, backed by the East India Company, led to conversions among lower castes seeking liberation from an oppressive system.
- Maharaja Ayilyam Thirunal initiated several progressive reforms, notably the establishment of a modern education system providing free primary education for all, including lower castes.
- These reforms, alongside the influence of capitalism, contributed to the emergence of new social hierarchies, sometimes conflicting with traditional ones.
Commencement of Satyagraha:
- On March 30, 1924, the Satyagrahis embarked on a procession towards the restricted public roads, where a board warned oppressed communities against walking (near the Vaikom Mahadeva temple).
- Despite being halted 50 yards away, individuals such as Govinda Panikkar (Nair), Bahuleyan (Ezhava), and Kunjappu (Pulaya), adorned in khadi attire, courageously defied the prohibition orders.
- Subsequently, they were stopped by the police and, in protest, sat on the road, resulting in their arrest.
- Following this incident, three volunteers from different communities were designated each day to walk on the prohibited roads. Within a week, the movement's leaders were all apprehended by authorities.
Role of Women:
- Large-scale participation of women was witnessed for the first time during the Satyagraha, marking the passage of women into the socio-political consciousness of the country.
- Nagammai, the wife of Periyar, and Kannammal, his sister, played unprecedented roles in the struggle.
Arrival of Gandhi:
- In March 1925, Gandhi arrived at Vaikom and engaged in discussions with leaders from various caste groups.
- He also met with the Maharani Regent at her Varkala camp.
Withdrawal of Vaikom Satyagraha:
- The Vaikom Satyagraha was officially terminated on November 30, 1925, following consultations between Gandhi and W.H. Pitt, the police commissioner of Travancore.
- A compromise was reached, leading to the release of all prisoners and the granting of access to roads.
Temple Entry Proclamation:
- In 1936, the historic Temple Entry Proclamation was signed by the Maharaja of Travancore, abolishing the age-old ban on temple entry.
Significance:
- During a period of growing nationalist fervor and widespread agitation, the Vaikom Satyagraha emerged as a pivotal catalyst for social reform.
- Introducing Gandhian principles of nonviolent resistance to Travancore for the first time, marked a significant departure from traditional modes of protest.
- Enduring for over 600 consecutive days, despite social pressure, police interventions, and even a natural disaster in 1924, the steadfastness of the movement is commendable.
- The Vaikom Satyagraha fostered unprecedented unity across caste lines, showcasing a remarkable display of solidarity among diverse communities.
India-led ‘Group of Friends’

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a high-level meeting of the India-led 'Group of Friends (GOF), India launched a new database designed to record crimes against UN peacekeepers and monitor progress in holding perpetrators accountable.
About the 'Group of Friends':
- The Group of Friends (GOF) was launched by India in 2022 to promote accountability for crimes against the Blue Helmets during its presidency of the UN Security Council.
- India, Bangladesh, Egypt, France, Morocco, and Nepal are co-chairs of the GOF, which comprises 40 member states.
Key objectives of the group include:
- Engaging and sharing information with the UN Secretary-General to assist member states hosting or having hosted peacekeeping operations in bringing perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers to justice.
- Serving as an informal platform at the UN to exchange information, share best practices, and mobilize resources to facilitate accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- Monitoring progress on bringing accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- The 'Group of Friends' will convene two meetings of its members per year and organize one event annually involving Permanent Missions and other stakeholders, ensuring greater safety and security for peacekeepers.
- This initiative represents the political will of member states, particularly troop and police contributing countries, to champion the implementation of UN Security Council resolution 2589, adopted in August 2021 under India's Presidency of the Council.
- Resolution 2589 called upon member states hosting or having hosted UN peacekeeping operations to take all appropriate measures to bring to justice perpetrators of violence against UN personnel, including their detention and abduction.
- The 'Group of Friends serves as a crucial platform for advancing this resolution, promoting accountability, and enhancing the protection of peacekeepers worldwide.
India's Significant Role in UN Peacekeeping:
- As a longstanding advocate for global peace and stability, India has demonstrated its commitment to United Nations (UN) peacekeeping operations.
- Over the past seven decades, India has contributed more than 260,000 peacekeepers, making it the largest cumulative contributor to UN peacekeeping missions.
- Despite the risks associated with such endeavors, India has remained steadfast in its support of peacekeeping efforts.
- Tragically, 177 Indian peacekeepers have made the ultimate sacrifice in the line of duty, reflecting India's dedication to fostering stability worldwide.
- Presently, India has more than 6,000 peacekeepers deployed in nine out of the twelve UN peacekeeping missions.
- As a strong proponent of accountability for crimes against peacekeepers, India plays a crucial role in advocating for the safety and security of these dedicated personnel.
C-Vigil App

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ever since the general election was announced two weeks ago, a total of 79,000 violations have been reported on the Election Commission of India’s (ECI) cVigil app across the country.
About C-Vigil App:
- cVigil is a user-friendly and easy-to-operate application, that connects vigilant citizens with the District Control Room, Returning Officer and Field Unit (Flying Squads), or Static Surveillance Teams.
- By using this app, citizens can immediately report incidents of political misconduct within minutes and without having to rush to the office of the returning officer.
- As soon as the complaint is sent on the cVigil app, the complainant receives a unique ID, through which the person will be able to track the complaint on their mobile.
- This creates a rapid and accurate reporting, action, and monitoring system.
The cVIGIL app enabled voters to
- Register Complaints: The app allows every citizen within the election boundaries to report the Model Code of Conduct / Expenditure Violations by taking photos/audio/video through their mobile phones by signing into the application.
- Anonymous User: The app also allows the citizen to complain anonymously, without revealing their details/ identity.
- Geotagging: The app automatically enables a geo-tagging feature when users switch on their camera in the cVIGIL to report a violation, which helps the field unit to know the precise location of the incident.
Benefits of the Application:
- cVIGIL is a convenient and user-friendly app allowing citizens to send pictorial evidence of the model code of conduct violations in their vicinity.
- Each reported incident is tracked and scrutinized from the beginning to the endpoint, thus bringing accountability into the system.
- The immediate location verification feature of the cVIGIL will act as a strong deterrence for miscreants and wrong-doers as they can be easily tracked.
- A combination of all these factors will encourage citizens to keep vigil over unhealthy electoral practices and bring them to the notice of the Election Commission.
- This in turn will help the commission reach its objective of conducting free and fair elections.
Hume’s Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI startup Hume unveiled a new voice interface yesterday that the company claims is “the first conversational AI with emotional intelligence.
What is an Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)?
- Empathic Voice Interface (EVI) by Hume, a New York-based research lab and technology company, is the world’s first emotionally intelligent voice AI.
- It accepts live audio input and returns both generated audio and transcripts augmented with measures of vocal expression.
- By processing the tune, rhythm, and timbre of speech, EVI unlocks a variety of new capabilities, like knowing when to speak and generating more empathic language with the right tone of voice.
- These features enable smoother and more satisfying voice-based interactions between humans and AI, opening new possibilities for personal AI, customer service, accessibility, robotics, immersive gaming, VR experiences, and much more.
- Developers can now seamlessly integrate EVI into various applications using Hume’s API, offering a unique voice interface experience.
EVI boasts several distinctive empathic capabilities:
- Human-Like Tone: EVI responds with tones resembling human expressions, enhancing the conversational experience.
- Responsive Language: It adapts its language based on the user’s expressions, addressing their needs effectively.
- State-of-the-Art Detection: EVI uses the user’s tone to detect the end of a conversation turn accurately, ensuring seamless interactions.
- Interruption Handling: While it stops when interrupted, EVI can effortlessly resume from where it left off.
- Self-Improvement: EVI learns from user reactions to continuously improve and enhance user satisfaction over time.
- In addition to its empathic features, EVI offers fast, reliable transcription and text-to-speech capabilities, making it versatile and adaptable to various scenarios.
- It seamlessly integrates with any Language Model Library (LLM), adding to its flexibility and utility.
What is an AI with Emotional Intelligence and How Can it be Used?
- Artificial Intelligence with emotional intelligence, also known as affective computing or emotion AI, refers to the integration of emotional awareness and intelligence into AI systems, enabling them to recognize, understand, and respond to human emotions.
- This capability draws inspiration from the concept of emotional intelligence in humans, which involves perceiving and managing emotions in both oneself and others.
- The development of emotionally intelligent AI involves leveraging advanced techniques in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to enable AI systems to recognize emotions in facial expressions, speech, and text.
- These systems can adapt their responses based on recognized emotions, creating more empathetic and nuanced interactions between humans and AI.
Potential applications of AI with emotional intelligence include:
- Healthcare: Emotion-sensitive AI could help detect depression, anxiety, or other mental health issues by analyzing speech patterns, facial expressions, or social media posts.
- Education: AI systems could adapt to individual students' emotions, providing customized support and facilitating better learning experiences.
- Customer Service: Emotion AI could enable businesses to respond more appropriately to customer emotions, improving customer satisfaction and fostering long-term loyalty.
- Entertainment: Affective computing could make games and other entertainment experiences more immersive and engaging by adapting to users' emotions in real-time.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court last week said it will review its April 2021 order to bury underground all power lines in the habitat of the Great Indian Bustard (GIB), after the Centre found the order “practically impossible to implement” over long distances.
About Great Indian Bustard:
- Great Indian Bustard (GIB) is an agro-grassland bird endemic to the Indian Subcontinent.
- Known locally as Godawan in Rajasthan, it is a Critically Endangered species as per the IUCN Red List.
- It belongs to the family Otididae and exhibits sexual dimorphism.
- The GIB is an omnivorous bird.
- The species has a current viable population of around 150 individuals in India and mainly survives in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan which holds about 100 individuals.
- Of the remaining individuals, these birds are found in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh respectively.
- With fewer than 150 individuals, they are caught in a deadly maze of power lines that crisscross its last refuge in the Kutch and Thar deserts of western India.
Why Do Power Lines Kill Bustards?
- Power lines pose a risk to all flying birds.
- In 2020, a study carried out by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) in 4,200 sq km of GIB habitat in and around Desert National Park (DNP) in Rajasthan estimated that power lines killed around 84,000 birds of multiple species every year.
- GIBs are especially vulnerable because of their narrow frontal vision and large size.
- Unlike some birds that have a panoramic vision around the head, species like raptors and bustards have extensive blind areas above their heads.
- When they stretch their head forward to scan the ground below, they fly blind in the direction of travel.
Arguments of the Centre:
- The Centre said taking lines of 66 KV and higher voltage underground was not feasible for the evacuation of bulk power due to constraints such as transmission losses, maintenance challenges, multiple cable joints, increased time requirements, and safety concerns.
- The cost implications of undergrounding all power lines in the large area identified are very heavy — running into many thousands of crores and the cost of externalities that will burden the nation was “huge” and “disproportionate”.
- Harnessing renewable power from high-potential areas of Rajasthan and Gujarat was “essential for meeting rising power demand and India’s international commitments on climate change”.
Other threats faced by GIB:
- Free-ranging dogs pose a significant threat to the Great Indian Bustard (GIB) population, particularly in the Thar landscape, with feral packs responsible for a substantial portion of Chinkara depredation in the Desert National Park (DNP) as of 2017.
- Although sporadic hunting of GIBs persists, the prevalent use of pesticides in agricultural areas poses a more substantial risk to the bird's survival.
- Additionally, habitat loss, particularly the decline of grasslands essential for nesting, and diminishing support from local communities are growing concerns.
CoViNet
- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a global network of laboratories to identify and monitor potentially novel coronaviruses that could emerge shortly.
What is CoViNet?
- The Coronavirus Network (CoViNet) is a global collaboration of laboratories with expertise in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- This network aims to identify and monitor potential new coronaviruses that could emerge and impact public health worldwide.
- To enhance pandemic preparedness, CoViNet will expand its scope to include animal health and environmental surveillance, as well as timely risk assessments.
- This will allow the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop more informed policies and protective measures against future viral outbreaks.
- CoViNet will also play a pivotal role in building and supporting laboratory capacities in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health importance.
- By fostering knowledge exchange and capacity building, CoViNet aims to strengthen the global response to coronavirus threats.
- Furthermore, data generated through CoViNet's efforts will guide the work of the WHO's Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution (TAG-VE) and Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). These groups rely on cutting-edge research and surveillance data to inform public health policies and vaccination strategies.
- With 36 laboratories from 21 countries across all six WHO regions, CoViNet currently encompasses a wide range of expertise and resources.
- Three Indian institutions, namely, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, proudly represent the country in this global network dedicated to coronavirus surveillance and preparedness.
About the World Health Organization (WHO):
- The World Health Organization (WHO) stands as a paramount global health authority, dedicated to promoting health, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare systems worldwide.
- Established in 1948, WHO operates as a specialized agency of the United Nations, with its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It collaborates with governments, international organizations, and civil society to address pressing health challenges and provide guidance and support to countries in need.
- WHO's mandate encompasses a wide array of health-related issues, including infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, mental health, maternal and child health, and environmental health.
- Through research, policy development, and technical assistance, WHO plays a vital role in shaping health policies, setting standards, and coordinating responses to health emergencies such as pandemics and natural disasters.
- With a mission to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people, WHO continues to lead efforts in global health governance, advocacy, and capacity-building, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable world.
Food Waste Index Report 2024

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per the Food Waste Index Report for 2024, households worldwide discarded more than one billion meals daily in 2022.
About UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2024:
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Food Waste Index Report 2024, co-authored with the Waste and Resources Action Programme (WRAP), offers a comprehensive analysis of the state of global food waste.
- The report reveals alarming trends, including the wastage of over 1 billion meals per day in 2022, highlighting the urgency to address this critical issue.
Key findings from the report include:
- Per Capita Waste: The average annual food waste per person amounts to approximately 79 kilograms (or around 174 pounds).
- This equates to over a billion meals being wasted daily worldwide, underscoring the significant inefficiencies in current food consumption habits.
- Sources of Waste: Household waste constitutes the majority, around 60%, with food service establishments (such as restaurants) contributing approximately 28%, and retailers making up about 12%.
- This breakdown suggests that interventions targeting consumer behavior could have a substantial impact on reducing overall waste.
- Environmental Impact: Food loss and waste contribute to 8 to 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Comparatively, if food waste were considered a country, it would rank as the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases globally, trailing only China and the United States.
- This stark comparison underscores the urgent need to address food waste not only for resource efficiency but also as a crucial aspect of climate action on a global scale.
- Global vs. Local Impact: The report highlights that food waste is a pervasive issue affecting both high-income and lower-income countries alike.
- This universality implies that solutions must be adaptable and scalable across various socioeconomic contexts.
- Collaborative Solutions: Governments, regional entities, industry stakeholders, and non-profit organizations are increasingly involved in public-private partnerships to combat food waste.
- Effective strategies, such as food redistribution through initiatives like food banks and charities, are recognized as vital for reducing waste while simultaneously supporting vulnerable communities.
Recommendations:
- The Food Waste Index Report by UNEP emphasizes the urgent need for comprehensive action, both globally and locally, to tackle the issue of food waste.
- By illuminating the extent and origins of waste, as well as its significant environmental and social repercussions, the report advocates for collaborative efforts across all sectors to establish sustainable food systems.
- The target of halving food waste by 2030 is not only in line with environmental goals but also represents a crucial step towards reducing global hunger and promoting a fairer distribution of food resources.
- As nations strive to achieve this objective, the report underscores the interconnectedness of food security, environmental sustainability, and economic viability.
- It presents addressing food waste not only as a moral and environmental imperative but also as a practical opportunity to bolster global food security and combat climate change.
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala High Court has held that a child charged with offenses under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012, is to be prosecuted as per the provisions of the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) (JJ) Act.
About the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO Act):
- Enacted in 2012, the POCSO Act stands as India's pioneering legislation dedicated to addressing child sexual abuse comprehensively.
- Under the administration of the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD), its primary objective is safeguarding children under 18 from sexual assault, harassment, and exploitation, alongside establishing Special Courts to adjudicate such cases swiftly and efficiently, ensuring justice and protection for victims.
Salient Features of the Act:
- The POCSO Act adopts a gender-neutral approach, defining a child as "any person" under 18, ensuring inclusivity for all victims of child sexual abuse.
- It delineates various forms of sexual abuse, encompassing penetrative and non-penetrative assault, sexual harassment, and pornography.
- Certain circumstances, such as mental illness or abuse by a trusted individual like a family member, escalate the severity of sexual assault as per the Act.
- Individuals involved in trafficking children for sexual exploitation are subject to punishment under the Act's provisions on abetment.
- Attempting to commit an offense under the Act incurs penalties up to half the prescribed punishment for the completed offense.
- There's no time limit for reporting abuse, empowering victims to come forward at any point, regardless of when the abuse occurred.
- The Act mandates reporting of sexual abuse, penalizing failure to do so with imprisonment or fines.
- It includes child-friendly procedures for reporting, evidence recording, investigation, and trial, ensuring a supportive environment for victims.
- These procedures include recording the child's statement in a preferred location, preferably by a female officer, and avoiding aggressive questioning or character attacks.
- Medical examinations occur in the presence of a trusted individual, and the child is shielded from seeing the accused during testimony.
- Trials are held in camera, with the Special Court aiming to complete proceedings within a year of cognizance, prioritizing swift justice for victims.
Amendment to the Act:
- In 2019, the Act underwent its inaugural amendment to intensify penalties for particular offenses, aiming to dissuade perpetrators and safeguard the dignity of childhood.
- This amendment introduced the death penalty for aggravated penetrative sexual assault against children.
- Additionally, it empowered the imposition of fines and sentences of up to 20 years in prison to combat child pornography.
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), in 2023, more than 4,500 Rohingya refugees embarked on a perilous journey across the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
About the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR):
- UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency, is a global organization dedicated to saving lives, protecting rights, and building a better future for people forced to flee their homes because of conflict and persecution.
- It leads international action to protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people.
- Formally known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Refugees, UNHCR was established by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1950 in the aftermath of the Second World War to help the millions of people who had lost their homes.
- Today, UNHCR operates in 137 countries and provides life-saving assistance, including shelter, food, water, and medical care for people forced to flee conflict and persecution, many of whom have nobody left to turn to.
- UNHCR defends their right to reach safety and helps them find a place to call home so they can rebuild their lives.
- UNHCR also collaborates with countries to improve and monitor refugee and asylum laws and policies, ensuring that human rights are upheld.
- UNHCR considers refugees and those forced to flee as partners, putting those most affected at the center of planning and decision-making.
Who are the Rohingya Refugees?
- Rohingya are an ethnic group, largely comprising Muslims, who predominantly live in the Western Myanmar province of Rakhine.
- They speak a dialect of Bengali, as opposed to the commonly spoken Burmese language.
- Though they have been living in the South East Asian country for generations, Myanmar considers them as persons who migrated to their land during Colonial rule so, it has not granted Rohingyas full citizenship.
- According to the 1982 Burmese citizenship law, a Rohingya (or any ethnic minority) is eligible for citizenship only if he/she provides proof that his/her ancestors have lived in the country before 1823. Otherwise, they are classified as “resident foreigners” or as “associate citizens” (even if one of the parent is a Myanmar citizen).
- Since they are not citizens, they are not entitled to be part of civil service. Their movements are also restricted within the Rakhine state.
T+0 Settlement Cycle

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The BSE and NSE introduced trading in the T+0 rolling settlement cycle in the equity segment on an optional basis today.
What is Trade Settlement?
- Trade settlement encompasses the bilateral process of transferring funds and securities on the designated settlement date.
- It signifies the completion of a trade transaction when the purchased securities of a listed company are successfully delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the agreed-upon payment.
- The evolution of the trade settlement cycle in India has seen notable adjustments over time.
- Initially shortened by SEBI to T+3 from T+5 in 2002 and further to T+2 in 2003, the current cycle in the Indian stock market stands at T+1.
- This migration to the T+1 cycle took effect in January 2023, positioning India as the second country globally, after China, to implement the T+1 settlement cycle for top-listed securities.
What is the T+0 Trading Settlement Cycle?
- In December last year, the capital markets regulator SEBI proposed to introduce a facility for clearing and settlement of funds and securities on T+0 (same day) on an optional basis, in addition to the existing T+1 settlement cycle.
- The regulator has also proposed to introduce optional instant settlement at a later stage.
- Under the T+0 trade cycle, the settlement of trades will happen on the same day after the closure of the T+0 market.
- If investors sell a share, they will get the money credited to their account the same day, and the buyer will also get the shares in their demat account on the very day of the transaction.
What are the Benefits of T+0 Trade Settlement?
- A shortened settlement cycle will bring cost and time efficiency, transparency in charges to investors, and strengthen risk management at clearing corporations and the overall securities market ecosystem.
- The T+0 trade cycle is expected to provide flexibility in terms of faster pay-out of the funds against the securities to the sellers and faster pay-out of securities against the funds to the buyers.
- It will allow better control over funds and securities by the investors.
- For the securities market ecosystem, a shorter settlement cycle will further free up capital in the securities market, thereby enhancing the overall market efficiency.
- It will enhance the overall risk management of Clearing Corporations (CCs) as the trades are backed by upfront funds and securities.
Who can Participate in the T+0 Settlement Cycle?
- All investors are eligible to participate in the segment for the T+0 trade settlement cycle if they are able to meet the timelines, process, and risk requirements as prescribed by the Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs).
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
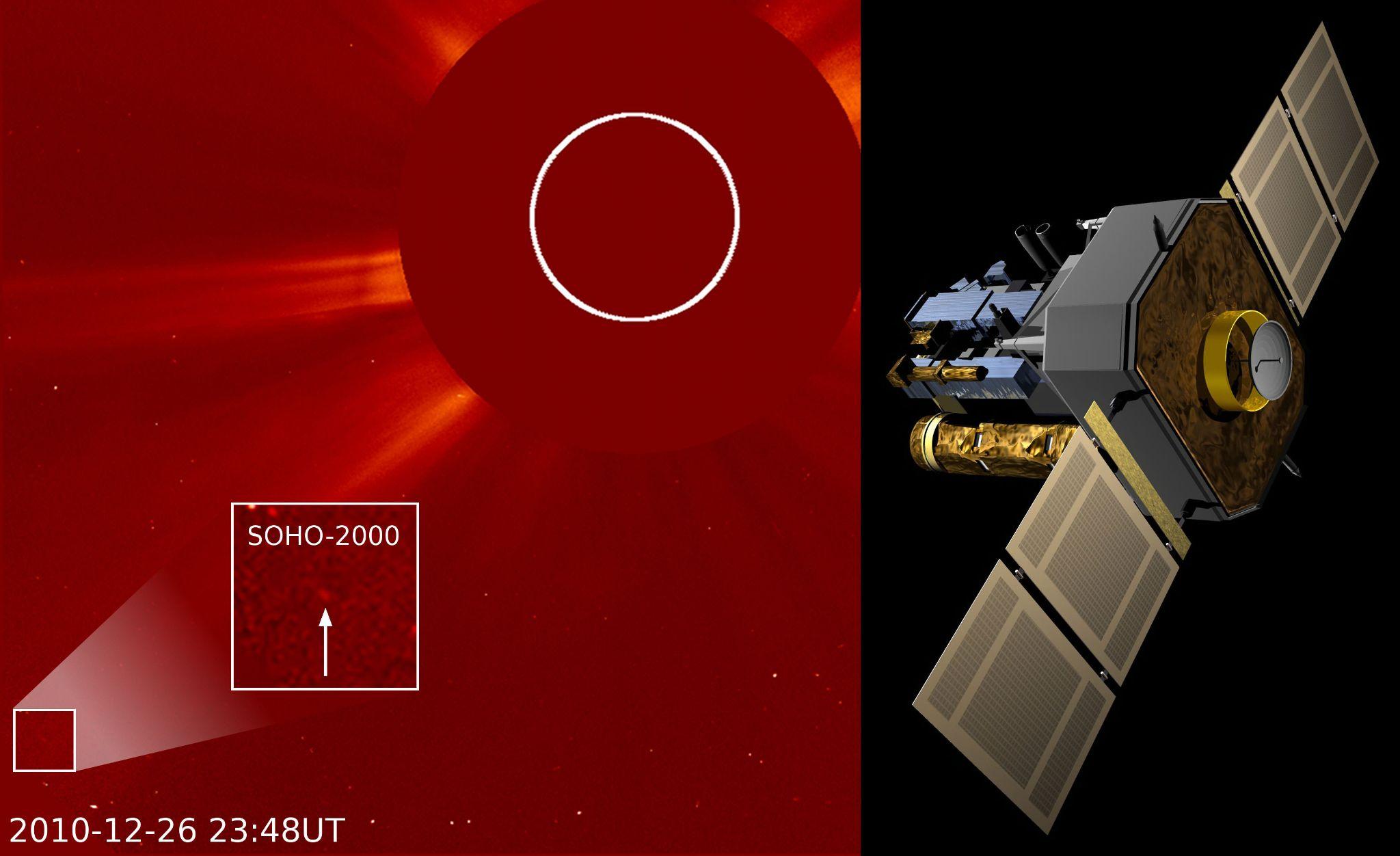
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
South East Africa Montane Archipelago (SEAMA)

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent investigation in southern Africa has revealed a plethora of previously undiscovered biodiversity within a newly identified ecoregion known as the South East Africa Montane Archipelago (SEAMA).
About South East Africa Montane Archipelago (SEAMA):
- It represents a newly identified mountainous ecoregion spanning from northern Mozambique to Mount Mulanje in Malawi, which is the second-highest peak in southern Africa.
- This ecoregion comprises 30 granitic inselbergs rising over 1000 meters above sea level, hosting both the largest (Mt Mabu) and smallest (Mt Lico) mid-elevation rainforests in southern Africa, alongside uniquely diverse montane grasslands.
- SEAMA experiences notably higher annual rainfall and humidity, particularly during the dry season, compared to its surrounding areas.
- Since 2000, SEAMA has witnessed a loss of 18% of its primary humid forest cover, with rates reaching up to 43% in certain locations—marking one of the most rapid deforestation rates across Africa.
- The principal cause of montane forest depletion in SEAMA stems from slash-and-burn agricultural practices, predominantly employed for subsistence food cultivation by local communities, alongside charcoal production for household cooking and economic purposes.
What are Inselbergs?
- Inselbergs are solitary geological formations characterized by isolated, steep-sided hills or small mountains rising abruptly from flat or gently sloping terrain.
- Composed of erosion-resistant rock, such as granite or quartzite, inselbergs stand out prominently in landscapes, with steep or even vertical sides resulting from differential erosion processes.
- These formations, found predominantly in arid or semi-arid regions, take various shapes, including dome-shaped hills, conical peaks, or sheer-sided cliffs.
- Despite their isolated nature, inselbergs support unique ecosystems and biodiversity, creating microclimates and habitats for specialized plant and animal species.
- Rock crevices, caves, and pockets of soil on inselbergs harbor distinct flora and fauna adapted to harsh conditions, making these formations biodiversity hotspots.
- Additionally, inselbergs often hold cultural and spiritual significance for indigenous peoples and local communities, serving as sites for religious rituals, cave paintings, or archaeological artifacts.
- However, inselbergs face threats such as deforestation and habitat degradation due to human activities like slash-and-burn agriculture and charcoal production.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these geological wonders and preserve their ecological and cultural significance for future generations.
Carlsberg Ridge & Afanasy-Nikitin Seamount
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian delegates have been visiting the International Seabed Authority (ISA), Jamaica to strengthen efforts to explore two deep sea regions in the Indian Ocean for mining, according to reports this week.
What is the Carlsberg Ridge?
- The Carlsberg Ridge is the northern section of the Central Indian Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the African Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate, traversing the western regions of the Indian Ocean.
- The ridge of which the Carlsberg Ridge is a part extends northward from a triple point junction near the island of Rodrigues (the Rodrigues Triple Point) to a junction with the Owen Fracture Zone.
- The ridge started its northwards propagation in the late Maastrichtian and reached the incipient Arabian Sea in the Eocene.
- Then it continued to accrete basalt but did not propagate for nearly 30 million years ago.
- Then, in the early Miocene, it started to propagate westwards towards the Afar hot spot, opening the Gulf of Aden.
- The Carlsberg Ridge is seismically active, with a major earthquake being recorded by the U.S. Geological Survey at 7.6 on the moment magnitude scale in July 2003.
- The ridge was discovered by the Danish research vessel Dana during the Carlsberg Foundation's Oceanographic Expedition around the world (1928–1930), better known as the 2nd Dana Expedition, and named after the Carlsberg Foundation, which funded the entire expedition and subsequent analysis and publication of results.
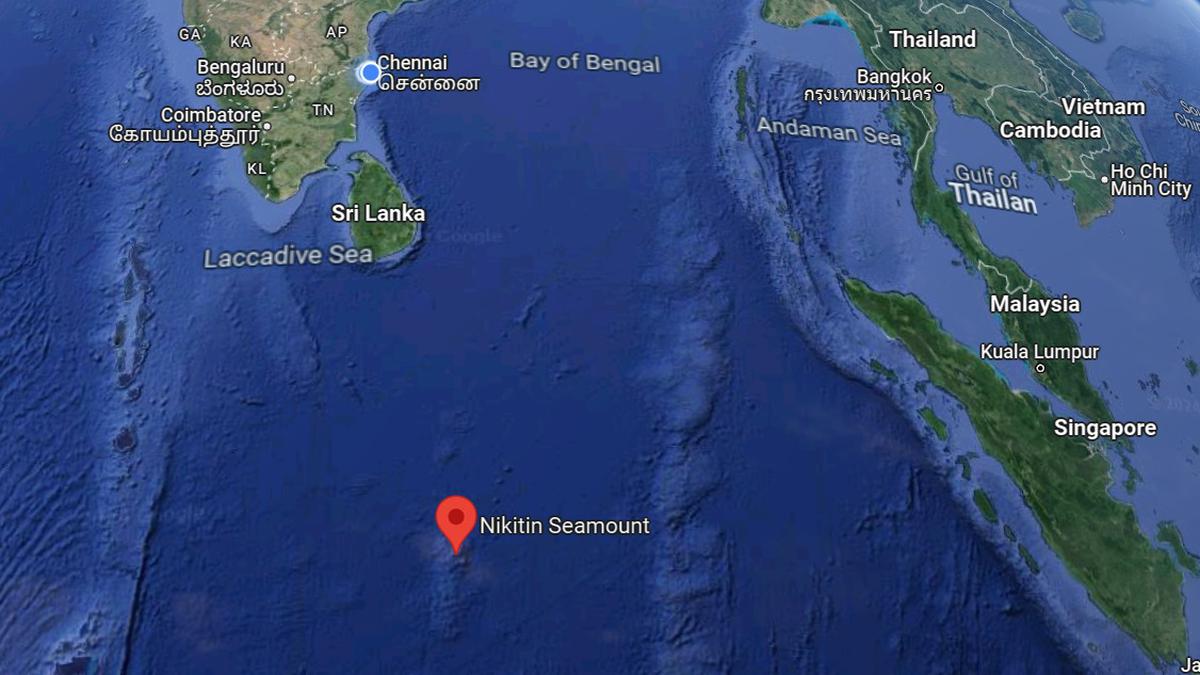
About the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (ANS) Seabed:
- The ANS is a major structural feature in the Indian Ocean, rising up above the sea bed but below the surface, and forming a seamount.
- It is 400 km long and 150 km wide, and is located in the Central Indian Basin — southeast of Sri Lanka, right below the equator, to the west of Singapore.
- It was formed about 80 million years ago, while dinosaurs still roamed the Earth.
- The Seamount is named after Afanasy Nikitin, a 15th-century Russian merchant who was one of the first to document his travels to India.
- A black monolith is also erected in his honor at Revdanda, about 100 km away from Mumbai, where he is thought to have first set foot in the country.
- The ANS seamount is about 3,000 km from India’s coast and is rich in cobalt, copper, manganese, and nickel.
What are Seamounts?
- Seamounts are submarine mountains originating from volcanic eruptions beneath the ocean's surface, serving as critical habitats for diverse marine ecosystems.
- Similar to terrestrial volcanoes, seamounts can exhibit varying states of activity, including active, dormant, or extinct stages.
- They typically form near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates separate, allowing magma to ascend and solidify on the seabed.
- Notably, seamounts also emerge near intraplate hotspots and oceanic island chains, such as island arcs, characterized by volcanic and seismic activity.
- These underwater formations hold significant scientific value, offering insights into mantle composition, plate tectonics, and oceanic circulation dynamics.
- Moreover, seamounts play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and marine life proliferation, fostering localized upwelling of nutrient-rich waters that support diverse biological communities.
Australia’s Carbon Credits System

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent study revealed that a prominent reforestation initiative operating within the Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU) Scheme has been deemed a significant underperformer, amounting to a 'catastrophe' in terms of its outcomes.
What is the Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU) Scheme?
- The ACCU Scheme plays a pivotal role in the Australian carbon market, incentivizing various entities including individuals, businesses, and governmental bodies to engage in endeavors aimed at mitigating emissions or sequestering carbon.
- Participants encompass a broad spectrum ranging from individuals and sole traders to corporations, local and state government entities, and trusts.
- Achievement of the scheme's objectives is facilitated through diverse means such as the adoption of innovative technologies, equipment upgrades, the adoption of sustainable business practices to enhance productivity or energy efficiency, and the implementation of novel vegetation management techniques.
How Does It Work?
- The ACCU Scheme operates by rewarding participants who execute projects focused on either reducing or avoiding greenhouse gas emissions (emissions avoidance) or capturing and storing atmospheric carbon (sequestration).
- These projects contribute significantly to mitigating climate change and advancing environmental sustainability in Australia.
- For each tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (t CO?-e) emissions that a participant's project successfully stores or avoids, they are eligible to earn one Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU).
- These ACCUs serve as a tangible representation of the project's positive environmental impact and can be traded on the secondary market or sold to the Australian Government through carbon abatement contracts.
- In essence, the ACCU Scheme establishes a robust framework for quantifying and monetizing emission reduction and carbon sequestration efforts, providing a strong financial incentive for individuals and businesses to actively engage in climate-friendly initiatives.
- By fostering an active carbon market, the scheme helps ensure the continued growth and development of innovative projects that combat climate change and support Australia's transition to a low-carbon economy.
Criticisms and Controversies:
- The ACCU Scheme has encountered criticisms and controversies regarding its overall effectiveness and the integrity of the carbon credits it generates.
- One such concern is based on research indicating that native forests in Australia's desert regions are experiencing either stagnant growth or shrinking woodlands.
- This finding raises questions about the capacity of these areas to sequester carbon at the levels claimed in ACCU projects.
- Furthermore, critics argue that Australia has amassed substantial quantities of carbon credits through these projects, despite the questionable integrity of the underlying data.
- The scheme's reliability and effectiveness are, thus, scrutinized, as the quality and accuracy of the carbon credits generated are essential to maintaining trust and credibility in the carbon market.
- As the ACCU Scheme evolves, addressing these concerns and ensuring that it genuinely contributes to emission reduction and carbon sequestration efforts is crucial.
- Regular evaluations and transparency in data collection and analysis will help enhance public confidence and secure the scheme's role as a central pillar of Australia's climate change mitigation strategy.
Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC)

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this month, Agriculture Minister Arjun Munda inaugurated a Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) set up at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi, a big-screen dashboard of all digital innovations in the sector.
What is the Krishi ICCC?
- The ICCC is a tech-based solution involving multiple IT applications and platforms, designed to help make informed decisions.
- The center is housed in the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare and is responsible for legislation, policy formation, and implementation of initiatives in the agriculture sector.
- The ICCC uses state-of-the-art technologies such as artificial intelligence, remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process large amounts of granular data.
- The ICCC uses platforms including the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) to collect micro-level data, process it, and present the macro picture.
How does the Krishi ICCC Operate?
- Using AI and machine learning, the system will initially identify a farmer either through their mobile number or Aadhaar details.
- Next, it will cross-reference this information with the farmer's field data retrieved from land records, as well as historical crop sowing data from the crop registry, and weather information from IMD, among other sources.
- Subsequently, the system will generate personalized advisories tailored to the farmer's needs, presented in their local language.
- This functionality will be facilitated through the Bhashini platform, enabling translations into multiple Indian languages.
What Information Does the Krishi ICCC Offer?
- Displayed on eight expansive 55-inch LED screens within the ICCC, the system provides comprehensive data covering various aspects such as temperatures, rainfall, wind speed, crop yields, production statistics, drought conditions, cropping patterns (both geographically and over time), and production forecasts.
- This information is presented in a graphical, map-based, timeline, and drill-down formats for enhanced visualization and analysis.
- Additionally, users can access pertinent trends, including periodic and non-periodic variations, outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), alongside receiving insights, alerts, and feedback concerning agriculture schemes, programs, projects, and initiatives.
- Moreover, the system facilitates direct interaction between farmer beneficiaries and officials or the Minister through video conferencing facilities, ensuring effective communication and support.
Practical Applications:
- Farmer’s Advisory: The ICCC allows visualization of GIS-based soil carbon mapping as well as soil health card data for a particular district together in one place.
- This, when visualized with weather-related data from IMD for the selected district, will allow a customized and authentic advisory to be sent to the farmer about the type of crops that can be grown, and water and fertilizer requirements.
- Drought Actions: An increase or decrease in yield from a specific region (as per GCES data) can be correlated with weather, rainfall, and other information visualized through the Drought Portal, enabling the administration to understand the reason for the increase/ decrease in yield and to take decisions proactively.
- Crop Diversification: An analysis of crop diversification maps, together with field variability for paddy, will enable decision-makers to identify regions with scope for diversified cropping so that farmers can be advised accordingly.
- Farm Data Depository: Krishi Decision Support System (K-DSS), a platform under development, will act as an agriculture data repository. Integrated spatial and non-spatial data will be superimposed as a layer on the GIS map, and various AI/ ML models will be run on the data.
- The K-DSS will help in evidence-based, efficient, and data-driven decision-making, and assist in preparing customized advisories for farmers.
- Validation of Yield: Yield, as captured through Krishi MApper, can be analyzed with the yield generated through GCES application for a plot.
Archaeological Survey of India will ‘Delist’ Some ‘Lost’ Monuments

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has decided to delist 18 “centrally protected monuments” because it has assessed that they do not have national importance.
Context:
- ASI has decided to delist 18 protected monuments
- ASI says the monuments have ceased to be of 'national importance'
- The 18 'lost' monuments include eleven in Uttar Pradesh
Significance of Delisting Monuments:
- Several monuments are currently facing the prospect of delisting, including historical landmarks such as a medieval highway milestone in Mujessar village, Barakhamba Cemetery in Delhi, Gunner Burkill’s tomb in Jhansi district, a cemetery at Gaughat in Lucknow, and Telia Nala Buddhist ruins in Varanasi.
- The exact whereabouts or condition of these monuments remain uncertain.
Meaning of Delisting:
- Delisting a monument entails its removal from the roster of protected sites, thereby relinquishing its conservation, protection, and maintenance responsibilities by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, delisted monuments no longer enjoy protection against construction-related activities in their vicinity, enabling regular urbanization and development activities to proceed uninhibited.
Status of Protected Monuments:
- The inventory of protected monuments is subject to change through additions and removals. Presently, the ASI oversees 3,693 monuments, a number set to decrease to 3,675 following the ongoing delisting initiative.
- This marks the first extensive delisting endeavor in several decades.
Procedures for Monument Delisting:
- The regulations governing the List of Protected Monuments are stipulated under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Rules, 1959.
- This legislation safeguards structures and sites aged over a century, encompassing a diverse array of architectural and historical marvels.
- The government possesses the authority to eliminate certain monuments from the protected list via official notification in the Gazette.
- Through such notifications, the government can declare that certain ancient monuments, archaeological sites, or relics no longer hold national significance under the purview of the AMASR Act (Section 35 of the AMASR Act).
Lost Monuments:
- The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act safeguards monuments and sites aged over a century.
- Nevertheless, numerous structures, particularly smaller or lesser-known ones, have gradually disappeared over time due to factors like urbanization, encroachments, dam and reservoir construction, or neglect.
- In some instances, the lack of public memory hampers efforts to locate these monuments.
Extent of Loss:
- According to a submission by the Ministry of Culture to the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism, and Culture in December 2022, 50 out of India's 3,693 centrally protected monuments were unaccounted for.
- Among these, 14 succumbed to rapid urbanization, 12 were submerged by reservoirs or dams, and the remaining 24 remain untraceable.
- The Committee noted that budget constraints limited the provision of security guards to historical sites, with only 2,578 guards assigned to 248 sites out of the required 7,000.
- Additionally, a 2013 report by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India highlighted the disappearance of at least 92 centrally protected monuments nationwide.
About the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI):
- Founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) was later formalized as a statutory body under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act) following India's independence.
- ASI's primary mandate encompasses archaeological research and the safeguarding, conservation, and preservation of cultural monuments across the nation.
- Its operational scope includes conducting surveys of antiquarian remains, exploring and excavating archaeological sites, and overseeing the conservation and maintenance of protected monuments, among other responsibilities.
- The ASI operates under the purview of the Ministry of Culture.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah has said the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections will be held before September and that the Centre will consider revoking the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act there.
What is AFSPA?
- The AFSPA empowers the armed forces to uphold law and order in “disturbed areas.”
- They have the right to prevent a gathering of five or more people in a given location, use force, or even open fire after providing a sufficient warning if they believe someone is breaking the law.
- Armed forces are also permitted to enter and search any location if they suspect illegal activity.
- According to the AFSPA Act, the Army also has the authority to detain someone without a warrant, seize weapons and ammunition, and offer protection to someone acting in good faith.
Salient features of the AFSPA Act:
- The Central Government or the Governor of a State has the right to declare all or a part of any state to be a disturbed region if they believe it is necessary to stop the terrorist activity or any other activity that could jeopardize India’s sovereignty or be disrespectful to the national anthem, flag, or constitution.
- According to Section 3 of the AFSPA, the Central Government may send out armed forces to support the civilian authorities if the governor of a state publishes a formal announcement in the Gazette of India.
- According to the Disturbed Areas Act of 1976, a territory must maintain the status quo for a minimum of three months after being designated “disturbed.”
- Section (4) of the AFSPA grants army officers specific authority to shoot the only requirement is that the officer must sound the alarm before firing.
- Security forces have the authority to search without permission and arrest anyone without a warrant.
- After being taken into custody, a person must be delivered to the closest police station as soon as possible.
- The Central Government must first provide its consent before prosecuting an on-duty officer for alleged human rights violations.
What are the “Disturbed areas” under the AFSPA Act?
- The state governor, the administrator of the union territory, or the central government may declare a region as a “disturbed area” by publishing a notice in the official gazette, the entire territory or an order to implement it may be declared disturbed.
- It is up to the state governments to decide whether or not to implement the Act.
- However, the governor or the Center may disregard their judgment under Section (3) of the Act.
- The state governor was the only person with the authority to confer AFSPA when the act came into force in 1958.
- The 1978 amendment granted the central government this authority.
List of states that implement the AFSPA Act:
- Four states and one union territory currently have AFPSA activities, while 12 districts are still partially subject to the act, and 31 districts have fully implemented the law.
The AFSPA states include:
-
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Nagaland
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Manipur
Black Carbon

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per a study, the residential sector is responsible for 47% of India's overall black carbon emissions.
What is Black Carbon?
- Black carbon is the dark, sooty material emitted alongside other pollutants when biomass and fossil fuels are not fully combusted.
- It contributes to global warming and poses severe risks.
- Studies have found a direct link between exposure to black carbon and a higher risk of heart disease, birth complications, and premature death.
- Most black carbon emissions in India arise from burning biomass, such as cow dung or straw, in traditional cookstoves.
- According to a 2016 study, the residential sector contributes 47% of India’s total black carbon emissions.
- Industries contribute a further 22%, diesel vehicles 17%, open burning 12%, and other sources 2%.
- Decarbonization efforts in the industry and transport sectors in the past decade have yielded reductions in black carbon emissions, but the residential sector remains a challenge.
- Black carbon is a potent contributor to global warming due to its efficient absorption of light and subsequent heating of its surroundings.
- This process leads to the conversion of incoming solar radiation into heat.
- Moreover, black carbon influences cloud formation and affects regional circulation and precipitation patterns.
- When deposited on ice and snow, it diminishes surface albedo, reducing their ability to reflect sunlight and causing surface warming.
Impacts:
- Black carbon significantly contributes to global warming and poses substantial risks to human health.
- Exposure to black carbon has been linked to increased incidences of heart disease, birth complications, and premature mortality.
- Its warming effect on climate is estimated to be 460-1,500 times more potent than that of CO2.
Magnetofossils
- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
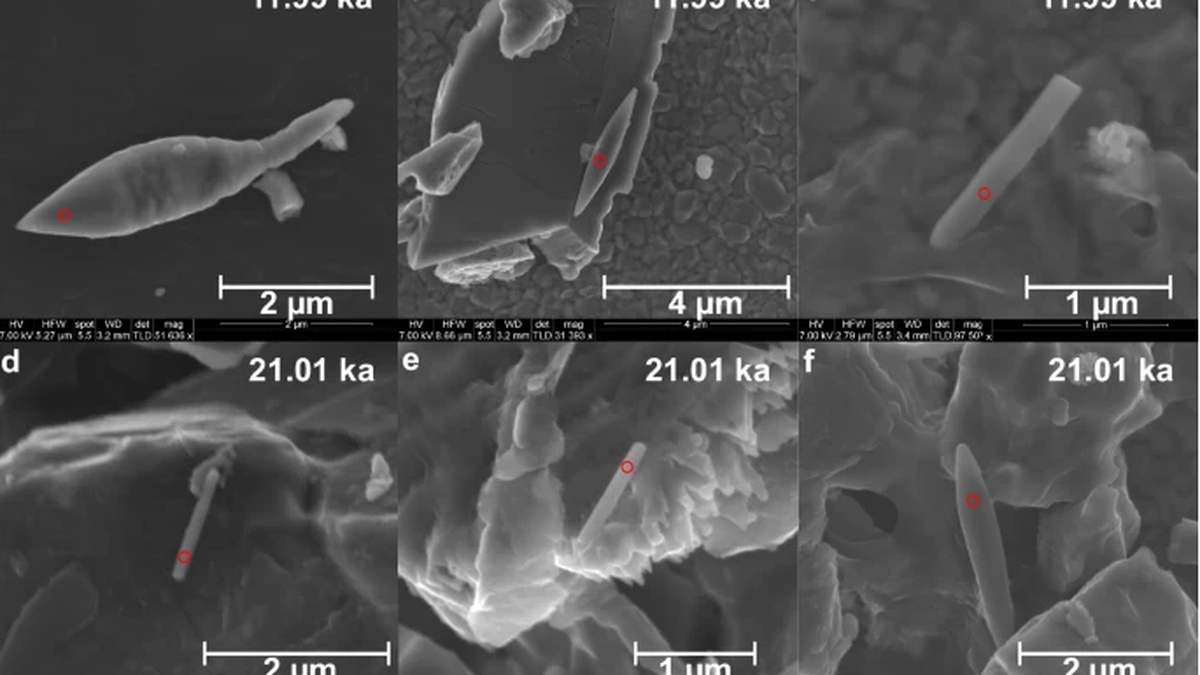
In the depths of the Bay of Bengal, scientists have discovered a 50,000-year-old sediment — a giant magnetofossil and one of the youngest to be found yet.
What are Magnetofossils?
- Magnetofossils represent the fossilized remnants of magnetic particles originated by magnetotactic bacteria, also referred to as magnetobacteria, encapsulated within the geological archives.
About Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria, predominantly prokaryotic microorganisms, possess the unique ability to align themselves in alignment with Earth's magnetic field.
- These organisms were traditionally believed to utilize the Earth's magnetic field as a navigational aid to locate environments with optimal oxygen levels.
- Comprising distinctively structured particles abundant in iron, these bacteria harbor small sacs that function akin to a compass.
- Magnetotactic bacteria synthesize minute crystals composed of iron-rich minerals such as magnetite or greigite, facilitating their navigation amidst fluctuations in oxygen concentrations within their aquatic habitats.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Sediment Composition: The sediment core, measuring three meters in length and extracted from the southwestern Bay of Bengal, primarily comprised "pale green silty clays."
- Foraminifera Abundance: Researchers observed abundant benthic and planktic foraminifera, which are single-celled organisms characterized by shells found near the seabed and freely floating in water.
- Oxygen Concentration: At depths ranging from approximately 1,000 to 1,500 meters, the Bay of Bengal exhibited notably low oxygen levels.
- Analysis of the sediment sample confirmed fluctuations in monsoon activity, as evidenced by the presence of magnetic mineral particles from distinct geological periods.
- Role of Rivers: Rivers such as the Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner, which discharge into the Bay of Bengal, played a pivotal role in magnetofossil formation.
- Nutrient Supply: The nutrient-rich sediment transported by these rivers supplied reactive iron, which, combined with organic carbon in the suboxic conditions of the Bay of Bengal, created a conducive environment for magnetotactic bacteria growth.
- Impact of Oceanographic Processes: Factors such as freshwater discharge from rivers and oceanographic phenomena like eddy formation influenced the oxygen content in these waters, distinguishing them from other low-oxygen zones.
- Persistence of Suboxic Conditions: The presence of magnetofossils indicated the prolonged persistence of suboxic conditions in the Bay of Bengal, fostering an environment conducive to the proliferation of magnetotactic bacteria.
Ola’s ‘Krutrim AI’

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this year, Ola, the Indian multinational ridesharing company, introduced Krutrim AI as "India's own AI," with plans for substantial enhancements to its initial iteration to expand its foundation upon launch.
What is Krutrim AI?
- Krutrim AI is a generative AI assistant that converses in 10+ languages, including Hindi, English, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Bengali, Marathi, Kannada, Gujarati, etc., making it India’s own AI by an artificial intelligence startup.
- It was founded by Bhavish Aggarwal, the founder of Ola Cabs.
- Krutrim AI has been natively created to ensure a creative AI tool designed for over 1.4 billion Indians to provide 100% contextually relevant responses.
- It is a critical milestone in developing public-facing artificial intelligence in India.
These are 4 benefits of Krutrim AI:
-
- Supports multiple Indian languages.
- Native experience is built to cater to cultural diversity.
- They are trained on local language tokens and sources.
- Allows user interaction without charge on its free version.
What is the Tech Behind Krutrim AI?
- Krutrim AI uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) — a component of AI — to understand the nuances of human language, including colloquialisms and cultural contexts.
- Machine Learning (ML) algorithms enable it to learn from vast data sets and improve its responses over time.
- Moreover, Deep Learning, a sophisticated branch of ML, helps it recognize patterns and analyze complex data, which could be crucial for Krutrim AI’s performance.
- While the exact technologies used are not disclosed, these methodologies align with the AI’s demonstrated functions.
How Krutrim AI Works?
- Krutrim AI works through prompts given in the chat field, similar to other generative AI chatbots.
- Generative AI chatbots like Krutrim AI are large language models that understand prompts in the language used for daily communication and respond with language similar to humans.
- Krutrim AI allows users to reply, modify the details, or add additional elements to the response, similar to the experience a user would have with a human assistant.
Benefits of Using Krutrim AI:
- Krutrim AI offers 4 benefits.
- Multilingual as it responds in over 10 Indian languages, which is helpful for users not proficient in English.
- Cultural context provides a native experience, as Krutrim’s training data was specifically geared towards being culturally relevant and understanding the Indian context.
- The development of (AI) start-up Krutrim was done natively from the ground up.
- It is trained on over 2 trillion language tokens, with the largest representation of Indian languages in the artificial intelligence landscape.
- Krutrim’s base model offers a free AI chatbot experience, with a premium version (Krutrim Pro) in the works, that will have larger knowledge-based capabilities.
Post-Vaccination Immunity
- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent review revealed that only a handful of vaccines offer durable protection lasting beyond 20 years.
About Post-vaccination immunity:
Mechanism:
- The fundamental immunological process involves the production of memory B cells in lymph nodes, providing long-term protection against diseases.
- These memory B cells recognize antigens delivered by vaccines, prompting the production of potent antibodies upon encountering similar antigens from foreign objects like viruses, effectively eliminating infections.
- T cell support is essential for the activation of memory B cells, thus vaccines stimulating T cells are capable of inducing their production.
- Notably, certain vaccines, such as polysaccharide typhoid and pneumococcal vaccines, may not prompt the production of B cells.
- To extend the duration of immunity conferred by memory B cells, frequent boosters may be necessary, ranging from six months to several years.
- However, the presence of memory B cells alone does not guarantee protection, as the effectiveness of vaccines in triggering their production varies.
- Long-lasting plasma cells (LLPCs) migrate from lymph nodes to the bone marrow, where they may persist for decades, constituting a crucial aspect of vaccine-induced immunity.
- Every vaccine aims to generate LLPCs in the bone marrow for lifelong protection, with vaccines like those for measles and rubella known to stimulate LLPC production.
- Notably, some potent vaccines, such as mRNA COVID-19 shots, may not effectively activate LLPCs in the bone marrow.
- For vaccines to confer long-term protection, they must generate both memory B cells and LLPCs in the bone marrow, with variations in vaccine effectiveness in producing these cells explaining differences in their durability.
Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP)

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kerala's shift towards an alternative approach for the implementation of smart electricity meters, sidelining the Central government's Rs 3 lakh crore project, poses a challenge to the Union Government's initiative of replacing 250 million traditional meters with smart meters in all households by March 2025.
About the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP):
- The Indian government has initiated the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) to revolutionize the country's energy sector through the implementation of smart meters.
- By replacing 25 crore conventional meters, the SMNP aims to enhance the operational efficiency and revenue management of distribution companies (DISCOMs).
- Under the leadership of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of four National Public Sector Enterprises, the scheme is set to make waves in the energy sector.
- EESL, comprised of NTPC Limited, PFC, REC, and POWERGRID, operates under the Ministry of Power and is committed to undertaking the necessary capital and operational expenditures with zero upfront investment from states and utilities.
- The Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) model facilitates the recovery of smart meter costs via the monetization of energy savings resulting from improved billing accuracy, reduced meter reading costs, and increased efficiency.
- In accordance with guidelines set forth by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), the strategic deployment of these smart meters adheres to industry standards.
Smart meters offer a multitude of advantages:
-
- Consumers can monitor their electricity usage and make informed decisions to reduce their bills.
- Utilities benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, enabling better power demand management.
- Web-based Monitoring: The interconnected smart meter network can mitigate utilities' commercial losses, enhance revenue generation, and propel power sector reforms.
- The Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) paves the way for a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape in India, revolutionizing the way utilities operate and consumers engage with their electricity usage.
What are Smart Meters?
- A smart meter serves as an advanced tool for recording electricity consumption and voltage levels, offering a significant upgrade over traditional metering systems.
- While conventional meters simply measure power usage, smart meters take it a step further by transmitting real-time data to utility providers at intervals of 15 minutes or hourly.
- Smart meters truly live up to their name by utilizing internet connectivity to facilitate two-way communication.
- On one hand, they empower consumers with up-to-date information on energy usage patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions and manage consumption more efficiently.
- On the other hand, utility providers gain valuable insights for monitoring purposes and ensuring accurate billing.
- In essence, smart meters pave the way for improved energy management, increased transparency, and enhanced efficiency, catering to the evolving needs of both consumers and utility providers in today's digital era.
Cannabis

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
During the celebration of Holi across India, Bhang, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant or true hemp, is widely favored for consumption.
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis is found mainly in the Indo-Gangetic plains – in Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal – along with the Deccan region.
- Cannabis is termed Ganzai in Telugu, Ganja in Tamil, and Bangi in Kannada.
- The cannabis plant can be 4 to 10 feet tall at maturity.
- Its plant also grows on wastelands and can easily be spotted on roadsides.
- Three products can be obtained from the plant – fiber, oil, and narcotics.
- Bhang is obtained from the seeds and leaves of the plant, which are reduced to powder.
- Then, the powder is filtered and prepared for drinking, mixed often with cold, flavored milk or thandai on Holi.
Additional Uses and Benefits of Cannabis:
- According to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), cannabis ash can be applied to animals' skin in cases of hematoma, a condition characterized by blood clotting outside of blood vessels.
- Hemp-seed oil is employed in varnish industries as a substitute for linseed oil and in soft soap manufacturing, as well as possessing numerous medicinal properties.
- In Himachal Pradesh, cannabis cultivation is concentrated in Chhota/Bada Bhangal of Kangra and the Karsog area of Mandi district.
- While cultivating cannabis for addictive narcotics is illegal, states permit regulated cultivation for industrial or horticultural purposes, focusing on fiber and seed extraction.
- Cannabis-based treatments, such as bhang application on paddy seeds, can enhance germination and control threadworms in paddy nurseries, particularly in the temperate regions of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Heated and crushed cannabis leaves are often transformed into a paste to alleviate pain from a honey bee or wasp stings.
District Election Management Plan

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Effective execution of elections demands thorough planning, where a crucial aspect is the meticulous formulation and implementation of the District Election Management Plan (DEMP).
About the District Election Management Plan (DEMP):
- The District Election Management Plan (DEMP) is a comprehensive document designed to ensure the smooth conduct of elections, employing statistics and analysis.
- According to the Election Commission of India, the DEMP must be prepared at least six months before the tentative poll day.
- Collaboration among election officials, administrative authorities, law enforcement agencies, etc., is crucial for the execution of the DEMP.
Key components of the DEMP include:
- District Profile: A district profile providing foundational electoral strategy, featuring political maps outlining constituencies, key demographic and infrastructure statistics, and a brief on the district’s administrative setup and socio-economic features.
- Polling Stations: Detailed strategies for enhancing the availability and accessibility of polling stations, ensuring essential facilities such as ramps, electricity, lighting, drinking water, toilets, and internet connectivity.
- Special Attention to PwD and Senior Citizens: Addressing the requirements of voters with disabilities and senior citizens through dedicated help desks, round-the-clock control rooms, home voting options, and advanced postal ballot voting for essential service personnel.
- Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) Plan: Integration of the Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) plan, focused on increasing electoral participation.
-
- Planning, training, welfare, and deployment strategies for election personnel, along with training initiatives for district-level teams to enforce the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) and equip all election personnel with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Regarding Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs)?
- Management of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) is vital to uphold the integrity of the electoral process, encompassing strategies for secure storage, availability, transportation, and maintenance of both EVMs and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs).
- The District Election Management Plan (DEMP) contributes to enhancing the voting process by ensuring its organization and accessibility to all voters.
- Furthermore, the principles employed in the DEMP, such as meticulous planning, collaboration, and transparency, offer valuable insights applicable beyond elections, providing lessons for broader governance.
- The emphasis on advanced planning, data-driven decision-making, and stakeholder collaboration highlighted by the DEMP is instrumental in addressing challenges effectively.
ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 Landing Experiment
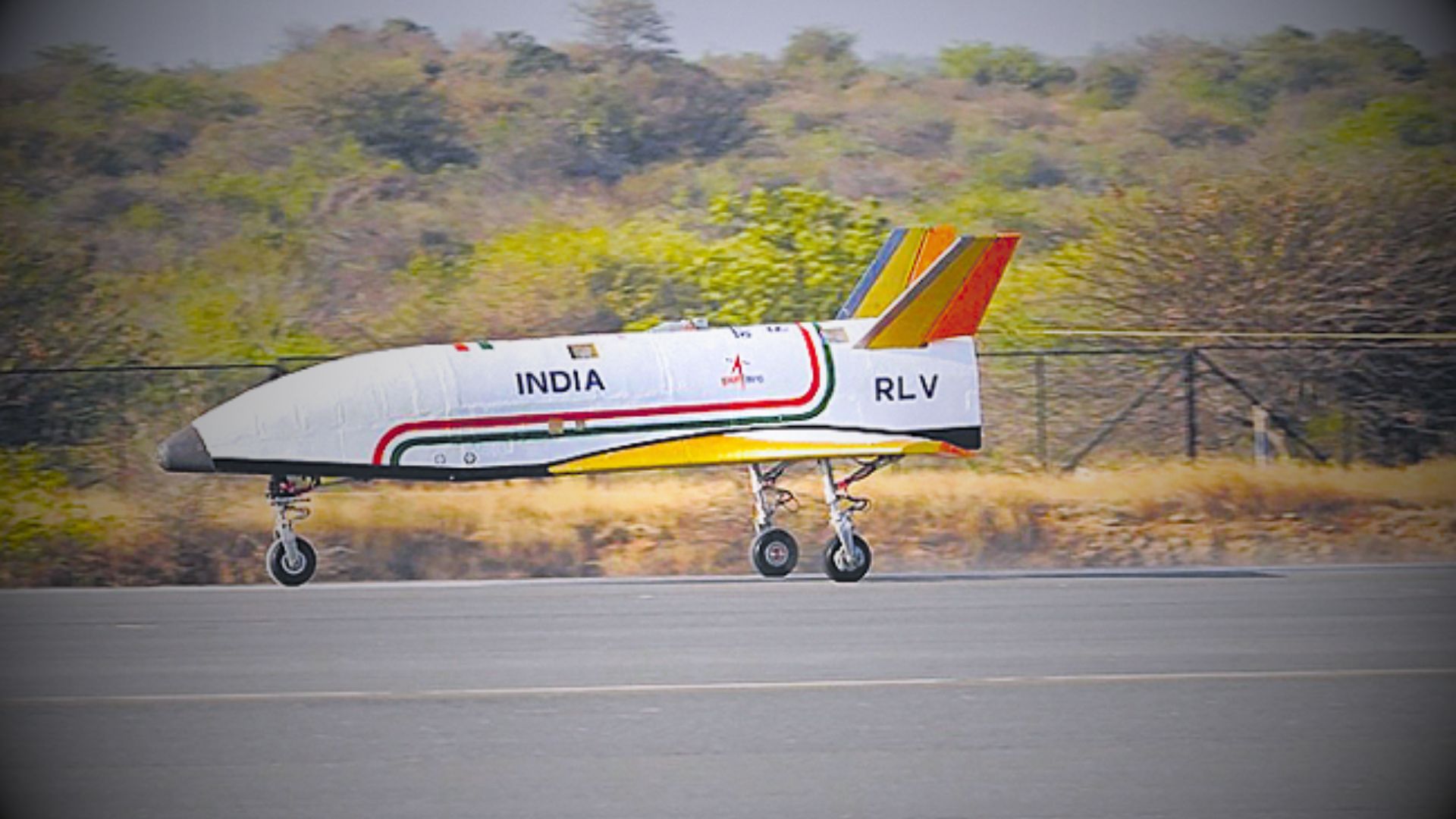

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully conducted the Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 landing experiment at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga recently.
What is a Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02?
- Continuing our exploration into reusable landing vehicles, RLV-LEX-02 marks the second mission in our series conducted at the Aeronautical Test Range.
- Following the success of RLV-LEX-01 last year, this latest endeavor showcases the remarkable autonomous landing capability of our reusable launch vehicle (RLV).
- Notably, RLV-LEX-02 demonstrates the vehicle's ability to navigate and safely land from off-nominal initial conditions immediately upon release from a helicopter.
Methodology of the Experiment:
- The RLV LEX-02 mission showcased the autonomous landing prowess of our reusable launch vehicle under demanding circumstances following its release from a helicopter.
- Dubbed 'Pushpak', this winged vehicle was airlifted by an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter and released from a height of 4.5 km.
- Navigating autonomously, it adeptly approached the runway, making precise cross-range corrections before executing a flawless landing.
- Utilizing a combination of its brake parachute, landing gear brakes, and nose wheel steering system, it safely came to a stop.
- Notably, the winged body and all flight systems previously employed in RLV-LEX-01 were repurposed for RLV-LEX-02 after undergoing necessary certification and clearances.
- This remarkable mission was executed collaboratively by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Liquid Propulsion System Centre (LPSC), and the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU).
What is the Reusable Launch Vehicle?
- The reusable launch vehicle represents a pioneering space plane design characterized by a low lift-to-drag ratio, which mandates high glide angles during approach and consequently requires landing at velocities reaching 350 kmph.
- Integral to its innovation are a multitude of indigenous systems developed meticulously. These encompass sophisticated navigation systems, leveraging pseudolite technology for precise localization, as well as instrumentation and sensor arrays, among other advancements, all spearheaded by ISRO.
Order of the Druk Gyalpo

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently received Bhutan’s highest civilian award, the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’, during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
What is the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’ Award?
- The Order of the Druk Gyalpo, Bhutan's most prestigious civilian award, was recently conferred upon Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
- As the first foreign Head of Government to receive this esteemed accolade, Prime Minister Modi joins a select group of individuals honored for their exceptional contributions to Bhutanese society, service, integrity, and leadership.
- According to the ranking and precedence established within Bhutan's honor system, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo represents the pinnacle of lifetime achievement, taking precedence over all other orders, decorations, and medals.
- Prime Minister Modi received the award in recognition of his outstanding contributions to strengthening India-Bhutan relations and his dedicated service to the Bhutanese nation and its people.
- Past recipients of the Order of the Druk Gyalpo include:
- Her Majesty The Royal Queen Grandmother Ashi Kesang Choden Wangchuck in 2008
- His Holiness Je Thrizur Tenzin Dendup in 2008, and
- His Holiness Je Khenpo Trulku Ngawang Jigme Choedra in 2018.
- With Prime Minister Modi's recent addition to this esteemed list, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo continues to symbolize Bhutan's appreciation for remarkable individuals who significantly impact the country and its people.
Netravati River

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The principal bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in New Delhi has initiated action on the Netravati Waterfront Promenade Development Project in Mangaluru.
About the Netravati River:
- The Netravati River, also known as Netravathi Nadi, originates from the Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka, India.
- It passes through the revered pilgrimage site Dharmasthala, earning recognition as one of India's sacred rivers.
- Converging with the Kumaradhara River at Uppinangadi, it eventually flows into the Arabian Sea, south of Mangalore city, serving as the primary water source for Bantwal and Mangalore.
- The Netravati railway bridge, a prominent structure, acts as the gateway to Mangalore.
- Historically known as the Bantwal River, it was documented as unfordable during the South-West Monsoon in the 1855 Gazetteer of Southern India.
- The river's navigability by small country craft and its influence on local geography and transport, including the naming of the Netravati Express train, underscores its significance in the region's history.
- Instances of flooding, notably in 1928 and 1974, have shaped the lives of residents, prompting relocations and resilience
About the National Green Tribunal:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) was established under the National Green Tribunal Act of 2010.
- While its principal seat is located in New Delhi, it also holds sessions in Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- The NGT is entrusted with the responsibility of adjudicating applications or appeals, ensuring their final disposition within six months of filing.
Composition:
- The tribunal comprises a Chairperson, Judicial Members, and Expert Members, each serving a non-renewable term of five years.
- The appointment of the Chairperson is made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- A Selection Committee, constituted by the Central Government, is responsible for appointing both Judicial and Expert Members.
- The tribunal can accommodate a minimum of 10 and a maximum of 20 full-time Judicial and Expert Members.
Powers & Jurisdiction:
- Established to efficiently handle cases concerning environmental protection and conservation of natural resources, including forests.
- It possesses appellate jurisdiction akin to a court.
- While not bound by the procedural formalities outlined in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, the NGT operates based on the principles of natural justice.
Hepatitis B
- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Public knowledge and awareness about Hepatitis B, a deadly disease that can cause end-stage liver cirrhosis and liver cancer, is dismal in India, according to a new study conducted by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi.
What is Hepatitis B?
- It is a severe liver infection that can lead to liver damage, cancer, and death.
- The virus spreads through contact with an infected person's blood or bodily fluids.
- One can get hepatitis B through sexual contact, sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is a severe viral infection of the liver that can cause inflammation and scarring.
- Symptoms include fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice.
Causes of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- HBV is found in the blood and body fluids of an infected person. It can spread through contact with fluids, such as:
- Blood, through needle sharing or accidental needle sticks
- Contact with body fluids, such as saliva, etc.
- Sexual contact with someone who has HBV
- From a mother to a child through childbirth
- Hepatitis B can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as:
- Sharing personal items like toothbrushes or razors with someone who has HBV
- Getting a tattoo or body piercing with contaminated equipment
Types of Hepatitis B:
- There are three main types of hepatitis B: acute, chronic, and carriers.
- Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after exposure to the virus. It is the most common type of hepatitis B in children.
- Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term illness that can lead to serious health problems, including liver failure and liver cancer.
- Carriers of hepatitis B have the virus in their blood but do not show any symptoms.
Treatment for Hepatitis B
- Several medications can help treat hepatitis B.
- These include antiviral drugs, which can help reduce the amount of virus in the body, and immunomodulators, which can help boost the immune system to better fight the virus.
- If the liver is damaged, one may also need medication to help protect it from further damage.
- HBIG (Hepatitis B Immuno Globulin) is one of the best ways to treat hepatitis B.
- Adults who have been exposed to hepatitis should get HBIG and vaccination as soon as possible, preferably within 24 hours but not later than 14 days after the exposure.
Prevention of Hepatitis B:
- The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated.
- The vaccine is given as a series of shots.
- The first shot is usually given at birth; the rest at 1–2 months old, 6–18 months old, and 4–6 years old.
- If one was not vaccinated as a child, they can receive the vaccines as an adult.
Jaipur’s traditional celebrations with ‘Gulaal Gota’

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In Jaipur, Rajasthan, a centuries-old tradition called "Gulaal Gota" will be observed during Holi, involving the throwing of colors through a unique medium, dating back around 400 years.
What is a Gulaal Gota?
- A Gulaal Gota is a small ball made of lac, filled with dry gulaal.
- Weighing around 20 grams when filled with gulaal, these balls are thrown at people on Holi, getting smashed to bits on impact.
- Local artisans say that making Gulaal Gotas involves first boiling the lac in water to make it flexible.
- Lac is a resinous substance that is secreted by certain insects. It is also used to make bangles.
- After shaping the lac, colour is added to it. At first red, yellow, and green are added as other colours can be obtained through their combinations.
- After the processing is done, artisans heat the lac.
- It is then blown into a spherical shape with the help of a blower called “phunkni”.
- Then, gulaal is filled in the balls before they are sealed with lac.
Where does the raw material for Gulaal Gota come from?
- Lac is brought from Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand.
- The female scale insect is one of the sources of lac.
- To produce 1 kg of lac resin, around 300,000 insects are killed.
- The lac insects also yield resin, lac dye, and lac wax.
How did Gulaal Gotas become a tradition in Jaipur?
- Gulaal Gotas are made by Muslim lac makers, called Manihaars, only in Jaipur.
- Manihaars’ ancestors were shepherds and horse traders who arrived from Afghanistan.
- They settled in Bagru, a town located close to Jaipur, and learned lac-making from Hindu lac makers or Lakhere.
- The city of Jaipur was established in 1727. Its founder Sawai Jai Singh II, an admirer of art, dedicated a lane at the Tripoliya Bazaar to the Manihaar community.
- This is where lac bangles, jewelry, and Gulaal Gota are mostly sold, to date.
What is the economics of this tradition?
- One box of six Gulaal Gota balls is sold for Rs 150, which is much costlier than water balloons.
- Usually, the whole family of artisans is engaged in this work, including women.
- For Manihaars, lac bangles are the main source of sustenance as making Gulaal Gota is a seasonal work.
- Artisans say that the bangles are eco-friendly as they are made without any chemicals.
Why the demand is falling?
- Jaipur has of late become a hub of many factories where cheap, chemical-based bangles are made with minimum lac.
- Original lac bangles are costlier than the manufactured ones. Hence, the demand for lac-only bangles has fallen.
- Many of the community’s younger members are also more interested in taking up blue-collar jobs instead of artisan work.
Government Support and Artisan Empowerment:
- The Indian government has issued artisan cards to Lac Bangle and Gulaal Gota craftsmen, enabling them to access benefits under various government schemes.
- Many artisans have ventured abroad to exhibit their craft, such as Awaz Mohammad, who was invited to showcase his work at the G20 summit in New Delhi last year.
- In efforts to preserve tradition, some Gulaal Gota artisans are advocating for a Geographical Indication (GI) tag, which can enhance product visibility and underscore its unique regional identity.
PIB Fact Check Unit (FCU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court stayed the Centre’s notification of the Fact Check Unit (FCU) under the Press Information Bureau (PIB) until the Bombay High Court arrives at a final decision on the challenge to the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules.
Background:
- Under the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules, 1961, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) is entrusted with the responsibility of disseminating information about government policies, schemes, and programs through various mediums of communication.
- In fulfilling its role, the Ministry publicizes the policies, initiatives, schemes, and programs of the Government of India through press releases, press conferences, webinars, publication of books, etc.
- To carry out this crucial function, the Ministry has several attached and subordinate offices, including the Press Information Bureau (PIB).
- A significant aspect of the responsibility of facilitating public information about the functioning of the Government of India involves countering the dissemination of fake, false, and misleading information.
- The PIB has been carrying out this function for a long through a wide distribution of accurate and reliable information, issuing rebuttals, etc.
- In the age of social media where information spreads rapidly, the spread of fake and manipulated information, especially related to the functioning of a democratically elected Government, is dangerous to society as it has the potential to intensify social, economic, and political conflicts, weaken public trust in democratic institutions, and even endanger the life of the citizens.
What is the PIB Fact Check Unit (FCU)?
- The Press Information Bureau has been at the forefront of taking proactive measures to combat fake news related to the Government of India.
- In November 2019, PIB established a Fact Check Unit (FCU) to tackle the issue of fake news about the Government of India, its various ministries, Departments, Public Sector Undertakings, and other Central Government organizations.
- The unit verifies claims about government policies, regulations, announcements, and measures.
- Through an established rigorous fact-checking procedure, the PIB Fact Check Unit helps dispel myths, rumors, and false claims and provides accurate and reliable information to the public.
Organization
- The PIB Fact Check Unit is headed by a senior DG/ADG level officer of the Indian Information Service (IIS).
- The day-to-day operations of the Unit are handled by IIS officers at various levels. The Unit reports to the Principal Director General, PIB who functions as the Principal Spokesperson of the Government of India.
Fact-Check Mechanism
- Users send requests over WhatsApp, email, or a web portal. Each such request received is considered a ‘Query’.
- Queries are segregated by the Unit based on their relevance to matters about the Government of India.
- Only queries about the Government of India are considered and taken up as Actionable Queries, while others are deemed not relevant for action.
- The information in question is checked rigorously through multiple layers of cross-checking through Government Open-source information, use of technological tools, and verification from the concerned Government of India organization.
- Should the Unit come across a piece of information that the Unit ascertains must be busted publicly for the larger benefit of the people of India, after investigation and verification from official & authoritative sources, it publishes a 'Fact Check' on its social media platforms.
- Often a single fact check can be a result of multiple queries.
Fact-checked content can be segregated into the following three categories:
- Fake: any factually incorrect news, content, or, piece of information related to the Government of India, spread intentionally or unintentionally, that can deceive or manipulate the audience, with or without the intention to cause potential harm, can be flagged as Fake
- Misleading: any information presented, either partially true or with selective presentation of facts or figures or with distortion of facts or figures and to deceive or mislead the recipient of the information.
- True: any information that is found to be factually correct after investigation
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will host the fifth meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation startup forum in January next year according to the commerce and industry ministry.
About the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Startup Forum:
- The SCO Startup Forum is a platform for the stakeholders from the startup ecosystems from all SCO Member States to interact and collaborate.
- The entrepreneurial activities aim to empower the local startup communities in the SCO Member States.
- The SCO Startup Forum aims to create multilateral cooperation and engagement for startups among the SCO Member States.
- This engagement will empower the local startup ecosystems in the SCO Member States.
The following are the objectives of the engagement:
- Sharing of best practices to promote entrepreneurship and innovation to build knowledge-exchange systems
- Bringing Corporations and Investors across to work closely with startups and provide local entrepreneurs with much-needed support and market access
- Increasing scaling opportunities for startups by providing solutions in the field of social innovation and providing Governments with a plethora of innovative solutions
- Creating open procurement channels to enable matchmaking for procuring innovative solutions from startups
- Facilitating cross-border incubation and acceleration programs that will enable the startups to explore international markets and get focused mentorship.
Upcoming Events:
- India is set to host the second meeting of the Special Working Group for Startups and Innovation (SWG) in November 2024 and the SCO Startup Forum 5.0 in January 2025.
Past Initiatives:
- SCO Startup Forum 1.0: Established in 2020, laying the groundwork for multilateral cooperation among SCO Member States' startups.
- SCO Startup Forum 2.0: Held virtually in 2021, introducing the SCO Startup Hub, a centralized platform for the SCO startup ecosystem.
- SCO Startup Forum 3.0: Organized physically in 2023 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), marking a significant milestone for SCO Member States' startup collaboration.
- 1st Meeting of the SWG: Led by India, the first meeting of the SCO Special Working Group on Startups and Innovation in 2023 focused on the theme 'Growing from Roots', emphasizing foundational growth within the startup ecosystem.
Usha Mehta

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent film has been launched, depicting the inspiring life story of Indian freedom fighter Usha Mehta.
About Usha Mehta:
- Born in 1920 in the village of Saras, near Surat in Gujarat, Usha Mehta, affectionately known as Ushaben, embodied the Gandhian principles of non-violence and civil disobedience from a young age.
Early Activism:
- At the tender age of eight in 1928, she participated in a protest march against the Simon Commission, demonstrating her early commitment to India's independence struggle.
- The Secret Congress Radio: In 1942, amidst the fervor of the Quit India Movement, Usha Mehta and her colleagues boldly established the Secret Congress Radio.
- This clandestine radio station played a pivotal role in connecting freedom movement leaders with the masses, ensuring the dissemination of crucial information, and maintaining the spirit of resistance against colonial rule.
Establishing an Underground Radio Station:
- With the outbreak of the War in 1939, the British government imposed stringent measures, including the suspension of all amateur radio licenses throughout the Empire.
- Operators were mandated to surrender their equipment to the authorities, under threat of severe repercussions for non-compliance.
Key Figures in the Operation:
- Usha Mehta, alongside Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, and Chandrakant Jhaveri, played instrumental roles in orchestrating the Congress Radio initiative, defying the ban on amateur radio broadcasting.
The Congress Radio Trial:
- The trial of the five accused individuals—Usha Mehta, Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, Chandrakant Jhaveri, and Nanak Gainchand Motwane, who facilitated crucial equipment—captivated public attention in Bombay.
- While Vithalbhai and Motwane were acquitted, Mehta, Babubhai, and Chandrakant faced severe sentences for their involvement.
Usha Mehta's Legacy:
- Following her release from Pune's Yerawada Jail in March 1946, Usha Mehta was lauded in nationalist circles as "Radio-ben," symbolizing her courageous defiance and commitment to the freedom struggle through underground broadcasting.
Independence, PhD, & Padma Vibhushan
- When India finally achieved independence in 1947, the British had divided the country into two parts – India and Pakistan, sending the region into chaos.
- The divide results in massive bloodshed with more than 10 million Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs seeking to find their home.
- Mehta was torn. “In a way, I was very happy, but sad at the same time because of partition.
- It was an independent India but a divided India,” she was quoted as saying in the book Freedom Fighters Remembered.
- She was away from active politics in independent India due to her ill health but continued to remain a staunch Gandhian till the very end.
- She penned the script for a documentary on Gandhi produced by her colleague at the radio station, and earned a PhD in Gandhian thought at the University of Bombay.
- She taught political science and ran the politics department at the university.
- She also taught at Wilson College for 30 years.
- She was also the president of the Gandhi Peace Foundation.
- In 1998, she was awarded India’s highest civilian honor, the Padma Vibhushan.
- She lived a simple life and never married or had children.
- She died on 11 August 2000 at the age of 80.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Dr. Neeraj Mittal's unanimously elected as co-chair of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s digital innovation board recently.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Established in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, the ITU has evolved into the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICT).
- Recognized as a vital intergovernmental organization, the ITU facilitates collaboration between governments and private sector entities to advance global telecommunication and ICT services.
Key Points:
- Status: Designated as a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Membership: Boasting a diverse membership of 193 countries and over 1000 companies, universities, and international and regional organizations.
Functions:
- Allocation of global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordination and establishment of technical standards about telecommunication/ICT.
- Initiatives to enhance ICT accessibility in underserved communities worldwide.
- India's Engagement: India has maintained an active presence within the ITU since 1869, consistently participating in its endeavors.
- Notably, India has been a regular member of the ITU Council since 1952.
- Headquarters: Located in Geneva, Switzerland, the ITU serves as the global epicenter for fostering collaboration and innovation in the realm of ICT.
What is the Digital Innovation Board?
- The Digital Innovation Board is a pivotal component of the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development, aimed at addressing pressing needs within the realm of innovation as outlined in the Kigali Action Plan, which was adopted at the World Telecommunication Development Conference 2022.
- Comprised of Ministers and Vice Ministers of Telecom/ICT from 23 Member Countries of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), spanning across Asia, Europe, Africa, and North, and South America, this board serves as a strategic advisory body.
- ITU initiated the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development to tackle significant challenges and opportunities in innovation.
- This alliance operates through three key mechanisms:
- The Digital Transformation Lab
- The Network of Acceleration Centers, and
- The Digital Innovation Board.
- The Digital Innovation Board's primary objective is to offer strategic guidance, expertise, and advocacy in promoting local capacity building, fostering innovation, and encouraging entrepreneurship in digital development.
- Its overarching mission is to cultivate a more inclusive and equitable digital future for all stakeholders.
Enforcement Directorate (ED) Arrests Delhi Chief Minister

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal was recently arrested in the Delhi excise policy case, in which he had been issued multiple summons by the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
About the Enforcement Directorate (ED):
- Established in 1956 as the 'Enforcement Unit' under the Department of Economic Affairs, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) underwent a name change in 1957.
- Presently, ED operates under the Department of Revenue (Ministry of Finance) administrative control for operational purposes.
Roles and Responsibilities:
- ED is responsible for enforcing the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) and certain provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
- In case of FEMA violations, ED has the authority to attach the assets of offenders.
- ED is also empowered to conduct searches, seizures, arrests, prosecutions, and surveys against PMLA offenses.
Appointment Process for ED Director:
- The Central Government appoints the ED Director based on the recommendations of a committee, which comprises:
Chairperson: Central Vigilance Commissioner
Members: Vigilance Commissioners, Home Secretary, Secretary DOPT, and Revenue Secretary.
What is the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22?
- The Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22, also known as the new liquor policy, was introduced on November 17, 2021, to transform liquor sales in the city.
- This policy marked a significant departure from the traditional model by privatizing liquor shops and aiming to enhance customer experience while curbing black market activities.
- However, amidst controversy and allegations of procedural irregularities, Delhi ultimately reverted to its previous excise regime.
Key Features:
- The new policy divided Delhi into 32 zones, each open for bidding by firms, departing from individual licenses to zone-based bidding.
- 849 retail vend licenses were auctioned by the Excise department.
- Notably, the policy allowed for discounts to retail customers and reduced dry days to three from 21.
- It proposed innovative measures such as home delivery of liquor and lowering the drinking age from 25 to 21, although these were not implemented.
Controversy:
- Before implementation, the policy underwent scrutiny by the Chief Secretary, who alleged procedural lapses and irregularities.
- The report implicated the Deputy CM for making unilateral decisions, leading to financial losses and allegations of kickbacks.
- These kickbacks were purportedly used to influence elections in other states, leading to a CBI investigation and subsequent arrest of the Deputy CM and others.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) also initiated investigations into alleged money laundering, with claims of substantial proceeds of crime and kickbacks reaching prominent political figures.
- In essence, the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22, while aiming for modernization and improved governance in liquor sales, was marred by controversy and allegations of corruption, prompting a thorough investigation into its implementation and aftermath.
International Day of Forests 2024

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On March 21, 2024, people around the world celebrate World Forest Day. It's a day to remind everyone about how important forests are and all the good things they do for us.
About World Forest Day:
- World Forestry Day, also known as International Day of Forests, is celebrated on March 21 each year.
- The day aims to promote the sustainable management, conservation, and development of all types of forests for the benefit of current and future generations.
The theme for International Day of Forests 2024:
- This year's theme, "Forests and Innovation: New Solutions for a Better World" highlights the critical role of innovation and technology in protecting our forests.
- From advanced monitoring systems that track deforestation to sustainable forestry practices, innovation is key to overcoming the challenges threatening our forests.
History of International Day of Forests:
- The United Nations General Assembly announced March 21 to be the International Day of Forests in 2012.
- The day aims to respect and promote the value of a wide range of forests. Countries are encouraged to take part in regional, global, and local drives to set up a scope of forest and tree-related campaigns, like planting campaigns.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the United Nations Forum on Forests are the coordinators of the International Day of Forests.
Importance of International Day of Forests:
- As per the UNGA, "The United Nations Forum on Forests and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), in collaboration with Governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests and other relevant organizations in the field are responsible for organizing the events and campaigns related to the World Forestry Day."
- The importance of the International Day of Forests is to spread awareness and give instruction at all levels to guarantee feasible forest management and biodiversity preservation.
The Enduring Significance of Forests:
- Forests are often referred to as the "lungs of the planet" for a reason.
They play a vital role in:
- Combating Climate Change: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Protecting Biodiversity: Forests provide habitats for countless species of plants and animals, ensuring the health and balance of ecosystems.
- Providing Clean Air and Water: Forests filter air and water, regulating our climate and providing us with essential resources.
- Supporting Livelihoods: Millions of people around the world depend on forests for food, medicine, and income generation.
Celebrating and Taking Action:
- World Forestry Day is a springboard for action and we can get involved by:
- Support Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working towards forest conservation and sustainable forestry practices.
- Reduce Consumption: Make conscious choices to reduce consumption of paper and wood products, minimizing environmental footprint.
- Plant a Tree: Plant a tree in our community or support tree-planting initiatives.
- Spread Awareness: Educate ourselves and others about the importance of forests and the threats they face.
- By taking action, big or small, we can all contribute to a future where our forests continue to thrive, ensuring a healthier planet for generations to come.
World Inequality Lab Report

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India’s top 1 percent income and wealth shares have reached historical highs and are among the very highest in the world, according to a paper released by World Inequality Lab.
What is the World Inequality Lab?
- The World Inequality Lab is a global research center that focuses on studying inequality and public policies that promote social, economic, and environmental justice.
The lab's main missions include:
- Expanding the World Inequality Database: The lab gathers and analyzes data on income, wealth, and capital asset distribution across various countries.
- Publishing research: The lab releases working papers, reports, and methodological handbooks to contribute to the understanding of global inequality dynamics.
- Collaborating with international researchers: The lab works with a network of researchers from around the world to compile and analyze data for the World Inequality Database.
- Promoting public debate: The lab aims to raise awareness about inequality by disseminating their findings and engaging in public discourse.
- The World Inequality Lab is known for producing the World Inequality Report, which offers up-to-date and comprehensive data on different aspects of inequality globally, including wealth, income, gender, and ecological inequality.
Key Insights from the Research Paper Released by the WIL:
- A team of four economists, including Nitin Kumar Bharti, Lucas Chancel, Thomas Piketty, and Anmol Somanchi, has compiled comprehensive time series data on income and wealth inequality in India.
- Titled "The Billionaire Raj," the paper asserts that India's current level of inequality surpasses that of the British Raj era.
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, India witnessed its highest recorded levels of income and wealth concentration among the top 1%: 22.6% and 40.1%, respectively.
- India's top 1% income share is noted to be among the highest globally, even surpassing countries like South Africa, Brazil, and the US.
- While India's top 1% holds a significant share of income, the wealth share of this segment is comparatively lower than in South Africa and Brazil.
- The paper accentuates the stark disparities among various income groups in India.
- For instance, the wealthiest 1% possess an average wealth of Rs 5.4 crore, 40 times the national average, whereas the bottom 50% and the middle 40% hold significantly lower amounts: Rs 1.7 lakh (0.1 times the national average) and Rs 9.6 lakh (0.7 times the national average), respectively.
- At the pinnacle of the wealth distribution, approximately 10,000 individuals out of 92 million Indian adults possess an average wealth of Rs 2,260 crore, a staggering 16,763 times the average Indian wealth.
Key Recommendations from the Research Paper:
- The research paper has meticulously compiled data from various sources to construct its estimates on income and wealth inequality.
- Given the absence of official income estimates and wealth statistics based on surveys in India, the paper underscores the necessity for reliable data sources in these domains.
- To tackle the issue of inequality in India, the paper proposes a range of policy interventions.
- These measures encompass a comprehensive overhaul of the tax structure to encompass both income and wealth considerations, alongside substantial public investments in critical areas such as healthcare, education, and nutrition.
- A notable suggestion outlined in the report is the implementation of a "super tax" of 2% on the net wealth of the 167 wealthiest families recorded in 2022-23. This levy is projected to generate revenues equivalent to 0.5% of the national income.
- Furthermore, the imposition of such a tax is envisaged not only to create fiscal leeway for essential investments but also to serve as an effective tool in combatting entrenched inequality within the society.
Project GR00T

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI chip leader Nvidia on Tuesday (March 19) announced Project GR00T or Generalist Robot 00 Technology, which promises to revolutionize the evolution of humanoid robots.
What is Project GR00T?
- Project GR00T stands for Generalist Robot 00 Technology.
- It is essentially a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots.
- This ambitious project aims to create a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots, enabling them to understand natural language, learn new skills from observing humans, and solve various tasks in real-time.
- Robots built on this platform are designed to understand natural language and emulate movements by observing human actions, such as instantly learning coordination, dexterity, and other skills.
- This can help the robots navigate and engage with the real world around them.
- The goal of Project GR00T is to advance the field of embodied artificial general intelligence (AGI) and drive breakthroughs in robotics.
- NVIDIA intends to leverage its expertise in AI and its technological resources to develop this foundational model, which would provide humanoid robots with human-like abilities, such as emotion, reaction, and movement.
The Potential Consequences of Project GR00T and Humanoid Robots in the Workforce:
- As humanoid robots, such as those envisioned by NVIDIA's Project GR00T, become more advanced and capable of handling various hazardous or repetitive tasks, concerns arise over potential job displacement.
- For instance, Nvidia's partnership with Hippocratic AI to develop AI-powered healthcare agents may lead to a reduction in the demand for nurses.
- However, proponents argue that these robots can serve as valuable aids for humans, enhancing their quality of life and complementing their skills rather than supplanting them entirely.
- Consequently, the impact of humanoid robots on the workforce may ultimately depend on their successful integration into existing labor structures, as well as the willingness and ability of society to adapt to this transformative technology.
Lianas and its Impact on Forest Ecosystem

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amidst escalating global temperatures, a pioneering study spearheaded by the University of the Sunshine Coast, Australia, sheds light on an unexpected threat posed by Lianas.
What are Lianas?
- Lianas are long-stemmed, woody vines that have their roots in the ground but use the trunks and branches of trees to climb their way up toward the canopy in order to reach sunlight.
- The term “liana” applies more to this type of lifestyle than to any specific family of plants, as lianas come from a variety of different taxonomic groups.
- They are found in tropical forests all over the world.
- These plants have developed a unique climbing strategy to reach the forest canopy and maximize their access to sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Their flexible stems, adventitious roots, and specialized structures such as tendrils and hooks allow them to twist, twine, and ascend the trunks and branches of trees.
How do Lianas Impact the Forest Ecosystem?
- Lianas can have both positive and negative influences on forest ecosystems, depending on their abundance and the specific environmental context.
Positive Impacts of Lianas on Forests:
- Biodiversity: Lianas enhance forest biodiversity by creating additional habitats, providing food resources, and supporting the life cycles of numerous organisms.
- Insects, birds, mammals, and even some epiphytic plants rely on lianas for food, shelter, and reproductive sites.
- Nutrient Cycling: Lianas play a crucial role in nutrient cycling within forests. By absorbing nutrients from the forest floor and transferring them to the canopy through their stems, lianas facilitate nutrient exchange between different vertical layers of the forest.
Negative Impacts of Lianas on Forests:
- Competition for Resources: High densities of lianas can lead to competition with trees for essential resources like light, water, and nutrients.
- This competition may impede tree growth, reduce seedling establishment, and hinder forest regeneration.
- Impact on Forest Structure and Stability: By increasing the likelihood of tree fall during storms or strong winds, lianas can negatively affect forest structure and composition.
- When lianas grow on tree crowns, they increase the weight and wind resistance of trees, making them more susceptible to uprooting.
- Economic Implications: Lianas can also impact the growth and reproduction of commercially valuable tree species, which has economic implications for forest management and timber production.
- Moreover, liana-infested trees often have reduced timber quality due to distortions in the tree trunk and branches.
- Low Carbon Sequestration: Their lower carbon sequestering capacity compared to trees further exacerbates the threat to carbon storage.
Pusa Basmati Rice

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as basmati rice exports from the country are poised to scale a new high, scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) have red-flagged the “illegal” cultivation of its blockbuster varieties in Pakistan.
Unauthorized Cultivation and Export of Pusa Basmati Rice Varieties in Pakistan:
- Despite being officially registered and protected Indian varieties, several IARI-bred Basmati rice varieties, such as Pusa Basmati 1121, Pusa Basmati-6, and Pusa Basmati 1509, are being illegally cultivated and marketed in Pakistan.
- Recent YouTube videos even feature newer IARI varieties like Pusa Basmati-1847, PB-1885, and PB-1886, released in late 2021.
- Pakistan's unauthorized Basmati exports have been substantial, with 7.58 lt ($694.55 million) in 2021-22 and 5.95 lt ($650.42 million) in 2022-23 (July-June).
- This growth is partly due to the depreciation of the Pakistani rupee, allowing the country to offer lower export prices than India.
- The proliferation of these protected varieties in Pakistan can be attributed to the ease of seed multiplication.
- With just a small quantity of seeds, large-scale cultivation can be established within two years of the variety's release in India.
- This unauthorized cultivation not only undermines India's intellectual property rights but also impacts the competitiveness of India's Basmati rice exports in the global market.
What is the Basmati Crop Improvement Program?
- The Basmati Crop Improvement Program focuses on refining the unique qualities of Basmati rice, such as its distinct grain characteristics, cooking properties, and pleasing aroma.
- IARI has played a crucial role in the genetic enhancement, leading to the development of high-yielding, semi-dwarf, and photo-insensitive Basmati varieties like Pusa Basmati 1.
- These improvements have significantly reduced the crop duration from 160 to 120 days and increased productivity from 2.5 to 6-8 tons per hectare.
- As a result, these advanced Basmati varieties account for approximately 90% of India's projected $5.5 billion exports in 2023-24.
- This achievement contributes to substantial foreign exchange earnings and economic growth for the country.
Key Features of IARI-Developed Basmati Rice Varieties:
- IARI has cultivated various Basmati rice varieties with distinct characteristics, including:
- Pusa Basmati 1121: Known as the world's longest Basmati rice, it matures in 145 days with an average yield of 45 q/ha.
- Pusa Basmati 1509: Derived from Pusa 1121 x Pusa 1301, this variety addresses Pusa Basmati 1121's weaknesses, matures in 115 days, and yields 5 tons/ha.
- Improved Pusa Basmati 1 (Pusa 1460): This variety, the first product of molecular breeding in Indian rice, is an enhanced Pusa Basmati 1 with bacterial leaf blight resistance.
- Pusa Basmati 6 (Pusa 1401): Offering superior grain quality, this variety improves upon Pusa 1121's yielding ability, agronomy, and cooking quality.
- Pusa RH10: The world's first superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid, it was released in 2001 for commercial cultivation in specific irrigated ecosystems.
Registration and Cultivation Areas of Pusa Basmati Rice in India:
- All Pusa Basmati rice varieties are officially recognized under the Seeds Act 1966 and can be cultivated within the designated Geographical Indication (GI) area of Basmati rice in India, encompassing seven northern states.
- These varieties are further registered under the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act 2001, which permits only Indian farmers to sow, save, re-sow, exchange, or share the seeds of protected/registered varieties.
Six Heritage Sites on Tentative UNESCO List

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant boost to its rich cultural and historical legacy, 6 new sites from Madhya Pradesh have found a place in the tentative UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites (WHS).
Six New Sites From MP In the UNESCO Tentative List:
- The sites included in the tentative list are Gwalior Fort, the Historical Group of Dhamnar, Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple, Rock Art Sites of Chambal Valley, Khooni Bhandara, Burhanpur, and God Memorial of Ramnagar, Mandla.
- The UNESCO tentative list includes those that provide a forecast of the properties that a State Party may decide to submit for inscription in the next five to ten years.
- Gwalior Fort: An imposing fortress atop a hill, featuring impenetrable walls, exquisite sculptures, and stunning architecture.
- Built-in the 6th century AD by Rajput warrior Suraj Sen and expanded by Tomar ruler Maan Singh in 1398.
- Dhamnar Caves: Rock-cut temple site in Mandsaur district, constructed in the 7th century AD.
- It comprises 51 caves, stupas, chaityas, and dwellings, with a colossal Gautam Buddha statue.
- Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple: Located near Bhopal, this temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, with a huge Linga carved from a single stone.
- Built between 1010 and 1053 AD by Raja Bhoj but was never completed.
- Chambal Valley Rock Art Sites: The world's largest concentration of rock art sites across MP, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, depicting ancient daily life, rituals, and hunting scenes.
- Khooni Bhandara: A unique water supply system built in Burhanpur in 1615 by ruler Abdurrahim Khankhana, still operational today.
- Gond Statue, Mandla: Moti Mahal, a five-storied palace built in Mandla in 1667 by Gond king Hriday Shah, showcasing the strong willpower of the king despite limited resources.
What is UNESCO’s Tentative List?
- A World Heritage Site is a site with outstanding universal value.
- It also denotes cultural and natural significance that transcends national boundaries and is of common importance for current and future generations of all humanity.
- According to UNESCO, a tentative list lists the properties each State Party intends to consider for nomination.
- The government of any nation must have a nomination document ready for the UNESCO World Heritage Committee to review once as soon as UNESCO includes it in a location on the Tentative List.
- After this, a UNESCO representative will evaluate the situation and inspect it.
What is the Tentative List Process?
- The States Parties are encouraged to submit their Tentative Lists of properties that they consider cultural and natural heritage of outstanding universal value and, therefore, suitable for inscription on the World Heritage List.
- The States Parties are encouraged to prepare their Tentative Lists with the participation of stakeholders such as site managers, local and regional governments, local communities, NGOs, and other interested parties and partners.
- The States Parties should submit the Tentative Lists to the World Heritage Centre at least one year before submitting any nomination.
- The list should not be exhaustive.
- The States Parties can re-examine and re-submit their list at least every ten years.
- The States Parties are also requested to submit their lists using a submission format (English or French) that should contain the name of the properties, geographical location, a brief description of the properties, and why the property is of outstanding universal value.
- Nomination will only be considered once the property is added to the State Party's Tentative List.
State of Global Climate Report 2023

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with a host of observations by climate agencies in the preceding three months, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has officially confirmed 2023 to be the hottest year on record.
About the State of Global Climate Report 2023:
- Published annually by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the State of Global Climate Report provides a detailed analysis of the Earth's climate system.
- Contributors to the report include various UN organizations, National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, Global Data and Analysis Centers, Regional Climate Centres, the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), and more.
Highlights of the 2023 Report:
- Record-Breaking Global Temperatures: 2023 was the hottest year on record, with a global average near-surface temperature of 1.45°Celsius (±0.12°C) above the pre-industrial baseline.
- The past ten years were also the warmest decade recorded.
- Extensive Marine Heatwaves: Nearly one-third of the global ocean experienced a marine heatwave on an average day in 2023.
- Over 90% of the ocean had faced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, negatively impacting ecosystems and food systems.
- Unprecedented Glacier Ice Loss: Preliminary data reveals the largest loss of ice since 1950 for the global set of reference glaciers, driven by extreme melt in western North America and Europe.
- Surge in Renewable Energy Capacity: Renewable capacity additions in 2023 increased by almost 50% from 2022, totaling 510 gigawatts (GW) and marking the highest rate in the past two decades.
- These findings emphasize the pressing need to address climate change through effective international cooperation, policymaking, and sustainable practices.
About the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that fosters international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Founded in 1950, WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization established in 1873 to facilitate the exchange of weather data and research.
- Today, WMO comprises 193 member countries and territories and promotes the free exchange of meteorological and hydrological data, information, and research.
- By collaborating with various partners, WMO contributes to environmental protection, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's largest gas utility GAIL (India) Ltd commissioned the country's first SSLNG unit at its Vijaipur complex in Madhya Pradesh recently.
India Unveils Its First Small-Scale LNG Plant:
- In a significant step towards a cleaner energy mix, GAIL (India) Ltd. has commissioned India's first Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) plant in Vijaipur, Madhya Pradesh.
- This plant will produce 36 tonnes of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) daily, utilizing cutting-edge technology like treatment skids and liquefaction skids to convert natural gas into LNG.
- As part of India's commitment to increasing the proportion of natural gas in its primary energy mix from 6% to 15% by 2030, the SSLNG plant will play a pivotal role in reducing pollution emissions while catering to the nation's growing energy demands.
- This milestone achievement paves the way for a greener future and positions India as a significant player in the global LNG landscape.
What is Small-Scale LNG?
- Small-scale LNG (SSLNG) is an emerging industry that offers a novel approach to natural gas distribution.
- While there is no standard international definition, SSLNG typically involves the liquefaction and transportation of natural gas in smaller quantities using specialized trucks and vessels.
- This allows for the supply of LNG to industrial and commercial consumers in regions without pipeline connectivity.
- SSLNG can be sourced from existing large-scale LNG import terminals or small liquefaction plants in gas-rich locations.
- End-users regasify the LNG using small vaporizers for traditional use cases like supplying Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles and piped gas for households and industries.
- Alternatively, LNG can be supplied in its liquid form for direct use.
Benefits of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG):
- Expanded Accessibility: SSLNG overcomes the constraints of traditional pipeline infrastructure, enabling natural gas delivery to regions previously lacking access.
- This opens new avenues for cleaner fuel alternatives and widespread energy availability.
- Operational Flexibility: SSLNG's modular design allows for rapid deployment in response to local demand fluctuations, making it an ideal solution for remote locations, industrial environments, and diverse transportation requirements.
- Sustainability Promotion: By fostering the adoption of cleaner fuels, SSLNG significantly reduces emissions in various transportation sectors, including trucks, buses, and marine vessels. This contributes to a greener future and combats climate change.
- Strengthened Energy Security: Decentralized SSLNG distribution systems diversify fuel sources and bolster energy security, ensuring reliable and stable energy supply amid global fluctuations and uncertainties.
Challenges of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) Implementation:
- Vehicle Availability Constraints: Limited options for LNG-powered vehicles impede the widespread adoption of LNG as a fuel source, underscoring the need for increased production and diversification of vehicle models.
- Insufficient Retail Infrastructure: The lack of a well-established LNG retail network hinders convenient consumer access to LNG fuel, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure expansion and enhancement.
- Higher Upfront Investment: The comparatively higher initial costs of LNG vehicles compared to traditional diesel options may deter potential buyers, necessitating innovative financial solutions and incentives.
- Financing Barriers: The absence of dedicated financing options for LNG vehicles poses obstacles for interested buyers, requiring tailored financial instruments to support SSLNG uptake.
- Restricted Pipeline Coverage: SSLNG faces logistical challenges in areas without existing natural gas pipeline networks, highlighting the need for infrastructure development to extend its reach to remote regions.
- Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: SSLNG projects may encounter regulatory and permitting setbacks, including environmental and safety concerns, potentially prolonging project timelines and inflating costs.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for expediting SSLNG implementation and fostering its growth.
FSSAI Launches Comprehensive Lab Network for Pathogen Testing

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
With food poisoning and diarrhea becoming a common occurrence, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is working towards creating a network of 34 microbiology labs across the country that will be equipped to test food products for 10 pathogens, including E coli, salmonella, and listeria.
About the Initiative:
- To address the growing concern of microbial contamination in food products, a network of 34 advanced microbiology laboratories has been established across the country.
- These state-of-the-art facilities are specifically designed to test and monitor a wide range of food products for the presence of harmful pathogens, including E. coli, salmonella, and listeria, among others.
- The nationwide initiative aims to strengthen the existing food safety framework by enhancing the early detection and prevention of foodborne illnesses.
- By analyzing food samples collected during routine surveillance, the labs will play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and quality of consumable goods.
- With a focus on safeguarding public health and well-being, this collaborative effort will contribute significantly to the overall improvement of food security and foster greater confidence in the food industry.
- As the network continues to expand and evolve, it will undoubtedly become an essential asset in the ongoing battle against foodborne pathogens and contamination.
Need for the Initiative:
- India has witnessed a surge in food poisoning and diarrhea cases in recent years, emphasizing the critical need for improved food safety measures.
- According to data from the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), over 1,100 outbreaks of acute diarrhoeal disease and around 550 incidents of food poisoning occurred within the last four years.
- These troubling statistics underscore the urgency to address this pressing public health issue.
- State food safety laboratories, responsible for ensuring the safety of consumable products, currently lack the necessary resources and infrastructure to effectively identify and mitigate the presence of dangerous pathogens.
- The complexities of maintaining live reference samples, the high costs of reagents, and the requisite expertise of microbiologists pose significant challenges in maintaining optimal food safety standards.
- Consequently, the establishment of a comprehensive microbiology lab network becomes crucial in effectively addressing the growing threat of foodborne illnesses.
- By enhancing testing capabilities and promoting early detection, this initiative will ultimately contribute to a safer food supply, improved public health outcomes, and increased consumer confidence in the food industry.
About the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI):
- As an autonomous body under India's Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the FSSAI was established in 2006 under the Food Safety and Standards Act.
- This act serves as a consolidating statute focusing on food safety and regulation in India.
- The FSSAI's mission is to set global standards for food, encourage adherence to these standards, promote good manufacturing and hygiene practices, and enable citizens' access to safe and nutritious food.
Key functions include:
-
- Protecting public health by regulating and supervising food safety.
- Setting standards and guidelines for food articles.
- Issuing licenses, registrations, and accreditations for food businesses.
- Controlling food imports to prevent harmful ingredients.
- Accrediting food testing laboratories nationwide.
- Overseeing food certification in India, including accreditation of certification systems and food safety management systems for food businesses.
- Through these efforts, the FSSAI plays a vital role in maintaining high food safety standards and safeguarding the well-being of India's citizens.
Reverse Flipping
- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Payments major Pine Labs and quick commerce firm Zepto are among the startups looking to relocate their headquarters from foreign shores to India, to capitalize on the country's burgeoning tech landscape.
What is Reverse Flipping?
- Reverse flipping is a growing trend where overseas startups relocate their domicile to India and list on Indian stock exchanges.
- The primary motivation behind this shift is the potential for a higher valuation and more certain exit opportunities in India's thriving economic landscape.
Several factors contribute to the rise of reverse flipping:
- Access to a large, expanding economy: India's significant market size and sustained economic growth offer foreign startups attractive prospects for business expansion and success.
- Abundant venture capital: India's substantial venture capital resources provide a strong financial foundation for startups, fueling innovation and growth.
- Favorable tax policies: The country's tax regulations encourage foreign startups to establish operations in India, helping them maximize profits and minimize costs.
- Enhanced intellectual property protection: India's robust IP protection framework fosters innovation and creativity, safeguarding the unique ideas and technologies of startups.
- Skilled, youthful workforce: The availability of a talented, young, and educated population provides startups with a valuable human resource pool to drive growth and success.
- Supportive government policies: The Indian government actively promotes entrepreneurship and innovation through various initiatives and policies, creating a conducive environment for startups.
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 acknowledged the importance of reverse flipping and suggested measures to expedite the process, including simplifying tax vacation procedures, ESOP taxation, capital movement, and reducing tax layers.
- These efforts aim to further enhance India's appeal as a destination for foreign startups and foster economic growth.
What is Flipping?
- Flipping refers to the process by which an Indian company becomes a 100% subsidiary of a foreign entity after moving its headquarters overseas, involving a transfer of intellectual property (IP) and other assets.
- This transforms an Indian startup into a fully-owned subsidiary of a foreign entity, with founders and investors maintaining their ownership through the new overseas structure by exchanging their shares.
The process of flipping poses several concerns for India:
- The brain drain of entrepreneurial talent: As Indian startups move their operations overseas, India experiences a loss of innovative and entrepreneurial talent, which could otherwise contribute to the country's economic growth and development.
- Value creation in foreign jurisdictions: Flipping redirects potential value creation to foreign countries, depriving India of the economic benefits that could result from successful startups and innovations.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: When companies relocate and transfer their intellectual property overseas, India loses valuable IP assets, undermining the country's competitive advantage and innovation potential.
- Reduced tax revenue: Flipping also contributes to decreased tax revenue for India as companies shift their operations and profits to other jurisdictions, which may have more favorable tax policies.
Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS)

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exporters seeking to avail duty concessions on shipments to the UK will have to adhere to the new British rules under the Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS).
What is the Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS)?
- The Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS) is a preferential trading scheme introduced by the United Kingdom to promote trade with developing countries and support their economic growth.
- The DCTS is designed to support sustainable growth in these countries through a more generous unilateral offer compared to the current Generalised Scheme of Preferences (GSP).
Key provisions of the DCTS include:
- Tariff Reduction: Lowering tariffs facilitates easier exportation of goods from developing countries to the UK market.
- Liberalized Rules of Origin: Simplifying rules of origin requirements streamlines trade between developing nations and the UK.
- Simplified Conditions: The scheme's conditions are simplified to facilitate easier access for developing nations.
- The DCTS extends to countries currently benefiting under the UK's GSP, encompassing 47 Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and 18 additional low-income (LIC) and lower-middle-income (LMIC) countries or territories identified by the World Bank.
- However, it excludes countries classified as upper-middle income by the World Bank for three consecutive years or those with a free trade agreement (FTA) with the UK.
- The UK government's policy response to the DCTS introduction is structured into four sections, addressing rules of origin, tariffs, goods graduation, and scheme conditions.
- Overall, the DCTS signifies the UK's commitment to bolstering trade opportunities and sustainable growth in developing countries by providing improved market access and favorable trade terms.
Significance For India:
- The Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS) has significant implications for India, as it offers preferential access to the United Kingdom's market.
- India, being classified as a lower-middle-income country by the World Bank, is eligible to benefit from the DCTS.
- Trade opportunities: The scheme provides reduced or eliminated tariffs on various goods, making it easier for Indian exporters to access the UK market.
- This results in enhanced trade opportunities and increased competitiveness for Indian products.
- Economic growth: By improving access to a major global market, the DCTS can contribute to India's economic growth, creating jobs and boosting the country's export sector.
- Diversification: The scheme encourages Indian businesses to diversify their export portfolio, helping to reduce reliance on specific sectors or trading partners.
- Sustainable development: Through its focus on promoting sustainable development and economic growth in participating countries, the DCTS aligns with India's own goals to foster inclusive and sustainable economic progress.
Overall, the DCTS presents a positive outlook for trade between India and the UK. It offers Indian exporters improved access to the UK market, reduced trade barriers, and a conducive environment for sustainable growth. India can leverage the opportunities provided by the DCTS to strengthen its trade relationship with the UK and potentially increase its exports, benefiting its economy and the livelihoods of its people.
Haemodialysis
- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Findings from a nationwide private hemodialysis network show that there is a variation in the survival of patients receiving hemodialysis in India depending on various factors, and stress on the need to standardize dialysis care across centers.
What is Hemodialysis?
- Haemodialysis, also known as dialysis, is a medical procedure that helps individuals with kidney failure by removing waste products and excess fluid from their blood.
- This procedure essentially performs the functions of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste and maintaining the body's electrolyte balance.
Key points about hemodialysis:
- Process: During hemodialysis, a patient's blood is circulated through a machine with a semipermeable membrane, called a dialyzer or an artificial kidney.
- The dialyzer filters out waste products, such as urea and creatinine, and excess fluid from the blood, which is then discarded, while essential components are returned to the patient's bloodstream.
- Access: To perform hemodialysis, a patient typically requires vascular access, which is a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein, usually in the arm.
- This connection allows for the efficient flow of blood from the patient to the dialysis machine and back.
- Duration: Haemodialysis treatment typically lasts for around 3-5 hours and is performed several times per week, depending on the patient's needs and kidney function.
- Indications: Haemodialysis is prescribed for patients with end-stage kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), who need immediate intervention while waiting for a kidney transplant or when a transplant is not a suitable option.
- Side effects: Some common side effects of hemodialysis include low blood pressure, muscle cramps, itching, and fatigue.
- Complications such as infection, access problems, and blood clotting may also occur, but these risks can be minimized with proper medical supervision and management.
- In summary, hemodialysis is a life-sustaining treatment for patients with kidney failure, offering a means to maintain their health and well-being despite the loss of kidney function.
SAKHI App To Assist Gaganyaan Crew

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) facility at Thumba in Thiruvananthapuram, has developed a multi-purpose app that will help astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission carry out a range of tasks such as looking up vital technical information or communicating with one another.
About SAKHI App:
- The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), an ISRO facility in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, has created the versatile 'SAKHI' app for astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission.
- SAKHI stands for 'Space-borne Assistant and Knowledge Hub for Crew Interaction'.
Purpose:
- During the mission, the app will assist Gaganyaan crew members in various tasks such as accessing vital technical information and communicating with each other.
Utility:
- Health Monitoring: It will monitor key health parameters like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, providing crucial insights into the crew's physical condition during the mission.
- Additionally, it will remind them of hydration, dietary schedules, and sleep patterns.
- Connectivity:
- Astronauts can use the app to maintain mission logs in various formats, including voice recordings, texts, and images.
- It will ensure seamless communication between the crew, the onboard computer, and ground-based stations.
- Current Status: An engineering model of the custom-built hand-held smart device featuring SAKHI has been tested, with the development of a flight model underway.
About the Gaganyaan Mission:
- The primary objective of the mission is to demonstrate the capability to launch and safely return three crew members to low Earth orbit.
- The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) is designated as the launch vehicle for the Gaganyaan mission.
- Crew Escape System (CES): A vital component of the mission, CES is powered by quick-acting, high-burn rate solid motors.
- It ensures the safe evacuation of the Crew Module and crew in case of emergencies during launch or ascent.
- Orbital Module: Comprising the Crew Module (CM) and Service Module (SM), the Orbital Module orbits the Earth, providing safety and support throughout the mission phases.
- Crew Module (CM): Designed to offer a habitable space with Earth-like conditions for the crew during their time in space.
- Service Module (SM): This module supports the CM during orbit, containing essential systems such as thermal, propulsion, power, avionics, and deployment mechanisms.
- This will mark ISRO's inaugural manned spaceflight mission, joining the ranks of the US, Russia, and China, which have previously conducted human spaceflights.
Nilgiris Forest Fire

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has deployed its assets to aid the local administration in dousing the raging forest fire that started recently in Tamil Nadu's Nilgiris district.
What is a Forest Fire?
- A forest fire, also known as a wildfire, is an uncontrolled fire that occurs in forested areas or other vegetated landscapes.
- These fires can spread rapidly, fueled by dry vegetation, high temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds.
- Once ignited, they can quickly grow in size, consuming vast areas of land, vegetation, and wildlife habitat.
- Wildfires pose significant risks to human safety, property, ecosystems, and air quality.
Causes of Forest Fire:
- Forest fires are caused by Natural causes as well as man-made causes.
- Natural causes: Many forest fires start from natural causes such as lightning which sets trees on fire.
- However, rain extinguishes such fires without causing much damage. High atmospheric temperatures and dryness (low humidity) offer favorable circumstances for a fire to start.
- Man-made causes: Fire is caused when a source of fire like naked flame, cigarette or bidi, electric spark, or any source of ignition comes into contact with inflammable material.
- Natural causes: Many forest fires start from natural causes such as lightning which sets trees on fire.
Types of forest fire:
- Surface Fire: This type of forest fire spreads primarily along the ground, consuming surface litter such as dry leaves, twigs, and grasses.
- The flames engulf the forest floor as they advance.
- Underground Fire: Underground fires, also known as muck fires, burn with low intensity beneath the surface, consuming organic matter and surface litter.
- These fires often spread slowly and can continue burning for months, destroying vegetative cover.
- Ground Fire: Ground fires occur in sub-surface organic fuels such as duff layers under forest stands or organic soils of swamps.
- They burn herbaceous growth and organic matter beneath the surface, often transitioning from smoldering underground fires.
- Crown Fire: Crown fires involve the burning of the crowns of trees and shrubs, sustained by a surface fire.
- They are particularly hazardous in coniferous forests, where resinous material can fuel intense flames.
Frequency of Forest Fire in India:
- Seasonality: Forest fires in India are prevalent from November to June, with peak activity typically occurring in April and May, encompassing both small-scale and large-scale incidents.
- Vulnerability: The 2019 India State of Forest Report (ISFR) highlighted that over 36% of the country's forest cover is susceptible to frequent fires, with 4% categorized as extremely prone and an additional 6% as highly fire-prone.
- Affected Regions: Dry deciduous forests experience severe fires, with Northeast India, Odisha, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Uttarakhand being particularly vulnerable areas.
- Recent Incidents: Notable fire outbreaks occurred in 2021 across Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Nagaland-Manipur border, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, including wildlife sanctuaries.
- In 2023, Goa faced large bushfires under investigation for potential human causes.
- 2024 Trends: Recent reports indicate heightened fire activity in Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Meghalaya, and Maharashtra, with increased incidents along the Konkan belt, coastal Gujarat, southern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, coastal Odisha, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Southern India: While Andhra Pradesh and Telangana witness fire incidents, forests in southern India, primarily evergreen or semi-evergreen, are less prone to fires, although Tamil Nadu has experienced recent wildfires.
Reasons Behind This Year's Fires:
- Climate Factors: Dry conditions, high temperatures, clear skies, and light winds have fueled forest fires in southern India.
- Temperature Trends: February 2024 was exceptionally hot, making it the hottest month in southern India since 1901.
- Heat Accumulation: Above-average temperatures over the past months led to a buildup of heat, drying out biomass in forests ahead of the summer season.
- Excess Heat Factor: Western Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are experiencing higher-than-normal EHF values, increasing the risk of heat waves.
- Mild Aridity: Lack of rain and high temperatures have classified most districts in southern India as mildly arid.
World Air Quality Report 2023

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India had the third worst air quality out of 134 countries in 2023 after Bangladesh and Pakistan according to the World Air Quality Report 2023 by IQAir.
About World Air Quality Report 2023:
- The World Air Quality Report is an annual publication by IQAir, a Swiss air quality monitoring firm.
- The report provides an in-depth analysis of global air quality, shedding light on the impact of air pollution on human health and the environment.
Key highlights from the report include:
- India ranks third in poor air quality: With an average annual particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) concentration of 54.4 micrograms per cubic meter, India trails only Bangladesh and Pakistan in terms of poor air quality.
- South Asian dominance in pollution rankings: Bangladesh and Pakistan occupy the top two positions in the air pollution rankings, while ten out of the eleven most polluted cities in the world are in India.
- Delhi's alarming status: For the fourth consecutive year, Delhi has been identified as the world's most polluted capital city.
- Additionally, Bihar's Begusarai has been termed the world's most polluted metropolitan area.
- India's widespread exposure: An overwhelming 96% of the Indian population experiences PM2.5 levels more than seven times the WHO annual PM2.5 guideline, emphasizing the need for urgent interventions to mitigate the health impacts of air pollution.
What is Particulate Matter (PM)?
- Particulate Matter (PM) is a term used to describe a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
- These particles can be made up of various components such as dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and organic chemicals.
- They are classified based on their size, with PM2.5 and PM10 being the most commonly referenced categories.
- PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less, which is about 30 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
- These particles are produced by various sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and wildfires.
- Due to their small size, they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, posing significant health risks.
- PM10, on the other hand, refers to coarse particulate matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less.
- These particles are larger and primarily originate from activities such as construction, road dust, and agricultural practices.
- While not as harmful as PM2.5, they can still enter the respiratory system and cause health problems.
Equity Issues in IPCC Reports

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a study published recently, researchers analyzed more than 500 future emissions scenarios the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessed in its latest reports.
About the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC):
- The IPCC was created in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It is the leading international body for the assessment of climate change.
- It is a key source of scientific information and technical guidance to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement.
- The IPCC provides governments with scientific information for use in developing climate policies.
- The IPCC currently has 195 members.
- The IPCC does not undertake new research. Instead, it synthesizes published and peer-reviewed literature to develop a comprehensive assessment of scientific understanding.
- These assessments are published in IPCC reports.
- They are subject to multiple drafting and review processes to promote an objective, comprehensive, and transparent assessment of current knowledge.
- The IPCC’s work is guided by principles and procedures that govern all main activities of the organization.
- IPCC member governments and observer organizations nominate experts and the IPCC's scientific governing body, the IPCC Bureau, selects authors and editors with expertise in a range of scientific, technical, and socio-economic fields.
What are IPCC Assessment Reports?
- Typically, IPCC reports comprise three Working Group reports:
- One on physical science
- One on climate adaptation, and
- One on mitigation action.
- One synthesis report consolidates findings from the three Working Group reports.
- Then there are thematic special reports.
- Each report assesses climate-related scientific literature to capture the state of scientific, technical, and socio-economic knowledge on climate change.
- The IPCC is currently in its Seventh Assessment cycle (AR7).
How Does it Assess Future Scenarios?
- The IPCC uses ‘modelled pathways’ to estimate what it will take to limit the warming of the earth’s surface.
- These pathways are drawn using Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) that describe human and earth systems.
- IAMs are complex models that examine possible futures of the energy and climate systems and economies.
- Its macroeconomic models can point to future growth levels in terms of GDP;
- Its energy models can project future consumption
- Vegetation models can examine land-use changes; and
- Earth-system models use the laws of physics to understand how climate evolves.
- With such integration across disciplines, IAMs are meant to provide policy-relevant guidelines on climate action.
- However, these models also have shortcomings. They prioritize least-cost assessments — for example, the absolute cost of setting up a solar plant or undertaking afforestation in India is lower than in the U.S.
- However, experts have said they could exercise the option of enabling countries to equitably share the burden of action, where the richest undertake more drastic mitigation action more immediately.
About the Latest Study:
- Conducted by a team of specialists from Bengaluru and Chennai, the study scrutinized 556 scenarios outlined in the IPCC's AR6 report.
- Their findings indicate that by 2050, per-capita GDP in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, West Asia, and other parts of Asia will remain below the global average.
- Collectively, these regions account for 60% of the global population.
- Additionally, the study highlighted disparities in the consumption of goods and services, as well as energy and fossil fuel consumption, between the Global North and the Global South.
Why Does Equity Matter?
- Equity is crucial in climate action as per the UNFCCC, which mandates developed nations to lead in combating climate change.
- However, current modeling approaches often overlook equity, burdening poorer nations disproportionately.
- Researchers highlight the need for modeling techniques that prioritize climate justice and equitable distribution of responsibilities.
- They argue that mitigation pathways should ensure developed regions accelerate towards net negative emissions and allocate carbon budgets to less developed regions.
- Addressing this gap requires a paradigm shift in scenario building, emphasizing both equity and environmental sustainability.
- This approach is vital for fostering global cooperation and achieving meaningful climate action.
Lisu and Singpho Communities

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Children of the Lisu and Singpho communities in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam are named according to the order they are born in the family, incorporating numbers into their names.
News Summary:
- In the Lisu or Yobin community of Arunachal Pradesh, names reflect the birth order of children, a tradition emphasizing familial hierarchy and cultural heritage.
- This practice underscores the community's deep-rooted connection to family and tradition.
- Recently, Birdwatchers discovered a new species of wren babblers in remote northeastern Arunachal Pradesh, aptly named the Lisu wren babbler.
Lisu and Singpho communities:
- The Lisu and Singpho communities, belonging to the Tibeto-Burman ethnic family, share a unique tradition of employing numbered names to denote birth order within their families, serving as a testament to their ethnic cohesion and rich cultural legacy.
- This naming tradition is prevalent among the Lisus, spanning regions such as Arunachal Pradesh, China, Myanmar, and Thailand, as well as the Singphos, who are prominent in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India.
- The Singphos, an ethnic community believed to have originated from the Kachin peoples, migrated from regions including upper Myanmar, Southwestern China, and Northern Thailand to settle in the eastern areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Both communities adhere to specific naming sequences for boys and girls, supplemented by strategies to prevent confusion in cases of similar name counts within families, such as the use of prefixes or suffixes.
- Furthermore, names may incorporate clan or ancestral references, adding layers of cultural and familial significance to the naming tradition, which underscores the profound connection to tradition and the enduring importance of family and clan identities within these communities.
About Wren Babblers:
- Belonging to the babbler family Timaliidae, Wren Babblers encompass approximately 20 small Asian bird species.
- Characteristics: These birds typically measure between 10 to 15 centimeters (4 to 6 inches) in length, featuring short tails and straight bills.
- Natural Habitat: Primarily found in southern Asia, Wren Babblers inhabit various ecological niches.
- Grey-bellied Wren Babblers: A closely resembling species to this newly discovered one, predominantly inhabit regions of Myanmar, with smaller populations also found in China and Thailand.
Revenue-Based Financing

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Revenue-based financing (RBF) is increasingly popular among startups and digital SMEs due to a lack of venture capital and limited access to traditional credit options.
What Is Revenue-Based Financing?
- Revenue-based financing is a method of raising capital for a business from investors who receive a percentage of the enterprise's ongoing gross revenues in exchange for the money they invested.
- In a revenue-based financing investment, investors receive a regular share of the business's income until a predetermined amount has been paid.
- Typically, this predetermined amount is a multiple of the principal investment and usually ranges between three to five times the original amount invested.
How Revenue-Based Financing Works?
- Capital investment: An investor or a group of investors provides capital to a company (but not as a traditional loan nor in exchange for equity in the company).
- Revenue percentage agreement: In return for the capital, the company agrees to give the investor a fixed percentage of its gross revenues each month.
- Repayment structure: The company repays the invested capital through payments based on monthly or annual revenue.
- The amount paid each month varies as it is directly tied to the company’s revenue for that month.
- Repayment cap or term: There is usually a cap on the total amount to be repaid, often set as a multiple of the original investment (e.g., 1.5x or 2x the initial amount).
- Alternatively, the repayment might continue until a specific term is reached, such as a number of years.
Comparing Revenue-based Financing to Debt and Equity-based Models:
- While revenue-based financing shares similarities with debt financing in terms of regular investor repayments, it differs notably as it doesn't involve interest payments.
- Instead, repayments are based on a predetermined multiple, yielding returns higher than the initial investment.
- Moreover, unlike traditional debt arrangements, revenue-based financing doesn't necessitate collateral.
- Additionally, unlike equity-based models, it doesn't entail transferring ownership stakes in the company to investors.
Chausath Khamba

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Characterized by its marble pillars and intricate latticework, Chausath Khamba (64 pillars) stands adjacent to the Nizamuddin dargah, a 14th-century shrine erected in honor of the revered Sufi saint Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
About the Chausath Khamba:
- Chausath Khamba was built in AD 1623 - 24 to serve as a tomb for Mirza Aziz Koka, the foster brother of Mughal Emperor Akbar.
- It is so called on account of the 64 (chausath) monolithic marble pillars (khamba) and stands close to his father, Atgah Khan’s tomb, at the edge of the Dargah of Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
- The tomb enclosure is entered through a lofty arched gateway and has a large sunken forecourt.
- The mausoleum is unique on account of it being built entirely of marble, with 25 marble domes supporting the flat roof of the structure.
- The plan for Chausath Khamba could have been inspired by the wooden garden pavilions from Persia - such as the Chihil Sutun, and in turn, the Chausath Khamba seems to have inspired the architectural design for Emperor Shahjahan’s Diwan-i-Aam, Hall of Audience.
- Each facade of the square structure has five marble arches inset with marble jaallis or lattice screens and a doorway in the central arch providing access to the tomb.
- The column capitals are intricately carved with simple yet striking pendentives bridging the square floor plan to the circular dome above.
- The structure also finds mention in Sir Gordon Risley Hearn’s book The Seven Cities of Delhi.
- As per author and historian Sam Dalrymple, the edifice embodies the architectural style of Gujarat and Ahmedabad within Delhi, serving as the Urs Mahal for hosting festivities during the commemoration of Nizamuddin's passing.
- This illustrates the historical dissemination of regional architectural influences across India over centuries.
Predictive AI: Its Applications and Advantages

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Predictive AI is revolutionizing data analysis, decision-making, and industry leadership, offering businesses unprecedented insights and strategic advantages.
What is Predictive Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Predictive artificial intelligence (AI) utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and forecast future events, distinguishing it from traditional AI focused solely on retrospective analysis.
- This cutting-edge technology employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to sift through extensive datasets, identifying subtle patterns and trends.
- Unlike conventional approaches, Predictive AI doesn't just analyze data; it transforms it into actionable insights, enabling organizations to:
- Anticipate future outcomes,
- Predict market shifts, and
- Make strategic decisions with unprecedented foresight.
- By continuously learning from past data and adapting to changing trends, Predictive AI becomes an invaluable tool, guiding businesses through uncertain landscapes.
How Predictive AI Work?
- Leveraging Big Data: Predictive AI relies on access to extensive datasets, often referred to as "big data," as larger datasets typically lead to more accurate analyses.
- Utilizing Machine Learning (ML): As a subset of AI, ML involves training computer programs to analyze data autonomously, without human intervention.
- In the realm of predictive AI, ML algorithms are applied to vast datasets to extract valuable insights.
- Autonomous Processing: Predictive AI models are capable of autonomously processing massive datasets, eliminating the need for human oversight.
- Pattern Recognition: Through ML techniques, predictive AI learns to recognize patterns within datasets, associating specific data points or occurrences with potential future events.
- By examining numerous factors, predictive AI can identify intricate patterns indicative of recurring events, enabling organizations to anticipate future outcomes effectively.
Difference Between Predictive AI and Generative AI:
- Predictive AI and generative AI both employ machine learning techniques and leverage extensive datasets to generate their outputs.
- However, while predictive AI utilizes machine learning to forecast future outcomes, generative AI employs machine learning to produce original content.
- For instance, a predictive AI model may inform fishermen about impending storms, whereas a generative AI model may craft a fictional narrative depicting various scenarios involving weather and fishing expeditions.
- While both types of AI rely on statistical analysis to discern patterns, their objectives, machine learning methodologies, and applications differ significantly.
Various Applications of Predictive AI:
- Assessing the Impact of Natural Disasters: With the recent eruption of a volcano in Iceland, the potential repercussions on air travel echo concerns from a similar event in 2010, which disrupted flights across Europe.
- Predictive AI leverages data analysis to identify patterns and anticipate the impact of such extreme weather events on air travel. Platforms like Yandex offer interactive maps for real-time monitoring of ash clouds post-eruption.
- Enhancing Oil and Gas Exploration: In the realm of oil and gas exploration, companies possess extensive historical geological data that can inform predictive AI systems.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- For instance, Saudi Aramco utilizes its meta-brain generative AI to optimize drilling plans, analyze geological data, and forecast drilling outcomes accurately.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- Inventory and Supply chain management: Predictive AI aids in inventory and supply chain management by identifying peak consumer demand periods, facilitating proactive stock adjustments, and optimizing resource allocation to address fluctuations in road congestion and meet increased user demands.
- Marketing campaigns: Just as predictive AI can anticipate user or customer behavior, it can help prognosticate what kinds of content or products prospective customers may be interested in.
- Advancing Medical Research: Predictive AI plays a pivotal role in drug discovery, a cornerstone of contemporary medical research.
- Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating to leverage predictive AI models for analyzing vast datasets and identifying potential drug candidates. Initiatives like the 'MELLODDY Project', supported by the EU Innovative
- Medicines Initiative and multiple pharmaceutical firms, exemplify this collaborative effort in pooling data and leveraging predictive AI for drug discovery.
First Drug to Treat Common, Lethal Liver Disease Gets US Nod
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Inc.’s drug Rezdiffra gained the first US approval to treat a potentially deadly liver disease that affects millions worldwide, succeeding in an area where some bigger rivals have failed.
What is Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)?
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver.
- NASH (or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) is a type of NAFLD that can damage the liver.
- NASH occurs when the fat buildup in the liver leads to inflammation (hepatitis) and scarring.
- NASH can be life-threatening, as it can cause liver scarring (called cirrhosis) or liver cancer.
- It is estimated that 3% to 5% of the global population is affected by NASH, though the disease is considered to be underdiagnosed.
Who gets NASH?
- The condition may be hereditary.
- If a person has family members who have had NASH or NAFLD, they are at risk.
- Additionally, having certain health conditions may increase a person’s risk of developing NASH. These include:
- Being overweight or obese.
- Having high cholesterol or high triglyceride levels.
- Having type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or prediabetes.
What are the signs and symptoms of NASH?
- NASH is known as a “silent” disease because many people present with few or no symptoms.
- However, some people will experience tiredness, pain, and discomfort in the upper right part of the abdomen.
How is NASH diagnosed?
- Diagnosing NASH can be challenging because symptoms may not be noticeable until the disease progresses.
- Healthcare providers typically suspect NASH based on abnormal blood or liver test results or imaging showing liver fat.
- Confirmation requires a liver biopsy, an invasive procedure with risks and expenses, involving taking a small liver sample for microscopic examination.
How is NASH treated?
- To manage NASH, losing weight is often recommended as it can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and scarring.
- This involves losing around 3% to 5% of body weight by limiting fats and sugars in the diet.
- Heavy alcohol use should also be avoided to prevent further liver damage.
- If NASH progresses to cirrhosis, treatment may involve medications, medical procedures, or even a liver transplant.
- Currently, there are no approved medications specifically for treating NASH, but ongoing research aims to develop new treatments.
Google Deepmind’s new AI that can play video games with you

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google DeepMind recently revealed its latest AI gaming agent called SIMA or Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent, which can follow natural language instructions to perform tasks across video game environments.
What is SIMA?
- Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) is an AI Agent, which is different from AI models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google Gemini.
- AI models are trained on a vast data set and are limited when it comes to working on their own.
- On the other hand, an AI Agent can process data and take action themselves.
- SIMA can be called a generalist AI Agent that is capable of doing different kinds of tasks.
- It is like a virtual buddy who can understand and follow instructions in all sorts of virtual environments – from exploring mysterious dungeons to building lavish castles.
- It can accomplish tasks or solve challenges assigned to it.
- It is essentially a super-smart computer program that can be thought of as a digital explorer, having the ability to understand what you want and help create it in the virtual world.
How does SIMA work?
- SIMA can understand commands as it has been trained to process human language.
- So when we ask it to build a castle or find the treasure chest, it understands exactly what these commands mean.
- One distinct feature of this AI Agent is that it is capable of learning and adapting.
- SIMA does this through the interactions it has with the user.
- The more we interact with SIMA, the smarter it gets by learning from its experiences and improves over time.
- This makes it better at understanding and fulfilling user requests.
- Based on the current stage of AI development, it is a big feat for an AI system to be able to play even one game.
- However, SIMA goes beyond that and can follow instructions in a variety of game settings.
- This could potentially introduce more helpful AI agents for other environments.
Tesla’s India entry gets boost as government approves new EV policy
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government announced a new electric vehicle (EV) policy recently that is expected to provide a major boost to Tesla's plans to start operations in India.
What is the Revised EV Policy Offering Tax Incentives?
- The Government of India has sanctioned a new initiative aimed at positioning India as a premier manufacturing hub, fostering the production of cutting-edge electric vehicles (EVs) within the nation.
- Crafted to entice investments from renowned global EV manufacturers, this policy seeks to provide Indian consumers access to state-of-the-art EV technology while bolstering the Make in India campaign.
- By cultivating a competitive environment among EV players, the policy endeavors to fortify the EV ecosystem, stimulating innovation and efficiency.
- Furthermore, it is anticipated to stimulate substantial production rates, capitalize on economies of scale, and drive down production costs, consequently curbing crude oil imports, narrowing trade imbalances, and mitigating urban air pollution, thereby fostering a healthier environment for all.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Minimum Investment Requirement: Companies are mandated to invest a minimum of Rs 4,150 Crores.
- Investment Ceiling: There is no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Manufacturing Timeline: Companies must establish manufacturing facilities in India within 3 years and commence commercial production of e-vehicles.
- Within 5 years, they should achieve 50% domestic value addition.
- Domestic Value Addition (DVA): Localization levels of 25% by the 3rd year and 50% by the 5th year are mandatory during manufacturing.
- Customs Duty: A customs duty of 15%, applicable to Completely Knocked Down (CKD) units, will be enforced for 5 years.
- Import Limits: Import of at most 8,000 EVs annually is permitted under this scheme, with provisions for carrying forward unutilized import quotas.
- Bank Guarantee Requirement: Investment commitments necessitate bank guarantees to cover the forgone customs duty.
EV Adoption in India:
- In 2023, electric vehicle sales in India surged by 49.25% year-on-year, surpassing 15 lakh units, as the Federation of Automobile Dealers' Association (FADA) reported.
- This notable increase follows a total sale of approximately 10 lakh units recorded in 2022, indicating a rapid growth trajectory.
- Factors contributing to this surge include improved product availability, escalating fuel prices, state subsidies, and incentives provided under the FAME-II Initiative.
What is the FAME-II Scheme?
- The FAME India scheme, initiated in 2015, serves as an incentive program aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, with its acronym standing for "Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles in India."
- In 2019, the Central government sanctioned Phase II of the FAME Scheme with a budgetary allocation of 10,000 Crore over three years, extending until March 31, 2024.
- The primary objective of Phase II is to stimulate demand by facilitating the deployment of 7000 e-Buses, 5 lakh e-3 Wheelers, 55,000 e-4 Wheeler Passenger Cars (including Strong Hybrid), and 10 lakh e-2 Wheelers, thereby fostering the growth of the electric vehicle ecosystem.
- Under the FAME-II scheme, nearly 2 lakh vehicles have received support, signifying a significant stride towards electric vehicle adoption in the country.
Government Initiatives to Promote EV Usage:
- Battery Swapping Policy: The Battery Swapping Policy offers an alternative approach wherein discharged batteries are exchanged for charged ones, enabling efficient charging without vehicle downtime.
- NITI Aayog has recently unveiled a draft battery-swapping policy, prioritizing metropolitan cities with populations exceeding 40 lakh for the establishment of battery-swapping networks in the initial phase.
- Switching to EVs: Central and State governments extend upfront subsidies to mitigate the overall costs associated with electric vehicles, incentivizing consumers to transition towards cleaner mobility options.
- E-AMRIT Portal: The e-AMRIT portal serves as a comprehensive platform, furnishing resources and support to facilitate the seamless transition to electric vehicles, thereby bolstering the nation's electrification agenda.
Pandavula Gutta designated an exclusive Geo-heritage site in Telangana

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Pandavula Gutta, a geological marvel older than the Himalayan hills, has been officially recognized as the sole Geo-heritage site in Telangana.
What is Pandavula Gutta?
- Pandavula Gutta holds historical significance, being older than the Himalayas and renowned for its ancient rock paintings portraying diverse animals such as bison, antelope, tiger, and leopard, along with intricate geometric designs and symbols like swastikas, circles, and squares.
- These paintings indicate continuous human habitation from the Mesolithic period (around 12,000 to 6,000 BCE) through medieval times.
About Geo-heritage Sites:
- Geo-heritage sites encompass geological features of inherent or cultural significance, providing insights into the Earth's evolution or history, valuable for earth science and educational purposes.
- In India, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) identifies and designates these special places as Geo-Heritage Sites (GHS) to ensure their preservation, akin to UNESCO's protection of world heritage sites worldwide.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI), established in 1851 initially to locate coal deposits for the Railways, has evolved into a comprehensive repository of geo-science information vital for various sectors in India.
- Its objective is to provide impartial and current geological expertise and geoscientific data to inform policy-making decisions and address commercial and socio-economic needs.
- Designated as the primary agency for geological mapping and regional mineral resources assessment under the National Mineral Policy (NMP) 2008, GSI emphasizes systematic documentation of geological processes across India and its offshore areas.
- Utilizing advanced techniques and methodologies, including geological, geophysical, and geochemical surveys, the organization operates from its headquarters in Kolkata, along with six regional offices and state units across the country.
- Presently, GSI operates as an attached office to the Ministry of Mines.
'ETHANOL 100' hits the road at 183 Indian Oil stations in five states

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a strategic advance towards cleaner fuel alternatives, India commenced the sale of ETHANOL 100 across 183 Indian Oil outlets in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, New Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
What is ETHANOL 100 Fuel?
- ETHANOL 100 fuel represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, offering a high-octane rating ranging from 100 to 105.
- This elevated octane level is particularly advantageous for high-performance engines, delivering improved efficiency and power output while simultaneously reducing environmental impact.
- One of the key features of ETHANOL 100 is its remarkable versatility, making it suitable for a diverse range of vehicles, including flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) designed to accommodate various fuel types such as gasoline, ethanol, or any blend thereof.
- This adaptability ensures that ETHANOL 100 can seamlessly integrate into existing automotive fleets without requiring extensive modifications or infrastructure upgrades.
- The composition of ETHANOL 100 consists of approximately 93 to 93.5 percent ethanol blended with 5 percent petrol and 1.5 percent co-solvent acting as a binder.
- This well-balanced formulation not only enhances fuel performance but also contributes to its practicality as a mainstream fuel option.
- In addition to its performance benefits, ETHANOL 100 stands out as a cleaner and greener alternative to traditional gasoline.
- By emitting lower levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and particulate matter, ETHANOL 100 plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and improving air quality in our communities.
- With the right infrastructure and support mechanisms in place, ETHANOL 100 has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry by offering a sustainable and eco-friendly fuel solution that aligns with the global efforts to combat environmental degradation and promote sustainable development.
What are Flex-fuel Vehicles?
- Flex-fuel vehicles are engineered to operate on a diverse range of fuels, offering consumers the flexibility to choose between petrol, ethanol, or methanol at the point of refueling.
- Equipped with an internal combustion engine (ICE), these vehicles can seamlessly switch between different fuel types, providing versatility and convenience to drivers.
- While possessing similarities to conventional petrol-only cars, flex-fuel vehicles undergo minor modifications to accommodate the use of alternative fuels, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various fuel options.
Devin AI, an AI software engineer, can handle coding projects end-to-end

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a US-based startup Cognition has unveiled an AI-powered tool, Devin, which it calls the “world’s first fully autonomous AI software engineer”.
What is Devin?
- Devin is a super-smart computer program created by a company called Cognition.
- It's like having a clever assistant for software engineering tasks.
- With just a simple instruction, Devin can write code, build websites, and make software all on its own.
- But Devin isn't trying to replace human engineers, instead, it's meant to work together with them to make their jobs easier.
- The special feature of Devin is its ability to think ahead and solve tricky problems.
- It can learn from its mistakes and keep getting better over time.
- Plus, it has all the tools that a human engineer needs, like a way to write code and browse the internet.
- Devin has been tested against other AI programs, and it did way better, solving almost 14 out of 100 problems compared to just under 2 for others.
- So, in simple terms, Devin is like a super-smart assistant that helps engineers do their work faster and better, without taking their jobs away.
How does Devin work?
- Devin works by using advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to understand and execute tasks related to software engineering.
- When given a prompt or instruction, Devin analyzes the request and uses its vast database of knowledge and problem-solving techniques to generate code, design websites, or develop software.
- One of Devin's key features is its ability to think ahead and plan complex tasks.
- It can make thousands of decisions based on the given task and learn from its mistakes to improve its performance over time.
- Devin also has access to essential tools like a code editor and web browser, enabling him to complete tasks from start to finish.
- It can learn new technologies, tackle a wide range of engineering challenges, and even train its own AI models.
- Additionally, Devin can collaborate with human engineers in real time, providing updates, accepting feedback, and contributing to design choices.
- Overall, Devin works by harnessing the power of AI to automate routine tasks, streamline workflows, and empower engineers to focus on more complex problems.
- By combining human expertise with machine intelligence, Devin represents a significant advancement in software engineering technology.
Conservationists to propose Kazhuveli watershed region in T.N. for nomination to World Monuments Fund Watch 2025

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eri (tank) network in the Kazhuveli watershed region in the Villupuram district which comprises an incredible network of tanks created thousands of years ago is to be proposed for nomination to the World Monuments Fund Watch 2025 program.
About the World Monuments Fund (WMF)?
- The World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a non-profit organization headquartered in New York, committed to safeguarding and conserving endangered ancient and historic sites worldwide.
- Collaborating with local partners globally, the WMF offers financial and technical assistance to support preservation efforts.
- With a track record of raising over $300 million and securing an additional $400 million from other entities, the WMF has successfully preserved over 700 sites and championed the protection of more than 800 cherished landmarks since its establishment.
World Monuments Watch:
- The World Monuments Watch, initiated in 1996, is a program centered on nominations, fostering a link between local heritage conservation and international engagement.
- Through this initiative, the WMF has allocated over $110 million towards projects at over 300 Watch sites, enabling communities to utilize the platform's visibility to secure an additional $300 million from various funding sources.
World Monuments Fund in India:
In India, the World Monuments Fund (WMF) has focused on conserving significant cultural and ecological sites, including:
- The Kazhuveli Watershed Region: Renowned for its ancient 'Eri' network, an intricate system of tanks dating back thousands of years.
- Situated in the Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu, spanning from Gingee to Marakkanam and extending to the Auroville plateau.
- Proposed pilot projects in Munnur village aim to develop a heritage toolkit applicable across the watershed and beyond if the nomination is successful.
- Suranga Bawadi: An ancient water management system located on the Deccan Plateau in Karnataka.
- Included in the World Monument Watch list for 2020, highlighting its significance for preservation efforts.
Vision for Edible Oil Self-Reliance takes root in the North-East

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has reiterated the Government’s commitment to move towards self-sufficiency in edible oils production and harped on the importance of oil palm cultivation in the northeast region.
About the National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP):
- The National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) is an initiative launched by the Government of India in August 2021 to significantly enhance oil palm cultivation and crude palm oil production.
- This centrally sponsored scheme prioritizes the North East region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, aiming to boost the area and productivity of oilseeds and Oil Palm.
- The targets of NMEO-OP include expanding the oil palm area to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26, a substantial increase from 3.5 lakh hectares in 2019-20, along with elevating Crude Palm Oil production to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 from 0.27 lakh tonnes in 2019-20.
- Furthermore, the mission seeks to enhance consumer awareness to maintain a consumption level of 19.00 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
- Implementation of NMEO-Oil Palm involves various stakeholders such as the State Departments of Agriculture and Horticulture, Central University, ICAR-Institutions, CDDs, SAUs, KVKs, Central Agencies/Cooperatives, Oil palm processors/ Associations, DD Kisan, AIR, DD, TV channels.
- The salient features of NMEO-OP encompass assistance for planting material, inputs for intercropping up to a gestation period of 4 years, the establishment of seed gardens and nurseries, micro-irrigation, bore well/pump set/water harvesting structure, vermicompost units, solar pumps, harvesting tools, custom hiring center cum harvester groups, farmers and officers training, and replanting of old oil palm gardens, among others.
Oil Palm Production in India:
- Originating in West Africa, Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis) is a relatively recent crop in India known for its high vegetable oil yield per hectare.
- It yields two main oils, palm oil, and palm kernel oil, utilized in both culinary and industrial applications.
- The primary oil palm-growing states in India include Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Kerala, which collectively contribute to 98% of the total production.
- Additionally, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Mizoram also have significant areas dedicated to oil palm cultivation.
India ranks 134th in global human development index

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has moved up a rank on the global Human Development Index (HDI), according to the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) report ‘Breaking the gridlock: Reimagining cooperation in a polarised world’ released recently.
Highlights of the Recent Report:
- The latest report revealed that India's global ranking improved slightly from 135th in 2021 to 134th in 2022, with a total of 193 countries assessed in 2022 compared to 191 in the previous year.
- In 2022, India exhibited progress across all Human Development Index (HDI) parameters, including life expectancy, education, and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
- Notable advancements were observed in life expectancy, which increased from 67.2 to 67.7 years, while expected years of schooling reached 12.6, mean years of schooling rose to 6.57, and GNI per capita saw an uptick from $6,542 to $6,951.
- Despite these positive strides, India continues to lag behind its South Asian counterparts, such as Bangladesh (129th), Bhutan (125th), Sri Lanka (78th), and China (75th).
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
- The Human Development Index is published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is the most well-known index of human development.
- It is based on the idea that human development means that people have long and healthy lives, are knowledgeable, and have a decent standard of living.
- More specifically, these three dimensions are measured with four indicators:
- A long and healthy life: measured by life expectancy at birth
- Knowledge: measured by expected years of schooling (for children of school entering age) and average years of schooling (for adults aged 25 and older)
- A decent standard of living: measured by Gross National Income (GNI) per capita
- Represented on a scale from 0 to 1, the HDI value reflects a country's level of human development, with higher values indicating greater development.
- Computed as the geometric mean of normalized indices for each dimension, it offers a nuanced understanding of a nation's progress.
- Furthermore, the HDI aligns with Amartya Sen's 'capabilities' approach, emphasizing the significance of achieving substantive ends in human well-being beyond mere economic indicators.
- Since its inception in 1990, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has annually published the Human Development Report, which incorporates the latest HDI findings and insights.
Honoring, the Architect of Mumbai (Bombay)

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maharashtra cabinet recently decided to ask the Ministry of Railways to rename Mumbai Central Station after Nana Jagannath Shankarseth.
Who was Nana Jagannath Shankarseth?
- Nana Jagannath Shankarseth was a social reformer, educationist, and philanthropist and often described as the “architect” of Mumbai (then Bombay).
- He made extremely valuable contributions in terms of both ideas and money to multiple sectors, to lay a strong foundation for the city.
- Shankarseth was greatly inspired by the legendary merchant and philanthropist Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy.
- As a social reformer and community leader, Shankarseth earned the goodwill of both Indians and the British.
- He became the first Indian to be nominated to the Legislative Council of Bombay.
Shankarseth’s Most Significant Contributions:
- Education: Shankarseth was deeply committed to the growth and spread of education in Bombay, and donated land owned by his family for educational institutions.
- Like many social reformers of his age, he believed that Indians could progress through education.
- He also worked for the education of girls and women.
- Shankarseth founded the Native School of Bombay, which was renamed first as the Bombay Native Institution, and then as the Board of Education.
- Finally, this institution evolved into the prestigious Elphinstone College.
- Museum, Temples: Shankarseth was among the wealthy donors who helped promote Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum in Byculla, which was designed by a famous London-based architect.
- The Bhawani Shankar Temple near Nana Chowk was Shankarseth’s tribute to his late mother Bhawanibai Murkute.
- He also built a Ram temple.
- Railways: The first train in India ran between Boribunder and Thane on April 16, 1853.
- The 34-km project was undertaken by the Great Indian Peninsular Railway Company.
- The committee that gave the project impetus included Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and Nana Shankarseth.
World Pi Day 2024: International Day Of Mathematics And Worldwide Celebrations

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
About International Day of Mathematics:
- Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the International Day of Mathematics at the 40th General Conference on November 19, 2019.
- This day also sheds light on Mathematics' importance in different areas like climate change, energy, artificial intelligence, and sustainable development.
- International Day of Mathematics coincides with International Pi Day.
- Pi is one of the most widely known mathematical constants and it is rounded to 3.14, which is why it is observed on March 14.
- IDM is an opportunity to educate students about the role and importance of mathematics in improving quality of life.
- It also empowers women and girls to contribute to achieving sustainable development goals for the 2030 agenda.
History:
- The 205th session of UNESCO’s Executive Council adopted the International Day of Mathematics.
- The 40th session of UNESCO's General Conference adopted March 14 as the International Day of Mathematics, which was the first official celebration with the theme 'Mathematics is Everywhere'.
- It is an opportunity to understand the importance of mathematics in daily life promoting mathematics use for the advancement of society.
Significance:
- International Day of Mathematics is celebrated to promote Mathematics in different fields highlighting the role of mathematics in solving the real-life world and addressing social concerns.
- IDM shows the application of mathematics in different fields of life including science, technology, engineering, and economics.
- IDM promotes mathematics at different levels encouraging educators, policymakers, parents and to stress the importance of mathematics and inspire students to pursue careers in STEM fields.
- STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It is an opportunity to share research, discoveries, and insights with the general public and demystify the subject to make it more accessible.
- International Day of Mathematics is a global initiative to foster collaboration and exchange ideas across borders, cultures, and disciplines.
- The day aims to promote mathematics and help address global challenges through it.
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024:
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024 is 'Playing With Math.'
News-sharing service by Prasar Bharati launched, content to be ‘free of copyright’

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the Lok Sabha polls, public broadcaster Prasar Bharati launched a news-wire-like service to offer free content across mediums, which will be free of copyright or credit obligations.
What is PB-SHABD?
- PB-SHABD, an acronym for Prasar Bharti - Shared Audio Visuals for Broadcast and Dissemination, is a comprehensive platform designed to deliver daily news feeds encompassing video, audio, text, photos, and other formats to media subscribers.
- Leveraging the expansive network of Prasar Bharati reporters, correspondents, and stringers, the service offers up-to-the-minute news coverage spanning various regions of the country.
- Functioning as a centralized hub for news content, SHABD serves as a valuable resource for organizations, offering a wide array of news stories across fifty categories in all major Indian languages.
- Furthermore, the shared feeds facilitate tailored storytelling across diverse platforms, catering to the specific needs of newspapers, TV channels, and digital portals.
- In an inaugural gesture, the service is provided free of charge for the initial year, extending invaluable support to smaller media outlets and contributing to enhanced accessibility to news content.
About Prasar Bharti:
- Prasar Bharti functions as the nation's Public Service Broadcaster, operating under the Prasar Bharati Act established in 1997 as a statutory autonomous body.
- Its primary objective is to deliver public broadcasting services aimed at informing and entertaining the public.
- Comprising the former media units of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, namely the Doordarshan Television Network and All India Radio, Prasar Bharti plays a vital role in disseminating news and entertainment content.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, Prasar Bharti serves as a cornerstone of India's media landscape, dedicated to fulfilling its mandate of public service broadcasting.
Lab to monitor seawater quality and testbed to track monsoon systems inaugurated
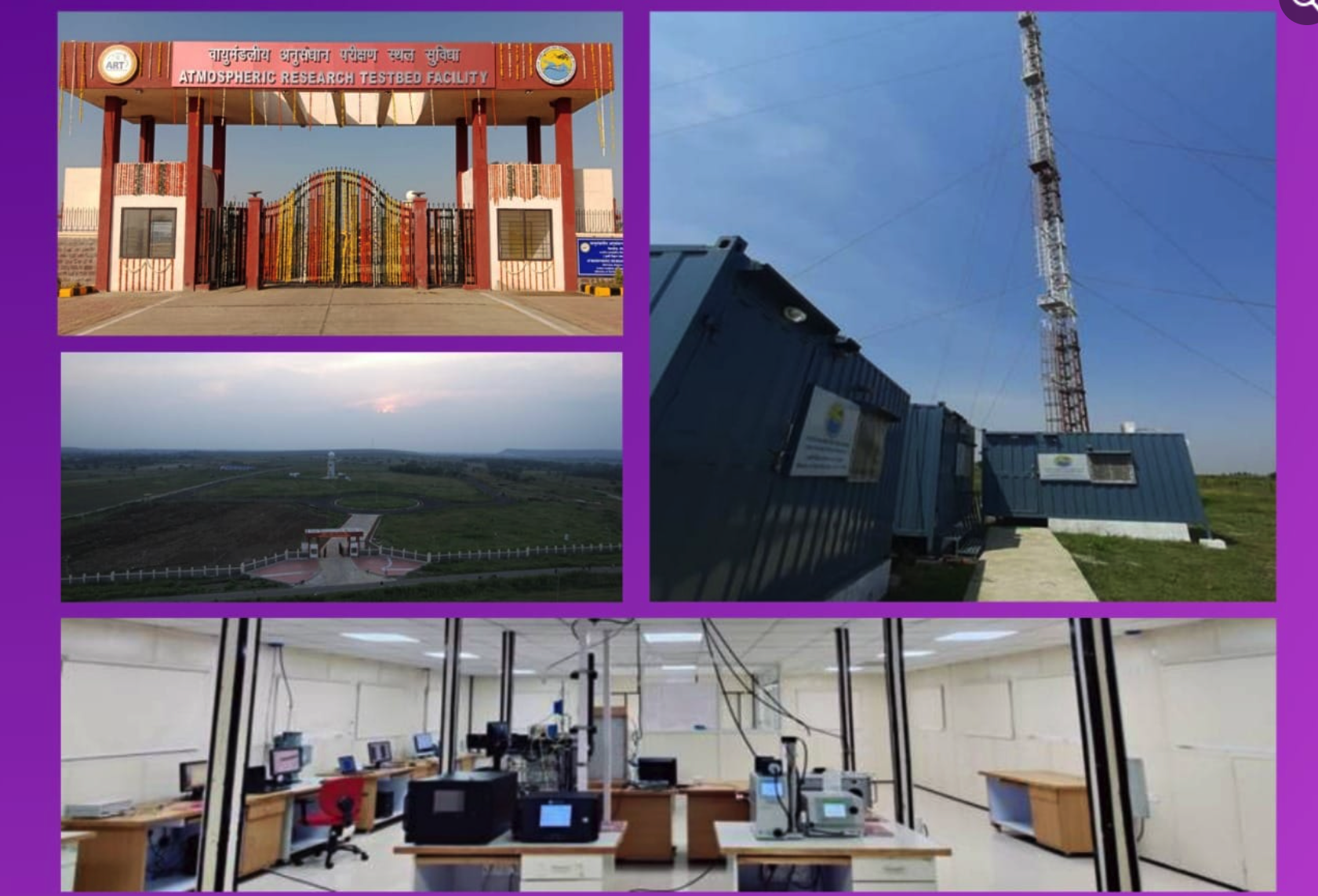

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India commissioned the atmospheric testbed facility near Bhopal, equipped with high-end instruments to record vital parameters for enhancing weather models and conducting advanced studies on the Indian monsoons, with construction commencing in early 2018.
What is the Atmospheric Research Testbed (ART)?
- The ART is an open-field, focused observational and analytical research programme at Silkheda.
- The facility aims to conduct ground-based observations of weather parameters like temperature, wind speeds, etc., and in-situ (on-site) observations of the transient synoptic systems – like low-pressure areas and depressions that form in the Bay of Bengal – during the southwest monsoon season from June to September.
- Studying these systems and their associated cloud parameters will be used to generate high volumes of data over a long period.
- It can then be compared with the existing weather models so that improvements can be made to obtain accurate rainfall predictions.
- The setup at ART will also be used for calibrating and validating various satellite-based observations, part of weather predictions and forecasting.
- Spread over 100 acres, the ART has been developed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences for Rs 125 crore.
- The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, is in charge of the operations.
- Under the first phase, remote sensing-based and in-situ measurements using 25 meteorological instruments have commenced.
- In the second phase, ART will deploy instruments such as a radar wind profiler and balloon-bound radiosonde, and soil moisture and temperature measuring equipment.
What instruments are ART equipped with?
- To obtain continuous observations of convection, clouds, and precipitation, and monitor the major modes of variabilities, the ART is equipped with over two dozen high-end instruments, radars, and more.
- At 72 meters, ART will house India’s tallest meteorological tower.
- Some of the instruments deployed are an aethalometer for performing aerosol studies, a cloud condensation nuclei counter, a laser ceilometer to measure cloud sizes, a micro rain radar to calculate raindrop size and its distribution, and a Ka-band cloud radar and a C-band Doppler weather radar to help track the movement of rain-bearing systems over this zone.
Why is having an Atmospheric Research Testbed important?
- At present, 45% of India’s labor force is employed in the agriculture sector and much of Indian agriculture is rain-fed.
- Cultivation along the Monsoon Core Zone (MCZ), which spans the central India region from Gujarat to West Bengal, is primarily rainfall-fed.
- The southwest monsoon season accounts for 70 percent of the country’s annual average rainfall (880mm).
- Throughout India, the majority of Kharif cultivation is undertaken between July and August, which see an average monthly rainfall of 280.4mm and 254.9mm (1971–2020 average), respectively.
- During this four-month-long season, several rain-bearing synoptic systems, namely the low pressures or depressions, develop in the Bay of Bengal.
- Inherently, these systems move westwards/northwestwards over to the Indian mainland and pass through the MCZ, causing bountiful rainfall.
Why is it important to have data about monsoons over central India?
- Studies have correlated the all-India rainfall performance to the rainfall received over the central India region, highlighting its importance.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issues rainfall forecasts for the country’s four homogeneous regions – north, west, east, and south peninsular India.
- In addition, it issues a special rainfall forecast for the MCZ, which is considered India’s food bowl.
- However, there is still limited understanding of the role of these synoptic systems, their associated cloud physics, cloud properties, and their overall role in enhancing the monsoon rainfall.
- Central India, therefore, acts as a natural laboratory for scientists and meteorologists to perform a hands-on study of the Indian monsoons.
- They can record data and make observations about the allied systems, clouds, and other associated physical and atmospheric parameters.
- Additionally, climate change is driving erratic rainfall patterns in tropical regions, like India.
- It has also strengthened the low-pressure systems, which are aided by high temperatures.
- This results in very heavy rainfall recorded along their trajectory during the monsoons.
- Now, with ART, scientists will be able to generate and obtain long-term observations on cloud microphysics, precipitation, convection, and land-surface properties, among a host of other parameters.
- This information will be assimilated and fed into the numerical weather models to enhance forecast output, especially the rainfall forecasts.
- More accurate forecasts will ultimately help the farming community plan their activities better.
Why Madhya Pradesh?
- The ART has been established at Silkheda, a location that falls directly in line with the path of major rain-bearing synoptic systems.
- This will facilitate direct monitoring and tracking.
- Besides, the locality is pristine and free of anthropogenic and other pollutants, making it the best site in central India for setting up sensitive, high-end meteorological instruments and observatories for recording data.
Methane emissions from fossil fuels remain high despite progress, US tops list of emitters: IEA

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Global Methane Tracker 2024, methane emissions from fuel consumption in 2023 approached record levels, nearing their highest point in history.
About the Global Methane Tracker:
- The Global Methane Tracker is an annual publication issued by the International Energy Agency (IEA), presenting the latest data on methane emissions primarily from the energy sector. It integrates recent scientific research, measurement campaigns, and satellite data.
Key Highlights from the Global Methane Tracker 2024:
- Methane emissions from fuel usage in 2023 approached record levels, reaching approximately 120 million tonnes (Mt), marking a slight increase from the previous year.
- Bioenergy, derived from plant and animal waste, contributed an additional 10 million tons of emissions.
- Out of the total methane emissions, around 80 million tons originated from ten countries, with the United States and Russia leading in emissions from oil and gas operations, and China leading in emissions from coal operations.
- Despite indications of declining emissions in certain regions, the overall methane emissions remain alarmingly high, posing a significant challenge to achieving global climate objectives.
- To align with the Paris Agreement goal of limiting warming to 1.5°C, there is a critical need to reduce methane emissions from fossil fuels by 75 percent by 2030.
- Achieving this target would require an estimated investment of approximately $170 billion, representing less than 5 percent of the revenue generated by the fossil fuel industry in 2023.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Paris, established in 1974.
- Its primary mandate is to ensure stability in the international oil supply, a response to the oil crisis of 1973, which led to temporary disruptions in the global oil supply chain.
- Operational Framework: The IEA functions within the broader scope of the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership: As of 2022, the IEA comprises 31 member nations, with India joining as an associate member in 2017.
- Key Requirement: Member countries are obligated to maintain reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net oil imports.
- These reserves must be readily accessible by the government to address potential disruptions in the global oil supply chain, even if the reserves are not owned directly by the government.
NITI Aayog launches 'vocal for local' initiative to promote grassroots-level entrepreneurship

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog on Wednesday launched the 'Vocal for Local' initiative under its Aspirational Blocks Programme to bolster local economies and foster grassroots-level entrepreneurship, an official statement said.
What is the ‘Vocal for Local’ Initiative?
- The 'Vocal for Local' initiative, led by NITI Aayog through its Aspirational Blocks Programme, aims to foster self-reliance and sustainable development.
- Under this initiative, products from 500 aspirational blocks have been curated and unified under the Aakanksha brand.
- Aakanksha is an overarching brand, with potential extensions into various sub-brands to tap into global markets.
- A dedicated section has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal under the Aakanksha brand to promote these products.
- Additionally, partners in the initiative offer support in areas such as e-commerce facilitation, establishing market linkages, financial and digital literacy, documentation and certification, and skill enhancement.
About Aspirational Blocks Programme:
- Inspired by the Aspirational District Programme launched in 2018, the Aspirational Blocks Programme extends its reach to 112 districts nationwide.
- This new initiative targets the enhancement of underperforming blocks across various development indicators.
- It aims to foster comprehensive growth in regions requiring additional support.
- Initially encompassing 500 districts across 31 States and Union Territories, the programme focuses on blocks in six key states: Uttar Pradesh (68 blocks), Bihar (61), Madhya Pradesh (42), Jharkhand (34), Odisha (29), and West Bengal (29).
What is the Government e-Marketplace (GeM)?
- Established in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) serves as an online platform for public procurement.
- GeM acts as a centralized portal, streamlining the procurement process for common-use Goods & Services required by various Government Departments, Organizations, and PSUs.
- Purchases made through GeM by Government users are mandated by the Ministry of Finance under the General Financial Rules, 2017.
- GeM is operated by GeM SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle), a 100% Government-owned, non-profit company operating under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
On Dandi March anniversary, PM Modi launches master plan for Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Describing various initiatives of his government as “a way of its dedication towards Mahatma Gandhi”, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a master plan for the Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project in Ahmedabad recently, on the anniversary of the historic Dandi March.
About Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project:
- On the anniversary of the historic Dandi March, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a master plan for the Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project in Ahmedabad.
- This joint initiative by the central government and the Gujarat government, known as the Gandhi Ashram Memorial and Precinct Development Project, is set to cost around Rs 1,200 crore.
- During the inauguration, PM Modi emphasized the importance of conserving heritage sites, stating that "a country which cannot conserve its heritage also loses its future."
- He highlighted the collective responsibility of all Indians to preserve this globally renowned site, which holds immense historical and cultural significance.
- The government's commitment to restoring old buildings to their original form, with the aim of eliminating the need for new constructions, was outlined by PM Modi.
- This approach aligns with the principle of preserving the authenticity and integrity of heritage sites, ensuring that future generations can experience and appreciate their true essence.
- The Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram, established by Mahatma Gandhi in 1917, played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence.
- By undertaking this redevelopment project, the government seeks to honor the legacy of the father of the nation and create a space that inspires future generations to learn from his life and teachings.
About Dandi March:
- The Dandi March, also known as the Salt March or Salt Satyagraha, was a significant non-violent protest action led by Mahatma Gandhi in March-April 1930.
- This landmark event marked the beginning of a larger civil disobedience campaign that Gandhi waged against British rule in India, which extended into early 1931.
- The Dandi March garnered widespread support for Gandhi among the Indian populace and drew considerable international attention.
- The motivations behind the Dandi March were rooted in the British monopoly over salt production and distribution in India.
- A series of laws prohibited Indians from producing or selling salt independently, forcing them to purchase heavily taxed salt that was often imported.
- This affected the majority of Indians, who were poor and could not afford the high cost of salt. Indian protests against the salt tax had begun in the 19th century and remained a major point of contention throughout British rule.
- By undertaking the Dandi March and defying the salt laws, Gandhi sought to mobilize the Indian populace against British oppression and galvanize support for the Indian independence movement.
- The march, which covered over 240 miles from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi, symbolized the spirit of nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience that would come to characterize India's struggle for freedom.
Impact of Dandi March:
- The Dandi March had a profound impact on the Indian independence movement and left an indelible mark on the country's history.
- The mass civil disobedience that ensued after Gandhi's iconic march led to millions of Indians breaking the salt laws by making or buying illegal salt.
- Gandhi's unwavering commitment to satyagraha against the salt tax inspired countless others to join the movement, including prominent leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Thousands were arrested and imprisoned, including Gandhi himself, but the spirit of resistance only grew stronger.
- News of Gandhi's detention galvanized tens of thousands more to join the satyagraha, and the march on the Dharasana salt works went ahead as planned in May 1931.
- Despite facing violent opposition from the police, the peaceful marchers, led by the poet Sarojini Naidu, persisted in their nonviolent resistance.
- Gandhi's release from custody in January 1931 marked a turning point, as he began negotiations with Lord Irwin aimed at ending the satyagraha campaign.
- These efforts culminated in the Gandhi-Irwin Pact, signed on March 5, 1931, which formalized a truce between the Indian independence movement and the British government.
- The Dandi March, therefore, served as a catalyst for change, uniting Indians from all walks of life in a shared struggle for freedom and justice.
- The events of the Salt Satyagraha remain an enduring symbol of the power of nonviolent resistance and the indomitable spirit of the Indian people in their quest for self-determination.
Khelo India Rising Talent Identification will take sports to the doorstep of aspiring champions

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, Shri Anurag Singh Thakur inaugurated the unique Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme amidst much enthusiasm at the Sector 7 sports complex, in Chandigarh recently.
About the KIRTI Programme:
- The KIRTI Programme is an ambitious nationwide initiative aimed at school children between the ages of nine and 18.
- With a dual focus, the scheme strives to uncover hidden talent from every corner of the country while simultaneously utilizing sports as a powerful tool to combat addiction to drugs and digital distractions.
Primary Objectives of KIRTI's Programme:
- Identifying and nurturing talented young athletes from across India, ensuring that no potential goes unnoticed.
- Leveraging sports as a means to steer youth away from harmful addictions and encourage a healthier, more active lifestyle.
- To achieve these goals, KIRTI plans to conduct 20 lakh assessments throughout the year at designated Talent Assessment Centres across the nation.
- The programme launched with a strong start at 50 centers in India, assessing 50,000 applicants in the first phase across 10 sports such as athletics, boxing, wrestling, hockey, and football.
- KIRTI's athlete-centric approach is characterized by its transparent selection methodology, which is grounded in Information Technology.
- The programme employs data analytics based on Artificial Intelligence to predict sporting potential in aspiring athletes, ensuring that talent identification is both objective and data-driven.
- By channeling India's youth towards sports and providing them with the necessary support, KIRTI aims to foster a new generation of athletes and promote a healthier, more active society.
About Khelo India Scheme:
- The Khelo India Scheme is the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India.
- This Central Sector Scheme is designed to instill a sports culture and achieve sporting excellence in the country by leveraging the transformative power of sports and its cross-cutting influence.
- The Khelo India Scheme encompasses multiple verticals, with "Sports Competitions and Talent Development" being a key focus area.
- Within this vertical, the "Talent Identification and Development" component plays a crucial role in identifying and nurturing athletes at both the grassroots and elite levels.
- The primary objective is to strengthen the sports ecosystem in India by cultivating talent and providing athletes with the necessary resources and support to excel in their respective disciplines.
- Through the Khelo India Scheme, the government aims to promote sports as a way of life, encouraging greater participation and creating a robust platform for athletes to showcase their skills.
- By investing in sports infrastructure, training, and competition opportunities, the scheme seeks to establish India as a global sporting powerhouse and inspire future generations to embrace the spirit of sportsmanship and athletic achievement.
Govt's new code bars unethical marketing of drugs by pharma firms

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has notified a new legal code to curb the unethical marketing of drugs and banning medical representatives from using “inducement” to access healthcare professionals
About the Uniform Code of Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (UCPMP) 2024:
- The UCPMP 2024 has been implemented to regulate unethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on promoting transparency and ethical conduct.
- The updated guidelines encompass various aspects, including drug endorsement, promotion, ethical behavior for medical representatives, and the maintenance of professional relationships with healthcare professionals.
Key provisions of the UCPMP 2024 include:
- Prohibiting the offering of gifts and travel facilities to healthcare professionals or their family members by pharmaceutical companies.
- Mandating that medical representatives should not use any form of inducement or subterfuge to gain interviews with healthcare professionals, nor should they provide payment for access under any guise.
- Holding pharmaceutical companies responsible for the actions of their medical representatives.
- Banning the supply of free drug samples to individuals who are not qualified to prescribe such products.
- Requiring each pharmaceutical company to maintain detailed records of free samples provided to healthcare practitioners, with the total value of distributed samples not exceeding two percent of the company's domestic sales per year.
- Compulsory constitution of an Ethics Committee for Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (ECPMP) by all pharmaceutical associations, along with the establishment of a dedicated UCPMP portal on their websites for implementation and monitoring purposes.
- Detailed guidelines on how drugs should be promoted in textual and audio-visual marketing materials, ensuring that information is balanced, up-to-date, verifiable, and non-misleading.
- Restrictions on making unverified claims and comparisons about a drug's usefulness, as well as using terms like "safe" and "new" without proper qualification.
- Assigning responsibility for adherence to the UCPMP 2024 to the Chief Executive Officers of pharmaceutical companies.
- Outlining penalties for violating the code and establishing a clear process for handling complaints, ensuring accountability and effective oversight.
- The UCPMP 2024 serves as a comprehensive framework for promoting ethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, aiming to protect the interests of patients, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders while fostering an environment of transparency and integrity.
India world’s top arms importer between 2019-23: SIPRI

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India was the world’s top arms importer for the period 2019-23 with imports having gone up by 4.7% compared to the period 2014-18, according to the SIPRI.
Highlights from the SIPRI Report 2023:
- The report highlights that India continues as the world’s largest arms importer, maintaining this position despite ongoing efforts to enhance its defense-industrial base, accounting for a significant 9.8% of global arms imports between 2019 and 2023.
- There has been a steady increase in India's arms imports, with a 4.7% rise observed between 2014-18 and 2019-23, attributed in part to emergency procurements prompted by the prolonged military standoff with China.
- The dynamics of arms suppliers are changing, with Russia historically serving as India's primary weapons supplier, still accounting for 36% of its arms imports, although there is a shift towards diversification, with India increasingly turning to Western countries and domestic manufacturers.
- Notably, between 2019-23, Russian deliveries constituted less than half of India's arms imports for the first time since 1960-64.
- Western suppliers like France and the United States are emerging as key players, collectively accounting for 46% of India's arms imports, with significant contracts in progress, such as India's procurement of 31 armed MQ-9B Sky Guardian drones from the US and 26 Rafale-M fighters from France.
- In the global arms trade landscape, India ranks as the top importer, followed by Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Ukraine, Pakistan, Japan, Egypt, Australia, South Korea, and China, while the United States leads among exporters with a 42% share, followed by France and Russia.
- India's role as a major arms customer is underscored by its position as the largest arms customer for France, Russia, and Israel, highlighting its significance in global arms procurement.
- Meanwhile, China remains a dominant supplier to Pakistan, accounting for 61% of its exports, and also exports 11% of its arms to Bangladesh, consolidating its influence in the region.
Challenges Encountered by India in Indigenous Production of Defense Equipment:
- Efforts to promote indigenous defense production, exemplified by initiatives like 'Make in India', have encountered persistent challenges, notably the failure to materialize any projects under the Strategic Partnership (SP) model, which was introduced to foster collaboration between the public and private sectors within the defense industry.
- The SP model, designed to facilitate joint endeavors between government-owned defense entities and private companies, has yet to yield tangible results, necessitating a thorough review of the policy framework.
- Key areas for improvement include a reevaluation of pricing methodologies, ensuring long-term orders to sustain production, and addressing bottlenecks that impede project implementation.
- Furthermore, India's defense sector has seen minimal Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), amounting to only Rs 5,077 crore since the sector was opened to private companies in 2001.
- Despite efforts to liberalize FDI regulations, such as allowing up to 74% through the automatic route and up to 100% through the government route in 2020, investment inflows remain disproportionately low.
About Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI):
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) is a renowned independent international institute committed to investigating various aspects of conflict, armaments, arms control, and disarmament.
- Founded in 1966 and headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, SIPRI consistently ranks among the world's most respected think tanks.
SIPRI's mission is multi-faceted and encompasses the following key objectives:
- Conducting in-depth research and activities related to security, conflict, and peace, with the aim of developing a deeper understanding of the complex factors that influence global stability.
- Providing insightful policy analysis and recommendations to policymakers, international organizations, and civil society actors, helping them make informed decisions and develop strategies to address security challenges.
- Facilitating dialogue and building capacities among various stakeholders, including governments, academia, and non-governmental organizations, to foster cooperation and promote mutual understanding on peace and security issues.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in the field of international security by maintaining comprehensive databases on arms transfers, military expenditure, and other relevant data, which contribute to a more accurate assessment of global security trends.
- By adhering to these core principles and objectives, SIPRI plays a vital role in advancing the global discourse on peace and security, while supporting efforts to mitigate conflict and promote stability worldwide.
Decoding the Trillion-Dollar Impact of GPUs on the AI Industry
- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the global demand for the latest AI technologies surges, one unexpected item has emerged as a highly sought-after commodity: the graphics processing unit (GPU).
What is a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)?
- A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized computer chip designed to efficiently render graphics and images by performing rapid mathematical calculations.
- Widely used in both professional and personal computing, GPUs were initially developed to handle the rendering of 2D and 3D images, animations, and video content.
- Similar to a Central Processing Unit (CPU), a GPU is an integral component of computing devices.
- However, the primary distinction lies in the GPU's specialized design to handle and accelerate graphics workloads and display graphics content on devices like PCs or smartphones.
- While a typical modern CPU consists of between 8 and 16 "cores" that process complex tasks sequentially, GPUs contain thousands of smaller cores.
- These cores are engineered to work simultaneously ("in parallel") to achieve fast overall processing, making GPUs ideal for tasks involving numerous simple operations that can be executed concurrently.
- GPUs operate using a technique called parallel processing, where multiple processors manage separate parts of a single task.
- They also possess their own dedicated RAM to store and process large amounts of data for graphics-intensive applications.
- In graphics applications, the CPU sends instructions to the GPU for drawing graphics content on the screen.
- The GPU then executes these instructions in parallel at high speeds, displaying the content on the device—a process known as the graphics or rendering pipeline.
- They also possess their own dedicated RAM to store and process large amounts of data for graphics-intensive applications.
- Modern GPUs have expanded beyond their traditional role in graphics rendering and are now employed in various applications such as creative content production, video editing, high-performance computing (HPC), and artificial intelligence (AI).
- By offloading graphics-related tasks from the CPU, GPUs enable fast and smooth rendering of content on computer screens.
- As technology continues to advance, the applications of GPUs will likely expand even further, solidifying their position as an essential component in the computing landscape.
Mission Divyastra: India's Agni-V missile makes maiden flight with MIRV

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India on Monday announced the successful testing of an Agni missile capable of carrying multiple warheads meant to hit multiple targets simultaneously.
What are Agni-5 Missiles?
- Agni is a long-range missile developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation, DRDO.
- The family of Agni missiles has been in the arsenal of the Indian armed forces since the early 1990s.
- This latest variant of the missile is equipped with what is known as MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology, first developed at least five decades ago but in possession of only a handful of countries.
Salient Features of Agni-5:
- Powered by a three-stage solid-fuel engine, Agni-5 boasts a range exceeding 5,000km.
- The Agni series encompasses medium to Intercontinental variants, spanning Agni-1 to Agni-5, with ranges varying from 700 km to over 5,000 km.
- DRDO’s successful June 2021 test of Agni P, a canisterized missile, demonstrated a range capability ranging between 1,000 and 2,000 km.
- With its ability to be launched from both road and rail platforms, Agni-5 ensures ease of deployment and swift launch capabilities.
What is MIRV Technology?
- The MIRV have revolutionized the concept of ballistic missile payloads by enabling a single missile to carry multiple warheads, each capable of targeting enemies at different locations.
- The technology was first introduced in the US with the successful test of the Minuteman III in 1968, which brought the technology into actual use in the 1970.
- The Soviet Union developed their own MIRV-enabled ICBM and SLBM technology by the end of the 1970s.
- The strategic shift started by MIRV has enabled many nations to greater target damage and reduce the effectiveness of enemy missile systems, altering the landscape of global nuclear deterrence.
- The warheads on MIRVs can be launched at different speeds and in different directions.
- Some MIRVed missiles can hit targets as far as 1,500 km apart.
- The technology requires a delicate combination of large missiles, small warheads, precise guidance, and a complex mechanism for releasing warheads sequentially during flight.
How does MIRV Work?
- The MIRV-equipped missile follows a trajectory into space similar to other ballistic missiles.
- After the boost phase, the missile’s upper stage, known as ‘bus’, reaches suborbital spaceflight, and aligns itself based on designated targets.
- The ‘bus’ sequentially deploys multiple warheads along with decoys and countermeasures.
- Each warhead can be assigned a different target or trajectory.
- After the deployment, the warheads re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere and proceed to their respective targets.
What are the Challenges?
- The MIRV technology enhances first-strike proficiency and complicates the calculus of mutual assured destruction.
- With the ability to deploy multiple warheads from a single missile, nations can achieve a broader spread of targets, making the defense system less effective and more costly.
- Although MIRVs were not initially made to defeat ballistic missile defenses, they are much more difficult to defend against than traditional missiles.
- Possession of MIRV technology not only exhibits a country’s nuclear prowess but plays a crucial role in shaping international security and nuclear deterrence strategies.
STPI launches 24th Centre of Entrepreneurship FinGlobe in Gandhinagar to nurture startups in fintech & banking services

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) recently launched its 24th Center of Entrepreneurship (CoE) - "FinGlobe," dedicated to fostering innovation and growth in the financial technology sector, at STPI-Gandhinagar, GIFT City.
About Software Technology Parks of India (STPI):
- Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) was set up in 1991 as an autonomous society under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- STPI’s main objective has been the promotion of software exports from the country. STPI acts as ‘single-window in providing services to the software exporters.
- The services rendered by STPI for the software exporting community have been statutory services, data communications services, incubation facilities, training and value-added services.
- STPI has played a key developmental role in the promotion of software exports with a special focus on SMEs and start-up units.
Services of STPI:
- Main services of STPI include Statutory services, Incubation and Data communication services to the IT/ITES/ESDM sector.
- Statutory services: STPI has been implementing the Software Technology Park (STP) scheme and the Electronics Hardware Technology Park (EHTP) scheme for the promotion of the IT/ITES industry.
- STP Scheme is a unique scheme, designed to promote the software industry and growth of start-ups and SMEs without any locational constraints.
- Incubation services: STPI is offering ultra-modern office facilities to small units and entrepreneurs.
- Plug-n-Play facilities for start-ups enable a short gestation period.
- This has encouraged many entrepreneurs to start their own operations and grow in a competitive environment.
Objectives of STPI:
- Promotion of software and software services development and exports, including IT Enabled Services (ITES)/Bio-IT.
- Provision of statutory and promotional services to exporters through the implementation of schemes like Software Technology Park/Electronics and Hardware Technology Park, among others.
- Offering data communication services, along with value-added services, to industries related to IT/ITES.
- Encouraging micro, small, and medium entrepreneurs by fostering an entrepreneurial environment in the IT/ITES sector.
. India ‘one of the worst autocratisers’: V-Dem report on democracy

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India, which was downgraded to the status of an “electoral autocracy” in 2018, has declined even further on multiple metrics to emerge as “one of the worst autocratizers”, according to the ‘Democracy Report 2024’ released by the Gothenburg-based V-Dem Institute that tracks democratic freedoms worldwide.
About V-Dem (Varieties of Democracy):
- The V-Dem Institute, established in 2014 by Swedish political scientist Staffan Lindberg, is a research institution dedicated to studying the various forms of democratic governance around the world.
- Headquartered at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden, V-Dem produces several high-profile datasets that assess the qualities of different governments based on hundreds of indicator variables.
- These datasets are widely used by political scientists due to their comprehensive coverage of various aspects of government and are freely available to the public.
- V-Dem's annual publications provide valuable insights into the functioning of governments worldwide, promoting transparency and understanding of democratic institutions.
About The Democracy Report:
- The Democracy Report presents a comprehensive analysis of the state of democracy worldwide, with a particular focus on the trends of democratization and autocratization.
- The report classifies countries into four distinct regime types based on their performance on the Liberal Democracy Index (LDI): Liberal Democracy, Electoral Democracy, Electoral Autocracy, and Closed Autocracy.
- The LDI is a composite index that encompasses both liberal and electoral dimensions of democracy.
- It is based on 71 indicators, which are grouped into the Liberal Component Index (LCI) and the Electoral Democracy Index (EDI).
- The LCI assesses various aspects of individual and minority rights, as well as legislative constraints on the executive.
- The EDI evaluates the extent to which elections are free and fair, considering factors such as freedom of expression and association.
- In addition to the LCI and EDI, the LDI also incorporates three other component indices:
- The Egalitarian Component Index (measuring social group equality)
- The Participatory Component Index (assessing the vibrancy of citizen groups and civil society organizations), and
- The Deliberative Component Index (evaluating whether political decisions are based on public reasoning or emotional appeals, solidarity attachments, and coercion).
- The Democracy Report, along with the underlying dataset, scientific articles, and working papers, is publicly available for download on the V-Dem Institute's website.
- The website also offers interactive graphic tools to facilitate the exploration and visualization of the data.
Key Insights from the Democracy Report 2024:
- The Democracy Report 2024, a collaborative effort involving 4,200 scholars from 180 countries, draws from 31 million datasets spanning 202 countries from 1789 to 2023.
Global Trends:
- In 2023, 42 countries (home to 35% of the world’s population) experienced autocratization.
- Autocracies now encompass 71% of the world's population, up from 48% a decade ago.
- The overall level of democracy has regressed to 1985 levels for the average global citizen.
- Eastern Europe, South, and Central Asia witnessed the most significant decline in democracy.
- Freedom of expression, clean elections, and civil society engagement were the most affected aspects in autocratizing nations.
Focus on 2024 Elections:
- Of the 60 countries holding elections in 2024, 31 are experiencing democratic backsliding.
India's Situation:
- India, classified as an electoral autocracy since 2018, has further deteriorated, earning the title of "one of the worst autocratizers."
- The report notes that India's level of liberal democracy has plummeted to levels comparable to those during the 1975 emergency declared by Indira Gandhi.
- Under the V-Dem classification, a liberal democracy requires robust mechanisms for judicial independence, checks on executive power, and strong protection of civil liberties and equality under the law.
- India currently falls into the category of electoral autocracy, characterized by multiparty elections but lacking adequate freedom of expression and fair electoral processes.
India launches revamped scheme to help advance pharma industry's tech capabilities

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's Department of Pharmaceuticals recently unveiled the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (RPTUAS) to help advance the technological capabilities of India's pharmaceutical industry and align it with global standards.
What is the Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme?
- In an effort to support pharma companies aligned with global quality standards, the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) has announced a revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme.
- It has been incorporated as a sub-scheme under the Scheme - Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI), which was launched in July 2022.
Objective:
- To facilitate Micro, Small and Medium Pharma Enterprises (MSME) of proven track record to upgrade their technology to meet WHO-GMP or Schedule M standards.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises of the pharma sector.
Key Features of the Revised Scheme:
- Broadened Eligibility Criteria: Reflecting a more inclusive approach, eligibility for the PTUAS has been expanded beyond Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to include any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit with a turnover of less than 500 crores that requires technology and quality upgradation.
- Preference remains for MSMEs, supporting smaller players in achieving high-quality manufacturing standards.
- Flexible Financing Options: The scheme introduces more flexible financing options, emphasizing subsidies on reimbursement basis, over traditional credit-linked approaches.
- Comprehensive Support for Compliance with New Standards: In alignment with revised Schedule-M and WHO- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, the scheme now supports a broader range of technological upgrades.
- Eligible activities include improvements such as HVAC systems, water and steam utilities, testing laboratories etc.
- State Government Scheme Integration: The revised scheme allows integration with state government schemes, enabling units to benefit from additional top-up assistance. This collaborative approach aims to maximize support for the pharmaceutical industry in their technology upgradation efforts.
- The new benefit limit is based on turnover of the company. Units with less than Rs 5 crore turnover will get an incentive of 20 percent of investment under eligible activities.
- The units with turnover ranging from Rs 50 crore to less than Rs 250 crore will get an incentive of 15 percent of investment, while for those with turnover ranging from Rs 250 crore to less than Rs 500 crore, it will be 10 percent of investment under eligible expenses.
New sensor can detect 'forever chemicals' in drinking water

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A team of chemists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has designed a breakthrough method for the detection of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
What are Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)?
- Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a class of man-made chemicals that have been in use since the 1940s.
- Due to their unique properties, such as high chemical stability and resistance to heat, grease, and water, PFAS have been widely used in various industrial and commercial applications.
- They are commonly found in products such as stain- and water-resistant fabrics, cleaning products, paints, and fire-fighting foams.
- PFAS are often referred to as "forever chemicals" because they do not break down naturally in the environment.
- This is due to the strong carbon-fluorine bond that characterizes these compounds, making them highly persistent and resistant to degradation.
- The widespread use of PFAS has resulted in increasing levels of environmental contamination, with PFAS being detected in air, water, and soil samples worldwide.
- Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to a range of health risks, including decreased fertility, developmental effects in children, interference with body hormones, increased cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Due to their persistent nature and potential health risks, there is growing concern about the widespread use of PFAS and the need for improved regulation and remediation strategies to manage their environmental and health impacts.
- Environmental Persistence: Due to their strong carbon-fluorine bonds, PFAS do not break down easily in the environment.
- They can accumulate in soil, water, and living organisms, posing a long-term risk to ecosystems and human health.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in living organisms, including humans, through the food chain.
- Even small amounts of PFAS in the environment can build up to harmful levels in animals and humans over time.
- Regulatory Action: Due to the potential health and environmental risks associated with PFAS, many countries are taking regulatory action to restrict their use and manage their environmental impacts.
- This includes banning certain PFAS-containing products, setting drinking water standards, and requiring the clean-up of contaminated sites.
MNRE to discuss specialized cylinders for hydrogen storage with stakeholders

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) plans to convene a meeting with relevant stakeholders to discuss the development of specialized cylinders for green hydrogen storage.
What is Green Hydrogen?
- Green Hydrogen is produced through the process of electrolysis of water, utilizing electricity generated from renewable energy sources.
- The carbon intensity of green hydrogen depends on the carbon neutrality of the electricity source, with higher renewable energy content resulting in greener hydrogen.
- With its potential to decarbonize various sectors, reduce carbon emissions, and achieve energy independence, green hydrogen holds significant promise.
- Its production from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower makes it a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels in transportation and industry, offering a consistent and reliable energy source.
- Storage: Hydrogen is stored in cylinders at high pressure, categorized into four types based on materials used. Type 1 and Type 2 are suited for storage, while Type 3 is ideal for storage and transportation, and Type 4 is recommended for on-board storage.
- Unlike compressed natural gas (CNG) stored at around 3,600 psi, hydrogen is stored at 5,000-10,000 psi.
- Vehicles can utilize hydrogen either by burning it in an internal combustion engine or by using a fuel cell to convert it into electricity to charge on-board batteries.
- Type 3 and Type 4 cylinders are reinforced with carbon fiber, making them lightweight and suitable for vehicles.
- Type 4 cylinders, lined with a polymer instead of aluminum like Type 3, are even lighter.
Application of Green Hydrogen:
- Green hydrogen finds diverse applications, including powering vehicles and generating electricity through fuel cells.
- It also serves in heating systems and the production of chemicals and fertilizers.
- Additionally, green hydrogen supports microgrids, facilitating electricity provision to remote areas and fostering energy independence.
Advantages and disadvantages of green hydrogen:
- 100 % sustainable: Green hydrogen does not emit polluting gasses either during combustion or during production.
- Storable: Hydrogen is easy to store, which allows it to be used subsequently for other purposes and at times other than immediately after its production.
- Versatile: Green hydrogen can be transformed into electricity or synthetic gas and used for commercial, industrial or mobility purposes.
However, green hydrogen also has negative aspects that should be borne in mind:
- High cost: Energy from renewable sources, which are key to generating green hydrogen through electrolysis, is more expensive to generate, which in turn makes hydrogen more expensive to obtain.
- High energy consumption: The production of hydrogen in general and green hydrogen in particular requires more energy than other fuels.
- Safety issues: Hydrogen is a highly volatile and flammable element and extensive safety measures are therefore required to prevent leakage and explosions.
NHAI to start rolling out satellite-based tolling on national highways soon

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said in Parliament in February that the government plans to implement a new highway toll collection system based on the global navigation satellite system before the model code of conduct for the 2024 election kicks in.
What is the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)?
- GNSS refers to a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers.
- The receivers then use this data to determine location.
- Examples of GNSS include Europe’s Galileo, the USA’s GPS, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou
How will the GNSS-Based Toll System work?
- The system will use an automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) system through cameras installed on highways and deduct tolls based on the distance traveled by a vehicle.
- The device monitors the movements while driving, accurately marking the entry and exit points on tolled segments. By analyzing travel distance, it computes the charges accordingly.
- This eliminates the uniformity of fixed tolls at booths, ensuring fairness for drivers traversing shorter distances.
Difference between FASTags and ANPR technology:
- FASTags streamline electronic toll payments at toll plazas equipped with scanners, enabling vehicles to pass through without stopping.
- Conversely, GNSS-based systems utilize ANPR technology to deduct tolls based on distance traveled, rendering traditional toll plazas unnecessary.
What are the Challenges?
- Detection of Non-Compliance: Without physical barriers, detecting non-compliant vehicles, such as those without an On-Board Unit (OBU) or engaging in fraudulent activities, poses a challenge.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying gantry-mounted Automatic Number-Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems along highways is essential for capturing violations and enforcing toll payments.
- License Plate Quality: The effectiveness of ANPR systems relies on the quality of license plates; subpar plates hinder accurate recognition and enforcement efforts.
- Data Privacy and Security: GNSS-based toll systems entail collecting and processing sensitive location data, necessitating robust privacy and security measures.
Inflection AI rolls out new large language model to its Pi chatbot

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Inflection AI launched its latest LLM, Inflection 2.5, an upgrade to its model that powers its friendly chatbot Pi personal assistant.
About Inflection 2.5:
- Inflection-2.5 is an “upgraded in-house model that is competitive with all the world’s leading LLMs like GPT-4 and Gemini.
- The newly upgraded LLM comes with its signature personality and uniquely empathetic fine-tuning.
- Its latest model achieved GPT-4’s performance with only 40 per cent of the OpenAI model’s computation power for training.
- Besides, it seems Inflection 2.5 has made some stellar strides in areas of IQ such as coding and mathematics.
- This means that the model has made substantial improvements on key benchmarks.
- With the new upgrade, Pi has now been endowed with world-class real-time web search capabilities to ensure that users get access to high-quality and up-to-date information in real-time.
What is the Pi chatbot?
- Pi is an advanced chatbot powered by Inflection AI's cutting-edge language model, Inflection 2.5 which allows one to have deep and meaningful conversations.
- To access the chatbot, one needs to log on to Inflection.AI, click on Meet Pi, and simply start talking to the chatbot right away.
- Pi is more humane and has been promoted as a chatbot that has a personality.
- In other words, Inflection AI dubbed it as a chatbot that is “supportive, smart, and there for you anytime”.
- Pi is more like a companion to humans and is free to use.
- The chatbot comes with a voice, in six distinct voices, to choose from adding life to conversations.
Pi chatbot boasts a number of impressive features that make it stand out from other conversational AI systems:
- Real-time web search capabilities: Pi can access and present up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, ensuring that users always have access to accurate and relevant information.
- Empathetic personality: Pi's unique empathetic fine-tuning allows it to understand and respond to the emotional nuances of human communication, making it a more engaging and personable conversational partner.
- Versatile conversation topics: Whether you're discussing current events, asking for local recommendations, studying for an exam, drafting a business plan, coding, or just talking about hobbies, Pi is equipped to handle a wide range of conversational topics.
- User-friendly interface: Designed with accessibility in mind, Pi's intuitive interface makes it easy for users of all technical abilities to engage with the chatbot and get the most out of their conversations.
Health ministers of 11 African countries commit to end malaria deaths

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic gathering in Cameroon’s capital Yaoundé, African health ministers, global malaria partners, funding agencies, scientists, civil society organizations and other principal malaria stakeholders pledged to end malaria deaths, especially given the tools and systems available.
What is the Yaounde Declaration?
- The Yaounde Declaration was endorsed by health ministers from 11 African nations with the highest malaria burden, aiming to expedite efforts to eliminate malaria-related deaths.
- Signed during the Yaoundé conference, co-hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Cameroon, the declaration underscores a collective commitment to combat malaria.
- The signatory countries include Burkina Faso, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania, together accounting for approximately 70% of the global malaria burden.
- Commitments entail stronger leadership and increased domestic funding for malaria control programs, leveraging data technology, adhering to updated technical guidance, and intensifying efforts at national and sub-national levels.
- Ministers pledged augmented health sector investments to fortify infrastructure, personnel, and program implementation, fostering multi-sectoral collaboration, and cultivating partnerships for funding, research, and innovation.
- Signatories affirmed their resolute dedication to hasten malaria mortality reduction and to ensure mutual accountability for the declaration's outlined commitments.
Current Status of Malaria:
- Between 2019 and 2022, global malaria cases increased from 233 million to 249 million, with Africa experiencing a substantial rise from 218 million to 233 million cases, highlighting the continent as the epicenter of the malaria crisis.
- The 11 African countries represented at the conference bear the highest burden of malaria infections and deaths.
Progress and Challenges:
- Despite some progress, malaria incidence has only declined by 7.6% and mortality by 11.3%, falling short of the African Union’s interim goals.
- Only seven out of 46 member states have achieved a 40% reduction in malaria incidence or mortality.
- Urgent action is imperative to bridge a financial gap of $1.5 billion to sustain basic malaria services, especially for vector control.
- Additional funding of $5.2 billion annually for progress towards elimination and $11 billion for climate adaptation in the health sector is crucial to avert significant surges in cases and deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women.
UGC notifies framework for private universities to set up off-campus centers

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with the “future academic vision” instead of “commercial interests”, the UGC has notified modalities on March 6 for state private universities to set up off campus centers within their respective states.
News Summary:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) recently permitted private universities to establish off-campus centers and outlined regulations for the same.
- Previously, private universities in the country were restricted from opening off-campus centers in other states.
- In a meeting held on March 5, the UGC decided to authorize state private universities to establish off-campus centers across the country, provided they meet specific criteria.
- Criteria include a minimum of five years of establishment and accreditation from the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), without requiring an A or B grade.
- Universities seeking to establish off-campus centers must meet staff, infrastructure, and financial requirements mandated by the commission and obtain approvals from statutory and regulatory bodies.
- These universities must ensure the provision of infrastructure, faculty, and courses offered at the main campus to students at their off-campus centers.
- A one-time establishment fee of Rs 10 lakh is required to be paid to the UGC by the universities.
- The UGC reserves the right to conduct inspections and take punitive actions against universities in case of irregularities or complaints.
- Additionally, the UGC may order the closure of a university’s off-campus center for violations, with the university responsible for relocating affected students to the main campus.
About University Grants Commission (UGC):
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) of India operates as a statutory body established under the UGC Act, 1956.
- Its primary mandate encompasses coordinating, determining, and upholding standards within higher education institutions across India.
- UGC holds the authority to grant recognition to universities and colleges within the country and allocates funds to these recognized institutions.
- Nodal Ministry: Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education.
Mandate of UGC:
- Facilitating and coordinating university education initiatives.
- Establishing and maintaining standards in teaching, examination, and research activities within universities.
- Formulating regulations to define minimum education standards.
- Monitoring advancements in collegiate and university education while disbursing grants to these institutions.
- Serving as a crucial intermediary between the Union and State governments and higher education institutions.
- Providing advisory services to the Central and State governments concerning measures aimed at enhancing university education standards.
Conclusion
Academic experts said that this decision may prove beneficial for students as they will get more options to choose from. However, it also means that the 16 government-run universities in the state will face more competition. More students may shift to these centers, leaving a large number of approved seats in the public universities vacant every year.
India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
India to restart Penicillin G manufacture
- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will start manufacturing the common antibiotic Penicillin G later this year, three decades after the country’s last plant shut down, Union health minister Mansukh Mandaviya announced last week.
What is Penicillin G?
- Penicillin G serves as a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) utilized in the production of various common antibiotics.
- Its molecular formula is C16H18N2O4S.
- Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an FDA-approved antibacterial medication primarily indicated for treating severe bacterial infections like pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, among others.
- This natural penicillin antibiotic is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly due to limited oral absorption.
- Additionally, Penicillin G may be employed in certain instances as prophylaxis against susceptible organisms.
Why did Penicillin Manufacturing Stopped in India?
- The discontinuation of Penicillin G production in India, along with numerous other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), resulted from the influx of cheaper Chinese products driven by subsidies.
- Torrent Pharma in Ahmedabad was the final plant to halt Penicillin G production, with at least five companies, including Torrent, manufacturing the antibiotic in the country during the 1990s.
- In the early 1990s, India boasted nearly 2,000 API manufacturers, while approximately 10,000 units produced formulations. However, the allure of cheaper Chinese alternatives grew, particularly with the relaxation of customs rules during the country's economic liberalization.
- The Drug Prices Control Order, which imposed price caps on essential medicines, further incentivized companies to opt for cheaper imported products.
- While India previously sold Penicillin G for around Rs 800 per kg, China drastically reduced prices to nearly Rs 400 per kg, rendering domestic manufacturing economically unviable.
Why the Delay in Restarting Production?
- Lack of Urgency: Despite awareness within the industry and government about the decline in API production in India due to the availability of cheaper alternatives globally, there was limited emphasis on restarting domestic production.
- The supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic highlighted the need for self-reliance, prompting the government to launch initiatives like the PLI scheme to bolster domestic manufacturing.
- High Initial Investment: API manufacturing, particularly for fermented compounds like Penicillin G, entails significant upfront costs.
- Establishing a production facility requires substantial capital investment, with companies often needing several years to break even.
- Dominance of China: China has emerged as a dominant supplier, significantly expanding its manufacturing capacity over the past three decades.
- Competing with Chinese prices would necessitate substantial investments in larger facilities.
What's the Impact of PLI Schemes?
- Reduction in API Imports: Since the implementation of the PLI scheme, there has been a notable decrease in API imports.
- For instance, the import dependency for paracetamol, which was previously two-thirds of the required volume, has now halved.
- Incentive Structure: The PLI scheme offers incentives structured as follows:
- 20% support for the first four years, gradually reducing to 15% in the fifth year and 5% in the sixth year for eligible sales of fermentation-based bulk drugs like antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones such as insulin.
- Chemically synthesized drugs receive a 10% incentive for six years on eligible sales.
The ‘Architecture Nobel’: Why Pritzker laureate Riken Yamamoto’s work stands out

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Japanese architect Riken Yamamoto was this week declared winner of the 2024 Pritzker Architecture Prize, the highest international award in the field, which is sometimes referred to as the “Architecture Nobel”.
About Pritzker Architecture Prize:
- The Pritzker Architecture Prize is an international prize awarded each year to a living architect or a group of architects for significant achievements.
- It was established by the Pritzker family of Chicago in 1979 through their Hyatt Foundation, which until today is responsible for the prestigious award.
- The idea behind the Pritzker Prize is to honor contemporary architects “whose built work demonstrates a combination of those qualities of talent, vision, and commitment, which has produced consistent and significant contributions to humanity and the built environment through the art of architecture.”
- The award consists of a bronze medallion and a prize money of 100,000 USD.
- It is conferred during a ceremony held at an architecturally significant site throughout the world.
- The prize, which is also known as the Nobel Prize of architecture, is awarded “irrespective of nationality, race, creed, or ideology”.
- Nominations come from a range of architects, academics, and critics and the jury consists of five to nine experts.
History of the Prize:
- The idea for the Pritzker Prize came from Jay and Cindy Pritzker, who wanted to encourage and stimulate a greater public awareness of architecture, while also inspiring more creativity in the profession.
- The name Pritzker comes from the family who are based in Chicago and own the Hyatt Hotels.
Riken Yamamoto's Notable Works:
- Yamamoto, the ninth laureate from Japan, is known for his iconic architectural designs, such as the Hiroshima Nishi Fire Station (2000), featuring a transparent façade with glass walls and floors, offering passersby a glimpse inside.
- His design of the Koyasu Elementary School (2018) incorporates spacious, open terraces that facilitate arts education in dance, music, and painting while fostering student interaction.
Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay, the unsung feminist freedom fighter in the history of India

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Post-Independence, the revival of the crafts sector began with Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay who strongly championed the handicrafts movement for the role it could play in social and economic upliftment.
About Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay:
- Kamaladevi was born in April 1903 in a liberal Chitrapur Saraswat Brahmin family in Mangalore (now Mangaluru).
- She completed her primary education at the local St Ann’s Convent.
- Growing up in a land with a rich cultural heritage, especially of the music and dance form Yakshagana, she developed a taste for traditional art forms.
- After her father’s untimely death, Kamaladevi moved to her maternal uncle’s house.
- There, she met renowned freedom fighters, including Gopalkrishna Gokhale, Srinivasa Shastri, Ramabai Ranade and Annie Besant.
- Kamaladevi was married off at the age of 14 and widowed two years later.
- Unperturbed by these life events, she joined Queen Mary’s College in Madras (now Chennai) for higher studies.
- There, she met Sarojini (Chattopadhyay) Naidu’s brother Harindranath Chattopadhyay which led to their wedlock.
- However, their marriage ended over incompatibility issues and this, too, created history – Kamaladevi was the first legal divorce granted through an Indian court of law.
- Kamaladevi played a prominent role in political reforms and India’s freedom struggle.
- She was the first woman to contest the Madras provincial elections.
- Though she lost by a narrow margin, she got recognition and was appointed secretary of the All-India Women’s Conference.
- She joined Indian National Congress in 1927 and was elected to the All-India Congress Committee within a year.
- During the Salt March to Dandi, she convinced Gandhi to give women equal opportunity to be in the forefront of the march.
- Later, she joined Seva Dal and trained women activists.
- However, the British government banned Seva Dal and threw Kamaladevi into jail.
- There, she contracted jaundice. Having experienced the pathetic condition of the prison hospital, she built a hospital for inmates upon release.
- Kamaladevi got attracted to socialism and took up the problems of laborers and peasants.
- During World War II, she visited America and met several political activists, mostly blacks, and shared with them India’s non-violent approach to freedom struggle.
- The British got wind of her activism and banned her from returning to India.
- Unmoved, Kamaladevi continued on her journey, visiting South Africa, China, Japan and Vietnam.
- Kamaladevi was inarguably the embodiment of women’s empowerment.
- She was an advocate of female sexual freedom and birth control.
- Her remarriage after widowhood and legal divorce from her second marriage were symbolic of her self-empowerment.
- She acted in many films (a Kannada film, too) when the film industry was not considered a respectable place for women.
- Indeed, Kamaladevi’s immense travel and experiences shaped her as a secular, socialist world citizen.
- Such were her ideals that led to her building the city of Faridabad to rehabilitate some 50,000 craftsmen who moved to India from Pakistan during Partition.
- Post-independence, she helped revive Indian handicrafts and built institutions for a ‘New India’-- to name a few, the National School of Drama, Bharatiya Natya Sangha, Lady Irwin College, Sangeet Natak Academy, Central Cottage Industries Emporium, World Craft Council, Craft Council of India, and the Delhi Craft Council.
- Kamaladevi was a prolific writer, too and wrote 18 books altogether, touching upon women’s issues, Indian handicrafts and her foreign visits.
- She published her autobiography, “Inner Recesses, Outer Spaces: Memoir” (1986).
- She received several awards in recognition of her public service, like Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan, the Ramon Magsaysay Award and the UNESCO Award.
- She died in Mumbai on October 29, 1988, aged 85.
Every village to have agricultural credit societies by 2027

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah Friday said that the Centre has decided to ensure formation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027.
Context:
- Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah recently announced the Centre's commitment to establishing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027, introducing 20 new activities to enhance their profitability.
- Emphasizing the significance of computerization in PACS, Shah highlighted its role in fostering development opportunities.
- He also inaugurated the National Cooperative Database and unveiled the 'National Cooperative Database 2023: A Report' to bridge existing gaps through comprehensive analysis.
- The database initiative progressed through three phases, including mapping approximately 2.64 lakh societies across agriculture, dairy, and fisheries sectors in the first phase.
- Subsequent phases involved data collection from various federations, banks, and mapping of the remaining 8 lakh primary cooperative societies in other sectors.
- The unveiling revealed over 8 lakh registered societies in the country, connecting more than 30 crore citizens.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
- PACS are grassroots cooperative credit societies, constituting the final tier in a three-tier cooperative credit system led by State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) at the state level.
- SCBs channel credit to District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) operating at the district level, which collaborate with PACS, directly serving farmers.
- PACS operate as cooperative entities, with individual farmers as members and elected office-bearers from within the community. Villages may host multiple PACS.
- These societies extend short-term and medium-term agricultural loans to farmers for various farming activities.
Number of PACS in India:
- Established since 1904, India currently boasts over 1,00,000 PACS nationwide, engaging a significant member base exceeding 13 crore farmers.
- However, operational PACS stand at only 63,000, indicating the need for enhanced functionality and outreach.
Why are PACS Appealing?
- PACS offer crucial last-mile connectivity, ensuring farmers have access to capital at the onset of agricultural activities.
- They streamline credit extension processes, providing farmers with timely financial support with minimal paperwork, unlike traditional banks known for cumbersome procedures.
- PACS simplify paperwork and administrative tasks, offering farmers collective strength and assistance from PACS office-bearers.
- Unlike individual interactions required with commercial banks, PACS enable farmers to navigate loan processes collectively, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Challenges Faced by PACS:
- Political influences often overshadow financial prudence within PACS, impacting loan recovery.
- Various committees have highlighted systemic issues within the cooperative system, including low member participation, lack of professionalism, inadequate governance, bureaucratic hurdles, and a workforce with aging and disengaged employees.
Union Cabinet approves India AI Mission with 10,372 cr outlay

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
India has made its first move to address a key shortcoming it currently has in unlocking opportunities around generative artificial intelligence (AI) – that of computing hardware.
What is IndiaAI Mission?
- India's AI Mission entails the launch of an artificial intelligence (AI) initiative, announced by the Prime Minister at the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi, with implementation overseen by the 'IndiaAI' Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- Led by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the mission aims to establish a computing capacity exceeding 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and develop foundational models trained on datasets encompassing major Indian languages, focusing on priority sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Additionally, the mission will involve the establishment of AI Curation Units (ACUs) in 50-line ministries and the creation of an AI marketplace to provide AI services and pre-trained models to AI application developers.
- Implementation of the AI computer infrastructure will follow a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding, with Rs 4,564 crore allocated from the total outlay of Rs 10,372 crore for building computing infrastructure.
Key Features of the IndiaAI Mission:
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Establishing a scalable AI computing ecosystem to meet the growing demands of India's burgeoning AI start-ups and research community.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Focusing on the development and deployment of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and domain-specific foundational models in critical sectors.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: Streamlining access to high-quality non-personal datasets to fuel AI innovation.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promoting the adoption of AI applications in critical sectors, addressing problem statements sourced from Central Ministries, State Departments, and other entities.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Mitigating barriers to entry into AI programs by expanding AI courses at undergraduate, master's, and Ph.D. levels.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Supporting and accelerating deep-tech AI startups by providing streamlined access to funding for futuristic AI projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Ensuring the responsible implementation of AI projects through the development of indigenous tools and frameworks to foster trust and safety in AI applications.
The Significance of the IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission aligns with the vision of fostering indigenous AI development and leveraging AI technology for the benefit of India.
- It aims to demonstrate to the international community the positive impact of AI technology on society, thereby enhancing India's global competitiveness.
- By establishing a comprehensive ecosystem for AI innovation through strategic partnerships across public and private sectors, the mission will catalyze AI-driven advancements.
- It will foster creativity and bolster internal capabilities, ensuring India's technological sovereignty.
- Furthermore, the mission is poised to create employment opportunities that demand advanced skills, leveraging India's demographic advantage.
After 10 years struggle, Mendha gets separate Panchayat status under Gramdan Act

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Maharashtra government recently notified Mendha, a village deep inside the forests of the state’s Gadchiroli district, as a separate Gram Panchayat under The Maharashtra Gramdan Act, 1964.
What is Gramdan?
- Gramdan is an expansion of the Bhoodan Movement started in 1951 by Aacharya Vinoba Bhave.
- ‘Bhoodan’ meant redistribution of land from bigger landowners to the landless.
- Under Gramdan, the entire village will put its land under a common trust.
- This way, the land will not be sold outside the village or to one who has not joined Gramdan in the village.
- But the landowners can continue to cultivate it and reap the benefits.
- The Movement paved the way for the protection of natural resources by giving equal rights and responsibilities to everyone in the community and empowering communities to move towards self-governance.
- Under the Act, at least 75 percent of landowners in the village should surrender land ownership to the village community for it to be declared as ‘gramdan’.
- Such land should at least be 60 percent of the village land. Five per cent of the surrendered land is distributed to the landless in the village for cultivation.
- Recipients of such land cannot transfer the same without the permission of the community.
- The rest remains with the donors.
- They and their descendants can work on it and reap the benefits.
- But they cannot sell it outside the village or to a village resident who has not joined Gramdan.
- Today, seven states in India have 3,660 Gramdan villages, the highest being in Odisha (1,309).
- The states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- In September 2022, the Assam government repealed the Assam Gramdan Act, 1961 and Assam Bhoodan Act, 1965, bypassing The Assam Land and Revenue Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
- This, it said, was done to counter encroachment on donated lands in the state.
- Till that time, Assam had 312 Gramdan villages.
About Mendha’s Village Struggle:
- The village, comprising around 500 Gond Adivasis, has fought for its forests for years.
- It is popular as the first village in India to secure community forest rights (CFR), following the passing of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- Some 80 per cent of the area in the village is covered with dense forest.
- People here believe that land is not a private property but a collective resource that provides food and livelihood and should be saved and passed on to the next generation.
- All villagers in Mendha have surrendered their land, which is unique. In all other villages, only about 75-80 per cent of landowners had agreed to do so.
- The village fulfilled these conditions of the Act in 2013 and notified the district collector about its decision to implement the Act.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
Kerala declares man-animal conflict a state-specific disaster

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid repeated deaths from animal attacks and rising anger over them, Kerala recently declared man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, becoming the first state in the country to do so.
What is Man-animal Conflict?
- Man-animal conflict refers to the interaction between wild animals and humans, resulting in adverse outcomes for both people and wildlife, as well as their habitats.
- Escalating Conflict: In states across India, human-wildlife conflict has intensified, leading to a significant rise in human casualties.
- For instance, in Maharashtra, the conflict resulted in 86 in 2021 and 105 deaths in 2022, marking a sharp increase compared to previous decades.
Causes:
- Factors contributing to this conflict include the encroachment of grodeathswing human and animal populations into each other's territories, habitat fragmentation due to legal and illegal land use changes, alterations in cropping patterns attracting wildlife to agriculture, and habitat destruction from invasive alien species.
- Despite having over 700 protected areas, a substantial portion of elephant, lion, and tiger ranges lie outside these protected zones, exacerbating the conflict.
Ecologist Perspective:
- Ecologist Madhav Gadgil highlights that the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 has inadvertently facilitated an environment where wild animals can invade human habitats with impunity.
- He cites the optimal foraging theory in ecology, which underscores animals' efforts to maximize nutrient intake while minimizing time, effort, and risks.
Solutions:
- Addressing the issue requires robust enforcement and pragmatic policies to mitigate conflict incidences.
- Engaging local communities, as suggested by the Future for All Report 2021 (by WWF and UNEP), fosters coexistence between humans and wildlife, acknowledging that complete elimination of conflicts is impractical.
- Additionally, awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about man-animal conflict and skill development initiatives for communities living near forests can alleviate pressures on agricultural and forest lands.
Kerala's Decision to Declare Man-Animal Conflict as a State-Specific Disaster:
- Implications of the Decision: Currently, the management of man-animal conflict falls under the jurisdiction of the forest department, operating in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Act.
- By designating man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, the responsibility for addressing it shifts to the state disaster management authority, empowered by the Disaster Management Act, enabling swifter and more decisive action.
- Rationale for the Decision: Instances of loss of life due to man-animal conflict have prompted calls to tranquilize, capture, or eliminate the responsible animals.
- Presently, the chief wildlife warden, holding the sole authority in the state, makes decisions regarding wild animals causing disturbances in human settlements.
- Past decisions to tranquilize aggressive animals, like wild elephants, have faced legal challenges.
- Under the disaster management authority, actions can be taken that supersede other regulations, including those outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act.
- According to the Disaster Management Act, except for the Supreme Court or a High Court, no court has jurisdiction to entertain suits or proceedings regarding actions taken by relevant authorities in line with the Act.
- Additionally, the Act stipulates that its provisions hold precedence over any other law during the specific period of a declared disaster.
Kerala's Success in Managing Man-Animal Conflict:
- Kerala, with approximately 5,700 wild elephants in 2017, comprising 19% of the nationwide population of 30,000, witnessed a significantly lower incidence of human fatalities caused by elephants, accounting for only 81 (4%) of the 2,036 deaths recorded in India between 2018 and 2021.
- Factors Contributing to Kerala's Effective Management of Man-Animal Conflict:
- Maintenance of Unchanged Wilderness Boundaries: Kerala has largely preserved the boundaries between wilderness and civilization in recent years, contributing to the mitigation of man-animal conflicts.
- Evolution of Agricultural Practices: Changes in agricultural practices, such as the cultivation of crops like coffee, pepper, and tea, which hold less appeal for elephants, have helped reduce conflicts between humans and elephants.
- Unique Elephant Characteristics: Individual elephants are identified and named based on their distinct characteristics, such as Kabali, an elephant residing in the Athirapally jungle in Thrissur district, known for its tendency to attack or chase automobiles.
- These factors collectively contribute to Kerala's successful management of man-animal conflict, resulting in relatively fewer human fatalities caused by elephants compared to other regions in India.
Countries hope to bring BBNJ or High Seas treaty into force by 2025

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Blue Leaders High-Level Event on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction was held in Belgium on March 7, 2024, to urge nations to ratify a new treaty to protect the high seas from pollution, climate change and overfishing.
What is the BBNJ Treaty?
- The BBNJ Treaty, also referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas, is an international agreement aimed at conserving and sustainably managing marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, operating within the framework of the UNCLOS.
- These areas encompass the high seas beyond exclusive economic zones or national waters.
- It represents nearly half of the Earth's surface and is characterized by minimal regulation and understanding of their biodiversity, with only 1% currently under protection.
- Launched at the One Ocean Summit in February 2022, the High Ambition Coalition on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction seeks to unite various delegations involved in BBNJ negotiations toward a comprehensive and ambitious outcome.
- The negotiations focus on key elements agreed upon in 2015, including the conservation and sustainable use of marine genetic resources, area-based management tools such as marine protected areas, environmental impact assessments, and initiatives for capacity-building and technology transfer in marine science and management.
- India is yet to sign the treaty. However, it called on efforts for entry into force and implementation of the treaty at the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration held in September 2023.
The Importance of a Legally Binding Instrument for BBNJ:
- Biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction is crucial for ocean health, coastal communities' welfare, and global sustainability, constituting 95% of the ocean and offering essential ecological, economic, social, cultural, scientific, and food-security benefits.
- Despite their significance, these areas face escalating threats such as pollution, overexploitation, and the impacts of climate change, compounded by the anticipated rise in demand for marine resources in the future.
- Even the deep seafloors, considered one of the most inhospitable habitats, are experiencing the onset of extinction processes, with alarming statistics showing that 62% of assessed mollusc species are threatened, including critically endangered, endangered, and vulnerable species, while the International Seabed Authority permits deep sea mining contracts.
- It is imperative to establish a legally binding framework for managing and regulating biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, as over 60% of this resource in the global seas remains unmanaged and unprotected, necessitating comprehensive conservation measures.
ISRO’s second rocket launchport in Tamil Nadu’s Kulasekarapattinam

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the second rocket launchport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at Kulasekarapattinam on February 28.
Why does India need a new launchport?
- With the Union government’s recent policy announcing the opening of the space sector to private players, a sharp rise in the number of commercial launches is certain.
- To ensure that ISRO’s first launchport, the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota, is not overburdened with a high number of launches, the space agency has decided to build another facility.
- While SHAR will be only used for launching bigger and heavy-lift-off missions, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport will be used to launch smaller payloads.
- SHAR will also be available for India’s big ticket missions to the Moon, Venus, and much touted human-flight mission, the Gaganyaan.
- Private players could develop space-qualified sub-systems, build satellites, and even launch vehicles using the new launchport.
- It will also facilitate dedicated launch infrastructure for all the on-demand commercial launches.
Why is the new ISRO launchport located in Tamil Nadu?
- Geographically, scientifically, and strategically, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport provides a natural advantage to ISRO’s future launches pertaining to the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
- Allowing a direct southward and smaller launch trajectory for the light weight SSLVs carrying less fuel, the Kulasekarapattinam facility will boost ISRO’s attempts to enhance payload capacities.
- Currently, the trajectory followed by all launches from SHAR are longer as they follow a path which requires the vehicle to skirt eastwards around Sri Lanka before taking the actual southward flight.
- This consumes additional fuel. However, the same would not be required for future launches from Kulasekarapattinam, which is geographically located several kilometers to the west of Colombo, thereby allowing a straight southward flight and simultaneously saving the already limited fuel available onboard SSLV.
- Notably, both the launch ports are located in Southern India, near the equator.
- For a launch site close to equator the magnitude of the velocity imparted due to Earth’s rotation is about 450 m/s, which can lead to substantial increase in the payload for a given launch vehicle.
- Geostationary satellites must necessarily be in the equatorial plane.
- So, for such satellites, the closer the launch site is to the equator the better it is.
What are SSLVs?
- SSLV is the new small satellite launch vehicle developed by ISRO to cater for the launch of small satellites.
- It has a three-stage launch vehicle, having a lift-off weight of about 120 tonnes and is 34 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter.
- SSLV is designed with a three-stage solid propulsion and a liquid propulsion stage, which is the terminal stage.
- The SSLV missions are useful to launch small-sized satellites weighing anywhere between 10 to 500kg into the Low Earth Orbit.
- Going by their size and weight, these are typically referred to as mini, micro or nano satellites.
- They are low on cost and intended satellite insertion into orbits takes a shorter flight time.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
- Previously, satellite projects built by college students and private players involved in the space sector have benefitted from SSLV missions.
What are the features of SHAR?
- SHAR is situated along the east coast of Andhra Pradesh and is located 80 km off Chennai.
- It currently provides launch infrastructure to all ISRO missions.
- It is equipped with a solid propellant processing setup, static testing, and launch vehicle integration facilities, telemetry services — tracking and command network to oversee the launch — and a mission control center.
- SHAR has two launch complexes that are routinely used to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the Geosynchronous Space Launch Vehicles (GSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III, now renamed as LVM3.
Haiper, the text-to-video model created by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a company founded by former members of Google DeepMind, TikTok, and top labs from research academia — introduced an eponymous new text-to-video model Haiper.
What is Haiper?
- Haiper is an all-in-one visual foundation model that allows everyone, with or without technical training, to generate high-quality video content with ease.
- The founders claim that Haiper brings forward cutting-edge machine learning with the belief that creativity should be “fun, surprising, and shareable”.
- The company has built Haiper as a powerful, industry-agnostic creativity tool.
- It was released by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni.
What does Haiper do?
- Haiper offers tools such as text-to-video, animated static images, video repainting tools, etc.
- Users can go on to the website, log in with their email addresses, and start generating videos for free by typing in text prompts.
- At present, users can only generate HD video spanning 2 seconds, and a slightly lower-quality video could go up to four seconds.
Strengths and limitations:
- While the short length is a limitation, the company is working towards extending the video outputs.
- Presently, the tool is free to use, with an aim to build a community.
- While OpenAI’s Sora is still not available for the public, Haiper is offering users to try its tool for free on its website.
Controversy Erupts as Tamil Nadu Governor Refers to Ayya Vaikundar as 'Sanatan Dharma Savior'

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu Governor R N Ravi’s recent remarks about the 19th-century social reformer Ayya Vaikundar — that he was Lord Vishnu incarnated to prevent the destruction of Sanatan Dharma — have evoked sharp reactions in the state, from politicians as well as Vaikundar’s followers.
Who was Ayya Vaikundar?
- Ayya Vaikundar, born in 1809, is revered as a social reformer and the founder of the Ayyavazhi sect, primarily in southern Tamil Nadu.
- His teachings focused on equality, fraternity, and the eradication of caste-based discrimination, challenging the established religious and social hierarchies of the time.
- At a time when rigid casteism and caste-based atrocities were the norm, Vaikundar introduced measures to challenge these divisions.
- He organized Samapanthi-bhojana or community eateries for people from all backgrounds.
- He would send his disciples to the homes of lower castes to eat with them.
- When lower castes were not allowed to fetch water from wells used by upper caste Hindus, Vaikundar initiated the digging of common wells, called Muthirikinarus.
- At a time when priests threw vibhuti and sandal paste at devotees from a distance to avoid touching them and lower castes were not allowed to enter temples at all, Vaikundar introduced Thottu Namam, in which he inspired priests to apply the sacred paste on devotees’ forehead, irrespective of their caste.
- The paste would be applied in the form of a lamp, indicating the soul and God, representing the form of God inside every life.
- Vaikundar also encouraged all devotees to wear turbans and dhotis, promoting equality.
- He initiated the Thuvayal Panthy programme, teaching vegetarianism and discipline to followers, who spread these teachings across Tamil Nadu.
- He established Nizhal Thangals as community worship spaces, which did not have any idol or deity, and only Tamil was used for worship.
- These community worship centers also had community kitchens and even basic schools.
- He pioneered education for the lower castes and opposed discriminatory taxes.
- One of his significant interventions was the introduction of simplified, inclusive marriage customs without a Brahmin priest or Sanskrit mantras.
Trees in Corbett fell prey to greedy nexus, says Supreme Court

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Wednesday condemned the illegal felling of over 6,000 trees to construct buildings, ostensibly for “eco-tourism” at the Jim Corbett National Park in Uttarakhand, as a “classic case” of nexus between politicians and officials working to ransack the environment for short-term commercial ends.
News Summary:
- In 2023, a series of applications brought attention to the creation of alleged illegal buildings and encroachment on water bodies, prompting court intervention.
- Petitioners highlighted violations of environmental norms and encroachment into core wildlife habitats.
- Evidence presented during proceedings revealed unauthorized constructions within the national park, including concrete and iron enclosures purportedly intended for a 'safari' experience.
- Moreover, it was disclosed that over 6,000 trees had been felled in the national park under the pretext of safari development.
Supreme Court’s Observations:
- The Court has raised concerns regarding the necessity of developing facilities within natural forest environments, particularly in areas designated for the protection of endangered species like tigers.
- Directing the Government to establish a committee, the Supreme Court seeks recommendations on whether tiger safaris should be permitted in buffer or fringe areas and what guidelines should govern their establishment if allowed.
- Additionally, the Court has strongly criticized the illegal constructions and extensive tree felling in Uttarakhand's Corbett National Park.
What are the Core and Buffer Areas in Tiger Reserves?
- As per the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act of 2006, a Tiger Reserve comprises core or critical habitat and a buffer zone surrounding it.
- Core areas hold the legal status of a National Park or a Sanctuary.
- Buffer zones consist of a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple-use area.
- The buffer area acts as a protective barrier, absorbing the impact of poaching pressure on tiger and other wildlife populations.
About Jim Corbett National Park:
- Location: Situated in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand, Jim Corbett National Park is renowned for its rich biodiversity.
Key Facts:
- Established in 1935, it is India’s oldest national park.
- Initially named Hailey National Park after its founder Sir Malcolm Hailey, it was renamed Corbett National Park in 1956 to honor Jim Corbett's contributions to wildlife preservation in India.
- Corbett National Park boasts the highest population of tigers in India, highlighting its importance for tiger conservation efforts.
- Flora: Dominated by Sal, Semal, Kharpat, Sissoo, Khair, Dhak, Khingan, Bakli, Bel, Ber, Bamboo, Khingam, Jamun, Kanju, Rohini, and Pula trees.
- Sal, Khair, and Sissoo are prominently featured throughout the park.
- Fauna: Home to diverse wildlife including Tiger, Leopard, Elephant, Chital Deer, Sambar Deer, Hogg Deer, Barking Deer, Wild Boar, Langur, Wild pig, Rhesus Monkey, Jackal, Rabbit, Yellow Throated Martin, and Otters.
- Various reptiles such as Crocodile, Gharial, King Cobra, Common Krait, Cobra, Russell's Viper, Rock Python, and Monitor Lizard inhabit the park.
- The Kosi River feeds the eastern periphery of Corbett National Park.
- The Ramganga River (West) and its tributaries Sonanadi, Palain, and Mandal serve as significant hydrological resources for the park.
Vaishnaw bats for further simplification of economic laws at ‘NITI for States’ platform launch

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union IT, Communications, and Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw Thursday stressed on the need to further simplify economic laws in a modern and relevant way at the launch of NITI Aayog’s ‘NITI for States’ platform.
About “NITI For States” Platform:
- It serves as a cross-sectoral knowledge hub envisioned to be a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Policy and Good Governance.
Key features include:
- A comprehensive repository comprising Best Practices, Policy documents, datasets, data profiles, and NITI publications across various sectors.
- Knowledge products spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes (Gender and Climate Change), such as Agriculture, Education, Energy, Health, Manufacturing, MSME, Tourism, Urban, and Water resources & WASH.
- An intuitive and user-friendly interface accessible via multiple devices, including mobile phones.
- The platform aims to catalyze digital governance transformation by providing government officials with contextualized, actionable knowledge and insights, thereby enhancing decision-making quality.
- It supports district collectors and block-level functionaries by granting access to innovative best practices from various States and Union Territories.
What is the Viksit Bharat Strategy Room?
- It serves as an interactive platform enabling users to visualize data, trends, best practices, and policies in an immersive manner, facilitating a comprehensive assessment of any problem statement.
- The platform features voice-enabled AI for user interaction and facilitates connectivity with multiple stakeholders through video conferencing.
- Designed as a plug-and-play model, it enables replication by states, districts, and blocks for widespread adoption.
- Collaboration with various government organizations by NITI Aayog includes:
- iGOT Karmayogi's "SAMARTH" online training modules accessible through the platform.
- Integration of NITI Aayog’s National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) to provide access to government datasets.
- Support from the National E-Governance Division (NeGD) in developing the innovative Viksit Bharat Strategy Room.
- Multi-lingual support provided by Bhashini.
- Integration of PM Gatishakti BISAG-N team, with DPIIT support, to offer geospatial tools for Area Based Planning.
INS Jatayu, India’s new naval base in Lakshadweep

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Wednesday (March 6), Naval Detachment Minicoy will be commissioned as INS Jatayu, an upgraded naval base, marking an important milestone in the Indian Navy’s resolve to incrementally augment security infrastructure at the strategic Lakshadweep Islands.
About INS Jatayu Naval Base:
- The existing Naval Detachment Minicoy, which is under the operational command of the Naval Officer-in-Charge (Lakshadweep), will be commissioned as INS Jatayu.
- A naval detachment has administrative, logistics, and medical facilities.
- INS Jatayu will be upgraded to a naval base with additional infrastructure such as an airfield, housing, and personnel, after obtaining the requisite environmental and other clearances.
- The fragile ecology of the island may pose challenges for the construction but there are plans to construct a new airfield that will be capable of operating both military and civil aircraft.
Significance of INS Jatayu?
- The basing of an independent naval unit with requisite infrastructure and resources will enhance its overall operational capability in the islands.
- The establishment of the base is in line with the government’s focus on comprehensive development of the islands.
- The base will enhance its operational reach, facilitate its anti-piracy and anti-narcotics operations in the western Arabian Sea, and augment its capability as the first responder in the region.
- With the commissioning of INS Jatayu, the Indian Navy will add to its strength on the western seaboard.
- The proposed airfield will allow operations for a range of aircraft, including P8I maritime reconnaissance aircraft and fighter jets, and extend the Navy’s reach and operational surveillance capabilities at a time when India is seeking to counter the growing Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- This has an immediate bearing at a time when India’s relations with the Maldives have come under strain since the election of the pro-China President Mohamed Muizzu.
About the Lakshadweep Islands:
- Lakshadweep, ‘a hundred thousand islands’ in Sanskrit and Malayalam, is an archipelago of 36 islands located between 220 km and 440 km from Kochi.
- The islands, only 11 of which are inhabited, have a total area of only 32 sq km.
- The Lakshadweep are part of a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean that includes Maldives to the south, and the Chagos archipelago farther beyond, to the south of the equator.
- Given their location in the Indian Ocean, the Lakshadweep are of huge strategic importance to India.
- Minicoy straddles vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs) — the world’s main maritime highways — including the Eight Degree Channel (between Minicoy and Maldives) and the Nine Degree Channel (between Minicoy and the main cluster of Lakshadweep islands).
- In consequence, the Lakshadweep Islands are also vulnerable to marine pollution.
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
Holistic Progress Card: How NCERT is planning to change student assessment

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The New Education Policy (NEP), established in 2020, proposed redesigning the assessment system of school students in India recently.
About the Holistic Progress Card (HPC):
- It Is Developed by Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development (PARAKH), a standard-setting body under the NCERT.
- The Holistic Progress Card (HPC) marks a significant departure from traditional assessment methods for students in the foundational stage (Classes 1 and 2), preparatory stage (Classes 3 to 5), and middle stage (Classes 6 to 8), aligning with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Features:
- Incorporates feedback from parents, classmates, and self-evaluation by students.
- Aims to provide a comprehensive view of students' academic performance, cognitive abilities, socio-emotional skills, and creativity during class activities.
- Aligns with the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE) to prioritize learner-centric evaluation.
- Emphasizes a shift from numerical grades to a 360-degree evaluation, focusing on students' active engagement in class activities and the demonstration of diverse skills and competencies.
- Enables teachers to identify students' strengths and weaknesses, fostering personalized support and intervention.
- Encourages students to reflect on their progress and set academic and personal goals, fostering self-awareness and accountability.
- Involves parents in the learning process, integrating their insights on homework, classroom engagement, and extracurricular activities.
- Includes peer evaluation, allowing students to assess their classmates' contributions to activities.
Benefits:
- Goes beyond numerical grades, providing descriptive and analytical evaluations that encompass academic achievements and critical skill development.
- Promotes a shift from summative to formative assessment, fostering competency-based evaluation and holistic growth.
Majuli Island's Mask Craft Celebrated With Geographical Indication Tag

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Adding to their growing national and international recognition, the traditional Majuli masks in Assam were given a Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Centre recently.
What are Majuli Masks?
- These handmade masks are traditionally used to depict characters in bhaonas, or theatrical performances with devotional messages under the neo-Vaishnavite tradition.
- Majuli, the largest river island in the world and the seat of Assam’s neo-Vaishnavite tradition, has been home to the art of mask-making since the 16th century.
- It was introduced by the 15th-16th century reformer saint Srimanta Sankardeva.
- The masks can depict gods, goddesses, demons, animals and birds — Ravana, Garuda, Narasimha, Hanuman, Varaha Surpanakha all feature among the masks.
- They can range in size from those covering just the face (mukh mukha), which take around five days to make, to those covering the whole head and body of the performer (cho mukha), which can take up to one-and-a-half months to make.
- According to the application made for the patent, the masks are made of bamboo, clay, dung, cloth, cotton, wood and other materials available in the riverine surroundings of their makers.
Why is This Art Practiced in Monasteries?
- Sattras are monastic institutions established by Srimanta Sankardev and his disciples as centers of religious, social and cultural reform.
- Today, they are also centers of traditional performing arts such as borgeet (songs), sattriya (dance) and bhaona (theater), which are an integral part of the Sankardev tradition.
- Majuli has 22 sattras, and the patent application states that the mask-making tradition is by and large concentrated in four of them:
- Samaguri Sattra
- Natun Samaguri Sattra
- Bihimpur Sattra and
- Alengi Narasimha Sattra
What is Majuli Manuscript Painting?
- It is a form of painting which also received the GI tag.
- It originated in the 16th century done on sanchi pat, or manuscripts made of the bark of the sanchi or agar tree, using homemade ink.
- The earliest example of an illustrated manuscript is said to be a rendering of the Adya Dasama of the Bhagwat Purana in Assamese by Srimanta Sankardev.
- This art was patronized by the Ahom kings.
- It continues to be practiced in every sattra in Majuli.
India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s legal gender gap index

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's ranked improved to 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s Women, Business and Law index, according to the 10th edition of the report released Monday.
About Women, Business and Law Index:
- The "Women, Business and the Law (WBL)" index is a project of the World Bank Group, specifically designed to measure the legal environment for women's economic opportunities across 190 economies.
- It's distinct from a general "Gender Equality Index" as it focuses specifically on legal frameworks and their impact on women's involvement in business and professional life.
What does it Measure?
- The WBL index assesses legal frameworks across eight indicators:
- Mobility (freedom of movement)
- Workplace (discrimination, maternity leave, etc.)
- Pay (equal pay for equal work)
- Marriage (property rights, domestic violence)
- Parenthood (parental leave, child custody)
- Entrepreneurship (starting and running a business)
- Assets (ownership and inheritance)
- Pension (access to and benefits)
- Scoring: Each indicator is scored on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 representing the highest level of legal rights and protections for women.
- The overall score for a country is the average of these eight indicators.
- Latest version: The latest edition is "Women, Business and the Law 2024", released in October 2023.
- This version also introduces two new indicators:
- Safety (addressing violence against women)
- Childcare (availability, affordability, and quality)
Highlights of the Report:
- Women spend an average of 2.4 more hours a day on unpaid care work than men—much of it on the care of children.
- Only 62 economies—fewer than a third—have quality standards governing childcare services, which has an adverse impact on the employment opportunity of women as mothers with young children have their battles to pick.
- Women face hindrances in areas such as entrepreneurship as just one in every five economies mandate gender-sensitive criteria for public procurement processes, meaning women are deprived of significant economic opportunities.
About India:
- According to the 10th edition of the Women, Business and Law index, India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the Index.
- The addition of Safety and childcare as indicators in the new index is believed to have improved India’s ranking slightly.
- The index shows that in India, women enjoy 60% of the legal rights compared to men, which is lower than the global average of 64.2%, but much higher than the 45.9% of the legal protections compared to men.
- Over the years, India’s score has remained constant at 74.4%, whereas a total of 14 countries around the world, including Denmark, Canada, and Finland, score a perfect 100 in the legal framework score.
- Some of the less developed countries like Ethiopia, Namibia, and even Burundi have better scores than India.
- India’s performance is much lower in providing supportive frameworks, such as programs, services, budgets, procedures, inspections, and sanctions for non-compliance with quality standards.
- Only 54.2% of the supportive frameworks needed were established in the country.
Venice Biennale, ‘the Olympics of the art world’, set to open on April 20

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 60th edition of the Venice Biennale, known as “the Olympics of the art world”, will open on April 20.
What is the Venice Biennale?
- The Venice Biennale is one of the biggest and most prestigious art fairs in the world.
- Biennale is an Italian word which means ‘every other year’. Over the years, however, it has come to mean a large international exhibition that takes place every two years.
- A biennale exhibition is different from a regular exhibition as it is organized on a large scale and involves multiple venues.
- Biennales feature contemporary art by artists from various countries that are usually linked by a common curatorial theme, providing a framework for exploring contemporary social, economic and political ideas in an international context.
India’s participation:
- India made its debut at the Biennale in 1954. Recording robust sales, the exhibition comprised over 50 paintings of masters such as M F Husain, S H Raza, Jamini Roy, Amrita Sher-Gil, and Francis Newton Souza.
- After 1954, the country officially participated in the event in 2011. The exhibition was organized by Lalit Kala Akademi and curated by Ranjit Hoskote.
- It featured works by artists like Zarina Hashmi, Gigi Scaria, Praneet Soi, and the Desire Machine Collective.
- At the 2019 Venice Biennale, the Ministry of Culture, Confederation of Indian Industry, National Gallery of Modern Art, and Kiran Nadar Museum of Art (KNMA) in collaboration organized the Indian pavilion.
Will India have a presence at the 2024 Venice Biennale?
- This year, the Biennale is helmed by its first Latin American curator — the artistic director of the São Paulo Museum of Art, Adriano Pedrosa.
- His theme for the event is “Foreigners Everywhere”, which will delve into the experiences of those living on the margins, as outsiders, immigrants or indigenous populations.
- Works by Indian artists will also feature in this central exhibition.
- This includes the late modernists Ram Kumar, B Prabha, SH Raza, Jamini Roy, Amrita Sher-Gil, FN Souza, and Goa-based Monika Correa.
- Representing the contemporary will be the public art collective Aravani Art Project, led by trans and cis women.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi witnessed the start of the process of core-loading the indigenous prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) at the Madras Atomic Power Station in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
What is the PFBR?
- The PFBR, or Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, is a nuclear reactor designed to produce more nuclear fuel than it consumes.
- In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom absorbs a neutron, becomes unstable, and splits into two, releasing energy.
- If the unstable nucleus releases additional neutrons, the reactor’s facilities can utilize them to initiate more fission reactions.
How does the PFBR work?
- PHWRs use natural or low-enriched U-238 as the fissile material and produce Pu-239 as a byproduct.
- This Pu-239 is combined with more U-238 into a mixed oxide and loaded into the core of a new reactor together with a blanket.
- This is a material the fission products in the core react with to produce more Pu-239.
- A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor that produces more fissile material than it consumes.
- In a ‘fast’ breeder reactor, the neutrons aren’t slowed, allowing them to trigger specific fission reactions.
- The PFBR is designed to produce more Pu-239 than it consumes.
- It uses liquid sodium, a highly reactive substance, as coolant in two circuits. Coolant in the first circuit enters the reactor and leaves with (heat) energy and radioactivity.
- Via heat-exchangers, it transfers only the heat to the coolant in a secondary circuit.
- The latter transfers the heat to generators to produce electricity.
DoT launches Digital Intelligence Portal, ‘Chakshu’ facility to curb cyber crimes, financial frauds

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) recently launched its ‘Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)’ to curb the misuse of telecom resources in cybercrimes and financial frauds, and the ‘Chakshu’ facility on the Sanchar Saathi portal to enable citizens to report suspected fraud communication.
About Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP):
- Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) is developed by the Department of Telecommunications.
- It is a secure and integrated platform for real time intelligence sharing, information exchange and coordination among the stakeholders i.e. Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), law enforcement agencies (LEAs), banks and financial institutions (FIs), social media platforms, identity document issuing authorities etc.
- The portal also contains information regarding the cases detected as misuse of telecom resources. The shared information could be useful to the stakeholders in their respective domains.
- It also works as a backend repository for the citizen-initiated requests on the Sanchar Saathi portal for action by the stakeholders.
- The DIP is accessible to the stakeholders over secure connectivity and the relevant information is shared based on their respective roles.
- The said platform is not accessible to citizens.
What is the Chakshu Facility?
- Chakshu is the latest addition to the citizen centric facilities already available on the Sanchar Saathi portal of DoT.
- It facilitates citizens to report suspected fraud communication received over call, SMS or WhatsApp with the intention of defrauding like KYC expiry or update of bank account / payment wallet / SIM / gas connection / electricity connection, sextortion, impersonation as government official / relative for sending money, disconnection of all mobile numbers by Department of Telecommunications etc.
- In case, a citizen is already a victim of cyber-crime or financial fraud, it is advised to report at cyber-crime helpline number 1930 or website https://www.cybercrime.gov.in of Government of India.
Carbon Capture and How it Can Help Save the Planet

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Germany has recently declared its approval for carbon capture and offshore storage for specific industrial sectors.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage?
- CCS refers to a host of different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large point sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- Notably, CCS is different from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), where CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
- CCS involves three different techniques of capturing carbon, including: Post-combustion, Pre-combustion, and Oxyfuel combustion.
- In post-combustion, CO2 is removed after the fossil fuel has been burnt. By using a chemical solvent, CO2 is separated from the exhaust or ‘flue’ gasses and then captured.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel. “First, the fossil fuel is partially burned in a ‘gasifier’ to form synthetic gas. CO2 can be captured from this relatively pure exhaust stream,” according to a report by the British Geological Survey. The method also generates hydrogen, which is separated and can be used as fuel.
- In oxyfuel combustion, the fossil fuel is burnt with almost pure oxygen, which produces CO2 and water vapor. The water is condensed through cooling and CO2 is separated and captured. Out of the three methods, oxyfuel combustion is the most efficient but the oxygen burning process needs a lot of energy.
- Post-combustion and oxyfuel combustion equipment can be retro-fitted in existing plants that were originally built without them. Pre-combustion equipment, however, needs “larger modifications to the operation of the facility and are therefore more suitable to new plants.
- After capture, CO2 is compressed into a liquid state and transported to suitable storage sites.
- Although CO2 can be transported through ship, rail, or road tanker, pipeline is the cheapest and most reliable method.
Can Carbon Capture Help Save the world?
- Operational CCS projects generally claim to be 90 percent efficient, meaning they can capture 90 per cent of carbon and store it.
- Studies, however, have shown that a number of these projects are not as efficient as they claim to be.
- For example, a 2022 study by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) found most of the 13 flagship CCS projects worldwide that it analyzed have either underperformed or failed entirely.
- Moreover, CCS technologies are quite expensive.
- When CCS is attached to coal and gas power stations it is likely to be at least six times more expensive than electricity generated from wind power backed by battery storage.
- It is far cheaper and more efficient to avoid CO2 emissions in the first place.
- There are also only a few operational CCS projects across the world even though the technology has been pushed for decades.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there were 40 operational CCS projects in 2023, which captured more than 45 metric tonnes (Mt) of CO2 annually.
- To ensure the planet doesn’t breach the 1.5 degree Celsius temperature increase limit, it would take an “inconceivable” amount of carbon capture “if oil and natural gas consumption were to evolve as projected under today’s policy settings.
- It added that the electricity required to capture that level of carbon as of 2050 would be more than the entire planet’s use of electricity in 2022.
- Therefore, there couldn’t be an overreliance on carbon capture as a solution to tackle climate change.
Grey-zone Warfare Latest Entry in Lexicon of Warfare

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the last day of the 2024 Raisina Dialogue (February 24), India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan said that “grey zone warfare” is the latest in informal warfare.
What is the Grey Zone Warfare?
- Grey zone warfare refers to a strategic approach where a nation seeks to gain advantages over others without engaging in overt conflict.
- It involves a series of tactics, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and economic pressures, aimed at subtly undermining or destabilizing adversaries.
- China has notably employed this strategy against India and neighboring countries.
What are the China's Grey Zone Tactics Against India?
- South China Sea Activities: China asserts its dominance in the South China Sea using naval and civilian vessels, raising tensions with neighboring countries like India.
- Infrastructure Near Borders: China constructs infrastructure and settlements near India's borders, bolstering territorial claims and strategic positioning.
- Digital Investments: China invests in Indian digital platforms and media, influencing public narratives and perceptions.
India's Counter-Measures:
- Inter-Agency Collaboration: India promotes collaboration among defense, intelligence, and law enforcement agencies to devise comprehensive strategies to counter grey zone threats.
- Enhanced Vigilance: India increases surveillance and presence in border areas and strategic locations to detect and respond to covert Chinese activities.
- Regulating Foreign Investments: India scrutinizes foreign investments in critical sectors, particularly technology, to safeguard national security interests.
Long-Term Implications for India:
- Information Warfare: Grey zone conflicts often involve digital misinformation, influencing public opinion and perceptions.
- Economic Leverage: Dependency on foreign investments poses vulnerabilities if used as leverage by investing nations.
- Technology Dependency: Heavy reliance on foreign technology exposes India to risks, emphasizing the need to bolster indigenous technological capabilities.
Conclusion
Grey zone warfare encompasses a multifaceted strategic landscape, blending digital, economic, and geopolitical tactics. India recognizes these challenges and is actively devising strategies to navigate this complex terrain.
PM Modi hails those supporting wildlife conservation efforts on World Wildlife Day

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of World Wildlife Day on March 3, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded those at the forefront of sustainable practices and supporting wildlife conservation efforts.
About the World Wildlife Day:
- World Wildlife Day is observed to advocate for sustainable practices that contribute to biodiversity conservation and to enhance public consciousness about the importance of safeguarding and nurturing animals.
- It endeavors to underscore the interconnectedness of all life forms on Earth and to foster harmonious coexistence between humans and animals through activism, advocacy, and education.
Origins:
- Initially proposed by Thailand to the UN General Assembly in 2013, World Wildlife Day aimed to dedicate a day to spotlight the significance of wild animals and plants worldwide.
- On December 20, 2013, the General Assembly adopted a resolution, designating March 3 as World Wildlife Day from 2014 onwards.
- Coinciding with the day, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) was signed in 1973, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding species from the threats of international trade.
The theme of WWD 2024:
- The theme, "Connecting People and Planet: Exploring Digital Innovation in Wildlife Conservation," underscores the potential of technological advancements to revolutionize conservation efforts.
- In today's digital era, technological breakthroughs offer novel solutions to persistent conservation challenges, making this theme particularly relevant.
Significance:
- World Wildlife Day serves as a vital global awareness platform for animal protection and conservation.
- It reinforces the intrinsic value of animals and advocates for treating them with compassion, integrity, and reverence.
About the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- CITES is an international treaty that aims to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered plants and animals, including their parts and derivatives, to ensure their survival in the wild.
- Under CITES, member countries are required to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered species through a system of permits and quotas.
- They must also report regularly on their implementation of the treaty and collaborate with other countries to ensure its effectiveness.
- Currently, CITES has 184 parties.
Supreme Court’s ban on Patanjali ads

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court restrained Patanjali Ayurved from discrediting allopathy in its campaigns, and from advertising products that claim to cure chronic conditions.
What is the Magic Remedies Act?
- The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act of 1954 is a legislative framework to control the advertisement of drugs and prohibit claims of magical qualities in remedies.
- The Act encompasses various forms of advertisements, including written, oral, and visual mediums.
What does the Magic Remedies Act entail?
- Under the Act, “drug” refers to medicines intended for human or animal use, substances for diagnosis or treatment of diseases, and articles affecting the body’s functions.
- Other than articles meant for consumption, the definition of “magic remedy” under this Act also extends to talismans, mantras, and charms that allegedly possess miraculous healing powers or influence bodily functions.
Regulations on advertisements under the Magic Remedies Act:
- The Act imposes strict regulations on the publication of advertisements related to drugs.
- It prohibits advertisements that give false impressions, make false claims, or are otherwise misleading.
- The term “advertisement,” under the Act, extends to all notices, labels, wrappers, and oral announcements.
- Violations of these provisions can result in penalties upon conviction, including imprisonment or fines.
Punishment:
- Violating the Act can result in imprisonment, fines, or both.
- If this is the first conviction for the violator, they may face up to six months in prison, fines, or both.
- For a subsequent conviction, imprisonment may extend to one year, a fine, or both.
- The Act does not include any limits for the fines that may be imposed on individuals or organizations.
Who comes under the Magic Remedies Act?
- The Act applies to all individuals and entities involved in the publication of advertisements, including manufacturers, distributors, and advertisers.
- The Act can hold both individuals and companies accountable for contraventions.
Several OPEC+ nations extend oil cuts to boost prices

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Moscow, Riyadh, and several other OPEC+ members announced extensions to oil production cuts first announced in 2023 as part of an agreement among oil producers to boost prices following economic uncertainty.
What is the OPEC+ Oil Alliance?
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-exporting nations that convenes regularly to determine the quantity of crude oil to offer on the global market.
- Origin: This alliance was established in late 2016 to formalize a framework for collaboration between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations on a consistent and sustainable basis.
- The primary objective of these nations is to collaborate on regulating crude oil production to stabilize the oil market.
- OPEC+ collectively controls approximately 40% of global oil supplies and holds over 80% of proven oil reserves.
- At its core, OPEC+ consists of OPEC member states, predominantly comprising nations from the Middle East and Africa.
- Membership: It includes OPEC member states along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- OPEC, short for the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent intergovernmental organization comprised of oil-exporting nations.
Mission:
- To coordinate and harmonize the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- To ensure the stability of oil prices in global oil markets, aiming to eliminate detrimental and unnecessary fluctuations.
- Formation: Founded in 1960 by the five original members - Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Presently, it consists of 13 member countries, which include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Headquarters: Located in Vienna, Austria.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Indian security agencies have intercepted a Pakistan-bound ship from China at Mumbai's Nhava Sheva port.
What are CNC Machines and Wassenaar Arrangements?
- CNC machines are controlled by a computer and offer efficiency, consistency, and accuracy not possible manually.
- These machines have been included in the Wassenaar Arrangement since 1996.
- This international arms control regime aims to stop the proliferation of equipment with both civilian and military uses, with India being among the 42 member countries exchanging information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies.
About the Wassenaar Arrangement:
- The Wassenaar Arrangement is a voluntary export control framework established in July 1996.
- Comprising 42 member nations, it facilitates the exchange of information regarding transfers of conventional weaponry and dual-use goods and technologies.
- Dual-use items possess the capacity for both civilian and military applications.
- The arrangement's secretariat is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
Membership:
- The arrangement boasts 42 member states, predominantly consisting of NATO and EU nations.
- Members are obligated to report arms transfers and dual-use goods and technology transfers or denials to destinations beyond the arrangement biannually.
- India became a member of the Arrangement in 2017.
Objectives:
- Central to its operation is the continual exchange of technology-related information, encompassing both conventional and nuclear-capable technologies, among member states.
- This information exchange involves the maintenance and refinement of comprehensive lists of materials, technologies, processes, and products deemed militarily significant.
- The primary goal is to regulate the movement of technology, materials, or components to entities or nations that could jeopardize global security and stability.
Wassenaar Arrangement Plenary:
- The WA Plenary is the decision-making and governing body of the Arrangement.
- It is composed of representatives of all Participating States who normally meet once a year, usually in December.
- Chairmanship of the Plenary is subject to annual rotation among Participating States.
- In 2018, the United Kingdom held the Plenary Chair, while Greece assumed the position in 2019.
- Decisions within the Plenary are made through consensus.
Bengaluru's Rameshwaram cafe blast puts the spotlight on IEDs

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least nine people were injured after an explosion at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area recently, possibly by an improvised explosive device (IED).
What is Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)?
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) refers to a makeshift explosive device constructed and deployed unorthodoxly or improvised.
- These devices are typically crafted using commonly available materials, including explosives, triggers, and containers, often to cause destruction, injury, or death.
- IEDs can vary widely in design and complexity, ranging from simple pipe bombs to more intricate devices incorporating timers, remote controls, or even cellular communication for activation.
- IEDs can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- Due to their adaptable nature, IEDs are commonly used by insurgents, terrorists, and other malicious actors to carry out attacks against both military and civilian targets.
- Their unpredictable nature and often concealed placement make them particularly challenging for security forces to detect and mitigate.
- Efforts to counter IED threats involve a combination of technological advancements, intelligence gathering, and counterinsurgency strategies aimed at identifying and neutralizing these devices before they can cause harm.
Types of IEDs:
- Vehicle-Borne IEDs: Among the most destructive forms of IEDs are those concealed within vehicles. These can be driven to specific locations and detonated, causing massive explosions capable of levelling buildings.
- Suicide Bombings: Suicide bombings involve individuals strapping IEDs to their bodies, becoming human carriers of destruction. This method inflicts maximum damage in densely populated areas.
- Package IEDs: Package IEDs are small devices hidden in innocuous-looking packages. They are often placed in public spaces, targeting unsuspecting victims.
Methods of IED Initiation:
- Remote Control: IEDs can be remotely triggered using various methods, such as cell phones or radio signals, allowing attackers to maintain a safe distance from the explosion.
- Pressure Activation: Pressure-sensitive IEDs detonate when a certain amount of pressure is applied, making them lethal traps for those who inadvertently trigger them.
- Timers: IEDs can also be equipped with timers, which delay the explosion to occur at a specific time, further complicating detection and prevention.
The Devastating Impact of IEDs:
- The aftermath of IED explosions is often catastrophic, leading to loss of life, severe injuries, and widespread damage to infrastructure.
- The psychological impact on survivors and affected communities can be long-lasting.
Detection Technologies and Challenges:
- Detection technologies such as (Metal Detectors, X-ray and Imaging Scanners, Explosive Trace Detection (ETD), and Sniffer Dogs) play a critical role in countering the threat of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), but they also face numerous challenges due to the evolving nature of these devices.
India to Make Climate Risk Disclosures Mandatory for Banks

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
While acknowledging the importance of the environment and its long-term impact on organizations and the economy as a whole, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has now released a draft framework for banks to follow.
What are Climate-led Financial Risks?
- “Climate-related financial risks” means the potential risks that may arise from climate change or from efforts to mitigate climate change, their related impacts, and economic and financial consequences according to RBI.
- These risks manifest through two primary channels: physical risks and transition risks.
- Physical Risks: These entail the economic and financial consequences arising from the escalating frequency and severity of extreme weather events linked to climate change. Such events can exert pressure on the financial sector in various ways:
- Renewable Energy Sector (REs) Vulnerability: The occurrence of local or regional weather events may strain the anticipated cash flows to REs, impacting their financial stability. Furthermore, chronic flooding or landslides pose risks to the collateral that REs have pledged as security for loans.
- Infrastructure and Property Damage: Severe weather phenomena can inflict damage on the physical assets and data centres owned or leased by REs, impairing their capacity to deliver financial services effectively.
- Transition Risks: These risks stem from the transition toward a low-carbon economy, influenced by factors such as evolving climate-related policies, technological advancements, and changing consumer behaviours. Key considerations include:
- Policy and Regulatory Shifts: Changes in climate-related regulations and policies, along with advancements in technologies, can significantly influence the transition process. Moreover, alterations in customer sentiments and behaviour patterns play a pivotal role in shaping this transition.
- Economic Impact: The transition toward reducing carbon emissions carries substantial implications for the economy at large. It entails a shift toward sustainable practices and investments, which can impact various sectors and industries differently.
- Recognizing and addressing these climate-related financial risks is imperative for ensuring the resilience and stability of the financial sector in the face of evolving environmental challenges.
About the Framework:
- Commencing from the financial year 2025-26, all major financial institutions across India, including top-tier NBFCs and renowned NBFCs, will be mandated to furnish details about governance, strategy, and risk management strategies.
- Additionally, they will be required to initiate disclosure of metrics and targets from the fiscal year 2027-28.
Key highlights of the framework include:
- Enhanced Disclosure Requirements: Banks will be obligated to unveil climate-related risks that could potentially impact their financial stability.
- This measure aims to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of climate-related financial risks and opportunities, fostering early assessment and proactive management.
- Scope of Coverage: The framework encompasses various financial entities, including scheduled commercial banks (excluding local area banks, payments banks, and regional rural banks), Tier-IV primary urban cooperative banks (UCBs), and top and upper layer non-banking financial companies (NBFCs).
- Disclosure Obligations for Renewable Energy Sector (REs): REs are mandated to disclose crucial information related to climate-related risks and opportunities across short-, medium-, and long-term horizons. Key areas of disclosure include:
- Identification of Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities: REs are required to identify and disclose climate-related risks and opportunities relevant to their operations and financial outlook.
- Assessment of Impact: REs must delineate the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on their business strategies and financial planning, enabling stakeholders to comprehend the implications on their overall strategy.
- Resilience Evaluation: REs are tasked with evaluating the resilience of their strategies in light of diverse climate scenarios, thereby ensuring robustness in navigating potential challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Significance:
- A pressing requirement exists for an improved and standardized disclosure framework for regulated entities to mitigate financial risks.
- Without such a framework, there is a risk of assets being mispriced and capital being misallocated, which could have adverse repercussions on financial stability. Consequently, the imperative for a standardized disclosure framework on climate-related financial risks became evident.
How India’s first semiconductor fabrication plant can help plug into the global value chain

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved the country's first semiconductor fab to be made by the Tata Group in collaboration with Powerchip Taiwan.
What is Semiconductor Fabrication?
- The semiconductor fabrication process is a complex and highly specialized series of steps that transform raw materials into functional electronic components.
- This process involves a multitude of techniques and technologies, with each stage requiring precise control and attention to detail.
- A semiconductor fab -- short for fabrication -- is a manufacturing plant in which raw silicon wafers are turned into integrated circuits (ICs).
- A fab lab features a clean room where ICs are etched onto wafers.
- The completed chips are sent to a back-end assembly and test facility before they are packaged and sold.
- A semiconductor fab facility always includes a clean room -- so known because its environment is carefully controlled to eliminate dust and vibrations and to keep the temperature and humidity within a specific narrow range.
- Contamination can enter the fab environment through external sources, resulting in damage to products that can affect overall yield.
- To minimize the losses, all potential sources of contamination are thoroughly analysed and cleaned.
- For example, the tools used in the chip manufacturing process have low levels of particulates and fibres.
- The goal is to ensure that extraneous contamination is not introduced into the semiconductor fab to ensure the highest quality of the final products.
Technology Used in Semiconductor Fab Labs:
- Photolithography: Photolithography is a crucial optical process in the fabrication process, as it is used to create intricate circuit patterns on a single wafer's surface.
- This is achieved by coating the wafer with a photosensitive material, called a photoresist, and then exposing it to high-wavelength deep ultraviolet (DUV) or extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light through a mask containing the desired pattern.
- The exposed photoresist undergoes a chemical change, which allows it to be selectively removed.
- It leaves behind a patterned layer that serves as a protective layer for subsequent processing steps, such as etching and deposition.
Minimum age to cast postal ballots hiked to 85 years

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the upcoming Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, senior citizens who are 85 years and older will be able to opt for postal ballots as the government recently amended the rule to increase the eligibility from the current limit of 80 years and above.
News Summary:
- The government, in collaboration with the Election Commission, has introduced amendments to the Conduct of Election Rules (1961), specifically targeting the eligibility criteria for voting by postal ballot.
- Notably, the minimum age for senior citizens eligible for postal voting has been increased from 80 years to 85 years.
- Previously, Rule 27A of the Conduct of Election Rules had extended the postal ballot facility to senior citizens above 80 years, persons with disabilities, poll officers, and individuals diagnosed with COVID-19.
- This provision was first implemented during the 2020 Bihar assembly polls, coinciding with the onset of the pandemic.
- Despite the initial extension of postal voting rights to senior citizens aged 80 and above, a subsequent review by the Election Commission revealed that only a small fraction, approximately 2-3%, of eligible voters in this age group opted for postal ballots.
- The majority preferred to physically visit polling stations to cast their votes.
- Considering the statistics indicating that the total number of senior citizens above 80 years stands at 1.75 crore, with 98 lakh falling within the age range of 80-85 years, the government deemed it necessary to amend the existing rule.
- This adjustment reflects a nuanced approach aimed at ensuring efficient electoral processes while addressing the preferences and needs of elderly voters.
What is Postal Voting?
- Postal voting is only available to a specific group of voters.
- By retyping her choices on the ballot paper and returning it to the inspection officer before counting, a voter can remotely cast her ballot using this feature.
Who Can Avail This?
- Armed forces members such as those in the Army, Navy, and Air Force, armed police officers serving outside their home states, government workers stationed outside of India, and their wives are only eligible to vote by mail.
Features:
- Voters may use this service from any location outside of the designated constituency.
- This system makes it easier to create voter electoral roll data for services.
- It has two layers of security, making it a secure system:
- 1. Downloading the encrypted electronically transmitted postal ballot (ETPB) file requires an OTP (one-time password).
- 2. To decrypt, print, and deliver ETPB, a PIN is necessary.
- By sending postal ballots electronically to eligible service voters, this system addresses the time constraint associated with mailing postal ballots.
- The specific quick response code ensures confidentiality and prevents the duplication of cast ETPB.
Concerned Raised by Political Parties:
- Parties argue that allowing voters 65 and older to cast postal ballots violates voting confidentiality since many of the population lacks education and may ask for help from others at various points, ultimately identifying their chosen candidate.
- Their exposure to "administrative influence or influence by the government or the ruling party" also results from this.
How the development of Agaléga figures in India’s vision for its maritime neighbourhood
- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Ministers Narendra Modi and Pravind Jugnauth jointly inaugurated an airstrip and the St James Jetty on North Agaléga Island in the Indian Ocean.
About Agalega Islands:
- Agaléga Island comprises two islets, a long and thin northern island and a shorter, round southern island.
- It is slightly over 3,000 kilometres from the nearest mainland Indian coast, deep in the Indian Ocean near Madagascar.
- Despite its pristine appeal, Agaléga remains largely undiscovered by tourists and there are no hotels, water bungalows, or bustling tourist shops.
- Instead, approximately 300 islanders sustain themselves through coconut cultivation and fishing, maintaining a way of life passed down through generations.
Importance of Agalega Islands:
- The development of the Agalega Islands holds significant socio-economic and national security implications for Mauritius, aligning closely with India's maritime vision.
- Despite being a dependency of Mauritius, the islands have long remained underdeveloped, posing challenges to the sustainability and well-being of their inhabitants.
- Necessities often required referral to Mauritius due to the lack of infrastructure.
- Moreover, the absence of an official government or security presence posed a serious vulnerability, necessitating urgent attention.
- Recognizing the potential to transform this vulnerability into a strategic asset, Mauritius prioritized the development of the islands and the establishment of facilities capable of accommodating ships and aircraft.
- In this regard, the construction of a jetty and an airstrip emerged as imperative steps to bolster the islands' infrastructure.
- Given the shared interests and cooperation between Mauritius and India, the government of Mauritius selected India as its preferred development partner for this ambitious initiative.
Why did Mauritians Choose India?
- Ties between India and Mauritius go back to 1948, 20 years before the country’s independence from Britain.
- Seventy percent of the inhabitants of Mauritius are of Indian origin, and the two countries share deep historical, social, and cultural bonds.
- The consistent feature in the history of bilateral relations has been friendship and trust at all levels — the political leadership, the diplomatic and military communities, as well as between the peoples of the two countries.
- The development of these strategically located islands required trust more than anything else. India was the obvious choice.
Significance for India:
- The goodwill and trust between the two countries will be further enhanced. India will welcome opportunities to further develop these islands in collaboration with Mauritius as the latter deems appropriate.
- The joint development of Agaléga underscores India’s commitment to the vision of Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), and its willingness to assist smaller maritime nations in building capacity and developing capability.
- It will indicate to other maritime neighbours that India is a benign and friendly country that respects the sovereignty of independent nations.
- India would like to emerge as the preferred development and security partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
PM Modi launches India’s first hydrogen-powered ferry built at Cochin Shipyard
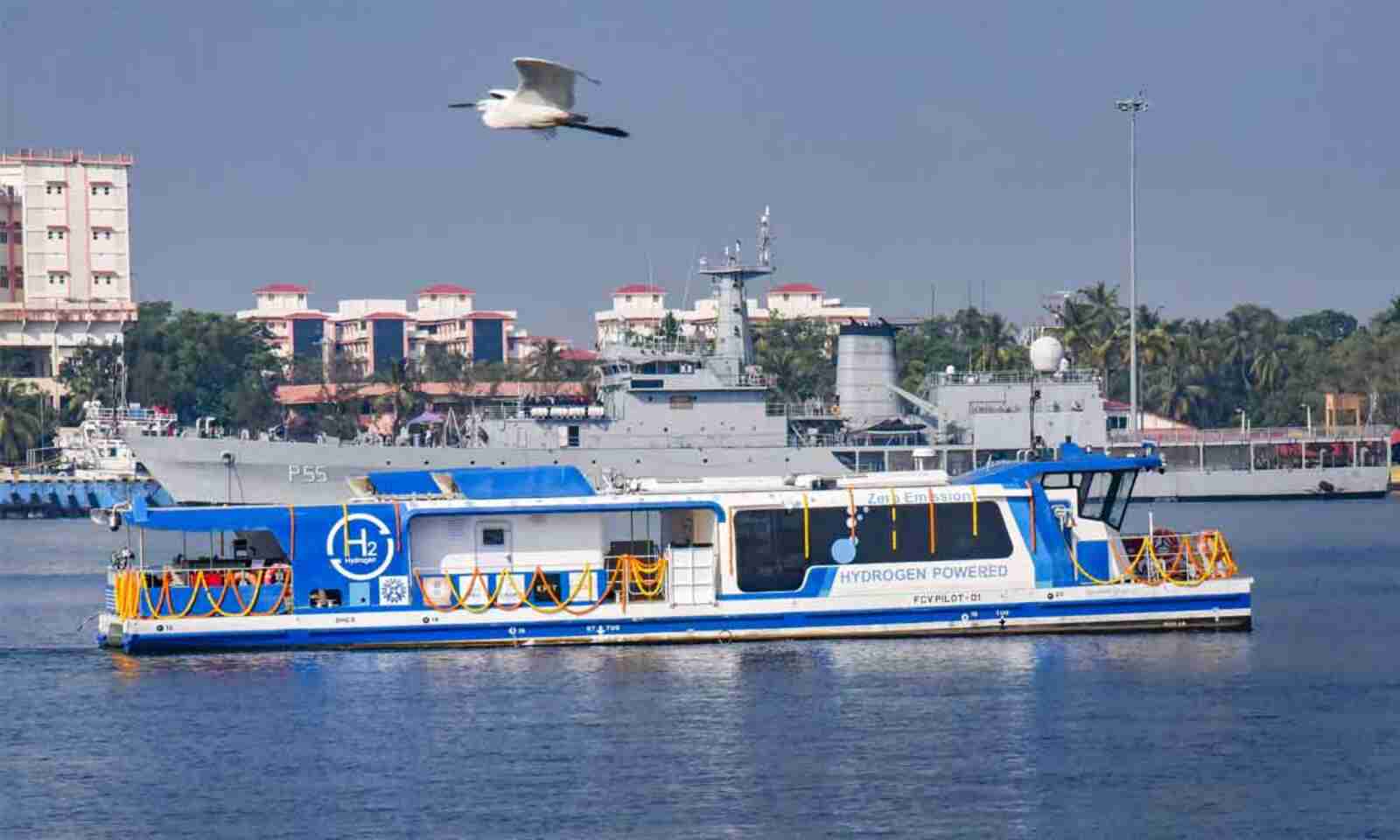

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi recently virtually launched India’s first indigenously developed hydrogen fuel cell ferry manufactured by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), which will be deployed for service at Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh.
What is the "Harit Nauka" (Green Boat) Initiative?
- Initiated by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways, "Harit Nauka" aims to facilitate a sustainable transition of inland vessels.
- In January 2024, the shipping ministry introduced the "Harit Nauka" guidelines, outlining the path towards environmentally friendly practices for inland vessels.
- According to these guidelines, all states are mandated to progressively adopt green fuels for 50% of their inland waterway-based passenger fleets within the next decade, to achieve 100% adoption by 2045. This initiative aligns with the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- The implementation of this initiative not only contributes to reducing emissions but also paves the way for replicating such environmentally friendly ferry models across the country to enhance urban mobility.
- Furthermore, it serves as a significant catalyst for advancing the objectives of the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
What are Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
- Hydrogen fuel cells harness the chemical energy of hydrogen to generate electricity, offering a clean energy solution with electricity, heat, and water as the sole products and by-products.
Functioning:
- Similar to batteries, fuel cells continuously produce electricity and heat as long as fuel is supplied. A typical fuel cell comprises two electrodes—an anode (negative electrode) and a cathode (positive electrode)—surrounding an electrolyte.
- Hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode, while air is directed to the cathode. At the anode, a catalyst separates hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons, which then travel different paths.
- Electrons create an electric current through an external circuit, while protons migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, combining with oxygen and electrons to form water and heat.
Challenges in India:
- High Cost: Fuel cell systems remain relatively expensive compared to conventional energy sources.
- Infrastructure Deficiency: India currently lacks the necessary infrastructure for the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology, including hydrogen production and distribution networks.
- Technical Hurdles: Despite ongoing advancements, fuel cell technology is still in its nascent stages, facing persistent technical challenges.
- Policy Constraints: The absence of a comprehensive policy framework from the Indian government has constrained the development and adoption of fuel cell technology, impeding research and investment.
India's Initiatives:
- In response to these challenges, India has formulated the National Green Hydrogen Policy, delineating a vision for the growth of the hydrogen and fuel cell industry.
- The policy aims to position India as a global hub for the production, utilization, and export of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives, signalling a strategic commitment to advancing sustainable energy solutions.
Characteristics of the Hydrogen-Powered Ferry:
- Length and Capacity: The hydrogen fuel cell vessel is a 24-meter-long catamaran, capable of accommodating up to 50 passengers in its air-conditioned passenger area.
- Battery-Free Operation: Distinguished by its innovative design, this ferry does not rely on conventional batteries for storing electrical energy.
- Instead, it utilizes hydrogen fuel, stored in cylinders onboard the vessel. With five hydrogen cylinders capable of carrying 40kg of hydrogen, the ferry can sustain operations for eight hours. Additionally, it features a 3-kW solar panel to complement its power source.
- Fuel Cell Technology: Equipped with a 50-kW PEM (proton-exchange membrane) fuel cell, coupled with Lithium-Ion Phosphate batteries, the ferry boasts adaptability in response to varying power demands.
- PEM fuel cells, renowned for their lower operating temperature, lightweight, and compactness, are commonly employed in automotive applications.
- Environmental Sustainability: With zero emissions and noise, coupled with enhanced energy efficiency, the hydrogen fuel cell-powered ferry stands as an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Its minimal moving parts contribute to reduced maintenance requirements compared to combustion vessels.
- Additional Advantages: While hydrogen fuel cell technology has been in development for maritime purposes, only a handful of countries worldwide have executed demonstration projects.
- Thus, this ferry positions India at the forefront, providing an early advantage in harnessing the potential of hydrogen as an emerging green fuel within the marine sector.
Doomsday Glacier has lost 50 billion tons of ice, melting began 80 years ago

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Antarctica's Doomsday Glacier, the world's widest glacier, has lost over 50 billion tons of ice and the melting rate is on the rise as the continent gets warmer.
What is Doomsday Glacier?
- The Thwaites Glacier (also known as Doomsday Glacier), a massive and world’s widest glacier is located in West Antarctica.
- The Doomsday nickname reflects the potential for catastrophic flooding if the glacier were to collapse completely.
- Scientists are particularly concerned about Thwaites Glacier because of its size and location.
- If it were to collapse or significantly retreat, it could lead to a more rapid flow of ice from the interior of West Antarctica into the ocean, contributing to rising sea levels.
- The collapse could lead to a 65 cm rise in global sea level.
- The ice loss in the region has been observed to be accelerating since the 1970s, however, so far it remained unclear as to when this retreat began.
- The significant glacial retreat began in the 1940s and the findings coincide with previous work that studied retreat on Pine Island Glacier and found glacial retreat began in the ‘40s as well.
- This change is not random nor specific to one glacier but It is part of a larger context of a changing climate.
Why Did the Melting Begin?
- The meeting was kicked off by an extreme El Nino climate pattern that warmed the west Antarctic, and since then the glacier has not been able to recover from the damage.
- It is significant that El Niño only lasted a couple of years, but the two glaciers, Thwaites and Pine Island remain in significant retreat.
- Once the system is kicked out of balance, the retreat is ongoing.
- The Doomsday Glacier's melting remains one of the most crucial events triggered and accelerated by climate change and could lead to the submergence of several coastal regions of the world.
ZSI names a newly discovered head-shield sea slug after President Droupadi Murmu
- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zoological Survey of India named a new marine species of head-shield sea slug with ruby red spot which was discovered from West Bengal and Odisha coast after President of India Droupadi Murmu.
About Melanochlamys Droupadi:
- Melanochlamys Droupadi is a newly discovered marine species of head-shield sea slug distinguished by its striking ruby red spot.
- This species, belonging to the Melanochlamys genus, was first identified along the coasts of Digha in West Bengal and Udaipur in Odisha.
Key Features:
- This small invertebrate typically measures up to 7 mm in length.
- It primarily inhabits wet and soft sandy beaches.
- Adorned in brownish-black hues, it features a distinctive ruby-red spot towards its hind end.
- Melanochlamys Droupadi exhibits hermaphroditic characteristics, possessing both male and female reproductive organs. However, it requires another sea slug for successful reproduction.
- Internally, it possesses a shell and a posterior segment comprising 61 per cent of its body length.
- To safeguard against sand infiltration, it continuously secretes transparent mucus, forming a protective sheath around its body.
- When in motion, it burrows beneath smooth sand, creating a moving capsule where its body remains mostly concealed, akin to a turtle, leaving behind a discernible trail.
What are Sea Slugs?
- Sea slugs are a diverse group of molluscs inhabiting marine environments, characterized by their slug-like appearance.
- They occupy a wide range of habitats, spanning from shallow intertidal zones to the depths of the ocean, and from polar regions to tropical waters.
- As agile predators, sea slugs prey on mobile organisms such as other shelled and unshelled sea slugs, roundworms, marine worms, and small fish.
- Currently, researchers have identified 18 species of sea slugs worldwide.
- While sea slugs predominantly inhabit temperate regions within the Indo-Pacific Oceanic realm, three species exhibit truly tropical distributions: Melanochlamys papillata from the Gulf of Thailand, Melanochlamys bengalensis from the West Bengal and Odisha coast, and the newly discovered species.
World's First Vedic Clock to be Unveiled by PM Modi in Ujjain

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Vedic Clock in Ujjain as part of the 'Vikramotsav' celebration in Madhya Pradesh.
Features of the Vikramaditya Vedic Clock:
- This is the world's first 'Vedic Clock', designed to display time according to the ancient Indian traditional Panchang (time calculation system).
- The clock is installed on an 85-foot high tower constructed at Jantar Mantar in Ujjain, adjacent to the Government Jiwaji Observatory.
- It will display 30 Muhurats, tithi, and all other time calculations of Vedic Hindu panchang.
- Additionally, Samvat, Mas, moon position, Parva, Shubhshubh Muhurat, Ghati, Nakshatra, solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse, among other things
- It will be the world’s first clock in which Indian time calculation will be displayed.
- The Vedic clock installed in Ujjain as the city has been considered the centre of time calculation.
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through Ujjain.
Time calculation:
- The unique timepiece calculates time-based on Vedic Hindu Panchang, planetary positions, Muhurat, astrological calculations, solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse, among other things, and also indicates the Indian Standard Time (IST) and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- The period from one sunrise to the next is used to calculate time.
- The clock will calculate time from one sunrise to another.
- The time period between the two sunrises will be divided into 30 parts, with each hour consisting of 48 minutes according to ISD.
- The reading will start from 0.00 with the sunrise functions for 30 hours (an hour of 48 minutes).
- Also, there will be a dedicated mobile application for the readings of the Vedic Clock, and citizens will be able to use it on their smartphones, computers, televisions, and other devices.
Why It is Located in Ujjain?
- The standard time of the world was determined from Ujjain 300 years ago.
- Throughout the world, the time prescribed and transmitted from Ujjayini (Ujjain) has been followed.
- The shortest fraction of time is included in Indian time calculations based on the Indian astronomical theory and the motions of planetary constellations.
- Ujjain was previously thought to be India’s central meridian, and the city determined the nation’s time zones and time differences, according to Hindu astronomical belief.
- The city of Lord Mahakal is situated exactly where the Tropic of Cancer and Zero Meridians meet.
- Additionally, it is situated in the oldest observatory in India, which Sawai Jai Singh II of Jaipur constructed in the early 1700s.
- Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh, which is located at 82°30’ East longitude, is the location of the zero meridians on the Prime Meridian, or IST, four hours ahead of GMT, according to the 1884 convention on meridians.
India to set up International Big Cat Alliance

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Environment Ministry plans to set up and coordinate an International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), along the lines of the International Solar Alliance, an India-headquartered initiative to promote solar installations globally.
About the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- The idea of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was first given by Prime Minister Modi during his speech on the occasion of Global Tiger Day in 2019.
- He called for developing an alliance of global leaders to curb poaching in Asia.
- The alliance was formally announced on April 9, 202, in Mysuru, as India commemorated the completion of 50 years of Project Tiger.
- The alliance will focus on the conservation of seven big cats, which include Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah. Out of these, five are found in India.
- Membership to the IBCA is open to 97 'range' countries, encompassing the natural habitats of these big cats, as well as other interested nations and international organizations.
- The alliance aims to facilitate cooperation among countries to advance the conservation agenda for mutual benefit.
- Operating with a multifaceted approach, the IBCA endeavours to establish robust linkages across various domains, including knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, financial and resource support, research, technical assistance, education, and awareness.
- Governance of the alliance consists of a General Assembly comprising all member countries, a Council comprised of seven to fifteen member countries elected by the General Assembly for a five-year term, and a Secretariat.
- The IBCA Secretary General, appointed by the General Assembly upon the Council's recommendation, serves a specific term.
- To support its initiatives, the IBCA has secured initial funding of Rs. 150 crore from the Government of India for the period spanning from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
