La Nina impacted air quality in India in the winter of 2022
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study suggests that monsoon rainfall over India, which is strongly influenced by El Niño and La Niña events—alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean impacting global weather may also affect air quality in the country.
Key Findings of the New Study on the Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- According to the researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Studies (Bengaluru) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (Pune), the strong influence of El Niño and La Niña events on monsoon rainfall over India, driven by the alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, with far-reaching effects on global weather patterns.
- Remarkably, this study marks the first time that air quality in Indian cities has been directly linked to a La Niña event, suggesting an indirect connection to climate change, which intensifies the severity of El Niño and La Niña occurrences.
- Traditionally, northern Indian cities, notably Delhi, face elevated concentrations of PM2.5 pollutants from October to January.
- However, the winter of 2022 witnessed a notable deviation from this trend, with northern cities experiencing cleaner air than usual, while western and southern cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Chennai saw worsened air quality.
- Specifically, Delhi observed a 10% reduction in PM2.5 concentrations, contrasted with a 30% increase in Mumbai and a 20% rise in Bengaluru.
- The researchers, investigating this anomaly, identified the potent effects of the La Niña event, notably stronger than typical occurrences, leading to significant changes in wind circulation patterns over India.
- This impact became pronounced in the third year of La Niña, suggesting a cumulative effect that may amplify over time.
- While La Niña events are associated with improved air quality in northern India, the study emphasizes the need for further research to understand the potential impacts of El Niño events, which may produce contrasting effects on air quality across the country.
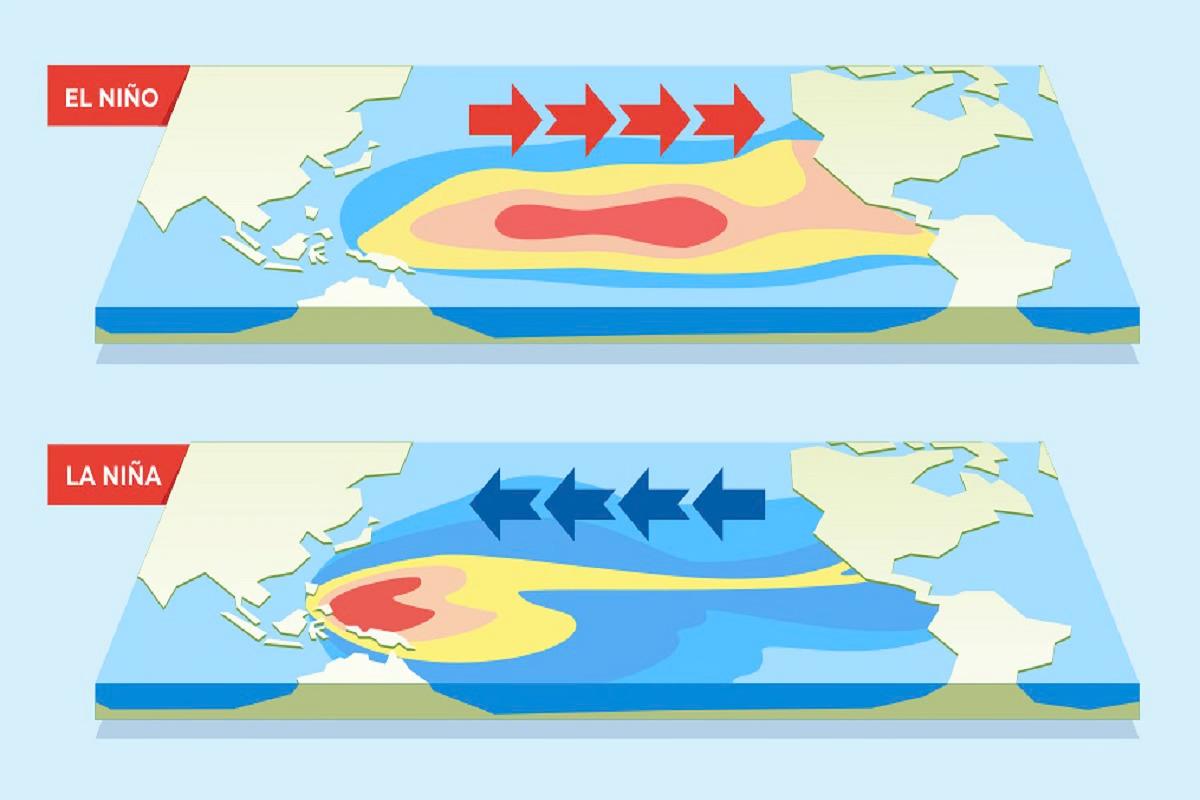
What are El Niño and La Niña?
- El Niño refers to a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Similarly, a La Niña occurs when the band of water spreads east to west and is cooler.
- Both phenomena affect the weather worldwide and can have drastic effects on economies that depend on rainfall.
- Together, El Niño and La Niña make up a cyclical process called the El Niño Southern Oscillation.
- An El Niño year creates a global warming crisis in miniature because the warm water spreading across the tropical Pacific releases a large amount of heat into the atmosphere.
- El Niño: El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, El Niño events often correlate with below-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to drought conditions in some regions, affecting agriculture and water resources.
- El Niño can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing warmer temperatures during El Niño events.
- La Niña: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, La Niña events often correlate with above-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to increased precipitation in some regions, potentially causing flooding, while other areas may experience drought conditions.
- La Niña can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing cooler temperatures during La Niña events.
Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- Altering Wind Patterns: During the winter of 2022, the typical north-westerly winds, carrying agricultural pollutants from Punjab and Haryana towards Delhi and the Gangetic plains, were disrupted.
- Instead, wind circulation shifted to a north-south direction, diverting pollutants away from Delhi.
- Consequently, pollutants bypassed Delhi, travelling over Rajasthan and Gujarat towards southern regions.
- Modifying Local Wind Circulation near Mumbai: In Mumbai, the local wind circulation, which alternates between land-to-sea and sea-to-land flows every few days, experienced prolonged unidirectional winds.
- This sustained wind pattern prevented the dispersal of pollutants from the city, leading to their accumulation within Mumbai's atmosphere throughout the winter of 2022.
- These changes in wind patterns, influenced by La Niña, significantly impacted air quality dynamics in India, highlighting the intricate relationship between climate phenomena and regional atmospheric conditions.
